CN114354870A - Unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm - Google Patents
Unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithmDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114354870A CN114354870ACN202111661953.9ACN202111661953ACN114354870ACN 114354870 ACN114354870 ACN 114354870ACN 202111661953 ACN202111661953 ACN 202111661953ACN 114354870 ACN114354870 ACN 114354870A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- unmanned ship
- longitude
- water quality
- latitude
- points
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Position, Course, Altitude, Or Attitude Of Moving Bodies (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及水面上利用无人船进行多点路径规划寻优及实时水质监测领域,具体涉及一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船最短路径水质监测系统及方法。The invention relates to the field of multi-point path planning and optimization and real-time water quality monitoring using an unmanned ship on the water surface, in particular to an unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm.
背景技术Background technique
我国是水资源利用大国,过去社会经济的发展,给我国的水资源带来很大的污染,随着人民生活质量的提高,人们对水质安全的需求也日益增高。水质监测不仅事关日常饮用水安全,也是水产养殖、湖泊水质管理重要的一环,水中的温度、气压、溶氧值等参数是常用的水质评价指标,快速、准确、安全、智能化的对这些参数进行监测是十分重要的。my country is a big country in the utilization of water resources. The social and economic development in the past has brought great pollution to my country's water resources. With the improvement of people's quality of life, people's demand for water safety is also increasing. Water quality monitoring is not only related to daily drinking water safety, but also an important part of aquaculture and lake water quality management. Parameters such as temperature, air pressure, dissolved oxygen value in water are commonly used water quality evaluation indicators. It is important to monitor these parameters.
传统的水质监测方式主要有两种。一种是技术人员携带相关仪器和设备在现场取样检测并记录,这种方式存在人工成本高、耗时、费力、低效等缺点。另一种水质监测方式是采用固定点搭建漂浮式监测仪器进行实时监测,将监测的数据以无线数传的方式上传到服务器中,这种方式当需要监测的范围很大的时候,需要搭建多个漂浮式监测站,存在成本高、不灵活、拓展性差、不易维护等不足。There are two main types of traditional water quality monitoring methods. One is that technicians carry relevant instruments and equipment to sample, detect and record on site. This method has disadvantages such as high labor cost, time-consuming, laborious, and inefficient. Another water quality monitoring method is to use a fixed point to build a floating monitoring instrument for real-time monitoring, and upload the monitored data to the server in the form of wireless data transmission. A floating monitoring station has shortcomings such as high cost, inflexibility, poor expansion, and difficult maintenance.
近年来,随着科技的发展,将无人船用于水质监测领域已成为无人船的研究趋势之一。水质检测无人船具有布放灵活、实时性好、成本低、智能化程度高、可扩展性好等优点,且可以在人迹罕至或人迹难至的水域自动测量等明显的技术优势。但是目前的水质检测无人船大多采用手动控制航行并检测的方式,需要人工观察实时的动态环境,或者在多个监测点任务下只能按照已设定的固定路线自动航行,消耗电量较多。本发明在服务器中加入一个百度地图,可在地图中看到所测湖泊的轮廓和周边的环境信息,并实时的显示无人船的位置和轨迹跟踪,同时,在自动模式下,可在地图上的待测水域随意设置多个监测点并规划出一条最短路径并按照最短路径执行监测任务。In recent years, with the development of science and technology, the use of unmanned ships in the field of water quality monitoring has become one of the research trends of unmanned ships. Unmanned ships for water quality testing have the advantages of flexible deployment, good real-time performance, low cost, high intelligence, and good scalability, and have obvious technical advantages such as automatic measurement in inaccessible or inaccessible waters. However, most of the current water quality testing unmanned ships use manual control of navigation and detection, which requires manual observation of the real-time dynamic environment, or can only navigate automatically according to the fixed route that has been set under the tasks of multiple monitoring points, which consumes a lot of electricity. . In the present invention, a Baidu map is added to the server, the outline of the measured lake and the surrounding environmental information can be seen in the map, and the position and track tracking of the unmanned ship can be displayed in real time. A number of monitoring points are randomly set in the water area to be measured on the surface, and a shortest path is planned and monitoring tasks are performed according to the shortest path.
因此,本发明针对无人船路径规划和水质在线监测情况,提出一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船最短路径水质监测系统及方法。Therefore, the present invention proposes a water quality monitoring system and method for the shortest path of an unmanned ship based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm, aiming at the path planning of the unmanned ship and the online monitoring of water quality.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
为了解决当前无人船存在多个监测点任务下路径规划的问题及智能监测水质问题,本发明提出一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船最短路径水质监测系统及方法。通过该路径规划方法及水质监测系统,无人船可在服务器的地图中手动设置多个监测点并快速的规划出一条最短的路径,控制无人船按照规划出的路径依次到达指定的点测量水质参数,并将测得的各个水质参数上传到服务器实时显示和保存。In order to solve the problem of path planning under the task of multiple monitoring points and the problem of intelligent monitoring of water quality in current unmanned ships, the present invention proposes a water quality monitoring system and method for the shortest path of unmanned ships based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Through the path planning method and water quality monitoring system, the unmanned ship can manually set multiple monitoring points in the map of the server and quickly plan a shortest path, and control the unmanned ship to follow the planned path to arrive at the designated point for measurement. Water quality parameters, and upload the measured water quality parameters to the server for real-time display and storage.
本发明通过以下技术方案予以实现:The present invention is achieved through the following technical solutions:
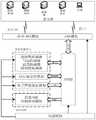
一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船最短路径水质监测系统包括:感知层、传输层、应用层三部分;An unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm includes three parts: perception layer, transmission layer and application layer;
第一部分,所述感知层由主控芯片、测量装置、动力系统、电源模块组成。In the first part, the perception layer is composed of a main control chip, a measurement device, a power system, and a power supply module.
所述主控芯片采用基于Cortex-M4内核的STM32单片机;The main control chip adopts the STM32 single-chip microcomputer based on the Cortex-M4 core;
所述测量装置包括GPS/BD定位模块、电子罗盘模块、水质参数检测模块;The measuring device includes a GPS/BD positioning module, an electronic compass module, and a water quality parameter detection module;
所述GPS/BD定位模块用于测量无人船的实时经纬度数据;The GPS/BD positioning module is used to measure the real-time latitude and longitude data of the unmanned ship;
所述电子罗盘模块用于测量无人船实时的航向角数据;The electronic compass module is used to measure the real-time heading angle data of the unmanned ship;
所述水质参数检测模块为四合一传感器,包括:溶解氧传感器、温度传感器、气压传感器、饱和度传感器,用于测量溶解氧浓度、水温、气压值和饱和度数据;The water quality parameter detection module is a four-in-one sensor, including: a dissolved oxygen sensor, a temperature sensor, an air pressure sensor, and a saturation sensor for measuring dissolved oxygen concentration, water temperature, air pressure and saturation data;
所述动力系统包括船体两侧的水下直流电机和无刷电调;The power system includes underwater DC motors and brushless ESCs on both sides of the hull;
所述水下直流电机驱动螺旋桨用于无人船的直行和转向;The underwater DC motor drives the propeller for straight running and steering of the unmanned ship;
所述无刷电调通过PWM波对电机调速。The brushless ESC adjusts the speed of the motor through PWM waves.
所述电源模块为可充电锂电池,为其他模块供电。The power module is a rechargeable lithium battery, which supplies power to other modules.
第二部分,所述无线数传模块采用GPRS—DTU模块和LORA模块,用于与服务器后台程序通信。In the second part, the wireless data transmission module adopts the GPRS-DTU module and the LORA module to communicate with the server background program.
第三部分,所述应用层采用C/S结构建立应用层与所述无线数传模块的连接。In the third part, the application layer uses a C/S structure to establish a connection between the application layer and the wireless data transmission module.
所述服务器后台程序基于Qt5.9平台使用C++语言开发一个可视化的上位机界面,通过串口或者TCP/IP协议接收测量装置发送的数据并进行解算,将解算的各个数据实时的显示在对应的LineEdit中;在服务器后台程序中嵌入由HTML、CSS以及JavaScript语言开发的百度地图HTML文件,编写改进粒子群优化算法,在地图中设置多个监测任务点,通过改进粒子群优化算法调用各个点的经纬度坐标值计算得到一条最短路径,控制无人船按照规划出的最短路径执行监测任务。The server background program uses the C++ language to develop a visual host computer interface based on the Qt5.9 platform, receives the data sent by the measuring device through the serial port or the TCP/IP protocol and solves it, and displays the calculated data in real time in the corresponding data. In LineEdit; embed the Baidu map HTML file developed by HTML, CSS and JavaScript language in the server background program, write an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm, set multiple monitoring task points in the map, and call each point through the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm A shortest path is obtained by calculating the latitude and longitude coordinates of , and the unmanned ship is controlled to perform monitoring tasks according to the planned shortest path.
基于上述系统,本发明提出了一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船最短路径水质监测方法包括如下步骤:Based on the above system, the present invention proposes a water quality monitoring method for the shortest path of an unmanned ship based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm, which includes the following steps:
步骤1:无人船与上位机建立通信连接,电子罗盘获取无人船的实时航向角数据,GPS/BD模块获取无人船实时的经纬度数据,将数据上传到上位机。上位机解析收到的经纬度数据,将其转换为百度地图格式,统一经纬度坐标。Step 1: The unmanned ship establishes a communication connection with the host computer, the electronic compass obtains the real-time heading angle data of the unmanned ship, the GPS/BD module obtains the real-time latitude and longitude data of the unmanned ship, and uploads the data to the host computer. The host computer parses the received longitude and latitude data, converts it into Baidu map format, and unifies the longitude and latitude coordinates.
步骤2:在上位机界面的百度地图中手动设置各个水质监测的目标点并保存各个目标点的经纬度坐标值,设置无人船为自动导航模式,将无人船目前所处的位置作为起点,点击路径规划按钮通过改进的粒子群优化算法调用起点和各个目标点的经纬度坐标值进行计算,并保存最短路径的各个点的先后顺序,点击自动航行按钮开启自动航行。Step 2: Manually set the target points of each water quality monitoring in the Baidu map of the host computer interface and save the latitude and longitude coordinates of each target point, set the unmanned ship to the automatic navigation mode, and use the current position of the unmanned ship as the starting point. Click the path planning button to use the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm to call the longitude and latitude coordinates of the starting point and each target point for calculation, and save the sequence of each point of the shortest path. Click the automatic navigation button to start the automatic navigation.
步骤3:上位机取出当前位置的经纬度值和下一目标点的经纬度值,计算两个点之间的距离和方位角。Step 3: The host computer takes out the latitude and longitude value of the current position and the latitude and longitude value of the next target point, and calculates the distance and azimuth between the two points.
步骤4:将方位角与步骤1中上位机收到的航向角对比得出无人船的转向角,经过逻辑判断后发给单片机相应的指令以控制无人船转向。随着无人船的运动,通过虚折线在百度地图上实时的显示无人船的航迹。Step 4: Comparing the azimuth angle with the heading angle received by the host computer in step 1, the steering angle of the unmanned ship is obtained, and after logical judgment, a corresponding command is sent to the microcontroller to control the steering of the unmanned ship. With the movement of the unmanned ship, the track of the unmanned ship is displayed on the Baidu map in real time through the dotted line.
步骤5:判断无人船是否到达目标点,如果没有,重复执行步骤3,如果到达目标点,上位机发送相应控制指令给单片机对目标点的水质进行检测,将检测的数据发送给上位机进行显示并保存到数据库。Step 5: Determine whether the unmanned ship has reached the target point. If not, repeat
步骤6:判断无人船是否遍历所有目标点,若完成遍历,本次任务结束,若尚未遍历所有目标点,重复执行步骤3到步骤5,直到完成遍历监测任务。Step 6: Determine whether the unmanned ship has traversed all the target points. If the traversal is completed, the task is over. If all the target points have not been traversed, repeat
进一步,所述步骤2的具体执行以下步骤:Further, the specific implementation of the
步骤2.1:在上位机的百度地图中设置n个目标点,记录各个目标点的经纬度值和序号,在自动导航模式下,点击路径规划按钮,调用改进粒子群优化算法,初始化粒子群的群体规模N以及每个粒子的初始位置xi和初始速度vi。Step 2.1: Set n target points in the Baidu map of the host computer, record the latitude and longitude value and serial number of each target point, in the automatic navigation mode, click the path planning button, call the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm, and initialize the group size of the particle swarm N and the initial positionxi and initial velocity vi of each particle.
步骤2.2:每个粒子在n个设定的目标点中单独的遍历所有点,遍历的各个点的顺序记为该粒子的历史最优位置Pbest(i),并记录其对应的适应度值Fit[Pbest(i)]。Step 2.2: Each particle traverses all the points individually in the n set target points, and the order of the traversed points is recorded as the historical optimal position Pbest (i) of the particle, and its corresponding fitness value is recorded Fit[Pbest (i)].
步骤2.3:对每个粒子的适应度值做比较,找出全局最优粒子,记录其位置为全局最优位置Gbest,记录其适应度值为Fit[Gbest];Step 2.3: compare the fitness value of each particle, find out the global optimal particle, record its position as the global optimal position Gbest , and record its fitness value as Fit[Gbest ];
步骤2.4:更新每个粒子的速度vi和位置xi。Step 2.4: Update the velocity vi and positionxi of each particle.
速度vi的更新公式为:The update formula of velocityvi is:
位置xi的更新公式为:The update formula for position xi is:
xi=xi+vi (2)xi = xi +vi (2)
公式(1)和(2)中i=1,2,...,N,N是群体规模,w为惯性因子,其值为非负,α,β为加速度,其值为介于(0,1)之间的随机数,xi是粒子的当前位置。In formulas (1) and (2) i=1,2,...,N, N is the size of the group, w is the inertia factor, its value is non-negative, α, β is the acceleration, its value is between (0 , 1), where xi is the current position of the particle.
式中定义运算符号:The operator symbol is defined in the formula:
-:当“-”号的两边均为位置时,其结果为交换序列,表示速度。-: When both sides of the "-" sign are positions, the result is an exchange sequence, indicating the speed.
假设速度v的长度为k,加速度的长度为l,运算操作是:从第k*ω(取整)位置开始,把速度v的置换序列替换为加速度的前α*l(取整)个交换序列; Assuming that the length of the velocity v is k and the length of the acceleration is l, the operation operation is: starting from the k*ω (rounding) position, replace the permutation sequence of the velocity v with the first α*l (rounding) exchanges of the acceleration sequence;
×:对实数c∈(0,1),假设速度v的长度为k个置换序列,乘法操作是截取速度列表,使得新的速度的长度等于c×k(取整);×: For the real number c∈(0,1), assuming that the length of the velocity v is k permutation sequences, the multiplication operation is to truncate the velocity list, so that the length of the new velocity is equal to c×k (rounded);
+:当“+”号的两边分别为位置和速度时,原位置通过速度的交换序列依次作用于粒子的某个位置,结果得到一个新的位置;+: When the two sides of the "+" sign are position and velocity respectively, the original position acts on a certain position of the particle in turn through the exchange sequence of velocity, and a new position is obtained as a result;
α×(Pbest(i)-xi)表示基本交换序(Pbest(i)-xi)中的所有交换子以概率α保留,β×(Gbest-xi)表示基本交换序(Gbest-xi)中的所有交换子以概率β保留。α×(Pbest (i)-xi ) indicates that all commutators in the basic exchange order (Pbest (i)-xi ) are retained with probability α, and β×(Gbest -xi ) indicates that the basic exchange order ( All commutators in Gbest-xi ) are retained with probability β.
步骤2.5:计算更新后的粒子的适应度值,与当前粒子的历史最优位置比较,如果适应度得到改善,则将更新后的位置记录该粒子的历史最优Pbest(i),适应度值记为Fit[Pbest(i)]。Step 2.5: Calculate the fitness value of the updated particle and compare it with the historical optimal position of the current particle. If the fitness is improved, the updated position will be recorded as the historical optimal Pbest (i) of the particle, and the fitness The value is recorded as Fit[Pbest (i)].
步骤2.6:将步骤2.5中各粒子的适应度值与全局最优适应度值Fit[Gbest]作比较,如果适应度得到改善,则更新种群的全局最优位置Gbest和其对应的全局最优Fit[Gbest]。Step 2.6: Compare the fitness value of each particle in step 2.5 with the global optimal fitness value Fit[Gbest ], if the fitness is improved, update the global optimal position Gbest of the population and its corresponding global optimal value. Excellent Fit[Gbest ].
步骤2.7:判断是否满足结束条件(最大迭代次数),若满足结束条件,改进粒子群优化算法结束,输出全局最优位置Gbest和其对应的最优距离Fit[Gbest],调用全局最优位置Gbest的各个点的先后顺序保存在数据结构中供服务器界面调用。若不满足结束条件,重复步骤2.4到2.6。Step 2.7: Determine whether the end condition (maximum number of iterations) is met. If the end condition is met, the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm ends, output the global optimal position Gbest and its corresponding optimal distance Fit[Gbest ], and call the global optimal The sequence of each point of the position Gbest is stored in the data structure for the server interface to call. If the end condition is not met, repeat steps 2.4 to 2.6.
本发明的有益效果为:The beneficial effects of the present invention are:
(1)克服传统水质监测方式成本高、效率低、测量范围有限、不灵活、可扩展性差的缺点,能移动测量水域内多个点的水质情况。(1) Overcoming the shortcomings of traditional water quality monitoring methods such as high cost, low efficiency, limited measurement range, inflexibility, and poor scalability, it can measure the water quality of multiple points in the water area.
(2)克服无人船存在多个监测点任务时,耗时、耗电高的顺序执行监测任务的缺点,采用改进的粒子群算法能快速的规划出一条最短路径并按此路径作业,在自动航行模式下,无人船按照规划的路径先后到达指定的监测点作业。本发明具有成本低、效率高、定位精度高、多监测点路径寻优、水质实时测量显示、耗电量低等优点,可以有效提高水质监测无人船的工作效率和节约无人船的电量消耗。(2) Overcoming the shortcomings of time-consuming and high-power-consumption sequential monitoring tasks when the unmanned ship has multiple monitoring point tasks, the improved particle swarm algorithm can quickly plan a shortest path and operate according to this path. In the automatic sailing mode, the unmanned ship arrives at the designated monitoring point successively according to the planned path. The invention has the advantages of low cost, high efficiency, high positioning accuracy, multi-monitoring point path optimization, real-time water quality measurement and display, low power consumption, etc., and can effectively improve the working efficiency of the water quality monitoring unmanned ship and save the power of the unmanned ship consume.
(3)无人船可以在服务器界面的地图中随意设置监测点并可查看无人船的实时的位置。(3) The unmanned ship can freely set monitoring points in the map of the server interface and view the real-time position of the unmanned ship.
(4)无人船采用GPS和北斗综合定位的方式,定位精度更高,响应速度更快。(4) The unmanned ship adopts the comprehensive positioning method of GPS and Beidou, which has higher positioning accuracy and faster response speed.
(5)补充了监测点的位置信息,有助于对区域内不同位置的水质变化进行监控分析。(5) The location information of the monitoring points is supplemented, which is helpful for monitoring and analyzing the water quality changes at different locations in the region.
(6)可将采集的各个数据在服务器中实时的查看并保存数据库中。(6) The collected data can be viewed on the server in real time and saved in the database.
(7)服务器后台程序采用多线程技术接收数据,各线程负责每一种数据的解算,有序无误地展现在电脑端界面上。(7) The server background program uses multi-thread technology to receive data, and each thread is responsible for the solution of each data, which is displayed on the computer interface in an orderly and error-free manner.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1本发明系统结构图;Fig. 1 system structure diagram of the present invention;
图2本发明无人船测量装置示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of the unmanned ship measuring device of the present invention;
图3改进粒子群优化算法流程图;Figure 3 is a flowchart of the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm;
图4改进粒子群优化算法生成最短路径示意图;Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the shortest path generated by the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm;
图5本发明程序流程图;Fig. 5 program flow chart of the present invention;
图6本发明服务器后台程序主界面图;Fig. 6 main interface diagram of server background program of the present invention;
图7本发明水质参数监测数据库图;Fig. 7 water quality parameter monitoring database diagram of the present invention;
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图对本发明作进一步说明。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
如图1所示,一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船最短路径水质监测系统主要由感知层、传输层、应用层三部分组成;As shown in Figure 1, an unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm is mainly composed of three parts: perception layer, transmission layer and application layer;
第一部分,所述感知层由主控芯片、测量装置、动力系统、电源模块组成,实现无人船对应用层规划出的一条多点最短路径按照路线各点的顺序巡航并监测各点的水质参数,将测得的水质参数保存到数据库中。In the first part, the perception layer consists of a main control chip, a measuring device, a power system, and a power supply module, and realizes a multi-point shortest path planned by the unmanned ship to the application layer according to the sequence of each point of the route and monitors the water quality of each point. parameters, and save the measured water quality parameters to the database.
如图2所示,所述无人船由主控芯片、测量装置、动力系统、电源模块组成;As shown in Figure 2, the unmanned ship consists of a main control chip, a measurement device, a power system, and a power module;
所述主控芯片采用基于Cortex-M4内核的STM32单片机;The main control chip adopts the STM32 single-chip microcomputer based on the Cortex-M4 core;
所述测量装置包括GPS/BD定位模块、电子罗盘模块、水质参数检测模块;The measuring device includes a GPS/BD positioning module, an electronic compass module, and a water quality parameter detection module;
所述GPS/BD定位模块用于测量无人船的实时经纬度数据;The GPS/BD positioning module is used to measure the real-time latitude and longitude data of the unmanned ship;
所述电子罗盘模块用于测量无人船实时的航向角数据;The electronic compass module is used to measure the real-time heading angle data of the unmanned ship;
所述水质参数检测模块为四合一传感器,包括:溶解氧传感器、温度传感器、气压传感器、饱和度传感器,用于测量溶解氧浓度、水温、气压值和饱和度数据;The water quality parameter detection module is a four-in-one sensor, including: a dissolved oxygen sensor, a temperature sensor, an air pressure sensor, and a saturation sensor for measuring dissolved oxygen concentration, water temperature, air pressure and saturation data;
所述动力系统包括船体两侧的水下直流电机和无刷电调;The power system includes underwater DC motors and brushless ESCs on both sides of the hull;
所述水下直流电机驱动螺旋桨用于无人船的直行和转向;The underwater DC motor drives the propeller for straight running and steering of the unmanned ship;
所述无刷电调通过PWM波对电机调速。The brushless ESC adjusts the speed of the motor through PWM waves.
所述电源模块为可充电锂电池,为其他模块供电。The power module is a rechargeable lithium battery, which supplies power to other modules.
第二部分,所述无线数传模块采用GPRS—DTU模块和LORA模块,用于与服务器后台程序通信。In the second part, the wireless data transmission module adopts the GPRS-DTU module and the LORA module to communicate with the server background program.
第三部分,所述应用层采用C/S结构建立应用层与所述无线数传模块的连接。In the third part, the application layer uses a C/S structure to establish a connection between the application layer and the wireless data transmission module.
所述服务器后台程序基于Qt5.9平台使用C++语言开发一个可视化的上位机界面,通过串口或者TCP/IP协议接收测量装置测得的数据,上位机通过提取收到的数据段的关键字对数据进行分割并实时的显示在数据对应的LineEdit中,如无人船的实时经纬度数据、实时航向角数据、溶解氧浓度、水温等数据,同时,将各个数据保存到上位机的数据库中,用户可在数据库中查看各个历史数据。在服务器后台程序中嵌入由HTML、CSS以及JavaScript语言开发的百度地图HTML文件,上位机界面运行时,能在可视化界面中加载百度地图,将解析的无人船实时的经纬度数据格式转换为地图的数据格式实现在地图中实时的显示无人船的航迹,用户可通过鼠标在地图中设置多个任务点,将各个点的坐标保存,通过编写的改进粒子群优化算法调用各个点的经纬度坐标值计算得到一条最短路径,并将各个点的顺序保存,无人船按照最短路径的顺序点,发送指令给下位机控制无人船按照规划出的最短路径执行监测任务。The server background program uses C++ language to develop a visual host computer interface based on the Qt5.9 platform, receives the data measured by the measuring device through the serial port or the TCP/IP protocol, and the host computer compares the data by extracting the keywords of the received data segment. Segment and display the data in the corresponding LineEdit in real time, such as real-time latitude and longitude data, real-time heading angle data, dissolved oxygen concentration, water temperature and other data of the unmanned ship. At the same time, each data is saved to the database of the host computer. View individual historical data in the database. The Baidu map HTML file developed by HTML, CSS and JavaScript language is embedded in the server background program. When the host computer interface is running, the Baidu map can be loaded in the visual interface, and the parsed real-time latitude and longitude data format of the unmanned ship can be converted into the map. The data format realizes the real-time display of the track of the unmanned ship in the map. The user can set multiple task points in the map through the mouse, save the coordinates of each point, and call the latitude and longitude coordinates of each point through the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm written. The value is calculated to obtain a shortest path, and the order of each point is saved. The unmanned ship sends instructions to the lower computer to control the unmanned ship to perform monitoring tasks according to the planned shortest path.
如图3所示,一种改进的粒子群优化算法的流程图如下:As shown in Figure 3, the flowchart of an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm is as follows:
步骤1:初始化粒子群的群体规模N以及每个粒子的初始位置xi和初始速度vi。本步骤的初始化含义是指每个粒子随机的遍历n个目标点,产生的一个路径顺序和交换序,路径顺序是初始位置,交换序是初始速度。Step 1: Initialize the swarm size N of the particle swarm and the initial positionxi and initial velocity vi of each particle. The initialization meaning of this step means that each particle randomly traverses n target points, and generates a path sequence and exchange order. The path order is the initial position, and the exchange order is the initial speed.
步骤2:每个粒子在n个设定的目标点中单独的遍历所有点,遍历的各个点的顺序记为该粒子的历史最优位置Pbest(i),并记录其对应的适应度值Fit[Pbest(i)]。Step 2: Each particle traverses all the points individually in the n set target points, and the order of the traversed points is recorded as the historical optimal position Pbest (i) of the particle, and its corresponding fitness value is recorded Fit[Pbest (i)].
步骤3:对每个粒子的适应度值做比较,找出全局最优粒子,记录其位置为全局最优位置Gbest,记录其适应度值为Fit[Gbest];Step 3: compare the fitness value of each particle, find out the global optimal particle, record its position as the global optimal position Gbest , record its fitness value as Fit[Gbest ];
步骤4:更新每个粒子的速度vi和位置xi。Step 4: Update the velocity vi and positionxi of each particle.
速度vi的更新公式为:The update formula of velocityvi is:
位置xi的更新公式为:The update formula for position xi is:
xi=xi+vi (2)xi = xi +vi (2)
公式(1)和(2)中i=1,2,...,N,N是群体规模,w为惯性因子,其值为非负,α,β为加速度,其值为介于(0,1)之间的随机数,xi是粒子的当前位置。In formulas (1) and (2), i=1,2,...,N, N is the population size, w is the inertia factor, its value is non-negative, α, β is the acceleration, its value is between (0 , 1), where xi is the current position of the particle.
式中定义运算符号:The operator symbol is defined in the formula:
-:当“-”号的两边均为位置时,其结果为交换序列,表示速度。-: When both sides of the "-" sign are positions, the result is an exchange sequence, indicating the speed.
假设速度v的长度为k,加速度的长度为l,运算操作是:从第k*ω(取整)位置开始,把速度v的置换序列替换为加速度的前α*l(取整)个交换序列; Assuming that the length of the velocity v is k and the length of the acceleration is l, the operation operation is: starting from the k*ω (rounding) position, replace the permutation sequence of the velocity v with the first α*l (rounding) exchanges of the acceleration sequence;
×:对实数c∈(0,1),假设速度v的长度为k个置换序列,乘法操作是截取速度列表,使得新的速度的长度等于c×k(取整);×: For the real number c∈(0,1), assuming that the length of the velocity v is k permutation sequences, the multiplication operation is to truncate the velocity list, so that the length of the new velocity is equal to c×k (rounded);
+:当“+”号的两边分别为位置和速度时,原位置通过速度的交换序列依次作用于粒子的某个位置,结果得到一个新的位置;+: When the two sides of the "+" sign are position and velocity respectively, the original position acts on a certain position of the particle in turn through the exchange sequence of velocity, and a new position is obtained as a result;
α×(Pbest(i)-xi)表示基本交换序(Pbest(i)-xi)中的所有交换子以概率α保留,β×(Gbest-xi)表示基本交换序(Gbest-xi)中的所有交换子以概率β保留。α×(Pbest (i)-xi ) indicates that all commutators in the basic exchange order (Pbest (i)-xi ) are retained with probability α, and β×(Gbest -xi ) indicates that the basic exchange order ( All commutators in Gbest-xi ) are retained with probability β.
步骤5:计算更新后的粒子的适应度值,与当前粒子的历史最优位置比较,如果适应度得到改善,则将更新后的位置记录该粒子的历史最优Pbest(i),适应度值记为Fit[Pbest(i)]。Step 5: Calculate the fitness value of the updated particle and compare it with the historical optimal position of the current particle. If the fitness is improved, record the updated position as the historical optimal Pbest (i) of the particle, and the fitness The value is recorded as Fit[Pbest (i)].
步骤6:将步骤5中各粒子的适应度值与全局最优适应度值Fit[Gbest]作比较,如果适应度得到改善,则更新种群的全局最优位置Gbest和其对应的全局最优Fit[Gbest]。Step 6: Compare the fitness value of each particle in Step 5 with the global optimal fitness value Fit[Gbest ]. If the fitness is improved, update the global optimal position Gbest of the population and its corresponding global optimal fitness value. Excellent Fit[Gbest ].
步骤7:判断是否满足结束条件(最大迭代次数),若满足结束条件,改进粒子群优化算法结束,输出全局最优位置Gbest和其对应的最优距离Fit[Gbest],调用全局最优位置Gbest的各个点的先后顺序保存在数据结构中供服务器界面调用。若不满足结束条件,重复步骤4到6。Step 7: Determine whether the end condition (maximum number of iterations) is met. If the end condition is met, the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm ends, output the global optimal position Gbest and its corresponding optimal distance Fit[Gbest ], and call the global optimal The sequence of each point of the position Gbest is stored in the data structure for the server interface to call. If the end condition is not met, repeat steps 4 to 6.
如图4所示,为无人船在有多个监测点任务时调用改进粒子群优化算法规划的最短路径示意图。As shown in Figure 4, it is a schematic diagram of the shortest path planned by the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for the unmanned ship when there are multiple monitoring point tasks.
如图5所示,一种基于改进粒子群优化算法的无人船多点最短路径水质监测系统的程序流程图如下:As shown in Figure 5, the program flow chart of an unmanned ship multi-point shortest path water quality monitoring system based on the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm is as follows:
步骤1:无人船与上位机建立通信连接,电子罗盘获取无人船的实时航向角数据,GPS/BD模块获取无人船实时的经纬度数据,将数据上传到上位机。Step 1: The unmanned ship establishes a communication connection with the host computer, the electronic compass obtains the real-time heading angle data of the unmanned ship, the GPS/BD module obtains the real-time latitude and longitude data of the unmanned ship, and uploads the data to the host computer.
步骤2:上位机解析收到的经纬度数据,将其转换为百度地图格式,统一经纬度坐标。Step 2: The host computer parses the received latitude and longitude data, converts it into Baidu map format, and unifies the latitude and longitude coordinates.
步骤3:在上位机界面的百度地图中手动设置各个水质监测的目标点并保存各个目标点的经纬度坐标值,将无人船目前所处的位置作为起点。Step 3: Manually set the target points of each water quality monitoring in the Baidu map of the host computer interface and save the latitude and longitude coordinates of each target point, taking the current position of the unmanned ship as the starting point.
步骤4:设置无人船为自动导航模式,上位机中的改进粒子群优化算法调用起点和各个目标点的经纬度坐标值进行计算,得到一条最短路径,并保存最短路径的各个点的先后顺序。Step 4: Set the unmanned ship to the automatic navigation mode, and the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm in the host computer calls the starting point and the latitude and longitude coordinates of each target point for calculation to obtain a shortest path, and save the sequence of each point of the shortest path.
步骤5:上位机取出无人船当前位置的经纬度值和下一目标点的经纬度值,计算两个点之间的距离和方位角。Step 5: The host computer takes out the latitude and longitude value of the current position of the unmanned ship and the latitude and longitude value of the next target point, and calculates the distance and azimuth between the two points.
两点间的距离计算公式为:The formula for calculating the distance between two points is:
式中D为地球上两个点的距离,单位为m,R=6378137m为地球半径,a为当前点与目标点的纬度差,b为当前点与目标点的经度差,lat1为当前点的纬度、lat2为目标点的纬度。In the formula, D is the distance between two points on the earth, the unit is m, R=6378137m is the radius of the earth, a is the latitude difference between the current point and the target point, b is the longitude difference between the current point and the target point, and lat1 is the current point. Latitude and lat2 are the latitude of the target point.
两点之间的方位角计算公式为:The formula for calculating the azimuth angle between two points is:
式中α为两点之间的方位角,其正方向为地理北极顺时针旋转的方向,其中X、Y分别为两点直线距离在纬线和经线上的投影,其公式为式(3)。where α is the azimuth angle between two points, and its positive direction is the clockwise direction of the geographic North Pole, where X and Y are the projections of the straight-line distance between the two points on the latitude and longitude, respectively, and the formula is Equation (3).
步骤6:将方位角与无人船实时的航向角对比得出无人船的转向角。Step 6: Compare the azimuth angle with the real-time heading angle of the unmanned ship to obtain the steering angle of the unmanned ship.
转向角的计算公式为:The formula for calculating the steering angle is:
γ=|α-(heading+d)|γ=|α-(heading+d)|
式中γ为无人船的转向角,heading为上位机收到的航向角,其正方向为磁北极顺时针旋转的方向,d是磁偏角,是磁北极与地理北极之间的夹角。In the formula, γ is the steering angle of the unmanned ship, heading is the heading angle received by the host computer, the positive direction is the clockwise direction of the magnetic north pole, and d is the magnetic declination angle, which is the angle between the magnetic north pole and the geographic north pole. .
步骤7:经过逻辑判断是否需要转向,如果需要转向,上位机通过无线数传模块发送相应的指令给单片机以控制电机转向。如果不需要转向,继续直行。Step 7: It is logically judged whether steering is required. If steering is required, the host computer sends corresponding instructions to the single-chip microcomputer through the wireless data transmission module to control the steering of the motor. If you don't need to turn, keep going straight.
步骤8:随着无人船的运动,通过虚折线在上位机的百度地图上实时的标记无人船的航迹。Step 8: With the movement of the unmanned ship, mark the track of the unmanned ship in real time on the Baidu map of the host computer through the dotted line.
步骤9:判断无人船是否到达目标点,如果没有,执行步骤5。Step 9: Determine whether the unmanned ship has reached the target point, if not, go to Step 5.
步骤10:如果到达目标点,上位机发送相应控制指令给单片机对目标点的水质进行检测,将检测的数据发送给上位机进行显示并保存到数据库。Step 10: If the target point is reached, the host computer sends corresponding control instructions to the single-chip microcomputer to detect the water quality of the target point, and sends the detected data to the host computer for display and saves it to the database.
步骤11:重复执行步骤5到步骤10,依次遍历并测量剩余目标点。Step 11: Repeat steps 5 to 10, traverse and measure the remaining target points in turn.
如图6所示,为本发明的服务器后台程序的上位机可视化界面,界面分为数据显示区、地图显示区、模式切换区、手动控制区、数据库窗口区。As shown in FIG. 6 , it is a visual interface of the host computer of the server background program of the present invention. The interface is divided into a data display area, a map display area, a mode switching area, a manual control area, and a database window area.
所述数据显示区显示测量装置测得的数据,如经纬度、航向角、水质参数以及设定的目标点的经纬度坐标。The data display area displays the data measured by the measuring device, such as longitude and latitude, heading angle, water quality parameters and the longitude and latitude coordinates of the set target point.
所述地图显示区能加载百度地图,在地图上通过虚折线实时的显示接收的无人船的经纬度数据形成一条航迹,能通过鼠标在地图上设置目标点并记录各目标点的经纬度数据。The map display area can load Baidu map, display the received latitude and longitude data of the unmanned ship in real time on the map through dotted lines, and form a track, set target points on the map through the mouse, and record the latitude and longitude data of each target point.
所述模式切换区包括两个部分,其一为切换所述无线数传方式为GPRS-DTU通信或LORA通信,其二将无人船设置为手动控制模式和自动导航模式,在手动控制模式下通过鼠标点击所述手动控制区按钮控制无人船的运动,在所述地图显示区设置好目标点后点击自动导航模式,上位机通过嵌入的改进粒子群优化算法规划出一条最短路径并依次巡航。The mode switching area includes two parts, one is to switch the wireless data transmission mode to GPRS-DTU communication or LORA communication, the other is to set the unmanned ship to manual control mode and automatic navigation mode, in manual control mode Control the movement of the unmanned ship by clicking the button of the manual control area with the mouse, and click the automatic navigation mode after setting the target point in the map display area. The host computer plans a shortest path through the embedded improved particle swarm optimization algorithm and cruises in sequence .
所述手动控制区可以通过鼠标点击相应的控制按钮实现无人船的前进、后退、左转和右转。In the manual control area, the unmanned ship can move forward, backward, turn left and turn right by clicking the corresponding control button with the mouse.
所述数据库窗口区为显示二级子窗口,该窗口记录并显示目标点的经纬度数据以及水质参数信息。The database window area is a secondary sub-window, which records and displays the latitude and longitude data and water quality parameter information of the target point.
如图7所示,为数据库窗口区的二级子窗口,在该窗口下可查看历史数据。表格里记录测量日期、目标点的经纬度位置数据及水质参数数据。As shown in Figure 7, it is a secondary sub-window of the database window area, and historical data can be viewed under this window. The table records the measurement date, the latitude and longitude position data of the target point and the water quality parameter data.
上文所列出的一系列的详细说明仅仅是针对本发明的可行性实施方式的具体说明,它们并非用以限制本发明的保护范围,凡未脱离本发明技术所创的等效方式或变更均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The series of detailed descriptions listed above are only specific descriptions for the feasible embodiments of the present invention, and they are not used to limit the protection scope of the present invention. All should be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111661953.9ACN114354870A (en) | 2021-12-30 | 2021-12-30 | Unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111661953.9ACN114354870A (en) | 2021-12-30 | 2021-12-30 | Unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114354870Atrue CN114354870A (en) | 2022-04-15 |
Family
ID=81105993
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111661953.9APendingCN114354870A (en) | 2021-12-30 | 2021-12-30 | Unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114354870A (en) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111174794A (en)* | 2020-03-12 | 2020-05-19 | 青岛蓝海未来海洋科技有限责任公司 | Unmanned ship path planning method and system based on improved particle swarm algorithm |
| CN112000115A (en)* | 2020-09-15 | 2020-11-27 | 湖南文理学院 | A path planning method and related equipment for an autonomous underwater robot |
| CN112631293A (en)* | 2020-12-16 | 2021-04-09 | 江苏大学 | Unmanned ship anti-collision Internet of things control system and method based on artificial potential field method |
| CN113110439A (en)* | 2021-04-08 | 2021-07-13 | 江苏大学 | Real-time anti-storm unmanned ship air route control method and water quality monitoring system thereof |
| CN113112065A (en)* | 2021-04-09 | 2021-07-13 | 山东交通学院 | Route planning method for multiple unmanned ships for ocean pollution inspection and sampling |
| CN113721620A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2021-11-30 | 山东交通学院 | Particle swarm-genetic hybrid algorithm-based vehicle transverse PID control method |
- 2021
- 2021-12-30CNCN202111661953.9Apatent/CN114354870A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111174794A (en)* | 2020-03-12 | 2020-05-19 | 青岛蓝海未来海洋科技有限责任公司 | Unmanned ship path planning method and system based on improved particle swarm algorithm |
| CN112000115A (en)* | 2020-09-15 | 2020-11-27 | 湖南文理学院 | A path planning method and related equipment for an autonomous underwater robot |
| CN112631293A (en)* | 2020-12-16 | 2021-04-09 | 江苏大学 | Unmanned ship anti-collision Internet of things control system and method based on artificial potential field method |
| CN113110439A (en)* | 2021-04-08 | 2021-07-13 | 江苏大学 | Real-time anti-storm unmanned ship air route control method and water quality monitoring system thereof |
| CN113112065A (en)* | 2021-04-09 | 2021-07-13 | 山东交通学院 | Route planning method for multiple unmanned ships for ocean pollution inspection and sampling |
| CN113721620A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2021-11-30 | 山东交通学院 | Particle swarm-genetic hybrid algorithm-based vehicle transverse PID control method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN104267723B (en) | Ocean vessel navigation automatic sailing system and navigation method | |
| CN206178469U (en) | Unmanned ship control system | |
| US20080294308A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for real-time polars | |
| US12242270B2 (en) | Method and system for controlling multi-unmanned surface vessel collaborative search | |
| CN117053793A (en) | Water quality monitoring and inspection method, device and equipment based on sea-air cross-domain cooperation | |
| CN114281083A (en) | Unmanned ship water quality monitoring Internet of things control system and method based on hybrid path planning autonomous navigation | |
| CN110608744A (en) | A water quality sampling unmanned boat path planning method with dynamic obstacle avoidance function | |
| CN110597937B (en) | Unmanned intelligent inspection method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN110968108A (en) | Unmanned ship autonomous navigation method and control system | |
| CN104850120B (en) | Wheeled mobile robot air navigation aid based on IHDR autonomous learning frameworks | |
| CN119512157B (en) | An offshore wind turbine inspection system and method based on drone hangar | |
| CN113671508B (en) | Underwater sludge measurement method, device and system | |
| CN113110439B (en) | Real-time anti-storm unmanned ship air route control method and water quality monitoring system thereof | |
| CN112560207A (en) | Unmanned ship sailing type submarine cable passive electromagnetic detection system and positioning method | |
| CN108592910A (en) | A kind of agricultural unmanned aerodynamic ship paths planning method based on wind direction | |
| CN115435845A (en) | An intelligent wide-area water quality monitoring and analysis system, method, and water quality analysis method based on unmanned ships and integrated learning | |
| CN111947655A (en) | Precise determination method and underwater positioning system of underwater monitoring robot based on autonomous snorkeling | |
| CN103336887A (en) | Method for identifying water power coefficient based on bee colony algorithm | |
| CN110908404B (en) | AUV intelligent observation motion method based on data driving | |
| CN112631293A (en) | Unmanned ship anti-collision Internet of things control system and method based on artificial potential field method | |
| CN114237253B (en) | A Hadoop-based autonomous navigation performance testing device and method for unmanned boats | |
| CN114354870A (en) | Unmanned ship shortest path water quality monitoring system and method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm | |
| CN107014374A (en) | A kind of underwater glider Energy Saving Algorithm based on complementary filter | |
| CN119596301A (en) | Moving target monitoring method based on unmanned aerial vehicle | |
| CN118112923A (en) | A data-driven adaptive control system for marine robot swarms |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20220415 | |
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |