CN113268339A - Dynamic load balancing method and system based on differential evolution algorithm - Google Patents
Dynamic load balancing method and system based on differential evolution algorithmDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113268339A CN113268339ACN202110425030.7ACN202110425030ACN113268339ACN 113268339 ACN113268339 ACN 113268339ACN 202110425030 ACN202110425030 ACN 202110425030ACN 113268339 ACN113268339 ACN 113268339A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- load balancing
- differential evolution
- evolution algorithm
- server
- rate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5005—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request
- G06F9/5027—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request the resource being a machine, e.g. CPUs, Servers, Terminals
- G06F9/505—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request the resource being a machine, e.g. CPUs, Servers, Terminals considering the load
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/004—Artificial life, i.e. computing arrangements simulating life
- G06N3/006—Artificial life, i.e. computing arrangements simulating life based on simulated virtual individual or collective life forms, e.g. social simulations or particle swarm optimisation [PSO]
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/12—Computing arrangements based on biological models using genetic models
- G06N3/126—Evolutionary algorithms, e.g. genetic algorithms or genetic programming
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y04—INFORMATION OR COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES HAVING AN IMPACT ON OTHER TECHNOLOGY AREAS
- Y04S—SYSTEMS INTEGRATING TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO POWER NETWORK OPERATION, COMMUNICATION OR INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES FOR IMPROVING THE ELECTRICAL POWER GENERATION, TRANSMISSION, DISTRIBUTION, MANAGEMENT OR USAGE, i.e. SMART GRIDS
- Y04S10/00—Systems supporting electrical power generation, transmission or distribution
- Y04S10/50—Systems or methods supporting the power network operation or management, involving a certain degree of interaction with the load-side end user applications
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Multi Processors (AREA)
- Debugging And Monitoring (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及一种基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法及系统,属于负载均衡领域。The invention relates to a dynamic load balancing method and system based on a differential evolution algorithm, and belongs to the field of load balancing.
背景技术Background technique
随着电力市场的放开,我国电力市场的接入成员数量和市场交易规模将呈爆炸式增长,这就要求新一代电力交易平台能够支持数百万用户的便捷接入和数据的高效采集与传输。这对电力交易技术支持系统的服务器提出了更高的要求,要求服务器保持快速的响应,同时为大量并发客户提供高质量的服务。With the liberalization of the electricity market, the number of access members and the scale of market transactions in my country's electricity market will explode, which requires a new generation of electricity trading platforms to support the convenient access of millions of users and efficient data collection and transmission. This puts forward higher requirements for the server of the power trading technical support system, requiring the server to maintain a fast response and provide high-quality services for a large number of concurrent customers.
Nginx服务器作为一种优秀的HTTP和反向代理服务器,以其稳定性、高并发性、低系统资源消耗和开放源代码等优点,常被广泛应用于高并发电力交易技术支持系统,Nginx服务器内置了许多第三方负载均衡算法,如轮询算法(RR)、最小连接算法(LC),内置这些算法的Nginx服务器并不能满足快速响应、处理大量并发请求的要求,因此现在急需一种新的负载均衡方法。As an excellent HTTP and reverse proxy server, Nginx server is often widely used in high-concurrency power trading technical support systems for its advantages of stability, high concurrency, low system resource consumption and open source code. Nginx server has built-in There are many third-party load balancing algorithms, such as round robin algorithm (RR) and least connection algorithm (LC). The Nginx server built with these algorithms cannot meet the requirements of fast response and processing a large number of concurrent requests, so a new load is urgently needed. Balance method.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明提供了一种基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法及系统,解决了背景技术中披露的问题。The present invention provides a dynamic load balancing method and system based on a differential evolution algorithm, which solves the problems disclosed in the background art.
为了解决上述技术问题,本发明所采用的技术方案是:In order to solve the above-mentioned technical problems, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法,包括:Dynamic load balancing methods based on differential evolution algorithm, including:
计算服务器群的若干负载均衡指标;Calculate several load balancing indicators of the server farm;
响应于任意一负载均衡指标超过对应的阈值,采用差分进化算法进行动态负载均衡;其中,差分进化算法以所有负载均衡指标之和最小为目标,服务器的动态权值为优化量;差分进化算法中的变异率和交叉率为自适应调整的变异率和交叉率。In response to any load balancing index exceeding the corresponding threshold, the differential evolution algorithm is used for dynamic load balancing; among them, the differential evolution algorithm takes the minimum sum of all load balancing indicators as the goal, and the dynamic weight of the server is the optimization amount; in the differential evolution algorithm The mutation rate and crossover rate are adaptively adjusted for the mutation rate and crossover rate.
负载均衡指标包括服务器群的综合负载均衡度和服务器群的链路负载均衡度。The load balancing index includes the comprehensive load balancing degree of the server group and the link load balancing degree of the server group.
服务器群综合负载均衡度的计算公式如下,The calculation formula of the comprehensive load balance degree of the server group is as follows:
其中,δp为服务器群的综合负载均衡度;TK为当前周期;m为分析时长;N为服务器群内的服务器数量;PUt(Svi)为服务器Svi当前周期的实时综合利用率;为服务器群中所有服务器实时综合利用率的均值;Among them, δp is the comprehensive load balancing degree of the server group; TK is the current cycle; m is the analysis duration;N is the number of servers in the server group; PUt (Svi ) is the real-time comprehensive utilization rate of the server Svi in the current cycle ; is the average real-time comprehensive utilization of all servers in the server farm;
PUt(Svi)=R1PUCPU(Svi)+R2PUMemory(Svi)+R3PUBd(Svi)PUt (Svi )=R1 PUCPU (Svi )+R2 PUMemory (Svi )+R3 PUBd (Svi )
其中,R1、R2、R3为CPU、内存和带宽的服务影响权;PUCPU(Svi)、PUMemory(Svi)、PUBd(Svi)分别为服务器Svi当前周期的CPU、内存和带宽占用比。Among them, R1 , R2 , and R3 are the service influence rights of CPU, memory and bandwidth; PUCPU (Svi ), PUMemory (Svi ), and PUBd (Svi ) are the CPU of the current cycle of server Svi respectively , memory and bandwidth usage ratio.
服务器群链路负载均衡度的计算公式如下,The calculation formula of the link load balance degree of the server group is as follows:
其中,δDL为服务器群的链路负载均衡度;loadi(t)为第i个链路当前周期的已用带宽;为所有链路已用带宽的平均值;TK为当前周期;m为分析时长;N为服务器群内的服务器数量。Among them, δDL is the link load balance degree of the server group; loadi (t) is the used bandwidth of the i-th link in the current cycle; is the average of the bandwidth used by all links; TK is the current cycle; m is the analysis time;N is the number of servers in the server group.
变异率自适应调整的公式为,The formula for adaptive adjustment of the mutation rate is,
其中,Fn+1为第n+1代种群的变异率;Fn为第n代种群的变异率;λ为变异率衰减系数;C为与目标函数f最大值相对的常数;为第n+1代种群的最优个体;为第n代种群的最优个体。Among them,Fn+1 is the mutation rate of the n+1th generation population;Fn is the mutation rate of the nth generation population; λ is the decay rate of mutation coefficient; C is a constant relative to the maximum value of the objective function f; is the optimal individual of the n+1 generation population; is the optimal individual of the nth generation population.
交叉率自适应调整的公式为,The formula for adaptive adjustment of the crossover rate is,
其中,n为当前迭代数;Crn为当前迭代对应的交叉率;D为最大迭代数。Among them, n is the current iteration number; Crn is the crossover rate corresponding to the current iteration; D is the maximum iteration number.
响应于所有负载均衡指标均不超过对应的阈值,选择负载最小的服务器处理请求。In response to all load balancing metrics not exceeding the corresponding thresholds, the server with the least load is selected to process the request.
基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡系统,包括:A dynamic load balancing system based on differential evolution algorithm, including:
负载均衡指标计算模块:计算服务器群的若干负载均衡指标;Load balancing indicator calculation module: calculate several load balancing indicators of the server group;
负载均衡模块:响应于任意一负载均衡指标超过对应的阈值,采用差分进化算法进行动态负载均衡;其中,差分进化算法以所有负载均衡指标之和最小为目标,服务器的动态权值为优化量;差分进化算法中的变异率和交叉率为自适应调整的变异率和交叉率。Load balancing module: In response to any load balancing index exceeding the corresponding threshold, the differential evolution algorithm is used to perform dynamic load balancing; wherein, the differential evolution algorithm takes the minimum sum of all load balancing indicators as the goal, and the dynamic weight of the server is the optimization amount; The mutation rate and crossover rate in the differential evolution algorithm are adaptively adjusted mutation rate and crossover rate.
一种存储一个或多个程序的计算机可读存储介质,所述一个或多个程序包括指令,所述指令当由计算设备执行时,使得所述计算设备执行基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法。A computer-readable storage medium storing one or more programs, the one or more programs comprising instructions that, when executed by a computing device, cause the computing device to perform a differential evolution algorithm-based dynamic load balancing method .
一种计算设备,包括一个或多个处理器、一个或多个存储器以及一个或多个程序,其中一个或多个程序存储在所述一个或多个存储器中并被配置为由所述一个或多个处理器执行,所述一个或多个程序包括用于执行基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法的指令。A computing device comprising one or more processors, one or more memories, and one or more programs, wherein the one or more programs are stored in the one or more memories and configured to be executed by the one or more A plurality of processors execute, the one or more programs including instructions for executing a differential evolution algorithm based dynamic load balancing method.
本发明所达到的有益效果:本发明采用变异率和交叉率自适应调整的差分进化算法进行负载均衡,相较于现有的方法更能满足快速响应、处理大量并发请求的要求。Beneficial effects achieved by the present invention: the present invention adopts the differential evolution algorithm with adaptive adjustment of mutation rate and crossover rate for load balancing, which can better meet the requirements of fast response and processing a large number of concurrent requests compared with the existing method.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明方法的流程图;Fig. 1 is the flow chart of the inventive method;
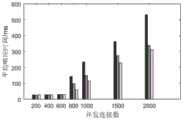
图2为本发明方法与现有两种方法的平均响应时间对比结果Fig. 2 is the average response time comparison result of the method of the present invention and the existing two methods
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图对本发明作进一步描述。以下实施例仅用于更加清楚地说明本发明的技术方案,而不能以此来限制本发明的保护范围。The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. The following examples are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention more clearly, and cannot be used to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
如图1所示,基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法,包括以下步骤:As shown in Figure 1, the dynamic load balancing method based on differential evolution algorithm includes the following steps:
步骤1,计算服务器群的若干负载均衡指标。Step 1: Calculate several load balancing indicators of the server farm.
步骤2,响应于所有负载均衡指标均不超过对应的阈值,选择负载最小的服务器处理请求;响应于任意一负载均衡指标超过对应的阈值,采用差分进化算法进行动态负载均衡;其中,差分进化算法以所有负载均衡指标之和最小为目标,服务器的动态权值为优化量;差分进化算法中的变异率和交叉率为自适应调整的变异率和交叉率。Step 2, in response to all load balancing indicators not exceeding the corresponding threshold, select the server with the smallest load to process the request; in response to any load balancing indicator exceeding the corresponding threshold, adopt the differential evolution algorithm to perform dynamic load balancing; among them, the differential evolution algorithm Taking the minimum sum of all load balancing indicators as the goal, the dynamic weight of the server is the optimization amount; the mutation rate and crossover rate in the differential evolution algorithm are adaptively adjusted mutation rate and crossover rate.
上述方法采用变异率和交叉率自适应调整的差分进化算法进行负载均衡,相较于现有的方法更能满足快速响应、处理大量并发请求的要求。The above method adopts a differential evolution algorithm with adaptive adjustment of mutation rate and crossover rate for load balancing, which can better meet the requirements of fast response and processing a large number of concurrent requests compared with existing methods.
这里的负载均衡指标主要有两个,包括服务器群的综合负载均衡度和服务器群的链路负载均衡度。There are two main load balancing indicators here, including the comprehensive load balancing degree of the server group and the link load balancing degree of the server group.
1)服务器群的综合负载均衡度1) Comprehensive load balancing degree of the server group
为了评估服务器群的服务能力,从CPU、内存(RAM)、服务器带宽三个方面分析了运行项目的服务器资源消耗;In order to evaluate the service capability of the server farm, the server resource consumption of running the project was analyzed from three aspects: CPU, memory (RAM), and server bandwidth;
假设服务器群中有N个服务器,度量服务器的综合服务性能,如下所示:Assuming that there are N servers in the server farm, measure the comprehensive service performance of the servers as follows:
P(Svi)=R1PCPU(Svi)+R2PMemory(Svi)+R3PBd(Svi)P(Svi )=R1 PCPU (Svi )+R2 PMemory (Svi )+R3 PBd (Svi )
其中,P(Svi)为服务器Svi的综合服务性能,R1、R2、R3为CPU、内存和带宽的服务影响权,PCPU(Svi)、PMemory(Svi)、PBd(Svi)为服务器Svi的CPU负载能力、内存负载能力和带宽负载能力;Among them, P(Svi ) is the comprehensive service performance of the server Svi, R1 , R2 , and R3 are the service influence weights of CPU, memory and bandwidth, PCPU (Svi) , PMemory (Svi) , PBd (Svi ) is the CPU load capacity, memory load capacity and bandwidth load capacity of the serverSvi ;
这样,服务器的实时综合利用率可定义为:In this way, the real-time comprehensive utilization of the server can be defined as:
PUt(Svi)=R1PUCPU(Svi)+R2PUMemory(Svi)+R3PUBd(Svi)PUt (Svi )=R1 PUCPU (Svi )+R2 PUMemory (Svi )+R3 PUBd (Svi )
其中,PUCPU(Svi)、PUMemory(Svi)、PUBd(Svi)分别为服务器Svi当前周期的CPU、内存和带宽占用比,PUt(Svi)为服务器Svi当前周期的实时综合利用率;Among them, PUCPU (Svi ), PUMemory (Svi ), and PUBd (Svi ) are the CPU, memory and bandwidth occupancy ratios of the current cycle of the server Svi respectively, and PUt (Svi ) is the current cycle of the server Svi . real-time comprehensive utilization rate;
那么服务器群的综合负载均衡度为:Then the comprehensive load balancing degree of the server group is:
其中,δp为服务器群的综合负载均衡度,TK为当前周期,m为分析时长,为服务器群中所有服务器实时综合利用率的均值;Among them, δp is the comprehensive load balance degree of the server group, TK is the current cycle, m is the analysis time, is the average real-time comprehensive utilization of all servers in the server farm;
服务器的当前默认权重可表示为:The current default weight of the server can be expressed as:
其中,Wt(Svi)为服务器Svi的当前(即当前周期)默认权重,Pt(Svi)为服务器Svi当前周期的综合服务性能。Wherein, Wt (Svi ) is the current (ie, current cycle) default weight of the serverSvi , and Pt (Svi ) is the comprehensive service performance of the serverSvi in the current cycle.
2)服务器群的链路负载均衡度2) Link load balance of the server farm
为了反映网络的链路负载衡度,定义了一个链路负载衡度性参数。在统计学中,方差是用来衡量随机变量的离散度的。对于一个网络,链路负载衡度参数可以定义为网络中所有链路使用带宽的方差,但直接监测方差是不合适的。网络中短期链路负载不衡度的状态可以忽略,直接监控方差可能会触发不必要的负载衡度算法。因此,这里通过计算一段时间内所用链路带宽的标准差值,可以平滑瞬时的短期流量波动。计算过程如式下所示:In order to reflect the link load balance of the network, a link load balance parameter is defined. In statistics, variance is used to measure the dispersion of random variables. For a network, the link load balance parameter can be defined as the variance of the bandwidth used by all links in the network, but it is not suitable to monitor the variance directly. The state of short-term link load imbalance in the network can be ignored, and direct monitoring of the variance may trigger unnecessary load balancing algorithms. Therefore, by calculating the standard deviation value of the link bandwidth used in a period of time, the instantaneous short-term traffic fluctuation can be smoothed. The calculation process is as follows:
其中,δDL为服务器群的链路负载均衡度,loadi(t)为第i个链路当前周期的已用带宽,为所有链路已用带宽的平均值。Among them, δDL is the link load balance degree of the server group, loadi (t) is the used bandwidth of the i-th link in the current cycle, is the average of the bandwidth used by all links.
这样,根据服务器群两个负载均衡指标δp和δDL,可有效动态评估服务器群性能和链路负载均衡性;设定两个阈值当任一负载均衡指标超过对应阈值时,网络链路处于较强不平衡状态,采用差分进化算法进行动态负载均衡;否则选择负载最小的服务器处理请求,即当前默认权重最大的服务器。In this way, according to the two load balancing indicators δp and δDL of the server group, the performance of the server group and the link load balance can be effectively and dynamically evaluated; two thresholds are set. When any load balancing indicator exceeds the corresponding threshold, the network link is in a strong unbalanced state, and the differential evolution algorithm is used for dynamic load balancing; otherwise, the server with the least load is selected to process the request, that is, the server with the current default weight is the largest.
传统的差分进化算法的基本思想是:在可行解的范围内,根据自然生存规律进行随机优化的方法。首先随机生成初始种群,对初始种群进行交叉和变异操作,然后,根据优胜劣汰的生存规律,对种群进行选择和操作;具体如下:The basic idea of the traditional differential evolution algorithm is: within the scope of feasible solutions, it is a method of stochastic optimization according to the laws of natural survival. First randomly generate an initial population, perform crossover and mutation operations on the initial population, and then select and operate the population according to the survival law of the survival of the fittest; the details are as follows:
11)种群初始化11) Population initialization
生成初始种群如下:The initial population is generated as follows:
X0=Xmin+rand()(Xmax-Xmin)X0 =Xmin +rand( )(Xmax -Xmin )
其中,X0为第0代种群,rand()用以产生(0,1)之间的随机数,Xmax、Xmin分别为个体的最大值和最小值,在种群初始化后,得到NP个初始个体;Among them, X0 is the 0th generation population, rand() is used to generate random numbers between (0, 1), Xmax and Xmin are the maximum and minimum values of the individual, respectively. After the population is initialized, NP numbers are obtained. initial individual;
12)种群变异12) Population variation
差分进化算法的变异操作不同于其他智能优化算法,如遗传算法和粒子群优化算法。这也是该优化算法的一个重要特点,变异模式的不同选择对种群的优化效率有一定的影响。The mutation operation of differential evolution algorithm is different from other intelligent optimization algorithms, such as genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization algorithm. This is also an important feature of the optimization algorithm, and the different choices of mutation modes have a certain impact on the optimization efficiency of the population.
采用以下变异策略为:The following mutation strategies are used:
其中,为通过变异操作获得的第n+1代种群的第j个个体,为第n代种群的第t1个个体和第t2个个体,t1和t2为(1,NP)之间的两个随机正整数,为通过变异操作获得的第n代种群的第j个个体,为第n代种群的最优个体,F为变异率,一般F∈[0,2];in, is the jth individual of the n+1th generation population obtained by mutation operation, is the t1th individual and the t2th individual of the nth generation population, t1 and t2 are two random positive integers between (1, NP), is the jth individual of the nth generation population obtained by mutation operation, is the optimal individual of the nth generation population, F is the mutation rate, generally F∈[0,2];
13)种群交叉13) Population crossover
在传统的差分进化算法中,交叉率设置为一个固定的常数,一般Cr∈[0,2],种群交叉方法:In the traditional differential evolution algorithm, the crossover rate is set to a fixed constant, generally Cr ∈ [0,2], the population crossover method:
其中,为通过交叉操作获得的第n+1代种群的第j个个体,为突变操作后n+1代第j个个体的第j′染色体进行交叉,为第n代第j个个体的第j′染色体;in, is the jth individual of the n+1th generation population obtained by the crossover operation, Crossover is performed for the j'th chromosome of the jth individual of the n+1 generation after the mutation operation, is the j'th chromosome of the jth individual of the nth generation;
14)种群选择14) Population selection
差分进化算法的选择操作基于贪婪搜索机制,根据初始个体和交叉个体的适应度进行选择,适应性较差的个体进入下一代群体;选择方法如下:The selection operation of the differential evolution algorithm is based on the greedy search mechanism, and the selection is made according to the fitness of the initial individual and the cross individual, and the individuals with poor adaptability enter the next generation group; the selection method is as follows:
其中,为经过选择操作后获得的第n+1代种群的第j个个体,为经过前面交叉操作后获得的第n+1代种群的第j个个体,f为差分进化算法的目标函数。in, is the jth individual of the n+1th generation population obtained after the selection operation, is the jth individual of the n+1th generation population obtained after the previous crossover operation, and f is the objective function of the differential evolution algorithm.
在传统的差分进化算法中,固定的变异率和交叉率不能有效地平衡搜索范围和搜索方向之间的矛盾,因此,为了提高优化能力,设计了一种具有自适应调整的变异率和交叉率的差分进化算法。In the traditional differential evolution algorithm, the fixed mutation rate and crossover rate cannot effectively balance the contradiction between the search range and the search direction. Therefore, in order to improve the optimization ability, a mutation rate and crossover rate with adaptive adjustment are designed. differential evolution algorithm.
在交易支持系统的负载均衡处理过程中,变异率可在权值动态优化中缩放种群向量。在权重优化的初始阶段,为了保证种群的多样性,需要较大的变异率来防止进化过程陷入局部最优解,在权重优化的后期,为了有效地保留种群中的优秀个体,需要较小的变异率,这样可以有效地提高最优解的搜索速度。During the load balancing process of the transaction support system, the mutation rate can scale the population vector in the dynamic optimization of weights. In the initial stage of weight optimization, in order to ensure the diversity of the population, a large mutation rate is required to prevent the evolution process from falling into a local optimal solution. In the later stage of weight optimization, in order to effectively retain the excellent individuals in the population, a small The mutation rate can effectively improve the search speed of the optimal solution.
因此,自适应变异率的设计可有效地平衡电力交易技术支持系统动态权重优化的全局搜索和局部搜索能力,对于动态权重优化,变异率的自适应调整可以表示为:Therefore, the design of the adaptive mutation rate can effectively balance the global search and local search capabilities of the power trading technology to support the dynamic weight optimization of the system. For the dynamic weight optimization, the adaptive adjustment of the mutation rate can be expressed as:
其中,Fn+1为第n+1代种群的变异率,Fn为第n代种群的变异率,λ为变异率衰减系数,一般为0.1,C为与目标函数f最大值相对的常数,为第n+1代种群的最优个体,为第n代种群的最优个体。Among them, Fn+1 is the mutation rate of the n+1 generation population, Fn is the mutation rate of the nth generation population, λ is the mutation rate attenuation coefficient, generally 0.1, and C is a constant relative to the maximum value of the objective function f , is the optimal individual of the n+1 generation population, is the optimal individual of the nth generation population.
那么,自适应调整变异率后,权重优化的变异率序列为[F0,F1,F2,…,FD]。Then, after adaptively adjusting the mutation rate, the weight-optimized mutation rate sequence is [F0 , F1 , F2 ,…,FD ].
为了进一步提高交易支撑系统的服务器负载权重优化效果,在自适应调整变异率后继续对交叉率进行自适应调整,交叉率自适应调整具体如下:In order to further improve the server load weight optimization effect of the transaction support system, the adaptive adjustment of the crossover rate is continued after the adaptive adjustment of the mutation rate. The adaptive adjustment of the crossover rate is as follows:
其中,n为当前迭代数,Crn为当前迭代对应的交叉率,D为最大迭代数。Among them, n is the current iteration number, Crn is the crossover rate corresponding to the current iteration, and D is the maximum iteration number.
由于变异因子和交叉因子的适应性,差分进化在迭代开始时具有较强的全局搜索能力,在迭代结束时具有较高的计算精度和较快的收敛速度,而且变异率和交叉率不需要人工干预,适应性强。Due to the adaptability of mutation factor and crossover factor, differential evolution has strong global search ability at the beginning of the iteration, high calculation accuracy and fast convergence speed at the end of the iteration, and the mutation rate and crossover rate do not need artificial Intervention and adaptability.
为了验证上述方法的效果,进行仿真实验,在虚拟机中构建了五台服务器,一台作为客户端测试连接,一台作为反向代理服务器,另外三台作为后端服务器。在后端服务器上搭建Nginx+PHP环境,实现动态网站运行环境。Nginx通过fastcgi接口与PHP文件交互。PHP动态资源文件被引入并放置在根目录中的位置。搭建实验环境后,采用Httperf和Autobench进行了性能测试。Httperf可以根据不同的测试需求生成不同的工作负载。Autobench是基于Httperf开发的一个脚本工具,它可以根据参数设置自动执行并行测试,并将结果保存在数据库中。In order to verify the effect of the above method, a simulation experiment was carried out, and five servers were built in the virtual machine, one was used as a client test connection, one was used as a reverse proxy server, and the other three were used as back-end servers. Build the Nginx+PHP environment on the back-end server to realize the dynamic website running environment. Nginx interacts with PHP files through the fastcgi interface. The location where PHP dynamic resource files are imported and placed in the root directory. After building the experimental environment, Httperf and Autobench were used for performance testing. Httperf can generate different workloads according to different test requirements. Autobench is a script tool developed based on Httperf, which can automatically execute parallel tests according to parameter settings and save the results in the database.
在仿真实验中,分别对默认轮询算法(RR)、最小连接算法(LC)和上述方法进行了测试,统计数据如图2和表1所示。In the simulation experiments, the default round-robin algorithm (RR), the least connection algorithm (LC) and the above methods are tested respectively, and the statistical data are shown in Figure 2 and Table 1.
由图2可以清楚发现,上述方法的平均响应时间基本在不同的请求速率下是最短的,特别是在较高的并发访问数时,因此它的性能优于其他两种算法。It can be clearly found from Figure 2 that the average response time of the above method is basically the shortest under different request rates, especially when the number of concurrent accesses is high, so its performance is better than the other two algorithms.
表1实际并发连接数结果对比Table 1 Comparison of the actual number of concurrent connections
表1结果显示,当并发请求数小于2000时,三种算法的实际连接数对比,可以看出,在算法执行过程中,当请求数增加到2000个时,虽然三种算法都失败了,但在相同并发数请求数的情况下,上述方法能够处理的并发请求数明显高于其他两种算法;而并发请求数小于1000时,上述方法能够处理的并发请求数也显著高于其他两种算法。The results in Table 1 show that when the number of concurrent requests is less than 2000, compared with the actual number of connections of the three algorithms, it can be seen that when the number of requests increases to 2000 during the execution of the algorithm, although all three algorithms fail, In the case of the same number of concurrent requests, the number of concurrent requests that can be processed by the above method is significantly higher than that of the other two algorithms; and when the number of concurrent requests is less than 1000, the number of concurrent requests that can be processed by the above method is also significantly higher than the other two algorithms. .
基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡系统,包括:A dynamic load balancing system based on differential evolution algorithm, including:
负载均衡指标计算模块:计算服务器群的若干负载均衡指标;Load balancing indicator calculation module: calculate several load balancing indicators of the server group;
负载均衡模块:响应于任意一负载均衡指标超过对应的阈值,采用差分进化算法进行动态负载均衡;其中,差分进化算法以所有负载均衡指标之和最小为目标,服务器的动态权值为优化量;差分进化算法中的变异率和交叉率为自适应调整的变异率和交叉率。Load balancing module: In response to any load balancing index exceeding the corresponding threshold, the differential evolution algorithm is used to perform dynamic load balancing; wherein, the differential evolution algorithm takes the minimum sum of all load balancing indicators as the goal, and the dynamic weight of the server is the optimization amount; The mutation rate and crossover rate in the differential evolution algorithm are adaptively adjusted mutation rate and crossover rate.
一种存储一个或多个程序的计算机可读存储介质,所述一个或多个程序包括指令,所述指令当由计算设备执行时,使得所述计算设备执行基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法。A computer-readable storage medium storing one or more programs, the one or more programs comprising instructions that, when executed by a computing device, cause the computing device to perform a differential evolution algorithm-based dynamic load balancing method .
一种计算设备,包括一个或多个处理器、一个或多个存储器以及一个或多个程序,其中一个或多个程序存储在所述一个或多个存储器中并被配置为由所述一个或多个处理器执行,所述一个或多个程序包括用于执行基于差分进化算法的动态负载均衡方法的指令。A computing device comprising one or more processors, one or more memories, and one or more programs, wherein the one or more programs are stored in the one or more memories and configured to be executed by the one or more A plurality of processors execute, the one or more programs including instructions for executing a differential evolution algorithm based dynamic load balancing method.
本领域内的技术人员应明白,本申请的实施例可提供为方法、系统、或计算机程序产品。因此,本申请可采用完全硬件实施例、完全软件实施例、或结合软件和硬件方面的实施例的形式。而且,本申请可采用在一个或多个其中包含有计算机可用程序代码的计算机可用存储介质(包括但不限于磁盘存储器、CD-ROM、光学存储器等)上实施的计算机程序产品的形式。As will be appreciated by those skilled in the art, the embodiments of the present application may be provided as a method, a system, or a computer program product. Accordingly, the present application may take the form of an entirely hardware embodiment, an entirely software embodiment, or an embodiment combining software and hardware aspects. Furthermore, the present application may take the form of a computer program product embodied on one or more computer-usable storage media (including, but not limited to, disk storage, CD-ROM, optical storage, etc.) having computer-usable program code embodied therein.
本申请是参照根据本申请实施例的方法、设备(系统)、和计算机程序产品的流程图和/或方框图来描述的。应理解可由计算机程序指令实现流程图和/或方框图中的每一流程和/或方框、以及流程图和/或方框图中的流程和/或方框的结合。可提供这些计算机程序指令到通用计算机、专用计算机、嵌入式处理机或其他可编程数据处理设备的处理器以产生一个机器,使得通过计算机或其他可编程数据处理设备的处理器执行的指令产生用于实现在流程图一个流程或多个流程和/或方框图一个方框或多个方框中指定的功能的装置。The present application is described with reference to flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams of methods, apparatus (systems), and computer program products according to embodiments of the present application. It will be understood that each flow and/or block in the flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams, and combinations of flows and/or blocks in the flowchart illustrations and/or block diagrams, can be implemented by computer program instructions. These computer program instructions may be provided to the processor of a general purpose computer, special purpose computer, embedded processor or other programmable data processing device to produce a machine such that the instructions executed by the processor of the computer or other programmable data processing device produce Means for implementing the functions specified in a flow or flow of a flowchart and/or a block or blocks of a block diagram.
这些计算机程序指令也可存储在能引导计算机或其他可编程数据处理设备以特定方式工作的计算机可读存储器中,使得存储在该计算机可读存储器中的指令产生包括指令装置的制造品,该指令装置实现在流程图一个流程或多个流程和/或方框图一个方框或多个方框中指定的功能。These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer-readable memory capable of directing a computer or other programmable data processing apparatus to function in a particular manner, such that the instructions stored in the computer-readable memory result in an article of manufacture comprising instruction means, the instructions The apparatus implements the functions specified in the flow or flow of the flowcharts and/or the block or blocks of the block diagrams.
这些计算机程序指令也可装载到计算机或其他可编程数据处理设备上,使得在计算机或其他可编程设备上执行一系列操作步骤以产生计算机实现的处理,从而在计算机或其他可编程设备上执行的指令提供用于实现在流程图一个流程或多个流程和/或方框图一个方框或多个方框中指定的功能的步骤。These computer program instructions can also be loaded on a computer or other programmable data processing device to cause a series of operational steps to be performed on the computer or other programmable device to produce a computer-implemented process such that The instructions provide steps for implementing the functions specified in the flow or blocks of the flowcharts and/or the block or blocks of the block diagrams.
以上仅为本发明的实施例而已,并不用于限制本发明,凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所做的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均包含在申请待批的本发明的权利要求范围之内。The above are only examples of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the present invention. Any modifications, equivalent replacements, improvements, etc. made within the spirit and principles of the present invention are included in the application for pending approval of the present invention. within the scope of the claims.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110425030.7ACN113268339B (en) | 2021-04-20 | 2021-04-20 | Dynamic load balancing method and system based on differential evolution algorithm |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110425030.7ACN113268339B (en) | 2021-04-20 | 2021-04-20 | Dynamic load balancing method and system based on differential evolution algorithm |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113268339Atrue CN113268339A (en) | 2021-08-17 |
| CN113268339B CN113268339B (en) | 2022-08-19 |
Family
ID=77229064
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110425030.7AExpired - Fee RelatedCN113268339B (en) | 2021-04-20 | 2021-04-20 | Dynamic load balancing method and system based on differential evolution algorithm |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113268339B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114237872A (en)* | 2021-11-24 | 2022-03-25 | 金梦笔 | High-performance memory management method and system based on differential evolution |
| CN114422517A (en)* | 2022-01-24 | 2022-04-29 | 广东三合电子实业有限公司 | Server load balancing system and method thereof |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20200210864A1 (en)* | 2018-01-15 | 2020-07-02 | Dalian Minzu University | Method for detecting community structure of complicated network |
| CN112380016A (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2021-02-19 | 华南理工大学 | Cloud computing resource load balancing scheduling method based on improved genetic algorithm and application |
- 2021
- 2021-04-20CNCN202110425030.7Apatent/CN113268339B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20200210864A1 (en)* | 2018-01-15 | 2020-07-02 | Dalian Minzu University | Method for detecting community structure of complicated network |
| CN112380016A (en)* | 2020-11-30 | 2021-02-19 | 华南理工大学 | Cloud computing resource load balancing scheduling method based on improved genetic algorithm and application |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114237872A (en)* | 2021-11-24 | 2022-03-25 | 金梦笔 | High-performance memory management method and system based on differential evolution |
| CN114237872B (en)* | 2021-11-24 | 2025-03-25 | 金梦笔 | A high-performance memory management method and system based on differential evolution |
| CN114422517A (en)* | 2022-01-24 | 2022-04-29 | 广东三合电子实业有限公司 | Server load balancing system and method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113268339B (en) | 2022-08-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113938488A (en) | Load balancing method based on dynamic and static weighted polling | |
| Ye et al. | Energy-efficient many-objective virtual machine placement optimization in a cloud computing environment | |
| CN113268339B (en) | Dynamic load balancing method and system based on differential evolution algorithm | |
| CN114741955B (en) | A multi-objective optimization task scheduling method based on secure cloud | |
| CN106790726A (en) | A kind of priority query's dynamic feedback of load equilibrium resource regulating method based on Docker cloud platforms | |
| CN108363643A (en) | A kind of HDFS copy management methods based on file access temperature | |
| Fallah et al. | NASLA: Novel auto scaling approach based on learning automata for web application in cloud computing environment | |
| Singh et al. | Crow–penguin optimizer for multiobjective task scheduling strategy in cloud computing | |
| CN118232352B (en) | Power distribution network self-adaptive power flow optimization method and system | |
| CN117033004B (en) | Load balancing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| Cheng et al. | Optimal placement of distributed generation units in distribution systems via an enhanced multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm | |
| CN107707680A (en) | A kind of distributed data load-balancing method and system based on node computing capability | |
| CN110225096B (en) | Server load balancing method based on genetic algorithm | |
| CN106657399B (en) | Background server selection method and device based on middleware | |
| CN111858029A (en) | Storm cluster load balancing method and system based on discrete particle swarm | |
| Ogden et al. | Many models at the edge: Scaling deep inference via model-level caching | |
| CN105005501B (en) | A kind of second order optimizing and scheduling task method towards cloud data center | |
| CN114945024B (en) | Server load balancing optimization method based on long short-term memory network | |
| Zhang et al. | A dynamic placement policy of virtual machine based on MOGA in cloud environment | |
| CN116962419A (en) | Method and device for generating server allocation policy, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN116799826A (en) | Distributed photovoltaic energy storage system optimal configuration method and related device | |
| Tong et al. | An efficient dynamic load balancing scheme for heterogenous processing system | |
| CN115202591A (en) | Storage device, method and storage medium of distributed database system | |
| CN111290853A (en) | Cloud data center scheduling method based on self-adaptive improved genetic algorithm | |
| Peng et al. | The realization of load balancing algorithm in cloud computing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20220819 |