CN114366309A - Surgical robot with nerve monitoring function - Google Patents
Surgical robot with nerve monitoring functionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114366309A CN114366309ACN202210050059.6ACN202210050059ACN114366309ACN 114366309 ACN114366309 ACN 114366309ACN 202210050059 ACN202210050059 ACN 202210050059ACN 114366309 ACN114366309 ACN 114366309A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- nerve
- surgical
- end effector
- joystick
- signal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 210000005036nerveAnatomy0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription104
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription64
- 239000012636effectorSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription43
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 230000001537neural effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000claimsdescription27
- 230000007658neurological functionEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000001225therapeutic effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000037361pathwayEffects0.000claims1
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000abstractdescription16
- 208000028389Nerve injuryDiseases0.000abstractdescription4
- 230000008764nerve damageEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 210000000988bone and boneAnatomy0.000description35
- 210000000944nerve tissueAnatomy0.000description8
- 230000006837decompressionEffects0.000description7
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000description6
- 208000005198spinal stenosisDiseases0.000description5
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description5
- 210000004872soft tissueAnatomy0.000description4
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description4
- 241000283984RodentiaSpecies0.000description3
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description3
- 230000000399orthopedic effectEffects0.000description3
- 210000000278spinal cordAnatomy0.000description3
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 208000031481Pathologic ConstrictionDiseases0.000description2
- 210000003484anatomyAnatomy0.000description2
- 238000013473artificial intelligenceMethods0.000description2
- 238000002591computed tomographyMethods0.000description2
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 239000003989dielectric materialSubstances0.000description2
- 230000007831electrophysiologyEffects0.000description2
- 238000002001electrophysiologyMethods0.000description2
- 229910021389grapheneInorganic materials0.000description2
- 210000004749ligamentum flavumAnatomy0.000description2
- 210000003141lower extremityAnatomy0.000description2
- 206010025005lumbar spinal stenosisDiseases0.000description2
- 238000002595magnetic resonance imagingMethods0.000description2
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000description2
- 230000000926neurological effectEffects0.000description2
- 210000000273spinal nerve rootAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000036262stenosisEffects0.000description2
- 208000037804stenosisDiseases0.000description2
- 230000004936stimulating effectEffects0.000description2
- 230000008733traumaEffects0.000description2
- 238000002604ultrasonographyMethods0.000description2
- 208000012260Accidental injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 208000026350Inborn Genetic diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 206010061246Intervertebral disc degenerationDiseases0.000description1
- 208000034819Mobility LimitationDiseases0.000description1
- 208000010428Muscle WeaknessDiseases0.000description1
- 206010028372Muscular weaknessDiseases0.000description1
- 208000002193PainDiseases0.000description1
- 206010033799ParalysisDiseases0.000description1
- 230000002159abnormal effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000013459approachMethods0.000description1
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 208000018180degenerative disc diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 230000003412degenerative effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 230000004927fusionEffects0.000description1
- 208000016361genetic diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003384imaging methodMethods0.000description1
- 208000021600intervertebral disc degenerative diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 238000002684laminectomyMethods0.000description1
- 210000000653nervous systemAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000012829orthopaedic surgeryMethods0.000description1
- 208000035824paresthesiaDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003825pressingMethods0.000description1
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description1
- 206010039073rheumatoid arthritisDiseases0.000description1
- 206010062261spinal cord neoplasmDiseases0.000description1
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B17/16—Instruments for performing osteoclasis; Drills or chisels for bones; Trepans
- A61B17/1659—Surgical rasps, files, planes, or scrapers
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/388—Nerve conduction study, e.g. detecting action potential of peripheral nerves
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B17/00—Surgical instruments, devices or methods
- A61B2017/00017—Electrical control of surgical instruments
- A61B2017/00115—Electrical control of surgical instruments with audible or visual output
- A61B2017/00128—Electrical control of surgical instruments with audible or visual output related to intensity or progress of surgical action
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/20—Surgical navigation systems; Devices for tracking or guiding surgical instruments, e.g. for frameless stereotaxis
- A61B2034/2046—Tracking techniques
- A61B2034/2065—Tracking using image or pattern recognition
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B2034/301—Surgical robots for introducing or steering flexible instruments inserted into the body, e.g. catheters or endoscopes
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B2034/302—Surgical robots specifically adapted for manipulations within body cavities, e.g. within abdominal or thoracic cavities
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Dentistry (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Surgical Instruments (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于医疗器械领域,具体涉及一种具有神经监测功能的手术机器人。The invention belongs to the field of medical devices, and in particular relates to a surgical robot with a nerve monitoring function.
背景技术Background technique
具有手术导航系统的外科手术机器人是集机械电子、影像学、外科临床等诸多技术于一体的综合医疗手术设备,目前已应用于神经系统、心血管系统、消化系统、泌尿系统、骨外科等手术中。手术导航系统将病人术前或术中影像数据和手术床上病人解剖结构准确对应,手术中跟踪手术器械并将手术器械的位置在病人影像上以虚拟探针的形式实时更新显示,使医生对手术器械相对病人解剖结构的位置一目了然,使外科手术更快速、更精确、更安全。The surgical robot with surgical navigation system is a comprehensive medical and surgical equipment that integrates many technologies such as mechatronics, imaging, and clinical surgery. middle. The surgical navigation system accurately corresponds the preoperative or intraoperative image data of the patient with the patient's anatomical structure on the operating bed, tracks the surgical instruments during the operation, and updates and displays the position of the surgical instruments on the patient image in real time in the form of a virtual probe, so that the doctor can understand the operation. The position of the instruments relative to the patient's anatomy can be seen at a glance, making surgery faster, more precise, and safer.
然而在一些神经外科手术或是骨外科中,手术部位及附近存在丰富的神经组织,手术导航系统不显示神经定位,即使使用精细操作的外科手术机器人也存在盲打盲切误伤神经的风险。However, in some neurosurgery or orthopedic surgery, there are abundant nerve tissues in and near the operation site, and the surgical navigation system does not display the nerve location. Even if a surgical robot with fine operation is used, there is a risk of accidentally injuring the nerve by blind typing and blind cutting.
椎管狭窄是由于椎孔或椎间孔不正常狭窄而压迫到脊髓或神经根的一种状态。椎管狭窄以腰椎狭窄最常见,其次是颈椎狭窄。腰椎椎管狭窄引起的症状包括下肢的疼痛、感觉异常、肌肉减弱、步行困难,症状渐进发展,严重时影响到尿失禁、排便困难和性功能障碍。椎管狭窄的成因很多,包括退化性椎间盘疾病(degenerative disc disease)、脊髓肿瘤、创伤、类风湿性关节炎、遗传性疾病。最为多见的退化性腰椎椎管狭窄,人群发病率50-65岁达 8%,65岁以上人群发病率达20%。传统开放椎板切除减压术具有疗效确定的优点,但对脊柱稳定性影响较大,常需内固定和融合,其存在手术创伤大、并发症较多等缺点。Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the spinal cord or nerve roots are compressed due to abnormal narrowing of the vertebral foramen or intervertebral foramen. The most common spinal stenosis is lumbar stenosis, followed by cervical stenosis. Symptoms caused by lumbar spinal stenosis include lower extremity pain, paresthesias, muscle weakness, and difficulty walking. Spinal stenosis can have many causes, including degenerative disc disease, spinal cord tumors, trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, and genetic diseases. The most common type of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis is 8% of the population aged 50-65, and 20% of the population over the age of 65. Traditional open laminectomy and decompression has the advantages of definite curative effect, but it has a great impact on the stability of the spine, often requires internal fixation and fusion, and has disadvantages such as large surgical trauma and many complications.
现有技术下,椎管减压手术过程中,手术入路从椎板间入,内镜下使用高速磨钻、椎板咬骨钳等手术器械切除椎板骨性结构,达到椎管成形减压的目的。然而手术对操作的精细程度要求很高,控制不好容易伤到脊髓。Under the prior art, during spinal canal decompression surgery, the surgical approach is from the interlaminar, and surgical instruments such as a high-speed drill, a lamina rongeur and other surgical instruments are used to remove the laminar bony structure under the endoscope, so as to achieve the reduction of laminoplasty. the purpose of pressing. However, the operation requires a high degree of precision, and it is easy to damage the spinal cord if the control is not good.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明针对现有技术不足,提供了一种具备神经监测功能的手术机器人,监测术中神经电生理信号,进行神经功能定位和功能评估,辅助指导手术操作,避免损伤神经,提高手术的安全性。Aiming at the deficiencies in the prior art, the present invention provides a surgical robot with a nerve monitoring function, which can monitor intraoperative nerve electrophysiological signals, perform nerve function positioning and function evaluation, assist in guiding surgical operations, avoid nerve damage, and improve the safety of surgery. .
本发明具体技术方案如下:The specific technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
一种具有神经监测功能的手术机器人,包括主控系统、机械臂/操纵杆、末端执行器和与末端执行器相配的手术器械以及神经功能监测系统,末端执行器和/或手术器械上具有神经监测元件,神经功能监测系统通过神经监测元件探测并处理患者手术部位的阻抗信号和/或神经电生理信号,并将信号反馈给主控系统,主控系统根据阻抗信号特点和/或神经电生理信号的有无、强弱或者信号特征,控制机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动或停止,或者调整机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动轨迹。A surgical robot with nerve monitoring function, comprising a main control system, a mechanical arm/joystick, an end effector, a surgical instrument matched with the end effector, and a nerve function monitoring system, the end effector and/or the surgical instrument having nerves Monitoring element, the nerve function monitoring system detects and processes the impedance signal and/or nerve electrophysiology signal of the patient's surgical site through the nerve monitoring element, and feeds back the signal to the main control system, which is based on the characteristics of the impedance signal and/or nerve electrophysiology. The presence or absence, strength or signal characteristics of the signal, control the movement or stop of the robot arm/joystick and/or the end effector, or adjust the movement trajectory of the robot arm/joystick and/or the end effector.
所述主控系统包括计算机中央控制系统,机械驱动主机,手术操作监视器、机器人控制监视器、操作手柄和输入输出等设备。手术时,外科医生可通过主控系统控制操作手柄,手部动作传达到机械臂/操纵杆的尖端,完成手术操作,或者手术机器人根据预设程序或者人工智能系统实现自动化无人操作。The main control system includes a computer central control system, a mechanical drive host, a surgical operation monitor, a robot control monitor, an operation handle, and input and output devices. During surgery, the surgeon can control the operating handle through the main control system, and the hand movements are transmitted to the tip of the robotic arm/joystick to complete the surgical operation, or the surgical robot can realize automatic unmanned operation according to preset programs or artificial intelligence systems.
所述神经功能监测系统包括对电生理信号(如阻抗)或神经电生理信号的采集、刺激、计算分析、处理的设备或模块(如:阻抗监测仪、神经功能监测仪或者具有相同功能的模块)。The neurological function monitoring system includes equipment or modules for collecting, stimulating, calculating and analyzing, and processing electrophysiological signals (such as impedance) or neurological electrophysiological signals (such as: impedance monitor, neurological function monitor, or modules with the same function) ).
所述神经监测元件能够传出和/或传入信号,通过对阻抗信号的探测区分骨组织、神经组织或其他软组织;或者探测神经因被直接或间接刺激而产生的神经电生理信号,定位神经精确位置。The nerve monitoring element can transmit and/or afferent signals, distinguish bone tissue, nerve tissue or other soft tissue by detecting impedance signals; or detect nerve electrophysiological signals generated by direct or indirect stimulation of nerves, and locate nerves. precise location.
所述神经监测元件设于手术器械的端部、表面或外缘中的一种或几种,导线埋设于手术器械内部。末端执行器内设有与神经功能监测系统电路连接的导线,末端执行器上设有与神经监测元件的电路连接的接口。优选的,电路连接的接口设于末端执行器与手术器械固定接触处。The nerve monitoring element is arranged on one or more of the end, the surface or the outer edge of the surgical instrument, and the wire is embedded inside the surgical instrument. The end effector is provided with a wire connected with the circuit of the nerve function monitoring system, and the end effector is provided with an interface connected with the circuit of the nerve monitoring element. Preferably, the interface for electrical connection is provided at the fixed contact point between the end effector and the surgical instrument.
本发明所述的手术机器人可以为适用于各种外科手术的机器人,根据手术类型、手术部位以及操作需要的不同,具有相适应的末端执行器以及相配的手术器械。The surgical robot of the present invention can be a robot suitable for various surgical operations, and has a suitable end effector and a matching surgical instrument according to the type of operation, the surgical site and the operation needs.
进一步的,所述神经功能监测系统记录并存储记忆术中阻抗信号和/或神经电生理信号形成患者的神经定位信息,主控系统根据神经定位的信息规划、调整机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动轨迹。Further, the nerve function monitoring system records and stores the intraoperative impedance signal and/or nerve electrophysiological signal to form the nerve location information of the patient, and the main control system plans and adjusts the robotic arm/joystick and/or according to the nerve location information. The trajectory of the end effector.
优选的,所述手术机器人还包括手术导航系统,主控系统根据手术导航系统的影像信号(如三维数字化影像)以及神经功能监测系统的阻抗信号和/或神经电生理信号,控制机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动或停止,或者调整机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动轨迹。Preferably, the surgical robot further includes a surgical navigation system, and the main control system controls the robotic arm/manipulation according to the image signals (such as three-dimensional digital images) of the surgical navigation system and the impedance signals and/or neurophysiological signals of the neurological function monitoring system Movement or stop of the rod and/or end effector, or adjustment of the motion trajectory of the robotic arm/joystick and/or end effector.
所述手术导航系统包括对图像进行采集、处理的设备或模块,例如内窥镜、超声、X光、CT或MRI扫描装置或模块,以及对图像进行处理的软件系统或模块。The surgical navigation system includes a device or module for acquiring and processing images, such as an endoscope, ultrasound, X-ray, CT or MRI scanning device or module, and a software system or module for processing images.
本发明所述神经监测元件选自电极、传感器、传感性能的外包膜、传感性能贴片或涂层、具有传导神经信号的介质制成的传导通路中的一种或几种,所述介质包括但不限于金属、光、声、石墨烯、新介质材料等以上一种或几种中的一种或几种。The nerve monitoring element of the present invention is selected from one or more of electrodes, sensors, outer envelopes with sensing properties, patches or coatings with sensing properties, and conduction paths made of media with conduction nerve signals. The medium includes, but is not limited to, one or more of the above one or more of metal, light, sound, graphene, and new dielectric materials.
所述手术器械可以为本领域下所有可以用于手术机器人的手术器械,包括工具类、治疗类、诊断类器械,如各种钳、剪、夹、刀、针、管、镊、钩、锉、锯、丝、线等。The surgical instruments can be all surgical instruments that can be used for surgical robots in the field, including tools, therapeutic, and diagnostic instruments, such as various forceps, scissors, clips, knives, needles, tubes, forceps, hooks, and files. , saw, wire, wire, etc.
优选的,所述手术器械可以为骨外科手术中实施手术操作的器械,例如导引管、开路器、咬骨钳、扩孔器、克氏针、穿刺针、导引丝、骨锉、骨锯等。Preferably, the surgical instrument may be an instrument for performing surgical operations in bone surgery, such as guide tube, circuit opener, rongeur, reamer, Kirschner wire, puncture needle, guide wire, bone rasp, bone saw etc.
一个具体的示例,所述的手术机器人为骨科手术机器人,手术器械为导引管、导丝或线状骨锉中的一种或几种,所述导引管、导丝的头端,线状骨锉的表面设有至少一个神经监测元件。A specific example, the surgical robot is an orthopaedic surgical robot, the surgical instrument is one or more of a guide tube, a guide wire or a wire rasp, the guide tube, the head end of the guide wire, the wire The surface of the rasp is provided with at least one nerve monitoring element.
优选的,所述线状骨锉为扁平带状,具有工作部和牵拉部,工作部表面具有锉磨纹路,如磨砂颗粒状、齿状、斜纹状纹路等,背面(与非手术部位组织接触面)光滑。工作部表面上设有至少一个神经监测元件。所述牵拉部具有与手术机器人的末端执行器固定的固定孔或固定件,神经监测元件的导线可经固定孔或固定件与手术机器人末端执行器的电路接口连接,Preferably, the linear bone rasp is in the shape of a flat band, with a working part and a pulling part, and the surface of the working part has rasping patterns, such as frosted grain-like, tooth-like, twill-like patterns, etc. contact surface) smooth. At least one nerve monitoring element is provided on the working part surface. The pulling part has a fixing hole or a fixing piece fixed with the end effector of the surgical robot, and the wire of the nerve monitoring element can be connected with the circuit interface of the end effector of the surgical robot through the fixing hole or fixing piece,
使用时,线状骨锉的工作部表面贴合骨骼,牵拉部受手术操作者或手术机器人牵拉,光滑的背面能够保证锉磨骨骼(如椎板)时,避免误伤神经或其他组织。与神经监测元件连接的导线埋设于骨锉内部,使用时与具有阻抗监测和/或神经功能监测系统的手术机器人连接。所述神经监测元件能够传出和/或传入信号,通过对阻抗信号的探测区分骨组织、神经组织或其他软组织;或者探测神经因被直接或间接刺激而产生的神经电生理信号,定位神经精确位置。当骨锉工作面探测到神经组织的阻抗信号或神经电生理信号时,神经监测元件能够将探测到的信号传输至手术机器人的主控系统,主控系统控制机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器停止锉磨。When in use, the surface of the working part of the linear bone file fits the bone, and the pulling part is pulled by the surgical operator or the surgical robot. The smooth back can ensure that when the bone (such as the lamina) is rasped, the nerve or other tissue can be avoided by accident. The wire connected with the nerve monitoring element is embedded in the bone rasp, and is connected to a surgical robot with an impedance monitoring and/or nerve function monitoring system when in use. The nerve monitoring element can transmit and/or afferent signals, distinguish bone tissue, nerve tissue or other soft tissue by detecting impedance signals; or detect nerve electrophysiological signals generated by direct or indirect stimulation of nerves, and locate nerves. precise location. When the working surface of the bone rasp detects the impedance signal or neurophysiological signal of the nerve tissue, the nerve monitoring element can transmit the detected signal to the main control system of the surgical robot, which controls the robotic arm/joystick and/or end The actuator stops filing.
骨锉的长度和宽度可以有多种规格。Bone rasps are available in a variety of lengths and widths.
以椎管减压手术为例,结合导引管、导丝和线状骨锉对本发明所述手术机器人的使用过程进行说明。具体步骤为:Taking spinal canal decompression surgery as an example, the use process of the surgical robot of the present invention will be described in combination with a guide tube, a guide wire and a linear bone rasp. The specific steps are:
(1)利用导引管头端穿入椎间孔,并利用导引管的硬度松解黄韧带与锥板的缝隙;(1) Use the head end of the guide tube to penetrate the intervertebral foramen, and use the hardness of the guide tube to release the gap between the ligamentum flavum and the cone plate;
(2)将导丝与线状骨锉固定,导丝一端沿导引管内穿入,骨锉随导丝通过黄韧带、经关节突、穿椎间孔,弯曲穿过锥板;(2) Fix the guide wire and the linear bone rasp, one end of the guide wire is inserted into the guide tube, and the bone rasp follows the guide wire through the ligamentum flavum, through the articular process, through the intervertebral foramen, and bends through the cone and plate;
(3)线状骨锉到达手术部位后,解除与导丝的连接,导引管先行退出,导丝再退出锥板缝隙。导引管、导丝、线状骨锉上的神经监测元件在执行上述操作过程中进行实时监测;(3) After the linear bone file reaches the surgical site, the connection with the guide wire is released, the guide tube is withdrawn first, and then the guide wire exits the cone-plate gap. The nerve monitoring elements on the guide tube, guide wire and wire rasp perform real-time monitoring during the above-mentioned operations;
(4)线状骨锉的固定孔或固定件与外科手术机器人的末端执行器固定,同时神经监测元件也与手术机器人的神经功能监测系统电路连接。使用手术机器人利用骨锉进行磨骨时,神经监测元件实时监测骨锉触及组织的阻抗和/或神经电生理信号,阻抗信号显示为非神经组织或无神经电生理信号时,机械臂带动骨锉工作,椎间孔扩大,达到减压目的,一旦探测到信号,机械臂立即停止工作,避免神经损伤。(4) The fixing hole or the fixing piece of the linear bone file is fixed with the end effector of the surgical robot, and the nerve monitoring element is also connected with the circuit of the nerve function monitoring system of the surgical robot. When using a surgical robot to grind bone with a bone rasp, the nerve monitoring element monitors the impedance and/or nerve electrophysiological signal of the tissue touched by the bone rasp in real time. When the impedance signal shows non-nervous tissue or no nerve electrophysiological signal, the robotic arm drives the bone rasp. When working, the intervertebral foramen will expand to achieve the purpose of decompression. Once a signal is detected, the robotic arm will stop working immediately to avoid nerve damage.
本发明优点:Advantages of the present invention:
1.手术流程的最大风险是操作中误伤神经系统,造成病人永久性功能丧失,例如瘫痪、下肢行走运动功能丧失。本发明所述手术机器人在使用手术器械进行外科手术的同时,实时监测手术部位的阻抗和/或神经电生理信号,探测到非神经组织的阻抗信号或无神经电生理信号时,机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器正常运动,当探测到神经组织的阻抗信号或神经电生理信号时,发出探测警报的同时立即停止工作。神经功能监测系统记忆、记录术中神经电生理信号形成患者的神经定位信息,可根据定位信息将机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器调整至新的非神经组织的位置后再进行手术操作,同时根据已经记录的神经定位信息指导建立机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器新的运动轨迹,避开已经定位的神经位点,使手术更为顺畅。1. The biggest risk of the surgical procedure is the accidental injury to the nervous system during the operation, resulting in permanent loss of patient function, such as paralysis and loss of lower limb walking movement. The surgical robot of the present invention monitors the impedance and/or nerve electrophysiological signals of the surgical site in real time while using surgical instruments for surgical operations. The rod and/or the end effector moves normally, when the impedance signal or neurophysiological signal of the nerve tissue is detected, the detection alarm is issued and the work is stopped immediately. The nerve function monitoring system memorizes and records the intraoperative nerve electrophysiological signals to form the patient's nerve positioning information. According to the positioning information, the robotic arm/joystick and/or the end effector can be adjusted to the position of the new non-nervous tissue before performing the operation. At the same time, according to the nerve positioning information that has been recorded, a new movement trajectory of the robotic arm/joystick and/or end effector is established to avoid the already positioned nerve sites and make the operation smoother.
2.本发明所述外科手术机器人还可以结合手术导航系统的影像信号以及神经功能监测系统的阻抗和/或神经电生理信号,协同控制机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动或停止,或者调整机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动轨迹。2. The surgical robot of the present invention can also be combined with the image signal of the surgical navigation system and the impedance and/or nerve electrophysiological signal of the nerve function monitoring system to coordinately control the movement or stop of the robotic arm/joystick and/or end effector , or adjust the motion trajectory of the robotic arm/joystick and/or end effector.
3.本发明还提供了一种具备神经信号探测功能的骨科手术机器人,配合使用具有神经监测元件的导引管、导丝、线状骨锉,用于骨科手术,如椎管减压手术。该骨科手术机器人将手术最高风险的减压操作彻底转变,从机械性去除骨组织,转变为片状的锉纹贴合骨组织,进行摩擦,一点一点磨去骨组织。去除骨组织的厚度能够以毫米等级控制,完全避开手术工具操作的空间要求,完全不损伤脊髓和脊神经根的前提下,达到减压手术目的。该设计避免了现有技术使用高速磨钻、椎板咬骨钳切除椎板存在损伤神经的风险。采用骨锉锉磨椎板,操作简单,工作面只与椎板接触,具有更高的安全性。3. The present invention also provides an orthopedic surgery robot with nerve signal detection function, which is used in conjunction with a guide tube, a guide wire, and a linear bone file with a nerve monitoring element for orthopedic surgery, such as spinal canal decompression surgery. This orthopaedic surgery robot completely changes the decompression operation with the highest risk of surgery, from mechanically removing bone tissue to a sheet-like rasping to fit the bone tissue, rubbing and grinding away the bone tissue bit by bit. The thickness of the removed bone tissue can be controlled in millimeters, completely avoiding the space requirements of surgical tools, and achieving the purpose of decompression surgery without damaging the spinal cord and spinal nerve roots. The design avoids the risk of nerve damage in the prior art using a high-speed drill and a lamina rongeur to remove the lamina. Using bone rasp to grind the lamina, the operation is simple, and the working surface is only in contact with the lamina, which has higher safety.
附图说明Description of drawings
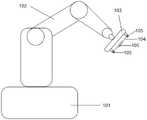
图1为本发明所述手术机器人系统连接示意图。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of the connection of the surgical robot system according to the present invention.
图2为本发明所述手术机器人结构示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of the surgical robot according to the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下通过实施例说明本发明的具体步骤,但不受实施例限制。The specific steps of the present invention are illustrated by the following examples, but are not limited by the examples.
在本发明中所使用的术语,除非另有说明,一般具有本领域普通技术人员通常理解的含义。Terms used in the present invention generally have the meanings commonly understood by those of ordinary skill in the art unless otherwise specified.
下面结合具体实例并参照数据进一步详细描述本发明。应理解,这些实施例只是为了举例说明本发明,而非以任何方式限制本发明的范围。The present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to specific examples and data. It should be understood that these examples are intended to illustrate the invention only and not to limit the scope of the invention in any way.
在以下实施例中,未详细描述的各种过程和方法是本领域中公知的常规方法。In the following examples, various procedures and methods not described in detail are conventional methods well known in the art.
实施例1Example 1
如图1和2所示,一种具有神经监测功能的手术机器人,包括主控系统101、机械臂/操纵杆 102、末端执行器103和与末端执行器相配的手术器械104、神经功能监测系统201和手术导航系统301,末端执行器103和/或手术器械104上具有神经监测元件105,神经功能监测系统201通过神经监测元件105探测并处理患者手术部位的阻抗信号和/或神经电生理信号,并将信号反馈给主控系统101,手术导航系统301形成影像信号,主控系统101根据手术导航系统的影像信号以及神经功能监测系统的阻抗信号特点和/或神经电生理信号的有无、强弱或者信号特征,控制机械臂/操纵杆102和/或末端执行器103的运动或停止,或者调整机械臂/操纵杆102和/或末端执行器103的运动轨迹。As shown in Figures 1 and 2, a surgical robot with nerve monitoring function includes a
所述主控系统包括计算机中央控制系统,机械驱动主机,手术操作监视器、机器人控制监视器、操作手柄和输入输出等设备。手术时,外科医生可通过主控系统控制操作手柄,手部动作传达到机械臂/操纵杆的尖端,完成手术操作,或者手术机器人根据预设程序或者人工智能系统实现自动化无人操作。The main control system includes a computer central control system, a mechanical drive host, a surgical operation monitor, a robot control monitor, an operation handle, and input and output devices. During surgery, the surgeon can control the operating handle through the main control system, and the hand movements are transmitted to the tip of the robotic arm/joystick to complete the surgical operation, or the surgical robot can realize automatic unmanned operation according to preset programs or artificial intelligence systems.
所述神经功能监测系统包括对电生理信号(如阻抗)或神经电生理信号的采集、刺激、计算分析、处理的设备或模块(如:阻抗监测仪、神经功能监测仪或者具有相同功能的模块)。神经监测元件能够传出和/或传入信号,通过对阻抗信号的探测区分骨组织、神经组织或其他软组织;或者探测神经因被直接或间接刺激而产生的神经电生理信号,定位神经精确位置。The neurological function monitoring system includes equipment or modules for collecting, stimulating, calculating and analyzing, and processing electrophysiological signals (such as impedance) or neurological electrophysiological signals (such as: impedance monitor, neurological function monitor, or modules with the same function) ). The nerve monitoring element can send and/or afferent signals, distinguish bone tissue, nerve tissue or other soft tissue by detecting impedance signals; or detect nerve electrophysiological signals generated by direct or indirect stimulation of nerves, and locate the precise location of nerves .
所述手术导航系统包括对图像进行采集、处理的设备或模块,例如内窥镜、超声、X光、CT或MRI扫描装置或模块,以及对图像进行处理的软件系统或模块。The surgical navigation system includes a device or module for acquiring and processing images, such as an endoscope, ultrasound, X-ray, CT or MRI scanning device or module, and a software system or module for processing images.
所述神经监测元件设于手术器械的端部、表面或外缘中的一种或几种,导线埋设于手术器械内部。末端执行器内设有与神经功能监测系统电路连接的导线,末端执行器上设有与神经监测元件的电路连接的接口。优选的,电路连接的接口设于末端执行器与手术器械固定接触处。The nerve monitoring element is arranged on one or more of the end, the surface or the outer edge of the surgical instrument, and the wire is embedded inside the surgical instrument. The end effector is provided with a wire connected with the circuit of the nerve function monitoring system, and the end effector is provided with an interface connected with the circuit of the nerve monitoring element. Preferably, the interface for electrical connection is provided at the fixed contact point between the end effector and the surgical instrument.
本发明所述的手术机器人可以为适用于各种外科手术的机器人,根据手术类型、手术部位以及操作需要的不同,具有相适应的末端执行器以及相配的手术器械。The surgical robot of the present invention can be a robot suitable for various surgical operations, and has a suitable end effector and a matching surgical instrument according to the type of operation, the surgical site and the operation needs.
进一步的,所述神经功能监测系统记录并存储记忆术中阻抗信号和/或神经电生理信号形成患者的神经定位信息,主控系统根据神经定位的信息规划、调整机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器的运动轨迹。Further, the nerve function monitoring system records and stores the intraoperative impedance signal and/or nerve electrophysiological signal to form the nerve location information of the patient, and the main control system plans and adjusts the robotic arm/joystick and/or according to the nerve location information. The trajectory of the end effector.
本发明所述神经监测元件选自电极、传感器、传感性能的外包膜、传感性能贴片或涂层、具有传导神经信号的介质制成的传导通路中的一种或几种,所述介质包括但不限于金属、光、声、石墨烯、新介质材料等以上一种或几种中的一种或几种。The nerve monitoring element of the present invention is selected from one or more of electrodes, sensors, outer envelopes with sensing properties, patches or coatings with sensing properties, and conduction paths made of media with conduction nerve signals. The medium includes, but is not limited to, one or more of the above one or more of metal, light, sound, graphene, and new dielectric materials.
所述手术器械可以为本领域下所有可以用于手术机器人的手术器械,包括但不限于工具类、治疗类、诊断类器械,如各种钳、剪、夹、刀、针、管、镊、钩、锉、锯、丝、线等。The surgical instruments can be all surgical instruments that can be used for surgical robots in the field, including but not limited to tools, treatment, and diagnostic instruments, such as various forceps, scissors, clips, knives, needles, tubes, forceps, Hook, file, saw, wire, thread, etc.
一个示例,手术器械104为线性骨锉,以此为例进一步说明本发明技术方案。所述线状骨锉两端与手术机器人的末端执行器103固定,神经监测元件105的导线可与手术机器人末端执行器103连接处的电路接口连接。In one example, the
使用时,线状骨锉的工作部表面贴合骨骼,牵拉部受手术操作者或手术机器人牵拉,光滑的背面能够保证锉磨骨骼(如椎板)时,避免误伤神经或其他组织。与神经监测元件连接的导线埋设于骨锉内部,使用时与具有阻抗监测和/或神经功能监测系统的手术机器人连接。所述神经监测元件101能够传出和/或传入信号,通过对阻抗信号的探测区分骨组织、神经组织或其他软组织;或者探测神经因被直接或间接刺激而产生的神经电生理信号,定位神经精确位置。当骨锉工作面探测到神经组织的阻抗信号或神经电生理信号时,神经监测元件105能够将探测到的信号传输至手术机器人的主控系统101,主控系统101控制机械臂/操纵杆和/或末端执行器停止锉磨。When in use, the surface of the working part of the linear bone file fits the bone, and the pulling part is pulled by the surgical operator or the surgical robot. The smooth back can ensure that when the bone (such as the lamina) is rasped, the nerve or other tissue can be avoided by accident. The wire connected with the nerve monitoring element is embedded in the bone rasp, and is connected to a surgical robot with an impedance monitoring and/or nerve function monitoring system when in use. The
Claims (5)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210050059.6ACN114366309A (en) | 2022-01-17 | 2022-01-17 | Surgical robot with nerve monitoring function |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210050059.6ACN114366309A (en) | 2022-01-17 | 2022-01-17 | Surgical robot with nerve monitoring function |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114366309Atrue CN114366309A (en) | 2022-04-19 |
Family
ID=81143775
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202210050059.6APendingCN114366309A (en) | 2022-01-17 | 2022-01-17 | Surgical robot with nerve monitoring function |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114366309A (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114947750A (en)* | 2022-06-08 | 2022-08-30 | 张霞玲 | Intelligent nerve function positioning and evaluating system |
| CN115137487A (en)* | 2022-07-13 | 2022-10-04 | 山东大学 | Spine endoscopic surgery robot system and method based on intraoperative physiological monitoring |
| CN119564282A (en)* | 2023-08-30 | 2025-03-07 | 重庆西山科技股份有限公司 | Surgical power equipment and equipment control method |
Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060178593A1 (en)* | 2005-02-07 | 2006-08-10 | Neubardt Seth L | Device and method for operating a tool relative to bone tissue and detecting neural elements |
| CN101677778A (en)* | 2007-01-25 | 2010-03-24 | 华沙整形外科股份有限公司 | Have surgical navigational and neuromonitoring integrated system from have an operation auxiliary and control appliance |
| CN102470013A (en)* | 2009-06-29 | 2012-05-23 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | Visualizing surgical trajectories |
| CN104116558A (en)* | 2014-07-25 | 2014-10-29 | 中国医学科学院北京协和医院 | Surgical equipment, surgical instrument control equipment and medical equipment |
| CN104203129A (en)* | 2012-04-09 | 2014-12-10 | 伊西康内外科公司 | Surgical instrument with nerve detection feature |
| CN107468237A (en)* | 2017-08-24 | 2017-12-15 | 郭铮蔚 | A kind of Multifunctional nerve monitoring investigation system and its implementation |
| KR20190023914A (en)* | 2017-08-30 | 2019-03-08 | 부산대학교 산학협력단 | Intraoperative Neuromonitoring System Using Bio-pressure Sensor |
| CN209153962U (en)* | 2018-03-29 | 2019-07-26 | 浙江大学 | A nerve monitoring operation component and an electrosurgical control system with automatic power-off |
| CN111184539A (en)* | 2019-04-26 | 2020-05-22 | 张霞玲 | Neural scope with monitoring function |
| CN112656510A (en)* | 2020-12-21 | 2021-04-16 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | Spinal surgery robot puncture early warning method and system based on electromyographic signals |
| CN113081269A (en)* | 2020-01-08 | 2021-07-09 | 格罗伯斯医疗有限公司 | Surgical robotic system for performing surgery on anatomical features of a patient |
- 2022
- 2022-01-17CNCN202210050059.6Apatent/CN114366309A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20060178593A1 (en)* | 2005-02-07 | 2006-08-10 | Neubardt Seth L | Device and method for operating a tool relative to bone tissue and detecting neural elements |
| CN101677778A (en)* | 2007-01-25 | 2010-03-24 | 华沙整形外科股份有限公司 | Have surgical navigational and neuromonitoring integrated system from have an operation auxiliary and control appliance |
| CN102470013A (en)* | 2009-06-29 | 2012-05-23 | 皇家飞利浦电子股份有限公司 | Visualizing surgical trajectories |
| CN104203129A (en)* | 2012-04-09 | 2014-12-10 | 伊西康内外科公司 | Surgical instrument with nerve detection feature |
| CN104116558A (en)* | 2014-07-25 | 2014-10-29 | 中国医学科学院北京协和医院 | Surgical equipment, surgical instrument control equipment and medical equipment |
| CN107468237A (en)* | 2017-08-24 | 2017-12-15 | 郭铮蔚 | A kind of Multifunctional nerve monitoring investigation system and its implementation |
| KR20190023914A (en)* | 2017-08-30 | 2019-03-08 | 부산대학교 산학협력단 | Intraoperative Neuromonitoring System Using Bio-pressure Sensor |
| CN209153962U (en)* | 2018-03-29 | 2019-07-26 | 浙江大学 | A nerve monitoring operation component and an electrosurgical control system with automatic power-off |
| CN111184539A (en)* | 2019-04-26 | 2020-05-22 | 张霞玲 | Neural scope with monitoring function |
| CN113081269A (en)* | 2020-01-08 | 2021-07-09 | 格罗伯斯医疗有限公司 | Surgical robotic system for performing surgery on anatomical features of a patient |
| CN112656510A (en)* | 2020-12-21 | 2021-04-16 | 山东大学齐鲁医院 | Spinal surgery robot puncture early warning method and system based on electromyographic signals |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114947750A (en)* | 2022-06-08 | 2022-08-30 | 张霞玲 | Intelligent nerve function positioning and evaluating system |
| CN115137487A (en)* | 2022-07-13 | 2022-10-04 | 山东大学 | Spine endoscopic surgery robot system and method based on intraoperative physiological monitoring |
| CN119564282A (en)* | 2023-08-30 | 2025-03-07 | 重庆西山科技股份有限公司 | Surgical power equipment and equipment control method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114366309A (en) | Surgical robot with nerve monitoring function | |
| KR20180027540A (en) | Percutaneous System and Method for Improved Epidural Approach for Spinal Surgery | |
| CN109925058B (en) | Spinal surgery minimally invasive surgery navigation system | |
| DE69528998T2 (en) | SURGICAL NAVIGATION ARRANGEMENTS INCLUDING REFERENCE AND LOCATION SYSTEMS | |
| AU2004257657B2 (en) | Instrumentation and method for performing image-guided spinal surgery | |
| JP6268087B2 (en) | Spinal stenosis treatment device | |
| US8454583B2 (en) | Robotic surgical device implant system | |
| US20030196671A1 (en) | Instrumentation and method for mounting a surgical navigation reference device to a patient | |
| JPH07184929A (en) | Surgical instrument | |
| AU2020357745B2 (en) | Modular implant delivery and positioning system | |
| JP2003275223A (en) | Surgical instrument unit | |
| Li et al. | Ultrasonic osteotome assisted full-endoscopic en block resection of thoracic ossified ligamentum flavum: technical note and 2 years follow-up | |
| CN217548207U (en) | Orthopedic surgery robot with nerve monitoring function | |
| CN108135441A (en) | Illuminated endoscopic pedicle probe with dynamic real-time monitoring of proximal nerves | |
| Yang et al. | Two-dimensional fluoroscopy-guided robot-assisted percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy: a retrospective cohort study | |
| CN116269800A (en) | A robotic system for spinal endoscopic surgery | |
| CN209789815U (en) | Vertebral canal endoscope system | |
| CN210249923U (en) | Neural scope and video system with monitoring function | |
| Tew Jr et al. | Application of stereotactic principles to the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia | |
| JP2022524203A (en) | Multi-shield spine access system | |
| CN114376667B (en) | Linear bone file with nerve monitoring function | |
| CN216985080U (en) | Puncture positioning double needle | |
| CN111184539A (en) | Neural scope with monitoring function | |
| Woo et al. | Instruments and Settings of Unilateral Biportal Spinal Endoscopic Surgery | |
| Girardo et al. | Comparison of free-hand technique and patient-specific guiding template for pedicle screws positioning in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery using neurophysiological monitoring |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20220419 |