CN114832012A - Ce-MOF nano material with oxidation resistance, preparation method and application - Google Patents
Ce-MOF nano material with oxidation resistance, preparation method and applicationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114832012A CN114832012ACN202210292346.8ACN202210292346ACN114832012ACN 114832012 ACN114832012 ACN 114832012ACN 202210292346 ACN202210292346 ACN 202210292346ACN 114832012 ACN114832012 ACN 114832012A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- mof
- preparation
- nanomaterials
- oxidation resistance
- terephthalic acid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000002086nanomaterialSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription46
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription16
- 230000003647oxidationEffects0.000titleclaims9
- 238000007254oxidation reactionMethods0.000titleclaims9
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-NN,N-DimethylformamideChemical compoundCN(C)C=OZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription27
- KKEYFWRCBNTPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-NTerephthalic acidChemical compoundOC(=O)C1=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C1KKEYFWRCBNTPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription25
- 208000003556Dry Eye SyndromesDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription21
- 206010013774Dry eyeDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 239000007810chemical reaction solventSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- 239000012046mixed solventSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-OAmmoniumChemical compound[NH4+]QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O0.000claims3
- 229910002651NO3Inorganic materials0.000claims3
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-NNitrateChemical compound[O-][N+]([O-])=ONHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims3
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000claims1
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000claims1
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000claims1
- XMPZTFVPEKAKFH-UHFFFAOYSA-Pceric ammonium nitrateChemical compound[NH4+].[NH4+].[Ce+4].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OXMPZTFVPEKAKFH-UHFFFAOYSA-P0.000abstractdescription7
- 230000003064anti-oxidating effectEffects0.000abstractdescription6
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000abstractdescription4
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 230000001276controlling effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000001590oxidative effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 239000012621metal-organic frameworkSubstances0.000description30
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description13
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000description8
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000description8
- 230000003078antioxidant effectEffects0.000description7
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description7
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description6
- 239000000376reactantSubstances0.000description5
- 230000002000scavenging effectEffects0.000description5
- 229910000667(NH4)2Ce(NO3)6Inorganic materials0.000description3
- 239000003963antioxidant agentSubstances0.000description3
- 238000005119centrifugationMethods0.000description3
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description3
- 230000036542oxidative stressEffects0.000description3
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000description3
- PWKSKIMOESPYIA-BYPYZUCNSA-NL-N-acetyl-CysteineChemical compoundCC(=O)N[C@@H](CS)C(O)=OPWKSKIMOESPYIA-BYPYZUCNSA-N0.000description2
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description2
- 238000002441X-ray diffractionMethods0.000description2
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description2
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 230000004438eyesightEffects0.000description2
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description2
- 230000003834intracellular effectEffects0.000description2
- 201000004569BlindnessDiseases0.000description1
- 206010006784Burning sensationDiseases0.000description1
- 229910052684CeriumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 208000017667Chronic DiseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 102000004127CytokinesHuman genes0.000description1
- 108090000695CytokinesProteins0.000description1
- 206010052140Eye pruritusDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003917TEM imageMethods0.000description1
- 206010047513Vision blurredDiseases0.000description1
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000010171animal modelMethods0.000description1
- 230000002238attenuated effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- GWXLDORMOJMVQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NceriumChemical compound[Ce]GWXLDORMOJMVQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 210000000795conjunctivaAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000004087corneaAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description1
- 230000004064dysfunctionEffects0.000description1
- 210000002919epithelial cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000012530fluidSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001727in vivoMethods0.000description1
- 230000002757inflammatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000013067intermediate productSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000description1
- 230000008506pathogenesisEffects0.000description1
- 239000013641positive controlSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001878scanning electron micrographMethods0.000description1
- 230000035807sensationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000007visual effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004382visual functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000004393visual impairmentEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K33/00—Medicinal preparations containing inorganic active ingredients
- A61K33/24—Heavy metals; Compounds thereof
- A61K33/244—Lanthanides; Compounds thereof
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/69—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit
- A61K47/6949—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit inclusion complexes, e.g. clathrates, cavitates or fullerenes
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P27/00—Drugs for disorders of the senses
- A61P27/02—Ophthalmic agents
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P39/00—General protective or antinoxious agents
- A61P39/06—Free radical scavengers or antioxidants
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y40/00—Manufacture or treatment of nanostructures
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y5/00—Nanobiotechnology or nanomedicine, e.g. protein engineering or drug delivery
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Ophthalmology & Optometry (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于新型纳米生物医药领域,具体涉及一种具有抗氧化性能的Ce-MOF纳米材料、制备方法及应用。The invention belongs to the field of novel nano-biomedicine, and in particular relates to a Ce-MOF nano-material with anti-oxidation performance, a preparation method and application.
背景技术Background technique
干眼(Dry Eye Disease,DED)是由于泪液的量或质或流体动力学异常引起的泪膜不稳定和/或眼表损害,从而引起眼不适症状及视功能障碍的一类疾病。干眼是临床常见的眼表慢性疾病,表现为眼部干涩感、异物感、烧灼感、眼痒、视物模糊、视力波动等,严重干眼可导致角膜上皮缺损及视力下降等,在我国的发病率约为21%~30%,且该数值还将继续上升。DED对患者视觉功能、日常生活能力、专业工作均有不同程度的影响。很多体内和体外的研究证明氧化应激与干眼的发生密不可分。氧化应激可以对角膜及结膜等眼表造成损害,其在干眼的发病中起着重要作用。DED动物模型研究表明,通过降低ROS水平和抑制炎性细胞因子,可以显著减轻氧化应激损伤。因此,用广谱抗氧化剂清除ROS可能是治疗这一类DED的有效方案,即通过降低角膜和结膜上皮细胞的ROS水平来缓解DED。Dry Eye Disease (DED) is a class of diseases that cause eye discomfort and visual dysfunction due to tear film instability and/or ocular surface damage caused by abnormal tear quantity or quality or fluid dynamics. Dry eye is a common clinical chronic disease of the ocular surface, manifested as dry eye, foreign body sensation, burning sensation, eye itching, blurred vision, vision fluctuation, etc. Severe dry eye can lead to corneal epithelial defect and vision loss. The incidence of the disease is about 21% to 30%, and the value will continue to rise. DED has varying degrees of influence on patients' visual function, ability of daily living, and professional work. Many in vivo and in vitro studies have demonstrated that oxidative stress is inseparable from the occurrence of dry eye. Oxidative stress can cause damage to the ocular surface such as the cornea and conjunctiva, which plays an important role in the pathogenesis of dry eye. DED animal model studies have shown that oxidative stress damage can be significantly attenuated by reducing ROS levels and inhibiting inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, scavenging ROS with broad-spectrum antioxidants may be an effective regimen to treat this type of DED by reducing ROS levels in corneal and conjunctival epithelial cells to alleviate DED.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的是为了克服现有技术存在的缺点和不足,而提供一种具有抗氧化性能的Ce-MOF纳米材料、制备方法及应用。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the shortcomings and deficiencies of the prior art, and provide a Ce-MOF nanomaterial with antioxidant properties, a preparation method and an application.
本发明所采取的技术方案如下:一种具有抗氧化性能的Ce-MOF纳米材料的制备方法,包括以下步骤:以硝酸铈铵和对苯二甲酸为原料,N,N-二甲基甲酰胺和水的混合溶剂体系为反应溶剂,得到反应体系,将反应体系在密封条件下于80-120 ℃下反应0.5-1.5 h,冷却至室温后离心洗涤得到Ce-MOF纳米材料。The technical scheme adopted in the present invention is as follows: a preparation method of Ce-MOF nanomaterial with anti-oxidation performance, comprising the following steps: using ceric ammonium nitrate and terephthalic acid as raw materials, N,N-dimethylformamide A mixed solvent system with water is used as a reaction solvent to obtain a reaction system. The reaction system is reacted at 80-120 °C for 0.5-1.5 h under sealed conditions, cooled to room temperature, and then centrifuged and washed to obtain Ce-MOF nanomaterials.
所述对苯二甲酸溶于N,N-二甲基甲酰胺中,所述硝酸铈铵溶于水中,待二者充分溶解后将二者混合均匀得到反应体系。The terephthalic acid is dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide, and the ceric ammonium nitrate is dissolved in water. After the two are fully dissolved, the two are mixed uniformly to obtain a reaction system.
所述N,N-二甲基甲酰胺和水的体积比为1:1。The volume ratio of the N,N-dimethylformamide and water is 1:1.
所述对苯二甲酸与硝酸铈铵的摩尔浓度比值为1:1-1.2。The molar concentration ratio of the terephthalic acid and ceric ammonium nitrate is 1:1-1.2.
所述对苯二甲酸的浓度为10-100mM。该浓度范围制备得到的产物粒径为纳米级的,且均具备抗氧化性能,随着原料浓度的降低,产物粒径也会随之降低,可以轻松实现对所得产物的尺寸的调控。The concentration of the terephthalic acid is 10-100 mM. The particle size of the products prepared in this concentration range is nano-scale, and all have antioxidant properties. As the concentration of raw materials decreases, the particle size of the product will also decrease, and the size of the obtained product can be easily adjusted.
所述对苯二甲酸的浓度为10-30mM。该浓度范围制备得到的产物为超小Ce-MOF纳米材料,且可以缓解干眼症状。The concentration of the terephthalic acid is 10-30 mM. The products prepared in this concentration range are ultra-small Ce-MOF nanomaterials, and can relieve dry eye symptoms.
如上所述的具有抗氧化性能的Ce-MOF纳米材料的制备方法制备得到的Ce-MOF纳米材料。The Ce-MOF nanomaterial prepared by the above-mentioned preparation method of the Ce-MOF nanomaterial with anti-oxidation properties.
如上所述的Ce-MOF纳米材料在制备缓解干眼症的药物的应用。Application of the above Ce-MOF nanomaterials in the preparation of medicines for relieving dry eye.
本发明的有益效果如下:本发明所提供的方法制备得到的Ce-MOF纳米材料具有显著的抗氧化性能,且通过对原料浓度的控制,可实现对所得产物的尺寸的调控,随着产物粒径的降低,产物的抗氧化能力逐渐增强。在缓解干眼症的应用结果显示,所得Ce-MOF纳米材料在一定程度上可以缓解干眼症状。这对于扩大铈基金属-有机骨架纳米材料在眼科领域里的应用具有重要的研究意义。The beneficial effects of the present invention are as follows: the Ce-MOF nanomaterial prepared by the method provided by the present invention has remarkable anti-oxidation performance, and by controlling the concentration of the raw materials, the size of the obtained product can be regulated. As the diameter decreased, the antioxidant capacity of the product gradually increased. The application results in relieving dry eye symptoms show that the obtained Ce-MOF nanomaterials can alleviate dry eye symptoms to a certain extent. This has important research significance for expanding the application of cerium-based metal-organic framework nanomaterials in the field of ophthalmology.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动性的前提下,根据这些附图获得其他的附图仍属于本发明的范畴。In order to illustrate the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art more clearly, the following briefly introduces the accompanying drawings that are used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only These are some embodiments of the present invention, and for those of ordinary skill in the art, obtaining other drawings according to these drawings still belongs to the scope of the present invention without any creative effort.
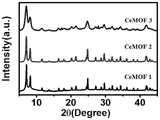
图1为本发明制得的三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的XRD图谱;Fig. 1 is the XRD pattern of three kinds of Ce-MOF nanomaterials obtained by the present invention;
图2为本发明实例制得的三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的SEM照片及超小Ce-MOF的TEM照片,其中,(a)为Ce-MOF1的SEM照片,(b)为为Ce-MOF2的SEM照片,(c)为为Ce-MOF3的SEM照片,(d)为Ce-MOF3的TEM照片;Fig. 2 is the SEM photograph of three kinds of Ce-MOF nanomaterials and the TEM photograph of ultra-small Ce-MOF prepared in the example of the present invention, wherein (a) is the SEM photograph of Ce-MOF1, (b) is Ce-MOF2 The SEM photo of , (c) is the SEM photo of Ce-MOF3, (d) is the TEM photo of Ce-MOF3;
图3为本发明实例制得的三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的清除H2O2能力的评价。FIG. 3 is an evaluation of the H2 O2 scavenging ability of three Ce-MOF nanomaterials prepared in an example of the present invention.
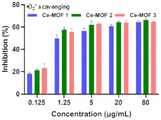
图4为本发明实例制得的三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的清除O2-能力的评价Fig. 4 is the evaluation of the O2-scavenging ability of three kinds of Ce-MOF nanomaterials prepared in the example of the present invention
图5为本发明实例制得的三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的细胞内抗氧化性能的评价;Fig. 5 is the evaluation of the intracellular antioxidant properties of three kinds of Ce-MOF nanomaterials prepared in the example of the present invention;
图6为本发明实例制得的超小Ce-MOF纳米材料(Ce-MOF3)缓解干眼症的评价。FIG. 6 is the evaluation of the ultra-small Ce-MOF nanomaterial (Ce-MOF3) prepared in the example of the present invention for relieving dry eye.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合附图对本发明作进一步地详细描述。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
实施例1:Example 1:
将0.708 g H2BDC(终浓度为80.98mM)溶入到24 mL DMF中,2.32 g (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6(终浓度为88.16 mM)溶于24 mL水中,待二者充分溶解后将二者混,继续搅拌10 min。最后将所得混合物转移到50 ml的聚四氟乙烯内衬的反应釜中,密封,在100 ℃ 下反应1 h,自然冷却至室温后离心洗涤即可得到产物一(Ce-MOF1)。Dissolve 0.708 g of H2 BDC (final concentration of 80.98 mM) in 24 mL of DMF, and dissolve 2.32 g of (NH4 )2 Ce(NO3 )6 (final concentration of 88.16 mM) in 24 mL of water. After fully dissolving, mix the two and continue stirring for 10 min. Finally, the obtained mixture was transferred to a 50 ml PTFE-lined reaction kettle, sealed, reacted at 100 °C for 1 h, cooled to room temperature naturally, and washed by centrifugation to obtain product one (Ce-MOF1).
实施例2:Example 2:
将0.304 g H2BDC(终浓度为40.49mM)溶入到24 mL DMF中,1.16g (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6(终浓度为44.08mM)溶于24 mL水中,待二者充分溶解后将二者混,继续搅拌10 min。最后将所得混合物转移到50 ml的聚四氟乙烯内衬的反应釜中,密封,在100 ℃ 下反应1 h,自然冷却至室温后离心洗涤即可得到产物一(Ce-MOF2)。Dissolve 0.304 g of H2 BDC (final concentration of 40.49 mM) into 24 mL of DMF, and dissolve 1.16 g of (NH4 )2 Ce(NO3 )6 (final concentration of 44.08 mM) in 24 mL of water. After fully dissolving, mix the two and continue stirring for 10 min. Finally, the obtained mixture was transferred to a 50 ml PTFE-lined reaction kettle, sealed, reacted at 100 °C for 1 h, cooled to room temperature naturally, and washed by centrifugation to obtain product one (Ce-MOF2).
实施例3:Example 3:
将0.152g H2BDC(终浓度为20.25mM)溶入到24 mL DMF中,0.58g (NH4)2Ce(NO3)6(终浓度为22.04mM)溶于24 mL水中,待二者充分溶解后将二者混,继续搅拌10 min。最后将所得混合物转移到50 ml的聚四氟乙烯内衬的反应釜中,密封,在100 ℃ 下反应1 h,自然冷却至室温后离心洗涤即可得到产物一(Ce-MOF3)。Dissolve 0.152g H2 BDC (final concentration of 20.25mM) in 24 mL of DMF, and dissolve 0.58g of (NH4 )2 Ce(NO3 )6 (final concentration of 22.04 mM) in 24 mL of water. After fully dissolving, mix the two and continue stirring for 10 min. Finally, the obtained mixture was transferred to a 50 ml PTFE-lined reaction kettle, sealed, reacted at 100 °C for 1 h, cooled to room temperature naturally, and washed by centrifugation to obtain product one (Ce-MOF3).
以下为对实施例1-3所得产物的相关性能的研究分析结果。The following are the research and analysis results of the relevant properties of the products obtained in Examples 1-3.
由图1通过调控不同反应物的浓度所得三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的XRD图谱,可以看出所得三种尺寸的Ce-MOF纳米材料的相结构是一致的,反应物浓度的不同对产物相结构的影响不大。From Figure 1, the XRD patterns of the three Ce-MOF nanomaterials obtained by adjusting the concentrations of different reactants, it can be seen that the phase structures of the obtained three sizes of Ce-MOF nanomaterials are consistent, and the different concentrations of reactants have the same effect on the product phase. The structure has little effect.
由图2通过调控不同反应物的浓度所制备的三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的SEM 照片及超小尺寸Ce-MOF纳米材料的TEM照片,可以看出随着反应物浓度的降低产物的粒径依次降低,从初始的500-1000 nm(Ce-MOF1),到中间产物的50 nm(Ce-MOF2),以及最后的3-5 nm的超小纳米颗粒(SEM 及TEM)(Ce-MOF3)。可以看出通过简单的调节反应物的浓度就可以很好的控制产物的粒径。From Figure 2, the SEM images of the three Ce-MOF nanomaterials prepared by adjusting the concentrations of different reactants and the TEM images of the ultra-small Ce-MOF nanomaterials, it can be seen that the particle size of the products decreases with the decrease of the reactant concentration. Decrease sequentially, from the initial 500-1000 nm (Ce-MOF1), to the intermediate product of 50 nm (Ce-MOF2), and finally 3-5 nm of ultra-small nanoparticles (SEM and TEM) (Ce-MOF3) . It can be seen that the particle size of the product can be well controlled by simply adjusting the concentration of the reactants.
由图3三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的清除H2O2能力的评价,可以看出所合成的三种不同尺寸的Ce-MOF纳米材料都具有清除H2O2的能力,并且随着材料粒径的降低,清除能力逐渐增强。From the evaluation of the H2 O2 scavenging ability of the three Ce-MOF nanomaterials in Fig. 3, it can be seen that the synthesized three Ce-MOF nanomaterials with different sizes all have the ability to scavenge H2 O2 , and with the material particles As the diameter decreases, the removal capacity gradually increases.
由图4三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的清除O2-能力的评价,可以看出所合成的三种不同尺寸的Ce-MOF纳米材料都具有清除O2-的能力,并且随着材料粒径的降低,清除能力逐渐增强,Ce-MOF2和Ce-MOF3的效能相近。From the evaluation of the O2- scavenging ability of the three Ce-MOF nanomaterials in Fig. 4, it can be seen that the synthesized Ce-MOF nanomaterials with different sizes all have the ability to scavenge O2- , and with the increase of the particle size of the material. decreased, the scavenging ability gradually increased, and the efficacy of Ce-MOF2 and Ce-MOF3 were similar.
由图5三种Ce-MOF纳米材料的体外细胞内抗氧化性能的评价;可以看出相对于目前常用的阳性对照的N-乙酰-L-半胱氨酸(NAC),所合成的三种不同粒径的Ce-MOF纳米材料都有一定的抗氧化效果,并且随着材料粒径的降低,抗氧化能力有所增强,视野中绿色明显的更少。From the evaluation of the in vitro intracellular antioxidant properties of the three Ce-MOF nanomaterials in Figure 5; it can be seen that compared with the currently commonly used positive control N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), the synthesized three Ce-MOF nanomaterials with different particle sizes have a certain antioxidant effect, and with the decrease of the particle size of the material, the antioxidant capacity is enhanced, and the greenness in the field of vision is significantly less.
由图6超小Ce-MOF纳米材料(Ce-MOF3)在缓解动物干眼症的评价结果显示,相对于PBS组,滴加含有超小Ce-MOF纳米材料的动物干眼症的分值更低,说明干眼症得到了缓解。According to the evaluation results of ultra-small Ce-MOF nanomaterials (Ce-MOF3) in relieving dry eye in animals in Figure 6, compared with the PBS group, the scores of dry eye in animals containing ultra-small Ce-MOF nanomaterials were better than those in the PBS group. low, indicating that the dry eye has been alleviated.
以上所揭露的仅为本发明较佳实施例而已,当然不能以此来限定本发明之权利范围,因此依本发明权利要求所作的等同变化,仍属本发明所涵盖的范围。The above disclosures are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and of course, the scope of the rights of the present invention cannot be limited by this. Therefore, equivalent changes made according to the claims of the present invention are still within the scope of the present invention.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210292346.8ACN114832012B (en) | 2022-03-23 | 2022-03-23 | Ce-MOF nano material with oxidation resistance, preparation method and application |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210292346.8ACN114832012B (en) | 2022-03-23 | 2022-03-23 | Ce-MOF nano material with oxidation resistance, preparation method and application |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114832012Atrue CN114832012A (en) | 2022-08-02 |
| CN114832012B CN114832012B (en) | 2023-10-31 |
Family
ID=82561758
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210292346.8AActiveCN114832012B (en) | 2022-03-23 | 2022-03-23 | Ce-MOF nano material with oxidation resistance, preparation method and application |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114832012B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118048102A (en)* | 2024-02-07 | 2024-05-17 | 甘肃金宏桥集团有限公司 | A multifunctional environmentally friendly coating and preparation method thereof |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109012722A (en)* | 2018-06-12 | 2018-12-18 | 广东工业大学 | It is a kind of using Ce-MOF as the ceria of presoma/titanium nitride nano pipe and its preparation method and application |
| CN110585169A (en)* | 2019-09-12 | 2019-12-20 | 郑州大学 | Preparation method of glucose oxidase modified metal organic framework pharmaceutical composition |
| CN110787584A (en)* | 2019-11-11 | 2020-02-14 | 中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所 | Application of cerium-based metal organic framework structure material in CO2Adsorption separation application of |
| CN113441114A (en)* | 2021-08-04 | 2021-09-28 | 辽宁大学 | Mixed metal MOF and preparation method and application thereof |
- 2022
- 2022-03-23CNCN202210292346.8Apatent/CN114832012B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109012722A (en)* | 2018-06-12 | 2018-12-18 | 广东工业大学 | It is a kind of using Ce-MOF as the ceria of presoma/titanium nitride nano pipe and its preparation method and application |
| CN110585169A (en)* | 2019-09-12 | 2019-12-20 | 郑州大学 | Preparation method of glucose oxidase modified metal organic framework pharmaceutical composition |
| CN110787584A (en)* | 2019-11-11 | 2020-02-14 | 中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所 | Application of cerium-based metal organic framework structure material in CO2Adsorption separation application of |
| CN113441114A (en)* | 2021-08-04 | 2021-09-28 | 辽宁大学 | Mixed metal MOF and preparation method and application thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| FAN YU等: "A cerium oxide loaded glycol chitosan nano-system for the treatment of dry eye disease", 《JOURNAL OF CONTROLLED RELEASE》, no. 315, pages 40 - 54, XP085936070, DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.10.039* |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118048102A (en)* | 2024-02-07 | 2024-05-17 | 甘肃金宏桥集团有限公司 | A multifunctional environmentally friendly coating and preparation method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114832012B (en) | 2023-10-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111110636B (en) | High-efficiency loading and sustained-release anti-glaucoma drug by using nano mesoporous silica | |
| Singh et al. | Chitosan nanoparticles for controlled delivery of brimonidine tartrate to the ocular membrane | |
| Chi et al. | Multifunctional organic–inorganic hybrid nanoparticles and nanosheets based on chitosan derivative and layered double hydroxide: Cellular uptake mechanism and application for topical ocular drug delivery | |
| CN114832012B (en) | Ce-MOF nano material with oxidation resistance, preparation method and application | |
| CN113307970B (en) | Preparation method of ultra-small polydopamine/polydopamine cysteine nanoparticles | |
| CN117224706A (en) | Anti-nitrification NO nano-drug, preparation method and application thereof | |
| JP2018525370A5 (en) | Drug-mounted nano-resin particles | |
| KR102718421B1 (en) | Prussian blue/polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticle complex and its use | |
| CN111096950B (en) | Curcumin double-layer emulsion with colon-targeted delivery function and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN106112006A (en) | A kind of golden nanometer particle aqueous solution and its preparation method and application | |
| CN111110629B (en) | Curcumin multi-layer emulsion with colon-targeted delivery function and preparation method and application thereof | |
| Zhang et al. | Design of hydrophobic zein/dye-LDHs biohybrid pigments for cosmetic applications | |
| Zou et al. | Multifunctional cerium oxide nanozymes with high ocular surface retention for dry eye disease treatment achieved by restoring redox balance | |
| CN108727507A (en) | Oxycellulose is prepared and its in the application for washing and carrying prescription face | |
| CN101081214A (en) | Methodc for preparing sub-micron gemfibrozil medicament powder | |
| CN101530394B (en) | A preparation method of polypeptide-chitosan composite nanoparticles loaded with coenzyme Q10 | |
| CN115487143B (en) | Sodium hyaluronate eye drops and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114146065A (en) | Chloroquine-coated denatured albumin nano-particle for selectively resisting inflammatory cells and preparation method and application thereof | |
| KR0181973B1 (en) | Process for preparing an aqueous suspension | |
| CN114773251B (en) | L-tryptophan spherical crystal and preparation method and application thereof | |
| Dias et al. | Optimizing Retinal Imaging: Evaluation of ultrasmall TiO2 nanoparticle-fluorescein conjugates for improved Fundus Fluorescein Angiography | |
| CN109568273A (en) | A kind of Florfenicol instant capacity particle and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110804180A (en) | Preparation method of polydopamine nanosheets | |
| CN116549638A (en) | A composite material of photothermal conversion nanomaterial loaded with ellagic acid and its preparation method and application | |
| CN114869805A (en) | A kind of cinnamon essential oil microcapsule and its preparation method and application |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |