CN114469940A - Application of Small Molecular Compound AQ-390 in Preparation of Anti-Pyroptosis Drugs and Inhibitors - Google Patents
Application of Small Molecular Compound AQ-390 in Preparation of Anti-Pyroptosis Drugs and InhibitorsDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114469940A CN114469940ACN202210253238.XACN202210253238ACN114469940ACN 114469940 ACN114469940 ACN 114469940ACN 202210253238 ACN202210253238 ACN 202210253238ACN 114469940 ACN114469940 ACN 114469940A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- gsdmd
- inhibitor
- reperfusion injury
- cell apoptosis
- prepared
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription40
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription33
- 239000003112inhibitorSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription25
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription5
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription8
- 102100037388Gasdermin-DHuman genes0.000claimsabstractdescription55
- 206010063837Reperfusion injuryDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription39
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription24
- 208000012947ischemia reperfusion injuryDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 230000003110anti-inflammatory effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 101001026262Homo sapiens Gasdermin-DProteins0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 230000006907apoptotic processEffects0.000claimsabstract8
- -1small molecule compoundChemical class0.000claimsdescription15
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium chlorideChemical compound[Na+].[Cl-]FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000000969carrierSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000000725suspensionSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000011780sodium chlorideSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000003826tabletSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000010521absorption reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000839emulsionSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000003623enhancerSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000945fillerSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000008187granular materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000314lubricantSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 229940100691oral capsuleDrugs0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000008194pharmaceutical compositionSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000006187pillSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000001179sorption measurementMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000004094surface-active agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000080wetting agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 206010061218InflammationDiseases0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000004054inflammatory processEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 229940023488pillDrugs0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000000853adhesiveSubstances0.000claims1
- 230000001070adhesive effectEffects0.000claims1
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claims1
- 239000004480active ingredientSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000012752auxiliary agentSubstances0.000abstract1
- 230000002401inhibitory effectEffects0.000abstract1
- 101710087939Gasdermin-DProteins0.000description45
- 241000699670Mus sp.Species0.000description28
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description24
- 208000031225myocardial ischemiaDiseases0.000description23
- 230000006010pyroptosisEffects0.000description20
- 210000004413cardiac myocyteAnatomy0.000description19
- 239000002158endotoxinSubstances0.000description18
- 229920006008lipopolysaccharidePolymers0.000description18
- 210000002540macrophageAnatomy0.000description13
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description11
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description11
- 206010021143HypoxiaDiseases0.000description10
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000description10
- 206010040047SepsisDiseases0.000description10
- 230000002107myocardial effectEffects0.000description10
- DANUORFCFTYTSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NepinigericinNatural productsO1C2(C(CC(C)(O2)C2OC(C)(CC2)C2C(CC(O2)C2C(CC(C)C(O)(CO)O2)C)C)C)C(C)C(OC)CC1CC1CCC(C)C(C(C)C(O)=O)O1DANUORFCFTYTSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description9
- DANUORFCFTYTSZ-BIBFWWMMSA-NnigericinChemical compoundC([C@@H]1C[C@H]([C@H]([C@]2([C@@H](C[C@](C)(O2)C2O[C@@](C)(CC2)C2[C@H](CC(O2)[C@@H]2[C@H](C[C@@H](C)[C@](O)(CO)O2)C)C)C)O1)C)OC)[C@H]1CC[C@H](C)C([C@@H](C)C(O)=O)O1DANUORFCFTYTSZ-BIBFWWMMSA-N0.000description9
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000description7
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description7
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description7
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description7
- 208000010125myocardial infarctionDiseases0.000description6
- 239000000546pharmaceutical excipientSubstances0.000description6
- 150000003384small moleculesChemical class0.000description6
- 108091006057GST-tagged proteinsProteins0.000description5
- 239000002552dosage formSubstances0.000description5
- 231100000673dose–response relationshipToxicity0.000description5
- 230000035699permeabilityEffects0.000description5
- 210000002966serumAnatomy0.000description5
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description5
- 239000006144Dulbecco’s modified Eagle's mediumSubstances0.000description4
- 241000700159RattusSpecies0.000description4
- 238000010171animal modelMethods0.000description4
- 239000011324beadSubstances0.000description4
- 239000002775capsuleSubstances0.000description4
- 230000001413cellular effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description4
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description4
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description4
- 230000007954hypoxiaEffects0.000description4
- 230000002757inflammatory effectEffects0.000description4
- 230000001404mediated effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000description4
- XJMOSONTPMZWPB-UHFFFAOYSA-Mpropidium iodideChemical compound[I-].[I-].C12=CC(N)=CC=C2C2=CC=C(N)C=C2[N+](CCC[N+](C)(CC)CC)=C1C1=CC=CC=C1XJMOSONTPMZWPB-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description4
- 108091003079Bovine Serum AlbuminProteins0.000description3
- 238000011740C57BL/6 mouseMethods0.000description3
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NDimethylsulphoxideChemical compoundCS(C)=OIAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-NGlycerineChemical compoundOCC(O)COPEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 241000699666Mus <mouse, genus>Species0.000description3
- 239000012091fetal bovine serumSubstances0.000description3
- 210000005003heart tissueAnatomy0.000description3
- 239000007928intraperitoneal injectionSubstances0.000description3
- 239000002609mediumSubstances0.000description3
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description3
- 235000013336milkNutrition0.000description3
- 239000008267milkSubstances0.000description3
- 210000004080milkAnatomy0.000description3
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description3
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description3
- 238000013146percutaneous coronary interventionMethods0.000description3
- 108010051423streptavidin-agaroseProteins0.000description3
- 239000006228supernatantSubstances0.000description3
- YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N(+)-BiotinChemical compoundN1C(=O)N[C@@H]2[C@H](CCCCC(=O)O)SC[C@@H]21YBJHBAHKTGYVGT-ZKWXMUAHSA-N0.000description2
- HJXMNVQARNZTEE-UHFFFAOYSA-NButylphthalideChemical compoundC1=CC=C2C(CCCC)OC(=O)C2=C1HJXMNVQARNZTEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-LCalcium carbonateChemical compound[Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=OVTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- 102000011727CaspasesHuman genes0.000description2
- 108010076667CaspasesProteins0.000description2
- 102400000484Gasdermin-D, N-terminalHuman genes0.000description2
- 101800000973Gasdermin-D, N-terminalProteins0.000description2
- 206010061216InfarctionDiseases0.000description2
- 208000007201Myocardial reperfusion injuryDiseases0.000description2
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium bicarbonateChemical compound[Na+].OC([O-])=OUIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description2
- 239000011230binding agentSubstances0.000description2
- 238000012575bio-layer interferometryMethods0.000description2
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description2
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description2
- 239000006143cell culture mediumSubstances0.000description2
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description2
- 238000007405data analysisMethods0.000description2
- 230000034994deathEffects0.000description2
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description2
- 239000007884disintegrantSubstances0.000description2
- BXWNKGSJHAJOGX-UHFFFAOYSA-Nhexadecan-1-olChemical compoundCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOBXWNKGSJHAJOGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000007574infarctionEffects0.000description2
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000description2
- 208000028867ischemiaDiseases0.000description2
- 230000000302ischemic effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000description2
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description2
- 208000037891myocardial injuryDiseases0.000description2
- 230000007959normoxiaEffects0.000description2
- 230000010412perfusionEffects0.000description2
- 230000009873pyroptotic effectEffects0.000description2
- 239000000523sampleSubstances0.000description2
- IZTQOLKUZKXIRV-YRVFCXMDSA-NsincalideChemical compoundC([C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C(N)=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O)C1=CC=C(OS(O)(=O)=O)C=C1IZTQOLKUZKXIRV-YRVFCXMDSA-N0.000description2
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 238000010186stainingMethods0.000description2
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description2
- 229960005322streptomycinDrugs0.000description2
- 230000004083survival effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000013268sustained releaseMethods0.000description2
- 239000012730sustained-release formSubstances0.000description2
- 230000008685targetingEffects0.000description2
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000002861ventricularEffects0.000description2
- 238000003041virtual screeningMethods0.000description2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 229920001817AgarPolymers0.000description1
- 239000005995Aluminium silicateSubstances0.000description1
- 201000001320AtherosclerosisDiseases0.000description1
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description1
- 238000010356CRISPR-Cas9 genome editingMethods0.000description1
- 208000031229CardiomyopathiesDiseases0.000description1
- 102400000888Cholecystokinin-8Human genes0.000description1
- 101800005151Cholecystokinin-8Proteins0.000description1
- 108010010803GelatinProteins0.000description1
- 208000032843HemorrhageDiseases0.000description1
- PIWKPBJCKXDKJR-UHFFFAOYSA-NIsofluraneChemical compoundFC(F)OC(Cl)C(F)(F)FPIWKPBJCKXDKJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-NMagnesiumChemical compound[Mg]FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 101000933115Mus musculus Caspase-4Proteins0.000description1
- 206010057249PhagocytosisDiseases0.000description1
- 239000002202Polyethylene glycolSubstances0.000description1
- 229920001213Polysorbate 20Polymers0.000description1
- 239000012980RPMI-1640 mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 238000011529RT qPCRMethods0.000description1
- 206010058156Reperfusion arrhythmiaDiseases0.000description1
- 241000283984RodentiaSpecies0.000description1
- 108010087230SincalideProteins0.000description1
- 229920002472StarchPolymers0.000description1
- 229930006000SucroseNatural products0.000description1
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-NSucroseChemical compoundO[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N0.000description1
- 241000700605VirusesSpecies0.000description1
- 230000004913activationEffects0.000description1
- 206010000891acute myocardial infarctionDiseases0.000description1
- 239000008272agarSubstances0.000description1
- 229920000615alginic acidPolymers0.000description1
- 235000010443alginic acidNutrition0.000description1
- 235000012211aluminium silicateNutrition0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000000440bentoniteSubstances0.000description1
- 229910000278bentoniteInorganic materials0.000description1
- SVPXDRXYRYOSEX-UHFFFAOYSA-NbentoquatamChemical compoundO.O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=OSVPXDRXYRYOSEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 229960002685biotinDrugs0.000description1
- 235000020958biotinNutrition0.000description1
- 239000011616biotinSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004204blood vesselAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000009835boilingMethods0.000description1
- 239000000872bufferSubstances0.000description1
- 229950005197butylphthalideDrugs0.000description1
- 229910000019calcium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcalcium stearateChemical compound[Ca+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=OCJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 239000008116calcium stearateSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013539calcium stearateNutrition0.000description1
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000010609cell counting kit-8 assayMethods0.000description1
- 230000005779cell damageEffects0.000description1
- 208000037887cell injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 210000000170cell membraneAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000001913celluloseSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002678cellulosePolymers0.000description1
- 229960000541cetyl alcoholDrugs0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 230000002060circadianEffects0.000description1
- 238000003776cleavage reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000001427coherent effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000012059conventional drug carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description1
- 230000002950deficientEffects0.000description1
- 230000003111delayed effectEffects0.000description1
- UQLDLKMNUJERMK-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldi(octadecanoyloxy)leadChemical compound[Pb+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=OUQLDLKMNUJERMK-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 239000003085diluting agentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000010494dissociation reactionMethods0.000description1
- 230000005593dissociationsEffects0.000description1
- 238000009472formulationMethods0.000description1
- 239000000499gelSubstances0.000description1
- 229920000159gelatinPolymers0.000description1
- 239000008273gelatinSubstances0.000description1
- 235000019322gelatineNutrition0.000description1
- 235000011852gelatine dessertsNutrition0.000description1
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001146hypoxic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000010166immunofluorescenceMethods0.000description1
- 230000008595infiltrationEffects0.000description1
- 238000001764infiltrationMethods0.000description1
- 230000028709inflammatory responseEffects0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 230000009878intermolecular interactionEffects0.000description1
- 238000007918intramuscular administrationMethods0.000description1
- 238000001990intravenous administrationMethods0.000description1
- 230000002427irreversible effectEffects0.000description1
- 229960002725isofluraneDrugs0.000description1
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-NkaolinChemical compoundO.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=ONLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 210000005240left ventricleAnatomy0.000description1
- 150000002632lipidsChemical class0.000description1
- 239000012160loading bufferSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011777magnesiumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052749magnesiumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 230000010534mechanism of actionEffects0.000description1
- 239000012982microporous membraneSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009456molecular mechanismEffects0.000description1
- 238000010172mouse modelMethods0.000description1
- 208000002089myocardial stunningDiseases0.000description1
- 239000002547new drugSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000399optical microscopyMethods0.000description1
- 230000000242pagocytic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000007310pathophysiologyEffects0.000description1
- 230000008782phagocytosisEffects0.000description1
- 229920002401polyacrylamidePolymers0.000description1
- 229920001223polyethylene glycolPolymers0.000description1
- 239000000256polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurateSubstances0.000description1
- 235000010486polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurateNutrition0.000description1
- 235000010482polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleateNutrition0.000description1
- 229920000053polysorbate 80Polymers0.000description1
- 229920000036polyvinylpyrrolidonePolymers0.000description1
- 239000001267polyvinylpyrrolidoneSubstances0.000description1
- 235000013855polyvinylpyrrolidoneNutrition0.000description1
- 239000011148porous materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description1
- 150000003856quaternary ammonium compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 230000010410reperfusionEffects0.000description1
- 230000029058respiratory gaseous exchangeEffects0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 230000033764rhythmic processEffects0.000description1
- 230000007017scissionEffects0.000description1
- 230000028327secretionEffects0.000description1
- 230000019491signal transductionEffects0.000description1
- 239000011734sodiumSubstances0.000description1
- 235000017557sodium bicarbonateNutrition0.000description1
- 229910000030sodium bicarbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000012453sprague-dawley rat modelMethods0.000description1
- 239000008107starchSubstances0.000description1
- 235000019698starchNutrition0.000description1
- 238000007920subcutaneous administrationMethods0.000description1
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 239000005720sucroseSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 239000006188syrupSubstances0.000description1
- 235000020357syrupNutrition0.000description1
- 239000000454talcSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052623talcInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
- 229940126585therapeutic drugDrugs0.000description1
- 230000002537thrombolytic effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000001262western blotMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/41—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with two or more ring hetero atoms, at least one of which being nitrogen, e.g. tetrazole
- A61K31/415—1,2-Diazoles
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及化学生物学领域,具体涉及小分子化合物AQ-390在制备抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物中的应用,还公开了一种基于该药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂。The invention relates to the field of chemical biology, in particular to the application of a small molecular compound AQ-390 in the preparation of a drug against pyroptosis and exerting an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury. GSDMD inhibitor.
背景技术Background technique
目前,最接近的现有技术:急性心肌梗死最有效的治疗干预是及时有效的心肌再灌注溶栓治疗或直接经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PPCI),但是心肌血流恢复灌注时会诱导心肌细胞的进一步死亡,这种现象叫做心肌再灌注损伤(Myocardial ischemia-reperfusioninjury,IRI),其不可逆转的结局包括心肌顿抑、再灌注心律失常、微血管阻塞、心肌内出血和致死性心肌再灌注损伤等。现有预防和控制心肌缺血再灌注损伤的有效措施十分有限,临床上预防和控制心肌缺血再灌注损伤仍是一个巨大的挑战。At present, the closest existing technology: the most effective therapeutic intervention for acute myocardial infarction is timely and effective myocardial reperfusion thrombolysis or direct percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI). This phenomenon is called myocardial reperfusion injury (Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, IRI), and its irreversible outcomes include myocardial stunning, reperfusion arrhythmia, microvascular occlusion, intramyocardial hemorrhage and fatal myocardial reperfusion injury. The existing effective measures to prevent and control myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury are very limited, and clinical prevention and control of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury is still a huge challenge.
目前的学术观点认为,无菌性炎症在心肌缺血再灌注损伤(IRI)病理生理中发挥关键作用。而相关研究报道,Gasdermin-D(GSDMD)蛋白所介导的细胞焦亡在心肌缺血再灌注损伤无菌性炎症反应中占据主导作用。Gasdermin-D(GSDMD)分子是细胞焦亡的执行蛋白,它是由N-末端结构域通过茎环结构共同组成。正常情况下,GSDMD蛋白不具有活性,当细胞受到病毒、细菌或者脂多糖(LPS)刺激时,通过经典的caspase-1信号通路或者非经典caspase-4/5/11信号通路,Gasdermin-D(GSDMD)的caspase识别位点被切割,从而形成具有活性GSDMD-N基端,随后N端结构域与膜脂结合并通过在膜内形成内径为10-14nm的孔隙,IL-1β等炎性因子即可被释放于胞外引起炎症放大反应。因此,Gasdermin-D(GSDMD)分子的域间切割是炎症性半胱天冬酶激活和细胞焦亡的可靠指标。最新的研究揭示,GSDMD介导的心肌细胞焦亡通过caspase-11/GSDMD信号通路促进心肌I/R损伤。因此发掘GSDMD与心肌缺血再灌注损伤的相关机制,并将其作为分子靶点发挥抗心肌缺血再灌注损伤具有非常重要的意义。The current academic view holds that aseptic inflammation plays a key role in the pathophysiology of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). Related studies reported that pyroptosis mediated by Gasdermin-D (GSDMD) protein played a dominant role in the aseptic inflammatory response of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Gasdermin-D (GSDMD) molecule is the executive protein of pyroptosis, which is composed of N-terminal domains through a stem-loop structure. Under normal circumstances, the GSDMD protein is inactive. When cells are stimulated by viruses, bacteria or lipopolysaccharide (LPS), Gasdermin-D ( The caspase recognition site of GSDMD) is cleaved to form an active GSDMD-N base, and then the N-terminal domain binds to membrane lipids and forms a pore with an inner diameter of 10-14 nm in the membrane, inflammatory factors such as IL-1β It can be released extracellularly to cause inflammatory amplifying response. Therefore, interdomain cleavage of the Gasdermin-D (GSDMD) molecule is a reliable indicator of inflammatory caspase activation and pyroptosis. Recent studies reveal that GSDMD-mediated cardiomyocyte pyroptosis promotes myocardial I/R injury through the caspase-11/GSDMD signaling pathway. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the related mechanism of GSDMD and myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and use it as a molecular target to fight myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
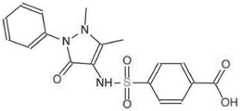
AQ-390,是一种通过计算机虚拟筛选所得到的与GSDMD蛋白存在潜在结合的小分子物质。结构如图1所示。目前,医学界尚未关于AQ-390在抑制细胞焦亡的报道,并且目前临床也并没有专门针对细胞焦亡的药物使用。本发明一方面,为治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤提供了新的药物及新的作用机制及靶点;另一方面,揭示AQ-390与细胞焦亡执行分子GSDMD的分子结合机制,为AQ-390应用于临床治疗PCI患者心肌缺血再灌注损伤提供理论依据。AQ-390 is a small molecule with potential binding to GSDMD protein obtained by computer virtual screening. The structure is shown in Figure 1. At present, there is no report in the medical community that AQ-390 inhibits pyroptosis, and there are no drugs specifically targeting pyroptosis in clinical practice. On the one hand, the present invention provides a new drug and a new mechanism of action and target for the treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury; The application of 390 in clinical treatment of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in patients with PCI provides a theoretical basis.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于克服治疗或预防PCI患者心肌缺血再灌注损伤药物的空白,开辟了AQ-390在医学上的用途。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the blank of drugs for treating or preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in patients with PCI, and to open up the use of AQ-390 in medicine.
本发明提供了一种小分子化合物AQ-390在制备抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物中的应用,涉及小分子化合物AQ-390在制备治疗心肌缺血再灌注损伤药物中的用途,还涉及小分子化合物AQ-390在制备具有抗细胞焦亡活性GSDMD抑制剂中的用途。The invention provides the application of a small molecule compound AQ-390 in preparing a drug against pyroptosis and exerting an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury, and relates to the application of the small molecule compound AQ-390 in the preparation of a drug for treating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. The use in perfusion injury medicine also relates to the use of small molecule compound AQ-390 in the preparation of GSDMD inhibitor with anti-pyroptosis activity.
本发明是这样实现的,一种抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物,所述治疗或预防心肌缺血再灌注损伤药物为小分子化合物AQ-390。小分子化合物AQ-390可用于注射用的针剂或口服的胶囊。The present invention is achieved in this way, a drug for preventing or treating ischemia-reperfusion injury by resisting cell pyroptosis and exerting an anti-inflammatory effect is a small molecule compound AQ-390. The small molecule compound AQ-390 can be used for injection or oral capsule.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的针剂(25-50mg/kg/天)。Another object of the present invention is to provide an injection (25-50 mg/kg/day) prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的口服胶囊(25-50mg/kg/天)。Another object of the present invention is to provide an oral capsule (25-50 mg/kg/day) prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂(25-50mg/kg/天),所述具有抗细胞焦亡活性GSDMD抑制剂由AQ-390和药学上可接受的辅料配制而成。Another object of the present invention is to provide a GSDMD inhibitor (25-50 mg/kg/day) prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury. The anti-pyroptotic activity GSDMD inhibitor is formulated from AQ-390 and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
进一步,可接受的辅料为可接受的载体或填充剂或粘合剂或湿润剂或崩解剂或吸收促进剂或表面活性剂或吸附载体或润滑剂或0.9%氯化钠,(“辅料”指药学领域常规的药物载体,例如:稀释剂、赋形剂如水等,填充剂如淀粉、蔗糖等;粘合剂如纤维素衍生物、藻酸盐、明胶和聚乙烯吡咯烷酮;湿润剂如甘油;崩解剂如琼脂、碳酸钙和碳酸氢钠;吸收促进剂如季铵化合物;表面活性剂如十六烷醇;吸附载体如高岭土和皂粘土;润滑剂如滑石粉、硬脂酸钙/镁、聚乙二醇等。配制比例以0.9%氯化钠为例为丁苯酞:0.9%氯化钠=1:20)Further, acceptable excipients are acceptable carriers or fillers or binders or wetting agents or disintegrants or absorption enhancers or surfactants or adsorption carriers or lubricants or 0.9% sodium chloride, ("excipients" Refers to the conventional pharmaceutical carriers in the pharmaceutical field, such as: diluents, excipients such as water, etc., fillers such as starch, sucrose, etc.; binders such as cellulose derivatives, alginates, gelatin and polyvinylpyrrolidone; wetting agents such as glycerol ; disintegrants such as agar, calcium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate; absorption enhancers such as quaternary ammonium compounds; surfactants such as cetyl alcohol; adsorption carriers such as kaolin and bentonite; lubricants such as talc, calcium stearate/ Magnesium, polyethylene glycol, etc. The preparation ratio is 0.9% sodium chloride as an example: butylphthalide: 0.9% sodium chloride = 1:20)
按质量比,AQ-390和药学上可接受的辅料配比质量比例为1:20。According to the mass ratio, the mass ratio of AQ-390 and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients is 1:20.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂制成的片剂。Another object of the present invention is to provide a tablet made of a GSDMD inhibitor prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂制成的丸剂。Another object of the present invention is to provide a pill made of a GSDMD inhibitor prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂制成的混悬剂。Another object of the present invention is to provide a suspension made of a GSDMD inhibitor prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂制成的颗粒剂。Another object of the present invention is to provide a granule made of a GSDMD inhibitor prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明的另一目的在于提供一种利用所述抵抗细胞焦亡发挥抗炎效应以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤药物制成的GSDMD抑制剂制成的乳液剂。Another object of the present invention is to provide an emulsion made of a GSDMD inhibitor prepared by using the anti-pyroptosis drug to exert an anti-inflammatory effect to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury.
本发明通过虚拟筛选方法获得潜在的GSDMD小分子抑制剂AQ-390。通过PMA诱导的THP-1细胞上利用LPS联合Nigericin刺激构建细胞焦亡模型以及小鼠腹腔注射LPS构建脓毒症模型,发现100μMAQ-390可明显缓解细胞焦亡减轻炎症所引起的细胞损伤并提高脓毒症小鼠的存活率。随后,本发明利用生物膜光相干生物传感器(bio-layerinferferometry,BLI),蛋白pulldown技术发现AQ-390与GSDMD蛋白可存在直接结合且动力学稳定。在小鼠心肌缺血再灌注动物模型中,AQ-390可以减轻细胞焦亡,改善心肌缺血再灌注损伤,减少心梗面积,抑制梗死区心肌组织中IL-1β和IL-18的表达以及血液中LDH及CK-MB的含量,保护心肌组织。在细胞层面,AQ-390在安全药物浓度范围内,可以明显改善以乳大鼠原代心肌细胞构建的缺氧再复氧模型所引起的细胞损伤。根据以上的结果,AQ-390具有特异性靶向抑制GSDMD抵抗细胞焦亡所引起的炎症效应,进而缓解心肌缺血再灌注损伤。The present invention obtains potential GSDMD small molecule inhibitor AQ-390 through virtual screening method. The pyroptosis model was established by stimulation of LPS combined with Nigericin on THP-1 cells induced by PMA, and the sepsis model was established by intraperitoneal injection of LPS in mice. Survival of septic mice. Subsequently, the present invention utilizes bio-layer inferferometry (BLI) and protein pulldown technology to find that AQ-390 and GSDMD protein can be directly combined and kinetically stable. In the mouse model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion, AQ-390 can attenuate pyroptosis, improve myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, reduce myocardial infarction size, inhibit the expression of IL-1β and IL-18 in myocardial tissue in the infarcted area, and reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. The content of LDH and CK-MB in blood can protect myocardial tissue. At the cellular level, within the safe drug concentration range, AQ-390 can significantly improve the cell damage caused by the hypoxia-reoxygenation model constructed with primary cardiomyocytes of milk rats. According to the above results, AQ-390 can specifically target and inhibit GSDMD to resist the inflammatory effect caused by pyroptosis, thereby alleviating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
具体应用时,所述的药物为AQ-390和药学上可接受的辅料而配制成的各种制剂。其中优选与注射用的针剂和口服的胶囊。本发明的制剂可以为单位计量形式,如针剂、胶囊(包括持续释放或延迟释放形式)、片剂、丸剂、混悬剂、颗粒剂、酊剂、糖浆剂、乳液剂、悬浮液等剂型以及各种缓释剂型,从而适合各种给药方式,例如口服、非肠道注射、粘膜、肌肉、静脉内、皮下、眼内、皮内或经过皮肤等的给药形式(其中优选于用于注射用的针剂和口服的胶囊)。In specific applications, the drugs are various preparations prepared from AQ-390 and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. Among them, injections for injection and capsules for oral administration are preferred. The formulations of the present invention can be in unit dosage forms, such as injections, capsules (including sustained-release or delayed-release forms), tablets, pills, suspensions, granules, tinctures, syrups, emulsions, suspensions, etc. A sustained-release dosage form, which is suitable for various modes of administration, such as oral, parenteral injection, mucosal, intramuscular, intravenous, subcutaneous, intraocular, intradermal or transdermal, etc. injections and oral capsules).
本发明的特点在于药物中的活性成分合成简单,其特异性靶向消皮素(GasderminD,GSDMD)抑制细胞焦亡从而发挥良好的抗炎活性以预防或治疗缺血再灌注损伤,最适抑制浓度为100μM,可以作为心肌缺血再灌注损伤、脓毒心肌症、动脉粥样硬化等的治疗药物,治疗效果显著。The present invention is characterized in that the synthesis of the active components in the medicine is simple, the specific targeting of Gasdermin D (GSDMD) to inhibit cell pyroptosis, thereby exerting a good anti-inflammatory activity to prevent or treat ischemia-reperfusion injury, and the optimal inhibition With a concentration of 100 μM, it can be used as a therapeutic drug for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury, septic cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis, etc., and has a significant therapeutic effect.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明所述的小分子化合物AQ-390的分子结构式。Figure 1 is the molecular structural formula of the small molecule compound AQ-390 according to the present invention.
图2为本发明所述的小分子化合物AQ-390对脓毒症及巨噬细胞模型中GSDMD介导的细胞焦亡损伤的影响图。Figure 2 is a graph showing the effect of the small molecule compound AQ-390 of the present invention on GSDMD-mediated pyroptotic injury in sepsis and macrophage models.
图3为本发明所述的小分子化合物AQ-390与GSDMD蛋白结合的结构及相关分子机制的结果图。FIG. 3 is a result diagram of the structure and related molecular mechanism of the small molecule compound AQ-390 of the present invention binding to GSDMD protein.
图4为本发明所述的小分子化合物AQ-390对原代心肌细胞缺氧再复氧细胞损伤的影响图。Figure 4 is a graph showing the effect of the small molecule compound AQ-390 according to the present invention on the injury of primary cardiomyocytes by hypoxia-reoxygenation.
图5为本发明所述的小分子化合物AQ-390对小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤心肌损伤的影响图。Figure 5 is a graph showing the effect of the small molecule compound AQ-390 of the present invention on myocardial injury in mice with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
图6为本发明所述的小分子化合物AQ-390对小鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤心肌细胞焦亡程度的影响图。Fig. 6 is a graph showing the effect of the small molecule compound AQ-390 according to the present invention on the degree of myocardial cell pyroptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合实施例对本发明的具体实施方式做详细的说明。The specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the examples.
本发明所使用的原代心肌细胞提取自新生Sprague-Dawley(SD)大鼠的左心室,所用培养基为Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基(DMEM,ThermoFisher Scientific,UnitedStates),添加10%胎牛血清(FBS,Thermo Fisher Scientific)和1%青霉素-链霉素(Thermo Fisher Scientific)。本发明所使用的Thp-1巨噬细胞采购自美国典型菌种保藏中心(ATCC),所用培养基为RPMI1640培养基,添加10%胎牛血清和1%青霉素-链霉素。所使用培养基,血清以及双抗均为商购来源,按照生产厂家所提供的使用说明使用。细胞常规培养于37℃,5%CO2培养箱,原代心肌细胞贴壁生长,Thp-1巨噬细胞悬浮生长。本发明所使用的GSDMD纯化蛋白采购自杭州华安生物技术有限公司。本发明所使用的AQ-390药物购买自Specs公司。本发明所使用LPS药物购买自Sigma-Aldrich公司,尼日利亚菌素(Nigericin,Nig)购买自aladdin公司。其余试剂与材料也均为商购来源,按照生产厂家所提供的使用说明使用。The primary cardiomyocytes used in the present invention are extracted from the left ventricle of newborn Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, and the medium used is Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium (DMEM, ThermoFisher Scientific, United States), supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). , Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The Thp-1 macrophages used in the present invention were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), and the medium used was RPMI1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. The medium, serum and double antibody used were all from commercial sources and were used according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer. Cells were routinely cultured at 37°C in a 5% CO2 incubator. Primary cardiomyocytes were grown adherently, and Thp-1 macrophages were grown in suspension. The GSDMD purified protein used in the present invention was purchased from Hangzhou Huaan Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The AQ-390 drug used in the present invention was purchased from Specs Company. The LPS drugs used in the present invention were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Company, and Nigericin (Nigericin, Nig) was purchased from Aladdin Company. The remaining reagents and materials were also purchased from commercial sources and were used according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer.
实验动物:本发明所使用的C57BL/6雄性小鼠购买自浙江维通利华实验动物技术有限公司,饲养于温州医科大学附属第一医院动物实验中心。利用CRISPR-Cas9技术培育GSDMD-/-小鼠。小鼠用标准啮齿类动物食物和水饲养在恒温昼夜12-12h节律的动物房内。动物在实验开始前至少花一周时间进行环境适应性生长。Experimental animals: C57BL/6 male mice used in the present invention were purchased from Zhejiang Weitong Lihua Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd., and were raised in the Animal Experimental Center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University. GSDMD-/- mice were bred using CRISPR-Cas9 technology. Mice were housed with standard rodent chow and water in animal rooms with a constant temperature circadian 12-12 h rhythm. Animals were acclimated for at least one week prior to the start of the experiment.
实施例1:AQ-390对脓毒症以及巨噬细胞经典焦亡模型中的细胞焦亡损伤具有抵抗作用Example 1: AQ-390 is resistant to sepsis and pyroptotic injury in a classical macrophage model of pyroptosis
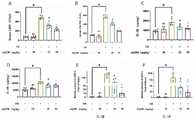
在本发明动物实验中所用的AQ-390为制成的可溶于0.25%的tween-80的CMC-Na溶液的剂型。溶液的PH值为7.36并经0.22微孔滤膜过滤。选用6-8周龄C57BL/6健康小鼠(WT)和6-8周龄GSDMD-/-健康小鼠腹腔注射低剂量LPS(15mg/kg)构建脓毒症动物模型。AQ-390药物处理组则为AQ-390(25mg/kg)(腹腔注射25小时)预处理后腹腔注射低剂量LPS(15mg/kg)构建脓毒症动物模型。细胞实验则将Thp-1巨噬细胞铺至六孔板中,培养基2ml。利用LPS(10μg/ml)处理6小时,尼日利亚菌素(Nigericin,Nig)(10μM)1小时刺激巨噬细胞以构建经典细胞焦亡模型。AQ-390药物处理组则为不同药物浓度的AQ-390预处理巨噬细胞1小时,随后利用LPS(10μg/ml)处理4小时,尼日利亚菌素(Nigericin,Nig)(10μM)1小时刺激巨噬细胞以构建经典细胞焦亡模型。在动物层面,我们发现GSDMD-/-鼠相对野生型小鼠可以有效抵抗由LPS诱导的脓毒症小鼠的死亡(图2A),而AQ-390作为GSDMD潜在的小分子抑制剂,同样可以降低LPS诱导的脓毒症小鼠的死亡率(图2B);在细胞层面,AQ-390在安全的药物浓度范围内,可以有效改善LPS联合Nigericin刺激的巨噬细胞活性(图2C),减少IL-1β和IL-18的分泌(图2D),减少GSDMD-NT的膜结合数量(图2E),改善细胞形态和通透性(图2F),抑制巨噬细胞焦亡。The AQ-390 used in the animal experiments of the present invention is a dosage form prepared in a CMC-Na solution soluble in 0.25% tween-80. The solution had a pH of 7.36 and was filtered through a 0.22 microporous membrane. The 6-8 week old C57BL/6 healthy mice (WT) and 6-8 week old GSDMD-/- healthy mice were intraperitoneally injected with low-dose LPS (15 mg/kg) to construct the sepsis animal model. The AQ-390 drug treatment group was treated with AQ-390 (25mg/kg) (intraperitoneal injection for 25 hours), followed by intraperitoneal injection of low-dose LPS (15mg/kg) to establish a sepsis animal model. For cell experiments, Thp-1 macrophages were plated in six-well plates with 2ml of culture medium. Macrophages were stimulated with LPS (10 μg/ml) for 6 hours and Nigericin (Niger) (10 μM) (10 μM) for 1 hour to construct a classical pyroptosis model. In the AQ-390 drug treatment group, macrophages were pretreated with different drug concentrations of AQ-390 for 1 hour, then treated with LPS (10 μg/ml) for 4 hours, and Nigericin (10 μM) (10 μM) stimulated macrophages for 1 hour. Phagocytosis to construct a classical model of pyroptosis. At the animal level, we found that GSDMD-/- mice can effectively resist the death of LPS-induced sepsis mice compared with wild-type mice (Fig. 2A), and AQ-390, as a potential small molecule inhibitor of GSDMD, can also Reduced mortality in mice with LPS-induced sepsis (Fig. 2B); at the cellular level, AQ-390 could effectively improve macrophage activity stimulated by LPS combined with Nigericin within a safe drug concentration range (Fig. 2C), reducing The secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 (Fig. 2D), decreased the membrane-bound amount of GSDMD-NT (Fig. 2E), improved cell morphology and permeability (Fig. 2F), and inhibited macrophage pyroptosis.
其中,图2A表示的是GSDMD-/-小鼠较野生型(WT)小鼠能有效抵抗LPS诱导的脓毒症死亡,延长小鼠的生存时间;图2B表示的是经AQ-390治疗小鼠与野生型(WT)小鼠相比较,AQ-390能有效降低LPS诱导的脓毒症小鼠的死亡率;图2C表示的是CCK8检测梯度浓度的潜在小分子抑制剂AQ-390对巨噬细胞活性的影响;图2D表示的是AQ-390能减少利用LPS联合Nigericin(Nig)刺激巨噬细胞的模型中细胞上清的IL-1β和IL-18含量;图2E表示的是利用PI(Propidium iodide)检测细胞通透性,观察AQ-390对LPS联合Nigericin(Nig)刺激巨噬细胞的形态及通透性的影响(细胞膜通透性正常情况下PI不能渗入细胞内,通透性受影响的细胞由于PI渗入细胞中显现为红色荧光);图2F利用细胞免疫荧光观察AQ-390对LPS联合Nigericin(Nig)刺激巨噬细胞中GSDMD-NT生成的影响。Among them, Figure 2A shows that GSDMD-/- mice can effectively resist LPS-induced sepsis death and prolong the survival time of mice compared with wild-type (WT) mice; Figure 2B shows that treated with AQ-390 Compared with wild-type (WT) mice, AQ-390 can effectively reduce the mortality of LPS-induced sepsis mice; Figure 2C shows that the potential small molecule inhibitor AQ-390, a potential small molecule inhibitor of CCK8 detection gradient concentration, is effective in reducing the mortality of mice with LPS-induced sepsis. The effect of phagocytic activity; Figure 2D shows that AQ-390 can reduce the IL-1β and IL-18 content of cell supernatant in the model of macrophage stimulation with LPS combined with Nigericin (Nig); Figure 2E shows the use of PI (Propidium iodide) to detect cell permeability, observe the effect of AQ-390 on the morphology and permeability of macrophages stimulated by LPS combined with Nigericin (Nig) (under normal cell membrane permeability, PI cannot penetrate into cells, permeability Affected cells appear as red fluorescence due to PI infiltration into cells); Figure 2F uses cellular immunofluorescence to observe the effect of AQ-390 on LPS combined with Nigericin (Nig) stimulated GSDMD-NT production in macrophages.
实施例2:AQ-390与GSDMD蛋白有直接的结合作用且动力学稳定Example 2: AQ-390 has direct binding effect with GSDMD protein and is kinetically stable
本发明利用生物膜光相干生物传感器(bio-layer interferometry,BLI),蛋白pulldown技术分析AQ-390与GSDMD蛋白的结合关系:生物膜相干生物传感器利用ForteBioOctet检测方法,主要采用由ForteBio公司生产的全自动测试平台即Octet RED96分子间相互作用检测系统进行评估AQ-390与GSDMD蛋白结合作用。使用PBS Buffer(PH7.4)将GST标记的GSDMD纯化蛋白(GST-GSDMD)和GST标签蛋白(GST)稀释为分别稀释成10μg/mL,体积分别为400μL;使用5%DMSO+PBST[PH7.4PBS+0.02%Tween20]将AQ-390稀释成1000μM,以此为最高浓度,倍比稀释成6个浓度,用于后续检测;使用GST探针(ForteBio,18-5096)固化GST-GSDMD以及GST;将上述样品及试剂按顺序置入样品板中,用Octet RED96程序运行,用fortebio data analysis 10.0软件采用双扣除的计算方式,即扣除缓冲液信号和GST的结合信号,随即将扣除后的信号数据进行Align处理,Baseline 55-59.8s(是将结合信号的起点进行归零处理,Baseline步骤中60s的信号进行归零处理,该相互作用完整的实验流程为Baseline 60s,结合60s,解离60s),最后将所得数据进行拟合分析(拟合模型1:1)。对于Pulldown实验,本发明使用BeaverbeadsTM链霉亲和素-琼脂糖珠和生物素化AQ-390。将100μL的1mM生物素化AQ-390添加到10μL链霉亲和素-琼脂糖珠中,以单独使用生物素、未生物素化的AQ-390以及未处理的珠子作为对照组,然后将GSDMD纯化蛋白添加到带有Bio-AQ-390的链酶亲和素-琼脂糖珠中,将混合物25℃温育3小时,同时轻轻摇动,随后将样品洗涤3次,用5x上样缓冲液煮沸洗脱蛋白,样品按分组上样于10%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶上进行WesternBlot分析。根据BLI以及pulldown实验相关数据分析,AQ-390可与GSDMD纯化蛋白存在结合且动力学稳定(图3B、C)。The present invention utilizes bio-layer interferometry (bio-layer interferometry, BLI) and protein pulldown technology to analyze the binding relationship between AQ-390 and GSDMD protein: the bio-film coherent biosensor utilizes the ForteBioOctet detection method, and mainly adopts the whole product produced by ForteBio Company. An automatic test platform, the Octet RED96 intermolecular interaction detection system, was used to evaluate the binding effect of AQ-390 to GSDMD protein. Use PBS Buffer (PH7.4) to dilute GST-tagged GSDMD purified protein (GST-GSDMD) and GST-tagged protein (GST) to 10 μg/mL, respectively, in a volume of 400 μL; use 5% DMSO+PBST [PH7. 4PBS+0.02%Tween20] AQ-390 was diluted to 1000μM, which was the highest concentration, and was diluted to 6 concentrations for subsequent detection; GST-GSDMD and GST were immobilized with GST probe (ForteBio, 18-5096). ; Put the above-mentioned samples and reagents into the sample plate in sequence, run with the Octet RED96 program, and use the fortebio data analysis 10.0 software to adopt the calculation method of double deduction, that is, deduct the binding signal of the buffer signal and GST, and then deduct the signal after the deduction. The data is processed by Align, Baseline 55-59.8s (the starting point of the binding signal is reset to zero, and the signal of 60s in the Baseline step is reset to zero. The complete experimental process of the interaction is Baseline 60s, binding 60s, dissociation 60s ), and finally perform fitting analysis on the obtained data (fitting model 1:1). For Pulldown experiments, the present invention used BeaverbeadsTM streptavidin-agarose beads and biotinylated AQ-390. 100 μL of 1 mM biotinylated AQ-390 was added to 10 μL streptavidin-agarose beads to use biotin alone, unbiotinylated AQ-390, and untreated beads as controls, followed by GSDMD Purified protein was added to streptavidin-agarose beads with Bio-AQ-390 and the mixture was incubated at 25°C for 3 hours with gentle shaking, then the samples were washed 3 times with 5x loading buffer The proteins were eluted by boiling, and the samples were loaded in groups on a 10% polyacrylamide gel for Western Blot analysis. According to the data analysis of BLI and pulldown experiments, AQ-390 could bind to GSDMD purified protein with stable kinetics (Figure 3B, C).
其中,图3A表示的是AQ-390和GSDMD蛋白结合位点示意图;图3B表示的是生物素化AQ-390与GSDMD纯化蛋白pulldown实验结果示意图;图3C表示的是AQ-390与GSDMD纯化蛋白BLI结果示意图。Among them, Figure 3A shows the schematic diagram of the binding site of AQ-390 and GSDMD protein; Figure 3B shows the schematic diagram of the pulldown experiment results of biotinylated AQ-390 and GSDMD purified protein; Figure 3C shows AQ-390 and GSDMD purified protein Schematic diagram of BLI results.
实施例3:AQ-390可靶向抑制GSDMD蛋白缓解细胞焦亡减轻心肌缺血再灌注损伤的作用Example 3: AQ-390 can target the inhibition of GSDMD protein to alleviate cell pyroptosis and reduce myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
细胞层面:利用乳大鼠原代心肌细胞,置于无糖无血清的DMEM细胞培养液中,分别放入低氧工作站(1%O2、5%CO2、约95%N2)培养2小时,然后再将各组细胞放入常氧培养箱分别复氧4小时构建缺氧再复氧损伤的心肌细胞模型。AQ-390药物处理组则为,使用安全范围内的AQ-390剂量预处理心肌细胞1小时,置于无糖无血清的DMEM细胞培养液中,分别放入低氧工作站(1%O2、5%CO2、约95%N2)培养2小时,然后再将各组细胞放入常氧培养箱分别复氧4小时构建缺氧再复氧损伤的心肌细胞模型。具体细胞实验分组分为:正常对照组、单纯药物处理组、H/R组、AQ-390(100μM)+H/R组、AQ-390(200μM)+H/R组(选用100μM、200μMAQ-390药物浓度理由由下图4B阐述)。Cell level: The primary cardiomyocytes of milk rats were used, placed in DMEM cell culture medium without sugar and serum, and placed in a hypoxic workstation (1% O2, 5% CO2, about 95% N2) for 2 hours, and then The cells in each group were then placed in a normoxia incubator for 4 hours of reoxygenation to construct a myocardial cell model of hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. In the AQ-390 drug treatment group, cardiomyocytes were pretreated with a dose of AQ-390 within the safe range for 1 hour, placed in sugar-free and serum-free DMEM cell culture medium, and placed in a hypoxia workstation (1% O2, 5 %CO2, about 95%N2) were cultured for 2 hours, and then the cells of each group were put into a normoxia incubator for reoxygenation for 4 hours to build a myocardial cell model of hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. The specific cell experimental groups are divided into: normal control group, simple drug treatment group, H/R group, AQ-390(100μM)+H/R group, AQ-390(200μM)+H/R group (select 100μM, 200μM MAQ- The rationale for the 390 drug concentration is illustrated in Figure 4B below).
动物层面:挑选健康雄性6-8周龄的C57BL/6小鼠,(相关动物信息见前详细阐述),平均体重20-24g,小鼠采用异氟烷气麻,待呼吸平稳后开胸利用5-0细线结扎左前降支,可观察到左心室壁变白,留置活结后闭胸,30分钟后松开活结再灌注4小时后开胸留取样本。假手术(Sham)组开胸后穿线但不结扎血管。采用造模前4小时腹腔注射25mg/kg以及50mg/kg的AQ-390,对照组使用生理盐水腹腔注射,每组8只。将6-8周小鼠随机分为5组:假手术组(Sham)、AQ-390(50mg/kg)+假手术组、I/R组、AQ-390(25mg/kg)+I/R组、AQ-390(50mg/kg)+I/R组。Animal level: Select healthy male C57BL/6 mice aged 6-8 weeks, (relevant animal information is described in detail above), with an average weight of 20-24g, the mice are anesthetized with isoflurane, and the chest is opened after breathing is stable. The left anterior descending branch was ligated with 5-0 thin thread, and the left ventricular wall was observed to be white. The chest was closed after indwelling the slip knot. After 30 minutes, the slip knot was loosened and reperfused for 4 hours, and then the chest was opened to collect samples. The sham operation (Sham) group was threaded but not ligated blood vessels after thoracotomy. 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg of AQ-390 were intraperitoneally injected 4 hours before modeling, and the control group was intraperitoneally injected with normal saline, with 8 rats in each group. 6-8 week old mice were randomly divided into 5 groups: sham operation group (Sham), AQ-390 (50mg/kg)+sham operation group, I/R group, AQ-390 (25mg/kg)+I/R group, AQ-390 (50mg/kg)+I/R group.
在细胞层面中,本发明首先检验了不同浓度的AQ390药物本身是否会对原代心肌细胞的活性造成影响,在0-400μM之间任意终浓度的AQ390均不会对原代心肌细胞活性造成影响。因此本发明最终挑选浓度为100μM以及200μM的药物浓度进行后续实验(图4A)。随后本发明在光镜下观察心肌细胞,发现缺复氧的心肌细胞结构紊乱,梭形心肌细胞拉长变细,细胞活性下降,LDH和IL-18释放增加,经AQ390药物预处理后心肌细胞形态均有所改善,细胞活性也均有所提高,LDH、IL-18释放减少,并呈现一定的剂量依赖性。而对照组心肌细胞形态及活性无明显改变(图4B、C、D、E)。At the cellular level, the present invention firstly tested whether different concentrations of AQ390 drug itself would affect the activity of primary cardiomyocytes, and any final concentration of AQ390 between 0-400 μM would not affect the activity of primary cardiomyocytes . Therefore, the present invention finally selected drug concentrations of 100 μM and 200 μM for subsequent experiments ( FIG. 4A ). Subsequently, the present invention observes cardiomyocytes under a light microscope, and finds that the cardiomyocytes of hypo-reoxygenation are structurally disordered, spindle cardiomyocytes elongate and thin, cell activity decreases, and the release of LDH and IL-18 increases. After pretreatment with AQ390, cardiomyocytes The morphology was improved, the cell activity was also improved, and the release of LDH and IL-18 was decreased in a dose-dependent manner. In the control group, there was no significant change in the morphology and activity of cardiomyocytes (Fig. 4B, C, D, E).
在动物层面中,本发明利用Evans Blue/TTC染色观察心梗面积,发现经两种药物浓度治疗的缺灌组剂量依赖性的改善了心肌梗死面积(图5A、B、C),这说明AQ390能够保护缺血再灌注的心脏组织,减少心梗面积。本发明检测了各组小鼠血清中的LDH(图6A)、CK-MB(图6B),小鼠心脏组织中的IL-1β和IL-18(图6C、D),用qPCR法分析小鼠心脏组织中的IL-1β、IL-18(图6E、F),所得的结果均可以显示AQ390能够改善GSDMD介导的细胞焦亡所引起的心肌缺血再灌注损伤。In the animal level, the present invention uses Evans Blue/TTC staining to observe the myocardial infarction area, and found that the myocardial infarction area was improved in a dose-dependent manner in the deficient perfusion group treated with two drug concentrations (Figure 5A, B, C), which indicates that AQ390 It can protect the ischemia-reperfusion heart tissue and reduce the size of myocardial infarction. The present invention detected LDH (Fig. 6A), CK-MB (Fig. 6B), IL-1β and IL-18 in mouse heart tissue (Fig. 6C, D) in the serum of each group of mice. The results of IL-1β and IL-18 in mouse heart tissue (Figure 6E, F) all showed that AQ390 can improve myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury caused by GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis.
其中,图4A表示的是利用光学显微镜观察AQ-390对缺氧再复氧模型的原代心肌细胞形态的影响;图4B表示的是利用CCK-8检测梯度浓度的潜在小分子抑制剂AQ-390对乳大鼠原代心肌细胞活性的影响;图4C表示的是AQ-390能够明显以剂量依赖性的改善原代心肌细胞缺氧再复氧后的细胞活性;图4D表示的是AQ-390能够明显以剂量依赖性的减少原代心肌细胞缺氧再复氧后细胞上清中LDH的释放量;图4E表示的是AQ-390能够明显以剂量依赖性的减少原代心肌细胞缺氧再复氧后细胞上清中的IL-18释放量。Among them, Figure 4A shows the effect of AQ-390 on the morphology of primary cardiomyocytes in the hypoxia-reoxygenation model by optical microscopy; Figure 4B shows the use of CCK-8 to detect gradient concentrations of potential small molecule inhibitors AQ- The effect of 390 on the activity of primary cardiomyocytes in milk rats; Figure 4C shows that AQ-390 can significantly improve the cell activity of primary cardiomyocytes after hypoxia and reoxygenation in a dose-dependent manner; Figure 4D shows AQ-390 390 can significantly reduce the release of LDH in the supernatant of primary cardiomyocytes after hypoxia and reoxygenation in a dose-dependent manner; Figure 4E shows that AQ-390 can significantly reduce the hypoxia of primary cardiomyocytes in a dose-dependent manner. IL-18 release in cell supernatants after reoxygenation.
其中,图5A表示的构建小鼠心肌缺血再灌注模型,根据Evans Blue/TTC染色观察AQ-390对心梗面积的影响(一般采用的是以白色区域代表梗死区,红色区域代表缺血危险区,蓝色区域代表非缺血区(附图由左至右依次从白-红-蓝的转变);图5B表示的是五组小鼠心脏缺血危险区的百分比统计图(AAR:缺血危险区;LV:左心室面积);图5C表示的是五组小鼠心梗面积百分比统计图(IFN:梗死区;AAR:缺血危险区)。Among them, the mouse myocardial ischemia-reperfusion model shown in Figure 5A was constructed, and the effect of AQ-390 on myocardial infarction area was observed according to Evans Blue/TTC staining (generally, the white area represents the infarct area, and the red area represents the ischemic risk The blue area represents the non-ischemic area (the figure changes from white-red-blue from left to right); Figure 5B shows the percentage statistics of the risk area of cardiac ischemia in five groups of mice (AAR: lack of Blood risk area; LV: left ventricular area); Fig. 5C shows a graph of the percentage of myocardial infarction area in five groups of mice (IFN: infarct area; AAR: ischemia risk area).
其中,图6A表示的是AQ-390剂量依赖性的减少I/R小鼠血清中LDH的含量;图6B表示的是AQ-390能减少I/R动物组血清中心肌损伤指标CK-MB的含量;图6C、D表示的是AQ-390剂量依赖性的减少I/R小鼠梗死区心肌组织中IL-1β、IL-18的表达量;图6E、F表示的是利用qPCR法检测各分组小鼠梗死区心肌组织中IL-1β、IL-18的表达量。AQ-390可呈剂量依赖性的减少I/R小鼠梗死区心肌组织中IL-1β、IL-18的表达量。Among them, Figure 6A shows that AQ-390 dose-dependently reduces the content of LDH in serum of I/R mice; Figure 6B shows that AQ-390 can reduce the level of myocardial injury index CK-MB in serum of I/R animal group. Figure 6C and D show that AQ-390 dose-dependently reduces the expression of IL-1β and IL-18 in the myocardial tissue of the infarcted area of I/R mice; Figure 6E and F show that the qPCR method was used to detect The expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in myocardial tissue in the infarcted area of mice were grouped. AQ-390 can dose-dependently reduce the expression of IL-1β and IL-18 in the myocardial tissue of the infarcted area of I/R mice.
本发明实施例提供的治疗或预防心肌缺血再灌注损伤药物制备方法包括:本发明药物组合物的各种剂型可以按照药学领域的常规生产方法制备。例如使活性成分AQ-390与一种或多种载体辅料混合,然后将其制成所需的剂型,如针剂、胶囊及片剂等。The preparation method of the medicine for treating or preventing myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury provided in the embodiment of the present invention includes: various dosage forms of the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be prepared according to the conventional production methods in the pharmaceutical field. For example, the active ingredient AQ-390 is mixed with one or more carrier auxiliary materials, and then it is made into the desired dosage form, such as injection, capsule and tablet.
显然,本领域的技术人员可以对本发明进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本发明的精神和范围。这样,倘若本发明的这些修改和变型属于本发明权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则本发明也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made in the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. Thus, provided that these modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and their equivalents, the present invention is also intended to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210253238.XACN114469940B (en) | 2022-03-15 | 2022-03-15 | Application of small molecule compound AQ-390 in preparing medicine and inhibitor for resisting cell apoptosis |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210253238.XACN114469940B (en) | 2022-03-15 | 2022-03-15 | Application of small molecule compound AQ-390 in preparing medicine and inhibitor for resisting cell apoptosis |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114469940Atrue CN114469940A (en) | 2022-05-13 |
| CN114469940B CN114469940B (en) | 2023-03-31 |
Family
ID=81486291
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210253238.XAActiveCN114469940B (en) | 2022-03-15 | 2022-03-15 | Application of small molecule compound AQ-390 in preparing medicine and inhibitor for resisting cell apoptosis |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114469940B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116919955A (en)* | 2023-08-30 | 2023-10-24 | 温州医科大学附属第一医院 | Application of small molecular compound GI-Y2 in preparation of medicines and inhibitors |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117159533A (en)* | 2023-07-07 | 2023-12-05 | 中山大学 | Application of a sesquiterpenoid compound in the preparation of drugs that inhibit inflammasome activation and/or block pyroptosis |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB916456A (en)* | 1960-06-02 | 1963-01-23 | Solco Basel Ag | New and useful pyrazoline derivatives and a process of making same |
| CN1578767A (en)* | 2001-11-22 | 2005-02-09 | 小野药品工业株式会社 | Piperidin-2-one derivative compounds and drugs containing these compounds as the active ingredient |
| WO2017153952A1 (en)* | 2016-03-10 | 2017-09-14 | Glaxosmithkline Intellectual Property Development Limited | 5-sulfamoyl-2-hydroxybenzamide derivatives |
| CN109071454A (en)* | 2016-02-16 | 2018-12-21 | 昆士兰大学 | Sulfonylureas and related compound and application thereof |
| CN112076189A (en)* | 2020-09-23 | 2020-12-15 | 唐怡庭 | Application of amide compound in preparation of medicine for treating sepsis |
- 2022
- 2022-03-15CNCN202210253238.XApatent/CN114469940B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB916456A (en)* | 1960-06-02 | 1963-01-23 | Solco Basel Ag | New and useful pyrazoline derivatives and a process of making same |
| CN1578767A (en)* | 2001-11-22 | 2005-02-09 | 小野药品工业株式会社 | Piperidin-2-one derivative compounds and drugs containing these compounds as the active ingredient |
| CN109071454A (en)* | 2016-02-16 | 2018-12-21 | 昆士兰大学 | Sulfonylureas and related compound and application thereof |
| WO2017153952A1 (en)* | 2016-03-10 | 2017-09-14 | Glaxosmithkline Intellectual Property Development Limited | 5-sulfamoyl-2-hydroxybenzamide derivatives |
| CN112076189A (en)* | 2020-09-23 | 2020-12-15 | 唐怡庭 | Application of amide compound in preparation of medicine for treating sepsis |
Non-Patent Citations (4)
| Title |
|---|
| LI-WEN REN等: "Benzimidazoles induce concurrent apoptosis and pyroptosis of human glioblastoma cells via arresting cell cycle", 《ACTA PHARMACOL SIN.》* |
| REGISTRY: "31816-70-3", 《STN》* |
| YASUHIRO ISHIHARA等: "Effects of sulfaphenazole derivatives on cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: association of cytochrome P450 activity and infarct size", 《JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGICAL SCIENCES》* |
| YASUHIRO ISHIHARA等: "Sulfaphenazole attenuates myocardial cell apoptosis accompanied with cardiac ischemia-reperfusion by suppressing the expression of BimEL and Noxa", 《JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGICAL SCIENCES》* |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116919955A (en)* | 2023-08-30 | 2023-10-24 | 温州医科大学附属第一医院 | Application of small molecular compound GI-Y2 in preparation of medicines and inhibitors |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114469940B (en) | 2023-03-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2022200570B2 (en) | Compositions and methods for treating anemia | |
| KR100386229B1 (en) | Inhibition of smooth muscle migration and proliferation of hydroxycarbazole compounds | |
| JP5827962B2 (en) | Cdc7 kinase inhibitors and uses thereof | |
| CN114469940B (en) | Application of small molecule compound AQ-390 in preparing medicine and inhibitor for resisting cell apoptosis | |
| CH661871A5 (en) | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION FOR THE TREATMENT OF STATES OF ACUTE RENAL INSUFFICIENCY. | |
| CN106692150B (en) | Use of nintedanib in the preparation of drugs for the prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis and liver cirrhosis | |
| US20090062338A1 (en) | Nitroxides for use in treating or preventing cardiovascular disease | |
| WO2020252937A1 (en) | Application of heterocyclic compound extracted from solanaceae in preparing medicine for treating multiple sclerosis and medicine | |
| RU2825648C1 (en) | Methods of treating coronavirus infections | |
| CN118717774A (en) | Preparation method of small molecule compound GI-Y3 and its application in preparing anti-cell pyroptosis drugs and inhibitors | |
| KR20250124425A (en) | Novel PRMT5 Inhibitors and Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising the Same | |
| JPS62129218A (en) | Remedy for hepatic disease containing thiaprostaglandin as active component | |
| JP2016141669A (en) | Chronic myeloid leukemia treating agent | |
| HK1216844B (en) | Compositions and methods for treating anemia | |
| JPH02286617A (en) | Arterialization inhibitor |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20230831 Address after:Building 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7, 112-118 Gaoyi Road, Baoshan District, Shanghai, 201900 Patentee after:Shenlu Yaoxin Pharmaceutical (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd. Address before:325000 nanbaixiang, Ouhai District, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province Patentee before:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL University |