CN113535656A - Data access method, device, device and storage medium - Google Patents
Data access method, device, device and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113535656A CN113535656ACN202110709977.0ACN202110709977ACN113535656ACN 113535656 ACN113535656 ACN 113535656ACN 202110709977 ACN202110709977 ACN 202110709977ACN 113535656 ACN113535656 ACN 113535656A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- target
- storage
- read
- index
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/10—File systems; File servers
- G06F16/17—Details of further file system functions
- G06F16/1734—Details of monitoring file system events, e.g. by the use of hooks, filter drivers, logs
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/10—File systems; File servers
- G06F16/18—File system types
- G06F16/1805—Append-only file systems, e.g. using logs or journals to store data
- G06F16/1815—Journaling file systems
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/22—Indexing; Data structures therefor; Storage structures
- G06F16/2228—Indexing structures
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/27—Replication, distribution or synchronisation of data between databases or within a distributed database system; Distributed database system architectures therefor
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及数据库技术领域,特别涉及一种数据访问方法、装置、设备及存储介质。The present application relates to the technical field of databases, and in particular, to a data access method, apparatus, device and storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
随着数据库技术的发展,为了提高分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能以及可用性,将数据以多副本的形式进行存储已成为一种共识。多副本技术是指将一份数据复制多份,并将各数据副本分别存储在分布式数据库系统的不同节点上。例如,按照数据的价值高低,将不同价值的数据副本分别存储在不同的存储介质中。又例如,按照数据的数据类型,将不同类型的数据副本分别存储在不同的数据存储区域中。然而,基于上述多副本技术进行数据访问时,所有数据访问请求需要集中到一个主节点上进行处理,增加了负载均衡的实现难度,且容易造成较高的时间开销,导致数据访问延迟较高,分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能不佳。With the development of database technology, in order to improve the data access performance and availability of distributed database systems, it has become a consensus to store data in the form of multiple copies. Multi-copy technology refers to copying a piece of data into multiple copies, and storing each copy of the data on different nodes of the distributed database system. For example, according to the value of the data, data copies of different values are stored in different storage media. For another example, according to the data type of the data, different types of data copies are respectively stored in different data storage areas. However, when data access is performed based on the above-mentioned multi-copy technology, all data access requests need to be processed on one master node, which increases the difficulty of implementing load balancing, and easily causes high time overhead, resulting in high data access latency. Distributed database systems have poor data access performance.
因此,亟需一种能够提升分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能的数据访问方法。Therefore, there is an urgent need for a data access method that can improve the data access performance of a distributed database system.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本申请实施例提供了一种数据访问方法、装置、设备及存储介质,能够有效提升分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。该技术方案如下:The embodiments of the present application provide a data access method, apparatus, device, and storage medium, which can effectively improve the data access performance of a distributed database system. The technical solution is as follows:
一方面,提供了一种数据访问方法,应用于分布式数据库系统,该分布式数据库系统包括计算节点和多个存储节点,该方法包括:In one aspect, a data access method is provided, applied to a distributed database system, the distributed database system includes a computing node and a plurality of storage nodes, and the method includes:
计算节点响应于第一数据读取请求,确定该第一数据读取请求的第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片,基于该第一数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第一存储节点,该多个第一存储节点用于存储该第一目标数据的多个副本;In response to the first data read request, the computing node determines a first data fragment to which the first target data of the first data read request belongs, and determines a plurality of storage nodes based on the first data fragment from the plurality of storage nodes. a first storage node, where the plurality of first storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the first target data;
计算节点基于该第一数据读取请求,从该多个第一存储节点中确定第一目标存储节点,向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件;The computing node determines a first target storage node from the plurality of first storage nodes based on the first data read request, and sends the first data read request to the first target storage node. The data access cost meets the first target condition;
第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求,读取该第一目标数据,向该计算节点发送第一数据读取结果。The first target storage node reads the first target data based on the first data read request, and sends the first data read result to the computing node.
另一方面,提供了一种数据访问装置,应用于分布式数据库系统,该装置包括:On the other hand, a data access device is provided, which is applied to a distributed database system, and the device includes:
第一确定模块,用于响应于第一数据读取请求,确定该第一数据读取请求的第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片,基于该第一数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第一存储节点,该多个第一存储节点用于存储该第一目标数据的多个副本;a first determination module, configured to determine, in response to a first data read request, a first data fragment to which the first target data of the first data read request belongs, and based on the first data fragment, obtain data from the plurality of storage A plurality of first storage nodes are determined in the nodes, and the plurality of first storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the first target data;
第二确定模块,用于基于该第一数据读取请求,从该多个第一存储节点中确定第一目标存储节点,向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件;A second determination module, configured to determine a first target storage node from the plurality of first storage nodes based on the first data read request, and send the first data read request to the first target storage node, the first target storage node The data access cost of a target storage node meets the first target condition;
第一读取模块,用于基于该第一数据读取请求,读取该第一目标数据,向该计算模块发送第一数据读取结果。The first reading module is configured to read the first target data based on the first data reading request, and send the first data reading result to the computing module.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取模块包括:In an optional implementation, the first reading module includes:
第一读取单元,用于若该第一目标数据为当前态数据,基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标存储节点的节点类型,读取该第一目标数据;a first reading unit, configured to read the first target data based on the first data read request and the node type of the first target storage node if the first target data is current state data;
第二读取单元,用于若该第一目标数据为历史态数据,基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标数据的事务完成时间,读取该第一目标数据。The second reading unit is configured to read the first target data based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time of the first target data if the first target data is historical data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取单元用于下述任一项:In an optional implementation, the first reading unit is used for any of the following:
若该第一目标存储节点为主存储节点,基于该第一数据读取请求,确定该第一目标数据的第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据,该第一读索引用于指示基于该第一数据读取请求读取该第一目标数据的最小读索引;If the first target storage node is the main storage node, based on the first data read request, determine the first read index of the first target data, take the first read index as the starting point, and start from the first read index corresponding to the first target data. The first target data is read in the state machine, and the first read index is used to indicate the minimum read index for reading the first target data based on the first data read request;
若该第一目标存储节点为从存储节点,基于该第一数据读取请求,从该主存储节点中获取该第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。If the first target storage node is a slave storage node, based on the first data read request, obtain the first read index from the master storage node, take the first read index as a starting point, and retrieve the corresponding data from the first target data The first target data is read in the state machine of .
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the first reading unit is used for:
更新当前时刻的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引;Update the commit index at the current moment, which is used to indicate the maximum index of the committed logs in the log list;
按照第一顺序,扫描该日志列表中存储的日志,该第一顺序是指从该提交索引至该日志列表的执行索引,该执行索引用于指示该日志列表中已执行日志的最大索引;Scan the logs stored in the log list according to the first order, where the first order refers to the execution index from the submission index to the log list, and the execution index is used to indicate the largest index of the executed log in the log list;
若存在第一目标日志,基于该第一目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第一目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据;若不存在该第一目标日志,该第一目标存储节点基于该执行索引,确定该第一读索引。If there is a first target log, the first read index is determined based on the log index of the first target log, and the data operated by the first target log is the first target data; if the first target log does not exist, the first target log The first target storage node determines the first read index based on the execution index.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第一存储模块,用于将该第一读索引存储至第一列表,该第一列表包括该第一目标数据、该第一读索引以及第一校验索引,该第一校验索引用于指示该第一目标存储节点确定该第一读索引时对应的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引;The first storage module is used to store the first read index in a first list, where the first list includes the first target data, the first read index and the first check index, and the first check index is used for Instruct the first target storage node to determine the corresponding submission index when the first read index is used, and the submission index is used to indicate the largest index of the submitted log in the log list;
第一查询模块,用于当该分布式数据库系统处理第二数据读取请求时,若该第二数据读取请求的数据为该第一目标数据,查询该第一列表以读取该第一目标数据。The first query module is used for querying the first list to read the first data when the distributed database system processes the second data reading request, if the data of the second data reading request is the first target data target data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the first reading unit is used for:
若该第一目标存储节点中存在该第一读索引对应的日志,对该第一读索引对应的日志进行持久化存储,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据;If the log corresponding to the first read index exists in the first target storage node, the log corresponding to the first read index is persistently stored, and the first read index is used as the starting point, and the state corresponding to the first target data is read the first target data in the machine;
若该第一目标存储节点中不存在该第一读索引对应的日志,从该主存储节点中获取该第一读索引对应的日志,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。If the log corresponding to the first read index does not exist in the first target storage node, obtain the log corresponding to the first read index from the main storage node, take the first read index as the starting point, and obtain the log corresponding to the first read index from the first target data The first target data is read in the corresponding state machine.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第二读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the second reading unit is used for:
若该第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之前,基于该第一数据读取请求和该事务完成时间,按照第二顺序,扫描日志列表中存储的日志,确定第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据;If the data submission time of the first target data is before the transaction completion time, based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time, the logs stored in the log list are scanned in the second order to determine the first read index, Taking the first read index as a starting point, read the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data;
若该第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之后,基于该第一数据读取请求和该事务完成时间,按照第三顺序,扫描该日志列表中存储的日志,确定该第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据;If the data submission time of the first target data is after the transaction completion time, based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time, the logs stored in the log list are scanned in the third order to determine the first read request. index, taking the first read index as a starting point, and reading the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data;
其中,该第二顺序是指从该日志列表的提交索引至该日志列表的执行索引,该第三顺序是指从该日志列表的执行索引至该日志列表的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示该日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引,该执行索引用于指示该日志列表中已执行日志的最大索引,该第一读索引用于指示基于该第一数据读取请求读取该第一目标数据的最小读索引。Wherein, the second order refers to from the commit index of the log list to the execution index of the log list, the third order refers to from the execution index of the log list to the commit index of the log list, and the commit index is used to indicate The maximum index of the submitted log in the log list, the execution index is used to indicate the maximum index of the executed log in the log list, and the first read index is used to indicate that the first target is read based on the first data read request The minimum read index for the data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第二读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the second reading unit is used for:
若存在第二目标日志,且该第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该第二目标日志的事务完成时间相同,或该第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第二目标日志的事务完成时间之后,基于该第二目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第二目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据;If there is a second target log, and the transaction completion time of the first target data is the same as the transaction completion time of the second target log, or the transaction completion time of the first target data is after the transaction completion time of the second target log , determine the first read index based on the log index of the second target log, and the data operated by the second target log is the first target data;
若不存在该第二目标日志,基于该日志列表的执行索引,确定该第一读索引。If the second target log does not exist, the first read index is determined based on the execution index of the log list.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该数据访问代价用于指示存储节点的执行时间、等待时间以及传输时间;In an optional implementation manner, the data access cost is used to indicate the execution time, waiting time and transmission time of the storage node;
该执行时间包括存储节点查询该第一目标数据的时间、处理数据量的时间以及元组构建时间;The execution time includes the time for the storage node to query the first target data, the time for processing the amount of data, and the time for tuple construction;
该等待时间包括存储节点的请求队列时间、设备负载延迟时间以及数据同步时间;The waiting time includes the request queue time of the storage node, the device load delay time and the data synchronization time;
该传输时间包括网络传输时间。The transmission time includes network transmission time.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件,包括下述任一项:In an optional implementation manner, the data access cost of the first target storage node meets the first target condition, including any of the following:
该第一目标存储节点中该第一目标数据的存储模式为列存模式,且该数据读取请求所需访问的列数与总列数之间的比值小于第一阈值,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式;The storage mode of the first target data in the first target storage node is a column storage mode, and the ratio between the number of columns to be accessed by the data read request and the total number of columns is less than a first threshold, and the storage mode is used for Indicates the storage format of the data in the storage node;
该第一目标存储节点的节点负载小于该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点的节点负载;The node load of the first target storage node is smaller than the node load of the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes;
该第一目标存储节点与该计算节点之间的物理距离小于该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点与该计算节点之间的物理距离;The physical distance between the first target storage node and the computing node is smaller than the physical distance between the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes and the computing node;
该第一目标存储节点的数据同步状态在该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点的数据同步状态之后。The data synchronization state of the first target storage node is after the data synchronization state of the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
调整模块,用于对该第一目标数据的多个副本的存储模式进行动态调整,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。The adjustment module is configured to dynamically adjust the storage mode of the multiple copies of the first target data, where the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该调整模块用于下述任一项:In an optional implementation, the adjustment module is used for any of the following:
基于该多个第一存储节点的负载情况,切换该多个副本的存储模式;switching the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the load conditions of the multiple first storage nodes;
若该多个副本中存在至少一个副本异常,基于该至少一个副本,建立至少一个新副本;If there is at least one copy exception in the multiple copies, at least one new copy is established based on the at least one copy;
若该第一数据分片发生数据分裂,生成至少一个第二数据分片,基于该至少一个第二数据分片,建立该至少一个第二数据分片对应的多个副本;If data splitting occurs in the first data fragment, at least one second data fragment is generated, and based on the at least one second data fragment, multiple copies corresponding to the at least one second data fragment are established;
基于该多个第一存储节点的节点类型,调整该多个副本的存储模式。Based on the node types of the plurality of first storage nodes, the storage modes of the plurality of replicas are adjusted.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该基于该多个第一存储节点的负载情况,切换该多个副本的存储模式,包括下述任一项:In an optional implementation manner, the switching of the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the load conditions of the multiple first storage nodes includes any one of the following:
基于该多个第一存储节点的节点负载大小和可用空间,切换该多个副本的存储模式;switching the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the node load size and available space of the multiple first storage nodes;
基于该多个第一存储节点的节点负载大小和每个存储模式下副本的数量,切换该多个副本的存储模式。The storage modes of the multiple copies are switched based on the node load size of the multiple first storage nodes and the number of copies in each storage mode.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第三确定模块,用于响应于数据写入请求,若该数据写入请求的第二目标数据存在所属的第三数据分片,基于该第三数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第二存储节点,该多个第二存储节点用于存储该第二目标数据的多个副本;The third determining module is configured to, in response to the data write request, determine from the plurality of storage nodes based on the third data fragment if the second target data of the data write request exists in the third data fragment to which it belongs. multiple second storage nodes, the multiple second storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the second target data;
发送模块,用于向该多个第二存储节点中的主存储节点发送该数据写入请求;a sending module, configured to send the data write request to the main storage node in the plurality of second storage nodes;
第一写入模块,用于基于该数据写入请求,写入该第二目标数据,向该计算节点发送第一数据写入结果。The first writing module is configured to write the second target data based on the data writing request, and send the first data writing result to the computing node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一写入模块用于:In an optional implementation manner, the first writing module is used for:
基于该数据写入请求,写入该第二目标数据,生成数据操作日志,向该多个存储节点中的从存储节点发送日志同步请求,该日志同步请求用于指示该从存储节点同步该数据操作日志后向该主存储节点发送数据同步消息;Based on the data writing request, write the second target data, generate a data operation log, and send a log synchronization request to a slave storage node among the plurality of storage nodes, where the log synchronization request is used to instruct the slave storage node to synchronize the data Send a data synchronization message to the primary storage node after operating the log;
若该主存储节点接收到的该数据同步消息的数量大于或等于从存储节点数量的半数,确认该数据写入请求已操作成功。If the number of the data synchronization messages received by the master storage node is greater than or equal to half of the number of slave storage nodes, it is confirmed that the data write request has been successfully operated.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第一持久化存储模块,用于对该第二目标数据进行持久化存储;a first persistent storage module for persistently storing the second target data;
第二持久化存储模块,用于基于该数据操作日志和该第二目标数据在该从存储节点中的存储模式,对该第二目标数据进行格式转换,对转换后的该第二目标数据进行持久化存储,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。The second persistent storage module is configured to perform format conversion on the second target data based on the data operation log and the storage mode of the second target data in the slave storage node, and perform format conversion on the converted second target data Persistent storage, the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of data in the storage node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第四确定模块,用于基于该数据操作日志的日志索引,确定该第二目标数据的第二读索引,该第二读索引用于指示基于第三数据读取请求读取该第二目标数据的最小读索引;a fourth determination module, configured to determine a second read index of the second target data based on the log index of the data operation log, where the second read index is used to indicate that the second target data is read based on the third data read request The minimum read index of ;
第二存储模块,用于将该第二读索引存储至第二列表,该第二列表包括该第二目标数据、该第二读索引以及第二校验索引,该第二校验索引为该数据操作日志的日志索引;The second storage module is configured to store the second read index in a second list, where the second list includes the second target data, the second read index and a second check index, and the second check index is the The log index of the data operation log;
第二查询模块,用于当该分布式数据库系统处理该第三数据读取请求时,若该第三数据读取请求的数据为该第二目标数据,查询该第二列表以读取该第二目标数据。The second query module is configured to query the second list to read the first data when the distributed database system processes the third data read request, if the data of the third data read request is the second target data Two target data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第一建立模块,用于若该数据写入请求的第二目标数据不存在所属的第三数据分片,建立该第二目标数据的第三数据分片,向该多个存储节点发送副本创建请求;The first establishment module is used to establish a third data fragment of the second target data if the second target data of the data write request does not have a third data fragment to which it belongs, and send the copy creation to the plurality of storage nodes ask;
第二建立模块,用于基于该副本创建请求,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本。The second establishment module is configured to establish multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment based on the copy creation request.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第二建立模块用于:In an optional implementation manner, the second establishment module is used for:
基于该副本创建请求和该第二目标数据在该多个存储节点中的存储模式,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。Based on the copy creation request and the storage mode of the second target data in the multiple storage nodes, multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment are established, where the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第五确定模块,用于响应于数据读写请求,若该数据读写请求的第三目标数据存在所属的第四数据分片,基于该第四数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第三存储节点,该多个第三存储节点用于存储该第三目标数据的多个副本;The fifth determination module is used to respond to the data read and write request, if the third target data of the data read and write request has a fourth data fragment to which it belongs, determine from the plurality of storage nodes based on the fourth data fragment multiple third storage nodes, the multiple third storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the third target data;
第二读取模块,用于对于该数据读写请求中的读操作,基于该数据读写请求,从该多个第三存储节点中确定第二目标存储节点,向该第二目标存储节点发送该数据读写请求,该第二目标存储节点基于该数据读写请求,读取该第三目标数据,向该计算节点发送第二数据读取结果,该第二目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第二目标条件;The second read module is configured to, for the read operation in the data read/write request, determine a second target storage node from the plurality of third storage nodes based on the data read/write request, and send the data to the second target storage node In the data read/write request, the second target storage node reads the third target data based on the data read/write request, and sends the second data read result to the computing node, and the data access cost of the second target storage node is consistent with the second target condition;
第二写入模块,用于对于该数据读写请求中的写操作,向该多个第三存储节点中的主存储节点发送该数据读写请求,该主存储节点基于该数据读写请求,写入该第三目标数据,向该计算节点发送第二数据写入结果。The second writing module is configured to send the data reading and writing request to the main storage node among the plurality of third storage nodes for the writing operation in the data reading and writing request, and the main storage node is based on the data reading and writing request, Write the third target data, and send the second data writing result to the computing node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该多个第三存储节点中的从存储节点配置有内存锁,该内存锁用于在该写操作尚未完成时锁定该第三目标数据。In an optional implementation manner, a slave storage node among the plurality of third storage nodes is configured with a memory lock, and the memory lock is used to lock the third target data when the write operation has not been completed.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第六确定模块,用于当该多个存储节点中存在第四存储节点通过选举成为主存储节点时,该多个存储节点中的从存储节点基于当前存储模式和该从存储节点的写性能参数,确定超时时间,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式;The sixth determination module is used for when a fourth storage node in the plurality of storage nodes becomes the master storage node through election, the slave storage node in the plurality of storage nodes is based on the current storage mode and the write performance parameter of the slave storage node , determine the timeout period, the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node;
状态切换模块,用于若存在第一从存储节点在对应的超时时间内,未接收到该主存储节点的消息,该第一从存储节点切换至候选状态,参与下一次选举。The state switching module is configured to switch the first slave storage node to the candidate state and participate in the next election if the first slave storage node does not receive the message of the master storage node within the corresponding timeout period.
另一方面,提供了一种计算机设备,该计算机设备包括处理器和存储器,该存储器用于存储至少一条计算机程序,该至少一段计算机程序由该处理器加载并执行以实现本申请实施例中的数据访问方法中所执行的操作。In another aspect, a computer device is provided, the computer device includes a processor and a memory, the memory is used to store at least one computer program, and the at least one computer program is loaded and executed by the processor to implement the embodiments of the present application. The operation performed in the data access method.
另一方面,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质中存储有至少一条计算机程序,该至少一条计算机程序由处理器加载并执行以实现如本申请实施例中数据访问方法中所执行的操作。In another aspect, a computer-readable storage medium is provided, where at least one computer program is stored in the computer-readable storage medium, and the at least one computer program is loaded and executed by a processor to implement the data access method in the embodiment of the present application operations performed in .
另一方面,提供了一种计算机程序产品或计算机程序,该计算机程序产品或计算机程序包括计算机程序代码,该计算机程序代码存储在计算机可读存储介质中。计算机设备的处理器从计算机可读存储介质读取该计算机程序代码,处理器执行该计算机程序代码,使得该计算机设备执行上述各种可选实现方式中提供的数据访问方法。In another aspect, a computer program product or computer program is provided, the computer program product or computer program comprising computer program code stored in a computer-readable storage medium. The processor of the computer device reads the computer program code from the computer-readable storage medium, and the processor executes the computer program code, so that the computer device executes the data access methods provided in the various optional implementations described above.
本申请实施例提供的技术方案带来的有益效果是:The beneficial effects brought by the technical solutions provided in the embodiments of the present application are:
在分布式数据库系统中,当计算节点接收到数据读取请求时,先根据该数据读取请求的目标数据所属的数据分片,来确定存储有该目标数据的多个副本的多个存储节点,然后按照存储节点访问目标数据的数据访问代价,从这些存储节点中选出符合目标条件的目标存储节点,由该目标存储节点来读取目标数据。上述方法中,由于该目标存储节点是根据数据访问代价来确定的,因此主存储节点和从存储节点都可能成为目标存储节点,避免了由主存储节点处理所有的数据读取请求,从而既保证了多副本带来的高可用性,又提高了数据读取速度,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。In a distributed database system, when a computing node receives a data read request, it first determines multiple storage nodes that store multiple copies of the target data according to the data shard to which the target data of the data read request belongs. , and then select a target storage node that meets the target condition from these storage nodes according to the data access cost of the storage node to access the target data, and the target storage node reads the target data. In the above method, since the target storage node is determined according to the data access cost, both the master storage node and the slave storage node may become the target storage node, avoiding the master storage node processing all data read requests, thus ensuring that both It improves the high availability brought by multiple copies, improves the data reading speed, and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本申请实施例中的技术方案,下面将对实施例描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本申请的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application more clearly, the following briefly introduces the drawings that are used in the description of the embodiments. Obviously, the drawings in the following description are only some embodiments of the present application. For those of ordinary skill in the art, other drawings can also be obtained from these drawings without creative effort.
图1是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法的实施环境示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of an implementation environment of a data access method provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图2是根据本申请实施例提供的一种HTAP数据库系统的架构示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of the architecture of a HTAP database system provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图3是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法流程图;3 is a flowchart of a data access method provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图4是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法流程图;4 is a flowchart of a data access method provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图5是根据本申请实施例提供的一种确定第一读索引的示意图;5 is a schematic diagram of determining a first read index according to an embodiment of the present application;
图6是根据本申请实施例提供的一种存储第一读索引的示意图;6 is a schematic diagram of storing a first read index according to an embodiment of the present application;
图7是根据本申请实施例提供的一种主节点读请求处理流程的示意图;7 is a schematic diagram of a master node read request processing flow provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图8是根据本申请实施例提供的一种从节点读请求处理流程的示意图;8 is a schematic diagram of a processing flow of a read request from a node provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图9是根据本申请实施例提供的一种确定第一读索引的示意图;9 is a schematic diagram of determining a first read index according to an embodiment of the present application;
图10是根据本申请实施例提供的一种旧数据读请求处理流程的示意图;10 is a schematic diagram of a processing flow of an old data read request provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图11是根据本申请实施例提供的一种非最新数据读请求处理流程的示意图;11 is a schematic diagram of a non-latest data read request processing flow provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图12是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法流程图;12 is a flowchart of a data access method provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图13是根据本申请实施例提供的一种存储第二读索引的示意图;FIG. 13 is a schematic diagram of storing a second read index according to an embodiment of the present application;
图14是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法流程图;14 is a flowchart of a data access method provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图15是根据本申请实施例提供的一种读半已提交问题的示意图;15 is a schematic diagram of a read half-submitted question provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图16是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问装置的结构示意图;16 is a schematic structural diagram of a data access device provided according to an embodiment of the present application;
图17是根据本申请实施例提供的一种服务器的结构示意图。FIG. 17 is a schematic structural diagram of a server provided according to an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本申请的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合附图对本申请实施方式作进一步地详细描述。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present application clearer, the embodiments of the present application will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
这里将详细地对示例性实施例进行说明,其示例表示在附图中。下面的描述涉及附图时,除非另有表示,不同附图中的相同数字表示相同或相似的要素。以下示例性实施例中所描述的实施方式并不代表与本申请相一致的所有实施方式。相反,它们仅是与如所附权利要求书中所详述的、本申请的一些方面相一致的装置和方法的例子。Exemplary embodiments will be described in detail herein, examples of which are illustrated in the accompanying drawings. Where the following description refers to the drawings, the same numerals in different drawings refer to the same or similar elements unless otherwise indicated. The implementations described in the illustrative examples below are not intended to represent all implementations consistent with this application. Rather, they are merely examples of apparatus and methods consistent with some aspects of the present application as recited in the appended claims.
本申请中术语“第一”“第二”等字样用于对作用和功能基本相同的相同项或相似项进行区分,应理解,“第一”、“第二”、“第n”之间不具有逻辑或时序上的依赖关系,也不对数量和执行顺序进行限定。还应理解,尽管以下描述使用术语第一、第二等来描述各种元素,但这些元素不应受术语的限制。In this application, the terms "first", "second" and other words are used to distinguish the same or similar items with basically the same function and function, and it should be understood that between "first", "second" and "nth" There are no logical or timing dependencies, and no restrictions on the number and execution order. It will also be understood that, although the following description uses the terms first, second, etc. to describe various elements, these elements should not be limited by the terms.
这些术语只是用于将一个元素与另一个元素区别开。例如,在不脱离各种示例的范围的情况下,第一存储节点能够被称为第二存储节点,并且类似地,第二存储节点也能够被称为第一存储节点。第一存储节点和第二存储节点都可以是存储节点,并且在某些情况下,可以是单独且不同的存储节点。These terms are only used to distinguish one element from another. For example, a first storage node could be termed a second storage node, and, similarly, a second storage node could be termed a first storage node, without departing from the scope of the various examples. Both the first storage node and the second storage node may be storage nodes, and in some cases may be separate and distinct storage nodes.
其中,至少一个是指一个或一个以上,例如,至少一个存储节点可以是一个存储节点、两个存储节点、三个存储节点等任意大于等于一的整数个存储节点。而多个是指两个或者两个以上,例如,多个存储节点可以是两个存储节点、三个存储节点等任意大于等于二的整数个存储节点。Wherein, at least one refers to one or more than one, for example, at least one storage node may be any integer number of storage nodes greater than or equal to one, such as one storage node, two storage nodes, and three storage nodes. The multiple refers to two or more than two. For example, the multiple storage nodes may be any integer number of storage nodes greater than or equal to two, such as two storage nodes, three storage nodes, or the like.
在介绍本申请实施例之前,需要引入一些云技术领域内的基本概念:Before introducing the embodiments of this application, it is necessary to introduce some basic concepts in the field of cloud technology:
云技术(Cloud Technology):是指在广域网或局域网内将硬件、软件、网络等系列资源统一起来,实现数据的计算、储存、处理和共享的一种托管技术,也即是基于云计算商业模式应用的网络技术、信息技术、整合技术、管理平台技术、应用技术等的总称,可以组成资源池,按需所用,灵活便利。云计算技术将变成云技术领域的重要支撑。技术网络系统的后台服务需要大量的计算、存储资源,如视频网站、图片类网站和更多的门户网站。伴随着互联网行业的高度发展和应用,将来每个物品都有可能存在自己的识别标志,都需要传输到后台系统进行逻辑处理,不同程度级别的数据将会分开处理,各类行业数据皆需要强大的系统后盾支撑,均能通过云计算来实现。Cloud Technology: It refers to a hosting technology that unifies hardware, software, network and other series of resources in a wide area network or a local area network to realize the calculation, storage, processing and sharing of data, that is, a business model based on cloud computing The general term for applied network technology, information technology, integration technology, management platform technology, and application technology, etc., can form a resource pool, which can be used on demand and is flexible and convenient. Cloud computing technology will become an important support in the field of cloud technology. Background services of technical network systems require a lot of computing and storage resources, such as video websites, picture websites and more portal websites. With the high development and application of the Internet industry, in the future, each item may have its own identification mark, which needs to be transmitted to the back-end system for logical processing. Data of different levels will be processed separately, and all kinds of industry data need to be strong. The system backing support can be realized through cloud computing.
云存储(Cloud Storage):是在云计算概念上延伸和发展出来的一个新的概念,分布式云存储系统(以下简称存储系统)是指通过集群应用、网格技术以及分布存储文件系统等功能,将网络中大量各种不同类型的存储设备(存储设备也称之为存储节点)通过应用软件或应用接口集合起来协同工作,共同对外提供数据存储和业务访问功能的一个存储系统。Cloud Storage: It is a new concept extended and developed in the concept of cloud computing. Distributed cloud storage system (hereinafter referred to as storage system) refers to the functions of cluster application, grid technology and distributed storage file system. , a storage system that integrates a large number of different types of storage devices (also called storage nodes) in the network through application software or application interfaces to work together to provide external data storage and business access functions.
数据库(Database):简而言之可视为一种电子化的文件柜,也即是存储电子文件的处所,用户可以对文件中的数据进行新增、查询、更新、删除等操作。所谓“数据库”是以一定方式储存在一起、能与多个用户共享、具有尽可能小的冗余度、与应用程序彼此独立的数据集合。Database: In short, it can be regarded as an electronic filing cabinet, that is, a place where electronic files are stored. Users can add, query, update, delete and other operations on the data in the file. The so-called "database" is a collection of data that is stored together in a certain way, can be shared with multiple users, has as little redundancy as possible, and is independent of applications.
本申请实施例所涉及的分布式数据库系统可以为基于多版本并发控制(Multi-Version Concurrency Control,MVCC)的任一类型的数据库系统。在本申请实施例中,对该分布式数据库系统的类型不作具体限定。The distributed database system involved in the embodiments of the present application may be any type of database system based on multi-version concurrency control (Multi-Version Concurrency Control, MVCC). In this embodiment of the present application, the type of the distributed database system is not specifically limited.
在分布式数据库系统中可以包括至少一个节点设备,每个节点设备的数据库中可以存储有多个数据表,每个数据表可以用于存储一个或多个数据项(也称为变量版本)。其中,节点设备的数据库可以为任一类型的分布式数据库,可以包括关系型数据库或者非关系型数据库中至少一项,例如结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language,SQL)数据库、NoSQL、NewSQL(泛指各种新式的可拓展/高性能数据库)等,在本申请实施例中对数据库的类型不作具体限定。The distributed database system may include at least one node device, and the database of each node device may store multiple data tables, and each data table may be used to store one or more data items (also called variable versions). The database of the node device may be any type of distributed database, and may include at least one of a relational database or a non-relational database, such as Structured Query Language (SQL) database, NoSQL, NewSQL (pan- Refers to various new scalable/high-performance databases), etc., and the types of databases are not specifically limited in the embodiments of this application.
在一些实施例中,本申请实施例还可以应用于一种基于区块链技术的分布式数据库系统(以下简称为“区块链系统”),上述区块链系统在本质上属于一种去中心化式的分布式数据库系统,采用共识算法保持区块链上不同节点设备所记载的账本数据一致,通过密码算法保证不同节点设备之间账本数据的加密传送以及不可篡改,通过脚本系统来拓展账本功能,通过网络路由来进行不同节点设备之间的相互连接。In some embodiments, the embodiments of the present application can also be applied to a distributed database system based on blockchain technology (hereinafter referred to as "blockchain system"), and the above blockchain system is essentially a kind of blockchain system. The centralized distributed database system adopts the consensus algorithm to keep the ledger data recorded by different node devices on the blockchain consistent, and ensures the encrypted transmission of ledger data between different node devices and cannot be tampered with through the cryptographic algorithm, and can be expanded through the script system The ledger function is used to connect different node devices through network routing.
在区块链系统中可以包括一条或多条区块链,区块链是一串使用密码学方法相关联产生的数据块,每一个数据块中包含了一批次网络交易的信息,用于验证其信息的有效性(防伪)和生成下一个区块。A blockchain system can include one or more blockchains. A blockchain is a series of data blocks that are associated with cryptographic methods. Each data block contains a batch of network transaction information, which is used for Verify the validity of its information (anti-counterfeiting) and generate the next block.
区块链系统中节点设备之间可以组成点对点(Peer To Peer,P2P)网络,P2P协议是一个运行在传输控制协议(Transmission Control Protocol,TCP)协议之上的应用层协议。在区块链系统中,任一节点设备可以具备如下功能:1)路由,节点设备具有的基本功能,用于支持节点设备之间的通信;2)应用,用于部署在区块链中,根据实际业务需求而实现特定业务,记录实现功能相关的数据形成账本数据,在账本数据中携带数字签名以表示数据来源,将账本数据发送至区块链系统中的其他节点设备,供其他节点设备在验证账本数据来源以及完整性成功时,将账本数据添加至临时区块中,其中,应用实现的业务可以包括钱包、共享账本、智能合约等;3)区块链,包括一系列按照先后的时间顺序相互接续的区块,新区块一旦加入到区块链中就不会再被移除,区块中记录了区块链系统中节点设备提交的账本数据。A peer-to-peer (P2P) network can be formed between node devices in a blockchain system. The P2P protocol is an application layer protocol running on top of the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) protocol. In the blockchain system, any node device can have the following functions: 1) routing, the basic functions of node devices, used to support communication between node devices; 2) applications, used to deploy in the blockchain, Implement specific services according to actual business needs, record data related to the realization of functions to form ledger data, carry digital signatures in the ledger data to indicate the source of the data, and send the ledger data to other node devices in the blockchain system for other node devices. When verifying the source and integrity of the ledger data is successful, the ledger data is added to the temporary block, in which the business implemented by the application can include wallets, shared ledger, smart contracts, etc.; 3) Blockchain, including a series of sequential Blocks that follow each other in time sequence. Once a new block is added to the blockchain, it will not be removed. The block records the ledger data submitted by node devices in the blockchain system.
在一些实施例中,每个区块中可以包括本区块存储交易记录的哈希值(本区块的哈希值)以及前一区块的哈希值,各区块通过哈希值连接形成区块链,另,区块中还可以包括有区块生成时的时间戳等信息。In some embodiments, each block may include the hash value of the transaction record stored in the current block (the hash value of the current block) and the hash value of the previous block, and each block is formed by connecting the hash values. In addition, the block can also include information such as the timestamp when the block was generated.
下面对本申请实施例所涉及到的一些基本术语进行介绍:Some basic terms involved in the embodiments of the present application are introduced below:
多副本异构:同一份数据的多个副本在磁盘上采取了不同的存储结构。例如,一个副本是按照行存格式对数据进行存储,每一条存储记录是table的一整行数据的内容。一个副本是按照列存格式对数据进行存储,每一条存储记录是table一行数据的某个或某些列值的内容。Multi-copy heterogeneity: Multiple copies of the same data take different storage structures on disk. For example, a copy stores data according to the row storage format, and each storage record is the content of a whole row of data in the table. A copy stores data according to the column storage format, and each storage record is the content of one or some column values of a row of data in the table.
数据分片:是指在分布式数据库系统中数据管理的最小逻辑单元,一个数据分片会拥有多个副本,这多个副本通过多副本一致性协议来控制数据间的副本一致性。在一些实施例中,当分布式数据库系统新建一个数据分片时,将该数据分片的分片信息进行存储。例如,该分片信息包括该数据分片的数据范围、多个副本各自的节点信息以及各个副本的存储模式信息等,本申请实施例对此不作限定。Data sharding: refers to the smallest logical unit of data management in a distributed database system. A data shard will have multiple copies, and these multiple copies will control the copy consistency between data through a multi-copy consistency protocol. In some embodiments, when a distributed database system creates a new data shard, the shard information of the data shard is stored. For example, the fragmentation information includes the data range of the data fragmentation, the node information of each of the multiple copies, and the storage mode information of each copy, etc., which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
事务:事务是数据库系统在执行操作的过程中的一个逻辑单位,由一个有限的数据库操作序列构成,是数据库系统操作的最小执行单位。Transaction: A transaction is a logical unit of the database system in the process of performing operations. It consists of a limited sequence of database operations and is the smallest execution unit of database system operations.
数据项:事务是数据库系统中的一个数据单位,数据项是数据库操作的作用者(或者说被操作的数据对象),在一些实施例中,数据项也称为变量。其中,一个数据项可以是一个元组(tuple)或者记录(record),也可以是一个页面(page)或者一个表(table)对象等。一个数据项可以包含若干数据项版本(在后文中也简称为“版本”),每当事务对数据项进行更新时,则会添加新的数据项版本,数据项的各个数据项版本可以以自然数作为版本号标识,版本号越大,则表示数据项版本越新。在一些实施例中,分布式数据库系统在接收到数据访问请求时,根据数据访问请求所需访问的数据项来确定所属的数据分片,例如,分布式数据库系统可以根据数据项标识来计算数据项所属的数据范围,从而确定该数据项所属的数据分片,本申请实施例对此不作限定。Data item: A transaction is a data unit in a database system, and a data item is an actor (or a data object to be operated) of database operations. In some embodiments, a data item is also called a variable. Wherein, a data item may be a tuple (tuple) or a record (record), or may be a page (page) or a table (table) object and so on. A data item can contain several data item versions (also referred to as "versions" in the following text). Whenever a transaction updates a data item, a new data item version will be added. Each data item version of a data item can be a natural number. As a version number identifier, the larger the version number, the newer the data item version. In some embodiments, when receiving a data access request, the distributed database system determines the data shard to which it belongs according to the data item to be accessed by the data access request. For example, the distributed database system can calculate the data according to the data item identifier. The data range to which the item belongs, so as to determine the data slice to which the data item belongs, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
操作:一个数据库操作由操作类型、事务、数据项版本三部分构成,其中,操作类型可以包括读(Read,R)和写(Write,W)两种。Operation: A database operation consists of three parts: operation type, transaction, and data item version. The operation type can include read (Read, R) and write (Write, W).
分布式共识:共识是分布式系统最重要的抽象之一,具体是指分布式系统中所有的节点就某一项提议达成一致。即一个或多个进程对某个值进行提议后,采用一种全体认可的方法,使分布式系统中所有进程对这个值达成一致意见。Distributed Consensus: Consensus is one of the most important abstractions of distributed systems, which means that all nodes in a distributed system agree on a proposal. That is, after one or more processes propose a certain value, a method of unanimous approval is adopted to make all processes in the distributed system reach an agreement on this value.
Raft:一种分布式共识协议,用于管理日志一致性,是一种在工程上使用较为广泛的一致性算法,具有强一致性、去中心化、易于理解和开发实现等特点。Raft将分布式系统中的角色分为领导者(Leader)、跟从者(Follower)和候选者(Candidate)。在一个Raft集群中,有且只有一个Leader节点(也可以称为主节点),该Leader节点负责处理请求,并把数据同步到Follower节点(也可以称为从节点)。同时,Raft提供了完善的错误处理机制,从而保证了数据的高可用性。Raft: A distributed consensus protocol for managing log consistency. It is a consensus algorithm widely used in engineering. It has the characteristics of strong consistency, decentralization, easy understanding and development and implementation. Raft divides the roles in distributed systems into leaders, followers, and candidates. In a Raft cluster, there is only one leader node (also called master node), which is responsible for processing requests and synchronizing data to follower nodes (also called slave nodes). At the same time, Raft provides a complete error handling mechanism to ensure the high availability of data.
Leader节点:Raft协议通过选举机制来选出Leader节点,负责接受终端请求和日志复制,Leader节点接收请求后,将其写入自己的日志并向Follower节点同步请求日志,当日志同步到大多数节点上后告诉Follower节点提交日志。其中,Leader节点在任期内采用“心跳”机制以通知Follower节点该Leader节点仍在正常工作。Leader node: The Raft protocol selects the leader node through the election mechanism, which is responsible for accepting terminal requests and log replication. After the leader node receives the request, it writes it to its own log and synchronizes the request log to the follower node. When the log is synchronized to most nodes After going up, tell the Follower node to submit the log. Among them, the leader node adopts the "heartbeat" mechanism during the term of office to notify the follower node that the leader node is still working normally.
Follower节点:用于接受并持久化Leader同步的日志,在Leader告之日志可以提交之后,提交日志。其中,Follower节点在选举超时时间内没有收到Leader节点发送的“心跳”,就会转换状态为Candidate状态,并向其他节点发送消息以发起新一轮Leader节点的选举。Follower node: It is used to accept and persist the logs synchronized by the Leader. After the Leader informs that the logs can be submitted, the logs are submitted. Among them, if the follower node does not receive the "heartbeat" sent by the leader node within the election timeout period, it will switch the state to the Candidate state and send a message to other nodes to initiate a new round of leader node election.
MVCC:是数据库系统常用的一种并发控制。意图解决读写锁造成的多个或长时间的读操作阻塞写操作的问题。每个事务读到的数据项都是一个快照。写操作不覆盖已有数据项,而是创建一个新的数据项版本,直至操作提交时才变为可见。MVCC: It is a kind of concurrency control commonly used in database systems. It is intended to solve the problem of multiple or long-term read operations blocking write operations caused by read-write locks. The data item read by each transaction is a snapshot. A write operation does not overwrite an existing data item, but instead creates a new version of the data item that is not visible until the operation commits.
全态数据:分布式数据库系统中的数据基于状态属性,可以包括三种状态:当前态、过渡态和历史态,该三种状态合称为“数据的全态”,简称全态数据,全态数据中的各个不同状态属性,可以用于标识数据在其生命周期轨迹中所处的状态。其中,当前态(CurrentState):元组的最新版本的数据,是处于当前阶段的数据,换言之,处于当前阶段的数据的状态,称为当前态。过渡态(Transitional State):不是元组的最新的版本也不是历史态版本,处于从当前态向历史态转变的过程中,处于过渡态的数据,称为半衰数据。历史态(Historical State):元组在历史上的一个状态,其值是旧值,不是当前值。处于历史阶段的数据的状态,称为历史态。一个元组的历史态,可以有多个,反映了数据的状态变迁的过程。处于历史态的数据,只能被读取而不能被修改或删除。Full state data: The data in the distributed database system is based on state attributes, which can include three states: current state, transition state and historical state. These three states are collectively called "full state of data", referred to as full state data. Different state attributes in state data can be used to identify the state the data is in in its life cycle trajectory. Among them, the current state (CurrentState): the data of the latest version of the tuple is the data in the current stage, in other words, the state of the data in the current stage is called the current state. Transitional State: It is neither the latest version of the tuple nor the historical state version. In the process of transitioning from the current state to the historical state, the data in the transitional state is called half-dead data. Historical State: A state in the history of the tuple whose value is the old value, not the current value. The state of the data in the historical stage is called the historical state. There can be multiple historical states of a tuple, reflecting the state transition process of the data. The data in the historical state can only be read and cannot be modified or deleted.
元数据:又称中介数据、中继数据,是指描述数据的数据(Data about Data),是关于数据的组织、数据域及其关系的信息,主要是描述数据属性(Property)的信息,用来支持如指示数据分片的分片信息、存储位置、历史数据、资源查找、文件记录等功能。Metadata: Also known as intermediary data and relay data, it refers to the data that describes the data (Data about Data), which is the information about the organization of the data, the data domain and its relationship, mainly the information describing the data properties (Property). To support functions such as fragmentation information indicating data fragmentation, storage location, historical data, resource search, file recording, etc.
状态机(State Machine):是有限状态自动机的简称,是现实事物运行规则抽象而成的一个数学模型。State Machine: It is the abbreviation of finite state automata, which is a mathematical model abstracted from the running rules of real things.
下面对本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法的实施环境进行介绍。The implementation environment of the data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application is introduced below.
图1是本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法的实施环境示意图。如图1所示,本申请实施例可以应用于分布式数据库系统,该系统中可以包括网关服务器101、全局时间戳生成集群102、分布式存储集群103以及分布式协调系统104(例如ZooKeeper),在分布式存储集群103中可以包括数据节点设备和协调节点设备。FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an implementation environment of a data access method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 1 , the embodiments of the present application can be applied to a distributed database system, and the system can include a
其中,网关服务器101用于接收外部的读写请求,并将读写请求对应的读写事务分发至分布式存储集群103,比如,用户在登录终端上的应用终端之后,触发应用终端生成读写请求,调用分布式数据库系统提供的应用程序编程接口(Application ProgrammingInterface,API)将该读写请求发送至网关服务器101,比如,该API可以是MySQL API(一种关系型数据库系统提供的API)。The
在一些实施例中,该网关服务器101可以与分布式存储集群103中的任一个数据节点设备或任一协调节点设备合并在同一个物理机上,也即是,让某个数据节点设备或协调节点设备充当网关服务器101。In some embodiments, the
全局时间戳生成集群102用于生成全局事务的全局提交时间戳(GlobalTimestamp,Gts),该全局事务又称为分布式事务,是指涉及到多个数据节点设备的事务,例如全局读事务可以涉及到对多个数据节点设备上存储数据的读取,又例如,全局写事务可以涉及到对多个数据节点设备上的数据写入。全局时间戳生成集群102在逻辑上可以视为一个单点,但在一些实施例中可以通过一主三从的架构来提供具有更高可用性的服务,采用集群的形式来实现该全局提交时间戳的生成,可以防止单点故障,也就规避了单点瓶颈问题。The global
可选地,全局提交时间戳是一个在分布式数据库系统中全局唯一且单调递增的时间戳标识,能够用于标志每个事务全局提交的顺序,以此来反映出事务之间在真实时间上的先后关系(事务的全序关系),全局提交时间戳可以采用物理时钟、逻辑时钟、混合物理时钟或者混合逻辑时钟(Hybrid Logical Clock,HLC)中至少一项,本申请实施例不对全局提交时间戳的类型进行具体限定。Optionally, the global commit timestamp is a globally unique and monotonically increasing timestamp identifier in the distributed database system, which can be used to mark the order of the global commit of each transaction, so as to reflect the real time between transactions. The sequence relationship (the total order relationship of the transaction), the global submission time stamp can be at least one of a physical clock, a logical clock, a hybrid physical clock, or a hybrid logical clock (Hybrid Logical Clock, HLC). The type of stamp is specifically limited.
在一个示例性场景中,全局提交时间戳可以采用混合物理时钟的方式生成,全局提交时间戳可以由八字节组成,其中,前44位可以为物理时间戳的取值(也即Unix时间戳,精确到毫秒),这样共计可以表示244个无符号整数,因此理论上一共可以表示约为年的物理时间戳,其中,后20位可以为在某一毫秒内的单调递增计数,这样每毫秒有220个(约100万个)计数,基于上述数据结构,如果单机(任一数据节点设备)的事务吞吐量为10w/s,理论上可以支持包含1万个节点设备的分布式存储集群103,同时,全局提交时间戳的数量代表了系统理论上所能支持的总事务数,基于上述数据结构,理论上系统可以支持(244-1)*220个事务。这里仅仅是对一种全局提交时间戳的定义方法的示例性说明,根据业务需求的不同,可以对全局提交时间戳的位数进行扩展,以满足对更多的节点数、事务处理数的支持,本申请实施例不对全局提交时间戳的定义方法进行具体限定。In an exemplary scenario, the global commit timestamp can be generated by mixing physical clocks, and the global commit timestamp can be composed of eight bytes, wherein the first 44 bits can be the value of the physical timestamp (that is, the Unix timestamp , accurate to milliseconds), so that a total of 244 unsigned integers can be represented, so theoretically a total of about The physical timestamp of the year, of which the last20 bits can be counted monotonically within a certain millisecond, so that there are 220 (about 1 million) counts per millisecond. Based on the above data structure, if a single machine (any data node) The transaction throughput of the device) is 10w/s, which can theoretically support a distributed
在一些实施例中,该全局时间戳生成集群102可以是物理独立的,也可以和分布式协调系统104(例如ZooKeeper)合并到一起。In some embodiments, the global
其中,分布式存储集群103可以包括数据节点设备和协调节点设备,每个协调节点设备可以对应于至少一个数据节点设备,数据节点设备与协调节点设备的划分是针对不同事务而言的,以某一全局事务为例,全局事务的发起节点可以称为协调节点设备,全局事务所涉及的其他节点设备称为数据节点设备,数据节点设备或协调节点设备的数量可以是一个或多个,本申请实施例不对分布式存储集群103中数据节点设备或协调节点设备的数量进行具体限定。由于本实施例所提供的分布式数据库系统中缺乏全局事务管理器,因此在该系统中可以采用XA(eXtended Architecture,X/Open组织分布式事务规范)/2PC(Two-Phase Commit,二阶段提交)技术来支持跨节点的事务(全局事务),保证跨节点写操作时数据的原子性和一致性,此时,协调节点设备用于充当2PC算法中的协调者,而该协调节点设备所对应的各个数据节点设备用于充当2PC算法中的参与者。The distributed
可选地,每个数据节点设备或协调节点设备可以是单机设备,也可以采用主备结构(也即是为一主多备集群),如图1所示,以节点设备(数据节点设备或协调节点设备)为一主两备集群为例进行示意,每个节点设备中包括一个主机和两个备机,可选地,每个主机或备机都对应配置有代理(agent)设备,代理设备可以与主机或备机是物理独立的,当然,代理设备还可以作为主机或备机上的一个代理模块,以节点设备1为例,节点设备1包括一个主数据库及代理设备(主database+agent,简称主DB+agent),此外还包括两备数据库及代理设备(备database+agent,简称备DB+agent)。Optionally, each data node device or coordinating node device can be a stand-alone device, or a master-standby structure (that is, a master-multiple-standby cluster), as shown in FIG. Coordination node device) is an example of one master and two standby clusters for illustration, each node device includes one host and two standby machines, optionally, each host or standby machine is correspondingly configured with an agent device. The device can be physically independent from the host or standby. Of course, the agent device can also be used as an agent module on the host or standby. Taking
在一个示例性场景中,每个节点设备所对应的主机或备机的数据库实例集合称为一个SET(集合),例如,假设某一节点设备为单机设备,那么该节点设备的SET仅为该单机设备的数据库实例,假设某一节点设备为一主两备集群,那么该节点设备的SET为主机数据库实例以及两个备机数据库实例的集合,此时可以基于云数据库的强同步技术来保证主机的数据与备机的副本数据之间的一致性,可选地,每个SET可以进行线性扩容,以应付大数据场景下的业务处理需求,在一些金融业务场景下,全局事务通常是指跨SET的转账。In an exemplary scenario, the set of database instances of the host or standby machine corresponding to each node device is called a SET (set). For example, if a node device is a stand-alone device, the SET of the node device is only the A database instance of a stand-alone device, assuming that a node device is a cluster with one master and two backups, then the SET of the node device is the set of the master database instance and the two backup database instances. At this time, it can be guaranteed based on the strong synchronization technology of cloud database. The consistency between the data of the host and the copy data of the standby machine. Optionally, each SET can be linearly expanded to meet the business processing requirements in big data scenarios. In some financial business scenarios, global transactions usually refer to Transfers across SETs.
分布式协调系统104可以用于对网关服务器101、全局时间戳生成集群102或者分布式存储集群103中至少一项进行管理,可选地,技术人员可以通过终端上的调度器(scheduler)访问该分布式协调系统104,从而基于前端的调度器来控制后端的分布式协调系统104,实现对各个集群或服务器的管理。例如,技术人员可以通过调度器来控制ZooKeeper将某一个节点设备从分布式存储集群103中删除,也即是使得某一个节点设备失效。The distributed
上述图1仅是提供了一种轻量级的全局事务处理的架构图,是一种类分布式数据库系统。整个分布式数据库系统可以看作是共同维护一个逻辑上的大表,这个大表中存储的数据通过主键被打散到分布式存储集群103中的各个节点设备中,每个节点设备上存储的数据是独立于其他节点设备的,从而实现了节点设备对逻辑大表的水平切分。由于在上述系统中能够将各个数据库中各个数据表水平切分后进行分布式地存储,因此,这种系统也可以形象地称为具有“分库分表”的架构。The above-mentioned FIG. 1 is only an architecture diagram that provides a lightweight global transaction processing, which is a kind of distributed database system. The entire distributed database system can be regarded as jointly maintaining a large logical table. The data stored in this large table is scattered to each node device in the distributed
在一些实施例中,上述网关服务器101、全局时间戳生成集群102、分布式存储集群103以及分布式协调系统104所构成的分布式数据库系统,可以视为一种向用户终端提供数据服务的服务器,该服务器可以是独立的物理服务器,也可以是多个物理服务器构成的服务器集群或者分布式系统,还可以是提供云服务、云数据库、云计算、云函数、云存储、网络服务、云通信、中间件服务、域名服务、安全服务、内容分发网络(Content DeliveryNetwork,CDN)、以及大数据和人工智能平台等基础云计算服务的云服务器。可选地,上述用户终端可以是智能手机、平板电脑、笔记本电脑、台式计算机、智能音箱、智能手表等,但并不局限于此。终端以及服务器可以通过有线或无线通信方式进行直接或间接地连接,本申请在此不做限制。In some embodiments, the distributed database system formed by the
基于上述实施环境,在一些实施例中,上述分布式数据库系统可以为混合事务和分析处理(Hybrid Transaction and Analytical Process,HTAP)数据库系统。HTAP数据库系统是一种支持联机事务处理(On-Line Transaction Processing,OLTP)业务和联机分析处理(On-Line Analytical Processing,OLAP)业务同时处理的数据库系统。换言之,HTAP数据库系统是一种既支持在线更新任务、又支持在线分析查询请求的数据库系统。需要说明的是,HTAP数据库避免了在线与离线数据的大量数据交互,其创新的计算存储框架也可以支持弹性扩容,更好的应对高并发带来的挑战。Based on the foregoing implementation environment, in some embodiments, the foregoing distributed database system may be a hybrid transaction and analytical processing (Hybrid Transaction and Analytical Process, HTAP) database system. The HTAP database system is a database system that supports simultaneous processing of online transaction processing (On-Line Transaction Processing, OLTP) services and online analytical processing (On-Line Analytical Processing, OLAP) services. In other words, the HTAP database system is a database system that supports both online update tasks and online analysis of query requests. It should be noted that the HTAP database avoids a large amount of data interaction between online and offline data, and its innovative computing and storage framework can also support elastic expansion to better cope with the challenges brought by high concurrency.
下面参考图2,对本申请实施例提供的一种HTAP数据库系统的架构进行说明。图2是本申请实施例提供的一种HTAP数据库系统的架构示意图。如图2所示,HTAP数据库系统可以包括四个部分:计算层201、分布式一致性协议层202、存储层203以及元数据管理层204。其中,The following describes the architecture of an HTAP database system provided by an embodiment of the present application with reference to FIG. 2 . FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of the architecture of an HTAP database system provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 2 , the HTAP database system may include four parts: a
计算层201具有下述几种功能:The
1)连接处理功能,用于根据终端发来的连接请求,与终端建立可靠连接。1) The connection processing function is used to establish a reliable connection with the terminal according to the connection request sent by the terminal.
2)查询计划的制定功能,用于接收终端发送的数据访问请求,并对该数据访问请求进行语法分析等处理,从而生成查询计划(此部分内容会在后续实施例中进行详细说明,故在此不赘述)。2) The function of formulating a query plan, which is used to receive the data access request sent by the terminal, and perform grammatical analysis and other processing on the data access request, thereby generating a query plan (this part of the content will be described in detail in the subsequent embodiments, so in the This is not repeated).
3)执行功能(也可以称为封装功能),用于将数据访问请求涉及的操作用事务进行封装,并根据查询计划,将数据访问请求发送到对应的节点。3) The execution function (also called the encapsulation function) is used to encapsulate the operations involved in the data access request with transactions, and according to the query plan, send the data access request to the corresponding node.
在一些实施例中,计算层201配置有至少一个计算节点,用于实现上述功能,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, the
分布式一致性协议层202具有下述几种功能:The distributed
1)日志同步功能,用于控制数据同步,保证各个副本之间的数据一致性。可选地,该日志同步功能用于保证从节点执行读操作时,从节点具有与主节点同步的数据(此部分内容会在后续实施例中进行详细说明,故在此不赘述)。1) The log synchronization function is used to control data synchronization and ensure data consistency between copies. Optionally, the log synchronization function is used to ensure that when the slave node performs a read operation, the slave node has data synchronized with the master node (this part of the content will be described in detail in subsequent embodiments, so it is not repeated here).
2)主节点选举功能,用于在主节点失效时,重新选举主节点(此部分内容会在后续实施例中进行详细说明,故在此不赘述)。2) The master node election function is used to re-elect the master node when the master node fails (this part of the content will be described in detail in subsequent embodiments, so it will not be repeated here).
3)状态机安全功能,用于接收和处理计算层201的数据访问请求,控制访问存储层203中的数据(此部分内容会在后续实施例中进行详细说明,故在此不赘述)。3) The state machine security function is used to receive and process data access requests from the
在一些实施例中,上述分布式一致性协议层202的功能由计算层201中所配置的至少一个计算节点实现,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, the functions of the above-mentioned distributed
存储层203具有下述几种功能:The
1)数据访问请求处理功能,用于接收和处理分布式一致性协议层202的数据访问请求。1) The data access request processing function is used to receive and process the data access request of the distributed
2)副本管理功能,用于管理数据的多个副本,保证各个副本之间的数据一致性。2) The copy management function is used to manage multiple copies of data to ensure data consistency between each copy.
在一些实施例中,存储层203包括状态机和格式转换器。其中,状态机中具有不同存储模式的数据分片,一个数据分片存在多个副本,存放于不同的存储节点中,副本之间按照分布式一致性协议,通过日志(Log)进行数据同步。Log中的数据会经过日志回放的步骤持久化到状态机中,便于数据访问。格式转换器用于按照指定的存储模式,将数据转换成对应的存储格式,再由状态机进行持久化存储。例如,数据的多个副本的存储模式为行存格式和列存格式,本申请实施例对此不作限定。需要说明的是,图2所示的存储模式的组合方式仅为示意性地,各存储模式的副本数量可以依照系统和负载的实际情况进行组合配置,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments,
在一些实施例中,存储层203配置有至少一个存储节点,用于实现上述功能,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, the
元数据管理层204具有下述几种功能:The
1)记录功能,用于记录数据分片的分片信息以及数据各个副本的日志同步情况。1) The recording function is used to record the fragmentation information of the data fragmentation and the log synchronization of each copy of the data.
2)路由功能,用于为计算层201和存储层203提供路由服务。2) The routing function is used to provide routing services for the
需要说明的是,在上述图2所示的架构中,计算节点和存储节点的数量仅为示意性地,在一些实施例中,该HTAP数据库系统还可以包括更多或更少的计算节点和存储节点,本申请实施例对此不作限定。通过采用这种计算与存储分离的架构,便于改变存储节点的分布和配置,从而增加了分布式数据库系统的灵活性,使得分布式数据库系统适用于多种不同的场景,具有广泛的适用性。It should be noted that in the above architecture shown in FIG. 2 , the numbers of computing nodes and storage nodes are only illustrative, and in some embodiments, the HTAP database system may further include more or less computing nodes and storage nodes. A storage node, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. By adopting this architecture of separation of computing and storage, it is easy to change the distribution and configuration of storage nodes, thereby increasing the flexibility of the distributed database system, making the distributed database system suitable for a variety of different scenarios and having a wide range of applicability.
另外,上述计算层204可以配置有上述图1所示的网关服务器101,且上述图1所示的分布式协调系统104可以用于管理整个HTAP系统,也即是由分布式协调系统104来调度HTAP系统中涉及到的节点设备中的至少一项,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In addition, the
示意性地,上述图2所示的分布式数据库系统具有存储和计算功能。在存储层,系统会对数据进行分片,每个数据分片对应有若干个副本,理论上来说每个副本都提供数据访问功能。对于数据分片的不同副本,其存储模式不一定相同。在计算层,系统会根据分析统计,来判断数据访问请求的类型,从而确定性能更优的副本,考虑负载均衡,将数据访问请求发送给被选定的副本。该副本所在节点执行数据访问请求后,将数据返回给计算层,再经由计算层返回给终端。对于上层用户来说,并不会感知到底层存储模式的异构,而是由分布式数据库系统本身完成多副本异构的管理。基于这种分布式数据库系统,对数据采用多副本异构数据模型存储及访问的方法,既保证了多副本带来的高可用性以及多副本间的数据一致性,又增加了系统的并发度,提高了系统在混合负载下的性能表现。Illustratively, the distributed database system shown in FIG. 2 above has storage and computing functions. In the storage layer, the system will shard the data, and each data shard corresponds to several copies. In theory, each copy provides data access functions. For different copies of data shards, their storage modes are not necessarily the same. At the computing layer, the system will determine the type of data access request based on analysis and statistics, so as to determine the replica with better performance, consider load balancing, and send the data access request to the selected replica. After the node where the replica is located executes the data access request, the data is returned to the computing layer, and then returned to the terminal via the computing layer. For upper-level users, the heterogeneity of the underlying storage mode is not perceived, but the heterogeneous management of multiple copies is completed by the distributed database system itself. Based on this distributed database system, the multi-copy heterogeneous data model storage and access method for data not only ensures the high availability brought by multiple copies and the data consistency between multiple copies, but also increases the concurrency of the system. Improved system performance under mixed loads.
接下来将以上述图1和图2所示的分布式数据库系统为基础,对本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法进行说明。Next, the data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application will be described based on the distributed database system shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 above.
首先,数据多副本存储是分布式数据库系统中普遍采用的技术,多副本机制可以保证数据高可用性。但目前,分布式数据库系统普遍采用同构的多副本机制,即数据的副本采用相同的组织模型和存储结构。这种存储机制使得用户请求在各个副本上表现性能一样(在不考虑节点负载和硬件差异的情况下)。其次,采用分布式一致性协议管理数据的多个副本,可以保证数据的一致性,但相关分布式一致性协议中严格的主从机制使得所有请求需要集中到一个副本上处理,增加了负载均衡的实现难度,更有可能造成性能瓶颈。再次,在分布式一致性协议(例如Raft)中,在执行读请求时必须先把数据从日志中执行(Apply)到状态机,在执行写请求时必须等待主节点将相关日志执行(Apply)到状态机才会认为写事务成功,这些过程引起较高的时间开销,导致读写操作延迟比较高,使得分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能不佳。First of all, data multi-copy storage is a technology commonly used in distributed database systems, and the multi-copy mechanism can ensure high data availability. But at present, the distributed database system generally adopts the homogeneous multi-copy mechanism, that is, the copy of the data adopts the same organizational model and storage structure. This storage mechanism enables user requests to perform equally across replicas (regardless of node load and hardware differences). Secondly, using a distributed consistency protocol to manage multiple copies of data can ensure data consistency, but the strict master-slave mechanism in the relevant distributed consistency protocol makes all requests need to be processed on one copy, which increases load balancing The implementation difficulty is more likely to cause performance bottlenecks. Again, in a distributed consensus protocol (such as Raft), when executing a read request, the data must first be executed (Apply) from the log to the state machine, and when executing a write request, it must wait for the master node to execute (Apply) the relevant log. It is not until the state machine that the write transaction is considered successful. These processes cause high time overhead, resulting in high latency of read and write operations, and poor data access performance in the distributed database system.
因此,传统的多副本技术并没有充分发挥多副本的性能优势,仅仅只是提高了数据的可用性,同时传统的分布式一致性协议具有读写操作延迟开销高的问题。Therefore, the traditional multi-copy technology does not give full play to the performance advantages of multiple copies, but only improves the availability of data. At the same time, the traditional distributed consensus protocol has the problem of high latency and overhead of read and write operations.
有鉴于此,本申请实施例提供了一种数据访问方法,在综合考虑负载均衡、数据同步状态以及用户请求类型等因素的前提下,为每个数据访问请求选择最合适的副本,从而提升分布式数据库系统整体的访问性能。针对数据读取请求,对管理数据副本所用的分布式一致性协议进行了修改,在保证数据一致性正确的前提下,增加了从节点响应数据读取请求的流程,并提出了基于放宽读索引(Relaxed Read Index,RRI)的数据读取方法,从而增大了系统并发度,加快了数据读取请求的处理速度,提高了分布式数据库系统整体的读性能。针对数据写入请求,对分布式一致性协议的写流程进行了优化,提出了基于提交退回(Commit Return,CR)的数据写入方法,从而提高了数据写入的速度,加快了数据写入请求的返回速度,提高了分布式数据库系统整体的写性能。针对数据读写请求,结合上述基于RRI的数据读取方法和基于CR的数据写入方法,提高了读写事务的处理速度,加快了数据读写请求的返回速度,提高了分布式数据库系统整体的读写性能,提高了系统并发度,减少了磁盘和网络带宽的占用,有效提高了系统的吞吐量。In view of this, the embodiments of the present application provide a data access method, which selects the most suitable copy for each data access request under the premise of comprehensively considering factors such as load balancing, data synchronization status, and user request type, thereby improving distribution. The overall access performance of the database system. For data read requests, the distributed consistency protocol used to manage data copies is modified. On the premise of ensuring correct data consistency, the process of responding to data read requests from slave nodes is added, and a method based on relaxed read indexes is proposed. (Relaxed Read Index, RRI) data reading method, thereby increasing the concurrency of the system, speeding up the processing speed of data read requests, and improving the overall read performance of the distributed database system. For data writing requests, the writing process of the distributed consistency protocol is optimized, and a data writing method based on Commit Return (CR) is proposed, thereby improving the speed of data writing and speeding up data writing. The return speed of the request improves the overall write performance of the distributed database system. For data read and write requests, combined with the above RRI-based data read method and CR-based data write method, the processing speed of read and write transactions is improved, the return speed of data read and write requests is accelerated, and the overall distributed database system is improved. The read and write performance improves the system concurrency, reduces the occupation of disk and network bandwidth, and effectively improves the system throughput.
下面将通过几个实施例,以不同类型的数据访问请求为例,对本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法进行说明。在下述实施例中,针对不同的数据访问请求,提供了相应的数据访问方法,从而有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。The data access methods provided by the embodiments of the present application will be described below by taking different types of data access requests as examples through several embodiments. In the following embodiments, corresponding data access methods are provided for different data access requests, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
图3是本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法的流程图,如图3所示,该实施例应用于分布式数据库系统,该分布式数据库系统包括计算节点和多个存储节点。示意性地,在图3所示的实施例中,该数据访问方法适用于数据访问请求的请求类型为数据读取请求,该数据访问方法应用于如图2所示的HTAP数据库系统,以计算节点和存储节点之间的交互为例来进行说明。该实施例包括下述步骤。FIG. 3 is a flowchart of a data access method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 3 , the embodiment is applied to a distributed database system, and the distributed database system includes a computing node and a plurality of storage nodes. Schematically, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 3 , the data access method is applicable to the request type of the data access request as a data read request, and the data access method is applied to the HTAP database system shown in FIG. 2 to calculate The interaction between nodes and storage nodes is taken as an example to illustrate. This embodiment includes the following steps.
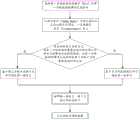
301、计算节点响应于第一数据读取请求,确定该第一数据读取请求的第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片,基于该第一数据分片,从多个存储节点中确定多个第一存储节点,该多个第一存储节点用于存储该第一目标数据的多个副本。301. In response to the first data read request, the computing node determines a first data fragment to which the first target data of the first data read request belongs, and based on the first data fragment, determines the number of data fragments from the plurality of storage nodes. a plurality of first storage nodes, and the plurality of first storage nodes are used for storing multiple copies of the first target data.
在本申请实施例中,第一数据读取请求用于请求读取第一目标数据。可选地,该第一目标数据为当前态数据或历史态数据,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In this embodiment of the present application, the first data read request is used to request to read the first target data. Optionally, the first target data is current state data or historical state data, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
可选地,计算节点对第一数据读取请求进行解析,得到第一目标数据的数据项标识,根据该数据项标识,确定该第一目标数据在当前分布式数据库系统中所属的第一数据分片,并根据该第一数据分片的分片信息,从多个存储节点中确定多个第一存储节点。Optionally, the computing node parses the first data read request to obtain a data item identifier of the first target data, and determines the first data to which the first target data belongs in the current distributed database system according to the data item identifier. sharding, and according to the sharding information of the first data shard, determine a plurality of first storage nodes from the plurality of storage nodes.
可选地,该分布式数据库系统包括元数据管理层,计算节点在确定第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片后,根据该第一数据分片的分片信息,向元数据管理层发送信息获取请求,并接收该元数据管理层返回的该第一数据分片的分片信息。例如,该分片信息包括:第一目标数据的多个副本各自对应的存储节点的节点信息(包括节点类型、节点负载、与计算节点之间的物理距离等等)、该多个副本各自对应的存储模式的存储信息、该多个副本的数据范围以及主存储节点的节点信息等,本申请实施例对于第一数据分片的分片信息的具体内容不作限定。Optionally, the distributed database system includes a metadata management layer, and after determining the first data fragment to which the first target data belongs, the computing node sends the data to the metadata management layer according to fragmentation information of the first data fragment. information acquisition request, and receive the fragmentation information of the first data fragment returned by the metadata management layer. For example, the sharding information includes: node information (including node type, node load, physical distance from the computing node, etc.) of the storage nodes corresponding to the multiple copies of the first target data, and the multiple copies of the first target data correspond to each other. The storage information of the storage mode, the data range of the multiple copies, and the node information of the primary storage node, etc., the specific content of the fragmentation information of the first data fragmentation is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
302、计算节点基于该第一数据读取请求,从该多个第一存储节点中确定第一目标存储节点,向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件。302. Based on the first data read request, the computing node determines a first target storage node from the plurality of first storage nodes, and sends the first data read request to the first target storage node, and the first target storage node The data access cost of the node meets the first objective condition.
在本申请实施例中,多个第一存储节点基于分布式一致性协议实现数据一致性。其中,该多个第一存储节点包括主存储节点和至少一个从存储节点,每个第一存储节点均可以响应该第一数据读取请求,以读取对应节点中存储的第一目标数据的副本。可选地,多个第一存储节点基于分布式一致性协议实现数据一致性,例如,该分布式一致性协议为Raft协议,本申请实施例对此不做限定。In the embodiment of the present application, a plurality of first storage nodes implement data consistency based on a distributed consistency protocol. The plurality of first storage nodes include a master storage node and at least one slave storage node, and each first storage node can respond to the first data read request to read the first target data stored in the corresponding node. copy. Optionally, the multiple first storage nodes implement data consistency based on a distributed consistency protocol. For example, the distributed consistency protocol is a Raft protocol, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
可选地,该分布式数据库系统包括元数据管理层,计算节点在确定第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片后,基于该元数据管理层,获取到该第一数据分片的相关信息,并根据该相关信息和第一数据读取请求,从多个第一存储节点中选出数据访问代价符合第一目标条件的存储节点,将该存储节点确定为第一目标存储节点(确定第一目标存储节点的具体实施方式将在后文进行介绍,此处不再赘述),向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求。Optionally, the distributed database system includes a metadata management layer, and after determining the first data fragment to which the first target data belongs, the computing node obtains the relevant information of the first data fragment based on the metadata management layer. , and according to the relevant information and the first data read request, select a storage node whose data access cost meets the first target condition from a plurality of first storage nodes, and determine the storage node as the first target storage node (determine the first target storage node). The specific implementation manner of a target storage node will be introduced later, and will not be repeated here), and the first data read request is sent to the first target storage node.
303、第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求,读取该第一目标数据,向该计算节点发送第一数据读取结果。303. The first target storage node reads the first target data based on the first data read request, and sends the first data read result to the computing node.
在本申请实施例中,该第一目标存储节点在接收到该第一数据读取请求后,基于该第一数据读取请求,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据,并将读取结果发送给计算节点。可选地,该第一目标存储节点根据自身的节点类型和第一目标数据的数据类型,确定相应的读取流程(确定读取流程的具体实施方式将在后文进行介绍,此处不再赘述),并根据该读取流程从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据,并将读取结果发送给计算节点,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In this embodiment of the present application, after receiving the first data read request, the first target storage node reads the first data read request from a state machine corresponding to the first target data based on the first data read request target data, and send the read result to the compute node. Optionally, the first target storage node determines a corresponding read process according to its own node type and the data type of the first target data (the specific implementation of determining the read process will be introduced later, and will not be described here. Repeat), and read the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data according to the reading process, and send the read result to the computing node, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
在本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法中,在分布式数据库系统中,当计算节点接收到数据读取请求时,先根据该数据读取请求的目标数据所属的数据分片,来确定存储有该目标数据的多个副本的多个存储节点,然后按照存储节点访问目标数据的数据访问代价,从这些存储节点中选出符合目标条件的目标存储节点,由该目标存储节点来读取目标数据。上述方法中,由于该目标存储节点是根据数据访问代价来确定的,因此主存储节点和从存储节点都可能成为目标存储节点,避免了由主存储节点处理所有的数据读取请求,从而既保证了多副本带来的高可用性,又提高了数据读取速度,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。In the data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application, in a distributed database system, when a computing node receives a data read request, it first determines the data shards to which the target data of the data read request belongs to determine the stored data. There are multiple storage nodes for multiple copies of the target data, and then according to the data access cost of the storage nodes accessing the target data, a target storage node that meets the target conditions is selected from these storage nodes, and the target storage node reads the target data. . In the above method, since the target storage node is determined according to the data access cost, both the master storage node and the slave storage node may become the target storage node, avoiding the master storage node processing all data read requests, thus ensuring that both It improves the high availability brought by multiple copies, improves the data reading speed, and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
上述图3所示的实施例是对本申请提供的数据访问方法的简要说明,下面结合图4,对本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法进行详细介绍。The above-mentioned embodiment shown in FIG. 3 is a brief description of the data access method provided by the present application. The following describes the data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application in detail with reference to FIG. 4 .
图4是本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法的流程图,如图4所示,该实施例应用于分布式数据库系统,该分布式数据库系统包括计算节点和多个存储节点。示意性地,在图4所示的实施例中,该数据访问方法适用于数据访问请求的请求类型为数据读取请求,该数据访问方法应用于如图2所示的HTAP数据库系统,以计算节点和存储节点之间的交互为例来进行说明。该实施例包括下述步骤。FIG. 4 is a flowchart of a data access method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 4 , the embodiment is applied to a distributed database system, and the distributed database system includes a computing node and a plurality of storage nodes. Schematically, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 , the data access method applicable to the request type of the data access request is a data read request, and the data access method is applied to the HTAP database system shown in FIG. 2 to calculate The interaction between nodes and storage nodes is taken as an example to illustrate. This embodiment includes the following steps.
401、计算节点基于终端发送的连接请求,与终端建立连接。401. The computing node establishes a connection with the terminal based on the connection request sent by the terminal.
在本申请实施例中,计算节点通过无线网络或有线网络与终端相连,终端响应于用户的操作,向计算节点发送连接请求,计算节点接收该连接请求,并基于该连接请求,与终端建立可靠连接。In this embodiment of the present application, the computing node is connected to the terminal through a wireless network or a wired network, the terminal sends a connection request to the computing node in response to the user's operation, the computing node receives the connection request, and based on the connection request, establishes a reliable connection with the terminal connect.
402、计算节点响应于第一数据读取请求,确定该第一数据读取请求的第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片,基于该第一数据分片,从多个存储节点中确定多个第一存储节点,该多个第一存储节点用于存储该第一目标数据的多个副本。402. The computing node determines, in response to the first data read request, a first data fragment to which the first target data of the first data read request belongs, and based on the first data fragment, determines the number of data fragments from the plurality of storage nodes. a plurality of first storage nodes, and the plurality of first storage nodes are used for storing multiple copies of the first target data.
在本申请实施例中,计算节点确定多个第一存储节点的方式与上述步骤301同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, the manner in which the computing node determines a plurality of first storage nodes is the same as that in the foregoing step 301, and thus will not be repeated here.
在一些实施例中,该多个副本的存储模式包括行存模式、列存模式以及交叉模式等,本申请实施例对此不作限定。其中,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。下面对上述涉及到的几种存储模式进行介绍。In some embodiments, the storage modes of the multiple copies include row storage mode, column storage mode, and cross mode, etc., which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node. The following describes several storage modes involved in the above.
第一种、行存模式。The first is the row storage mode.
示意性地,参考表1(表中m和n为正整数),在存储节点的状态机中,每一个数据对应表1中的一行完整的记录,如表1中行(Row)2所示。需要说明的是,在一些实施例中,行存模式的表格中,行序列(也可以称为排序列,本申请对此不作限定)可以根据需求进行调整。例如,以某一个数据为学生成绩为例,该数据表示为学生(学号,姓名,分数),则可以将学号对应的列(Column,Col)、姓名对应的列以及分数对应的列作为主行序列,本申请实施例对此不作限定。Illustratively, referring to Table 1 (where m and n are positive integers), in the state machine of the storage node, each data corresponds to a complete row of records in Table 1, as shown in row (Row) 2 in Table 1. It should be noted that, in some embodiments, in the table in the row storage mode, the row sequence (also referred to as a sorting sequence, which is not limited in this application) can be adjusted according to requirements. For example, taking a certain data as student grades as an example, the data is represented as students (student number, name, score), then the column corresponding to the student number (Column, Col), the column corresponding to the name, and the column corresponding to the score can be used as The main row sequence is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
表1Table 1
第二种、列存模式。The second, column storage mode.
示意性地,参考表2(表中m和n为正整数),在存储节点的状态机中,每一个数据对应表2中的某一行数据中某个列的值,如表2中行(Row)3列(Col)3所示。Schematically, referring to Table 2 (m and n in the table are positive integers), in the state machine of the storage node, each data corresponds to the value of a certain column in a certain row of data in Table 2, such as the row (Row ) 3 shown in column (Col) 3.
表2Table 2
第三种、交叉模式。The third, the cross mode.
示意性地,参考表3(表中m和n为正整数),在存储节点的状态机中,每一个数据对应表3中的若干行和若干列交叉的数据范围,如表3所示。在一些实施例中,该交叉模式也称为拼贴/瓦片(Tile)模式,本申请实施例对此不作限定。Illustratively, referring to Table 3 (m and n are positive integers in the table), in the state machine of the storage node, each data corresponds to the data range intersected by several rows and several columns in Table 3, as shown in Table 3. In some embodiments, the cross mode is also called a tile/tile mode, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
表3table 3
需要说明的是,上述几种存储模式仅为示意性地,在一些实施例中,该多个副本还可以以其他存储模式存储于存储节点中,本申请实施例对于存储模式的具体类型不作限定。It should be noted that the above several storage modes are only illustrative. In some embodiments, the multiple copies may also be stored in the storage node in other storage modes. The embodiments of this application do not limit the specific types of storage modes. .
在一些实施例中,在分布式数据库系统的运行过程中,该多个第一存储节点对该多个副本的存储模式进行动态调整(也可以理解为对数据的多个副本进行动态管理)。下面对动态调整的几种情况进行介绍:In some embodiments, during the operation of the distributed database system, the multiple first storage nodes dynamically adjust the storage modes of the multiple copies (which can also be understood as dynamically managing multiple copies of data). Several situations of dynamic adjustment are described below:
情况一、多个第一存储节点基于该多个第一存储节点的负载情况,切换该多个副本的存储模式。Case 1: The multiple first storage nodes switch the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the load conditions of the multiple first storage nodes.
其中,情况一包括下述两种场景:Among them,
场景一、多个第一存储节点基于该多个第一存储节点的节点负载大小和可用空间,切换该多个副本的存储模式。
其中,根据存储节点的节点负载大小和可用空间,场景一可以包括两种切换方案。下面以第一数据分片在存储节点A中存储的副本为例,记该副本的原存储模式为S1模式,切换后的该副本的存储模式为S2模式为例,对这两种切换方案进行介绍。Among them, according to the node load size and available space of the storage node,
第一种方案、存储节点A的节点负载较小且该节点的可用空间较大,在该存储节点A上切换副本的存储模式。In the first solution, the node load of the storage node A is small and the available space of the node is large, and the storage mode of the copy is switched on the storage node A.
示意性地,以分布式一致性协议为Raft协议为例,存储节点A建立该第一数据分片的一个新的临时副本,该临时副本不计入Raft成员(也即是该临时副本不参与Raft的所有流程,只同步数据),存储节点A读取所有S1模式的副本的数据,将这些数据转换为存储模式为S2模式的新数据,通过该临时副本将S2模式的新数据持久化存储到状态机中,并将S1模式的副本还未持久化存储的日志同步到该临时副本中,当同步完成后,销毁S1模式的副本,将S2模式的临时副本作为新副本(也可以理解为新成员)加入Raft组。Illustratively, taking the distributed consistency protocol as the Raft protocol as an example, the storage node A establishes a new temporary copy of the first data fragment, and the temporary copy is not counted as a Raft member (that is, the temporary copy does not participate in the All processes of Raft, only synchronize data), storage node A reads the data of all copies in S1 mode, converts these data into new data whose storage mode is S2 mode, and stores the new data in S2 mode persistently through the temporary copy into the state machine, and synchronize the log of the S1 mode copy that has not been persisted to the temporary copy. When the synchronization is completed, destroy the S1 mode copy and use the S2 mode temporary copy as a new copy (which can also be understood as new member) to join the Raft group.
第二种方案、存储节点A的节点负载较大或该节点的可用空间较小,在存储节点B上切换副本的存储模式,该存储节点B的节点负载较小且该节点的可用空间较大。In the second solution, the node load of storage node A is large or the free space of the node is small, and the storage mode of the copy is switched on the storage node B. The node load of the storage node B is small and the free space of the node is large. .
示意性地,以分布式一致性协议为Raft协议为例,存储节点B建立该第一数据分片的一个新的临时副本,该临时副本不计入Raft成员(也即是该临时副本不参与Raft的所有流程,只同步数据),将S1模式的副本的数据通过快照转移到存储节点B,将这些数据转换为存储模式为S2模式的新数据,通过该临时副本将S2模式的新数据持久化存储到状态机中,并将S1模式的副本还未持久化存储的日志同步到该临时副本中,当同步完成后,销毁S1模式的副本,将S2模式的临时副本作为新副本(也可以理解为新成员)加入Raft组。Illustratively, taking the distributed consistency protocol as the Raft protocol as an example, the storage node B establishes a new temporary copy of the first data fragment, and the temporary copy is not counted as a Raft member (that is, the temporary copy does not participate in the All processes of Raft, only synchronize data), transfer the data of the replica in S1 mode to storage node B through snapshots, convert these data into new data in S2 mode, and persist the new data in S2 mode through the temporary replica After the synchronization is completed, destroy the copy of S1 mode and use the temporary copy of S2 mode as a new copy (or understood as a new member) to join the Raft group.
需要说明的是,在上述两种切换方案中,Raft组成员变更、数据在存储节点之间的转移以及快照持久化存储到状态机等,都可以通过Raft协议的原有过程实现,因此,上述切换方案保证了分布式数据库系统的正确性。另外,由于存储模式的切换涉及状态机的读取和写入,因此,在切换过程中,通过节点负载大小和可用空间来选择相应的切换方案,充分考虑了状态机的运行情况,保证了分布式数据库系统的可用性。It should be noted that in the above two switching schemes, the change of Raft group members, the transfer of data between storage nodes, and the persistent storage of snapshots to the state machine can all be implemented through the original process of the Raft protocol. Therefore, the above The switching scheme ensures the correctness of the distributed database system. In addition, since the switching of the storage mode involves the reading and writing of the state machine, during the switching process, the corresponding switching scheme is selected according to the node load size and available space, and the operation of the state machine is fully considered to ensure distribution. availability of database systems.
场景二、多个第一存储节点基于该多个第一存储节点的节点负载大小和每个存储模式下副本的数量,切换该多个副本的存储模式。Scenario 2: The multiple first storage nodes switch the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the node load size of the multiple first storage nodes and the number of copies in each storage mode.
其中,在分布式数据库系统中,每个存储模式下副本的数量并不是一成不变的,也可以理解为,多个副本的配置策略并不是一成不变的。多个第一存储节点根据自身的节点负载大小,在保证每个存储模式有可用副本的前提下,将节点负载较小的存储节点对应副本的存储模式切换为节点负载较大的存储节点对应副本的存储模式。Among them, in a distributed database system, the number of replicas in each storage mode is not static, and it can also be understood that the configuration strategy of multiple replicas is not static. The multiple first storage nodes switch the storage mode of the copy corresponding to the storage node with a smaller node load to the copy corresponding to the storage node with a larger node load on the premise of ensuring that each storage mode has available copies according to their own node load. storage mode.
示意性地,以多个副本的存储模式包括行存模式、列存模式以及交叉模式,行存模式下副本的数量为L,列存模式下副本的数量为M,交叉模式下副本的数量为N为例(L、M、N为正整数),当系统在某一时间段内,列存模式下副本所在存储节点处理的数据访问请求较多,且该列存模式下副本所在存储节点的节点负载较大时,将该时间段内处理数据访问请求较少(也即是节点负载较小)且副本数量大于1(也即是确保每个存储模式下存在可用副本)的存储模式下的副本切换为列存模式。Illustratively, the storage modes of multiple copies include row storage mode, column storage mode and cross mode, the number of copies in the row storage mode is L, the number of copies in the column storage mode is M, and the number of copies in the cross mode is Take N as an example (L, M, and N are positive integers), when the system is in a certain period of time, the storage node where the replica is located in the column storage mode processes more data access requests, and the storage node where the replica is located in the column storage mode has more data access requests. When the node load is large, the data access request is less processed during the period (that is, the node load is small) and the number of copies is greater than 1 (that is, to ensure that there are available copies in each storage mode) in the storage mode. The replica is switched to columnar storage mode.
需要说明的是,在系统运行的过程中,根据节点负载大小和每个存储模式下副本的数量来切换多个副本的存储模式,在保证每个存储模式有可用副本的前提下,及时切换副本的存储模式,可以更好的应对系统运行过程中负载发生变化的情况,从而有效提升分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。It should be noted that during the operation of the system, the storage mode of multiple copies is switched according to the node load size and the number of copies in each storage mode. On the premise that each storage mode has available copies, the copies are switched in time. The storage mode of the distributed database system can better cope with the load changes during the operation of the system, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
情况二、若该多个副本中存在至少一个副本异常,多个第一存储节点基于该至少一个副本,建立至少一个新副本。Case 2: If at least one copy of the multiple copies is abnormal, the multiple first storage nodes establish at least one new copy based on the at least one copy.
其中,副本异常是指副本不可用,也可以理解为副本出现错误导致副本无法正常工作。当多个副本中存在至少一个副本异常,则多个第一存储节点基于该至少一个副本的数量,建立至少一个新副本,也即是副本的总数符合预设总数。Among them, the replica exception means that the replica is unavailable, and it can also be understood that the replica fails to work properly due to an error in the replica. When at least one copy is abnormal in the multiple copies, the multiple first storage nodes create at least one new copy based on the number of the at least one copy, that is, the total number of copies conforms to the preset total number.
对于至少一个新副本中的任一新副本,若系统中已存在同样存储模式的其他副本,且该其他副本已与主存储节点完成同步,则该新副本所在存储节点从该其他副本同步数据,若系统中不存在同样存储模式的其他副本,则通过快照转移的方式,从主存储节点中同步数据,并将数据转换为相应的存储模式进行持久化存储。For any new copy in at least one new copy, if another copy with the same storage mode already exists in the system, and the other copy has been synchronized with the primary storage node, the storage node where the new copy is located synchronizes data from the other copy, If there are no other copies of the same storage mode in the system, the data is synchronized from the primary storage node by means of snapshot transfer, and the data is converted to the corresponding storage mode for persistent storage.
在一些实施例中,至少一个新副本的存储模式与出现异常的至少一个副本的存储模式相同。在一些实施例中,至少一个新副本的存储模式与出现异常的至少一个副本的存储模式不同,由分布式数据库系统当前的副本配置策略决定,也即是,至少一个新副本的存储模式不一定与出现异常前的状态保持一致,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, the storage mode of the at least one new replica is the same as the storage mode of the at least one replica in which the exception occurred. In some embodiments, the storage mode of the at least one new copy is different from the storage mode of the at least one copy in which the exception occurs, and is determined by the current copy configuration policy of the distributed database system, that is, the storage mode of the at least one new copy is not necessarily It is consistent with the state before the abnormality occurs, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
需要说明的是,在该情况二中,副本异常、建立新副本的过程中以及新副本建立后数据分片的可用性和副本数据的正确性由分布式一致性协议保证,例如,该分布式一致性协议为Raft协议。另外,在系统运行的过程中,通过在副本出现异常的情况下及时建立新副本,确保了系统中各个副本的可用性,从而有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。It should be noted that, in the second case, the availability of data fragments and the correctness of the copy data are guaranteed by the distributed consistency protocol during the process of creating a new copy and the process of establishing a new copy. For example, the distributed consistency The sex protocol is the Raft protocol. In addition, during the operation of the system, by establishing a new copy in time when the copy is abnormal, the availability of each copy in the system is ensured, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
情况三、若该第一数据分片发生数据分裂,生成至少一个第二数据分片,该多个第一存储节点基于该至少一个第二数据分片,建立该至少一个第二数据分片对应的多个副本。Case 3: If the first data fragment is split, at least one second data fragment is generated, and the plurality of first storage nodes establish the at least one second data fragment corresponding to the at least one second data fragment based on the at least one second data fragment. of multiple copies.
其中,数据分裂是指当一个数据分片过大或该数据分片过热时,为了均衡负载,分布式数据库系统对该数据分片进行再分裂操作,使该数据分片裂变为两个数据分片。Among them, data splitting means that when a data fragment is too large or the data fragment is overheated, in order to balance the load, the distributed database system performs a split operation on the data fragment, so that the data fragment is split into two data fragments. piece.
在一些实施例中,该至少一个第二数据分片对应的多个副本的存储模式与第一数据分片的多个副本的存储模式相同。在一些实施例中,该至少一个第二数据分片对应的多个副本的存储模式与第一数据分片的多个副本的存储模式不同,由分布式数据库系统当前的副本配置策略决定,也即是,该至少一个第二数据分片对应的多个副本的存储模式不一定与发生数据分裂前的状态保持一致,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, the storage mode of the multiple copies corresponding to the at least one second data fragment is the same as the storage mode of the multiple copies of the first data fragment. In some embodiments, the storage mode of the multiple copies corresponding to the at least one second data fragment is different from the storage mode of the multiple copies of the first data fragment, and is determined by the current copy configuration policy of the distributed database system, and also That is, the storage modes of the multiple copies corresponding to the at least one second data fragment are not necessarily consistent with the state before the data split occurs, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
在一些实施例中,当行存模式副本进行数据分裂时,只需要分别迁移部分数据即可;当列存模式副本进行数据分裂时,由于列存模式下重新组织所有行代价较大,因此行存模式副本进行数据分裂后,将分裂后的数据转换为列存模式,完成转换后销毁被分裂的列存模式副本。通过这种方式,能够减少分布式数据库系统在数据分裂时所需处理的数据量,从而提高数据分裂效率。In some embodiments, when data splitting is performed on the row-based copy, only part of the data needs to be migrated; when the column-based copy splits data, because the cost of reorganizing all rows in the column-based mode is relatively high, the row-based storage After the schema copy is split, the split data is converted to the column storage mode, and the split column storage mode copy is destroyed after the conversion is completed. In this way, the amount of data that needs to be processed by the distributed database system during data splitting can be reduced, thereby improving the efficiency of data splitting.
情况四、多个第一存储节点基于该多个第一存储节点的节点类型,调整该多个副本的存储模式。Case 4: The multiple first storage nodes adjust the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the node types of the multiple first storage nodes.
其中,多个第一存储节点中存在主存储节点和从存储节点,对于不同节点类型的存储节点,其存储模式不同。例如,主存储节点的存储模式为列存模式,从存储节点的存储模式包括行存模式以及交叉模式等,当某一存储节点通过选举称为主存储节点时,该存储节点将副本的存储模式调整为列存模式,本申请实施例对此不作限定。Among the plurality of first storage nodes, there are master storage nodes and slave storage nodes, and storage nodes of different node types have different storage modes. For example, the storage mode of the master storage node is column storage mode, and the storage mode of the slave storage node includes row storage mode and cross mode. When a storage node is elected as the master storage node, the storage node will copy the storage mode It is adjusted to the column storage mode, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
需要说明的是,上述几种动态调整的情况仅为示意性地,在一些实施例中,该多个第一存储节点还可以以其他方式对多个副本进行动态调整,本申请实施例对于动态调整的具体方式不作限定。另外,在一些实施例中,多个第一存储节点通过格式转换器来实现存储模式的切换,具体可参考上述图2所示的HTAP数据库系统中的存储层203,本申请在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the above situations of dynamic adjustment are only illustrative. In some embodiments, the multiple first storage nodes may also dynamically adjust multiple replicas in other ways. The specific method of adjustment is not limited. In addition, in some embodiments, multiple first storage nodes use format converters to switch storage modes. For details, please refer to the
通过在分布式数据库系统的运行过程中,对数据的多个副本进行动态调整,能够更好的应对系统运行过程中负载发生变化的情况,从而有效提升分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。By dynamically adjusting multiple copies of data during the operation of the distributed database system, it can better cope with the load changes during the operation of the system, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
403、计算节点基于该第一数据读取请求,从该多个第一存储节点中确定第一目标存储节点,向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件。403. Based on the first data read request, the computing node determines a first target storage node from the plurality of first storage nodes, sends the first data read request to the first target storage node, and the first target storage node The data access cost of the node meets the first objective condition.
在本申请实施例中,计算节点基于该第一数据读取请求和多个第一存储节点的节点信息,确定多个第一存储节点的数据访问代价,将符合第一目标条件的第一存储节点作为第一目标存储节点,并向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求。在一些实施例中,第一目标条件是指对应第一存储节点的数据访问代价最低。In the embodiment of the present application, the computing node determines the data access cost of the multiple first storage nodes based on the first data read request and the node information of the multiple first storage nodes, and selects the first storage node that meets the first target condition. The node acts as a first target storage node, and sends the first data read request to the first target storage node. In some embodiments, the first target condition refers to the lowest data access cost corresponding to the first storage node.
在一些实施例中,数据访问代价用于指示存储节点的执行时间、等待时间以及传输时间。其中,执行时间包括存储节点查询第一目标数据的时间、处理数据量(也即是输入输出(Input Output,IO)数据量)的时间以及元组构建时间;等待时间包括存储节点的请求队列时间、设备负载延迟时间以及数据同步时间;传输时间包括网络传输时间。In some embodiments, the data access cost is used to indicate the execution time, latency and transfer time of the storage node. The execution time includes the time for the storage node to query the first target data, the time for processing the amount of data (that is, the amount of input and output (IO) data), and the tuple construction time; the waiting time includes the request queue time of the storage node , device load delay time and data synchronization time; transmission time includes network transmission time.
示意性地,为了便于描述,上述数据访问代价所涉及的各项时间的表示形式如表4所示:Schematically, for the convenience of description, the representations of the various times involved in the above data access cost are shown in Table 4:
表4Table 4
由表4可知,数据访问代价T=执行时间Tproc+等待时间Twait+传输时间Ttrans。其中,执行时间Tproc=查询时间Tsearch+处理时间Tio+元组构建时间Tcons,等待时间Twait=请求队列时间Tqueue+设备负载延迟时间Tload+数据同步时间Tsync。It can be known from Table 4 that the data access cost T = execution time Tproc + waiting time Twait + transmission time Ttrans . Wherein, execution time Tproc = query time Tsearch + processing time Tio + tuple construction time Tcons , waiting time Twait = request queue time Tqueue + device load delay time Tload + data synchronization time Tsync .
在一些实施例中,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件,包括下述几种情况:In some embodiments, the data access cost of the first target storage node meets the first target condition, including the following situations:
情况一、该第一目标存储节点中该第一目标数据的存储模式为列存模式,且该数据读取请求所需访问的列数与总列数之间的比值小于第一阈值。Case 1: The storage mode of the first target data in the first target storage node is a column storage mode, and the ratio between the number of columns to be accessed by the data read request and the total number of columns is less than a first threshold.
其中,第一阈值为预设阈值,在一些实施例中,该第一阈值可以根据需求进行调整,本申请实施例对此不作限定。上述情况一还可以概括为该数据读取请求为宽表少列查询请求,也即是,该数据读取请求为在一个列的数量比较多的表(即“宽表”)上只涉及少部分列(即“少列”)的查询请求。The first threshold is a preset threshold. In some embodiments, the first threshold may be adjusted according to requirements, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. The
需要说明的是,在分布式数据库系统中,副本的存储模式与存储节点的执行时间相关。示意性地,参考表4,查询列存模式副本所涉及的查询时间Tsearch和处理时间Tio少于查询行存模式副本所涉及的查询时间Tsearch和处理时间Tio,查询列存模式副本所涉及的列数越多,元组构建时间Tcons越久。因此,对于数据读取请求,若该请求所需访问的列数与表中总列数之间的比值小于第一阈值,则存储有列存模式副本的存储节点的执行时间Tproc最少,相应地,该存储节点的数据访问代价最低。It should be noted that, in a distributed database system, the storage mode of the replica is related to the execution time of the storage node. Illustratively, with reference to Table 4, the query time Tsearch and processing time Tio involved in querying a copy of the column storage mode are less than the query time Tsearch and processing time Tio involved in querying a copy of the row storage mode, and querying a copy of the column storage mode The more columns involved, the longer the tuple construction time Tcons . Therefore, for a data read request, if the ratio between the number of columns accessed by the request and the total number of columns in the table is less than the first threshold, the execution time Tproc of the storage node storing the copy of the column storage mode is the least, and the corresponding Therefore, the data access cost of this storage node is the lowest.
情况二、该第一目标存储节点的节点负载小于该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点的节点负载。Case 2: The node load of the first target storage node is smaller than the node load of the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes.
其中,副本所在存储节点的节点负载与存储节点的等待时间相关。示意性地,参考表4,存储节点的节点负载越小,该存储节点的请求队列时间Tqueue和设备负载延迟时间Tload越少。因此,若某一存储节点的节点负载最小,则该存储节点的等待时间Twait最少,相应地,该存储节点的数据访问代价最低。The node load of the storage node where the replica is located is related to the waiting time of the storage node. Illustratively, referring to Table 4, the smaller the node load of the storage node, the smaller the request queue time Tqueue and the device load delay time Tload of the storage node. Therefore, if the node load of a certain storage node is the smallest, the waiting time Twait of the storage node is the smallest, and accordingly, the data access cost of the storage node is the lowest.
情况三、该第一目标存储节点与该计算节点之间的物理距离小于该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点与该计算节点之间的物理距离。Case 3: The physical distance between the first target storage node and the computing node is smaller than the physical distance between the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes and the computing node.
其中,副本所在存储节点与计算节点之间的物理距离与传输时间相关。示意性地,参考表4,存储节点与计算节点之间的物理距离越小,该存储节点的网络传输时间Ttrans越少。因此,若某一存储节点与计算节点之间的物理距离最小,则该存储节点的传输时间Ttrans最少,相应地,该存储节点的数据访问代价最低。另外,由于多个副本可能分散在不同机房甚至不同的数据中心,因此将距离计算节点最近的第一存储节点作为第一目标存储节点,可以有效减少网络传输的开销。The physical distance between the storage node where the replica is located and the computing node is related to the transmission time. Illustratively, referring to Table 4, the smaller the physical distance between the storage node and the computing node, the shorter the network transmission time Ttrans of the storage node. Therefore, if the physical distance between a storage node and a computing node is the smallest, the transmission time Ttrans of the storage node is the smallest, and accordingly, the data access cost of the storage node is the lowest. In addition, since multiple copies may be scattered in different computer rooms or even different data centers, using the first storage node closest to the computing node as the first target storage node can effectively reduce the overhead of network transmission.
情况四、该第一目标存储节点的数据同步状态在该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点的数据同步状态之后。Case 4: The data synchronization state of the first target storage node is after the data synchronization state of the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes.
其中,副本所在存储节点的数据同步状态与存储节点的等待时间相关。示意性地,参考表4,存储节点的数据同步状态越新,该存储节点的数据同步时间Tsync越少。因此,对于数据读取请求而言,该请求需要等待存储节点的日志同步到最新状态,若存在某一存储节点的数据同步状态最新,则该存储节点的等待时间Twait最少,相应地,该存储节点的数据访问代价最低。The data synchronization state of the storage node where the replica is located is related to the waiting time of the storage node. Illustratively, referring to Table 4, the newer the data synchronization state of the storage node, the less the data synchronization time Tsync of the storage node. Therefore, for a data read request, the request needs to wait for the log of the storage node to be synchronized to the latest state. If there is a storage node with the latest data synchronization state, the waiting time Twait of the storage node is the least. Correspondingly, the The data access cost of the storage node is the lowest.
在一些实施例中,上述所示的四种情况也可以理解为计算节点通过数据访问代价来确定第一目标存储节点的四种策略,也即是,通过上述策略,从多个第一存储节点中选出数据访问代价最低的存储节点,将该存储节点作为第一目标存储节点。In some embodiments, the four situations shown above can also be understood as four strategies for the computing node to determine the first target storage node according to the data access cost, that is, through the above strategy, from multiple first storage nodes The storage node with the lowest data access cost is selected from among them, and the storage node is used as the first target storage node.
在一些实施例中,计算节点根据上述任一种策略来确定第一目标存储节点。在另一些实施例中,计算节点通过权重等方式将上述几种策略结合以确定第一目标存储节点。例如,参考表4,对于任一第一存储节点,其数据访问代价表示为:T1=a1(Tsearch+Tio)+1/a1(Tcons)+a2(Tqueue+Tload)+a3(Ttrans)+a4(Tsync),其中,a1、a2、a3以及a4分别表示上述四种策略对应的权重。应理解,上述权重以及策略的选择可以根据实际情况进行调整,例如,仅选择两种策略以权重的方式结合等等,本申请实施例对此不作限定。另外,在一些实施例中,由于节点性能、网络速度等因素的影响,存储节点的执行时间Tproc、等待时间Twait以及传输时间Ttrans的量级存在差异,因此,权重的设置应保证尽可能加速总时间较长的部分。In some embodiments, the computing node determines the first target storage node according to any one of the above policies. In other embodiments, the computing node determines the first target storage node by combining the above several strategies by means of weights or the like. For example, referring to Table 4, for any first storage node, its data access cost is expressed as: T1 =a1 (Tsearch +Tio )+1/a1 (Tcons )+a2 (Tqueue +Tload )+a3 (Ttrans )+a4 (Tsync ), wherein a1 , a2 , a3 and a4 respectively represent the weights corresponding to the above four strategies. It should be understood that the selection of the above weights and strategies may be adjusted according to actual conditions, for example, only two strategies are selected to be combined in a weighted manner, etc., which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application. In addition, in some embodiments, due to the influence of factors such as node performance, network speed, etc., the execution time Tproc , the waiting time Twait and the transmission time Ttrans of the storage nodes are different in magnitude. Therefore, the setting of the weight should ensure that the maximum It is possible to speed up the part with a longer total time.
在一些实施例中,数据访问代价用于指示存储节点在单位时间内的执行时间、等待时间以及传输时间。也即是,在上述表4所示的数据访问代价T的基础上,将数据访问代价T与存储节点随机读取一个数据页的时间T0之比作为数据访问代价T′。通过这种方式,能够统一各个存储节点的数据访问代价,从而提高了计算节点确定第一目标存储节点的准确性。In some embodiments, the data access cost is used to indicate the execution time, waiting time and transmission time of the storage node per unit time. That is, on the basis of the data access cost T shown in Table 4 above, the ratio of the data access cost T to the time T0 for the storage node to randomly read a data page is taken as the data access cost T′. In this way, the data access cost of each storage node can be unified, thereby improving the accuracy of the computing node in determining the first target storage node.
需要说明的是,经过上述步骤403,计算节点将多个第一存储节点中数据访问代价符合目标条件的存储节点作为第一目标存储节点,这一过程也可以称为计算节点制定查询计划的过程,在这一过程中,考虑到了存储模式、负载均衡以及请求的延迟时间等多方面的因素,最大限度发挥了多副本存储的并发和存储优势,提高系统整体性能。根据每个存储节点的数据访问代价,选择最佳副本作为访问目标,并向该副本对应的存储节点发送数据读取请求,有利于降低瓶颈发生的可能,提高系统的整体吞吐量。而且,在这一过程中,计算节点是根据数据访问代价来确定第一目标存储节点的,因此,无论是主存储节点还是从存储节点都有可能成为第一目标存储节点,换言之,在本申请实施例所涉及的分布式数据库系统中,允许从不同类型的存储节点中读取数据,从而提高了多副本存储的读操作并发度,保证了多副本带来的高可用性以及多副本间的数据一致性,又增加了系统的并发度,有效提高了系统的数据访问性能。It should be noted that, after the above step 403, the computing node uses the storage node whose data access cost meets the target condition among the plurality of first storage nodes as the first target storage node. This process may also be referred to as the process of formulating a query plan by the computing node. , in this process, taking into account factors such as storage mode, load balancing and request delay time, the concurrency and storage advantages of multi-copy storage are maximized, and the overall performance of the system is improved. According to the data access cost of each storage node, the best replica is selected as the access target, and a data read request is sent to the storage node corresponding to the replica, which is conducive to reducing the possibility of bottlenecks and improving the overall throughput of the system. Moreover, in this process, the computing node determines the first target storage node according to the data access cost. Therefore, both the master storage node and the slave storage node may become the first target storage node. In other words, in this application In the distributed database system involved in the embodiment, data is allowed to be read from different types of storage nodes, thereby improving the read operation concurrency of multi-copy storage, ensuring high availability brought by multiple copies and data between multiple copies. Consistency increases the concurrency of the system and effectively improves the data access performance of the system.
经过上述步骤401至步骤403,计算节点在接收到终端发送的数据读取请求后,确定了该数据读取请求的第一目标数据的多个副本所在的存储节点,并根据各个存储节点的数据访问代价,从中确定了第一目标存储节点。下面将通过步骤404至步骤411,对第一目标存储节点读取第一目标数据的实施方式进行介绍。After the above steps 401 to 403, after receiving the data read request sent by the terminal, the computing node determines the storage node where the multiple copies of the first target data of the data read request are located, and calculates the The access cost, from which the first target storage node is determined. The following will introduce the implementation manner of reading the first target data by the first target storage node through steps 404 to 411 .
404、第一目标存储节点基于第一目标数据的数据类型,确定该第一目标数据为当前态数据。404. The first target storage node determines, based on the data type of the first target data, that the first target data is current state data.
在本申请实施例中,第一目标存储节点根据第一目标数据的数据类型不同,采用不同的数据读取方式来读取第一目标数据。其中,当第一目标数据为当前态数据时,第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标存储节点的节点类型,读取该第一目标数据(也即是下述步骤405至步骤408)。In this embodiment of the present application, the first target storage node uses different data reading methods to read the first target data according to different data types of the first target data. Wherein, when the first target data is current state data, the first target storage node reads the first target data (that is, the following
405、若第一目标存储节点为主存储节点,则第一目标存储节点执行下述步骤406和步骤408,若第一目标存储节点为从存储节点,则第一目标存储节点执行下述步骤407和步骤408。405. If the first target storage node is the master storage node, the first target storage node executes the following steps 406 and 408; if the first target storage node is the slave storage node, the first target storage node executes the following step 407 and step 408.
在本申请实施例中,第一目标存储节点在接收到计算节点发送的数据读取请求时,根据当前节点的节点类型,采用不同的数据读取方式来读取第一目标数据。其中,当第一目标存储节点为主存储节点时,第一目标存储节点根据放宽读索引(Relaxed ReadIndex,RRI(为便于描述,以下均简称为RRI))来读取第一目标数据(也即是下述步骤406,RRI的含义会在下述步骤406中进行详细介绍,此处不再赘述)。当第一目标存储节点为从存储节点时,第一目标存储节点从主存储节点中获取RRI后读取第一目标数据(也即是下述步骤407)。In this embodiment of the present application, when the first target storage node receives the data read request sent by the computing node, it uses different data reading methods to read the first target data according to the node type of the current node. Wherein, when the first target storage node is the main storage node, the first target storage node reads the first target data according to a relaxed read index (Relaxed ReadIndex, RRI (hereinafter referred to as RRI for ease of description)) It is the following step 406, and the meaning of the RRI will be introduced in detail in the following step 406, and will not be repeated here). When the first target storage node is the slave storage node, the first target storage node obtains the RRI from the master storage node and then reads the first target data (that is, the following step 407).
406、第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求,确定该第一目标数据的第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据,该第一读索引用于指示基于该第一数据读取请求读取该第一目标数据的最小读索引。406. The first target storage node determines the first read index of the first target data based on the first data read request, and reads the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data with the first read index as a starting point For the first target data, the first read index is used to indicate a minimum read index for reading the first target data based on the first data read request.
在本申请实施例中,第一目标存储节点为主存储节点,该第一目标数据的第一读索引即为第一目标数据的RRI,该第一读索引的值小于等于读索引(Read Index)的值。通俗来讲,RRI表示当前存储节点基于数据读取请求,能够接受的最小的读索引(Read Index),只要保证执行索引(Apply Index)大于RRI,就能确保当前存储节点读到的都是最新的数据。在一些实施例中,第一目标存储节点根据RRI读取第一目标数据的方式也可以称为放宽读(Relaxed Read Read,RRR)。In the embodiment of the present application, the first target storage node is the main storage node, the first read index of the first target data is the RRI of the first target data, and the value of the first read index is less than or equal to the read index (Read Index). ) value. In layman's terms, RRI indicates the smallest read index (Read Index) that the current storage node can accept based on data read requests. As long as the execution index (Apply Index) is greater than RRI, it can ensure that the current storage node reads the latest data. The data. In some embodiments, the manner in which the first target storage node reads the first target data according to the RRI may also be referred to as a relaxed read (Relaxed Read Read, RRR).
应理解,在相关分布式一致性协议(例如Raft协议)中,为保证数据的一致性,存储节点需要在读取数据之前将已经提交(Commit)的日志全部执行(Apply)到状态机中,以保证数据的一致性,这一过程引起较高的时间开销,导致数据访问性能不佳。而在本申请实施例中,通过引入RRI这一索引,使得存储节点在保证读取的数据正确性的前提下,减少需要执行的日志的数量,实现了提前读取数据,提高了数据读取请求的处理效率,从而有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。It should be understood that in a related distributed consistency protocol (such as the Raft protocol), in order to ensure data consistency, the storage node needs to execute (Apply) all the logs that have been committed (Commit) to the state machine before reading the data. In order to ensure data consistency, this process causes high time overhead, resulting in poor data access performance. In the embodiment of the present application, by introducing the index RRI, the storage node reduces the number of logs to be executed on the premise of ensuring the correctness of the read data, realizes the data read in advance, and improves the data read The processing efficiency of the request, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
下面对本步骤406中第一目标存储节点确定第一目标数据的第一读索引的具体实施方式进行介绍,包括下述步骤4061至步骤4063:The following describes the specific implementation of the first target storage node determining the first read index of the first target data in this step 406, including the following steps 4061 to 4063:
4061、第一目标存储节点更新当前时刻的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引。4061. The first target storage node updates the commit index at the current moment, where the commit index is used to indicate the largest index of the committed log in the log list.
其中,第一目标存储节点更新当前时刻的提交索引(Commit Index)是指将数据读取请求所需的读索引(Read Index)设置为当前节点的提交索引(Commit Index)。The updating of the commit index (Commit Index) at the current moment by the first target storage node refers to setting the read index (Read Index) required by the data read request as the commit index (Commit Index) of the current node.
在一些实施例中,第一目标存储节点在确认节点类型为主存储节点之后,更新当前时刻的提交索引(Commit Index)。由于可能出现的网络分区会导致该第一目标存储节点仍认为自己是主存储节点,但在集群中已经存在更新的主存储节点的情况,因此,通过这种先确认身份再更新提交索引的方式,能够避免上述情况的出现,从而确保数据读取的准确性。In some embodiments, after confirming that the node type is the primary storage node, the first target storage node updates the commit index (Commit Index) at the current moment. Since the possible network partition may cause the first target storage node to still think that it is the primary storage node, but there is already an updated primary storage node in the cluster, this method of confirming the identity first and then updating the submitted index , can avoid the occurrence of the above situation, so as to ensure the accuracy of data reading.
4062、第一目标存储节点按照第一顺序,扫描该日志列表中存储的日志,该第一顺序是指从该提交索引至该日志列表的执行索引,该执行索引用于指示该日志列表中已执行日志的最大索引。4062. The first target storage node scans the logs stored in the log list according to the first order, the first order refers to the execution index from the submission index to the log list, and the execution index is used to indicate that the log list has been The maximum index of the execution log.
其中,在日志列表中,执行索引(Apply Index)的值小于提交索引(Commit Index)的值。第一目标存储节点按照第一顺序扫描日志列表中存储的日志也可以理解为第一目标存储节点从提交索引(Commit Index)开始从后向前反向扫描日志列表,一直到执行索引(Apply Index)为止。Wherein, in the log list, the value of the execution index (Apply Index) is smaller than the value of the commit index (Commit Index). The first target storage node scans the logs stored in the log list in the first order. It can also be understood that the first target storage node scans the log list from the back to the front from the commit index (Commit Index) until the execution of the index (Apply Index). )until.
4063、若存在第一目标日志,该第一目标存储节点基于该第一目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第一目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据;若不存在该第一目标日志,该第一目标存储节点基于该执行索引,确定该第一读索引。4063. If there is a first target log, the first target storage node determines the first read index based on the log index of the first target log, and the data operated by the first target log is the first target data; if not The first target log exists, and the first target storage node determines the first read index based on the execution index.
其中,第一目标存储节点在执行上述步骤4062的过程中,若扫描到一条日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据,则该条日志即为第一目标日志,将该第一读索引设置为该第一目标日志的日志索引(Log Index);若扫描结束后,该日志列表中不存在上述第一目标日志,则将该第一读索引设置为该日志列表的执行索引(Apply Index)。Wherein, in the process of performing the above step 4062 on the first target storage node, if the data operated by a log scanned is the first target data, the log is the first target log, and the first read index is set is the log index (Log Index) of the first target log; if the above-mentioned first target log does not exist in the log list after scanning, then the first read index is set as the execution index (Apply Index) of the log list .
下面参考图5,对上述步骤4061至步骤4063所示的确定第一读索引的方式进行举例说明。图5是本申请实施例提供的一种确定第一读索引的示意图。如图5所示,日志列表中日志索引(Log Index)的值为1至8,分别代表日志1(Log1)至日志8(Log 8),执行索引(Apply Index)为2,提交索引(Commit Index)为7。示意性地,第一目标存储节点从日志7(Log 7)开始,逐个向前扫描,若存在一条日志满足“日志所操作的数据为第一目标数据”,将第一读索引(也即RRI)设置为该条日志的日志索引(Log Index),并提前结束扫描。例如,以第一目标数据为x为例,该第一目标数据x的RRI为7。同理,以第一目标数据为y为例,该第一目标数据y的RRI为6;以第一目标数据为z为例,该第一目标数据z的RRI为3;以第一目标数据为w为例,该第一目标数据w的RRI为2。Referring to FIG. 5 below, the manner of determining the first read index shown in the above steps 4061 to 4063 will be described by way of example. FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of determining a first read index according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 5, the value of the log index (Log Index) in the log list is 1 to 8, representing log 1 (Log1) to log 8 (Log 8) respectively, the execution index (Apply Index) is 2, and the commit index (Commit) Index) is 7. Schematically, the first target storage node starts from log 7 (Log 7) and scans forward one by one. If there is a log that satisfies "the data operated by the log is the first target data", the first read index (that is, the RRI ) is set to the Log Index of the log, and the scan ends early. For example, taking the first target data as x as an example, the RRI of the first target data x is 7. Similarly, taking the first target data as y as an example, the RRI of the first target data y is 6; taking the first target data as z as an example, the RRI of the first target data z is 3; Taking w as an example, the RRI of the first target data w is 2.
经过上述步骤4061至步骤4063,第一目标存储节点确定了第一目标数据的第一读索引,当该第一目标存储节点的状态机中的执行索引大于该第一读索引,即能以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。通过这种方式,在确保读取的第一目标数据的正确性的前提下,减少了数据读取请求的处理时间,从而有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。After the above steps 4061 to 4063, the first target storage node determines the first read index of the first target data. When the execution index in the state machine of the first target storage node is greater than the first read index, the first target storage node can use the first read index. The first read index is the starting point, and the first target data is read from the state machine corresponding to the first target data. In this way, on the premise of ensuring the correctness of the read first target data, the processing time of the data read request is reduced, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
在一些实施例中,当第一目标存储节点确定第一目标数据的第一读索引之后,将该第一读索引进行存储,以便再次接收到相同的数据读取请求时,通过查表来读取相应的数据。下面通过下述两个步骤来对这种可选实施方式进行介绍:In some embodiments, after the first target storage node determines the first read index of the first target data, the first read index is stored, so that when the same data read request is received again, the first read index is read by looking up the table. Get the corresponding data. This optional implementation is described below through the following two steps:
步骤一、第一目标存储节点将该第一读索引存储至第一列表,该第一列表包括该第一目标数据、该第一读索引以及第一校验索引,该第一校验索引用于指示该第一目标存储节点确定该第一读索引时对应的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引。Step 1: The first target storage node stores the first read index in a first list, where the first list includes the first target data, the first read index and the first check index, and the first check index is When instructing the first target storage node to determine the first read index, the corresponding commit index is used to indicate the largest index of the committed log in the log list.
步骤二、当该分布式数据库系统处理第二数据读取请求时,若该第二数据读取请求的数据为该第一目标数据,查询该第一列表以读取该第一目标数据。Step 2: When the distributed database system processes the second data read request, if the data of the second data read request is the first target data, query the first list to read the first target data.
其中,当该分布式数据库系统处理查询第一列表以读取该第一目标数据的方式包括下述两种情况:Wherein, when the distributed database system processes and queries the first list to read the first target data, the following two situations are included:
情况一、第一列表中第一目标数据的提交索引(Commit Index)等于对应的第一校验索引(Check Index),则将第一列表中该第一目标数据对应的RRI作为第二数据读取请求对应的RRI,用于读取第一目标数据。Situation 1: The Commit Index (Commit Index) of the first target data in the first list is equal to the corresponding first check index (Check Index), then the RRI corresponding to the first target data in the first list is read as the second data The RRI corresponding to the fetch request is used to read the first target data.
情况二、第一列表中第一目标数据的提交索引(Commit Index)大于对应的第一校验索引(Check Index),表明此时的RRI并不一定是最新的,也即是根据此时的RRI读取到的数据并不一定是最新的数据。在该情况下,分布式数据库系统需要按照上述步骤4062至步骤4063所示的方法,扫描日志列表中存储的日志,来确定第二数据读取请求对应的RRI。需要说明的是,在扫描时,从日志列表中提交索引(Commit Index)对应的日志开始扫描,直至第一校验索引(Check Index)为止。Case 2: The Commit Index of the first target data in the first list is greater than the corresponding first Check Index, indicating that the RRI at this time is not necessarily the latest, that is, according to the current RRI The data read by RRI is not necessarily the latest data. In this case, the distributed database system needs to scan the logs stored in the log list according to the methods shown in the above steps 4062 to 4063 to determine the RRI corresponding to the second data read request. It should be noted that, during scanning, scanning starts from the log corresponding to the commit index (Commit Index) in the log list until the first check index (Check Index).
在一些实施例中,若该第一列表中数据项的数量大于或等于预设阈值,则删除该第一列表中的至少一个数据项和对应的RRI,该至少一个数据项的RRI小于执行索引(ApplyIndex)。例如,该预设阈值为100,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, if the number of data items in the first list is greater than or equal to a preset threshold, at least one data item and corresponding RRI in the first list are deleted, and the RRI of the at least one data item is smaller than the execution index (ApplyIndex). For example, the preset threshold is 100, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
下面参考图6,对上述存储第一读索引以及处理第二数据读取请求的可选实施方式进行举例说明。图6是本申请实施例提供的一种存储第一读索引的示意图。如图6图所示,第一目标存储节点将扫描日志列表后的结果存储在列表中,该列表中包括数据项、数据项对应的RRI以及校验索引(Check Index),其中,校验索引(Check Index)的值等于提交索引(Commit Index)的值。当分布式数据库系统处理第二数据读取请求时,先在表中查看RRI和校验索引(Check Index)。如果提交索引(Commit Index)等于校验索引(Check Index),则按照表中RRI的值作为第二数据读取请求对应的RRI。示意性地,如图6中(a)和(b)图所示,当第二数据读取请求读取x时,由于表中的提交索引(Commit Index)等于校验索引(CheckIndex),所以无需做额外操作。如果提交索引(Commit Index)大于校验索引(CheckIndex),说明此时的RRI不一定是最新的,需要扫描日志列表,扫描时从日志列表中提交索引(Commit Index)对应的日志开始扫描,直至校验索引(Check Index)为止。图6中(c)和(d)图与(a)和(b)图同理,故在此不再赘述。Referring to FIG. 6 , the foregoing optional implementation manner of storing the first read index and processing the second data read request will be described by way of example. FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of storing a first read index according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 6 , the first target storage node stores the result of scanning the log list in a list, where the list includes data items, RRIs corresponding to the data items, and a check index (Check Index), wherein the check index The value of Check Index is equal to the value of Commit Index. When the distributed database system processes the second data read request, the RRI and the check index (Check Index) are first checked in the table. If the commit index (Commit Index) is equal to the check index (Check Index), the value of the RRI in the table is used as the RRI corresponding to the second data read request. Schematically, as shown in (a) and (b) of FIG. 6, when the second data read request reads x, since the commit index (Commit Index) in the table is equal to the check index (CheckIndex), so No additional action is required. If the commit index (Commit Index) is greater than the check index (CheckIndex), it means that the RRI at this time is not necessarily the latest, and the log list needs to be scanned. Check Index (Check Index). The diagrams (c) and (d) in FIG. 6 are the same as the diagrams (a) and (b), so they will not be repeated here.
需要说明的是,通过这种将第一读索引存储至第一列表的方式,能够避免多次重复扫描日志列表,减少数据处理量,从而节约计算资源。另外,由于该第一列表的信息是在每次处理数据读取请求时更新的,所以这种可选实施方法也可以称为读时更新法。应理解,实验表明执行索引(Apply Index)和提交索引(Commit Index)之间的差距一般不会超过10,因此第一列表的大小足以放置于内存中。如果出现了第一列表满了的情况,就说明此时当前存储节点的状态机远远落后于日志。因此可以暂停维护这张表,阻塞数据读取请求,等待执行索引(Apply Index)等于提交索引(Commit Index)时,再恢复服务。进一步地,因为第一列表的信息完全可以由任意时刻的分布式一致性协议的状态推出,所以不需要存放于持久化存储中。当需要做故障恢复时,只需要根据分布式一致性协议当时的状态,利用上述方法重构该表即可。It should be noted that, by storing the first read index in the first list in this manner, repeated scanning of the log list can be avoided, data processing amount can be reduced, and computing resources can be saved. In addition, since the information in the first list is updated each time a data read request is processed, this optional implementation method can also be called a read-time update method. It should be understood that experiments show that the gap between the Apply Index and the Commit Index generally does not exceed 10, so the size of the first list is sufficient to fit in the memory. If the first list is full, it means that the state machine of the current storage node is far behind the log. Therefore, you can suspend the maintenance of this table, block the data read request, wait for the execution index (Apply Index) to be equal to the commit index (Commit Index), and then resume the service. Further, because the information in the first list can be derived from the state of the distributed consensus protocol at any time, it does not need to be stored in persistent storage. When failure recovery is required, it is only necessary to reconstruct the table according to the current state of the distributed consistency protocol using the above method.
经过步骤406,在第一目标存储节点为主存储节点的情况下,通过确定RRI的方式,读取到了第一目标数据。这种数据读取的过程也可以概括为主节点读请求(Leader Read)处理流程,下面参考图7,对这一主节点读请求处理流程进行示意性说明。图7是本申请实施例提供的一种主节点读请求处理流程的示意图。如图7所示,该主节点读请求处理流程由第一目标存储节点执行,包括下述步骤(1)至步骤(7):After step 406, when the first target storage node is the primary storage node, the first target data is read by determining the RRI. This data reading process can also be summarized as a master node read request (Leader Read) processing flow, the following is a schematic illustration of the master node read request processing flow with reference to FIG. 7 . FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of a processing flow of a master node read request provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 7, the master node read request processing flow is executed by the first target storage node, including the following steps (1) to (7):
(1)接收数据读取请求。(1) Receive a data read request.
(2)判断当前存储节点是否为主存储节点,若是,执行下述步骤(4),若不是,执行下述步骤(3)。(2) Determine whether the current storage node is the primary storage node, if so, execute the following step (4), if not, execute the following step (3).
(3)将数据读取请求转发给主存储节点。(3) Forward the data read request to the main storage node.
(4)更新当前时刻的提交索引(Commit Index)。(4) Update the commit index (Commit Index) at the current moment.
(5)确定第一读索引(也即是RRI)。(5) Determine the first read index (ie, RRI).
(6)按照第一读索引,将日志执行到状态机中。(6) According to the first read index, the log is executed into the state machine.
(7)从状态机中读取数据。(7) Read data from the state machine.
需要说明的是,上述步骤(1)至步骤(7)的具体实施方式与步骤406同理,故在此不再赘述。It should be noted that, the specific implementation manners of the above steps (1) to (7) are the same as those of step 406, so they are not repeated here.
应理解,相关技术中,Raft协议为保障严格的一致性,确保上层应用不会因为读到旧的数据而导致业务逻辑出错,每次在读取数据之前都必须保证执行索引(Apply Index)超过读索引(Read Index)。由于Raft协议在处理数据访问请求时,只有日志写入是同步的,而执行到状态机的过程是异步的,因此在Raft正常运行时,经常会出现执行索引(ApplyIndex)小于读索引(Read Index)的情况。在执行索引(Apply Index)增加到读索引(ReadIndex)的这段时间里,用户都无法读取数据,即使要读的数据与这些操作没有关系。这一严格的限制提高了数据读取请求的延迟,降低了整体系统的性能。而本申请通过引入放宽读索引RRI,不再要求存储节点必须在执行索引(Apply Index)超过读索引(Read Index)时才可以读取结果,而是在与数据读取请求相关指令日志执行到状态机后(也即是执行索引(Apply Index)超过RRI)即可从状态机中读取数据,从而减少数据读取请求的等待时间,并且确保了所读取的数据是最新的,有效提高了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。It should be understood that in the related art, in order to ensure strict consistency, the Raft protocol ensures that the upper-layer application will not cause business logic errors due to reading old data. Before reading data, it must ensure that the index (Apply Index) exceeds Read Index. Since the Raft protocol processes data access requests, only log writing is synchronous, and the process to the state machine is asynchronous. Therefore, when Raft is running normally, it often occurs that the execution index (ApplyIndex) is smaller than the read index (Read Index). )Case. During the period when the execution index (Apply Index) is increased to the read index (ReadIndex), the user cannot read the data, even if the data to be read has nothing to do with these operations. This strict limit increases the latency of data read requests and reduces overall system performance. In this application, by introducing the relaxation of the read index RRI, it is no longer required that the storage node can read the result only when the application index (Apply Index) exceeds the read index (Read Index), but when the instruction log related to the data read request is executed to After the state machine (that is, the execution index (Apply Index) exceeds the RRI), data can be read from the state machine, thereby reducing the waiting time of data read requests, and ensuring that the read data is the latest, effectively improving The data access performance of the distributed database system.
407、第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求,从该主存储节点中获取该第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。407. Based on the first data read request, the first target storage node obtains the first read index from the main storage node, and uses the first read index as a starting point to read from the state machine corresponding to the first target data Get the first target data.
在本申请实施例中,当第一目标存储节点为从存储节点时,该第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求,向主存储节点发送读索引获取请求,以获取第一目标数据的第一读索引。在一些实施例中,第一目标存储节点通过远程过程调用(Remote ProcedureCall,RPC)与主存储节点通信,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In this embodiment of the present application, when the first target storage node is a slave storage node, the first target storage node sends a read index obtaining request to the master storage node based on the first data read request to obtain the first target data The first read index of . In some embodiments, the first target storage node communicates with the primary storage node through a remote procedure call (Remote Procedure Call, RPC), which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
在一些实施例中,该第一目标存储节点以该第一读索引为起点,从第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取第一目标数据的方式包括下述任一种情况:In some embodiments, the first target storage node starts from the first read index, and reads the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data. The manner includes any of the following situations:
情况一、若第一目标存储节点中存在该第一读索引对应的日志,该第一目标存储节点对该第一读索引对应的日志进行持久化存储,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。
其中,第一目标存储节点在获取到第一读索引后,通过查询本地的日志列表,确定存在索引为第一读索引的日志记录,然后进行日志回放,将该条日志进行持久化存储(也即是将数据持久化到状态机),完成与主存储节点的数据同步,之后,第一目标存储节点以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标存储节点对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。Wherein, after obtaining the first read index, the first target storage node determines that there is a log record with the index as the first read index by querying the local log list, then performs log playback, and stores the log persistently (also called the first read index). That is, the data is persisted to the state machine), and the data synchronization with the main storage node is completed. After that, the first target storage node uses the first read index as a starting point to read from the state machine corresponding to the first target storage node. the first target data.
需要说明的是,在一些实施例中,由于网络、机器硬件、IO调度等原因,从存储节点和主存储节点持久化存储的时机不一定保持一致(也可以理解为日志和数据落盘的时机不一定保持一致),因此通过上述日志回放以持久化存储的方式能够确保数据一致性。It should be noted that, in some embodiments, due to reasons such as network, machine hardware, IO scheduling, etc., the timing of persistent storage of the slave storage node and the primary storage node may not always be consistent (it can also be understood as the timing of the log and data being placed on the disk). It is not necessarily consistent), so data consistency can be ensured by persistent storage through the above log playback.
情况二、若该第一目标存储节点中不存在该第一读索引对应的日志,该第一目标存储节点从该主存储节点中获取该第一读索引对应的日志,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。Case 2: If the log corresponding to the first read index does not exist in the first target storage node, the first target storage node obtains the log corresponding to the first read index from the main storage node, and uses the first read index As a starting point, the first target data is read from the state machine corresponding to the first target data.
其中,第一目标存储节点在获取到第一读索引后,通过查询本地的日志列表,未查询到索引为第一读索引的日志记录,然后该第一目标存储节点向主存储节点发送日志获取请求,以获取第一读索引对应的日志,之后,第一目标存储节点以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标存储节点对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。Wherein, after obtaining the first read index, the first target storage node queries the local log list and fails to find any log records whose index is the first read index, and then the first target storage node sends the log to the main storage node to obtain the log record. request to obtain the log corresponding to the first read index, and then the first target storage node reads the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target storage node using the first read index as a starting point.
经过步骤407,在第一目标存储节点为从存储节点的情况下,通过向主存储节点获取第一读索引的方式,读取到了第一目标数据。这种数据读取的过程也可以概括为从节点读请求(Follower Read)处理流程,下面参考图8,对这一从节点读请求处理流程进行示意性说明。图8是本申请实施例提供的一种从节点读请求处理流程的示意图。如图8所示,该从节点读请求处理流程包括下述步骤(1)至步骤(5):After step 407, when the first target storage node is a slave storage node, the first target data is read by acquiring the first read index from the master storage node. This data reading process can also be summarized as a slave node read request (Follower Read) processing flow. The following describes the slave node read request processing flow with reference to FIG. 8 . FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of a processing flow of a read request from a node provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 8, the slave node read request processing flow includes the following steps (1) to (5):
(1)从存储节点接收数据读取请求。(1) Receive a data read request from the storage node.
(2)从存储节点向主存储节点请求第一读索引(也即是RRI)。(2) Request the first read index (ie, RRI) from the storage node to the primary storage node.
(3)主存储节点确定第一读索引(这一过程参考上述步骤406,在此不再赘述),并将第一读索引发送给从存储节点。(3) The master storage node determines the first read index (for this process, refer to the above step 406, which is not repeated here), and sends the first read index to the slave storage node.
(4)从存储节点按照第一读索引,将日志执行到状态机中。(4) Execute the log into the state machine from the storage node according to the first read index.
(5)从存储节点从状态机中读取数据。(5) Read data from the state machine from the storage node.
需要说明的是,上述步骤(1)至步骤(5)的具体实施方式与步骤407同理,故在此不再赘述。It should be noted that, the specific implementation manners of the above steps (1) to (5) are the same as those of step 407, so they are not repeated here.
经过上述步骤405至步骤407,当第一目标数据为当前态数据时,第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标存储节点的节点类型,采用不同的数据读取方式,读取到了该第一目标数据。下面将通过步骤408至步骤410,对第一目标数据为历史态数据时,第一目标存储节点读取第一目标数据的方式进行介绍。After the
408、第一目标存储节点向该计算节点发送第一数据读取结果。408. The first target storage node sends the first data read result to the computing node.
在本申请实施例中,第一目标存储节点基于从第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取到的第一目标数据,生成第一数据读取结果,将该第一数据读取结果发送给计算节点,由计算节点将第一数据读取结果反馈至终端。在一些实施例中,第一目标存储节点将从第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取到的第一目标数据作为第一数据读取结果,发送给计算节点,由计算节点将第一数据读取结果反馈至终端,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In this embodiment of the present application, the first target storage node generates a first data read result based on the first target data read from the state machine corresponding to the first target data, and sends the first data read result to A computing node, the computing node feeds back the first data reading result to the terminal. In some embodiments, the first target storage node sends the first target data read from the state machine corresponding to the first target data as the first data reading result to the computing node, and the computing node stores the first data The read result is fed back to the terminal, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
需要说明的是,上述步骤404至步骤408是第一目标数据为当前态数据时,第一目标存储节点读取第一目标数据的方式,在一些实施例中,上述步骤404至步骤408能够替换为下述步骤404′至步骤408′。It should be noted that the above-mentioned steps 404 to 408 are the methods for the first target storage node to read the first target data when the first target data is current state data. In some embodiments, the above-mentioned steps 404 to 408 can be replaced It is the following steps 404' to 408'.
404′、第一目标存储节点基于第一目标数据的数据类型,确定该第一目标数据为历史态数据。404'. The first target storage node determines, based on the data type of the first target data, that the first target data is historical data.
其中,当第一目标数据为历史态数据时,第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标数据的事务完成时间,读取该第一目标数据(也即是下述步骤405′至步骤408′)。Wherein, when the first target data is historical data, the first target storage node reads the first target data (that is, the following step 405' to step 408').
405′、若该第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之前,则该第一目标存储节点执行下述步骤406′和步骤408′,若该第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之后,则第一目标存储节点执行下述步骤407′和步骤408′。405'. If the data submission time of the first target data is before the transaction completion time, the first target storage node executes the following steps 406' and 408', if the data submission time of the first target data is within the After the transaction completion time, the first target storage node executes the following steps 407' and 408'.
在本申请实施例中,第一目标存储节点在接收到计算节点发送的数据读取请求时,获取第一目标数据的关键字(Key)和该第一目标数据对应的事务完成时间,根据第一目标数据的数据提交时间是否在事务完成时间之前,采用不同的数据读取方式来读取第一目标数据。其中,当第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之前时,第一目标存储节点按照第二顺序扫描日志列表,以确定第一读索引(也即是RRI),从而读取第一目标数据(也即是下述步骤406′)。当第一目标数据的数据提交时间在事务完成时间之后时,第一目标存储节点按照第三顺序扫描日志列表,以确定第一读索引,从而读取第一目标数据(也即是下述步骤407′)。In this embodiment of the present application, when receiving the data read request sent by the computing node, the first target storage node obtains the keyword (Key) of the first target data and the transaction completion time corresponding to the first target data. Whether the data submission time of a target data is before the transaction completion time, different data reading methods are used to read the first target data. Wherein, when the data submission time of the first target data is before the completion time of the transaction, the first target storage node scans the log list in the second order to determine the first read index (that is, the RRI), so as to read the first target data (ie, step 406' described below). When the data submission time of the first target data is after the transaction completion time, the first target storage node scans the log list in the third order to determine the first read index, so as to read the first target data (that is, the following steps 407′).
406′、第一目标存储节点基于第一数据读取请求和事务完成时间,按照第二顺序,扫描日志列表中存储的日志,确定第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。406'. Based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time, the first target storage node scans the logs stored in the log list according to the second order, determines the first read index, and takes the first read index as the starting point, and starts from the first read index. The first target data is read from a state machine corresponding to a target data.
在本申请实施例中,该第二顺序是指从该日志列表的提交索引(Commit Index)至该日志列表的执行索引(Apply Index)。第一目标存储节点按照第二顺序扫描日志列表中存储的日志也可以理解为第一目标存储节点从提交索引(Commit Index)开始从后向前反向扫描日志列表,一直到执行索引(Apply Index)为止。In this embodiment of the present application, the second order refers to from a commit index (Commit Index) of the log list to an execution index (Apply Index) of the log list. The first target storage node scans the logs stored in the log list in the second order. It can also be understood that the first target storage node starts from the commit index (Commit Index) and scans the log list backwards and forwards until the execution of the index (Apply Index). )until.
其中,第一目标存储节点通过扫描日志列表来确定第一读索引,包括下述任一种情况:Wherein, the first target storage node determines the first read index by scanning the log list, including any of the following situations:
情况一、若存在第二目标日志,且该第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该第二目标日志的事务完成时间相同,或该第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第二目标日志的事务完成时间之后,基于该第二目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第二目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据。
其中,日志列表中包括日志时间信息,该日志时间信息用于指示每条日志的事务完成时间。第一目标存储节点在扫描日志列表的过程中,扫描到一条日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据,且第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该条日志的事务完成时间相同,或,第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第二目标日志的事务完成时间之后,则该条日志即为上述第二目标日志,将该第一读索引设置为该第二目标日志的日志索引(Log Index)。The log list includes log time information, where the log time information is used to indicate the transaction completion time of each log. In the process of scanning the log list, the first target storage node scans a log that operates on data that is the first target data, and the transaction completion time of the first target data is the same as the transaction completion time of the log, or, the first The transaction completion time of a target data is after the transaction completion time of the second target log, then the log is the above-mentioned second target log, and the first read index is set as the log index (Log Index) of the second target log. ).
情况二、若不存在该第二目标日志,基于该日志列表的执行索引,确定该第一读索引。Case 2: If the second target log does not exist, the first read index is determined based on the execution index of the log list.
其中,第一目标存储节点扫描日志列表后,未扫描到上述第二目标日志,则将该第一读索引设置为该日志列表的执行索引(Apply Index)。Wherein, after the first target storage node scans the log list, and fails to scan the second target log, the first read index is set as the execution index (Apply Index) of the log list.
下面参考图9,对本步骤406′所示的确定第一读索引的方式进行举例说明。图9是本申请实施例提供的一种确定第一读索引的示意图。如图9所示,日志列表中包括日志时间信息,用于指示每条日志的事务完成时间,也可以称为事务完成时间戳(Txn Commit TS)。日志列表中日志索引(Log Index)的值为1至8,分别代表日志1(Log 1)至日志8(Log 8),执行索引(Apply Index)为2,提交索引(Commit Index)为7。示意性地,第一目标存储节点从日志7(Log 7)开始,逐个向前扫描,若存在一条日志满足“日志所操作的数据为第一目标数据”且“第一目标数据的事务完成时间戳大于或等于该条日志的事务完成时间戳”(这一过程也可以理解为旨在发现日志列表中未被执行的、且接下来会被读到的旧数据),将第一读索引(也即RRI)设置为该条日志的日志索引(Log Index),并提前结束扫描。若扫描结束后,不存在上述所示的日志,则将第一读索引设置为该条日志的执行索引(Apply Index)。Referring to FIG. 9 , the manner of determining the first read index shown in this step 406 ′ will be illustrated below with reference to FIG. 9 . FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of determining a first read index according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 9 , the log list includes log time information, which is used to indicate the transaction completion time of each log, which may also be referred to as a transaction completion timestamp (Txn Commit TS). The values of the Log Index (Log Index) in the log list are 1 to 8, representing Log 1 (Log 1) to Log 8 (Log 8), respectively, the Apply Index (Apply Index) is 2, and the Commit Index (Commit Index) is 7. Schematically, the first target storage node starts from log 7 (Log 7) and scans forward one by one. If there is a log that satisfies "the data operated by the log is the first target data" and "the transaction completion time of the first target data" The stamp is greater than or equal to the transaction completion timestamp of the log" (this process can also be understood as the purpose of discovering the old data in the log list that has not been executed and will be read next), and the first read index ( That is, RRI) is set as the log index (Log Index) of the log, and the scan is ended in advance. If the above-mentioned log does not exist after the scanning is completed, the first read index is set as the execution index (Apply Index) of the log.
需要说明的是,对于本申请实施例所应用的分布式数据库系统而言,该分布式数据库系统为支持MVCC的数据库,读取某一版本之前的数据是一种需求。比如OLAP需要分析前天的统计数据,此时不需要最新的数据在状态机中,底层存储提供最新的数据并不是必要的。因此,上述步骤406′所示的读取第一目标数据的方式也可以称为读取旧数据,这一过程简称为旧数据读请求处理流程。下面参考图10,对这一旧数据读请求处理流程进行示意性说明。图10是本申请实施例提供的一种旧数据读请求处理流程的示意图。如图10所示,该旧数据读请求处理流程由第一目标存储节点执行,包括下述步骤(1)至步骤(7):It should be noted that, for the distributed database system applied in the embodiments of the present application, the distributed database system is a database supporting MVCC, and it is a requirement to read data before a certain version. For example, OLAP needs to analyze the statistical data of the day before yesterday. At this time, the latest data does not need to be in the state machine, and it is not necessary for the underlying storage to provide the latest data. Therefore, the method of reading the first target data shown in the above step 406' may also be referred to as reading old data, and this process is simply referred to as an old data read request processing flow. Referring to FIG. 10 below, a schematic illustration of the processing flow of this old data read request will be given. FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram of a processing flow of an old data read request provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 10, the old data read request processing flow is executed by the first target storage node, including the following steps (1) to (7):
(1)获取第一目标数据的关键字(Key)和第一目标数据的事务完成时间。(1) Obtain the keyword (Key) of the first target data and the transaction completion time of the first target data.
(2)从提交索引(Commit Index)开始从后向前进行反向扫描日志列表,一直到执行索引(Apply Index)为止。(2) From the commit index (Commit Index), the log list is reversely scanned from the back to the front until the index (Apply Index) is executed.
(3)判断日志列表中是否存在第二目标日志,且该第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该第二目标日志的事务完成时间相同,或该第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第二目标日志的事务完成时间之后,若是,执行下述步骤(4),若不是,执行下述步骤(5)。(3) Determine whether there is a second target log in the log list, and the transaction completion time of the first target data is the same as the transaction completion time of the second target log, or the transaction completion time of the first target data is in the second target log. After the transaction completion time of the target log, if yes, execute the following step (4), if not, execute the following step (5).
(4)基于第二目标日志的日志索引确定第一读索引。(4) Determine the first read index based on the log index of the second target log.
(5)基于日志列表的执行索引确定第一读索引。(5) Determine the first read index based on the execution index of the log list.
(6)按照第一读索引,将日志执行到状态机中。(6) According to the first read index, the log is executed into the state machine.
(7)从状态机中读取数据。(7) Read data from the state machine.
需要说明的是,上述步骤(1)至步骤(7)的具体实施方式与步骤406′同理,故在此不再赘述。It should be noted that, the specific implementations of the above steps (1) to (7) are the same as those of step 406', so they are not repeated here.
经过步骤406′,第一目标存储节点在第一目标数据为旧数据时,通过确定第一读索引,引入放宽读方法,从而减少了数据读取请求的处理时间,提高了分布式数据库系统的数据访问效率。After step 406 ′, when the first target data is old data, the first target storage node determines the first read index and introduces a relaxed read method, thereby reducing the processing time of the data read request and improving the performance of the distributed database system. Data access efficiency.
407′、该第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求和该事务完成时间,按照第三顺序,扫描该日志列表中存储的日志,确定该第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。407'. Based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time, the first target storage node scans the logs stored in the log list in a third order, determines the first read index, and uses the first read index As a starting point, the first target data is read from the state machine corresponding to the first target data.
在本申请实施例中,该第三顺序是指从该日志列表的执行索引(Apply Index)至该日志列表的提交索引(Commit Index)。第一目标存储节点按照第三顺序扫描日志列表中存储的日志也可以理解为第一目标存储节点从执行索引(Apply Index)开始向前往后正向扫描日志列表,一直到提交索引(Commit Index)为止。In the embodiment of the present application, the third order refers to from the execution index (Apply Index) of the log list to the commit index (Commit Index) of the log list. The first target storage node scans the logs stored in the log list in the third order. It can also be understood that the first target storage node scans the log list forward and backward from the execution index (Apply Index) until the commit index (Commit Index). until.
其中,第一目标存储节点通过扫描日志列表来确定第一读索引,包括下述任一种情况:Wherein, the first target storage node determines the first read index by scanning the log list, including any of the following situations:
情况一、若存在第三目标日志,且该第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该第三目标日志的事务完成时间相同,或该第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第三目标日志的事务完成时间之后,基于该第三目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第三目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据。
其中,日志列表中包括日志时间信息,该日志时间信息用于指示每条日志的事务完成时间。第一目标存储节点在扫描日志列表的过程中,扫描到一条日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据,且第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该条日志的事务完成时间相同,或,第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第三目标日志的事务完成时间之后,则该条日志即为上述第三目标日志,将该第一读索引设置为该第三目标日志的日志索引(Log Index)。The log list includes log time information, where the log time information is used to indicate the transaction completion time of each log. In the process of scanning the log list, the first target storage node scans a log that operates on data that is the first target data, and the transaction completion time of the first target data is the same as the transaction completion time of the log, or, the first The transaction completion time of a target data is after the transaction completion time of the third target log, then the log is the above-mentioned third target log, and the first read index is set as the log index (Log Index) of the third target log. ).
情况二、若不存在该第三目标日志,基于该日志列表的执行索引,确定该第一读索引。Case 2: If the third target log does not exist, the first read index is determined based on the execution index of the log list.
其中,第一目标存储节点扫描日志列表后,未扫描到上述第三目标日志,则将该第一读索引设置为该日志列表的执行索引(Apply Index)。Wherein, after the first target storage node scans the log list, and fails to scan the third target log, the first read index is set as the execution index (Apply Index) of the log list.
下面继续参考图9,对本步骤407′所示的确定第一读索引的方式进行举例说明。如图9所示,日志列表中包括日志时间信息,用于指示每条日志的事务完成时间,也可以称为事务完成时间戳(Txn Commit TS)。日志列表中日志索引(Log Index)的值为1至8,分别代表日志1(Log 1)至日志8(Log 8),执行索引(Apply Index)为2,提交索引(Commit Index)为7。示意性地,第一目标存储节点从日志2(Log 2)开始,逐个向后扫描,若存在一条日志满足“日志所操作的数据为第一目标数据”且“第一目标数据的事务完成时间戳大于或等于该条日志的事务完成时间戳”(这一过程也可以理解为旨在发现日志列表中未被执行的、且接下来会被读到的非最新数据),将第一读索引(也即RRI)设置为该条日志的日志索引(LogIndex),并提前结束扫描。若扫描结束后,不存在上述所示的日志,则将第一读索引设置为该条日志的执行索引(Apply Index)。Continuing to refer to FIG. 9 , the manner of determining the first read index shown in this step 407 ′ will be illustrated by an example. As shown in FIG. 9 , the log list includes log time information, which is used to indicate the transaction completion time of each log, which may also be referred to as a transaction completion timestamp (Txn Commit TS). The values of the Log Index (Log Index) in the log list are 1 to 8, representing Log 1 (Log 1) to Log 8 (Log 8), respectively, the Apply Index (Apply Index) is 2, and the Commit Index (Commit Index) is 7. Schematically, the first target storage node starts from log 2 (Log 2) and scans backward one by one. The stamp is greater than or equal to the transaction completion timestamp of the log" (this process can also be understood as the purpose of discovering the non-latest data in the log list that has not been executed and will be read next), index the first read (that is, RRI) is set to the log index (LogIndex) of the log, and the scan ends early. If the above-mentioned log does not exist after the scanning is completed, the first read index is set as the execution index (Apply Index) of the log.
需要说明的是,对于本申请实施例所应用的分布式数据库系统而言,该分布式数据库系统为支持MVCC的数据库,读取某一版本之后的数据也是一种需求。比如事务需要读取某一时间戳之后的数据即可,并不需要数据是最新的。因此,上述步骤407′所示的读取第一目标数据的方式也可以称为读取非最新数据,这一过程简称为非最新数据读请求处理流程。下面参考图11,对这一非最新数据读请求处理流程进行示意性说明。图11是本申请实施例提供的一种非最新数据读请求处理流程的示意图。如图11所示,该非最新数据读请求处理流程由第一目标存储节点执行,包括下述步骤(1)至步骤(7):It should be noted that, for the distributed database system applied in the embodiments of the present application, the distributed database system is a database supporting MVCC, and reading data after a certain version is also a requirement. For example, the transaction needs to read the data after a certain timestamp, and the data does not need to be the latest. Therefore, the method of reading the first target data shown in the above step 407' may also be referred to as reading non-latest data, and this process is simply referred to as a non-latest data read request processing flow. Referring to FIG. 11 , a schematic illustration of the processing flow of this non-latest data read request will be given below. FIG. 11 is a schematic diagram of a processing flow of a non-latest data read request provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 11, the non-latest data read request processing flow is executed by the first target storage node, including the following steps (1) to (7):
(1)获取第一目标数据的关键字(Key)和第一目标数据的事务完成时间。(1) Obtain the keyword (Key) of the first target data and the transaction completion time of the first target data.
(2)从执行索引(Apply Index)开始向前往后进行正向扫描日志列表,一直到提交索引(Commit Index)为止。(2) From the execution of the index (Apply Index), the log list is scanned forward and backward until the index (Commit Index) is submitted.
(3)判断日志列表中是否存在第三目标日志,且该第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该第三目标日志的事务完成时间相同,或该第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第三目标日志的事务完成时间之后,若是,执行下述步骤(4),若不是,执行下述步骤(5)。(3) Determine whether there is a third target log in the log list, and the transaction completion time of the first target data is the same as the transaction completion time of the third target log, or the transaction completion time of the first target data is in the third target log. After the transaction completion time of the target log, if yes, execute the following step (4), if not, execute the following step (5).
(4)基于第三目标日志的日志索引确定第一读索引。(4) Determine the first read index based on the log index of the third target log.
(5)基于日志列表的执行索引确定第一读索引。(5) Determine the first read index based on the execution index of the log list.
(6)按照第一读索引,将日志执行到状态机中。(6) According to the first read index, the log is executed into the state machine.
(7)从状态机中读取数据。(7) Read data from the state machine.
需要说明的是,上述步骤(1)至步骤(7)的具体实施方式与步骤407′同理,故在此不再赘述。It should be noted that, the specific implementations of the above steps (1) to (7) are the same as those of step 407 ′, so they are not repeated here.
经过步骤407′,第一目标存储节点在第一目标数据为非最新数据时,通过确定第一读索引,引入放宽读方法,从而减少了数据读取请求的处理时间,提高了分布式数据库系统的数据访问效率。After step 407 ′, when the first target data is not the latest data, the first target storage node determines the first read index and introduces the relaxed read method, thereby reducing the processing time of the data read request and improving the distributed database system. data access efficiency.
408′、第一目标存储节点向该计算节点发送第一数据读取结果。408': The first target storage node sends the first data read result to the computing node.
在本申请实施例中,步骤408′与上述步骤408同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, step 408' is the same as the above-mentioned step 408, and thus will not be repeated here.
经过上述步骤404′至步骤408′,当第一目标数据为历史态数据时,第一目标存储节点基于该第一数据读取请求和第一目标数据的事务完成时间,采用不同的数据读取方式,读取到了该第一目标数据。这一过程也可以称为特殊时间版本数据的读取过程。通过确定放宽读索引的方式,减少了数据读取请求的处理时间,从而有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。After the above steps 404' to 408', when the first target data is historical data, the first target storage node uses different data read requests based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time of the first target data. mode, the first target data is read. This process can also be referred to as the reading process of the special time version data. By determining the way to relax the read index, the processing time of the data read request is reduced, thereby effectively improving the data access performance of the distributed database system.
在本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法中,当计算节点接收到数据读取请求时,先根据该数据读取请求的目标数据所属的数据分片,来确定存储有该目标数据的多个副本的多个存储节点,然后按照存储节点访问目标数据的数据访问代价,从这些存储节点中选出符合目标条件的目标存储节点,由该目标存储节点来读取目标数据。上述方法中,由于该目标存储节点是根据数据访问代价来确定的,因此主存储节点和从存储节点都可能成为目标存储节点,避免了由主存储节点处理所有的数据读取请求,从而既保证了多副本带来的高可用性,又提高了数据读取速度,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。In the data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application, when a computing node receives a data read request, it first determines that multiple copies of the target data are stored according to the data fragment to which the target data of the data read request belongs. Then, according to the data access cost of the storage nodes accessing the target data, a target storage node that meets the target conditions is selected from these storage nodes, and the target storage node reads the target data. In the above method, since the target storage node is determined according to the data access cost, both the master storage node and the slave storage node may become the target storage node, avoiding the master storage node processing all data read requests, thus ensuring that both It improves the high availability brought by multiple copies, improves the data reading speed, and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
通过上述图4所示的实施例,以数据访问请求的请求类型为数据读取请求为例,对本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法进行了介绍。下面结合图12,对本申请实施例提供的另一种数据访问方法进行详细介绍。The data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application is introduced by taking the request type of the data access request as a data read request as an example through the above-mentioned embodiment shown in FIG. 4 . The following describes in detail another data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application with reference to FIG. 12 .
图12是本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法的流程图,如图12所示,该实施例应用于分布式数据库系统,该分布式数据库系统包括计算节点和多个存储节点。示意性地,在图12所示的实施例中,该数据访问方法适用于数据访问请求的请求类型为数据写入请求,该数据访问方法应用于如图2所示的HTAP数据库系统,以计算节点和存储节点之间的交互为例来进行说明。该实施例包括下述步骤。FIG. 12 is a flowchart of a data access method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 12 , this embodiment is applied to a distributed database system, and the distributed database system includes a computing node and a plurality of storage nodes. Schematically, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 12 , the data access method applicable to the request type of the data access request is a data write request, and the data access method is applied to the HTAP database system shown in FIG. 2 to calculate The interaction between nodes and storage nodes is taken as an example to illustrate. This embodiment includes the following steps.
1201、计算节点基于终端发送的连接请求,与终端建立连接。1201. The computing node establishes a connection with the terminal based on the connection request sent by the terminal.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1201与上述步骤401同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, step 1201 is the same as step 401 above, and thus will not be repeated here.
1202、计算节点响应于数据写入请求,确定该数据写入请求的第二目标数据是否存在所属的第三数据分片,若不存在,则由计算节点和多个存储节点分别执行下述步骤1203和步骤1204,若存在,则由计算节点执行下述步骤1205。1202. In response to the data writing request, the computing node determines whether the second target data of the data writing request has a third data fragment to which it belongs, and if not, the computing node and multiple storage nodes perform the following steps respectively Step 1203 and step 1204, if there is, the computing node will execute the following step 1205.
在本申请实施例中,计算节点接收终端发送的数据写入请求,根据该数据写入请求的第二目标数据的数据内容,计算该第二目标数据所属的第三数据分片,判断该当前多个存储节点中是否存在该第三数据分片。若不存在,则需建立该第二目标数据所属的第三数据分片及对应的多个副本(也即是下述步骤1203和步骤1204),若存在,则计算节点根据第二目标数据的数据内容,确定该第二目标数据在当前分布式数据库系统中所属的第三数据分片,并根据该第三数据分片的分片信息,从多个存储节点中确定多个第二存储节点(也即是下述步骤1205)。In the embodiment of the present application, the computing node receives the data writing request sent by the terminal, calculates the third data fragment to which the second target data belongs according to the data content of the second target data of the data writing request, and judges the current Whether the third data fragment exists in multiple storage nodes. If it does not exist, the third data fragment to which the second target data belongs and the corresponding multiple copies need to be established (that is, the following steps 1203 and 1204). data content, determine the third data fragment to which the second target data belongs in the current distributed database system, and determine a plurality of second storage nodes from a plurality of storage nodes according to fragment information of the third data fragment (that is, the following step 1205).
1203、计算节点建立该第二目标数据所属的第三数据分片,向该多个存储节点发送副本创建请求。1203. The computing node creates a third data fragment to which the second target data belongs, and sends a copy creation request to the multiple storage nodes.
在本申请实施例中,计算节点基于第二目标数据的数据内容,建立该第二目标数据所属的第三数据分片,基于该第三数据分片的分片信息,向多个存储节点发送副本创建请求。可选地,该副本创建请求携带第二目标数据的数据内容、第三数据分片的分片信息以及副本的存储模式等,本申请实施例对此不作限定。在一些实施例中,计算节点将该第三数据分片的分片信息存储至元数据管理层。In this embodiment of the present application, the computing node creates a third data fragment to which the second target data belongs based on the data content of the second target data, and sends the data to multiple storage nodes based on fragmentation information of the third data fragment. Copy creation request. Optionally, the copy creation request carries the data content of the second target data, the fragmentation information of the third data fragment, the storage mode of the copy, and the like, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application. In some embodiments, the computing node stores the fragmentation information of the third data fragment in the metadata management layer.
1204、多个存储节点基于该副本创建请求,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本。1204. Multiple storage nodes create multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment based on the copy creation request.
在本申请实施例中,多个存储节点接收到计算节点发送的副本创建请求后,基于该副本创建请求,在各自的存储节点上建立该第三数据分片对应的副本。In the embodiment of the present application, after receiving the replica creation request sent by the computing node, multiple storage nodes create replicas corresponding to the third data fragment on their respective storage nodes based on the replica creation request.
在一些实施例中,多个存储节点基于该副本创建请求和该第二目标数据在多个存储节点中的存储模式,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。In some embodiments, multiple storage nodes create multiple copies corresponding to the third data slice based on the copy creation request and storage modes of the second target data in the multiple storage nodes, where the storage mode is used to indicate The storage format of the data in the storage node.
在一些实施例中,多个存储节点根据预设副本配置策略,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本。例如,预设副本配置策略如下:每个数据分片共建立N个副本,其中K个副本的存储模式为行存模式,N-K个副本的存储模式为列存模式,其中,N和K为正整数,N个副本分散在N个物理节点上进行存储,通过分布式一致性协议管理,并通过选举机制选出主存储节点。应理解,副本的配置策略可根据实际情况进行调整,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, multiple storage nodes establish multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment according to a preset copy configuration policy. For example, the preset copy configuration strategy is as follows: a total of N copies are established for each data shard, wherein the storage mode of K copies is row storage mode, and the storage mode of N-K copies is column storage mode, where N and K are positive Integer, N copies are scattered on N physical nodes for storage, managed through a distributed consensus protocol, and the primary storage node is elected through an election mechanism. It should be understood that the configuration policy of the replica may be adjusted according to the actual situation, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
需要说明的是,第三数据分片对应的多个副本的存储模式的具体内容可参考上述步骤402,故在此不再赘述。另外,在该第三数据分片对应的多个副本建立完成后,该多个存储节点对该多个副本的存储模式进行动态调整。这一过程与上述步骤402中所示的“多个第一存储节点对多个副本的存储模式进行动态调整”同理,故在此不再赘述。It should be noted that, for the specific content of the storage modes of the multiple copies corresponding to the third data slice, reference may be made to the foregoing step 402, and thus will not be repeated here. In addition, after the establishment of multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment is completed, the multiple storage nodes dynamically adjust the storage modes of the multiple copies. This process is the same as the "multiple first storage nodes dynamically adjust the storage modes of multiple copies" shown in the foregoing step 402, and thus will not be repeated here.
1205、计算节点基于该第三数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第二存储节点,该多个第二存储节点用于存储第二目标数据的多个副本。1205. The computing node determines, based on the third data fragment, a plurality of second storage nodes from the plurality of storage nodes, where the plurality of second storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the second target data.
在本申请实施例中,计算节点确定多个第二存储节点的方式与上述步骤301和步骤402同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, the manner in which the computing node determines a plurality of second storage nodes is the same as the above-mentioned step 301 and step 402, and thus will not be repeated here.
1206、计算节点向该多个第二存储节点中的主存储节点发送该数据写入请求。1206. The computing node sends the data write request to the primary storage node among the plurality of second storage nodes.
1207、主存储节点基于该数据写入请求,写入该第二目标数据,生成数据操作日志,向该多个存储节点中的从存储节点发送日志同步请求,该日志同步请求用于指示从存储节点同步该数据操作日志后向该主存储节点发送数据同步消息。1207. Based on the data writing request, the master storage node writes the second target data, generates a data operation log, and sends a log synchronization request to the slave storage node in the plurality of storage nodes, where the log synchronization request is used to indicate the slave storage node. The node sends a data synchronization message to the primary storage node after synchronizing the data operation log.
在本申请实施例中,主存储节点在接收到数据写入请求后,先进行合法性判断,在数据写入请求合法的前提下,写入该第二目标数据,生成数据操作日志,向从存储节点发送日志同步请求,等待从存储节点返回数据同步消息。在一些实施例中,该数据操作日志包括操作类型、被操作的数据项以及操作时间等,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In the embodiment of the present application, after receiving the data write request, the primary storage node firstly judges the validity, and on the premise that the data write request is legal, writes the second target data, generates a data operation log, and sends the data to the slave. The storage node sends a log synchronization request and waits for a data synchronization message to be returned from the storage node. In some embodiments, the data operation log includes the operation type, the operated data item, and the operation time, etc., which are not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
在一些实施例中,当主存储节点基于该数据写入请求,写入第二目标数据,生成数据操作日志之后,主存储节点确定该第二目标数据的第二读索引,并将该第二读索引进行存储,以便分布式数据库系统在接收到需要读取第二目标数据的数据读取请求时,通过查表来读取相应的数据。下面通过下述三个步骤来对这一可选实施方式进行介绍:In some embodiments, after the primary storage node writes the second target data and generates a data operation log based on the data write request, the primary storage node determines a second read index of the second target data, and writes the second read index to the second target data. The index is stored, so that the distributed database system can read the corresponding data by looking up the table when receiving a data read request that needs to read the second target data. This alternative implementation is described in the following three steps:
步骤一、主存储节点基于该数据操作日志的日志索引,确定该第二目标数据的第二读索引,该第二读索引用于指示基于第三数据读取请求读取该第二目标数据的最小读索引。Step 1: The main storage node determines the second read index of the second target data based on the log index of the data operation log, and the second read index is used to indicate the read request of the second target data based on the third data read request. Minimum read index.
需要说明的是,第二目标数据的第二读索引也即是第二目标数据的RRI,RRI的具体含义与上述图4所示的实施例同理,故在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the second read index of the second target data is also the RRI of the second target data, and the specific meaning of the RRI is the same as the embodiment shown in FIG.
步骤二、将该第二读索引存储至第二列表,该第二列表包括该第二目标数据、该第二读索引以及第二校验索引,该第二校验索引为该数据操作日志的日志索引。Step 2: Store the second read index in a second list, where the second list includes the second target data, the second read index, and a second check index, where the second check index is an index of the data operation log. log index.
其中,对于每条数据操作日志,该数据操作日志所操作的数据的RRI为该条日志的日志索引(Log Index),第二校验索引(Check Index)也为该条日志的日志索引(LogIndex)。Among them, for each data operation log, the RRI of the data operated by the data operation log is the log index (Log Index) of the log, and the second check index (Check Index) is also the log index (LogIndex) of the log. ).
在一些实施例中,若该第二列表中数据项的数量大于或等于预设阈值,则删除该第二列表中的至少一个数据项和对应的RRI,该至少一个数据项的RRI小于执行索引(ApplyIndex)。例如,该预设阈值为100,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In some embodiments, if the number of data items in the second list is greater than or equal to a preset threshold, at least one data item and corresponding RRI in the second list are deleted, and the RRI of the at least one data item is smaller than the execution index (ApplyIndex). For example, the preset threshold is 100, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present application.
步骤三、当分布式数据库系统处理第三数据读取请求时,若该第三数据读取请求所需读取的数据为该第二目标数据,查询该第二列表以读取该第二目标数据。Step 3: When the distributed database system processes the third data read request, if the data to be read by the third data read request is the second target data, query the second list to read the second target data.
其中,该分布式数据库系统处理查询第二列表以读取该第二目标数据的方式与上述步骤406同理,故在此不再赘述。The manner in which the distributed database system processes the query of the second list to read the second target data is the same as that in the above-mentioned step 406, and thus will not be repeated here.
下面参考图13,对上述存储第二读索引以及处理第三数据读取请求的可选实施方式进行举例说明。图13是本申请实施例提供的一种存储第二读索引的示意图。如图13所示,主存储节点将数据操作日志的结果存储在列表中,该列表中包括数据项以及对应的RRI和校验索引(Check Index),其中,校验索引(Check Index)的值等于日志索引(Log Index)的值;该数据操作日志所操作的数据的RRI为该条日志的日志索引(Log Index)。示意性地,如图13中(a)和(b)图所示,当第二目标数据为x时,其对应的RRI的值为7,当第二目标数据为y时,其对应的RRI的值为6,等等。图13中(c)和(d)图与(a)和(b)图同理,故在此不再赘述。Referring to FIG. 13 , the foregoing optional implementation manner of storing the second read index and processing the third data read request will be described by way of example. FIG. 13 is a schematic diagram of storing a second read index according to an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 13 , the main storage node stores the results of the data operation log in a list, which includes data items and corresponding RRIs and a check index (Check Index), wherein the value of the check index (Check Index) Equal to the value of the log index (Log Index); the RRI of the data operated by the data operation log is the log index (Log Index) of the log. Schematically, as shown in (a) and (b) of FIG. 13 , when the second target data is x, the corresponding RRI value is 7, and when the second target data is y, the corresponding RRI value is 7. is 6, and so on. The diagrams (c) and (d) in FIG. 13 are the same as the diagrams (a) and (b), so they will not be repeated here.
需要说明的是,通过这种将第二读索引存储至第二列表的方式,能够避免多次重复扫描日志列表,减少数据处理量,从而节约计算资源。另外,由于该第二列表的信息是在每次处理数据写入请求时更新的,所以这种可选实施方法也可以称为写时更新法。应理解,由于每次只需要更新与数据写入请求相关数据的参数,这种方法的单次更新量要小于上述步骤406中介绍的读时更新方法。与读时更新方法同理,第二列表的大小一般不会超过10项,足以存放于内存中,并且不需要同步到持久化存储中,故障恢复时按照相同策略重构该表即可。It should be noted that, by storing the second read index in the second list in this manner, repeated scanning of the log list can be avoided, data processing amount can be reduced, and computing resources can be saved. In addition, since the information in the second list is updated each time a data write request is processed, this optional implementation method may also be called an update-on-write method. It should be understood that since only the parameters related to the data writing request need to be updated each time, the single update amount of this method is smaller than the update-on-read method introduced in the above step 406 . Similar to the update-on-read method, the size of the second list generally does not exceed 10 items, which is enough to store in memory and does not need to be synchronized to persistent storage. The table can be reconstructed according to the same strategy during failure recovery.
1208、若主存储节点接收到的数据同步消息的数量大于或等于从存储节点数量的半数,该主存储节点确认该数据写入请求已操作成功。1208. If the number of data synchronization messages received by the master storage node is greater than or equal to half of the number of slave storage nodes, the master storage node confirms that the data write request has been successfully operated.
在本申请实施例中,当从存储节点接收到主存储节点发送的日志同步请求后,将数据操作日志同步到各自的日志记录中,并将主存储节点发送数据同步消息,以通知主存储节点日志已同步成功。当主存储节点接收到的数据同步消息的数量大于或等于从存储节点数量的半数,则确认该数据写入请求已操作成功。In the embodiment of the present application, after receiving the log synchronization request sent by the main storage node from the storage node, the data operation log is synchronized to the respective log records, and the main storage node sends a data synchronization message to notify the main storage node. Logs have been synced successfully. When the number of data synchronization messages received by the master storage node is greater than or equal to half of the number of slave storage nodes, it is confirmed that the data write request has been successfully operated.
需要说明的是,在相关分布式一致性协议(例如Raft协议)中,主存储节点接收到数据写入请求后,把数据写入请求作为日志条目加入到自己的日志中,然后向其他从存储节点复制日志。当这条日志被复制到大多数从存储节点上时,主存储节点将这条日志持久化存储到自己的状态机中,之后才能将执行结果返回到终端,表示写入成功。在这个过程中,从存储节点的持久化是异步完成的,无需等待,但是主存储节点的持久化是同步的,需要等待持久化成功后才能返回执行结果。而在本申请实施例中,将主存储节点的持久化改为异步,即保证半数从存储节点复制了日志后,即可返回执行结果,不需要等待主存储节点持久化成功,从而减少了数据写入请求的等待时间,有效提升了数据写入请求的处理效率,提高了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。It should be noted that in related distributed consistency protocols (such as Raft protocol), after the master storage node receives a data write request, it adds the data write request as a log entry to its own log, and then sends the data write request to other slave storage nodes. Node replication log. When the log is copied to most of the slave storage nodes, the master storage node persistently stores the log in its own state machine, and then returns the execution result to the terminal, indicating that the writing is successful. In this process, the persistence of the slave storage node is completed asynchronously without waiting, but the persistence of the primary storage node is synchronous, and the execution result can be returned only after the persistence is successful. However, in the embodiment of the present application, the persistence of the main storage node is changed to asynchronous, that is, it is guaranteed that after half of the logs are copied from the storage nodes, the execution result can be returned, and there is no need to wait for the main storage node to be successfully persisted, thereby reducing the number of data The waiting time of the write request effectively improves the processing efficiency of the data write request and improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
1209、主存储节点向计算节点发送第一数据写入结果。1209. The primary storage node sends the first data writing result to the computing node.
在本申请实施例中,主存储节点基于数据写入请求已操作成功,生成第一数据写入结果,将该第一数据写入结果发送给计算节点,由计算节点将第一数据写入结果反馈至终端。In this embodiment of the present application, the primary storage node generates a first data writing result based on the successful operation of the data writing request, sends the first data writing result to the computing node, and the computing node writes the first data writing result feedback to the terminal.
在一些实施例中,主存储节点向计算节点发送第一数据写入结果后,该数据访问方法还包括:主存储节点对该第二目标数据进行持久化存储;从存储节点基于该数据操作日志和该第二目标数据在该从存储节点中的存储模式,对该第二目标数据进行格式转换,对转换后的第二目标数据进行持久化存储。需要说明的是,这一过程也即是主从节点对写入数据进行异步持久化操作的过程。示意性地,主存储节点对数据根据本节点的配置进行落盘;从存储节点逐步进行数据落盘工作:取出一条日志记录,获得操作类型、数据项。从存储节点访问格式转换器,指定本节点所需记录的数据存储模式及数据项,得到转换后的数据,并对数据落盘至状态机。In some embodiments, after the primary storage node sends the first data writing result to the computing node, the data access method further includes: the primary storage node persistently stores the second target data; the secondary storage node operates the log based on the data and the storage mode of the second target data in the slave storage node, perform format conversion on the second target data, and perform persistent storage on the converted second target data. It should be noted that this process is also the process in which the master-slave node performs an asynchronous persistent operation on the written data. Schematically, the main storage node places data on the disk according to the configuration of the node; the data is placed on the disk step by step from the storage node: a log record is taken out to obtain the operation type and data item. Access the format converter from the storage node, specify the data storage mode and data items to be recorded by this node, obtain the converted data, and put the data into the state machine.
在上述步骤1201至步骤1209所示的数据访问方法中,当计算节点接收到数据写入请求时,先根据该数据写入请求的目标数据所属的数据分片,来确定存储有该目标数据的多个副本的多个存储节点,然后向多个存储节点的主存储节点发送该数据写入请求,当超过一半数量的从存储节点日志同步完成,则允许主存储节点未将日志信息持久化到状态机中就返回执行结果,这一过程也可以称为基于提交退回(Commit Return)的数据写入方法。这种方法加快了数据写入请求的返回速度,提高了整体系统的写性能,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。In the data access method shown in the above steps 1201 to 1209, when the computing node receives a data write request, it first determines the data shard that stores the target data according to the data fragment to which the target data of the data write request belongs. Multiple storage nodes with multiple copies, and then send the data write request to the master storage node of multiple storage nodes. When more than half of the slave storage node logs are synchronized, the master storage node is allowed to not persist log information to The execution result is returned in the state machine, and this process can also be called a data writing method based on Commit Return. This method speeds up the return speed of data write requests, improves the write performance of the overall system, and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
通过上述图4和图12所示的实施例,分别以数据访问请求为数据读取请求和数据写入请求为例,对本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法进行了介绍。下面结合图14,对本申请实施例提供的另一种数据访问方法进行详细介绍。The data access method provided by the embodiment of the present application is introduced by taking the data access request as a data read request and a data write request as an example through the above embodiments shown in FIG. 4 and FIG. 12 . Another data access method provided by this embodiment of the present application will be described in detail below with reference to FIG. 14 .
图14是本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问方法的流程图,如图14所示,该实施例应用于分布式数据库系统,该分布式数据库系统包括计算节点和多个存储节点。示意性地,在图14所示的实施例中,该数据访问方法适用于数据访问请求为数据读写请求,该数据访问方法应用于如图2所示的HTAP数据库系统,以计算节点和存储节点之间的交互为例来进行说明。该实施例包括下述步骤。FIG. 14 is a flowchart of a data access method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 14 , this embodiment is applied to a distributed database system, and the distributed database system includes a computing node and a plurality of storage nodes. Schematically, in the embodiment shown in FIG. 14, the data access method is applicable to the data access request being a data read/write request, and the data access method is applied to the HTAP database system shown in FIG. The interaction between nodes is described as an example. This embodiment includes the following steps.
1401、计算节点基于终端发送的连接请求,与终端建立连接。1401. The computing node establishes a connection with the terminal based on the connection request sent by the terminal.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1401与上述步骤401同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, step 1401 is the same as step 401 above, and thus is not repeated here.
1402、计算节点响应于数据读写请求,确定该数据读写请求的第三目标数据是否存在所属的第四数据分片,若不存在,则由计算节点和多个存储节点分别执行下述步骤1403和步骤1404,若存在,则由计算节点执行下述步骤1405至步骤1407。1402. In response to the data read/write request, the computing node determines whether the third target data of the data read/write request has a fourth data fragment to which it belongs, and if not, the computing node and multiple storage nodes perform the following steps respectively: Steps 1403 and 1404, if exist, the computing node executes the following steps 1405 to 1407.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1402与上述步骤1202同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application,
1403、计算节点建立该第三目标数据所属的第四数据分片,向该多个存储节点发送副本创建请求。1403. The computing node creates a fourth data fragment to which the third target data belongs, and sends a copy creation request to the plurality of storage nodes.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1403与上述步骤1203同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, step 1403 is the same as the above-mentioned step 1203, and thus will not be repeated here.
1404、多个存储节点基于该副本创建请求,建立该第四数据分片对应的多个副本。1404. Multiple storage nodes create multiple copies corresponding to the fourth data fragment based on the copy creation request.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1404与上述步骤1204同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, step 1404 is the same as the above-mentioned step 1204, and thus will not be repeated here.
1405、计算节点基于该第四数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第三存储节点,该多个第三存储节点用于存储第三目标数据的多个副本。1405. The computing node determines, based on the fourth data fragment, a plurality of third storage nodes from the plurality of storage nodes, where the plurality of third storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the third target data.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1405与上述步骤1205同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, step 1405 is the same as the above-mentioned step 1205, and thus will not be repeated here.
1406、对于数据读写请求中的读操作,计算节点基于数据读写请求,从多个第三存储节点中确定第二目标存储节点,向第二目标存储节点发送数据读写请求,该第二目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第二目标条件。1406. For the read operation in the data read/write request, the computing node determines a second target storage node from a plurality of third storage nodes based on the data read/write request, and sends a data read/write request to the second target storage node. The data access cost of the target storage node meets the second target condition.
1407、第二目标存储节点基于数据读写请求,读取该第三目标数据,向该计算节点发送第二数据读取结果。1407. The second target storage node reads the third target data based on the data read/write request, and sends the second data read result to the computing node.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1406和步骤1407与上述步骤403至步骤411同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, steps 1406 and 1407 are the same as the above-mentioned steps 403 to 411, and thus are not repeated here.
1408、对于该数据读写请求中的写操作,该计算节点向该多个第三存储节点中的主存储节点发送该数据读写请求。1408. For the write operation in the data read/write request, the computing node sends the data read/write request to the main storage node among the plurality of third storage nodes.
1409、主存储节点基于该数据读写请求,写入该第三目标数据,向该计算节点发送第二数据写入结果。1409. The main storage node writes the third target data based on the data read/write request, and sends the second data write result to the computing node.
在本申请实施例中,步骤1408和步骤1409与上述步骤1206至步骤1209同理,故在此不再赘述。In this embodiment of the present application, steps 1408 and 1409 are the same as the above-mentioned steps 1206 to 1209 , and thus are not repeated here.
需要说明的是,在本申请实施例中,分布式数据库系统是按照上述步骤1406至步骤1409来执行的,在一些实施例中,分布式数据库系统先执行步骤1408和步骤1409,再执行步骤1406和步骤1407。在另一些实施例中,分布式数据库系统同步执行上述步骤1406至步骤1409,本申请实施例对于上述步骤1406至步骤1409的执行顺序不作限定。It should be noted that, in this embodiment of the present application, the distributed database system executes steps 1406 to 1409 above. In some embodiments, the distributed database system executes steps 1408 and 1409 first, and then executes step 1406 and step 1407. In other embodiments, the distributed database system synchronously executes the foregoing steps 1406 to 1409 , and the embodiment of the present application does not limit the execution order of the foregoing steps 1406 to 1409 .
在一些实施例中,该多个第三存储节点中的从存储节点配置有内存锁,该内存锁用于在该写操作尚未完成时锁定该第三目标数据。通过这种方式能够确保并发事务的可串行化调度。In some embodiments, a slave storage node among the plurality of third storage nodes is configured with a memory lock, and the memory lock is used to lock the third target data when the write operation has not been completed. In this way, serializable scheduling of concurrent transactions can be ensured.
在上述步骤1401至步骤1409所示的数据访问方法中,当计算节点接收到数据读写请求时,先根据该数据读写请求的目标数据所属的数据分片,来确定存储有该目标数据的多个副本的多个存储节点,然后针对数据读写请求中的读操作和写操作,分别进行数据读取和数据写入。In the data access method shown in the above steps 1401 to 1409, when the computing node receives a data read/write request, it firstly determines the data fragment that stores the target data according to the data fragment to which the target data of the data read/write request belongs. Multiple storage nodes with multiple copies, and then perform data reading and data writing respectively for the read and write operations in the data read and write requests.
对于读操作,按照目标数据的数据访问代价,从这些存储节点中选出符合目标条件的目标存储节点,由该目标存储节点来读取目标数据,这一过程中,由于该目标存储节点是根据数据访问代价来确定的,因此主存储节点和从存储节点都可能成为目标存储节点,避免了由主存储节点处理所有的数据读取请求,从而既保证了多副本带来的高可用性,又提高了数据读取速度,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。For the read operation, according to the data access cost of the target data, the target storage node that meets the target conditions is selected from these storage nodes, and the target storage node reads the target data. The data access cost is determined, so both the primary storage node and the secondary storage node may become the target storage node, avoiding the primary storage node to process all data read requests, thus not only ensuring the high availability brought by multiple copies, but also improving It improves the data reading speed and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
对于写操作,向多个存储节点的主存储节点发送该数据写入请求,当超过一半数量的从存储节点日志同步完成,则允许主存储节点未将日志信息持久化到状态机中就返回执行结果,这一方法加快了数据写入请求的返回速度,提高了整体系统的写性能,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。For write operations, the data write request is sent to the master storage nodes of multiple storage nodes. When more than half of the slave storage nodes log synchronization is completed, the master storage node is allowed to return to execution without persisting the log information to the state machine. As a result, this method speeds up the return speed of data write requests, improves the write performance of the overall system, and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
经过上述图3、图4、图12以及图14所示的实施例,对本申请提供的数据访问方法进行了介绍,下面对上述数据访问方法中涉及的选举机制进行介绍,其中,从存储节点参与选举的处理流程包括下述步骤1501和步骤1502:The data access method provided by this application is introduced through the embodiments shown in the above-mentioned FIG. 3 , FIG. 4 , FIG. 12 and FIG. 14 , and the election mechanism involved in the above-mentioned data access method is introduced below. The process of participating in the election includes the following steps 1501 and 1502:
1501、当多个存储节点中存在第三存储节点通过选举成为主存储节点时,该多个存储节点中的从存储节点基于当前存储模式和该从存储节点的写性能参数,确定超时时间,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。1501. When a third storage node in the plurality of storage nodes is elected as the master storage node, the slave storage node in the plurality of storage nodes determines the timeout time based on the current storage mode and the write performance parameter of the slave storage node, the The storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node.
其中,主存储节点的选举机制也称为Leader选举机制,用于保证顺序一致性。当第三存储节点通过选举称为主存储节点时,该第三存储节点向多个存储节点中的从存储节点发送通知消息以确立Leader身份。从存储节点在接收到主存储节点发送的通知消息后,基于当前存储模式和该存储节点的写性能参数,设置超时时间。在一些实施中,不同存储模式的存储节点设置不同的随机时间范围。例如,某一存储节点的随机超时范围为(t1,t2),该存储节点的写性能参数为p,则该存储节点从(t1-p/f,t2-p/f)的时间范围内确定超时时间,写性能参数p越大,超时时间越短,也即是写性能越好的存储节点,其超时时间越短,其中,f为规范因子,可根据集群性能合理设定,本申请实施例对此不作限定。需要说明的是,此处举例仅为示意性地,在一些实施例中,存储节点的超时时间的设置有多种方式,只要是将存储模式和存储节点的写性能参数纳入超时时间的确定过程的方案,均落在本申请的保护范围内。Among them, the election mechanism of the main storage node is also called the leader election mechanism, which is used to ensure sequential consistency. When the third storage node is called the master storage node through election, the third storage node sends a notification message to the slave storage node among the plurality of storage nodes to establish the identity of the leader. After receiving the notification message sent by the master storage node, the slave storage node sets the timeout period based on the current storage mode and the write performance parameters of the storage node. In some implementations, storage nodes of different storage modes set different random time ranges. For example, if the random timeout range of a storage node is (t1 , t2 ), and the write performance parameter of the storage node is p, then the storage node changes from (t1 -p/f, t2 -p/f) Determine the timeout period within the time range. The larger the write performance parameter p, the shorter the timeout period, that is, the storage node with better write performance will have a shorter timeout period. Among them, f is the norm factor, which can be set reasonably according to the cluster performance. , which is not limited in the embodiments of the present application. It should be noted that the examples here are only illustrative, and in some embodiments, the timeout period of the storage node can be set in various ways, as long as the storage mode and the write performance parameters of the storage node are included in the determination process of the timeout period solutions, all fall within the protection scope of the present application.
通过将存储模式和存储节点的写性能参数纳入超时时间的确定过程,使得写性能好的存储节点更有可能称为主存储节点,从而提升分布式数据库系统整体的数据访问性能。By incorporating the storage mode and the write performance parameters of the storage node into the determination process of the timeout period, the storage node with good write performance is more likely to be called the primary storage node, thereby improving the overall data access performance of the distributed database system.
1502、若存在第一从存储节点在对应的超时时间内,未接收到该主存储节点的消息,该第一从存储节点切换至候选状态,参与下一次选举。1502. If there is a first slave storage node that does not receive a message from the master storage node within the corresponding timeout period, the first slave storage node switches to a candidate state and participates in the next election.
其中,第一从存储节点在对应的超时时间内,未接收到该主存储节点的消息,表明主存储节点已经失效,则该第一从存储节点切换至候选状态,参与下一次选举。需要说明的是,由于写性能好的存储节点被设置了更短的超时时间,因此有更大概率率先切换至候选状态并参与下一次选举,从而更有可能成为主存储节点。Wherein, if the first slave storage node does not receive a message from the master storage node within the corresponding timeout period, indicating that the master storage node has failed, the first slave storage node switches to the candidate state and participates in the next election. It should be noted that since a storage node with good write performance is set with a shorter timeout period, it has a higher probability of being the first to switch to the candidate state and participate in the next election, so it is more likely to become the primary storage node.
另外,当主存储节点失效后,新主尚未选出的期间,分布式数据库系统不支持任何数据读写请求,也不支持从存储节点数据读取请求。原因在于,如果选择的从存储节点上没有最新版本的数据,而此时主存储节点不工作,从存储节点无法获得数据一致性点,如果服务上层发送的数据读取请求,则有可能造成数据不一致的状况。因此,这种方式能够避免出现数据不一致的状况出现,保证系统的正确性。In addition, when the primary storage node fails, the distributed database system does not support any data read and write requests, nor does it support data read requests from the storage node during the period when the new master has not been elected. The reason is that if the selected slave storage node does not have the latest version of data, and the master storage node does not work at this time, the slave storage node cannot obtain the data consistency point. If the data read request sent by the upper layer is served, it may cause data inconsistent condition. Therefore, this method can avoid data inconsistency and ensure the correctness of the system.
由于在本申请所提供的数据访问方法中,对分布式一致性协议进行了修改,因此,下面将对本申请所涉及的修改对分布式事务的影响进行介绍,包括下述两个部分,分别是“线性一致性证明”以及“分布式事务设置内存锁”。Since the distributed consistency protocol has been modified in the data access method provided by this application, the following will introduce the impact of the modification involved in this application on distributed transactions, including the following two parts, which are: "Proof of Linear Consistency" and "Memory Locks Set by Distributed Transactions".
第一部分、线性一致性证明。The first part, the linear consistency proof.
在本申请实施例中,上述数据访问方法确保了数据的线性一致性,即只要一个新的值vnew被写入或者被读到,后续的所有数据读取请求都可以读到这个新值vnew,直到vnew被覆盖。In the embodiment of the present application, the above data access method ensures the linear consistency of data, that is, as long as a new value vnew is written or read, all subsequent data read requests can read the new value vnew , until vnew is overwritten.
以Raft协议为例,虽然上述数据访问方法放宽了Raft协议中读流程和写流程的限制,但是并不会改变Raft协议的线性一致性。上述图12所示的数据访问方法对数据写入流程进行了从数据落盘后返回写成功到更新日志达成共识即返回写成功的改动(即基于CR的数据写入方法);上述图4所示的数据访问方法对数据读取流程放松了等待执行索引(ApplyIndex)与读索引(Read Index)相同的限制,记录每个数据项的更新索引,只要写索引与写请求涉及数据项的更新索引相同即可进行读取(即基于RRI的数据读取方法)。关于从节点读请求处理流程中,从节点处理数据读取请求前会强制与主节点进行数据同步,因此从节点读请求处理流程在一致性角度与主节点处理数据读取请求没有区别。Taking the Raft protocol as an example, although the above data access method relaxes the restrictions on the read process and write process in the Raft protocol, it does not change the linear consistency of the Raft protocol. The data access method shown in the above Figure 12 changes the data writing process from returning the write success after the data is placed to the update log and reaching a consensus to return the write success (that is, the CR-based data writing method); the above-mentioned Figure 4 shows. The shown data access method relaxes the same restrictions on the waiting execution index (ApplyIndex) and the read index (Read Index) for the data reading process, and records the update index of each data item, as long as the write index and write request involve the update index of the data item The same can be read (ie, RRI-based data read method). Regarding the read request processing flow of the slave node, the slave node will force data synchronization with the master node before processing the data read request. Therefore, the read request processing flow of the slave node is no different from the master node processing data read requests in terms of consistency.
下面以主节点处理数据读取请求为例,通过形式化证明这一组改动(CR和RRI)没有破坏Raft协议的线性一致性,包括下述两种情况:The following takes the master node's processing of data read requests as an example to formally prove that this group of changes (CR and RRI) does not destroy the linear consistency of the Raft protocol, including the following two cases:
情况一、写后读。
在本申请实施例中,一个新值vnew被写入是指,对vnew的更新日志已经在Raft集群中达成共识(即过半节点已保存更新日志)。假设对vnew的更新日志索引为n1,当前的CommitIndex为c1,可知c1≥n1,vnew的放宽读索引i1=n1。当主节点在上述的数据写入请求返回之后接收新的数据读取请求,假设此时的Apply Index是a2,当前的Commit Index是c2,数据读取请求的Read Index(r2)将被设为c2,即r2=c2,因此我们可以得到r2=c2≥c1≥n1且c2≥a2,即r2≥n1与r2≥a2。In the embodiment of the present application, the writing of a new value vnew means that a consensus has been reached on the update log of vnew in the Raft cluster (that is, more than half of the nodes have saved the update log). Assuming that the update log index of vnew is n1 and the current CommitIndex is c1 , it can be known that c1 ≥ n1 , and the relaxed read index of vnew i1 =n1 . When the master node receives a new data read request after the above-mentioned data write request is returned, assuming that the Apply Index at this time is a2 and the current Commit Index is c2 , the Read Index (r2 ) of the data read request will be Let c2 , that is, r2 =c2 , so we can get r2 =c2 ≥c1 ≥n1 and c2 ≥a2 , that is, r2 ≥n1 and r2 ≥a2 .
此时,假如n1>a2,vnew还未落盘,此时i2=i1,此时数据读取请求将被阻塞,直到Apply Index更新到a3=n1=i2,数据读取请求将从状态机中读取数据并返回结果。由于此时a3=n1,对vnew的更新已经落盘,因此从状态机中读取数据可以获得最新的vnew的值。At this time, if n1 >a2 , vnew has not yet been placed on the disk, at this time i2 =i1 , and the data read request will be blocked until the Apply Index is updated to a3 =n1 =i2 , the data A read request will read data from the state machine and return the result. Since a3 =n1 at this time, the update to vnew has already been placed on the disk, so the latest value of vnew can be obtained by reading data from the state machine.
若假设n1≤a2,此时对vnew的放宽读索引i2=a2,数据读取请求可以直接从状态机中读取数据并返回结果。由于n1≤a2,vnew已经落盘,因此数据读取请求可以读到最新的vnew的值。If it is assumed that n1 ≤ a2 , and the relaxed read index i2 =a2 for vnew at this time, the data read request can directly read data from the state machine and return the result. Since n1 ≤a2 , vnew has already been placed on the disk, so the data read request can read the latest value of vnew .
假设上述两种情况(n1>a2以及n1≤a2)下读到的vnew不是最新,说明在这个数据读取请求到达之前有对vnew的最新的更新操作被提交,与RRI的设计矛盾。因此本申请提供的数据访问方法保证了在新的值vnew的数据写入请求被提交后,后续数据读取请求可以在vnew被覆盖之前读到vnew。Assuming that the vnew read in the above two cases (n1 >a2 and n1 ≤ a2 ) is not the latest, it means that the latest update operation for vnew is submitted before the data read request arrives, which is consistent with the RRI design contradictions. Therefore, the data access method provided by this application ensures that after a data write request for a new value vnew is submitted, subsequent data read requests can read vnew before vnew is overwritten.
情况二、读后读。Second, read after reading.
当新值vnew被读索引为r1的读请求读到后,设第一次读到vnew的数据读取请求返回时节点的Commit Index为c1,写入vnew的数据写入请求的索引为n1,vnew的放宽读索引为i1,数据读取请求读到vnew,此时的Apply Index(设为a1)不小于i1,则有r1=c1≥a1≥i1≥n1,新的放宽读索引i2=a1。当有新的数据读取请求到来时,设其Read Index为r2,有r2>r1,设主节点接收这个新的数据读取请求时的Commit Index为c2、Apply Index为a2,有r2=c2≥c1≥n1,那么可以得到r2≥n1和r2≥a2,与上述情况一中同理,可以证明新的数据读取请求依然能在vnew被覆盖之前读到vnew。When the new value vnew is read by the read request with the read index r1 , set the Commit Index of the node to be c1 when the data read request that reads vnew for the first time returns, and write the data write request of vnew The index of vnew is n1 , the relaxed read index of v new is i1 , the data read request reads vnew , and the Apply Index (set as a1 ) at this time is not less than i1 , then r1 =c1 ≥a1 ≥ i1 ≥ n1 , the new relaxed read index i2 =a1 . When a new data read request arrives, set its Read Index to r2 , and r2 >r1 , set the Commit Index to c2 and the Apply Index to a2 when the master node receives this new data read request , there is r2 =c2 ≥c1 ≥n1 , then r2 ≥n1 and r2 ≥a2 can be obtained, the same as the
综上,根据本申请实施例提供的数据访问方法,只要一个新的值vnew被写入或者被读到,后续的所有数据读取请求都可以读到这个新值vnew,直到vnew被覆盖。本申请提供的数据访问方法维持了Raft算法的线性一致性。To sum up, according to the data access method provided by the embodiments of the present application, as long as a new value vnew is written or read, all subsequent data read requests can read the new value vnew until vnew is cover. The data access method provided in this application maintains the linear consistency of the Raft algorithm.
第二部分、分布式事务设置内存锁。The second part, distributed transactions set memory locks.
在本申请实施例中,增加了从节点读取数据的功能,而从节点在读取数据时,可能会出现读半已提交问题。针对读半已提交问题,本申请在从节点中增加内存锁,基于封锁并发访问机制实现并发事务的可串行化调度。In the embodiment of the present application, the function of reading data from the slave node is added, but when the slave node reads data, the problem of read half-submitted may occur. Aiming at the problem of read half-submitted, the present application adds a memory lock in the slave node, and realizes serializable scheduling of concurrent transactions based on the blocking concurrent access mechanism.
下面通过一个例子来证明。The following is demonstrated by an example.
首先参考图15,对读半已提交问题进行介绍。图15是本申请实施例提供的一种读半已提交问题的示意图。如图15所示,图中包括两个物理节点,分别为节点node a和节点node b,其中,node a对应账户X,node b对应账户Y,X与Y的初始值都为1。两个物理节点都可以从从节点读取数据。Referring first to Figure 15, an introduction to the read half-committed problem is presented. FIG. 15 is a schematic diagram of a read half-submitted question provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in Figure 15, the figure includes two physical nodes, namely node a and node b, where node a corresponds to account X, node b corresponds to account Y, and the initial values of X and Y are both 1. Both physical nodes can read data from slave nodes.
例如,现在第一个写事务,要从X账户向Y账户转账1元,当此写事务在node a节点完成提交,但node b节点尚没有提交,从节点还未同步日志信息。此时,另外一个分布式事务读事务要做对账操作,需要分别读取两个物理节点上X、Y的值。由于node a的写事务已提交,则读事务读到的X的值为0。在读取Y的值时,计算层指定从节点响应数据读取请求,但是由于对Y值修改的操作还未提交,所以读事务从从节点读到的Y的值为1,则总账为“X-1+Y”,出现了数据不一致,称为读半已提交。For example, now the first write transaction needs to transfer 1 yuan from account X to account Y. When this write transaction is submitted on node a, but node b has not yet submitted, the slave node has not yet synchronized the log information. At this time, another distributed transaction read transaction needs to perform the reconciliation operation, which needs to read the values of X and Y on the two physical nodes respectively. Since the write transaction of node a has been committed, the value of X read by the read transaction is 0. When reading the value of Y, the computing layer specifies the slave node to respond to the data read request, but since the operation of modifying the Y value has not been submitted, the value of Y read by the read transaction from the slave node is 1, and the general ledger is " X-1+Y", there is data inconsistency, which is called read half-committed.
为解决该读半已提交问题,本申请实施例在从节点中增加内存锁,这样,对于上述读写事务,在对Y的修改没有提交之前(即出现图15中的状态),不允许对账读事务从任何节点读取Y数据项的值,只能令读事务等待。直到对X和Y的修改都提交之后,才允许读事务读取X和Y的值。In order to solve the read half-committed problem, the embodiment of the present application adds a memory lock to the slave node, so that, for the above-mentioned read-write transaction, before the modification to Y is not committed (that is, the state in FIG. 15 occurs), it is not allowed to The account read transaction reads the value of the Y data item from any node, and can only make the read transaction wait. Read transactions are not allowed to read the values of X and Y until the modifications to both X and Y are committed.
通过上述图2至图15,从分布式数据库系统的架构、不同类型的数据访问请求对应不同的数据访问方法以及对分布式事务的影响等多个方面,对本申请提供的数据访问方法进行了介绍,下面将以上述内容为基础,对本申请提供的数据访问方法所带来的有益效果进行总结性说明,主要包括下述9点。2 to 15, the data access methods provided by this application are introduced from the aspects of the architecture of the distributed database system, the different data access methods corresponding to different types of data access requests, and the impact on distributed transactions. , the following will summarize the beneficial effects brought by the data access method provided by the present application based on the above content, mainly including the following 9 points.
1、本申请的数据访问方法基于多副本异构存储模型的支持,使得系统在混合负载下,不同类型的数据访问请求可以在不同存储模式的副本上,从而更好的发挥磁盘读取优势,减少网络带宽的占用(详见图4所示实施例)。1. The data access method of this application is based on the support of the multi-copy heterogeneous storage model, so that under the mixed load of the system, different types of data access requests can be made on copies of different storage modes, so as to better utilize the advantages of disk reading, The occupation of network bandwidth is reduced (see the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 for details).
2、本申请的数据访问方法允许从不同类型的节点读取数据,从而提高了多副本存储的读操作并发度,保证了多副本带来的高可用性以及多副本间的数据一致性,又增加了系统的并发度(详见图4所示实施例中的步骤403)。2. The data access method of the present application allows data to be read from different types of nodes, thereby improving the read operation concurrency of multi-copy storage, ensuring high availability brought by multiple copies and data consistency between multiple copies, and increasing the concurrency of the system (see step 403 in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 for details).
3、本申请的数据访问方法提出了多副本动态管理策略,可以更好的应对系统运行过程中负载发生变化的情况(详见图4所示实施例中的步骤402)。3. The data access method of the present application proposes a multi-copy dynamic management strategy, which can better cope with changes in load during system operation (see step 402 in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 for details).
4、本申请的数据访问方法对查询计划的制订进行了修改,在计算节点制定查询计划的过程中,增加了多因素的考量,对请求类型和系统状态综合判断,选择最佳数据副本作为访问目标,有利于降低瓶颈发生可能,提高系统的整体吞吐(详见图4所示实施例中的步骤403)。4. The data access method of this application modifies the formulation of the query plan. In the process of formulating the query plan by the computing node, multi-factor considerations are added, and the request type and system status are comprehensively judged, and the best data copy is selected as the access. The goal is to help reduce the possibility of bottlenecks and improve the overall throughput of the system (see step 403 in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 for details).
5、本申请的数据访问方法通过基于放宽读索引(Relaxed Read Index,RRI)的数据读取方法,增大了系统并发度,加快了数据读取请求的处理速度,提高了分布式数据库系统整体的读性能。读取数据时允许不将所有的日志信息持久化到状态机中,够缩短底层状态机处理的时间,加快读请求返回的速度,提高整体系统的读性能(详见图4所示实施例中的步骤406和步骤407)。5. The data access method of the present application increases the system concurrency, speeds up the processing speed of data read requests, and improves the overall distributed database system through the data read method based on the Relaxed Read Index (RRI). read performance. When reading data, it is allowed not to persist all log information to the state machine, which can shorten the processing time of the underlying state machine, speed up the return of read requests, and improve the read performance of the overall system (see the embodiment shown in Figure 4 for details). steps 406 and 407).
6、本申请的数据访问方法通过读取特殊版本数据,读取某个时间戳之前或者之后的特殊版本数据时,可以通过日志时间信息允许不将所有的日志信息持久化到状态机中,提高这类特殊读请求的返回时间(详见图4所示实施例中的步骤409和步骤410)。6. When the data access method of the present application reads the special version data and reads the special version data before or after a certain time stamp, the log time information can be used to allow all log information not to be persisted in the state machine, thereby improving the performance of the state machine. Return time of this type of special read request (see steps 409 and 410 in the embodiment shown in FIG. 4 for details).
7、本申请的数据访问方法通过基于提交退回(Commit Return)的数据写入方法,在处理数据写入请求时,允许主节点未将日志信息持久化到状态机中就返回执行结果,加快写请求的返回速度,提高整体系统的写性能(详见图12所示实施例中的步骤1208)。7. The data access method of the present application, through the data writing method based on Commit Return, allows the master node to return the execution result without persisting the log information to the state machine when processing the data writing request, thereby speeding up writing The return speed of the request improves the write performance of the overall system (see step 1208 in the embodiment shown in FIG. 12 for details).
8、本申请的数据访问方法采用计算与存储分离架构,方便改变存储节点分布和配置(详见图2所示的HTAP数据库系统)。8. The data access method of the present application adopts a computing and storage separation architecture, which is convenient to change the distribution and configuration of storage nodes (see the HTAP database system shown in FIG. 2 for details).
9、整体而言,本申请的数据访问方法解决了多副本存储模式下,系统并发度和存储优势没有被完全发挥的问题,提高了系统并发度,减少了磁盘和网络带宽的占用,最终达到提高系统吞吐的效果。9. On the whole, the data access method of the present application solves the problem that the system concurrency and storage advantages are not fully utilized in the multi-copy storage mode, improves the system concurrency, reduces the occupation of disk and network bandwidth, and finally achieves the Improve system throughput.
图16是根据本申请实施例提供的一种数据访问装置的结构示意图。该数据访问装置应用于分布式数据库系统,参见图16,该数据访问装置包括:第一确定模块1601、第二确定模块1602以及第一读取模块1603。FIG. 16 is a schematic structural diagram of a data access apparatus provided according to an embodiment of the present application. The data access device is applied to a distributed database system. Referring to FIG. 16 , the data access device includes: a
第一确定模块1601,用于响应于第一数据读取请求,确定该第一数据读取请求的第一目标数据所属的第一数据分片,基于该第一数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第一存储节点,该多个第一存储节点用于存储该第一目标数据的多个副本;The
第二确定模块1602,用于基于该第一数据读取请求,从该多个第一存储节点中确定第一目标存储节点,向该第一目标存储节点发送该第一数据读取请求,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件;The second determining
第一读取模块1603,用于基于该第一数据读取请求,读取该第一目标数据,向该计算模块发送第一数据读取结果。The
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取模块1603包括:In an optional implementation manner, the
第一读取单元,用于若该第一目标数据为当前态数据,基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标存储节点的节点类型,读取该第一目标数据;a first reading unit, configured to read the first target data based on the first data read request and the node type of the first target storage node if the first target data is current state data;
第二读取单元,用于若该第一目标数据为历史态数据,基于该第一数据读取请求和该第一目标数据的事务完成时间,读取该第一目标数据。The second reading unit is configured to read the first target data based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time of the first target data if the first target data is historical data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取单元用于下述任一项:In an optional implementation, the first reading unit is used for any of the following:
若该第一目标存储节点为主存储节点,基于该第一数据读取请求,确定该第一目标数据的第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据,该第一读索引用于指示基于该第一数据读取请求读取该第一目标数据的最小读索引;If the first target storage node is the main storage node, based on the first data read request, determine the first read index of the first target data, take the first read index as the starting point, and start from the first read index corresponding to the first target data. The first target data is read in the state machine, and the first read index is used to indicate the minimum read index for reading the first target data based on the first data read request;
若该第一目标存储节点为从存储节点,基于该第一数据读取请求,从该主存储节点中获取该第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。If the first target storage node is a slave storage node, based on the first data read request, obtain the first read index from the master storage node, take the first read index as a starting point, and retrieve the corresponding data from the first target data The first target data is read in the state machine of .
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the first reading unit is used for:
更新当前时刻的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引;Update the commit index at the current moment, which is used to indicate the maximum index of the committed logs in the log list;
按照第一顺序,扫描该日志列表中存储的日志,该第一顺序是指从该提交索引至该日志列表的执行索引,该执行索引用于指示该日志列表中已执行日志的最大索引;Scan the logs stored in the log list according to the first order, where the first order refers to the execution index from the submission index to the log list, and the execution index is used to indicate the largest index of the executed log in the log list;
若存在第一目标日志,基于该第一目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第一目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据;若不存在该第一目标日志,该第一目标存储节点基于该执行索引,确定该第一读索引。If there is a first target log, the first read index is determined based on the log index of the first target log, and the data operated by the first target log is the first target data; if the first target log does not exist, the first target log The first target storage node determines the first read index based on the execution index.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第一存储模块,用于将该第一读索引存储至第一列表,该第一列表包括该第一目标数据、该第一读索引以及第一校验索引,该第一校验索引用于指示该第一目标存储节点确定该第一读索引时对应的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引;The first storage module is used to store the first read index in a first list, where the first list includes the first target data, the first read index and the first check index, and the first check index is used for Instruct the first target storage node to determine the corresponding submission index when the first read index is used, and the submission index is used to indicate the largest index of the submitted log in the log list;
第一查询模块,用于当该分布式数据库系统处理第二数据读取请求时,若该第二数据读取请求的数据为该第一目标数据,查询该第一列表以读取该第一目标数据。The first query module is used for querying the first list to read the first data when the distributed database system processes the second data reading request, if the data of the second data reading request is the first target data target data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the first reading unit is used for:
若该第一目标存储节点中存在该第一读索引对应的日志,对该第一读索引对应的日志进行持久化存储,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据;If the log corresponding to the first read index exists in the first target storage node, the log corresponding to the first read index is persistently stored, and the first read index is used as the starting point, and the state corresponding to the first target data is read the first target data in the machine;
若该第一目标存储节点中不存在该第一读索引对应的日志,从该主存储节点中获取该第一读索引对应的日志,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据。If the log corresponding to the first read index does not exist in the first target storage node, obtain the log corresponding to the first read index from the main storage node, take the first read index as the starting point, and obtain the log corresponding to the first read index from the first target data The first target data is read in the corresponding state machine.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第二读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the second reading unit is used for:
若该第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之前,基于该第一数据读取请求和该事务完成时间,按照第二顺序,扫描日志列表中存储的日志,确定第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据;If the data submission time of the first target data is before the transaction completion time, based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time, the logs stored in the log list are scanned in the second order to determine the first read index, Taking the first read index as a starting point, read the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data;
若该第一目标数据的数据提交时间在该事务完成时间之后,基于该第一数据读取请求和该事务完成时间,按照第三顺序,扫描该日志列表中存储的日志,确定该第一读索引,以该第一读索引为起点,从该第一目标数据对应的状态机中读取该第一目标数据;If the data submission time of the first target data is after the transaction completion time, based on the first data read request and the transaction completion time, the logs stored in the log list are scanned in the third order to determine the first read request. index, taking the first read index as a starting point, and reading the first target data from the state machine corresponding to the first target data;
其中,该第二顺序是指从该日志列表的提交索引至该日志列表的执行索引,该第三顺序是指从该日志列表的执行索引至该日志列表的提交索引,该提交索引用于指示该日志列表中已提交日志的最大索引,该执行索引用于指示该日志列表中已执行日志的最大索引,该第一读索引用于指示基于该第一数据读取请求读取该第一目标数据的最小读索引。Wherein, the second order refers to from the commit index of the log list to the execution index of the log list, the third order refers to from the execution index of the log list to the commit index of the log list, and the commit index is used to indicate The maximum index of the submitted log in the log list, the execution index is used to indicate the maximum index of the executed log in the log list, and the first read index is used to indicate that the first target is read based on the first data read request The minimum read index for the data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第二读取单元用于:In an optional implementation manner, the second reading unit is used for:
若存在第二目标日志,且该第一目标数据的事务完成时间与该第二目标日志的事务完成时间相同,或该第一目标数据的事务完成时间在该第二目标日志的事务完成时间之后,基于该第二目标日志的日志索引,确定该第一读索引,该第二目标日志所操作的数据为该第一目标数据;If there is a second target log, and the transaction completion time of the first target data is the same as the transaction completion time of the second target log, or the transaction completion time of the first target data is after the transaction completion time of the second target log , determine the first read index based on the log index of the second target log, and the data operated by the second target log is the first target data;
若不存在该第二目标日志,基于该日志列表的执行索引,确定该第一读索引。If the second target log does not exist, the first read index is determined based on the execution index of the log list.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该数据访问代价用于指示存储节点的执行时间、等待时间以及传输时间;In an optional implementation manner, the data access cost is used to indicate the execution time, waiting time and transmission time of the storage node;
该执行时间包括存储节点查询该第一目标数据的时间、处理数据量的时间以及元组构建时间;The execution time includes the time for the storage node to query the first target data, the time for processing the amount of data, and the time for tuple construction;
该等待时间包括存储节点的请求队列时间、设备负载延迟时间以及数据同步时间;The waiting time includes the request queue time of the storage node, the device load delay time and the data synchronization time;
该传输时间包括网络传输时间。The transmission time includes network transmission time.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第一目标条件,包括下述任一项:In an optional implementation manner, the data access cost of the first target storage node meets the first target condition, including any of the following:
该第一目标存储节点中该第一目标数据的存储模式为列存模式,且该数据读取请求所需访问的列数与总列数之间的比值小于第一阈值,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式;The storage mode of the first target data in the first target storage node is a column storage mode, and the ratio between the number of columns to be accessed by the data read request and the total number of columns is less than a first threshold, and the storage mode is used for Indicates the storage format of the data in the storage node;
该第一目标存储节点的节点负载小于该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点的节点负载;The node load of the first target storage node is smaller than the node load of the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes;
该第一目标存储节点与该计算节点之间的物理距离小于该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点与该计算节点之间的物理距离;The physical distance between the first target storage node and the computing node is smaller than the physical distance between the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes and the computing node;
该第一目标存储节点的数据同步状态在该多个存储节点中除该第一目标存储节点以外的存储节点的数据同步状态之后。The data synchronization state of the first target storage node is after the data synchronization state of the storage nodes other than the first target storage node among the plurality of storage nodes.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
调整模块,用于对该第一目标数据的多个副本的存储模式进行动态调整,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。The adjustment module is configured to dynamically adjust the storage mode of the multiple copies of the first target data, where the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该调整模块用于下述任一项:In an optional implementation, the adjustment module is used for any of the following:
基于该多个第一存储节点的负载情况,切换该多个副本的存储模式;switching the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the load conditions of the multiple first storage nodes;
若该多个副本中存在至少一个副本异常,基于该至少一个副本,建立至少一个新副本;If there is at least one copy exception in the multiple copies, at least one new copy is established based on the at least one copy;
若该第一数据分片发生数据分裂,生成至少一个第二数据分片,基于该至少一个第二数据分片,建立该至少一个第二数据分片对应的多个副本;If data splitting occurs in the first data fragment, at least one second data fragment is generated, and based on the at least one second data fragment, multiple copies corresponding to the at least one second data fragment are established;
基于该多个第一存储节点的节点类型,调整该多个副本的存储模式。Based on the node types of the plurality of first storage nodes, the storage modes of the plurality of replicas are adjusted.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该基于该多个第一存储节点的负载情况,切换该多个副本的存储模式,包括下述任一项:In an optional implementation manner, the switching of the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the load conditions of the multiple first storage nodes includes any one of the following:
基于该多个第一存储节点的节点负载大小和可用空间,切换该多个副本的存储模式;switching the storage modes of the multiple copies based on the node load size and available space of the multiple first storage nodes;
基于该多个第一存储节点的节点负载大小和每个存储模式下副本的数量,切换该多个副本的存储模式。The storage modes of the multiple copies are switched based on the node load size of the multiple first storage nodes and the number of copies in each storage mode.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第三确定模块,用于响应于数据写入请求,若该数据写入请求的第二目标数据存在所属的第三数据分片,基于该第三数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第二存储节点,该多个第二存储节点用于存储该第二目标数据的多个副本;The third determining module is configured to, in response to the data write request, determine from the plurality of storage nodes based on the third data fragment if the second target data of the data write request exists in the third data fragment to which it belongs. multiple second storage nodes, the multiple second storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the second target data;
发送模块,用于向该多个第二存储节点中的主存储节点发送该数据写入请求;a sending module, configured to send the data write request to the main storage node in the plurality of second storage nodes;
第一写入模块,用于基于该数据写入请求,写入该第二目标数据,向该计算节点发送第一数据写入结果。The first writing module is configured to write the second target data based on the data writing request, and send the first data writing result to the computing node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第一写入模块用于:In an optional implementation manner, the first writing module is used for:
基于该数据写入请求,写入该第二目标数据,生成数据操作日志,向该多个存储节点中的从存储节点发送日志同步请求,该日志同步请求用于指示该从存储节点同步该数据操作日志后向该主存储节点发送数据同步消息;Based on the data writing request, write the second target data, generate a data operation log, and send a log synchronization request to a slave storage node among the plurality of storage nodes, where the log synchronization request is used to instruct the slave storage node to synchronize the data Send a data synchronization message to the primary storage node after operating the log;
若该主存储节点接收到的该数据同步消息的数量大于或等于从存储节点数量的半数,确认该数据写入请求已操作成功。If the number of the data synchronization messages received by the master storage node is greater than or equal to half of the number of slave storage nodes, it is confirmed that the data write request has been successfully operated.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第一持久化存储模块,用于对该第二目标数据进行持久化存储;a first persistent storage module for persistently storing the second target data;
第二持久化存储模块,用于基于该数据操作日志和该第二目标数据在该从存储节点中的存储模式,对该第二目标数据进行格式转换,对转换后的该第二目标数据进行持久化存储,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。The second persistent storage module is configured to perform format conversion on the second target data based on the data operation log and the storage mode of the second target data in the slave storage node, and perform format conversion on the converted second target data Persistent storage, the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of data in the storage node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第四确定模块,用于基于该数据操作日志的日志索引,确定该第二目标数据的第二读索引,该第二读索引用于指示基于第三数据读取请求读取该第二目标数据的最小读索引;a fourth determination module, configured to determine a second read index of the second target data based on the log index of the data operation log, where the second read index is used to indicate that the second target data is read based on the third data read request The minimum read index of ;
第二存储模块,用于将该第二读索引存储至第二列表,该第二列表包括该第二目标数据、该第二读索引以及第二校验索引,该第二校验索引为该数据操作日志的日志索引;The second storage module is configured to store the second read index in a second list, where the second list includes the second target data, the second read index and a second check index, and the second check index is the The log index of the data operation log;
第二查询模块,用于当该分布式数据库系统处理该第三数据读取请求时,若该第三数据读取请求的数据为该第二目标数据,查询该第二列表以读取该第二目标数据。The second query module is configured to query the second list to read the first data when the distributed database system processes the third data read request, if the data of the third data read request is the second target data Two target data.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第一建立模块,用于若该数据写入请求的第二目标数据不存在所属的第三数据分片,建立该第二目标数据的第三数据分片,向该多个存储节点发送副本创建请求;The first establishment module is used to establish a third data fragment of the second target data if the second target data of the data write request does not have a third data fragment to which it belongs, and send the copy creation to the plurality of storage nodes ask;
第二建立模块,用于基于该副本创建请求,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本。The second establishment module is configured to establish multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment based on the copy creation request.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该第二建立模块用于:In an optional implementation manner, the second establishment module is used for:
基于该副本创建请求和该第二目标数据在该多个存储节点中的存储模式,建立该第三数据分片对应的多个副本,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式。Based on the copy creation request and the storage mode of the second target data in the multiple storage nodes, multiple copies corresponding to the third data fragment are established, where the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第五确定模块,用于响应于数据读写请求,若该数据读写请求的第三目标数据存在所属的第四数据分片,基于该第四数据分片,从该多个存储节点中确定多个第三存储节点,该多个第三存储节点用于存储该第三目标数据的多个副本;The fifth determination module is used to respond to the data read and write request, if the third target data of the data read and write request has a fourth data fragment to which it belongs, determine from the plurality of storage nodes based on the fourth data fragment multiple third storage nodes, the multiple third storage nodes are used to store multiple copies of the third target data;
第二读取模块,用于对于该数据读写请求中的读操作,基于该数据读写请求,从该多个第三存储节点中确定第二目标存储节点,向该第二目标存储节点发送该数据读写请求,该第二目标存储节点基于该数据读写请求,读取该第三目标数据,向该计算节点发送第二数据读取结果,该第二目标存储节点的数据访问代价符合第二目标条件;The second read module is configured to, for the read operation in the data read/write request, determine a second target storage node from the plurality of third storage nodes based on the data read/write request, and send the data to the second target storage node In the data read/write request, the second target storage node reads the third target data based on the data read/write request, and sends the second data read result to the computing node, and the data access cost of the second target storage node is consistent with the second target condition;
第二写入模块,用于对于该数据读写请求中的写操作,向该多个第三存储节点中的主存储节点发送该数据读写请求,该主存储节点基于该数据读写请求,写入该第三目标数据,向该计算节点发送第二数据写入结果。The second writing module is configured to send the data reading and writing request to the main storage node among the plurality of third storage nodes for the writing operation in the data reading and writing request, and the main storage node is based on the data reading and writing request, Write the third target data, and send the second data writing result to the computing node.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该多个第三存储节点中的从存储节点配置有内存锁,该内存锁用于在该写操作尚未完成时锁定该第三目标数据。In an optional implementation manner, a slave storage node among the plurality of third storage nodes is configured with a memory lock, and the memory lock is used to lock the third target data when the write operation has not been completed.
在一种可选地实现方式中,该装置还包括:In an optional implementation, the device further includes:
第六确定模块,用于当该多个存储节点中存在第四存储节点通过选举成为主存储节点时,该多个存储节点中的从存储节点基于当前存储模式和该从存储节点的写性能参数,确定超时时间,该存储模式用于指示数据在存储节点中的存储格式;The sixth determination module is used for when a fourth storage node in the plurality of storage nodes becomes the master storage node through election, the slave storage node in the plurality of storage nodes is based on the current storage mode and the write performance parameter of the slave storage node , determine the timeout period, the storage mode is used to indicate the storage format of the data in the storage node;
状态切换模块,用于若存在第一从存储节点在对应的超时时间内,未接收到该主存储节点的消息,该第一从存储节点切换至候选状态,参与下一次选举。The state switching module is configured to switch the first slave storage node to the candidate state and participate in the next election if the first slave storage node does not receive the message of the master storage node within the corresponding timeout period.
在本申请实施例中,提供了一种数据访问装置,当接收到数据读取请求时,先根据该数据读取请求的目标数据所属的数据分片,来确定存储有该目标数据的多个副本的多个存储节点,然后按照存储节点访问目标数据的数据访问代价,从这些存储节点中选出符合目标条件的目标存储节点,由该目标存储节点来读取目标数据。上述过程中,由于该目标存储节点是根据数据访问代价来确定的,因此主存储节点和从存储节点都可能成为目标存储节点,避免了由主存储节点处理所有的数据读取请求,从而既保证了多副本带来的高可用性,又提高了数据读取速度,有效提升了分布式数据库系统的数据访问性能。In the embodiment of the present application, a data access device is provided. When a data read request is received, it firstly determines a plurality of pieces of data storing the target data according to the data fragment to which the target data of the data read request belongs. The multiple storage nodes of the copy, and then according to the data access cost of the storage node accessing the target data, the target storage node that meets the target condition is selected from these storage nodes, and the target storage node reads the target data. In the above process, since the target storage node is determined according to the data access cost, both the master storage node and the slave storage node may become the target storage node, avoiding the master storage node to process all data read requests, thus ensuring that both It improves the high availability brought by multiple copies, improves the data reading speed, and effectively improves the data access performance of the distributed database system.
需要说明的是:上述实施例提供的数据访问装置在进行数据访问时,仅以上述各功能模块的划分进行举例说明,实际应用中,可以根据需要而将上述功能分配由不同的功能模块完成,即将装置的内部结构划分成不同的功能模块,以完成以上描述的全部或者部分功能。另外,上述实施例提供的数据访问装置与数据访问方法实施例属于同一构思,其具体实现过程详见方法实施例,这里不再赘述。It should be noted that: when the data access device provided in the above embodiment performs data access, only the division of the above-mentioned functional modules is used as an example for illustration. In practical applications, the above-mentioned functions can be allocated according to different functional modules. That is, the internal structure of the device is divided into different functional modules to complete all or part of the functions described above. In addition, the data access device and the data access method embodiments provided by the above embodiments belong to the same concept, and the specific implementation process thereof is detailed in the method embodiments, which will not be repeated here.
本申请实施例还提供了一种计算机设备,该计算机设备包括处理器和存储器,该存储器用于存储至少一条计算机程序,该至少一段计算机程序由该处理器加载并执行以实现本申请实施例中的数据访问方法中计算节点或存储节点所执行的操作。An embodiment of the present application further provides a computer device, the computer device includes a processor and a memory, where the memory is used to store at least one computer program, and the at least one computer program is loaded and executed by the processor to implement the embodiments of the present application. The operations performed by the compute node or storage node in the data access method.
在一些实施例中,本申请实施例所涉及的计算机程序可被部署在一个计算机设备上执行,或者在位于一个地点的多个计算机设备上执行,又或者,在分布在多个地点且通过有线网络或无线网络互连的多个计算机设备上执行,分布在多个地点且通过有线网络或无线网络互连的多个计算机设备可以组成区块链系统。In some embodiments, the computer programs involved in the embodiments of the present application may be deployed and executed on one computer device, or executed on multiple computer devices located at one location, or distributed in multiple locations and via wired Executed on multiple computer devices interconnected by a network or wireless network, and multiple computer devices distributed in multiple locations and interconnected through wired or wireless networks can form a blockchain system.
以计算机设备为服务器为例,图17是根据本申请实施例提供的一种服务器的结构示意图,该服务器1700可因配置或性能不同而产生比较大的差异,能够包括一个或一个以上处理器(Central Processing Units,CPU)1701和一个或一个以上的存储器1702,其中,该存储器1702中存储有至少一条计算机程序,该至少一条计算机程序由处理器1701加载并执行以实现上述各个方法实施例提供的数据访问方法。当然,该服务器还能够具有有线或无线网络接口、键盘以及输入输出接口等部件,以便进行输入输出,该服务器还能够包括其他用于实现设备功能的部件,在此不做赘述。Taking a computer device as a server as an example, FIG. 17 is a schematic structural diagram of a server provided according to an embodiment of the present application. The
本申请实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质应用于计算机设备,该计算机可读存储介质中存储有至少一条计算机程序,该至少一条计算机程序由处理器加载并执行以实现上述实施例的数据访问方法中计算机设备所执行的操作。Embodiments of the present application further provide a computer-readable storage medium, where the computer-readable storage medium is applied to a computer device, where at least one computer program is stored in the computer-readable storage medium, and the at least one computer program is loaded by a processor and executed. Execute to realize the operations performed by the computer device in the data access method of the above-mentioned embodiment.
本申请实施例还提供了一种计算机程序产品或计算机程序,该计算机程序产品或计算机程序包括计算机程序代码,该计算机程序代码存储在计算机可读存储介质中。计算机设备的处理器从计算机可读存储介质读取该计算机程序代码,处理器执行该计算机程序代码,使得该计算机设备执行上述各种可选实现方式中提供的数据访问方法。Embodiments of the present application also provide a computer program product or computer program, where the computer program product or computer program includes computer program code, and the computer program code is stored in a computer-readable storage medium. The processor of the computer device reads the computer program code from the computer-readable storage medium, and the processor executes the computer program code, so that the computer device executes the data access methods provided in the various optional implementations described above.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例的全部或部分步骤可以通过硬件来完成,也可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件完成,所述的程序可以存储于一种计算机可读存储介质中,上述提到的存储介质可以是只读存储器,磁盘或光盘等。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps of implementing the above embodiments can be completed by hardware, or can be completed by instructing relevant hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. The storage medium mentioned may be a read-only memory, a magnetic disk or an optical disk, etc.
以上所述仅为本申请的可选实施例,并不用以限制本申请,凡在本申请的精神和原则之内,所作的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本申请的保护范围之内。The above descriptions are only optional embodiments of the present application, and are not intended to limit the present application. Any modifications, equivalent replacements, improvements, etc. made within the spirit and principles of the present application shall be included in the protection of the present application. within the range.
Claims (25)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110709977.0ACN113535656B (en) | 2021-06-25 | 2021-06-25 | Data access method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110709977.0ACN113535656B (en) | 2021-06-25 | 2021-06-25 | Data access method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113535656Atrue CN113535656A (en) | 2021-10-22 |
| CN113535656B CN113535656B (en) | 2022-08-09 |
Family
ID=78125940
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110709977.0AActiveCN113535656B (en) | 2021-06-25 | 2021-06-25 | Data access method, device, equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113535656B (en) |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114244859A (en)* | 2022-02-23 | 2022-03-25 | 阿里云计算有限公司 | Data processing method and device and electronic equipment |
| CN114637475A (en)* | 2022-04-13 | 2022-06-17 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A distributed storage system control method, device and readable storage medium |
| CN114969072A (en)* | 2022-06-06 | 2022-08-30 | 北京友友天宇系统技术有限公司 | Data transmission method, device and equipment based on state machine and data persistence |
| CN114969035A (en)* | 2022-05-17 | 2022-08-30 | 度小满科技(北京)有限公司 | Data redundancy storage method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN115103011A (en)* | 2022-06-24 | 2022-09-23 | 北京奥星贝斯科技有限公司 | A cross-data center business processing method, device, and device |
| CN115114374A (en)* | 2022-06-27 | 2022-09-27 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Transaction execution method and device, computing equipment and storage medium |
| CN115114344A (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2022-09-27 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Transaction processing method and device, computing equipment and storage medium |
| CN115563221A (en)* | 2022-10-25 | 2023-01-03 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Data synchronization method, storage system, device and storage medium |
| CN116561097A (en)* | 2022-11-16 | 2023-08-08 | 天翼云科技有限公司 | A big data distributed storage incentive method and system based on blockchain and hybrid database |
| WO2023193495A1 (en)* | 2022-04-07 | 2023-10-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for processing read request, distributed database and server |
| WO2023236629A1 (en)* | 2022-06-07 | 2023-12-14 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data access method and apparatus, and storage system and storage medium |
| WO2024040902A1 (en)* | 2022-08-22 | 2024-02-29 | 华为云计算技术有限公司 | Data access method, distributed database system and computing device cluster |
| CN118093647A (en)* | 2024-03-13 | 2024-05-28 | 星环信息科技(上海)股份有限公司 | Distributed database query system, method, equipment and medium supporting multi-copy consistency reading |
| CN118981506A (en)* | 2024-10-21 | 2024-11-19 | 平凯星辰(北京)科技有限公司 | Data storage method, reading method, device and electronic device |
| CN119292997A (en)* | 2024-09-20 | 2025-01-10 | 北京火山引擎科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device of data service system based on read-write separation architecture |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140324785A1 (en)* | 2013-04-30 | 2014-10-30 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Efficient read replicas |
| CN105516263A (en)* | 2015-11-28 | 2016-04-20 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data distribution method, device in storage system, calculation nodes and storage system |
| CN106406758A (en)* | 2016-09-05 | 2017-02-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data processing method based on distributed storage system, and storage equipment |
| CN106844399A (en)* | 2015-12-07 | 2017-06-13 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Distributed data base system and its adaptive approach |
| CN112148798A (en)* | 2020-10-10 | 2020-12-29 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Data processing method and device applied to distributed system |
- 2021
- 2021-06-25CNCN202110709977.0Apatent/CN113535656B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20140324785A1 (en)* | 2013-04-30 | 2014-10-30 | Amazon Technologies, Inc. | Efficient read replicas |
| CN105516263A (en)* | 2015-11-28 | 2016-04-20 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data distribution method, device in storage system, calculation nodes and storage system |
| CN106844399A (en)* | 2015-12-07 | 2017-06-13 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Distributed data base system and its adaptive approach |
| CN106406758A (en)* | 2016-09-05 | 2017-02-15 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data processing method based on distributed storage system, and storage equipment |
| CN112148798A (en)* | 2020-10-10 | 2020-12-29 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Data processing method and device applied to distributed system |
Cited By (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115114344A (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2022-09-27 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Transaction processing method and device, computing equipment and storage medium |
| CN115114344B (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2023-06-23 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Transaction processing method, device, computing equipment and storage medium |
| CN114244859A (en)* | 2022-02-23 | 2022-03-25 | 阿里云计算有限公司 | Data processing method and device and electronic equipment |
| WO2023193495A1 (en)* | 2022-04-07 | 2023-10-12 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method for processing read request, distributed database and server |
| CN114637475A (en)* | 2022-04-13 | 2022-06-17 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A distributed storage system control method, device and readable storage medium |
| CN114969035A (en)* | 2022-05-17 | 2022-08-30 | 度小满科技(北京)有限公司 | Data redundancy storage method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN114969072A (en)* | 2022-06-06 | 2022-08-30 | 北京友友天宇系统技术有限公司 | Data transmission method, device and equipment based on state machine and data persistence |
| WO2023236629A1 (en)* | 2022-06-07 | 2023-12-14 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data access method and apparatus, and storage system and storage medium |
| CN115103011A (en)* | 2022-06-24 | 2022-09-23 | 北京奥星贝斯科技有限公司 | A cross-data center business processing method, device, and device |
| CN115103011B (en)* | 2022-06-24 | 2024-02-09 | 北京奥星贝斯科技有限公司 | Cross-data center service processing method, device and equipment |
| CN115114374A (en)* | 2022-06-27 | 2022-09-27 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Transaction execution method and device, computing equipment and storage medium |
| WO2024040902A1 (en)* | 2022-08-22 | 2024-02-29 | 华为云计算技术有限公司 | Data access method, distributed database system and computing device cluster |
| CN115563221A (en)* | 2022-10-25 | 2023-01-03 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Data synchronization method, storage system, device and storage medium |
| CN116561097A (en)* | 2022-11-16 | 2023-08-08 | 天翼云科技有限公司 | A big data distributed storage incentive method and system based on blockchain and hybrid database |
| CN118093647A (en)* | 2024-03-13 | 2024-05-28 | 星环信息科技(上海)股份有限公司 | Distributed database query system, method, equipment and medium supporting multi-copy consistency reading |
| CN118093647B (en)* | 2024-03-13 | 2024-11-05 | 星环信息科技(上海)股份有限公司 | A distributed database query system, method, device and medium supporting multi-copy consistent reading |
| WO2025189868A1 (en)* | 2024-03-13 | 2025-09-18 | 星环信息科技(上海)股份有限公司 | Distributed database query system and method supporting multi-replica consistent read, device, and medium |
| CN119292997A (en)* | 2024-09-20 | 2025-01-10 | 北京火山引擎科技有限公司 | Data processing method and device of data service system based on read-write separation architecture |
| CN118981506A (en)* | 2024-10-21 | 2024-11-19 | 平凯星辰(北京)科技有限公司 | Data storage method, reading method, device and electronic device |
| CN118981506B (en)* | 2024-10-21 | 2025-01-21 | 平凯星辰(北京)科技有限公司 | Data storage method, reading method, device and electronic device |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113535656B (en) | 2022-08-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113535656B (en) | Data access method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| Akkoorath et al. | Cure: Strong semantics meets high availability and low latency | |
| CN111338766B (en) | Transaction processing method, apparatus, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111143389B (en) | Transaction execution method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111597015B (en) | Transaction processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| US11822540B2 (en) | Data read method and apparatus, computer device, and storage medium | |
| WO2020224374A1 (en) | Data replication method and apparatus, and computer device and storage medium | |
| CN115098229A (en) | Transaction processing method, device, node device and storage medium | |
| US11461201B2 (en) | Cloud architecture for replicated data services | |
| US12111817B2 (en) | Log execution method and apparatus, computer device and storage medium | |
| US11360866B2 (en) | Updating stateful system in server cluster | |
| CN117931531B (en) | Data backup system, method, device, equipment, storage medium and program product | |
| CN115114294A (en) | Adaptive method, device and computer equipment for database storage mode | |
| US20250200070A1 (en) | Consensus Protocol For Asynchronous Database Transaction Replication With Fast, Automatic Failover, Zero Data Loss, Strong Consistency, Full SQL Support And Horizontal Scalability | |
| CN114003580A (en) | A database construction method and device for distributed scheduling system | |
| CN118796932A (en) | Data synchronization method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113297159B (en) | Data storage method and device | |
| US12399909B2 (en) | Configuration and management of replication units for asynchronous database transaction replication | |
| Radi | Improved aggressive update propagation technique in cloud data storage | |
| Sarr et al. | Transpeer: Adaptive distributed transaction monitoring for web2. 0 applications | |
| Butler et al. | Distributed Lucene: A distributed free text index for Hadoop | |
| Sapate et al. | Survey on comparative analysis of database replication techniques | |
| Arrieta-Salinas et al. | Epidemia: Variable consistency for transactional cloud databases | |
| CN117762656A (en) | Data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| WO2024081140A1 (en) | Configuration and management of replication units for asynchronous database transaction replication |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |