CN114569070A - Ring type integrated fluorography operation imaging guide system and application - Google Patents
Ring type integrated fluorography operation imaging guide system and applicationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114569070A CN114569070ACN202210110880.2ACN202210110880ACN114569070ACN 114569070 ACN114569070 ACN 114569070ACN 202210110880 ACN202210110880 ACN 202210110880ACN 114569070 ACN114569070 ACN 114569070A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- miniature
- light source
- image
- module
- ring
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0059—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence
- A61B5/0071—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons using light, e.g. diagnosis by transillumination, diascopy, fluorescence by measuring fluorescence emission
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B90/37—Surgical systems with images on a monitor during operation
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B90/00—Instruments, implements or accessories specially adapted for surgery or diagnosis and not covered by any of the groups A61B1/00 - A61B50/00, e.g. for luxation treatment or for protecting wound edges
- A61B90/36—Image-producing devices or illumination devices not otherwise provided for
- A61B90/37—Surgical systems with images on a monitor during operation
- A61B2090/373—Surgical systems with images on a monitor during operation using light, e.g. by using optical scanners
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Gynecology & Obstetrics (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Investigating, Analyzing Materials By Fluorescence Or Luminescence (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及医疗器械领域,具体涉及一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统及应用。The invention relates to the field of medical devices, in particular to a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgery imaging guidance system and application.
背景技术Background technique
根据世界卫生组织国际癌症研究机构发布的数据显示,2020年全球新发癌症病例达到了1929万例,新增死亡病例达到了996万例。而据相关数据显示,目前的所有抗肿瘤药物治疗基本上都未改变中晚期肿瘤患者的生存率,与不治疗患者的生存率不存在统计学差异。这就表明:肿瘤患者的治疗还是高度依赖于早期发现,早期诊断,早期治疗,而手术仍然是第一选择。早期发现的肿瘤患者和癌前病变患者,通过手术有更大希望实现治愈。According to data released by the World Health Organization's International Agency for Research on Cancer, the number of new cancer cases worldwide in 2020 reached 19.29 million, and the number of new deaths reached 9.96 million. According to relevant data, all current antitumor drug treatments have basically not changed the survival rate of patients with advanced tumors, and there is no statistical difference between the survival rate of patients with no treatment. This shows that the treatment of cancer patients is still highly dependent on early detection, early diagnosis and early treatment, and surgery is still the first choice. Patients with tumors and precancerous lesions detected at an early stage have greater hope of achieving cure through surgery.
但是目前大多数的肿瘤切除手术,或是癌前病变、转移淋巴结等病变的切除手术,基本上还是凭借医生的经验来对病变的手术边界进行定位,如何精确定位病变手术边界是临床手术的一大关键技术问题。而随着分子影像技术的发展,特别是多功能分子影像示踪造影剂的出现,给相关疾病患者的精准诊断,精准治疗与精准手术导航提供了一个全新的手段和有力的技术支持。随即也出现了基于分子影像示踪造影剂的成像设备,用于指导癌前病变、肿瘤、转移淋巴结等病变的切除手术。例如吲哚菁绿在780nm附近较宽范围波段内的近红外光照射下会被激发出波段820nm附近的近红外光,通过将其作为示踪造影剂,选择性地靶向点亮肿瘤,可协助医生实现对病变的精准定位,并帮助医生找到通过肉眼及超声难以发现的微小病灶及并未带来形态明显变化的病灶。而对于部分癌前病变而言,已有众多可靠研究表明,部分癌前病变组织内的一些内源性荧光物质的含量在癌变后会发生改变,则不需要外界示踪造影剂的前提下,通过紫外光激发,可以产生不同于正常组织的自体荧光,从而可以和正常组织进行有效区分。However, most of the current tumor resection operations, or the resection of precancerous lesions, metastatic lymph nodes and other lesions, basically rely on the experience of doctors to locate the surgical boundary of the lesion. How to accurately locate the surgical boundary of the lesion is one of the clinical operations. Big key technical issues. With the development of molecular imaging technology, especially the emergence of multi-functional molecular imaging tracer contrast agents, it has provided a new means and strong technical support for accurate diagnosis, precise treatment and precise surgical navigation of patients with related diseases. Imaging equipment based on molecular imaging tracer contrast agents has also appeared, which is used to guide the resection of precancerous lesions, tumors, metastatic lymph nodes and other lesions. For example, when indocyanine green is irradiated with near-infrared light in a wide band around 780nm, it will be excited to emit near-infrared light in the band around 820nm. By using it as a tracer contrast agent, it can selectively target and light up tumors, which can be Assist doctors to achieve precise localization of lesions, and help doctors to find small lesions that are difficult to detect by naked eyes and ultrasound, and lesions that do not cause obvious changes in morphology. For some precancerous lesions, many reliable studies have shown that the content of some endogenous fluorescent substances in some precancerous lesions will change after canceration, and no external tracer contrast agent is required. Through ultraviolet light excitation, autofluorescence that is different from normal tissue can be generated, so that it can be effectively distinguished from normal tissue.
而目前在荧光手术引导方面的相关产品或相关专利,都是较为大型的设备,在不调整的情况下,在手术中只可放置于固定位置,在固定高度下对固定角度进行静态成像,得到的是静态二维图像。然而肿瘤等病变都是三维立体的,并且形状无规则,例如菜花状、分叶状、绒毛状、弥漫性肥厚状、浸润性包块状、溃疡状等等,因此肿瘤等病变和正常组织的边界也是毫无规则的立体形状,在切除过程中,需要进行多方位多角度的成像,才能对肿瘤等病变和正常组织的复杂立体边界做一个清晰的判定,尤其对于边界把控十分重要的病变而言,例如脑瘤。若只有一个角度成像的话,存在很大的视觉盲区,极大影响了手术的精确性。在现有相关产品及相关专利的技术限制下,在手术过程中,若要对盲区进行成像,则需要除主刀医生以外的助手,根据主刀医生的手术进度和授意对光源的位置、高度和照射角度,以及成像设备的位置、高度和照射角度这六个参数进行调整,以对医生需要的目标部位进行实时成像。这样不断的对设备进行移动不仅会严重耽误手术进程,还需要医生和助手具有极高的默契度和配合度,否则若光源和成像设备未达到医生所要的理想参数,将会影响医生的发挥进而影响手术精度。并且目前在荧光手术引导方面的相关产品或相关专利都不具备通过紫外光对癌前病变的自体荧光进行激发成像引导的功能。At present, the related products or related patents in the field of fluorescent surgical guidance are relatively large-scale equipment. Without adjustment, they can only be placed in a fixed position during the operation, and static imaging is performed at a fixed angle at a fixed height. is a static 2D image. However, lesions such as tumors are three-dimensional and irregular in shape, such as cauliflower-like, lobulated, villous, diffuse hypertrophic, infiltrating mass, ulcer-like, etc., so the tumor and other lesions and normal tissue The boundary is also an irregular three-dimensional shape. During the excision process, multi-directional and multi-angle imaging is required to make a clear judgment on the complex three-dimensional boundary of the tumor and other lesions and normal tissues, especially for lesions where boundary control is very important. For example, brain tumors. If there is only one angle of imaging, there is a large blind spot, which greatly affects the accuracy of surgery. Under the technical limitations of existing related products and related patents, during the operation, if the blind spot is to be imaged, an assistant other than the chief surgeon is required to determine the position, height and irradiation of the light source according to the surgical progress and instructions of the chief surgeon. The angle, as well as the six parameters of the position, height and irradiation angle of the imaging device are adjusted to perform real-time imaging of the target site required by the doctor. Such constant movement of the equipment will not only seriously delay the operation process, but also require a high degree of tacit understanding and cooperation between the doctor and the assistant. Otherwise, if the light source and imaging equipment do not meet the ideal parameters required by the doctor, it will affect the doctor's performance and further affect the precision of surgery. And at present, the related products or related patents in the aspect of fluorescence surgical guidance do not have the function of exciting and imaging the autofluorescence of precancerous lesions through ultraviolet light.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
基于这种现状,本发明目的在于:提供一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统。Based on this situation, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgery imaging guidance system.
本发明的另一目的在于提供指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的应用。Another object of the present invention is to provide the application of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopy imaging guidance system.
本发明目的通过下述方案实现:一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统,该系统将摄像头模组和光纤扩束器微型化处理并与微型光源进行一体化集成,根据医生的习惯,可以配戴在医生的任何一根手指上,医生在手术中持刀的同时,可根据自己的需求自主地对任何形状的病变进行全方位多角度实时动态成像引导,可无线使用也可有线使用,以解决现有技术中荧光导航系统只能对单一角度进行静态成像而造成视觉盲区过大进而影响手术精度的问题;同时,制备了可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变的示踪造影剂,在搭配使用下可有效提高手术的精确性、成功率和效率;此外,该系统与现有大型的荧光引导系统可以很好的兼容,可进行配合使用,以进一步增强使用效果。系统还具备了在不需要使用示踪造影剂的情况下通过紫外光对癌前病变的自体荧光进行激发成像并引导手术的功能。The object of the present invention is achieved through the following scheme: a ring-type integrated fluoroscopy surgery imaging guidance system, which miniaturizes the camera module and the optical fiber beam expander and integrates them with the miniature light source. According to the doctor's habit, It can be worn on any finger of the doctor. While holding the knife during the operation, the doctor can autonomously conduct all-round, multi-angle real-time dynamic imaging guidance for lesions of any shape according to their own needs. It can be used wirelessly or wiredly. , in order to solve the problem that the fluorescent navigation system in the prior art can only perform static imaging at a single angle, which causes the visual blind area to be too large and affects the accuracy of the operation; The accuracy, success rate and efficiency of surgery can be effectively improved when used in combination; in addition, the system is well compatible with existing large-scale fluorescence guidance systems, and can be used in conjunction to further enhance the use effect. The system also has the ability to excite the autofluorescence of precancerous lesions with ultraviolet light and guide surgery without the use of tracer contrast agents.
本发明的其一目的在于提供一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统,包括微型白光光源,微型近红外光源,外接光纤口,微型光纤扩束器,光源供电模块,安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一,安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,指环型支架,可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变的示踪造影剂,图像接收模块,图像处理和显示模块。One of the purposes of the present invention is to provide a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic imaging guidance system, including a miniature white light source, a miniature near-infrared light source, an external optical fiber port, a miniature optical fiber beam expander, a light source power supply module, and a near-infrared light source installed with Micro-camera module 1 with optical filters, micro-camera module 2 with visible and ultraviolet filters installed, ring-shaped bracket, which can specifically target the tracer contrast agent adsorbed on specific lesions, image receiving module, image Processing and display modules.
其中,所述的微型白光光源,可为贴片形白光发光二极管,发出白光照射病变部位。Wherein, the miniature white light source can be a patch-shaped white light emitting diode, which emits white light to illuminate the diseased part.
所述的微型近红外光源,可为微型近红外激光二极管,发出一区近红外光照射病变部位,激发吸附在病变上的示踪造影剂以产生荧光。当在无线模式下工作时,仅可使用微型近红外光源进行照射。当在有线模式下工作时,可使用微型近红外光源进行照射,也可使用外接光纤进行照射。The miniature near-infrared light source can be a miniature near-infrared laser diode, which emits a region of near-infrared light to illuminate the lesion, and excites the tracer contrast agent adsorbed on the lesion to generate fluorescence. When working in wireless mode, only a tiny near-infrared light source can be used for illumination. When working in wired mode, a miniature near-infrared light source can be used for illumination, or an external optical fiber can be used for illumination.
所述的外接光纤口,可用于固定具有基于SMA905接口的光纤跳线的光纤,光纤通过通用的SMA905接口,可以与外界一切具有SMA905接口的激光器连接。可根据实际需要,选择不同的光纤与不同的激光器,例如:可选择与一区近红外激光器,或二区近红外激光器,或紫外光激光器等进行连接,进而将外界激光器产生的一区近红外光,或二区近红外光,或紫外光等光源通过微型光纤扩束器进行发散后对病变部位进行照射。此种照射方式仅可在有线模式下工作,发光功率和发光波段均取决于外界激光器,激光器由外界电源供电。近红外光用于照射吸附在病变上的示踪造影剂以激发产生荧光,紫外光用于直接照射部分癌前病变以激发产生自体荧光。The external optical fiber port can be used to fix the optical fiber with the optical fiber jumper based on the SMA905 interface, and the optical fiber can be connected with all the lasers with the SMA905 interface in the outside world through the general SMA905 interface. Different optical fibers and different lasers can be selected according to actual needs. For example, you can choose to connect with a near-infrared laser in the first zone, a near-infrared laser in the second zone, or an ultraviolet laser, etc., and then connect the near-infrared laser in the first zone generated by the external laser. Light, or near-infrared light in the second zone, or ultraviolet light and other light sources are diffused through a micro-fiber beam expander and then irradiated to the lesion. This irradiation method can only work in wired mode, and the luminous power and luminous band depend on the external laser, which is powered by the external power supply. Near-infrared light is used to irradiate the tracer contrast agent adsorbed on the lesion to generate fluorescence, and ultraviolet light is used to directly irradiate part of the precancerous lesions to generate autofluorescence.
所述的微型光纤扩束器,为若干透镜组成的透镜组,用于对光纤射出的光线进行发散。The miniature optical fiber beam expander is a lens group composed of several lenses, and is used for diffusing the light emitted by the optical fiber.
所述光源供电模块,用于为微型白光光源和微型近红外光源供电。其具备电池接口和外接电源接口,当在无线模式下工作时,光源供电模块由电池供电,当在有线模式下工作时,光源供电模块由外接电源供电。The light source power supply module is used for supplying power to the miniature white light source and the miniature near-infrared light source. It has a battery interface and an external power supply interface. When working in wireless mode, the light source power supply module is powered by the battery, and when working in wired mode, the light source power supply module is powered by an external power supply.
所述的安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一,包括近红外光滤光片,可安装于微型图像传感器的感光面前,用于仅允许波长大于所采用的近红外光源波长至少10纳米的近红外波段的光进入微型图像传感器,可根据使用的光源不同而进行更换。包括微型镜头,用于收集广角范围内的光线并传递给微型图像传感器。包括微型图像传感器,用于将光学信号转换成电学信号。包括中央控制模块,用于和微型图像传感器的各引脚连接,对其进行参数配置并对其输出信号进行处理。包括通讯模块,用于接收中央控制模块传出的图像数据,并将其传输至图像接收模块上。当在无线工作模式下,微型摄像头模组由电池供电,通讯模块通过天线将数据无线传输给图像接收模块。当在有线工作模式下,微型摄像头模组由USB(通用串行总线)供电,通讯模块通过USB将图像直接传输到图像接收模块上。The first micro-camera module equipped with a near-infrared light filter includes a near-infrared light filter, which can be installed in front of the photosensitive surface of the micro-image sensor, and is used to only allow the wavelength of the near-infrared light source to be greater than that of the near-infrared light source used. Light in the near-infrared band of 10 nanometers enters the miniature image sensor, which can be replaced according to the light source used. Includes a tiny lens that collects light in a wide-angle range and passes it to a tiny image sensor. Includes a miniature image sensor for converting optical signals into electrical signals. It includes a central control module, which is used to connect with each pin of the miniature image sensor, configure its parameters and process its output signal. It includes a communication module for receiving image data from the central control module and transmitting it to the image receiving module. When in the wireless working mode, the miniature camera module is powered by the battery, and the communication module wirelessly transmits the data to the image receiving module through the antenna. When in wired working mode, the micro camera module is powered by USB (Universal Serial Bus), and the communication module directly transmits the image to the image receiving module through USB.
所述安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,包括可见及紫外光滤光片,可安装于微型图像传感器的感光面前,用于仅允许可见光及紫外光波段的光进入图像传感器。其余部分包括微型镜头,微型图像传感器,中央控制模块,通讯模块,所采用的选型及要求均可与安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一相同。The second micro camera module with visible and ultraviolet light filters, including visible and ultraviolet light filters, can be installed in front of the photosensitive front of the micro image sensor to allow only visible light and ultraviolet light to enter the image. sensor. The other parts include miniature lens, miniature image sensor, central control module, and communication module. The selection and requirements used are the same as the miniature camera module 1 with the near-infrared light filter installed.
所述的指环型支架,包括保护玻璃和圆柱形支架,用于固定和封装微型白光光源,微型近红外光源,外接光纤口,微型光纤扩束器,光源供电模块,安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一,以及安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二;包括具有松紧调节功能的指环,用于将支架固定在手指上。The ring-shaped bracket includes a protective glass and a cylindrical bracket for fixing and encapsulating a miniature white light source, a miniature near-infrared light source, an external optical fiber port, a miniature optical fiber beam expander, a light source power supply module, and a near-infrared light filter installed. Micro-camera module 1 of the film, and micro-camera module 2 installed with visible and ultraviolet light filters; including a ring with elastic adjustment function for fixing the bracket on the finger.
所述的图像接收模块,用于接收摄像头模组采集的图像并将图像传输给图像处理和显示模块。The image receiving module is used for receiving the image collected by the camera module and transmitting the image to the image processing and display module.
所述的图像处理和显示模块,用于接收图像接收模块所传输的图像,并对图像进行快速滤波、增强等处理后进行实时显示,同时,可对视频图像进行保存;并可把近红外荧光图像按照预设样式处理成伪彩图并将其与可见光图片进行叠加融合。The image processing and display module is used to receive the image transmitted by the image receiving module, and perform real-time display on the image after processing such as fast filtering and enhancement. At the same time, the video image can be saved; The image is processed into a pseudo-color image according to the preset style and superimposed and fused with the visible light image.
所述的可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变的示踪造影剂,主要包括靶向分子和近红外荧光分子。靶向分子为可以特异性靶向吸附于特定病变例如癌前病变、肿瘤、转移淋巴结等的物质,例如在癌变组织中高度表达的基因所对应的蛋白质所对应的抗体。近红外荧光分子在近红外光激发下会发出更高波段的荧光。将靶向分子和近红外荧光分子通过化学合成偶联在一起后,荧光分子便能随着靶向分子,一同特异性靶向吸附到特定病变上,因而特定病变在近红外光激发下将发出更高波段的荧光,从而将特定病变“点亮”,以供医生更为高效准确地确定病变的位置、尺寸和边界。还可根据需要加入纳米材料等材料用于富集靶向分子和近红外荧光分子,以对信号进行放大。The tracer contrast agent that can be specifically targeted and adsorbed on a specific lesion mainly includes targeting molecules and near-infrared fluorescent molecules. Targeting molecules are substances that can specifically target and adsorb to specific lesions such as precancerous lesions, tumors, metastatic lymph nodes, etc., such as antibodies corresponding to proteins corresponding to genes highly expressed in cancerous tissues. Near-infrared fluorescent molecules emit higher-band fluorescence when excited by near-infrared light. After the target molecule and the near-infrared fluorescent molecule are coupled together by chemical synthesis, the fluorescent molecule can be specifically targeted and adsorbed to a specific lesion along with the target molecule, so the specific lesion will emit light under the excitation of near-infrared light. Higher wavelengths of fluorescence, which "light up" specific lesions, allowing physicians to more efficiently and accurately determine the location, size, and boundaries of lesions. Materials such as nanomaterials can also be added to enrich target molecules and near-infrared fluorescent molecules to amplify the signal as needed.
本发明还提供了一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的应用。The invention also provides the application of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgery imaging guidance system.
1、利用外源性荧光进行造影,即使用示踪造影剂特异性靶向吸附于病变时的应用:第一步:针对特定病变类型,对靶向分子和近红外荧光分子进行选择并进行化学合成,制备相应示踪造影剂,这步可提前完成并于2-8℃下保存。第二步:根据病变类型及靶向分子类型,选择注射示踪造影剂或者将病变部位及周围部位浸泡于示踪造影剂后再进行清洗,目的是让示踪造影剂完成对病变的靶向吸附同时去除非特异性吸附的影响。第三步:医生在手指上佩戴系统,开启白光光源及近红外光源,对病变进行照射,被示踪剂靶向吸附的病变被照射后被激发出荧光,因此和正常组织产生明显区别。同时开启安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一及安装有可见光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,对病变图像进行采集。由于可见及紫外光滤光片的阻隔,因此仅有可见光及紫外光可以进入摄像头模组二,由于近红外光滤光片的阻隔,因此仅有波长大于微型近红外光源波长至少10纳米的近红外光可以进入摄像头模组一,即只有病变部位上的靶向示踪剂被近红外光源照射后产生的近红外激发光可以进入摄像头模组一。第四步:图像处理和显示模块对图像进行滤波、增强等处理,并将近红外荧光图像按照预设样式处理成伪彩图并将其与可见光图片进行叠加融合并实时显示及存储。第五步:医生参考叠加图像对病变边界进行实时判定,并完成手术。1. The use of exogenous fluorescence for contrast imaging, that is, the application of specific targeting and adsorption of tracer contrast agents to lesions: the first step: for specific lesion types, select and chemically target molecules and near-infrared fluorescent molecules. Synthesis, preparation of the corresponding tracer contrast agent, this step can be completed in advance and stored at 2-8 ℃. Step 2: According to the type of lesion and the type of target molecule, choose to inject the tracer contrast agent or soak the lesion and surrounding parts in the tracer contrast agent before cleaning, so that the tracer contrast agent can complete the target of the lesion Adsorption simultaneously removes the effects of non-specific adsorption. Step 3: The doctor wears the system on the finger, turns on the white light source and the near-infrared light source, and irradiates the lesion. The lesion targeted and adsorbed by the tracer is irradiated and excited to fluoresce, so it is obviously different from normal tissue. At the same time, the first micro-camera module installed with the near-infrared light filter and the second micro-camera module installed with the visible light filter are turned on to collect images of lesions. Due to the blocking of the visible and ultraviolet light filters, only visible light and ultraviolet light can enter the camera module 2. Due to the blocking of the near-infrared light filter, only the near-infrared light sources whose wavelength is at least 10 nanometers larger than the wavelength of the near-infrared light source can enter the camera module 2. Infrared light can enter the first camera module, that is, only the near-infrared excitation light generated after the target tracer on the lesion is irradiated by the near-infrared light source can enter the first camera module. Step 4: The image processing and display module filters and enhances the image, and processes the near-infrared fluorescence image into a pseudo-color image according to a preset style, and superimposes and fuses it with the visible light image for real-time display and storage. Step 5: The doctor refers to the superimposed image to determine the boundary of the lesion in real time, and completes the operation.
2、利用自体荧光对癌前病变进行造影,即不使用示踪造影剂时的应用:第一步:医生在手指上佩戴系统,开启白光光源及紫外光源,对癌前病变进行照射,病变被照射后被激发出自体荧光,因此和正常组织产生明显区别,同时开启安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,对病变图像进行采集,由于滤光片不对可见及紫外光进行阻隔,因此可见光及紫外光可以进入摄像头模组二。第二步:图像处理和显示模块对图像进行滤波、增强等处理,并将图像进行实时显示及存储。第三步:医生参考图像对癌前病变边界进行实时判定,并完成手术。2. The use of autofluorescence to contrast precancerous lesions, that is, the application when no tracer contrast agent is used: Step 1: The doctor wears the system on the finger, turns on the white light source and ultraviolet light source, and irradiates the precancerous lesions. Autofluorescence is excited after irradiation, so it is obviously different from normal tissue. At the same time, the second micro camera module equipped with visible and ultraviolet light filters is turned on to collect images of lesions. Therefore, visible light and ultraviolet light can enter the second camera module. Step 2: The image processing and display module filters and enhances the image, and displays and stores the image in real time. Step 3: The doctor makes a real-time determination of the boundary of the precancerous lesion with reference to the image, and completes the operation.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益效果在于,通过制备出具有成像和通讯功能的微型摄像头模组、微型光纤扩束器,并与微型光源配合使用,从而将光源和摄像头模组一体化集成于指环支架内,因而本发明的引导系统可直接配戴在医生的手指上,可无线使用也可有线使用,可灵活地随着医生手指的运动而指向不同的方位,当医生在进行荧光造影下切除病变的手术时,在持刀的同时可以根据自己的需求自主地对任何复杂形状的立体病变进行全方位的动态成像引导,不产生任何盲区,同时制备了可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变的示踪造影剂,在搭配使用下可大大提高手术的精确性、成功率和效率。此外该系统与现有大型的荧光引导系统可以很好的兼容,可进行配合使用,以进一步增强使用效果。系统还具备了在不需要使用示踪造影剂的情况下通过紫外光对癌前病变的自体荧光进行激发成像并引导手术的功能。Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effect of the present invention is that the light source and the camera module are integrated by preparing a miniature camera module and a miniature optical fiber beam expander with imaging and communication functions, and using them together with a miniature light source. It is integrated in the ring holder, so the guiding system of the present invention can be directly worn on the doctor's finger, and can be used wirelessly or wiredly, and can be flexibly pointed to different directions with the movement of the doctor's finger. When excising lesions under angiography, while holding the knife, you can autonomously conduct a full range of dynamic imaging guidance for any complex shape of three-dimensional lesions according to your own needs, without any blind spots, and at the same time, a specific target adsorption can be prepared. Tracer contrast agents for specific lesions can greatly improve the accuracy, success rate and efficiency of surgery when used in combination. In addition, the system is well compatible with the existing large-scale fluorescence guidance system, and can be used in conjunction to further enhance the use effect. The system also has the ability to excite the autofluorescence of precancerous lesions with ultraviolet light and guide surgery without the use of tracer contrast agents.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的一种佩戴示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of wearing a ring-type integrated fluoroscopy imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图2:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的另一种佩戴示意图;Figure 2: Another wearing schematic diagram of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopy imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的结构示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic structural diagram of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的指环支架及其内部模块结构示意图;Figure 4: A schematic structural diagram of a ring support and its internal modules of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图5:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的微型近红外激光二极管发光光谱示意图;Figure 5: A schematic diagram of the luminescence spectrum of a miniature near-infrared laser diode of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopy surgery imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图6:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的微型光纤扩束器光学组成及光路示意图;Fig. 6 is a schematic diagram of the optical composition and optical path of the miniature optical fiber beam expander of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopic surgery imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图7:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的近红外光滤光片的透光光谱图;FIG. 7 : a light transmittance spectrum diagram of a near-infrared light filter of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgical imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图8:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的圆柱形支架示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of a cylindrical support of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic surgery imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图9:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的示踪造影剂示意图;FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of the tracer contrast agent of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgical imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图10:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的示踪造影剂近红外光图像示意图;FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram of a near-infrared light image of a tracer contrast agent of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgical imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图11:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的示踪造影剂靶向胃癌细胞MGC-803的近红外光示意图;FIG. 11 is a near-infrared light schematic diagram of the tracking contrast agent targeting gastric cancer cell MGC-803 of the ring-type integrated fluorescence angiography surgical imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图12:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的示踪造影剂靶向肿瘤的白光和近红外光示意图;FIG. 12 is a schematic diagram of white light and near-infrared light of the tracking contrast agent targeting tumor of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgical imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图13:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的一种应用流程简图;FIG. 13 is a schematic diagram of an application flow of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgical imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图14:本发明一个实施例的指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的另一种应用流程简图。FIG. 14 is another application flow chart of the ring-type integrated fluoroscopy imaging guidance system according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
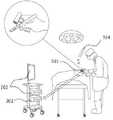
参考图1-图4所示,本发明提供了一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统,根据医生的习惯,系统可以在医生持刀的同时配戴在医生的任何一根手指的任何位置上,图1和图2为其中两种指环型支架301佩戴在医生持手术刀1的手指上的示意图。Referring to Figures 1-4, the present invention provides a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic imaging guidance system. According to the doctor's habit, the system can be worn on any part of the doctor's finger while the doctor is holding the knife. In terms of position, FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 are schematic diagrams in which two kinds of ring-shaped
该系统包括微型白光光源401,微型近红外光源402,外接光纤口403,微型光纤扩束器404,光源供电模块405,安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一406,安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二407,被指环型支架301集合成一体结构;系统还包括了图像接收模块302,图像处理和显示模块303,可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变的示踪造影剂304。The system includes a miniature
其中,微型白光光源401,可为贴片形白光发光二极管,用于发出白光照射病变部位。Wherein, the miniature
微型近红外光源402,可为微型近红外激光二极管,型号可以是SS-D6-7-780-200,其直径为5.6毫米,功率为200mw,发光波段为780-793纳米,发光光谱图如图5所示,用于发出一区近红外光照射病变部位,激发吸附在病变上的示踪造影剂以产生更长波段的近红外荧光。当在无线模式下工作时,仅可使用微型近红外光源进行照射。当在有线模式下工作时,可使用微型近红外光源进行照射,也可使用外接光纤进行照射。The miniature near-infrared
外接光纤口403,可用于固定安装有SMA905接口光纤跳线的光纤,光纤通过通用的SMA905接口,可以与外界一切具有SMA905接口的激光器连接。可根据实际需要选择不同的光纤与不同的激光器,可选择与一区近红外激光器,或二区近红外激光器,或紫外光激光器等进行连接,用于将外界的一区近红外光,或二区近红外光,或紫外光等光源通过微型光纤扩束器进行扩束后对病变部位进行照射,例如可选用芯径尺寸为200微米,包层直径为220微米的光纤,和型号为MW-GX-808/5000mW的一区近红外激光器进行连接。此种照射方式仅可在有线模式下工作,发光功率和发光波段均取决于外界激光器,激光器由外接电源供电。近红外光用于照射激发吸附在病变上的示踪造影剂以产生更长波段的近红外荧光。紫外光用于直接照射部分癌前病变以产生自体荧光,紫外光可选择不会损伤正常组织的波段,可选择中心波长在365纳米附近的紫外光源。The external
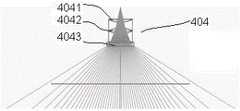
微型光纤扩束器404,可以为由若干透镜组成的透镜组,用于对光纤内的光线进行扩束,在和芯径尺寸为200微米,包层直径为220微米的光纤,和型号为MW-GX-808/5000mW的一区近红外激光器配合的情况下,微型光纤扩束器可由两片凹透镜一、二4041、4042和一片凸透镜4043组成,其光学组成及光路示意图如图6所示。The miniature optical
光源供电模块405,具有稳压稳流功能,用于为微型白光光源和微型近红外光源供电。其具备电池接口和外接电源接口,当在无线模式下工作时,光源供电模块由电池供电,当在有线模式下工作时,光源供电模块由外接电源供电。The light source
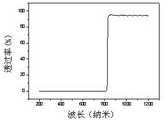
安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一406,包括近红外光滤光片,可安装于微型图像传感器的感光面前,用于仅允许波长大于所采用的近红外光源波长至少10纳米的近红外波段的光进入微型图像传感器,可根据使用的光源不同而进行更换,例如当使用光源的中心波段为780纳米或808纳米时,均可选择825纳米以上可通过的半通滤光片,其透光光谱图如图7所示。包括微型镜头,其为若干透镜组成的透镜组,用于收集广角范围内的光线并传递给微型图像传感器,可选择四块微型透镜组合而成的视场角为75°,最小焦距为8毫米的透镜组。包括微型图像传感器,用于将光学信号转换成电学信号,型号可以是OV9734,其为超低功耗微型图像传感器,感光面积为1/9英寸,像素为100万,像素尺寸为1.4微米*1.4微米。包括中央控制模块,其核心可以为一块单片微控制器,可以是MSP430系列,PIC系列,或STM32系列等,优选为MSP430系列。其用于和微型图像传感器的各引脚连接,对其进行参数配置并对其输出信号进行处理。包括通讯模块,用于接收中央控制模块传出的图像数据,并将其传输至图像接收模块上。当在无线工作模式下,微型摄像头模组由电池供电,通讯模块通过天线将数据无线传输到图像接收模块上。当在有线工作模式下,微型摄像头模组由USB供电,通讯模块通过USB将图像直接传输到图像接收模块上。Micro camera module one 406 with a near-infrared light filter installed, including a near-infrared light filter, which can be installed in front of the photosensitive front of the micro-image sensor to allow only wavelengths greater than the wavelength of the near-infrared light source used by at least 10 nanometers The light in the near-infrared band enters the miniature image sensor and can be replaced according to the light source used. For example, when the central wavelength band of the light source is 780 nm or 808 nm, a half-pass filter above 825 nm can be selected. , and its transmittance spectrum is shown in Figure 7. Including a miniature lens, which is a lens group composed of several lenses, used to collect light in a wide-angle range and transmit it to a miniature image sensor. The field of view angle formed by the combination of four miniature lenses is 75°, and the minimum focal length is 8 mm lens group. Including a miniature image sensor for converting optical signals into electrical signals, the model can be OV9734, which is an ultra-low power miniature image sensor with a photosensitive area of 1/9 inch, 1 million pixels, and a pixel size of 1.4 microns * 1.4 microns. Including a central control module, the core of which can be a single-chip microcontroller, which can be MSP430 series, PIC series, or STM32 series, etc., preferably MSP430 series. It is used to connect with each pin of the miniature image sensor, configure its parameters and process its output signal. It includes a communication module for receiving image data from the central control module and transmitting it to the image receiving module. When in the wireless working mode, the miniature camera module is powered by the battery, and the communication module wirelessly transmits the data to the image receiving module through the antenna. When in the wired working mode, the micro camera module is powered by USB, and the communication module directly transmits the image to the image receiving module through USB.
安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二407,包括可见光滤光片,可安装于微型图像传感器的感光面前,用于仅允许可见光及紫外光波段的光进入图像传感器,可选择760纳米以下可通过的半通滤光片。其余部分包括微型镜头,微型图像传感器,中央控制模块,通讯模块,所采用的选型及要求均可与安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一相同。Micro camera module 2 407 with visible and ultraviolet light filters installed, including visible light filters, can be installed in front of the photosensitive front of the micro image sensor to allow only visible light and ultraviolet light to enter the image sensor, optional Passable half-pass filters below 760 nm. The other parts include miniature lens, miniature image sensor, central control module, and communication module. The selection and requirements used are the same as the miniature camera module 1 with the near-infrared light filter installed.
指环型支架301,具有松紧调节功能的指环,用于将支架固定在手指上,包括保护玻璃和圆柱形支架3011,其中圆柱形支架3011外径可为13毫米,内部上半部分可具有3个空心圆柱通孔,如图8所示,其中第一个孔30111可用于固定安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一,第二个孔30112可用于固定安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,第三个孔30113可用于固定微型近红外光源或用于在固定外接光纤口和微型光纤扩束器,当使用微型近红外光源进行照射时,用于固定微型近红外光源,当使用光纤进行照射时,则用于固定外接光纤口和微型光纤扩束器。圆柱形支架3011下半部可为整个空心通孔,可用于固定光源供电模块及电池。微型白光光源则可固定于保护玻璃和圆柱形支架之间的缝隙。Ring-
图像接收模块302,其核心可以为一块单片微控制器,可以是MSP430系列,PIC系列,或STM32系列等,优选为MSP430系列,用于接收摄像头模组采集的图像并将图像传输到图像处理和显示模块。The
图像处理和显示模块303,可为安装有特定图像处理软件的电脑机箱和显示屏幕,用于接收图像接收模块所传输的图像,并对图像进行快速滤波,增强等处理后进行实时显示,同时可对视频图像进行保存。并可把近红外荧光图像按照预设样式处理成伪彩图并将其与可见光图片进行叠加融合。The image processing and
可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变的示踪造影剂304,主要包括靶向分子和近红外荧光分子,靶向分子为可特异性靶向吸附于特定病变例如癌前病变、肿瘤、转移淋巴结等的物质,包括在癌变组织中高度表达的基因所对应的蛋白质所对应的抗体,例可选用BRCAA1抗体、HAI-178人源性抗体、PLCe1抗体或胃泌素G-17抗体等用于靶向识别早期胃癌,也可选择广泛用于癌症靶向的叶酸,因为叶酸受体在癌细胞上的表达会显著增强。近红外荧光分子在近红外光激发下会发出更高波段的荧光,可使用吲哚菁绿,其在730-800纳米近红外光的照射下均会发出820纳米左右的荧光。将靶向分子和近红外荧光分子通过化学合成偶联在一起后,荧光分子便能随着靶向分子,一同特异性靶向吸附到特定病变上,因而特定病变在近红外光激发下将发出更高波段的荧光,将特定病变“点亮”,以供医生更为高效准确地确定病变的位置、尺寸和边界。还可根据需要加入纳米材料等材料例如金纳米棒、金纳米星等,用于富集靶向分子和近红外荧光分子,以对信号进行放大。本实施例选择叶酸和吲哚菁绿作为示踪造影剂的成分。具体合成方法如下:首先将一定量的带有羧基的吲哚菁绿(ICG-COOH),1-乙基-(3-二甲基氨基丙基)碳酰二亚胺(EDC)和N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺(NHS)溶于二甲基亚砜(DMSO),均匀混合后避光保存30分钟,其中EDC用于活化羧基,NHS用作共反应剂。随后加入过量的叶酸,均匀混合后避光保存2小时。随后加入三倍体积的纯水,均匀混合后,重复三次:离心-重悬-混匀的过程,最后一次根据所需的ICG浓度而加入一定体积的纯水即可,制备完毕后避光保存于2-8℃环境下。制备好的示踪造影剂如图9所示,将其滴在猪胃上后在微型近红外激光二极管照射下的荧光图像如图10所示。制备好的示踪造影剂对肿瘤具有靶向效应,可特异性吸附于肿瘤细胞,并在近红外光激发下将发出更高波段的荧光,以特异性点亮肿瘤细胞, 通过安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组对激发光进行拍摄,从而可根据荧光来判断肿瘤的位置、尺寸和边界,其吸附于人胃癌细胞MGC-803后,细胞可在荧光显微镜下进行荧光成像,示意图如图11所示。其以猪胃为背景,吸附于通过人胃癌细胞MGC-803在小鼠身上制备的肿瘤后,肿瘤可在本实施例的系统下进行荧光成像,示意图如图12所示。The
应用例1Application example 1
以下为本实施例的一种指环式一体化荧光造影手术成像引导系统的应用实例。The following is an application example of a ring-type integrated fluoroscopic angiography surgery imaging guidance system of the present embodiment.
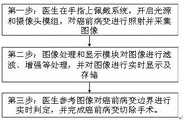
为利用外源性荧光造影的情况,即使用示踪造影剂特异性靶向吸附于病变,流程简图如图13所示,具体流程如下:第一步:针对特定病变类型,对靶向分子和近红外荧光分子进行选择并进行化学合成,制备相应示踪造影剂,这步可提前完成并于2-8℃下保存。第二步:根据病变类型及靶向分子类型,选择注射示踪造影剂或者将病变部位及周围部位浸泡于示踪造影剂后再进行清洗,目的是让示踪造影剂完成对病变的靶向吸附同时去除非特异性吸附的影响。第三步:医生在手指上佩戴系统,开启白光光源及近红外光源,对病变进行照射,被示踪剂靶向吸附的病变被照射后被激发出荧光,因此和正常组织产生明显区别。同时开启安装有近红外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组一及安装有可见光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,对病变图像进行采集。第四步:图像处理和显示模块对图像进行滤波、增强等处理,并将把近红外荧光图像按照预设样式处理成伪彩图并将其与可见光图片进行叠加融合并实时显示及存储。第五步:医生参考叠加图像对病变边界进行实时判定,并完成病变切除手术。In the case of using exogenous fluorescence angiography, that is, using a tracer contrast agent to specifically target and adsorb to the lesion, the flowchart is shown in Figure 13, and the specific process is as follows: Step 1: For specific lesion types, target Select and chemically synthesize near-infrared fluorescent molecules to prepare corresponding tracer contrast agents. This step can be completed in advance and stored at 2-8°C. Step 2: According to the type of lesion and the type of target molecule, choose to inject the tracer contrast agent or soak the lesion and surrounding parts in the tracer contrast agent before cleaning, so that the tracer contrast agent can complete the target of the lesion Adsorption simultaneously removes the effects of non-specific adsorption. Step 3: The doctor wears the system on the finger, turns on the white light source and the near-infrared light source, and irradiates the lesion. The lesion targeted and adsorbed by the tracer is irradiated and excited to fluoresce, so it is obviously different from normal tissue. At the same time, the first micro-camera module installed with the near-infrared light filter and the second micro-camera module installed with the visible light filter are turned on to collect images of lesions. Step 4: The image processing and display module performs filtering, enhancement and other processing on the image, and will process the near-infrared fluorescent image into a pseudo-color image according to a preset style, and superimpose and fuse it with the visible light image, and display and store it in real time. Step 5: The doctor refers to the superimposed image to determine the lesion boundary in real time, and completes the lesion resection.
应用例2Application example 2
利用自体荧光对癌前病变进行造影的情况,即不使用示踪造影剂,流程简图如图14所示,具体流程如下:第一步:医生在手指上佩戴系统,开启白光光源及紫外光源,对癌前病变进行照射,病变被照射后被激发出自体荧光,因此和正常组织产生明显区别,同时开启安装有可见及紫外光滤光片的微型摄像头模组二,对病变图像进行采集。第二步:图像处理和显示模块对图像进行滤波、增强等处理并进行实时显示及存储。第三步:医生参考图像对癌前病变边界进行实时判定,并完成癌前病变切除手术。In the case of using autofluorescence to contrast precancerous lesions, that is, no tracer contrast agent is used, the flow chart is shown in Figure 14. The specific flow is as follows: Step 1: The doctor wears the system on the finger, and turns on the white light source and the ultraviolet light source. , irradiate precancerous lesions, and the lesions are excited by autofluorescence after being irradiated, so they are significantly different from normal tissues. At the same time, the second micro camera module installed with visible and ultraviolet filters is turned on to collect lesions images. Step 2: The image processing and display module filters and enhances the image and displays and stores it in real time. Step 3: The doctor makes a real-time determination of the boundary of the precancerous lesion with reference to the image, and completes the resection of the precancerous lesion.
Claims (26)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210110880.2ACN114569070A (en) | 2022-01-29 | 2022-01-29 | Ring type integrated fluorography operation imaging guide system and application |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210110880.2ACN114569070A (en) | 2022-01-29 | 2022-01-29 | Ring type integrated fluorography operation imaging guide system and application |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114569070Atrue CN114569070A (en) | 2022-06-03 |
Family
ID=81769466
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210110880.2APendingCN114569070A (en) | 2022-01-29 | 2022-01-29 | Ring type integrated fluorography operation imaging guide system and application |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114569070A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115981001A (en)* | 2022-12-02 | 2023-04-18 | 浙江迈视医疗科技有限公司 | Head-mounted vision auxiliary equipment |
| WO2024045507A1 (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2024-03-07 | 南京诺源医疗器械有限公司 | Data processing-based three-dimensional fluorescence imaging method and apparatus |
| CN118766613A (en)* | 2024-09-05 | 2024-10-15 | 天津大学 | A safe and accurate segmented positioning guidance system for deep tissue based on near-infrared second-zone light |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090318758A1 (en)* | 2004-09-24 | 2009-12-24 | Vivid Medical, Inc. | Pluggable vision module and portable display for endoscopy |
| US20100262020A1 (en)* | 2009-01-08 | 2010-10-14 | American Biooptics Llc | Probe apparatus for recognizing abnormal tissue |
| US20110152692A1 (en)* | 2009-12-15 | 2011-06-23 | Emory University Office Of Technology Transfer | System and methods for providing real-time anatomical guidance in a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure |
| CN102319059A (en)* | 2011-10-28 | 2012-01-18 | 北京天助基业科技发展有限公司 | Near-infrared fluorescence imaging surgery guide device and application thereof |
| CN104826127A (en)* | 2015-04-25 | 2015-08-12 | 郑州大学 | Preparation method and applications of photo-thermal and photodynamic co-used antitumor drug delivery system taking gold nano star mediated by folic acid as carrier |
| US20150296111A1 (en)* | 2012-11-26 | 2015-10-15 | Mayo Foundation For Medical Education And Research | Finger cot camera system |
| CN106963744A (en)* | 2017-02-21 | 2017-07-21 | 上海工程技术大学 | A kind of nano-complex particle for being coupled folate-targeted and preparation method and application |
| JP2021010713A (en)* | 2019-07-09 | 2021-02-04 | 国立大学法人高知大学 | Medical equipment |
| CN113331767A (en)* | 2021-07-05 | 2021-09-03 | 上海交通大学 | Diagnosis and treatment system for gastrointestinal precancerous lesions |
- 2022
- 2022-01-29CNCN202210110880.2Apatent/CN114569070A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20090318758A1 (en)* | 2004-09-24 | 2009-12-24 | Vivid Medical, Inc. | Pluggable vision module and portable display for endoscopy |
| US20100262020A1 (en)* | 2009-01-08 | 2010-10-14 | American Biooptics Llc | Probe apparatus for recognizing abnormal tissue |
| US20110152692A1 (en)* | 2009-12-15 | 2011-06-23 | Emory University Office Of Technology Transfer | System and methods for providing real-time anatomical guidance in a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure |
| CN102319059A (en)* | 2011-10-28 | 2012-01-18 | 北京天助基业科技发展有限公司 | Near-infrared fluorescence imaging surgery guide device and application thereof |
| US20150296111A1 (en)* | 2012-11-26 | 2015-10-15 | Mayo Foundation For Medical Education And Research | Finger cot camera system |
| CN104826127A (en)* | 2015-04-25 | 2015-08-12 | 郑州大学 | Preparation method and applications of photo-thermal and photodynamic co-used antitumor drug delivery system taking gold nano star mediated by folic acid as carrier |
| CN106963744A (en)* | 2017-02-21 | 2017-07-21 | 上海工程技术大学 | A kind of nano-complex particle for being coupled folate-targeted and preparation method and application |
| JP2021010713A (en)* | 2019-07-09 | 2021-02-04 | 国立大学法人高知大学 | Medical equipment |
| CN113331767A (en)* | 2021-07-05 | 2021-09-03 | 上海交通大学 | Diagnosis and treatment system for gastrointestinal precancerous lesions |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024045507A1 (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2024-03-07 | 南京诺源医疗器械有限公司 | Data processing-based three-dimensional fluorescence imaging method and apparatus |
| CN115981001A (en)* | 2022-12-02 | 2023-04-18 | 浙江迈视医疗科技有限公司 | Head-mounted vision auxiliary equipment |
| CN118766613A (en)* | 2024-09-05 | 2024-10-15 | 天津大学 | A safe and accurate segmented positioning guidance system for deep tissue based on near-infrared second-zone light |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114569070A (en) | Ring type integrated fluorography operation imaging guide system and application | |
| ES2967384T3 (en) | Systems, methods and devices for three-dimensional imaging, measurement and visualization of wounds and tissue samples | |
| US11765340B2 (en) | Goggle imaging systems and methods | |
| Loschenov et al. | Photodynamic therapy and fluorescence diagnostics | |
| CN1976639B (en) | Lymph node detector | |
| US8865128B2 (en) | Folate targeted enhanced tumor and folate receptor positive tissue optical imaging technology | |
| US20100305436A1 (en) | Systems, devices, and methods for photoactive assisted resection | |
| JP6420446B2 (en) | Intraoperative diagnostic system comprising a combination of a photodynamic diagnostic device equipped with a collimator and a surgical microscope having a fluorescence diagnostic mode | |
| US8858914B2 (en) | Folate targeted enhanced tumor and folate receptor positive tissue optical imaging technology | |
| JP3579424B2 (en) | Analyte detection by the duration of luminescence at steady state. | |
| CA3148654A1 (en) | Systems and methods for vascular and structural imaging | |
| US10288568B2 (en) | Raman probe and methods of imaging | |
| US20070269837A1 (en) | Devices and methods for fluorescent inspection and/or removal of material in a sample | |
| CN201578365U (en) | A fluorescent navigation system in tumor surgery | |
| JP2006512109A (en) | Identification technology of molecular structure using fluorescent light emission, and treatment technology of cell types lined inside the body lumen | |
| CN106937884A (en) | Operation guiding system based near infrared imaging | |
| CN116250803A (en) | Methods and systems for peripheral nerve reflex imaging | |
| CN207821799U (en) | 2nd area of near-infrared and the imaging of nano target fluorescence probe indicate system with tumor operation real-time navigation | |
| US20130085385A1 (en) | Surgical lighting sources for use with fluophore-tagged monoclonal antibodies or fluorophore-tagged tumor avid compounds | |
| JP6044012B2 (en) | Detection system for detection target part | |
| Papayan et al. | Video-endoscopy system for photodynamic theranostics of central lung cancer | |
| EP2228003A1 (en) | Multifunctional endoscopic device and methods employing said device | |
| Messadi et al. | Oral cancer | |
| Leon et al. | Development of a portable intraoral camera and a smartphone application for oral cancer PDT treatment guidance and monitoring | |
| Kercher | New Methods and Tools for Optimizing Translational Precision Photomedicine |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |