CN114781508A - Clustering-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system - Google Patents
Clustering-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method and systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114781508A CN114781508ACN202210407679.0ACN202210407679ACN114781508ACN 114781508 ACN114781508 ACN 114781508ACN 202210407679 ACN202210407679 ACN 202210407679ACN 114781508 ACN114781508 ACN 114781508A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- task
- time
- population
- count
- antenna
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/23—Clustering techniques
- G06F18/232—Non-hierarchical techniques
- G06F18/2321—Non-hierarchical techniques using statistics or function optimisation, e.g. modelling of probability density functions
- G06F18/23213—Non-hierarchical techniques using statistics or function optimisation, e.g. modelling of probability density functions with fixed number of clusters, e.g. K-means clustering
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/12—Computing arrangements based on biological models using genetic models
- G06N3/126—Evolutionary algorithms, e.g. genetic algorithms or genetic programming
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0631—Resource planning, allocation, distributing or scheduling for enterprises or organisations
- G06Q10/06316—Sequencing of tasks or work
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Probability & Statistics with Applications (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于卫星任务规划领域,尤其是涉及一种基于聚类的卫星测控调度方法及系统。The invention belongs to the field of satellite task planning, in particular to a cluster-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system.
背景技术Background technique
近些年来,随着太空技术的快速发展,卫星作为一种可以在很多领域具有应用价值的太空平台愈发扮演着一个不可或缺的角色。卫星被用来完成目标观测、导航定位、通信传输等多种类型的任务,这取决于用户任务要求。无论卫星需要执行什么样的任务,都需要由卫星地面站以直接或者间接(先传输到中继卫星)的方式将任务以指令的形式由上行链路传输。地面站给卫星上传任务、动作指令并获取卫星运行状态的过程被称为卫星测控。卫星测控调度系统通过使用高效率的调度算法实现对卫星和地面站资源的有效管理。随着在轨运行卫星数量快速增加和卫星管理控制的需要,卫星测控调度问题的有效任务调度变得更加具有挑战性。In recent years, with the rapid development of space technology, satellites play an increasingly indispensable role as a space platform that can be applied in many fields. Satellites are used to complete various types of tasks such as target observation, navigation and positioning, and communication transmission, depending on the user's mission requirements. No matter what kind of task the satellite needs to perform, the satellite ground station needs to transmit the task in the form of instructions by the uplink directly or indirectly (transmitting to the relay satellite first). The process that the ground station uploads tasks and action instructions to the satellite and obtains the operating status of the satellite is called satellite measurement and control. The satellite measurement and control scheduling system realizes the effective management of satellite and ground station resources by using efficient scheduling algorithms. With the rapid increase in the number of satellites in orbit and the need for satellite management and control, the effective task scheduling of satellite measurement and control scheduling problems becomes more challenging.
卫星测控调度描述的是合理安排卫星和地面站的通信以实现卫星状态监测和指令上注的过程,也可简单描述为:为一系列卫星和一系列卫星地面站在相互可见的时间窗内找到合适的执行测控任务组合。卫星测控调度问题难以解决的主要原因在于,序列依赖和超额订购的特征。序列依赖是指一个任务的调度结果会影响到后续任务。这使得找到可行方案存在困难。超额订购是指地面站时间窗即便完全被使用也会有一部分任务没有被成功执行。这两个特征的同时存在使得测控调度问题变得尤为困难。卫星测控调度问题已经被证明复杂度为NP-complete。Satellite measurement and control scheduling describes the process of arranging the communication between satellites and ground stations to achieve satellite status monitoring and command annotation. A suitable combination of execution measurement and control tasks. The main reason why the satellite measurement and control scheduling problem is difficult to solve lies in the characteristics of sequence dependence and oversubscription. Sequence dependency means that the scheduling result of a task will affect subsequent tasks. This makes finding feasible solutions difficult. Oversubscription means that even if the ground station time window is fully used, a portion of the mission is not successfully performed. The coexistence of these two features makes the measurement and control scheduling problem particularly difficult. The satellite TT&C scheduling problem has been proved to be NP-complete.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明要解决的技术问题是怎样快速给出大规模卫星测控方案,提出了一种基于聚类的卫星测控调度方法及系统。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is how to quickly provide a large-scale satellite measurement and control scheme, and a cluster-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system are proposed.
为解决上述技术问题,本发明所采用的技术方案是:For solving the above-mentioned technical problems, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一种基于聚类的卫星测控调度方法,包括以下步骤:A cluster-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method, comprising the following steps:
步骤1:获取可调度的卫星资源、地面站资源、任务集以及可见时间窗集合;Step 1: Obtain schedulable satellite resources, ground station resources, task sets and visible time window sets;
步骤2:根据步骤1中所获取的内容构建混合整数规划模型;Step 2: build a mixed integer programming model according to the content obtained in step 1;
步骤3:对所述混合整数规划模型进行求解;Step 3: solving the mixed integer programming model;
步骤4:将求解得到的测控方案输出。Step 4: Output the obtained measurement and control scheme.
进一步地,所述混合整数规划模型是:Further, the mixed integer programming model is:
目标函数为:The objective function is:
其中,pt表示任务t的收益,为0-1决策变量,表示任务t是否安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗,1为安排,0为否,t表示任务,T表示任务集,a表示天线,A表示天线集合,表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗,TWta表示任务t安排在天线a上的时间窗集合;Among them, pt represents the income of task t, is a 0-1 decision variable, indicating whether task t is arranged in the ith visible time window on antenna a, 1 is the arrangement, 0 is no, t represents the task, T represents the task set, a represents the antenna, and A represents the antenna set, Indicates that task t is arranged on the ith visible time window on antenna a, and TWta represents the set of time windows in which task t is arranged on antenna a;
约束条件是:The constraints are:
式2表明任务需要在允许的开始时间之后开始执行任务;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的实际的测控时间长度,dt表示任务t要求的测控时间长度;Equation 2 indicates that the task needs to start executing the task after the allowed start time; Represents the actual measurement and control time length that task t arranges on the i-th visible time window on antenna a, and dt represents the measurement and control time length required by task t;
式3表明任务需要在允许的结束时间之前完成任务;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的实际开始时间,表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的结束时间;Equation 3 indicates that the task needs to be completed by the allowed end time; represents the actual start time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a, Represents the end time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a;
式4表明任务最多可以执行一次;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的的最早允许开始时间;Equation 4 indicates that the task can be executed at most once; Represents the earliest allowable start time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a;
式5表明任务实际执行时间应当与要求时间相同;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的的最晚允许结束时间;Equation 5 indicates that the actual execution time of the task should be the same as the required time; Represents the latest allowable end time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a;
式6表明任务执行过程需要在一个地面站时间范围内;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗的开始时间;Equation 6 indicates that the task execution process needs to be within a ground station time range; Represents the start time of the i-th visible time window scheduled for task t on antenna a;
式7表明每个任务只能由一个天线服务;Equation 7 indicates that each task can only be served by one antenna;
式8表明每个任务只能在一个可见的时间窗口内执行;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗的结束时间;Equation 8 indicates that each task can only be executed within a visible time window; Represents the end time of the i-th visible time window scheduled for task t on antenna a;
式9表明每个任务在全部天线上最多执行一次;Equation 9 indicates that each task is performed at most once on all antennas;
式10表明每个任务在全部时间窗内最多执行一次;Equation 10 indicates that each task is executed at most once in the entire time window;
式11表明任务在规划周期内最多被执行一次;Equation 11 indicates that the task is executed at most once in the planning period;
式12表明两个任务要满足任务转换时间的间隔要求;γ表示任务之间的转换时间。Equation 12 indicates that the two tasks must meet the task transition time interval requirement; γ represents the transition time between tasks.
进一步地,步骤3中对所述混合整数规划模型进行求解的方法是基于聚类的遗传算法。Further, the method for solving the mixed integer programming model in step 3 is a genetic algorithm based on clustering.
进一步地,所述基于聚类的遗传算法是:Further, the cluster-based genetic algorithm is:
步骤3.1:初始化遗传算法参数、聚类K-means方法参数;Step 3.1: Initialize genetic algorithm parameters and cluster K-means method parameters;
步骤3.2:生成初始化种群,种群中的每一个个体为任务集中的所有任务进行编码后的编码序列;Step 3.2: Generate an initialization population, and each individual in the population encodes a coding sequence for all tasks in the task set;
步骤3.3:当迭代代数没有达到最大迭代代数时,执行步骤3.3.1;否则,执行步骤3.4;Step 3.3: When the iteration algebra does not reach the maximum iteration algebra, go to Step 3.3.1; otherwise, go to Step 3.4;
步骤3.3.1:对种群内每一个个体生成测控方案初始解并计算目标函数值;Step 3.3.1: Generate the initial solution of the measurement and control plan for each individual in the population and calculate the objective function value;
步骤3.3.2:如果当代种群中的最大目标函数值大于最优目标函数值,则更新最优目标函数值并计数count1=count1+1;Step 3.3.2: If the maximum objective function value in the contemporary population is greater than the optimal objective function value, update the optimal objective function value and count count1 =count1 +1;
如果当代种群中最大目标函数值大于上一代种群中最大目标函数值,则更新计数count2=count2+1;If the maximum objective function value in the current population is greater than the maximum objective function value in the previous generation population, update the count count2 =count2 +1;
如果当代种群中最大目标函数值小于上一代种群中最大函数值乘以比例per,则更新计数count3=count3+1;If the maximum objective function value in the current population is less than the maximum function value in the previous generation population multiplied by the proportion per, then update the count count3 = count3 +1;
步骤3.3.3:根据目标函数值使用轮盘赌选择个体生成新的种群;Step 3.3.3: Use roulette to select individuals to generate a new population according to the objective function value;
步骤3.3.4:对新的种群使用基于聚类的交叉和变异方法进行更新;Step 3.3.4: Update the new population using a cluster-based crossover and mutation method;
步骤3.3.5:如果count1等于阈值Thre1,则更新k-means方法的参数K值并重新基于任务属性对任务集中的任务进行聚类,重置计数参数count1;Step 3.3.5: If count1 is equal to the threshold Thre1 , update the parameter K value of the k-means method and re-cluster the tasks in the task set based on the task attributes, and reset the count parameter count1 ;
如果count2等于Thre2,则用最优目标函数值对应的最优个体替换掉新的种群内目标函数值最小的个体,并重置计数参数count2;If count2 is equal to Thre2 , replace the individual with the smallest objective function value in the new population with the optimal individual corresponding to the optimal objective function value, and reset the count parameter count2 ;
如果count3等于Thre3,则对新的种群中目标函数值最大的个体进行局部优化,随机生成一个新的个体并删除新的种群中目标函数值最小的个体,重置计数参数count3;If count3 is equal to Thre3 , perform local optimization on the individual with the largest objective function value in the new population, randomly generate a new individual and delete the individual with the smallest objective function value in the new population, and reset the count parameter count3 ;
步骤3.3.6:将新的种群中最大目标函数值记录为上一代种群最大目标函数值;Step 3.3.6: Record the maximum objective function value in the new population as the maximum objective function value of the previous generation population;
步骤3.4:将最优目标函数值对应的个体作为测控方案输出。Step 3.4: Output the individual corresponding to the optimal objective function value as the measurement and control plan.
进一步地,步骤3.3.1中:对种群内每一个个体生成测控方案初始解的方法是任务安排算法,具体为:Further, in step 3.3.1: the method of generating the initial solution of the measurement and control plan for each individual in the population is the task scheduling algorithm, specifically:
对任务集中的所有任务按照编码序列依次按照可见时间窗顺序尝试安排给每个任务,如果全部时间窗都已经尝试且安排成功,则输出安排成功的结果作为初始解,否则,继续尝试安排;对每一个任务的具体安排方法为:For all tasks in the task set, try to arrange each task in the order of visible time windows according to the coding sequence. If all time windows have been tried and the arrangement is successful, the result of the successful arrangement will be output as the initial solution, otherwise, continue to try to arrange; The specific arrangements for each task are as follows:
1):计算任务t最早实际可用时间eatt和最晚实际可用时间latt;1): Calculate the earliest actual available time eatt and the latest actual available time latt of the task t ;
2):如果任务t在天线a的第i个时间窗长度大于任务t要求的测控时间长度,即并且任务t实际可用时间长度大于任务t的测控时间长度,即(latt-eatt)≥dt,则转至步骤3);否则,继续安排下一个任务;2): If the length of the i-th time window of the task t in the antenna a is greater than the length of the measurement and control time required by the task t, that is, And the actual available time length of task t is greater than the measurement and control time length of task t, that is (latt -eatt )≥dt , then go to step 3); otherwise, continue to arrange the next task;
3):将任务t最早实际可用时间eatt作为任务开始时间,如果任务t最早实际可用时间eatt等于任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗的开始时间转至步骤4);否则,转至步骤5);3): Take the earliest actual available time eatt of task t as the task start time, if the earliest actual available time eatt of task t is equal to the start time of the i-th visible time window arranged by task t on antenna a Go to step 4); otherwise, go to step 5);
4):将任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗将该窗口剩余时间窗更新为一个新时间窗4): Schedule task t in the ith visible time window on antenna a Update the remaining time window of this window to a new time window
5):将任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗将该窗口剩余时间窗更新为两个新的时间窗和5): Schedule task t in the ith visible time window on antenna a Update the remaining time window of this window to two new time windows and
进一步地,步骤3.2中生成初始化种群的方法是使用多种启发式初始化方法生成初始化种群,所述初始化种群中存在各种启发式初始化方法生成的个体。Further, the method for generating the initialization population in step 3.2 is to use multiple heuristic initialization methods to generate the initialization population, and there are individuals generated by various heuristic initialization methods in the initialization population.
进一步地,步骤3.3.4中使用基于聚类的交叉方法是指:Further, using the cluster-based crossover method in step 3.3.4 means:
将所有任务按照任务属性使用k-means聚类方法划分成K类任务;Divide all tasks into K types of tasks using k-means clustering method according to task attributes;
交叉时,分别从属于两组不同类别的任务中选择相等长度的基因片段进行交叉,任务的类别根据目标函数值使用轮盘赌进行选择。During crossover, gene fragments of equal length were selected from tasks belonging to two different categories for crossover, and the task category was selected using a roulette wheel based on the objective function value.
进一步地,步骤3.3.4中使用基于聚类的变异方法包括两种,一种是同一类别中的变异,另一种是不同类别中变异,在每一次变异操作中随机选择两种变异方式中的一种执行变异操作;Further, the clustering-based mutation method used in step 3.3.4 includes two types, one is mutation in the same category, and the other is mutation in different categories. In each mutation operation, one of the two mutation methods is randomly selected. A kind of perform mutation operation;
同一类别中的变异是指将个体内处在同一个类别内的两个任务进行位置交换。Variation in the same category refers to the swapping of two tasks within the same category within an individual.
不同类别中的变异是指将个体内处在不同类别中的两个任务交换位置。Variation in different classes refers to the swapping of two tasks in different classes within an individual.
进一步地,步骤3.1中基于聚类的方法是基于任务的属性进行聚类,所述任务的属性包括任务的最早允许开始时间、最晚允许结束时间、收益、任务要求测控时间长度,当K值更新重新进行聚类时,增加任务是否被成功安排这个特征。。Further, the method based on clustering in step 3.1 is to perform clustering based on the attribute of the task, and the attribute of the task includes the earliest allowable start time of the task, the latest allowable end time, income, and the length of the task required measurement and control time. When the K value is When updating re-clustering, add the feature of whether the task was successfully scheduled. .
本发明还提供了一种基于聚类的卫星测控调度系统,包括以下模块:The present invention also provides a cluster-based satellite measurement and control scheduling system, comprising the following modules:
输入模块:用于获取可调度的卫星资源、地面站资源、任务集以及卫星看见地面站的时间窗集合;Input module: used to obtain schedulable satellite resources, ground station resources, task sets, and time window sets for satellites to see ground stations;
模型构建模块:用于根据步骤1中所获取的内容构建混合整数规划模型;Model building module: used to build a mixed integer programming model based on the content obtained in step 1;
求解模块:用于对所述混合整数规划模型进行求解;Solving module: used to solve the mixed integer programming model;
方案输出模块:用于将求解得到的测控方案输出。Scheme output module: used to output the obtained measurement and control scheme.
采用上述技术方案,本发明具有如下有益效果:Adopt above-mentioned technical scheme, the present invention has following beneficial effect:
本发明一种基于聚类的卫星测控调度方法及系统,使用基于聚类的遗传算法C-BGA(Cluster-based genetic algorithm)求解卫星测控调度问题SRSP(satellite rangescheduling problem)问题。根据任务特征将任务分为K类,评估了任务与任务之间的相近关系,让相似的任务尽可能距离近而不同的任务尽可能远,在种群进行交叉和变异时,选择两个不同类别也就是不相似的两个任务类别中的个体进行交叉变异,实现了全局搜索和局部搜索的平衡,使得可以得到更高质量的解,很好的解决了序列依赖问题。通过任务安排算法对种群内每一个个体生成测控方案初始解,判断任务执行可行性,并进行有效安排。在初始化种群时,使用多种启发式初始化方法生成初始化种群,并不局限于一种策略来进行生成,使得解多样化。实验表明,使用本发明的C-BGA方法只需要KBGA大概三分之一的时间即可达到相同的优化效果。The present invention is a cluster-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system, which uses a cluster-based genetic algorithm C-BGA (Cluster-based genetic algorithm) to solve the satellite measurement and control scheduling problem SRSP (satellite rangescheduling problem). The tasks are divided into K categories according to the task characteristics, and the similarity between tasks is evaluated, so that similar tasks are as close as possible and different tasks are as far away as possible. When the population is crossed and mutated, two different categories are selected. That is, individuals in two dissimilar task categories are cross-mutated to achieve a balance between global search and local search, so that higher-quality solutions can be obtained, and the problem of sequence dependence can be well solved. Through the task scheduling algorithm, the initial solution of the measurement and control plan is generated for each individual in the population, and the feasibility of the task execution is judged and effectively arranged. When initializing the population, a variety of heuristic initialization methods are used to generate the initialization population, and the generation is not limited to one strategy, so that the solutions are diversified. Experiments show that using the C-BGA method of the present invention only needs about one third of the time of KBGA to achieve the same optimization effect.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明系统流程图;Fig. 1 is the system flow chart of the present invention;
图2为聚类方法中K值的变化曲线;Fig. 2 is the change curve of K value in the clustering method;
图3为L_L-5和L-H-5例子箱线图;Figure 3 is a boxplot of L_L-5 and L-H-5 examples;
图4为中等规模测试集结果;Figure 4 shows the results of the medium-scale test set;
图5为大规模测试集结果。Figure 5 shows the results of the large-scale test set.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将结合附图对本发明的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。The technical solutions of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings. Obviously, the described embodiments are a part of the embodiments of the present invention, but not all of the embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
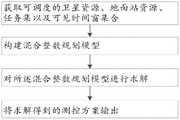
一种基于聚类的卫星测控调度方法,如图1所示,包括以下步骤:A cluster-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method, as shown in Figure 1, includes the following steps:
步骤1:获取可调度的卫星资源、地面站资源、任务集以及卫星看见地面站的时间窗集合;Step 1: Obtain schedulable satellite resources, ground station resources, task sets, and time window sets for satellites to see the ground station;
步骤2:根据步骤1中所获取的内容构建混合整数规划模型。Step 2: Build a mixed integer programming model based on the content obtained in Step 1.
本实施例中,混合整数规划模型是:In this embodiment, the mixed integer programming model is:
目标函数为:The objective function is:
其中,pt表示任务t的收益,为0-1决策变量,表示任务t是否安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗,1为安排,0为否,t表示任务,T表示任务集,a表示天线,A表示天线集合,表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗,TWta表示任务t安排在天线a上的时间窗集合;Among them, pt represents the income of task t, is a 0-1 decision variable, indicating whether task t is arranged in the ith visible time window on antenna a, 1 is the arrangement, 0 is no, t represents the task, T represents the task set, a represents the antenna, and A represents the antenna set, Indicates that task t is arranged on the ith visible time window on antenna a, TWta represents the set of time windows in which task t is arranged on antenna a;
约束条件是:The constraints are:
式2表明任务需要在允许的开始时间之后开始执行任务;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的实际的测控时间长度,dt表示任务t要求的测控时间长度;Equation 2 indicates that the task needs to start executing the task after the allowed start time; Represents the actual measurement and control time length that task t arranges on the i-th visible time window on antenna a, and dt represents the measurement and control time length required by task t;
式3表明任务需要在允许的结束时间之前完成任务;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的实际开始时间,表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的结束时间;Equation 3 indicates that the task needs to be completed by the allowed end time; represents the actual start time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a, Represents the end time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a;
式4表明任务最多可以执行一次;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的的最早允许开始时间;Equation 4 indicates that the task can be executed at most once; Represents the earliest allowable start time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a;
式5表明任务实际执行时间应当与要求时间相同;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗上的的最晚允许结束时间;Equation 5 indicates that the actual execution time of the task should be the same as the required time; Represents the latest allowable end time of task t scheduled on the ith visible time window on antenna a;
式6表明任务执行过程需要在一个地面站时间范围内;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗的开始时间;Equation 6 indicates that the task execution process needs to be within a ground station time range; Represents the start time of the i-th visible time window scheduled for task t on antenna a;
式7表明每个任务只能由一个天线服务;Equation 7 indicates that each task can only be served by one antenna;
式8表明每个任务只能在一个可见的时间窗口内执行;表示任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗的结束时间;Equation 8 indicates that each task can only be executed within a visible time window; Represents the end time of the i-th visible time window scheduled for task t on antenna a;
式9表明每个任务在全部天线上最多执行一次;Equation 9 indicates that each task is performed at most once on all antennas;
式10表明每个任务在全部时间窗内最多执行一次;Equation 10 indicates that each task is executed at most once in the entire time window;
式11表明任务在规划周期内最多被执行一次;Equation 11 indicates that the task is executed at most once in the planning period;
式12表明两个任务要满足任务转换时间的间隔要求;γ表示任务之间的转换时间。Equation 12 indicates that the two tasks must meet the task transition time interval requirement; γ represents the transition time between tasks.
步骤3:对所述混合整数规划模型进行求解。Step 3: Solve the mixed integer programming model.
本实施例中,对所述混合整数规划模型进行求解的方法是基于聚类的遗传算法。In this embodiment, the method for solving the mixed integer programming model is a genetic algorithm based on clustering.
基于聚类的遗传算法是:The genetic algorithm based on clustering is:
步骤3.1:初始化遗传算法参数、聚类K-means方法参数;Step 3.1: Initialize genetic algorithm parameters and cluster K-means method parameters;
步骤3.2:生成初始化种群,种群中的每一个个体为任务集中的所有任务进行编码后的编码序列;Step 3.2: Generate an initialization population, and each individual in the population encodes a coding sequence for all tasks in the task set;
本实施例中,生成初始化种群的方法是使用多种启发式初始化方法生成初始化种群,所述初始化种群中存在各种启发式初始化方法生成的个体。In this embodiment, the method for generating an initialization population is to use a variety of heuristic initialization methods to generate an initialization population, and there are individuals generated by various heuristic initialization methods in the initialization population.
在本实施例中,使用的多种启发式初始化方法包括四种启发式种群初始化方式和一种随机初始化种群方式。In this embodiment, the multiple heuristic initialization methods used include four heuristic population initialization methods and one random initialization population method.
四种启发式种群初始化分别被称为基于最早允许开始时间排序的初始化方法、基于最晚允许结束时间排序的初始化方式、基于任务收益排序的初始化方式和基于任务持续时间排序的初始化方式。The four heuristic population initializations are called the initialization method based on the earliest allowable start time, the initialization method based on the latest allowable end time, the initialization method based on the task revenue order and the initialization method based on the task duration order.
基于最早允许开始时间排序的初始化(EST):按照测控任务的最早允许开始时间从前至后的顺序依次排序,根据排序后的顺序生成个体。Initialization based on the earliest allowable start time (EST): sort according to the earliest allowable start time of the measurement and control tasks from front to back, and generate individuals according to the sorted order.
基于最晚允许结束时间排序的初始化(LET):按照测控任务的最晚允许结束时间从前至后的顺序依次排序,根据排序后的顺序生成个体。Initialization based on the latest allowable end time (LET): sort according to the latest allowable end time of the measurement and control tasks from front to back, and generate individuals according to the sorted order.
基于任务收益排序的初始化(TP):按照测控任务的任务收益从大到小的顺序降序排序,根据排序后的顺序生成个体。Initialization based on task revenue sorting (TP): sort in descending order according to the task revenue of the measurement and control tasks from large to small, and generate individuals according to the sorted order.
基于任务持续时间排序的初始化(TD):按照测控任务的任务持续时间从小到大的顺序升序排序,根据排序后的顺序生成个体。Initialization based on task duration sorting (TD): Sort in ascending order according to the task duration of the measurement and control tasks from small to large, and generate individuals according to the sorted order.
在采取每一种启发式规则生成种群个体后,需要通过个体部分序列调整的方式让个体更具有多样性。将启发式和局部随机的方式结合,可以让每一个个体更容易找到一个好的搜索起始位置。四种启发式方法和随机方法分别占据种群全部个体的各20%。当然,四种启发式方法和随机方法分别占据种群全部个体的比例也可以根据需要进行调整,为了增加解的多样性,启发式初始化方法还可以包括别的不限于上面提到的四种启发式方法。After each heuristic rule is used to generate population individuals, it is necessary to adjust the individual parts of the sequence to make the individuals more diverse. Combining heuristics and local randomization makes it easier for each individual to find a good search starting position. The four heuristic methods and random methods account for 20% of all individuals in the population respectively. Of course, the proportion of the four heuristic methods and random methods respectively occupying all individuals in the population can also be adjusted as needed. In order to increase the diversity of solutions, the heuristic initialization method can also include other but not limited to the four heuristics mentioned above. method.
步骤3.3:当迭代代数没有达到最大迭代代数时,执行步骤3.3.1;否则,执行步骤3.4;Step 3.3: When the iteration algebra does not reach the maximum iteration algebra, go to Step 3.3.1; otherwise, go to Step 3.4;
步骤3.3.1:对种群内每一个个体生成测控方案初始解并计算目标函数值。Step 3.3.1: Generate the initial solution of the measurement and control plan for each individual in the population and calculate the objective function value.
本实施例中,步骤3.3.1中:对种群内每一个个体生成测控方案初始解的方法是任务安排算法,具体为:In this embodiment, in step 3.3.1: the method for generating the initial solution of the measurement and control scheme for each individual in the population is a task scheduling algorithm, specifically:
对任务集中的所有任务按照编码序列依次按照可见时间窗顺序尝试安排给每个任务,如果全部时间窗都已经尝试且安排成功,则输出安排成功的结果作为初始解,否则,继续尝试安排;对每一个任务的具体安排方法为:For all tasks in the task set, try to arrange each task in the order of visible time windows according to the coding sequence. If all time windows have been tried and the arrangement is successful, the result of the successful arrangement will be output as the initial solution, otherwise, continue to try to arrange; The specific arrangements for each task are as follows:
1):计算任务t最早实际可用时间eatt和最晚实际可用时间latt;1): Calculate the earliest actual available time eatt and the latest actual available time latt of the task t ;
2):如果任务t在天线a的第i个时间窗长度大于任务t要求的测控时间长度,即并且任务t实际可用时间长度大于任务t的测控时间长度,即(latt-eatt)≥dt,则转至步骤3);否则,继续安排下一个任务;2): If the i-th time window length of task t in antenna a is greater than the measurement and control time length required by task t, that is, And the actual available time length of task t is greater than the measurement and control time length of task t, that is (latt -eatt )≥dt , then go to step 3); otherwise, continue to arrange the next task;
3):将任务t最早实际可用时间eatt作为任务开始时间,如果任务t最早实际可用时间eatt等于任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗的开始时间转至步骤4);否则,转至步骤5);3): Take the earliest actual available time eatt of task t as the task start time, if the earliest actual available time eatt of task t is equal to the start time of the i-th visible time window arranged by task t on antenna a Go to step 4); otherwise, go to step 5);
4):将任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗将该窗口剩余时间窗更新为一个新时间窗4): Schedule task t in the ith visible time window on antenna a Update the remaining time window of this window to a new time window
5):将任务t安排在天线a上第i个可见时间窗将该窗口剩余时间窗更新为两个新的时间窗和5): Schedule task t in the ith visible time window on antenna a Update the remaining time window of this window to two new time windows and
本实施例中,对任务集中的所有任务依次判断每一个时间窗是否能够执行任务。如果时间窗长度超过测控任务要求的时间则尝试安排任务。本发明采用一种快速判断方法确定任务是否具有被安排的可能,首先需要引入两个新的变量eatt和latt,分别表示最早实际可用时间和最晚实际可用时间,计算方法如公式13所示。如果实际可用时间超过测控任务要求时间则可以成功安排,任务被安排在最早实际可用时间开始执行。任务被成功安排后需要更新剩余的可用时间窗资源,如果任务的最早实际可用时间等于任务最早允许开始时间则将该窗口剩余的时间窗裁剪为一个新的时间窗,否则,将该窗口剩余的时间窗裁剪为两个新的时间窗。完成时间窗裁剪后更新时间窗集合,并开始安排下一任务。In this embodiment, all tasks in the task set are sequentially judged whether each time window can execute the task. If the time window length exceeds the time required by the measurement and control task, try to schedule the task. The present invention adopts a quick judgment method to determine whether the task has the possibility of being scheduled. First, two new variables eatt and latt need to be introduced, which represent the earliest actual available time and the latest actual available time respectively. The calculation method is as shown in formula 13. Show. If the actual available time exceeds the time required by the measurement and control task, it can be successfully scheduled, and the task is scheduled to be executed at the earliest actual available time. After the task is successfully scheduled, the remaining available time window resources need to be updated. If the earliest actual available time of the task is equal to the earliest allowable start time of the task, the remaining time window of the window will be cut into a new time window, otherwise, the remaining time window of the window will be cut into a new time window. The time window is clipped to two new time windows. After finishing the time window clipping, update the time window set and start scheduling the next task.
步骤3.3.2:如果当代种群中的最大目标函数值大于最优目标函数值,则更新最优目标函数值并计数count1=count1+1;本实施例中的最优目标函数值是整个优化过程中的最优目标函数值,其初始值可以设置为0,然后在每一次迭代中,将每一代种群中的最大目标函数值与其进行比较更新得到的最优值。Step 3.3.2: If the maximum objective function value in the contemporary population is greater than the optimal objective function value, update the optimal objective function value and count count1 =count1 +1; the optimal objective function value in this embodiment is the entire The initial value of the optimal objective function value in the optimization process can be set to 0, and then in each iteration, the optimal value obtained by comparing the maximum objective function value in each generation of the population with it is updated.
如果当代种群中最大目标函数值大于上一代种群中最大目标函数值,则更新计数count2=count2+1;If the maximum objective function value in the current population is greater than the maximum objective function value in the previous generation population, update the count count2 =count2 +1;
如果当代种群中最大目标函数值小于上一代种群中最大函数值乘以比例per,则更新计数count3=count3+1;If the maximum objective function value in the current population is less than the maximum function value in the previous generation population multiplied by the proportion per, then update the count count3 = count3 +1;
步骤3.3.3:根据目标函数值使用轮盘赌选择个体生成新的种群;Step 3.3.3: Use roulette to select individuals to generate a new population according to the objective function value;
本实施例中,使用轮盘赌方法选择出个体生成新的种群,然后对该新种群进行交叉和变异。In this embodiment, individuals are selected by the roulette method to generate a new population, and then crossover and mutation are performed on the new population.
使用轮盘赌选择过程需要更好地反映出种群内个体之间的表现差异,本发明根据个体的目标函数值利用轮盘赌的方法进行个体和任务类别的选择,让具有更好表现的个体和所处的类别更容易被选择。利用轮盘赌选择个体的概率公式如下所示:Using the roulette wheel selection process needs to better reflect the performance differences between individuals in the population. The present invention uses the roulette wheel method to select individuals and task categories according to the individual's objective function value, so that individuals with better performance can be selected. and the category in which it is placed is easier to select. The probability formula for selecting an individual using the roulette wheel is as follows:
其中,是个体j的概率,fj是个体j的目标函数值,P为种群。in, is the probability of individual j, fj is the objective function value of individual j, and P is the population.
步骤3.3.4:对新的种群使用基于聚类的交叉和变异方法进行更新。Step 3.3.4: Update the new population using a cluster-based crossover and mutation method.
本实施例中,基于聚类的交叉方法是指:In this embodiment, the clustering-based crossover method refers to:
将所有任务按照任务属性使用k-means聚类方法划分成K类任务;Divide all tasks into K types of tasks using k-means clustering method according to task attributes;
交叉时,分别从属于两组不同类别的任务中选择相等长度的基因片段进行交叉。具体是根据轮盘赌选择一个类别,在该类别中随机选择一个任务,以随机选择的这个任务作为基因片段的开始。然后根据轮盘赌选择另外一个类别,选择时,去除当前已选的任务类别。根据轮盘赌选择类别的概率公式为:During crossover, gene fragments of equal length were selected from the tasks belonging to two different categories for crossover. Specifically, a category is selected according to the roulette wheel, and a task is randomly selected in this category, and the randomly selected task is used as the beginning of the gene segment. Then select another category according to the roulette wheel, and when selected, remove the currently selected task category. The formula for the probability of choosing a class according to the roulette wheel is:
其中,是类别k的概率,是类别k中任务tk的目标函数值,ft表示任务t的目标函数值,K为类别集。in, is the probability of class k, is the objective function value of task tk in category k, ft represents the objective function value of task t, and K is the category set.
基于聚类的变异方法包括两种,一种是同一类别中的变异,另一种是不同类别中变异,在每一次变异操作中随机选择两种变异方式中的一种执行变异操作;There are two kinds of mutation methods based on clustering, one is mutation in the same category, and the other is mutation in different categories. In each mutation operation, one of the two mutation methods is randomly selected to perform mutation operation;
同一类别中的变异是指将个体内处在同一个类别内的两个任务进行位置交换。Variation in the same category refers to the swapping of two tasks within the same category within an individual.
不同类别中的变异是指将个体内处在不同类别中的两个任务交换位置。Variation in different classes refers to the swapping of two tasks in different classes within an individual.
采用这两种变异方式既可以实现具有相似数据特征任务之间的执行位置交换,也可以让被选中任务与特征差异性较大任务之间完成对换。采用两种变异方式可以增加变异的多样性,让算法更有机会找到更好的任务执行顺序。通过基于聚类的交叉和变异更新种群中的个体,从两个不同类别也就是不相似的两个任务类别中的个体进行交叉变异,实现了全局搜索和局部搜索的平衡,使得可以得到更高质量的解,很好的解决了序列依赖问题。Using these two mutation methods can not only realize the execution position exchange between tasks with similar data characteristics, but also complete the exchange between the selected task and the task with large difference in characteristics. Using two mutation methods can increase the diversity of mutation and give the algorithm a better chance to find a better task execution order. Through cluster-based crossover and mutation update individuals in the population, crossover and mutation are performed from individuals in two different categories, that is, two dissimilar task categories, to achieve a balance between global search and local search, so that higher The quality of the solution is a good solution to the sequence dependence problem.
步骤3.3.5:如果count1等于阈值Thre1,则更新k-means方法的参数K值并重新基于任务属性对任务集中的任务进行聚类,重置计数参数count1;Step 3.3.5: If count1 is equal to the threshold Thre1 , update the parameter K value of the k-means method and re-cluster the tasks in the task set based on the task attributes, and reset the count parameter count1 ;
如果count2等于Thre2,则用最优目标函数值对应的最优个体替换掉新的种群内目标函数值最小的个体,并重置计数参数count2;If count2 is equal to Thre2 , replace the individual with the smallest objective function value in the new population with the optimal individual corresponding to the optimal objective function value, and reset the count parameter count2 ;
如果count3等于Thre3,则对新的种群中目标函数值最大的个体进行局部优化,随机生成一个新的个体并删除新的种群中目标函数值最小的个体,,重置计数参数count3;If count3 is equal to Thre3 , perform local optimization on the individual with the largest objective function value in the new population, randomly generate a new individual and delete the individual with the smallest objective function value in the new population, and reset the count parameter count3 ;
步骤3.3.6:将新的种群中最大目标函数值记录为上一代种群最大目标函数值;Step 3.3.6: Record the maximum objective function value in the new population as the maximum objective function value of the previous generation population;
聚类方法目标是将样本集合根据数据特征分割成多个子集合。这种方法根据数据特征的相似度,将数据分成多组离散或者层次结构的方法。分类最终要达到的效果是在一个组内的各个样本之间尽可能接近,不是一个组的样本差异明显。本发明选择聚类算法的原因一方面是想要充分利用卫星任务数据,利用数据驱动优化过程,另一方面是卫星任务数据在规划调度方面存在难以确定的分类标准,采用聚类方法可以更好地实现任务根据特征分类。为了防止由于部分特征由于量纲过大导致计算聚类结果存在偏差,需要先对特征数据进行归一化(normalization)。通过归一化可以让数据不受量纲和单位的影响,更加凸显数据特征本身的内容。归一化的计算公式如下:The goal of clustering methods is to divide the sample set into multiple subsets according to data characteristics. This method divides data into multiple groups of discrete or hierarchical structures according to the similarity of data features. The final effect of classification is to be as close as possible between the samples in a group, not the samples of a group are significantly different. The reason why the present invention selects the clustering algorithm is that on the one hand, it wants to make full use of the satellite mission data and use the data to drive the optimization process; The realization tasks are classified according to their characteristics. In order to prevent the deviation of the calculated clustering results due to the excessive dimension of some features, it is necessary to normalize the feature data first. Through normalization, the data can be freed from the influence of dimensions and units, and the content of the data characteristics itself can be more prominent. The normalization calculation formula is as follows:
其中,y是特征值,ymax是特征y的最大值,ymin是特征y的最小值。where y is the feature value, ymax is the maximum value of feature y, and ymin is the minimum value of feature y.
本实施例中聚类方法的步骤为:The steps of the clustering method in this embodiment are:
输入:任务特征矩阵(每一列表示一种特征),特征数量,分类的数量KInput: task feature matrix (each column represents a feature), the number of features, the number of categories K
输出:聚类结果Output: Clustering results
1):随机从特征集合中选择K个样本作为聚类中心(1,2,…,K);1): randomly select K samples from the feature set as cluster centers (1,2,...,K);
2):计算数据到各个中心点的欧式距离,选择最近的中心点作为数据的类别;2): Calculate the Euclidean distance from the data to each center point, and select the nearest center point as the data category;
3):对每一类重新计算得到新的中心点,根据公式|Cj|为属于j类数据的数量,x表示数据;3): Recalculate the new center point for each class, according to the formula |Cj | is the number of data belonging to class j, and x represents the data;
4):如果中心点发生变化,转至步骤2;否则,转至步骤5;4): If the center point changes, go to step 2; otherwise, go to step 5;
5):输出聚类结果。5): Output the clustering results.
本实施例中,基于聚类的方法是基于任务的特征进行聚类,所述任务的特征包括任务的最早允许开始时间、最晚允许结束时间、收益、任务要求测控时间长度,任务特征矩阵每一列表示一种任务特征,构成矩阵,当发生重新计算聚类时,将从开始优化至今最优方案的任务执行结果加入到特征矩阵最右侧一列,即在达到某个条件需要重新进行聚类时,增加任务是否被成功安排这个特征,已安排的任务标记为1,未安排的标记为0。本发明的聚类方法根据任务特征将任务数据分成K个类别,评估了任务与任务之间的相近关系,让相似的任务尽可能距离近而不同的任务尽可能远,在种群进行交叉和变异时,从两个不同类别也就是不相似的两个任务类别中的个体进行交叉变异,使得可以得到更高质量的解,改进了遗传算法的优化过程。聚类方法的类别数随着优化过程发生改变,下面也将通过实验来证明聚类为遗传算法提供的信息更有价值。In this embodiment, the method based on clustering is to perform clustering based on the characteristics of the tasks, and the characteristics of the tasks include the earliest allowable start time of the task, the latest allowable end time, revenue, and the length of the measurement and control time required by the task. One column represents a task feature and forms a matrix. When recalculation of clustering occurs, the task execution results from the beginning of optimization to the optimal solution are added to the rightmost column of the feature matrix, that is, when a certain condition is reached, clustering needs to be performed again. When , add the feature of whether the task is successfully scheduled, the scheduled task is marked as 1, and the unscheduled task is marked as 0. The clustering method of the present invention divides task data into K categories according to task characteristics, evaluates the similarity between tasks, makes similar tasks as close as possible and different tasks as far as possible, and performs crossover and mutation in the population. When , cross-mutation is performed from individuals in two different categories, that is, two dissimilar task categories, so that a higher quality solution can be obtained and the optimization process of the genetic algorithm is improved. The number of categories of the clustering method changes with the optimization process, and the following experiments will also prove that the information provided by the clustering for the genetic algorithm is more valuable.
对于SRSP问题而言,聚类分成的簇的数量K应该随着优化过程发生改变,固定的一个值容易在优化过程进行到一定阶段后由于分类不够准确而产生无效搜索。为了提升搜索效率和搜索效果,本实施例中K值更新是当count1等于阈值Thre1,更新k-means方法的参数K值并重新基于任务特征对任务集中的任务进行聚类,K值的更新曲线可以预先进行设定,本实施例中选择让分类数量K以触发改变条件数量减少1的方式在[上届、下届]区间范围不断变化,K值变化的过程如图2所示,重新进行聚类时,增加任务是否被成功执行这个特征。For the SRSP problem, the number K of clusters into which the clustering is divided should change with the optimization process, and a fixed value is likely to cause invalid search due to inaccurate classification after the optimization process reaches a certain stage. In order to improve the search efficiency and search effect, the K value update in this embodiment is to update the parameter K value of the k-means method when count1 is equal to the threshold Thre1 , and re-cluster the tasks in the task set based on the task characteristics. The update curve can be set in advance. In this embodiment, the number of classifications K is selected to change continuously in the interval range of [last session, next session] in the manner of reducing the number of triggering change conditions by 1. The process of changing the value of K is shown in Figure 2. When re-clustering, add the feature of whether the task was successfully executed.
步骤3.4:将最优目标函数值对应的个体作为测控方案输出。Step 3.4: Output the individual corresponding to the optimal objective function value as the measurement and control plan.
本发明基于聚类的遗传算法改善了遗传算法全局搜索较好而局部搜索性能力差的情况,提升了遗传算法的局部搜索表现。The cluster-based genetic algorithm of the present invention improves the situation that the genetic algorithm has good global search ability and poor local search ability, and improves the local search performance of the genetic algorithm.
步骤4:将求解得到的测控方案输出。Step 4: Output the obtained measurement and control scheme.
实验验证Experimental verification
1)不同任务规模下规划结果1) Planning results under different task scales
不同密度的30个instances被用来验证算法的规划表现。结果如表1所示,算例规模的增长伴随而来的是得到收益值的增多,表1中最左列的场景编号表达式中,最左边的三个符号S表示小规模,M表示中规模,L表示大规模;中间的两个符号L表示低密度,H表示高密度;最右边的数字表示序号。当任务规模增加到中等后,收益的增长幅度开始放缓。这是由于有限的卫星和地面站资源在众多的任务中找到一个更好的任务执行方案变得格外困难。C-BGA算法在30个场景中均取得了很好的规划结果。在小规模和中等场景中,规划结果由好到差依次由C-BGA、烟花算法FWA(Fireworks algorithm)、带禁忌策略的自适应大邻域搜索算法ALNS/TPF(Tabu-based adaptive large neighborhood search)、基于知识的遗传算法KBGA(Knowledge based genetic algorithm)算法。大规模场景中,KBGA和ALNS/TPF算法介于C-BGA和FWA算法之间。从整体趋势上可以看出,C-BGA算法在较大规模场景中更容易获得超过其他对比算法的表现。Thirty instances of different densities are used to verify the planning performance of the algorithm. The results are shown in Table 1. The increase in the scale of the calculation example is accompanied by an increase in the obtained income value. In the scene number expression in the leftmost column of Table 1, the three symbols S on the left represent small scale, and M represents medium. Scale, L indicates large scale; the two symbols in the middle L indicate low density, H indicates high density; the rightmost number indicates the serial number. When the mission size increases to moderate, the growth rate of revenue starts to slow down. This is due to the limited resources of satellites and ground stations that make it particularly difficult to find a better mission execution plan among the numerous missions. The C-BGA algorithm achieves good planning results in all 30 scenarios. In small-scale and medium-scale scenarios, the planning results are ranked from good to bad by C-BGA, FWA (Fireworks algorithm), and ALNS/TPF (Tabu-based adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm) with tabu strategy. ), knowledge-based genetic algorithm KBGA (Knowledge based genetic algorithm) algorithm. In large-scale scenarios, KBGA and ALNS/TPF algorithms are between C-BGA and FWA algorithms. It can be seen from the overall trend that the C-BGA algorithm is more likely to outperform other comparison algorithms in larger-scale scenarios.
表1 30个场景不同任务规模下的收益对比表Table 1 Comparison of benefits under different task scales in 30 scenarios
2)算法稳定性分析2) Algorithm stability analysis
大规模instances更容易反映算法的稳定性表现,L-L-5和L-H-5例子箱线图如图3所示。C-BGA算法的稳定性是最好的,在1000个任务的instance下保持着较小的波动性。表现最差的是ALNS/TPF,最为容易获得离平均值偏差比较大的结果。FWA算法和KBGA算法处在C-BGA算法和ALNS/TPF算法之间。Large-scale instances are more likely to reflect the stability performance of the algorithm. The boxplots of the L-L-5 and L-H-5 examples are shown in Figure 3. The stability of the C-BGA algorithm is the best, maintaining a small volatility under the instance of 1000 tasks. The worst performance is ALNS/TPF, and it is easiest to obtain results with a large deviation from the average. The FWA algorithm and the KBGA algorithm are between the C-BGA algorithm and the ALNS/TPF algorithm.
3)优化时间分析3) Optimization time analysis
本文对比了基于聚类的遗传算法C_BGA算法达到KBGA相同平均优化结果所需要的时间,结果如图4和图5所示,图4和图5分别表示的是中等规模和大规模的优化结果,但是通过实验,得出的结果是一致的,图中100%的柱表示KBGA算法达到每一个实例平均表现所用的时间,黑色的柱表示本发明基于聚类的遗传算法C-BGA算法占参考算法时间的百分比。从结果可以看出,C-BGA算法只需要KBGA大概三分之一的时间即可达到相同的优化效果。也就是说,在种群初始化之后的很短时间便可以找到一个质量很好的解。This paper compares the time required for the cluster-based genetic algorithm C_BGA algorithm to achieve the same average optimization result of KBGA. However, through experiments, the results obtained are consistent. The 100% column in the figure represents the time it takes for the KBGA algorithm to achieve the average performance of each instance, and the black column represents the cluster-based genetic algorithm C-BGA algorithm of the present invention accounts for the reference algorithm. percentage of time. It can be seen from the results that the C-BGA algorithm only needs about one third of the time of KBGA to achieve the same optimization effect. That is, a solution of good quality can be found a short time after the population is initialized.
最后应说明的是:以上各实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述各实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分或者全部技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的范围。Finally, it should be noted that the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, but not to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: The technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments can still be modified, or some or all of the technical features thereof can be equivalently replaced; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention. scope.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210308731 | 2022-03-28 | ||
| CN2022103087317 | 2022-03-28 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114781508Atrue CN114781508A (en) | 2022-07-22 |
| CN114781508B CN114781508B (en) | 2024-11-01 |
Family
ID=82431851
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210407679.0AActiveCN114781508B (en) | 2022-03-28 | 2022-04-19 | Satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system based on clustering |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114781508B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115460304A (en)* | 2022-11-10 | 2022-12-09 | 广州铭创通讯科技有限公司 | Protocol layer data analysis method and system for intercepting wireless communication |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040158832A1 (en)* | 2003-01-28 | 2004-08-12 | Gal Chechik | Method and system for scheduling image acquistion events based on dynamic programming |
| CN107678850A (en)* | 2017-10-17 | 2018-02-09 | 合肥工业大学 | Repeater satellite method for scheduling task and device |
| WO2021035911A1 (en)* | 2019-08-28 | 2021-03-04 | 青岛蓝海未来海洋科技有限责任公司 | Method and system for planning path of unmanned surface vehicle based on forward/reverse data-driven linear parameter-varying genetic algorithm |
| CN112766813A (en)* | 2021-02-05 | 2021-05-07 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Air-space cooperative observation complex task scheduling method and system |
- 2022
- 2022-04-19CNCN202210407679.0Apatent/CN114781508B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040158832A1 (en)* | 2003-01-28 | 2004-08-12 | Gal Chechik | Method and system for scheduling image acquistion events based on dynamic programming |
| CN107678850A (en)* | 2017-10-17 | 2018-02-09 | 合肥工业大学 | Repeater satellite method for scheduling task and device |
| WO2021035911A1 (en)* | 2019-08-28 | 2021-03-04 | 青岛蓝海未来海洋科技有限责任公司 | Method and system for planning path of unmanned surface vehicle based on forward/reverse data-driven linear parameter-varying genetic algorithm |
| CN112766813A (en)* | 2021-02-05 | 2021-05-07 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Air-space cooperative observation complex task scheduling method and system |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 宋彦杰等: "面向多星任务规划问题的改进遗传算法", 《控制理论与应用》, vol. 36, no. 09, 30 September 2019 (2019-09-30)* |
| 张超;李艳斌;: "多敏捷卫星协同任务规划调度方法", 科学技术与工程, no. 22, 8 August 2017 (2017-08-08)* |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115460304A (en)* | 2022-11-10 | 2022-12-09 | 广州铭创通讯科技有限公司 | Protocol layer data analysis method and system for intercepting wireless communication |
| CN115460304B (en)* | 2022-11-10 | 2023-01-31 | 广州铭创通讯科技有限公司 | Protocol layer data analysis method and system for intercepting wireless communication |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114781508B (en) | 2024-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN118798588B (en) | Reservoir group multi-target intelligent optimal scheduling method based on multi-constraint coupling | |
| CN108053119A (en) | A kind of Modified particle swarm optimization algorithm for solving zero-waiting Flow Shop Scheduling | |
| CN102063339B (en) | Resource load balancing method and equipment based on cloud computing system | |
| CN112995289A (en) | Internet of vehicles multi-target computing task unloading scheduling method based on non-dominated sorting genetic strategy | |
| CN102609714A (en) | Novel classifier based on information gain and online support vector machine, and classification method thereof | |
| CN117077981B (en) | Method and device for distributing stand by fusing neighborhood search variation and differential evolution | |
| CN114781508A (en) | Clustering-based satellite measurement and control scheduling method and system | |
| CN108022045A (en) | A distribution estimation method | |
| CN117519244A (en) | Unmanned plane cluster collaborative detection multi-target path planning method and system | |
| CN116629586A (en) | Airport guarantee vehicle scheduling method and system based on ALNS | |
| CN110300417A (en) | The energy efficiency optimization method and device of Communication Network for UAVS | |
| CN113657958B (en) | A customized product demand transformation method based on directional optimization of association rules | |
| CN114330891B (en) | A multi-objective resource scheduling method for cloud computing | |
| CN118365065B (en) | A multi-task resource allocation method and system based on social genetic algorithm | |
| CN119211041A (en) | Bandwidth fragment adaptive arrangement method and device based on DT algorithm | |
| CN118863501A (en) | Workshop scheduling method, device, storage medium and equipment based on adaptive genetic algorithm | |
| CN117579500B (en) | A network traffic prediction method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN116502776B (en) | A flight recovery modeling method, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114298376B (en) | Software project scheduling method based on heuristic discrete artificial bee colony algorithm | |
| Ying et al. | Hybrid-directional planning: improving improvement heuristics for scheduling resource-constrained projects | |
| D’Ambrosio et al. | Optimizing cellular automata through a meta-model assisted memetic algorithm | |
| CN110297977B (en) | Personalized recommendation single-target evolution method for crowd funding platform | |
| CN111800310B (en) | Scheduling method for task management module of Internet of things test cloud platform | |
| CN119010082B (en) | Operation optimization method, device, electronic device and storage medium of photovoltaic charging station | |
| CN117745042B (en) | Multi-disaster-point emergency material scheduling method, device, medium and equipment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |