CN114470523A - A plastic magnetic stimulator - Google Patents
A plastic magnetic stimulatorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114470523A CN114470523ACN202111538311.XACN202111538311ACN114470523ACN 114470523 ACN114470523 ACN 114470523ACN 202111538311 ACN202111538311 ACN 202111538311ACN 114470523 ACN114470523 ACN 114470523A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- muscle
- magnetic
- stimulation
- state
- coil
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N2/00—Magnetotherapy
- A61N2/004—Magnetotherapy specially adapted for a specific therapy
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/22—Ergometry; Measuring muscular strength or the force of a muscular blow
- A61B5/224—Measuring muscular strength
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/389—Electromyography [EMG]
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/45—For evaluating or diagnosing the musculoskeletal system or teeth
- A61B5/4519—Muscles
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61N—ELECTROTHERAPY; MAGNETOTHERAPY; RADIATION THERAPY; ULTRASOUND THERAPY
- A61N2/00—Magnetotherapy
- A61N2/02—Magnetotherapy using magnetic fields produced by coils, including single turn loops or electromagnets
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Radiology & Medical Imaging (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Magnetic Treatment Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及塑形磁技术领域,尤其涉及一种实时监测刺激肌肉状态并自适应调节刺激强度的塑形磁刺激仪。The invention relates to the technical field of shaping magnetism, in particular to a shaping magnetic stimulator which can monitor the state of a stimulated muscle in real time and adjust the stimulation intensity adaptively.
背景技术Background technique
目前主流的塑形技术包括药物治疗、电刺激、磁刺激。其中药物治疗因为较强的副作用越来越引起人们的警惕,而近年来兴起的电刺激和磁刺激技术因为其效果明显且见效快而越来越受到推崇。The current mainstream shaping techniques include drug therapy, electrical stimulation, and magnetic stimulation. Among them, drug therapy has attracted more and more people's vigilance because of its strong side effects. In recent years, the electric stimulation and magnetic stimulation technology that has emerged in recent years has been more and more respected because of its obvious effect and quick effect.
相比于目前使用较多的电刺激塑形技术,磁刺激塑形技术有以下三个方面的优势:1、刺激没有电流密度十分集中的区域,因此受试者无疼痛感;2、肌肉、骨骼等不良导体对磁脉冲进入人体没有衰减作用,因此磁刺激可以达到深部组织,特别是塑形磁刺激用户目标部位通常有较厚的脂肪层,对电流的衰减作用十分大,而磁刺激可以透过脂肪层直达目标肌肉,达到更好的塑形效果;3、磁刺激的操纵十分简单,只需将刺激线圈放在目标刺激部位旁边,中间可以有各种衣服,线圈位置方便改变。Compared with the current electric stimulation shaping technology, the magnetic stimulation shaping technology has the following three advantages: 1. The stimulation does not have a very concentrated area of current density, so the subjects have no pain; 2. Muscle, Bad conductors such as bones have no attenuation effect on the magnetic pulse entering the human body, so the magnetic stimulation can reach deep tissues, especially the target part of the shaping magnetic stimulation user usually has a thicker fat layer, which has a great attenuation effect on the current, while the magnetic stimulation can It can reach the target muscle directly through the fat layer to achieve better shaping effect; 3. The operation of magnetic stimulation is very simple, just place the stimulation coil next to the target stimulation site, there can be various clothes in the middle, and the position of the coil can be easily changed.
但是,目前磁刺激塑形领域还没有实时监测刺激肌肉状态的技术方案,处于“盲刺”的阶段,对于刺激部位的准确性和效果完全靠用户的口头反馈,无可量化的指标用来指示肌肉是否进入最大收缩状态、以及治疗过程中肌肉是否进入疲劳状态。因此治疗过程中耐受强度均是依靠询问用户体验感或者是全部调节强度至最大,无法确保每次都达到肌肉最大收缩状态,也就无法确保每次治疗效果最大化,并且无法针对治疗过程中用户可能出现的肌肉疲劳状态来调节强度,因此治疗过后,用户会普遍出现肌肉酸痛。However, at present, there is no technical solution for real-time monitoring of the state of stimulated muscles in the field of magnetic stimulation and shaping, and it is in the stage of "blind stab". The accuracy and effect of the stimulation site are completely dependent on the user's oral feedback, and there is no quantifiable index to indicate. Whether the muscle has entered a state of maximum contraction, and whether the muscle has entered a state of fatigue during the treatment. Therefore, the tolerance intensity during the treatment process depends on asking the user's experience or adjusting the intensity to the maximum. It is impossible to ensure that the maximum muscle contraction state is reached every time, and it is impossible to ensure the maximum effect of each treatment. The user may have muscle fatigue to adjust the intensity, so after the treatment, the user will generally experience muscle soreness.
为解决上述问题,本发明公开了一种实时监测刺激肌肉状态并自适应调节刺激强度的塑形磁刺激仪。In order to solve the above problems, the present invention discloses a shaping magnetic stimulator that monitors the state of the stimulated muscles in real time and adaptively adjusts the stimulation intensity.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于提供一种塑形磁刺激仪,相比于现有的自适应调节磁刺激强度,本发明提出自适应调节磁刺激强度的算法不需要使用神经网络、深度学习等非解析类方法建模,不需要前期花费大量资源训练模型拟合参数,采用临床经验总结出的计算方法,成本大幅降低,更加简洁、更为直观、能很好的提高塑形效果。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a shaping magnetic stimulator. Compared with the existing self-adaptive adjustment of magnetic stimulation intensity, the algorithm proposed by the present invention for self-adaptive adjustment of magnetic stimulation intensity does not require the use of non-analytical methods such as neural networks and deep learning. Method modeling does not require a large amount of resources to train the model fitting parameters in the early stage, and the calculation method summed up by clinical experience is used, which greatly reduces the cost, is more concise, more intuitive, and can improve the shaping effect.
为实现上述目的,本发明的技术方案如下:For achieving the above object, technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
作为本发明公开了一种塑形磁刺激仪,包括控制运算模块,与所述控制运算模块输入端相连的肌肉状态监测模块,以及与所述控制运算模块输出端相连的刺激线圈;The present invention discloses a shaping magnetic stimulator, comprising a control arithmetic module, a muscle state monitoring module connected to the input end of the control arithmetic module, and a stimulation coil connected to the output end of the control arithmetic module;
所述刺激线圈为跑道型线圈结构,用于对目标肌肉发送磁脉冲;所述肌肉状态监测模块在磁脉冲刺激下实时采集肌肉状态值;The stimulation coil is a track-type coil structure, and is used for sending magnetic pulses to the target muscle; the muscle state monitoring module collects muscle state values in real time under the stimulation of the magnetic pulse;
所述控制运算模块用于接收肌肉状态值并将肌肉状态值运算成肌力特征值,通过调节磁刺激强度,根据肌力特征值的变化与目标肌肉收缩状态的理论关系自适应调节磁刺激强度,刺激线圈根据控制运算模块更新后的磁脉冲刺激参数作用于目标肌肉。The control computing module is used to receive the muscle state value and calculate the muscle state value into a muscle strength characteristic value, and adjust the magnetic stimulation intensity adaptively according to the theoretical relationship between the change of the muscle strength characteristic value and the target muscle contraction state by adjusting the magnetic stimulation intensity. , the stimulation coil acts on the target muscle according to the magnetic pulse stimulation parameters updated by the control operation module.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益效果包括:Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of the present invention include:
刺激线圈采用弧形跑道绕制,根据不同体型及磁刺激强度的需求选择相对应的刺激面,实现更好的磁刺激效果;The stimulation coil is wound by an arc-shaped track, and the corresponding stimulation surface is selected according to the needs of different body shapes and magnetic stimulation strengths to achieve better magnetic stimulation effects;
在刺激线圈基础上新增肌肉状态监测设计,采用包括但不限于压力信号、肌电信号、图像信号等方式,达成磁刺激过程中实时监测肌肉状态的目的;On the basis of the stimulation coil, a new muscle state monitoring design is added, including but not limited to pressure signals, EMG signals, image signals, etc., to achieve the purpose of real-time monitoring of muscle state during the magnetic stimulation process;
根据肌肉收缩过程中的肌力特征值,能够更直观地评估指示磁场强度是否引起肌肉最大收缩,保证每一次治疗效果最大化;According to the muscle strength characteristic value in the process of muscle contraction, it can more intuitively evaluate whether the indicated magnetic field strength causes the maximum muscle contraction, so as to ensure the maximum effect of each treatment;
在治疗过程中,评估并指示用户是否进入肌肉疲劳状态,同时可结合肌肉疲劳度适当调节刺激强度,保证疗效的基础上,减少肌肉酸痛感,提高治疗体验。During the treatment process, assess and indicate whether the user is in a state of muscle fatigue. At the same time, the stimulation intensity can be adjusted appropriately according to the degree of muscle fatigue, so as to reduce muscle soreness and improve the treatment experience on the basis of ensuring the curative effect.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例的技术方案,下面将对实施例描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例。其中:In order to illustrate the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention more clearly, the following briefly introduces the drawings used in the description of the embodiments. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present invention. in:
图1为本发明实施例塑形磁刺激仪的结构示意图;1 is a schematic structural diagram of a shaping magnetic stimulator according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明实施例塑形磁刺激仪的原理框图;Fig. 2 is the principle block diagram of the shaping magnetic stimulator according to the embodiment of the present invention;
图3为本发明实施例刺激线圈与现有圆形线圈的结构对比图;3 is a structural comparison diagram of a stimulation coil according to an embodiment of the present invention and an existing circular coil;
图4为本发明实施例刺激线圈与现有圆形线圈X轴磁场变化对比图;4 is a comparison diagram of the X-axis magnetic field change of the stimulation coil according to the embodiment of the present invention and the existing circular coil;
图5为本发明实施例刺激线圈与现有圆形线圈Y轴磁场变化对比图;FIG. 5 is a comparison diagram of the Y-axis magnetic field change of the stimulation coil according to the embodiment of the present invention and the existing circular coil;
图6为本发明实施例刺激线圈的结构示意图;6 is a schematic structural diagram of a stimulation coil according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图7为本发明实施例刺激线圈凹面磁场分布图;Fig. 7 is the magnetic field distribution diagram of the concave surface of the stimulation coil according to the embodiment of the present invention;
图8为本发明实施例刺激线圈凸面磁场分布图;Fig. 8 is the magnetic field distribution diagram of the convex surface of the stimulation coil according to the embodiment of the present invention;
图9为本发明实施例刺激线圈为弧形结构的磁场聚焦示意图;9 is a schematic diagram of magnetic field focusing in which the stimulation coil is an arc structure according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图10为本发明实施例肌肉状态监测模块与刺激线圈的位置关系图;FIG. 10 is a positional relationship diagram of a muscle state monitoring module and a stimulation coil according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图11为本发明实施例塑形磁刺激仪的工作流程图;Fig. 11 is the working flow chart of the shaping magnetic stimulator according to the embodiment of the present invention;
图12为本发明实施例塑形磁刺激仪自适应调节磁刺激强度的流程图;FIG. 12 is a flow chart of adaptively adjusting the magnetic stimulation intensity of the shaping magnetic stimulator according to the embodiment of the present invention;
图13为本发明实施例塑形磁刺激过程中肌力波形图;13 is a waveform diagram of muscle strength during the shaping magnetic stimulation process according to the embodiment of the present invention;
图14为本发明实施例塑形磁刺激过程中肌力特征值图;14 is a graph of muscle strength characteristic values in the process of shaping magnetic stimulation according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图中,1-刺激线圈;101-跑道型线圈,102-中空跑道型线圈,103-圆形线圈;2-肌肉状态监测模块;3-控制运算模块;4-可视化终端;5-目标肌肉。In the figure, 1-stimulation coil; 101-track-type coil, 102-hollow track-type coil, 103-circular coil; 2-muscle state monitoring module; 3-control operation module; 4-visualization terminal; 5-target muscle.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和实施例对本发明的技术方案做进一步的详细说明。The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
如图1和图2所示,本发明实施例公开了一种塑形磁刺激仪,包括肌肉状态监测模块2、控制运算模块3、通信模块、可视化终端4和刺激线圈1;其中刺激线圈1为跑道型绕制,肌肉状态监测模块2用于实时采集磁刺激状态下的肌肉状态值;控制运算模块3的输入端与肌肉状态监测模块2相连,用于接收肌肉状态监测模块2采集的肌肉状态值并转成肌力特征值,通过调节磁刺激强度,根据肌力特征值的变化与目标肌肉收缩状态的理论关系自适应调节磁刺激强度;控制运算模块3的输出端与刺激线圈1相连,刺激线圈1根据控制运算模块3发送的电磁波刺激参数作用于目标肌肉。As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, an embodiment of the present invention discloses a shaping magnetic stimulator, including a muscle
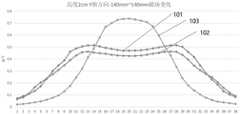
图3至图5示出本发明实施例现有圆形线圈103,跑道型线圈101与中空跑道型线圈102 的结构示意图及磁场分布情况,具体的中空跑道型线圈102与跑道型线圈101的结构区别在于线圈只沿跑道两侧绕制。以高度2cmX轴方向和Y轴方向-140mm至+140mm磁场变化显示,圆形线圈103的磁场分布尖而窄,跑道型线圈101的磁场分布扁而宽,中空跑道型线圈102的磁场分布相比较跑道型线圈略窄,但比现有的圆形线圈103的磁场分布宽。因此,跑道型线圈101与中空跑道型线圈102的结构设计均能实现更宽的磁场分布。3 to 5 show the structure schematic diagram and magnetic field distribution of the conventional
如图6至图8所示,针对不同体型采用同样的磁场对于体型偏瘦者的刺激面太大,对于体型偏胖者刺激面太小。为适应不同体型的用户,本发明进一步将跑道绕制的刺激线圈1设计成弧形结构,正反两个刺激面的磁刺激强度及磁场分布均不同。弧形结构的跑道型线圈或中空跑道型线圈凹面刺激面广,磁场分布宽而广,如图7两侧颜色较深的区域所示,主要集中在刺激线圈的两端部位置;而凸面刺激面窄,如图8中间区域所示,主要集中在刺激线圈的中部,磁场强度高,具有聚磁效果。As shown in Fig. 6 to Fig. 8 , using the same magnetic field for different body types has too much stimulation surface for thin people, and too small stimulation surface for obese people. In order to adapt to users of different body shapes, the present invention further designs the
在实际应用中,当作用于腹部肌肉时,由于分娩或其他原因导致腹直肌分离,采用凹面刺激面进行刺激时,位于腹白线处无肌肉,无需进行磁刺激,磁场主要集中在腹白线两侧的肌肉,从而实现更好的治疗效果。因此,弧形结构跑道型线圈或弧形结构中空跑道型线圈可针对用户对磁刺激强度及用户体型需求选择使用刺激线圈的凸面或凹面作用于目标肌肉,保证更好的磁刺激效果。In practical applications, when acting on the abdominal muscles, the rectus abdominis is separated due to childbirth or other reasons. When the concave stimulation surface is used for stimulation, there is no muscle located at the linea alba, and no magnetic stimulation is required. The magnetic field is mainly concentrated in the white line of the abdomen Muscles on both sides of the line for better treatment results. Therefore, the arc-shaped track-shaped coil or the arc-shaped hollow track-shaped coil can choose to use the convex or concave surface of the stimulation coil to act on the target muscle according to the user's demand for magnetic stimulation intensity and user body shape, so as to ensure a better magnetic stimulation effect.
由图9所示,平面线圈两面的磁场分布相同,但当平面线圈压制成弧形,其凹面的磁场分布即发生变化,根据麦克斯韦方程Γ为曲面Ω的边界,J为传导电流密度矢量,为位移电流密度(A/m2),D为电通密度(C/m2),同一个线圈等式右边一样,左边dL减少H就会变大,对于线圈边缘参考B至刺激点的距离大于线圈边缘参考 A,进一步证实弧形结构的刺激线圈的凹面具有聚磁效果。As shown in Figure 9, the magnetic field distribution on both sides of the planar coil is the same, but when the planar coil is pressed into an arc shape, the magnetic field distribution on the concave surface changes. According to Maxwell's equation Γ is the boundary of the surface Ω, J is the conduction current density vector, is the displacement current density (A/m2), D is the electric flux density (C/m2), the same as the right side of the same coil equation, the left dL decreases H will become larger, for the coil edge, the distance from B to the stimulation point is greater than the coil Refer to A for the edge, which further confirms that the concave surface of the stimulation coil of the arc-shaped structure has a magnetic concentrating effect.
在一实施例中,跑道型线圈101或中空跑道型线圈102的内径尺寸为30*50~80*100mm,外径尺寸为80*100~200*220mm,线圈的圈数根据性能指标具体定制,采用编制铜线制作、铜线与铜线之间采用环氧树脂灌封粘接。在跑道型线圈101或中空跑道型线圈102的基础上进行弧度处理,形成凹刺激面和凸刺激面两个不同磁刺激强度的刺激面,即可满足不同体型人群的磁刺激需求。In one embodiment, the inner diameter of the
进一步说明,肌肉状态监测模块2用于实时采集磁刺激目标肌肉5收缩状态,采集的信号可以为皮肤表面肌电信号,或使用压力传感器和流体装置采集的压力信号,或基于机械波 (频率在10Hz~1010Hz)或电磁波(频率在10Hz~1020Hz)的采集的皮肤表面图像信号,从而实现实时监测目标肌肉状态的目的。Further description, the muscle
在一实施例中,如图10所示,肌肉状态监测模块2包括流体结构及安装在流体结构内的压力传感器,流体结构安装在刺激线圈1的正反刺激面上,如气囊机构,其内填充有气体或液体,当刺激线圈1磁刺激目标肌肉,压力传感器采集目标肌肉在被磁刺激时形变引起气体或液体变化的压力信号,即为肌肉状态值或肌力值。In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 , the muscle
或者,肌肉状态监测模块2还可为贴于目标肌肉5对应部位的采集电极,刺激线圈1磁刺激目标肌肉时,电流经过神经通路传递到目标肌肉,目标肌肉5产生动作即可采集到皮肤表面肌电信号。基于采集到的肌电信号转化成肌力特征值,在通过调节磁刺激强度,通过肌力特征值的变化情况,自适应的调节磁刺激强度。Alternatively, the muscle
或者,肌肉状态监测模块2还可采用红外传感器、激光传感器或超声波传感器等采集目标肌肉产生形变的图像信号,如超声成像、可见光成像、红外、微波成像、X线成像、X-CT成像、磁共振成像、核素成像、分子成像等。同样,基于图像信号转化成肌力特征值。Alternatively, the muscle
控制运算模块3包括信号处理单元和单片机,信号处理单元用于对肌肉状态监测模块2 采集的信号进行处理,消除信号中的噪声和干扰,将肌电信号或压力信号或图像信号变换成单片机容易处理和识别的肌力特征值;单片机接收、储存、并处理肌力特征值,实现强度自适应调节算法,根据肌力特征值计算出实时最优刺激强度,并传递磁刺激参数和用户状态给可视化终端4;单片机已实现但不限于STM32、GD32。The
根据肌肉收缩过程中的肌电特征值,能够更直观地评估指示磁场强度是否引起肌肉最大收缩,保证每一次治疗效果最大化。本发明的肌力特征值为脉冲持续时间内所有肌肉状态值的平均值、中位数、平均振幅值、积分肌电值、均方根平均功率频率值、中位频率值、信号上升或下降通过零线的比率、协同收缩率的一种或多种组合计算而成。通常情况下,肌力特征值为磁脉冲持续时间内所有肌肉状态值,即肌力值的平均值,或平均值与中位数或平均振幅值或其他的结合运算。According to the EMG characteristic value in the process of muscle contraction, it is possible to more intuitively evaluate whether the indicated magnetic field strength causes the maximum contraction of the muscle, so as to ensure the maximum effect of each treatment. The muscle strength characteristic value of the present invention is the average value, median value, average amplitude value, integral EMG value, RMS average power frequency value, median frequency value, signal rise or fall of all muscle state values within the pulse duration Calculated by one or more combinations of the ratio of the zero line and the synergistic shrinkage rate. Usually, the muscle strength characteristic value is the average value of all muscle state values during the duration of the magnetic pulse, that is, the average value of the muscle strength value, or the combination of the average value and the median or average amplitude value or others.
通信模块用于连接单片机、可视化终端4和刺激线圈1。目前可实现有线(包括但不限于STD和CAMAC总线、ISA总线、VXI总线、PCI、Compact及PXI总线、RS-232C、RS-422A、 RS-485、USB、IEEE-1943、IEEE488、SCSI总线、MXI总线)和无线(包括但不限于自定义协议、IEEE802.15.4协议、ZigBee协议、蓝牙协议、LoRa以及UWB通信方式)的方式连接。The communication module is used to connect the single chip microcomputer, the
可视化终端4用于图形化显示实时肌力曲线、肌肉收缩时的肌力特征值、磁刺激参数等。The
刺激线圈1根据单片机发射的磁脉冲刺激参数作用于目标肌肉、神经肌肉或肌纤维,以达到塑形效果。刺激线圈1将磁脉冲刺激作用于人体目标肌肉,包括磁刺激频率、强度、脉冲数、间隔、时长等参数。The
但在塑形过程中,磁刺激强度过低,目标肌群无法实现最大收缩,则达不到较好的塑形效果;磁刺激强度过高,导致用户进入疲劳状态,则可能产生痛感,甚至肌肉痉挛。因此,自动找到最适合用户的磁刺激强度对于提高治疗效果和提高体验至关重要。However, during the shaping process, if the magnetic stimulation intensity is too low, the target muscle group cannot achieve the maximum contraction, and a good shaping effect cannot be achieved; if the magnetic stimulation intensity is too high, the user may enter a state of fatigue, which may cause pain, or even Muscle spasms. Therefore, automatically finding the most suitable magnetic stimulation intensity for the user is crucial to improve the therapeutic effect and enhance the experience.
为解决这一问题,作为本发明的一实施例,实时采集磁刺激状态下的肌力特征值P(t),调节磁刺激强度,根据临床实验肌力特征值与肌肉收缩状态的理论关系自适应调节刺激强度,从而使得用户在每一时刻都能接收到最合适当前肌力的磁刺激强度,提高治疗效果。In order to solve this problem, as an embodiment of the present invention, the muscle strength characteristic value P(t) under the magnetic stimulation state is collected in real time, and the magnetic stimulation intensity is adjusted. According to the theoretical relationship between the muscle strength characteristic value and the muscle contraction state in clinical experiments, Adjust the stimulation intensity adaptively, so that the user can receive the magnetic stimulation intensity most suitable for the current muscle strength at every moment, and improve the treatment effect.
具体的,如图11至图12所示,实现塑形磁刺激仪实时监测刺激肌肉状态并自适应调节刺激强度的具体方法为:Specifically, as shown in Fig. 11 to Fig. 12, the specific method for realizing the real-time monitoring of the stimulated muscle state by the shaping magnetic stimulator and adaptively adjusting the stimulation intensity is as follows:
记录目标肌肉在t时刻的肌力特征值;用户进入塑形阶段,根据塑形方案(Treatment_No),塑形磁刺激仪发射相对应电磁波,包括频率(Treatment_No_Freq)、强度(Treatment_No_Stren(t))、脉冲数(Treatment_No_Cycle)、间隔(Treatment_No_Gap)、时长(Treatment_No_Dura)。Record the muscle strength characteristic value of the target muscle at time t; the user enters the shaping stage, and according to the shaping plan (Treatment_No), the shaping magnetic stimulator emits corresponding electromagnetic waves, including frequency (Treatment_No_Freq), intensity (Treatment_No_Stren(t)), Number of pulses (Treatment_No_Cycle), interval (Treatment_No_Gap), duration (Treatment_No_Dura).
基于采集到的肌肉状态值即肌力值,计算出每个治疗脉冲的肌力特征值P_Eig(k)。经过实验和对比,本发明使用复杂度和效果均较好的平均值指标,即肌力特征值P_Eig(k)为单位脉冲持续时间内所有肌力值的平均值,同时基于临床实验肌力特征值与肌肉收缩状态的理论关系自适应调节刺激强度。Based on the collected muscle state value, that is, the muscle strength value, the muscle strength characteristic value P_Eig(k) of each treatment pulse is calculated. After experiments and comparisons, the present invention uses an average index with better complexity and effect, that is, the muscle strength characteristic value P_Eig(k) is the average value of all muscle strength values within the unit pulse duration, and is based on clinical experimental muscle strength characteristics. The theoretical relationship between the value and the state of muscle contraction adaptively modulates the stimulus intensity.
若调高磁刺激强度,P_Eig(k)持续增大,则认为肌肉未达到最大收缩状态,调高下一时刻磁刺激强度为:If the magnetic stimulation intensity is increased and P_Eig(k) continues to increase, it is considered that the muscle has not reached the maximum contraction state, and the magnetic stimulation intensity at the next moment is:
Treatment_No_Stren(t+1)=Treatment_No_Stren(t)*(1+Stren_Tune)Treatment_No_Stren(t+1)=Treatment_No_Stren(t)*(1+Stren_Tune)
其中,Stren_Tune为微调系数,取值区间为:[0,1],通常取值5%。Among them, Stren_Tune is the fine-tuning coefficient, the value range is: [0, 1], usually the value is 5%.
若调高磁刺激强度,P_Eig(k)基本不变,则认为肌肉已经达到最大收缩状态,取上一磁刺激强度为最优磁刺激强度:If the magnetic stimulation intensity is increased, P_Eig(k) is basically unchanged, it is considered that the muscle has reached the maximum contraction state, and the last magnetic stimulation intensity is taken as the optimal magnetic stimulation intensity:
若刺激过程中,磁刺激强度不变,P_Eig(k)下降,则认为肌肉已经进入疲劳状态,则降低下一时刻磁刺激强度为:If during the stimulation process, the magnetic stimulation intensity remains unchanged and P_Eig(k) decreases, it is considered that the muscle has entered a state of fatigue, and the magnetic stimulation intensity at the next moment is reduced as follows:
Treatment_No_Stren(t+1)=Treatment_No_Stren(t)*(1-Stren_Tune)Treatment_No_Stren(t+1)=Treatment_No_Stren(t)*(1-Stren_Tune)
其中,Stren_Tune为微调系数,取值区间为:[0,1],通常取值5%-10%。Among them, Stren_Tune is the fine-tuning coefficient, the value range is: [0, 1], usually the value is 5%-10%.
图13至图14进一步说明塑形过程中随刺激强度的变化与肌力特征值之间的关系。Figures 13 to 14 further illustrate the relationship between the change with the stimulus intensity and the muscle strength characteristic value during the shaping process.
在0s至100s阶段,为用户自主呼吸状态,不接受磁刺激,肌力图显示用户呼吸时的肌力状态值。In the stage from 0s to 100s, the user is in the state of spontaneous breathing and does not receive magnetic stimulation.
在100s至440s阶段,随着磁刺激强度的增加,用户的肌力状态值和肌力特征值处于稳步增加的状态,则下一时刻磁刺激强度为上一时刻磁刺激强度的基础上适度增加磁刺激强度。From 100s to 440s, with the increase of the magnetic stimulation intensity, the user's muscle strength state value and muscle strength characteristic value are in a state of steady increase, then the magnetic stimulation intensity at the next moment will be moderately increased on the basis of the magnetic stimulation strength at the previous moment. Magnetic stimulation intensity.
450s往后阶段,在磁刺激强度不变的情况下,用户的肌力状态值和肌力特征值有所下降,显示目标肌肉有所疲劳,则下一时刻磁刺激强度为上一时候磁刺激强度的基础上适度降低刺激强度,使得目标肌肉仍处于最佳刺激状态。保证刺激强度的同时降低目标肌肉的疲劳,加速刺激后的恢复,提高塑形效果。In the later stage of 450s, when the magnetic stimulation intensity remains unchanged, the user's muscle strength state value and muscle strength characteristic value decrease, indicating that the target muscle is fatigued, and the magnetic stimulation intensity at the next moment is the magnetic stimulation at the previous time. On the basis of the intensity, the stimulation intensity is moderately reduced, so that the target muscle is still in the best stimulation state. While ensuring the stimulation intensity, it reduces the fatigue of the target muscles, accelerates the recovery after stimulation, and improves the shaping effect.
在整个塑形过程中,实时采集肌肉收缩过程中的肌肉状态值,并转化成相对应的肌力特征值,根据肌肉收缩过程中肌力特征值的变化判定刺激过程中肌肉收缩程度,能够更直观地评估指示磁场强度是否引起肌肉最大收缩或已进入疲劳状态,从而自适应调整刺激强度,此过程为治疗过程中持续监测并不断调整的过程,保证每一次治疗效果最大化。相比于现有的自适应调节刺激强度技术,本发明提出自适应调节算法不需要使用神经网络、深度学习等非解析类方法建模,不需要前期花费大量资源训练模型拟合参数,采用临床经验总结出的计算方法,成本大幅降低,更加简洁、更为直观、能很好的提高塑形效果。During the whole shaping process, the muscle state value during the muscle contraction process is collected in real time, and converted into the corresponding muscle strength characteristic value. Intuitively assess whether the indicated magnetic field strength causes the muscle to contract the maximum or has entered a state of fatigue, so as to adjust the stimulation intensity adaptively. This process is a process of continuous monitoring and continuous adjustment during the treatment process to ensure the maximum effect of each treatment. Compared with the existing self-adaptive adjustment stimulation intensity technology, the self-adaptive adjustment algorithm proposed in the present invention does not need to use non-analytical methods such as neural network and deep learning for modeling, and does not need to spend a lot of resources in the early stage to train model fitting parameters. The calculation method summed up by experience has greatly reduced the cost, is more concise, more intuitive, and can improve the shaping effect.
以上所述的具体实施方式,对本发明的目的、技术方案和有益效果进行了进一步详细说明,所应理解的是,以上所述仅为本发明的具体实施方式,并不用于限定本发明保护范围,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所做的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应含在本发明的保护范围之内。The specific embodiments described above further describe the objectives, technical solutions and beneficial effects of the present invention in detail. It should be understood that the above descriptions are only specific embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention. , any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made within the spirit and principle of the present invention shall be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (12)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111538311.XACN114470523A (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | A plastic magnetic stimulator |
| PCT/CN2022/076282WO2023108881A1 (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2022-02-15 | Sculpting magnetic stimulator |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111538311.XACN114470523A (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | A plastic magnetic stimulator |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114470523Atrue CN114470523A (en) | 2022-05-13 |
Family
ID=81493543
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111538311.XAPendingCN114470523A (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2021-12-15 | A plastic magnetic stimulator |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114470523A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2023108881A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115364376A (en)* | 2022-07-12 | 2022-11-22 | 南京伟思医疗科技股份有限公司 | Pulse magnetic shaping instrument and automatic identification method, system, control method and circuit thereof |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20180001107A1 (en) | 2016-07-01 | 2018-01-04 | Btl Holdings Limited | Aesthetic method of biological structure treatment by magnetic field |
| US11534619B2 (en) | 2016-05-10 | 2022-12-27 | Btl Medical Solutions A.S. | Aesthetic method of biological structure treatment by magnetic field |
| US11141219B1 (en) | 2016-08-16 | 2021-10-12 | BTL Healthcare Technologies, a.s. | Self-operating belt |
| US12156689B2 (en) | 2019-04-11 | 2024-12-03 | Btl Medical Solutions A.S. | Methods and devices for aesthetic treatment of biological structures by radiofrequency and magnetic energy |
| ES2926904T3 (en) | 2019-04-11 | 2022-10-31 | Btl Medical Solutions A S | Device for the aesthetic treatment of biological structures using radiofrequency and magnetic energy |
| US11878167B2 (en) | 2020-05-04 | 2024-01-23 | Btl Healthcare Technologies A.S. | Device and method for unattended treatment of a patient |
| WO2021224678A1 (en) | 2020-05-04 | 2021-11-11 | Btl Medical Technologies S.R.O. | Device and method for unattended treatment of a patient |
| EP4415812A1 (en) | 2021-10-13 | 2024-08-21 | BTL Medical Solutions a.s. | Devices for aesthetic treatment of biological structures by radiofrequency and magnetic energy |
| US11896816B2 (en) | 2021-11-03 | 2024-02-13 | Btl Healthcare Technologies A.S. | Device and method for unattended treatment of a patient |
| CN117883706B (en)* | 2024-01-12 | 2024-09-10 | 中国人民解放军军事科学院军事医学研究院 | Magnetic stimulation control system and method |
| CN119112199B (en)* | 2024-09-12 | 2025-07-18 | 天津大学 | Wearable electromyography monitoring and electrical stimulation intervention integrated device |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN201324444Y (en)* | 2008-08-18 | 2009-10-14 | 武汉依瑞德医疗设备新技术有限公司 | Stimulating bat for magnetic field stimulator |
| CN104869902A (en)* | 2012-12-18 | 2015-08-26 | 莫库比技术有限公司 | Biofeedback device using magnetic stimulator and control method thereof |
| CN214512282U (en)* | 2020-08-26 | 2021-10-29 | 郑州品正科技有限公司 | Electromagnetic slimming therapeutic instrument |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102553077A (en)* | 2012-03-02 | 2012-07-11 | 天津工业大学 | Uniform muscle magnetic stimulation induction system |
| CN104587605A (en)* | 2015-01-11 | 2015-05-06 | 北京工业大学 | Electromyographic signal controlled peripheral magnetic stimulation system and method |
| US20170001025A1 (en)* | 2015-07-01 | 2017-01-05 | Btl Holdings Limited | Aesthetic method of biological structure stimulation by magnetic field |
| US9849302B1 (en)* | 2015-10-23 | 2017-12-26 | Zygood, Llc | Three-coil magnetic pulsations system for the treatment of foot pain |
| CZ308216B6 (en)* | 2018-10-19 | 2020-03-04 | Fakultní nemocnice Hradec Králové | Device for measuring muscle strength and method of testing the muscle performance of athletes |
| CN109550146A (en)* | 2018-11-16 | 2019-04-02 | 上海交通大学 | A kind of fatigue mitigation device based on electro photoluminescence Yu muscle infomation detection |
- 2021
- 2021-12-15CNCN202111538311.XApatent/CN114470523A/enactivePending
- 2022
- 2022-02-15WOPCT/CN2022/076282patent/WO2023108881A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN201324444Y (en)* | 2008-08-18 | 2009-10-14 | 武汉依瑞德医疗设备新技术有限公司 | Stimulating bat for magnetic field stimulator |
| CN104869902A (en)* | 2012-12-18 | 2015-08-26 | 莫库比技术有限公司 | Biofeedback device using magnetic stimulator and control method thereof |
| CN214512282U (en)* | 2020-08-26 | 2021-10-29 | 郑州品正科技有限公司 | Electromagnetic slimming therapeutic instrument |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115364376A (en)* | 2022-07-12 | 2022-11-22 | 南京伟思医疗科技股份有限公司 | Pulse magnetic shaping instrument and automatic identification method, system, control method and circuit thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2023108881A1 (en) | 2023-06-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114470523A (en) | A plastic magnetic stimulator | |
| CN215309722U (en) | Active and passive combined pelvic floor magnetic stimulation treatment device | |
| CN112546448B (en) | Active and passive combined pelvic floor magnetic stimulation treatment device and method | |
| CN101259302A (en) | Intelligent Brain Nerve Nucleus Electrical Stimulation System | |
| CN107050645A (en) | A kind of adjusting method of the frequency of stimulation of sacral nerve stimulator | |
| CN114949602A (en) | A closed-loop control method and system for online monitoring of neuromuscular electrical stimulation responses | |
| CN107158564B (en) | Low-frequency modulated intermediate-frequency electric stimulation external diaphragm pacemaker | |
| CN102247652A (en) | Neuromuscular electric stimulation device | |
| CN113713333B (en) | A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation | |
| CN106139405A (en) | A kind of vagus nerve magnetic stimulating device | |
| CN111939068A (en) | A kind of myoelectric feedback intelligent acupuncture physiotherapy instrument | |
| CN108261607A (en) | A kind of functional transcutaneous electrical stimulation device for motion function regulation and control | |
| CN115887911A (en) | Nerve regulation and control method and device with stimulation and induction loops | |
| CN114904140A (en) | Physical therapy equipment, control method thereof and physical therapy system | |
| CN208130251U (en) | A kind of external diaphragm pacemaker of the medium frequency electric stimulation of low frequency modulations | |
| CN114377296A (en) | Non-invasive deep brain electromagnetic coupling neuromodulation device | |
| CN119499544A (en) | A transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation device for the ear and neck based on interoceptive signals | |
| CN212327192U (en) | A mental fatigue intervention device | |
| CN117138233A (en) | Medium-low frequency physiotherapy instrument control method and system based on data acquisition | |
| CN2768819Y (en) | Nerve function rebuilding instrument | |
| CN111973880A (en) | Mental fatigue intervention equipment and intervention method | |
| CN105435371A (en) | 8-shaped coil transcranial magnetic stimulation system based on magnetic resonant coupling principle | |
| CN109954209A (en) | A kind of high-voltage driving circuit system for functional electrostimulation | |
| CN111544289A (en) | Intelligent eye physiotherapy equipment with electroencephalogram feedback | |
| CN211214974U (en) | Electrical stimulation device with fatigue assessment |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |