CN114736820B - Pseudomonas orange strain and application thereof - Google Patents
Pseudomonas orange strain and application thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114736820B CN114736820BCN202210347984.5ACN202210347984ACN114736820BCN 114736820 BCN114736820 BCN 114736820BCN 202210347984 ACN202210347984 ACN 202210347984ACN 114736820 BCN114736820 BCN 114736820B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- strain
- pseudoalteromonas
- aurantia
- pathogenic bacteria
- preservation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 241000589516PseudomonasSpecies0.000titleclaimsdescription3
- 244000052616bacterial pathogenSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 241000519590PseudoalteromonasSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 238000004321preservationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 241000158004Pseudoalteromonas aurantiaSpecies0.000claimsdescription14
- 241000191967Staphylococcus aureusSpecies0.000claimsdescription8
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 241000588724Escherichia coliSpecies0.000claimsdescription4
- 241000589517Pseudomonas aeruginosaSpecies0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000003674animal food additiveSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 244000005700microbiomeSpecies0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000003975animal breedingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 244000037640animal pathogenSpecies0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 244000052769pathogenSpecies0.000claims1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000abstractdescription12
- 230000000171quenching effectEffects0.000abstractdescription8
- 238000010791quenchingMethods0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000006698inductionEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000002779inactivationEffects0.000abstract1
- 238000012827research and developmentMethods0.000abstract1
- 230000001580bacterial effectEffects0.000description10
- 238000009395breedingMethods0.000description8
- 230000001488breeding effectEffects0.000description8
- 239000003242anti bacterial agentSubstances0.000description6
- 208000035143Bacterial infectionDiseases0.000description5
- 229940088710antibiotic agentDrugs0.000description5
- 230000003042antagnostic effectEffects0.000description4
- 208000022362bacterial infectious diseaseDiseases0.000description4
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description4
- 230000011664signalingEffects0.000description4
- 10802000446516S ribosomal RNAProteins0.000description3
- 241000607598VibrioSpecies0.000description3
- 241000544286Vibrio anguillarumSpecies0.000description3
- 230000000844anti-bacterial effectEffects0.000description3
- 230000003385bacteriostatic effectEffects0.000description3
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description3
- 208000031295Animal diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 241001135140Vibrio orientalisSpecies0.000description2
- 239000013543active substanceSubstances0.000description2
- 230000003321amplificationEffects0.000description2
- 230000001276controlling effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description2
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description2
- 238000003199nucleic acid amplification methodMethods0.000description2
- 230000007918pathogenicityEffects0.000description2
- 239000006041probioticSubstances0.000description2
- 235000018291probioticsNutrition0.000description2
- 238000012216screeningMethods0.000description2
- 239000007787solidSubstances0.000description2
- 239000000304virulence factorSubstances0.000description2
- 230000007923virulence factorEffects0.000description2
- 229920001817AgarPolymers0.000description1
- 241000194103Bacillus pumilusSpecies0.000description1
- 102100026189Beta-galactosidaseHuman genes0.000description1
- 239000002028BiomassSubstances0.000description1
- 241000588879Chromobacterium violaceumSpecies0.000description1
- 206010059866Drug resistanceDiseases0.000description1
- 108010059881LactaseProteins0.000description1
- JKEJEOJPJVRHMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-NN-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactoneNatural productsCCCCCCCC(=O)NC1CCOC1=OJKEJEOJPJVRHMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000007990PIPES bufferSubstances0.000description1
- 206010034133Pathogen resistanceDiseases0.000description1
- 241000238552Penaeus monodonSpecies0.000description1
- 241000607142SalmonellaSpecies0.000description1
- 241000607768ShigellaSpecies0.000description1
- 241000194017StreptococcusSpecies0.000description1
- 239000008272agarSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000137annealingMethods0.000description1
- 230000008485antagonismEffects0.000description1
- 108010005774beta-GalactosidaseProteins0.000description1
- 230000033228biological regulationEffects0.000description1
- 230000000903blocking effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000015556catabolic processEffects0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 238000012258culturingMethods0.000description1
- 238000006731degradation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000004925denaturationMethods0.000description1
- 230000036425denaturationEffects0.000description1
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000009792diffusion processMethods0.000description1
- 238000007865dilutingMethods0.000description1
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description1
- 239000012154double-distilled waterSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003640drug residueSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 235000013305foodNutrition0.000description1
- 125000001475halogen functional groupChemical group0.000description1
- 230000036039immunityEffects0.000description1
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000description1
- 239000002054inoculumSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000968intestinal effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007413intestinal healthEffects0.000description1
- 229940116108lactaseDrugs0.000description1
- 238000009629microbiological cultureMethods0.000description1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description1
- JKEJEOJPJVRHMQ-JTQLQIEISA-Nn-(2-oxotetrahydrofuran-3-yl)octanamideChemical compoundCCCCCCCC(=O)N[C@H]1CCOC1=OJKEJEOJPJVRHMQ-JTQLQIEISA-N0.000description1
- 235000015097nutrientsNutrition0.000description1
- 238000002205phenol-chloroform extractionMethods0.000description1
- 239000002504physiological saline solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 239000013641positive controlSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012257pre-denaturationMethods0.000description1
- 235000013406prebioticsNutrition0.000description1
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000description1
- 230000000529probiotic effectEffects0.000description1
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000001228spectrumMethods0.000description1
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description1
- 238000000844transformationMethods0.000description1
- 238000011144upstream manufacturingMethods0.000description1
- 230000001018virulenceEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A23—FOODS OR FOODSTUFFS; TREATMENT THEREOF, NOT COVERED BY OTHER CLASSES
- A23K—FODDER
- A23K10/00—Animal feeding-stuffs
- A23K10/10—Animal feeding-stuffs obtained by microbiological or biochemical processes
- A23K10/16—Addition of microorganisms or extracts thereof, e.g. single-cell proteins, to feeding-stuff compositions
- A23K10/18—Addition of microorganisms or extracts thereof, e.g. single-cell proteins, to feeding-stuff compositions of live microorganisms
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K35/00—Medicinal preparations containing materials or reaction products thereof with undetermined constitution
- A61K35/66—Microorganisms or materials therefrom
- A61K35/74—Bacteria
- A61K35/741—Probiotics
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/04—Antibacterial agents
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N1/00—Microorganisms, e.g. protozoa; Compositions thereof; Processes of propagating, maintaining or preserving microorganisms or compositions thereof; Processes of preparing or isolating a composition containing a microorganism; Culture media therefor
- C12N1/20—Bacteria; Culture media therefor
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02A50/00—TECHNOLOGIES FOR ADAPTATION TO CLIMATE CHANGE in human health protection, e.g. against extreme weather
- Y02A50/30—Against vector-borne diseases, e.g. mosquito-borne, fly-borne, tick-borne or waterborne diseases whose impact is exacerbated by climate change
Landscapes
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Tropical Medicine & Parasitology (AREA)
- Animal Husbandry (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于微生物技术领域,特别是涉及一种橙色假交替单胞菌菌株。The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes, in particular to a strain of Pseudoalteromonas aurantiac.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,我国的畜牧业取得了飞速的发展,畜牧业养殖规模日益扩大,养殖模式已经由家庭农场向规模化养殖场转换,畜牧业效益逐渐增加,为国民经济做出了突出贡献。随着养殖模式的集约化和规模化发展,养殖密度增加也为动物疫病防控带来新的挑战。细菌感染也是动物疫病中的重要组成部分,目前应对细菌感染主要依靠抗生素,但抗生素的使用又带来了严重的细菌耐药问题和动物性食品中和药物残留超标问题,阻碍了养殖业的健康可持续发展。尤其是随着禁抗令的颁布和实行,寻找好的抗生素替代品保障养殖安全变得尤为重要。In recent years, my country's animal husbandry has achieved rapid development, the scale of animal husbandry has been expanding day by day, the breeding mode has been transformed from family farms to large-scale farms, and the benefits of animal husbandry have gradually increased, making outstanding contributions to the national economy. With the intensive and large-scale development of breeding models, the increase in breeding density has also brought new challenges to the prevention and control of animal diseases. Bacterial infection is also an important part of animal diseases. At present, antibiotics are mainly used to deal with bacterial infections. However, the use of antibiotics has brought about serious bacterial resistance and excessive drug residues in animal foods, hindering the health of the breeding industry. sustainable development. Especially with the promulgation and implementation of the ban on antibiotics, it is particularly important to find good alternatives to antibiotics to ensure the safety of breeding.
有益菌也称为益生菌,是来源于自然界中,具有益生作用的一类有益微生物的统称。从50多年前使用的乳酶生至今,有益菌微生态制剂已在畜牧养殖业中得到广泛应用,并已经成为减抗、替抗的较优选择。有益菌可以抑制病原菌生长、提高机体免疫力、提供机体所需营养物质等,可以实现防病治病、提高养殖效益的作用。而且随着养殖成本的日益增加,有益菌却具有成本低廉、适应性强、环境友好、使用简便等优点,更加成为养殖业健康管理的热点。Beneficial bacteria, also known as probiotics, is a general term for a class of beneficial microorganisms that come from nature and have a prebiotic effect. Since the use of lactase more than 50 years ago, probiotic microecological preparations have been widely used in animal husbandry, and have become a better choice for reducing and replacing antibiotics. Beneficial bacteria can inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, improve the body's immunity, provide the nutrients needed by the body, etc., and can prevent and cure diseases and improve the efficiency of breeding. Moreover, with the increasing cost of breeding, beneficial bacteria have the advantages of low cost, strong adaptability, environmental friendliness, and easy use, and have become a hot spot for health management in the breeding industry.
筛选针对某些特定病原菌的拮抗菌是获得有益菌的一种快速有效的手段,拮抗现象在自然界中普遍存在。利用有益菌来拮抗病原菌,不仅可以抑制病原菌的生长、降低其毒力因子的表达,而且可以改善动物的肠道环境,提高动物肠道健康水平,从而实现微生态调节的功效。细菌的信号系统是菌体之间信息交流的主要渠道,在调控细菌耐药性方面也发挥重要的作用。通过淬灭细胞间的信号分子,阻断病原菌之间的交流,可以有效干扰致病菌毒力因子的表达,降低病原菌的致病性。因此,开发既具有抑菌功能,又兼具淬灭病原菌信号系统的有益菌,有望成为控制细菌感染的新途径和新策略。Screening antagonistic bacteria against certain specific pathogenic bacteria is a fast and effective way to obtain beneficial bacteria, and antagonism phenomena are ubiquitous in nature. The use of beneficial bacteria to antagonize pathogenic bacteria can not only inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria and reduce the expression of their virulence factors, but also improve the intestinal environment of animals and improve the intestinal health of animals, thereby achieving the effect of microecological regulation. The bacterial signaling system is the main channel for information exchange between bacteria, and also plays an important role in regulating bacterial drug resistance. By quenching the signaling molecules between cells and blocking the communication between pathogenic bacteria, it can effectively interfere with the expression of virulence factors of pathogenic bacteria and reduce the pathogenicity of pathogenic bacteria. Therefore, the development of beneficial bacteria with both antibacterial function and quenching pathogenic bacteria signaling system is expected to become a new way and new strategy to control bacterial infection.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明的目的是提供一株橙色假交替单胞菌菌株及其应用,即一种可以抑制多种病原菌的生长、并具有密度感应淬灭活性的海洋源有益菌,可以作为潜在的有益菌为控制细菌性病害提供新的方案。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a strain of Pseudoalteromonas aurantiac and its application, that is, a marine-derived beneficial bacterium that can inhibit the growth of various pathogenic bacteria and has density induction quenching activity, which can be used as a potential beneficial bacterium Provide new solutions for controlling bacterial diseases.
为解决上述技术问题,本发明采用的一个技术方案是:一种橙色假交替单胞菌菌株,所述橙色假交替单胞菌菌株的保藏名称为橙色假交替单胞菌(Pseudoalteromonasaurantia)DL1,保藏单位为中国微生物菌种保藏管理委员会普通微生物中心,保藏号为CGMCC No.8687。In order to solve the above-mentioned technical problems, a technical scheme adopted in the present invention is: a kind of Pseudoalteromonas aurantias strain, the preserved name of described Pseudoalteromonas aurantias strain is Pseudoalteromonas aurantia (Pseudoalteromonasaurantia) DL1, deposit The unit is the General Microbiology Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.8687.
所述的一种橙色假交替单胞菌菌株在制备抑制动物病原菌中的应用。The application of the described Pseudoalteromonas aurantiacens strain in the preparation of inhibiting animal pathogens.
进一步地说,所述病原菌为金黄色葡萄球菌、绿脓杆菌、大肠杆菌或鳗弧菌。Further, the pathogenic bacteria are Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli or Vibrio anguillarum.
一种由所述的橙色假交替单胞菌菌株制成的菌剂。A bacterial agent made from the Pseudoalteromonas aurantiacus strain.
所述的一种橙色假交替单胞菌菌株制成得菌剂在制备饲料添加剂或动物养殖过程中的药品的应用。The application of the bacterium prepared from the Pseudoalteromonas aurantiacus strain in the preparation of feed additives or medicines in the process of animal breeding.
本发明的有益效果:本发明的橙色假交替单胞菌DL1菌株可通过产生抑菌活性物质抑制多种常见病原菌,并可产生密度感应淬灭活性物质,降低或消除致病菌的毒力和致病性。Beneficial effects of the present invention: the Pseudomonas aurantiacus DL1 strain of the present invention can inhibit a variety of common pathogenic bacteria by producing antibacterial active substances, and can produce density induction quenching active substances to reduce or eliminate the virulence of pathogenic bacteria and pathogenicity.
附图说明Description of drawings
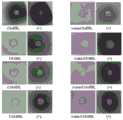
图1是本发明基于16S rRNA序列构建的菌株DL1系统发育树;Fig. 1 is the strain DL1 phylogenetic tree constructed based on the 16S rRNA sequence of the present invention;
图2是本发明不同培养时间对菌株DL1生物量(图a)以及不同培养时间菌株DL1对VBI72产生抑菌圈的范围(图b);Fig. 2 is the scope (figure b) that bacterial strain DL1 of different culture times of the present invention produces the bacteriostatic zone to VBI72 to bacterial strain DL1 biomass (figure a) and different culture time;
图3是本发明菌株DL1降解AHL类信号分子结果图。Fig. 3 is a graph showing the results of the degradation of AHL signal molecules by the strain DL1 of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图对本发明的较佳实施例进行详细阐述,以使本发明的优点和特征能更易于被本领域技术人员理解,从而对本发明的保护范围做出更为清楚明确的界定。The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, so that the advantages and features of the present invention can be more easily understood by those skilled in the art, so as to define the protection scope of the present invention more clearly.
实施例1、一种橙色假交替单胞菌DL1菌株的筛选Embodiment 1, the screening of a kind of Pseudoalteromonas aurantiacens DL1 bacterial strain
选取五条健康斑节对虾,研磨后涂布于海洋细菌培养基2216E平板上,28℃恒温培养48h。随机挑取若干单菌落点种于涂有鳗弧菌的平板上,发现一个淡黄色的菌落周围有抑菌圈,随即挑取该单菌落进行继代培养,直至得到纯化菌株,编号为DL1。该菌种已在国家知识产权局中国微生物菌种保藏管理委员会普通微生物中心(地址为北京朝阳区北辰西路1号院3号)保藏,保藏日期为2014年01月06日,保藏编号为CGMCC No.8687。Select five healthy Penaeus monodon prawns, grind them, spread them on the plate of Marine Bacteria Medium 2216E, and culture them at a constant temperature of 28°C for 48 hours. A number of single colonies were randomly selected and planted on a plate coated with Vibrio anguillarum, and a light yellow colony was found to have a bacteriostatic zone around it, and then the single colony was picked for subculture until a purified strain was obtained, numbered DL1. This strain has been preserved in the General Microbiology Center of the China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee of the State Intellectual Property Office (address: No. 3, No. 1 Yard, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing). The preservation date is January 06, 2014, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 8687.
将菌株在2216E培养基中培养过夜,酚氯仿抽提法抽提菌株DL1的基因组DNA,使用细菌通用引物,上游引物序列为27F(5')-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-(3'),下游引物序列为1492R(5')-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-(3'),对其16S rRNA基因序列进行PCR扩增。The strain was cultured overnight in 2216E medium, and the genomic DNA of the strain DL1 was extracted by phenol-chloroform extraction, using bacterial universal primers, the sequence of the upstream primer was 27F(5')-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-(3'), and the sequence of the downstream primer was 1492R (5')-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-(3'), the 16S rRNA gene sequence was amplified by PCR.
具体采用的扩增体系为:2×Taq Master Mix 12.5μL、正反向引物(10μM)各1μL、DNA模板2μL、ddH2O 8.5μL,总体系25μL;扩增条件为:95℃预变性5min;95℃变性1min、55℃退火1min、72℃延伸1.5min,循环30次;最后72℃延伸10min。The specific amplification system used is: 2×Taq Master Mix 12.5 μL, forward and reverse primers (10 μM) 1 μL each, DNA template 2 μL, ddH2O 8.5 μL,
PCR产物经测序后在NCBI中进行序列比对,和橙色假交替单胞菌(Pseudoalteromonas aurantia)NCIMB 2033T的同源性最高,达到100%。采用MEGA5.1构建系统发育进化树(如图1所示),其与Pseudoalteromonas aurantia NCIMB 2033T的亲缘关系最近,初步确定该菌株为假交替单胞菌属(pseudoalteromonas)。16S rRNA序列如SEQ IDNO.1。After the PCR product was sequenced, the sequence was compared in NCBI, and the homology with Pseudoalteromonas aurantia (Pseudoalteromonas aurantia) NCIMB 2033T was the highest, reaching 100%. Using MEGA5.1 to construct a phylogenetic tree (as shown in Figure 1), it has the closest relationship with Pseudoalteromonas aurantia NCIMB 2033T , and the strain was preliminarily determined to be pseudoalteromonas (pseudoalteromonas). 16S rRNA sequence as SEQ ID NO.1.
实施例2、橙色假交替单胞菌DL1能够降解AHL类信号分子Example 2, Pseudoalteromonas aurantiacens DL1 can degrade AHL signal molecules
将菌株DL1接种于2216E液体培养基中,于摇床170rpm、28℃培养12h。The strain DL1 was inoculated in 2216E liquid medium, and cultured on a shaker at 170 rpm at 28°C for 12 hours.
AHL报告菌紫色色杆菌CV026和VIR24分别用于检测短链(C4~C8)和长链(C8~C14),将其分别接种于LB液体培养基中,转速170rpm、28℃培养24h。AHL reporter bacteria Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 and VIR24 were used to detect short chains (C4-C8) and long chains (C8-C14), respectively, which were inoculated in LB liquid medium at 170 rpm and cultured at 28°C for 24 hours.
将培养好的DL1菌液、PIPES缓冲液(1M,pH 6.7)以及AHL类信号分子(1mM)按比例为10:1:0.1混匀准备反应液,在28℃反应24h。The cultured DL1 bacterial solution, PIPES buffer (1M, pH 6.7) and AHL signal molecules (1mM) were mixed in a ratio of 10:1:0.1 to prepare the reaction solution, and reacted at 28°C for 24h.
报告菌按3%接种量加入到温度为45℃左右的半固体LB培养基中,将其混匀后倒至平板,待凝固后打孔后,将上述反应液取10μl加入检测孔,28℃培养观察蓝色或紫色晕圈的出现。信号分子采用AHL报告菌CVO26和VIR24检测剩余的AHL分子,检测孔周围的紫色圈的深浅和无色代表着剩余的AHL分子,通过与阳性对照的结果发现,菌株DL1能够降解一部分短链C6-HSL分子和C8-HSL分子,对长链信号分子均具有较强的淬灭活性,说明通过淬灭病原菌分泌的信号分子可能是菌株DL1发挥有益作用的一种方式。具体结果如下表1和图3。Add the reporter bacteria to the semi-solid LB medium at a temperature of about 45°C according to the inoculum amount of 3%. Incubate to watch for the appearance of a blue or purple halo. The signal molecule uses AHL reporter bacteria CVO26 and VIR24 to detect the remaining AHL molecules. The depth and colorlessness of the purple circle around the detection hole represent the remaining AHL molecules. Through the results of the positive control, it is found that the strain DL1 can degrade a part of the short chain C6- Both HSL molecules and C8-HSL molecules have strong quenching activity on long-chain signal molecules, indicating that quenching the signal molecules secreted by pathogenic bacteria may be a way for strain DL1 to exert beneficial effects. The specific results are shown in Table 1 and Figure 3 below.
表1菌株DL1对不同信号分子的淬灭效果Table 1 Quenching effect of strain DL1 on different signaling molecules
-不显紫色,+浅紫色,++较深紫色,+++深紫色。- No purple, + light purple, ++ darker purple, +++ dark purple.
实施例3、橙色假交替单胞菌DL1菌株可以抑制常见病原菌
采用琼脂扩散法检测菌株DL1对常见病原菌的抑制活性。21株病原菌均由本实验室分离保存,包括大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌、鳗弧菌、河弧菌、哈维氏弧菌、东方弧菌、短小芽孢杆菌、志贺氏杆菌、绿脓杆菌、沙门氏菌、链球菌。分别接种于2216E和LB液体培养基,制成菌液。用生理盐水稀释至一定浓度后涂布于2216E和LB固体培养基上,挑取菌株DL1点种在平板上。培养24-96h后,观察菌株DL1周围是否有透明圈,并测量直径(如图2所示)。实验结果表明橙色假交替单胞菌DL1对这21株病原菌具有较为广泛的抑菌谱,对其中的21株病原菌均具有较好的抑制作用,抑菌圈直径在10mm以上。其中,尤其对金黄色葡萄球菌PMJ4-1、金黄色葡萄球菌QTB1-1、金黄色葡萄球菌TTB2-1的拮抗作用最强,对金黄色葡萄球菌TTB1-1、鳗弧菌VIB72、东方弧菌VIB303拮抗作用次之,具体结果如表2所示。The inhibitory activity of strain DL1 against common pathogenic bacteria was detected by agar diffusion method. 21 strains of pathogenic bacteria were isolated and preserved by our laboratory, including Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio river, Vibrio harvey, Vibrio orientalis, Bacillus pumilus, Shigella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella, Streptococcus. Inoculated in 2216E and LB liquid medium respectively to make bacterial liquid. After diluting to a certain concentration with physiological saline, it was spread on 2216E and LB solid medium, and the strain DL1 was picked and planted on the plate. After culturing for 24-96 hours, observe whether there is a transparent circle around the strain DL1, and measure the diameter (as shown in FIG. 2 ). The experimental results showed that Pseudoalteromonas aurantiacens DL1 had a relatively broad antibacterial spectrum against these 21 strains of pathogenic bacteria, and had a good inhibitory effect on all 21 strains of pathogenic bacteria, and the diameter of the inhibition zone was more than 10 mm. Among them, the antagonistic effect on Staphylococcus aureus PMJ4-1, Staphylococcus aureus QTB1-1, Staphylococcus aureus TTB2-1 is the strongest, and it has the strongest antagonistic effect on Staphylococcus aureus TTB1-1, Vibrio eel VIB72, Vibrio orientalis The antagonistic effect of VIB303 was second, and the specific results are shown in Table 2.
表2菌株DL1对不同病原菌的抑菌结果Table 2 Bacteriostatic results of bacterial strain DL1 to different pathogenic bacteria
因此,本发明的橙色假交替单胞菌DL1菌株可以作为有效的抑菌制剂应用于动物养殖中,成为控制细菌感染的新方法。Therefore, the pseudoalteromonas aurantiacus DL1 strain of the present invention can be used as an effective antibacterial agent in animal breeding, and becomes a new method for controlling bacterial infection.
以上所述仅为本发明的实施例,并非因此限制本发明的专利范围,凡是利用本发明说明书及附图内容所作的等效结构变换,或直接或间接运用在其他相关的技术领域,均同理包括在本发明的专利保护范围内。The above is only an embodiment of the present invention, and does not limit the patent scope of the present invention. All equivalent structural transformations made by using the description of the present invention and the contents of the accompanying drawings, or directly or indirectly used in other related technical fields, are all the same. The theory is included in the patent protection scope of the present invention.
SEQUENCE LISTINGSEQUENCE LISTING
<110> 青岛农业大学<110> Qingdao Agricultural University
<120> 一种橙色假交替单胞菌菌株及其应用<120> A Pseudoalteromonas aurantias strain and its application
<130> 2022<130> 2022
<160> 1<160> 1
<170> PatentIn version 3.5<170> PatentIn version 3.5
<210> 1<210> 1
<211> 1444<211> 1444
<212> DNA<212>DNA
<213> 人工序列<213> Artificial sequence
<400> 1<400> 1
gcgatttggg gggccggccc taacacatgc aagtcgagcg gtaacatttc tagcttgcta 60gcgatttggg gggccggccc taacacatgc aagtcgagcg gtaacatttc tagcttgcta 60
gaagatgacg agcggcggac gggtgagtaa tgcttgggaa catgccttga ggtgggggac 120gaagatgacg agcggcggac gggtgagtaa tgcttgggaa catgccttga ggtggggac 120
aaccattgga aacgatggct aataccgcat aatgtctacg gaccaaaggg ggcttcggct 180aaccattgga aacgatggct aataccgcat aatgtctacg gaccaaaggg ggcttcggct 180
ctcgccttta gattggccca agtgggatta gctagttggt gaggtaaagg ctcaccaagg 240ctcgccttta gattggccca agtgggatta gctagttggt gaggtaaagg ctcaccaagg 240
cgacgatccc tagctggttt gagaggatga tcagccacac tggaactgag acacggtcca 300cgacgatccc tagctggttt gagaggatga tcagccacac tggaactgag acacggtcca 300
gactcctacg ggaggcagca gtggggaata ttgcacaatg ggcgcaagcc tgatgcagcc 360gactcctacg ggaggcagca gtggggaata ttgcacaatg ggcgcaagcc tgatgcagcc 360
atgccgcgtg tgtgaagaag gccttcgggt tgtaaagcac tttcagtcag gaggaaaggt 420atgccgcgtg tgtgaagaag gccttcgggt tgtaaagcac tttcagtcag gaggaaaggt 420
tagtagttaa tacctgctag ctgtgacgtt actgacagaa gaagcaccgg ctaactccgt 480tagtagttaa tacctgctag ctgtgacgtt actgacagaa gaagcaccgg ctaactccgt 480
gccagcagcc gcggtaatac ggagggtgcg agcgttaatc ggaattactg ggcgtaaagc 540gccagcagcc gcggtaatac ggagggtgcg agcgttaatc ggaattactg ggcgtaaagc 540
gtacgcaggc ggtttgttaa gcgagatgtg aaagccccgg gcttaacctg ggaactgcat 600gtacgcaggc ggtttgttaa gcgagatgtg aaagccccgg gcttaacctg ggaactgcat 600
ttcgaactgg caaactagag tgtgatagag ggtggtagaa tttcaggtgt agcggtgaaa 660ttcgaactgg caaactagag tgtgatagag ggtggtagaa tttcaggtgt agcggtgaaa 660
tgcgtagaga tctgaaggaa taccgatggc gaaggcagcc acctgggtca acactgacgc 720tgcgtagaga tctgaaggaa taccgatggc gaaggcagcc acctgggtca acactgacgc 720
tcatgtacga aagcgtgggg agcaaacagg attagatacc ctggtagtcc acgccgtaaa 780tcatgtacga aagcgtgggg agcaaacagg attagatacc ctggtagtcc acgccgtaaa 780
cgatgtctac taggagctgg ggtcttcgga caacttttcc aaagctaacg cattaagtag 840cgatgtctac taggagctgg ggtcttcgga caacttttcc aaagctaacg cattaagtag 840
accgcctggg gagtacggcc gcaaggttaa aactcaaatg aattgacggg ggcccgcaca 900accgcctggg gagtacggcc gcaaggttaa aactcaaatg aattgacggg ggcccgcaca 900
agcggtggag catgtggttt aattcgatgc aacgcgaaga accttaccta cacttgacat 960agcggtggag catgtggttt aattcgatgc aacgcgaaga accttaccta cacttgacat 960
acagagaact taccagagat ggtttggtgc cttcgggaac tctgatacag gtgctgcatg 1020acagagaact taccagagat ggtttggtgc cttcgggaac tctgatacag gtgctgcatg 1020
gctgtcgtca gctcgtgttg tgagatgttg ggttaagtcc cgcaacgagc gcaaccccta 1080gctgtcgtca gctcgtgttg tgagatgttg ggttaagtcc cgcaacgagc gcaacccccta 1080
tccttagttg ccagcgattc ggtcgggaac tctaaggaga ctgccggtga taaaccggag 1140tccttagttg ccagcgattc ggtcgggaac tctaaggaga ctgccggtga taaaccggag 1140
gaaggtgggg acgacgtcaa gtcatcatgg cccttacgtg tagggctaca cacgtgctac 1200gaaggtgggg acgacgtcaa gtcatcatgg cccttacgtg tagggctaca cacgtgctac 1200
aatggcaggt acagagagca gcgagctagc gatagtgagc gaatccctta aagcctgtcg 1260aatggcaggt acagagagca gcgagctagc gatagtgagc gaatccctta aagcctgtcg 1260
tagtccggat tggagtctgc aactcgactc catgaagtcg gaatcgctag taatcgcaaa 1320tagtccggat tggagtctgc aactcgactc catgaagtcg gaatcgctag taatcgcaaa 1320
tcagaatgtt gcggtgaata cgttcccggg ccttgtacac accgcccgtc acaccatggg 1380tcagaatgtt gcggtgaata cgttcccggg ccttgtacacaccgcccgtcacaccatggg 1380
agtgggttgc tccagaagtg gatagtctaa ccttcgggag gacgtcaacc caacccggaa 1440agtgggttgc tccagaagtg gatagtctaa ccttcgggag gacgtcaacc caacccggaa 1440
gggt 1444gggt 1444
Claims (2)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210347984.5ACN114736820B (en) | 2022-04-01 | 2022-04-01 | Pseudomonas orange strain and application thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210347984.5ACN114736820B (en) | 2022-04-01 | 2022-04-01 | Pseudomonas orange strain and application thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114736820A CN114736820A (en) | 2022-07-12 |
| CN114736820Btrue CN114736820B (en) | 2023-06-27 |
Family
ID=82280278
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210347984.5AActiveCN114736820B (en) | 2022-04-01 | 2022-04-01 | Pseudomonas orange strain and application thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114736820B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115975872A (en)* | 2022-11-25 | 2023-04-18 | 浙江大学杭州国际科创中心 | A kind of culture medium for conjugative transfer of Pseudoalteromonas chromatogenes and its application |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110241049A (en)* | 2019-07-04 | 2019-09-17 | 福州大学 | A strain of Pseudoalteromonas with alginolytic ability and its application to red tide of Karenia militaris |
| CN114774310A (en)* | 2022-04-01 | 2022-07-22 | 青岛农业大学 | A kind of pseudoalteromonas strain and its application |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20110110894A1 (en)* | 2009-11-10 | 2011-05-12 | Novozymes Biologicals, Inc. | Methods, compositions and systems for controlling fouling of a membrane |
| CN102304484B (en)* | 2011-08-16 | 2012-10-03 | 中国海洋大学 | New strain of pseudoalteromonas flavipulchra and use thereof |
| CN113234615B (en)* | 2021-03-18 | 2022-05-03 | 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所 | A fish-killing pseudoalteromonas and its application in aquaculture |
- 2022
- 2022-04-01CNCN202210347984.5Apatent/CN114736820B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110241049A (en)* | 2019-07-04 | 2019-09-17 | 福州大学 | A strain of Pseudoalteromonas with alginolytic ability and its application to red tide of Karenia militaris |
| CN114774310A (en)* | 2022-04-01 | 2022-07-22 | 青岛农业大学 | A kind of pseudoalteromonas strain and its application |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114736820A (en) | 2022-07-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107937300B (en) | Bacillus subtilis and application thereof in aquaculture | |
| CN106190933B (en) | The bacillus subtilis of the anti-pathogenic bacteria of wide spectrum and its application | |
| CN109439577B (en) | Broad-spectrum antibacterial bacillus amyloliquefaciens and application thereof | |
| CN107868763B (en) | Bacillus coagulans E21 for improving antioxidant stress capability of livestock and poultry after challenge and application thereof | |
| CN113549578B (en) | A strain of Bacillus siamese BsNlG13 inhibiting rice blast fungus and promoting seed germination and its application | |
| CN109777758B (en) | Bacillus licheniformis HYT-9 with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and preparation method and application of microbial inoculum thereof | |
| CN111269865B (en) | A strain of Brevibacterium lateralis S62-9 and use thereof | |
| Sivasubramanian et al. | Isolation and characterization of gut micro biota from some estuarine fishes | |
| CN108611299A (en) | One plant of lactobacillus plantarum for producing bacteriostatic peptide and its application | |
| CN108048373B (en) | A strain of Bacillus subtilis AH1005 and its application | |
| CN114736820B (en) | Pseudomonas orange strain and application thereof | |
| CN109136126B (en) | A strain of Pediococcus pentosaceus used to prevent diarrhea in weaned piglets | |
| CN104498385B (en) | High yield antibacterial peptide Bacillus licheniformis and application thereof | |
| KR101494230B1 (en) | Novel strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and animal feed additive containing it | |
| CN111004741B (en) | Deep-sea-derived campylobacter R29-2, microecological preparation and application thereof | |
| CN114480185B (en) | A kind of Sinorhizobium meliloti degrading zearalenone and its application | |
| CN112266890A (en) | A strain of Lactobacillus casei and its application | |
| CN113151113B (en) | A strain of Clostridium butyricum with strong antibacterial ability and its application | |
| KR100371503B1 (en) | Probiotic preparations for aquacultured fish and its production method | |
| CN114774310B (en) | A kind of pseudoalteromonas bacterial strain and application thereof | |
| Zhang et al. | Screening and identification of organics-degrading bacteria from the sediment of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus ponds | |
| Gheibipour et al. | Screening the Rumen of Balochi Camel (Camelus dromedarius) and Cashmere Goat (Capra hircus) to isolate enzyme-producing bacteria as potential additives for animal feed | |
| CN115651860B (en) | Bacillus coagulans BC-HYC strain and application thereof | |
| CN106635878A (en) | Streptomyces sp. 5X4 and applications thereof as biocontrol bacterium in preventing and treating plant diseases | |
| CN106190919B (en) | Application of the thermophilic cock Salmonella in degradative fungi toxin |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |