CN114748644A - Preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrix - Google Patents
Preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrixDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114748644A CN114748644ACN202210548537.6ACN202210548537ACN114748644ACN 114748644 ACN114748644 ACN 114748644ACN 202210548537 ACN202210548537 ACN 202210548537ACN 114748644 ACN114748644 ACN 114748644A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- zif
- pbs solution
- volume ratio
- dox
- drug
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000013154zeolitic imidazolate framework-8Substances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription108
- MFLKDEMTKSVIBK-UHFFFAOYSA-Nzinc;2-methylimidazol-3-ideChemical compound[Zn+2].CC1=NC=C[N-]1.CC1=NC=C[N-]1MFLKDEMTKSVIBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription108
- 108010053210PhycocyaninProteins0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription46
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription34
- 239000003937drug carrierSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription26
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription20
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription5
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription89
- LXBGSDVWAMZHDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-methyl-1h-imidazoleChemical compoundCC1=NC=CN1LXBGSDVWAMZHDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription22
- CERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethacrylic acidChemical compoundCC(=C)C(O)=OCERQOIWHTDAKMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription20
- ROOXNKNUYICQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-Nammonium persulfateChemical compound[NH4+].[NH4+].[O-]S(=O)(=O)OOS([O-])(=O)=OROOXNKNUYICQNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription18
- 239000002202Polyethylene glycolSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- 229920001223polyethylene glycolPolymers0.000claimsdescription15
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterChemical compoundOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription13
- 239000011259mixed solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 229910001870ammonium persulfateInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription9
- QNILTEGFHQSKFF-UHFFFAOYSA-Nn-propan-2-ylprop-2-enamideChemical compoundCC(C)NC(=O)C=CQNILTEGFHQSKFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000claimsdescription8
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription8
- 238000005119centrifugationMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000006228supernatantSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000003760magnetic stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000claimsdescription4
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000001291vacuum dryingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 241000195493CryptophytaSpecies0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000002156mixingMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- XLSZMDLNRCVEIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NmethylimidazoleNatural productsCC1=CNC=N1XLSZMDLNRCVEIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000claims1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000abstractdescription72
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000abstractdescription72
- AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-NDoxorubicinChemical compoundO([C@H]1C[C@@](O)(CC=2C(O)=C3C(=O)C=4C=CC=C(C=4C(=O)C3=C(O)C=21)OC)C(=O)CO)[C@H]1C[C@H](N)[C@H](O)[C@H](C)O1AOJJSUZBOXZQNB-TZSSRYMLSA-N0.000abstractdescription24
- 206010028980NeoplasmDiseases0.000abstractdescription21
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-LCalcium carbonateChemical compound[Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=OVTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000abstractdescription16
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription16
- 238000011068loading methodMethods0.000abstractdescription15
- 201000011510cancerDiseases0.000abstractdescription14
- 229920000344molecularly imprinted polymerPolymers0.000abstractdescription14
- 229960004679doxorubicinDrugs0.000abstractdescription11
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000abstractdescription10
- 229910000019calcium carbonateInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription8
- 231100000331toxicToxicity0.000abstractdescription8
- 230000002588toxic effectEffects0.000abstractdescription8
- OVBPIULPVIDEAO-LBPRGKRZSA-Nfolic acidChemical compoundC=1N=C2NC(N)=NC(=O)C2=NC=1CNC1=CC=C(C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1OVBPIULPVIDEAO-LBPRGKRZSA-N0.000abstractdescription7
- 230000008685targetingEffects0.000abstractdescription7
- 235000019152folic acidNutrition0.000abstractdescription6
- 239000011724folic acidSubstances0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000002195synergetic effectEffects0.000abstractdescription6
- 238000012377drug deliveryMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000006116polymerization reactionMethods0.000abstractdescription4
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000009977dual effectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- OVBPIULPVIDEAO-UHFFFAOYSA-NN-Pteroyl-L-glutaminsaeureNatural productsC=1N=C2NC(N)=NC(=O)C2=NC=1CNC1=CC=C(C(=O)NC(CCC(O)=O)C(O)=O)C=C1OVBPIULPVIDEAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstract1
- 229960000304folic acidDrugs0.000abstract1
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description27
- 239000002246antineoplastic agentSubstances0.000description10
- 229940041181antineoplastic drugDrugs0.000description10
- 235000010216calcium carbonateNutrition0.000description7
- 239000007853buffer solutionSubstances0.000description5
- 231100000135cytotoxicityToxicity0.000description5
- 230000003013cytotoxicityEffects0.000description5
- 229940014144folateDrugs0.000description5
- 230000002378acidificating effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000005538encapsulationMethods0.000description4
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NDimethylsulphoxideChemical groupCS(C)=OIAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 206010060862Prostate cancerDiseases0.000description3
- 208000000236Prostatic NeoplasmsDiseases0.000description3
- 230000000259anti-tumor effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000015556catabolic processEffects0.000description3
- 238000006731degradation reactionMethods0.000description3
- 102000006815folate receptorHuman genes0.000description3
- 108020005243folate receptorProteins0.000description3
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description3
- 239000003446ligandSubstances0.000description3
- 239000002609mediumSubstances0.000description3
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000description3
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description3
- 239000012621metal-organic frameworkSubstances0.000description3
- 239000000178monomerSubstances0.000description3
- 210000005267prostate cellAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000001681protective effectEffects0.000description3
- 239000013153zeolitic imidazolate frameworkSubstances0.000description3
- AZKSAVLVSZKNRD-UHFFFAOYSA-M3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromideChemical compound[Br-].S1C(C)=C(C)N=C1[N+]1=NC(C=2C=CC=CC=2)=NN1C1=CC=CC=C1AZKSAVLVSZKNRD-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- 206010006187Breast cancerDiseases0.000description2
- 208000026310Breast neoplasmDiseases0.000description2
- 206010058467Lung neoplasm malignantDiseases0.000description2
- 125000003178carboxy groupChemical group[H]OC(*)=O0.000description2
- 230000009920chelationEffects0.000description2
- 238000000354decomposition reactionMethods0.000description2
- 239000012737fresh mediumSubstances0.000description2
- 230000002147killing effectEffects0.000description2
- 231100000225lethalityToxicity0.000description2
- 201000005202lung cancerDiseases0.000description2
- 208000020816lung neoplasmDiseases0.000description2
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description2
- 239000002904solventSubstances0.000description2
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description2
- 210000004881tumor cellAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000003981vehicleSubstances0.000description2
- 206010005003Bladder cancerDiseases0.000description1
- 208000003174Brain NeoplasmsDiseases0.000description1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-NCalciumChemical compound[Ca]OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 208000030453Drug-Related Side Effects and Adverse reactionDiseases0.000description1
- 108090000790EnzymesProteins0.000description1
- 102000004190EnzymesHuman genes0.000description1
- 231100000002MTT assayToxicity0.000description1
- 238000000134MTT assayMethods0.000description1
- 206010033128Ovarian cancerDiseases0.000description1
- 206010061535Ovarian neoplasmDiseases0.000description1
- 206010039491SarcomaDiseases0.000description1
- 208000007097Urinary Bladder NeoplasmsDiseases0.000description1
- 238000002835absorbanceMethods0.000description1
- 229940009456adriamycinDrugs0.000description1
- 230000006907apoptotic processEffects0.000description1
- 230000004888barrier functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004071biological effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000017531blood circulationEffects0.000description1
- 229910052791calciumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000011575calciumSubstances0.000description1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncarbonic acidChemical compoundOC(O)=OBVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000030833cell deathEffects0.000description1
- 230000003833cell viabilityEffects0.000description1
- 230000007541cellular toxicityEffects0.000description1
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000004087circulationEffects0.000description1
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000013270controlled releaseMethods0.000description1
- 239000002178crystalline materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001186cumulative effectEffects0.000description1
- 231100000433cytotoxicToxicity0.000description1
- 230000001472cytotoxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000009792diffusion processMethods0.000description1
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description1
- 238000010828elutionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002708enhancing effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description1
- 125000003929folic acid groupChemical group0.000description1
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002163immunogenEffects0.000description1
- 238000011534incubationMethods0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 238000010253intravenous injectionMethods0.000description1
- 150000002500ionsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000001665lethal effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 230000002035prolonged effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005588protonationEffects0.000description1
- 230000010837receptor-mediated endocytosisEffects0.000description1
- 102000005962receptorsHuman genes0.000description1
- 108020003175receptorsProteins0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- BOLDJAUMGUJJKM-LSDHHAIUSA-Nrenifolin DNatural productsCC(=C)[C@@H]1Cc2c(O)c(O)ccc2[C@H]1CC(=O)c3ccc(O)cc3OBOLDJAUMGUJJKM-LSDHHAIUSA-N0.000description1
- 230000000087stabilizing effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000002560therapeutic procedureMethods0.000description1
- 231100000419toxicityToxicity0.000description1
- 230000001988toxicityEffects0.000description1
- 230000001960triggered effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000000870ultraviolet spectroscopyMethods0.000description1
- 201000005112urinary bladder cancerDiseases0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/69—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit
- A61K47/6949—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the conjugate being characterised by physical or galenical forms, e.g. emulsion, particle, inclusion complex, stent or kit inclusion complexes, e.g. clathrates, cavitates or fullerenes
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/70—Carbohydrates; Sugars; Derivatives thereof
- A61K31/7028—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages
- A61K31/7034—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin
- A61K31/704—Compounds having saccharide radicals attached to non-saccharide compounds by glycosidic linkages attached to a carbocyclic compound, e.g. phloridzin attached to a condensed carbocyclic ring system, e.g. sennosides, thiocolchicosides, escin, daunorubicin
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
- A61K38/16—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- A61K38/41—Porphyrin- or corrin-ring-containing peptides
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/54—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic compound
- A61K47/545—Heterocyclic compounds
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K47/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient
- A61K47/50—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates
- A61K47/51—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent
- A61K47/56—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic macromolecular compound, e.g. an oligomeric, polymeric or dendrimeric molecule
- A61K47/59—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic macromolecular compound, e.g. an oligomeric, polymeric or dendrimeric molecule obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyureas or polyurethanes
- A61K47/60—Medicinal preparations characterised by the non-active ingredients used, e.g. carriers or inert additives; Targeting or modifying agents chemically bound to the active ingredient the non-active ingredient being chemically bound to the active ingredient, e.g. polymer-drug conjugates the non-active ingredient being a modifying agent the modifying agent being an organic macromolecular compound, e.g. an oligomeric, polymeric or dendrimeric molecule obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyureas or polyurethanes the organic macromolecular compound being a polyoxyalkylene oligomer, polymer or dendrimer, e.g. PEG, PPG, PEO or polyglycerol
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G83/00—Macromolecular compounds not provided for in groups C08G2/00 - C08G81/00
- C08G83/008—Supramolecular polymers
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/30—Against vector-borne diseases, e.g. mosquito-borne, fly-borne, tick-borne or waterborne diseases whose impact is exacerbated by climate change
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于功能材料制备领域,具体涉及一种以ZIF-8为基质的藻蓝蛋白分子印迹药物载体的制备方法。The invention belongs to the field of functional material preparation, in particular to a preparation method of a phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as a matrix.
背景技术Background technique
阿霉素是一种广谱抗肿瘤药物,对乳腺癌、肉瘤、肺癌、膀胱癌等癌症都有一定疗效,但其具有强烈的细胞毒性作用,因此多与其他抗癌药联合使用。藻蓝素是藻类抗肿瘤药物中最有效和最具有代表性的,有良好的生物活性,可以提高调节酶的活性和多种蛋白的合成,有良好的抗肿瘤活性,对多种癌细胞系有明显的杀伤作用,毒副作用小,对正常细胞组织没有影响,对自由基导致的细胞凋亡死亡具有保护作用。将藻蓝素和阿霉素药物联合使用,通过抗癌药物的协同作用,可显著的增强治疗效果,而且不受剂量影响,还可以使药物的副作用最小化。Doxorubicin is a broad-spectrum antitumor drug, which has certain curative effect on breast cancer, sarcoma, lung cancer, bladder cancer and other cancers, but it has strong cytotoxic effect, so it is often used in combination with other anticancer drugs. Phycocyanin is the most effective and representative algal anti-tumor drug, has good biological activity, can improve the activity of regulating enzymes and the synthesis of various proteins, has good anti-tumor activity, and has good anti-tumor activity against a variety of cancer cell lines. It has obvious killing effect, small toxic and side effects, has no effect on normal cells and tissues, and has a protective effect on cell apoptosis and death caused by free radicals. The combined use of phycocyanin and doxorubicin can significantly enhance the therapeutic effect through the synergistic effect of anticancer drugs, and is not affected by the dose, and can also minimize the side effects of the drug.
然而,一般药物传递载体存在一些局限性,主要涉及在药物的负载量不足,难以响应释药和药物易泄露。分子印迹聚合物(MIPs)可以选择性识别和携带模板分子及其结构类似物。因其独特的性质,如选择性识别能力及由聚合物结构中的印迹位点引发的可控制药物释放,常被选用为药物递送载体。但如同时负载两种药物,两种模板分子的印迹易造成印迹位点分布不均匀,印迹位点的互相占据等问题。沸石咪唑酯骨架系列材料(ZIFs)是一种具有类似沸石结构的多孔晶态材料,可归属为一类特殊的金属有机框架MOFs材料,具有四面体型三维网状结构,具有较大的比表面积、孔隙率高、超高的药物装载效率、可生物降解、生物相容性好等优点;然而其稳定性和药物易泄露,限制了其作为药物载体的实际应用。However, general drug delivery vehicles have some limitations, mainly related to insufficient drug loading, difficulty in responding to drug release and easy drug leakage. Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) can selectively recognize and carry template molecules and their structural analogs. Due to its unique properties, such as selective recognition ability and controllable drug release triggered by imprinted sites in the polymer structure, it is often chosen as a drug delivery vehicle. However, if two kinds of drugs are loaded at the same time, the imprinting of the two template molecules is likely to cause uneven distribution of imprinted sites and mutual occupation of the imprinted sites. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) are porous crystalline materials with a zeolite-like structure, which can be classified as a special class of metal-organic framework MOFs with a tetrahedral three-dimensional network structure, large specific surface area, It has the advantages of high porosity, ultra-high drug loading efficiency, biodegradability, and good biocompatibility; however, its stability and easy drug leakage limit its practical application as a drug carrier.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明是为了解决现有药物载体药物协同作用差,载药率低,药物易提前泄露,靶向性受限,毒副作用大的问题,提供了一种以ZIF-8为基质的藻蓝蛋白分子印迹药物载体的制备方法。The invention provides a phycocyanin with ZIF-8 as a matrix in order to solve the problems of poor synergy of the existing drug carriers, low drug loading rate, easy leakage of drugs in advance, limited targeting and large toxic and side effects. Preparation method of molecularly imprinted drug carrier.
本发明中一种以ZIF-8为基质的藻蓝蛋白分子印迹药物载体的制备方法具体是按以下步骤进行:A preparation method of a phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as a matrix in the present invention is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
一、ZIF-8的制备:1. Preparation of ZIF-8:
将 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和2-甲基咪唑分别加入到去离子水中超声3~6min,得到 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液和2-甲基咪唑溶液;在室温下将 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液和2-甲基咪唑溶液混合搅拌,混合液依次采用水和乙醇洗涤,真空干燥得到ZIF-8;所述Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和2-甲基咪唑的质量比为1:(8~12);所述Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液的浓度为0.01~0.015g/mL;所述2-甲基咪唑溶液的浓度为0.1~0.15g/mL;Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O and 2-methylimidazole were respectively added to deionized water for 3-6 min to obtain Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O solution and 2-methylimidazole solution; at room temperature Next, the Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O solution and the 2-methylimidazole solution were mixed and stirred, the mixed solution was washed with water and ethanol in turn, and vacuum dried to obtain ZIF-8; the Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 The mass ratio of O and 2-methylimidazole is 1:(8~12); the concentration of the Zn(NO3 )2 ·6H2 O solution is 0.01~0.015g/mL; the 2-methylimidazole solution The concentration is 0.1~0.15g/mL;
二、ZIF-8/DOX的制备:2. Preparation of ZIF-8/DOX:
将DOX和ZIF-8分散在PBS溶液中,超声处理50~70 min;然后避光搅拌22~26h,离心后收集上清液,得到ZIF-8/DOX;所述DOX的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(1200~1400)mL;所述ZIF-8的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(180~220)mL;DOX and ZIF-8 were dispersed in PBS solution, and ultrasonically treated for 50-70 min; then stirred in the dark for 22-26 h, and the supernatant was collected after centrifugation to obtain ZIF-8/DOX; the mass of DOX was the same as that of PBS solution. The volume ratio is 1g:(1200~1400)mL; the volume ratio of the mass of the ZIF-8 to the PBS solution is 1g:(180~220)mL;
三、ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA的制备:3. Preparation of ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA:
将ZIF-8/DOX分散在PBS溶液中,然后依次加入藻蓝蛋白和α-甲基丙烯酸,得到混合溶液;将混合溶液磁力搅拌0.8~1.2h,通入N2去除氧气后依次向其中加入N-异丙基丙烯酰胺、聚乙二醇2000和过硫酸铵在温度为20~30℃的条件下聚合反应22~26h,再向其中加入PEG-FA和CaCO3在磁力搅拌下继续反应4~6h,采用去离子水洗涤,真空干燥得到ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA;所述ZIF-8/DOX的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(180~220)mL;所述藻蓝蛋白与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(900~1100)mL;所述α-甲基丙烯酸与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(350~400)mL;所述N-异丙基丙烯酰胺与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(280~320)mL;所述聚乙二醇2000与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(180~220)mL;所述过硫酸铵与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(1700~1900)mL;所述PEG-FA与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(90~110)mL;所述CaCO3与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(3800~4200)mL。ZIF-8/DOX was dispersed in PBS solution, and then phycocyanin and α-methacrylic acid were added in sequence to obtain a mixed solution; the mixed solution was magnetically stirred for 0.8-1.2 h, and N2 was introduced to remove oxygen and then added to it in turn N-isopropylacrylamide, polyethylene glycol 2000 and ammonium persulfate were polymerized for 22 to 26 h at a temperature of 20 to 30 °C, and then PEG-FA and CaCOwere added to them to continue the reaction under magnetic stirring 4 For ~6h, wash with deionized water, and vacuum dry to obtain ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA; the mass ratio of the ZIF-8/DOX to the PBS solution is 1 g:(180~220) mL; the algae The volume ratio of blue protein to PBS solution is 1g:(900~1100)mL; the volume ratio of the α-methacrylic acid to PBS solution is 1g:(350~400)mL; the N-isopropylacrylamide The volume ratio to the PBS solution is 1g:(280~320)mL; the volume ratio of the polyethylene glycol 2000 to the PBS solution is 1g:(180~220)mL; the volume ratio of the ammonium persulfate to the PBS solution is 1g:(1700~1900)mL; the volume ratio of the PEG-FA to the PBS solution is 1g:(90~110)mL; the volume ratio of the CaCO3 to the PBS solution is 1g:(3800~4200)mL .
本发明的优点:Advantages of the present invention:
1、本发明制备的药物载体可以同时对两种抗癌药物均有较高的负载量, 协同抗癌的同时降低阿霉素对正常细胞毒副作用。1. The drug carrier prepared by the present invention can simultaneously have higher loadings for two anticancer drugs, and can synergistically resist cancer while reducing the toxic side effects of adriamycin on normal cells.
2、本发明应用分子印迹技术在载药ZIF-8表面制备载药印迹聚合物。表面印迹聚合物层对ZIF-8起到稳定作用和避免药物提前泄露而在肿瘤微环境下响应释药的效果。2. The present invention uses molecular imprinting technology to prepare drug-loaded imprinted polymer on the surface of drug-loaded ZIF-8. The surface-imprinted polymer layer has the effect of stabilizing ZIF-8 and preventing the drug from leaking in advance and releasing the drug in response to the tumor microenvironment.
3、本发明将阿霉素负载在ZIF-8内,在其表面制备藻蓝蛋白分子印迹聚合物,在非印迹区修饰PEG-FA,获得良好生物相容性和靶向性。避免靶向识别和释药均由印迹位点效应产生而互相干扰,也避免二次药物印迹减少溶剂使用和残留。3. In the present invention, doxorubicin is loaded in ZIF-8, phycocyanin molecularly imprinted polymer is prepared on its surface, and PEG-FA is modified in the non-imprinted area to obtain good biocompatibility and targeting. It is avoided that both target recognition and drug release interfere with each other due to the effect of imprinting sites, and also avoid secondary drug imprinting to reduce solvent use and residues.
4、碳酸钙的掺杂起到对印迹聚合物表面药物的保护作用,印迹位点中的藻蓝蛋白在肿瘤微环境中响应释放后,暴露印迹位点而促进内部阿霉素有效释放,确保阿霉素和藻蓝蛋白的协同释药,减小对正常细胞的毒副作用。4. The doping of calcium carbonate plays a protective role for the drug on the surface of the imprinted polymer. After the phycocyanin in the imprinted site is released in response to the tumor microenvironment, the imprinted site is exposed to promote the effective release of internal doxorubicin, ensuring that The synergistic release of doxorubicin and phycocyanin reduces the toxic and side effects on normal cells.
5、本发明还能够解决现有药物载体难以生物降解的问题。5. The present invention can also solve the problem that the existing drug carriers are difficult to biodegrade.
附图说明Description of drawings
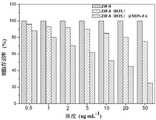
图1为ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA对DOX和PC的载药率和包封率的柱状对比图;Figure 1 is a bar comparison chart of the drug loading and encapsulation efficiency of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA on DOX and PC;
图2为在5.0(a)和7.4(b)的pH值下,ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA中DOX和PC的释放量的对比曲线;Figure 2 is the comparison curve of DOX and PC release from ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA at pH values of 5.0(a) and 7.4(b);
图3为ZIF-8、ZIF-8(DOX)和ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA对正常前列腺细胞RWPE-2的细胞毒性柱状对比图;Figure 3 is a bar graph comparing the cytotoxicity of ZIF-8, ZIF-8(DOX) and ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA on normal prostate cells RWPE-2;
图4为ZIF-8、ZIF-8(DOX)和ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA对前列腺癌细胞DU 145的细胞毒性柱状对比图;Figure 4 is a bar graph comparing the cytotoxicity of ZIF-8, ZIF-8(DOX) and ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA on prostate cancer cell DU 145;
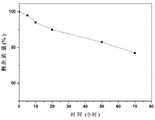
图5为ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA体外降解中的剩余质量百分比曲线。Figure 5 is the residual mass percentage curve of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA in vitro degradation.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
具体实施方式一:本实施方式一种以ZIF-8为基质的藻蓝蛋白分子印迹药物载体的制备方法具体是按以下步骤进行:Embodiment 1: The preparation method of a phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as a matrix of this embodiment is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
一、ZIF-8的制备:1. Preparation of ZIF-8:
将 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和2-甲基咪唑分别加入到去离子水中超声3~6min,得到 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液和2-甲基咪唑溶液;在室温下将 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液和2-甲基咪唑溶液混合搅拌,混合液依次采用水和乙醇洗涤,真空干燥得到ZIF-8;所述Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和2-甲基咪唑的质量比为1:(8~12);所述Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液的浓度为0.01~0.015g/mL;所述2-甲基咪唑溶液的浓度为0.1~0.15g/mL;Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O and 2-methylimidazole were respectively added to deionized water for 3-6 min to obtain Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O solution and 2-methylimidazole solution; at room temperature Next, the Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O solution and the 2-methylimidazole solution were mixed and stirred, the mixed solution was washed with water and ethanol in turn, and vacuum dried to obtain ZIF-8; the Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 The mass ratio of O and 2-methylimidazole is 1:(8~12); the concentration of the Zn(NO3 )2 ·6H2 O solution is 0.01~0.015g/mL; the 2-methylimidazole solution The concentration is 0.1~0.15g/mL;
二、ZIF-8/DOX的制备:2. Preparation of ZIF-8/DOX:
将DOX和ZIF-8分散在PBS溶液中,超声处理50~70 min;然后避光搅拌22~26h,离心后收集上清液,得到ZIF-8/DOX;采用紫外分光光度法确定纳米颗粒的载药量和药物包封率;所述DOX的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(1200~1400)mL;所述ZIF-8的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(180~220)mL;DOX and ZIF-8 were dispersed in PBS solution, and ultrasonically treated for 50-70 min; then stirred in the dark for 22-26 h, and the supernatant was collected after centrifugation to obtain ZIF-8/DOX; UV spectrophotometry was used to determine the nanoparticle size. Drug loading and drug encapsulation efficiency; the volume ratio of the mass of the DOX to the PBS solution is 1g:(1200~1400) mL; the volume ratio of the mass of the ZIF-8 to the PBS solution is 1g:(180~220 ) mL;
三、ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA的制备:3. Preparation of ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA:
将ZIF-8/DOX分散在PBS溶液中,然后依次加入藻蓝蛋白和α-甲基丙烯酸,得到混合溶液;将混合溶液磁力搅拌0.8~1.2h,通入N2去除氧气后依次向其中加入N-异丙基丙烯酰胺、聚乙二醇2000和过硫酸铵在温度为20~30℃的条件下聚合反应22~26h,再向其中加入PEG-FA和CaCO3在磁力搅拌下继续反应4~6h,采用去离子水洗涤,真空干燥得到ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA;所述ZIF-8/DOX的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(180~220)mL;所述藻蓝蛋白与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(900~1100)mL;所述α-甲基丙烯酸与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(350~400)mL;所述N-异丙基丙烯酰胺与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(280~320)mL;所述聚乙二醇2000与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(180~220)mL;所述过硫酸铵与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(1700~1900)mL;所述PEG-FA与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(90~110)mL;所述CaCO3与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:(3800~4200)mL。ZIF-8/DOX was dispersed in PBS solution, and then phycocyanin and α-methacrylic acid were added in sequence to obtain a mixed solution; the mixed solution was magnetically stirred for 0.8-1.2 h, and N2 was introduced to remove oxygen and then added to it in turn N-isopropylacrylamide, polyethylene glycol 2000 and ammonium persulfate were polymerized for 22 to 26 h at a temperature of 20 to 30 °C, and then PEG-FA and CaCOwere added to them to continue the reaction under magnetic stirring 4 For ~6h, wash with deionized water, and vacuum dry to obtain ZIF-8/DOX@MIPs-FA; the mass ratio of the ZIF-8/DOX to the PBS solution is 1 g:(180~220) mL; the algae The volume ratio of blue protein to PBS solution is 1g:(900~1100)mL; the volume ratio of the α-methacrylic acid to PBS solution is 1g:(350~400)mL; the N-isopropylacrylamide The volume ratio to the PBS solution is 1g:(280~320)mL; the volume ratio of the polyethylene glycol 2000 to the PBS solution is 1g:(180~220)mL; the volume ratio of the ammonium persulfate to the PBS solution is 1g:(1700~1900)mL; the volume ratio of the PEG-FA to the PBS solution is 1g:(90~110)mL; the volume ratio of the CaCO3 to the PBS solution is 1g:(3800~4200)mL .
本实施方式中DOX为阿霉素。In this embodiment, DOX is doxorubicin.
本实施方式创新性的提出了以可降解的金属有机骨架ZIF-8为载药基质装载抗肿瘤药物阿霉素,并在此基础上不洗脱模板分子藻蓝蛋白,进一步合成载药型MIPs,增加药物携带量的同时,也对药物起到保护作用,防止药物提前泄露,提高药物递送和癌症治疗的效率。将DOX包封于MIPs的承载基质中,聚合物的承载基质可以通过聚合物涂层的分解使被封装的抗癌药物缓慢扩散释放。在聚合过程中加入ZIF-8,不仅增加了比表面积,提高了印迹位点的可达性,还减少模板分子的包埋,具有可降解的特质和可控的释放药物能力。而未印迹区可进一步靶向修饰,使材料表面功能化的结合靶向配体。通过这种方式,聚合物可通过受体介导的内吞作用,使配体能够识别特定癌细胞表面过表达的受体实现主动靶向。人体的大多数肿瘤,如卵巢癌、乳腺癌、肺癌、和脑癌等癌细胞表面叶酸受体(FRs)高度表达,此外,靶向配体叶酸(FA)是非免疫原性的,在存储过程中稳定,分子量较低,可以很容易地通过生物屏障扩散。聚乙二醇(PEG)是一种高分子聚合物,具有良好的水溶性,生物相容性和分散性。在生物医学中,常用PEG修饰药物载体,增强其在血液中的稳定性,延长其血液循环,从而累计增加药物浓度。将PEG和FA以序列连接,叶酸侧链可通过叶酸受体进入靶细胞,将药物传递到肿瘤部位。This embodiment innovatively proposes to use the degradable metal-organic framework ZIF-8 as the drug-loading matrix to load the antitumor drug doxorubicin, and on this basis, the template molecule phycocyanin is not eluted to further synthesize drug-loaded MIPs , while increasing the drug carrying capacity, it also protects the drug, prevents the drug from leaking in advance, and improves the efficiency of drug delivery and cancer treatment. The DOX is encapsulated in the MIPs carrier matrix, and the polymer carrier matrix can release the encapsulated anticancer drugs by slow diffusion through the decomposition of the polymer coating. The addition of ZIF-8 during the polymerization process not only increases the specific surface area and improves the accessibility of imprinted sites, but also reduces the entrapment of template molecules, with degradable properties and controllable drug release capabilities. The unimprinted region can be further modified in a targeted manner, so that the surface of the material can be functionalized to bind targeting ligands. In this way, polymers can be actively targeted through receptor-mediated endocytosis, enabling ligands to recognize overexpressed receptors on the surface of specific cancer cells. Most human tumors, such as ovarian cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, and brain cancer, are highly expressed on the surface of folate receptors (FRs). In addition, the targeting ligand folate (FA) is non-immunogenic, and is stored during storage. Medium stability, low molecular weight, can easily diffuse through biological barriers. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a high molecular polymer with good water solubility, biocompatibility and dispersibility. In biomedicine, PEG is commonly used to modify drug carriers to enhance their stability in blood and prolong their blood circulation, thereby increasing the drug concentration cumulatively. By linking PEG and FA in sequence, the folic acid side chain can enter the target cell through the folic acid receptor and deliver the drug to the tumor site.
本实施方式将DOX包封于ZIF-8中为承载基质,采用表面印迹聚合法,以藻蓝素(PC)为模板分子,甲基丙烯酸为功能单体,制备分子印迹聚合物。在此基础上,通过PEG序列连接FA,掺杂碳酸钙,制备响应释药靶向载药型分子印迹聚合物(ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA)。PC作为抗肿瘤药物发挥作用,增强DOX的抗肿瘤效果,同时降低DOX的副作用。双药物的同时携带和FA的靶向功能性,使两种抗癌药物精准的同时到达疾病处,响应释药,更好的发挥协同作用。PEG改善了ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA的亲水性,增强了其在生物体系中的稳定性,延长其循环时间,从而增加癌细胞周围的药物浓度。ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA兼顾了优越的药物负载量,较高的生物相容性和良好的药物释放效果及精准的靶向功能性。本研究提出了一种有效的药物协同治疗的新策略,为发展复方配方的给药系统提供了一条行之有效的新思路。In this embodiment, DOX is encapsulated in ZIF-8 as a carrier matrix, and a molecularly imprinted polymer is prepared by using a surface imprinting polymerization method with phycocyanin (PC) as a template molecule and methacrylic acid as a functional monomer. On this basis, FA was linked with PEG sequence and doped with calcium carbonate to prepare a drug-loaded molecularly imprinted polymer (ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA) with responsive drug release. PC acts as an anti-tumor drug, enhancing the anti-tumor effect of DOX while reducing the side effects of DOX. The simultaneous carrying of the dual drugs and the targeting functionality of FA enable the two anticancer drugs to reach the disease at the same time, respond to the drug release, and play a better synergistic effect. PEG improved the hydrophilicity of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA, enhanced its stability in biological systems, and prolonged its circulation time, thereby increasing the drug concentration around cancer cells. ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA combines superior drug loading, high biocompatibility, good drug release effect and precise targeting functionality. This study proposes a new strategy of effective drug synergistic therapy, and provides an effective new idea for the development of drug delivery system of compound formula.
具体实施方式二:本实施方式与具体实施方式一不同的是:步骤一中所述混合搅拌是以1000rpm的转速剧烈搅拌30min。其他与具体实施方式一相同。Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and
具体实施方式三:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至二之一不同的是:步骤一中所述真空干燥是在50℃下真空干燥12h。其他与具体实施方式一至二之一相同。Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and one of
具体实施方式四:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至三之一不同的是:步骤一中所述Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和2-甲基咪唑的质量比为1:(10);所述Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液的浓度为0.0125g/mL;所述2-甲基咪唑溶液的浓度为0.125g/mL。其它与具体实施方式一至三之一相同。Embodiment 4: The difference between this embodiment and one of
具体实施方式五:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至四之一不同的是:步骤二中所述PBS溶液的pH为7,浓度为20 mmol·L-1。其它与具体实施方式一至四之一相同。Embodiment 5: The difference between this embodiment and one of
具体实施方式六:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至五之一不同的是:步骤二中所述离心是以5000rpm的转速离心20min。其它与具体实施方式一至五之一相同。Embodiment 6: The difference between this embodiment and one of
具体实施方式七:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至六之一不同的是:步骤二中所述DOX的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为0.75g:1000mL;所述ZIF-8的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:200mL。其它与具体实施方式一至六之一相同。Embodiment 7: This embodiment is different from one of
具体实施方式八:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至六之一不同的是:步骤三中所述ZIF-8/DOX的质量与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:200mL;所述藻蓝蛋白与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:1000mL;所述α-甲基丙烯酸与PBS溶液的体积比为26g:10000mL。其它与具体实施方式一至六之一相同。Embodiment 8: The difference between this embodiment and one of
具体实施方式九:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至六之一不同的是:步骤三中所述N-异丙基丙烯酰胺与PBS溶液的体积比为34g:10000mL;所述聚乙二醇2000与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:200mL;所述过硫酸铵与PBS溶液的体积比为5.5g:10000mL。其它与具体实施方式一至六之一相同。Embodiment 9: This embodiment differs from one of
具体实施方式十:本实施方式与具体实施方式一至六之一不同的是:步骤三中所述PEG-FA的MW=2000Da;所述PEG-FA与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:100mL;所述CaCO3与PBS溶液的体积比为1g:4000mL。其它与具体实施方式一至六之一相同。Embodiment 10: This embodiment differs from one of
通过以下实施例验证本发明的有益效果:The beneficial effects of the present invention are verified by the following examples:
实施例1:一种以ZIF-8为基质的藻蓝蛋白分子印迹药物载体的制备方法具体是按以下步骤进行:Embodiment 1: a kind of preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrix is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
一、ZIF-8的制备:1. Preparation of ZIF-8:
将1.0g Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和10g 2-甲基咪唑分别加入到80mL去离子水中超声5min,得到 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液和2-甲基咪唑溶液;在室温下将 Zn(NO3)2·6H2O溶液和2-甲基咪唑溶液混合以1000rpm的转速剧烈搅拌30min,混合液依次采用水和乙醇洗涤,然后在50℃下真空干燥12h得到ZIF-8;1.0g of Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O and 10g of 2-methylimidazole were respectively added to 80 mL of deionized water for 5 min to obtain Zn(NO3 )2 .6H2 O solution and 2-methylimidazole solution; The Zn(NO3 )2 ·6H2 O solution and the 2-methylimidazole solution were mixed vigorously at room temperature and stirred vigorously at 1000 rpm for 30 min. The mixed solution was washed with water and ethanol in turn, and then vacuum-dried at 50 °C for 12 h to obtain ZIF. -8;
二、ZIF-8(DOX)的制备:2. Preparation of ZIF-8(DOX):
将15mg DOX和100mg ZIF-8分散在20mL PBS溶液(pH=7.0,20 mmol·L-1)中,超声处理60 min;然后避光搅拌24h,以5000rpm离心20min,离心后收集上清液,得到ZIF-8(DOX);15mg DOX and 100mg ZIF-8 were dispersed in 20mL PBS solution (pH=7.0, 20 mmol·L-1 ), and ultrasonically treated for 60 min; then stirred in the dark for 24 h, centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 20 min, and the supernatant was collected after centrifugation. Get ZIF-8(DOX);
三、ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA的制备:3. Preparation of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA:
将100mg ZIF-8(DOX)分散在20mL PBS溶液(pH=7.0,20 mmol·L-1)中,然后依次加入20mg藻蓝蛋白和52mg(6mmol) α-甲基丙烯酸,得到混合溶液;将混合溶液磁力搅拌1h,通入N2去除氧气后依次向其中加入68mg(6mmol)N-异丙基丙烯酰胺、100mg聚乙二醇2000和11mg过硫酸铵在温度为25℃的条件下聚合反应24h,再向其中加入200mg PEG-FA(MW=2000Da)和5mg CaCO3在磁力搅拌下继续反应5h,采用去离子水洗涤除去PBS和其他残留成分,真空干燥得到ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA。Disperse 100 mg of ZIF-8 (DOX) in 20 mL of PBS solution (pH=7.0, 20 mmol·L-1 ), then add 20 mg of phycocyanin and 52 mg (6 mmol) of α-methacrylic acid in turn to obtain a mixed solution; The mixed solution was magnetically stirred for 1 h, and N2 was introduced to remove oxygen. Then, 68 mg (6 mmol) of N-isopropylacrylamide, 100 mg of polyethylene glycol 2000 and 11 mg of ammonium persulfate were added to it in turn to polymerize at a temperature of 25 °C. After 24h, 200mg PEG-FA (MW=2000Da) and 5mg CaCO3were added to it, and the reaction was continued for 5h under magnetic stirring, washed with deionized water to remove PBS and other residual components, and vacuum dried to obtain ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs -FA.
1、ZIF-8-(DOX)@MIPs-FA载药量的研究1. Study on drug loading of ZIF-8-(DOX)@MIPs-FA
载药量(DLC)和药物包封率(DEE)公式(2-1)、(2-2)如下:Drug Loading Capacity (DLC) and Drug Encapsulation Efficiency (DEE) formulas (2-1) and (2-2) are as follows:
(2-1) (2-1)
(2-2) (2-2)
其中M1(mg)为上清液中药物的质量,M0(mg)为加入药物的质量,M为包封药物的质量与加入负载材料的质量之和。Wherein M1 (mg) is the mass of the drug in the supernatant, M0 (mg) is the mass of the drug added, and M is the sum of the mass of the encapsulated drug and the mass of the loaded material.
由图1可知,ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA对DOX和PC的载药量及药物包封率均较高,这是由于ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA以ZIF-8为承载基质,增大了比表面积、提高了药物装载效率。将阿霉素负载在ZIF-8内,在其表面制备藻蓝蛋白分子印迹聚合物,两种药物在负载过程中互不干扰,制备简单,减少溶剂的使用和模板分子的洗脱。DOX被很好的包覆在聚合物层中,同时碳酸钙在PC释放前对药物PC具有一定的保护作用,该制备方案避免了药物的提前泄露。It can be seen from Figure 1 that the drug loading and drug encapsulation efficiency of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA for DOX and PC are higher, which is because ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA uses ZIF-8 as the The carrier matrix increases the specific surface area and improves the drug loading efficiency. Doxorubicin is loaded in ZIF-8, and phycocyanin molecularly imprinted polymer is prepared on its surface. The two drugs do not interfere with each other during the loading process, the preparation is simple, and the use of solvent and the elution of template molecules are reduced. The DOX is well coated in the polymer layer, and the calcium carbonate has a certain protective effect on the drug PC before the PC is released, and the preparation scheme avoids the early leakage of the drug.
2、体外释药实验2. In vitro drug release experiment
装载DOX 和 PC的ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs分散在pH值为5.0或7.4的PBS溶液中。上述体系在37±1℃环境中,在指定的时间间隔,样品离心10min,测定释放的药物浓度。并测量材料剩余的质量。ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs loaded with DOX and PC were dispersed in PBS solution at pH 5.0 or 7.4. In the above system, the samples were centrifuged for 10 min at the specified time interval in the environment of 37±1°C, and the concentration of the released drug was determined. And measure the remaining mass of the material.
为了模拟肿瘤间质或肿瘤细胞和静脉注射条件下ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA的药物释放行为。本研究在pH值分别为5.0和7.4的两种缓冲溶液中考查了载药ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA的体外药物释放,图2为不同释药条件下ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA中DOX和PC的释药量。在缓冲溶液的pH值为5.0的条件下ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs中DOX和PC的释药量分别为100 mg·g-1和135mg·g-1,均高于在缓冲溶液pH值为7.4的条件下的药物释放量。根据结果显示,在不同pH值下的累积的药物释放量有显著性差异。与pH值为7.0的缓冲溶液相比,pH值为5.0的缓冲溶液中药物总释放要高得多,造成这种现象的原因是微酸环境导致ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA表面碳酸钙分解析出,同时MAA的羧基质子化可以破坏功能单体与模板分子之间的相互作用从而实现药物释放。ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA表面PC位点中的药物暴露在外,首先释放,避免了阿霉素提前释放导致的毒副作用。 PC释放后暴露的印迹位点导致ZIF-8暴露在微酸环境下,进一步有效释放药物阿霉素。众所周知癌细胞周围微环境的pH值为5.0左右,因此本研究制备的ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA可以在癌细胞存在的微酸性条件中伴随着碳酸钙分解,金属螯合作用和功能单体与药物之间的氢键破坏,从而达到药物控制性释放,同时避免在正常组织中的释放,降低对正常细胞的杀伤性。并且制备的ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA可以在肿瘤微酸环境中构架分解,使深层包覆的药物DOX释放的更加完全,发挥药物的相互协同作用。To simulate the drug release behavior of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA under tumor stroma or tumor cells and intravenous injection conditions. In this study, the in vitro drug release of drug-loaded ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA was investigated in two buffer solutions with pH values of 5.0 and 7.4, respectively. Figure 2 shows ZIF-8(DOX)@ The amount of DOX and PC released in MIPs-FA. The release amounts of DOX and PC in ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs were 100 mg·g-1 and 135 mg·g-1 , respectively, at the pH value of the buffer solution at 5.0, which were higher than those in the buffer solution at pH value of 5.0. The drug release amount under the condition of 7.4. According to the results, there were significant differences in the cumulative drug release at different pH values. Compared with the buffer solution with pH 7.0, the total drug release was much higher in the buffer solution with pH 5.0, which was caused by the slightly acidic environment leading to carbonic acid on the surface of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA Calcium was resolved, and the carboxyl protonation of MAA could disrupt the interaction between functional monomers and template molecules to achieve drug release. The drug in the PC site on the surface of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA is exposed and released first, avoiding the toxic and side effects caused by the early release of doxorubicin. The exposed imprinted sites after PC release led to the exposure of ZIF-8 to a slightly acidic environment, which further effectively released the drug doxorubicin. It is well known that the pH value of the microenvironment around cancer cells is around 5.0, so the ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA prepared in this study can be accompanied by calcium carbonate decomposition, metal chelation and function in the slightly acidic conditions in which cancer cells exist The hydrogen bond between the monomer and the drug is broken, so as to achieve the controlled release of the drug, while avoiding the release in normal tissues and reducing the cytotoxicity to normal cells. Moreover, the prepared ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA can decompose the framework in the slightly acidic environment of the tumor, so that the deeply coated drug DOX can be released more completely, and the synergistic effect of the drug can be exerted.
3、细胞毒性研究3. Cytotoxicity study
为了研究ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA对肿瘤细胞的细胞毒性,进行了MTT测定。将前列腺癌细胞DU 145和正常前列腺细胞RWPE-2以每孔1×104个细胞的密度接种在培养基(80 μL)中,在37 ℃下孵育20 h。然后,将培养基替换为80 μL的含有特定试剂(ZIF-8,ZIF-8(DOX),ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA)的不同新鲜培养基,孵育5 h。随后,将培养基更换为含有3-(4, 5-二甲基噻唑-2-基)-2, 5-二苯基溴化四唑(MTT)(最终浓度为0.5 mg·mL-1)的新鲜培养基。将细胞再孵育3 h。然后,用DMSO(80 μL)替换上清液,并在摇床上振摇10 min。通过酶标仪获得溶液的吸光度以测量光密度(OD)值。细胞存活率根据公式(2-3)进行计算:To investigate the cytotoxicity of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA on tumor cells, MTT assay was performed. Prostate cancer cells DU 145 and normal prostate cells RWPE-2 were seeded in culture medium (80 μL) at a density of 1×104 cells per well, and incubated at 37 °C for 20 h. Then, the medium was replaced with 80 μL of different fresh medium containing specific reagents (ZIF-8, ZIF-8(DOX), ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA) and incubated for 5 h. Subsequently, the medium was changed to contain 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) (final concentration 0.5 mg·mL-1 ) of fresh medium. The cells were incubated for an additional 3 h. Then, the supernatant was replaced with DMSO (80 μL) and shaken on a shaker for 10 min. The absorbance of the solution was obtained by a microplate reader to measure the optical density (OD) value. Cell viability was calculated according to formula (2-3):
(2-3) (2-3)
其中ODtreated是从特定药物处理的细胞中获得的,ODcontrol是从没有任何处理的细胞中获得的。ODtreated was obtained from cells treated with specific drugs, and ODcontrol was obtained from cells without any treatment.
图3、图4中显示了不同浓度的ZIF-8,ZIF-8(DOX)和ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA分别处理前列腺癌细胞DU 145和正常前列腺细胞RWPE-2的相对细胞生存力。孵育5小时后,装载DOX的药物载体ZIF-8(DOX)对癌细胞具有一定的杀伤力,说明对细胞的致死作用是由抗癌药物DOX引起的。与ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs和ZIF-8(DOX)相比较看出,在各种浓度下,ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA对癌细胞均具有较大的癌细胞毒性,且对正常细胞的毒副作用较低,这是由于ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA表面印迹了PC药物,同时ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA在癌细胞周围靶向富集作用,因此增强了对癌细胞的杀伤作用,并且减少了药物对正常细胞的毒副作用,根据实验结果可以说明ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs对正常细胞具有较低的毒副作用,对癌细胞具有较高的杀伤性。Figures 3 and 4 show the relative cell survival of different concentrations of ZIF-8, ZIF-8(DOX) and ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA in prostate cancer cells DU 145 and normal prostate cells RWPE-2, respectively force. After 5 hours of incubation, the DOX-loaded drug carrier ZIF-8 (DOX) had a certain lethality to cancer cells, indicating that the lethal effect on cells was caused by the anticancer drug DOX. Compared with ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs and ZIF-8(DOX), ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA has greater cancer cell toxicity to cancer cells at various concentrations, and The toxicity to normal cells is low, which is due to the imprinting of PC drugs on the surface of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA, and the targeted enrichment of ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs-FA around cancer cells, so It enhances the killing effect on cancer cells and reduces the toxic and side effects of drugs on normal cells. According to the experimental results, it can be shown that ZIF-8(DOX)@MIPs has lower toxic and side effects on normal cells and higher on cancer cells. lethality.
4、降解研究4. Degradation research
从图5可以看出,ZIF-8-(DOX)@MIPs-FA在pH值为5.0PBS溶液中降解70小时剩下的质量大约77%,降解开始于碳酸钙吸出,药物释放,接下来聚合物中甲基丙烯酸的羧基与ZIF-8中金属Zn离子的金属螯合作用被打破,印迹层分解,ZIF-8逐渐生物降解,ZIF-8-(DOX)@MIPs-FA表现出良好的可生物降解性。As can be seen from Figure 5, ZIF-8-(DOX)@MIPs-FA degraded in pH 5.0 PBS solution for 70 hours and the remaining mass was about 77%. The degradation started with calcium carbonate suction, drug release, followed by polymerization The metal chelation between the carboxyl group of methacrylic acid and the metal Zn ions in ZIF-8 was broken, the imprinted layer was decomposed, and ZIF-8 was gradually biodegraded. ZIF-8-(DOX)@MIPs-FA showed good biodegradability. Biodegradability.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210548537.6ACN114748644B (en) | 2022-05-20 | 2022-05-20 | Preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrix |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210548537.6ACN114748644B (en) | 2022-05-20 | 2022-05-20 | Preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrix |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114748644Atrue CN114748644A (en) | 2022-07-15 |
| CN114748644B CN114748644B (en) | 2023-08-18 |
Family
ID=82334447
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210548537.6AActiveCN114748644B (en) | 2022-05-20 | 2022-05-20 | Preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrix |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114748644B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115028853A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2022-09-09 | 广东石油化工学院 | A kind of construction method of phycocyanin-metal organic framework |
| CN115181739A (en)* | 2022-08-09 | 2022-10-14 | 宁波大学 | Metal framework material capable of adjusting selective catalysis of lipase, preparation method and application |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050272806A1 (en)* | 2004-06-02 | 2005-12-08 | Robert Falotico | Injectable formulations of taxanes for cad treatment |
| US20120093720A1 (en)* | 2010-10-16 | 2012-04-19 | Robert Jones | Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Use as Imaging and Therapeutics Agents |
| CN104492396A (en)* | 2014-12-10 | 2015-04-08 | 西南大学 | Targeted liposome based on protein molecular imprinting and preparation method thereof |
| CN105873569A (en)* | 2013-11-06 | 2016-08-17 | 芝加哥大学 | Nanoscale carriers for the delivery or co-delivery of chemotherapeutics, nucleic acids and photosensitizers |
| CN110664778A (en)* | 2019-10-11 | 2020-01-10 | 上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院 | Composite microparticles, method for preparing same and use thereof as carrier in drug delivery |
| CN112694577A (en)* | 2020-12-02 | 2021-04-23 | 江苏科技大学 | Imprinted mesoporous material and preparation method and application thereof |
- 2022
- 2022-05-20CNCN202210548537.6Apatent/CN114748644B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20050272806A1 (en)* | 2004-06-02 | 2005-12-08 | Robert Falotico | Injectable formulations of taxanes for cad treatment |
| US20120093720A1 (en)* | 2010-10-16 | 2012-04-19 | Robert Jones | Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Use as Imaging and Therapeutics Agents |
| CN105873569A (en)* | 2013-11-06 | 2016-08-17 | 芝加哥大学 | Nanoscale carriers for the delivery or co-delivery of chemotherapeutics, nucleic acids and photosensitizers |
| CN104492396A (en)* | 2014-12-10 | 2015-04-08 | 西南大学 | Targeted liposome based on protein molecular imprinting and preparation method thereof |
| CN110664778A (en)* | 2019-10-11 | 2020-01-10 | 上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院 | Composite microparticles, method for preparing same and use thereof as carrier in drug delivery |
| CN112694577A (en)* | 2020-12-02 | 2021-04-23 | 江苏科技大学 | Imprinted mesoporous material and preparation method and application thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| SHUANG HAN ET AL.: "A dual-template imprinted polymer based on amino-functionalized zirconium-based metal-organic framework for delivery of doxorubicin and phycocyanin with synergistic anticancer effect", EUROPEAN POLYMER JOURNAL, vol. 170, no. 5, pages 1 - 10* |
| YA-TING QIN ET AL: "Tumor-Sensitive Biodegradable Nanoparticles of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Stabilized Fluorescent Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 for Targeted Imaging and Drug Delivery", ACS APPL. MATER. INTERFACES, vol. 12, no. 22, pages 24585* |
| YUZHUO SONG ET AL.: "Biodegradable Imprinted Polymer Based on ZIF-8/DOX-HA for Synergistically Targeting Prostate Cancer Cells and Controlled Drug Release with Multiple Responses", ACS APPL. MATER. INTERFACES, vol. 15, no. 21, pages 25339* |
| 张柯林: "还原响应型分子印迹纳米药物载体制备及应用", 中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 (工程科技Ⅰ辑), pages 016 - 696* |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115028853A (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2022-09-09 | 广东石油化工学院 | A kind of construction method of phycocyanin-metal organic framework |
| CN115028853B (en)* | 2022-07-29 | 2024-03-29 | 广东石油化工学院 | A method for constructing phycocyanin-metal organic framework |
| CN115181739A (en)* | 2022-08-09 | 2022-10-14 | 宁波大学 | Metal framework material capable of adjusting selective catalysis of lipase, preparation method and application |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114748644B (en) | 2023-08-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107095859B (en) | Drug-loaded nanocapsule with tumor cell bioreductive microenvironment sensitivity and preparation method thereof | |
| US11638700B2 (en) | Iron/shikonin nano-composite and use thereof and method for preparing the same by supermolecular self-assembly | |
| CN114748644B (en) | Preparation method of phycocyanin molecularly imprinted drug carrier with ZIF-8 as matrix | |
| CN103920153A (en) | Chitosan-modified pH responsive medicine-loading controlled release material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110652497B (en) | A kind of targeted drug delivery system for dual-effect therapy and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN105030795A (en) | Nanometer drug-loading system as well as preparation method and application thereof | |
| Far et al. | Co-delivery of doxorubicin/sorafenib by DNA-decorated green ZIF-67-based nanocarriers for chemotherapy and hepatocellular carcinoma treatment | |
| JP4991563B2 (en) | Dosage form in which hydrophobic anticancer agent is encapsulated inside bile acid-chitosan complex and method for producing the same | |
| CN112826939A (en) | Abdominal perfusion nano-medicine and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN114748634A (en) | Preparation and application of phenylboronic acid/folic acid dual-targeting nano delivery carrier | |
| CN103768598B (en) | A kind of implantable fullerene polylactic acid is from the preparation method of reunion carried medicine sustained-release microsphere and application | |
| CN113750245A (en) | Double-cavity type nano-scale drug carrier, drug loading system, preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN103239718B (en) | Method for preparing adriamycin-loaded polycaprolactone-block-polyethylene glycol nano microspheres | |
| CN106474049A (en) | A kind of photopolymerized hydrogel topical drug delivery systems and preparation method and application | |
| CN112608398A (en) | reduction/pH sensitive polysaccharide-based nano prodrug carrying adriamycin and platinum drugs together, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN111686258A (en) | T7 polypeptide modified targeting nano system and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN102793671A (en) | Human recombinant epidermal growth factor (hrEGF)-modified cisplatin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN101690820B (en) | Nano microspheres loaded with platinum-based drugs and their hydrogels wrapped by natural polymers and their preparation and use | |
| CN116602931A (en) | Preparation method of biodegradable molecularly imprinted polymer for synergistically targeting prostate cancer cells and controlling drug release through multiple responses | |
| Feng et al. | Mussel biomimetic ZIF-8 nanoscale metal organic frameworks as stable and pH-responsive platforms for enhanced drug delivery | |
| CN112315940B (en) | Nanoparticle for promoting tumor coagulation and enzyme/ATP dual-responsive drug release, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN113456611A (en) | Double-response rapid controlled release nano-carrier and preparation method of nano-drug formed by nano-carrier | |
| CN116327687B (en) | Stimulus-responsive injectable composite carrier hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110772496A (en) | Paclitaxel nanoparticles applied to liver cancer interventional therapy | |
| CN110742874B (en) | Polymer-coated cisplatin nanoparticle and preparation method and application thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |