CN114569105A - Cerebral blood flow detection method based on diffusion coherent spectrum image - Google Patents
Cerebral blood flow detection method based on diffusion coherent spectrum imageDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114569105A CN114569105ACN202210462086.4ACN202210462086ACN114569105ACN 114569105 ACN114569105 ACN 114569105ACN 202210462086 ACN202210462086 ACN 202210462086ACN 114569105 ACN114569105 ACN 114569105A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- value
- image sequence
- flow velocity
- image
- sequence
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/026—Measuring blood flow
- A61B5/0261—Measuring blood flow using optical means, e.g. infrared light
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0033—Features or image-related aspects of imaging apparatus, e.g. for MRI, optical tomography or impedance tomography apparatus; Arrangements of imaging apparatus in a room
- A61B5/004—Features or image-related aspects of imaging apparatus, e.g. for MRI, optical tomography or impedance tomography apparatus; Arrangements of imaging apparatus in a room adapted for image acquisition of a particular organ or body part
- A61B5/0042—Features or image-related aspects of imaging apparatus, e.g. for MRI, optical tomography or impedance tomography apparatus; Arrangements of imaging apparatus in a room adapted for image acquisition of a particular organ or body part for the brain
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7203—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes for noise prevention, reduction or removal
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7225—Details of analogue processing, e.g. isolation amplifier, gain or sensitivity adjustment, filtering, baseline or drift compensation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/0002—Inspection of images, e.g. flaw detection
- G06T7/0012—Biomedical image inspection
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B2576/00—Medical imaging apparatus involving image processing or analysis
- A61B2576/02—Medical imaging apparatus involving image processing or analysis specially adapted for a particular organ or body part
- A61B2576/026—Medical imaging apparatus involving image processing or analysis specially adapted for a particular organ or body part for the brain
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30016—Brain
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/30—Subject of image; Context of image processing
- G06T2207/30004—Biomedical image processing
- G06T2207/30101—Blood vessel; Artery; Vein; Vascular
- G06T2207/30104—Vascular flow; Blood flow; Perfusion
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及光谱图像处理的技术领域,具体涉及一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法。The invention relates to the technical field of spectral image processing, in particular to a method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images.
背景技术Background technique
脑血流量(cerebral blood flow, CBF)是临床上诊断脑梗塞、脑出血等脑血管疾病的主要依据,测定CBF可以为研究人脑在不同病理和生理条件下的功能提供客观指标。针对如癫痫、阿尔兹海默症等特定脑血管病症诊治,需要长期监测局部CBF的慢性变化过程。目前,临床上治疗脑血管疾病多采用经颅多普勒超声检测,但单点监测导致空间分辨率低且成像深度浅,难以满足临床需求。Cerebral blood flow (CBF) is the main basis for the clinical diagnosis of cerebral infarction, cerebral hemorrhage and other cerebrovascular diseases. Determination of CBF can provide objective indicators for studying the function of human brain under different pathological and physiological conditions. For the diagnosis and treatment of specific cerebrovascular diseases such as epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease, it is necessary to monitor the chronic changes of local CBF for a long time. At present, transcranial Doppler ultrasound is mostly used in clinical treatment of cerebrovascular diseases, but single-point monitoring results in low spatial resolution and shallow imaging depth, which is difficult to meet clinical needs.
而无创光谱血流检测技术在近年来得到了快速发展,有望发展为一种标准的临床血流监测手段。其中扩散相关光谱技术能实现深层组织的血流检测,但检测精度受限于头皮血流干扰且采集速率低,难以实现长时间检测CBF的慢性变化。而扩散相干光谱技术结合了光外差检测原理,其扩散相干光能穿透头皮、颅骨等进入脑组织深层内部被多次散射,利用强参考光与信号光的相干过程增强系统的检测灵敏度,有望改善头皮血流等因素干扰。但是,目前扩散相干光谱成像系统还存在一些不足之处,如仍缺乏一种高效且准确的光谱图像处理方法,难以从光谱图像中提取深层CBF的流速特征,成像系统噪声干扰较大导致测量准确性较低等问题。The non-invasive spectral blood flow detection technology has developed rapidly in recent years, and is expected to develop into a standard clinical blood flow monitoring method. Among them, diffusion correlation spectroscopy can realize blood flow detection in deep tissue, but the detection accuracy is limited by the interference of scalp blood flow and the acquisition rate is low, so it is difficult to detect chronic changes in CBF for a long time. The diffused coherent spectroscopy technology combines the principle of optical heterodyne detection. The diffused coherent light can penetrate the scalp, skull, etc. into the deep interior of the brain tissue and be scattered multiple times. The coherent process of the strong reference light and the signal light is used to enhance the detection sensitivity of the system. It is expected to improve the interference of factors such as scalp blood flow. However, the current diffusion coherent spectral imaging system still has some shortcomings. For example, there is still a lack of an efficient and accurate spectral image processing method, it is difficult to extract the flow velocity characteristics of the deep CBF from the spectral image, and the noise interference of the imaging system is large, which leads to accurate measurement. issues of lower sexuality.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
鉴于以上所述现有方法的局限,本发明的目的在于提供一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法。利用扩散相干光谱成像系统探测待测局部脑组织表面漫反射的扩散相干光束,在CMOS相机光敏面上记录得到扩散相干光谱图像序列。并对扩散相干光谱图像序列进行流速特征增强处理、动态散射特征提取和图像校正处理等方法过程。最终计算得到局部脑血流相对指数,并结合血管管径测量方法得到该待测局部脑组织随时间变化的局部脑血流量,从而有望实现高效且高灵敏度的无创脑血流量检测。本发明提供的脑血流量检测方法高效准确,解决了目前的技术难点,有利于长期地实时检测脑血流量,为脑血管疾病的早期诊断与治疗提供一种理论依据。In view of the limitations of the above-mentioned existing methods, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a cerebral blood flow detection method based on diffuse coherent spectral images. The diffused coherent spectral imaging system is used to detect the diffused coherent light beams diffusely reflected on the surface of the brain tissue to be measured, and the diffused coherent spectral image sequence is obtained by recording on the photosensitive surface of the CMOS camera. The process of flow velocity feature enhancement, dynamic scattering feature extraction and image correction processing is carried out for the diffusion coherent spectral image sequence. The relative index of local cerebral blood flow is finally calculated, and the local cerebral blood flow of the local brain tissue to be measured changes with time is obtained in combination with the vascular diameter measurement method, which is expected to achieve efficient and high-sensitivity non-invasive cerebral blood flow detection. The cerebral blood flow detection method provided by the invention is efficient and accurate, solves the current technical difficulties, is conducive to long-term real-time detection of cerebral blood flow, and provides a theoretical basis for early diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular diseases.
为了实现上述目的,根据本公开的一方面,提供一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法,所述方法包括以下步骤:In order to achieve the above object, according to an aspect of the present disclosure, a method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on a diffuse coherent spectral image is provided, the method comprising the following steps:
S100,利用扩散相干光谱成像系统测定待测局部脑组织,获得扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列;S100, use a diffusion coherent spectral imaging system to measure the local brain tissue to be tested, and obtain a diffusion coherent spectral image sequence and a dark current image sequence;
S200,根据所述扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列,进行流速特征增强处理,得到特征增强图像序列和流速特征区域图像序列;S200, according to the diffusion coherent spectral image sequence and the dark current image sequence, perform flow velocity feature enhancement processing to obtain a feature enhanced image sequence and a flow velocity feature region image sequence;
S300,根据所述流速特征区域图像序列,计算局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列;S300, according to the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence, calculate the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence;
S400,根据所述局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列,计算动态散射流速图像序列;S400, according to the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence, calculate a dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence;
S500,根据所述特征增强图像序列和动态散射流速图像序列,进行图像校正处理,得到相对流速图像序列;S500, performing image correction processing according to the feature enhancement image sequence and the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence to obtain a relative flow velocity image sequence;
S600,根据所述相对流速图像序列,得到局部脑血流相对指数序列;S600, obtain a local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence according to the relative flow velocity image sequence;
S700,根据所述局部脑血流相对指数序列结合血管管径测量方法,得到该待测局部脑组织随时间变化的局部脑血流量。S700, according to the local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence combined with the blood vessel diameter measurement method, obtain the time-varying local cerebral blood flow of the local brain tissue to be measured.
进一步地,在S100中,利用扩散相干光谱成像系统测定待测局部脑组织,获得扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列的方法为:Further, in S100, using the diffusion coherent spectral imaging system to measure the local brain tissue to be measured, the methods for obtaining the diffusion coherent spectral image sequence and the dark current image sequence are:
S101,设定扩散相干光谱成像系统的CMOS相机的曝光时间为T ms,即在每秒内采集1/T×103帧;设置所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的激光光源关闭输入,在采集时间t秒内,所述CMOS相机记录t/T×103帧暗电流图像;由计算机进行灰度预处理后得到暗电流图像序列;S101, set the exposure time of the CMOS camera of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system to T ms, that is, to collect 1/T×103 frames per second; set the laser light source of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system to turn off the input, and at the acquisition time Within t seconds, the CMOS camera records t/T×103 frames of dark current images; the dark current image sequence is obtained after grayscale preprocessing by the computer;
S102,设定在采集时间t秒内,设置所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的激光光源打开输入,将所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的入射光源光纤探头和探测光纤探头之间的距离设定在1.5~2.5 cm范围之间,接触于待测局部脑组织表面进行测定;S102, set within the acquisition time t seconds, set the laser light source of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system to turn on the input, and set the distance between the incident light source fiber probe of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system and the detection fiber probe at 1.5 Within the range of ~2.5 cm, contact the surface of the local brain tissue to be measured for measurement;
S103,所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的探测光纤采集所述待测局部脑组织表面漫反射的扩散相干光束,传输至CMOS相机的光敏面上形成扩散相干光谱图像;S103, the detection fiber of the diffused coherent spectral imaging system collects the diffused coherent light beam that is diffusely reflected on the surface of the local brain tissue to be measured, and transmits it to the photosensitive surface of the CMOS camera to form a diffused coherent spectral image;
S104,设定在采集时间t秒内,所述CMOS相机总记录t/T×103帧所述扩散相干光谱图像,由计算机进行灰度预处理后得到扩散相干光谱图像序列。S104 , within the acquisition time t seconds, the CMOS camera records t/T×103 frames of the diffuse coherent spectral images in total, and a computer performs grayscale preprocessing to obtain a sequence of diffuse coherent spectral images.
进一步地,在S200中,根据扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列,进行流速特征增强处理,得到特征增强图像序列和流速特征区域图像序列的方法为:Further, in S200, according to the diffusion coherent spectrum image sequence and the dark current image sequence, the flow velocity feature enhancement process is performed, and the method for obtaining the feature enhanced image sequence and the flow velocity feature region image sequence is:
S201,设定所述扩散相干光谱图像序列为I(x, y, z),所述暗电流图像序列为O(x, y, z),其中I(x, y, z)和O(x, y, z)分别表示在第z帧所述扩散相干光谱图像和所述暗电流图像在像素点坐标(x, y)上的灰度值,初始化x = 1, y = 1, z = 1;其中设定图像分辨率尺寸大小为[M, N],x值取值范围为[1, M],y值取值范围为[1, N],z值取值范围为[1, t/T×103];设定时间域窗口长度大小为Nt帧,时间域窗口序号为n,n值取值范围为[1,floor(z/Nt)];其中floor函数为高斯取整,即n值不超过z/Nt的最大整数,初始化n = 1;S201, set the diffusion coherence spectrum image sequence to be I(x, y, z), and the dark current image sequence to be O(x, y, z), where I(x, y, z) and O(x , y, z) respectively represent the grayscale values of the diffuse coherent spectral image and the dark current image at the pixel coordinates (x, y) in the zth frame, and initialize x = 1, y = 1, z = 1 ;The size of the image resolution is set to [M, N], the value range of x value is [1, M], the value range of y value is [1, N], and the value range of z value is [1, t] /T×103 ]; set the length of the time domain window to Nt frames, the time domain window serial number to n, and the value range of n to be [1, floor(z/Nt)]; where the floor function is Gaussian rounding, That is, the value of n does not exceed the largest integer of z/Nt, and initializes n = 1;
S202,在第z帧时遍历像素点坐标(x, y)的取值范围,根据所述扩散相干光谱图像I(x, y, z)和所述暗电流图像序列为O(x, y, z),计算特征校准图像序列Q(x, y, z):S202, traverse the value range of the pixel coordinates (x, y) in the zth frame, according to the diffusion coherent spectral image I(x, y, z) and the dark current image sequence O(x, y, z), calculate the feature calibration image sequence Q(x, y, z):
其中Q(x, y, z)表示为在第z帧所述特征校准图像的像素点坐标为(x, y)上的特征校准值,na(z)表示为在第z帧所述暗电流图像中的校准因子;where Q(x, y, z) is the feature calibration value at the pixel point coordinates (x, y) of the feature calibration image in the zth frame, and na (z) is the dark value in the zth frame. calibration factor in the current image;
S203,判断z值是否等于n×Nt,是则根据所述特征校准图像序列Q(x, y, z),在第n个时间域窗口内遍历z = [Nt(n-1)+1, ..., nNt ]时,对应遍历像素点坐标(x, y)的取值范围,计算特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n):S203, determine whether the z value is equal to n×Nt, if yes, calibrate the image sequence Q(x, y, z) according to the feature, and traverse z = [Nt(n-1)+1 in the nth time domain window, ..., nNt ], correspondingly traverse the range of pixel coordinates (x, y) to calculate the feature enhanced image sequence R(x, y, n):
其中R(x, y, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口中所述特征增强图像在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的灰度值;为R(x, y, n)在第n个时间域窗口内对应像素点坐标为(x, y)上的特征相关因子,为R(x, y, n)在第n个时间域窗口内对应像素点坐标为(x, y)上的特征增强因子,为所述特征校准图像序列Q(x, y, z)遍历z = [Nt(n-1)+1,..., nNt ],对应第n个时间域窗口内共Nt帧在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的灰度均值,和分别为所述暗电流图像序列O(x, y, z)遍历z = [Nt(n-1)+1, ...,nNt ],对应第n个时间域窗口内共Nt帧在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的灰度均值和标准方差,为流速规范化算子;where R(x, y, n) represents the gray value of the feature-enhanced image in the nth time domain window at the pixel coordinate (x, y); For R(x, y, n) in the nth time domain window, the corresponding pixel coordinates are the feature correlation factor on (x, y), is the feature enhancement factor of R(x, y, n) corresponding to the pixel coordinates in the nth time domain window (x, y), Traverse z = [Nt(n-1)+1,..., nNt ] for the feature calibration image sequence Q(x, y, z), corresponding to the pixel coordinates of Nt frames in the nth time domain window is the gray mean value on (x, y), and Respectively, traverse z = [Nt(n-1)+1, ..., nNt ] for the dark current image sequence O(x, y, z), corresponding to a total of Nt frames in the nth time domain window at the pixel point The coordinates are the gray mean and standard deviation on (x, y), is the flow rate normalization operator;
否则令z值增加1,跳转至步骤S202;Otherwise, increase the z value by 1, and jump to step S202;
S204,判断n值是否小于floor(z/Nt),是则令n值增加1,z值增加1,跳转至步骤S202;否则跳转至步骤S205;S204, determine whether the value of n is less than floor(z/Nt), if yes, increase the value of n by 1 and the value of z by 1, and jump to step S202; otherwise, jump to step S205;
S205,根据所述特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n),计算得到流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n)。S205, according to the feature enhancement image sequence R(x, y, n), calculate and obtain the flow velocity feature region image sequence RI(x, y, n).
其中,在步骤S205中,计算得到流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n)的方法为:Wherein, in step S205, the method for calculating the flow velocity characteristic region image sequence RI(x, y, n) is:
S2051,设定空间域窗口长度大小为Ns个像素点,则一个空间域窗口单元大小为Ns×Ns个像素点;其中Ns = gcd(M-2, N-2),gcd函数为求最大公约数,即Ns为二维图像分辨率尺寸大小[M-2, N-2]的最大公约数;初始化x = 2,y = 2,n = 1;空间域窗口的扫描序号为k,k值取值范围为[1, floor((M-2)(n-2)/Ns2)],floor函数为高斯取整,初始化k = 1;S2051, set the size of the spatial domain window length to Ns pixels, then the size of one spatial domain window unit is Ns×Ns pixels; where Ns = gcd(M-2, N-2), the gcd function is to find the greatest convention number, that is, Ns is the greatest common divisor of the two-dimensional image resolution size [M-2, N-2]; initialization x = 2, y = 2, n = 1; the scan sequence number of the spatial domain window is k, the value of k The value range is [1, floor((M-2)(n-2)/Ns2 )], the floor function is Gaussian rounding, and the initialization k = 1;
S2052,在第n个时间域窗口时,根据所述特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n),遍历(x,y)计算流速特征梯度图像序列G(x, y, n):S2052, in the nth time domain window, according to the feature enhancement image sequence R(x, y, n), traverse (x, y) to calculate the flow velocity feature gradient image sequence G(x, y, n):
G(x, y, n)表示为第z帧时所述流速特征梯度图像在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的梯度大小;其中,G(x, y, n) is expressed as the gradient size of the flow velocity characteristic gradient image on the pixel coordinate (x, y) at the zth frame; wherein,
Gx(x, y, n),Gy(x, y, n)和Gz(x, y, n)分别表示为在第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征梯度图像在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的水平梯度,垂直梯度大小和时间轴梯度大小;Gx (x, y, n), Gy (x, y, n) and Gz (x, y, n) are respectively expressed as the pixel coordinates of the flow velocity characteristic gradient image in the nth time domain window is the horizontal gradient on (x, y), the vertical gradient size and the time axis gradient size;
S2053,判断n值是否大于1,是则在第n个时间域窗口时,在二维图像尺寸大小为(M-2)×(N-2)个像素点内遍历所述空间域窗口序号k值的取值范围,以Ns个像素点为步长,从x = 2, y = 2开始水平方向和垂直方向移动扫描第k个所述空间域窗口单元,在Ns×Ns个像素点内计算流速特征度量序列D(k, n)和流动特征序列F(k, n):S2053, determine whether the value of n is greater than 1, and if so, in the nth time domain window, traverse the spatial domain window sequence number k within the two-dimensional image size of (M-2)×(N-2) pixels. The value range of the value, with Ns pixels as the step size, starts from x = 2, y = 2 and moves horizontally and vertically to scan the kth spatial domain window unit, calculated within Ns×Ns pixels Flow velocity characteristic metric sequence D(k, n) and flow characteristic sequence F(k, n):
其中D(k, n)表示为第n个和第n-1个相邻的时间域窗口之间,计算在第k个空间域窗口单元内与流速线性相关的特征度量值;为归一化参数;where D(k, n) is expressed as between the nth and n-1th adjacent time domain windows, and the characteristic metric value linearly related to the flow velocity in the kth space domain window unit is calculated; is the normalization parameter;
Rv(k, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述特征增强图像在第k个空间域窗口单元内计算的特征增强均值;Gv(k, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征梯度图像在第k个空间域窗口单元内计算的特征梯度均值;Rv(k, n) is the feature enhancement mean value of the feature-enhanced image calculated in the k-th space-domain window unit when the n-th time-domain window; Gv(k, n) is the n-th time-domain window the mean value of the characteristic gradient calculated in the kth spatial domain window unit of the flow velocity characteristic gradient image;
其中F(k, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述特征增强图像在第k个空间域窗口单元内的流动特征灰度值,min函数为求最小值;where F(k, n) represents the gray value of the flow feature of the feature-enhanced image in the kth spatial domain window unit in the nth time domain window, and the min function is the minimum value;
否则跳转至步骤S2052;Otherwise, jump to step S2052;
S2054,判断n值是否小于floor(z/Nt)-1,是则n值增加1,跳转至步骤S2052;否则令n = 1,跳转至步骤S2055;S2054, determine whether the value of n is less than floor(z/Nt)-1, if yes, the value of n is increased by 1, and jump to step S2052; otherwise, set n = 1, and jump to step S2055;
S2055,根据所述流速特征度量序列D(k, n)和流动特征序列F(k, n),遍历k值取值范围,计算流速特征序列L(k):S2055, according to the flow velocity characteristic measurement sequence D(k, n) and the flow characteristic sequence F(k, n), traverse the value range of the k value, and calculate the flow velocity characteristic sequence L(k):
L(k)表示为在第k个空间域窗口单元内的流速特征序列;L(k) is expressed as the flow velocity characteristic sequence in the kth spatial domain window unit;
S2056,遍历k值的取值范围,判断所述流速特征序列L(k)内是否存在大于流速相关性阈值的流速特征值,是则遍历x和y的取值范围,标记k值对应的空间域窗口单元内的流速特征值V(x, y) = 1;否则标记k值对应的空间域窗口单元内的流速特征值V(x, y) = 0;S2056, traverse the value range of the k value, and determine whether there is a flow velocity characteristic value greater than the flow velocity correlation threshold in the flow velocity characteristic sequence L(k), and if yes, traverse the value range of x and y, and mark the space corresponding to the k value The flow velocity characteristic value V(x, y) = 1 in the domain window unit; otherwise, the flow velocity characteristic value V(x, y) = 0 in the space domain window unit corresponding to the marked k value;
V(x, y)表示在像素坐标(x, y)上的流速特征值;其中,V(x, y) represents the flow velocity eigenvalue at pixel coordinates (x, y); where,
S2057,根据所述流速特征值V(x, y),遍历n值的取值范围,计算得到流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n) = R(x, y, n)×V(x, y);其中RI(x, y, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征区域图像在像素坐标(x, y)上的灰度值。S2057, according to the flow velocity characteristic value V(x, y), traverse the value range of the n value, and calculate the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence RI(x, y, n) = R(x, y, n)×V( x, y); wherein RI(x, y, n) represents the gray value of the flow velocity characteristic region image at pixel coordinates (x, y) in the nth time domain window.
进一步地,在S300中,根据所述流速特征区域图像序列,计算局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列的方法为:Further, in S300, according to the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence, the method for calculating the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence is:
S301,设定所述流速特征区域图像序列的像素尺寸为M1×N1×L1,图像序列坐标为(x1, y1, n1),图像像素坐标为(x1, y1);其中x1的取值范围为[1, M1],y1的取值范围为[1, N1],n1的取值范围为[1, L1];S301, set the pixel size of the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence to be M1×N1×L1, the image sequence coordinates to be (x1, y1, n1), and the image pixel coordinates to be (x1, y1); wherein the value range of x1 is [1, M1], the value range of y1 is [1, N1], and the value range of n1 is [1, L1];
遍历x,y和n值的取值范围,根据所述流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n),令局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1, n1) = RI(x, y, n),即同样遍历x1,y1和n1值的取值范围,将第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征区域图像在像素坐标为(x, y)上的灰度值,对应存入第n1个时间域窗口时所述局部区域图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的灰度值;初始化x1= 1,y1 = 1,n1 = 1;Traverse the value range of x, y and n values, according to the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence RI(x, y, n), let the local flow velocity characteristic area image sequence ROI(x1, y1, n1) = RI(x, y , n), that is, the value range of x1, y1 and n1 values is also traversed, and the gray value of the flow velocity characteristic area image at the pixel coordinate (x, y) in the nth time domain window is stored in the corresponding In the n1th time domain window, the gray value of the local area image at the pixel coordinates (x1, y1); initialize x1 = 1, y1 = 1, n1 = 1;
S302,在第n1个时间域窗口时,遍历所述局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1,n1) 上的所有像素坐标(x1, y1),经过标准偏差滤波处理,得到标准偏差散射特征区域图像序列Std(x1, y1, n1);S302, in the n1th time domain window, traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) on the local flow velocity characteristic region image sequence ROI (x1, y1, n1), and obtain standard deviation scattering features through standard deviation filtering processing Region image sequence Std(x1, y1, n1);
其中Std(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述标准散射特征区域图像在像素坐标(x1, y1)上的灰度值;where Std(x1, y1, n1) represents the gray value of the standard scattering feature region image at pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the n1th time domain window;
S303,在第n1个时间域窗口时,遍历所述局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1,n1) 上的所有像素坐标(x1, y1),经过平均滤波处理,得到平均散射特征区域图像序列Ave(x1, y1, n1);S303, in the n1th time domain window, traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) on the local flow velocity characteristic area image sequence ROI(x1, y1, n1), and obtain an average scattering characteristic area image through an average filtering process sequence Ave(x1, y1, n1);
其中Ave(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述平均散射特征区域图像在像素坐标(x1, y1)上的灰度值;where Ave(x1, y1, n1) represents the gray value of the average scattering feature area image at pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the n1th time domain window;
S304,设定空间统计步长为offset,根据所述标准散射特征区域图像序列Std(x1,y1, n1)和平均散射特征区域图像序列Ave(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1,y1)计算静态散射图像序列Static(x1, y1, n1):S304, set the spatial statistical step size to offset, and traverse all pixel coordinates in the image according to the standard scattering characteristic area image sequence Std(x1, y1, n1) and the average scattering characteristic area image sequence Ave(x1, y1, n1). (x1, y1) computes the static scatter image sequence Static(x1, y1, n1):
其中,Static(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述静态散射图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的静态散射值;mean函数为在空间统计窗口大小为offset×offset个像素点内计算均值;Among them, Static(x1, y1, n1) represents the static scattering value of the static scattering image at the pixel coordinate of (x1, y1) when the n1th time domain window; the mean function is the size of the spatial statistical window is offset× Calculate the mean within offset pixels;
S305,判断n1值是否小于L1,是则令n1值增加1,跳转至步骤S302;否则令n1 = 1,跳转至步骤S400。S305, determine whether the value of n1 is less than L1, if yes, increase the value of n1 by 1, and jump to step S302; otherwise, set n1 = 1, and jump to step S400.
进一步地,在S400中,根据所述局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列,计算动态散射流速图像序列的方法为:Further, in S400, according to the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence, the method for calculating the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence is:
S401,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1,n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算系统相干因子beta(n1)和动态算子:S401, traverse the value range of the n1 value, according to the local flow velocity characteristic region image sequence ROI (x1, y1, n1), traverse all pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the system coherence factor beta (n1) and dynamic calculation son :
其中,beta(n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时,所述系统相干因子的数值;为遍历所有x1值和y1值计算在M1×N1像素范围内的均值;表示为在第n1个时间域窗口时,所述动态算子的数值;Wherein, beta(n1) is expressed as the numerical value of the system coherence factor in the n1th time domain window; Calculate the mean in the range of M1×N1 pixels for traversing all x1 values and y1 values; is expressed as the value of the dynamic operator in the n1th time domain window;
S402,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述静态散射图像序列Static(x1, y1, n1)、系统相干因子beta(n1)和动态算子,遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算动态散射流速图像序列Dynamic(x1, y1, n1):S402, traverse the value range of the n1 value, according to the static scattering image sequence Static(x1, y1, n1), the system coherence factor beta(n1) and the dynamic operator , traverse all pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence Dynamic(x1, y1, n1):
其中,Dynamic(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述动态散射流速图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的动态散射值。Wherein, Dynamic(x1, y1, n1) represents the dynamic scattering value at the pixel coordinate of (x1, y1) of the dynamic scattering flow velocity image in the n1th time domain window.
进一步地,在S500中,根据所述特征增强图像序列和动态散射流速图像序列,进行图像校正处理,得到相对流速图像序列的方法为:Further, in S500, image correction processing is performed according to the feature enhancement image sequence and the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence, and the method for obtaining the relative flow velocity image sequence is:
S501,遍历x,y和n值的取值范围,根据所述特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n),令局部特征增强图像序列ROI2(x1, y1, n1) = R(x, y, n),即同样遍历x1,y1和n1值的取值范围,将第n个时间域窗口时所述特征增强图像在像素坐标为(x, y)上的灰度值,对应存入第n1个时间域窗口时所述局部特征增强图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的灰度值;初始化x1 =1,y1 = 1,n1 = 1;S501, traverse the value ranges of x, y and n values, and according to the feature enhancement image sequence R(x, y, n), make the local feature enhancement image sequence ROI2(x1, y1, n1) = R(x, y , n), that is, the value range of x1, y1 and n1 values is also traversed, and the gray value of the feature-enhanced image at the pixel coordinate of (x, y) in the nth time domain window is stored in the corresponding When there are n1 time domain windows, the gray value of the local feature enhancement image at the pixel coordinates (x1, y1); initialize x1 =1, y1 = 1, n1 = 1;
S502,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据局部特征增强图像序列ROI2(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算系统噪声估值Knoise(n1):S502, traverse the value range of the n1 value, enhance the image sequence ROI2 (x1, y1, n1) according to the local features, and traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the system noise estimate Knoise (n1):
其中,Knoise(n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时的系统噪声估值,为遍历所有x1值和y1值计算在M1×N1像素范围内的均值,为计算均值,nd为系统噪声因子,定义为系统输入和输出信噪比的比值,是归一化噪声系数;Among them, Knoise (n1) is expressed as the estimated system noise at the n1th time domain window, Calculate the mean over M1×N1 pixels for iterating over all x1 and y1 values, To calculate the mean, nd is the system noise factor, defined as the ratio of the system input and output signal-to-noise ratios, is the normalized noise figure;
S503,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述系统噪声估值Knoise(n1)和动态散射流速图像序列Dynamic(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算相对流速图像序列FK(x1, y1, n1):S503, traverse the value range of the n1 value, according to the estimated system noise Knoise (n1) and the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence Dynamic (x1, y1, n1), traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the relative Flow velocity image sequence FK(x1, y1, n1):
其中FK(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述相对流速图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的相对流速值,为在第n1个时间域窗口的动态算子。where FK(x1, y1, n1) represents the relative flow velocity value of the relative flow velocity image at the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the n1th time domain window, is the dynamic operator in the n1th time domain window.
进一步地,在S600中,根据所述相对流速图像序列,得到局部脑血流相对指数序列的方法为:Further, in S600, according to the relative flow velocity image sequence, the method for obtaining the local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence is:
S601,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述相对流速图像序列FK(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算相对流速指数序列FV(n1):S601, traverse the value range of the n1 value, and according to the relative flow velocity image sequence FK(x1, y1, n1), traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the relative flow velocity index sequence FV(n1):
其中,FV(n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口的相对流速指数,为遍历所有x1值和y1值计算在M1×N1像素范围内的均值;Among them, FV(n1) is expressed as the relative velocity index of the n1th time domain window, Calculate the mean in the range of M1×N1 pixels for traversing all x1 values and y1 values;
S602,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述相对流速指数序列FV(n1),计算得到局部脑血流相对指数序列BFI (n1)= c / FV(n1)2,其中BFI(n1)为第n1个时间域窗口的局部脑血流相对指数,c为归一化比例常数。S602, traverse the value range of the n1 value, and according to the relative flow velocity index sequence FV(n1), calculate and obtain the local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence BFI(n1)=c / FV(n1)2 , where BFI(n1) is The relative index of regional cerebral blood flow in the n1th time domain window, c is the normalized proportionality constant.
如上所述,本发明所述的一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法,具有以下有益效果:As described above, the method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images according to the present invention has the following beneficial effects:
(1)基于扩散相干光谱图像进行流速特征增强处理,能高效且准确地从光谱图像中提取流速特征值,避免了复杂的频域转换和积分计算过程;(1) The flow velocity feature enhancement processing based on the diffusion coherent spectral image can efficiently and accurately extract the flow velocity characteristic value from the spectral image, avoiding the complicated frequency domain conversion and integration calculation process;
(2)基于扩散相干光谱图像进行进行图像校正处理,能有效地消除系统噪声干扰导致的测量误差,提高系统抗干扰能力;(2) Image correction processing based on diffuse coherent spectral images can effectively eliminate measurement errors caused by system noise interference and improve system anti-interference capabilities;
(3)基于扩散相干光谱成像系统,结合该脑血流量检测方法能有望提高对局部深层脑血流的检测精度和测量灵敏度,能有效避免头皮血流的干扰。(3) Based on the diffusion coherent spectral imaging system, combined with the cerebral blood flow detection method, it is expected to improve the detection accuracy and measurement sensitivity of local deep cerebral blood flow, and can effectively avoid the interference of scalp blood flow.
附图说明Description of drawings
通过对结合附图所示出的实施方式进行详细说明,本公开的上述以及其他特征将更加明显,本公开附图中相同的参考标号表示相同或相似的元素,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本公开的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图,在附图中:The above-mentioned and other features of the present disclosure will become more apparent from the detailed description of the embodiments shown in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, in which the same reference numerals refer to the same or similar elements of the present disclosure. The drawings are only some embodiments of the present disclosure. For those of ordinary skill in the art, other drawings can also be obtained from these drawings without creative efforts. In the drawings:
图1所示为一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法于一实施例中的的流程图;FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectroscopic images in one embodiment;
图2所示为一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法于一实施例中的扩散相干光谱成像系统的硬件结构框图组成示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram showing the composition of a hardware structure block diagram of a diffusion coherent spectral imaging system in an embodiment of a cerebral blood flow detection method based on a diffusion coherent spectral image;
图3所示为一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法于一实施例中基于动物实验测量的局部脑血流相对指数与同步测量随时间变化的血压曲线对比示意图。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing the comparison of the relative index of local cerebral blood flow measured based on animal experiments and the blood pressure curve measured synchronously over time in an embodiment of a method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectroscopic images.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下将结合实施例和附图对本公开的构思、具体结构及产生的技术效果进行清楚、完整的描述,以充分地理解本公开的目的、方案和效果。需要说明的是,在不冲突的情况下,本申请中的实施例及实施例中的特征可以相互组合。以下实施例中所提供的图示仅以示意方式说明本发明的基本构想,旨在用于解释本申请,而不能理解为对本申请的限制。The concept, specific structure and technical effects of the present disclosure will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the embodiments and accompanying drawings, so as to fully understand the purpose, solutions and effects of the present disclosure. It should be noted that the embodiments in the present application and the features of the embodiments may be combined with each other in the case of no conflict. The illustrations provided in the following embodiments merely illustrate the basic idea of the present invention in a schematic manner, and are intended to be used to explain the present application, but should not be construed as a limitation to the present application.
本发明所述的一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法,能有望提高对局部深层脑血流的检测精度和测量灵敏度,有效地避免头皮血流的干扰;且实现高效且准确地从光谱图像中提取流速特征,避免了复杂的频域转换和积分计算过程;有效地消除系统噪声干扰导致的测量误差,提高系统抗干扰能力。The cerebral blood flow detection method based on the diffusion coherent spectral image described in the present invention is expected to improve the detection accuracy and measurement sensitivity of local deep cerebral blood flow, effectively avoid the interference of scalp blood flow; Extracting flow velocity features from spectral images avoids complex frequency domain conversion and integral calculation processes; effectively eliminates measurement errors caused by system noise interference and improves system anti-interference ability.
如图1所示为根据本发明的一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法的流程图,下面结合图1来阐述根据本发明的实施方式的一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法。FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on a diffuse coherent spectral image according to the present invention. The following describes a cerebral blood flow detection method based on a diffuse coherent spectral image according to an embodiment of the present invention with reference to FIG. 1 . Flow detection method.
本公开提出一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法,所述方法具体包括以下步骤:The present disclosure proposes a method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images, the method specifically includes the following steps:
S100,利用扩散相干光谱成像系统测定待测局部脑组织,获得扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列;S100, use a diffusion coherent spectral imaging system to measure the local brain tissue to be tested, and obtain a diffusion coherent spectral image sequence and a dark current image sequence;
S200,根据所述扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列,进行流速特征增强处理,得到特征增强图像序列和流速特征区域图像序列;S200, according to the diffusion coherent spectral image sequence and the dark current image sequence, perform flow velocity feature enhancement processing to obtain a feature enhanced image sequence and a flow velocity feature region image sequence;
S300,根据所述流速特征区域图像序列,计算局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列;S300, according to the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence, calculate the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence;
S400,根据所述局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列,计算动态散射流速图像序列;S400, according to the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence, calculate a dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence;
S500,根据所述特征增强图像序列和动态散射流速图像序列,进行图像校正处理,得到相对流速图像序列;S500, performing image correction processing according to the feature enhancement image sequence and the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence to obtain a relative flow velocity image sequence;
S600,根据所述相对流速图像序列,得到局部脑血流相对指数序列;S600, obtain a local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence according to the relative flow velocity image sequence;
S700,根据所述局部脑血流相对指数序列结合血管管径测量方法,得到该待测局部脑组织随时间变化的局部脑血流量。S700, according to the local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence combined with the blood vessel diameter measurement method, obtain the time-varying local cerebral blood flow of the local brain tissue to be measured.
进一步地,在S100中,利用扩散相干光谱成像系统测定待测局部脑组织,获得扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列的方法为:Further, in S100, using the diffusion coherent spectral imaging system to measure the local brain tissue to be measured, the methods for obtaining the diffusion coherent spectral image sequence and the dark current image sequence are:
S101,设定扩散相干光谱成像系统的CMOS相机的曝光时间为T ms,即在每秒内采集1/T×103帧;设置所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的激光光源关闭输入,在采集时间t秒内,所述CMOS相机记录t/T×103帧暗电流图像;由计算机进行灰度预处理后得到暗电流图像序列;S101, set the exposure time of the CMOS camera of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system to T ms, that is, to collect 1/T×103 frames per second; set the laser light source of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system to turn off the input, and at the acquisition time Within t seconds, the CMOS camera records t/T×103 frames of dark current images; the dark current image sequence is obtained after grayscale preprocessing by the computer;
优选地,T值取值范围为1.0~5.0 ms;Preferably, the T value ranges from 1.0 to 5.0 ms;
S102,设定在采集时间t秒内,设置所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的激光光源打开输入,将所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的入射光源光纤探头和探测光纤探头之间的距离设定在1.5~2.5 cm范围之间,接触于待测局部脑组织表面进行测定;S102, set within the acquisition time t seconds, set the laser light source of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system to turn on the input, and set the distance between the incident light source fiber probe of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system and the detection fiber probe at 1.5 Within the range of ~2.5 cm, contact the surface of the local brain tissue to be measured for measurement;
S103,所述扩散相干光谱成像系统的探测光纤采集所述待测局部脑组织表面漫反射的扩散相干光束,传输至CMOS相机的光敏面上形成扩散相干光谱图像;S103, the detection fiber of the diffused coherent spectral imaging system collects the diffused coherent light beam that is diffusely reflected on the surface of the local brain tissue to be measured, and transmits it to the photosensitive surface of the CMOS camera to form a diffused coherent spectral image;
S104,设定在采集时间t秒内,所述CMOS相机总记录t/T×103帧所述扩散相干光谱图像,由计算机进行灰度预处理后得到扩散相干光谱图像序列。S104 , within the acquisition time t seconds, the CMOS camera records t/T×103 frames of the diffuse coherent spectral images in total, and a computer performs grayscale preprocessing to obtain a sequence of diffuse coherent spectral images.
可选地,本具体实施例中的扩散相干光谱成像系统的硬件结构构成如图2所示,可见成像系统的硬件组成包括光源模块,光外差模块以及成像采集模块;其中,Optionally, the hardware structure of the diffuse coherent spectral imaging system in this specific embodiment is shown in FIG. 2 , and the hardware structure of the visible imaging system includes a light source module, an optical heterodyne module, and an imaging acquisition module; wherein,
光源模块包括激光驱动和激光器,优选地采用光纤布拉格光栅激光器,中心波长为850 nm;The light source module includes a laser driver and a laser, preferably a fiber Bragg grating laser with a center wavelength of 850 nm;
光外差模块包括分束器、源光纤探头、移动量杆、探光纤探头、光衰减器和耦合器;其中耦合器将探光纤探头采集的信号光束和另一路参考光束耦合输出扩散相干光束;移动量杆可用于调整源光纤探头与探光纤探头之间的最佳范围;源光纤选择单模光纤,探光纤选择多模光纤;优选地,本实施例中的扩散相干光谱成像系统中所述分束器的分光比为1:9,所述耦合器的分光比为5:5;The optical heterodyne module includes a beam splitter, a source fiber probe, a moving measuring rod, a probe fiber probe, an optical attenuator and a coupler; the coupler couples the signal beam collected by the probe fiber probe and another reference beam to output a diffused coherent beam; The moving measuring rod can be used to adjust the optimal range between the source fiber probe and the probe fiber probe; single-mode fiber is selected for the source fiber, and multi-mode fiber is selected for the probe fiber; preferably, the diffusion coherent spectral imaging system in this embodiment is described in The splitting ratio of the beam splitter is 1:9, and the splitting ratio of the coupler is 5:5;
成像采集模块包括光准直器、相机和处理器;其中耦合器输出的扩散相干光由光准直器调整为平行光束,投入相机的光敏面形成扩散相干光谱图像;传输至处理器记录一定采集时间内得到扩散相干光谱图像序列,并利用本公开的一种基于扩散相干光谱图像的脑血流量检测方法进行流速特征提取。The imaging acquisition module includes a light collimator, a camera and a processor; the diffused coherent light output by the coupler is adjusted by the optical collimator into a parallel beam, and is put into the photosensitive surface of the camera to form a diffused coherent spectral image; transmitted to the processor to record certain acquisitions The diffusion coherent spectral image sequence is obtained in time, and the flow velocity feature extraction is performed by using the cerebral blood flow detection method based on the diffusion coherent spectral image of the present disclosure.
进一步地,在S200中,根据扩散相干光谱图像序列和暗电流图像序列,进行流速特征增强处理,得到特征增强图像序列和流速特征区域图像序列的方法为:Further, in S200, according to the diffusion coherent spectrum image sequence and the dark current image sequence, the flow velocity feature enhancement process is performed, and the method for obtaining the feature enhanced image sequence and the flow velocity feature region image sequence is:
S201,设定所述扩散相干光谱图像序列为I(x, y, z),所述暗电流图像序列为O(x, y, z),其中I(x, y, z)和O(x, y, z)分别表示在第z帧所述扩散相干光谱图像和所述暗电流图像在像素点坐标(x, y)上的灰度值,初始化x = 1, y = 1, z = 1;其中设定图像分辨率尺寸大小为[M, N],x值取值范围为[1, M],y值取值范围为[1, N],z值取值范围为[1, t/T×103];设定时间域窗口长度大小为Nt帧,时间域窗口序号为n,n值取值范围为[1,floor(z/Nt)];其中floor函数为高斯取整,即n值不超过z/Nt的最大整数,初始化n = 1;S201, set the diffusion coherence spectrum image sequence to be I(x, y, z), and the dark current image sequence to be O(x, y, z), where I(x, y, z) and O(x , y, z) respectively represent the grayscale values of the diffuse coherent spectral image and the dark current image at the pixel coordinates (x, y) in the zth frame, and initialize x = 1, y = 1, z = 1 ;The size of the image resolution is set to [M, N], the value range of x value is [1, M], the value range of y value is [1, N], and the value range of z value is [1, t] /T×103 ]; set the length of the time domain window to Nt frames, the time domain window serial number to n, and the value range of n to be [1, floor(z/Nt)]; where the floor function is Gaussian rounding, That is, the value of n does not exceed the largest integer of z/Nt, and initializes n = 1;
优选地,本实施例中选择Nt = 20;Preferably, Nt=20 is selected in this embodiment;
S202,在第z帧时遍历像素点坐标(x, y)的取值范围,根据所述扩散相干光谱图像I(x, y, z)和所述暗电流图像序列为O(x, y, z),计算特征校准图像序列Q(x, y, z):S202, traverse the value range of the pixel coordinates (x, y) in the zth frame, according to the diffusion coherent spectral image I(x, y, z) and the dark current image sequence O(x, y, z), calculate the feature calibration image sequence Q(x, y, z):
其中Q(x, y, z)表示为在第z帧所述特征校准图像的像素点坐标为(x, y)上的特征校准值,na(z)表示为在第z帧所述暗电流图像中的校准因子;where Q(x, y, z) is the feature calibration value at the pixel point coordinates (x, y) of the feature calibration image in the zth frame, and na (z) is the dark value in the zth frame. calibration factor in the current image;
S203,判断z值是否等于n×Nt,是则根据所述特征校准图像序列Q(x, y, z),在第n个时间域窗口内遍历z = [Nt(n-1)+1, ..., nNt ]时,对应遍历像素点坐标(x, y)的取值范围,计算特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n):S203, determine whether the z value is equal to n×Nt, if yes, calibrate the image sequence Q(x, y, z) according to the feature, and traverse z = [Nt(n-1)+1 in the nth time domain window, ..., nNt ], correspondingly traverse the range of pixel coordinates (x, y) to calculate the feature enhanced image sequence R(x, y, n):
其中R(x, y, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口中所述特征增强图像在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的灰度值;为R(x, y, n)在第n个时间域窗口内对应像素点坐标为(x, y)上的特征相关因子,为R(x, y, n)在第n个时间域窗口内对应像素点坐标为(x, y)上的特征增强因子,为所述特征校准图像序列Q(x, y, z)遍历z = [Nt(n-1)+1,..., nNt ],对应第n个时间域窗口内共Nt帧在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的灰度均值,和分别为所述暗电流图像序列O(x, y, z)遍历z = [Nt(n-1)+1, ...,nNt ],对应第n个时间域窗口内共Nt帧在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的灰度均值和标准方差,为流速规范化算子;where R(x, y, n) represents the gray value of the feature-enhanced image in the nth time domain window at the pixel coordinate (x, y); For R(x, y, n) in the nth time domain window, the corresponding pixel coordinates are the feature correlation factor on (x, y), is the feature enhancement factor of R(x, y, n) corresponding to the pixel coordinates in the nth time domain window (x, y), Traverse z = [Nt(n-1)+1,..., nNt ] for the feature calibration image sequence Q(x, y, z), corresponding to the pixel coordinates of Nt frames in the nth time domain window is the gray mean value on (x, y), and Respectively, traverse z = [Nt(n-1)+1, ..., nNt ] for the dark current image sequence O(x, y, z), corresponding to a total of Nt frames in the nth time domain window at the pixel point The coordinates are the gray mean and standard deviation on (x, y), is the flow rate normalization operator;
否则令z值增加1,跳转至步骤S202;Otherwise, increase the z value by 1, and jump to step S202;
S204,判断n值是否小于floor(z/Nt),是则令n值增加1,z值增加1,跳转至步骤S202;否则跳转至步骤S205;S204, determine whether the value of n is less than floor(z/Nt), if yes, increase the value of n by 1 and the value of z by 1, and jump to step S202; otherwise, jump to step S205;
S205,根据所述特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n),计算得到流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n)。S205, according to the feature enhancement image sequence R(x, y, n), calculate and obtain the flow velocity feature region image sequence RI(x, y, n).
其中,在步骤S205中,计算得到流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n)的方法为:Wherein, in step S205, the method for calculating the flow velocity characteristic region image sequence RI(x, y, n) is:
S2051,设定空间域窗口长度大小为Ns个像素点,则一个空间域窗口单元大小为Ns×Ns个像素点;其中Ns = gcd(M-2, N-2),gcd函数为求最大公约数,即Ns为二维图像分辨率尺寸大小[M-2, N-2]的最大公约数;初始化x = 2,y = 2,n = 1;空间域窗口的扫描序号为k,k值取值范围为[1, floor((M-2)(n-2)/Ns2)],floor函数为高斯取整,初始化k = 1;S2051, set the size of the spatial domain window length to Ns pixels, then the size of one spatial domain window unit is Ns×Ns pixels; where Ns = gcd(M-2, N-2), the gcd function is to find the greatest convention number, that is, Ns is the greatest common divisor of the two-dimensional image resolution size [M-2, N-2]; initialization x = 2, y = 2, n = 1; the scan sequence number of the spatial domain window is k, the value of k The value range is [1, floor((M-2)(n-2)/Ns2 )], the floor function is Gaussian rounding, and the initialization k = 1;
优选地,本实施例中选择Ns = 7;Preferably, Ns=7 is selected in this embodiment;
S2052,在第n个时间域窗口时,根据所述特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n),遍历(x,y)计算流速特征梯度图像序列G(x, y, n):S2052, in the nth time domain window, according to the feature enhancement image sequence R(x, y, n), traverse (x, y) to calculate the flow velocity feature gradient image sequence G(x, y, n):
G(x, y, n)表示为第z帧时所述流速特征梯度图像在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的梯度大小;其中,G(x, y, n) is expressed as the gradient size of the flow velocity characteristic gradient image on the pixel coordinates (x, y) at the zth frame; wherein,
Gx(x, y, n),Gy(x, y, n)和Gz(x, y, n)分别表示为在第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征梯度图像在像素点坐标为(x, y)上的水平梯度,垂直梯度大小和时间轴梯度大小;Gx (x, y, n), Gy (x, y, n) and Gz (x, y, n) are respectively expressed as the pixel coordinates of the flow velocity characteristic gradient image in the nth time domain window is the horizontal gradient on (x, y), the vertical gradient size and the time axis gradient size;
S2053,判断n值是否大于1,是则在第n个时间域窗口时,在二维图像尺寸大小为(M-2)×(N-2)个像素点内遍历所述空间域窗口序号k值的取值范围,以Ns个像素点为步长,从x = 2, y = 2开始水平方向和垂直方向移动扫描第k个所述空间域窗口单元,在Ns×Ns个像素点内计算流速特征度量序列D(k, n)和流动特征序列F(k, n):S2053, determine whether the value of n is greater than 1, and if so, in the nth time domain window, traverse the spatial domain window sequence number k within the two-dimensional image size of (M-2)×(N-2) pixels. The value range of the value, with Ns pixels as the step size, starts from x = 2, y = 2 and moves horizontally and vertically to scan the kth spatial domain window unit, calculated within Ns×Ns pixels Flow velocity characteristic metric sequence D(k, n) and flow characteristic sequence F(k, n):
其中D(k, n)表示为第n个和第n-1个相邻的时间域窗口之间,计算在第k个空间域窗口单元内与流速线性相关的特征度量值;为归一化参数;where D(k, n) is expressed as between the nth and n-1th adjacent time domain windows, and the characteristic metric value linearly related to the flow velocity in the kth space domain window unit is calculated; is the normalization parameter;
Rv(k, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述特征增强图像在第k个空间域窗口单元内计算的特征增强均值;Gv(k, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征梯度图像在第k个空间域窗口单元内计算的特征梯度均值;Rv(k, n) is the feature enhancement mean value of the feature-enhanced image calculated in the k-th space-domain window unit when the n-th time-domain window; Gv(k, n) is the n-th time-domain window the mean value of the characteristic gradient calculated in the kth spatial domain window unit of the flow velocity characteristic gradient image;
其中F(k, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述特征增强图像在第k个空间域窗口单元内的流动特征灰度值,min函数为求最小值;where F(k, n) represents the gray value of the flow feature of the feature-enhanced image in the kth spatial domain window unit in the nth time domain window, and the min function is the minimum value;
否则跳转至步骤S2052;Otherwise, jump to step S2052;
S2054,判断n值是否小于floor(z/Nt)-1,是则n值增加1,跳转至步骤S2052;否则令n = 1,跳转至步骤S2055;S2054, determine whether the value of n is less than floor(z/Nt)-1, if yes, the value of n is increased by 1, and jump to step S2052; otherwise, set n = 1, and jump to step S2055;
S2055,根据所述流速特征度量序列D(k, n)和流动特征序列F(k, n),遍历k值取值范围,计算流速特征序列L(k):S2055, according to the flow velocity characteristic measurement sequence D(k, n) and the flow characteristic sequence F(k, n), traverse the value range of the k value, and calculate the flow velocity characteristic sequence L(k):
L(k)表示为在第k个空间域窗口单元内的流速特征序列;L(k) is expressed as the flow velocity characteristic sequence in the kth spatial domain window unit;
S2056,遍历k值的取值范围,判断所述流速特征序列L(k)内是否存在大于流速相关性阈值的流速特征值,是则遍历x和y的取值范围,标记k值对应的空间域窗口单元内的流速特征值V(x, y) = 1;否则标记k值对应的空间域窗口单元内的流速特征值V(x, y) = 0;S2056, traverse the value range of the k value, and determine whether there is a flow velocity characteristic value greater than the flow velocity correlation threshold in the flow velocity characteristic sequence L(k), and if yes, traverse the value range of x and y, and mark the space corresponding to the k value The flow velocity characteristic value V(x, y) = 1 in the domain window unit; otherwise, the flow velocity characteristic value V(x, y) = 0 in the space domain window unit corresponding to the marked k value;
V(x, y)表示在像素坐标(x, y)上的流速特征值;其中,V(x, y) represents the flow velocity eigenvalue at pixel coordinates (x, y); where,
S2057,根据所述流速特征值V(x, y),遍历n值的取值范围,计算得到流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n) = R(x, y, n)×V(x, y);其中RI(x, y, n)表示为第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征区域图像在像素坐标(x, y)上的灰度值。S2057, according to the flow velocity characteristic value V(x, y), traverse the value range of the n value, and calculate the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence RI(x, y, n) = R(x, y, n)×V( x, y); wherein RI(x, y, n) represents the gray value of the flow velocity characteristic region image at pixel coordinates (x, y) in the nth time domain window.
进一步地,在S300中,根据所述流速特征区域图像序列,计算局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列的方法为:Further, in S300, according to the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence, the method for calculating the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence is:
S301,设定所述流速特征区域图像序列的像素尺寸为M1×N1×L1,图像序列坐标为(x1, y1, n1),图像像素坐标为(x1, y1);其中x1的取值范围为[1, M1],y1的取值范围为[1, N1],n1的取值范围为[1, L1];S301, set the pixel size of the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence to be M1×N1×L1, the image sequence coordinates to be (x1, y1, n1), and the image pixel coordinates to be (x1, y1); wherein the value range of x1 is [1, M1], the value range of y1 is [1, N1], and the value range of n1 is [1, L1];
遍历x,y和n值的取值范围,根据所述流速特征区域图像序列RI(x, y, n),令局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1, n1) = RI(x, y, n),即同样遍历x1,y1和n1值的取值范围,将第n个时间域窗口时所述流速特征区域图像在像素坐标为(x, y)上的灰度值,对应存入第n1个时间域窗口时所述局部区域图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的灰度值;初始化x1= 1,y1 = 1,n1 = 1;Traverse the value range of x, y and n values, according to the flow velocity characteristic area image sequence RI(x, y, n), let the local flow velocity characteristic area image sequence ROI(x1, y1, n1) = RI(x, y , n), that is, the value range of x1, y1 and n1 values is also traversed, and the gray value of the flow velocity characteristic area image at the pixel coordinate (x, y) in the nth time domain window is stored in the corresponding In the n1th time domain window, the gray value of the local area image at the pixel coordinates (x1, y1); initialize x1 = 1, y1 = 1, n1 = 1;
S302,在第n1个时间域窗口时,遍历所述局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1,n1) 上的所有像素坐标(x1, y1),经过标准偏差滤波处理,得到标准偏差散射特征区域图像序列Std(x1, y1, n1);S302, in the n1th time domain window, traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) on the local flow velocity characteristic region image sequence ROI (x1, y1, n1), and obtain standard deviation scattering features through standard deviation filtering processing Region image sequence Std(x1, y1, n1);
其中Std(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述标准散射特征区域图像在像素坐标(x1, y1)上的灰度值;where Std(x1, y1, n1) represents the gray value of the standard scattering feature region image at pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the n1th time domain window;
S303,在第n1个时间域窗口时,遍历所述局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1,n1) 上的所有像素坐标(x1, y1),经过平均滤波处理,得到平均散射特征区域图像序列Ave(x1, y1, n1);S303, in the n1th time domain window, traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) on the local flow velocity characteristic area image sequence ROI(x1, y1, n1), and obtain an average scattering characteristic area image through an average filtering process sequence Ave(x1, y1, n1);
其中Ave(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述平均散射特征区域图像在像素坐标(x1, y1)上的灰度值;where Ave(x1, y1, n1) represents the gray value of the average scattering feature area image at pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the n1th time domain window;
S304,设定空间统计步长为offset,根据所述标准散射特征区域图像序列Std(x1,y1, n1)和平均散射特征区域图像序列Ave(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1,y1)计算静态散射图像序列Static(x1, y1, n1):S304, set the spatial statistical step size to offset, and traverse all pixel coordinates in the image according to the standard scattering characteristic area image sequence Std(x1, y1, n1) and the average scattering characteristic area image sequence Ave(x1, y1, n1). (x1, y1) computes the static scatter image sequence Static(x1, y1, n1):
其中,Static(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述静态散射图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的静态散射值;mean函数为在空间统计窗口大小为offset×offset个像素点内计算均值;Among them, Static(x1, y1, n1) represents the static scattering value of the static scattering image at the pixel coordinate of (x1, y1) when the n1th time domain window; the mean function is the size of the spatial statistical window is offset× Calculate the mean within offset pixels;
S305,判断n1值是否小于L1,是则令n1值增加1,跳转至步骤S302;否则令n1 = 1,跳转至步骤S400。S305, determine whether the value of n1 is less than L1, if yes, increase the value of n1 by 1, and jump to step S302; otherwise, set n1 = 1, and jump to step S400.
进一步地,在S400中,根据所述局部区域图像序列和静态散射图像序列,计算动态散射流速图像序列的方法为:Further, in S400, according to the local area image sequence and the static scattering image sequence, the method for calculating the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence is:
S401,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述局部流速特征区域图像序列ROI(x1, y1,n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算系统相干因子beta(n1)和动态算子:S401, traverse the value range of the n1 value, according to the local flow velocity characteristic region image sequence ROI (x1, y1, n1), traverse all pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the system coherence factor beta (n1) and dynamic calculation son :
其中,beta(n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时,所述系统相干因子的数值;为遍历所有x1值和y1值计算在M1×N1像素范围内的均值;表示为在第n1个时间域窗口时,所述动态算子的数值;Wherein, beta(n1) is expressed as the numerical value of the system coherence factor in the n1th time domain window; Calculate the mean in the range of M1×N1 pixels for traversing all x1 values and y1 values; is expressed as the value of the dynamic operator in the n1th time domain window;
S402,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述静态散射图像序列Static(x1, y1, n1)、系统相干因子beta(n1)和动态算子,遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算动态散射流速图像序列Dynamic(x1, y1, n1):S402, traverse the value range of the n1 value, according to the static scattering image sequence Static(x1, y1, n1), the system coherence factor beta(n1) and the dynamic operator , traverse all pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence Dynamic(x1, y1, n1):
其中,Dynamic(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述动态散射流速图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的动态散射值。Wherein, Dynamic(x1, y1, n1) represents the dynamic scattering value at the pixel coordinate of (x1, y1) of the dynamic scattering flow velocity image in the n1th time domain window.
进一步地,在S500中,根据所述特征增强图像序列和动态散射流速图像序列,进行图像校正处理,得到相对流速图像序列的方法为:Further, in S500, image correction processing is performed according to the feature enhancement image sequence and the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence, and the method for obtaining the relative flow velocity image sequence is:
S501,遍历x,y和n值的取值范围,根据所述特征增强图像序列R(x, y, n),令局部特征增强图像序列ROI2(x1, y1, n1) = R(x, y, n),即同样遍历x1,y1和n1值的取值范围,将第n个时间域窗口时所述特征增强图像在像素坐标为(x, y)上的灰度值,对应存入第n1个时间域窗口时所述局部特征增强图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的灰度值;初始化x1 =1,y1 = 1,n1 = 1;S501, traverse the value ranges of x, y and n values, and according to the feature enhancement image sequence R(x, y, n), make the local feature enhancement image sequence ROI2(x1, y1, n1) = R(x, y , n), that is, the value range of x1, y1 and n1 values is also traversed, and the gray value of the feature-enhanced image at the pixel coordinate of (x, y) in the nth time domain window is stored in the corresponding When there are n1 time domain windows, the gray value of the local feature enhancement image at the pixel coordinates (x1, y1); initialize x1 =1, y1 = 1, n1 = 1;
S502,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据局部特征增强图像序列ROI2(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算系统噪声估值Knoise(n1):S502, traverse the value range of the n1 value, enhance the image sequence ROI2 (x1, y1, n1) according to the local features, and traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the system noise estimate Knoise (n1):
其中,Knoise(n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时的系统噪声估值,为遍历所有x1值和y1值计算在M1×N1像素范围内的均值,为计算均值,nd为系统噪声因子,定义为系统输入和输出信噪比的比值,是归一化噪声系数;Among them, Knoise (n1) is expressed as the estimated system noise at the n1th time domain window, Calculate the mean over M1×N1 pixels for iterating over all x1 and y1 values, To calculate the mean, nd is the system noise factor, defined as the ratio of the system input and output signal-to-noise ratios, is the normalized noise figure;
S503,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述系统噪声估值Knoise(n1)和动态散射流速图像序列Dynamic(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算相对流速图像序列FK(x1, y1, n1):S503, traverse the value range of the n1 value, according to the estimated system noise Knoise (n1) and the dynamic scattering flow velocity image sequence Dynamic (x1, y1, n1), traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the relative Flow velocity image sequence FK(x1, y1, n1):
其中FK(x1, y1, n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口时所述相对流速图像在像素坐标为(x1, y1)上的相对流速值,为在第n1个时间域窗口的动态算子。where FK(x1, y1, n1) represents the relative flow velocity value of the relative flow velocity image at the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the n1th time domain window, is the dynamic operator in the n1th time domain window.
进一步地,在S600中,根据所述相对流速图像序列,得到局部脑血流相对指数序列的方法为:Further, in S600, according to the relative flow velocity image sequence, the method for obtaining the local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence is:
S601,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述相对流速图像序列FK(x1, y1, n1),遍历图像中所有像素坐标(x1, y1)计算相对流速指数序列FV(n1):S601, traverse the value range of the n1 value, and according to the relative flow velocity image sequence FK(x1, y1, n1), traverse all the pixel coordinates (x1, y1) in the image to calculate the relative flow velocity index sequence FV(n1):
其中,FV(n1)表示为第n1个时间域窗口的相对流速指数,为遍历所有x1值和y1值计算在M1×N1像素范围内的均值;Among them, FV(n1) is expressed as the relative velocity index of the n1th time domain window, Calculate the mean in the range of M1×N1 pixels for traversing all x1 values and y1 values;
S602,遍历n1值的取值范围,根据所述相对流速指数序列FV(n1),计算得到局部脑血流相对指数序列BFI (n1)= c / FV(n1)2,其中BFI(n1)为第n1个时间域窗口的局部脑血流相对指数,c为归一化比例常数。S602, traverse the value range of the n1 value, and according to the relative flow velocity index sequence FV(n1), calculate and obtain the local cerebral blood flow relative index sequence BFI(n1)=c / FV(n1)2 , where BFI(n1) is The relative index of regional cerebral blood flow in the n1th time domain window, c is the normalized proportionality constant.
另一实施例中基于扩散相干光谱成像系统进行大脑局部仿体流速实验,进一步验证该脑血流检测方法的定量分析能力。其中待测大脑局部组织模型由固体和液体两个部分:固体部分为中空立方体模型,一侧面为琼脂层模拟头皮和头骨层组成的表层组织,其余侧面及底面为黑色聚甲醛硬体材料;液体部分是利用3%脂肪乳溶液模拟脑脊液和灰质+白质层组成的内层组织的生理环境。实验设计软管管径可选,计算得到的局部脑血流相对指数与流量的关系。实验结果表明检测得到的局部脑血流相对指数与流量能建立较好的相关性,线性相关系数在0.98左右;且相同流量时,不同的血管管径下的BFI值不一致,管径越小对应的BFI越大,符合横截面积与流速的一般变化规律。由此验证了本公开的脑血流检测方法可以通过计算得到局部脑血流相对指数,结合血管管径测量方法计算待测血管的局部横截面积,根据流速与流量的一般规律可得到待测局部脑组织的局部脑血流量。In another embodiment, a flow velocity experiment of a local phantom of the brain is performed based on the diffusion coherent spectroscopy imaging system, to further verify the quantitative analysis capability of the cerebral blood flow detection method. The local tissue model of the brain to be tested consists of two parts: solid and liquid: the solid part is a hollow cube model, one side is an agar layer to simulate the surface tissue composed of the scalp and the skull layer, and the other sides and bottom are black polyoxymethylene hard material; liquid In part, 3% fat emulsion solution was used to simulate the physiological environment of the inner tissue composed of cerebrospinal fluid and gray matter + white matter layer. The tube diameter of the experimental design is optional, and the relationship between the relative index of local cerebral blood flow and the flow rate is calculated. The experimental results show that the detected local cerebral blood flow relative index and flow can establish a good correlation, and the linear correlation coefficient is about 0.98; and when the flow is the same, the BFI values under different vessel diameters are inconsistent, and the smaller the diameter, the corresponding The larger the BFI of , is in line with the general variation law of cross-sectional area and flow velocity. Therefore, it is verified that the cerebral blood flow detection method of the present disclosure can obtain the relative index of local cerebral blood flow through calculation, and the local cross-sectional area of the blood vessel to be measured can be calculated in combination with the blood vessel diameter measurement method. Regional cerebral blood flow in regional brain tissue.
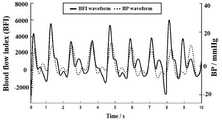
另一实施例中开展动物实验,选择健康幼猪的前额叶皮质为待测组织对象;利用多参数监护仪同步有创测量该健康幼猪的颈动脉血压数据作为标准对照。如图3所示,为计算得到的局部脑血流相对指数与同步测量随时间变化的血压曲线对比示意图。图中实线波形是BFI waveform,表示为局部脑血流相对指数曲线;虚线波形为BP waveform,表示为有创血压曲线;由于血压波形在一个心动周期内中主要表现为收缩压和舒张压,当心脏搏动时心室收缩将血液泵入主动脉,管壁压力升高至最大值称为收缩压,同时血管内血液急速流动,局部脑血流相对指数达最高峰;当心室舒张时压力下降,血管壁弹性回缩,会引起血管内血液流速瞬时小幅度上升形成次峰。其后血液流动速度缓慢下降,导致血管内存留血量增加,又引起舒张压升高,进入第二个心动周期。可见两者具有相似的波动规律和频率范围,证明测得了真实有效的局部脑血流相对指数。In another embodiment, an animal experiment is carried out, and the prefrontal cortex of a healthy young pig is selected as the tissue object to be tested; the carotid artery blood pressure data of the healthy young pig is synchronously and invasively measured by a multi-parameter monitor as a standard control. As shown in FIG. 3 , it is a schematic diagram showing the comparison between the calculated relative index of local cerebral blood flow and the synchronously measured blood pressure curve. The solid line waveform in the figure is the BFI waveform, which is the relative exponential curve of local cerebral blood flow; the dashed waveform is the BP waveform, which is the invasive blood pressure curve. When the heart beats, the ventricle contracts to pump blood into the aorta, and the pressure on the wall of the vessel increases to a maximum value, which is called systolic blood pressure. The elastic retraction of the blood vessel wall will cause the blood flow rate in the blood vessel to rise instantaneously and slightly to form a secondary peak. After that, the blood flow rate decreases slowly, resulting in an increase in the amount of blood retained in the blood vessels, which in turn causes an increase in diastolic blood pressure and enters the second cardiac cycle. It can be seen that the two have similar fluctuation laws and frequency ranges, which proves that a real and effective relative index of local cerebral blood flow has been measured.
尽管本公开的描述已经相当详尽且特别对几个所述实施例进行了描述,但其并非旨在局限于任何这些细节或实施例或任何特殊实施例,从而有效地涵盖本公开的预定范围。此外,上文以发明人可预见的实施例对本公开进行描述,其目的是为了提供有用的描述,而那些目前尚未预见的对本公开的非实质性改动仍可代表本公开的等效改动。Although the present disclosure has been described in considerable detail and with particular reference to a few of the described embodiments, it is not intended to be limited to any of these details or embodiments or any particular embodiment so as to effectively encompass the intended scope of the present disclosure. Furthermore, the foregoing description of the disclosure in terms of embodiments foreseen by the inventors is intended to provide a useful description, and those insubstantial modifications of the disclosure that are not presently foreseen may still represent equivalent modifications of the disclosure.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210462086.4ACN114569105B (en) | 2022-04-29 | 2022-04-29 | A method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210462086.4ACN114569105B (en) | 2022-04-29 | 2022-04-29 | A method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114569105Atrue CN114569105A (en) | 2022-06-03 |
| CN114569105B CN114569105B (en) | 2022-08-09 |
Family
ID=81785141
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210462086.4AActiveCN114569105B (en) | 2022-04-29 | 2022-04-29 | A method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114569105B (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140206980A1 (en)* | 2013-01-23 | 2014-07-24 | Nanyang Technological University | Deep tissue flowmetry using diffuse speckle contrast analysis |
| CN105342597A (en)* | 2015-12-01 | 2016-02-24 | 华中科技大学 | Quantitative laser blood flow detection method |
| CN106236068A (en)* | 2016-08-25 | 2016-12-21 | 中国科学院苏州生物医学工程技术研究所 | A kind of cerebral blood flow measurement apparatus, system and the helmet |
| CN107452029A (en)* | 2017-07-31 | 2017-12-08 | 中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所 | A kind of optics microvascular blood flow imaging method |
| WO2020243658A1 (en)* | 2019-05-29 | 2020-12-03 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Real-time methods to enable precision-guided cpr to improve neurological outcome and predict brain damage |
| CN112263225A (en)* | 2020-10-26 | 2021-01-26 | 中国人民解放军总医院第一医学中心 | Collateral blood vessel and tissue function evaluation method based on cerebral blood flow |
| CN112716471A (en)* | 2013-08-14 | 2021-04-30 | 佩德拉科技私人有限公司 | System and method for assessing vascular remodeling |
| CN113100823A (en)* | 2021-04-08 | 2021-07-13 | 苏州苏穗绿梦生物技术有限公司 | Noninvasive cerebral blood flow detection system |
| CN114081483A (en)* | 2021-12-28 | 2022-02-25 | 北京工业大学 | A Tissue Blood Flow and Blood Oxygen Saturation Measurement Method Based on Deep Learning Diffusion Correlation Spectroscopy |
- 2022
- 2022-04-29CNCN202210462086.4Apatent/CN114569105B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140206980A1 (en)* | 2013-01-23 | 2014-07-24 | Nanyang Technological University | Deep tissue flowmetry using diffuse speckle contrast analysis |
| CN112716471A (en)* | 2013-08-14 | 2021-04-30 | 佩德拉科技私人有限公司 | System and method for assessing vascular remodeling |
| CN105342597A (en)* | 2015-12-01 | 2016-02-24 | 华中科技大学 | Quantitative laser blood flow detection method |
| CN106236068A (en)* | 2016-08-25 | 2016-12-21 | 中国科学院苏州生物医学工程技术研究所 | A kind of cerebral blood flow measurement apparatus, system and the helmet |
| CN107452029A (en)* | 2017-07-31 | 2017-12-08 | 中国医学科学院生物医学工程研究所 | A kind of optics microvascular blood flow imaging method |
| WO2020243658A1 (en)* | 2019-05-29 | 2020-12-03 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Real-time methods to enable precision-guided cpr to improve neurological outcome and predict brain damage |
| CN112263225A (en)* | 2020-10-26 | 2021-01-26 | 中国人民解放军总医院第一医学中心 | Collateral blood vessel and tissue function evaluation method based on cerebral blood flow |
| CN113100823A (en)* | 2021-04-08 | 2021-07-13 | 苏州苏穗绿梦生物技术有限公司 | Noninvasive cerebral blood flow detection system |
| CN114081483A (en)* | 2021-12-28 | 2022-02-25 | 北京工业大学 | A Tissue Blood Flow and Blood Oxygen Saturation Measurement Method Based on Deep Learning Diffusion Correlation Spectroscopy |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114569105B (en) | 2022-08-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7995814B2 (en) | Dynamic motion contrast and transverse flow estimation using optical coherence tomography | |
| WO2020155415A1 (en) | Feature-space-based optical coherence tomography three-dimensional angiography method and system | |
| JP5294340B2 (en) | Ultrasonic diagnostic equipment | |
| Nair et al. | Regularized autoregressive analysis of intravascular ultrasound backscatter: improvement in spatial accuracy of tissue maps | |
| CN109662735B (en) | Method for measuring skin blood perfusion | |
| Katouzian et al. | Challenges in atherosclerotic plaque characterization with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS): from data collection to classification | |
| JPH08224238A (en) | Method and equipment for ultrasonic wave doppler power measurement | |
| KR101746763B1 (en) | Diagnostic technique and imaging method of retinal and choroidal optical coherence tomography angiography | |
| US20180268542A1 (en) | Processing optical coherency tomography scans | |
| JP2023528679A (en) | Methods for estimating hemodynamic parameters | |
| CN117197096B (en) | Blood vessel function assessment method and system based on blood vessel image | |
| Guo et al. | Quantitative investigation of in vitro flow using three-dimensional colour Doppler ultrasound | |
| CN103735287B (en) | A kind of intravascular ultrasound elastogram two-dimensional multistage mixing displacement estimation method | |
| Turner et al. | Brain tissue pulsation in healthy volunteers | |
| Johnson et al. | Detecting aortic valve-induced abnormal flow with seismocardiography and cardiac MRI | |
| Thomas | Tissue Doppler echocardiography–A case of right tool, wrong use | |
| Raj et al. | Image-free fast Ultrasound for Measurement of local pulse Wave Velocity: in Vitro Validation and in vivo feasibility | |
| JP4918369B2 (en) | Ultrasonic diagnostic equipment | |
| CN114569105B (en) | A method for detecting cerebral blood flow based on diffuse coherent spectral images | |
| CN110522438B (en) | Method, device and medium for calculating blood flow velocity and blood flow imaging method and system | |
| Lindén et al. | Evaluation of Enhanced High-Resolution Laser Doppler Imaging in anin VitroTube Model with the Aim of Assessing Blood Flow in Separate Microvessels | |
| van den Bos–van et al. | In vivo comparison of pulse wave velocity estimation based on ultrafast plane wave imaging and high-frame-rate focused transmissions | |
| CN111631700B (en) | System for regulating blood pressure according to optimal blood pressure target value | |
| Serov et al. | Combined laser Doppler and laser speckle imaging for real-time blood flow measurements | |
| Zhu et al. | Quantification of shunt volume through ventricular septal defect by real-time 3-D color Doppler echocardiography: an in vitro study |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |