CN113522895B - Pipeline flushing method and device - Google Patents
Pipeline flushing method and deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113522895B CN113522895BCN202110816301.1ACN202110816301ACN113522895BCN 113522895 BCN113522895 BCN 113522895BCN 202110816301 ACN202110816301 ACN 202110816301ACN 113522895 BCN113522895 BCN 113522895B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- thickness
- layer
- flushing
- scouring
- deposition layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000011010flushing procedureMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription169
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription49
- 230000008021depositionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription134
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription23
- 239000010410layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription242
- 238000009991scouringMethods0.000claimsdescription75
- 238000005265energy consumptionMethods0.000claimsdescription19
- 239000002344surface layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription18
- 238000004590computer programMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000006378damageEffects0.000claims1
- 239000013049sedimentSubstances0.000abstractdescription34
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000abstractdescription5
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000abstractdescription3
- 230000007269microbial metabolismEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 241000894006BacteriaSpecies0.000description10
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000description10
- 230000002503metabolic effectEffects0.000description9
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description7
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-NmethaneChemical compoundCVNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 239000010865sewageSubstances0.000description5
- 230000006870functionEffects0.000description4
- 230000000696methanogenic effectEffects0.000description4
- 244000005700microbiomeSpecies0.000description4
- RWSOTUBLDIXVET-UHFFFAOYSA-NDihydrogen sulfideChemical compoundSRWSOTUBLDIXVET-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 230000003628erosive effectEffects0.000description3
- 229910000037hydrogen sulfideInorganic materials0.000description3
- 239000002207metaboliteSubstances0.000description3
- 230000000813microbial effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description2
- 238000013461designMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000description2
- UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-NSulphideChemical compound[S-2]UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000009825accumulationMethods0.000description1
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 238000013500data storageMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000004880explosionMethods0.000description1
- 238000007689inspectionMethods0.000description1
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000004060metabolic processEffects0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 230000003287optical effectEffects0.000description1
- 231100000572poisoningToxicity0.000description1
- 230000000607poisoning effectEffects0.000description1
- 229920001690polydopaminePolymers0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 238000003672processing methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000004062sedimentationMethods0.000description1
- 230000003068static effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000001360synchronised effectEffects0.000description1
- 150000003568thioethersChemical class0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B08—CLEANING
- B08B—CLEANING IN GENERAL; PREVENTION OF FOULING IN GENERAL
- B08B9/00—Cleaning hollow articles by methods or apparatus specially adapted thereto
- B08B9/02—Cleaning pipes or tubes or systems of pipes or tubes
- B08B9/027—Cleaning the internal surfaces; Removal of blockages
- B08B9/032—Cleaning the internal surfaces; Removal of blockages by the mechanical action of a moving fluid, e.g. by flushing
- B08B9/0321—Cleaning the internal surfaces; Removal of blockages by the mechanical action of a moving fluid, e.g. by flushing using pressurised, pulsating or purging fluid
- B08B9/0325—Control mechanisms therefor
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16L—PIPES; JOINTS OR FITTINGS FOR PIPES; SUPPORTS FOR PIPES, CABLES OR PROTECTIVE TUBING; MEANS FOR THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16L55/00—Devices or appurtenances for use in, or in connection with, pipes or pipe systems
- F16L55/24—Preventing accumulation of dirt or other matter in pipes, e.g. by traps, by strainers
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F17—STORING OR DISTRIBUTING GASES OR LIQUIDS
- F17D—PIPE-LINE SYSTEMS; PIPE-LINES
- F17D5/00—Protection or supervision of installations
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Length Measuring Devices Characterised By Use Of Acoustic Means (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及环境治理领域,尤其涉及一种管道冲刷方法及装置。The invention relates to the field of environmental governance, in particular to a pipeline flushing method and device.
背景技术Background technique
城市的污水管道中普遍存在沉积现象,沉积物中含有大量的有机物质,污水管道的空间相对封闭、空气的流通性差,容易形成厌氧环境,为沉积物中的产甲烷菌、硫酸盐还原菌等的代谢活动提供和了物质基础和环境基础。Sedimentation is common in urban sewage pipes. Sediments contain a large amount of organic substances. The space of sewage pipes is relatively closed and the air circulation is poor. An anaerobic environment is easy to form. Methanogenic bacteria and sulfate-reducing bacteria in sediments And other metabolic activities provide and provide the material basis and environmental basis.
在厌氧环境下,产甲烷菌等通过代谢活动会产生甲烷等有害气体,硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)等通过代谢活动会产生硫化氢等有害气体,这些有害气体如果处理不当将造成气体积蓄,达到一定浓度后会发生泄漏,可能造成人员中毒,甚至遇明火时发生爆炸等事故,而且污水中硫化物的总浓度为2.0mg/L时,排水管道将发生严重腐蚀。在现有技术中,为避免上述事故的发生,往往通过一些化学手段使产生的甲烷、硫化氢气体等通过化学反应转化为其它物质,从而实现无害处理的目的,但现有技术中的这些处理方法比较复杂,而且成本较高。In an anaerobic environment, methanogenic bacteria will produce harmful gases such as methane through metabolic activities, and sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) will produce harmful gases such as hydrogen sulfide through metabolic activities. If these harmful gases are not handled properly, they will cause gas accumulation. Leakage will occur after reaching a certain concentration, which may cause personnel poisoning, and even explosions and other accidents when exposed to open flames, and when the total concentration of sulfides in sewage is 2.0mg/L, the drainage pipes will be severely corroded. In the prior art, in order to avoid the occurrence of the above-mentioned accidents, some chemical means are often used to convert the generated methane, hydrogen sulfide gas, etc. into other substances through chemical reactions, thereby achieving the purpose of harmless treatment, but these in the prior art The processing method is more complicated and the cost is higher.
发明内容Contents of the invention
基于此,本发明提供了一种管道冲刷方法及装置,用于解决现有技术中处理管道内微生物代谢产生的有害物质的方法复杂和成本高的问题。Based on this, the present invention provides a method and device for flushing pipelines, which are used to solve the problems of complex and high-cost methods for treating harmful substances produced by microbial metabolism in pipelines in the prior art.
为了实现上述目的,本发明实施例提供的技术方案如下:In order to achieve the above object, the technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present invention are as follows:
第一方面,本发明实施例提供了一种管道冲刷方法,所述方法包括:In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a pipeline flushing method, the method comprising:
获取沉积层厚度,所述沉积层厚度为管道中的沉积层的厚度;Obtain the thickness of the deposition layer, the thickness of the deposition layer being the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline;
根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件,所述预设对应关系包括:所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件;According to the thickness of the deposited layer and the preset corresponding relationship, the scouring condition is obtained, and the preset corresponding relationship includes: the corresponding relationship between the thickness of the deposited layer and the scouring condition, and the scouring condition corresponding to the thickness of the deposited layer is the minimum The condition that the power consumption destroys the thickness of the preset proportion of the corresponding deposited layer;
根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。The water flow is controlled according to the flushing condition to flush the deposition layer in the pipeline.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述冲刷条件包括:As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the flushing conditions include:
冲刷流速和冲刷时长,所述冲刷时长为水流以所述冲刷流速开始冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层至破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的时间。The flushing flow rate and the flushing duration, the flushing duration is the time from when the water flow begins to flush the sediment layer corresponding to the thickness of the sediment layer at the flushing flow rate to destroying the thickness of the sediment layer by a preset ratio.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述预设对应关系包括:各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系;As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the preset corresponding relationship includes: the corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and the flushing condition;
所述根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件,包括:The acquisition of scour conditions according to the thickness of the deposited layer and the preset corresponding relationship includes:
获取所述沉积层厚度所属的厚度区间;Obtain the thickness interval to which the thickness of the deposited layer belongs;
根据所述厚度区间和所述预设对应关系获取该沉积层厚度的沉积层对应的冲刷条件。According to the thickness interval and the preset corresponding relationship, the scour condition corresponding to the deposition layer with the thickness of the deposition layer is obtained.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,在根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件之前,所述方法还包括:As an optional implementation manner of the embodiment of the present invention, before obtaining the flushing condition according to the thickness of the deposited layer and the preset corresponding relationship, the method further includes:
建立多个冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件,各冲刷方案中的沉积层厚度不同,各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件下水流冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层的冲刷流速不同;Establish the preset scouring conditions of multiple scouring schemes, the thickness of the sedimentary layer in each scouring scheme is different, and the scouring flow rate of the sedimentary layer corresponding to the thickness of the sedimentary layer is different under the preset scouring conditions of each scouring scheme;
计算各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件所需的能耗;Calculate the energy consumption required for the preset flushing conditions of each flushing scheme;
基于所述能耗确定各冲刷方案对应的冲刷条件,所述冲刷条件为该冲刷方案下所述能耗最小的预设冲刷条件。The flushing condition corresponding to each flushing scheme is determined based on the energy consumption, and the flushing condition is a preset flushing condition with the minimum energy consumption under the flushing scheme.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系,包括:As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and the flushing condition includes:
若所述沉积层厚度属于厚度区间[0,3cm],则对应的冲刷流速为0.4m/s,冲刷时间为4分钟;If the thickness of the deposited layer belongs to the thickness interval [0, 3cm], the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.4m/s, and the flushing time is 4 minutes;
若所述沉积层厚度属于厚度区间(3cm,6cm],则对应的冲刷流速为0.6m/s,冲刷时间为6分钟;If the thickness of the deposited layer belongs to the thickness interval (3cm, 6cm], then the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.6m/s, and the flushing time is 6 minutes;
若所述沉积层厚度属于厚度区间(6cm,10cm],则对应的冲刷流速为0.7m/s,冲刷时间为10分钟;If the thickness of the deposited layer belongs to the thickness interval (6cm, 10cm], the corresponding scouring flow rate is 0.7m/s, and the scouring time is 10 minutes;
若所述沉积层厚度大于或等于10cm,则对应的冲刷流速为0.8m/s,冲刷时间为13分钟。If the thickness of the deposited layer is greater than or equal to 10 cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.8 m/s, and the flushing time is 13 minutes.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述获取沉积层厚度,包括:As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the acquisition of the thickness of the deposited layer includes:
通过声呐探测器获取所述管道中的沉积层厚度。The thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline is acquired by a sonar detector.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述通过声呐探测器获取所述管道中的沉积层厚度,包括:As an optional implementation manner of the embodiment of the present invention, the acquisition of the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline through the sonar detector includes:
通过声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度;Obtaining the thickness of the deposition layer at multiple positions in the pipeline through a sonar detector;
计算所述多个位置的沉积层厚度的平均值,作为所述管道中的沉积层厚度。calculating an average value of the thickness of the deposition layer at the plurality of positions as the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述声呐探测器设置于伸缩杆上,所述通过声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度,包括:As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the sonar detector is arranged on the telescopic rod, and the acquisition of the thickness of the deposition layer at multiple positions in the pipeline through the sonar detector includes:
通过调节所述伸缩杆的长度使所述声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度。By adjusting the length of the telescopic rod, the sonar detector acquires the thickness of the deposition layer at multiple positions in the pipeline.
第二方面,本发明实施例提供一种管道冲刷装置,包括:In the second aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a pipeline flushing device, comprising:
检测模块,用于获取沉积层厚度,所述沉积层厚度为管道中的沉积层的厚度;The detection module is used to obtain the thickness of the deposition layer, and the thickness of the deposition layer is the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline;
获取模块,用于根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件,所述预设对应关系包括:所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件;An acquisition module, configured to acquire scouring conditions according to the thickness of the deposition layer and a preset correspondence relationship, the preset correspondence relationship includes: the correspondence relationship between the thickness of the deposition layer and the scouring condition, and the corresponding relationship between the thickness of the deposition layer The flushing condition is a condition for destroying the thickness of the corresponding deposition layer with a preset ratio of minimum power consumption;
处理模块,用于根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。The processing module is used to control the water flow to scour the deposition layer in the pipeline according to the scour conditions.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述冲刷条件包括:冲刷流速和冲刷时长,所述冲刷时长为水流以所述冲刷流速开始冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层至破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的时间。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the flushing conditions include: a flushing flow rate and a flushing duration, and the flushing duration is when the water flow begins to flush the sedimentary layer corresponding to the thickness of the sedimentary layer at the flushing flow rate until the depositional layer is destroyed. A preset ratio of thickness to time.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述预设对应关系包括:各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系;As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the preset corresponding relationship includes: the corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and the flushing condition;
所述获取模块,具体用于获取所述沉积层厚度所属的厚度区间;以及根据所述厚度区间和所述预设对应关系获取该沉积层厚度的沉积层对应的冲刷条件。The acquiring module is specifically configured to acquire the thickness interval to which the thickness of the sediment layer belongs; and acquire the erosion condition corresponding to the sediment layer of the thickness of the sediment layer according to the thickness interval and the preset corresponding relationship.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述装置还包括:确定模块,在根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件之前,用于建立多个冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件,各冲刷方案中的沉积层厚度不同,各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件下水流冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层的冲刷流速不同;计算各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件所需的能耗;以及基于所述能耗确定各冲刷方案对应的冲刷条件,所述冲刷条件为该冲刷方案下所述能耗最小的预设冲刷条件。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the device further includes: a determination module, used to establish a plurality of preset flushing schemes before obtaining the flushing conditions according to the thickness of the deposited layer and the preset corresponding relationship Scouring conditions, the thickness of the sediment layer in each scouring scheme is different, and the scouring velocity of the sediment layer corresponding to the thickness of the sediment layer under the preset scouring conditions of each scouring scheme is different; the energy consumption required for the preset scouring conditions of each scouring scheme is calculated and determining flushing conditions corresponding to each flushing scheme based on the energy consumption, where the flushing condition is a preset flushing condition with the minimum energy consumption under the flushing scheme.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系,包括:As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and the flushing condition includes:
若所述沉积层厚度属于0~3cm的厚度区间,则对应的冲刷流速为0.4m/s,冲刷时间为4分钟;若所述沉积层厚度属于3~6cm的厚度区间,则对应的冲刷流速为0.6m/s,冲刷时间为6分钟;若所述沉积层厚度属于6~10cm的厚度区间,则对应的冲刷流速为0.7m/s,冲刷时间为10分钟;若所述沉积层厚度大于或等于10cm,则对应的冲刷流速为0.8m/s,冲刷时间为13分钟。If the thickness of the sediment layer belongs to the thickness interval of 0-3cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.4m/s, and the flushing time is 4 minutes; if the thickness of the deposition layer belongs to the thickness interval of 3-6cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.6m/s, and the flushing time is 6 minutes; if the thickness of the deposition layer belongs to the thickness range of 6-10cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.7m/s, and the flushing time is 10 minutes; if the thickness of the deposition layer is greater than Or equal to 10cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.8m/s, and the flushing time is 13 minutes.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述检测模块,具体用于通过声呐探测器获取所述管道中的沉积层厚度。As an optional implementation manner of the embodiment of the present invention, the detection module is specifically configured to obtain the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline through a sonar detector.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述检测模块,具体用于通过声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度;以及计算所述多个位置的沉积层厚度的平均值,作为所述管道中的沉积层厚度。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the detection module is specifically configured to obtain the thickness of the deposition layer at multiple positions in the pipeline through a sonar detector; and calculate the thickness of the deposition layer at the multiple positions average value, as the thickness of the deposited layer in the pipe.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述声呐探测器设置于伸缩杆上,所述检测模块,具体用于通过调节所述伸缩杆的长度使所述声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the sonar detector is arranged on a telescopic rod, and the detection module is specifically configured to enable the sonar detector to obtain the pipeline by adjusting the length of the telescopic rod Thicknesses of deposited layers at multiple locations within the
第三方面,本发明实施例提供一种电子设备,包括:存储器和处理器,所述存储器用于存储计算机程序;所述处理器用于在调用计算机程序时执行第一方面或第一方面任一种可选的实施方式所述方法的步骤。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic device, including: a memory and a processor, the memory is used to store a computer program; the processor is used to execute any one of the first aspect or the first aspect when calling the computer program. The steps of the method described in an optional embodiment.
第四方面,本发明实施例提供一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时实现第一方面或第一方面任一种可选的实施方式所述方法的步骤。In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored. When the computer program is executed by a processor, the method described in the first aspect or any optional implementation manner of the first aspect is implemented. A step of.
本发明实施例提供的管道冲刷方法通过获取管道中的沉积层厚度,根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件,所述预设对应关系包括:所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件,再根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。由于本发明实施例中沉积层厚度和冲刷条件存在对应关系,在获取到管道中的沉积层厚度之后,就能确定对应的冲刷条件,而冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件,因此在该冲刷条件下控制管道中的水流对管道中的沉积层进行冲刷,可以在损耗的功耗最小的情况下,破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的沉积物结构,从而破坏微生物的代谢环境,减小了有害气体的生成,该方法不仅简单,而且降低了处理微生物代谢产物的成本。The pipeline flushing method provided in the embodiment of the present invention obtains the flushing conditions by obtaining the thickness of the sediment layer in the pipeline, and according to the thickness of the sediment layer and a preset corresponding relationship, the preset corresponding relationship includes: the thickness of the deposited layer and the Corresponding relationship of flushing conditions, the flushing condition corresponding to the thickness of the deposition layer is the condition of destroying the thickness of the corresponding deposition layer with the minimum power consumption, and then controlling the flow of water to the deposition layer in the pipeline according to the flushing condition Flush. Since there is a corresponding relationship between the thickness of the deposition layer and the flushing condition in the embodiment of the present invention, after the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline is obtained, the corresponding flushing condition can be determined, and the flushing condition is a predetermined condition for destroying the corresponding deposition layer with the minimum power consumption. The condition of proportional thickness is set, so the water flow in the pipeline is controlled to scour the sediment layer in the pipeline under the flushing condition, and the deposition of the preset ratio thickness of the sediment layer can be destroyed with the minimum power consumption structure, thereby destroying the metabolic environment of microorganisms and reducing the generation of harmful gases. This method is not only simple, but also reduces the cost of processing microbial metabolites.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明实施例提供的一种管道冲刷方法的应用场景图;FIG. 1 is an application scene diagram of a pipeline flushing method provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明一个实施例提供的管道冲刷方法的步骤流程图;Fig. 2 is a flow chart of the steps of the pipeline flushing method provided by one embodiment of the present invention;
图3为本发明另一个实施例提供的管道冲刷方法的步骤流程图;Fig. 3 is a flow chart of the steps of the pipeline flushing method provided by another embodiment of the present invention;
图4为本发明又一个实施例提供的管道冲刷方法的步骤流程图;Fig. 4 is a flow chart of the steps of the pipeline flushing method provided by another embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明一个实施例提供的管道冲刷装置的结构框图;Fig. 5 is a structural block diagram of a pipeline flushing device provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明另一个实施例提供的管道冲刷装置的结构框图;Fig. 6 is a structural block diagram of a pipeline flushing device provided by another embodiment of the present invention;
图7为本发明实施例提供的一种电子设备的内部结构图。FIG. 7 is an internal structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了能够更清楚地理解本发明的上述目的、特征和优点,下面将对本发明的方案进行进一步描述。需要说明的是,在不冲突的情况下,本发明的实施例及实施例中的特征可以相互组合。In order to understand the above-mentioned purpose, features and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the solutions of the present invention will be further described below. It should be noted that, in the case of no conflict, the embodiments of the present invention and the features in the embodiments can be combined with each other.
在下面的描述中阐述了很多具体细节以便于充分理解本发明,但本发明还可以采用其他不同于在此描述的方式来实施;显然,说明书中的实施例只是本发明的一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。In the following description, many specific details have been set forth in order to fully understand the present invention, but the present invention can also be implemented in other ways different from those described here; obviously, the embodiments in the description are only some embodiments of the present invention, and Not all examples.
本发明的说明书和权利要求书中的术语“第一”和“第二”等是用于区别同步的对象,而不是用于描述对象的特定顺序。The terms "first" and "second" and the like in the specification and claims of the present invention are used to distinguish synchronized objects, rather than to describe a specific order of objects.
在本发明实施例中,“示例性的”或者“例如”等词用于表示作例子、例证或说明。本发明实施例中被描述为“示例性的”或者“例如”的任何实施例或设计方案不应被解释为比其它实施例或设计方案更优选或更具优势。确切而言,使用“示例性的”或者“例如”等词旨在以具体方式呈现相关概念,此外,在本发明实施例的描述中,除非另有说明,“多个”的含义是指两个或两个以上。In the embodiments of the present invention, words such as "exemplary" or "for example" are used as examples, illustrations or illustrations. Any embodiment or design solution described as "exemplary" or "for example" in the embodiments of the present invention shall not be construed as being more preferred or more advantageous than other embodiments or design solutions. To be precise, the use of words such as "exemplary" or "for example" is intended to present related concepts in a specific manner. In addition, in the description of the embodiments of the present invention, unless otherwise specified, the meaning of "plurality" refers to two one or more.
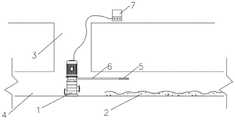
图1为本发明实施例的一个应用场景图,参照图1所示,管道2中的沉积物在管壁上形成沉积层2,推流泵1放置于污水管网的检查井3中,伸缩杆6的一端固定于推流泵1上,另一端与声呐探测器5相连,伸缩杆6的长度可以根据需要进行调节,通过调节伸缩杆6的长度可以使声呐探测器6发生移动,获取管道1中不同位置的沉积层厚度,推流泵1上连接有控制器7,控制器7可以调节伸缩杆的长度。Fig. 1 is an application scene diagram of an embodiment of the present invention. Referring to Fig. 1, the sediment in the
本发明实施例提供的管道冲刷方法的执行主体可以为:管道冲刷装置,该管道冲刷装置具体可以为图1中所示的控制器7,也可以为终端设备,该终端设备可以为手机、平板电脑、笔记本电脑、超级移动个人计算机(ultra-mobile personal computer,UMPC)、上网本、个人数字助理(personal digital assistant,PDA)、智能手表、智能手环等终端设备,或者该终端设备还可以为其他类型的终端设备。The execution subject of the pipeline flushing method provided in the embodiment of the present invention may be: a pipeline flushing device, the pipeline flushing device may specifically be the controller 7 shown in Figure 1, or a terminal device, the terminal device may be a mobile phone, a tablet Computers, laptops, ultra-mobile personal computers (ultra-mobile personal computers, UMPCs), netbooks, personal digital assistants (personal digital assistants, PDAs), smart watches, smart bracelets and other terminal equipment, or the terminal equipment can also be other type of terminal equipment.
在一个实施例中,如图2所示,图2为本发明实施例提供的一种管道冲刷方法的流程图。本实施例中,该方法包括以下步骤S110-S130:In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 2 , FIG. 2 is a flowchart of a pipeline flushing method provided by an embodiment of the present invention. In this embodiment, the method includes the following steps S110-S130:
S110、获取沉积层厚度。S110. Obtain the thickness of the deposited layer.
其中,所述沉积层厚度为管道中的沉积层的厚度。Wherein, the thickness of the deposited layer is the thickness of the deposited layer in the pipeline.
具体的,以城市中的污水管道为例,管道中的沉积层主要分为表层、中层和底层三部分,沉积层的表层的结构的特点是表面光滑、内部结构紧密,通过抵御水流变化来保护内部环境,为微生物提供代谢底物。中层是硫酸盐还原菌主要存在的区域,底层是产甲烷细菌主要存在的区域,硫酸盐还原菌与产甲烷菌存在着共生关系,硫酸盐还原菌代谢产生的甲基辅酶M可作为产甲烷菌代谢生成甲烷的直接前体物质,产甲烷菌能够以硫酸盐还原菌代谢产生的硫化物为反应底物进行代谢繁衍。Specifically, taking the sewage pipeline in the city as an example, the sedimentary layer in the pipeline is mainly divided into three parts: the surface layer, the middle layer and the bottom layer. The structure of the surface layer of the sedimentary layer is characterized by a smooth surface and a tight internal structure. The internal environment provides metabolic substrates for microorganisms. The middle layer is the area where sulfate-reducing bacteria mainly exist, and the bottom layer is the area where methanogenic bacteria mainly exist. There is a symbiotic relationship between sulfate-reducing bacteria and methanogenic bacteria. Methanogens can use the sulfide produced by the metabolism of sulfate-reducing bacteria as the reaction substrate for metabolic reproduction.
可选的,通过声呐探测器5获取所述管道中的沉积层厚度。Optionally, the thickness of the deposited layer in the pipeline is acquired by the
需要说明的是,本实施例中通过声呐探测器获取沉积层厚度是获取沉积层厚度的一种方式,但并不是唯一方式。It should be noted that in this embodiment, obtaining the thickness of the deposition layer by using the sonar detector is one way of obtaining the thickness of the deposition layer, but it is not the only way.
可选的,获取所述管道中的沉积层厚度包括如下步骤a和步骤b。Optionally, obtaining the thickness of the deposited layer in the pipeline includes the following steps a and b.
步骤a、通过声呐探测器5获取管道2内多个位置的沉积层厚度。Step a. Obtain the thickness of the deposition layer at multiple positions in the
步骤b、计算所述多个位置的沉积层厚度的平均值,作为管道2中的沉积层厚度。Step b. Calculating the average value of the thickness of the deposition layer at the multiple positions as the thickness of the deposition layer in the
通过获取管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度的平均值作为管道中的沉积层厚度,可以防止因管道中各位置的沉积层厚度之间的厚度差导致的冲刷效率差的问题。By obtaining the average value of the thickness of the sediment layer at multiple positions in the pipeline as the thickness of the sediment layer in the pipeline, the problem of poor flushing efficiency caused by the thickness difference between the thicknesses of the sediment layer at various positions in the pipeline can be prevented.
可选的,声呐探测器5设置于伸缩杆6上,通过调节所述伸缩杆6的长度使声呐探测器5获取管道2内多个位置的沉积层厚度。Optionally, the
S120、根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件。S120. Acquire flushing conditions according to the thickness of the deposited layer and a preset corresponding relationship.
其中,所述预设对应关系包括:所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件。Wherein, the preset corresponding relationship includes: the corresponding relationship between the thickness of the deposited layer and the scouring condition, and the scouring condition corresponding to the thickness of the deposited layer is to destroy the thickness of the preset proportion of the corresponding deposited layer with the minimum power consumption. condition.
可选的,所述冲刷条件包括冲刷流速和冲刷时长,所述冲刷时长为水流以所述冲刷流速开始冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层至破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的时间。Optionally, the flushing conditions include a flushing flow rate and a flushing duration, and the flushing duration is the time for water flow at the flushing flow rate to start flushing the sediment layer corresponding to the thickness of the sediment layer to destroy the thickness of the sediment layer at a preset ratio.
具体的,上述沉积层的预设比例的厚度为该沉积层的表层厚度,沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏该沉积层厚度的沉积层的表层时需要的条件。Specifically, the thickness of the preset proportion of the deposition layer is the surface thickness of the deposition layer, and the flushing conditions corresponding to the deposition layer thickness are the conditions required to destroy the surface layer of the deposition layer with the minimum power consumption.
S130、根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。S130. Control the water flow to scour the deposition layer in the pipeline according to the scour conditions.
具体的,图1所示的控制器7控制管道中的水流以冲刷条件下的冲刷流速对管道中的沉积层进行冲刷,冲刷时间达到该冲刷条件对应的冲刷时长时,停止控制管道中的水流流速,用声呐探测器5再次获取该管道中的沉积层的第二厚度,在第二厚度的值与沉积层的预设比例的厚度值之和小于或等于所述沉积层厚度的值的情况下,说明该沉积层的表层已经被破坏,硫酸盐还原菌与产甲烷菌的代谢环境已经被破坏,共生关系被打破,甲烷、硫化氢等有害气体在产生源头上得到了抑制。Specifically, the controller 7 shown in FIG. 1 controls the water flow in the pipeline to scour the sediment layer in the pipeline at the scouring flow rate under the scouring condition. When the scouring time reaches the scouring time corresponding to the scouring condition, stop controlling the water flow in the pipeline. Flow rate, use the
本发明实施例提供的管道冲刷方法通过获取管道中的沉积层厚度,根据所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系来获取冲刷条件,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件,再根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。由于本发明实施例中沉积层厚度和冲刷条件存在对应关系,在获取到管道中的沉积层厚度之后,就能确定对应的冲刷条件,而冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件,因此在该冲刷条件下控制管道中的水流对管道中的沉积层进行冲刷,可以在损耗的功耗最小的情况下,破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的沉积物结构,从而破坏微生物的代谢环境,减小了有害气体的生成,该方法不仅简单,而且降低了处理微生物代谢产物的成本。The pipeline scouring method provided in the embodiment of the present invention obtains the scouring condition according to the corresponding relationship between the deposition layer thickness and the scouring condition by obtaining the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline, and the scouring condition corresponding to the deposition layer thickness is The condition of destroying the thickness of the corresponding deposition layer at a preset ratio, and then controlling the water flow to flush the deposition layer in the pipeline according to the flushing condition. Since there is a corresponding relationship between the thickness of the deposition layer and the flushing condition in the embodiment of the present invention, after the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline is obtained, the corresponding flushing condition can be determined, and the flushing condition is a predetermined condition for destroying the corresponding deposition layer with the minimum power consumption. The condition of proportional thickness is set, so the water flow in the pipeline is controlled to scour the sediment layer in the pipeline under the flushing condition, and the deposition of the preset ratio thickness of the sediment layer can be destroyed with the minimum power consumption structure, thereby destroying the metabolic environment of microorganisms and reducing the generation of harmful gases. This method is not only simple, but also reduces the cost of processing microbial metabolites.
在本发明的另一个实施例中,所述预设对应关系包括:各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系。参照图3所示,图3是在图2的基础上,对步骤S120的一种可能的实现方式的描述,即步骤S120可以通过以下步骤S121-S122来实现。In another embodiment of the present invention, the preset corresponding relationship includes: a corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and scouring conditions. Referring to FIG. 3 , FIG. 3 is a description of a possible implementation of step S120 on the basis of FIG. 2 , that is, step S120 may be implemented through the following steps S121-S122.
S121、获取所述沉积层厚度所属的厚度区间。S121. Obtain the thickness interval to which the thickness of the deposited layer belongs.
具体的,所述厚度区间是根据事先进行的冲刷实验来划分的,处于同一个厚度区间的沉积层,可以用相同的冲刷条件控制管道中的水流破坏沉积层的表层,当沉积层的沉积层厚度处于[0,3cm]的厚度区间时,该沉积层的表层厚度为该沉积层厚度的15%-20%,沉积层的沉积层厚度处于(3cm,6cm]的厚度区间时,该沉积层的表层厚度为该沉积层厚度的18%-23%,沉积层的沉积层厚度处于(6cm,10cm]的厚度区间时,该沉积层的表层厚度为该沉积层厚度的20%-25%,沉积层的沉积层厚度处于大于或等于10cm时,该沉积层的表层厚度为该沉积层厚度的23%-30%。Specifically, the thickness interval is divided according to the scouring experiments carried out in advance. The sedimentary layer in the same thickness interval can use the same scouring conditions to control the water flow in the pipeline to destroy the surface layer of the sedimentary layer. When the sedimentary layer of the sedimentary layer When the thickness is in the thickness interval of [0, 3cm], the surface thickness of the deposition layer is 15%-20% of the thickness of the deposition layer, and when the thickness of the deposition layer is in the thickness interval of (3cm, 6cm), the deposition layer The thickness of the surface layer is 18%-23% of the thickness of the deposition layer, and when the thickness of the deposition layer of the deposition layer is in the thickness interval of (6cm, 10cm], the thickness of the surface layer of the deposition layer is 20%-25% of the thickness of the deposition layer, When the thickness of the deposition layer is greater than or equal to 10 cm, the thickness of the surface layer of the deposition layer is 23%-30% of the thickness of the deposition layer.
S122、根据所述厚度区间和所述预设对应关系获取该沉积层厚度的沉积层对应的冲刷条件。S122. According to the thickness interval and the preset corresponding relationship, obtain the flushing condition corresponding to the deposition layer with the thickness of the deposition layer.
可选的,所述各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系,包括:Optionally, the corresponding relationship between the various thickness intervals and scour conditions includes:
若所述沉积层厚度属于厚度区间[0,3cm],则对应的冲刷流速为0.4m/s,冲刷时间为4分钟;若所述沉积层厚度属于厚度区间(3cm,6cm],则对应的冲刷流速为0.6m/s,冲刷时间为6分钟;若所述沉积层厚度属于厚度区间(6cm,10cm],则对应的冲刷流速为0.7m/s,冲刷时间为10分钟;若所述沉积层厚度大于或等于10cm,则对应的冲刷流速为0.8m/s,冲刷时间为13分钟。If the thickness of the deposited layer belongs to the thickness interval [0, 3cm], then the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.4m/s, and the flushing time is 4 minutes; if the thickness of the deposited layer belongs to the thickness interval (3cm, 6cm], then the corresponding The scouring velocity is 0.6m/s, and the scouring time is 6 minutes; if the thickness of the deposited layer belongs to the thickness interval (6cm, 10cm], then the corresponding scouring velocity is 0.7m/s, and the scouring time is 10 minutes; if the deposition If the thickness of the layer is greater than or equal to 10cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.8m/s, and the flushing time is 13 minutes.
示例性的,当沉积层的厚度为5cm时,控制管道中水流以0.6m/s的冲刷流速冲刷6分钟,该沉积层的表层被破坏,再次获取该沉积层的第二厚度,第二厚度应小于或等于4.1cm。Exemplarily, when the thickness of the deposition layer is 5cm, control the water flow in the pipeline to flush for 6 minutes at a flushing flow rate of 0.6m/s, the surface layer of the deposition layer is destroyed, and obtain the second thickness of the deposition layer again, the second thickness Should be less than or equal to 4.1cm.
在本发明的又一个实施例中,参照图4所示,图4是在图2的基础上,进一步地,在步骤S120(根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件)之前还包括如下步骤S111-S113。In yet another embodiment of the present invention, refer to FIG. 4, which is based on FIG. 2, and further, before step S120 (obtaining the flushing condition according to the thickness of the deposited layer and the preset correspondence relationship) The following steps S111-S113 are also included.
S111、建立多个冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件,各冲刷方案中的沉积层厚度不同,各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件下水流冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层的冲刷流速不同。S111. Establish preset flushing conditions for multiple flushing schemes. The thickness of the sediment layer in each flushing scheme is different. Under the preset flushing conditions of each flushing scheme, the flushing flow rate of the water flow to flush the sedimentary layer corresponding to the thickness of the sedimentary layer is different.
示例性的,建立的冲刷方案有m个,即有m个沉积层厚度,对每个沉积层厚度的沉积层用预设的n个不同的流速分别冲刷,n个流速对应n个预设冲刷条件,记录每个流速下破坏对应的沉积层的表层所用的冲刷时间。Exemplarily, there are m flushing schemes established, that is, there are m sedimentary layer thicknesses, and the sedimentary layers of each sedimentary layer thickness are flushed with preset n different flow rates, and n flow rates correspond to n preset flushing Conditions, record the flushing time used to destroy the surface layer of the corresponding sediment layer at each flow rate.
S112、计算各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件所需的能耗。S112. Calculate the energy consumption required by the preset flushing conditions of each flushing scheme.
具体的,通过步骤S111中的多个流速和对应的冲刷时间计算在每个预设冲刷条件破坏对应的沉积层的表层所需的能耗,对每个沉积层厚度对应的n个预设冲刷条件所需的能耗进行排序。Specifically, calculate the energy consumption required to destroy the surface layer of the corresponding sediment layer under each preset flushing condition through multiple flow rates and corresponding flushing times in step S111, and for n preset flushes corresponding to the thickness of each sedimentary layer The energy consumption required by the conditions is sorted.
S113、基于所述能耗确定各冲刷方案对应的冲刷条件。S113. Determine flushing conditions corresponding to each flushing scheme based on the energy consumption.
其中,所述冲刷条件为该冲刷方案下所述能耗最小的预设冲刷条件。Wherein, the flushing condition is the preset flushing condition with the least energy consumption under the flushing scheme.
将能耗最小的预设冲刷条件确定为对应沉积层厚度的沉积层的冲刷条件,保证了在能耗最低的情况下可以破坏沉积层的表层,减少有害气体的产生。The preset flushing condition with the minimum energy consumption is determined as the flushing condition of the deposition layer corresponding to the thickness of the deposition layer, which ensures that the surface layer of the deposition layer can be destroyed and the generation of harmful gases can be reduced under the condition of the lowest energy consumption.
具体说明请参阅上述实施例中S110至S130的说明,此处不在赘述。For specific descriptions, please refer to the descriptions of S110 to S130 in the above embodiments, and details are not repeated here.
基于同一发明构思,作为对上述方法的实现,本发明实施例还提供了一种管道冲刷装置,该装置实施例与前述方法实施例对应,为便于阅读,本装置实施例不再对前述方法实施例中的细节内容进行逐一赘述,但应当明确,本实施例中的装置能够对应实现前述方法实施例中的全部内容。Based on the same inventive concept, as the realization of the above method, the embodiment of the present invention also provides a pipeline flushing device, the embodiment of the device corresponds to the embodiment of the method described above, for the sake of easy reading, the embodiment of the device does not implement the method described above The details in the examples are described one by one, but it should be clear that the device in this embodiment can correspondingly implement all the content in the foregoing method embodiments.
图5为本发明实施例提供的管道冲刷装置的结构框图,如图5所示,本实施例提供的管道冲刷装置5包括:Fig. 5 is a structural block diagram of a pipeline flushing device provided in an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in Fig. 5, the
检测模块501,用于获取沉积层厚度,所述沉积层厚度为管道中的沉积层的厚度;A
获取模块502,用于根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件,所述预设对应关系包括:所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件;The acquiring
处理模块503,用于根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。The
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述冲刷条件包括:冲刷流速和冲刷时长,所述冲刷时长为水流以所述冲刷流速开始冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层至破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的时间。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the flushing conditions include: a flushing flow rate and a flushing duration, and the flushing duration is when the water flow begins to flush the sedimentary layer corresponding to the thickness of the sedimentary layer at the flushing flow rate until the depositional layer is destroyed. A preset ratio of thickness to time.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述预设对应关系包括:各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系;As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the preset corresponding relationship includes: the corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and the flushing condition;
所述获取模块502,具体用于获取所述沉积层厚度所属的厚度区间;以及根据所述厚度区间和所述预设对应关系获取该沉积层厚度的沉积层对应的冲刷条件。The obtaining
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,参照图6所示,所述装置还包括:确定模块504,在根据所述沉积层厚度和预设对应关系,获取冲刷条件之前,用于建立多个冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件,各冲刷方案中的沉积层厚度不同,各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件下水流冲刷对应沉积层厚度的沉积层的冲刷流速不同;计算各冲刷方案的预设冲刷条件所需的能耗;以及基于所述能耗确定各冲刷方案对应的冲刷条件,所述冲刷条件为该冲刷方案下所述能耗最小的预设冲刷条件。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 6, the device further includes: a
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述各个厚度区间与冲刷条件的对应关系,包括:As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the corresponding relationship between each thickness interval and the flushing condition includes:
若所述沉积层厚度属于0~3cm的厚度区间,则对应的冲刷流速为0.4m/s,冲刷时间为4分钟;若所述沉积层厚度属于3~6cm的厚度区间,则对应的冲刷流速为0.6m/s,冲刷时间为6分钟;若所述沉积层厚度属于6~10cm的厚度区间,则对应的冲刷流速为0.7m/s,冲刷时间为10分钟;若所述沉积层厚度大于或等于10cm,则对应的冲刷流速为0.8m/s,冲刷时间为13分钟。If the thickness of the sediment layer belongs to the thickness interval of 0-3cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.4m/s, and the flushing time is 4 minutes; if the thickness of the deposition layer belongs to the thickness interval of 3-6cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.6m/s, and the flushing time is 6 minutes; if the thickness of the deposition layer belongs to the thickness range of 6-10cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.7m/s, and the flushing time is 10 minutes; if the thickness of the deposition layer is greater than Or equal to 10cm, the corresponding flushing flow rate is 0.8m/s, and the flushing time is 13 minutes.
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述检测模块501,具体用于通过声呐探测器获取所述管道中的沉积层厚度。As an optional implementation manner of the embodiment of the present invention, the
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述检测模块501,具体用于通过声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度;以及计算所述多个位置的沉积层厚度的平均值,作为所述管道中的沉积层厚度。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the
作为本发明实施例一种可选的实施方式,所述声呐探测器设置于伸缩杆上,所述检测模块501,具体用于通过调节所述伸缩杆的长度使所述声呐探测器获取所述管道内多个位置的沉积层厚度。As an optional implementation of the embodiment of the present invention, the sonar detector is arranged on a telescopic rod, and the
本发明实施例提供的管道冲刷装置通过获取管道中的沉积层厚度,根据所述沉积层厚度与所述冲刷条件的对应关系来获取冲刷条件,所述沉积层厚度对应的冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件,再根据所述冲刷条件控制水流对所述管道中的沉积层进行冲刷。由于本发明实施例中沉积层厚度和冲刷条件存在对应关系,在获取到管道中的沉积层厚度之后,就能确定对应的冲刷条件,而冲刷条件为以最小功耗破坏对应的沉积层的预设比例的厚度的条件,因此在该冲刷条件下控制管道中的水流对管道中的沉积层进行冲刷,可以在损耗的功耗最小的情况下,破坏该沉积层的预设比例的厚度的沉积物结构,从而破坏微生物的代谢环境,减小了有害气体的生成,该方法不仅简单,而且降低了处理微生物代谢产物的成本。The pipeline scouring device provided in the embodiment of the present invention obtains the scouring condition according to the corresponding relationship between the deposition layer thickness and the scouring condition by obtaining the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline, and the scouring condition corresponding to the deposition layer thickness is The condition of destroying the thickness of the corresponding deposition layer at a preset ratio, and then controlling the water flow to flush the deposition layer in the pipeline according to the flushing condition. Since there is a corresponding relationship between the thickness of the deposition layer and the flushing condition in the embodiment of the present invention, after the thickness of the deposition layer in the pipeline is obtained, the corresponding flushing condition can be determined, and the flushing condition is a predetermined condition for destroying the corresponding deposition layer with the minimum power consumption. The condition of proportional thickness is set, so the water flow in the pipeline is controlled to scour the sediment layer in the pipeline under the flushing condition, and the deposition of the preset ratio thickness of the sediment layer can be destroyed with the minimum power consumption structure, thereby destroying the metabolic environment of microorganisms and reducing the generation of harmful gases. This method is not only simple, but also reduces the cost of processing microbial metabolites.
本实施例提供的管道冲刷装置可以执行上述方法实施例提供的管道冲刷方法,其实现原理与技术效果类似,此处不再赘述。The pipeline flushing device provided in this embodiment can implement the pipeline flushing method provided in the above method embodiment, and its implementation principle and technical effect are similar, and will not be repeated here.
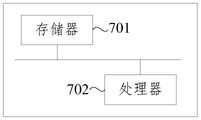
基于同一发明构思,本发明实施例还提供了一种电子设备。图7为本发明实施例提供的电子设备的结构示意图,如图7所示,本实施例提供的电子设备包括:存储器701和处理器702,存储器701用于存储计算机程序;处理器702用于在调用计算机程序时执行上述方法实施例提供的管道冲刷方法中的各步骤。Based on the same inventive concept, an embodiment of the present invention also provides an electronic device. FIG. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 7 , the electronic device provided by this embodiment includes: a
具体的,存储器701可用于存储软件程序以及各种数据。存储器601可主要包括存储程序区和存储数据区,其中,存储程序区可存储操作系统、至少一个功能所需的应用程序(比如声音播放功能、图像播放功能等)等;存储数据区可存储根据电子设备的使用所创建的数据等。此外,存储器701可以包括高速随机存取存储器,还可以包括非易失性存储器,例如至少一个磁盘存储器件、闪存器件、或其他易失性固态存储器件。Specifically, the
处理器702是电子设备的控制中心,利用各种接口和线路连接整个电子设备的各个部分,通过运行或执行存储在存储器701中的软件程序和/或模块,以及调用存储在存储器701中的数据,执行电子设备的各种功能和处理数据,从而对电子设备进行整体监控。处理器702可包括一个或多个处理单元。The
本发明实施例还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质上存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时实现上述方法实施例提供的管道冲刷方法的步骤。The embodiment of the present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium, on which a computer program is stored. When the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps of the pipeline flushing method provided by the above-mentioned method embodiments are implemented.
本领域技术人员应明白,本发明的实施例可提供为方法、系统、或计算机程序产品。因此,本发明可采用完全硬件实施例、完全软件实施例、或结合软件和硬件方面的实施例的形式。而且,本发明可采用在一个或多个其中包含有计算机可用程序代码的计算机可用存储介质上实施的计算机程序产品的形式。Those skilled in the art should understand that the embodiments of the present invention may be provided as methods, systems, or computer program products. Accordingly, the present invention can take the form of an entirely hardware embodiment, an entirely software embodiment, or an embodiment combining software and hardware aspects. Furthermore, the present invention may take the form of a computer program product embodied on one or more computer-usable storage media having computer-usable program code embodied therein.
计算机可读介质包括永久性和非永久性、可移动和非可移动存储介质。存储介质可以由任何方法或技术来实现信息存储,信息可以是计算机可读指令、数据结构、程序的模块或其他数据。计算机的存储介质的例子包括,但不限于相变内存(PRAM)、静态随机存取存储器(SRAM)、动态随机存取存储器(DRAM)、其他类型的随机存取存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、电可擦除可编程只读存储器(EEPROM)、快闪记忆体或其他内存技术、只读光盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、数字多功能光盘(DVD)或其他光学存储、磁盒式磁带,磁盘存储或其他磁性存储设备或任何其他非传输介质,可用于存储可以被计算设备访问的信息。根据本文中的界定,计算机可读介质不包括暂存电脑可读媒体(transitorymedia),如调制的数据信号和载波。Computer-readable media includes both volatile and non-volatile, removable and non-removable storage media. The storage medium may store information by any method or technology, and the information may be computer-readable instructions, data structures, program modules, or other data. Examples of computer storage media include, but are not limited to, phase change memory (PRAM), static random access memory (SRAM), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), other types of random access memory (RAM), read only memory (ROM), Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM), Flash memory or other memory technology, Compact Disc Read-Only Memory (CD-ROM), Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) or other optical storage, A magnetic tape cartridge, disk storage or other magnetic storage device or any other non-transmission medium that can be used to store information that can be accessed by a computing device. As defined herein, computer readable media does not include transitory computer readable media, such as modulated data signals and carrier waves.
以上实施例的各技术特征可以进行任意的组合,为使描述简洁,未对上述实施例中的各个技术特征所有可能的组合都进行描述,然而,只要这些技术特征的组合不存在矛盾,都应当认为是本说明书记载的范围。The technical features of the above embodiments can be combined arbitrarily. To make the description concise, all possible combinations of the technical features in the above embodiments are not described. However, as long as there is no contradiction in the combination of these technical features, they should be It is considered to be within the range described in this specification.
以上所述实施例仅表达了本申请的几种实施方式,其描述较为具体和详细,但并不能因此而理解为对发明专利范围的限制。应当指出的是,对于本领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本申请构思的前提下,还可以做出若干变形和改进,这些都属于本申请的保护范围。因此,本申请专利的保护范围应以所附权利要求为准。The above-mentioned embodiments only represent several implementation modes of the present application, and the description thereof is relatively specific and detailed, but it should not be construed as limiting the scope of the patent for the invention. It should be noted that those skilled in the art can make several modifications and improvements without departing from the concept of the present application, and these all belong to the protection scope of the present application. Therefore, the scope of protection of the patent application should be based on the appended claims.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110816301.1ACN113522895B (en) | 2021-07-20 | 2021-07-20 | Pipeline flushing method and device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110816301.1ACN113522895B (en) | 2021-07-20 | 2021-07-20 | Pipeline flushing method and device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113522895A CN113522895A (en) | 2021-10-22 |
| CN113522895Btrue CN113522895B (en) | 2022-11-15 |
Family
ID=78100338
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110816301.1AActiveCN113522895B (en) | 2021-07-20 | 2021-07-20 | Pipeline flushing method and device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113522895B (en) |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5746923A (en)* | 1993-09-28 | 1998-05-05 | Minister For Infrastructure | Control of iron deposition in borehole pumps |
| US6027572A (en)* | 1997-06-23 | 2000-02-22 | Princeton Trade And Technologt, Inc | Cleaning method for removing biofilm and debris from lines and tubing |
| WO2012025109A2 (en)* | 2010-06-20 | 2012-03-01 | Thomas Pfalz | Method for controlling the animal watering water supply for a pipeline and for sanitizing by flushing, cleaning, and disinfecting pipelines, in particular animal watering lines |
| CN102636329A (en)* | 2012-04-25 | 2012-08-15 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Device for simulating operating conditions of water supply network |
| DE102013203156A1 (en)* | 2013-02-26 | 2014-08-28 | Carela Gmbh | Method for removing biofilms from installations for the provision and distribution of drinking and service water |
| KR20190006207A (en)* | 2017-06-26 | 2019-01-18 | 지에스건설 주식회사 | Method for improving performance of pressure retarded osmosis process |
| US10350653B1 (en)* | 2018-06-21 | 2019-07-16 | Dabney Patents, L.L.C. | Method, system and device for reducing microbial concentration and/or biofilm formation |
| JP2019195386A (en)* | 2018-05-07 | 2019-11-14 | 早稲田ビジネスコンサルティング株式会社 | Washing water supply device for dental unit, dental unit and maintenance method thereof |
| WO2021056078A1 (en)* | 2019-09-27 | 2021-04-01 | Grenof Pty Ltd | A method for disrupting biofilms in wastewater systems |
Family Cites Families (24)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5674323A (en)* | 1993-02-12 | 1997-10-07 | American International, Inc. | Method and apparatus for cleaning columns by inducing vibrations in fouling material and the column |
| US20040007255A1 (en)* | 1997-06-20 | 2004-01-15 | Labib Mohamed Emam | Apparatus and method for cleaning pipelines, tubing and membranes using two-phase flow |
| US20030079758A1 (en)* | 1998-06-03 | 2003-05-01 | Siegel Phyllis B. | Process and composition for removing biofilm |
| CN1222668C (en)* | 1999-09-27 | 2005-10-12 | 东陶机器株式会社 | Flush toilet and flushing water supply |
| WO2003010094A1 (en)* | 2001-07-26 | 2003-02-06 | H20 Technologies, Ltd. | Apparatus and methods for cleaning and controlling bacteria growth in fluid supply lines |
| US7052614B2 (en)* | 2001-08-06 | 2006-05-30 | A.Y. Laboratories Ltd. | Control of development of biofilms in industrial process water |
| JP4709486B2 (en)* | 2001-10-09 | 2011-06-22 | アルベマール・コーポレーシヨン | Biofilm suppression in industrial water systems |
| US7329358B2 (en)* | 2004-05-27 | 2008-02-12 | Siemens Water Technologies Holding Corp. | Water treatment process |
| US8226964B2 (en)* | 2006-09-07 | 2012-07-24 | Biolargo Life Technologies, Inc. | Systems and methods for cleaning liquid carriers related applications data |
| SG11201401087WA (en)* | 2011-09-28 | 2014-08-28 | Univ Duke | Devices and methods for active biofouling control |
| US20180274905A1 (en)* | 2015-03-18 | 2018-09-27 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Method and apparatus for measuring biofilm thickness and topology |
| CN105618439B (en)* | 2016-01-31 | 2017-11-14 | 李志强 | A kind of crude oil pipeline cleaning system and crude oil pipeline cleaning construction method |
| CN106959356B (en)* | 2017-04-24 | 2023-06-23 | 中国石油大学(北京) | An integrated simulation experiment device for crude oil pipeline wax deposition and pigging |
| CN107842105B (en)* | 2017-10-27 | 2024-08-16 | 上海市政工程设计研究总院(集团)有限公司 | Handheld dredging equipment suitable for large-size box culvert and dredging method thereof |
| CN108296239A (en)* | 2017-12-23 | 2018-07-20 | 卞家福 | The working method of full angle rotating cleaning device based on PID control |
| CN109013576B (en)* | 2018-09-05 | 2021-06-01 | 吴先德 | Hydraulic pipeline cleaning system for ship |
| CN109235602A (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2019-01-18 | 上海市政工程设计研究总院(集团)有限公司 | A kind of pipeline deposit automatic clearing apparatus steaming again water pipe by pumping plant |
| CN109235604A (en)* | 2018-09-30 | 2019-01-18 | 上海市政工程设计研究总院(集团)有限公司 | A method of automatic removing pipeline deposit is responsible for suitable for multichannel |
| CN110240260B (en)* | 2019-05-28 | 2021-10-08 | 同济大学 | A sewage treatment equipment and method based on in-situ control of biofilm thickness |
| EP4049006B8 (en)* | 2019-10-24 | 2024-11-20 | Ecolab USA Inc. | System and method of inline deposit detection in process fluid |
| CN111299267B (en)* | 2020-02-12 | 2021-10-22 | 上海交通大学 | A biofilm control method for water supply pipe network based on quorum effect and its application |
| CN111501984B (en)* | 2020-04-16 | 2024-09-03 | 天津国投津能发电有限公司 | Large-scale vertical water pump forebay silt monitoring and cleaning device |
| CN111533344B (en)* | 2020-05-12 | 2021-01-01 | 上海市政工程设计研究总院(集团)有限公司 | Disinfection and sterilization system for long-distance pipeline and application method thereof |
| CN212835759U (en)* | 2020-06-04 | 2021-03-30 | 华夏鼎慧(宁夏)农业科技有限公司 | Agricultural greenhouse uses high-efficient drainage device |
- 2021
- 2021-07-20CNCN202110816301.1Apatent/CN113522895B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5746923A (en)* | 1993-09-28 | 1998-05-05 | Minister For Infrastructure | Control of iron deposition in borehole pumps |
| US6027572A (en)* | 1997-06-23 | 2000-02-22 | Princeton Trade And Technologt, Inc | Cleaning method for removing biofilm and debris from lines and tubing |
| WO2012025109A2 (en)* | 2010-06-20 | 2012-03-01 | Thomas Pfalz | Method for controlling the animal watering water supply for a pipeline and for sanitizing by flushing, cleaning, and disinfecting pipelines, in particular animal watering lines |
| CN102636329A (en)* | 2012-04-25 | 2012-08-15 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Device for simulating operating conditions of water supply network |
| DE102013203156A1 (en)* | 2013-02-26 | 2014-08-28 | Carela Gmbh | Method for removing biofilms from installations for the provision and distribution of drinking and service water |
| WO2014131648A1 (en)* | 2013-02-26 | 2014-09-04 | Carela Gmbh | Method for removing biofilms from systems for preparing and distributing drinking water and service water |
| KR20190006207A (en)* | 2017-06-26 | 2019-01-18 | 지에스건설 주식회사 | Method for improving performance of pressure retarded osmosis process |
| JP2019195386A (en)* | 2018-05-07 | 2019-11-14 | 早稲田ビジネスコンサルティング株式会社 | Washing water supply device for dental unit, dental unit and maintenance method thereof |
| US10350653B1 (en)* | 2018-06-21 | 2019-07-16 | Dabney Patents, L.L.C. | Method, system and device for reducing microbial concentration and/or biofilm formation |
| WO2021056078A1 (en)* | 2019-09-27 | 2021-04-01 | Grenof Pty Ltd | A method for disrupting biofilms in wastewater systems |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 城市污水管网中污染物冲刷与沉积规律;桑浪涛等;《环境科学》;20161231;第253-257页* |
| 城市污水管网污染物沉积与冲刷释放规律研究;金鹏康等;《安全与环境学报》;20161031;第1965-1971页* |
| 多点汇流下污水管网污染物迁变规律及其机制;石烜等;《中国环境科学》;20210331;第3615-3625页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113522895A (en) | 2021-10-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Jickells et al. | Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate | |
| Berntsen et al. | Effect of FeCO3 supersaturation and carbide exposure on the CO2 corrosion rate of carbon steel | |
| TW200745931A (en) | Apparatus and method to store information | |
| Kennelley et al. | Current and potential distribution on a coated pipeline with holidays part I—Model and experimental verification | |
| CN112694171B (en) | Aeration control method and device for sewage treatment, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| US12105045B2 (en) | Systems and methods for controlling oxygen levels | |
| CN113522895B (en) | Pipeline flushing method and device | |
| Nikolova-Kuscu et al. | Mechanisms of clogging in granular drainage systems permeated with low organic strength leachate | |
| Song et al. | Steel corrosion under a disbonded coating with a holiday—Part 1: The model and validation | |
| Liu et al. | Sulfur cycle by in situ analysis in the sediment biofilm of a sewer system | |
| Rittmann et al. | Design of fixed-film processes with steady-state-biofilm model | |
| Suflita et al. | Carbon dioxide corrosion and acetate: a hypothesis on the influence of microorganisms | |
| Rudelle et al. | Anaerobic transformations of organic matter in collection systems | |
| Maxwell | Predicting microbially influenced corrosion (MIC) in seawater injection systems | |
| Morizot et al. | A novel approach for monitoring of CaCO3 and BaSO4 scale formation | |
| Dias et al. | Microbially induced organic acid underdeposit attack in a gas pipeline | |
| Gross | Communicating ignorance and the development of post-mining landscapes | |
| Sharma et al. | Modeling biofilm and development of rate law expressions for biofilm kinetics | |
| Gali et al. | Biodegradation of phenol with wastewater as a cosubstrate in upflow anaerobic sludge blanket | |
| WO2006097903A3 (en) | Method of synchronization in a mobile system | |
| KR100958965B1 (en) | Generate multiplier products based on encoded data from addressable locations | |
| Melchers et al. | Extreme value statistics for pitting corrosion of steel pipelines | |
| Li et al. | Inequality, power, population and hydraulic works: a quantitative approach unraveling the emergence of the earliest state in the prehistoric Yangtze Plain | |
| César et al. | Modeling of an anoxic/methanogenic biofilm: effect of pH calculation within the biofilm | |
| Zhang et al. | Optimizing managed artificial recharge backwash using a multi-objective particle swarm optimization coupled with a clogging simulation model |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |