CN114697672B - Neural network quantization compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encoding - Google Patents
Neural network quantization compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encodingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114697672B CN114697672BCN202011607727.8ACN202011607727ACN114697672BCN 114697672 BCN114697672 BCN 114697672BCN 202011607727 ACN202011607727 ACN 202011607727ACN 114697672 BCN114697672 BCN 114697672B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- neural network
- character
- run
- length
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/42—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals characterised by implementation details or hardware specially adapted for video compression or decompression, e.g. dedicated software implementation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
- G06N3/082—Learning methods modifying the architecture, e.g. adding, deleting or silencing nodes or connections
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/10—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding
- H04N19/102—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the element, parameter or selection affected or controlled by the adaptive coding
- H04N19/12—Selection from among a plurality of transforms or standards, e.g. selection between discrete cosine transform [DCT] and sub-band transform or selection between H.263 and H.264
- H04N19/122—Selection of transform size, e.g. 8x8 or 2x4x8 DCT; Selection of sub-band transforms of varying structure or type
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/10—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding
- H04N19/102—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the element, parameter or selection affected or controlled by the adaptive coding
- H04N19/124—Quantisation
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/10—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding
- H04N19/102—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the element, parameter or selection affected or controlled by the adaptive coding
- H04N19/13—Adaptive entropy coding, e.g. adaptive variable length coding [AVLC] or context adaptive binary arithmetic coding [CABAC]
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Discrete Mathematics (AREA)
- Compression, Expansion, Code Conversion, And Decoders (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及神经网络运算领域,并特别涉及一种基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩方法及系统。The invention relates to the field of neural network computing, and in particular to a neural network quantization and compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encoding.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,人工智能在信息量和硬件算力双重爆发的背景下迅猛发展,已经日趋成为生产力发展和技术创新的主要推动力。作为人工智能技术的主要分支,神经网络算法为了进一步提高模型精度,已经遇到了结构复杂、参数量和计算量巨大的技术瓶颈,限制了神经网络模型在追求吞吐率和能效比场景下的应用,因此计算效率成为了下一阶段的主要研究目标。目前最有效的神经网络压缩方法结合了低精度和稀疏化,能够在一定程度上减少神经网络的参数量,但是无法进一步挖掘剪枝和量化后的神经网络模型中的数据冗余。In recent years, artificial intelligence has developed rapidly against the background of the double explosion of information volume and hardware computing power, and has increasingly become the main driving force for productivity development and technological innovation. As the main branch of artificial intelligence technology, in order to further improve the accuracy of the model, the neural network algorithm has encountered technical bottlenecks such as complex structure, large amount of parameters and huge amount of calculation, which limits the application of the neural network model in the pursuit of throughput and energy efficiency ratio scenarios. Therefore, computational efficiency becomes the main research goal in the next stage. Currently the most effective neural network compression method combines low precision and sparsification, which can reduce the number of parameters of the neural network to a certain extent, but cannot further exploit the data redundancy in the pruned and quantized neural network model.
剪枝(Pruning),如图1所示,也可以称作模型稀疏化,即直接将神经网络当中重要性较低的一部分参数裁剪为0,与这部分参数有关的计算也都被屏蔽,按照裁剪的基本单元可以分为单个参数剪枝和结构化参数剪枝。Pruning (Pruning), as shown in Figure 1, can also be called model sparsification, that is, directly cut some of the less important parameters in the neural network to 0, and the calculations related to these parameters are also shielded, according to The basic unit of pruning can be divided into single parameter pruning and structured parameter pruning.
量化(Quantization),如图2所示,也可以称作模型低比特化,即低精度表示的方法减少神经网络模型当中部分或全部数据存储所需要的比特数,进而在降低参数量的同时也简化了大部分的浮点运算,达到模型压缩的目的。Quantization, as shown in Figure 2, can also be called low-bit model, that is, the method of low-precision representation reduces the number of bits required for some or all data storage in the neural network model, thereby reducing the amount of parameters while also Simplifies most of the floating-point operations to achieve the purpose of model compression.
网络量化的合理性来自于神经网络本身的数据分布特性,例如经过激活层的输出神经元可能包含许多0,同时大部分权值的绝对值都落在[0,1]区间内,从而避免了大量的数据上溢,结合重训练过程我们可以很容易地恢复低精度量化后模型的精度。另一方面,为了保证神经网络的训练收敛速度和精度,如Caffe、Tensorflow和Pytorch这样的深度学习开发框架主要使用的都是32位或64位浮点数,这在ASIC或者FPGA硬件实现当中通常是一种浪费,不但会带来更多的存储和计算开销,也会显著增加芯片当中运算单元的面积和功耗。The rationality of network quantization comes from the data distribution characteristics of the neural network itself. For example, the output neurons after the activation layer may contain many 0s, and the absolute values of most weights fall within the [0,1] interval, thus avoiding A large amount of data overflow, combined with the retraining process, we can easily restore the accuracy of the model after low-precision quantization. On the other hand, in order to ensure the convergence speed and accuracy of neural network training, deep learning development frameworks such as Caffe, Tensorflow, and Pytorch mainly use 32-bit or 64-bit floating-point numbers, which are usually used in ASIC or FPGA hardware implementations. A kind of waste will not only bring more storage and computing overhead, but also significantly increase the area and power consumption of the computing unit in the chip.
对大多数网络模型的推理(Inference)运算来说,8bit左右的低精度数据已经能够满足网络性能的要求,因此工业界对神经网络量化的技术应用也已经非常成熟,Nvidia的TensorRT运算库和国内外的许多深度学习加速架构都已经支持并优化了8bit定点数的神经网络运算和存储。For the inference (Inference) operation of most network models, low-precision data of about 8 bits can already meet the requirements of network performance. Therefore, the industrial application of neural network quantization technology is also very mature. Nvidia's TensorRT computing library and domestic Many other deep learning acceleration architectures have already supported and optimized the neural network operation and storage of 8bit fixed-point numbers.
数据归约(DataReduction),如图3所示,即以一小部分数据替代原始数据的方法减少神经网络模型当中的参数数量。数据归约原本是数据预处理当中的概念,目前已经不再局限于缩小神经网络的数据集规模,而是逐渐用于探索神经网络参数甚至网络结构的压缩方法。按照被压缩的数据形式,数据归约又可被分为维度归约(DimensionalityReduction)和数量归约(DimensionalityReduction)两类。Data reduction (DataReduction), as shown in Figure 3, is to reduce the number of parameters in the neural network model by replacing the original data with a small part of the data. Data reduction was originally a concept in data preprocessing. At present, it is no longer limited to reducing the size of the neural network dataset, but is gradually used to explore the compression methods of neural network parameters and even network structures. According to the compressed data form, data reduction can be divided into two types: dimension reduction (Dimensionality Reduction) and quantity reduction (Dimensionality Reduction).
维度归约的目标为减少可学习参数的自变量个数,例如对模型当中的参数做小波变换、主成分分析或离散余弦变换等,然后利用数据的变换域特征进行量化或者熵编码等压缩操作,结合剪枝、量化和重训练等方法,能够从变换域角度削减神经网络模型的冗余性。这一思想与图像压缩的JPEG编码中对直流分量采取的处理方法类似,也是利用了神经网络当中的数据局部性,但还需要考虑到FeatureMap与自然图像具有本质区别,对于变换域参数的压缩策略需要谨慎探索,以避免逆变换后的模型精度受到不可恢复的损失,进而导致整个压缩方法失效。The goal of dimensionality reduction is to reduce the number of independent variables of learnable parameters, such as performing wavelet transform, principal component analysis or discrete cosine transform on the parameters in the model, and then use the transform domain characteristics of the data to perform quantization or entropy coding and other compression operations , combined with methods such as pruning, quantization and retraining, can reduce the redundancy of neural network models from the perspective of transform domain. This idea is similar to the processing method of the DC component in the JPEG encoding of image compression. It also uses the data locality in the neural network, but it also needs to consider that the FeatureMap is essentially different from the natural image. The compression strategy for the transformation domain parameters Careful exploration is required to avoid an irrecoverable loss of model accuracy after the inverse transformation, which in turn renders the entire compression method ineffective.
数量归约则聚焦于更加直观地减少参数数量的方法,例如线性回归、聚类和采样等,从而实现一定范围内的参数共享,共享粒度可以是参数矩阵、通道、卷积核、层甚至子网络。Quantity reduction focuses on methods to reduce the number of parameters more intuitively, such as linear regression, clustering and sampling, etc., so as to achieve parameter sharing within a certain range. The sharing granularity can be parameter matrix, channel, convolution kernel, layer or even sub network.
综合现有的研究成果,可以发现剪枝、量化和数据归约通常在一种综合性的神经网络压缩方法中同时出现,一定程度上为之后的硬件优化提供了方向。这一现象是因为在形成参数共享策略的过程中,势必要将模型当中的参数按照一定的评价指标进行分组,因此数量归约和前述的剪枝和量化方法具有天然的耦合关系,参数共享的粒度也可以非常自然地作为剪枝和量化的粒度。Combining the existing research results, it can be found that pruning, quantization and data reduction usually appear together in a comprehensive neural network compression method, which provides a direction for subsequent hardware optimization to a certain extent. This phenomenon is because in the process of forming the parameter sharing strategy, it is necessary to group the parameters in the model according to certain evaluation indicators, so the number reduction and the aforementioned pruning and quantification methods have a natural coupling relationship, and the parameter sharing Granularity can also be used very naturally as the granularity of pruning and quantization.
另一方面,传统的数据压缩尤其是图像压缩方法(熵编码、变换编码、游程编码和混合编码等)也在神经网络压缩方法中得到了广泛的运用,用于对各种经过剪枝、量化和数据归约的神经网络模型进行最后一步压缩,还能再节省20%-30%的存储开销,不仅能够提升压缩比,部署在相关硬件加速架构上之后也能显著地提高推理和训练的计算性能。On the other hand, traditional data compression methods, especially image compression methods (entropy coding, transform coding, run-length coding and hybrid coding, etc.) The last step of compression with the neural network model of data reduction can save another 20%-30% of storage overhead, which can not only improve the compression ratio, but also significantly improve the calculation of reasoning and training after being deployed on the relevant hardware acceleration architecture performance.
此外,神经网络压缩研究还引申了无损压缩的含义,无论是剪枝、量化还是数据归约,都会对神经网络当中的参数本身带来失真,虽然经过重训练可以恢复压缩后模型的精度,但是得到的模型数据已经发生了不可逆的变化,这进一步降低了神经网络算法的可解释性,也和经典的数据压缩当中对无损压缩的定义不同。因此需要在此说明,本文提到的无损压缩并不是指模型精度无损的神经网络压缩方法,而是数据本身可以无任何失真恢复的数据压缩方法。In addition, the research on neural network compression also extends the meaning of lossless compression. Whether it is pruning, quantization or data reduction, it will bring distortion to the parameters in the neural network. Although retraining can restore the accuracy of the compressed model, but The obtained model data has undergone irreversible changes, which further reduces the interpretability of the neural network algorithm, and is also different from the definition of lossless compression in classic data compression. Therefore, it needs to be explained here that the lossless compression mentioned in this article does not refer to the neural network compression method without loss of model accuracy, but the data compression method in which the data itself can be restored without any distortion.
剪枝和量化后的数据分布。神经网络当中的数据分布符合大数原理,因此预训练模型当中的数据大致呈现以0为均值的一个正态分布。由于数值分辨率的下降,低精度量化之后可能会成为一个离散的正态分布,并在超出表示范围的数值上出现溢出现象,但分布的包络保持不变,以AlexNet当中最后一个卷积层Conv5为例,图4给出了量化为8bit定点数后该层的权值分布。同时,剪枝会导致绝对值接近0的一部分参数被裁剪为0,如图5所示,在接近0的位置会出现一个分布上的空洞,其中的数据都集中在等于0的尖峰上。Data distribution after pruning and quantization. The data distribution in the neural network conforms to the principle of large numbers, so the data in the pre-training model roughly presents a normal distribution with 0 as the mean. Due to the decline in numerical resolution, low-precision quantization may become a discrete normal distribution, and overflow occurs on values beyond the range of representation, but the envelope of the distribution remains unchanged, taking the last convolutional layer in AlexNet Conv5 is taken as an example. Figure 4 shows the weight distribution of this layer after being quantized to 8bit fixed-point numbers. At the same time, pruning will cause some parameters whose absolute value is close to 0 to be pruned to 0. As shown in Figure 5, there will be a hole in the distribution near 0, and the data in it will be concentrated on the peak equal to 0.
在剪枝和量化的双重约束下,重训练虽然能恢复模型精度,但是无法找回预训练模型的正态分布,而是呈现如图6所示的双峰分布。从这一现象上我们能够看出,剪枝、量化和重训练结合的压缩方法不仅会引入大量的0,还会深刻地改变神经网络当中的数据分布。Under the dual constraints of pruning and quantization, although retraining can restore model accuracy, it cannot retrieve the normal distribution of the pre-trained model, but presents a bimodal distribution as shown in Figure 6. From this phenomenon, we can see that the compression method combining pruning, quantization and retraining will not only introduce a large number of 0s, but also profoundly change the data distribution in the neural network.
哈夫曼编码在频率分布符合2-n的字符序列上能够达到熵极限,同时游程编码不存在二阶编码,再结合上述数据分布的变化,我们可以挖掘出以下两个待优化之处:Huffman coding can reach the entropy limit on the character sequence whose frequency distribution conforms to 2-n. At the same time, there is no second-order coding in run-length coding. Combined with the above-mentioned changes in data distribution, we can dig out the following two areas to be optimized:
(1)相比于原先的正态分布,经过重训练后各个数字的出现频率更加平均,可能会导致哈夫曼编码的平均码长增加,因此必须在熵编码之前对数据进行预编码,以改善哈夫曼编码输入字符的出现频率。(1) Compared with the original normal distribution, the frequency of occurrence of each number after retraining is more even, which may lead to an increase in the average code length of Huffman coding. Therefore, the data must be pre-coded before entropy coding. Improve Huffman encoding of the frequency of input characters.
(2)尽管重训练能够使恢复一部分被裁剪的参数,但权值当中依然存在大量的0,并且不一定是连续出现的,因此需要一种能够全面压缩这些0的编码方法,从而提高剪枝后模型的压缩比。(2) Although retraining can restore some of the pruned parameters, there are still a large number of 0s in the weights, and they do not necessarily appear continuously. Therefore, a coding method that can fully compress these 0s is needed to improve pruning. The compression ratio of the post model.
神经网络压缩方法既是针对神经网络算法的改进,也是对数据压缩方法的设计和应用,因此评价神经网络压缩的效果必须从两方面出发,也就是精度和压缩比,为了更合理地度量对硬件带宽的影响,还应当引入码率作为评价指标。The neural network compression method is not only the improvement of the neural network algorithm, but also the design and application of the data compression method. Therefore, the evaluation of the effect of the neural network compression must start from two aspects, that is, the accuracy and the compression ratio. In order to measure the hardware bandwidth more reasonably The impact of the code rate should also be introduced as an evaluation index.
精度(Accuracy),前文介绍的各种神经网络压缩方法都会对神经网络作出改动,或是数值上或是结构上,这必然会影响模型在其目标任务上的表现,而能否恢复预训练的精度取决于神经网络压缩算法对模型造成的损伤是否可逆。因此,经过压缩和一系列重训练操作后,神经网络的识别精度是评价该压缩方法的首要指标,尤其是与预训练模型的对比。对于目标检测来说表现为Top-1和Top-5准确率,而在模式识别和场景分割的任务上则需要考虑mAP等。Accuracy, the various neural network compression methods introduced above will make changes to the neural network, either numerically or structurally, which will inevitably affect the performance of the model on its target task, and whether it can restore the pre-trained Accuracy depends on whether the damage done to the model by the neural network compression algorithm is reversible. Therefore, after compression and a series of retraining operations, the recognition accuracy of the neural network is the primary indicator for evaluating the compression method, especially compared with the pre-trained model. For target detection, it shows the accuracy of Top-1 and Top-5, while for the tasks of pattern recognition and scene segmentation, mAP needs to be considered.
压缩比(CompressionRatio),即为原始数据和压缩后数据的大小之比,这是对数据压缩方法的直观评判,也是所有压缩算法的通用评价标准。Compression ratio (CompressionRatio), which is the ratio of the size of the original data to the compressed data, is an intuitive judgment of the data compression method and a general evaluation standard for all compression algorithms.
码率(BitRate),即在压缩数据中表示一个字符所需要的平均bit数,其意义与哈夫曼编码当中的加权平均码长类似,码率约低表明当前压缩方法越契合原始的数据分布,搬运压缩数据所需的硬件带宽就越小。Code rate (BitRate), that is, the average number of bits required to represent a character in compressed data, its meaning is similar to the weighted average code length in Huffman coding, and the low code rate indicates that the current compression method is more in line with the original data distribution , the less hardware bandwidth required to move the compressed data.
基于以上三个评价指标,本发明提出一种全新的无损压缩算法,目标是在对现有技术基础和评价体系的参考下,设计出更加适合神经网络模型的编码方法,进而对神经网络压缩方法作出实质性的优化。Based on the above three evaluation indicators, the present invention proposes a brand-new lossless compression algorithm. The goal is to design a coding method that is more suitable for the neural network model under the reference of the existing technical foundation and evaluation system, and then further improve the neural network compression method. Make substantial optimizations.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明基于规范化的HSF(Huffman-Shannon-Fano)编码、游程编码以及进一步的全零替换编码,提出了多个流并行的编解码方法,通过流间数据混洗来提高压缩比的Shuffle方法,以及通过均衡流间压缩速度来避免死锁的FakeLiteralInsert方法,最终提出了一种高效的神经网络无损压缩编码及其硬件流水线实现方案。Based on standardized HSF (Huffman-Shannon-Fano) encoding, run-length encoding and further all-zero replacement encoding, the present invention proposes a parallel encoding and decoding method for multiple streams, and a Shuffle method that improves the compression ratio by shuffling data between streams. As well as the FakeLiteralInsert method that avoids deadlock by balancing the compression speed between streams, and finally proposes an efficient neural network lossless compression encoding and its hardware pipeline implementation.
具体来说,本发明提出一种基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩方法,其中包括:Specifically, the present invention proposes a neural network quantization compression method based on run-length all-zero encoding, which includes:
步骤1、获取经过量化处理后待压缩的神经网络数据,对该神经网络数据进行分块,得到多个数据块;
步骤2、对每一个该数据块分配一个数据流进行压缩,每条数据流的压缩包括:对该数据块进行游程全零编码,得到游程压缩数据,其中该游程全零编码仅对该神经网络数据中的零字符进行游程编码,对该游程压缩数据进行规范化哈夫曼编码,并对编码结果进行重整,得到规范哈夫曼编码,作为该数据块的压缩结果;
步骤3、集合各数据块的压缩结果,作为该神经网络数据的压缩结果;
其中该游程全零编码的游程位宽为2bit;The run-length bit width of the run-length all-zero encoding is 2 bits;
该游程全零编码进一步包括:对该神经网络数据中的零数据进行游程编码,得到第一中间数据;将该第一中间数据的游程为3的编码片段替换为ZeroLiteral字符,得到第二中间数据;判断该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符是否为该神经网络数据中的原字符,若是,则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为原字符的标志位,否则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为替换字符的标志位。The run-length all-zero encoding further includes: performing run-length encoding on the zero data in the neural network data to obtain the first intermediate data; replacing the code segment with a run length of 3 of the first intermediate data with a ZeroLiteral character to obtain the second intermediate data ; Judging whether the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data is the original character in the neural network data, if so, then replacing the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data with a ZeroExtra character, and at the same time Then increase the sign bit representing that it is the original character, otherwise replace the same character with the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data with the ZeroExtra character, and increase the sign bit representing it as the replacement character afterwards.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩方法,其中该ZeroLiteral字符和该ZeroExtra字符分别为该神经网络数据中出现频率最低的两种字符。In the neural network quantization compression method based on run-length all-zero encoding, the ZeroLiteral characters and the ZeroExtra characters are respectively the two characters with the lowest frequency in the neural network data.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩方法,其中该神经网络数据为神经网络运算中的权值数据和神经元输入数据。In the neural network quantization and compression method based on run-length all-zero encoding, the neural network data is weight data and neuron input data in neural network operations.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩方法,其中若该规范哈夫曼编码大于等于该神经网络数据,则放弃该规范哈夫曼编码,将该神经网络数据直接作为该压缩结果。In the neural network quantization compression method based on run-length all-zero encoding, if the canonical Huffman coding is greater than or equal to the neural network data, the canonical Huffman coding is discarded, and the neural network data is directly used as the compression result.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩方法,其中该步骤2中所有数据流的输入输出同步进行。In the neural network quantization and compression method based on run-length all-zero encoding, the input and output of all data streams in
本发明还提出了一种基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中包括:The present invention also proposes a neural network quantization compression system based on run-length all-zero coding, which includes:
模块1,用于获取经过量化处理后待压缩的神经网络数据,对该神经网络数据进行分块,得到多个数据块;
模块2,用于对每一个该数据块分配一个数据流进行压缩,每条数据流的压缩包括:对该数据块进行游程全零编码,得到游程压缩数据,其中该游程全零编码仅对该神经网络数据中的零字符进行游程编码,对该游程压缩数据进行规范化哈夫曼编码,并对编码结果进行重整,得到规范哈夫曼编码,作为该数据块的压缩结果;
模块3,用于集合各数据块的压缩结果,作为该神经网络数据的压缩结果;
其中该游程全零编码的游程位宽为2bit;The run-length bit width of the run-length all-zero encoding is 2 bits;
该游程全零编码进一步包括:对该神经网络数据中的零数据进行游程编码,得到第一中间数据;将该第一中间数据的游程为3的编码片段替换为ZeroLiteral字符,得到第二中间数据;判断该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符是否为该神经网络数据中的原字符,若是,则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为原字符的标志位,否则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为替换字符的标志位。The run-length all-zero encoding further includes: performing run-length encoding on the zero data in the neural network data to obtain the first intermediate data; replacing the code segment with a run length of 3 of the first intermediate data with a ZeroLiteral character to obtain the second intermediate data ; Judging whether the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data is the original character in the neural network data, if so, then replacing the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data with a ZeroExtra character, and at the same time Then increase the sign bit representing that it is the original character, otherwise replace the same character with the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data with the ZeroExtra character, and increase the sign bit representing it as the replacement character afterwards.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中该ZeroLiteral字符和该ZeroExtra字符分别为该神经网络数据中出现频率最低的两种字符。In the neural network quantization compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, the ZeroLiteral characters and the ZeroExtra characters are respectively the two characters with the lowest frequency in the neural network data.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中该神经网络数据为神经网络运算中的权值数据和神经元输入数据。In the neural network quantization and compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, the neural network data is weight data and neuron input data in neural network operations.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中若该规范哈夫曼编码大于等于该神经网络数据,则放弃该规范哈夫曼编码,将该神经网络数据直接作为该压缩结果。In the neural network quantization compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, if the normalized Huffman code is greater than or equal to the neural network data, the normalized Huffman code is discarded, and the neural network data is directly used as the compression result.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中该模块2中所有数据流的输入输出同步进行。In the neural network quantization and compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, the input and output of all data streams in the
由以上方案可知,本发明的优点在于:As can be seen from the above scheme, the present invention has the advantages of:
1、针对量化后神经网络数据具有稀疏性的特点,本发明对游程编码进行了改进提出了游程全零编码,可以更高效的无损压缩神经网络数据;1. In view of the sparsity of the quantized neural network data, the present invention improves the run-length coding and proposes a run-length all-zero coding, which can compress the neural network data more efficiently without loss;
2、本发明的游程全零编码包括二阶字符替换,进一步提高了压缩效率的同时减少了数据中0出现的数量,为后续的哈夫曼编码留出了更多的压缩空间;2. The run-length all-zero encoding of the present invention includes second-order character replacement, which further improves the compression efficiency and reduces the number of 0 occurrences in the data, leaving more compression space for subsequent Huffman encoding;
3、对哈夫曼树自上而下地进行重整,省去存储完整的哈夫曼树结构,显著降低了查表操作的复杂程度;3. Reorganize the Huffman tree from top to bottom, save the need to store the complete Huffman tree structure, and significantly reduce the complexity of table lookup operations;
4、通过向速度慢的数据流的输出缓存写入虚字符对应的虚编码,均衡流间压缩速度,缩小流水线之间的编码差距,进而避免产生死锁。4. By writing virtual codes corresponding to virtual characters to the output buffer of slow data streams, the compression speed between streams is balanced, and the coding gap between pipelines is narrowed, thereby avoiding deadlocks.
5、数据流随机选择输入缓存或根据预设规则选择输入缓存,避免了连续从同一个输入缓存读取数据,增加了单个数据流的输入随机性,进一步平衡各数据流的编码速率,从而提高硬件资源的利用效率。5. The data stream randomly selects the input buffer or selects the input buffer according to the preset rules, which avoids continuously reading data from the same input buffer, increases the input randomness of a single data stream, and further balances the encoding rate of each data stream, thereby improving Utilization efficiency of hardware resources.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为网络剪枝和参数恢复图;Figure 1 is a network pruning and parameter recovery diagram;
图2为网络参数渐进量化图;Figure 2 is a progressive quantization diagram of network parameters;
图3为参数共享和聚类中心微调图;Figure 3 is a graph of parameter sharing and clustering center fine-tuning;
图4为量化后的Conv5层权值分布图;Figure 4 is a quantized Conv5 layer weight distribution diagram;
图5为量化和剪枝后的Conv5层权值分布图;Figure 5 is a weight distribution diagram of the Conv5 layer after quantization and pruning;
图6为重训练后的Conv5层权值分布图;Figure 6 is a weight distribution diagram of the Conv5 layer after retraining;
图7为第一阶段编码结果图;Fig. 7 is a first-stage encoding result diagram;
图8为第二阶段编码规则图;Fig. 8 is the coding rule diagram of the second stage;
图9为第二阶段编码结果图;Fig. 9 is the second stage encoding result figure;
图10a和图10b为规范化哈夫曼树示例图;Figure 10a and Figure 10b are illustrations of normalized Huffman trees;
图11为并行压缩中的数据拆分图;Figure 11 is a data split diagram in parallel compression;
图12为多数据流编解码器图;Figure 12 is a multi-stream codec diagram;
图13为Last位的设计图;Figure 13 is a design diagram of the Last bit;
图14为Head-Data存储格式图;Figure 14 is a Head-Data storage format diagram;
图15为死锁的产生示意图;Figure 15 is a schematic diagram of deadlock generation;
图16为FakeLiteral替换规则图;Figure 16 is a FakeLiteral replacement rule diagram;
图17为本发明流程图。Fig. 17 is a flowchart of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为让本发明的上述特征和效果能阐述的更明确易懂,下文特举实施例,并配合说明书附图作详细说明如下。In order to make the above-mentioned features and effects of the present invention more clear and understandable, the following specific examples are given together with the accompanying drawings for detailed description as follows.
本文以优化神经网络压缩方法为目的,分析了经过剪枝和量化后神经网络模型中数据的分布特性,提出了一种结合熵编码、游程编码和全零编码的无损压缩算法,并对其在硬件上的部署形式进行了充分的探索,最后设计并实现了NNcodec神经网络编解码模拟器,在此基础上对目前比较成熟的7种神经网络模型进行了纵向和横向的对比实验,从软件层面证明了该混合编码对神经网络压缩方法的优化效果,也给出了一种易于实现的硬件设计方案。In order to optimize the neural network compression method, this paper analyzes the distribution characteristics of the data in the neural network model after pruning and quantization, and proposes a lossless compression algorithm that combines entropy coding, run-length coding and all-zero coding. The deployment form on the hardware has been fully explored, and finally the NNcodec neural network encoding and decoding simulator has been designed and implemented. On this basis, vertical and horizontal comparative experiments have been carried out on the seven mature neural network models. From the software level It proves the optimization effect of the hybrid encoding on the neural network compression method, and also provides an easy-to-implement hardware design scheme.
为让本发明的上述特征和效果能阐述的更明确易懂,下文特举实施例,并配合说明书附图作详细说明如下。In order to make the above-mentioned features and effects of the present invention more clear and understandable, the following specific examples are given together with the accompanying drawings for detailed description as follows.
游程编码,使用字符加游程的组合替代重复出现的若干个字符,同一个字符连续出现的次数被称作游程,例如字符序列{AABBCCCD}经过游程编码则被压缩为{A2B2C3D1}。Run-length encoding uses a combination of characters and run lengths to replace several repeated characters. The number of consecutive occurrences of the same character is called a run length. For example, the character sequence {AABBCCCD} is compressed into {A2B2C3D1} after run-length encoding.
游程编码是一种有效的数据压缩方法,具体实现当中需要设计出一个合理的游程位宽,既不能因为游程太短导致重复压缩,也不能因为游程太长降低压缩比。此外,从原理上我们即可以观察到,此方法不能对已经经过游程编码的数据使用。Run-length coding is an effective data compression method. In the specific implementation, a reasonable run-length bit width needs to be designed. It can neither cause repeated compression because the run length is too short, nor reduce the compression ratio because the run length is too long. In addition, we can observe in principle that this method cannot be used on data that has been run-length encoded.
首先应当为游程全零编码选定一个合理的游程位宽。考虑到目前的神经网络压缩模型更多地采用8bit或更低位宽的定点数进行量化,本发明采用了较短的2bit游程,即最多能够将4个连续出现的0压缩成数字0和游程3的形式。以8bit定点数格式的待编码序列{1,0,0,0,0,2,0,255,0,0}为例,其第一阶段的编码结果如图7所示。First, a reasonable run-length bit width should be selected for the run-length all-zero encoding. Considering that the current neural network compression model mostly uses 8bit or lower bit-width fixed-point numbers for quantization, the present invention adopts a shorter 2bit run length, that is, it can compress up to four consecutive 0s into digital 0 and run
上述的待编码数据总位宽为80bit,而经过第一阶段压缩后总码长为64bit,如果采用传统的游程编码得到的总码长为72bit,考虑到压缩后神经网络模型当大量连续出现的0,可以认为非零数据不带游程是对游程编码在神经网络计算中的一种改进。The total bit width of the above-mentioned data to be encoded is 80 bits, and the total code length after the first stage of compression is 64 bits. If the traditional run-length encoding is used, the total code length is 72 bits. 0, it can be considered that non-zero data without run length is an improvement of run length encoding in neural network calculations.
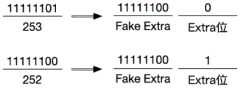
特殊字符替换和Extra位。为了进一步提升对全零数据的压缩比,同时不过多地引入开销,我们在第二阶段选择原始数据中出现可能性极低的某个字符(例如255)作为ZeroLiteral,替换掉现有数据中游程为3的编码片段;为了与数值上等于ZeroLiteral的字符进行区分,还需要将其替换为另一个出现可能性极低的字符(例如254),称作ZeroExtra,同时在其后增加1bit的Extra位,以便与数值上等于ZeroExtra的字符进行区分,如图8所示。Special character substitution and Extra bits. In order to further improve the compression ratio of all-zero data without introducing too much overhead, in the second stage, we select a character (such as 255) that is extremely unlikely to appear in the original data as ZeroLiteral to replace the existing data. is a coded fragment of 3; in order to distinguish it from a character equal to ZeroLiteral in value, it needs to be replaced with another character with a very low possibility of occurrence (such as 254), called ZeroExtra, and a 1-bit Extra bit is added after it , so as to be distinguished from characters numerically equal to ZeroExtra, as shown in Figure 8.
值得注意的是,这里没有选择直接在ZeroLiteral后面增加1bit的区分方法,而是采用了上述的二阶字符替换,是因为数值上等于ZeroLiteral和ZeroExtra的字符出现频率很低,相比于在连续出现的4个0对应编码上增加1bit的方法,再进行一次字符替换然后以Extra位进行区分的做法更加合理。第二阶段的编码结果如图9所示。It is worth noting that here, instead of directly adding 1 bit after ZeroLiteral, the above-mentioned second-order character replacement is used, because the characters that are numerically equal to ZeroLiteral and ZeroExtra have a very low frequency of occurrence, compared with consecutive occurrences The 4 0s correspond to the method of adding 1 bit to the encoding, and it is more reasonable to perform a character replacement and then use the Extra bit to distinguish. The encoding result of the second stage is shown in Figure 9.
至此我们完成了一次游程全零编码,进而可以总结出一般情况下的解码流程:So far we have completed a run-length all-zero encoding, and then we can summarize the decoding process in general:
(1)特殊字符还原,如果在压缩数据当中检查到了ZeroLiteral,则将其替换为数字0和游程3;如果在压缩数据当中检查到了ZeroExtra,则检查其后的Extra位,如果Extra位为0则替换为ZeroLiteral,否则替换为ZeroExtra。(1) Special characters are restored. If ZeroLiteral is detected in the compressed data, replace it with the
(2)游程解码,对经过特殊字符还原的数据当中的0进行游程解码,将其后的2bit游程展开,并向结果中写入对应个数的0。(2) Run-length decoding, perform run-length decoding on 0 in the data restored by special characters, expand the subsequent 2-bit run-length, and write the corresponding number of 0 into the result.
以上就是游程全零编码的算法描述,最终将例子中80bit的待编码数据压缩为49bit,由于采用全零编码和字符替换的策略,此方法在剪枝和量化后的模型当中表现明显优于游程编码。此外,它能够以4倍的压缩比将连续出现的0直接替换成ZeroLiteral,减少了数据中0出现的此处也为后续的哈夫曼编码留出了更多的压缩空间。The above is the algorithm description of run-length all-zero encoding. In the end, the 80-bit data to be encoded in the example is compressed into 49 bits. Due to the strategy of all-zero encoding and character replacement, this method performs significantly better than run-length in the model after pruning and quantization coding. In addition, it can directly replace consecutive 0s with ZeroLiteral with a compression ratio of 4 times, reducing the occurrence of 0s in the data and leaving more space for subsequent Huffman coding.
规范化哈夫曼编码。同一个数据分布对应的哈夫曼编码并不唯一,这是由于在构建哈夫曼树的过程中可能出现频率相同的节点,为了更好地应用哈夫曼编码,我们需要一种固定且高效的构建哈夫曼树的方法,而通过这种方法产生的唯一的哈夫曼编码被称作规范化哈夫曼编码。Normalized Huffman coding. The Huffman coding corresponding to the same data distribution is not unique, because nodes with the same frequency may appear in the process of constructing the Huffman tree. In order to better apply Huffman coding, we need a fixed and efficient The method of constructing a Huffman tree, and the unique Huffman code generated by this method is called a normalized Huffman code.
哈夫曼树重整。具体地,本发明采用HSF编码作为规范化的哈夫曼编码。此编码的主要思想是将哈夫曼树自上而下地进行重整,同一级节点当中的叶子节点优先移到二叉树的左侧,在不改变频率分布的前提下使得所有编码都可以通过加1和加1左移来得到,进而用比较和加法运算替代复杂的二叉树遍历或完整的查表操作,极大地缩减了编解码所需的存储和计算开销。如图10a、图10b和表1所示,给定字符序列{u1,u2,u3,u4,u5}和任意的两组哈夫曼树,都可以用上述的重整方法找到它们的规范化形式。Huffman tree reshaping. Specifically, the present invention adopts HSF coding as the normalized Huffman coding. The main idea of this encoding is to reorganize the Huffman tree from top to bottom, and the leaf nodes in the same level of nodes are moved to the left side of the binary tree first, so that all encodings can be added by adding 1 without changing the frequency distribution. It is obtained by adding 1 to the left, and then using comparison and addition operations to replace complex binary tree traversal or complete table lookup operations, which greatly reduces the storage and calculation overhead required for encoding and decoding. As shown in Figure 10a, Figure 10b and Table 1, given a character sequence {u1, u2, u3, u4, u5} and any two sets of Huffman trees, their normalized forms can be found by the above-mentioned reorganization method .
表1规范化哈夫曼编码示例Table 1 Normalized Huffman coding example
码表重定义。可以看到,每一棵哈夫曼树都对应有其规范化形式,同时规范化后的码字之间具有硬件友好的运算规律:相同码长+1,不同码长+1后左移1位,我们可以利用这一规律重新定义码表,从而彻底省去存储完整的哈夫曼树结构,显著降低了查表操作的复杂程度。Code table redefinition. It can be seen that each Huffman tree corresponds to its normalized form, and at the same time, the normalized codewords have hardware-friendly operation rules: the same code length + 1, different code lengths + 1 and then shifted to the left by 1 bit, We can use this rule to redefine the code table, thereby completely eliminating the need to store the complete Huffman tree structure, and significantly reducing the complexity of the table lookup operation.
以上一小节的待编码序列(a)为例,其HSF编解码过程需要以下几种码表:The sequence to be encoded (a) in the previous section is taken as an example, the HSF encoding and decoding process requires the following code tables:
(1)CharTable,所有待编码字符按照出现频率的降序排列,在例(a)当中即为{u1,u4,u5,u2,u3},编解码可以复用。(1) CharTable, all the characters to be encoded are arranged in descending order of frequency, which is {u1, u4, u5, u2, u3} in example (a), and the encoding and decoding can be reused.
(2)LenTable,所有有效码长的升序排列,例(a)当中的HSF编码只有2bit和3bit,对应的LenTable为{2,3},编解码可以复用。(2) LenTable, all effective code lengths are arranged in ascending order. The HSF code in example (a) is only 2bit and 3bit, and the corresponding LenTable is {2,3}, and the codec can be multiplexed.
(3)RangeTable,每个有效码长的最后一个码字对应的字符在CharTable当中的排序下标,例(a)当中2bit和3bit的最后一个码字分别对应u5和u3,因此RangeTable为{2,4},只在编码阶段使用。(3) RangeTable, the sort subscript of the characters corresponding to the last codeword of each effective code length in CharTable, the last codewords of 2bit and 3bit in example (a) correspond to u5 and u3 respectively, so the RangeTable is {2 ,4}, used only in the encoding phase.
(4)LimitTable,每个有效码长的最后一个码字的数值,例(a)当中2bit和3bit的最后一个码字分别为10和111,因此LimitTable为{2,7},只在解码阶段使用。(4) LimitTable, the value of the last codeword of each effective code length, in example (a), the last codewords of 2bit and 3bit are 10 and 111 respectively, so LimitTable is {2,7}, only in the decoding stage use.
(5)BaseTable,LimitTable减去RangeTable,例(a)当中的BaseTable为{0,3},编解码可以复用。(5) BaseTable, LimitTable minus RangeTable, BaseTable in example (a) is {0,3}, codec can be reused.
在此基础上,给定例(a)当中的字符u4和上述编码表,产生其HSF编码的流程可以分为以下三个步骤:On this basis, given the character u4 in example (a) and the above code table, the process of generating its HSF code can be divided into the following three steps:
Lookup,访问CharTable,得到u4的排序rank,即rank(u4)=1;Lookup, visit CharTable, get u4 sorting rank, that is, rank(u4)=1;
Compare,访问RangeTable,得到大于等于rank(u4)的第一项下标index,因为rank(u4)≤2,所以index(u3)=0;Compare, visit RangeTable, get the first subscript index greater than or equal to rank(u4), because rank(u4)≤2, so index(u3)=0;
Add,访问BaseTable和LenTable,得到下标index对应的基值base和码长len,base与rank相加即为码字的数值,结合len就能够得到字符u4的HSF编码:base(u4)=0,len(u4)=2,code(u4)=0+1=1,所以最终的编码结果为01。Add, visit BaseTable and LenTable, get the base value base and code length len corresponding to the subscript index, add base and rank to get the value of the code word, combine len to get the HSF code of character u4: base(u4)=0 , len(u4)=2, code(u4)=0+1=1, so the final encoding result is 01.
对应地,我们可以推导出从一串形如01xxx的HSF码流中解析出第一个字符u4的解码流程:Correspondingly, we can deduce the decoding process of parsing the first character u4 from a string of HSF code streams shaped like 01xxx:
Compare,访问LimitTable和LenTable,由一个从0开始累加的下标index进行遍历,直到满足limit≥码流的前len位,因为LimitTable当中的下标为0的值limit≥码流的前2bit,所以index=0,limit=2,len=2,code=1;Compare, access LimitTable and LenTable, traverse from a subscript index accumulated from 0 until limit≥the first len bits of the code stream, because the value of the
Sub,访问BaseTable,用code值减去下标index对应的base值得到字符排序,即rank=1-0=1;Sub, access BaseTable, subtract the base value corresponding to the subscript index from the code value to get the character sorting, that is, rank=1-0=1;
Lookup,访问CharTable,得到排序rank对应的字符,因此最终的解码结果为CharTable当中排序为1的项,也即字符u4。Lookup accesses the CharTable to obtain the character corresponding to the sort rank, so the final decoding result is the item ranked 1 in the CharTable, that is, the character u4.
以上就是对规范化哈夫曼编码算法的介绍,可以看出HSF编码能够简化哈夫曼编码的存储和运算结构,同时自然地将编解码流程都切分为3级流水线,为硬件部署提供了高效且合理的实现方案。The above is the introduction to the standardized Huffman coding algorithm. It can be seen that HSF coding can simplify the storage and operation structure of Huffman coding, and at the same time, the coding and decoding process is naturally divided into three-stage pipelines, which provides efficient hardware deployment. And a reasonable implementation plan.
多数据流并行压缩方法。将前述的游程全零编码和规范化哈夫曼编码结合起来,我们已经具备了本发明所提出的混合编码的算法基础,接下来需要讨论的是如何提高此编码方法在硬件上的压缩效率。Multi-stream parallel compression method. Combining the aforementioned run-length all-zero encoding and normalized Huffman encoding, we already have the algorithm basis of the hybrid encoding proposed by the present invention, and what needs to be discussed next is how to improve the compression efficiency of this encoding method on hardware.
在并行计算(ParallelComputing)的背景下,大多数串行操作都使用流水线(Pipeline)技术实现时间并行。另一方面,而随着多核架构的发展,针对数据级并行的单指令多数据流(SingleInstructionMultipleData,SIMD)等技术也开始被用在各种数据压缩方法中。在类似方法的启发下,本文提出了一种基于数据分块和流水线编解码的并行压缩方法,并且对它的硬件实现作出了思考和优化。In the context of parallel computing (Parallel Computing), most serial operations use pipeline (Pipeline) technology to achieve time parallelism. On the other hand, with the development of multi-core architecture, technologies such as Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) for data-level parallelism have also begun to be used in various data compression methods. Inspired by similar methods, this paper proposes a parallel compression method based on data partitioning and pipeline encoding and decoding, and considers and optimizes its hardware implementation.
流水级划分和数据分块。根据对各串行操作复杂度的预估,可以认为现有的压缩方法在硬件上能够被划分为5级流水线,如表2所示。并且由于编解码运算存在对称性,所以压缩和解压阶段还能够复用一部分的运算和存储结构,以此提高硬件单元的利用率。Pipeline division and data block. According to the estimation of the complexity of each serial operation, it can be considered that the existing compression methods can be divided into 5-stage pipelines in hardware, as shown in Table 2. And because of the symmetry of the encoding and decoding operations, part of the operations and storage structures can be reused in the compression and decompression stages, so as to improve the utilization rate of hardware units.
表2编解码流水级划分Table 2 Codec pipeline level division
在流水线编解码结构的基础上,我们需要对固定大小的批量(Chunk)待压缩数据进行分块(Block),如图11所示。同时为每个分块分配一个数据流(Stream)进行压缩或解压,其中每个数据流都包括上述的5级流水线所需的硬件单元,所有数据分块和编解码流共同完成本文所提出的并行压缩解压操作。On the basis of the pipeline codec structure, we need to block the fixed-size batch (Chunk) of data to be compressed, as shown in Figure 11. At the same time, a data stream (Stream) is assigned to each block for compression or decompression, where each data stream includes the hardware units required by the above-mentioned 5-stage pipeline, and all data blocks and codec streams jointly complete the proposed method. Parallel compression and decompression operations.
为了在后续的实验当中充分考量各种影响因素,从而更加科学地评估此并行压缩解压方法的性能,我们需要提前明确上述编解码器结构当中的自变量,并在此基础上对输入和输出的基本粒度进行命名。In order to fully consider various influencing factors in the follow-up experiments, so as to more scientifically evaluate the performance of this parallel compression and decompression method, we need to clarify the independent variables in the above codec structure in advance, and on this basis, the input and output The basic granularity is named.
Stream,即数据流的数量,从提高处理速度的角度出发我们当然希望数据流越多越好,但这会成倍增加编解码器的面积功耗开销,因此Stream数量是一个需要通过实验分析来权衡的参数。Stream, that is, the number of data streams. From the perspective of improving processing speed, we certainly hope that the more data streams the better, but this will multiply the area power consumption of the codec. Therefore, the number of Streams is a factor that needs to be determined through experimental analysis. trade-off parameters.
Chunk,即待压缩数据的批量大小,最直观的选择就是将全部待压缩数据作为一个Chunk,但这样无法通过复制多个编解码结构来进行更高层次的数据并行(例如多核处理结构等,由于硬件限制和数据局部性,单纯地铺开更多Stream并不能取得更好的压缩效果),因此我们将Chunk大小也作为实验当中受控制的变量之一。Chunk, that is, the batch size of the data to be compressed, the most intuitive choice is to use all the data to be compressed as a Chunk, but it is impossible to perform higher-level data parallelism by copying multiple codec structures (such as multi-core processing structures, etc., due to Due to hardware limitations and data locality, simply spreading more streams cannot achieve better compression results), so we also use the Chunk size as one of the controlled variables in the experiment.
Dword,即每个Stream的输入队列宽度,与Stream数量共同决定了Block大小,通常选择一个与待压缩数据类型的宽度相比拟的值,以避免由于游程编码的串行性在第1级流水线造成性能瓶颈或硬件资源的浪费。Dword, that is, the input queue width of each Stream, determines the Block size together with the number of Streams. Usually, a value comparable to the width of the data type to be compressed is selected to avoid the serialization of the run-length encoding in the first-level pipeline. Performance bottlenecks or waste of hardware resources.
Cword,即每个Stream的输出队列宽度,可以用Dword除以预期的压缩比来估算出一个合理的取值。Cword, that is, the output queue width of each Stream, can be estimated by dividing Dword by the expected compression ratio to a reasonable value.
图12给出了一个具体的编解码器结构,其中Dword为16bit,Cword为4bit,共有64个Stream,也即能够并行处理1024bit的Block,得到256bit的压缩数据。值得注意的是,各Stream输入和输出同步,内部异步,这是为了保证以Block粒度的操作同步,便于后续的硬件单元以固定的数据大小存储每个周期多个流同时产生的压缩数据。Figure 12 shows a specific codec structure, where Dword is 16bit, Cword is 4bit, and there are 64 Streams in total, that is, 1024bit Blocks can be processed in parallel to obtain 256bit compressed data. It is worth noting that the input and output of each Stream are synchronous and internally asynchronous. This is to ensure synchronous operation at the block granularity, so that subsequent hardware units can store compressed data simultaneously generated by multiple streams in each cycle with a fixed data size.
为了解决前面提到的Chunk不能被Block整除的问题,每个Stream当中的流水级除了必要的编解码硬件之外,还需要额外增加1bit的Last位,在输入输出同步的约束下允许一部分Stream提前清空流水线并结束压缩流程,当所有Stream的输出端口Last位都为1之后即代表对当前Block的压缩完成,如图13所示。In order to solve the aforementioned problem that the Chunk cannot be divisible by the Block, in addition to the necessary encoding and decoding hardware, the pipeline level in each Stream needs to add an additional 1-bit Last bit, allowing some Streams to advance under the constraints of input and output synchronization. Clear the pipeline and end the compression process. When the Last bits of the output ports of all Streams are 1, it means that the compression of the current Block is completed, as shown in Figure 13.
此外,由于我们采用是一种变长编码方法,即压缩后产生的码长不确定,出现几率较小的字符压缩后的码字可能超过其本身的数据位宽,极端情况下压缩数据大小可能超过Block的大小从而导致压缩失败。因此,上述编解码器结构的外围还应当加入旁路(Bypass)设计,也即当前Block压缩失败后的备选操作。In addition, since we use a variable-length encoding method, that is, the code length generated after compression is uncertain, and the compressed codeword of characters with a small probability of occurrence may exceed its own data bit width. In extreme cases, the compressed data size may If the size of the block is exceeded, the compression will fail. Therefore, a bypass (Bypass) design should also be added to the periphery of the above codec structure, that is, an alternative operation after the current Block compression fails.
具体地,如果输出端得到的压缩数据已经超过当前Block的大小,则放弃此次压缩,将原始数据直接作为当前Block的压缩结果,并在解压阶段跳过各级流水的运算。下一小节将会介绍能够实现压缩Bypass以及参数化流水线的存储格式。Specifically, if the compressed data obtained at the output end exceeds the size of the current block, the compression is discarded, the original data is directly used as the compression result of the current block, and the pipeline operations at all levels are skipped in the decompression stage. The next section will introduce the storage format that can realize compression bypass and parameterized pipeline.
Head-Data存储格式。为了实现Bypass操作和其他更加灵活的编解码方式,如前述的通过参数配置各级流水线当中的运算是否启用,从而在提升压缩效率的同时方便地评估每一级运算在整体方案当中所起到的作用,本文提出一种压缩数据的Head-Data存储格式,即压缩后的数据分为首部(Head)和数据(Data)两部分,其中Head当中存储Data部分的地址偏移、数据长度和压缩配置(例如每一级运算的使能、Bypass使能等),如图14所示。Head-Data storage format. In order to realize Bypass operation and other more flexible encoding and decoding methods, as mentioned above, configure whether the operations in the pipeline at all levels are enabled through parameters, so as to improve the compression efficiency and conveniently evaluate the role of each level of operation in the overall solution. Function, this paper proposes a Head-Data storage format for compressed data, that is, the compressed data is divided into two parts: the head (Head) and the data (Data), where the address offset, data length and compression configuration of the Data part are stored in the Head (such as the enablement of each stage of operation, the enablement of Bypass, etc.), as shown in Figure 14.
在此基础上,指令级别的压缩解压操作需要在编解码器完成编码运算之前增加一个配置(Configure)阶段,将每一级流水线运算所需的码表(CharTable等)和流水级使能等信号,然后在解码运算时从压缩数据的Head部分获取流水级使能和Bypass使能等信号,进而对Data部分执行正确的解码流程,完成解压操作。On this basis, the instruction-level compression and decompression operation needs to add a configuration (Configure) stage before the codec completes the encoding operation, and the code table (CharTable, etc.) , and then obtain signals such as pipeline level enable and bypass enable from the Head part of the compressed data during the decoding operation, and then execute the correct decoding process on the Data part to complete the decompression operation.
此外,由于使用地址偏移来定位Data部分,Head-Data存储格式也保证了图13当中一部分Stream提前结束压缩后输出数据补齐到256bit这一操作的正确性,即每个Block对应的压缩数据都有其精确的存储地址,因此在Data部分的末尾增加一些无意义数据也不会影响到解压流程的有效执行。In addition, because the address offset is used to locate the Data part, the Head-Data storage format also guarantees the correctness of the operation of filling the output data to 256 bits after part of the Stream in Figure 13 ends compression early, that is, the compressed data corresponding to each Block Each has its precise storage address, so adding some meaningless data at the end of the Data section will not affect the effective execution of the decompression process.
FakeLiteral与流水线平衡。由于上述的编解码器结构具有定长输入、变长输出、端口同步、内部异步的特点,在多个Stream的之间压缩速度极度不平衡的情况下,输入输出队列的同步约束可能会导致死锁(Deadlcok)的出现。FakeLiteral is balanced with the pipeline. Since the above-mentioned codec structure has the characteristics of fixed-length input, variable-length output, port synchronization, and internal asynchrony, when the compression speed between multiple Streams is extremely unbalanced, the synchronization constraints of the input and output queues may lead to deadlocks. The emergence of lock (Deadlock).
首先明确,所有Stream的输入输出同步进行,也就是所有的第一级流水线为空才进行输入,所有的最后一级流水线全满才进行输出,中间各级则可以独立执行操作,只有在前一级空或后一级满的情况下才会等待。不失一般性,我们假设出一个Stream总数2、Dword宽度为8、Cword宽度为8以及FIFO深度为4的例子,图15给出了其中死锁现象的产生原因。First of all, it is clear that the input and output of all Streams are performed synchronously, that is, all the first-stage pipelines are empty to input, all the last-stage pipelines are full to output, and the middle stages can perform operations independently. It will only wait when the level is empty or the next level is full. Without loss of generality, we assume an example where the total number of Streams is 2, the Dword width is 8, the Cword width is 8, and the FIFO depth is 4. Figure 15 shows the cause of the deadlock phenomenon.
为了模拟多个Stream之间不平衡的极端情况,我们假设Stream1将8bit数据编码为1bit,Stream2将8bit数据编码为16bit;经过前3个Cycle的输入,流水线当中的数据打满,从第4个Cycle开始产生输出,第5个Cycle时Stream2的输出FIFO的4项全满,但由于Stream1的输出FIFO当中目前只有2bit,并不足以提供一个完整的Cword,因此Stream2从此时开始阻塞,所有流水级都无法接收输入;第8个Cycle之后,Stream1当中的所有流水级排空,但输出FIFO中只有5bit,仍然不足以产生输出,输入端由于被Stream2的第一级流水线阻塞,因此也无法输入,从而进入死锁状态。In order to simulate the extreme situation of unbalance between multiple Streams, we assume that Stream1 encodes 8bit data into 1bit, and Stream2 encodes 8bit data into 16bit; after the input of the first 3 Cycles, the data in the pipeline is full, starting from the fourth Cycle starts to generate output. In the 5th Cycle, all 4 items of the output FIFO of Stream2 are full. However, since there are only 2 bits in the output FIFO of Stream1, which is not enough to provide a complete Cword, Stream2 starts to block from this moment, and all pipeline levels Neither can receive input; after the 8th Cycle, all pipeline stages in Stream1 are emptied, but there are only 5 bits in the output FIFO, which is still not enough to generate output, and the input terminal cannot be input because it is blocked by the first-stage pipeline of Stream2. Thus entering a deadlock state.
经过观察我们可以发现,截止到死锁产生,Stream1完成了对5个Dword的编码,而Stream2只完成了2个,二者相差的3个Dword都作为中间数据暂存在Stream2的流水级中,因此造成了流水线的全部阻塞。在这个结论的引导下,我们可以在编码速度最快的Stream当中适当地插入空泡,缩小流水线之间的差距,从而避免产生死锁。After observation, we can find that until the deadlock occurs, Stream1 has completed the encoding of 5 Dwords, while Stream2 has only completed 2, and the 3 Dwords that differ between the two are temporarily stored in the pipeline level of Stream2 as intermediate data, so Caused a total blockage of the pipeline. Guided by this conclusion, we can properly insert bubbles in the fastest-encoding Stream to narrow the gap between pipelines, thereby avoiding deadlocks.
为了解决这个问题,本文提出了FakeLiteral的概念,即“虚字符”:在编码时作为占位空泡输入,解码时被直接丢弃,不作为有效数据。与3.2节引入的特殊字符ZeroLiteral类似,FakeLiteral也使用待编码数据当中出现频率极低的某个字符来表示,并且也采用二阶替换和增加Extra位的策略与真实字符进行区分,如图16所示(给定FakeLiteral和FakeExtra分别为253和252),而解码阶段对FakeLiteral的识别和丢弃操作也能够合并到Alter这一级来完成。In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes the concept of FakeLiteral, that is, "virtual character": it is input as a space-occupied bubble during encoding, and it is directly discarded during decoding, not as valid data. Similar to the special character ZeroLiteral introduced in Section 3.2, FakeLiteral is also represented by a character with a very low frequency of occurrence in the data to be encoded, and also uses the strategy of second-order replacement and extra bits to distinguish it from real characters, as shown in Figure 16 (Given FakeLiteral and FakeExtra are 253 and 252 respectively), and the identification and discarding of FakeLiteral in the decoding stage can also be merged into the Alter level to complete.
从刚才的推导能够得知,死锁产生的条件为下式,其中Pcurrent为当前Stream已经编码的Dword数量,Pmin为编码速率最慢的Stream已经编码的Dword数量,S为流水线深度。From the derivation just now, it can be known that the condition for deadlock is the following formula, where Pcurrent is the number of Dwords encoded by the current Stream, Pmin is the number of Dwords encoded by the Stream with the slowest encoding rate, and S is the depth of the pipeline.
Pcurrent-Pmin≥SPcurrent -Pmin ≥S
对于我们刚才给出的例子,在第8个Cycle时P1=5,P2=2,并且S=3,已经满足向输出FIFO写入FakeCode的条件,因此进行FakeLiteral插入的改进后死锁问题已经被解决。For the example we just gave, in the 8th Cycle, P1=5, P2=2, and S=3, the condition of writing FakeCode to the output FIFO has been met, so the deadlock problem after the improvement of FakeLiteral insertion has been eliminated solve.
从上述的分析能够看出,各Stream的P值实际上对应输入次数。同时,我们需要在死锁条件被满足时向当前Stream的输出FIFO写入若干个FakeLiteral对应的编码FakeCode,保证它能够产生完整的Cword输出。为了减少死锁带来的性能损失,我们可以把FakeCode提前生成出来,并且作为编解码器的配置信息保存在每个Stream的输出FIFO中,从而省去了对FakeLiteral的重复编码。From the above analysis, it can be seen that the P value of each Stream actually corresponds to the number of inputs. At the same time, when the deadlock condition is met, we need to write several FakeLiteral corresponding codes FakeCode to the output FIFO of the current Stream to ensure that it can generate a complete Cword output. In order to reduce the performance loss caused by deadlock, we can generate FakeCode in advance and save it as codec configuration information in the output FIFO of each Stream, thus eliminating the need to repeatedly encode FakeLiteral.
混洗Shuffle方法。根据上一小节对流水线平衡方法的讨论,我们已经认识到同一个Stream的输入数据可能有连续多个高频字符,导致不同的Stream之间的编码速率相差太多,从而引起同步约束下的输入和输出FIFO的大量阻塞。尽管FakeLiteral的引入解决了死锁问题,但并没能改善流水线阻塞造成的性能浪费。Shuffle method. According to the discussion of the pipeline balance method in the previous section, we have realized that the input data of the same Stream may have multiple consecutive high-frequency characters, resulting in too much difference in the encoding rate between different Streams, which causes input under synchronization constraints and massive blocking of the output FIFO. Although the introduction of FakeLiteral solved the deadlock problem, it did not improve the performance waste caused by pipeline blocking.
针对这一问题,本文提出对Stream进行分组,混洗输入数据的方法,即连续两次输入可能来自与原先不同的两个Stream,如此可以增加单个Stream的输入随机性,进一步平衡各Stream的编码速率,从而提高硬件资源的利用效率。In response to this problem, this paper proposes a method of grouping Streams and shuffling input data, that is, two consecutive inputs may come from two different Streams from the original, so that the input randomness of a single Stream can be increased, and the encoding of each Stream can be further balanced rate, thereby improving the utilization efficiency of hardware resources.
经过定性分析的实验,在Stream数量为16的整数倍的情况下,以下4种Shuffle方式表现最好:After qualitative analysis experiments, when the number of Streams is an integer multiple of 16, the following four Shuffle methods perform best:
Adj4,相邻4个Stream分为一组,进行组内的循环混洗,Stream1顺序输入的Dword分别输入混洗之前的Stream1、2、3、4,以此类推。Adj4, the adjacent 4 Streams are divided into a group, and the group is cyclically shuffled, and the Dwords sequentially input by Stream1 are respectively input into Stream1, 2, 3, and 4 before shuffling, and so on.
Adj16,相邻16个Stream分为一组,进行组内的循环混洗,Stream1顺序输入的Dword分别输入混洗之前的Stream1、2、3、...、16,以此类推。Adj16, 16 adjacent Streams are divided into a group, and the cyclic shuffling in the group is performed. The Dwords input by Stream1 are respectively input into Stream1, 2, 3, ..., 16 before shuffling, and so on.
Every4,跳过4个Stream进行分组,进行组内的循环混洗,Stream1顺序输入的Dword分别输入混洗之前的Stream1、5、9、13,以此类推。Every4, skip 4 Streams for grouping, and perform cyclic shuffling within the group. The Dwords sequentially input by Stream1 are respectively input into Stream1, 5, 9, and 13 before shuffling, and so on.
Every16,跳过16个Stream进行分组,进行组内的循环混洗,Stream1顺序输入的Dword分别输入混洗之前的Stream1、17、33、49,以此类推。Every16, skip 16 Streams for grouping, and perform circular shuffling within the group. The Dwords input in order by Stream1 are respectively input into Stream1, 17, 33, and 49 before shuffling, and so on.
至此本章完成了对无损压缩方法的算法方案介绍,回顾我们在2.5节列举的神经网络压缩的评价指标,我们可以得到这样的结论:本文提出的混合编码是一种无损压缩算法,可以还原神经网络当中任意被编码的数值,从原理上规避了神经网络模型精度(Accuracy)的降低;而对于数据位宽和大小固定的原始数据来说,码率(BitRate)又和整体的压缩效果紧密相关,如下式所示。So far, this chapter has completed the introduction of the algorithm scheme of the lossless compression method. Looking back at the evaluation indicators of the neural network compression we listed in Section 2.5, we can draw the conclusion that the hybrid coding proposed in this paper is a lossless compression algorithm that can restore the neural network. Any encoded value among them avoids the reduction of the neural network model accuracy (Accuracy) in principle; and for the original data with fixed data bit width and size, the bit rate (BitRate) is closely related to the overall compression effect. As shown in the following formula.
BitRate=DataWidth×CompressionRatioBitRate = DataWidth × CompressionRatio
因此下一章的实验与分析将主要围绕压缩比(CompressionRatio)展开讨论,以图表的形式量化此混合编码的压缩效果,进而证明其在神经网络运算当中的优势,以及对神经网络压缩的优化作用。Therefore, the experiment and analysis in the next chapter will mainly discuss the compression ratio (CompressionRatio), quantify the compression effect of this hybrid code in the form of a graph, and then prove its advantages in neural network operations and optimize neural network compression. .
以下为与上述方法实施例对应的系统实施例,本实施方式可与上述实施方式互相配合实施。上述实施方式中提到的相关技术细节在本实施方式中依然有效,为了减少重复,这里不再赘述。相应地,本实施方式中提到的相关技术细节也可应用在上述实施方式中。The following are system embodiments corresponding to the foregoing method embodiments, and this implementation manner may be implemented in cooperation with the foregoing implementation manners. The relevant technical details mentioned in the foregoing implementation manners are still valid in this implementation manner, and will not be repeated here in order to reduce repetition. Correspondingly, the relevant technical details mentioned in this implementation manner may also be applied in the foregoing implementation manners.
本发明还提出了一种基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中包括:The present invention also proposes a neural network quantization compression system based on run-length all-zero coding, which includes:
模块1,用于获取经过量化处理后待压缩的神经网络数据,对该神经网络数据进行分块,得到多个数据块;
模块2,用于对每一个该数据块分配一个数据流进行压缩,每条数据流的压缩包括:对该数据块进行游程全零编码,得到游程压缩数据,其中该游程全零编码仅对该神经网络数据中的零字符进行游程编码,对该游程压缩数据进行规范化哈夫曼编码,并对编码结果进行重整,得到规范哈夫曼编码,作为该数据块的压缩结果;
模块3,用于集合各数据块的压缩结果,作为该神经网络数据的压缩结果;
其中该游程全零编码的游程位宽为2bit;The run-length bit width of the run-length all-zero encoding is 2 bits;
该游程全零编码进一步包括:对该神经网络数据中的零数据进行游程编码,得到第一中间数据;将该第一中间数据的游程为3的编码片段替换为ZeroLiteral字符,得到第二中间数据;判断该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符是否为该神经网络数据中的原字符,若是,则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为原字符的标志位,否则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为替换字符的标志位。The run-length all-zero encoding further includes: performing run-length encoding on the zero data in the neural network data to obtain the first intermediate data; replacing the code segment with a run length of 3 of the first intermediate data with a ZeroLiteral character to obtain the second intermediate data ; Judging whether the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data is the original character in the neural network data, if so, then replacing the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data with a ZeroExtra character, and at the same time Then increase the sign bit representing that it is the original character, otherwise replace the same character with the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data with the ZeroExtra character, and increase the sign bit representing it as the replacement character afterwards.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中该ZeroLiteral字符和该ZeroExtra字符分别为该神经网络数据中出现频率最低的两种字符。In the neural network quantization compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, the ZeroLiteral characters and the ZeroExtra characters are respectively the two characters with the lowest frequency in the neural network data.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中该神经网络数据为神经网络运算中的权值数据和神经元输入数据。In the neural network quantization and compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, the neural network data is weight data and neuron input data in neural network operations.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中若该规范哈夫曼编码大于等于该神经网络数据,则放弃该规范哈夫曼编码,将该神经网络数据直接作为该压缩结果。In the neural network quantization compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, if the normalized Huffman code is greater than or equal to the neural network data, the normalized Huffman code is discarded, and the neural network data is directly used as the compression result.
所述的基于游程全零编码的神经网络量化压缩系统,其中该模块2中所有数据流的输入输出同步进行。In the neural network quantization and compression system based on run-length all-zero encoding, the input and output of all data streams in the
如图17所示,本发明还提出了一种基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中包括:As shown in Figure 17, the present invention also proposes a neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, which includes:
模块1、获取经过量化处理后待压缩的神经网络数据,对该神经网络数据进行分块,得到多个数据块;
模块2、对每一个该数据块分配一个数据流进行压缩,每条数据流的压缩包括:对该数据块进行游程全零编码,得到游程压缩数据,其中该游程全零编码仅对该神经网络数据中的零字符进行游程编码,对该游程压缩数据进行规范化哈夫曼编码,并对编码结果进行重整,得到规范哈夫曼编码,作为该数据块的压缩结果;
模块3、集合各数据块的压缩结果,作为该神经网络数据的压缩结果。
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该模块2中所有数据流的输入输出同步进行。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the input and output of all data streams in the
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中每条该数据流具有独立的输入缓存和输出缓存,输入缓存用于缓存该数据块,输出缓存用于缓存该数据块的压缩结果。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, each data stream has an independent input cache and output cache, the input cache is used to cache the data block, and the output cache is used to cache the compression result of the data block.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中模块2包括:Described neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, wherein
模块21、监测各数据流已经压缩编码的数据量,判断是否满足Pcurrent-Pmin≥S,若满足,则向当前数据流的输出缓存写入虚字符对应的虚编码,否则再次执行模块21;其中Pcurrent为当前数据流已编码的输入队列宽度,Pmin为编码速率最慢的数据流已经编码的输入队列宽度,S为数据流的流水线深度。Module 21. Monitor the compressed and encoded data volume of each data stream, and judge whether Pcurrent -Pmin ≥ S is satisfied. If it is satisfied, write the dummy code corresponding to the dummy character to the output buffer of the current data stream, otherwise execute module 21 again ; where Pcurrent is the encoded input queue width of the current data stream, Pmin is the encoded input queue width of the data stream with the slowest encoding rate, and S is the pipeline depth of the data stream.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中向当前数据流的输出缓存写入虚编码的数据量为Pcurrent-Pmin。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the amount of dummy coded data written to the output buffer of the current data stream is Pcurrent -Pmin .
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该模块21包括:向当前数据流的输出缓存写入虚字符,得到第三中间数据;判断该第三中间数据中与该虚字符相同的字符是否为当前数据流的输出缓存中的原字符,若是,则将该第三中间数据中与该虚字符相同的字符替换为虚编码,同时在其后增加表示其为原字符的标志位,否则将该第三中间数据中与该虚字符相同的字符替换为虚编码,同时在其后增加表示其为替换字符的标志位。The neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, wherein the module 21 includes: writing dummy characters to the output buffer of the current data stream to obtain the third intermediate data; judging the characters identical to the dummy characters in the third intermediate data Whether it is the original character in the output buffer of the current data stream, if so, replace the character identical to the virtual character in the third intermediate data with a virtual code, and add a flag indicating that it is the original character, otherwise The character identical to the dummy character in the third intermediate data is replaced with a dummy code, and at the same time, a flag indicating that it is a replacement character is added thereafter.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该模块2包括:设置与数据流数量相同的输入缓存,用于缓存该数据块,每条该数据流具有输出缓存,用于缓存该数据块的压缩结果。The neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, wherein the
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该模块2包括:该数据流随机选择输入缓存,并从中获取该数据块。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该模块2包括:该数据流根据预设规则选择输入缓存,并从中获取该数据块。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该游程全零编码的游程位宽为2bit。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the run-length bit width of the run-length all-zero coding is 2 bits.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该游程全零编码进一步包括:对该神经网络数据中的零数据进行游程编码,得到第一中间数据;将该第一中间数据的游程为3的编码片段替换为ZeroLiteral字符,得到第二中间数据;判断该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符是否为该神经网络数据中的原字符,若是,则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为原字符的标志位,否则将该第二中间数据中与该ZeroLiteral字符相同的字符替换为ZeroExtra字符,同时在其后增加表示其为替换字符的标志位。The neural network compression system based on hybrid encoding, wherein the run-length all-zero encoding further includes: performing run-length encoding on the zero data in the neural network data to obtain the first intermediate data; the run length of the first intermediate data is 3 The coding segment of the code segment is replaced by a ZeroLiteral character to obtain the second intermediate data; judge whether the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data is the original character in the neural network data, and if so, then match the second intermediate data with the original character in the neural network data The same character as the ZeroLiteral character is replaced with a ZeroExtra character, and at the same time, a flag indicating that it is the original character is added, otherwise, the character identical to the ZeroLiteral character in the second intermediate data is replaced with a ZeroExtra character, and at the same time, it is added. Flag indicating that it is a replacement character.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该ZeroLiteral字符和该ZeroExtra字符分别为该神经网络数据中出现频率最低的两种字符。In the neural network compression system based on mixed coding, the ZeroLiteral characters and the ZeroExtra characters are respectively the two characters with the lowest frequency in the neural network data.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该编码结果为哈夫曼树。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the coding result is a Huffman tree.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该模块2包括:Described neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, wherein the
对该哈夫曼树自上而下地进行重整,重整具体为将该哈夫曼树同一级节点当中的叶子节点移到二叉树左侧。The Huffman tree is reorganized from top to bottom. Specifically, the reorganization is to move the leaf nodes in the same level nodes of the Huffman tree to the left side of the binary tree.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中该神经网络数据为神经网络运算中的权值数据和神经元输入数据。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, the neural network data is weight data and neuron input data in neural network operations.
所述的基于混合编码的神经网络压缩系统,其中若该规范哈夫曼编码大于等于该神经网络数据,则放弃该规范哈夫曼编码,将该神经网络数据直接作为该压缩结果。In the neural network compression system based on hybrid coding, if the canonical Huffman coding is greater than or equal to the neural network data, the canonical Huffman coding is discarded, and the neural network data is directly used as the compression result.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011607727.8ACN114697672B (en) | 2020-12-30 | 2020-12-30 | Neural network quantization compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encoding |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011607727.8ACN114697672B (en) | 2020-12-30 | 2020-12-30 | Neural network quantization compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encoding |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114697672A CN114697672A (en) | 2022-07-01 |
| CN114697672Btrue CN114697672B (en) | 2023-06-27 |
Family
ID=82132650
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011607727.8AActiveCN114697672B (en) | 2020-12-30 | 2020-12-30 | Neural network quantization compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encoding |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114697672B (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116645101B (en)* | 2023-06-16 | 2024-05-10 | 厦门快快网络科技有限公司 | Cloud resource settlement method and system based on blockchain |
| CN116702708B (en)* | 2023-08-04 | 2023-11-03 | 陕西交通电子工程科技有限公司 | Road pavement construction data management system |
| CN117272989B (en)* | 2023-11-21 | 2024-02-06 | 浙江无端科技股份有限公司 | Character encoding compression-based mask word recognition method, device, equipment and medium |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101917622B (en)* | 2010-08-24 | 2012-09-05 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | 14bit wide image compression hardware coder |
| DE102018203709A1 (en)* | 2018-03-12 | 2019-09-12 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Method and device for memory-efficient operation of a neural network |
| CN109859281B (en)* | 2019-01-25 | 2022-12-02 | 杭州国芯科技股份有限公司 | Compression coding method of sparse neural network |
| CN110619392A (en)* | 2019-09-19 | 2019-12-27 | 哈尔滨工业大学(威海) | Deep neural network compression method for embedded mobile equipment |
| CN111884660B (en)* | 2020-07-13 | 2022-06-17 | 山东云海国创云计算装备产业创新中心有限公司 | Huffman coding equipment |
- 2020
- 2020-12-30CNCN202011607727.8Apatent/CN114697672B/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114697672A (en) | 2022-07-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114697672B (en) | Neural network quantization compression method and system based on run-length all-zero encoding | |
| US10901948B2 (en) | Query predicate evaluation and computation for hierarchically compressed data | |
| CN114697654B (en) | Neural network quantization compression method and system | |
| CN103326730B (en) | Data parallel compression method | |
| CN106549673B (en) | Data compression method and device | |
| CN105306951B (en) | Pipeline Parallel Acceleration Method and System Architecture for Data Compression Coding | |
| CN108416427A (en) | Convolution kernel accumulates data flow, compressed encoding and deep learning algorithm | |
| CN110021369B (en) | Gene sequencing data compression and decompression method, system and computer readable medium | |
| CN109859281A (en) | A kind of compaction coding method of sparse neural network | |
| CN113055017A (en) | Data compression method and computing device | |
| CN116318172A (en) | Design simulation software data self-adaptive compression method | |
| CN104156990B (en) | A kind of lossless compression-encoding method and system for supporting super-huge data window | |
| JP5584203B2 (en) | How to process numeric data | |
| Sun et al. | ZFP-V: Hardware-optimized lossy floating point compression | |
| CN116743182A (en) | Lossless data compression method | |
| Andrzejewski et al. | GPU-WAH: Applying GPUs to compressing bitmap indexes with word aligned hybrid | |
| CN114697673B (en) | Neural network quantization compression method and system based on inter-stream data shuffling | |
| CN114697655B (en) | Neural network quantization compression method and system for equalizing compression speed between streams | |
| CN113902097A (en) | Run-length coding accelerator and method for sparse CNN neural network model | |
| CN112101548A (en) | Data compression method and device, data decompression method and device, and electronic device | |
| WO2020114283A1 (en) | Data processing method and device | |
| Hishida et al. | Beyond Compression: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Lossless Floating-Point Compression | |
| Loncaric et al. | Pcodec: Better Compression for Numerical Sequences | |
| KR20210119907A (en) | Compression and decompression of weight values | |
| Andrzejewski et al. | GPU-PLWAH: GPU-based implementation of the PLWAH algorithm for compressing bitmaps |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |