CN113713333B - A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation - Google Patents
A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113713333B CN113713333BCN202110984585.5ACN202110984585ACN113713333BCN 113713333 BCN113713333 BCN 113713333BCN 202110984585 ACN202110984585 ACN 202110984585ACN 113713333 BCN113713333 BCN 113713333B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- patient
- neural network
- rehabilitation training
- signal
- power frequency
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63B—APPARATUS FOR PHYSICAL TRAINING, GYMNASTICS, SWIMMING, CLIMBING, OR FENCING; BALL GAMES; TRAINING EQUIPMENT
- A63B23/00—Exercising apparatus specially adapted for particular parts of the body
- A63B23/035—Exercising apparatus specially adapted for particular parts of the body for limbs, i.e. upper or lower limbs, e.g. simultaneously
- A63B23/04—Exercising apparatus specially adapted for particular parts of the body for limbs, i.e. upper or lower limbs, e.g. simultaneously for lower limbs
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/369—Electroencephalography [EEG]
- A61B5/372—Analysis of electroencephalograms
- A61B5/374—Detecting the frequency distribution of signals, e.g. detecting delta, theta, alpha, beta or gamma waves
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/24—Detecting, measuring or recording bioelectric or biomagnetic signals of the body or parts thereof
- A61B5/316—Modalities, i.e. specific diagnostic methods
- A61B5/389—Electromyography [EMG]
- A61B5/397—Analysis of electromyograms
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63B—APPARATUS FOR PHYSICAL TRAINING, GYMNASTICS, SWIMMING, CLIMBING, OR FENCING; BALL GAMES; TRAINING EQUIPMENT
- A63B24/00—Electric or electronic controls for exercising apparatus of preceding groups; Controlling or monitoring of exercises, sportive games, training or athletic performances
- A63B24/0087—Electric or electronic controls for exercising apparatus of groups A63B21/00 - A63B23/00, e.g. controlling load
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A63—SPORTS; GAMES; AMUSEMENTS
- A63B—APPARATUS FOR PHYSICAL TRAINING, GYMNASTICS, SWIMMING, CLIMBING, OR FENCING; BALL GAMES; TRAINING EQUIPMENT
- A63B71/00—Games or sports accessories not covered in groups A63B1/00 - A63B69/00
- A63B71/06—Indicating or scoring devices for games or players, or for other sports activities
- A63B71/0619—Displays, user interfaces and indicating devices, specially adapted for sport equipment, e.g. display mounted on treadmills
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/08—Learning methods
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Psychology (AREA)
- Rehabilitation Tools (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于人体下肢康复技术领域,涉及一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导方法及系统。The invention belongs to the technical field of human lower limb rehabilitation, and relates to a dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation.
背景技术Background technique
随着社会人口老龄化的加剧,以及近年来由于交通事故,运动伤害以及自然灾难等引起的肢体损伤的人数不断上升,导致出现了大量的下肢运动功能障碍患者。传统的下肢康复训练需要多名康复医疗师的参与,成本较高且训练效果由于过于依赖医疗师的经验而难以保证。同时,传统的下肢康复治疗大多是重复性的康复训练,患者容易产生训练疲劳导致训练效果不佳。此外,对于老年人来说,在下肢功能障碍的同时可能还会伴有其他老年疾病,在康复训练过程中还会出现下肢疼痛等问题。With the aging of the social population and the increasing number of limb injuries caused by traffic accidents, sports injuries and natural disasters in recent years, a large number of patients with lower extremity motor dysfunction have appeared. Traditional lower extremity rehabilitation training requires the participation of multiple rehabilitation physicians, and the cost is high and the training effect is difficult to guarantee because it relies too much on the experience of the physicians. At the same time, traditional lower limb rehabilitation therapy is mostly repetitive rehabilitation training, and patients are prone to training fatigue, resulting in poor training effect. In addition, for the elderly, other senile diseases may be accompanied by lower limb dysfunction, and problems such as lower limb pain may also occur during the rehabilitation training process.
下肢康复训练机器人作为一款康复医疗设备,既可以提高训练效率又可以保证训练质量,现已成为下肢康复领域极受重视的一种替代传统康复训练方式的治疗手段。针对下肢功能训练过程中存在的训练乏味,训练疼痛的问题,部分科研团队已将虚拟现实应用到下肢康复训练机器人,用来诱导患者进行康复训练,使患者产生较强烈的康复训练的意愿。但是对于下肢功能障碍患者而言,在训练过程中极有可能会因为疼痛、乏味等各种负面因素导致训练意愿很低,进而导致训练效果不佳。而现有的康复训练系统无法实时地获取到患者自身的状态反馈,不能够及时根据患者的运动状态调整虚拟场景来更好地诱导患者进行康复训练,使得康复训练效果欠佳。As a rehabilitation medical equipment, the lower limb rehabilitation training robot can not only improve the training efficiency but also ensure the training quality. In view of the problems of tedious training and training pain in the process of lower extremity functional training, some scientific research teams have applied virtual reality to lower extremity rehabilitation training robots to induce patients to perform rehabilitation training, so that patients have a strong desire for rehabilitation training. However, for patients with lower extremity dysfunction, it is very likely that during the training process, due to various negative factors such as pain and boredom, the willingness to train is very low, resulting in poor training effect. However, the existing rehabilitation training system cannot obtain the patient's own state feedback in real time, and cannot timely adjust the virtual scene according to the patient's motion state to better induce the patient to perform rehabilitation training, resulting in poor rehabilitation training effect.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于解决现有技术中的问题,提供一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导方法及系统。The purpose of the present invention is to solve the problems in the prior art, and to provide a dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation.
为达到上述目的,本发明采用以下技术方案予以实现:To achieve the above object, the present invention adopts the following technical solutions to realize:
一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导方法,包括以下步骤:A dynamic virtual induction method for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation, comprising the following steps:
设定康复训练的时间和虚拟现实诱导界面;Set the time of rehabilitation training and virtual reality induction interface;
在训练中采集患者的脑电信号和肌电信号;Collect EEG and EMG signals of patients during training;
将采集的数据进行预处理;Preprocessing the collected data;
通过计算得到脑电信号波段的频谱能量和肌电信号的平均功率频率;Obtain the spectral energy of the EEG signal band and the average power frequency of the EMG signal by calculation;
将脑电信号波段实时产生频谱能量和脑电信号的频谱能量阈值进行比较,判断患者的运动意愿;将肌电信号的平均功率频率与肌电信号平均功率频率的阈值进行比较,判断患者的运动能力;基于运动意愿和运动能力,得出运动状态结果;Compare the spectral energy generated by the EEG signal band in real time with the spectral energy threshold of the EEG signal to judge the patient's willingness to exercise; Ability; based on exercise willingness and exercise ability, the exercise state results are obtained;
基于患者运动状态结果,对虚拟诱导场景动态进行实时调整,直至康复训练时间达到预先设定的时间。Based on the results of the patient's motion state, the virtual induction scene is dynamically adjusted in real time until the rehabilitation training time reaches a preset time.
本发明的进一步改进在于:A further improvement of the present invention is:
脑电信号波段包括枕骨和顶骨部位的α波和额叶部位的θ波;所述肌电信号包括与下肢行走动作相关的股外侧肌、股直肌、股二头肌和腓肠肌部位的肌电信号。The EEG signal band includes the alpha wave of the occipital bone and the parietal bone and the theta wave of the frontal lobe; the EMG signal includes the EMG of the vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, biceps femoris and gastrocnemius muscle related to the walking action of the lower limbs Signal.
所述α波段和θ波段产生的频谱能量的计算方法为:The calculation method of the spectral energy generated by the α-band and theta-band is:
所述α波段和θ波段的脑电信号频谱能量阈值分别用Tα和Tθ表示,所述脑电信号频谱能量阈值表示患者进入精神疲劳的临界值,脑电信号频谱能量阈值的建立方法如下:The EEG spectral energy thresholds of the α-band and θ-band are represented by Tα and Tθ respectively, the EEG spectral energy threshold represents the critical value of the patient entering mental fatigue, and the establishment method of the EEG spectral energy threshold is as follows :
将患者的频普能量Ex作为神经网络的输入,将患者的状态作为神经网络的输出来训练神经网络,得到患者脑电信号频谱能量Ex和患者状态之间的映射关系,表现为α波和θ波的阈值Tα和Tθ;The patient's frequency spectrum energy Exis used as the input of the neural network, and the patient's state is used as the output of the neural network to train the neural network, and the mapping relationship between the patient's EEG spectrum energy Ex and the patient's stateis obtained, which is expressed as an alpha wave and the theta wave thresholds Tα and Tθ ;
在运动过程中,当α波频谱能量Eα大于Tα或者θ波频谱能量Eθ大于Tθ时,判定患者出现了精神疲劳。During exercise, when the spectral energy Eα of the α wave is greater than Tα or the spectral energy Eθ of the theta wave is greater than Tθ , it is determined that the patient has mental fatigue.
所述肌电信号的平均功率频率的计算方法为:The calculation method of the average power frequency of the EMG signal is:
所述肌电信号平均功率频率的阈值用TEMG表示,所述肌电信号平均功率频率阈值表示患者进入肌肉疲劳状态的临界值,肌电信号平均功率频率阈值的建立方法如下:The threshold value of the average power frequency of the EMG signal is represented by TEMG, and the average power frequency threshold value of theEMG signal represents the critical value of the patient entering the muscle fatigue state. The establishment method of the average power frequency threshold value of the EMG signal is as follows:
将患者肌电信号的平均功率频率作为神经网络的输入,将患者的状态作为神经网络的输出来训练神经网络,得到患者肌电信号平均功率频率和患者状态之间的映射关系,具体表现为阈值TEMG;The average power frequency of the patient's EMG signal is used as the input of the neural network, and the state of the patient is used as the output of the neural network to train the neural network, and the mapping relationship between the average power frequency of the patient's EMG signal and the patient's state is obtained.TEMG ;
在运动过程中,当肌电信号的平均功率频率小于TEMG时,即MPF<TEMG,判定患者出现了肌肉疲劳。During exercise, when the average power frequency of theEMG signal is less than TEMG, ie MPF<T EMG, it is determined that the patient has muscle fatigue.
所述神经网络为RBF神经网络,所述RBF神经网络是由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成的一种三层神经网络,通过确定RBF神经网络的隐含层空间能够将输入矢量直接映射到隐空间,确定RBF神经网络的中心点从而确定输入输出的映射关系,RBF神经网络的激活函数表示为:The neural network is an RBF neural network, and the RBF neural network is a three-layer neural network composed of an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer, and the input vector can be directly mapped to the hidden layer space of the RBF neural network by determining the hidden layer space. In the latent space, the center point of the RBF neural network is determined to determine the mapping relationship between the input and output. The activation function of the RBF neural network is expressed as:
其中:损失函数where: loss function
所述动态调整的具体方法为:The specific method of the dynamic adjustment is:
当肌电信号的平均功率频率小于TEMG时,对虚拟场景中的环境参数进行调整;When the average power frequency of theEMG signal is less than TEMG, adjust the environmental parameters in the virtual scene;
当α波频谱能量Eα大于Tα或者θ波频谱能量Eθ大于Tθ时,对虚拟场景中的事件参数进行调整。When the alpha wave spectral energy Eα is greater than Tα or the theta wave spectral energy Eθ is greater than Tθ , the event parameters in the virtual scene are adjusted.
一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导系统,包括虚拟现实诱导模块、信号采集模块、预处理模块、人体运动状态识别模块、神经网络模块和动态调整模块;A dynamic virtual induction system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation, comprising a virtual reality induction module, a signal acquisition module, a preprocessing module, a human body motion state recognition module, a neural network module and a dynamic adjustment module;
所述虚拟现实诱导模块用于设定康复训练的时间和虚拟现实诱导界面;The virtual reality induction module is used to set the time of rehabilitation training and the virtual reality induction interface;
所述信号采集模块用于采集患者在康复训练中的脑电信号和肌电信号;The signal acquisition module is used to collect the EEG signal and the EMG signal of the patient during the rehabilitation training;
所述预处理模块用于对采集的数据进行预处理;The preprocessing module is used for preprocessing the collected data;
所述人体运动状态识别模块能够得到脑电信号波段的频谱能量和肌电信号的平均功率频率;The human body motion state identification module can obtain the spectral energy of the EEG signal band and the average power frequency of the EMG signal;
所述神经网络模块用于将脑电信号波段实时产生频谱能量和脑电信号的频谱能量阈值进行比较,判断患者的运动意愿;将肌电信号的平均功率频率与肌电信号平均功率频率的阈值进行比较,判断患者的运动能力;基于运动意愿和运动能力,得出运动状态结果;The neural network module is used to compare the spectral energy generated by the EEG signal band in real time with the spectral energy threshold of the EEG signal to determine the patient's willingness to exercise; the average power frequency of the EMG signal and the threshold of the average power frequency of the EMG signal Compare and judge the patient's exercise ability; based on exercise willingness and exercise ability, get the result of exercise state;
所述动态调整模块能够基于患者运动状态结果,对虚拟诱导场景动态进行实时调整,直至康复训练时间达到预先设定的时间。The dynamic adjustment module can dynamically adjust the virtual induction scene in real time based on the results of the patient's motion state until the rehabilitation training time reaches a preset time.
进一步的,所述信号采集模块包括脑电信号采集单元、肌电信号采集单元和无线传输单元。Further, the signal acquisition module includes an EEG signal acquisition unit, an EMG signal acquisition unit and a wireless transmission unit.
与现有技术相比,本发明具有以下有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following beneficial effects:
本发明公开了一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导方法及系统,将虚拟现实与下肢康复训练结合,借助虚拟现实技术沉浸式体验特点改善传统下肢康复训练中的枯燥乏味,训练疼痛等问题,增强患者进行康复训练的意愿,采集患者自身产生的脑电信号和肌电信号来判断患者运动意愿与运动能力,并根据人体的运动意愿和运动能力强弱实时动态调整虚拟现实中的场景参数与事件,可以诱导患者一直以比较积极的状态投入到下肢康复训练中;以患者的实时状态信息为指导,改善了传统虚拟诱导一成不变的方式,更好地激发患者的康复训练积极性,增强患者的运动意图,极大地改善了下肢康复训练与虚拟现实结合的不足,本发明能够有效弥补下肢康复训练体系的不足,推广价值高。The invention discloses a dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower extremity rehabilitation, which combines virtual reality with lower extremity rehabilitation training, and improves the problems such as dullness and training pain in traditional lower extremity rehabilitation training with the help of the immersive experience feature of virtual reality technology. , enhance the patient's willingness to perform rehabilitation training, collect the EEG and EMG signals generated by the patient to judge the patient's willingness to exercise and exercise ability, and dynamically adjust the scene parameters in virtual reality in real time according to the human body's willingness to exercise and exercise ability. With events, patients can be induced to devote themselves to lower extremity rehabilitation training in a more positive state; guided by the real-time status information of patients, the traditional immutable method of virtual induction can be improved, which can better stimulate the enthusiasm of patients for rehabilitation training and enhance the patient's performance. The motion intention greatly improves the deficiency of the combination of lower limb rehabilitation training and virtual reality, and the present invention can effectively make up for the deficiency of the lower limb rehabilitation training system, and has high promotion value.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚的说明本发明实施例的技术方案,下面将对实施例中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,应当理解,以下附图仅示出了本发明的某些实施例,因此不应被看作是对范围的限定,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他相关的附图。In order to describe the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention more clearly, the following briefly introduces the accompanying drawings that need to be used in the embodiments. It should be understood that the following drawings only show some embodiments of the present invention, and therefore do not It should be regarded as a limitation of the scope, and for those of ordinary skill in the art, other related drawings can also be obtained according to these drawings without any creative effort.
图1是本发明的总体框架图;Fig. 1 is the overall frame diagram of the present invention;
图2是本发明的患者脑肌电信号与运动状态之间映射关系的建立方法图;Fig. 2 is the establishment method diagram of the mapping relationship between the patient's brain electromyogram signal and the motion state of the present invention;
图3是本发明的虚拟场景参数调整方法图;Fig. 3 is the virtual scene parameter adjustment method diagram of the present invention;
图4是本发明的患者训练流程图。Figure 4 is a flow chart of patient training of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。通常在此处附图中描述和示出的本发明实施例的组件可以以各种不同的配置来布置和设计。In order to make the purposes, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments These are some embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. The components of the embodiments of the invention generally described and illustrated in the drawings herein may be arranged and designed in a variety of different configurations.
因此,以下对在附图中提供的本发明的实施例的详细描述并非旨在限制要求保护的本发明的范围,而是仅仅表示本发明的选定实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。Thus, the following detailed description of the embodiments of the invention provided in the accompanying drawings is not intended to limit the scope of the invention as claimed, but is merely representative of selected embodiments of the invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
应注意到:相似的标号和字母在下面的附图中表示类似项,因此,一旦某一项在一个附图中被定义,则在随后的附图中不需要对其进行进一步定义和解释。It should be noted that like numerals and letters refer to like items in the following figures, so once an item is defined in one figure, it does not require further definition and explanation in subsequent figures.
在本发明实施例的描述中,需要说明的是,若出现术语“上”、“下”、“水平”、“内”等指示的方位或位置关系为基于附图所示的方位或位置关系,或者是该发明产品使用时惯常摆放的方位或位置关系,仅是为了便于描述本发明和简化描述,而不是指示或暗示所指的装置或元件必须具有特定的方位、以特定的方位构造和操作,因此不能理解为对本发明的限制。此外,术语“第一”、“第二”等仅用于区分描述,而不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性。In the description of the embodiments of the present invention, it should be noted that if the terms "upper", "lower", "horizontal", "inside", etc. appear, the orientation or positional relationship indicated is based on the orientation or positional relationship shown in the accompanying drawings , or the orientation or positional relationship that the product of the invention is usually placed in use, it is only for the convenience of describing the present invention and simplifying the description, rather than indicating or implying that the device or element referred to must have a specific orientation, be constructed in a specific orientation and operation, and therefore should not be construed as limiting the present invention. Furthermore, the terms "first", "second", etc. are only used to differentiate the description and should not be construed to indicate or imply relative importance.
此外,若出现术语“水平”,并不表示要求部件绝对水平,而是可以稍微倾斜。如“水平”仅仅是指其方向相对“竖直”而言更加水平,并不是表示该结构一定要完全水平,而是可以稍微倾斜。Furthermore, the presence of the term "horizontal" does not imply that the component is required to be absolutely horizontal, but rather may be tilted slightly. For example, "horizontal" only means that its direction is more horizontal than "vertical", it does not mean that the structure must be completely horizontal, but can be slightly inclined.
在本发明实施例的描述中,还需要说明的是,除非另有明确的规定和限定,若出现术语“设置”、“安装”、“相连”、“连接”应做广义理解,例如,可以是固定连接,也可以是可拆卸连接,或一体地连接;可以是机械连接,也可以是电连接;可以是直接相连,也可以通过中间媒介间接相连,可以是两个元件内部的连通。对于本领域的普通技术人员而言,可以根据具体情况理解上述术语在本发明中的具体含义。In the description of the embodiments of the present invention, it should also be noted that, unless otherwise expressly specified and limited, the terms "set", "installed", "connected" and "connected" should be understood in a broad sense. It can be a fixed connection, a detachable connection, or an integral connection; it can be a mechanical connection or an electrical connection; it can be a direct connection, or an indirect connection through an intermediate medium, and it can be internal communication between two components. For those of ordinary skill in the art, the specific meanings of the above terms in the present invention can be understood according to specific situations.
下面结合附图对本发明做进一步详细描述:Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention is described in further detail:
参见图1,本发明实施例公开了一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导方法,包括以下步骤:Referring to FIG. 1 , an embodiment of the present invention discloses a dynamic virtual induction method for the entire training process of lower limb rehabilitation, including the following steps:
步骤1:根据患者所处的康复阶段,选择相应康复阶段的虚拟诱导场景,确定康复训练时长T,将人体表面肌电电极片帖至与患者下肢运动相关肌肉的表面,具体位置为股外侧肌、股直肌、股二头肌和腓肠肌处,将脑电帽按照10/20系统佩戴至患者头部,患者穿戴下肢康复外骨骼机器人,开启虚拟诱导系统,患者在虚拟环境的诱导下开始训练任务。Step 1: According to the rehabilitation stage of the patient, select the virtual induction scene of the corresponding rehabilitation stage, determine the rehabilitation training duration T, and attach the EMG electrode patch on the surface of the human body to the surface of the muscle related to the movement of the lower limb of the patient, the specific position is the vastus lateralis muscle , rectus femoris, biceps femoris and gastrocnemius muscle, the EEG cap is put on the patient's head according to the 10/20 system, the patient wears the lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton robot, the virtual induction system is turned on, and the patient starts training under the guidance of the virtual environment Task.
步骤2:患者在虚拟现实诱导界面的视觉刺激和听觉刺激下进行康复训练,训练过程中持续采集患者脑肌电信号,并对采集到的脑肌电信号进行预处理,去除信号中的噪声和伪迹。Step 2: The patient performs rehabilitation training under the visual stimulation and auditory stimulation of the virtual reality induction interface. During the training process, the patient's EMG signal is continuously collected, and the collected EEG signal is preprocessed to remove noise and noise in the signal. Artifacts.
步骤3:处理后通过人体运动状态识别模型计算患者训练过程中α波和θ波频谱能量Eα,Eθ和肌电信号的平均功率频率MPF,计算公式如下:Step 3: After processing, calculate the α-wave and theta-wave spectral energy Eα , Eθ and the average power frequency MPF of the electromyographic signal during the patient training process through the human body motion state recognition model. The calculation formula is as follows:
其中,脑电信号包括枕骨和顶骨部位的α波以及额叶部位的θ波,它们都是跟人体精神疲劳密切相关的脑电波;当一个人疲劳时,枕骨和顶骨部位的α波以及额叶部位的θ波的活性会增加,频谱能量增加;所述肌电信号包括与下肢行走动作相关的股外侧肌、股直肌、股二头肌和腓肠肌部位的肌电信号;而且在患者产生肌肉疲劳期间,肌电信号的平均功率频率(MPF)会下降。Among them, the EEG signals include alpha waves in the occipital and parietal bones and theta waves in the frontal lobe, which are brain waves closely related to human mental fatigue; when a person is fatigued, the alpha waves in the occipital and parietal bones and the frontal lobe The activity of the theta waves at the site will increase, and the spectral energy will increase; the EMG signals include the EMG signals of the vastus lateralis, rectus femoris, biceps femoris, and gastrocnemius muscles associated with lower extremity walking; During fatigue, the mean power frequency (MPF) of EMG signals decreases.
步骤4:将第步骤4种计算得到的患者实时脑电信号频谱能量特征Eα,Eθ与阈值Tα,Tθ分别进行比较,若Eα>Tα或Eθ>Tθ,则判定患者出现了精神疲劳,否则,判定患者没有出现精神疲劳;Step 4: Compare the spectral energy characteristics Eα , Eθ of the patient’s real-time EEG signal calculated in the fourth step with the thresholds Tα , Tθ respectively, if Eα >Tα or Eθ >Tθ , then determine The patient has mental fatigue, otherwise, it is determined that the patient does not have mental fatigue;
将第步骤4种计算得到的患者实时肌电信号平均功率频率特征MPF与阈值TEMG分别进行比较,若MPF<TEMG,则判定患者出现了肌肉疲劳,否则,判定患者没有出现肌肉疲劳。The average power frequency characteristic MPF of the patient's real-time EMG signal calculated in the fourth step is compared with the threshold TEMG . If MPF < TEMG , it is determined that the patient has muscle fatigue; otherwise, it is determined that the patient has no muscle fatigue.
步骤5:系统依照当前患者的运动意愿和运动能力的强弱实时动态地调整虚拟诱导场景的相关参数,在更新后的虚拟诱导场景下继续诱导患者进行下肢康复训练运动。Step 5: The system dynamically adjusts the relevant parameters of the virtual induction scene in real time according to the current patient's willingness to exercise and the strength of the exercise ability, and continues to induce the patient to perform lower limb rehabilitation training in the updated virtual induction scene.
步骤6:循环步骤2-6,直至患者的康复训练时间达到预先设定的时间长度T,完成康复训练任务。Step 6: Repeat steps 2-6 until the patient's rehabilitation training time reaches the preset time length T, and the rehabilitation training task is completed.
参见图2,脑肌电信号与患者运动意愿和运动能力映射关系建立方法如下:Referring to Figure 2, the method for establishing the mapping relationship between the EMG signal and the patient's willingness to exercise and exercise ability is as follows:
分别采集患者在正常状态下、精神疲劳状态下和肌肉疲劳状态下的脑电数据和下肢表面肌电数据;对采集到的脑肌电信号进行预处理,去除信号中的噪声和伪迹。The EEG data and lower extremity surface EMG data of patients in normal state, mental fatigue state and muscle fatigue state were collected respectively; the collected EEG signals were preprocessed to remove noise and artifacts in the signals.
将患者不同状态下的脑电信号频谱能量作为神经网络的输入,将患者的正常状态记为0,精神疲劳状态记为1,以患者的状态作为神经网络的输出来训练神经网络,得到患者不同状态下脑电信号频谱能量和患者状态之间的映射关系,具体表现为α波和θ波的阈值Tα、Tθ,该阈值表示患者进入精神疲劳状态的临界值。The spectral energy of the EEG signal of the patient in different states is used as the input of the neural network, the normal state of the patient is recorded as 0, and the mental fatigue state is recorded as 1, and the state of the patient is used as the output of the neural network to train the neural network, and the different patients are obtained. The mapping relationship between the spectral energy of the EEG signal and the state of the patient in the state, specifically expressed as the thresholds Tα and Tθ of the α wave and the theta wave, which represent the critical value of the patient entering the mental fatigue state.
类似的,将患者不同状态下的肌电信号的平均功率频率作为神经网络的输入,将患者的正常状态记为0,肌肉疲劳状态记为1,以患者的状态作为神经网络的输出来训练神经网络,得到患者不同状态下肌电信号平均功率频率和患者状态之间的映射关系,具体表现为阈值TEMG,该阈值表示患者进入肌肉疲劳状态的临界值。Similarly, the average power frequency of the EMG signal of the patient in different states is used as the input of the neural network, the normal state of the patient is recorded as 0, the muscle fatigue state is recorded as 1, and the state of the patient is used as the output of the neural network to train the neural network. The network is used to obtain the mapping relationship between the average power frequency of theEMG signal and the patient state in different states of the patient.
进一步地,所述神经网络为RBF神经网络,该网络是由输入层、隐藏层和输出层组成的一种三层神经网络,通过确定RBF的隐含层空间就可以将输入矢量直接映射到隐空间,确定RBF的中心点从而确定输入输出的映射关系。该网络的激活函数可表示为:Further, the neural network is an RBF neural network, which is a three-layer neural network composed of an input layer, a hidden layer and an output layer, and the input vector can be directly mapped to the hidden layer by determining the hidden layer space of the RBF. Space, determine the center point of the RBF to determine the mapping relationship between input and output. The activation function of this network can be expressed as:
其中损失函数where the loss function
进一步地,further,
当患者在运动过程中的α波频频谱能量Eα大于Tα或者θ波频谱能量Eθ大于Tθ,则判定为患者已经出现了精神疲劳。When the α-wave frequency spectral energy Eα of the patient during exercise is greater than Tα or the theta-wave spectral energy Eθ is greater than Tθ , it is determined that the patient has experienced mental fatigue.
当患者在运动过程中的肌电信号的平均功率频率小于TEMG,则判定为患者已经出现了肌肉疲劳。When the average power frequency of the electromyographic signal of the patient during exercise is less thanTEMG , it is determined that the patient has developed muscle fatigue.
所述运动意愿指患者愿不愿意继续进行下肢康复训练,具体衡量的指标是患者是否出现了精神疲劳;所述运动能力指患者能不能继续进行下肢康复训练,具体衡量的指标是患者是否出现了肌肉疲劳。The exercise willingness refers to whether the patient is willing to continue lower extremity rehabilitation training, and the specific measurement index is whether the patient has mental fatigue; the exercise ability refers to whether the patient can continue the lower limb rehabilitation training, and the specific measurement index is whether the patient has experienced mental fatigue. Muscle fatigue.
参见图3,动态虚拟诱导是通过实时采集患者的脑肌电信号,根据上一步骤确定的患者是否出现了肌肉疲劳和精神疲劳来判断患者的运动能力和运动意愿的强弱。规定患者处于正常状态时运动意愿强且运动能力强,若患者出现了肌肉疲劳规定患者运动能力弱,若患者出现了精神疲劳规定患者运动意愿弱。Referring to Figure 3, dynamic virtual induction is to determine the strength of the patient's exercise ability and exercise willingness by collecting the patient's brain EMG signal in real time, and according to whether the patient has muscle fatigue and mental fatigue determined in the previous step. It is stipulated that the patient is in a normal state with strong willingness to exercise and strong exercise ability. If the patient has muscle fatigue, the patient has weak exercise ability.
通过检测患者运动意愿强弱来决定是否调整以及如何调整事件参数,通过检测患者运动能力强弱来决定是否调整以及如何调整环境参数;当患者运动意愿强时,对事件参数不进行任何调整,当检测到患者运动意愿弱时,采取相关措施对虚拟场景的事件参数进行调整;当检测到患者运动能力强时,对环境参数不进行任何调整,当检测到患者的运动能力弱时,采取相关措施对虚拟场景的环境参数进行调整,其具体调整方式如下:Whether to adjust and how to adjust the event parameters is determined by detecting the patient's willingness to exercise, and whether to adjust and how to adjust the environmental parameters by detecting the patient's exercise ability; when the patient's willingness to exercise is strong, no adjustment is made to the event parameters. When it is detected that the patient's willingness to exercise is weak, relevant measures are taken to adjust the event parameters of the virtual scene; when it is detected that the patient's exercise ability is strong, no adjustment is made to the environmental parameters, and when it is detected that the patient's exercise ability is weak, relevant measures are taken To adjust the environmental parameters of the virtual scene, the specific adjustment methods are as follows:
1)训练过程中,当判断出患者运动能力弱时,患者出现了肌肉疲劳,这时采取措施一,对虚拟场景中的环境参数进行调整,具体措施包括场景中增加鼓励的声音与文字,播放一些舒缓的音乐,减缓虚拟诱导人物的运动速度以鼓励患者跟上虚拟人物的脚步继续康复训练等。1) During the training process, when it is judged that the patient's exercise ability is weak, the patient has muscle fatigue. At this time, measure 1 is taken to adjust the environmental parameters in the virtual scene. The specific measures include adding encouraging sounds and words in the scene, playing Some soothing music, slowing down the movement speed of the virtual induction characters to encourage patients to keep up with the steps of the virtual characters to continue rehabilitation training, etc.
2)训练过程中,当判断出患者运动意愿较弱时,患者出现了精神疲劳,这时采取措施二,对虚拟场景中的事件参数进行调整,具体是通过吸引患者注意力,提高患者兴趣的事件如发布寻宝任务来完成的。2) During the training process, when it is judged that the patient's willingness to exercise is weak, the patient is mentally fatigued. At this time, the second measure is taken to adjust the event parameters in the virtual scene, specifically by attracting the patient's attention and improving the patient's interest. Events such as posting treasure hunt quests are done.
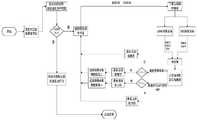
参见图4,医生根据患者的康复情况,设定训练时长T,选择对应不同的虚拟诱导场景和训练任务,对应的虚拟现实场景显示在显示界面上,并在康复训练过程中以图像、声音等形式诱导患者主动参与康复训练,康复训练场景根据人自身的运动意愿与运动能力强弱进行实时动态调整,使患者始终以积极的状态进行康复训练。Referring to Figure 4, the doctor sets the training duration T according to the patient's rehabilitation situation, and selects corresponding virtual induction scenarios and training tasks. The corresponding virtual reality scenarios are displayed on the display interface, and images, sounds, etc. are displayed during the rehabilitation training process. The form induces patients to actively participate in rehabilitation training, and the rehabilitation training scene is dynamically adjusted in real time according to the person's own exercise willingness and exercise ability, so that patients can always carry out rehabilitation training in a positive state.
虚拟诱导训练模块,基于计算机,具有虚拟现实显示界面,根据患者所处康复的不同阶段,会有不同阶段的虚拟诱导环境显示于虚拟现实显示界面上,并在康复训练过程中以图像、声音等形式诱导患者主动参与康复训练,康复训练场景根据人自身的运动意愿与运动能力实时动态调整,使患者始终以积极的状态进行康复训练。The virtual induction training module is based on a computer and has a virtual reality display interface. According to the different stages of the patient's rehabilitation, there will be different stages of virtual induction environments displayed on the virtual reality display interface, and images, sounds, etc. will be displayed during the rehabilitation training process. The form induces patients to actively participate in the rehabilitation training, and the rehabilitation training scene is dynamically adjusted in real time according to the person's own exercise willingness and exercise ability, so that the patient can always carry out the rehabilitation training in a positive state.
患者的康复阶段包括康复中期和康复后期。其中:康复中期指患者刚结束卧床期,能够独自站立,能独立行走但仅仅限于能够独立小幅度挪动行走;康复后期指患者具有稍强的行走能力,能够较大幅度行走,但肌肉耐力,对运动的控制能力以及运动模态等距离恢复还有一定距离。The patient's recovery stage includes the middle and late stages of recovery. Among them: the mid-rehabilitation period means that the patient has just finished the bedridden period, can stand alone, and can walk independently, but only limited to being able to move independently in small steps; in the later stage of rehabilitation, the patient has a slightly stronger walking ability and can walk in a large range, but muscle endurance is not enough. There is still a certain distance between the control ability of the movement and the equidistance recovery of the movement mode.
在康复中期,训练开始前根据患者的康复情况设置一个训练时长,在虚拟现实场景中预设一个虚拟人物,此虚拟人物的运动按照预先设定好的直线路线向前行走,进而诱导患者跟随虚拟人物向前行走;虚拟场景通过语音、图像等视听觉刺激诱导患者向前缓慢行走,期间会有金币奖励获取分数;同时,在患者运动过程中会对其运动意愿和运动能力进行实时的判断,并根据判断结果采取措施一或措施二对虚拟场景的参数进行实时动态调整,达到较好的诱导效果;当患者的运动时长达到预先设定的时长时将训练数据发送给康复治疗师,此次训练结束;In the mid-rehabilitation period, before the training starts, set a training time according to the patient's recovery situation, and preset a virtual character in the virtual reality scene. The character walks forward; the virtual scene induces the patient to walk slowly forward through visual and auditory stimuli such as voice and images, and gold coins will be rewarded to obtain points during the virtual scene; According to the judgment result, take measures 1 or 2 to dynamically adjust the parameters of the virtual scene in real time to achieve a better induction effect; when the patient's exercise duration reaches the preset duration, the training data is sent to the rehabilitation therapist. end of training;
在康复后期,患者可以自由地在虚拟场景中进行直线行走以及转弯等康复训练,患者在虚拟场景中在规定时间内尽可能收集多的金币,时间结束后训练结束。In the later stage of rehabilitation, patients can freely perform rehabilitation training such as walking in a straight line and turning in the virtual scene. The patient collects as many gold coins as possible in the virtual scene within the specified time, and the training ends after the time is up.
本发明实施例还公开了一种下肢康复全训练过程的动态虚拟诱导系统,包括虚拟现实诱导模块、信号采集模块、预处理模块、人体运动状态识别模块、神经网络模块和动态调整模块;The embodiment of the present invention also discloses a dynamic virtual induction system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation, including a virtual reality induction module, a signal acquisition module, a preprocessing module, a human body motion state recognition module, a neural network module and a dynamic adjustment module;
虚拟现实诱导模块用于在视觉刺激和听觉刺激下诱导患者进行训练,为患者康复提供沉浸式的康复训练环境;The virtual reality induction module is used to induce patients to train under visual stimulation and auditory stimulation, providing an immersive rehabilitation training environment for patients to recover;
所述信号采集模块包括脑电信号采集单元,肌电信号采集单元以及无线传输单元,用于患者在康复过程中的脑电信号和肌电信号采集;The signal acquisition module includes an EEG signal acquisition unit, an EMG signal acquisition unit and a wireless transmission unit, which are used for EEG signal and EMG signal acquisition of the patient during the rehabilitation process;
预处理模块用于对虚拟现实诱导模块采集的数据进行去除噪声和伪迹;The preprocessing module is used to remove noise and artifacts from the data collected by the virtual reality induction module;
人体运动状态识别模块用于识别患者训练过程中脑电信号波段的频谱能量特征和肌电信号的平均功率频率;The human body motion state identification module is used to identify the spectral energy characteristics of the EEG signal band and the average power frequency of the EMG signal during the patient training process;
神经网络模块用于判断患者不同状态下脑电信号频谱能量和患者状态之间的映射关系,以及肌电信号平均功率频率和患者状态之间的映射关系。The neural network module is used to judge the mapping relationship between the spectral energy of the EEG signal and the patient state in different states of the patient, as well as the mapping relationship between the average power frequency of the EMG signal and the patient state.
动态调整模块根据患者的运动状态,能够对虚拟诱导场景进行实时调整。The dynamic adjustment module can adjust the virtual induction scene in real time according to the motion state of the patient.
以上仅为本发明的优选实施例而已,并不用于限制本发明,对于本领域的技术人员来说,本发明可以有各种更改和变化。凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所作的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. For those skilled in the art, the present invention may have various modifications and changes. Any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made within the spirit and principle of the present invention shall be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (3)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110984585.5ACN113713333B (en) | 2021-08-25 | 2021-08-25 | A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110984585.5ACN113713333B (en) | 2021-08-25 | 2021-08-25 | A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113713333A CN113713333A (en) | 2021-11-30 |
| CN113713333Btrue CN113713333B (en) | 2022-08-05 |
Family
ID=78678031
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110984585.5AActiveCN113713333B (en) | 2021-08-25 | 2021-08-25 | A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113713333B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114587276A (en)* | 2022-03-04 | 2022-06-07 | 首都医科大学宣武医院 | A nursing system and method for monitoring exercise |
| CN114797007B (en)* | 2022-04-02 | 2023-06-06 | 中国科学技术大学先进技术研究院 | Wearable underwater exoskeleton robot for rehabilitation and method of use thereof |
| CN114694448B (en)* | 2022-06-01 | 2022-08-30 | 深圳市心流科技有限公司 | Concentration training method and device, intelligent terminal and storage medium |
| CN115494955A (en)* | 2022-10-13 | 2022-12-20 | 深圳市智鼎自动化技术有限公司 | Industrial control method based on deep learning and related device |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN203043423U (en)* | 2013-01-22 | 2013-07-10 | 深圳市科瑞康实业有限公司 | Rehabilitation training device based on brain-computer interface |
| CN103431976B (en)* | 2013-07-19 | 2016-05-04 | 燕山大学 | Based on lower limb rehabilitation robot system and the control method thereof of electromyographic signal feedback |
| CN104000586B (en)* | 2014-05-12 | 2017-12-29 | 燕山大学 | Patients with cerebral apoplexy rehabilitation training system and method based on brain myoelectricity and virtual scene |
| US20180021629A1 (en)* | 2016-07-20 | 2018-01-25 | Strive VR, LLC | Interactive and Dynamic Fitness System |
| EP3743172A4 (en)* | 2018-01-23 | 2021-03-31 | AUT Ventures Limited | Uni-lateral sled |
| CN109331453A (en)* | 2018-08-07 | 2019-02-15 | 燕山大学 | Virtual rehabilitation system and training method based on EMG feedback and Kinect interaction |
| CN109363888A (en)* | 2018-11-14 | 2019-02-22 | 华南理工大学 | A kind of immersion rehabilitation training of upper limbs system |
| CN109568083B (en)* | 2018-12-15 | 2024-01-05 | 华南理工大学 | Multi-mode interaction upper limb rehabilitation robot training system |
| CN110711361A (en)* | 2019-10-29 | 2020-01-21 | 东北大学 | A virtual scene-based upper limb rehabilitation training method and system |
| CN111544854B (en)* | 2020-04-30 | 2021-05-25 | 天津大学 | Cerebral apoplexy motor rehabilitation method based on brain myoelectric signal deep learning fusion |
| CN113101612B (en)* | 2021-04-06 | 2023-01-10 | 合肥工业大学 | An immersive upper limb rehabilitation system |
- 2021
- 2021-08-25CNCN202110984585.5Apatent/CN113713333B/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113713333A (en) | 2021-11-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113713333B (en) | A dynamic virtual induction method and system for the whole training process of lower limb rehabilitation | |
| CN113398422B (en) | Rehabilitation training system and method based on motor imagery-brain-computer interface and virtual reality | |
| Masood et al. | Modeling mental stress using a deep learning framework | |
| CN105054927B (en) | The biological quantitative estimation method for degree of being actively engaged in a kind of lower limb rehabilitation system | |
| CN109864750A (en) | Based on the state of mind assessment and regulating system and its working method stimulated through cranium | |
| CN106913341A (en) | A kind of wearable device, system and method for disturbances in patients with Parkinson disease gait training and monitoring and evaluation | |
| CN106621287A (en) | Upper limb rehabilitation training method based on brain-computer interface and virtual reality technology | |
| CN106730238A (en) | The intelligent auxiliary sleeping device and method of a kind of environment self-adaption | |
| KR20120000564A (en) | Adaptive Performance Trainer | |
| CN104524742A (en) | Cerebral palsy child rehabilitation training method based on Kinect sensor | |
| CN107802262B (en) | A device for EEG combined with VR for the intervention and treatment of children with hyperactivity and attention deficit | |
| CN109276807A (en) | Functional electrical stimulation therapy device for lower limbs of hemiplegic patients based on mirror rehabilitation therapy | |
| CN109568897B (en) | Pelvic floor muscle function training device and system | |
| CN107822648A (en) | A kind of non-intrusion type intelligence basin bottom rehabilitation system | |
| CN111773539A (en) | A neurorehabilitation training device based on the combination of real scene and virtual scene | |
| JPWO2015152122A1 (en) | Rehabilitation device, rehabilitation system provided with the same, rehabilitation program and rehabilitation method | |
| CN108471977A (en) | Promote the system and method for the self-control and function motor development of psychology-body-emotional state by way of biofeedback and environmental monitoring | |
| CN108721048A (en) | Rehabilitation training control method, computer readable storage medium and terminal | |
| CN110993056A (en) | Hybrid active rehabilitation method and device based on mirror image neurons and brain-computer interface | |
| CN101574297A (en) | Rehabilitation system for disabled persons based on virtual reality | |
| CN110853753A (en) | A home rehabilitation nursing system for the elderly with cognitive dysfunction | |
| CN114569144B (en) | Knee joint tendon reflex state assessment method based on myoelectricity-inertia sensing | |
| Li et al. | A neuro-fuzzy fatigue-tracking and classification system for wheelchair users | |
| CN113614751A (en) | Electroencephalogram signal identification and extraction | |
| CN118098507B (en) | Adaptive upper limb rehabilitation training control method and system based on multi-source data |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |