CN113151312B - Novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2mRNA vaccine and its preparation method and application - Google Patents
Novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2mRNA vaccine and its preparation method and applicationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113151312B CN113151312BCN202110224383.0ACN202110224383ACN113151312BCN 113151312 BCN113151312 BCN 113151312BCN 202110224383 ACN202110224383 ACN 202110224383ACN 113151312 BCN113151312 BCN 113151312B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- mrna
- pharmaceutical composition
- cov
- sequence
- pseudouridine
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription12
- 229960005486vaccineDrugs0.000titleabstractdescription57
- 241000711573CoronaviridaeSpecies0.000titleabstractdescription8
- 241001678559COVID-19 virusSpecies0.000claimsabstractdescription54
- 230000009385viral infectionEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription5
- 108020004999messenger RNAProteins0.000claimsdescription89
- 150000002632lipidsChemical class0.000claimsdescription29
- 239000008194pharmaceutical compositionSubstances0.000claimsdescription28
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000claimsdescription27
- 230000000890antigenic effectEffects0.000claimsdescription25
- ISAKRJDGNUQOIC-UHFFFAOYSA-NUracilChemical compoundO=C1C=CNC(=O)N1ISAKRJDGNUQOIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription24
- 229920001184polypeptidePolymers0.000claimsdescription24
- 108090000765processed proteins & peptidesProteins0.000claimsdescription24
- 102000004196processed proteins & peptidesHuman genes0.000claimsdescription24
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription17
- -1cationic lipidChemical class0.000claimsdescription16
- 229940096437Protein SDrugs0.000claimsdescription12
- 101710198474Spike proteinProteins0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000012634fragmentSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 102000005962receptorsHuman genes0.000claimsdescription12
- 108020003175receptorsProteins0.000claimsdescription12
- 229940035893uracilDrugs0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000027455bindingEffects0.000claimsdescription11
- 102000029301Protein SHuman genes0.000claimsdescription10
- 125000003275alpha amino acid groupChemical group0.000claimsdescription10
- 238000007385chemical modificationMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- 108091026890Coding regionProteins0.000claimsdescription8
- 229930185560PseudouridineNatural products0.000claimsdescription8
- PTJWIQPHWPFNBW-UHFFFAOYSA-NPseudouridine CNatural productsOC1C(O)C(CO)OC1C1=CNC(=O)NC1=OPTJWIQPHWPFNBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- WGDUUQDYDIIBKT-UHFFFAOYSA-Nbeta-PseudouridineNatural productsOC1OC(CN2C=CC(=O)NC2=O)C(O)C1OWGDUUQDYDIIBKT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- OPTASPLRGRRNAP-UHFFFAOYSA-NcytosineChemical compoundNC=1C=CNC(=O)N=1OPTASPLRGRRNAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 230000008488polyadenylationEffects0.000claimsdescription8
- PTJWIQPHWPFNBW-GBNDHIKLSA-NpseudouridineChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1C1=CNC(=O)NC1=OPTJWIQPHWPFNBW-GBNDHIKLSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- UVBYMVOUBXYSFV-XUTVFYLZSA-N1-methylpseudouridineChemical compoundO=C1NC(=O)N(C)C=C1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1UVBYMVOUBXYSFV-XUTVFYLZSA-N0.000claimsdescription7
- LRSASMSXMSNRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N5-methylcytosineChemical compoundCC1=CNC(=O)N=C1NLRSASMSXMSNRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription7
- 229930182558SterolNatural products0.000claimsdescription7
- 230000007935neutral effectEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 150000003432sterolsChemical class0.000claimsdescription7
- 235000003702sterolsNutrition0.000claimsdescription7
- NRJAVPSFFCBXDT-HUESYALOSA-N1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholineChemical compoundCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCNRJAVPSFFCBXDT-HUESYALOSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 1080200053453' Untranslated RegionsProteins0.000claimsdescription6
- 1080200035895' Untranslated RegionsProteins0.000claimsdescription6
- AMMRPAYSYYGRKP-BGZDPUMWSA-N5-[(2s,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1-ethylpyrimidine-2,4-dioneChemical compoundO=C1NC(=O)N(CC)C=C1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1AMMRPAYSYYGRKP-BGZDPUMWSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-NcholesterolChemical compoundC1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N0.000claimsdescription6
- 108091028043Nucleic acid sequenceProteins0.000claimsdescription5
- KYEKLQMDNZPEFU-KVTDHHQDSA-N1-[(2r,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-dioneChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1N1C(=O)NC(=O)N=C1KYEKLQMDNZPEFU-KVTDHHQDSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- MUSPKJVFRAYWAR-XVFCMESISA-N1-[(2r,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)thiolan-2-yl]pyrimidine-2,4-dioneChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)S[C@H]1N1C(=O)NC(=O)C=C1MUSPKJVFRAYWAR-XVFCMESISA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- SXUXMRMBWZCMEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N2'-O-methyl uridineNatural productsCOC1C(O)C(CO)OC1N1C(=O)NC(=O)C=C1SXUXMRMBWZCMEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- SXUXMRMBWZCMEN-ZOQUXTDFSA-N2'-O-methyluridineChemical compoundCO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1N1C(=O)NC(=O)C=C1SXUXMRMBWZCMEN-ZOQUXTDFSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- JCNGYIGHEUKAHK-DWJKKKFUSA-N2-Thio-1-methyl-1-deazapseudouridineChemical compoundCC1C=C(C(=O)NC1=S)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)OJCNGYIGHEUKAHK-DWJKKKFUSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- CWXIOHYALLRNSZ-JWMKEVCDSA-N2-ThiodihydropseudouridineChemical compoundC1C(C(=O)NC(=S)N1)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)OCWXIOHYALLRNSZ-JWMKEVCDSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- VRVXMIJPUBNPGH-XVFCMESISA-N2-thio-dihydrouridineChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)N1CCC(=O)NC1=SVRVXMIJPUBNPGH-XVFCMESISA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- GJTBSTBJLVYKAU-XVFCMESISA-N2-thiouridineChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1N1C(=S)NC(=O)C=C1GJTBSTBJLVYKAU-XVFCMESISA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- VTGBLFNEDHVUQA-XUTVFYLZSA-N4-Thio-1-methyl-pseudouridineChemical compoundS=C1NC(=O)N(C)C=C1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1VTGBLFNEDHVUQA-XUTVFYLZSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- DDHOXEOVAJVODV-GBNDHIKLSA-N5-[(2s,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-2-sulfanylidene-1h-pyrimidin-4-oneChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1C1=CNC(=S)NC1=ODDHOXEOVAJVODV-GBNDHIKLSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- BNAWMJKJLNJZFU-GBNDHIKLSA-N5-[(2s,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-4-sulfanylidene-1h-pyrimidin-2-oneChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1C1=CNC(=O)NC1=SBNAWMJKJLNJZFU-GBNDHIKLSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- DWRXFEITVBNRMK-UHFFFAOYSA-NBeta-D-1-ArabinofuranosylthymineNatural productsO=C1NC(=O)C(C)=CN1C1C(O)C(O)C(CO)O1DWRXFEITVBNRMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- YKWUPFSEFXSGRT-JWMKEVCDSA-NDihydropseudouridineChemical compoundO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1C1C(=O)NC(=O)NC1YKWUPFSEFXSGRT-JWMKEVCDSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229940104302cytosineDrugs0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- DWRXFEITVBNRMK-JXOAFFINSA-NribothymidineChemical compoundO=C1NC(=O)C(C)=CN1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1DWRXFEITVBNRMK-JXOAFFINSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- WTBFLCSPLLEDEM-JIDRGYQWSA-N1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-L-serineChemical compoundCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP(O)(=O)OC[C@H](N)C(O)=O)OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCWTBFLCSPLLEDEM-JIDRGYQWSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- SNKAWJBJQDLSFF-NVKMUCNASA-N1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholineChemical compoundCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OC[C@H](COP([O-])(=O)OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCSNKAWJBJQDLSFF-NVKMUCNASA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- HOCJTJWYMOSXMU-XUTVFYLZSA-N4-MethoxypseudouridineChemical compoundCOC1=C(C=NC(=O)N1)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)OHOCJTJWYMOSXMU-XUTVFYLZSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 108091005634SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domainsProteins0.000claimsdescription3
- 235000012000cholesterolNutrition0.000claimsdescription3
- MWRBNPKJOOWZPW-CLFAGFIQSA-Ndioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamineChemical compoundCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(COP(O)(=O)OCCN)OC(=O)CCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCCMWRBNPKJOOWZPW-CLFAGFIQSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000001727in vivoMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000004519manufacturing processMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- ZXIATBNUWJBBGT-JXOAFFINSA-N5-methoxyuridineChemical compoundO=C1NC(=O)C(OC)=CN1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1ZXIATBNUWJBBGT-JXOAFFINSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 208000036142Viral infectionDiseases0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000002671adjuvantSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- DGNMJYUPWDTKJB-ZDSKVHJSSA-Nbis[(z)-non-2-enyl] 9-[4-(dimethylamino)butanoyloxy]heptadecanedioateChemical compoundCCCCCC\C=C/COC(=O)CCCCCCCC(OC(=O)CCCN(C)C)CCCCCCCC(=O)OC\C=C/CCCCCCDGNMJYUPWDTKJB-ZDSKVHJSSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- JUMHLCXWYQVTLL-KVTDHHQDSA-N2-thio-5-aza-uridineChemical compound[C@@H]1([C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1)N1C(=S)NC(=O)N=C1JUMHLCXWYQVTLL-KVTDHHQDSA-N0.000claims2
- PDXQSLIBLQMPJS-FDDDBJFASA-N1-[(2r,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-(methoxymethyl)pyrimidine-2,4-dioneChemical compoundO=C1NC(=O)C(COC)=CN1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1PDXQSLIBLQMPJS-FDDDBJFASA-N0.000claims1
- 241000700605VirusesSpecies0.000abstractdescription28
- 230000003472neutralizing effectEffects0.000abstractdescription27
- 210000002966serumAnatomy0.000abstractdescription27
- 108700021021mRNA VaccineProteins0.000abstractdescription24
- 229940126582mRNA vaccineDrugs0.000abstractdescription24
- 230000003053immunizationEffects0.000abstractdescription23
- 238000002649immunizationMethods0.000abstractdescription21
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000abstractdescription10
- 230000005847immunogenicityEffects0.000abstractdescription10
- 238000011830transgenic mouse modelMethods0.000abstractdescription9
- 101000929928Homo sapiens Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2Proteins0.000abstractdescription8
- 241000699660Mus musculusSpecies0.000abstractdescription8
- 102000048657human ACE2Human genes0.000abstractdescription8
- 239000000427antigenSubstances0.000abstractdescription6
- 102000036639antigensHuman genes0.000abstractdescription6
- 108091007433antigensProteins0.000abstractdescription6
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 238000012546transferMethods0.000abstractdescription6
- 210000004027cellAnatomy0.000description38
- 241000699670Mus sp.Species0.000description28
- 210000004072lungAnatomy0.000description20
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical compoundCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description15
- 239000000902placeboSubstances0.000description15
- 229940068196placeboDrugs0.000description15
- 241001112090PseudovirusSpecies0.000description14
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description13
- 238000013518transcriptionMethods0.000description13
- 230000035897transcriptionEffects0.000description13
- 239000002609mediumSubstances0.000description12
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000description11
- 230000003612virological effectEffects0.000description11
- 241000699666Mus <mouse, genus>Species0.000description10
- 239000013612plasmidSubstances0.000description10
- UQLDLKMNUJERMK-UHFFFAOYSA-Ldi(octadecanoyloxy)leadChemical group[Pb+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=OUQLDLKMNUJERMK-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description9
- 102000004190EnzymesHuman genes0.000description8
- 108090000790EnzymesProteins0.000description8
- KWGKDLIKAYFUFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-Mlithium chlorideChemical compound[Li+].[Cl-]KWGKDLIKAYFUFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description8
- 108091032973(ribonucleotides)n+mProteins0.000description7
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000description7
- 239000007924injectionSubstances0.000description7
- 238000002347injectionMethods0.000description7
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description7
- 239000000523sampleSubstances0.000description7
- 210000001744T-lymphocyteAnatomy0.000description6
- 210000004369bloodAnatomy0.000description6
- 239000008280bloodSubstances0.000description6
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description6
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description6
- 238000004806packaging method and processMethods0.000description6
- 238000002965ELISAMethods0.000description5
- GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-Nadenyl groupChemical classN1=CN=C2N=CNC2=C1NGFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description5
- 125000002091cationic groupChemical group0.000description5
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description5
- 238000011534incubationMethods0.000description5
- 150000007523nucleic acidsChemical group0.000description5
- 239000002773nucleotideSubstances0.000description5
- 125000003729nucleotide groupChemical group0.000description5
- 239000012071phaseSubstances0.000description5
- 238000010186stainingMethods0.000description5
- 208000025721COVID-19Diseases0.000description4
- 108090000695CytokinesProteins0.000description4
- 102000004127CytokinesHuman genes0.000description4
- 239000006144Dulbecco’s modified Eagle's mediumSubstances0.000description4
- 101000600434Homo sapiens Putative uncharacterized protein encoded by MIR7-3HGProteins0.000description4
- 102100037401Putative uncharacterized protein encoded by MIR7-3HGHuman genes0.000description4
- 101800000904Spike protein S1Proteins0.000description4
- 238000005119centrifugationMethods0.000description4
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description4
- 230000002163immunogenEffects0.000description4
- 208000015181infectious diseaseDiseases0.000description4
- 230000003834intracellular effectEffects0.000description4
- 238000001556precipitationMethods0.000description4
- 230000001681protective effectEffects0.000description4
- 108090000623proteins and genesProteins0.000description4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 238000011725BALB/c mouseMethods0.000description3
- 108010074328Interferon-gammaProteins0.000description3
- 108010047620PhytohemagglutininsProteins0.000description3
- 231100000645Reed–Muench methodToxicity0.000description3
- 208000037847SARS-CoV-2-infectionDiseases0.000description3
- 201000003176Severe Acute Respiratory SyndromeDiseases0.000description3
- NRLNQCOGCKAESA-KWXKLSQISA-N[(6z,9z,28z,31z)-heptatriaconta-6,9,28,31-tetraen-19-yl] 4-(dimethylamino)butanoateChemical compoundCCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCCCCCC(OC(=O)CCCN(C)C)CCCCCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCCNRLNQCOGCKAESA-KWXKLSQISA-N0.000description3
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description3
- 230000000120cytopathologic effectEffects0.000description3
- 238000010790dilutionMethods0.000description3
- 239000012895dilutionSubstances0.000description3
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description3
- 210000001163endosomeAnatomy0.000description3
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description3
- 238000007490hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stainingMethods0.000description3
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description3
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000description3
- 230000001885phytohemagglutininEffects0.000description3
- 238000003757reverse transcription PCRMethods0.000description3
- FGFVODMBKZRMMW-XUTVFYLZSA-N4-Methoxy-2-thiopseudouridineChemical compoundCOC1=C(C=NC(=S)N1)[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)OFGFVODMBKZRMMW-XUTVFYLZSA-N0.000description2
- 239000005695Ammonium acetateSubstances0.000description2
- 102000053723Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2Human genes0.000description2
- 108090000975Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2Proteins0.000description2
- 102100031673CorneodesmosinHuman genes0.000description2
- 101710139375CorneodesmosinProteins0.000description2
- 208000032163Emerging Communicable diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 206010064571Gene mutationDiseases0.000description2
- NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-NGuanosineChemical compoundC1=NC=2C(=O)NC(N)=NC=2N1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1ONYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UUOKFMHZSA-N0.000description2
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrochloric acidChemical compoundClVEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 102000008070Interferon-gammaHuman genes0.000description2
- 108060001084LuciferaseProteins0.000description2
- 239000005089LuciferaseSubstances0.000description2
- 206010035664PneumoniaDiseases0.000description2
- 108091034057RNA (poly(A))Proteins0.000description2
- 101000629318Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 Spike glycoproteinProteins0.000description2
- 239000002253acidSubstances0.000description2
- 230000002378acidificating effectEffects0.000description2
- 229940043376ammonium acetateDrugs0.000description2
- 238000004113cell cultureMethods0.000description2
- 239000013592cell lysateSubstances0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 239000006196dropSubstances0.000description2
- 238000002296dynamic light scatteringMethods0.000description2
- 229930182470glycosideNatural products0.000description2
- 239000001963growth mediumSubstances0.000description2
- UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-NguanineChemical groupO=C1NC(N)=NC2=C1N=CN2UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000028993immune responseEffects0.000description2
- 238000000338in vitroMethods0.000description2
- 229960003130interferon gammaDrugs0.000description2
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description2
- 125000002496methyl groupChemical group[H]C([H])([H])*0.000description2
- 239000007923nasal dropSubstances0.000description2
- 239000013642negative controlSubstances0.000description2
- 238000006386neutralization reactionMethods0.000description2
- 108020004707nucleic acidsProteins0.000description2
- 102000039446nucleic acidsHuman genes0.000description2
- 239000012188paraffin waxSubstances0.000description2
- 238000010827pathological analysisMethods0.000description2
- 239000013641positive controlSubstances0.000description2
- 239000002244precipitateSubstances0.000description2
- 230000037452primingEffects0.000description2
- 102000004169proteins and genesHuman genes0.000description2
- 238000000746purificationMethods0.000description2
- 210000000952spleenAnatomy0.000description2
- 210000004989spleen cellAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000000638stimulationEffects0.000description2
- 239000006228supernatantSubstances0.000description2
- 230000008685targetingEffects0.000description2
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description2
- 239000003981vehicleSubstances0.000description2
- LRFJOIPOPUJUMI-KWXKLSQISA-N2-[2,2-bis[(9z,12z)-octadeca-9,12-dienyl]-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]-n,n-dimethylethanamineChemical compoundCCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCCCCCC1(CCCCCCCC\C=C/C\C=C/CCCCC)OCC(CCN(C)C)O1LRFJOIPOPUJUMI-KWXKLSQISA-N0.000description1
- FWMNVWWHGCHHJJ-SKKKGAJSSA-N4-amino-1-[(2r)-6-amino-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2r)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]piperidine-4-carboxylic acidChemical compoundC([C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)N1CCC(N)(CC1)C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@H](N)CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1FWMNVWWHGCHHJJ-SKKKGAJSSA-N0.000description1
- OGHAROSJZRTIOK-KQYNXXCUSA-O7-methylguanosineChemical compoundC1=2N=C(N)NC(=O)C=2[N+](C)=CN1[C@@H]1O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OOGHAROSJZRTIOK-KQYNXXCUSA-O0.000description1
- 208000010444AcidosisDiseases0.000description1
- 206010001052Acute respiratory distress syndromeDiseases0.000description1
- USFZMSVCRYTOJT-UHFFFAOYSA-NAmmonium acetateChemical compoundN.CC(O)=OUSFZMSVCRYTOJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 201000004813BronchopneumoniaDiseases0.000description1
- 238000011740C57BL/6 mouseMethods0.000description1
- 241000283707CapraSpecies0.000description1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 108020004705CodonProteins0.000description1
- 208000001528Coronaviridae InfectionsDiseases0.000description1
- 206010011224CoughDiseases0.000description1
- MIKUYHXYGGJMLM-GIMIYPNGSA-NCrotonosideNatural productsC1=NC2=C(N)NC(=O)N=C2N1[C@H]1O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1OMIKUYHXYGGJMLM-GIMIYPNGSA-N0.000description1
- 229930183912Cytidylic acidNatural products0.000description1
- NYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UHFFFAOYSA-ND-guanosineNatural productsC1=2NC(N)=NC(=O)C=2N=CN1C1OC(CO)C(O)C1ONYHBQMYGNKIUIF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- HMFHBZSHGGEWLO-SOOFDHNKSA-ND-ribofuranoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H]1OHMFHBZSHGGEWLO-SOOFDHNKSA-N0.000description1
- 108010041986DNA VaccinesProteins0.000description1
- 229940021995DNA vaccineDrugs0.000description1
- 102000007260Deoxyribonuclease IHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010008532Deoxyribonuclease IProteins0.000description1
- 206010012735DiarrhoeaDiseases0.000description1
- 208000000059DyspneaDiseases0.000description1
- 206010013975DyspnoeasDiseases0.000description1
- 238000011510Elispot assayMethods0.000description1
- 241000729176Fagopyrum dibotrysSpecies0.000description1
- 206010021143HypoxiaDiseases0.000description1
- 102100037850Interferon gammaHuman genes0.000description1
- 208000029523Interstitial Lung diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 239000012097Lipofectamine 2000Substances0.000description1
- 206010027417Metabolic acidosisDiseases0.000description1
- 206010028735Nasal congestionDiseases0.000description1
- 108700026244Open Reading FramesProteins0.000description1
- 206010068319Oropharyngeal painDiseases0.000description1
- 229930040373ParaformaldehydeNatural products0.000description1
- 201000007100PharyngitisDiseases0.000description1
- 229920001213Polysorbate 20Polymers0.000description1
- 206010037660PyrexiaDiseases0.000description1
- 230000004570RNA-bindingEffects0.000description1
- 208000013616Respiratory Distress SyndromeDiseases0.000description1
- 208000036071RhinorrheaDiseases0.000description1
- 206010039101RhinorrhoeaDiseases0.000description1
- PYMYPHUHKUWMLA-LMVFSUKVSA-NRiboseNatural productsOC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=OPYMYPHUHKUWMLA-LMVFSUKVSA-N0.000description1
- 241000315672SARS coronavirusSpecies0.000description1
- 206010040070Septic ShockDiseases0.000description1
- 108010008038Synthetic VaccinesProteins0.000description1
- 230000024932T cell mediated immunityEffects0.000description1
- 108020000999Viral RNAProteins0.000description1
- 238000001467acupunctureMethods0.000description1
- 201000000028adult respiratory distress syndromeDiseases0.000description1
- 239000000443aerosolSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000246agarose gel electrophoresisMethods0.000description1
- 239000003513alkaliSubstances0.000description1
- HMFHBZSHGGEWLO-UHFFFAOYSA-Nalpha-D-Furanose-RiboseNatural productsOCC1OC(O)C(O)C1OHMFHBZSHGGEWLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 235000019257ammonium acetateNutrition0.000description1
- 238000004458analytical methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000008350antigen-specific antibody responseEffects0.000description1
- 239000008346aqueous phaseSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003556assayMethods0.000description1
- 229940031567attenuated vaccineDrugs0.000description1
- 210000003719b-lymphocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000002585baseSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 239000006227byproductSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052799carbonInorganic materials0.000description1
- 210000000170cell membraneAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000012512characterization methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000005345coagulationMethods0.000description1
- 230000015271coagulationEffects0.000description1
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000012228culture supernatantSubstances0.000description1
- 238000012258culturingMethods0.000description1
- IERHLVCPSMICTF-XVFCMESISA-Ncytidine 5'-monophosphateChemical compoundO=C1N=C(N)C=CN1[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](COP(O)(O)=O)O1IERHLVCPSMICTF-XVFCMESISA-N0.000description1
- IERHLVCPSMICTF-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncytidine monophosphateNatural productsO=C1N=C(N)C=CN1C1C(O)C(O)C(COP(O)(O)=O)O1IERHLVCPSMICTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 210000000805cytoplasmAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000001419dependent effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description1
- 238000000502dialysisMethods0.000description1
- 231100000673dose–response relationshipToxicity0.000description1
- 239000003937drug carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 208000017574dry coughDiseases0.000description1
- 230000004064dysfunctionEffects0.000description1
- 238000000635electron micrographMethods0.000description1
- 238000001493electron microscopyMethods0.000description1
- 239000003480eluentSubstances0.000description1
- 238000005538encapsulationMethods0.000description1
- 230000012202endocytosisEffects0.000description1
- 238000003114enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assayMethods0.000description1
- 210000003743erythrocyteAnatomy0.000description1
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000description1
- 206010016256fatigueDiseases0.000description1
- 210000001035gastrointestinal tractAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000000499gelSubstances0.000description1
- 150000002338glycosidesChemical class0.000description1
- 229940029575guanosineDrugs0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 210000005260human cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000028996humoral immune responseEffects0.000description1
- 208000018875hypoxemiaDiseases0.000description1
- 210000002865immune cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000001900immune effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000036039immunityEffects0.000description1
- 239000012535impuritySubstances0.000description1
- 229940031551inactivated vaccineDrugs0.000description1
- 230000002779inactivationEffects0.000description1
- 230000001939inductive effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000008595infiltrationEffects0.000description1
- 238000001764infiltrationMethods0.000description1
- 230000005764inhibitory processEffects0.000description1
- 239000007928intraperitoneal injectionSubstances0.000description1
- NLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-NkaolinChemical compoundO.O.O=[Al]O[Si](=O)O[Si](=O)O[Al]=ONLYAJNPCOHFWQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 238000011031large-scale manufacturing processMethods0.000description1
- 239000006166lysateSubstances0.000description1
- 238000005259measurementMethods0.000description1
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000description1
- 238000010369molecular cloningMethods0.000description1
- 239000000178monomerSubstances0.000description1
- 230000000877morphologic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000035772mutationEffects0.000description1
- 229940100662nasal dropsDrugs0.000description1
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000description1
- 239000003960organic solventSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002866paraformaldehydePolymers0.000description1
- 231100000915pathological changeToxicity0.000description1
- 230000036285pathological changeEffects0.000description1
- 239000008188pelletSubstances0.000description1
- 230000008823permeabilizationEffects0.000description1
- 235000010486polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurateNutrition0.000description1
- 239000000256polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurateSubstances0.000description1
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description1
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003753real-time PCRMethods0.000description1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000description1
- 230000000241respiratory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 108091008146restriction endonucleasesProteins0.000description1
- 230000002441reversible effectEffects0.000description1
- 125000002652ribonucleotide groupChemical group0.000description1
- 238000013341scale-upMethods0.000description1
- 238000000926separation methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000036303septic shockEffects0.000description1
- 239000007974sodium acetate bufferSubstances0.000description1
- 230000003319supportive effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000024891symptomDiseases0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000001890transfectionMethods0.000description1
- 239000013638trimerSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001226triphosphateSubstances0.000description1
- 235000011178triphosphateNutrition0.000description1
- 229940045145uridineDrugs0.000description1
- 230000029812viral genome replicationEffects0.000description1
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/005—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from viruses
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K39/12—Viral antigens
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/48—Preparations in capsules, e.g. of gelatin, of chocolate
- A61K9/50—Microcapsules having a gas, liquid or semi-solid filling; Solid microparticles or pellets surrounded by a distinct coating layer, e.g. coated microspheres, coated drug crystals
- A61K9/51—Nanocapsules; Nanoparticles
- A61K9/5107—Excipients; Inactive ingredients
- A61K9/5123—Organic compounds, e.g. fats, sugars
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/48—Preparations in capsules, e.g. of gelatin, of chocolate
- A61K9/50—Microcapsules having a gas, liquid or semi-solid filling; Solid microparticles or pellets surrounded by a distinct coating layer, e.g. coated microspheres, coated drug crystals
- A61K9/51—Nanocapsules; Nanoparticles
- A61K9/5107—Excipients; Inactive ingredients
- A61K9/513—Organic macromolecular compounds; Dendrimers
- A61K9/5146—Organic macromolecular compounds; Dendrimers obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyamines, polyanhydrides
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
- A61P31/14—Antivirals for RNA viruses
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K39/00—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies
- A61K2039/51—Medicinal preparations containing antigens or antibodies comprising whole cells, viruses or DNA/RNA
- A61K2039/53—DNA (RNA) vaccination
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2310/00—Structure or type of the nucleic acid
- C12N2310/30—Chemical structure
- C12N2310/33—Chemical structure of the base
- C12N2310/335—Modified T or U
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2770/00—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA ssRNA viruses positive-sense
- C12N2770/00011—Details
- C12N2770/20011—Coronaviridae
- C12N2770/20022—New viral proteins or individual genes, new structural or functional aspects of known viral proteins or genes
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2770/00—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA ssRNA viruses positive-sense
- C12N2770/00011—Details
- C12N2770/20011—Coronaviridae
- C12N2770/20034—Use of virus or viral component as vaccine, e.g. live-attenuated or inactivated virus, VLP, viral protein
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及生物医药和病毒学领域,具体涉及新型冠状病毒 SARS-CoV-2 mRNA疫苗及其制备方法和应用。The invention relates to the fields of biomedicine and virology, in particular to a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine and its preparation method and application.
背景技术Background technique
目前SARS-CoV-2主要传染源是新冠病毒感染的患者,但无症状感染 者也可能成为传染源,病毒主要经由呼吸道飞沫和接触传播,气溶胶和消 化道等传播途径尚待明确,暂无证据表明可经由母婴垂直传播,潜伏期 1-14天,多数为3-7天。多数患者以发热、乏力和干咳为主,少数患者伴 有鼻塞、流涕、咽痛和腹泻等症状,重症患者多在发病1周或2周出现呼 吸困难或低氧血症,严重的患者会快速进展为急性呼吸窘迫综合征、脓毒 症休克,甚至出现难以纠正的代谢性酸中毒和凝血功能障碍。目前,临床 中主要以对症支持治疗为主,没有特效药和疫苗。此次新型冠状肺炎疫情 已给我国和全球经济、社会和人民生命健康等造成了巨大损失。快速开发 针对SARS-CoV-2的有效疫苗已成为广大医药科研工作者的重大任务。At present, the main source of infection of SARS-CoV-2 is patients infected with the new coronavirus, but asymptomatic patients may also become the source of infection. The virus is mainly transmitted through respiratory droplets and contact. The transmission routes such as aerosol and digestive tract have yet to be clarified. There is no evidence that it can be transmitted vertically from mother to child, and the incubation period is 1-14 days, most of which are 3-7 days. Most patients have fever, fatigue, and dry cough, and a few patients have symptoms such as nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, and diarrhea. Severe patients often have dyspnea or hypoxemia within 1 or 2 weeks of onset. Rapid progression to acute respiratory distress syndrome, septic shock, and even uncorrectable metabolic acidosis and coagulation dysfunction. Currently, symptomatic and supportive treatment is mainly used in clinical practice, and there are no specific drugs and vaccines. The novel coronavirus pneumonia epidemic has caused huge losses to my country and the global economy, society and people's lives and health. Rapid development of an effective vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 has become a major task for medical researchers.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本发明为解决现今未研发出针对新型冠状病毒SARS-CoV-2感染的特 效药和疫苗的问题,本发明提供三种mRNA疫苗,即RBD、S1和S疫苗。 本发明的RBD疫苗在一针免疫后便可诱导高滴度的抗原特异性IgG抗体 和病毒中和抗体,且高滴度中和抗体可至少维持26周,并在血清过继转 移保护实验中能够为人ACE2转基因小鼠提供显著的免疫保护。本发明的 RBD和S疫苗经两针免疫后在人ACE2转基因小鼠中可诱导能够完全抵 抗SARS-CoV-2病毒感染的免疫保护。大量实验结果表明,本发明的三种 mRNA疫苗具有良好的免疫原性,并在免疫机体后形成强效的免疫保护, 具有巨大的开发潜力。The present invention solves the problem that there are no specific drugs and vaccines for novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infection. The present invention provides three mRNA vaccines, namely RBD, S1 and S vaccines. The RBD vaccine of the present invention can induce high-titer antigen-specific IgG antibodies and virus neutralizing antibodies after one shot of immunization, and the high-titer neutralizing antibodies can be maintained for at least 26 weeks, and can be used in serum adoptive transfer protection experiments. Provides significant immune protection to human ACE2 transgenic mice. The RBD and S vaccines of the present invention can induce immune protection that can completely resist SARS-CoV-2 virus infection in human ACE2 transgenic mice after two shots of immunization. A large number of experimental results show that the three mRNA vaccines of the present invention have good immunogenicity and form strong immune protection after immunizing the body, and have great potential for development.
为此,本发明第一方面提供mRNA,其包括包含编码SARS-CoV-2的 抗原性多肽或其抗原性片段、变体或衍生物的编码区,其中所述抗原性多 肽选自SARS-CoV-2的受体结合结构域RBD,SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S1 亚基或SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S全长序列,To this end, the first aspect of the present invention provides mRNA comprising a coding region comprising an antigenic polypeptide encoding SARS-CoV-2 or an antigenic fragment, variant or derivative thereof, wherein the antigenic polypeptide is selected from the group consisting of SARS-CoV The receptor binding domain RBD of -2, the spike protein S1 subunit of SARS-CoV-2 or the full-length sequence of the spike protein S of SARS-CoV-2,
优选地,所述抗原性多肽与SARS-CoV-2的受体结合结构域RBD、 SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S1亚基或SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S全长序列具 有至少80%、至少85%、至少90%、至少91%、至少92%、至少93%、 至少94%、至少95%、至少96%、至少97%、至少98%、至少99%的同 源性,Preferably, the antigenic polypeptide and the receptor binding domain RBD of SARS-CoV-2, the spike protein S1 subunit of SARS-CoV-2 or the full-length sequence of the spike protein S of SARS-CoV-2 have at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90%, at least 91%, at least 92%, at least 93%, at least 94%, at least 95%, at least 96%, at least 97%, at least 98%, at least 99% homology ,
其中所述mRNA中部分或全部的尿嘧啶和/或胞嘧啶进行了能够提高 所述mRNA在生物体内稳定性的化学改性。Wherein part or all of the uracil and/or cytosine in the mRNA has been chemically modified to improve the stability of the mRNA in vivo.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述化学改性包括利用以下物质置换所 述mRNA中的至少50%、至少60%、至少70%、至少80%、至少90%或 100%的尿嘧啶,In some embodiments of the invention, said chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90%, or 100% of the uracil in said mRNA with,
其中,置换尿嘧啶的物质选自假尿苷、N1-甲基假尿苷、N1-乙基假尿 苷、2-硫尿苷、4′-硫尿苷、5-甲基胞嘧啶、5-甲基尿苷、2-硫基-1-甲基-1- 去氮杂-假尿苷、2-硫基T-甲基-假尿苷、2-硫基-5-氮杂-尿苷、2-硫基-二氢 假尿苷、2-硫基-二氢尿苷、2-硫基-假尿苷、4-甲氧基-2-硫基-假尿苷、4- 甲氧基-假尿苷、4-硫基-1-甲基-假尿苷、4-硫基-假尿苷、5-氮杂-尿苷、二 氢假尿苷或5-甲氧基尿苷和2′-O-甲基尿苷中的至少一种,优选假尿苷或 N1-甲基假尿苷或N1-乙基假尿苷,进一步优选N1-甲基假尿苷;Wherein, the substance replacing uracil is selected from pseudouridine, N1-methylpseudouridine, N1-ethylpseudouridine, 2-thiouridine, 4'-thiouridine, 5-methylcytosine, 5 -Methyluridine, 2-thio-1-methyl-1-deaza-pseudouridine, 2-thio-T-methyl-pseudouridine, 2-thio-5-aza-uridine Glycoside, 2-thio-dihydropseudouridine, 2-thio-dihydrouridine, 2-thio-pseudouridine, 4-methoxy-2-thio-pseudouridine, 4-methyl Oxy-pseudouridine, 4-thio-1-methyl-pseudouridine, 4-thio-pseudouridine, 5-aza-uridine, dihydropseudouridine, or 5-methoxyuridine At least one of glycoside and 2'-O-methyluridine, preferably pseudouridine or N1-methylpseudouridine or N1-ethylpseudouridine, more preferably N1-methylpseudouridine;
和/或,所述化学改性包括利用5-甲基胞嘧啶置换所述mRNA中的至 少50%、至少60%、至少70%、至少80%、至少90%或100%的胞嘧啶。And/or, the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90%, or 100% of the cytosines in the mRNA with 5-methylcytosine.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述mRNA编码的抗原性多肽为SEQ ID NO:1所示氨基酸序列所示的SARS-CoV-2的受体结合结构域RBD蛋 白,或与SEQ ID NO:1所示氨基酸序列具有至少80%、至少85%、至少 90%、至少91%、至少92%、至少93%、至少94%、至少95%、至少96%、 至少97%、至少98%、至少99%的同源性的序列。In some other embodiments of the present invention, the antigenic polypeptide encoded by the mRNA is the receptor binding domain RBD protein of SARS-CoV-2 shown in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, or with SEQ ID NO : The amino acid sequence shown in 1 has at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90%, at least 91%, at least 92%, at least 93%, at least 94%, at least 95%, at least 96%, at least 97%, at least 98% , sequences of at least 99% homology.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,编码SARS-CoV-2的受体结合结构域 RBD的核苷酸序列如SEQ ID NO:2所示。In some embodiments of the present invention, the nucleotide sequence encoding the receptor binding domain RBD of SARS-CoV-2 is shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
SARS-CoV-2的受体结合结构域RBD为SARS-CoV-2病毒的刺突蛋白 (S蛋白)的S1亚基中的受体结合结构域(receptor binding domain,RBD), SARS-CoV-2通过RBD与人细胞表面的ACE2受体结合进而感染人体,因 此RBD、S1亚基和S可作为制备疫苗时的免疫原。The receptor binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 is the receptor binding domain (RBD) in the S1 subunit of the spike protein (S protein) of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. SARS-CoV- 2. RBD binds to the ACE2 receptor on the surface of human cells to infect the human body. Therefore, RBD, S1 subunit and S can be used as immunogens in the preparation of vaccines.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述mRNA编码的抗原性多肽为SEQ ID NO:5所示氨基酸序列所示的SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S1亚基,或与 SEQ ID NO:5所示氨基酸序列具有至少80%、至少85%、至少90%、至 少91%、至少92%、至少93%、至少94%、至少95%、至少96%、至少 97%、至少98%、至少99%的同源性的序列。In other embodiments of the present invention, the antigenic polypeptide encoded by the mRNA is the spike protein S1 subunit of SARS-CoV-2 shown in the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 5, or with SEQ ID NO: The amino acid sequence shown in 5 has at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90%, at least 91%, at least 92%, at least 93%, at least 94%, at least 95%, at least 96%, at least 97%, at least 98%, Sequences with at least 99% homology.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,编码刺突蛋白S1亚基的核苷酸序列如 SEQ ID NO:6所示。In some embodiments of the present invention, the nucleotide sequence encoding the S1 subunit of the Spike protein is shown in SEQ ID NO:6.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述mRNA编码的抗原性多肽为SEQ ID NO:7所示氨基酸序列的SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S全长,或与SEQ ID NO:7所示氨基酸序列具有至少80%、至少85%、至少90%、至少91%、 至少92%、至少93%、至少94%、至少95%、至少96%、至少97%、至 少98%、至少99%的同源性的序列。In other embodiments of the present invention, the antigenic polypeptide encoded by the mRNA is the full length of the spike protein S of SARS-CoV-2 with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 7, or with the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 7 The amino acid sequence has at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90%, at least 91%, at least 92%, at least 93%, at least 94%, at least 95%, at least 96%, at least 97%, at least 98%, at least 99% % homology to the sequence.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,编码刺突蛋白S全长的核苷酸序列如 SEQ ID NO:8所示。In some embodiments of the present invention, the nucleotide sequence encoding the full length of Spike protein S is shown in SEQ ID NO:8.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述mRNA还包含:In other embodiments of the present invention, the mRNA further comprises:
1)5’帽结构;1) 5' cap structure;
2)5’UTR序列;2) 5'UTR sequence;
3)3’UTR序列;以及3) 3'UTR sequence; and
4)多聚腺苷酸序列,4) polyadenylation sequence,
其中,所述mRNA按照5’→3’方向依次包括如下元件:5’帽结构,5’UTR 序列,SARS-CoV-2的抗原性多肽或其抗原性片段、变体或衍生物,3’UTR 序列和多聚腺苷酸序列。Wherein, the mRNA includes the following elements in sequence according to the 5'→3' direction: 5'cap structure, 5'UTR sequence, antigenic polypeptide of SARS-CoV-2 or its antigenic fragment, variant or derivative, 3' UTR sequence and polyadenylation sequence.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述5’帽结构选自m7GpppG、 m27,3′-OGpppG、m7Gppp(5′)N1或m7Gppp(m2′-O)N1中的至少一种。In some embodiments of the present invention, the 5' cap structure is selected from m7 GpppG, m27 ,3'-O GpppG, m7 Gppp(5')N1 or m7 Gppp(m2'-O ) At least one of N1.
在本发明的一些优选的实施方案中,所述5’帽结构为m7Gppp(5′)N1 或m7Gppp(m2′-O)N1。In some preferred embodiments of the present invention, the 5' cap structure is m7 Gppp(5')N1 or m7 Gppp(m2′-O )N1.
根据不同mRNA的需求,可在mRNA 5’端灵活添加不同的5’帽结构。According to the needs of different mRNAs, different 5' cap structures can be flexibly added to the 5' end of the mRNA.
“m7G”代表7-甲基鸟苷帽核苷,“ppp”代表帽核苷的5′碳和初级RNA 转录物的第一个核苷酸之间的三磷酸键,N1是最5′的核苷酸,“G”代表 鸟嘌呤核苷,“m7”代表在鸟嘌呤的7-位上的甲基,“m2′-O”代表核苷酸2′-O 位上的甲基。"m7G" stands for7 -methylguanosine capnucleoside, "ppp" stands for the triphosphate bond between the 5′ carbon of capnucleoside and the first nucleotide of the primary RNA transcript, and N1 is the last 5 ', "G" represents guanosine, "m7" represents the methyl group at the 7-position of guanine, and "m2'-O " represents the methyl group at the 2'-O position of the nucleotide base.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述5’UTR序列选自SEQ ID NO:9-11 中任意一个所述的核酸序列所对应的RNA序列或其同源物、片段或变体。In some embodiments of the present invention, the 5'UTR sequence is selected from the RNA sequence corresponding to any one of the nucleic acid sequences in SEQ ID NO: 9-11 or its homologues, fragments or variants.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述3’UTR序列选自SEQ ID NO: 12-14中任意一个所述的核酸序列所对应的RNA序列或其同源物、片段或 变体。In other embodiments of the present invention, the 3'UTR sequence is selected from the RNA sequence corresponding to any one of the nucleic acid sequences described in SEQ ID NO: 12-14 or its homologues, fragments or variants.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述多聚腺苷酸序列包含25-400个腺苷 酸的序列。In some embodiments of the invention, the polyA sequence comprises a sequence of 25-400 adenine nucleotides.
在本发明的一些优选的实施方案中,所述多聚腺苷酸序列包含50-400 个腺苷酸的序列。In some preferred embodiments of the present invention, the polyA sequence comprises a sequence of 50-400 adenine nucleotides.
在本发明的一些进一步优选的实施方案中,所述多聚腺苷酸序列包含 50-300个腺苷酸的序列。In some further preferred embodiments of the present invention, said polyA sequence comprises a sequence of 50-300 adenine nucleotides.
在本发明的另一些进一步优选的实施方案中,所述多聚腺苷酸序列包 含50-250个腺苷酸的序列。In some further preferred embodiments of the present invention, said polyA sequence comprises a sequence of 50-250 adenine nucleotides.
在本发明的另一些更进一步优选的实施方案中,所述多聚腺苷酸序列 包含60-200个腺苷酸的序列。In some further preferred embodiments of the present invention, said polyadenylic acid sequence comprises a sequence of 60-200 adenine nucleotides.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述mRNA具有选自SEQ ID NO:15-50 所示的mRNA,或与SEQ ID NO:15-50的mRNA具有至少80%、、至少 85%、至少90%、至少91%、至少92%、至少93%、至少94%、至少95%、 至少96%、至少97%、至少98%、至少99%的同源性的mRNA。In some embodiments of the present invention, the mRNA has an mRNA selected from SEQ ID NO: 15-50, or has at least 80%, at least 85%, at least 90% with the mRNA of SEQ ID NO: 15-50 %, at least 91%, at least 92%, at least 93%, at least 94%, at least 95%, at least 96%, at least 97%, at least 98%, at least 99% homologous to mRNA.
本发明第二方面提供药物组合物,其包含第一方面所述的mRNA中 的至少一种,和任选的递送载体。The second aspect of the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition, which comprises at least one of the mRNAs described in the first aspect, and an optional delivery carrier.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述递送载体为纳米颗粒。In some embodiments of the invention, the delivery vehicle is a nanoparticle.
在本发明的一些优选的实施方案中,所述递送载体为脂质纳米颗粒。In some preferred embodiments of the present invention, the delivery vehicle is a lipid nanoparticle.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述脂质纳米颗粒在中性pH值下具 有净中性电荷。In other embodiments of the invention, the lipid nanoparticles have a net neutral charge at neutral pH.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述脂质纳米颗粒具有50-200nm的平 均直径,且具有小于0.4的多分散性系数值。In some embodiments of the invention, the lipid nanoparticles have an average diameter of 50-200 nm and have a polydispersity coefficient value of less than 0.4.
本发明中提供的纳米颗粒,可高效递送mRNA,具有如下特点和优势: 例如,在包封mRNA时,酸性pH条件使可电离的阳离子脂质带有正电荷, 压缩带负电荷的mRNA分子,进而获得较高的包封率;在生理pH条件下, 可电离的脂质纳米颗粒具有电中性,不与带负电的细胞膜作用,生物相容 性高;可电离的脂质纳米颗粒通过细胞内吞作用形成内涵体进入细胞后, 内涵体中的酸性条件使纳米颗粒再次带上正电荷,与带有负电荷的内涵体 膜发生静电相互作用,从而有利于mRNA的释放。The nanoparticles provided in the present invention can efficiently deliver mRNA, and have the following characteristics and advantages: For example, when encapsulating mRNA, acidic pH conditions make the ionizable cationic lipids positively charged, compressing negatively charged mRNA molecules, In turn, a higher encapsulation efficiency is obtained; under physiological pH conditions, ionizable lipid nanoparticles are electrically neutral, do not interact with negatively charged cell membranes, and have high biocompatibility; ionizable lipid nanoparticles pass through cells After endocytosis forms endosomes and enters the cell, the acidic conditions in the endosomes cause the nanoparticles to be positively charged again, and electrostatically interact with the negatively charged endosome membranes, thereby facilitating the release of mRNA.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述mRNA与递送载体的质量比为A: B,其中A选自0.05-2,B选自1-100,优选A为0.05,B为1;或者A为 1,B为100;或者A为2,B为1;或者A为1,B为50;或者A为1, B为5。In some embodiments of the present invention, the mass ratio of the mRNA to the delivery carrier is A: B, wherein A is selected from 0.05-2, B is selected from 1-100, preferably A is 0.05, and B is 1; or A is 1, B is 100; or A is 2, B is 1; or A is 1, B is 50; or A is 1, B is 5.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述脂质纳米颗粒包括阳离子脂质和 选自非阳离子脂质、固醇、PEG修饰脂质中的至少一种。In other embodiments of the present invention, the lipid nanoparticles include cationic lipids and at least one selected from non-cationic lipids, sterols, and PEG-modified lipids.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述脂质纳米颗粒为阳离子脂质、非阳 离子脂质、固醇和PEG修饰脂质,其摩尔比为20-60:5-25:25-55:0.5-15, 优选30-60:5-20:30-50:0.5-10,进一步优选40-60:5-15:35-45:0.5-5。In some embodiments of the present invention, the lipid nanoparticles are cationic lipids, non-cationic lipids, sterols and PEG-modified lipids, the molar ratio of which is 20-60:5-25:25-55:0.5- 15, preferably 30-60:5-20:30-50:0.5-10, more preferably 40-60:5-15:35-45:0.5-5.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述阳离子脂质为可电离的阳离子脂 质,选自以下一种或多种成分:2,2-二亚油基-4-二甲氨基乙基-[1,3]-二氧戊 环、二亚油基-甲基-4-二甲氨基丁酸酯和9-((4-(二甲氨基)丁酰基)氧基)十 七烷二酸二((Z)-壬-2-烯-1-基)酯,优选二亚油基-甲基-4-二甲氨基丁酸酯。 在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述非阳离子脂质为中性脂质,选自二硬脂 酰基磷脂酰胆碱(DSPC)、二油酰磷脂酰乙醇胺(DOPE)、二油酰基卵磷脂 (DOPC)和二油酰基磷脂酰丝氨酸(DOPS)中的至少一种,优选为DSPC。In other embodiments of the present invention, the cationic lipid is an ionizable cationic lipid, selected from one or more of the following components: 2,2-Dilinoleyl-4-dimethylaminoethyl- [1,3]-Dioxolane, dilinoleyl-methyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate and 9-((4-(dimethylamino)butyryl)oxy)heptadecandioic acid Bis((Z)-non-2-en-1-yl) esters, preferably dilinoleyl-methyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate. In some embodiments of the present invention, the non-cationic lipid is a neutral lipid selected from distearoylphosphatidylcholine (DSPC), dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine (DOPE), dioleoyl lecithin (DOPC) and dioleoylphosphatidylserine (DOPS), preferably DSPC.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述固醇为胆固醇。In other embodiments of the invention, the sterol is cholesterol.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述PEG修饰脂质选自PEG-DMG、 PEG-DSG和PEG-DMPE中的至少一种,优选为PEG-DMPE。In some embodiments of the present invention, the PEG-modified lipid is at least one selected from PEG-DMG, PEG-DSG and PEG-DMPE, preferably PEG-DMPE.
在本发明的另一些实施方案中,所述PEG修饰脂质的PEG长度为 0.5-200KDa,优选为1-50KDa,进一步优选为1-5KDa,更进一步优选为 2KDa。In other embodiments of the present invention, the PEG length of the PEG-modified lipid is 0.5-200KDa, preferably 1-50KDa, more preferably 1-5KDa, even more preferably 2KDa.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述药物组合物任选的含有佐剂。In some embodiments of the invention, the pharmaceutical composition optionally contains an adjuvant.
本发明第三方面提供试剂盒,其包含本发明第一方面所述的mRNA 和/或本发明第二方面所述的药物组合物。The third aspect of the present invention provides a kit comprising the mRNA described in the first aspect of the present invention and/or the pharmaceutical composition described in the second aspect of the present invention.
本发明第四方面提供本发明第一方面所述的mRNA,本发明第二方面 所述的药物组合物,本发明第三方面所述的试剂盒在制备预防和/或治疗 SARS-CoV-2病毒感染的药物中的应用。The fourth aspect of the present invention provides the mRNA described in the first aspect of the present invention, the pharmaceutical composition described in the second aspect of the present invention, the kit described in the third aspect of the present invention in the preparation of prevention and/or treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Drug application for viral infections.
本发明第五方面提供本发明第一方面所述的mRNA,本发明第二方面 所述的药物组合物,本发明第三方面所述的试剂盒的制备方法,包括对其 中含有的mRNA中的包括包含编码SARS-CoV-2的抗原性多肽或其抗原 性片段、变体或衍生物的编码区中的部分或全部的尿嘧啶和/或胞嘧啶进行 化学改性的步骤,其中所述抗原性多肽选自SARS-CoV-2的受体结合结构 域RBD,SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S1亚基或SARS-CoV-2的刺突蛋白S 全长序列。The fifth aspect of the present invention provides the mRNA described in the first aspect of the present invention, the pharmaceutical composition described in the second aspect of the present invention, and the preparation method of the kit described in the third aspect of the present invention, including the mRNA contained therein. Including the step of chemically modifying part or all of uracil and/or cytosine in the coding region of the antigenic polypeptide encoding SARS-CoV-2 or its antigenic fragment, variant or derivative, wherein the antigen The sex polypeptide is selected from the receptor binding domain RBD of SARS-CoV-2, the S1 subunit of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 or the full-length sequence of the spike protein S of SARS-CoV-2.
在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述化学改性包括利用以下物质置换所 述mRNA的编码区中的至少50%、至少60%、至少70%、至少80%、至 少90%或100%的尿嘧啶,其中,置换尿嘧啶的物质选自假尿苷、N1-甲基 假尿苷、N1-乙基假尿苷、2-硫尿苷、4′-硫尿苷、5-甲基胞嘧啶、5-甲基尿 苷、2-硫基-1-甲基-1-去氮杂-假尿苷、2-硫基T-甲基-假尿苷、2-硫基-5-氮 杂-尿苷、2-硫基-二氢假尿苷、2-硫基-二氢尿苷、2-硫基-假尿苷、4-甲氧 基-2-硫基-假尿苷、4-甲氧基-假尿苷、4-硫基-1-甲基-假尿苷、4-硫基-假尿 苷、5-氮杂-尿苷、二氢假尿苷或5-甲氧基尿苷和2′-O-甲基尿苷中的至少 一种,优选假尿苷或N1-甲基假尿苷或N1-乙基假尿苷,进一步优选N1- 甲基假尿苷;In some embodiments of the invention, the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90%, or 100% of the coding region of the mRNA with Uracil, wherein the substance replacing uracil is selected from pseudouridine, N1-methylpseudouridine, N1-ethylpseudouridine, 2-thiouridine, 4'-thiouridine, 5-methylcytidine Pyrimidine, 5-methyluridine, 2-thio-1-methyl-1-deaza-pseudouridine, 2-thio-T-methyl-pseudouridine, 2-thio-5-aza Hetero-uridine, 2-thio-dihydropseudouridine, 2-thio-dihydrouridine, 2-thio-pseudouridine, 4-methoxy-2-thio-pseudouridine, 4-methoxy-pseudouridine, 4-thio-1-methyl-pseudouridine, 4-thio-pseudouridine, 5-aza-uridine, dihydropseudouridine, or 5-methyl At least one of oxyuridine and 2'-O-methyluridine, preferably pseudouridine or N1-methylpseudouridine or N1-ethylpseudouridine, more preferably N1-methylpseudouridine ;
和/或,所述化学改性包括利用5-甲基胞嘧啶置换所述mRNA中的至 少50%、至少60%、至少70%、至少80%、至少90%或100%的胞嘧啶。And/or, the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90%, or 100% of the cytosines in the mRNA with 5-methylcytosine.
mRNA疫苗的关键技术在近几年取得突破性进展。mRNA疫苗在安全 性、快速制备和免疫原性方面具有颠覆性的优势。mRNA疫苗安全性高, 不存在减毒疫苗潜在的回复突变的风险,不存在灭活疫苗灭活不彻底的风 险,也不存在DNA疫苗被整合到宿主基因组中并导致基因突变的可能。 一般传统疫苗开发需要至少5-6个月的时间,而mRNA疫苗可以实现标准 化生产,在10天内便可生产出所需疫苗,在应对包括SARS-CoV-2在内 的新发突发传染病方面具有无可比拟的优势。同时,mRNA疫苗能够诱导 T细胞和B细胞免疫应答,具有良好的免疫原性,一般一针免疫便可诱导 高水平的中和抗体产生。The key technologies of mRNA vaccines have made breakthroughs in recent years. mRNA vaccines have subversive advantages in terms of safety, rapid preparation and immunogenicity. mRNA vaccines are highly safe, and there is no risk of potential reverse mutation of attenuated vaccines, no risk of incomplete inactivation of inactivated vaccines, and no possibility of DNA vaccines being integrated into the host genome and causing gene mutations. Generally, the development of traditional vaccines takes at least 5-6 months, while mRNA vaccines can achieve standardized production, and the required vaccines can be produced within 10 days. In response to emerging infectious diseases including SARS-CoV-2 has incomparable advantages. At the same time, mRNA vaccines can induce T-cell and B-cell immune responses and have good immunogenicity. Generally, a single dose of immunization can induce high levels of neutralizing antibodies.
本发明基于SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白(S蛋白)的受体结合结构域(RBD)、 S1亚基和S全长构建、制备了SARS-CoV-2 mRNA疫苗,提供可编码新 型冠状病毒SARS-CoV-2的抗原性多肽或免疫原性片段的mRNA和药学 上可接受的载体,并选择纳米颗粒进行包装递送,获得用于预防或治疗新 型冠状病毒SARS-CoV-2感染的信使核糖核酸(mRNA)疫苗。The present invention constructs and prepares a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine based on the receptor binding domain (RBD), S1 subunit and S full-length of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein (S protein), and provides an encoding novel coronavirus The mRNA of the antigenic polypeptide or immunogenic fragment of SARS-CoV-2 and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and select the nanoparticle for packaging and delivery, and obtain the messenger ribose for preventing or treating the new coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infection Nucleic acid (mRNA) vaccines.
本发明合成可编码SARS-CoV-2抗原性多肽或免疫原性片段的mRNA 所需的质粒模板。在本发明的一些实施方案中,所述mRNA质粒模板pHRT 关键元件按照5’→3’顺序依次包括:T7启动子、5’UTR序列、SARS-CoV-2 抗原性多肽或免疫原性片段的编码区、3’UTR序列、多聚腺苷酸序列和线 性化酶切位点。The present invention synthesizes the plasmid template required for the mRNA encoding the SARS-CoV-2 antigenic polypeptide or immunogenic fragment. In some embodiments of the present invention, the key elements of the mRNA plasmid template pHRT include: T7 promoter, 5'UTR sequence, SARS-CoV-2 antigenic polypeptide or immunogenic fragment in sequence according to the 5'→3' order Coding region, 3'UTR sequence, polyadenylation sequence and linearization restriction site.
本发明中可编码SARS-CoV-2抗原性多肽或免疫原性片段的mRNA 的制备方法的特点和优势:(1)选择线性化质粒作为mRNA转录模板, 与以PCR产物作模板相比,转录过程中产生的错误副产物更少,并且质 粒容易大量获得且质量稳定;(2)在mRNA转录合成中引入化学改性的 核糖核苷酸可降低mRNA在生物体内的免疫原性,延长mRNA半衰期进 而提高目的抗原表达量,最终提高mRNA疫苗的免疫保护效果;(3)由 于质粒模板中含有多聚腺苷酸序列,mRNA的加尾步骤可在转录中同时完 成,疫苗生产工艺更简单;(4)产率高,1μg模板最后可获得100-150μg mRNA。The characteristics and advantages of the mRNA preparation method that can encode SARS-CoV-2 antigenic polypeptides or immunogenic fragments in the present invention: (1) select the linearized plasmid as the mRNA transcription template, compared with using the PCR product as the template, the transcription There are fewer erroneous by-products in the process, and the plasmid is easy to obtain in large quantities and has stable quality; (2) The introduction of chemically modified ribonucleotides during mRNA transcription and synthesis can reduce the immunogenicity of mRNA in vivo and prolong the half-life of mRNA Then increase the expression level of the target antigen, and finally improve the immune protection effect of the mRNA vaccine; (3) because the plasmid template contains a polyadenylic acid sequence, the tailing step of the mRNA can be completed simultaneously in the transcription, and the vaccine production process is simpler; ( 4) High yield, 100-150 μg mRNA can be obtained from 1 μg template.
本发明提供采用上述可电离的纳米颗粒包封mRNA的制备方法。该 方法基于微流控技术开发,具有如下特点和优势:快速,24L纳米颗粒可 在4小时内完成制备;制备出的纳米颗粒粒径均一,多分散性系数值小于 0.4;容易放大,实验室规模的制备参数和条件基本可直接用于中试和大规 模生产。The invention provides a preparation method for encapsulating mRNA by using the above-mentioned ionizable nanoparticles. The method is developed based on microfluidic technology, and has the following characteristics and advantages: fast, 24L nanoparticles can be prepared within 4 hours; the prepared nanoparticles have uniform particle size, and the polydispersity coefficient value is less than 0.4; easy to scale up, and the laboratory The scale preparation parameters and conditions can basically be directly used in pilot and large-scale production.
本发明有益效果:本发明的SARS-CoV-2 mRNA疫苗研发周期短,特 别适合包括SARS-CoV-2在内的新发突发传染病疫苗的开发;安全性高, mRNA仅需在细胞质中合成抗原,随后被降解,不会进入细胞核,无诱发 基因突变的风险;免疫原性高,一针免疫即可诱导高水平的中和抗体,并 维持至少26周;保护效果好,疫苗经两针免疫后可诱导能够完全抵抗 SARS-CoV-2感染的免疫保护。Beneficial effects of the present invention: the development period of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine of the present invention is short, and it is especially suitable for the development of vaccines for emerging infectious diseases including SARS-CoV-2; the safety is high, and the mRNA only needs to be in the cytoplasm Synthetic antigens, which are subsequently degraded, will not enter the nucleus, and have no risk of inducing gene mutations; high immunogenicity, a high level of neutralizing antibodies can be induced by one shot of immunization, and can be maintained for at least 26 weeks; the protective effect is good, and the vaccine has been tested twice Acupuncture can induce immune protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection completely.
附图说明Description of drawings
下面将结合附图来说明本发明。The present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
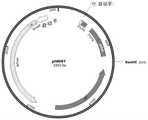
图1.mRNA转录模板空载体pHRNT质粒示意图;Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of mRNA transcription template empty vector pHRNT plasmid;
图2.mRNA转录模板pHRNT-COVID-19质粒示意图;Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the mRNA transcription template pHRNT-COVID-19 plasmid;
图3.mRNA转录模板线性化酶切结果,泳道1,pHRNT-RBD;泳道 2,线性化的pHRNT-RBD;泳道3,pHRNT-S1;泳道4,线性化的pHRNT-S1; 泳道5,pHRNT-S;泳道6,线性化的pHRNT-S;Figure 3. The results of linearization of mRNA transcription template,
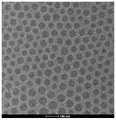
图4.mRNA疫苗动态光散射尺寸分析;Figure 4. Dynamic light scattering size analysis of mRNA vaccines;
图5.mRNA疫苗冷冻电镜照片;Fig. 5. Cryo-electron micrograph of mRNA vaccine;
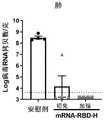
图6.不同构建疫苗诱导的IgG抗体滴度;Figure 6. IgG antibody titers induced by different construction vaccines;
图7.不同构建疫苗诱导的假病毒中和抗体滴度;Figure 7. The pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titers induced by different construction vaccines;
图8.不同构建疫苗诱导的SARS-CoV-2真病毒中和抗体滴度;Figure 8. SARS-CoV-2 true virus neutralizing antibody titers induced by different construction vaccines;
图9.酶联免疫斑点实验;Figure 9. Enzyme-linked immunospot assay;
图10.CD4阳性T细胞胞内细胞因子染色;Figure 10. Intracellular cytokine staining of CD4 positive T cells;
图11.CD8阳性T细胞胞内细胞因子染色;Figure 11. Intracellular cytokine staining of CD8 positive T cells;
图12.疫苗不同针次诱导的IgG抗体滴度;Figure 12. IgG antibody titers induced by different shots of the vaccine;
图13.疫苗不同针次诱导的SARS-CoV-2真病毒中和抗体滴度;Figure 13. SARS-CoV-2 true virus neutralizing antibody titers induced by different injections of the vaccine;
图14.肺组织病毒载量;Figure 14. Lung tissue viral load;
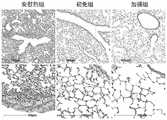
图15.肺组织H&E染色病理分析;Figure 15. H&E staining pathological analysis of lung tissue;
图16.肺组织病毒载量;Figure 16. Lung tissue viral load;
图17.疫苗诱导的IgG抗体水平的长时间监测;Figure 17. Long-term monitoring of vaccine-induced IgG antibody levels;
图18.疫苗诱导的假病毒中和抗体水平的长时间监测;Figure 18. Long-term monitoring of vaccine-induced pseudovirus neutralizing antibody levels;
图19.肺组织病毒载量。Figure 19. Lung tissue viral load.
具体实施方式detailed description
下面结合具体实施例,进一步阐述本发明。应理解,这些实施仅用于 说明本发明而不用于限制本发明的范围。下列实施例中未注明具体条件的 实验方法,通常按照常规条件如J.萨姆布鲁克等编著的分子克隆实验指南 (科学出版社出版的第三版)或按照制造商所建议的条件。实验所用到的 试剂,如无特殊说明,均可试剂公司购买到。Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further illustrate the present invention. It should be understood that these implementations are only used to illustrate the present invention and not to limit the scope of the present invention. The experimental method that does not indicate specific conditions in the following examples is usually according to conventional conditions such as the Molecular Cloning Experiment Guidebook (the third edition published by Science Press) edited by J. Sambrook et al. or according to the conditions suggested by the manufacturer. The reagents used in the experiment can be purchased from reagent companies unless otherwise specified.
实施例1:mRNA疫苗制备Embodiment 1: mRNA vaccine preparation
(1)目的基因获取:SARS-CoV-2受体结合结构域RBD、刺突蛋白 S1亚基和刺突蛋白S全长氨基酸序列来源于Genebank MN908947,经密 码子优化后,其核酸序列分别如SEQ IDNO:2、6和8所示,由北京擎科 新业生物技术有限公司合成后分别克隆至mRNA转录模板pHRNT载体 (例如购自北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司)(图1)后,获得mRNA转 录模板质粒pHRNT-RBD、pHRNT-S1和pHRNT-S(图2)。(1) Acquisition of target genes: The full-length amino acid sequences of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain RBD, spike protein S1 subunit, and spike protein S were obtained from Genebank MN908947. After codon optimization, the nucleic acid sequences are as follows: Shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, 6 and 8, synthesized by Beijing Qingke Xinye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. and cloned into the mRNA transcription template pHRNT vector (for example, purchased from Beijing Qingke Xinye Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) (Figure 1) , to obtain mRNA transcription template plasmids pHRNT-RBD, pHRNT-S1 and pHRNT-S (Fig. 2).
(2)mRNA转录(2) mRNA transcription
使用限制性内切酶BamHI对mRNA转录模板pHRNT-RBD、 pHRNT-S1和pHRNT-S分别进行酶切线性化,跑琼脂糖凝胶电泳(图3), 以确认线性化是否完全,然后用胶回收试剂盒回收线性化转录模板。Use the restriction endonuclease BamHI to linearize the mRNA transcription templates pHRNT-RBD, pHRNT-S1 and pHRNT-S respectively, and run agarose gel electrophoresis (Figure 3) to confirm whether the linearization is complete, and then use the gel The recovery kit recovers the linearized transcription template.
按下表配制mRNA体外转录反应体系(所用酶和试剂购自美国NEB 公司):Prepare the mRNA in vitro transcription reaction system according to the following table (the enzymes and reagents used were purchased from NEB Company, USA):
37℃,反应4小时后,加入1μl无RNase的DNase I,37℃,反应15 分钟。After reacting at 37°C for 4 hours, add 1 μl of RNase-free DNase I, and react at 37°C for 15 minutes.
然后进行分离RNA的分离纯化。有多种方法可进行RNA的分离纯化, 如醋酸铵沉淀法、LiCl沉淀法、有机溶剂抽提-醋酸铵沉淀法和RNA结合 柱纯化等。以LiCl沉淀法为例说明:The separation and purification of the isolated RNA is then carried out. There are many ways to separate and purify RNA, such as ammonium acetate precipitation, LiCl precipitation, organic solvent extraction-ammonium acetate precipitation and RNA binding column purification, etc. Take the LiCl precipitation method as an example to illustrate:
a)RNA溶液中加入7.5M LiCl,使LiCl终浓度为2.5M;a) Add 7.5M LiCl to the RNA solution to make the final concentration of LiCl 2.5M;
b)-20℃过夜;b) Overnight at -20°C;
c)12000rpm/min离心15分钟,弃溶液;c) Centrifuge at 12000rpm/min for 15 minutes, discard the solution;
d)向沉淀中加入-20℃预冷75%乙醇,清洗沉淀,然后12000rpm/min 离心1分钟,弃乙醇溶液,重复清洗三次;d) Add -20°C pre-cooled 75% ethanol to the precipitate, wash the precipitate, then centrifuge at 12000rpm/min for 1 minute, discard the ethanol solution, and repeat the washing three times;
e)室温晾干RNA沉淀,然后用无RNase水溶解RNA。使用Nanodrop 测定RNA浓度后,-80℃保存。e) Dry the RNA pellet at room temperature, and then dissolve the RNA with RNase-free water. After measuring the RNA concentration using Nanodrop, store at -80°C.
(2)mRNA加帽(2) mRNA capping
通过下面方法mRNA可加帽子m7Gppp(m2′-O)N1,具体方法如下:The mRNA can be capped with m7 Gppp(m2′-O )N1 by the following method, the specific method is as follows:
a)体外转录的mRNA,50-60μg,用无RNase水稀释至67μl;a) mRNA transcribed in vitro, 50-60 μg, diluted to 67 μl with RNase-free water;
b)65℃孵育5-10分钟,之后置于冰上冷却;b) Incubate at 65°C for 5-10 minutes, then place on ice to cool;
c)按下表配制反应体系混合液(所用酶和试剂购自美国NEB公司);c) Prepare the reaction system mixture according to the table below (the enzymes and reagents used are purchased from NEB Company in the United States);
d)反应开始前将b)中冷却的mRNA加入至c)混合液中,再加入4μl 加帽酶,37℃反应半小时。d) Add the cooled mRNA in b) to the mixture in c) before starting the reaction, then add 4 μl of capping enzyme, and react at 37° C. for half an hour.
然后对加帽后的mRNA进行分离纯化。具体方法如上所述,最后分 别获得mRNA-RBD、mRNA-S1和mRNA-S。The capped mRNA is then isolated and purified. The specific method was as above, and finally mRNA-RBD, mRNA-S1 and mRNA-S were obtained respectively.
(3)mRNA纳米颗粒包装(3) mRNA nanoparticle packaging
通过微流控技术对mRNA进行纳米颗粒包装。水相为mRNA溶液(50 mM醋酸钠缓冲溶液,pH 4.0),乙醇相为脂质混合液,由二亚油基-甲基-4- 二甲氨基丁酸酯、二硬脂酰基磷脂酰胆碱、胆固醇和PEG2K-DMPE按摩 尔比50:10:38.5:1.5比例配制。包装时水相和乙醇相的总流速为12ml/min, 水相和乙醇相体积比为3:1。包装完成的mRNA疫苗使用透析袋将缓冲 液置换成PBS后,分别获得mRNA疫苗RBD、S1和S。然后使用RiboGreen 试剂测定包封的mRNA浓度后,置于4℃保存待用。Nanoparticle packaging of mRNA by microfluidic technology. The aqueous phase is the mRNA solution (50 mM sodium acetate buffer solution, pH 4.0), the ethanol phase is the lipid mixture, composed of dilinoleyl-methyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate, distearoylphosphatidylcholine Alkali, cholesterol and PEG2K-DMPE were prepared in a molar ratio of 50:10:38.5:1.5. The total flow rate of the water phase and the ethanol phase during packaging is 12ml/min, and the volume ratio of the water phase and the ethanol phase is 3:1. After the packaged mRNA vaccine was replaced with PBS using a dialysis bag, the mRNA vaccines RBD, S1 and S were obtained respectively. Then use RiboGreen reagent to measure the concentration of encapsulated mRNA, and then store at 4°C until use.
(4)mRNA疫苗纳米颗粒形态表征(4) Morphological characterization of mRNA vaccine nanoparticles
疫苗溶液,使用动态光散射粒度分析仪进行脂质纳米颗粒尺寸测定, 结果表明疫苗中脂质纳米颗粒平均直径为78.4纳米,且均一性良好(图4)。 冷冻电镜结果也证明,疫苗颗粒大小比较均一(图5)。For the vaccine solution, the size of the lipid nanoparticles was measured using a dynamic light scattering particle size analyzer. The results showed that the average diameter of the lipid nanoparticles in the vaccine was 78.4 nanometers, and the uniformity was good ( FIG. 4 ). The results of cryo-electron microscopy also proved that the size of the vaccine particles was relatively uniform ( FIG. 5 ).
实施例2:疫苗诱导的体液免疫反应评价Example 2: Evaluation of Vaccine-Induced Humoral Immune Response
将36只雌性6-8周龄BALB/c小鼠分成6组,每组6只,分别肌肉注 射安慰剂(包装方法与疫苗组相同但包裹了聚胞苷酸的脂质纳米颗粒,其中 聚胞苷酸购自Sigma)、RBD(0.3μg,2μg和15μg)、S1(15μg)或S(15 μg)mRNA疫苗,并在免疫后的第4周取血,4℃分离血清并56℃灭活30 分钟后保存于-80℃待用。Divide 36 female BALB/c mice aged 6-8 weeks into 6 groups, 6 in each group, and inject placebo intramuscularly (the packaging method is the same as that of the vaccine group but lipid nanoparticles coated with polycytidylic acid, in which polycytidylic acid Cytidylic acid was purchased from Sigma), RBD (0.3 μg, 2 μg and 15 μg), S1 (15 μg) or S (15 μg) mRNA vaccine, and the blood was collected at the 4th week after immunization, and the serum was separated at 4°C and sterilized at 56°C Store at -80°C for 30 minutes before use.
(1)抗原特异性抗体滴度测定(1) Determination of antigen-specific antibody titer
将SARS-CoV-2S胞外段蛋白用ELISA包被液稀释至1μg/ml,96孔 板每孔加入100μl,4℃放置过夜。第二天封闭ELISA板,小鼠血清按照 2倍梯度稀释,加入到ELISA板中37℃孵育1小时,之后用含0.05%吐温 20的PBS(PBST)清洗三次后,加入羊抗鼠HRP二抗(购自北京中杉金 桥生物技术公司),37℃孵育1小时后,PBST清洗三次,加入TMB显色 液显示,并用2M盐酸终止,在酶标仪上用OD450读值。Dilute the SARS-CoV-2S extracellular segment protein with ELISA coating solution to 1 μg/ml, add 100 μl to each well of a 96-well plate, and place overnight at 4°C. The next day, the ELISA plate was closed, and the mouse serum was diluted in a 2-fold gradient, added to the ELISA plate and incubated at 37°C for 1 hour, then washed three times with PBS (PBST) containing 0.05
结果显示,RBD mRNA疫苗诱导的新冠病毒特异性抗体有剂量依赖 效应,剂量越高,抗体滴度越高(图6)。在15μg剂量时,RBD和S mRNA 疫苗经一针免疫便可诱导滴度高达105抗原特异性抗体反应,表明这两种 疫苗有良好的免疫原性;S1疫苗组抗体滴度低于104,表明S1mRNA疫 苗与另两种mRNA疫苗相比较,抗原免疫原性稍弱(图6)。The results showed that the RBD mRNA vaccine-induced new coronavirus-specific antibodies had a dose-dependent effect, and the higher the dose, the higher the antibody titer (Figure 6). At a dose of 15 μg, RBD and S mRNA vaccines can induce antigen-specific antibody responses with a titer as high as 105 after one injection, indicating that the two vaccines have good immunogenicity; the antibody titer of the S1 vaccine group is lower than 104 , indicating that compared with the other two mRNA vaccines, the S1 mRNA vaccine has slightly weaker antigen immunogenicity (Fig. 6).
(2)假病毒中和抗体滴度测定(2) Pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titer determination
假病毒包装:利用Lipofectamine2000将质粒pCAGGS-SARS-CoV-2 S(例如,由北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司合成SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白S 全长基因后克隆至pCAGGS载体)与假病毒骨架质粒HIV Pnl4-3.luc.RE (Invitrogen)共转染293T细胞。转染6小时后,PBS洗涤细胞2次,换 成无血清DMEM。48小时后收取细胞上清,离心去除细胞碎片,分装冻 存于-80℃。Pseudovirus packaging: use Lipofectamine2000 to clone the plasmid pCAGGS-SARS-CoV-2 S (for example, the full-length gene of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S synthesized by Beijing Qingke Xinye Biotechnology Co., Ltd. into the pCAGGS vector) and pseudovirus Viral backbone plasmid HIV Pnl4-3.luc.RE (Invitrogen) was co-transfected into 293T cells. Six hours after transfection, cells were washed twice with PBS and replaced with serum-free DMEM. After 48 hours, the cell supernatant was collected, centrifuged to remove cell debris, aliquoted and frozen at -80°C.
TCID50测定:将Huh7细胞(可商购,例如购自上海酶联生物)提前 一天铺96孔板。生长24小时后,第二天将收取的病毒液10倍比稀释, 依次为10-1、10-2……10-10,加入到96孔板中,此时Huh7细胞汇合度为 80%-100%。感染4小时后,弃掉病毒液,PBS洗涤细胞2次,换为含10% 血清的完全培养基DMEM。48小时后,弃掉培养液,PBS洗涤细胞2次, 加入细胞裂解液,利用GloMax 96Microplate Luminometer(Promega)检测 荧光素酶活性值。通过Reed-Muench法计算TCID50。TCID50 measurement: Huh7 cells (commercially available, for example, purchased from Shanghai Enzyme) were plated on a 96-well plate one day in advance. After growing for 24 hours, the next day, the collected virus solution was diluted 10 times, in order of 10-1 , 10-2 ... 10-10 , and added to the 96-well plate. At this time, the confluence of Huh7 cells was 80%- 100%. After 4 hours of infection, the virus liquid was discarded, the cells were washed twice with PBS, and replaced with complete medium DMEM containing 10% serum. After 48 hours, the culture medium was discarded, the cells were washed twice with PBS, the cell lysate was added, and the luciferase activity was detected by GloMax 96 Microplate Luminometer (Promega). TCID50 was calculated by the Reed-Muench method.
假病毒中和抗体滴度测定:提前一天在96孔板铺Huh7细胞,第二天 小鼠血清按2倍比进行梯度稀释,与1000TCID50假病毒混合,37℃孵育 30分钟后,将混合液加入到Huh7细胞上。37℃孵育4小时后,弃掉病毒 液,PBS洗涤细胞2次,更换为含10%血清的完全培养基DMEM。48小 时后,弃掉培养液,PBS洗涤细胞2次,加入细胞裂解液,检测荧光素酶 活性值。通过Reed-Muench法计算中和90%的细胞感染时的血清稀释倍数, 即为假病毒中和抗体滴度NT90值。Determination of pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titer: Pave Huh7 cells on a 96-well plate one day in advance, and the next day, the mouse serum is serially diluted by 2 times, mixed with 1000TCID50 pseudovirus, incubated at 37°C for 30 minutes, and then added to the mixture onto Huh7 cells. After incubation at 37°C for 4 hours, the virus solution was discarded, the cells were washed twice with PBS, and replaced with complete medium DMEM containing 10% serum. After 48 hours, discard the culture medium, wash the cells twice with PBS, add cell lysate, and detect the luciferase activity value. The serum dilution factor when 90% of the cells were infected was calculated by the Reed-Muench method, which was the NT90 value of the pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titer.
假病毒中和结果表明,与SARS-CoV-2特异性抗体结果相似,RBD疫 苗免疫2μg时,假病毒中和抗体滴度NT90为190,当免疫15μg时,NT90显著提高至700(图7)。同时,在15μg剂量下,S疫苗诱导的假病毒中 和抗体NT90为653,与RBD组相当,而S1疫苗组则仅为57,说明RBD 和S疫苗均具有良好的免疫原性,而S1疫苗较弱(图7)。The results of pseudovirus neutralization showed that, similar to the results of SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies, when the RBD vaccine was immunized with 2 μg, the titer of pseudovirus neutralizing antibody was190, and when immunized with 15 μg, the NT 90was significantly increased to 700 (Fig. 7). At the same time, at a dose of 15 μg, the pseudovirus neutralizing antibody NT90 induced by the S vaccine was 653, which was comparable to that of the RBD group, while that of the S1 vaccine group was only 57, indicating that both the RBD and the S vaccine had good immunogenicity, while the S1 vaccine The vaccine was weak (Figure 7).
(3)真病毒中和抗体滴度测定(3) Determination of true virus neutralizing antibody titer
提前一天在96孔板铺Vero E6细胞,第二天将小鼠血清或新冠康复病 人血清按2倍比进行梯度稀释,与100TCID50野生型SARS-CoV-2真病 毒(HB01株,例如购自中国科学院微生物研究所P3实验室)混合,37℃ 孵育30分钟后,将混合液加入到Vero E6细胞上。37℃孵育48小时后, 取培养上清100μl在全自动核酸提取仪进行病毒RNA提取,操作方法完 全按照仪器和试剂盒说明书进行,最后使用80μl洗脱液洗脱。之后使用 一步法荧光定量试剂盒在Light Cycler 480Real-Time PCR system仪器上对 样品进行实时荧光RT-PCR反应,将所测样品CT值代入标准曲线后计算 出样品中的病毒TCID50值。病毒复制抑制率(%)=(病毒对照组-样品对 照组)/病毒对照组*100%。最后通过Reed-Muench法计算中和50%的细 胞感染时的血清稀释倍数,即为真病毒中和抗体滴度NT50值。RT-PCR反 应中所用引物和探针如下:Spread Vero E6 cells on a 96-well plate one day in advance, and the next day, serially dilute the mouse serum or the serum of patients with new coronary pneumonia by 2 times, and mix with 100TCID50 wild-type SARS-CoV-2 true virus (HB01 strain, purchased from China Laboratory P3, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) were mixed, and after incubation at 37°C for 30 minutes, the mixture was added to Vero E6 cells. After incubating at 37°C for 48 hours, take 100 μl of the culture supernatant to extract viral RNA in an automatic nucleic acid extraction instrument. The operation method is completely in accordance with the instrument and kit instructions, and finally eluted with 80 μl of eluent. Then, the one-step fluorescent quantitative kit was used to perform real-time fluorescent RT-PCR reaction on the sample on the Light Cycler 480 Real-Time PCR system instrument, and the CT value of the measured sample was substituted into the standard curve to calculate the virus TCID50 value in the sample. Virus replication inhibition rate (%)=(virus control group−sample control group)/virus control group*100%. Finally, the serum dilution factor at the time of neutralizing 50% of the cell infection was calculated by the Reed-Muench method, which was the true virus neutralizing antibody titer NT50 value. The primers and probes used in the RT-PCR reaction are as follows:
正向引物:序列如SEQ ID NO:3所示Forward primer: the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:3
反应引物:序列如SEQ ID NO:4所示Reaction primer: the sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:4
探针:5′-FAM-TCCTCACTGCCGTCTTGTTGACCA-BHQ1-3′。Probe: 5'-FAM-TCCTCACTGCCGTCTTGTTGACCA-BHQ1-3'.
结果表明,RBD一针免疫后,2μg和15μg诱导的真病毒中和抗体滴 度分别为108和920,其中15μg剂量组抗体滴度水平与康复病人血清中 和滴度值(429)相当(图8)。The results showed that after one injection of RBD, the titers of true virus neutralizing antibodies induced by 2 μg and 15 μg were 108 and 920, respectively, and the antibody titers in the 15 μg dose group were equivalent to the serum neutralizing titers (429) of recovered patients (Fig. 8).
实施例3:疫苗诱导的细胞免疫反应评价Example 3: Evaluation of Vaccine-Induced Cellular Immune Response
将12只雌性6-8周龄C57BL/6小鼠分成2组,每组6只,分别肌肉 注射安慰剂和RBD(15μg),并在免疫后的第4周对小鼠实施安乐死,取 脾脏放置于预冷的1640培养基中。把40μm筛网放在50ml离心管上, 使用5ml注射器推头研磨脾脏,加1640培养基使细胞滴进50ml管中, 过滤掉杂质及大的细胞团。把所有细胞转移到15ml离心管中,室温2000 rpm离心收集细胞,再加入12ml的1640培养基洗一遍,再次离心收集 细胞。加入4ml的红细胞裂解液,悬浮细胞,室温放置5-10分钟,再 加入8ml的1640培养基,离心收集细胞,加入12ml 1640培养基洗一 遍,再次离心收集细胞。加入10ml的1640培养基,悬浮细胞,使用细 胞计数板计算细胞总数。再次离心收集细胞加入一定体积的10%FSB的 1640培养基,使细胞浓度为1*107个/ml。
酶联免疫斑点实验:平底96孔板中预先包被10μg/ml抗鼠IFN-γ 抗体(BDBiosciences),在4℃孵育过夜。第二天弃去液体,加入10%FBS 的1640培养基在室温封闭2小时。每孔加入2*105个小鼠脾脏细胞,补 充培养基使得每孔总体积为100μl,然后加入RBD多肽库,(每条多肽的 浓度为2μg/ml)。Phytohemagglutinin(PHA)作为阳性对照。不加任何刺 激物的细胞作为阴性对照。细胞培养箱中培养18小时。检测的步骤完全 按照BD公司提供的酶联免疫斑点读试剂盒说明书操作。形成的斑点数使 用酶联免疫斑点读板机读取。ELISpot assay: 10 μg/ml anti-mouse IFN-γ antibody (BD Biosciences) was pre-coated in a flat-bottomed 96-well plate, and incubated overnight at 4°C. The next day, the liquid was discarded, and 1640 medium added with 10% FBS was blocked at room temperature for 2 hours. 2*105 mouse spleen cells were added to each well, the medium was supplemented so that the total volume of each well was 100 μl, and then the RBD polypeptide library was added (the concentration of each polypeptide was 2 μg/ml). Phytohemagglutinin (PHA) served as a positive control. Cells without any stimulus were used as negative control. Incubate for 18 hours in a cell culture incubator. The detection steps were completely in accordance with the instructions of the enzyme-linked immunospot reading kit provided by BD company. The number of spots formed was read using an enzyme-linked immunospot plate reader.
胞内细胞因子染色实验:在圆底96孔板中每孔加入1*106个小鼠脾 脏细胞,然后加入RBD多肽库,(每条多肽的浓度为2μg/ml)刺激细胞, 分别设置加入PHA刺激组为阳性对照,不加任何刺激物的组为阴性对照。 刺激4小时后,加入GolgiStop接着在细胞培养箱中培养14小时。然后 离心收集细胞,进行抗体染色,其中操作步骤完全按照BD公司 Cytofix/CytopermTM Fixation/Permeabilization试剂盒说明书操作。之后在 FACSCanton流式细胞仪上检测细胞荧光。Intracellular cytokine staining experiment: Add1 *106 mouse spleen cells to each well of a round-bottomed 96-well plate, then add the RBD polypeptide library, (the concentration of each polypeptide is 2μg/ml) to stimulate the cells, set the addition The PHA stimulation group was the positive control, and the group without any stimulus was the negative control. After 4 hours of stimulation, GolgiStop was added followed by incubation for 14 hours in the cell culture incubator. Then the cells were collected by centrifugation for antibody staining, and the operating steps were completely in accordance with the instructions of the BD Cytofix/CytopermTM Fixation/Permeabilization kit. Cell fluorescence was then detected on a FACSCanton flow cytometer.
酶联免疫斑点实验结果表明,相比对照组,RBD疫苗一针免疫后便可 显著刺激T细胞分泌γ干扰素(图9)。胞内细胞因子染色实验结果表明, RBD疫苗组γ干扰素阳性的CD4和CD8阳性T细胞比例均显著高于对照 (图10和11)。因此,以上结果表明RBD疫苗一针免疫后便可诱导显著 的T细胞免疫应答。The results of the enzyme-linked immunospot test showed that, compared with the control group, the RBD vaccine could significantly stimulate T cells to secrete interferon-γ after one injection (Figure 9). The results of intracellular cytokine staining experiments showed that the proportion of interferon-γ-positive CD4 and CD8-positive T cells in the RBD vaccine group was significantly higher than that in the control group (Figures 10 and 11). Therefore, the above results indicate that a single dose of RBD vaccine can induce a significant T cell immune response.
实施例4:疫苗不同针次的免疫效果评价Example 4: Evaluation of the immune effect of different shots of the vaccine
将15只雌性6-8周龄BALB/c小鼠分成3组,每组5只,在第0周初 免,分别肌肉注射安慰剂、RBD(15μg)和S(15μg),在免疫后的第4 周眼眶取血分离血清,随后加强免疫一次,在初免后第8周,取血并分离 血清,使用ELISA方法测定初免和加强血清中RBD特异性抗体和S特异 性抗体滴度。用基于细胞病变效应(CPE)的微量中和方法测定初免和加 强血清中的SARS-CoV-2真病毒中和抗体滴度,其具体方法如下:Fifteen female BALB/c mice aged 6-8 weeks were divided into 3 groups, with 5 mice in each group. They were primed at
提前一天在96孔板铺Vero E6细胞,第二天小鼠血清按2倍比进行梯 度稀释,与100TCID50野生型SARS-CoV-2真病毒(HB01株)混合, 每孔设置4个复孔,37℃孵育30分钟后,将混合液加入到Vero E6细胞上。 设置不加血清只加病毒的病毒孔和不加病毒与血清的阴性孔。37℃培养箱 培养三天后观察并记录每孔CPE情况。抑制50%病毒感染的血清稀释度 即为真病毒中和抗体滴度NT50值。Spread Vero E6 cells on a 96-well plate one day in advance, and the next day, mouse serum was serially diluted at a 2-fold ratio, mixed with 100TCID50 wild-type SARS-CoV-2 true virus (HB01 strain), and 4 replicate wells were set in each well. After incubation at 37°C for 30 minutes, the mixture was added to Vero E6 cells. Set virus wells without adding serum and adding only virus and negative wells without adding virus and serum. Observe and record the CPE of each well after culturing in a 37°C incubator for three days. The serum dilution that inhibits 50% virus infection is the true virus neutralizing antibody titer NT50 value.
ELISA结果表明,一针免疫后,RBD和S疫苗均可诱导高水平的 SARS-CoV-2病毒特异性抗体,加强免疫后,抗体水平分别进一步提升170 和50倍,并且在S诱导的S特异性抗体中结合RBD单体的约占20%,表 明存在大量靶向非RBD区域的抗体或靶向S三聚体蛋白中特有的空间构 象表位的抗体(图12)。真病毒中和抗体实验结果表明,与初免相比,RBD 和S疫苗加强免疫后中和抗体水平均显著提升,分别达到58,000和159,000, 表明疫苗均具有很好的免疫原性(图13)。ELISA results showed that both RBD and S vaccines could induce high levels of SARS-CoV-2 virus-specific antibodies after one dose of immunization. About 20% of the antibodies bound to RBD monomers indicated that there were a large number of antibodies targeting non-RBD regions or antibodies targeting specific spatial conformation epitopes in S trimer proteins (Figure 12). The results of the true virus neutralizing antibody test showed that compared with the primary immunization, the neutralizing antibody levels of the RBD and S vaccines were significantly increased after booster immunization, reaching 58,000 and 159,000 respectively, indicating that the vaccines have good immunogenicity (Figure 13) .
实施例5:疫苗免疫攻毒保护效果评价Example 5: Evaluation of the protective effect of vaccine immune challenge
(1)RBD疫苗攻毒保护效果评价(1) Evaluation of RBD vaccine challenge protection effect
将18只雌性6-8周龄人ACE2转基因小鼠分成3组(安慰剂组、初免 组和加强组),每组6只。安慰剂组和初免组小鼠在第0周分别免疫一针 安慰剂和RBD疫苗(15μg),加强组在第0和2周分别免疫一针RBD疫 苗(15μg)。所有小鼠在初次免疫后的第4周通过滴鼻方式进行野生型 SARS-CoV-2攻毒,攻毒剂量为10^5FFU/50μl/只。在攻毒后第5天,对 小鼠实施安乐死,取肺脏。每组中四只小鼠肺脏称重并记录后,加入DMEM 培养基然后使用组织匀浆器匀浆,离心取上清通过实施例2中的RT-PCR 方法测定样品中的SARS-CoV-2病毒量,最后计算每克肺组织中的病毒拷 贝数。每组中剩余2只小鼠肺脏用4%多聚甲醛溶液固定72小时后,制备 石蜡切片(3-4μm),随后使用苏木素伊红(H&E)染色试剂盒对石蜡切片 进行H&E染色,分析肺部病理变化。Eighteen female human ACE2 transgenic mice aged 6-8 weeks were divided into 3 groups (placebo group, priming group and booster group), 6 in each group. Mice in the placebo group and priming group were immunized with a shot of placebo and RBD vaccine (15 μg) at
肺部病毒载量结果表明,安慰剂组小鼠病毒载量高达近10^8.5拷贝数 /克肺组织,一针RBD免疫组中一只小鼠可检测到10^7拷贝数/克肺组织, 病毒载量较安慰剂组减少97%,其余小鼠均检测不到病毒,;两针RBD疫 苗免疫后,全部小鼠检测不到病毒(图14)。肺组织H&E病理分析发现, 安慰剂组小鼠有严重的支气管肺炎和间质肺炎,以及大量的免疫细胞浸润; 一针免疫组小鼠仅有很少量的免疫细胞浸润,无其它病变,两针免疫组小 鼠肺部正常。上述结果表明,RBD疫苗一针便可诱导接近完全的免疫保护, 两针可完全保护小鼠肺组织抵抗新冠病毒感染(图15)。The results of lung viral load showed that the viral load of mice in the placebo group was as high as nearly 10^8.5 copies/gram of lung tissue, and 10^7 copies/gram of lung tissue could be detected in one mouse in the one-shot RBD immunization group , the viral load was reduced by 97% compared with the placebo group, and the virus was not detected in the remaining mice; after two doses of RBD vaccine immunization, the virus was not detected in all mice (Figure 14). H&E pathological analysis of lung tissue found that the mice in the placebo group had severe bronchial pneumonia and interstitial pneumonia, as well as a large number of immune cell infiltration; The lungs of mice in the needle-immunized group were normal. The above results show that one injection of RBD vaccine can induce nearly complete immune protection, and two injections can completely protect mouse lung tissue against the new coronavirus infection (Figure 15).
(2)S疫苗攻毒保护效果评价(2) Evaluation of the protective effect of S vaccine against virus
将12只雌性6-8周龄人ACE2转基因小鼠分成2组,每组6只。在第 0周分别免疫安慰剂和S疫苗(15μg),在第2周进行一次加强免疫。所 有小鼠在初次免疫后的第4周通过滴鼻方式进行野生型SARS-CoV-2攻毒, 攻毒剂量为10^5FFU/50μl/只。在攻毒后第5天,对小鼠实施安乐死,取 肺脏。按照(1)中方法测定肺组织中SARS-CoV-2病毒载量。Twelve female human ACE2 transgenic mice aged 6-8 weeks were divided into 2 groups with 6 mice in each group. Placebo and S vaccine (15 μg) were immunized at
结果表明,安慰剂组小鼠病毒载量约为10^8拷贝数/克肺组织,S疫 苗组小鼠均检测不到病毒,这表明两针免疫后,S疫苗可为人ACE2转基 因小鼠提供完全的免疫保护(图16)。The results showed that the viral load of mice in the placebo group was about 10^8 copies/gram of lung tissue, and no virus could be detected in the mice in the S vaccine group, which indicated that after two doses of immunization, the S vaccine could provide human ACE2 transgenic mice with Complete immune protection (Figure 16).
实施例6:疫苗免疫长期保护效果评价Example 6: Evaluation of long-term protective effect of vaccine immunity
将15只雌性6-8周龄BALB/c小鼠分成3组(安慰剂组、短期组和长 期组),每组5只。安慰剂组和长期组小鼠分别在第0周免疫安慰剂和RBD (15μg),并在第2、4、6、8、10、12、16、20周眼眶采血分离血清,在 第26周对小鼠实验安乐死,大量采血分离血清,用于后续的血清过继转 移攻毒保护实验。短期组小鼠在第0周免疫RBD疫苗(15μg),在第8 周对小鼠实验安乐死,大量采血分离血清,用于后续的血清过继转移攻毒 保护实验。所有血清均使用实施例2中方法测定RBD特异性抗体滴度和 假病毒中和抗体滴度。每组中大量收集的所有小鼠血清混合后,腹腔注射 方式过继转移到人ACE2转基因小鼠中,血清转移量为350μl/只。第二天 所有人ACE2转基因小鼠通过滴鼻方式进行野生型SARS-CoV-2攻毒,攻 毒剂量为10^5FFU/50μl/只。在攻毒后第5天,对小鼠实施安乐死,取肺 脏。按照实施例5中方法测定肺组织中SARS-CoV-2病毒载量。Fifteen female BALB/c mice aged 6-8 weeks were divided into 3 groups (placebo group, short-term group and long-term group), 5 mice in each group. Mice in the placebo group and the long-term group were immunized with placebo and RBD (15 μg) at
抗体长期监测结果表明,RBD免疫后,RBD特异性抗体和假病毒中和 抗体均在第8周到达峰值,滴度分别为10^5和10^3,随后在接下来的8-26 周保持基本稳定,并且在26周时,假病毒中和抗体水平NT90值仍可维持 在600左右(图17和18)。The results of long-term antibody monitoring showed that after RBD immunization, both RBD-specific antibodies and pseudovirus neutralizing antibodies peaked at
血清过继转移攻毒保护实验结果表明,两个疫苗组小鼠病毒载量均显 著低于安慰剂组,表明RBD一针免疫后便可为小鼠提供长达26周的显著 的免疫保护(图19)。The results of the serum adoptive transfer challenge protection experiment showed that the viral loads of mice in the two vaccine groups were significantly lower than those in the placebo group, indicating that a single injection of RBD can provide significant immune protection for mice for up to 26 weeks (Fig. 19).
Claims (37)
- Mrna comprising the following elements in order in the 5'→ 3' direction: a 5' cap structure, a 5' UTR sequence, a coding region for an antigenic polypeptide of SARS-CoV-2 or an antigenic fragment thereof, a 3' UTR sequence and a polyadenylation sequence, wherein the antigenic polypeptide is selected from the receptor binding domain RBD of SARS-CoV-2, or the full-length sequence of the spike protein S of SARS-CoV-2,wherein, the coding region of the antigenic polypeptide of SARS-CoV-2 or the antigenic fragment thereof is the RNA sequence coded by SEQ ID NO. 2 or 8; the 5' UTR sequence is selected from the RNA sequence of any one of SEQ ID NO 9-11; the 3' UTR sequence is selected from the RNA sequence of any one of SEQ ID NO 12-14,wherein some or all of the uracil and/or cytosine in the mRNA is chemically modified to increase the stability of the mRNA in vivo.
- 2. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or 100% of uracil in the mRNA,wherein the substance which replaces uracil is at least one selected from the group consisting of pseudouridine, N1-methylpseudouridine, N1-ethylpseudouridine, 2-thiouridine, 4 '-thiouridine, 5-methylcytosine, 5-methyluridine, 2-thio-1-methyl-1-deaza-pseudouridine, 2-thio T-methyl-pseudouridine, 2-thio-5-aza-uridine, 2-thio-dihydropseudouridine, 2-thio-dihydrouridine, 2-thio-pseudouridine, 4-methoxy-pseudouridine, 4-thio-1-methyl-pseudouridine, 4-thio-pseudouridine, 5-aza-uridine, dihydropseudouridine, 5-methoxy-uridine and 2' -O-methyluridine;and/or, the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or 100% of the cytosines in the mRNA with 5-methylcytosine.
- 3. The mRNA of claim 2, wherein the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or 100% of the uracils in the mRNA with pseudouridine or N1-methylpseuduridine or N1-ethylpseuduridine.
- 4. The mRNA of claim 1 or 2, wherein the antigenic polypeptide encoded by the mRNA is the receptor binding domain RBD protein of SARS-CoV-2 as shown in the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1.
- 5. The mRNA of claim 1 or 2, wherein the antigenic polypeptide encoded by the mRNA is the spike protein S full length of SARS-CoV-2 having the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO. 7.
- 6. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the 5' cap structure is selected from the group consisting of m7 GpppG、m27,3′-O GpppG、m7 Gppp (5') N1 or m7 Gppp(m2′-O ) At least one of N1.
- 7. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the 5' cap structure is selected from the group consisting of m7 Gppp (5') N1 or m7 Gppp(m2′-O )N1。
- 8. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the polyadenylation sequence comprises a sequence of 25 to 400 adenylates.
- 9. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the polyadenylation sequence comprises a sequence of 50 to 400 adenylates.
- 10. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the polyadenylation sequence comprises a sequence of 50 to 300 adenylates.
- 11. The mRNA of claim 1 wherein the polyadenylation sequence comprises a sequence of 50 to 250 adenylates.
- 12. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the poly A sequence comprises a sequence of 60-200 adenylates.
- 13. The mRNA of claim 1, wherein the mRNA has an mRNA selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NOS 15-50.
- 14. A pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one of the mrnas of any one of claims 1-13, and a delivery vehicle.
- 15. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 14, wherein the delivery vehicle is a nanoparticle.
- 16. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 14, wherein the delivery vehicle is a lipid nanoparticle.
- 17. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 15, wherein the lipid nanoparticle has a net neutral charge at neutral pH.
- 18. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 15, wherein the lipid nanoparticles have an average diameter of 50-200nm and a polydispersity index value of less than 0.4.
- 19. The pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 14-17, wherein the mRNA to delivery vehicle mass ratio is a: b, wherein A is selected from 0.05 to 2, and B is selected from 1 to 100.
- 20. The pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 14-17, wherein the mRNA to delivery vehicle mass ratio is a: b, wherein A is 0.05 and B is 1; or A is 1, B is 100; or A is 2, B is 1; or A is 1, B is 50; or A is 1 and B is 5.
- 21. The pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 15-17, wherein the lipid nanoparticle comprises a cationic lipid and at least one selected from the group consisting of a non-cationic lipid, a sterol, and a PEG-modified lipid.
- 22. The pharmaceutical composition according to any one of claims 15 to 17, wherein the lipid nanoparticle is a cationic lipid, a non-cationic lipid, a sterol and a PEG-modified lipid in a molar ratio of 20-60.
- 23. The pharmaceutical composition according to any one of claims 15 to 17, wherein the lipid nanoparticle is a cationic lipid, a non-cationic lipid, a sterol, and a PEG-modified lipid in a molar ratio of 30-60.
- 24. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21 or 22, wherein the cationic lipid is an ionizable cationic lipid selected from one or more of the following: 2, 2-dioleylene-4-dimethylaminoethyl- [1,3] -dioxolane, dioleylene-methyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate and di ((Z) -non-2-en-1-yl) 9- ((4- (dimethylamino) butanoyl) oxy) heptadecanedioate.
- 25. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21 or 22, wherein the cationic lipid is dioleyl-methyl-4-dimethylaminobutyrate.
- 26. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the non-cationic lipid is a neutral lipid selected from at least one of distearoylphosphatidylcholine, dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine, dioleoylphosphatidylcholine, and dioleoylphosphatidylserine.
- 27. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the non-cationic lipid is distearoylphosphatidylcholine.
- 28. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the sterol is cholesterol.
- 29. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the PEG-modified lipid is selected from at least one of PEG-DMG, PEG-DSG, and PEG-DMPE.
- 30. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the PEG-modified lipid is PEG-DMPE.
- 31. The pharmaceutical composition of claim 21, wherein the PEG of the PEG-modified lipid is 0.5-200KDa in length, alternatively 1-50KDa in length, alternatively 1-5KDa in length.
- 32. The pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 14-17, wherein the pharmaceutical composition comprises an adjuvant.
- 33. A kit comprising the mRNA of any one of claims 1 to 13 and/or the pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 14 to 32.
- 34. Use of the mRNA of any one of claims 1 to 13, the pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 14 to 32, the kit of claim 33 for the preparation of a medicament for the prevention and/or treatment of a SARS-CoV-2 viral infection.
- 35. The mRNA of any one of claims 1 to 13, the pharmaceutical composition of any one of claims 14 to 32, the method of making the kit of claim 33, comprising the step of chemically modifying uracil and/or cytosine in the mRNA contained therein, including in part or all of the coding region comprising an antigenic polypeptide encoding SARS-CoV-2, or an antigenic fragment, variant or derivative thereof, wherein the antigenic polypeptide is selected from the receptor binding domain RBD of SARS-CoV-2, or the full-length sequence of spike protein S of SARS-CoV-2.
- 36. The method of claim 35, wherein said chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or 100% of the uracil in the coding region of said mRNA with at least one member selected from the group consisting of pseudouridine, N1-methylpseuduridine, N1-ethylpseudouridine, 2-thiouridine, 4 '-thiouridine, 5-methylcytosine, 5-methyluridine, 2-thio-1-methyl-1-deaza-pseudouridine, 2-thio T-methyl-pseudouridine, 2-thio-5-aza-uridine, 2-thio-dihydropseudouridine, 2-thio-dihydrouridine, 2-thio-pseudouridine, 4-methoxy-pseudouridine, 4-thio-1-methyl-pseudouridine, 4-thio-pseudouridine, 5-aza-uridine, dihydropseudouridine or 5-methoxy-and 2' -O-methyluridine;and/or, the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or 100% of the cytosines in the mRNA with 5-methylcytosine.
- 37. The method of claim 35, wherein the chemical modification comprises replacing at least 50%, at least 60%, at least 70%, at least 80%, at least 90% or 100% of uracil in a coding region of the mRNA with pseudouridine or N1-methylpseuduridine or N1-ethylpseuduridine.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010137489 | 2020-03-02 | ||
| CN2020101374892 | 2020-03-02 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113151312A CN113151312A (en) | 2021-07-23 |
| CN113151312Btrue CN113151312B (en) | 2022-12-09 |
Family
ID=76883948
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110224383.0AActiveCN113151312B (en) | 2020-03-02 | 2021-03-01 | Novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2mRNA vaccine and its preparation method and application |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113151312B (en) |
Families Citing this family (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN117043343A (en)* | 2021-07-30 | 2023-11-10 | 苏州艾博生物科技有限公司 | Nucleic acid vaccine for mutant coronaviruses |
| AR127311A1 (en)* | 2021-10-08 | 2024-01-10 | Suzhou Abogen Biosciences Co Ltd | NUCLEIC ACID VACCINES FOR CORONAVIRUS BASED ON SEQUENCES DERIVED FROM THE DELTA STRAIN OF SARS-CoV-2 |
| CN114231502A (en)* | 2021-10-29 | 2022-03-25 | 吉林大学 | A recombinant rabies virus expressing novel coronavirus RBD protein and its application |
| CN114044814B (en)* | 2021-11-04 | 2024-07-23 | 深圳市人民医院 | MRNA encoding SARS-CoV-2 antigen and mRNA vaccine |
| CN116200403A (en)* | 2021-11-30 | 2023-06-02 | 石药集团巨石生物制药有限公司 | Novel coronavirus mRNA vaccine for preventing mutant strain |
| CN115813848B (en)* | 2021-12-10 | 2023-08-08 | 上海臻上医药科技有限公司 | Reagent, method and application of micro-needle injection mRNA encoding bispecific antibody drug |
| CN114404584B (en)* | 2022-04-01 | 2022-07-26 | 康希诺生物股份公司 | Novel coronavirus mRNA vaccine and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN116925195B (en)* | 2022-04-22 | 2024-06-21 | 仁景(苏州)生物科技有限公司 | MRNA vaccine based on novel coronavirus |
| CN114989308B (en)* | 2022-05-12 | 2023-04-04 | 中国科学院微生物研究所 | Novel coronavirus chimeric nucleic acid vaccine and use thereof |
| CN114752631B (en)* | 2022-06-15 | 2022-09-02 | 中国人民解放军军事科学院军事医学研究院 | RNA, novel coronavirus vaccine containing same and preparation method |
| CN117414418A (en)* | 2022-07-19 | 2024-01-19 | 深圳深信生物科技有限公司 | mRNA vaccine of novel coronavirus variant strain and application thereof |
| CN116514991B (en)* | 2022-08-20 | 2025-02-07 | 中国科学院微生物研究所 | A beta coronavirus and influenza chimeric antigen, preparation method and application thereof |
| CN115219726B (en)* | 2022-09-06 | 2024-04-09 | 昭衍(苏州)新药研究中心有限公司 | Method for detecting serum neutralizing antibody titer by SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus |
| CN117660494A (en)* | 2022-09-07 | 2024-03-08 | 远大赛威信生命科学(南京)有限公司 | mRNA for expressing varicella-zoster virus antigen protein and application thereof |
| CN118021957A (en)* | 2022-11-11 | 2024-05-14 | 深圳先进技术研究院 | MRNA for encoding anti-avian influenza H7N9 virus antibody and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN116042656A (en)* | 2022-11-25 | 2023-05-02 | 中山大学附属第七医院(深圳) | Monkey poxvirus mRNA vaccine and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN116036259B (en)* | 2022-11-30 | 2024-07-02 | 中国科学院微生物研究所 | Monkey pox virus multi-antigen mRNA vaccine and application thereof |
| WO2024239249A1 (en)* | 2023-05-23 | 2024-11-28 | Suzhou Abogen Biosciences Co., Ltd. | Nucleic acid vaccines for coronavirus based on sequences derived from sars-cov-2 omicron strains |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110352071A (en)* | 2016-10-26 | 2019-10-18 | 库瑞瓦格股份公司 | Lipidic nanoparticles mRNA vaccine |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6893177B2 (en)* | 2015-05-15 | 2021-06-23 | キュアバック アーゲー | PRIME-BOOST REGIMENS containing administration of at least one mRNA construct |
| SI3352584T1 (en)* | 2015-09-21 | 2021-09-30 | Trilink Biotechnologies, Llc | Compositions and methods for synthesizing 5'-capped rnas |
| CN110638759A (en)* | 2019-10-29 | 2020-01-03 | 珠海丽凡达生物技术有限公司 | A preparation for in vitro transfection and in vivo delivery of mRNA |
| CN110714015B (en)* | 2019-10-29 | 2021-03-16 | 珠海丽凡达生物技术有限公司 | mRNA rabies vaccine |
- 2021
- 2021-03-01CNCN202110224383.0Apatent/CN113151312B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110352071A (en)* | 2016-10-26 | 2019-10-18 | 库瑞瓦格股份公司 | Lipidic nanoparticles mRNA vaccine |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| mRNA疫苗研究进展及挑战;苗鹤凡等;《免疫学杂志》;20160501(第05期);446-449* |
| Towards an effective mRNA vaccine against 2019-nCoV: demonstration of virus-like particles expressed from an modified mRNA cocktail;Xia Jia 等;《ChinaXiv》;20200225;摘要,material and methods部分,图1* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113151312A (en) | 2021-07-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113151312B (en) | Novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2mRNA vaccine and its preparation method and application | |
| CN114081943B (en) | Varicella-zoster mRNA vaccine composition and preparation method and application thereof | |
| JP2023002709A (en) | Liposomes Containing Lipids with Favorable pKa Values for RNA Delivery | |
| US12083174B2 (en) | Immunogenic compositions and uses thereof | |
| CN114272369A (en) | mRNA vaccine composition for preventing varicella-zoster virus | |
| JP2016006128A (en) | Lipids suitable for liposomal delivery of protein-coding rna | |
| TW202216739A (en) | mRNA and novel coronavirus mRNA vaccine containing the same which is economical and efficient, safer and more efficient, more stable in structure, and more efficient in protein expression | |
| JP2025507227A (en) | Recombinant fusion protein derived from the HR region of the novel coronavirus S2 protein and its uses | |
| CN116082521B (en) | Poxvirus multi-antigen chimeric vaccines and their uses | |
| TW202330922A (en) | Compositions and methods of ribonucleic acid respiratory syncytial virus (rsv) vaccines | |
| CN116917470A (en) | PAN-RAS mRNA cancer vaccine | |
| CN117257929A (en) | Rabies virus mRNA vaccine and application thereof | |
| CN114668837A (en) | mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) -based novel coronavirus wild type and mutant combined vaccine and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116121282B (en) | A kind of mRNA vaccine expressing feline herpes virus protein and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116410992A (en) | mRNA and vaccine for preventing and/or treating novel coronavirus, and preparation method and application thereof | |
| WO2024055273A1 (en) | Rabies mrna vaccine and preparation and use thereof | |
| Di et al. | The self-assembled nanoparticle-based multi-epitope influenza mRNA vaccine elicits protective immunity against H1N1 and B influenza viruses in mice | |
| CN115960180A (en) | 2019-nCoV S protein mutant and genetically engineered mRNA and vaccine composition thereof | |
| KR20230005814A (en) | CPG-Adjuvanted SARS-COV-2 Virus Vaccine | |
| CN118064456A (en) | Novel RSV B mRNA vaccine for human syncytial virus | |
| US11730804B1 (en) | Compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of rabies virus infection | |
| WO2023202711A1 (en) | Mrna vaccine based on novel coronavirus | |
| CN115725613A (en) | mRNA vaccine aiming at novel coronavirus delta mutant strain and preparation method and application thereof | |
| EP4541806A1 (en) | Modified coronavirus spike antigen protein and uses thereof | |
| Chai et al. | Improved mRNA-based RSV vaccine with PreF forming enveloped virus-like particles |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |