CN114745309A - A method and system for microburst detection and elimination based on programmable data plane - Google Patents
A method and system for microburst detection and elimination based on programmable data planeDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114745309A CN114745309ACN202210233618.7ACN202210233618ACN114745309ACN 114745309 ACN114745309 ACN 114745309ACN 202210233618 ACN202210233618 ACN 202210233618ACN 114745309 ACN114745309 ACN 114745309A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- micro
- packet
- flow
- priority
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription33
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000titleabstractdescription12
- 230000008030eliminationEffects0.000titleabstractdescription11
- 238000003379elimination reactionMethods0.000titleabstractdescription11
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description4
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description3
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description3
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description2
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description2
- 230000002411adverseEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 230000001934delayEffects0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 230000006855networkingEffects0.000description1
- 230000000704physical effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000010076replicationEffects0.000description1
- 238000000926separation methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/08—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters
- H04L43/0876—Network utilisation, e.g. volume of load or congestion level
- H04L43/0894—Packet rate
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/08—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters
- H04L43/0852—Delays
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/16—Threshold monitoring
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/25—Flow control; Congestion control with rate being modified by the source upon detecting a change of network conditions
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L47/00—Traffic control in data switching networks
- H04L47/10—Flow control; Congestion control
- H04L47/32—Flow control; Congestion control by discarding or delaying data units, e.g. packets or frames
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于网络通信技术领域,更具体地,涉及一种基于可编程数据平面的微突发检测与消除方法、系统。The invention belongs to the technical field of network communication, and more particularly, relates to a method and a system for detecting and eliminating micro-bursts based on a programmable data plane.
背景技术Background technique
随着5G移动业务在全球范围内的普及,数据流量迅速增加。5G场景下物联网从网络边缘接入、承载大量数据,发挥着重要作用。物联网设备通过物联网网关连接到物联网服务器。物联网网关通过蜂窝、蓝牙等方式提供无线覆盖,多个网关构成边缘网络对其覆盖区域内的流量进行聚合,并发送到物联网远程核心服务器。大量物联网设备同时传输数据导致聚合流量突然增加称为微突发。微突发流量可能会超过边缘网络节点网关的队列缓存空间,导致数据包时延增加甚至被丢弃。同时物联网应用流量的需求特点具有差异性,如远程手术要求低时延低抖动;视频监控对时延几乎没什么要求。With the worldwide popularity of 5G mobile services, data traffic is rapidly increasing. In the 5G scenario, the Internet of Things accesses from the edge of the network and carries a large amount of data, which plays an important role. IoT devices connect to IoT servers through IoT gateways. The IoT gateway provides wireless coverage through cellular, Bluetooth, etc., and multiple gateways form an edge network to aggregate the traffic within its coverage area and send it to the IoT remote core server. The sudden increase in aggregated traffic caused by a large number of IoT devices transmitting data at the same time is called a microburst. Micro-burst traffic may exceed the queue buffer space of edge network node gateways, resulting in increased packet delay or even dropped packets. At the same time, the demand characteristics of IoT application traffic are different. For example, remote surgery requires low latency and low jitter; video surveillance has almost no requirements on latency.
物联网边缘网络具有一定的计算和存储资源同时距离微突发源头最近,是解决微突发的理想之处。微突发持续时间短且流量巨大,如何快速检测和消除一直是个难题。The IoT edge network has certain computing and storage resources and is the closest to the source of the micro-burst, which is an ideal place to solve the micro-burst. Micro-bursts have a short duration and huge traffic, so how to quickly detect and eliminate them has always been a difficult problem.
使用软件定义网络(Software-Defined Networking,SDN)来实现的边缘网络虽然具有控制与数据分离的体系结构带来的灵活优势,但也面临控制平面与数据平面存在通信、交互延迟的缺点。在一个集中的SDN控制器控制多个边缘交换机的体系结构中,边缘交换机依赖于控制器来获得指令。微突发持续时间很短,通常是几百毫秒,因此首要问题就是快速检测。控制平面对数据平面采取周期性地监控。网络测量周期较大而微突发持续时间较短导致无法发现微突发。微突发产生的流量巨大,通常达到TB级,会带来极高时延等不良后果,因此另一个重要问题则是快速消除。消除微突发的常见方法与相应不足如下:选择其他的交换机出口对微突发流进行重路由,该方法需要控制平面参与,通信与交互的延迟较大,不能及时消除微突发;以邻居交换机作为微突发流量的缓存空间,该方法无法应对邻居交换机队列也发生微突发的场景;在主机端进行发送速率调整等,该方法需要主机端修改网络协议;等等。Although the edge network implemented using Software-Defined Networking (SDN) has the advantages of flexibility brought by the separation of control and data architecture, it also faces the shortcomings of communication and interaction delay between the control plane and the data plane. In an architecture where a centralized SDN controller controls multiple edge switches, the edge switches rely on the controller for instructions. Microbursts are short in duration, typically a few hundred milliseconds, so fast detection is the primary concern. The control plane periodically monitors the data plane. The network measurement period is large and the microburst duration is short so that the microburst cannot be detected. The traffic generated by micro-burst is huge, usually reaching the terabyte level, which will bring adverse consequences such as extremely high latency. Therefore, another important problem is to eliminate it quickly. The common methods and corresponding deficiencies of eliminating micro-burst are as follows: Select other switch exports to re-route the micro-burst flow, this method requires the participation of the control plane, the delay of communication and interaction is large, and the micro-burst cannot be eliminated in time; The switch is used as a buffer space for micro-burst traffic, and this method cannot cope with the scenario where micro-burst occurs in the queue of neighboring switches; the sending rate is adjusted on the host side, etc., this method requires the host side to modify the network protocol; and so on.
近些年可编程交换机迅速发展,P4交换机(支持使用P4编程语言)构成的可编程数据平面提供了一种用户自定义数据包处理和转发行为的灵活方式,避免了与控制平面的通信延迟,因此采用P4交换机作为物联网边缘交换机的实体是更优的选择。P4交换机可以灵活编程,但由于要支持数据高速转发同时内部寄存器等资源较少,所以自定义的转发算法要有较低的时间和空间复杂度。因此在P4交换机上实现的微突发检测与消除方法也不得不考虑资源上的限制。Programmable switches have developed rapidly in recent years. The programmable data plane composed of P4 switches (supporting the use of the P4 programming language) provides a flexible way for users to customize packet processing and forwarding behavior, avoiding communication delays with the control plane. Therefore, it is a better choice to use the P4 switch as the entity of the IoT edge switch. The P4 switch can be programmed flexibly, but since it needs to support high-speed data forwarding and less resources such as internal registers, the self-defined forwarding algorithm must have lower time and space complexity. Therefore, the micro-burst detection and elimination method implemented on the P4 switch also has to consider resource constraints.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对现有技术的以上缺陷或改进需求,本发明提供了一种基于可编程数据平面的微突发检测与消除方法、系统,其目的在于如何同时考虑到微突发流的时延需求和物联网边缘网络的物理资源限制,实现快速检测和消除微突发。In view of the above defects or improvement requirements of the prior art, the present invention provides a method and system for microburst detection and elimination based on a programmable data plane, the purpose of which is how to simultaneously consider the delay requirements and physical properties of microburst streams Physical resource constraints of connected edge networks, enabling rapid detection and elimination of microbursts.
为实现上述目的,本发明提供了一种基于可编程数据平面的微突发检测与消除方法,包括:In order to achieve the above object, the present invention provides a micro-burst detection and elimination method based on a programmable data plane, including:
S1.设置各优先级队列的最大出口速率和最大排队时延,微突发流阈值速率;S1. Set the maximum egress rate and maximum queuing delay of each priority queue, and the threshold rate of micro-burst flow;
S2.解析入流水线中多个数据流的时延需求,按照数据流所需时延越低,队列优先级越高的原则,将数据流分配到不同的优先级队列;S2. Analyze the latency requirements of multiple data streams in the pipeline, and allocate the data streams to different priority queues according to the principle that the lower the latency required by the data stream, the higher the queue priority;
S3.对每个数据流,预估数据流进入所属优先级队列的入口速率,并根据数据流所属优先级队列的最大出口速率,预估数据流进入所属优先级队列的排队时延;S3. For each data flow, estimate the entry rate of the data flow entering the priority queue to which it belongs, and estimate the queuing delay of the data flow entering the priority queue according to the maximum egress rate of the priority queue to which the data flow belongs;
若预估的入口速率大于设置的微突发流阈值速率,并且预估的排队时延大于对应优先级队列设置的最大排队时延,则判断该数据流为微突发流,并执行步骤S4;否则,返回步骤S2;If the estimated ingress rate is greater than the set micro-burst flow threshold rate, and the estimated queuing delay is greater than the maximum queuing delay set by the corresponding priority queue, the data flow is judged to be a micro-burst flow, and step S4 is executed ; otherwise, return to step S2;
S4.以微突发流所需时延作为保障目标,对优先级比微突发流所属优先级低的流进行动态速率调整。S4. Take the delay required by the micro-burst flow as the guarantee target, and perform dynamic rate adjustment on the flow whose priority is lower than that of the micro-burst flow.
优选地,对每个数据流,预估数据流进入所属优先级队列的入口速率,具体为:Preferably, for each data flow, estimate the entry rate at which the data flow enters the priority queue to which it belongs, specifically:
01.判断数据流当前数据包进入交换机流水线的时间戳tc,与该流上一个数据包时间戳tp的大小;若tc大于tp,则设置当前数据包与上一个数据包的时间间隔Ti=tc-tp;否则,Ti设置为0;01. Determine the time stamp tc of the current data packet entering the switch pipeline of the data flow, and the size of the time stamp tp of the previous data packet in the flow; if tc is greater than tp , set the time between the current data packet and the previous data packet interval Ti =tc -tp ; otherwise, Ti is set to 0;
02.统计进入数据流所属优先级队列的数据包序列数目N;02. Count the number N of data packet sequences entering the priority queue to which the data flow belongs;
03.由以下公式计算数据流进入所属优先级队列的入口速率V:03. Calculate the entry rate V of the data flow entering the priority queue to which it belongs by the following formula:
i表示当前数据包与上一个数据包的时间间隔的序列标号。i represents the sequence number of the time interval between the current data packet and the previous data packet.
优选地,根据数据流所属优先级队列的最大出口速率,预估数据流进入所属优先级队列的排队时延,具体为:Preferably, according to the maximum egress rate of the priority queue to which the data stream belongs, estimate the queuing delay of the data stream entering the priority queue to which it belongs, specifically:
求解数据流所属优先级队列最大出口速率的倒数,得到相邻数据包的最小传输时延To;Solve the inverse of the maximum egress rate of the priority queue to which the data flow belongs, and obtain the minimum transmission delay To of adjacent data packets;
由以下公式计算数据流进入所属优先级队列的排队时延Tq:The queuing delay Tq of the data flow entering the priority queue to which it belongs is calculated by the following formula:
优选地,步骤S4具体为,Preferably, step S4 is specifically:
S4.1.如果存在多条数据流比微突发流所属优先级低,则优先丢弃优先级最低的数据流的数据包,再丢弃优先级次低的数据包,以此类推;S4.1. If there are multiple data streams with a lower priority than the micro-burst stream, the data packets of the data stream with the lowest priority will be discarded first, and then the data packets with the next lowest priority will be discarded, and so on;
S4.2.对于需要丢包的数据流,则设置丢包间隔W和监控时间Tm;S4.2. For the data flow that needs packet loss, set the packet loss interval W and monitoring timeTm ;
S4.3.每W个数据包丢弃第W个数据包;S4.3. Discard the Wth data packet every W data packets;
S4.4.若经过监控时间Tm,Tq仍大于设置的最大排队时延,则减小丢包间隔W;若否,则结束丢包。S4.4. If the monitoring time Tm elapses, and Tq is still greater than the set maximum queuing delay, reduce the packet loss interval W; if not, end the packet loss.
优选地,每次将丢包间隔W减小为原来的一半。Preferably, the packet loss interval W is reduced to half of the original value each time.
优选地,W最小为1且不再改变。Preferably, W is at least 1 and does not change.
总体而言,通过本发明所构思的以上技术方案与现有技术相比,能够取得下列有益效果。In general, compared with the prior art, the above technical solutions conceived by the present invention can achieve the following beneficial effects.
缩小检测微突发的时间。P4中的Meter测量流的速率,Meter三色标记(trTCM)测量IP数据流并将其数据包标记为绿色、黄色或红色。需要提前设置PIR、CIR两种速率,PIR大于CIR。如果数据流速率超过PIR,则将其标记为红色。否则,根据它是否超过CIR,将其标记为黄色或绿色。通常设置某一对固定的PIR、CIR无法达到预期测量效果。数据平面的Meter常需要联合控制平面去动态调整PIR、CIR来达到较为精确的测量效果,但由于控制平面和数据平面的延迟,对微突发流速率不能取得好的测量效果。本发明提出在数据平面快速估计速率的方法,不需要控制平面的参与,仅使用寄存器、计数器等资源和内置的时间戳等信息,便可以达到快速检测。Reduce the time to detect microbursts. The Meter in P4 measures the rate of the flow, and the Meter Tri-Color Marking (trTCM) measures IP traffic and marks its packets as green, yellow, or red. You need to set the PIR and CIR rates in advance, and the PIR is greater than the CIR. If the data flow rate exceeds the PIR, it is marked red. Otherwise, it is marked yellow or green depending on whether it exceeds the CIR. Usually, setting a fixed pair of PIR and CIR cannot achieve the expected measurement effect. The meter of the data plane often needs to work with the control plane to dynamically adjust the PIR and CIR to achieve a more accurate measurement effect. However, due to the delay between the control plane and the data plane, the micro-burst flow rate cannot be measured well. The present invention proposes a method for rapidly estimating the rate in the data plane, which does not require the participation of the control plane, and only uses resources such as registers, counters, and built-in time stamps to achieve rapid detection.
检测微突发时不会增加入流水线的输入带宽。P4交换机采用流水线的架构处理和转发数据包,数据包在入流水线上选择进入的出口队列或被丢弃,随后是不可编程的流量管理器(包含队列),在出流水线上可以获得在队列中的相关信息(队列长度、排队时延等)。相关队列信息可以作为判断微突发的标志,通常需要将相关队列信息通过包复制传递到入流水线,以对微突发流采取相应的处理策略。若对所有数据包都采取以队列信息作为包头的包复制加传递的方式,会增加入流水线的输入带宽同时处理代价较大。本发明提出快速估计排队时延的方法,通过记录数据包到达时间和已知的数据包离开时间来估计排队时延,不会增加入流水线的输入带宽。Detecting microbursts does not increase the input bandwidth into the pipeline. P4 switches use a pipelined architecture to process and forward data packets. The data packets are selected on the ingress pipeline to enter the egress queue or discarded, followed by a non-programmable traffic manager (including queues), which can obtain the data in the queue on the outgoing pipeline. Relevant information (queue length, queuing delay, etc.). The relevant queue information can be used as an indicator for judging micro-bursts, and it is usually necessary to transmit the relevant queue information to the incoming pipeline through packet replication, so as to adopt a corresponding processing strategy for the micro-burst flow. If all data packets are copied and transmitted with the queue information as the packet header, the input bandwidth of the pipeline will be increased and the processing cost will be high. The invention proposes a method for quickly estimating the queuing delay, which estimates the queuing delay by recording the arrival time of the data packet and the known departure time of the data packet, without increasing the input bandwidth of the pipeline.
快速消除微突发,保障微突发流的时延需求。背景介绍的微突发消除方法直接考虑流量的大小并没有直接针对流的时延需求。本发明的方法针对微突发流直接以估计的排队时延作为保障目标,通过在入流水线丢包的方式,即丢弃一定数量时延需求最低的流量数据包,来快速消除微突发并保障其时延需求。Quickly eliminate micro-bursts and ensure the latency requirements of micro-burst flows. The micro-burst elimination method introduced in the background directly considers the size of the traffic and does not directly address the delay requirement of the flow. The method of the invention directly regards the estimated queuing delay as the guarantee target for the micro-burst flow, and quickly eliminates the micro-burst and guarantees the guarantee its delay requirements.
附图说明Description of drawings
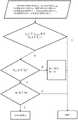
图1是一种基于可编程数据平面的微突发检测与消除方法流程图;Fig. 1 is a kind of micro-burst detection and elimination method flow chart based on programmable data plane;
图2是针对时延需求的微突发消除(丢包过程)示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of microburst elimination (packet loss process) for delay requirements.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。此外,下面所描述的本发明各个实施方式中所涉及到的技术特征只要彼此之间未构成冲突就可以相互组合。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as there is no conflict with each other.
一种基于可编程数据平面的微突发检测与消除方法,A micro-burst detection and elimination method based on programmable data plane,
本发明的方法所输入的微突发流量应当包括相应的时延需求,如经过某交换机的最大排队时延等,可以通过在IP包头携带相应的时延信息来生成相应流量。针对已经包含时延敏感需求的流量,本方法的处理流程包括以下步骤:The micro-burst traffic input by the method of the present invention should include the corresponding delay requirements, such as the maximum queuing delay passing through a switch, etc., and the corresponding traffic can be generated by carrying the corresponding delay information in the IP packet header. For traffic that already contains delay-sensitive requirements, the processing flow of this method includes the following steps:
步骤1:设置各优先级队列的最大出口速率和最大排队时延,微突发阈值速率。三个参数均在程序运行前设定,为可调整参数,速率表示方式为单位时间内经过的数据包数目。Step 1: Set the maximum egress rate and maximum queuing delay of each priority queue, and the micro-burst threshold rate. The three parameters are all set before the program runs and are adjustable parameters. The rate is expressed as the number of data packets that pass through in unit time.
步骤2:解析入流水线中多个数据流的时延需求,分配到优先级队列。该流要求时延越低,队列优先级越高。Step 2: Analyze the delay requirements of multiple data streams in the pipeline and assign them to priority queues. The lower the delay required by the flow, the higher the queue priority.
步骤3:微突发流检测。估算该流进入优先级队列的入口速率。结合该流所属优先级队列的最大出口速率,估算在优先级队列中的排队时延。若该流估算的入口速率大于设置的微突发流阈值速率,并且估算的排队时延大于设置的优先级队列最大排队时延,则认为该流是微突发流。Step 3: Microburst flow detection. Estimate the entry rate of this flow into the priority queue. Combined with the maximum egress rate of the priority queue to which the flow belongs, estimate the queuing delay in the priority queue. If the estimated ingress rate of the flow is greater than the set micro-burst flow threshold rate, and the estimated queuing delay is greater than the set maximum queuing delay of the priority queue, the flow is considered to be a micro-burst flow.
步骤4:以时延为保障目标的微突发消除。微突发消除具体方法为:对某些优先级比该流优先级低的流进行动态速率调整。Step 4: Micro-burst elimination with delay as the guarantee target. The specific method for eliminating the micro-burst is as follows: dynamic rate adjustment is performed on some flows with a lower priority than the flow.
优选地,步骤3包括以下子步骤:Preferably, step 3 includes the following sub-steps:
步骤3-1:记录该流的当前数据包进入交换机流水线的时间戳为tc,读出该流上一个数据包时间戳为tp。若tc大于tp,记录当前数据包与前一个数据包的时间间隔为Ti,即Ti=tc-tp。否则,Ti为0。Step 3-1: Record the time stamp of the current data packet of the flow entering the switch pipeline as tc , and read the time stamp of the previous data packet of the flow as tp . If tc is greater than tp , the time interval between recording the current data packet and the previous data packet is Ti , that is, Ti =tc -tp . Otherwise, Ti is zero.
步骤3-3:根据该流所属优先级队列的最大出口速率,得到相邻数据包的最小传输时延To。最小传输时延为最大出口速率的倒数,如设置最大出口速率为每秒1000个数据包,则To为0.001秒。Step 3-3: Obtain the minimum transmission delayTo of adjacent data packets according to the maximum egress rate of the priority queue to which the flow belongs. The minimum transmission delay is the reciprocal of the maximum egress rate. If the maximum egress rate is set to 1000 packets per second, thenTo is 0.001 seconds.
步骤3-4:记录进入该优先级队列的数据包数目为N。该流估算的排队时延Tq,估算的入口速率Vi由以下公式计算:Step 3-4: Record the number of packets entering the priority queue as N. The estimated queuing delay Tq for this flow, and the estimated ingress rate Vi are calculated by the following equations:
若该流估算的入口速率Vi大于设置的微突发流阈值速率,并且估算的排队时延Tq大于设置的优先级队列最大排队时延,则认为该流是微突发流并且需要保障时延。If the estimated ingress rate Vi of the flow is greater than the set micro-burst flow threshold rate, and the estimated queuing delay Tq is greater than the set maximum queuing delay of the priority queue, the flow is considered to be a micro-burst flow and needs to be guaranteed time delay.
优选地,步骤4包括以下子步骤:Preferably, step 4 includes the following sub-steps:
步骤4-1:对某些优先级比该微突发流优先级低的流进行动态速率调整。如果存在多条流比该流优先级低,则优先调整优先级最低的流的速率,比如本发明实例中该流优先级为7,则优先丢弃优先级为0的流的数据包,再丢弃优先级为1的流的数据包,依此类推。Step 4-1: Perform dynamic rate adjustment for some flows with a lower priority than the micro-burst flow. If there are multiple flows with a lower priority than the flow, the rate of the flow with the lowest priority will be adjusted first. For example, in the example of the present invention, if the flow priority is 7, the data packets of the flow with the priority of 0 will be discarded first, and then discarded. Packets for streams with priority 1, and so on.
步骤4-2:判断该优先级的流是否丢包。如果丢包,则设置丢包间隔W和监控时间Tm。每W个数据包丢弃第W个数据包(如,计数器统计10个数据包,当计数到10个数据包就丢弃第10个数据包),若经过监控时间Tm,Tq仍大于设置的最大排队时延,减小丢包间隔,具体流程参考图2,本发明实施例将丢包间隔W变为原来的一半,W最小为1且不再改变。如果不丢包,则无操作。Step 4-2: Determine whether the flow of this priority has lost packets. If the packet is lost, set the packet loss interval W and the monitoring time Tm . The W-th data packet is discarded every W data packets (for example, the counter counts 10 data packets, and when 10 data packets are counted, the 10th data packet is discarded). If the monitoring time Tm elapses, Tq is still greater than the set value The maximum queuing delay reduces the packet loss interval. Refer to FIG. 2 for the specific process. In this embodiment of the present invention, the packet loss interval W is changed to half of the original value, and W is at least 1 and will not change. If no packets are lost, no operation.
本领域的技术人员容易理解,以上所述仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,并不用以限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内所作的任何修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。Those skilled in the art can easily understand that the above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent replacements and improvements made within the spirit and principles of the present invention, etc., All should be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210233618.7ACN114745309B (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2022-03-10 | Micro burst detection and elimination method and system based on programmable data plane |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210233618.7ACN114745309B (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2022-03-10 | Micro burst detection and elimination method and system based on programmable data plane |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114745309Atrue CN114745309A (en) | 2022-07-12 |
| CN114745309B CN114745309B (en) | 2024-05-24 |
Family
ID=82274395
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210233618.7AActiveCN114745309B (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2022-03-10 | Micro burst detection and elimination method and system based on programmable data plane |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114745309B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116582507A (en)* | 2023-07-12 | 2023-08-11 | 华中科技大学 | Network microburst detection method and related equipment based on programmable switch |
| WO2024114642A3 (en)* | 2022-12-02 | 2024-08-02 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Data packet processing method and communication device |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140177443A1 (en)* | 2012-12-21 | 2014-06-26 | Fujitsu Limited | Relay apparatus and buffer control method |
| US20190334792A1 (en)* | 2018-04-30 | 2019-10-31 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Detecting microbursts |
| KR102064679B1 (en)* | 2018-07-25 | 2020-01-09 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | Method for processing data |
| CN112187586A (en)* | 2020-10-13 | 2021-01-05 | 盛科网络(苏州)有限公司 | Method and device for monitoring micro burst flow |
- 2022
- 2022-03-10CNCN202210233618.7Apatent/CN114745309B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140177443A1 (en)* | 2012-12-21 | 2014-06-26 | Fujitsu Limited | Relay apparatus and buffer control method |
| US20190334792A1 (en)* | 2018-04-30 | 2019-10-31 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Detecting microbursts |
| KR102064679B1 (en)* | 2018-07-25 | 2020-01-09 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | Method for processing data |
| CN112187586A (en)* | 2020-10-13 | 2021-01-05 | 盛科网络(苏州)有限公司 | Method and device for monitoring micro burst flow |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 张曼: "基于5G移动通信的集中式无线接入网络负载均衡算法研究", 《硕士电子期刊》, 15 September 2021 (2021-09-15)* |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024114642A3 (en)* | 2022-12-02 | 2024-08-02 | 维沃移动通信有限公司 | Data packet processing method and communication device |
| CN116582507A (en)* | 2023-07-12 | 2023-08-11 | 华中科技大学 | Network microburst detection method and related equipment based on programmable switch |
| CN116582507B (en)* | 2023-07-12 | 2023-10-03 | 华中科技大学 | Network microburst flow detection method and related equipment based on programmable switch |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114745309B (en) | 2024-05-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20210006482A1 (en) | Broadband communication link performance monitoring method for communication devices | |
| US8116225B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for estimating channel bandwidth | |
| JP4738148B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for estimating available bandwidth on a packet network | |
| US8229705B1 (en) | Performance monitoring in computer networks | |
| US20050232227A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for characterizing an end-to-end path of a packet-based network | |
| US10637792B2 (en) | Real-time analysis of quality of service for multimedia traffic in a local area network | |
| US20160192233A1 (en) | Congestion control for a multimedia session | |
| CN111316605A (en) | Layer 3 Fair Rate Congestion Control Notification | |
| WO2002087276A2 (en) | Method and device for robust real-time estimation of bottleneck bandwidth | |
| CN114745309A (en) | A method and system for microburst detection and elimination based on programmable data plane | |
| US20160337212A1 (en) | Uplink Performance Management | |
| CN112260899B (en) | Network monitoring method and device based on MMU (memory management unit) | |
| WO2021138604A1 (en) | Systems and methods for real-time monitoring and optimization of mobile networks | |
| US20080137540A1 (en) | Method And Apparatus For Analysing Traffic In A Network | |
| US8867350B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for packet buffering measurement | |
| US7889647B2 (en) | Switching apparatus for switching real-time packet in real time and packet switching method | |
| CN114629847A (en) | Coupling multi-flow TCP congestion control method based on available bandwidth allocation | |
| JP2003258881A (en) | Adaptive quality control method | |
| JP4766703B2 (en) | Edge node and bandwidth control method | |
| JP5528372B2 (en) | Flow quality degradation identification device and method | |
| JP7514970B1 (en) | Packet monitoring device, communication system, and program | |
| WO2025148816A1 (en) | Network measurement method and related device | |
| Yang et al. | Cross-Layer Assisted Early Congestion Control for Cloud VR Applications in 5G Edge Networks | |
| Antonyuk | Performance Evaluation of Computer Campus Network Segments | |
| CN116582507A (en) | Network microburst detection method and related equipment based on programmable switch |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |