CN114520972A - Interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in multi-channel system - Google Patents
Interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in multi-channel systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114520972A CN114520972ACN202210240847.1ACN202210240847ACN114520972ACN 114520972 ACN114520972 ACN 114520972ACN 202210240847 ACN202210240847 ACN 202210240847ACN 114520972 ACN114520972 ACN 114520972A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- information
- channel
- source node
- destination node
- node
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription52
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription16
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription48
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000002452interceptive effectEffects0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000006399behaviorEffects0.000description9
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description6
- 238000005562fadingMethods0.000description3
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description3
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description3
- 238000001228spectrumMethods0.000description3
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 238000004088simulationMethods0.000description2
- 230000003595spectral effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000009827uniform distributionMethods0.000description2
- 239000000654additiveSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000996additive effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000000969carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 230000002708enhancing effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 230000035755proliferationEffects0.000description1
- 239000013589supplementSubstances0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/02—Protecting privacy or anonymity, e.g. protecting personally identifiable information [PII]
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/04—Key management, e.g. using generic bootstrapping architecture [GBA]
- H04W12/041—Key generation or derivation
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W12/00—Security arrangements; Authentication; Protecting privacy or anonymity
- H04W12/04—Key management, e.g. using generic bootstrapping architecture [GBA]
- H04W12/043—Key management, e.g. using generic bootstrapping architecture [GBA] using a trusted network node as an anchor
- H04W12/0433—Key management protocols
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D30/00—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks
- Y02D30/70—Reducing energy consumption in communication networks in wireless communication networks
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于无线网络隐私信息安全传输技术领域,尤其涉及一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless network privacy information security transmission, and in particular relates to an interference-assisted concealed wireless communication method in a multi-channel system.
背景技术Background technique
随着技术的快速发展,越来越多的机密和敏感数据(如健康记录、身份认证等)通过无线信道传输。澳大利亚网络调查的数据“Australian Cyberawareness Index 2019,”https://channellife.com.au/story/eset-releases-aus-tralian-cyberawareness-index-2019-results,Accessed:2019-12-13表明,几乎所有(94%)的调查对象都在网上进行过金融交易,包括网上银行、支付账单和网上购物,这意味着在交换敏感和私人信息方面,人们更加依赖现代无线通信系统。由此可见,无线通信系统已经渗透到我们日常生活的方方面面,其安全性和隐私性也在我们的社会中占据了无可比拟的优先地位。但是,由于无线信道的开放特性(既可以被合法用户接收,也可以被非法用户接收),无线传输数据的安全问题一直是业界研究的重点。传统上,通过技术手段保护数据内容,提高无线传输的安全性。然而近年来,随着无线设备的激增和计算技术的进步,通信安全受到了较大的挑战,特别是量子计算的突破,极大地提高了潜在对手可用的计算资源,从而提高了打破传统无线信息传输的安全技术的可能性。作为传统安全机制的一种有效补充,物理层安全技术利用无线信道的衰落特性保证了信息传输的安全性,实现了香农信息论意义下的绝对安全。值得指出的是,基于传统加密和基于物理层安全的信息安全传输机制仅仅保护信息的内容不被非法的窃听节点破译,更多关注于传输信息本身的安全性,却忽视了信息传输过程的不可检测性。实际上,窃听节点进行信息破译的基础是对信息传输行为的正确检测,因此,通过隐藏无线传输行为可以实现更强的安全性能。并且在某些特殊场景中,比如军事指挥等场景中,不仅信息的隐私性和完整性很重要,传输信息的行为和传输者位置本身也是不能被暴露的信息。一旦监测到信息传输过程的发生,其可能会采取诸如全频段大功率干扰,甚至是采用物理攻击等手段破坏信息传输过程。此时,保证信息传输行为不可检测对于保护用户隐私和信息传输安全具有重要意义。With the rapid development of technology, more and more confidential and sensitive data (such as health records, identity authentication, etc.) are transmitted through wireless channels. Data from the Australian Cyber Survey "Australian Cyberawareness Index 2019," https://channellife.com.au/story/eset-releases-aus-tralian-cyberawareness-index-2019-results,Accessed:2019-12-13 shows that almost All (94%) of the respondents have conducted financial transactions online, including online banking, paying bills and shopping online, which means people are more reliant on modern wireless communication systems when it comes to exchanging sensitive and private information. It can be seen that the wireless communication system has penetrated into every aspect of our daily life, and its security and privacy also occupy an unparalleled priority in our society. However, due to the open nature of wireless channels (which can be received by both legitimate users and illegal users), the security of wirelessly transmitted data has always been the focus of research in the industry. Traditionally, data content is protected by technical means to improve the security of wireless transmission. However, in recent years, with the proliferation of wireless devices and the advancement of computing technology, communication security has been greatly challenged, especially the breakthrough of quantum computing, which has greatly improved the computing resources available to potential adversaries, thereby improving the ability to break through traditional wireless information. Possibility of transmission security technology. As an effective supplement to traditional security mechanisms, physical layer security technology utilizes the fading characteristics of wireless channels to ensure the security of information transmission, and achieves absolute security in the sense of Shannon's information theory. It is worth pointing out that the information security transmission mechanism based on traditional encryption and physical layer security only protects the content of the information from being deciphered by illegal eavesdropping nodes, and pays more attention to the security of the transmitted information itself, but ignores the impossibility of the information transmission process. detectability. In fact, the basis of the information deciphering of the eavesdropping node is the correct detection of the information transmission behavior. Therefore, stronger security performance can be achieved by concealing the wireless transmission behavior. And in some special scenarios, such as military command and other scenarios, not only the privacy and integrity of information are very important, but the behavior of transmitting information and the location of the transmitter itself are also information that cannot be exposed. Once the occurrence of the information transmission process is detected, it may take measures such as full-band high-power interference, or even use physical attacks to destroy the information transmission process. At this time, ensuring that the information transmission behavior is undetectable is of great significance for protecting user privacy and information transmission security.
在此背景下,隐蔽通信又称低概率检测通信受到越来越多的学者关注。隐蔽通信旨在令无线通信信号或通信行为具有较低的检测概率,避免被敌方检测到。隐蔽无线通信的应用场景很多,尤其是在军事通信中,低检测概率信号可以避免被敌方电子侦察设备获取情报,从而使军事行动更加隐蔽。隐蔽无线通信最早可以追溯到上世纪初兴起的无线扩频通信,扩频技术在传输信息时,实际所用的带宽远大于信息本身所需要的带宽,可以使发送功率谱密度低于背景噪声,从而具有隐蔽传输的能力。然而扩频技术的隐蔽性理论机理一直没有得到严谨的证明。直到文献“Limits of Reliable Communication with LowProbability of Detection on AWGN Channels,”in IEEE Journal on Selected Areasin Communications,vol.31,no.9,pp.1921–1930,Sep.2013.首次详细研究了加性高斯白噪声(AWGN)信道中隐蔽通信的基本性能界,奠定了隐蔽无线通信的信息论基础。文献“Covert Communication in the Presence of an Uninformed Jammer,”in IEEETransactions on Wireless Communications,vol.16,no.9,pp.6193–6206,Sep.2017.研究了隐蔽无线通信可以通过一个不知情的干扰器辅助发射机实现。研究表明,通过干扰辅助源节点通信,可以在满足隐蔽条件的基础上,可靠地给目的节点传输信息。然而,上述文献中考虑的源节点均是通过单信道系统发送信息;多信道系统由于具有频谱效率高的优点,在无线通信中得到了广泛的应用。多信道系统包含多个子信道(也称为子载波),使发射机可以选择其中一个子信道来传输信息,从而提供了另一个程度的自由度来迷惑监测者,提高通信隐蔽性;多信道系统中,可以通过子信道选择策略改善信道衰落对通信的影响,增强无线通信性能。因此,在多信道系统中,如何隐蔽且可靠的传输信息,以及挖掘多信道系统有效提升系统隐蔽吞吐量具有重要意义,而相关的研究却未有出现过。In this context, covert communication, also known as low-probability detection communication, has received more and more attention from scholars. Covert communication aims to make wireless communication signals or communication behaviors have a low probability of detection and avoid detection by adversaries. There are many application scenarios of covert wireless communication, especially in military communication, low detection probability signals can avoid intelligence obtained by enemy electronic reconnaissance equipment, thus making military operations more covert. Covert wireless communication can be traced back to the wireless spread spectrum communication that emerged at the beginning of the last century. When the spread spectrum technology transmits information, the actual bandwidth used is much larger than the bandwidth required by the information itself, which can make the transmission power spectral density lower than the background noise, so Capable of covert transmission. However, the hidden theoretical mechanism of spread spectrum technology has not been rigorously proved. Until the paper "Limits of Reliable Communication with LowProbability of Detection on AWGN Channels," in IEEE Journal on Selected Areasin Communications, vol.31, no.9, pp.1921–1930, Sep.2013. The first detailed study of additive Gaussian white The basic performance bounds of covert communication in noisy (AWGN) channel lays the foundation of information theory for covert wireless communication. The paper "Covert Communication in the Presence of an Uninformed Jammer," in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 16, no. 9, pp. 6193–6206, Sep. 2017. Researched that covert wireless communication can be transmitted by an uninformed jammer Auxiliary transmitter implementation. Research shows that by interfering with the communication of auxiliary source nodes, information can be reliably transmitted to the destination node on the basis of satisfying the concealment conditions. However, the source nodes considered in the above literature all send information through a single-channel system; multi-channel systems have been widely used in wireless communications due to their high spectral efficiency. Multi-channel systems contain multiple sub-channels (also called sub-carriers), allowing the transmitter to select one of the sub-channels to transmit information, thus providing another degree of freedom to confuse the monitor and improve communication concealment; multi-channel systems In the sub-channel selection strategy, the influence of channel fading on communication can be improved, and the wireless communication performance can be enhanced. Therefore, in a multi-channel system, how to transmit information covertly and reliably, and how to mine the multi-channel system to effectively improve the covert throughput of the system is of great significance, but no related research has appeared.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明目的是提供一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信方法,能够在多信道系统中充分利用选定子信道的不确定性,来提高源节点和目的节点之间的隐蔽通信性能。一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信方法,包括如下步骤:The purpose of the present invention is to provide an interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in a multi-channel system, which can fully utilize the uncertainty of selected sub-channels in the multi-channel system to improve the covert communication performance between the source node and the destination node. An interference-assisted concealed wireless communication method in a multi-channel system, comprising the following steps:
步骤S1:目的节点广播导频信号:源节点进行信道估计,并从K个子信道中,选择具有最大信道状态信息的子信道;Step S1: the destination node broadcasts the pilot signal: the source node performs channel estimation, and selects the subchannel with the largest channel state information from the K subchannels;
步骤S2:密钥交换与码本共享:在隐私信息传输之前,源节点与目的节点之间通过无线信道产生密钥,并利用密钥加密后共享隐私信息编码的码本;Step S2: key exchange and codebook sharing: before the privacy information is transmitted, a key is generated between the source node and the destination node through a wireless channel, and the codebook encoded by the privacy information is shared after the key is encrypted;
步骤S3:信息编码:源节点利用其与目的节点共享的码本对待传输的隐私信息进行编码,编码长度为N,表示源节点经过N次信道使用将隐私信息完整的发送出去;Step S3: information encoding: the source node uses the codebook shared with the destination node to encode the privacy information to be transmitted, and the encoding length is N, indicating that the source node transmits the privacy information completely through N times of channel use;
步骤S4:信息传输:源节点以最优发送功率在所选择的子信道上发送待传输的隐私信息;Step S4: Information transmission: the source node transmits at the optimal transmission power send the private information to be transmitted on the selected sub-channel;
步骤S5:信息译码:目的节点在每一个传输周期利用其与源节点共享的码本译码。Step S5: Information decoding: the destination node uses the codebook shared with the source node to decode in each transmission cycle.
一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信方法,系统由一对合法的收发对(源节点和目的节点)和一个友好的干扰节点组成,另外还存在于一个监测者不断地观察环境并检测源节点是否传输信息。所有节点均配置单天线,且工作在半双工模式下。具体的说,源节点从多个子信道中,选择信道系数最大的子信道发送信息,并且在源节点与目的节点之间共享密钥与码本;为了迷惑监测者,干扰节点发送功率均匀变化的干扰,并且每个子信道分配相同的干扰信号且在服从均匀分布;监测者持续地观测无线传输环境以判断源节点是否向目的节点发送了隐私信息。An interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in a multi-channel system. The system consists of a pair of legitimate transceiver pairs (source node and destination node) and a friendly interference node. In addition, there is a monitor who constantly observes the environment and detects Whether the source node transmits information. All nodes are configured with a single antenna and work in half-duplex mode. Specifically, the source node selects the sub-channel with the largest channel coefficient from multiple sub-channels to send information, and shares the key and codebook between the source node and the destination node. interference, and each sub-channel is assigned the same interference signal and is It obeys uniform distribution; the monitor continuously observes the wireless transmission environment to determine whether the source node sends private information to the destination node.
本发明所述的一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信方法在具体操作时,源节点通过在多个子信道中合理的选择子信道的方式,增加了源节点处信道选择的不确定性,进一步迷惑监测者,达到提升无线传输行为隐蔽性的目的。在源节点选择子信道的策略中,先进行信道估计再选择具有最大信道系数的子信道,减少衰落对信号的影响,达到了增强隐私信息传输可靠性的目的。与单信道隐蔽传输的隐蔽无线通信方法相比,本发明能获得更高的平均有效隐蔽速率。In the specific operation of the interference-assisted concealed wireless communication method in a multi-channel system according to the present invention, the source node increases the uncertainty of channel selection at the source node by reasonably selecting sub-channels from multiple sub-channels. , to further confuse the monitor and achieve the purpose of improving the concealment of wireless transmission behavior. In the sub-channel selection strategy of the source node, the channel estimation is performed first, and then the sub-channel with the largest channel coefficient is selected to reduce the influence of fading on the signal and achieve the purpose of enhancing the reliability of private information transmission. Compared with the covert wireless communication method of single-channel covert transmission, the present invention can obtain a higher average effective covert rate.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明的系统模型示意图。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a system model of the present invention.
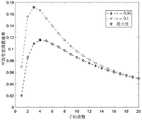
图2是采用本发明所提方法时不同的子信道数目对应的系统所能达到的平均有效隐蔽速率仿真对比图。FIG. 2 is a simulation comparison diagram of the average effective concealment rate that can be achieved by systems corresponding to different numbers of sub-channels when the method proposed in the present invention is adopted.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
如图1所示的一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信系统,由一对合法的收发方(源节点和目的节点)和一个友好的干扰节点组成,另外还存在一个监测者不断地观察环境并检测源节点是否传输信息。所有节点均配置单天线,且工作在半双工模式下。其中,源节点从多个子信道中,选择信道系数最大的子信道发送信息,并将所选择的子信道信息和发送时隙信息通过密钥与目的节点共享;为了迷惑监测者,干扰节点发送功率均匀变化的干扰,并且每个子信道分配相同的干扰信号且在服从均匀分布;监测者持续地观测无线传输环境以判断源节点是否向目的节点发送了隐私信息。As shown in Figure 1, an interference-assisted covert wireless communication system in a multi-channel system consists of a pair of legitimate transceivers (source node and destination node) and a friendly interference node. Observe the environment and detect if the source node transmits information. All nodes are configured with a single antenna and work in half-duplex mode. Among them, the source node selects the sub-channel with the largest channel coefficient from multiple sub-channels to send information, and shares the selected sub-channel information and transmission time slot information with the destination node through the key; in order to confuse the monitor, the interference node transmits power uniformly varying interference, and each subchannel is assigned the same interfering signal and is It obeys uniform distribution; the monitor continuously observes the wireless transmission environment to determine whether the source node sends private information to the destination node.
一种多信道系统中干扰辅助的隐蔽无线通信方法,包括以下步骤:An interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in a multi-channel system, comprising the following steps:
步骤S1:目的节点广播导频信号:源节点进行信号估计,并从K个子信道中,选择具有最大信道状态信息的子信道;Step S1: the destination node broadcasts the pilot signal: the source node performs signal estimation, and selects the subchannel with the largest channel state information from the K subchannels;
步骤S2:密钥交换与码本共享:在隐私信息传输之前,源节点与目的节点之间通过利用无线信道产生密钥,并利用密钥加密后共享隐私信息编码的码本;Step S2: key exchange and codebook sharing: before the transmission of privacy information, between the source node and the destination node, a key is generated by utilizing a wireless channel, and the codebook encoded by the privacy information is shared after the encryption of the key;
步骤S3:信息编码:源节点利用其与目的节点共享的码本对待传输的隐私信息进行编码,编码长度为N,表示源节点经过N次信道使用可以将该隐私信息完整的发送出去;Step S3: information encoding: the source node uses the codebook shared with the destination node to encode the privacy information to be transmitted, and the encoding length is N, which means that the source node can completely send the privacy information through N times of channel use;
步骤S4:信息传输:源节点以功率在所选择的子信道上发送待传输的隐私信息;Step S4: Information transmission: the source node transmits the power send the private information to be transmitted on the selected sub-channel;
为了在满足通信隐蔽性约束的条件下,最大化源节点与目的节点之间的平均有效隐蔽速率η,并且根据定义,平均有效速率(注:在隐蔽约束条件下求解成为平均有效隐蔽速率,这里没有设计隐蔽约束,只是单纯的平均有效速率),我们需要优化参数发送功率Pa和源节点发送信息的子信道数目K,因此建立如下优化问题:In order to maximize the average effective concealment rate η between the source node and the destination node under the condition of satisfying the communication concealment constraint, and by definition, the average effective rate (Note: The solution becomes the average effective concealment rate under the condition of concealment constraints. There is no concealment constraint designed here, but only the average effective rate). We need to optimize the parameter transmission power Pa and the number of sub-channels K that the source node sends information, so establish The optimization problem is as follows:
以最大化系统平均隐蔽吞吐量为目标,系统最优的子信道数目可根据如下方程式计算得到:In order to maximize the average stealth throughput of the system, the optimal number of sub-channels in the system can be calculated according to the following equation:
其中,∈为任意小的实数,表示隐蔽通信暴露容忍值,表示监测者的最小错判概率,则描述了监测者的最小错判概率大于源节点与目的节点之间要求隐蔽的概率值(例如:暴露容忍值∈=0.05,表示源节点的通信行为需要0.95的概率不暴露),即为隐蔽约束(源节点通信行为隐蔽的、秘密的传输的要求);Pa>0约束了发送功率为正值;Kmax指子信道数目能达到的最大值,K=1,2,…,Kmax约束了子信道数目K为小于Kmax的正整数。Among them, ∈ is an arbitrarily small real number, which represents the exposure tolerance value of covert communication, represents the minimum misjudgment probability of the monitor, Then it describes that the minimum misjudgment probability of the monitor is greater than the probability value that requires concealment between the source node and the destination node (for example, the exposure tolerance value ∈ = 0.05, indicating that the communication behavior of the source node requires a probability of 0.95 not to be exposed), that is, concealment Constraints (requirements for hidden and secret transmission of source node communication behavior); Pa > 0 constrains the transmission power to be a positive value; Kmax refers to the maximum number of sub-channels that can be achieved, K=1,2,...,Kmax The number of sub-channels K is constrained to be a positive integer less than Kmax .
为了求解上述优化问题,我们需要求解监测者的最小错判概率In order to solve the above optimization problem, we need to solve the minimum misjudgment probability of the monitor
监测者在一个传输周期(一个时隙)结束时,需要判断源节点是否发送信息,则监测者面临的是一个二元判决。由于监测者受到的观测值有限(有限个信道使用),因此在判断源节点通信行为时存在判断错误并且由虚警概率和漏检概率组成。不失一般性假设,通过计算可以得到:At the end of a transmission period (one time slot), the monitor needs to judge whether the source node sends information, and the monitor is faced with a binary decision. Since the observation value received by the monitor is limited (limited channels are used), there is a judgment error when judging the communication behavior of the source node and by false alarm probability and the probability of missed detection composition. Without loss of general assumptions, It can be obtained by calculation:
其中,表示监测者平均最小错检概率;λjw表示干扰节点到监测者的平均信道增益,λaw表示源节点到监测者的平均信道增益;表示监测者接收到的噪声方差,表示每个子信道上的干扰功率。通过设置最优门限τ*得到最小的错检概率错检概率是关于τ的凸函数,可通过简单的一维搜索得到最优门限τ*。in, represents the average minimum false detection probability of the monitor; λjw represents the average channel gain from the interfering node to the monitor, and λaw represents the average channel gain from the source node to the monitor; represents the noise variance received by the monitor, represents the interference power on each subchannel. Get the minimum false detection probability by setting the optimal threshold τ* false detection probability is a convex function with respect to τ, and the optimal threshold τ* can be obtained by a simple one-dimensional search.
通过对优化问题的简单分析,我们发现随Pa的单调增加而减少,随K的单调增加而增加;平均有效隐蔽速率η随Pa的单调增加而增加,随K的单调增加而减少。因此我们可以通过二维搜索发现优化问题的解K*与Through a simple analysis of the optimization problem, we find that It decreases with the monotonic increase ofPa and increases with the monotonic increase of K; the average effective concealment rate η increases with the monotonic increase ofPa and decreases with the monotonic increase of K. So we can find the solution of the optimization problem by two-dimensional search K* and
到这里,我们可以知道源节点使用K*个子信道与的发送功率发送信息时,可以在暴露容忍度内(隐蔽)的条件下,使源节点与目的节点的传输速率最大。At this point, we can know that the source node uses K* sub-channels with When sending information with the same transmission power, the transmission rate between the source node and the destination node can be maximized under the condition of exposure tolerance (concealment).
步骤S5:信息译码:信息译码目的节点在每一个传输周期,利用其与源节点共享的码本对接收信号进行译码。Step S5: information decoding: the information decoding destination node decodes the received signal by using the codebook shared with the source node in each transmission cycle.
在每个传输周期T内,目的节点的接收信号可以表示为:In each transmission period T, the received signal of the destination node can be expressed as:
其中i=1,2,…,N表示信道使用索引;是满足均值为零、方差为λab的复高斯随机变量,代表源节点所选择的到目的节点的瞬时子信道增益;xa[i]是满足均值为零、方差为1的复高斯随机变量,代表源节点第i次信道使用时发送的符号;xj[i]是满足均值为零、方差为1的复高斯随机变量,代表干扰节点第i次信道使用时发送的符号;nb[i]是满足均值为零、方差为的复高斯随机变量,代表目的节点在源节点第i次信道使用时观测到的噪声。where i=1,2,...,N represents the channel usage index; is a complex Gaussian random variable satisfying zero mean and variance λab , representing the instantaneous sub-channel gain selected by the source node to the destination node; xa [i] is a complex Gaussian random variable satisfying zero mean and variance 1 , represents the symbol sent by the source node when the channel is used for the i-th time; xj [i] is a complex Gaussian random variable that satisfies zero mean and variance of 1, representing the symbol sent by the interfering node when the channel is used for the i-th time; nb [ i] is to satisfy that the mean is zero and the variance is is a complex Gaussian random variable representing the noise observed by the destination node when the source node uses the i-th channel.
目的节点收到隐私信息后的接收信噪比为:The received signal-to-noise ratio of the destination node after receiving the private information is:
其中是满足均值为零、方差为λjb的复高斯随机变量,代表干扰节点所选择的到目的节点的瞬时子信道增益;Pmm是满足在区间上均匀分布的随机变量,代表干扰节点在每个子信道上发送的瞬时干扰信号的功率。in is a complex Gaussian random variable with a mean value of zero and a variance of λjb , representing the instantaneous sub-channel gain selected by the interferingnode to the destination node; A random variable uniformly distributed on the , representing the instantaneous power of the interfering signal sent by the interfering node on each sub-channel.
通过中断概率的定义,可以将中断概率用数学表达式表示为:Through the definition of outage probability, the outage probability can be expressed mathematically as:
其中,R为固定的常数,表示预期通信速率;r是公式中的中间变量,求和符号的求和范围;λab表示源节点到目的节点的平均信道增益;R表示预期通信速率;λjb表示干扰节点到目的节点的平均信道增益;表示目的节点接收到的噪声方差。Among them, R is a fixed constant, indicating the expected communication rate; r is the intermediate variable in the formula, the summation range of the summation symbol; λab is the average channel gain from the source node to the destination node; R is the expected communication rate; λjb Represents the average channel gain from the interfering node to the destination node; Represents the noise variance received by the destination node.
系统的平均吞吐量可以表示为:The average throughput of the system can be expressed as:
其中,δm表示系统中断概率。Among them, δm represents the probability of system outage.
本发明的传输方法中平均隐蔽吞吐量随子信道数目的变化仿真如图2所示。其中,源节点发送功率为满足隐蔽约束的最大发送功率,平均的信道增益λaw=λab=1dB,噪声功率干扰节点发送最大功率可以从图中看出,相比单信道传输,多信道传输方案提高了系统的平均有效隐蔽速率;并且存在最优的子信道数目使得平均有效隐蔽速率最大。The simulation of the variation of the average concealed throughput with the number of sub-channels in the transmission method of the present invention is shown in FIG. 2 . Among them, the transmission power of the source node is the maximum transmission power that satisfies the concealment constraint, the average channel gain λaw =λab =1dB, the noise power Interfering node transmits maximum power It can be seen from the figure that compared with single-channel transmission, the multi-channel transmission scheme improves the average effective concealment rate of the system; and there is an optimal number of sub-channels to maximize the average effective concealment rate.
上述实施例的描述较为具体和详细,但仅仅表达了本发明的一种可行的实施方式,并非对本发明专利范围的限制。需要指出的是,本领域的科研人员和工程人员,在本发明的框架下,可以在本实施例的基础上加入若干变形或改进,但这些都在本发明专利的保护范围之内,本发明专利的保护范围以权利要求为准。The description of the above embodiment is relatively specific and detailed, but only expresses a feasible implementation manner of the present invention, and does not limit the patent scope of the present invention. It should be pointed out that, under the framework of the present invention, scientific researchers and engineers in the field can add some modifications or improvements on the basis of this embodiment, but these are all within the protection scope of the patent of the present invention. The scope of protection of a patent is subject to the claims.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210240847.1ACN114520972A (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2022-03-10 | Interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in multi-channel system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210240847.1ACN114520972A (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2022-03-10 | Interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in multi-channel system |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114520972Atrue CN114520972A (en) | 2022-05-20 |
Family
ID=81599262
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210240847.1APendingCN114520972A (en) | 2022-03-10 | 2022-03-10 | Interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in multi-channel system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114520972A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115442829A (en)* | 2022-08-29 | 2022-12-06 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Selection and transmission power optimization method for hidden communication network jammer |
| CN115460597A (en)* | 2022-09-29 | 2022-12-09 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | A short-packet covert communication method against jamming attacks based on change point detection |
| CN116506859A (en)* | 2023-06-19 | 2023-07-28 | 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院 | Lightweight cooperative hidden wireless communication detection method and system |
| CN119210609A (en)* | 2024-11-28 | 2024-12-27 | 南京邮电大学 | A method for maximizing the security rate of artificial noise-assisted covert communication systems |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016123776A1 (en)* | 2015-02-05 | 2016-08-11 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus |
| CN109302250A (en)* | 2018-09-13 | 2019-02-01 | 西安交通大学 | Relay selection and transmit power allocation method for energy transmission full-duplex relays |
| CN112383380A (en)* | 2020-10-21 | 2021-02-19 | 西安交通大学 | Covert vehicle communication method based on non-orthogonal multiple access technology |
| WO2021136070A1 (en)* | 2019-12-30 | 2021-07-08 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | Resource allocation method for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer, device, and computer |
- 2022
- 2022-03-10CNCN202210240847.1Apatent/CN114520972A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016123776A1 (en)* | 2015-02-05 | 2016-08-11 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data transmission method and apparatus |
| CN109302250A (en)* | 2018-09-13 | 2019-02-01 | 西安交通大学 | Relay selection and transmit power allocation method for energy transmission full-duplex relays |
| WO2021136070A1 (en)* | 2019-12-30 | 2021-07-08 | 三维通信股份有限公司 | Resource allocation method for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer, device, and computer |
| CN112383380A (en)* | 2020-10-21 | 2021-02-19 | 西安交通大学 | Covert vehicle communication method based on non-orthogonal multiple access technology |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| BOHAN CHE等: "Covert Communication for Multi-Channel Transmission with A Full-Duplex Receiver", 2021 13TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS AND SIGNAL PROCESSING (WCSP), 22 October 2021 (2021-10-22), pages 1 - 5, XP034032849, DOI: 10.1109/WCSP52459.2021.9613571* |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115442829A (en)* | 2022-08-29 | 2022-12-06 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Selection and transmission power optimization method for hidden communication network jammer |
| CN115442829B (en)* | 2022-08-29 | 2025-02-11 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | A method for selecting jammers and optimizing transmission power in a covert communication network |
| CN115460597A (en)* | 2022-09-29 | 2022-12-09 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | A short-packet covert communication method against jamming attacks based on change point detection |
| CN116506859A (en)* | 2023-06-19 | 2023-07-28 | 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院 | Lightweight cooperative hidden wireless communication detection method and system |
| CN116506859B (en)* | 2023-06-19 | 2023-09-05 | 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院 | Lightweight cooperative hidden wireless communication detection method and system |
| CN119210609A (en)* | 2024-11-28 | 2024-12-27 | 南京邮电大学 | A method for maximizing the security rate of artificial noise-assisted covert communication systems |
| CN119210609B (en)* | 2024-11-28 | 2025-08-26 | 南京邮电大学 | A method for maximizing security rate in artificial noise-assisted covert communication system |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114520972A (en) | Interference-assisted covert wireless communication method in multi-channel system | |
| Zhang et al. | Covert communications for STAR-RIS-assisted industrial networks with a full duplex receiver and RSMA | |
| CN112383380B (en) | Covert vehicle communication method based on non-orthogonal multiple access technology | |
| CN111328079B (en) | Multi-antenna hidden communication method for movable eavesdropper | |
| Soderi et al. | Physical layer security based on spread‐spectrum watermarking and jamming receiver | |
| CN104378757A (en) | Method for guaranteeing physical layer security in multi-relay multi-interference wiretapping network | |
| CN115665729A (en) | A method of covert transmission under joint detection environment of multiple eavesdroppers | |
| CN106068032A (en) | Power distribution method in collaborative network based on man made noise under the conditions of main channel imperfect channel estimation | |
| Ahuja et al. | Optimal green hybrid attacks in secure IoT | |
| CN116916301A (en) | Multi-antenna covert communication method based on spectrum mask | |
| CN109039412A (en) | A kind of safe transmission method of physical layer based on random wave bundle figuration | |
| Xu et al. | Covert and reliable semantic communication against cross-layer privacy inference over wireless edge networks | |
| CN114531674B (en) | A joint confidentiality and covert communication method and system based on rate division | |
| CN114520973A (en) | Method for randomly selecting single sub-channel short packet covert wireless communication | |
| Fernandez et al. | Performance analysis of physical layer security in power line communication networks | |
| Fan et al. | Security analysis of cooperative jamming in internet of things with multiple eavesdroppers | |
| Ezzati Khatab et al. | A machine learning multi-hop physical layer authentication with hardware impairments | |
| CN118075735A (en) | A method for analyzing the safe location of eavesdroppers in a channel fading environment | |
| Yu et al. | Theoretical analysis of secrecy transmission capacity in wireless ad hoc networks | |
| Chen et al. | Secure short-packet communications using a full-duplex receiver | |
| Yin et al. | Covert Communication of Active RIS-Assisted Uplink SGF-NOMA Systems | |
| CN115460597A (en) | A short-packet covert communication method against jamming attacks based on change point detection | |
| Zhao et al. | Wireless Communication Network Security System Based on Big Data Information Transmission Technology | |
| Wei et al. | Physical Layer Security Technology Based on Nonorthogonal Multiple Access Communication | |
| Sondur et al. | Secure Communication in Gaussian Multiple Access Wiretap Channels: A Deep Learning and Friendly Jamming Approach |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |