CN113583257B - Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof - Google Patents
Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113583257B CN113583257BCN202110825998.9ACN202110825998ACN113583257BCN 113583257 BCN113583257 BCN 113583257BCN 202110825998 ACN202110825998 ACN 202110825998ACN 113583257 BCN113583257 BCN 113583257B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- electroadhesive
- hydrogel
- qca
- pva
- solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000000017hydrogelSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription52
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription7
- 239000004372Polyvinyl alcoholSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription27
- 229920002451polyvinyl alcoholPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription27
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 239000003431cross linking reagentSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription14
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription11
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 229910052757nitrogenInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription3
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthyl acetateChemical compoundCCOC(C)=OXEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription21
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethanolChemical compoundOCOKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000002156mixingMethods0.000claimsdescription8
- JKNCOURZONDCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-(dimethylamino)ethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoateChemical compoundCN(C)CCOC(=O)C(C)=CJKNCOURZONDCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription7
- LWTJEJCZJFZKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-chloro-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenoneChemical compoundOC1=CC=C(C(=O)CCl)C=C1OLWTJEJCZJFZKEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription7
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-NDiethyl etherChemical compoundCCOCCRTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription7
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NAtomic nitrogenChemical compoundN#NIJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000002244precipitateSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000001678irradiating effectEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000001376precipitating effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000claims1
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claims1
- YCIMNLLNPGFGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-NcatecholChemical compoundOC1=CC=CC=C1OYCIMNLLNPGFGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription18
- 239000000499gelSubstances0.000abstractdescription8
- 239000004327boric acidSubstances0.000abstractdescription7
- KGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-Nboric acidChemical compoundOB(O)OKGBXLFKZBHKPEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription6
- 230000002441reversible effectEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 239000000178monomerSubstances0.000abstractdescription4
- -13, 4-dihydroxyphenylChemical group0.000abstractdescription3
- HRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-NAcrylamideChemical compoundNC(=O)C=CHRPVXLWXLXDGHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription3
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-NAmmonium chlorideSubstances[NH4+].[Cl-]NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription3
- 238000004132cross linkingMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 238000007334copolymerization reactionMethods0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000005956quaternization reactionMethods0.000abstract1
- 150000003254radicalsChemical class0.000abstract1
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-MPotassium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[K+]KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description30
- 239000000853adhesiveSubstances0.000description11
- 229910021642ultra pure waterInorganic materials0.000description8
- 239000012498ultrapure waterSubstances0.000description8
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000description5
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000description5
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000description4
- 229920001940conductive polymerPolymers0.000description3
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000description3
- 229920001732LignosulfonatePolymers0.000description2
- ULVXDHIJOKEBMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N[3-(prop-2-enoylamino)phenyl]boronic acidChemical compoundOB(O)C1=CC=CC(NC(=O)C=C)=C1ULVXDHIJOKEBMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 125000005620boronic acid groupChemical group0.000description2
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description2
- 239000002131composite materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 229920001002functional polymerPolymers0.000description2
- 235000019357lignosulphonateNutrition0.000description2
- WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-o-gallateChemical compoundO([C@@H]1CC2=C(O)C=C(C=C2O[C@@H]1C=1C=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C=1)O)C(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1WMBWREPUVVBILR-WIYYLYMNSA-N0.000description1
- WMBWREPUVVBILR-UHFFFAOYSA-NGCGNatural productsC=1C(O)=C(O)C(O)=CC=1C1OC2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2CC1OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1WMBWREPUVVBILR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 244000269722Thea sinensisSpecies0.000description1
- 208000031737Tissue AdhesionsDiseases0.000description1
- 230000001070adhesive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000010382chemical cross-linkingMethods0.000description1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000description1
- 150000002009diolsChemical class0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 125000001495ethyl groupChemical group[H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])*0.000description1
- 235000013305foodNutrition0.000description1
- 235000009569green teaNutrition0.000description1
- 229920001477hydrophilic polymerPolymers0.000description1
- 230000001939inductive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description1
- 239000008204material by functionSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 239000002861polymer materialSubstances0.000description1
- 150000003242quaternary ammonium saltsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000001228spectrumMethods0.000description1
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 238000013268sustained releaseMethods0.000description1
- 239000012730sustained-release formSubstances0.000description1
- 238000001291vacuum dryingMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J3/00—Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances
- C08J3/02—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques
- C08J3/03—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques in aqueous media
- C08J3/075—Macromolecular gels
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C221/00—Preparation of compounds containing amino groups and doubly-bound oxygen atoms bound to the same carbon skeleton
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08F—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING CARBON-TO-CARBON UNSATURATED BONDS
- C08F261/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by polymerising monomers on to polymers of oxygen-containing monomers as defined in group C08F16/00
- C08F261/02—Macromolecular compounds obtained by polymerising monomers on to polymers of oxygen-containing monomers as defined in group C08F16/00 on to polymers of unsaturated alcohols
- C08F261/04—Macromolecular compounds obtained by polymerising monomers on to polymers of oxygen-containing monomers as defined in group C08F16/00 on to polymers of unsaturated alcohols on to polymers of vinyl alcohol
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2351/00—Characterised by the use of graft polymers in which the grafted component is obtained by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds; Derivatives of such polymers
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/38—Boron-containing compounds
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于功能聚合物技术领域,具体涉及一种电致黏附水凝胶及其制备方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of functional polymers, in particular to an electro-adhesion hydrogel and a preparation method thereof.
背景技术Background technique
高分子水凝胶是一种由亲水性聚合物通过物理或化学交联形成的新型功能高分子材料。由于其良好的生物相容性,水凝胶可以被应用到许多领域,如在医学领域用于药物缓释、组织工程支架材料,以及食品、通讯、环境保护等众多领域。传统水凝胶力学性能差,交联作用破坏后无法修复等特点限制了水凝胶的应用。Polymer hydrogel is a new type of functional polymer material formed by physical or chemical cross-linking of hydrophilic polymers. Due to its good biocompatibility, hydrogels can be used in many fields, such as drug sustained release in the medical field, tissue engineering scaffold materials, as well as food, communication, environmental protection and many other fields. Traditional hydrogels have poor mechanical properties and cannot be repaired after cross-linking damage, which limits the application of hydrogels.
现有技术中,酰腙键、亚胺键、硼酸酯键等多种可逆化学键可被引入水凝胶中以获得化学型自修复水凝胶。硼酸酯键存在于某些二醇和硼酸基团之间,硼酸基团在一定条件下能与顺式二醇分子(如聚乙烯醇)反应形成复合物,基于硼酸酯键的动态性质,使水凝胶具有自我修复能力。In the prior art, various reversible chemical bonds, such as acylhydrazone bonds, imine bonds, boronate ester bonds, etc., can be introduced into hydrogels to obtain chemically self-healing hydrogels. The boronic ester bond exists between some diols and boronic acid groups, and the boronic acid group can react with cis-diol molecules (such as polyvinyl alcohol) to form complexes under certain conditions. Based on the dynamic properties of boronic ester bonds, Make the hydrogel have self-healing ability.
邻苯二酚基团可与异物表面形成非共价、共价作用,从而使水凝胶对各种异物表面都具有坚韧耐久的粘附力。最近,Zhao等人[Xiaodan Zhao,Dandan Pei,et al.GreenTea Derivative Driven Smart Hydrogels with Desired Functions for ChronicDiabetic Wound Treatment[J].Advanced Functional Materials,2021.]将含邻苯二酚基团的表没食子儿茶素-3-没食子酸酯(EGCG)与3-丙烯酰胺基苯基硼酸(APBA)络合,与丙烯酰胺共聚得到智能水凝胶敷料。所得水凝胶具有足够的机械性能、自愈合能力和组织粘附性。Gan等人[Donglin Gan,Tao Shuai,et al.Mussel-Inspired Redox-Active andHydrophilic Conductive Polymer Nanoparticles for Adhesive HydrogelBioelectronics[J].Nano-Micro Letters,2020.]将含邻苯二酚的磺化木质素掺杂到不同的导电聚合物中,形成具有亲水性、导电性和氧化还原活性的导电聚合物/磺化木质素纳米粒子。这种复合纳米粒子作为纳米填料与丙烯酰胺复合来制备具有长期粘附性的导电水凝胶。尽管含邻苯二酚基团的水凝胶在皮肤黏附上已经取得了不少的成就,但是实现水凝胶本身对于皮肤的可逆黏附和脱黏附还是一个很大的问题。The catechol group can form non-covalent and covalent interactions with the surface of foreign objects, so that the hydrogel has tough and durable adhesion to the surfaces of various foreign objects. Recently, Zhao et al. [Xiaodan Zhao, Dandan Pei, et al. GreenTea Derivative Driven Smart Hydrogels with Desired Functions for ChronicDiabetic Wound Treatment [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021.] combined the catechol group-containing epigallium The tea-3-gallate (EGCG) was complexed with 3-acrylamidophenylboronic acid (APBA) and copolymerized with acrylamide to obtain a smart hydrogel dressing. The resulting hydrogel has sufficient mechanical properties, self-healing ability and tissue adhesion. Gan et al [Donglin Gan, Tao Shuai, et al. Mussel-Inspired Redox-Active and Hydrophilic Conductive Polymer Nanoparticles for Adhesive Hydrogel Bioelectronics [J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2020.] blended catechol-containing sulfonated lignin Hybrid into different conductive polymers to form conductive polymer/sulfonated lignin nanoparticles with hydrophilicity, conductivity and redox activity. The composite nanoparticles were used as nanofillers to composite with acrylamide to prepare conductive hydrogels with long-term adhesion. Although hydrogels containing catechol groups have achieved many achievements in skin adhesion, the realization of reversible adhesion and de-adhesion of hydrogels to skin is still a big problem.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于克服现有技术缺陷,提供一种电致黏附水凝胶。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the defects of the prior art and provide an electro-adhesive hydrogel.
本发明的另一目的在于提供上述电致黏附水凝胶的制备方法。Another object of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing the above electroadhesive hydrogel.
本发明的技术方案如下:The technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
一种电致黏附水凝胶,由如下质量百分比的原料组分制成:An electro-adhesive hydrogel is made from the following raw material components by mass percentage:
在本发明的一个优选实施方案中,所述PVA、QCA和AM的质量比为4-5:2.5-3.4:5.5-7.4。In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the mass ratio of the PVA, QCA and AM is 4-5:2.5-3.4:5.5-7.4.
进一步优选的,所述PVA、QCA和AM的质量比为4.5:3:6。Further preferably, the mass ratio of the PVA, QCA and AM is 4.5:3:6.
在本发明的一个优选实施方案中,所述PI2959的含量为1.5-3wt%。In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the content of the PI2959 is 1.5-3 wt%.
在本发明的一个优选实施方案中,所述聚乙烯醇的平均分子量为70000-80000。In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the average molecular weight of the polyvinyl alcohol is 70,000-80,000.
在本发明的一个优选实施方案中,所述QCA的合成路线为:In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the synthetic route of described QCA is:
进一步优选的,所述QCA的制备方法包括如下步骤:Further preferably, the preparation method of described QCA comprises the steps:
a、在室温下,将2-氯-3’,4’-二羟基苯乙酮溶于乙酸乙酯中,加入甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯,通氮气25-35min,在65-75℃反应40-50h,获得沉淀;a. Dissolve 2-chloro-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone in ethyl acetate at room temperature, add dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate, pass nitrogen for 25-35min, at 65-75℃ Reaction for 40-50h to obtain a precipitate;
b、将步骤a所得的沉淀依次经甲醇溶解、乙醚沉淀和真空干燥,获得QCA。b. Dissolving the precipitate obtained in step a through methanol, precipitating with ether and vacuum drying in sequence to obtain QCA.
更进一步优选的,所述2-氯-3’,4’-二羟基苯乙酮、乙酸乙酯和甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯的比例为4-5g:50mL:3-4mL。More preferably, the ratio of the 2-chloro-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone, ethyl acetate and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate is 4-5g:50mL:3-4mL.
再进一步优选的,所述2-氯-3’,4’-二羟基苯乙酮、乙酸乙酯和甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯的比例为4.2g:50mL:3.8mL。Still further preferably, the ratio of the 2-chloro-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone, ethyl acetate and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate is 4.2g:50mL:3.8mL.
上述电致黏附水凝胶的制备方法,包括如下步骤:The preparation method of the above-mentioned electro-adhesive hydrogel comprises the following steps:
(1)将PVA溶于水中,在80-100℃下搅拌1-2h,得到PVA溶液;(1) Dissolve PVA in water and stir at 80-100°C for 1-2h to obtain a PVA solution;
(2)将AM、QCA、PI2959、MBA和部分KOH溶于水中,得到预聚物溶液;(2) dissolving AM, QCA, PI2959, MBA and part of KOH in water to obtain a prepolymer solution;
(3)将上述预聚物溶液与上述PVA溶液混合后,用紫外光照射8-16h,得到聚合物溶液;(3) after mixing above-mentioned prepolymer solution with above-mentioned PVA solution, irradiate with ultraviolet light for 8-16h to obtain polymer solution;
(4)将剩余的KOH和H3BO3溶于水中,得到交联剂溶液;(4) dissolving the remaining KOH and H3 BO3 in water to obtain a cross-linking agent solution;
(5)将上述交联剂溶液与上述聚合物溶液于60-80℃下充分混合,冷却至室温后得到所述电致黏附水凝胶。(5) Fully mixing the above crosslinking agent solution and the above polymer solution at 60-80° C., and cooling to room temperature to obtain the electroadhesive hydrogel.
本发明的有益效果是:The beneficial effects of the present invention are:
1、本发明通过季铵化反应制备了一种水溶性邻苯二酚单体2-(3,4-二羟基苯基)-N-(2-(甲基丙烯酰氧)乙基)-N,N-二甲基-2-氧代乙醇-1-氯化铵,在聚乙烯醇存在下,与丙烯酰胺自由基共聚得到邻苯二酚基聚合物,再加入硼酸作为交联剂,形成硼酸酯键交联获得水凝胶,由于通电过程邻苯二酚基团在水凝胶表面的显现和隐藏,使凝胶获得电致可逆黏附性。1. The present invention prepares a water-soluble catechol monomer 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-(2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl)- N,N-dimethyl-2-oxoethanol-1-ammonium chloride, in the presence of polyvinyl alcohol, and acrylamide free radical copolymerization to obtain a catechol-based polymer, and then adding boric acid as a cross-linking agent, The hydrogel is obtained by forming boronic ester bonds and cross-linking. Due to the appearance and hiding of catechol groups on the surface of the hydrogel during the electrification process, the gel obtains electroreversible adhesion.
2、本发明将动态硼酸酯键引入凝胶以改善凝胶的机械性能,获得具有自修复性能的水凝胶。2. The present invention introduces dynamic boronate bonds into the gel to improve the mechanical properties of the gel and obtain a hydrogel with self-healing properties.
3、本发明在水凝胶内部引入邻苯二酚基团,其还具有正向通电可黏附皮肤,反向通电可脱黏的可逆黏附性。3. The present invention introduces a catechol group into the hydrogel, which also has the reversible adhesiveness of being able to adhere to the skin by forward electrification and de-adhesive by reverse electrification.
附图说明Description of drawings
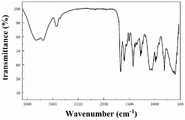
图1为本发明实施例1制得的QCA的红外光谱图。Fig. 1 is the infrared spectrogram of the QCA prepared in Example 1 of the present invention.
图2为本发明实施例1制得的QCA的1H NMR图。FIG. 2 is the1 H NMR chart of the QCA prepared in Example 1 of the present invention.
图3为本发明实施例1制得的QCA的13C NMR图。FIG. 3 is a13 C NMR chart of the QCA prepared in Example 1 of the present invention.
图4为本发明实施例2制得的电致黏附水凝胶的红外光谱图。FIG. 4 is an infrared spectrogram of the electroadhesive hydrogel prepared in Example 2 of the present invention.
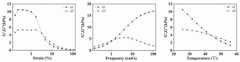
图5为本发明实施例2制得的电致黏附水凝胶的应变、频率、温度扫描流变谱。FIG. 5 is the strain, frequency and temperature sweep rheological spectrum of the electroadhesive hydrogel prepared in Example 2 of the present invention.
图6为本发明实施例2至5制得的电致黏附水凝胶的应力-应变曲线对比图。6 is a comparison diagram of the stress-strain curves of the electroadhesive hydrogels prepared in Examples 2 to 5 of the present invention.
图7为本发明实施例2至5制得的电致黏附水凝胶在通电5s下的对不锈钢的黏附强度对比图。FIG. 7 is a comparison diagram of the adhesion strength of the electro-adhesive hydrogels prepared in Examples 2 to 5 of the present invention to stainless steel under energization for 5 s.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下通过具体实施方式结合附图对本发明的技术方案进行进一步的说明和描述。The technical solutions of the present invention will be further illustrated and described below through specific embodiments in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
实施例1Example 1
实施例2至5所用的QCA的制备方法如下:The preparation method of the used QCA of
(1)在室温下,将4.2g 2-氯-3’,4’-二羟基苯乙酮溶于50mL乙酸乙酯中,加入3.8mL甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯,通氮气30min,在70℃反应48h。(1) At room temperature, 4.2 g of 2-chloro-3',4'-dihydroxyacetophenone was dissolved in 50 mL of ethyl acetate, 3.8 mL of dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate was added, and nitrogen was purged for 30 min. 70 ℃ reaction 48h.
(2)取沉淀用42mL甲醇溶解,500mL乙醚沉淀,真空干燥24h得到如图1至3所示的季铵盐单体QCA(2-(3,4-二羟基苯基)-N-(2-(甲基丙烯酰氧)乙基)-N,N-二甲基-2-氧代乙醇-1-氯化铵)。(2) Dissolve the precipitate with 42 mL of methanol, precipitate with 500 mL of ether, and vacuum dry for 24 h to obtain the quaternary ammonium salt monomer QCA (2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-(2) as shown in Figures 1 to 3 -(methacryloyloxy)ethyl)-N,N-dimethyl-2-oxoethanol-1-ammonium chloride).
实施例2Example 2
(1)将0.45gPVA(平均分子量74800)溶于1.8mL超纯水中,在90℃下搅拌1h,得到20wt%的PVA溶液。(1) Dissolve 0.45 g of PVA (average molecular weight 74800) in 1.8 mL of ultrapure water, and stir at 90° C. for 1 h to obtain a 20 wt % PVA solution.
(3)将0.6gAM、0.3gQCA、0.007gPI2959、0.07gKOH溶于3.5mL超纯水中,得到预聚物溶液。(3) Dissolve 0.6 g AM, 0.3 g QCA, 0.007 g PI2959, and 0.07 g KOH in 3.5 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a prepolymer solution.
(4)将(3)所得预聚物溶液与(2)所得PVA溶液混合,紫外光照射16h得到聚合物溶液。(4) mixing the prepolymer solution obtained in (3) with the PVA solution obtained in (2), and irradiating with ultraviolet light for 16 h to obtain a polymer solution.
(5)将0.04g氢氧化钾、0.05g硼酸溶于水中,得到交联剂溶液。(5) 0.04 g of potassium hydroxide and 0.05 g of boric acid were dissolved in water to obtain a crosslinking agent solution.
(6)将(5)所得交联剂溶液与(4)所得聚合物溶液在70℃下混合,冷却至室温后得到如图4所示的电致黏附水凝胶。如图5至图7所示,本实施例制得的电致黏附水凝胶的应变扫描初始模量为9.00kPa,凝胶点为43℃;以3v电压刺激5s,对不锈钢基体的粘附强度为3.50kPa;在100mm/min-1的拉伸速率下的断裂强度为11.52kPa,断裂伸长率为639%。(6) The crosslinking agent solution obtained in (5) and the polymer solution obtained in (4) are mixed at 70° C., and the electroadhesive hydrogel shown in FIG. 4 is obtained after cooling to room temperature. As shown in Fig. 5 to Fig. 7, the initial modulus of the electro-adhesive hydrogel prepared in this example is 9.00 kPa, and the gel point is 43 °C; the electro-adhesive hydrogel is stimulated with 3 v for 5 s, and the adhesion to the stainless steel substrate is 9.00 kPa. The strength was 3.50 kPa; the breaking strength at a tensile rate of 100 mm/min-1 was 11.52 kPa, and the breaking elongation was 639%.
实施例3Example 3
(1)将0.45gPVA(平均分子量74800)溶于1.8mL超纯水中,在90℃下搅拌1h,得到20wt%的PVA溶液。(1) Dissolve 0.45 g of PVA (average molecular weight 74800) in 1.8 mL of ultrapure water, and stir at 90° C. for 1 h to obtain a 20 wt % PVA solution.
(3)将0.6gAM、0.3gQCA、0.007gPI2959、0.0045gMBA、0.07gKOH溶于3.5mL超纯水中,得到预聚物溶液。(3) Dissolve 0.6 g AM, 0.3 g QCA, 0.007 g PI2959, 0.0045 g MBA, and 0.07 g KOH in 3.5 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a prepolymer solution.
(4)将(3)所得预聚物溶液与(2)所得PVA溶液混合,紫外光照射16h得到聚合物溶液。(4) mixing the prepolymer solution obtained in (3) with the PVA solution obtained in (2), and irradiating with ultraviolet light for 16 h to obtain a polymer solution.
(5)将0.038g氢氧化钾、0.048g硼酸溶于水中,得到交联剂溶液。(5) 0.038 g of potassium hydroxide and 0.048 g of boric acid were dissolved in water to obtain a crosslinking agent solution.
(6)将(5)所得交联剂溶液与(4)所得聚合物溶液在70℃下混合,冷却至室温后得到电致黏附水凝胶。如图6和图7所示,本实施例制得的电致黏附水凝胶的应变扫描初始模量为3.42kPa,凝胶点为32℃;以3v电压刺激5s,对不锈钢基体的粘附强度为3.05kPa;在100mm/min-1的拉伸速率下的断裂强度为8.15kPa,断裂伸长率为773%。(6) The crosslinking agent solution obtained in (5) and the polymer solution obtained in (4) are mixed at 70° C., and the electroadhesive hydrogel is obtained after cooling to room temperature. As shown in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7, the initial modulus of the electro-adhesive hydrogel prepared in this example is 3.42kPa, and the gel point is 32°C. When stimulated with a voltage of 3v for 5s, the adhesion to the stainless steel substrate The strength was 3.05 kPa; the breaking strength at a tensile rate of 100 mm/min-1 was 8.15 kPa, and the breaking elongation was 773%.
实施例4Example 4
(1)将0.45gPVA(平均分子量74800)溶于1.8mL超纯水中,在90℃下搅拌1h,得到20wt%的PVA溶液。(1) Dissolve 0.45 g of PVA (average molecular weight 74800) in 1.8 mL of ultrapure water, and stir at 90° C. for 1 h to obtain a 20 wt % PVA solution.
(3)将0.6gAM、0.3gQCA、0.007gPI2959、0.07gKOH溶于3.5mL超纯水中,得到预聚物溶液。(3) Dissolve 0.6 g AM, 0.3 g QCA, 0.007 g PI2959, and 0.07 g KOH in 3.5 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a prepolymer solution.
(4)将(3)所得预聚物溶液与(2)所得PVA溶液混合,紫外光照射16h得到聚合物溶液。(4) mixing the prepolymer solution obtained in (3) with the PVA solution obtained in (2), and irradiating with ultraviolet light for 16 h to obtain a polymer solution.
(5)将0.035g氢氧化钾、0.045g硼酸溶于水中,得到交联剂溶液。(5) Dissolve 0.035 g of potassium hydroxide and 0.045 g of boric acid in water to obtain a cross-linking agent solution.
(6)将(5)所得交联剂溶液与(4)所得聚合物溶液在70℃下混合,冷却至室温后得到致黏附水凝胶。如图6和图7所示,本实施例制得的电致黏附水凝胶的应变扫描初始模量为5.01kPa,凝胶点为36℃;以3v电压刺激5s,对不锈钢基体的粘附强度为2.80kPa;在100mm/min-1的拉伸速率下的断裂强度为10.95kPa,断裂伸长率为437%。(6) The crosslinking agent solution obtained in (5) and the polymer solution obtained in (4) are mixed at 70° C., and the adhesion-inducing hydrogel is obtained after cooling to room temperature. As shown in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7, the initial modulus of the electro-adhesive hydrogel prepared in this example is 5.01 kPa, and the gel point is 36 °C. The adhesion to the stainless steel substrate is stimulated by 3v for 5s. The strength was 2.80 kPa; the breaking strength at a tensile rate of 100 mm/min-1 was 10.95 kPa, and the breaking elongation was 437%.
实施例5Example 5
(1)将0.45gPVA(平均分子量74800)溶于1.8mL超纯水中,在90℃下搅拌1h,得到20wt%的PVA溶液。(1) Dissolve 0.45 g of PVA (average molecular weight 74800) in 1.8 mL of ultrapure water, and stir at 90° C. for 1 h to obtain a 20 wt % PVA solution.
(3)将0.6gAM、0.3gQCA、0.007gPI2959、0.009gMBA、0.07gKOH溶于3.5mL超纯水中,得到预聚物溶液。(3) Dissolve 0.6 g AM, 0.3 g QCA, 0.007 g PI2959, 0.009 g MBA, and 0.07 g KOH in 3.5 mL of ultrapure water to obtain a prepolymer solution.
(4)将(3)所得预聚物溶液与(2)所得PVA溶液混合,紫外光照射16h得到聚合物溶液。(4) mixing the prepolymer solution obtained in (3) with the PVA solution obtained in (2), and irradiating with ultraviolet light for 16 h to obtain a polymer solution.
(5)将0.035g氢氧化钾、0.045g硼酸溶于水中,得到交联剂溶液。(5) Dissolve 0.035 g of potassium hydroxide and 0.045 g of boric acid in water to obtain a cross-linking agent solution.
(6)将(5)所得交联剂溶液与(4)所得聚合物溶液在70℃下混合,冷却至室温后得到电致黏附水凝胶。如图6和图7所示,本实施例制得的电致黏附水凝胶的应变扫描初始模量为6.91kPa,凝胶点为38℃;以3v电压刺激5s,对不锈钢基体的粘附强度为3.51kPa;在100mm/min-1的拉伸速率下的断裂强度为13.10kPa,断裂伸长率为665%。(6) The crosslinking agent solution obtained in (5) and the polymer solution obtained in (4) are mixed at 70° C., and the electroadhesive hydrogel is obtained after cooling to room temperature. As shown in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7, the initial modulus of the electro-adhesive hydrogel prepared in this example is 6.91kPa in strain sweep, and the gel point is 38°C; stimulated with 3v voltage for 5s, the adhesion to the stainless steel substrate The strength was 3.51 kPa; the breaking strength at a tensile rate of 100 mm/min-1 was 13.10 kPa, and the breaking elongation was 665%.
表1 实施例中各组分用量The dosage of each component in the embodiment of table 1
以上所述,仅为本发明的较佳实施例而已,故不能依此限定本发明实施的范围,即依本发明专利范围及说明书内容所作的等效变化与修饰,皆应仍属本发明涵盖的范围内。The above descriptions are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, so the scope of implementation of the present invention cannot be limited accordingly, that is, equivalent changes and modifications made according to the patent scope of the present invention and the contents of the description should still be covered by the present invention. In the range.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110825998.9ACN113583257B (en) | 2021-07-21 | 2021-07-21 | Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
| PCT/CN2022/088969WO2023000744A1 (en) | 2021-07-21 | 2022-04-25 | Electro-adhesive hydrogel and preparation method therefor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110825998.9ACN113583257B (en) | 2021-07-21 | 2021-07-21 | Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113583257A CN113583257A (en) | 2021-11-02 |
| CN113583257Btrue CN113583257B (en) | 2022-06-07 |
Family
ID=78248792
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110825998.9AActiveCN113583257B (en) | 2021-07-21 | 2021-07-21 | Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113583257B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2023000744A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113583257B (en)* | 2021-07-21 | 2022-06-07 | 厦门大学 | Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
| CN116574212B (en)* | 2023-03-23 | 2024-07-19 | 厦门大学 | Polymer/liquid metal composite conductive solid material and preparation method thereof |
| CN116948215B (en)* | 2023-07-18 | 2024-03-29 | 四川大学华西医院 | A kind of polyphenol hydrogel, oxygen-carrying hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN118021711B (en)* | 2024-01-23 | 2025-01-28 | 四川大学 | Boric acid-polyphenol hydrogel targeting inflammatory aging microenvironment response and preparation method thereof |
| CN119925645B (en)* | 2025-01-24 | 2025-09-19 | 海南大学 | Hydrogel for injectable soft bioelectrode, and preparation method and application thereof |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012159106A2 (en)* | 2011-05-19 | 2012-11-22 | Northwestern University | Ph responsive self-healing hydrogels formed by boronate-catechol complexation |
| CN106633111A (en)* | 2017-01-11 | 2017-05-10 | 福州大学 | Method for preparing high-strength polyvinyl alcohol-based dual-network hydrogel |
| CN110628044A (en)* | 2019-08-30 | 2019-12-31 | 厦门大学 | A kind of ternary cross-linked hydrogel electrolyte, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN112457501A (en)* | 2020-11-11 | 2021-03-09 | 厦门大学 | Electro-reversible skin-adhesive hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0678460B2 (en)* | 1985-05-01 | 1994-10-05 | 株式会社バイオマテリアル・ユニバース | Porous transparent polyvinyl alcohol gel |
| WO2021081241A1 (en)* | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | Alfred E. Mann Institute For Biomedical Engineering At The University Of Southern California | Reversible adhesives |
| CN113583257B (en)* | 2021-07-21 | 2022-06-07 | 厦门大学 | Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
- 2021
- 2021-07-21CNCN202110825998.9Apatent/CN113583257B/enactiveActive
- 2022
- 2022-04-25WOPCT/CN2022/088969patent/WO2023000744A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012159106A2 (en)* | 2011-05-19 | 2012-11-22 | Northwestern University | Ph responsive self-healing hydrogels formed by boronate-catechol complexation |
| CN106633111A (en)* | 2017-01-11 | 2017-05-10 | 福州大学 | Method for preparing high-strength polyvinyl alcohol-based dual-network hydrogel |
| CN110628044A (en)* | 2019-08-30 | 2019-12-31 | 厦门大学 | A kind of ternary cross-linked hydrogel electrolyte, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN112457501A (en)* | 2020-11-11 | 2021-03-09 | 厦门大学 | Electro-reversible skin-adhesive hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 两亲型阳离子聚丙烯酰胺的合成及结构表征;高庆等;《石油化工》;20050115;第34卷(第01期);全文* |
| 高强度PAM/PVA互穿网络水凝胶的合成;林建明等;《华侨大学学报(自然科学版)》;20100120;第31卷(第01期);47-54* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| WO2023000744A1 (en) | 2023-01-26 |
| CN113583257A (en) | 2021-11-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113583257B (en) | Electroadhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110698697B (en) | A kind of preparation method of polyethyleneimine-polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel with self-healing properties | |
| CN104140630A (en) | Chitosan-based double-network hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106633111A (en) | Method for preparing high-strength polyvinyl alcohol-based dual-network hydrogel | |
| Chen et al. | Mussel-inspired ultra-stretchable, universally sticky, and highly conductive nanocomposite hydrogels | |
| CN106947020A (en) | A kind of preparation method of the chitosan-based hydrogel of high intensity | |
| CN112267167A (en) | Preparation method of self-healing luminous organic hydrogel fiber | |
| CN109836596B (en) | Preparation method of amylopectin composite hydrogel with strong hydrogen bonding, high strength and high adhesion | |
| CN111393675B (en) | Rapid-forming self-healing hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN103145914A (en) | Preparation method of high-strength nano-composite hydrogel with rapid dual responses of pH and temperature | |
| CN109970999A (en) | A kind of chitosan/polysulfobetaine ion supply double network hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110845743A (en) | Polyamino acid-based self-healing hydrogel based on quadruple hydrogen bonds and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106267366A (en) | A kind of method that high-strength and high ductility polyion hydrogel scaffold is prepared in the 3D of utilization printing | |
| CN117510704A (en) | Rapid-gelling conductive hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN114672044A (en) | A kind of cellulose conductive hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116854946A (en) | Preparation method and application of high-performance polyvinyl alcohol-based hydrogel | |
| CN113185725A (en) | Method for rapidly preparing silver nanoparticle/gelatin composite hydrogel in situ | |
| CN106380990A (en) | Preparation method of aldehyde-containing phosphorylcholine polymer and dopamine cross-linked coating | |
| CN108341972A (en) | Preparation method of ion coordination crosslinking natural polymer self-repairing hydrogel | |
| CN113861447B (en) | A modified hydroxypropyl chitosan adhesive self-healing hydrogel and its preparation method and application | |
| CN115746208A (en) | Cellulose/acrylamide super-stretching and adhering hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116178751A (en) | Self-healing hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN112354004B (en) | Medical hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN109260519B (en) | Adhesive type hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN115612009A (en) | Hydrogel tissue adhesive based on dicarboxyl amino acid and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |