CN114331286A - Spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment and medium - Google Patents
Spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment and mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN114331286A CN114331286ACN202111679536.7ACN202111679536ACN114331286ACN 114331286 ACN114331286 ACN 114331286ACN 202111679536 ACN202111679536 ACN 202111679536ACN 114331286 ACN114331286 ACN 114331286A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- spare parts
- data
- change
- reserved
- inventory
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及大数据技术领域,特别是涉及一种备件库存预测方法、装置、计算机设备、存储介质和计算机程序产品。The present application relates to the field of big data technology, and in particular, to a spare parts inventory forecasting method, apparatus, computer equipment, storage medium and computer program product.
背景技术Background technique
在日常的生产生活中,大型设备与系统常常需要进行维修与保养。In daily production and life, large-scale equipment and systems often need to be repaired and maintained.
以核电站系统为例,核电站的维修工作主要可以分为计划性维修和突发性维修两类,通常计划性维修工作都会对维修活动中所需要的备件提前进行预留。计划性维修中所需的备件也可细分为A类备件和B类备件,A类备件指维修活动必须更换的备件,B类备件指维修活动中根据现场设备的状态选择性更换的备件。突发性维修通常是指不可提前预估的维修活动。基于备件分类,对不同类别备件的需求进行预测,从而进一步对备件的库存进行预测,优化备件的库存参数,在保障现场备件维修需求的前提下,优化备件库存数据,减少库存积压。Taking the nuclear power plant system as an example, the maintenance work of the nuclear power plant can be mainly divided into two types: planned maintenance and unexpected maintenance. Usually, the planned maintenance work will reserve the spare parts needed in the maintenance activities in advance. The spare parts required in planned maintenance can also be subdivided into A-type spare parts and B-type spare parts. A-type spare parts refer to the spare parts that must be replaced in maintenance activities, and B-type spare parts refer to the spare parts that can be selectively replaced in maintenance activities according to the status of on-site equipment. Unexpected maintenance usually refers to maintenance activities that cannot be predicted in advance. Based on the classification of spare parts, the demand for different types of spare parts is predicted, so as to further predict the inventory of spare parts, optimize the inventory parameters of spare parts, and optimize the inventory data of spare parts to reduce the overstock of spare parts under the premise of ensuring the demand for on-site spare parts maintenance.
目前常规的备件库存预测一般是基于运维人员或者仓库管理人员的经验来进行的,这种单纯基于人工经验预测的方式容易受到人员经验因素的影响,导致最终预测结果不准确,不利于大型设备与系统运维。At present, conventional spare parts inventory forecasting is generally based on the experience of operation and maintenance personnel or warehouse managers. This method of forecasting based solely on manual experience is easily affected by personnel experience factors, resulting in inaccurate final forecast results, which is not conducive to large-scale equipment. and system operation.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
基于此,有必要针对上述技术问题,提供一种预测准确的备件库存预测方法、装置、计算机设备、存储介质和计算机程序产品。Based on this, it is necessary to provide an accurate prediction method, device, computer equipment, storage medium and computer program product for spare parts inventory forecasting in view of the above technical problems.
第一方面,本申请提供了一种备件库存预测方法。方法包括:In a first aspect, the present application provides a spare parts inventory forecasting method. Methods include:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
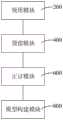
第二方面,本申请还提供了一种备件库存预测装置。装置包括:In a second aspect, the present application also provides a spare parts inventory prediction device. The device includes:
领用模块,用于根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;Requisition module, which is used to generate the change data of the requisition of spare parts over time according to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical requisition of spare parts;
预留模块,用于根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;The reservation module is used to obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the change of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change data of the quantity of the spare parts over time;
正订模块,用于获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;The correction module is used to obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the corrected quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change data of the reserved quantity of spare parts over time;
模型构建模块,用于根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The model building module is used to generate a spare parts inventory forecasting model according to the time change data of the amount of spare parts received, the time change data of the spare part reserved quantity, and the time change data of the spare parts correction quantity.
第三方面,本申请还提供了一种计算机设备。计算机设备包括存储器和处理器,存储器存储有计算机程序,处理器执行计算机程序时实现以下步骤:In a third aspect, the present application also provides a computer device. The computer device includes a memory and a processor, the memory stores a computer program, and the processor implements the following steps when executing the computer program:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
第四方面,本申请还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质。计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时实现以下步骤:In a fourth aspect, the present application also provides a computer-readable storage medium. A computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the following steps are implemented:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
第五方面,本申请还提供了一种计算机程序产品。计算机程序产品,包括计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时实现以下步骤:In a fifth aspect, the present application also provides a computer program product. A computer program product, including a computer program that, when executed by a processor, implements the following steps:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
上述备件库存预测方法、装置、计算机设备、存储介质和计算机程序产品,根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。整个过程中,基于历史备件历史数据,逐步得到备件的领用量随时间变化数据、预留量随时间变化数据、正订量随时间变化数据,并且基于这些数据生成备件库存预测模型,由于综合考虑备件领用、预留、验收以及正订方面的库存库存量的影响,可以实现准确的备件库存预测。The above-mentioned spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment, storage medium and computer program product, according to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical spare part demand amount, generate the data on the change of the spare part demand amount over time; obtain the spare parts according to the spare part historical reservation amount Reserve the configuration parameters, and generate the data of the reserve amount of spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the amount of spare parts over time; Data, historical acceptance data of spare parts, and time-varying data of reserved quantity of spare parts are generated to generate data of time-varying correction quantity of spare parts; The change data of the correction quantity over time is generated, and the spare parts inventory forecast model is generated. During the whole process, based on the historical data of historical spare parts, gradually obtain the data of the change of the amount of spare parts over time, the data of the change of the reserved amount over time, and the data of the change of the corrected amount over time, and generate the spare parts inventory prediction model based on these data. Accurate spare parts inventory forecasts can be achieved by taking into account the impact of inventory inventory in terms of spare parts requisition, reservation, acceptance, and revision.
附图说明Description of drawings
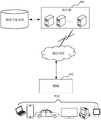
图1为一个实施例中备件库存预测方法的应用环境图;1 is an application environment diagram of a spare parts inventory forecasting method in one embodiment;
图2为一个实施例中备件库存预测方法的流程示意图;2 is a schematic flowchart of a method for predicting spare parts inventory in one embodiment;
图3为常用的MRP策略及其运算逻辑示意图;Figure 3 is a schematic diagram of a commonly used MRP strategy and its operation logic;
图4为另一个实施例中备件库存预测方法的流程示意图;4 is a schematic flowchart of a method for predicting spare parts inventory in another embodiment;
图5为总库存与有货率仿真结果示意图;Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of the simulation results of total inventory and availability;
图6为不同库存模型下的库存金额及有货率;Figure 6 shows the inventory amount and availability rate under different inventory models;
图7为模型效果网格分布图;Fig. 7 is a model effect grid distribution diagram;
图8为一个实施例中备件库存预测装置的结构框图;8 is a structural block diagram of an apparatus for predicting spare parts inventory in one embodiment;
图9为一个实施例中计算机设备的内部结构图。Figure 9 is a diagram of the internal structure of a computer device in one embodiment.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本申请的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本申请进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本申请,并不用于限定本申请。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the present application more clearly understood, the present application will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present application, but not to limit the present application.
本申请实施例提供的备件库存预测方法,可以应用于如图1所示的应用环境中。其中,终端102通过网络与服务器104进行通信。数据存储系统可以存储服务器104需要处理的数据。数据存储系统可以集成在服务器104上,也可以放在云上或其他网络服务器上。服务器104具体可以为备件库存管理的服务器,其存储有历史记录中备件库存量变化相关数据,终端102发起备件存储预测请求至服务器104,服务器104根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。其中,终端102可以但不限于是各种个人计算机、笔记本电脑、智能手机、平板电脑、物联网设备和便携式可穿戴设备,物联网设备可为智能音箱、智能电视、智能空调、智能车载设备等。便携式可穿戴设备可为智能手表、智能手环、头戴设备等。服务器104可以用独立的服务器或者是多个服务器组成的服务器集群来实现。The spare parts inventory prediction method provided in the embodiment of the present application can be applied to the application environment shown in FIG. 1 . The terminal 102 communicates with the
如图2所示,本申请提供一种备件库存预测方法,方法包括:As shown in FIG. 2 , the present application provides a spare parts inventory forecasting method, which includes:
S200:根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据。S200: According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical spare parts demand, the data on the change of spare parts demand over time is generated.
预设维修规范数据包括维修大纲、维修标准包等行业规范数据,基于这些规范数据可以知晓大型设备与系统的维修规范与标准,进而得知在正常运维条件下的所需备件种类与数量。备件历史领用量是指在历史运维过程中领用的备件种类及其对应的数量,通过分析这部分数据可以分析出备件领用量的规律,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据。在实际应用中,备件领用需求包括计划性A类需求、计划性B类需求以及突发性需求,其中计划性A类需求是指按照维修计划必须更换的备件、计划性B类需求是指按照维修计划选择性更换的备件、突发性需求是指运维过程突发性事件(故障)需求的备件,将这3类需求汇总之后,得到备件的领用量随时间变化数据。具体来说,备件的领用量随时间变化数据具体可以为备件在未来的领用表单,通过表单的方式展示备件的领用量。The preset maintenance specification data includes industry specification data such as maintenance outline and maintenance standard package. Based on these specification data, the maintenance specifications and standards of large-scale equipment and systems can be known, and then the types and quantities of spare parts required under normal operation and maintenance conditions can be known. Spare parts historical requisition refers to the types and corresponding quantities of spare parts used in the historical operation and maintenance process. By analyzing this part of the data, the regularity of the requisition of spare parts can be analyzed, and the data of the requisition of spare parts over time can be generated. In practical applications, the demand for spare parts includes planned demand of type A, planned demand of type B and unexpected demand, among which planned demand of type A refers to the spare parts that must be replaced according to the maintenance plan, and planned demand of type B refers to the spare parts that must be replaced according to the maintenance plan. The spare parts that are selectively replaced according to the maintenance plan and the sudden demand refer to the spare parts that are required by sudden events (failures) in the operation and maintenance process. Specifically, the data on the change of the amount of spare parts over time can be a form for the future use of spare parts, and the amount of spare parts is displayed in the form.
S400:根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据。S400: Acquire spare part reservation configuration parameters according to the historical reservation amount of spare parts, and generate time change data of the reserved amount of spare parts according to the spare part reservation configuration parameters and the change data of the amount of the spare parts over time.
预留是用户(运维管理人员)对备件未来领用提出的使用需求。具体来说,影响预留的有三个因素:预留提前期、预留比例以及预留准确率,因此,预留配置参数具体可以包括这三个维度的数据。由于预留是基于领用提出的,因此,可以根据上述的备件预留配置参数以及S200得到的备件的领用量随时间变化数据来得到备件的预留量随时间变化数据。进一步来说,不同类型的备件可能有着不同的预留提前期、预留比例、预留准确率,实际应用中,可以根据备件类型细化设置预留的三个因素设置值,也可简化将所有备件设置相同的设置值。Reservation is the usage demand put forward by the user (operation and maintenance manager) for the future use of spare parts. Specifically, there are three factors that affect the reservation: the reservation lead time, the reservation ratio, and the reservation accuracy rate. Therefore, the reservation configuration parameters can specifically include data of these three dimensions. Since the reservation is proposed based on the requisition, the time change data of the reserved quantity of the spare part can be obtained according to the above-mentioned spare part reservation configuration parameters and the time change data of the requisition quantity of the spare part obtained in S200. Further, different types of spare parts may have different reservation lead times, reservation ratios, and reservation accuracy rates. In practical applications, the setting values of the three reserved factors can be refined according to the type of spare parts, and the All spare parts are set to the same settings.
S600:获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据。S600: Acquire new purchase data of spare parts and historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate time change data of correct order quantity of spare parts according to the newly added purchase data, historical acceptance data of spare parts, and change data of reserved quantity of spare parts over time.
新增采购数据是指针对本期备件需求增加的采购数据,这些采购数据会在未来影响备件正订量。另外,正订量还与验收量以及预留量之间存在关系,通过分析新增采购数据、历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订单随时间变化数据。The newly added procurement data refers to the procurement data for the increased demand for spare parts in the current period, and these procurement data will affect the correct order quantity of spare parts in the future. In addition, there is a relationship between the positive order quantity and the acceptance quantity and the reserved quantity. By analyzing the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data and the time change data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts, the time change data of the positive order of the spare parts is generated.
进一步来说,备件的正订与新增正订(NPR)、验收量(Y)以及上一期的正订值有关。新增正订(NPR)与备件的库存量(S)、预留量(R)、库存参数(M)、正订(PR)有关,通过模拟MRP的运算逻辑,可利用公式计算NPR。常用的MRP策略及其运算逻辑如图3表格所示,将该逻辑转换为公式,通过输入库存参数、库存数量、正订数量、预留数量,由此计算新触发的采购数量。备件正订的计算公式为PRt=PRt-1+NPRt-1-Yt-1。Further, the revision of spare parts is related to the new revision (NPR), acceptance quantity (Y) and the revision value of the previous period. The newly added correction (NPR) is related to the stock quantity (S), reserved quantity (R), stock parameter (M), and correction (PR) of spare parts. By simulating the operation logic of MRP, the formula can be used to calculate the NPR. The commonly used MRP strategy and its operation logic are shown in the table in Figure 3. This logic is converted into a formula, and the newly triggered purchase quantity is calculated by entering the inventory parameters, inventory quantity, corrected quantity, and reserved quantity. The formula for calculating the correction of spare parts is PRt =PRt-1 +NPRt-1 -Yt-1 .
S800:根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。S800: Generate a spare parts inventory forecasting model according to the time change data of the amount of spare parts received, the time change data of the spare parts reserved quantity, and the time change data of the spare part correction quantity.
在经过上述处理得到备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据之后,可以基于这些数据生成备件库存预测模型。该备件库存预测模型可以预测在未来的备件库存参数。备件库存参数具体可以包括备件库存量,还可以进一步换算得到库存金额以及有货率等参数。进一步的,还可以对该备件库存参数进行进一步优化,以使最终得到的备件库存量既不会造成备件、资金长期无效占用,又能满足日常运维所需备件需求。After obtaining the data on the change of the quantity of spare parts with time, the data of the change of the reserved quantity of the spare parts with time, and the data of the change of the corrected quantity of the spare parts with time, the spare parts inventory prediction model can be generated based on these data. The spare parts inventory forecasting model can predict the spare parts inventory parameters in the future. Spare parts inventory parameters may specifically include spare parts inventory, and may be further converted to obtain parameters such as inventory amount and availability rate. Further, the spare parts inventory parameters can be further optimized, so that the finally obtained spare parts inventory will not cause long-term ineffective occupation of spare parts and funds, but also meet the demand for spare parts required for daily operation and maintenance.
具体来说,备件的库存与上一期库存、验收量和领用量有关。备件的库存计算公式为St=St-1+Yt-1-Lt-1。当库存数量<0时,即该期领用无法有效保障,当库存数量≥0时,该期的领用能够有效保障。假设有保障为1,无保障为0,有货率表为A,则若St≥0,则At=1,否则At=0。计算该备件在规定时间内的有货率,只要用A表中值为1的个数除以A表中的总个数。库存金额为库存数量*备件单价,当库存数量<0时,库存金额为0。库存金额表为SA,备件单价为SP,则若St≥0,则SAt=St*SP,否则SAt=0。计算该备件在规定时间内的平均库存金额,只要用SA表中的值求平均值即可。Specifically, the inventory of spare parts is related to the inventory of the previous period, the quantity accepted and the quantity received. The inventory calculation formula of spare parts is St =St-1 +Yt-1 -Lt-1 . When the inventory quantity is less than 0, that is, the collection in this period cannot be effectively guaranteed. When the inventory quantity is ≥ 0, the collection in this period can be effectively guaranteed. Assuming that the guarantee is 1, the non-guarantee is 0, and the availability rate table is A, then if St ≥0 , then At =1 , otherwise At = 0. To calculate the availability rate of the spare part within the specified time, just divide the number of 1 in table A by the total number in table A. The inventory amount is the inventory quantity * the unit price of spare parts. When the inventory quantity is less than 0, the inventory amount is 0. The inventory amount table is SA, and the unit price of spare parts is SP. If St ≥ 0, then SAt =St *SP, otherwise SAt =0. To calculate the average inventory amount of the spare part within the specified time, just use the value in the SA table to average.
上述备件库存预测方法,根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。整个过程中,基于历史备件历史数据,逐步得到备件的领用量随时间变化数据、预留量随时间变化数据、正订量随时间变化数据,并且基于这些数据生成备件库存预测模型,由于综合考虑备件领用、预留、验收以及正订方面的库存库存量的影响,可以实现准确的备件库存预测。The above-mentioned spare parts inventory forecasting method generates data on the change of the amount of spare parts over time according to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical amount of spare parts; according to the historical reserve amount of spare parts, the reserved configuration parameters of spare parts are obtained, and the configuration parameters are reserved according to the spare parts. As well as the data on the change of the amount of spare parts over time, generate the data on the change of the reserved amount of spare parts over time; obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the reserved amount of spare parts Time-varying data to generate the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts; according to the time-varying data of the quantity of spare parts, the quantity of the reserved quantity of the spare parts varying with time, and the data of the correct quantity of the spare parts varying over time, the spare-part inventory is generated. prediction model. During the whole process, based on the historical data of historical spare parts, gradually obtain the data of the change of the amount of spare parts over time, the data of the change of the reserved amount over time, and the data of the change of the corrected amount over time, and generate the spare parts inventory prediction model based on these data. Accurate spare parts inventory forecasts can be achieved by taking into account the impact of inventory inventory in terms of spare parts requisition, reservation, acceptance, and revision.
在其中一个实施例中,上述备件库存预测还包括:获取初始时刻的初始备件预留量;将初始备件预留量分解到未来领用量,得到备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据;In one embodiment, the above-mentioned spare parts inventory prediction further includes: obtaining an initial reserved amount of spare parts at an initial moment; decomposing the initial reserved amount of spare parts into a future demand amount to obtain data on the change of the initial spare part demand amount with time;
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据包括:根据预设维修规范数据、备件历史领用量以及备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据。According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical spare parts demand, the generation of the change data of the spare part demand over time includes: according to the preset maintenance specification data, the spare part historical demand amount and the spare part initial demand change data over time, the spare part demand change data is generated. Data on initial consumption over time.
对备件量进行仿真预测时,可以读取备件当前真实的库存数量、库存参数、正订、预留等数据。由于预留直接参与备件存量运算,为保障备件仿真的平稳性,需将当前的预留分解到未来的领用数据。进一步的,针对正订而言,需要将当前的正订分解到未来的验收数据。When simulating the spare parts quantity, you can read the current real inventory quantity, inventory parameters, correction, reservation and other data of the spare parts. Since the reservation directly participates in the calculation of spare parts inventory, in order to ensure the stability of the spare part simulation, it is necessary to decompose the current reservation into the future use data. Further, for the revision, it is necessary to decompose the current revision into the future acceptance data.
进一步的来说,进行分解可以包括详细分解和简化分解两种方式,其中以下会介绍详细分解和简化分解两种方法。其中详细分解需获取当前正订的具体到货时间,当前预留的类型以及工单开工日期。若无法获取备件的详细交货计划以及详细预留清单,可以通过简化的方法将正订和预留数据进行分解。Further, the decomposition can include detailed decomposition and simplified decomposition, and two methods of detailed decomposition and simplified decomposition will be introduced below. The detailed decomposition needs to obtain the specific arrival time of the current revision, the type of the current reservation and the start date of the work order. If the detailed delivery schedule and detailed reservation list for spare parts are not available, the revised and reserved data can be broken down in a simplified manner.
在其中一个实施例中,将初始备件预留量分解到未来领用量,得到备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据包括:In one of the embodiments, the initial reserved amount of spare parts is decomposed into the future consumption amount, and the data on the change over time of the initial consumption amount of the spare parts obtained includes:
提取初始备件预留量中预留提前周期和预留数量;根据预留提前周期确定分解到不同预留时间点的顺序;根据分解不同预留时间点的顺序以及预留数量,确定分解到未来不同时间点的领用量,得到备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据。Extract the reserved advance period and reserved quantity from the initial spare parts reservation; determine the sequence of decomposition to different reserved time points according to the reserved advance period; determine the decomposition to the future according to the order of decomposing different reserved time points and the reserved quantity Requisition at different time points, and obtain the change data of the initial requisition of spare parts over time.
预留提前周期是指需要提前预留的时间周期,例如需要预留未来12个月的备件量,则预留提前周期为12个月,又如需要预留未来6个月的备件量,则预留提前周期为6个月。预留数量是指初始总计预留数量。根据预留提前周期确定这些预留数据量分解到不同预留时间点的顺序,一般是取预留的时间周期中值向两端次序选择预留时间点,以预留提前周期为12个月为例,选取中间时间点6月份作为预留分解起始月份,向两端次序选择预留时间点,即6-7-5-8-4-9-3-10-2-11-1-12,直至将预留数量全部分解完,例如需要预留数量为19个,采取月度平均分配的方式,则需要分解到10个月度,分解之后两用数量和减少预留数量如下表1所示。The reserved advance period refers to the time period that needs to be reserved in advance. For example, if the amount of spare parts for the next 12 months needs to be reserved, the reserved advance period is 12 months, and if the amount of spare parts for the next 6 months needs to be reserved, then The reservation advance period is 6 months. The reserved quantity refers to the initial total reserved quantity. According to the reservation advance period, the order in which these reserved data volumes are decomposed into different reserved time points is determined. Generally, the median value of the reserved time period is used to select the reserved time points in the order of the two ends, and the reserved advance period is 12 months. For example, select the middle time point June as the starting month for reserved decomposition, and select the reserved time points in the order of both ends, that is, 6-7-5-8-4-9-3-10-2-11-1- 12. Until the reserved quantity is fully decomposed, for example, the reserved quantity is 19, and the monthly average distribution method is adopted, it needs to be decomposed into 10 monthly. After the decomposition, the dual-use quantity and the reduction of the reserved quantity are shown in Table 1 below. .
表1为基于初始备件预留量初始化领用、减少预留数据表Table 1 is the data table of initial requisition and reduction of reservation based on the initial reserve of spare parts
进一步的,针对正订分解也是采用上述类似的方式,下面将介绍针对初始正订简单分解的过程。Further, a similar method is used for the positive correction decomposition, and the simple decomposition process for the initial correction correction will be introduced below.
若无法获取备件的详细交货计划以及详细预留清单,可以通过简化的方法将正订和预留数据进行分解。针对正订PO,获取待交货数量N,在采购周期内分配验收数量,减少因正订初始化导致仿真前期的库存量出现大波动。每期的验收数量为即待交货数量除以采购周期(需向上取整),从时间(向上取整)开始计算验收数量,按照分解到验收表中,直至待交货数量N分解完成。例如某备件采购周期为7个月,待交货PO数量分别为6个,每期的验收数量为1,为4,则按照2021年4月、5月、3月、6月、2月、7月进行分配,每期验收1个,共验收6个。同理,若待交货PO数量为19个,则每期的验收数量为3,按照2021年4月、5月、3月、6月、2月、7月、1月进行分配,其中在2021年1月,只有1个待分配额度,故2021年1月分配一个,共验收19个。If the detailed delivery schedule and detailed reservation list for spare parts are not available, the revised and reserved data can be broken down in a simplified manner. For the revised PO, the quantity N to be delivered is obtained, and the acceptance quantity is allocated in the procurement cycle, so as to reduce the large fluctuation of the inventory in the early stage of simulation due to the initialization of the revised PO. The number of acceptances for each period is That is, the quantity to be delivered divided by the procurement cycle (to be rounded up), from Time (rounded up) starts to calculate the acceptance quantity, according to It is decomposed into the acceptance table until the decomposition of the quantity to be delivered N is completed. For example, the procurement cycle of a spare part is 7 months, the number of POs to be delivered is 6, and the acceptance quantity of each period is 1. If it is 4, it will be allocated according to April, May, March, June, February, and July of 2021, and 1 will be accepted in each period, and a total of 6 will be accepted. In the same way, if the number of POs to be delivered is 19, the number of acceptances in each phase is 3, which will be allocated according to April, May, March, June, February, July, and January in 2021. In January 2021, there is only one quota to be allocated, so one will be allocated in January 2021, and a total of 19 quotas will be accepted.
进一步的,除了可以采用简单分解方式之外,还可以采用详细分解方式。下面将针对初始正订和初始备用的详细分解方式展开描述。Further, in addition to a simple decomposition method, a detailed decomposition method can also be used. The detailed decomposition of the initial correction and the initial backup will be described below.
提取当前已经正式签署订单的正订(通常称为PO),若到货日期在当前日期之前,则按照计划到货日期+0.5*采购周期的时间后到货,若计划到货日期+0.5*采购周期仍小于当前日期,则按照当前日期+1时间到货。结合订单中的到货日期以及订单采购数量,初始化验收表数据。假设某备件的采购周期为12个月,有6个PO,当前日期为2021年1月,如下表2所示:Extract the current revision (usually called PO) of the order that has been officially signed. If the arrival date is before the current date, it will arrive after the planned arrival date + 0.5* purchase cycle time, if the planned arrival date + 0.5* If the procurement cycle is still less than the current date, the goods will arrive at the current date + 1 time. Combine the arrival date in the order and the purchase quantity of the order to initialize the acceptance table data. Suppose the procurement cycle of a spare part is 12 months, there are 6 POs, and the current date is January 2021, as shown in Table 2 below:
表2为已签署订单的PO及其到货日期与数量Table 2 is the PO of the signed order and its arrival date and quantity
其初始化的验收数据表如表3所示。The initial acceptance data table is shown in Table 3.
表3为基于已有PO初始化验收表Table 3 is the initial acceptance table based on the existing PO
其中表3中2021年4月的验收数量为7,其是表3中的2020年10月和2021年4月的到货数量之和。计划到货日期为POT,当前日期为NDT,到货数量为n,采购周期为ΔT,初始化验收表的计算逻辑如下:若POTi+0.5*ΔT<NDT,则Y2=ni;若POTi<NDT,则若POTi>NDT,则Y0.5*ΔT=ni。Among them, the acceptance quantity in April 2021 in Table 3 is 7, which is the sum of the arrival quantities in October 2020 and April 2021 in Table 3. The planned arrival date is POT, the current date is NDT, the arrival quantity is n, and the purchasing period is ΔT. The calculation logic of the initial acceptance table is as follows: if POTi +0.5*ΔT<NDT, then Y2 =ni ;i < NDT, then If POTi >NDT, then Y0.5*ΔT =ni .
针对初始预留数据来说,提取当前的有效预留数据,即工单预留中开工日期在当前日期之后的预留。基于该预留数据,初始化领用数据、减少预留和预留值。如果预留中涉及了计划性维护项目,则在领用表梳理环节,要剔除对应维护项目的备件需求。如表4所示,其中维护项目4002、4003、4004的备件需求已在预留中有体现,故在梳理领用表时,需剔除这几个维护项目的备件需求。For the initial reservation data, extract the current valid reservation data, that is, the reservation in the work order reservation with the start date after the current date. Based on the reserved data, initialize the requisition data, reduce the reservation, and reserve the value. If planned maintenance items are involved in the reservation, the spare parts requirements for the corresponding maintenance items should be eliminated in the process of sorting out the requisition table. As shown in Table 4, the spare parts requirements of maintenance items 4002, 4003, and 4004 have been reflected in the reservation. Therefore, when sorting out the requisition table, it is necessary to exclude the spare parts requirements of these maintenance items.
表4为已有预留数据梳理。Table 4 sorts out the existing reserved data.
基于已有的预留数据,初始化领用数据、减少预留、初始预留。由于表4中预留101的需求日期在当前日期之前,属于无效预留,不保留,其余预留都转换为领用数据和减少预留数据,如表5所示。由于当前日期为2021年1月,仿真从当前日期开始,故2021年1月的预留为表5中的有效预留数量,共计9个。后续时间的预留需通过预留、新增预留、减少预留进行迭代计算。Based on the existing reserved data, initialize the used data, reduce the reservation, and make the initial reservation. Since the demand date of
表5为基于已有预留数据初始化领用、减少预留、预留梳理Table 5 is based on the existing reserved data to initialize the use, reduce the reservation, and sort out the reservation
如图4所示,在其中一个实施例中,S200包括:As shown in Figure 4, in one embodiment, S200 includes:
S220:获取预设维修规范数据以及相邻预设时间段内备件历史领用量;S220: Acquire the preset maintenance specification data and the historical quantity of spare parts received in the adjacent preset time period;
S240:将相邻预设时间段内备件历史领用量分类为计划性A类备件的领用量、计划性B类备件的领用量以及突发性备件的领用量,A类备件是指运维必定更换的备件,B类备件是指运维选择性更换的备件;S240: Classify the historical spare parts demand in the adjacent preset time period into planned A-type spare parts, planned B-type spare parts, and unexpected spare parts. A-type spare parts refer to the spare parts that must be operated and maintained. Replacement spare parts, category B spare parts refer to spare parts that are selectively replaced by operation and maintenance;
S260:根据预设维修规范数据以及计划性A类备件的领用量,生成A类备件需求模型,根据预设维修规范数据以及计划性B类备件的领用量,生成B类备件需求模型,根据预设维修规范数据采用线性拟合的方法生成突发性备件未来领用量;S260: Generate a demand model for Type A spare parts according to the preset maintenance specification data and the planned demand for Type A spare parts, and generate a demand model for Type B spare parts according to the preset maintenance specification data and the planned demand for Type B spare parts. The maintenance specification data adopts the method of linear fitting to generate the future demand of emergency spare parts;
S280:根据A类备件需求模型、B类备件需求模型以及突发性备件未来领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据。S280: According to the demand model for type A spare parts, the demand model for type B spare parts, and the future demand for sudden spare parts, generate data on changes in the demand of spare parts over time.
相邻预设时间段是指与当前时间相邻的时间段,例如最近3年、最近5年获最近10年的备件历史领用量。具体来说,计算备件未来的领用即对备件在未来的需求进行预测,最简单的方案是假设备件未来的需求与历史需求一致,假设需要10年的仿真数据,可以按照如下方法梳理需求。从数据库导出该备件过去10年的领用数据,假设10年的领用数据分别为N1、N2、N3、......、N10,由此生成11~20年的领用数据,计算公式为由此生成了备件未来10年的领用需求。为提升预测的有效性,可以对备件的历史领用数据进行分类,针对计划性A类备件需求,根据维修大纲、标准包,生成备件未来的计划性A类备件领用需求;针对计划性B类备件需求,根据维修大纲、标准包、计划性B类备件需求模型,生成备件未来的计划性B类备件领用需求;针对突发性备件需求,可参照以上线性拟合的方法,生成备件未来领用需求,或者通过读取该备件的历史突发性备件领用数据,随机生成相同领用频次、相同领用均值、相同领用标准差的备件突发性领用需求。再对计划性A类备件需求、计划性B类备件需求、突发性备件需求进行求和,得到备件未来的总领用需求。The adjacent preset time period refers to the time period adjacent to the current time, such as the past 3 years, the last 5 years and the last 10 years of spare parts historical receipts. Specifically, calculating the future use of spare parts is to predict the demand for spare parts in the future. The simplest solution is to pretend that the future demand of equipment parts is consistent with the historical demand. Assuming that 10 years of simulation data are required, the demand can be sorted out as follows . From the database, export the spare part's usage data in the past 10 years, assuming that the 10-year usage data are respectively N1 , N2 , N3 , ..., N10 , so as to generate 11-20 years of usage data. Using the data, the calculation formula is This generates the demand for spare parts in the next 10 years. In order to improve the validity of the forecast, the historical data of spare parts can be classified, according to the planned A-class spare parts demand, according to the maintenance program and standard package, the planned spare parts' future planned A-class spare parts demand is generated; for the planned B-type spare parts Type B spare parts demand, according to the maintenance program, standard package, and planned Type B spare parts demand model, generate future planned Type B spare parts demand for spare parts; for sudden spare parts demand, you can refer to the above linear fitting method to generate spare parts The demand for future use, or by reading the historical data of sudden spare parts use of the spare part, randomly generate the sudden demand for spare parts with the same use frequency, the same use average value, and the same use standard deviation. Then sum up the planned A-type spare parts demand, the planned B-type spare parts demand, and the unexpected spare parts demand to obtain the future general demand for spare parts.
在其中一个实施例中,根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数包括:根据备件历史预留量,获取预留提前期、预留比例以及预留准确率。In one embodiment, acquiring the spare part reservation configuration parameter according to the historical reservation amount of the spare part includes: acquiring the reservation lead time, the reservation ratio, and the reservation accuracy rate according to the historical reservation amount of the spare part.
下面将详细介绍预留的三个因素确定方法,并举例说明完整的计算过程。The following will introduce the method of determining the three factors of reservation in detail, and illustrate the complete calculation process with an example.
预留提前期即提前多长时间对备件提出预留,例如针对大修PM项目(计划性维修),各核电厂约提前一年发出工单,下达备件预留(大亚湾是提前2C发出工单),日常PM项目,各核电厂也是约一年发出工单,下达备件预留。针对突发性项目,按照核电厂的管理规定,针对涉及核安全的项目,需在24小时内完成;针对相对重要的项目,需要在3周、12周内完成;针对普通项目,在下一个FEG(FEG Functional Equipment Group,功能设备组)完成,故可根据备件的重要性,设置不同预留提前期。可将重要备件(如CCM、H级)的突发性预留设置为1个月,其余备件的突发性预留设置为3个月;若不区分备件的重要性,可以将突发性预留的时间设置为2个月。The reservation lead time refers to how long in advance to reserve spare parts. For example, for overhaul PM projects (planned maintenance), each nuclear power plant will issue work orders about one year in advance and issue spare parts reservations (Daya Bay issues work orders 2C in advance) , For daily PM projects, each nuclear power plant also issues work orders for about a year and issues reservations for spare parts. For emergency projects, according to the management regulations of nuclear power plants, for projects involving nuclear safety, it needs to be completed within 24 hours; for relatively important projects, it needs to be completed within 3 weeks or 12 weeks; for ordinary projects, in the next FEG (FEG Functional Equipment Group, functional equipment group) is completed, so different reservation lead times can be set according to the importance of spare parts. The sudden reservation of important spare parts (such as CCM, H-level) can be set to 1 month, and the sudden reservation of other spare parts can be set to 3 months; if the importance of spare parts is not distinguished, the sudden reservation can be The reserved time is set to 2 months.
预留比例是指有多少比例的备件会进行预留,计划性A类备件绝大部分备件都会在大修前进行预留,计划性B类备件只有少数备件会提前进行预留,突发性备件一般只在领料前进行预留。经过对某核电厂6轮大修领用数据进行分析,大修计划性A类备件在预留提前期的预留比例约为93.3%,大修计划性B类备件在预留提前期的预留比例约为24.5%。按照某核电厂的现状,日常备件需求及时提报率比大修备件需求及时提报率低10%,故日常计划性A类备件在预留提前期的预留比例可设置为83.3%。由于当前大修计划性B类的预留比例较低,故可以将日常计划性B类备件的预留比例设置为与大修相同,即为24.5%。经对突发性备件领用工单进行分析可将突发性备件的整体预留比例设置为79.6%。The reserved ratio refers to the proportion of spare parts that will be reserved. Most of the planned Class A spare parts will be reserved before the overhaul. Only a few spare parts of the planned Class B spare parts will be reserved in advance, and emergency spare parts will be reserved in advance. Generally, reservations are only made before picking. After analyzing the data of 6 rounds of overhaul of a nuclear power plant, the reserve ratio of planned class A spare parts for major overhauls in the reserved lead time is about 93.3%, and the reserve ratio of planned class B spare parts for major repairs in the reserved lead time is about 93.3%. was 24.5%. According to the current situation of a nuclear power plant, the timely reporting rate of daily spare parts demand is 10% lower than that of overhaul spare parts. Therefore, the reserve ratio of daily planned Class A spare parts in the reserved lead time can be set to 83.3%. Due to the low reserve ratio of planned category B for overhaul at present, the reserved proportion of daily planned category B spare parts can be set to be the same as that of overhaul, that is, 24.5%. After analyzing the work order for unexpected spare parts, the overall reserve ratio of unexpected spare parts can be set to 79.6%.
预留准确率是指预留的备件中预测正确的比例,经过对某核电厂6轮大修领用数据进行分析,大修A类备件的预留准确率为87.4%,大修B类备件的预留准确率为75.6%。针对日常计划性备件,其计划性A/B类备件的需求准确率可设置为64%。通过对比分析突发性备件的预留和领用数据,突发性预留准确率可设置为64.3%,即每预留1个备件,实际领用的数量为0.643个。若通过领用计算预留,则为每领用一个备件,预留1.55个(可向上取值为2个),由于突发性备件的预留提前期远小于计划性备件,故突发性备件的整体预留准确率较高。预留提前期、预留比例、预留准确率汇总数据如表6所示。The reservation accuracy rate refers to the proportion of the reserved spare parts that are correctly predicted. After analyzing the data received for 6 rounds of overhaul of a nuclear power plant, the reservation accuracy rate of the overhaul type A spare parts is 87.4%, and the reservation accuracy of the overhaul type B spare parts is 87.4%. The accuracy rate is 75.6%. For daily planned spare parts, the demand accuracy rate of planned A/B spare parts can be set to 64%. By comparing and analyzing the reserved and used data of sudden spare parts, the accuracy rate of sudden reservation can be set to 64.3%, that is, for every reserved spare part, the actual number of reserved parts is 0.643. If the reservation is calculated by requisition, 1.55 spare parts are reserved for each requisition (the value can be upwards to 2). Since the reserved lead time of emergency spare parts is much smaller than that of planned spare parts, the The overall reservation accuracy of spare parts is relatively high. The summary data of reservation lead time, reservation ratio, and reservation accuracy are shown in Table 6.
表6为预留影响因素设置参考值Table 6 sets reference values for reserved influencing factors
基于备件的领用表以及设定预留的影响因素,即可计算备件的预留数据,以下举例说明如何将领用表转换为预留表。为了能够更清楚的展示转换的逻辑关系,在此简化了预留影响因素,假设只有计划性和突发性两类领用,其中计划性的预留提前期为2个月,预留比例为100%,预留准确率为100%;突发性的预留提前期为1个月,预留比例为50%,预留准确率为50%。如表7所示,首先梳理备件的领用数据,并标识领用类型。根据预留比例新增0-1的随机数列,若预留比例为50%,则0与1的比例各占50%。迭代计算“新增预留”和“减少预留”列,在t2时间时,有1个突发性领用,且突发性预留比例随机数为1,故在t1时间会出现2个预留(领用1个,预留准确率为50%,预留2个),该预留会随时t2时间备件领用而消失,故t2时间减少2个预留。t8时间的突发性领用1个和t9时间计划性领用3个都会在t7时间进行预留,故t7的预留为5个(2+3)。预留数据=上一期的预留+本期的新增预留-本期的减少预留,由此可计算出备件的预留数据。Based on the spare parts requisition table and setting the influencing factors of reservation, the reserved data of spare parts can be calculated. The following example shows how to convert the requisition table into a reservation table. In order to show the logical relationship of the conversion more clearly, the influencing factors of reservation are simplified here. It is assumed that there are only two types of requisitions: planned and unexpected. Among them, the planned reservation lead time is 2 months, and the reservation ratio is 100%, the reservation accuracy rate is 100%; the sudden reservation lead time is 1 month, the reservation ratio is 50%, and the reservation accuracy rate is 50%. As shown in Table 7, first sort out the spare parts usage data and identify the usage type. A random number sequence of 0-1 is added according to the reserved ratio. If the reserved ratio is 50%, the ratios of 0 and 1 will each account for 50%. Iteratively calculate the columns of "Add Reservation" and "Reduce Reservation". At t2 time, there is one sudden use, and the random number of the sudden reservation ratio is 1, so there will be two at t1 time. Reservation (1 piece is used, the reservation accuracy is 50%, 2 pieces are reserved), the reservation will disappear at the time of t2 when the spare parts are used, so the t2 time is reduced by 2 reservations. 1 sudden use at t8 time and 3 planned use at t9 time will be reserved at t7 time, so the reservation at t7 is 5 (2+3). Reservation data = reservation in the previous period + newly added reservation in this period - reduced reservation in this period, from which the reserved data of spare parts can be calculated.
若转换为程序流程,设定领用数量(L),预留提前期(ΔNi),预留比例(Ki),预留比例随机数为(f(K),0~1的随机数,0的概率为1-K,1的概率为K),预留准确率(P),新增预留(NR),减少预留(DR),预留(R)。迭代运算,IF Lt*f(k)t>0,Then其中t为时间维度,i为不同类型的备件(突发性、计划性)。先迭代进行新增预留和减少预留数据后,再通过Rt=Rt-1+NRt-DRt计算预留数量。If it is converted into a program flow, set the number of requisitions (L), the reserved lead time (ΔNi ), the reserved proportion (Ki ), and the random number of the reserved proportion is (f(K), a random number from 0 to 1) , the probability of 0 is 1-K, the probability of 1 is K), reservation accuracy rate (P), new reservation (NR), reduction reservation (DR), reservation (R). Iterative operation, IF Lt *f(k)t >0,Then where t is the time dimension, and i is the different types of spare parts (emergent, planned). After adding and reducing reserved data iteratively, the reserved quantity is calculated by Rt =Rt-1 +NRt -DRt .
表7领用数据转换为预留数据案例Table 7 Cases of conversion of used data to reserved data
在其中一个实施例中,根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型之后,还包括:In one of the embodiments, after generating the spare parts inventory prediction model according to the data of the change in the amount of spare parts over time, the data of the change of the reserved amount of the spare parts over time, and the data of the change of the correct amount of the spare parts over time, the method further includes:
根据备件库存预测模型获取本期备件库参数;采用预设参数优化方法对本期备件库参数进行参数优化,预设参数优化方法包括穷举法、改进遗传算法或需求概率模型优化法。According to the spare parts inventory prediction model, the parameters of the current spare parts warehouse are obtained; the parameters of the current spare parts warehouse are optimized by the preset parameter optimization method. The preset parameter optimization methods include the exhaustive method, the improved genetic algorithm or the demand probability model optimization method.
基于备件库存预测模型可以得到准确的本期备件库参数。进一步的,还可以对得到的本期备件库参数进行优化,以实现在备件的总库存金额和总有货率之间寻找到一个合适的平衡点。具体来说,按照仿真时运算逻辑基于备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据构建得到备件库存预测模型之后再对其进行优化。以图5中备件为例进行仿真,针对两组库存参数方案,计算的总库存金额和总有货率,如图6所示,其中TYP1组库存模型的平均库存金额为1094万元,平均有货率为97.3%,TYPE2组库存模型的平均库存金额为1121万元,平均有货率为96.4%。Based on the spare parts inventory prediction model, the accurate parameters of the spare parts inventory in the current period can be obtained. Further, the obtained parameters of the spare parts library in the current period can also be optimized, so as to find an appropriate balance point between the total inventory amount of spare parts and the total availability rate. Specifically, according to the calculation logic during the simulation, the spare parts inventory prediction model is constructed based on the data of the change of the quantity of spare parts over time, the data of the change of the reserved quantity of spare parts over time, and the change of the correct quantity of spare parts over time. optimization. Taking the spare parts in Figure 5 as an example for simulation, for the two sets of inventory parameter schemes, the total inventory amount and total availability rate are calculated, as shown in Figure 6, where the average inventory amount of the TYP1 group inventory model is 10.94 million yuan, and the average The stock rate is 97.3%, the average stock amount of the TYPE2 group stock model is 11.21 million yuan, and the average stock rate is 96.4%.
通过设置备件的库存参数,储备一定数量的库存,在不产生库存积压的情况下,保障备件未来的需求。备件库存参数设置的有效性,直接关系到备件库存金额以及保障情况。按照库存预测分析的逻辑,可以将备件的库存参数当作变量,基于库存金额和有货率设置适应度函数,将其转化为一个优化问题,对库存参数求最优解。By setting the inventory parameters of spare parts, a certain amount of inventory is reserved to ensure the future demand for spare parts without creating inventory backlog. The validity of the spare parts inventory parameter setting is directly related to the amount of spare parts inventory and the guarantee situation. According to the logic of inventory forecast analysis, the inventory parameters of spare parts can be regarded as variables, and the fitness function can be set based on the inventory amount and availability rate, and it can be transformed into an optimization problem to find the optimal solution to the inventory parameters.
备件库存预测模型评价优化方法Spare parts inventory forecast model evaluation and optimization method
当前常用的需求预测准确度检测方法主要用于比较两个模型偏离真实值的偏离程度,由于大型系统(例如核电站)目前应用的备件库存策略模型是通过设置库存参数,利用库存缓冲等方法来应对备件需求的发生,难以通过库存参数计算出未来某一时间端的准确需求数量,故该评价方法不适用评价当前的库存策略模型。若要评估突发性备件库存策略模型,可以从模型参数设置后在库存管理和备件保障领用的效果进行综合评价。The current commonly used demand forecasting accuracy detection method is mainly used to compare the degree of deviation of the two models from the true value. Because the spare parts inventory strategy model currently used in large systems (such as nuclear power plants) is to set inventory parameters, use inventory buffers and other methods to deal with Due to the occurrence of spare parts demand, it is difficult to calculate the exact demand quantity at a certain time in the future through inventory parameters, so this evaluation method is not suitable for evaluating the current inventory strategy model. To evaluate the emergency spare parts inventory strategy model, a comprehensive evaluation can be made on the effects of inventory management and spare parts guarantee receipt after the model parameters are set.
针对库存模型进行评价,需要计算备件在该模型下的平均库存金额、平均有货率、年均采购次数、备件的基准参数储备金额,其中平均库存金额和平均有货率是利用上述的内容得出,对备件在某库存参数下对未来的库存以及有货率进行预测,计算得到平均库存金额和平均有货率。备件有货率和库存金额是一对相互制约的指标,通常情况下,若要提升备件有货率,需增加库存储备,由此会提升库存金额。在计算出有货率和库存金额后,以平均库存金额为横坐标,以平均有货率为纵坐标,建立模型效果网格分布图。将采购周期内平均领用量*单价作为基准库存金额(代指横坐标的一格),将7%作为基准有货率(代指纵坐标的一格,72%~100%可以覆盖绝大部分有货率情况)。使用“距离法”进行评估,即通过计算各模型与理论最优值的距离,对各模型进行评估。图中约往左上处(即参数储备金额越低,有货率越高),模型的效果越好。模型效果网格分布图如图7所示,先计算X距离,再计算Y距离,最后根据X距离和Y距离计算离理论最优位置的总距离,总距离越小说明该模型离理论最优值最近,相对较优。For the evaluation of the inventory model, it is necessary to calculate the average inventory amount, average availability rate, annual average number of purchases, and the reserve amount of the benchmark parameters of spare parts under the model. The average inventory amount and average availability rate are obtained by using the above contents. Predict the future inventory and availability rate of spare parts under a certain inventory parameter, and calculate the average inventory amount and average availability rate. Spare parts availability rate and inventory amount are a pair of indicators that restrict each other. Usually, if you want to increase the spare parts availability rate, you need to increase the inventory reserve, which will increase the inventory amount. After calculating the availability rate and stock amount, take the average stock amount as the abscissa and the average stock rate as the ordinate to build the model effect grid distribution map. Take the average amount received in the procurement cycle * unit price as the benchmark inventory amount (referring to one grid on the abscissa), and 7% as the benchmark availability rate (referring to one grid on the ordinate, 72% to 100% can cover most of the availability). The "distance method" is used for evaluation, that is, each model is evaluated by calculating the distance between each model and the theoretical optimal value. About the upper left in the figure (that is, the lower the parameter reserve amount, the higher the availability rate), the better the effect of the model. The model effect grid distribution diagram is shown in Figure 7. The X distance is calculated first, then the Y distance is calculated, and finally the total distance from the theoretical optimal position is calculated according to the X distance and the Y distance. The smaller the total distance, the better the theoretical model is. The value is recent and relatively good.
例如某备件的基准库存金额为6000,通过计算各个库存策略模型的平均有货率、平均库存金额,进而计算模型效果网格分布图的X轴距离、Y轴距离,由此计算模型的评价分数。以下以Model1为例进行介绍,X轴距离为Model1的参数储备金额/基准参数储备金额,即8000/6000=1.33,Y轴距离为(1-85%)/7%=2.14。总距离为X轴距离的平方加上Y轴距离的平方,后开根号,即同理,可以求得Model2~Model6的总距离如表8所示。其中Model3的总距离最小,即离理论最优位置最近,所以Model3的效果相对更优。For example, the base inventory amount of a spare part is 6000. By calculating the average availability rate and average inventory amount of each inventory strategy model, the X-axis distance and Y-axis distance of the model effect grid distribution map are calculated, thereby calculating the evaluation score of the model. . The following takes Model1 as an example to introduce. The X-axis distance is the parameter reserve amount of Model1 / the reference parameter reserve amount, that is, 8000/6000=1.33, and the Y-axis distance is (1-85%)/7%=2.14. The total distance is the square of the X-axis distance plus the square of the Y-axis distance, followed by the square root, that is Similarly, the total distance of Model2 to Model6 can be obtained as shown in Table 8. Among them, the total distance of Model3 is the smallest, that is, it is the closest to the theoretical optimal position, so the effect of Model3 is relatively better.
表8某备件在不同库存策略模型的评价分数Table 8 Evaluation scores of a spare part in different inventory strategy models
明确了备件库存预测模型评价方法,可以将其转化为适应度函数,适应度函数的值越小,代表对应的库存模型越优。在实际应用中,增加年均采购次数,库存保障修正系数,采购频次修正系数,可以根据不同核电厂的现状和管理要求进行设置,提升了该方法的适用范围。The evaluation method of spare parts inventory prediction model is clarified, which can be transformed into a fitness function. The smaller the value of the fitness function, the better the corresponding inventory model. In practical applications, increasing the average annual purchase times, inventory guarantee correction factor, and purchase frequency correction factor can be set according to the status quo and management requirements of different nuclear power plants, which improves the scope of application of this method.
适应度函数的结构如下,其输入包含:平均有货率、平均库存金额、基准库存金额,年均采购次数,库存保障修正系数,采购频次修正系数;其输出包含:综合分数(总相对距离)。其中平均有货率、平均库存金额和年均采购次数为在该设定库存参数下,通过库存预测平台计算该备件在未来的平均有货率、平均库存金额以及年均采购次数。基准库存金额为库存参数设置为ZB+EX(仅设置最小库存),最小库存值为该备件在采购周期内平均领用量,由此通过库存预测平台计算该备件在未来平均库存金额,该值作为该备件的基准库存金额。库存保障修正系数,取值为0~1之间,若为趋向0则控制库存优先(库存金额低),若趋向于1则备件保障优先(保障率高)。采购次数修正系数,取值为0~1之间,若趋向0则严控年均采购发单次数(库存金额可能高),若趋向于1则采购发单次数约束越弱(库存金额可能低)。The structure of the fitness function is as follows. Its input includes: average availability rate, average inventory amount, benchmark inventory amount, average annual purchase times, inventory guarantee correction coefficient, and purchase frequency correction coefficient; its output includes: comprehensive score (total relative distance) . Among them, the average availability rate, average inventory amount, and average annual purchase times are calculated through the inventory forecast platform under the set inventory parameters. The base inventory amount is that the inventory parameter is set to ZB+EX (only the minimum inventory is set), and the minimum inventory value is the average consumption of the spare part in the procurement cycle, so the average inventory amount of the spare part in the future is calculated through the inventory forecast platform, and this value is used as The base inventory amount for this spare part. Inventory guarantee correction coefficient, the value is between 0 and 1. If it tends to 0, the control inventory will be prioritized (the inventory amount is low), and if it tends to 1, the spare parts guarantee will be prioritized (the guarantee rate is high). Purchase times correction coefficient, the value is between 0 and 1. If it tends to 0, the annual average number of purchase orders will be strictly controlled (the inventory amount may be high). If it tends to 1, the constraint on the number of purchase orders will be weaker (the inventory amount may be low ).
通过建立备件库存预测模型、适应度评价模型后,可以通过相关优化算法计算备件的最优库存参数,备件库存预测模型通过读取备件库存参数,进行运算,输出平均库存金额、平均有货率、年均采购次数,并将其传递给适应度评价模型,通过适应度函数算法,计算库存参数评价分数,并将其传达给优化算法模型库中的优化算法模型,由此计算新的库存参数,并传递给备件库存预测模型,通过不断迭代运算,计算最优的备件库存参数。以下以优化算法模型库中的穷举法和遗传算法为例,详细介绍其运算的逻辑。After establishing the spare parts inventory prediction model and fitness evaluation model, the optimal inventory parameters of spare parts can be calculated through relevant optimization algorithms. The annual average number of purchases is passed to the fitness evaluation model. Through the fitness function algorithm, the inventory parameter evaluation score is calculated, and it is transmitted to the optimization algorithm model in the optimization algorithm model library, thereby calculating the new inventory parameters. And pass it to the spare parts inventory prediction model, and calculate the optimal spare parts inventory parameters through continuous iterative operations. The following takes the exhaustive method and genetic algorithm in the optimization algorithm model library as examples to introduce the logic of its operation in detail.
基于穷举法的备件库存参数优化方法Parameter optimization method of spare parts inventory based on exhaustive method
库存参数通常是设置最小库存、最大库存(固定批量),因此通过设置不同的最小库存值、最大库存值、固定批量值,通过一系列组合,就能够构建一系列潜在最优的库存参数集合。例如某备件的采购周期内领用量为x个,按照经验,备件库存参数中最小库存ZB的取值范围为0.1x~3x,最大库存HB的取值范围为0.5x~3x(仅为采购批量,最大库存值为最小库存+采购批量),固定批量FX的取值范围为0.5~3x,由此可计算程序的计算数量为18x2+3x,当x为5时,运算次数为495次;当x为50时,运算次数为45150;当x为100时,运算次数为180300。由此可见,若要针对所有潜在参数都进行穷举法的话,随着领用量的增加,运算次数按照平方关系急剧增长,故需优化寻在最优解的穷举法。根据领用量值,若领用量较大,则每个潜在值得间隔越大;若领用量较小,则每个潜在值得间隔越小;根据经验,最小库存的最优值一般在采购周期的平均领用量附近,采购批量的最优值一般在年均领用量附近,因此在潜在最优值附近,可以增加搜寻密度,减少间隔。当年均领用数量k小于7个时,再订货点的基准间隔数量为1,在1~5k之间进行穷举求解;当年均领用数量k在7~15之间时,再订货点的基准间隔数量为2,分为三段,第一段在1~k之间,间隔为1,第二段在k~2k之间,间隔为2,第三段在2k~2.7k,间隔为3;当年均领用数量k在15~30之间,再订货点的基准间隔数量为3,分为四段,第一段在1~k/6之间,间隔为3,第二段在k/6~2k/3之间,间隔为2,第三段为2k/3~5k/3时,间隔为3,第四段在5k/3~2.4k,间隔为4;当年均领用数量k在30~101之间,再订货点的基准间隔数量为steps=4+k/20,分为四段,第一段在1~0.5*k/(1.2*steps),间隔为1.2*steps,第二段0.5*k/(1.2*steps)~0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)),间隔为0.6*steps,第三段在0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps))~0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)+k/(1.2*steps)),间隔为1.2*steps,第四段在0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)+k/(1.2*steps))~0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)+k/(1.2*steps)+1.5*k/(steps+1),间隔为2*steps;当年均领用数量k>101时,再订货点的基准间隔数量为steps=4*k/40,分为三段,第一段在1~0.5*k/steps,间隔为steps,第二段在0.5*k/steps~2.5*k/steps,间隔为0.4*steps,第三段在2.5*k/steps~40,间隔为2*steps。可参照再订货点的方法,分解最大库存和固定批量的潜在最优值。Inventory parameters are usually set to minimum inventory and maximum inventory (fixed batch). Therefore, by setting different minimum inventory values, maximum inventory values, and fixed batch values, a series of potentially optimal inventory parameter sets can be constructed through a series of combinations. For example, in the procurement cycle of a certain spare part, the number of purchases is x. According to experience, the value range of the minimum inventory ZB in the spare parts inventory parameter is 0.1x ~ 3x, and the value range of the maximum inventory HB is 0.5x ~ 3x (only for purchase batches). , the maximum inventory value is the minimum inventory + purchase batch), the value range of the fixed batch FX is 0.5 ~ 3x, the calculation quantity of the calculation program is 18x2 +3x, when x is 5, the number of operations is 495; When x is 50, the number of operations is 45150; when x is 100, the number of operations is 180300. It can be seen that if the exhaustive method is to be performed for all potential parameters, the number of operations increases sharply according to the square relationship with the increase of the amount of consumption, so it is necessary to optimize the exhaustive method to find the optimal solution. According to the amount of requisition, if the amount of requisition is large, the interval between each potential value is larger; if the amount of requisition is small, the interval between each potential value is smaller; according to experience, the optimal value of the minimum inventory is generally in the purchasing cycle. Near the average requisition, the optimal value of the purchase batch is generally near the average annual requisition. Therefore, in the vicinity of the potential optimal value, the search density can be increased and the interval can be reduced. When the average quantity k received in the current year is less than 7, the base interval quantity of the reorder point is 1, and the exhaustive solution is performed between 1 and 5k; when the average quantity k received in the current year is between 7 and 15, the reorder point The number of reference intervals is 2, which is divided into three sections. The first section is between 1 and k, and the interval is 1. The second section is between k and 2k, and the interval is 2. The third section is between 2k and 2.7k, and the interval is 2. 3; The average quantity k received in the current year is between 15 and 30, and the base interval quantity of the reorder point is 3, which is divided into four sections. The first section is between 1 and k/6, the interval is 3, and the second section is in Between k/6~2k/3, the interval is 2, when the third stage is 2k/3~5k/3, the interval is 3, and the fourth stage is 5k/3~2.4k, the interval is 4; The quantity k is between 30 and 101, and the base interval quantity of the reorder point is steps=4+k/20, which is divided into four stages, the first stage is 1~0.5*k/(1.2*steps), and the interval is 1.2* steps, the second stage is 0.5*k/(1.2*steps)~0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)), the interval is 0.6*steps, and the third stage is 0.5* k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps))~0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)+k/(1.2*steps) ), the interval is 1.2*steps, the fourth segment is 0.5*k/(1.2*steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)+k/(1.2*steps))~0.5*k/(1.2* steps)+(k/2)/(0.5*steps)+k/(1.2*steps)+1.5*k/(steps+1), the interval is 2*steps; The number of benchmark intervals at the order point is steps=4*k/40, which is divided into three stages, the first stage is 1~0.5*k/steps, the interval is steps, and the second stage is 0.5*k/steps~2.5*k/ steps, the interval is 0.4*steps, the third stage is 2.5*k/steps~40, and the interval is 2*steps. The potential optimum for maximum inventory and fixed lot size can be decomposed by referring to the reorder point method.
通过对不同类型的MRP类型进行组合,利用穷举法计算各类库存参数的综合分数,由此可以寻找到最优库存参数。以某核电厂某备件为例,该备件当前的库存参数为ZB+HB,再订货点为115,最大库存为500,其平均库存金额为241,平均有货率为88.3%,综合分数为4.22。经过计算,其最优库存参数为ZB+FX,再订货点为123,固定批量为116,其平均库存金额为107,有货率为98.3%,综合分数为1.75。By combining different types of MRP types and using the exhaustive method to calculate the comprehensive scores of various inventory parameters, the optimal inventory parameters can be found. Taking a spare part of a nuclear power plant as an example, the current inventory parameter of the spare part is ZB+HB, the reorder point is 115, the maximum inventory is 500, the average inventory amount is 241, the average availability rate is 88.3%, and the comprehensive score is 4.22 . After calculation, the optimal inventory parameter is ZB+FX, the reorder point is 123, the fixed batch is 116, the average inventory amount is 107, the availability rate is 98.3%, and the comprehensive score is 1.75.
基于改进遗传算法的备件库存参数优化方法Spare parts inventory parameter optimization method based on improved genetic algorithm
遗传算法是基于自然选择规律的全局概率搜索算法,可以用于计算非线性优化问题。遗传算法的实现过程主要包括初始化群体、数值转换、计算适应度、复制、交换、变异等操作。由于当前核电备件的库存策略主要包含:ZB+EX(仅设置最小库存)、ZB+HB(设置最大、最小库存)、ZB+FX(设置最小库存,触发采购时为固定采购数量)、PD+EX(不设置最大、最小库存)。由于PD+EX是通过预留触发采购,不主动储备库存,无库存参数需要设置,故在库存参数优化中暂不考虑该类情形。使用遗传算法计算备件的最优参数时,会分别对ZB+EX、ZB+HB、ZB+FX三种情形进行计算,再对比三种情形下的最优参数对应的综合分数,从而选择综合分数最优那个情形下的库存参数。Genetic algorithm is a global probabilistic search algorithm based on the law of natural selection, which can be used to calculate nonlinear optimization problems. The implementation process of genetic algorithm mainly includes operations such as initializing the population, numerical transformation, calculating fitness, copying, swapping, and mutating. Because the current inventory strategy of nuclear power spare parts mainly includes: ZB+EX (only minimum inventory is set), ZB+HB (maximum and minimum inventory is set), ZB+FX (minimum inventory is set, and the purchase is triggered when the purchase is a fixed quantity), PD+ EX (do not set the maximum and minimum inventory). Since PD+EX triggers procurement through reservation, it does not actively reserve inventory, and no inventory parameters need to be set, so this kind of situation is not considered in the optimization of inventory parameters. When using the genetic algorithm to calculate the optimal parameters of spare parts, the three cases of ZB+EX, ZB+HB, and ZB+FX will be calculated respectively, and then the comprehensive scores corresponding to the optimal parameters in the three cases will be compared, so as to select the comprehensive score Inventory parameters in the optimal case.
以下进一步介绍遗传算法的计算逻辑。The calculation logic of the genetic algorithm is further introduced below.
S1、为初始化种群,种群数量可设置为40,维度为1维或2维(ZB+EX情形下为1维,ZB+HB、ZB+FX情形下为2维),个体初始化位置在标准再订货点、标准最大库存、标准固定批量的±50%之间进行随机赋值,其中标准再订货点为采购周期内的领用数量,标准最大库存为采购周期内的领用量+年均领用量,标准固定批量为年均领用量,初始化时限制个体位置的最大值为备件年均领用数量的10倍~15倍,即个体是在1~最大值之间计算最优值。S1. In order to initialize the population, the population number can be set to 40, and the dimension is 1-dimensional or 2-dimensional (1-dimensional in the case of ZB+EX, 2-dimensional in the case of ZB+HB, ZB+FX), and the individual initialization position is in the standard Random assignments are made between the order point, standard maximum stock, and standard fixed batch ±50%, where the standard reorder point is the quantity received in the procurement cycle, and the standard maximum stock is the quantity received in the procurement cycle + the average annual consumption, The standard fixed batch is the average annual consumption, and the maximum limit of the individual position during initialization is 10 times to 15 times the average annual consumption of spare parts, that is, the optimal value of the individual is calculated between 1 and the maximum value.
S2、为数值转换,建立两个数组,其中一个数组存放原始十进制位置数据,令一个数组存在归一化后的二进制位置数据。原始十进制位置数据用于计算库存参数的适应度值,二进制位置数据用于参与遗传算法的负值、交叉、变异。原始十进制位置转换为二进制位置的方法如下:其将十进制的位置数据进行归一化,转换为0~1之间,可利用公式其中x为样本归一化后十进制位置,X为样本归一化前十进制位置,Xmin为所有样本位置中的最小值,可设置为1,Xmax为所有样本位置红的最大值,可设置为备件15倍年均领用数量。将0~1的十进制数值转换为二进制数值。二进制位置转换为原始十进制位置的方法如下:将二进制数值转换为0~1的十进制,若该值小于0,则将其转化为0,若该值大于1,则将其转换为1(在遗传算法交叉、变异的过程中,可能会导致出现大于1或小于0的异常情况)。将0~1的十进制位置转换为原始十进制位置,可领用公式X=(Xmax-Xmin)*x+Xmin。S2. For numerical conversion, two arrays are established, one of which stores the original decimal position data, and one array contains the normalized binary position data. The raw decimal position data is used to calculate the fitness value of the inventory parameter, and the binary position data is used to participate in the negative value, crossover, and mutation of the genetic algorithm. The method of converting the original decimal position to the binary position is as follows: it normalizes the decimal position data and converts it into a range between 0 and 1, and can use the formula where x is the decimal position after sample normalization, X is the decimal position before sample normalization, Xmin is the minimum value of all sample positions, which can be set to 1, and Xmax is the maximum value of all sample positions, which can be set It is 15 times the average annual quantity of spare parts. Converts a decimal value from 0 to 1 to a binary value. The method of converting the binary position to the original decimal position is as follows: convert the binary value to decimal from 0 to 1, if the value is less than 0, convert it to 0, if the value is greater than 1, convert it to 1 (in genetics In the process of algorithm crossover and mutation, it may cause abnormal situations greater than 1 or less than 0). To convert the decimal position from 0 to 1 to the original decimal position, the formula X=(Xmax -Xmin )*x+Xmin can be obtained.
S3、为计算适应度值,遗传算法将每个样本的位置(备件库存参数)传递给备件库存预测模型,由库存预测模型以及适应度评价模型,计算备件库存参数评价分数,并将该适应度值传递给遗传算法。S3. In order to calculate the fitness value, the genetic algorithm transmits the position of each sample (spare parts inventory parameter) to the spare parts inventory prediction model, and the inventory prediction model and the fitness evaluation model calculate the evaluation score of the spare parts inventory parameter, and use the fitness The value is passed to the genetic algorithm.
S4、为样本的复制,即根据每个样本的适应度值(备件库存参数评价分数),针对适应度值优的样本更有可能传递给下一代。可选用“轮盘算法”,即根据适应度值进行排序,适应度值优的样本复制概率较高,适应度值差的样本复制概率较低。S4 is the replication of the samples, that is, according to the fitness value of each sample (spare parts inventory parameter evaluation score), the samples with excellent fitness value are more likely to be passed on to the next generation. The "roulette algorithm" can be selected, that is, sorting is performed according to the fitness value. The samples with excellent fitness values have a higher replication probability, and the samples with poor fitness values have a lower replication probability.
S5、为样本的交叉,首先设定优秀父代的保留比例,即筛选出优秀的父代样本,其不进行交叉,直接保留到子代,该比例可设置为0.05。针对不是优秀父代的样本,进行交叉运算,即某样本随机与其他样本进行交叉运算,可选用两种方法进行交叉运算:1)选择两个样本,随机选择一个样本中的一半节点,将另一个样本对应节点的数值传递给该样本,进行交叉运算;2)随机选择一个样本中的某个节点,将另一个样本中对应节点后面的数值传递给该样本,进行交叉运算。S5. For the crossover of the samples, first set the retention ratio of the excellent parents, that is, filter out the excellent parent samples, which will not be crossed and directly retained to the offspring, and the ratio can be set to 0.05. For samples that are not excellent parents, perform crossover operation, that is, a sample is randomly crossed with other samples, and two methods can be used for crossover operation: 1) Select two samples, randomly select half of the nodes in one sample, and place the other The value of a node corresponding to a sample is passed to the sample for cross operation; 2) A node in one sample is randomly selected, and the value behind the corresponding node in another sample is passed to the sample for cross operation.
S6、为样本的变异,即每个样本中的每个节点,有一定概率发生变异,由0变为1或由1变为0,变异的概率可选为0.005。S6, is the variation of the sample, that is, each node in each sample has a certain probability of variation, from 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0, and the probability of variation can be selected as 0.005.
S7、为新增随机因子,可以有效防止算法陷入局部极值。随机挑选四个样本,对其进行重新赋值,其中第一个样本的位置赋值为随机数;第二个和第三个样本的位置在最优位置的±50%之间随机进行赋值;第四个样本的位置直接赋值为最优位置,由此可以保障每次迭代后的最优适应度值不高于迭代前的最优适应度值。S7. In order to add a random factor, it can effectively prevent the algorithm from falling into a local extreme value. Four samples are randomly selected and reassigned, where the position of the first sample is assigned a random number; the positions of the second and third samples are randomly assigned between ±50% of the optimal position; the fourth The position of each sample is directly assigned as the optimal position, which can ensure that the optimal fitness value after each iteration is not higher than the optimal fitness value before the iteration.
S8、为输出适应度值最优的个体。当迭代次数达到设定阈值后,直接输出适应度值最优的个体,即备件的库存参数。S8, is the individual with the best output fitness value. When the number of iterations reaches the set threshold, the individual with the best fitness value is directly output, that is, the inventory parameters of spare parts.
基于需求概率模型的备件库存参数优化方法Spare parts inventory parameter optimization method based on demand probability model
针对部分核电备件,由于备件的历史领用数量较少,未来的需求量较少,难以用备件库存模型对备件的库存进行预测,因此可采用确定需求概率函数的方法,通过分析备件的历史领用特征,假定起服从某种概率分布(目前选用的为二项分布和泊松分布),通过设定备件目标有货率,由此计算备件的库存参数。首先分析备件的历史领用数量,若属于高周转备件(三年内有两年及以上发生过领用或者五年内有三年及以上发生过领用),则采用基于备件库存预测的库存参数优化模型;若属于非高周转备件,则采用基于备件需求概率的库存参数优化模型。For some nuclear power spare parts, it is difficult to use the spare parts inventory model to predict the inventory of spare parts due to the small number of spare parts received in the past and the future demand. Using the feature, it is assumed that it obeys a certain probability distribution (the binomial distribution and Poisson distribution are currently selected), and the inventory parameters of spare parts are calculated by setting the target availability rate of spare parts. First, analyze the historically used quantity of spare parts. If it is a high-turnover spare part (two or more years in three years or three or more years in five years), an inventory parameter optimization model based on spare parts inventory forecast is used. ; If it belongs to non-high-turnover spare parts, the inventory parameter optimization model based on the probability of spare parts demand is used.
假设某批备件的需求特征符合某种概率密度,需要使用样本数据进行参数估计和假设检验,通过建立分布函数库,并通过K-S检验(Kolmogorov-Smirnvo test)等方法判断备件领用是否符合相应概率分布,从而选择合适的备件需求函数模型库。分布函数库中可设置泊松分布、正态分布、二项分布、Gamma、Lognorm、Weibull等分布函数,以下以泊松分布函数为例,进一步介绍备件库存参数优化方法。Assuming that the demand characteristics of a certain batch of spare parts conform to a certain probability density, it is necessary to use sample data for parameter estimation and hypothesis testing. By establishing a distribution function library, and by K-S test (Kolmogorov-Smirnvo test) and other methods to determine whether the spare parts are in compliance with the corresponding probability distribution, so as to select the appropriate spare parts demand function model library. Poisson distribution, normal distribution, binomial distribution, Gamma, Lognorm, Weibull and other distribution functions can be set in the distribution function library. The following takes the Poisson distribution function as an example to further introduce the optimization method of spare parts inventory parameters.
泊松分布是指在某段时间内,事件发生的具体概率,其是一种统计与概率学中常用到的离散几率分布。假设现场设备有n台,任意一台设备发生故障的概率为a,则在一定的时间段内,平均故障数量为λ=an,其发生m台设备故障的概率为假定设定的储备数为s,备件的采购周期为t天,则泊松分布的缺货概率为:有货率为:故只需要设置备件的有货率以及提取备件的采购周期、采购周期内的领用数量,就可以计算需储备的库存数量,由此设置备件的库存参数。实际应用中,在泊松分布模型中,若备件按照CCM/非CCM两级划分,可将CCM备件的有货率设置为99.5%,非CCM备件的有货率设置为90%。若按照备件分级H/M/L三级划分,可以考虑将H级的有货率设置为99%,M级的有货率设置为95%,L级的有货率设置为90%。例如某备件为非CCM备件,采购周期为1年,近五年的领用数量分别为0、2、0、0、2,经过K-S检验,领用数据符合泊松分布(K-S检验的显著水平设置为0.05),针对非CCM备件,有货率的设置值为90%,经过计算,在储备2个库存的情况下,满足90%的有货率要求,故该备件的库存参数为ZB+EX,再订货点为2。Poisson distribution refers to the specific probability of an event occurring within a certain period of time, which is a discrete probability distribution commonly used in statistics and probability. Assuming that there are n devices in the field, and the probability of failure of any device is a, then in a certain period of time, the average number of failures is λ=an, and the probability of failure of m devices is Assuming that the set number of reserves is s, and the procurement period of spare parts is t days, the probability of shortage of stock in Poisson distribution is: Availability rate: Therefore, it is only necessary to set the availability rate of spare parts, the procurement cycle for extracting spare parts, and the quantity to be used in the procurement cycle, and then the inventory quantity to be reserved can be calculated, thereby setting the inventory parameters of spare parts. In practical applications, in the Poisson distribution model, if the spare parts are divided into two levels of CCM/non-CCM, the availability rate of CCM spare parts can be set to 99.5%, and the availability rate of non-CCM spare parts can be set to 90%. If the spare parts are divided into three levels, H/M/L, you can consider setting the availability rate of H level to 99%, M level to 95%, and L level to 90%. For example, a spare part is a non-CCM spare part, the procurement cycle is 1 year, and the number of requisitions in the past five years is 0, 2, 0, 0, and 2, respectively. Set to 0.05), for non-CCM spare parts, the set value of the availability rate is 90%. After calculation, when 2 stocks are reserved, the availability rate of 90% can be satisfied, so the stock parameter of this spare part is ZB+ EX, the reorder point is 2.
针对部分非高周转备件,使用其领用数据进行K-S检验,需求函数库中的需求函数均无法通过检验,此时无法使用需求概率模型计算库存参数。针对该类备件,其库存参数可设置为ZB+EX,再订货点为采购周期内的领用数量,并根据备件的重要性,适当增加一定数量的安全库存。For some non-high-turnover spare parts, the K-S test is carried out using their requisition data. None of the demand functions in the demand function library can pass the test. At this time, the demand probability model cannot be used to calculate the inventory parameters. For this type of spare parts, the inventory parameter can be set to ZB+EX, the reorder point is the quantity to be received in the procurement cycle, and a certain amount of safety stock is appropriately increased according to the importance of the spare parts.
应该理解的是,虽然如上的各实施例所涉及的流程图中的各个步骤按照箭头的指示依次显示,但是这些步骤并不是必然按照箭头指示的顺序依次执行。除非本文中有明确的说明,这些步骤的执行并没有严格的顺序限制,这些步骤可以以其它的顺序执行。而且,如上的各实施例所涉及的流程图中的至少一部分步骤可以包括多个步骤或者多个阶段,这些步骤或者阶段并不必然是在同一时刻执行完成,而是可以在不同的时刻执行,这些步骤或者阶段的执行顺序也不必然是依次进行,而是可以与其它步骤或者其它步骤中的步骤或者阶段的至少一部分轮流或者交替地执行。It should be understood that, although the steps in the flowcharts involved in the above embodiments are sequentially displayed according to the arrows, these steps are not necessarily executed in the order indicated by the arrows. Unless explicitly stated herein, the execution of these steps is not strictly limited to the order, and these steps may be performed in other orders. Moreover, at least a part of the steps in the flowcharts involved in the above embodiments may include multiple steps or multiple stages. These steps or stages are not necessarily executed at the same time, but may be executed at different times. The order of execution of these steps or stages is also not necessarily sequential, but may be performed alternately or alternately with other steps or at least a portion of the steps or stages in the other steps.
基于同样的发明构思,本申请实施例还提供了一种用于实现上述所涉及的备件库存预测方法的备件库存预测装置。该装置所提供的解决问题的实现方案与上述方法中所记载的实现方案相似,故下面所提供的一个或多个备件库存预测装置实施例中的具体限定可以参见上文中对于备件库存预测方法的限定,在此不再赘述。Based on the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the present application also provides a spare parts inventory prediction device for implementing the above-mentioned spare parts inventory prediction method. The implementation solution for solving the problem provided by the device is similar to the implementation solution described in the above method, so the specific limitations in the embodiments of one or more spare parts inventory forecasting device provided below can refer to the above for the spare parts inventory prediction method. limitations, which are not repeated here.
另外,如图8所示,本申请还提供一种备件库存预测装置,装置包括:In addition, as shown in FIG. 8 , the present application also provides a spare parts inventory prediction device, which includes:
领用模块200,用于根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;The
预留模块400,用于根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;The
正订模块600,用于获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;The correcting
模型构建模块800,用于根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The
在其中一个实施例中,上述备件库存预测装置还包括:初始分解模块,用于获取初始时刻的初始备件预留量;将初始备件预留量分解到未来领用量,得到备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据;领用模块还用于根据预设维修规范数据、备件历史领用量以及备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据。In one embodiment, the above-mentioned spare parts inventory forecasting device further includes: an initial decomposition module, configured to obtain an initial reserved amount of spare parts at an initial moment; Time-varying data; the requisition module is also used to generate time-varying data of the initial requisition of spare parts according to preset maintenance specification data, historical requisition quantity of spare parts, and time-varying data of initial requisition quantity of spare parts.
在其中一个实施例中,初始分解模块还用于提取初始备件预留量中预留提前周期和预留数量;根据预留提前周期确定分解到不同预留时间点的顺序;根据分解不同预留时间点的顺序以及预留数量,确定分解到未来不同时间点的领用量,得到备件的初始领用量随时间变化数据。In one of the embodiments, the initial decomposition module is further configured to extract the reserved advance period and the reserved quantity in the initial spare parts reservation; determine the sequence of decomposition to different reserved time points according to the reserved advance period; The order of time points and the reserved quantity are determined to determine the amount of demand decomposed to different time points in the future, and the data of the change of the initial amount of spare parts with time can be obtained.
在其中一个实施例中,领用模块还用于获取预设维修规范数据以及相邻预设时间段内备件历史领用量;将相邻预设时间段内备件历史领用量分类为计划性A类备件的领用量、计划性B类备件的领用量以及突发性备件的领用量,A类备件是指运维必定更换的备件,B类备件是指运维选择性更换的备件;根据预设维修规范数据以及计划性A类备件的领用量,生成A类备件需求模型,根据预设维修规范数据以及计划性B类备件的领用量,生成B类备件需求模型,根据预设维修规范数据采用线性拟合的方法生成突发性备件未来领用量;根据A类备件需求模型、B类备件需求模型以及突发性备件未来领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据。In one embodiment, the requisition module is further configured to acquire preset maintenance specification data and the historical requisition amount of spare parts in an adjacent preset time period; classify the historical requisition amount of spare parts in the adjacent preset time period as planned class A The quantity of spare parts, the quantity of planned B-type spare parts, and the quantity of emergency spare parts. Type-A spare parts refer to the spare parts that must be replaced by operation and maintenance, and type-B spare parts refer to the spare parts that are selectively replaced by operation and maintenance; according to the preset The maintenance specification data and the planned quantity of A-type spare parts are used to generate a type-A spare parts demand model. The method of linear fitting is used to generate the future demand of sudden spare parts; according to the demand model of type A spare parts, the demand model of type B spare parts and the future demand of sudden spare parts, the data of the demand of spare parts over time is generated.
在其中一个实施例中,预留模块还用于根据备件历史预留量,获取预留提前期、预留比例以及预留准确率。In one embodiment, the reservation module is further configured to acquire the reservation lead time, the reservation ratio, and the reservation accuracy rate according to the historical reservation quantity of spare parts.
在其中一个实施例中,上述备件库存预测装置还包括:优化模块,用于根据备件库存预测模型获取本期备件库参数;采用预设参数优化方法对本期备件库参数进行参数优化,预设参数优化方法包括穷举法、改进遗传算法或需求概率模型优化法。In one of the embodiments, the above-mentioned spare parts inventory forecasting device further includes: an optimization module, configured to obtain the parameters of the spare parts warehouse in the current period according to the spare parts inventory prediction model; Parameter optimization methods include exhaustive method, improved genetic algorithm or demand probability model optimization method.
在一个实施例中,提供了一种计算机设备,该计算机设备可以是服务器,其内部结构图可以如图9所示。该计算机设备包括通过系统总线连接的处理器、存储器和网络接口。其中,该计算机设备的处理器用于提供计算和控制能力。该计算机设备的存储器包括非易失性存储介质和内存储器。该非易失性存储介质存储有操作系统、计算机程序和数据库。该内存储器为非易失性存储介质中的操作系统和计算机程序的运行提供环境。该计算机设备的数据库用于存储历史备件库存相关数据。该计算机设备的网络接口用于与外部的终端通过网络连接通信。该计算机程序被处理器执行时以实现一种备件库存预测方法。In one embodiment, a computer device is provided, and the computer device may be a server, and its internal structure diagram may be as shown in FIG. 9 . The computer device includes a processor, memory, and a network interface connected by a system bus. Among them, the processor of the computer device is used to provide computing and control capabilities. The memory of the computer device includes non-volatile storage media and internal memory. The nonvolatile storage medium stores an operating system, a computer program, and a database. The internal memory provides an environment for the execution of the operating system and computer programs in the non-volatile storage medium. The computer facility's database is used to store historical spare parts inventory related data. The network interface of the computer device is used to communicate with an external terminal through a network connection. The computer program, when executed by a processor, implements a spare parts inventory forecasting method.
在一个实施例中,提供了一种计算机设备,包括存储器和处理器,存储器中存储有计算机程序,该处理器执行计算机程序时实现以下步骤:In one embodiment, a computer device is provided, including a memory and a processor, a computer program is stored in the memory, and the processor implements the following steps when executing the computer program:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
在一个实施例中,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时实现以下步骤:In one embodiment, a computer-readable storage medium is provided on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the following steps are implemented:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
在一个实施例中,提供了一种计算机程序产品,包括计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时实现以下步骤:In one embodiment, a computer program product is provided, comprising a computer program that, when executed by a processor, implements the following steps:
根据预设维修规范数据以及备件历史领用量,生成备件的领用量随时间变化数据;According to the preset maintenance specification data and the historical demand of spare parts, generate data on the change of the demand of spare parts over time;
根据备件历史预留量,获取备件预留配置参数,并根据备件预留配置参数以及备件的领用量随时间变化数据,生成备件的预留量随时间变化数据;Obtain the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts according to the historical reserved quantity of the spare parts, and generate the data of the reserved quantity of the spare parts over time according to the reserved configuration parameters of the spare parts and the change of the quantity of the spare parts with time;
获取备件新增采购数据以及备件历史验收数据,根据新增采购数据、备件历史验收数据以及备件的预留量随时间变化数据,生成备件的正订量随时间变化数据;Obtain the new purchase data of spare parts and the historical acceptance data of spare parts, and generate the change data of the correct order quantity of spare parts over time according to the newly purchased data, the historical acceptance data of spare parts and the change of spare parts reserved quantity over time;
根据备件的领用量随时间变化数据、备件的预留量随时间变化数据以及备件的正订量随时间变化数据,生成备件库存预测模型。The spare parts inventory forecasting model is generated according to the time-varying data of spare parts demand, the time-varying data of the reserved quantity of spare parts, and the time-varying data of the correct quantity of spare parts.
需要说明的是,本申请所涉及的用户信息(包括但不限于用户设备信息、用户个人信息等)和数据(包括但不限于用于分析的数据、存储的数据、展示的数据等),均为经用户授权或者经过各方充分授权的信息和数据。It should be noted that the user information (including but not limited to user equipment information, user personal information, etc.) and data (including but not limited to data for analysis, stored data, displayed data, etc.) involved in this application are all Information and data authorized by the user or fully authorized by the parties.
以上实施例的各技术特征可以进行任意的组合,为使描述简洁,未对上述实施例中的各个技术特征所有可能的组合都进行描述,然而,只要这些技术特征的组合不存在矛盾,都应当认为是本说明书记载的范围。The technical features of the above embodiments can be combined arbitrarily. In order to make the description simple, all possible combinations of the technical features in the above embodiments are not described. However, as long as there is no contradiction in the combination of these technical features It is considered to be the range described in this specification.
以上实施例仅表达了本申请的几种实施方式,其描述较为具体和详细,但并不能因此而理解为对本申请专利范围的限制。应当指出的是,对于本领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本申请构思的前提下,还可以做出若干变形和改进,这些都属于本申请的保护范围。因此,本申请的保护范围应以所附权利要求为准。The above examples only represent several embodiments of the present application, and the descriptions thereof are relatively specific and detailed, but should not be construed as a limitation on the scope of the patent of the present application. It should be pointed out that for those skilled in the art, without departing from the concept of the present application, several modifications and improvements can be made, which all belong to the protection scope of the present application. Therefore, the scope of protection of the present application should be determined by the appended claims.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111679536.7ACN114331286B (en) | 2021-12-31 | 2021-12-31 | Spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment and medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111679536.7ACN114331286B (en) | 2021-12-31 | 2021-12-31 | Spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment and medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN114331286Atrue CN114331286A (en) | 2022-04-12 |
| CN114331286B CN114331286B (en) | 2025-08-08 |
Family
ID=81023134
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202111679536.7AActiveCN114331286B (en) | 2021-12-31 | 2021-12-31 | Spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment and medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN114331286B (en) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115146858A (en)* | 2022-07-13 | 2022-10-04 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | Nuclear power station spare part warehousing resource value prediction method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN115330294A (en)* | 2022-06-30 | 2022-11-11 | 张家口卷烟厂有限责任公司 | Automatic spare part purchasing system for cigarette enterprise |
| TWI847878B (en)* | 2023-07-31 | 2024-07-01 | 大陸商鼎捷軟件股份有限公司 | Inventory optimization device and inventory optimization method |
| CN118296294A (en)* | 2024-04-22 | 2024-07-05 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | Spare part parameter determination method, device and equipment |
| CN118313720A (en)* | 2024-03-29 | 2024-07-09 | 苏州知码芯信息科技有限公司 | Chip production data management system and method based on data analysis |
| CN118657472A (en)* | 2024-08-19 | 2024-09-17 | 苏州慧工云信息科技有限公司 | Material procurement plan information adjustment method and device |
| WO2024260526A1 (en)* | 2023-06-21 | 2024-12-26 | Maersk A/S | A method for predicting spare part usage and related electronic device |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09147041A (en)* | 1995-11-28 | 1997-06-06 | Hitachi Ltd | Inventory allocation management method |
| US20140082660A1 (en)* | 2012-09-19 | 2014-03-20 | Hulu, LLC | Ad inventory management system |
| CN106059661A (en)* | 2015-12-25 | 2016-10-26 | 国家电网公司 | Time sequence analysis based optical transmission network trend prediction method |
| CN108960741A (en)* | 2018-07-26 | 2018-12-07 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | A kind of nuclear power station group factory Spare Parts Inventory Management System |
| CN109002944A (en)* | 2018-10-10 | 2018-12-14 | 红云红河烟草(集团)有限责任公司 | Method for predicting spare part requirements of rolling and packing workshop |
| CN109117990A (en)* | 2018-07-26 | 2019-01-01 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | A kind of prediction of nuclear power station Parts Inventory and index decomposition device |
| US20200143313A1 (en)* | 2018-11-01 | 2020-05-07 | C3 loT, Inc. | Systems and methods for inventory management and optimization |
| CN111489037A (en)* | 2020-04-14 | 2020-08-04 | 青海绿能数据有限公司 | An optimization method of spare parts storage strategy for new energy wind turbines based on demand forecast |
| CN112132417A (en)* | 2020-09-02 | 2020-12-25 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | Multi-core power plant spare part overall planning and combined storage system |
| CN113793102A (en)* | 2021-09-18 | 2021-12-14 | 中广核风电有限公司 | Inventory management method and device based on platform |
- 2021
- 2021-12-31CNCN202111679536.7Apatent/CN114331286B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH09147041A (en)* | 1995-11-28 | 1997-06-06 | Hitachi Ltd | Inventory allocation management method |
| US20140082660A1 (en)* | 2012-09-19 | 2014-03-20 | Hulu, LLC | Ad inventory management system |
| CN106059661A (en)* | 2015-12-25 | 2016-10-26 | 国家电网公司 | Time sequence analysis based optical transmission network trend prediction method |
| CN108960741A (en)* | 2018-07-26 | 2018-12-07 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | A kind of nuclear power station group factory Spare Parts Inventory Management System |
| CN109117990A (en)* | 2018-07-26 | 2019-01-01 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | A kind of prediction of nuclear power station Parts Inventory and index decomposition device |
| CN109002944A (en)* | 2018-10-10 | 2018-12-14 | 红云红河烟草(集团)有限责任公司 | Method for predicting spare part requirements of rolling and packing workshop |
| US20200143313A1 (en)* | 2018-11-01 | 2020-05-07 | C3 loT, Inc. | Systems and methods for inventory management and optimization |
| CN111489037A (en)* | 2020-04-14 | 2020-08-04 | 青海绿能数据有限公司 | An optimization method of spare parts storage strategy for new energy wind turbines based on demand forecast |
| CN112132417A (en)* | 2020-09-02 | 2020-12-25 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | Multi-core power plant spare part overall planning and combined storage system |
| CN113793102A (en)* | 2021-09-18 | 2021-12-14 | 中广核风电有限公司 | Inventory management method and device based on platform |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 王坤其;谢宏志;邓重庆;刘淑慧;: "核电站高频领用备件采购批量参数设置研究", 设备管理与维修, no. 10, 25 May 2018 (2018-05-25)* |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115330294A (en)* | 2022-06-30 | 2022-11-11 | 张家口卷烟厂有限责任公司 | Automatic spare part purchasing system for cigarette enterprise |
| CN115146858A (en)* | 2022-07-13 | 2022-10-04 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | Nuclear power station spare part warehousing resource value prediction method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| WO2024260526A1 (en)* | 2023-06-21 | 2024-12-26 | Maersk A/S | A method for predicting spare part usage and related electronic device |
| TWI847878B (en)* | 2023-07-31 | 2024-07-01 | 大陸商鼎捷軟件股份有限公司 | Inventory optimization device and inventory optimization method |
| CN118313720A (en)* | 2024-03-29 | 2024-07-09 | 苏州知码芯信息科技有限公司 | Chip production data management system and method based on data analysis |
| CN118313720B (en)* | 2024-03-29 | 2024-11-15 | 苏州知码芯信息科技有限公司 | Chip production data management system and method based on data analysis |
| CN118296294A (en)* | 2024-04-22 | 2024-07-05 | 中广核核电运营有限公司 | Spare part parameter determination method, device and equipment |
| CN118657472A (en)* | 2024-08-19 | 2024-09-17 | 苏州慧工云信息科技有限公司 | Material procurement plan information adjustment method and device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN114331286B (en) | 2025-08-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN114331286A (en) | Spare parts inventory forecasting method, device, computer equipment and medium | |
| Blake et al. | The effects and interactions of data quality and problem complexity on classification | |
| CN106570778B (en) | A kind of method that data integration based on big data is calculated with line loss analyzing | |
| CN108389069A (en) | Top-tier customer recognition methods based on random forest and logistic regression and device | |
| CN108388955A (en) | Customer service strategies formulating method, device based on random forest and logistic regression | |
| CN113256020B (en) | A Cost Prediction Method for Power Supply System Considering Multi-scale Time Series | |
| CN109190902B (en) | Optimal allocation method of water resources considering supply and demand uncertainty based on newsboy model | |
| CN113869602A (en) | Method and system for predicting demand of spare parts of nuclear power plant, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN108364191A (en) | Top-tier customer Optimum Identification Method and device based on random forest and logistic regression | |
| CN110838076B (en) | A monthly cross-provincial renewable energy consumption method and terminal equipment | |
| CN109768540A (en) | Optimization scheduling method for power outages in distribution network based on big data analysis | |
| CN111680452A (en) | Simulation method for precise investment decision-making of power grid engineering based on total factor data mining | |
| CN108805388B (en) | A method and device for determining future annual load time series scenarios | |
| CN115375216A (en) | Method and device for determining safety stock | |
| CN118885912A (en) | An attribution analysis method and system applied to complex indicators | |
| CN116485256B (en) | Dynamic evaluation method for demand unit credibility based on product operation period | |
| CN115587865B (en) | Land price evaluation method, computing equipment and storage medium based on risk mapping | |
| Xiong et al. | Supplier selection model based on D numbers and transformation function | |
| CN116757717A (en) | Evaluation methods, devices, equipment, media and products for the coupled operation of the electricity and carbon market | |
| Abdou et al. | Modelling risk for construction cost estimating and forecasting: a review | |
| CN114037282B (en) | A power consumption labeling system based on power consumption characteristics | |
| Shurda | Basic risk assessment methods | |
| CN117035392A (en) | Enterprise shutdown correction risk assessment method based on multi-subject complex network | |
| Ermoliev et al. | Linking distributed sectorial and regional optimization models under asymmetric information: towards robust food-water-energy-environmental nexus | |
| Wei et al. | Optimization design method for biofuel resilient supply chain considering node disruption impacts in a two-stage stochastic programming framework |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |