CN114520519A - Virtual inertia control method and device for photovoltaic power station - Google Patents
Virtual inertia control method and device for photovoltaic power stationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114520519A CN114520519ACN202210316576.3ACN202210316576ACN114520519ACN 114520519 ACN114520519 ACN 114520519ACN 202210316576 ACN202210316576 ACN 202210316576ACN 114520519 ACN114520519 ACN 114520519A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- energy storage
- storage battery
- inertia control
- power station
- grid
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J3/00—Circuit arrangements for AC mains or AC distribution networks
- H02J3/38—Arrangements for parallely feeding a single network by two or more generators, converters or transformers
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J3/00—Circuit arrangements for AC mains or AC distribution networks
- H02J3/24—Arrangements for preventing or reducing oscillations of power in networks
- H02J3/241—The oscillation concerning frequency
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J3/00—Circuit arrangements for AC mains or AC distribution networks
- H02J3/28—Arrangements for balancing of the load in a network by storage of energy
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J3/00—Circuit arrangements for AC mains or AC distribution networks
- H02J3/28—Arrangements for balancing of the load in a network by storage of energy
- H02J3/32—Arrangements for balancing of the load in a network by storage of energy using batteries with converting means
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J3/00—Circuit arrangements for AC mains or AC distribution networks
- H02J3/38—Arrangements for parallely feeding a single network by two or more generators, converters or transformers
- H02J3/46—Controlling of the sharing of output between the generators, converters, or transformers
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02J—CIRCUIT ARRANGEMENTS OR SYSTEMS FOR SUPPLYING OR DISTRIBUTING ELECTRIC POWER; SYSTEMS FOR STORING ELECTRIC ENERGY
- H02J2300/00—Systems for supplying or distributing electric power characterised by decentralized, dispersed, or local generation
- H02J2300/20—The dispersed energy generation being of renewable origin
- H02J2300/22—The renewable source being solar energy
- H02J2300/24—The renewable source being solar energy of photovoltaic origin
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Charge And Discharge Circuits For Batteries Or The Like (AREA)
- Supply And Distribution Of Alternating Current (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及光伏发电技术领域,具体涉及一种光伏电站虚拟惯量控制方法及装置。The invention relates to the technical field of photovoltaic power generation, in particular to a method and device for virtual inertia control of a photovoltaic power station.
背景技术Background technique
随着新能源在电网占比的增大,电网的系统惯量随之减小,无法确保电网的稳定运行。相关技术中,公开号为CN 113541173 A的发明专利申请公开了一种弱电网条件下电池储能系统集群控制装置及控制方法,包括:多功能电力表模块、工厂层控制算法模块、变流器PCS功率分配模块、PCS虚拟同步控制算法模块和Profinet通信模块。该弱电网条件下电池储能系统集群控制装置及控制方法,基于此工作模式的设置和控制算法,实现了储能变流器PCS之间功率的分配功能,该系统解决了低短路容量的弱电网条件下规模化储能系统的稳定、可靠运行问题。但其采用多功能电力表模块采集UAct、Fact、Pact、及QAct信号,存在采样速度慢,响应时间长问题,抗谐波能力不足的缺陷。As the proportion of new energy in the power grid increases, the system inertia of the power grid decreases, which cannot ensure the stable operation of the power grid. In the related art, the invention patent application with publication number CN 113541173 A discloses a battery energy storage system cluster control device and control method under weak grid conditions, including: a multi-function power meter module, a factory-level control algorithm module, a converter PCS power distribution module, PCS virtual synchronization control algorithm module and Profinet communication module. The battery energy storage system cluster control device and control method under weak grid conditions, based on the setting and control algorithm of this working mode, realizes the power distribution function between the energy storage converters PCS, and the system solves the weak current with low short-circuit capacity. Stable and reliable operation of large-scale energy storage systems under grid conditions. However, it uses a multi-function power meter module to collect UAct, Fact, Pact, and QAct signals, which has the defects of slow sampling speed, long response time and insufficient anti-harmonic ability.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明所要解决的技术问题在于提供一种利用电池储能实现光伏电站虚拟惯量控制方法和设备,以保证电网稳定运行。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a method and device for realizing virtual inertia control of a photovoltaic power station by using battery energy storage to ensure stable operation of the power grid.
本发明通过以下技术手段实现解决上述技术问题的:The present invention realizes and solves the above-mentioned technical problems through the following technical means:
一方面,本发明提出了一种光伏电站虚拟惯量控制方法,所述方法包括:In one aspect, the present invention provides a virtual inertia control method for a photovoltaic power station, the method comprising:
采集采样信息,所述采样信息包括储能电池的电气信息、储能变流器PCS的电气信息以及并网点电流和电压;collecting sampling information, where the sampling information includes electrical information of the energy storage battery, electrical information of the energy storage converter PCS, and current and voltage of the grid connection point;
根据所述并网点的电流和电压,计算所述并网点的频率差值Δf;Calculate the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point according to the current and voltage of the grid-connected point;
在所述并网点的频率差值Δf超出或低于动作死区区间值时,开启惯量控制策略,控制所述储能电池的输出功率;When the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point exceeds or is lower than the action dead zone interval value, the inertia control strategy is activated to control the output power of the energy storage battery;
其中,所述惯量控制策略为跟随所述并网点的频率差值Δf增大所述储能电池的功率输出,公式表示为:The inertia control strategy is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery, and the formula is expressed as:
ΔP=k*ΔfΔP=k*Δf
其中,k是惯量输出线性度,ΔP是所述储能电池的功率输出。Among them, k is the inertia output linearity, and ΔP is the power output of the energy storage battery.
本发明通过直接采集采样信息,并根据并网点信息计算并网点的频率差值,在并网点的频率差值Δf不在动作死区区间内时,在储能最大的容量范围和PCS可控容量情况下,启动虚拟电站惯量的策略,该策略为跟随并网点的频率差值Δf增大储能电池的功率输出;储能通过该惯量控制策略,电站在配置时间内维持原功率输出、电站虚拟惯量和电站额定功率等效,且直接采集并网点信息,采样速度快,响应时间短。The invention directly collects the sampling information, and calculates the frequency difference of the grid connection point according to the grid connection point information. When the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is not within the action dead zone, the maximum capacity range of the energy storage and the controllable capacity of the PCS are obtained. The strategy of the inertia of the virtual power station is activated, which is to increase the power output of the energy storage battery by following the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point; through the inertia control strategy of the energy storage, the power station maintains the original power output and the virtual inertia of the power station within the configured time. It is equivalent to the rated power of the power station, and directly collects the information of the grid connection point, with fast sampling speed and short response time.
进一步地,所述方法还包括:Further, the method also includes:
通过电力系统规约,实现对所述储能电池所述储能变流器PCS的遥调遥控控制。Through the power system protocol, the remote control of the energy storage battery and the energy storage converter PCS is realized.
进一步地,所述储能电池配置为光伏额定容量的20%,所述储能变流器PCS配置为运行在80%的储能容量。Further, the energy storage battery is configured to be 20% of the rated photovoltaic capacity, and the energy storage converter PCS is configured to operate at 80% of the energy storage capacity.
进一步地,所述惯量控制策略的控制周期为小于100ms。Further, the control period of the inertia control strategy is less than 100ms.
进一步地,所述方法还包括:Further, the method also includes:
在所述并网点的频率差值Δf在所述动作死区区间范围内时,则退出本次惯量控制策略。When the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is within the action dead zone range, the current inertia control strategy is exited.
此外,本发明还提出了一种光伏电站虚拟惯量控制装置,所述设备包括:储能电池、储能变流器PCS和惯量控制设备,其中,所述惯量控制设备包括:In addition, the present invention also proposes a virtual inertia control device for a photovoltaic power station. The device includes: an energy storage battery, an energy storage converter PCS, and an inertia control device, wherein the inertia control device includes:
采集模块,用于采集采样信息,所述采样信息包括储能电池的电气信息、储能变流器PCS的电气信息以及并网点电流和电压;a collection module, used for collecting sampling information, the sampling information includes electrical information of the energy storage battery, electrical information of the energy storage converter PCS, and current and voltage of the grid connection point;
计算模块,用于根据所述并网点的电流和电压,计算所述并网点的频率差值Δf;a calculation module, configured to calculate the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point according to the current and voltage of the grid-connected point;
策略控制模块,用于在所述并网点的频率差值Δf超出或低于动作死区区间值时,开启惯量控制策略,控制所述储能电池的输出功率;A strategy control module, configured to open an inertia control strategy to control the output power of the energy storage battery when the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point exceeds or falls below the action dead zone value;
其中,所述惯量控制策略为跟随所述并网点的频率差值Δf增大所述储能电池的功率输出,公式表示为:The inertia control strategy is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery, and the formula is expressed as:
ΔP=k*ΔfΔP=k*Δf
其中,k是惯量输出线性度,ΔP是所述储能电池的功率输出。Among them, k is the inertia output linearity, and ΔP is the power output of the energy storage battery.
进一步地,所述装置还包括:Further, the device also includes:
遥调遥控模块,用于通过电力系统规约,实现对所述储能电池所述储能变流器PCS的遥调遥控控制。The remote adjustment and remote control module is used for realizing the remote adjustment and remote control of the energy storage battery and the energy storage converter PCS through the power system protocol.
进一步地,所述储能电池配置为光伏额定容量的20%,所述储能变流器PCS配置为运行在80%的储能容量。Further, the energy storage battery is configured to be 20% of the rated photovoltaic capacity, and the energy storage converter PCS is configured to operate at 80% of the energy storage capacity.
进一步地,所述惯量控制策略的控制周期为小于100ms。Further, the control period of the inertia control strategy is less than 100ms.
进一步地,所述装置还包括:Further, the device also includes:
策略退出模块,用于在所述并网点的频率差值Δf在所述动作死区区间范围内时,则退出本次惯量控制策略。The strategy exit module is used to exit the inertia control strategy when the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is within the action dead zone range.
本发明的优点在于:The advantages of the present invention are:
(1)本发明通过直接采集采样信息,并根据并网点信息计算并网点的频率差值,在并网点的频率差值Δf不在动作死区区间内时,在储能最大的容量范围和PCS可控容量情况下,启动虚拟电站惯量的策略,该策略为跟随并网点的频率差值Δf增大储能电池的功率输出;储能通过该惯量控制策略,电站在配置时间内维持原功率输出、电站虚拟惯量和电站额定功率等效,且直接采集并网点信息,采样速度快,响应时间短。(1) The present invention directly collects the sampling information and calculates the frequency difference of the grid-connected point according to the grid-connected point information. When the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point is not within the action dead zone, the maximum capacity range of the energy storage and the PCS can be used. In the case of capacity control, the strategy of virtual power station inertia is activated, which is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery; The virtual inertia of the power station is equivalent to the rated power of the power station, and the grid-connected point information is directly collected, with fast sampling speed and short response time.
(2)通过设置控制周期,保证计算一次抗谐波的频率计算有效性,使得新能源场站惯量响应的快速性。(2) By setting the control period, the validity of the frequency calculation for calculating the primary anti-harmonic is ensured, so that the inertia response of the new energy station is rapid.
(3)在当前并网点的频率差值在控制死区区间内时,即使还处于控制周期内,也会提前退出惯量控制过程,以减少电网频率电压波动。(3) When the frequency difference of the current grid connection point is within the control dead zone, even if it is still in the control period, the inertia control process will be exited in advance to reduce the frequency and voltage fluctuation of the grid.
本发明附加的方面和优点将在下面的描述中部分给出,部分将从下面的描述中变得明显,或通过本发明的实践了解到。Additional aspects and advantages of the present invention will be set forth, in part, from the following description, and in part will be apparent from the following description, or may be learned by practice of the invention.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明中光伏电站虚拟惯量控制方法的流程示意图;1 is a schematic flowchart of a method for controlling virtual inertia of a photovoltaic power station according to the present invention;
图2是本发明中光伏电站虚拟惯量控制装置的结构图示意图;2 is a schematic structural diagram of a virtual inertia control device for a photovoltaic power station according to the present invention;
图3是本发明中惯量控制设备的结构示意图。FIG. 3 is a schematic structural diagram of the inertia control device in the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the purposes, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are part of the present invention. examples, but not all examples. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
参照图1,本发明一实施例提出了一种光伏电站虚拟惯量控制方法,所述方法包括以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 1 , an embodiment of the present invention proposes a method for controlling virtual inertia of a photovoltaic power station. The method includes the following steps:
S10、采集采样信息,所述采样信息包括储能电池的电气信息、储能变流器PCS的电气信息以及并网点电流和电压;S10. Collect sampling information, where the sampling information includes electrical information of the energy storage battery, electrical information of the energy storage converter PCS, and the current and voltage of the grid connection point;
需要说明的是,储能电池的电气信息包括电池的最大容量Bm,当前容量Bd,输出电流Ib等信息;PCS的电气信息包括当前额运行状态Sp,控制有功容量Pp,无功容量Qp等信息。It should be noted that the electrical information of the energy storage battery includes information such as the maximum capacity Bm of the battery, the current capacity Bd, and the output current Ib; the electrical information of the PCS includes information such as the current operating state Sp, the control active capacity Pp, and the reactive capacity Qp. .
S20、根据所述并网点的电流和电压,计算所述并网点的频率差值Δf;S20. Calculate the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point according to the current and voltage of the grid-connected point;
需要说明的是,采集的并网点的电流I和电压U,用于计算有功功率P,无功功率Q和当前实时频率F,并根据当前实时频率和电网额定频率计算并网点的频率差值,形成控制指令。It should be noted that the collected current I and voltage U of the grid-connected point are used to calculate the active power P, reactive power Q and the current real-time frequency F, and the frequency difference of the grid-connected point is calculated according to the current real-time frequency and the rated frequency of the grid, Form control instructions.
其中,Δf=f0-fmea,f0为电网额定频率,fmea为当前并网点实时频率。Among them, Δf=f0-fmea, f0 is the rated frequency of the grid, and fmea is the real-time frequency of the current grid connection point.
S30、在所述并网点的频率差值Δf超出或低于动作死区区间值时,开启惯量控制策略,控制所述储能电池的输出功率;S30. When the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point exceeds or is lower than the action dead zone interval value, turn on the inertia control strategy to control the output power of the energy storage battery;
其中,所述惯量控制策略为跟随所述并网点的频率差值Δf增大所述储能电池的功率输出,公式表示为:The inertia control strategy is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery, and the formula is expressed as:
ΔP=k*ΔfΔP=k*Δf
其中,k是惯量输出线性度,ΔP是所述储能电池的功率输出。Among them, k is the inertia output linearity, and ΔP is the power output of the energy storage battery.
需要说明的是,本实施例通过直接采集采样信息,并根据并网点信息计算并网点的频率差值,在并网点的频率差值Δf不在动作死区区间内时,在储能最大的容量范围和PCS可控容量情况下,启动虚拟电站惯量的策略,该策略为跟随并网点的频率差值Δf增大储能电池的功率输出;储能通过该惯量控制策略,电站在配置时间内维持原功率输出、电站虚拟惯量和电站额定功率等效,且直接采集并网点信息,采样速度快,响应时间短。It should be noted that, in this embodiment, by directly collecting the sampling information, and calculating the frequency difference of the grid connection point according to the grid connection point information, when the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is not within the action dead zone, the maximum energy storage capacity is within the range. In the case of the controllable capacity of the virtual power station and the PCS, the strategy of starting the inertia of the virtual power station is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery; The power output, the virtual inertia of the power station and the rated power of the power station are equivalent, and the information of the grid connection point is directly collected, with fast sampling speed and short response time.
在一实施例中,所述方法还包括:In one embodiment, the method further includes:
通过电力系统规约,实现对所述储能电池所述储能变流器PCS的遥调遥控控制。Through the power system protocol, the remote control of the energy storage battery and the energy storage converter PCS is realized.
需要说明的是,本实施例根据采样信息计算本站的控制有功,无功容量,驱动pcs和储能电池输出支持电流和电压,完成虚拟电站惯量的策略,并通过电力系统规约,实现遥调遥控控制,完成pcs和储能BMS等控制。It should be noted that this embodiment calculates the control active power and reactive power capacity of the station according to the sampling information, drives the pcs and the energy storage battery to output the supporting current and voltage, completes the strategy of the inertia of the virtual power station, and realizes the remote adjustment through the power system protocol. Remote control, complete control of pcs and energy storage BMS.
应当理解的是,电力系统规约包括goose,104,modbus等规约,统一光伏电站数据格式,保证网络信息交换的准确快速。It should be understood that the power system protocols include goose, 104, modbus and other protocols, which unify the data format of photovoltaic power plants and ensure the accuracy and speed of network information exchange.
在一实施例中,所述储能电池配置为光伏额定容量的20%,所述储能变流器PCS配置为运行在80%的储能容量。In one embodiment, the energy storage battery is configured to operate at 20% of the photovoltaic rated capacity and the energy storage converter PCS is configured to operate at 80% of the energy storage capacity.
需要说明的是,在光伏电站配置光伏额定容量20%的电化学储能容量,配置PCS具有双向转换能力,正常运行在80%储能容量,以保证具备提供短时间有功输出,和空余容量来吸收有功的能力。It should be noted that the photovoltaic power station is equipped with an electrochemical energy storage capacity of 20% of the rated photovoltaic capacity, and the PCS is equipped with a bidirectional conversion capability, and the normal operation is at 80% of the energy storage capacity to ensure that it can provide short-term active power output and spare capacity. Ability to absorb active work.
在一实施例中,所述惯量控制策略的控制周期为小于100ms。In one embodiment, the control period of the inertia control strategy is less than 100ms.
需要说明的是,虚拟惯量采用整组控制策略,每组惯量控制在100ms以内,100ms计算一次当前频率,100ms计算周期保证计算一次抗谐波的频率计算有效性,通过设置控制周期为100ms,可以保证控制时效性,使得新能源场站惯量响应的快速性。It should be noted that the virtual inertia adopts a whole group of control strategies. Each group of inertia is controlled within 100ms. The current frequency is calculated once every 100ms. Ensure the control timeliness, making the inertia response of the new energy station fast.
在一实施例中,所述方法还包括:In one embodiment, the method further includes:
在所述并网点的频率差值Δf在所述动作死区区间范围内时,则退出本次惯量控制策略。When the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is within the action dead zone range, the current inertia control strategy is exited.
需要说明的是,在当前频率在动作死区区间范围内时,即便处在控制周期内,也提前退出惯量控制,以减少电网频率电压波动。It should be noted that when the current frequency is within the action dead zone range, even if it is within the control cycle, the inertia control is exited in advance to reduce the grid frequency and voltage fluctuations.
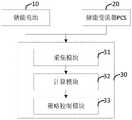
此外,参照图2至图3所示,本发明另一实施例提出了一种光伏电站虚拟惯量控制装置,所述装置包括储能电池10、储能变流器PCS20和惯量控制设备30,其中,所述惯量控制设备30包括:In addition, as shown in FIGS. 2 to 3 , another embodiment of the present invention provides a virtual inertia control device for a photovoltaic power station, the device includes an
采集模块31,用于采集采样信息,所述采样信息包括储能电池的电气信息、储能变流器PCS的电气信息以及并网点电流和电压;The
计算模块32,用于根据所述并网点的电流和电压,计算所述并网点的频率差值Δf;a
策略控制模块33,用于在所述并网点的频率差值Δf超出或低于动作死区区间值时,开启惯量控制策略,控制所述储能电池的输出功率;The
其中,所述惯量控制策略为跟随所述并网点的频率差值Δf增大所述储能电池的功率输出,公式表示为:The inertia control strategy is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery, and the formula is expressed as:
ΔP=k*ΔfΔP=k*Δf
其中,k是惯量输出线性度,ΔP是所述储能电池的功率输出。Among them, k is the inertia output linearity, and ΔP is the power output of the energy storage battery.
需要说明的是,采集模块31具体采用模拟量采样电路,用于采集并网点电流、电压,储能电池和PCS的电气信息。It should be noted that the
具体地,所述惯量控制设备还包括:Specifically, the inertia control device further includes:
开入开出电路:用于采集控制开关量信息,闭锁信号等输入,输出自身控制信息。Open-in-open-out circuit: used to collect control switch information, blocking signal and other inputs, and output its own control information.
对下光纤/网口/串口等通讯通道:用于根据核心运算单元计算的结果,通过goose,104,modbus等电力系统规约,实现遥调遥控控制,完成pcs和储能BMS等控制。For communication channels such as optical fiber/network port/serial port: It is used to realize remote adjustment and remote control through power system protocols such as goose, 104, and modbus according to the calculation result of the core operation unit, and complete the control of pcs and energy storage BMS.
模拟量输出电路:用于提供4-20ma等输出接口,用于匹配现场控制设备。Analog output circuit: used to provide 4-20ma and other output interfaces for matching on-site control equipment.
进一步地,所述惯量控制设备还包括人机交互模块,用于实现人机交互,完成状态显示,本地控制设置等操作。Further, the inertia control device further includes a human-computer interaction module, which is used to realize human-computer interaction, complete state display, local control settings and other operations.
本实施例通过直接采集采样信息,并根据并网点信息计算并网点的频率差值,在并网点的频率差值Δf不在动作死区区间内时,在储能最大的容量范围和PCS可控容量情况下,启动虚拟电站惯量的策略,该策略为跟随并网点的频率差值Δf增大储能电池的功率输出;储能通过该惯量控制策略,电站在配置时间内维持原功率输出、电站虚拟惯量和电站额定功率等效,且直接采集并网点信息,采样速度快,响应时间短。In this embodiment, the sampling information is directly collected, and the frequency difference of the grid connection point is calculated according to the grid connection point information. When the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is not within the action dead zone, the maximum capacity range of the energy storage and the controllable capacity of the PCS are obtained. In this case, start the strategy of virtual power station inertia, which is to follow the frequency difference Δf of the grid-connected point to increase the power output of the energy storage battery; The inertia is equivalent to the rated power of the power station, and the grid-connected point information is directly collected, with fast sampling speed and short response time.
在一实施例中,所述装置还包括:In one embodiment, the apparatus further includes:
遥调遥控模块,用于通过电力系统规约,实现对所述储能电池所述储能变流器PCS的遥调遥控控制。The remote adjustment and remote control module is used for realizing the remote adjustment and remote control of the energy storage battery and the energy storage converter PCS through the power system protocol.
在一实施例中,所述储能电池配置为光伏额定容量的20%,所述储能变流器PCS配置为运行在80%的储能容量。In one embodiment, the energy storage battery is configured to operate at 20% of the photovoltaic rated capacity and the energy storage converter PCS is configured to operate at 80% of the energy storage capacity.
在一实施例中,所述惯量控制策略的控制周期为小于100ms。In one embodiment, the control period of the inertia control strategy is less than 100ms.
在一实施例中,所述装置还包括:In one embodiment, the apparatus further includes:
策略退出模块,用于在所述并网点的频率差值Δf在所述动作死区区间范围内时,则退出本次惯量控制策略。The strategy exit module is used to exit the inertia control strategy when the frequency difference Δf of the grid connection point is within the action dead zone range.
需要说明的是,本发明所述光伏电站虚拟惯量控制装置的其他实施例或具有实现方法可参照上述各方法实施例,此处不再赘余。It should be noted that, for other embodiments of the virtual inertia control device for a photovoltaic power station according to the present invention or having an implementation method, reference may be made to the above method embodiments, and details are not repeated here.
在本说明书的描述中,参考术语“一个实施例”、“一些实施例”、“示例”、“具体示例”、或“一些示例”等的描述意指结合该实施例或示例描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点包含于本发明的至少一个实施例或示例中。在本说明书中,对上述术语的示意性表述不一定指的是相同的实施例或示例。而且,描述的具体特征、结构、材料或者特点可以在任何的一个或多个实施例或示例中以合适的方式结合。In the description of this specification, description with reference to the terms "one embodiment," "some embodiments," "example," "specific example," or "some examples", etc., mean specific features described in connection with the embodiment or example , structure, material or feature is included in at least one embodiment or example of the present invention. In this specification, schematic representations of the above terms do not necessarily refer to the same embodiment or example. Furthermore, the particular features, structures, materials or characteristics described may be combined in any suitable manner in any one or more embodiments or examples.
此外,术语“第一”、“第二”仅用于描述目的,而不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性或者隐含指明所指示的技术特征的数量。由此,限定有“第一”、“第二”的特征可以明示或者隐含地包括至少一个该特征。在本发明的描述中,“多个”的含义是至少两个,例如两个,三个等,除非另有明确具体的限定。In addition, the terms "first" and "second" are only used for descriptive purposes, and should not be construed as indicating or implying relative importance or implying the number of indicated technical features. Thus, a feature delimited with "first", "second" may expressly or implicitly include at least one of that feature. In the description of the present invention, "plurality" means at least two, such as two, three, etc., unless otherwise expressly and specifically defined.
尽管上面已经示出和描述了本发明的实施例,可以理解的是,上述实施例是示例性的,不能理解为对本发明的限制,本领域的普通技术人员在本发明的范围内可以对上述实施例进行变化、修改、替换和变型。Although the embodiments of the present invention have been shown and described above, it should be understood that the above embodiments are exemplary and should not be construed as limiting the present invention. Embodiments are subject to variations, modifications, substitutions and variations.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210316576.3ACN114520519A (en) | 2022-03-29 | 2022-03-29 | Virtual inertia control method and device for photovoltaic power station |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210316576.3ACN114520519A (en) | 2022-03-29 | 2022-03-29 | Virtual inertia control method and device for photovoltaic power station |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114520519Atrue CN114520519A (en) | 2022-05-20 |
Family
ID=81600347
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210316576.3APendingCN114520519A (en) | 2022-03-29 | 2022-03-29 | Virtual inertia control method and device for photovoltaic power station |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114520519A (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108599241A (en)* | 2018-04-28 | 2018-09-28 | 华北电力科学研究院有限责任公司 | Photovoltaic virtual synchronous machine primary frequency modulation control method and equipment |
| WO2020098242A1 (en)* | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | Photovoltaic power generation system and control method therefor |
| CN113224843A (en)* | 2021-05-17 | 2021-08-06 | 北京中泰华电科技有限公司 | Active support type wind-solar-storage integrated power control system and energy distribution method thereof |
| CN113890085A (en)* | 2021-09-09 | 2022-01-04 | 华中科技大学 | Non-communication distributed frequency supporting method and system for photovoltaic power station |
| CN114172199A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-11 | 国网辽宁省电力有限公司阜新供电公司 | Method for realizing frequency modulation and virtual inertia response by using energy storage wind power integrated unit |
- 2022
- 2022-03-29CNCN202210316576.3Apatent/CN114520519A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108599241A (en)* | 2018-04-28 | 2018-09-28 | 华北电力科学研究院有限责任公司 | Photovoltaic virtual synchronous machine primary frequency modulation control method and equipment |
| WO2020098242A1 (en)* | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-22 | 华为技术有限公司 | Photovoltaic power generation system and control method therefor |
| CN113224843A (en)* | 2021-05-17 | 2021-08-06 | 北京中泰华电科技有限公司 | Active support type wind-solar-storage integrated power control system and energy distribution method thereof |
| CN113890085A (en)* | 2021-09-09 | 2022-01-04 | 华中科技大学 | Non-communication distributed frequency supporting method and system for photovoltaic power station |
| CN114172199A (en)* | 2021-12-08 | 2022-03-11 | 国网辽宁省电力有限公司阜新供电公司 | Method for realizing frequency modulation and virtual inertia response by using energy storage wind power integrated unit |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108242819B (en) | Measurement and control device, system and method for wind farm | |
| CN102368620B (en) | Wind-energy/ solar-energy/ storage/ ocean-current-energy new-energy isolated network stabilization operation integration control system and method thereof | |
| CN102299520B (en) | Reactive power compensation method and system for micro power grid | |
| CN113949075B (en) | A new energy grid source coordinated frequency modulation and inertia support online monitoring and analysis system and method | |
| CN116388334B (en) | Reconfigurable battery energy storage system | |
| CN111030195B (en) | Control method, device and storage device for energy storage system to participate in grid power frequency regulation | |
| CN216312687U (en) | Photovoltaic energy storage direct current intelligent micro-grid monitoring management system | |
| CN104569691B (en) | The parameter detection method and system of polymorphic type energy-storage system | |
| CN114430170A (en) | Optimization control method and system for AVC system of energy storage power station | |
| CN114725929A (en) | Energy management control method and system for wind-solar energy storage micro-grid system | |
| CN116470527A (en) | Wind power plant frequency response control method and system for avoiding frequency secondary drop | |
| CN114144970B (en) | power conversion device | |
| CN114520519A (en) | Virtual inertia control method and device for photovoltaic power station | |
| KR20190064354A (en) | Remote controlling system for energy storage | |
| Fang et al. | Stability Analysis of Grid-forming and Grid-following VSCs in Parallel Connected to Weak Grid | |
| CN114123237B (en) | Cloud-edge collaborative thermal power and new energy frequency regulation, inertia online monitoring system and method | |
| CN214124859U (en) | Battery management system for lithium battery | |
| CN201699416U (en) | A megawatt-level wind power battery combined independent power system | |
| CN206096260U (en) | Little electric wire netting on -line monitoring system | |
| CN115566708A (en) | A flywheel lithium battery hybrid energy storage capacity configuration method and system | |
| CN206162121U (en) | Little load of power grid controller | |
| CN115173446A (en) | Electrochemical energy storage system and centralized control device | |
| CN117277356B (en) | Wind power plant using box transformer measurement and control primary frequency modulation response and related method | |
| CN222169333U (en) | Grid-connected energy storage system | |
| CN222976952U (en) | Control system of wind driven generator |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |