CN113143284B - Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction - Google Patents
Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode predictionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113143284B CN113143284BCN202110395294.2ACN202110395294ACN113143284BCN 113143284 BCN113143284 BCN 113143284BCN 202110395294 ACN202110395294 ACN 202110395294ACN 113143284 BCN113143284 BCN 113143284B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- prediction
- value
- wavelet
- frequency
- golomb
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription35
- 230000006835compressionEffects0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription21
- 238000007906compressionMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription21
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000titleclaimsdescription6
- 238000009499grossingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 238000000354decomposition reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 238000000306qrs intervalMethods0.000claimsdescription16
- 230000008569processEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000000717retained effectEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000012634fragmentSubstances0.000claims3
- 238000004806packaging method and processMethods0.000claims2
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000claims1
- 230000002902bimodal effectEffects0.000abstractdescription8
- 238000005538encapsulationMethods0.000abstractdescription4
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description5
- 230000018109developmental processEffects0.000description5
- 238000003745diagnosisMethods0.000description3
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description3
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description3
- 208000024172Cardiovascular diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description2
- 208000019622heart diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description2
- 230000032683agingEffects0.000description1
- 230000006399behaviorEffects0.000description1
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 230000007812deficiencyEffects0.000description1
- 238000001514detection methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 230000036541healthEffects0.000description1
- 230000003862health statusEffects0.000description1
- 230000010365information processingEffects0.000description1
- 238000012806monitoring deviceMethods0.000description1
- 230000004962physiological conditionEffects0.000description1
- 230000001766physiological effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000033764rhythmic processEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7232—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes involving compression of the physiological signal, e.g. to extend the signal recording period
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/72—Signal processing specially adapted for physiological signals or for diagnostic purposes
- A61B5/7235—Details of waveform analysis
- A61B5/7253—Details of waveform analysis characterised by using transforms
- A61B5/726—Details of waveform analysis characterised by using transforms using Wavelet transforms
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Measurement And Recording Of Electrical Phenomena And Electrical Characteristics Of The Living Body (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及生物医学信息处理领域,具体涉及一种基于小波变换和双模预测的心电信号压缩方法The invention relates to the field of biomedical information processing, in particular to an electrocardiographic signal compression method based on wavelet transform and bimodal prediction
背景技术Background technique
随着科技的发展和人类生活质量的提高,人们对自身的健康状况越来越重视,全球医疗费用也逐年增长。同时,老龄化的加剧使得更多的人需要实时的照顾,对医疗资源的需求日益增加。这一系列的社会问题极大促进了远程可穿戴健康监测设备的快速发展。可穿戴远程医疗设备通过实时监测,使得病人一旦产生患病趋势,在病情发展初期便能采取相应措施加以应对,极大地降低了病情进一步恶化的概率,同时,病人也能足不出户就能完成各项医疗行为,不必再定期往返医院做医疗检查,节省了大量的时间和经济成本。近年来,伴随物联网和无线通信的迅速发展,具有低成本、高效率等优点的可穿戴远程医疗设备开始得到应用,极大地降低了人工的成本,对现代医疗的发展具有重要意义。With the development of science and technology and the improvement of human life quality, people pay more and more attention to their own health status, and the global medical expenses are also increasing year by year. At the same time, the aggravation of aging makes more people need real-time care, and the demand for medical resources is increasing. This series of social problems has greatly promoted the rapid development of remote wearable health monitoring devices. Through real-time monitoring, wearable telemedicine devices enable patients to take corresponding measures in the early stage of disease development once they develop a disease trend, which greatly reduces the probability of further deterioration of the disease. At the same time, patients can also stay home. After completing various medical behaviors, there is no need to go to the hospital for medical examinations regularly, which saves a lot of time and economic costs. In recent years, with the rapid development of the Internet of Things and wireless communication, wearable telemedicine devices with the advantages of low cost and high efficiency have begun to be applied, which greatly reduces labor costs and is of great significance to the development of modern medical care.
心电信号(ECG)是一项重要的人体生理信号,它以时间为单位记录人体心脏的各种生理活动,可以反映出心脏的节律以及其电传导的生理信息,可以较为客观地反映出心脏各个部位的生理情况,被广泛应用于心血管疾病的诊断。远程可穿戴心电设备可以长时间监测人体的心电信号,用于诊断和预防可能发生的心血管疾病,相对于临床的检查和诊断具有明显的优势。为了应对突发的心脏疾病,需要长时间不间断地采集心电信号,这对心电信号地传输和存储造成了较大地压力,在可穿戴心电监测设备中,无线传输所占的功耗超过了70%,于是对心电信号进行压缩就变得尤为重要。Electrocardiogram (ECG) is an important human physiological signal. It records various physiological activities of the human heart in units of time, which can reflect the rhythm of the heart and the physiological information of its electrical conduction, and can objectively reflect the heart. Physiological conditions of various parts are widely used in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. Remote wearable ECG devices can monitor the human body's ECG signals for a long time to diagnose and prevent possible cardiovascular diseases, which has obvious advantages over clinical examination and diagnosis. In order to deal with sudden heart diseases, it is necessary to collect ECG signals for a long time without interruption, which causes great pressure on the transmission and storage of ECG signals. In wearable ECG monitoring equipment, the power consumption occupied by wireless transmission If it exceeds 70%, it is particularly important to compress the ECG signal.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
为了克服现有技术的不足,本发明提供了一种基于小波变换和双模预测的心电信号压缩方法,所述方法基于小波变换和双模预测对心电信号进行压缩,实现了较高的压缩率,同时保留了绝大部分有效信息,使压缩信号重构后的心电信号失真度较小,能够完成各种心脏疾病的诊断。In order to overcome the deficiencies of the prior art, the present invention provides an ECG signal compression method based on wavelet transform and bimodal prediction. The method compresses the ECG signal based on wavelet transform and bimodal prediction, and achieves higher At the same time, most of the effective information is retained, so that the distortion of the ECG signal after the reconstruction of the compressed signal is small, and the diagnosis of various heart diseases can be completed.
本发明可通过如下的技术方案实现:The present invention can be realized through the following technical scheme:
一种基于小波变换和双模预测的心电信号压缩方法,所述方法包括以下步骤:An electrocardiographic signal compression method based on wavelet transform and bimodal prediction, the method comprises the following steps:
第一步、信号分解:对心电信息的采样信号进行一级的提升小波变换,得到相同数量的高频系数和低频系数,去除高频系数保留低频系数;The first step, signal decomposition: perform first-level lifting wavelet transform on the sampled signal of ECG information to obtain the same number of high-frequency coefficients and low-frequency coefficients, remove the high-frequency coefficients and retain the low-frequency coefficients;
第二步、缩放平滑:对得到的小波系数低频部分做除法缩放和平滑操作;The second step, scaling and smoothing: perform division, scaling and smoothing operations on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficients;
第三步、预测:对系数采用线性预测和模板预测相结合的方法进行预测并得到预测误差;The third step, prediction: the coefficient is predicted by a combination of linear prediction and template prediction, and the prediction error is obtained;
第四步、编码:将预测误差应用二级golomb-rice编码方式编码;The fourth step, encoding: the prediction error is encoded by the secondary golomb-rice encoding method;
第五步、封装:将编码值和预测需要的信息一起打包形成最后的压缩数据流。The fifth step, encapsulation: encapsulate the encoded value and the information required for prediction together to form the final compressed data stream.
进一步,所述第一步中,所述小波变换采用了5/3提升小波变换,保留低频系数,其表达式为:Further, in the first step, the wavelet transform adopts 5/3 lifting wavelet transform, and the low-frequency coefficient is reserved, and its expression is:
式中X[2n+1]和X[2n]分别为输入信号X[n]分裂得到的奇偶两个序列,d[n]为提升小波变换得到的高频小波系数序列,s[n]为提升小波变换得到的低频尺度系数序列,在计算高频系数d[n]时,需要同时取得奇序列的值X[2n+1]和前后两个偶序列的值X[2n]和X[2n+2]进行计算,计算低频系数s[n]时,需要同时取得偶序列的值X[2n]和该偶序列值前后两个高频系数d[n]和d[n-1]的值。In the formula, X[2n+1] and X[2n] are the parity sequences obtained by splitting the input signal X[n], respectively, d[n] is the high-frequency wavelet coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, and s[n] is When calculating the high-frequency coefficient d[n] of the low-frequency scale coefficient sequence obtained by lifting the wavelet transform, it is necessary to obtain the value X[2n+1] of the odd sequence and the values X[2n] and X[2n of the two even sequences at the same time. +2] for calculation, when calculating the low-frequency coefficient s[n], it is necessary to obtain the value X[2n] of the even sequence and the values of the two high-frequency coefficients d[n] and d[n-1] before and after the even sequence value at the same time .
再进一步,所述第二步中,对得到的小波系数低频部分做除法缩放和平滑操作如下:对低频信号进行缩放,获得多种不同信号质量的心电信号,对小波系数做了平滑处理,对连续的三个小波系数x1、x2、x3,若满足x1=x3,|x2-x1|=1则使x2=x1,即将中间点视为毛刺,修改该值使其与前后值相等。Further, in the second step, the division, scaling and smoothing operations are performed on the low-frequency part of the obtained wavelet coefficients as follows: the low-frequency signal is scaled to obtain a variety of ECG signals with different signal qualities, and the wavelet coefficients are smoothed. For three consecutive wavelet coefficients x1 , x2 , x3 , if x1 =x3 , |x2 -x1 |=1, then x2 =x1 , that is, the middle point is regarded as a burr, and the value to make it equal to the value before and after.
所述第三步中,双模预测采用线性预测与模板预测相结合的方式,对于心电信号非QRS区域采用0阶线性预测,对于QRS区域采用模板预测和2阶线性预测。In the third step, the bi-modal prediction adopts a combination of linear prediction and template prediction, and adopts 0-order linear prediction for the non-QRS region of the ECG signal, and adopts template prediction and 2-order linear prediction for the QRS region.
所述第四步中,二级golomb-rice编码方式编码,参数k的大小与编码的效率紧密相关,即k为或时编码的码长最小,m为待编码的值,在进行golomb-rice编码前先对参数k的值进行预测,从而获得比较高的编码效率,预测的公式表示为:其中d为临时变量,初始值为64。In the fourth step, the second-level golomb-rice encoding method is encoded, and the size of the parameter k is closely related to the encoding efficiency, that is, k is or When the code length of the encoding is the smallest, m is the value to be encoded. Before the golomb-rice encoding, the value of the parameter k is predicted to obtain a relatively high encoding efficiency. The prediction formula is expressed as: where d is a temporary variable with an initial value of 64.
所述第四步中,将预测误差应用二级golomb-rice编码方式编码,为对golomb-rice编码算法做出改进使压缩性能更好,通过增加一前缀码“1110”,对于商值大于等于3且小于8的编码,需在商值的一元编码前增加一个比特“1”,当出现连续的数据0后,则使用该前缀码后配合自定义的游程编码对该片段进行编码,当出现QRS区间或连续数据0时需要使用前缀码和再次查表。In the fourth step, the prediction error is encoded by applying the second-level golomb-rice encoding method to improve the compression performance of the golomb-rice encoding algorithm. By adding a prefix code "1110", for the quotient greater than or equal to For codes of 3 and less than 8, a bit "1" needs to be added before the unary encoding of the quotient value. When there is
所述模板预测为:对于每个QRS区间的系数,都用已有的QRS模板中的值进行预测,在不同的模板中选取最为接近的一个进行预测,同时和应用2阶线性预测得到的值进行比较,选择误差最小的结果作为最终的预测结果。The template prediction is: for the coefficient of each QRS interval, use the value in the existing QRS template to predict, select the closest one in different templates to predict, and use the value obtained by applying the second-order linear prediction simultaneously. For comparison, the result with the smallest error is selected as the final prediction result.
进一步地,所述第五步中,将预测误差应用二级golomb-rice编码方式编码,和预测需要的信息一起打包形成最后的压缩数据流包括编码和数据封装,采用基于golomb-rice编码算法改进得到的二级golomb-rice编码对预测误差进行编码,将信号编码值和解码需要的信息一起封装。Further, in the described 5th step, the prediction error is encoded by applying the secondary golomb-rice encoding method, and the information required for the prediction is packaged together to form the final compressed data stream including encoding and data encapsulation, and the improvement based on the golomb-rice encoding algorithm is adopted. The resulting two-level golomb-rice encoding encodes the prediction error, encapsulating the encoded value of the signal with the information needed for decoding.
本发明与现有的技术相比,有以下优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
(1)本发明提供了一种基于小波变换和双模预测的心电信号压缩方法,在较低失真度下实现了较高的心电信号压缩率,同时也支持多种不同的压缩等级以适应不同的应用场景。(1) The present invention provides an electrocardiographic signal compression method based on wavelet transform and bimodal prediction, which achieves a higher electrocardiographic signal compression rate under lower distortion, and also supports a variety of different compression levels to Adapt to different application scenarios.
(2)应用5/3提升小波变换处理信号,降低数据的相关性提升压缩率,同时5/3提升小波变换只需要简单的加法运算,相比需要大量乘法运算的传统小波,拥有更低的运算复杂度(2) Apply 5/3 lifting wavelet transform to process signals, reduce the correlation of data and improve the compression rate. At the same time, 5/3 lifting wavelet transform only needs simple addition operation. Compared with traditional wavelet which requires a lot of multiplication operations, it has lower operational complexity
(3)将小波系数分为QRS区和非QRS区,对于非QRS区,采用线性预测的方法进行预测,对于QRS区域应用线性预测和模板预测相结合的方法进行预测,从而进一步降低数据间的相关性以实现更高的压缩率。(3) The wavelet coefficients are divided into QRS area and non-QRS area. For the non-QRS area, the linear prediction method is used for prediction. For the QRS area, the combination of linear prediction and template prediction is used for prediction, so as to further reduce the difference between the data. correlation to achieve higher compression ratios.
(4)设计的一种新型的编码方式——二级golomb-rice编码,将不同特性区域分开编码,进而得到比用其他编码方式更好的压缩效果。(4) A new type of coding method is designed—two-level golomb-rice coding, which encodes different characteristic regions separately, and then obtains a better compression effect than other coding methods.
附图说明Description of drawings
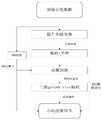
图1为本发明的流程图。FIG. 1 is a flow chart of the present invention.
图2为基于MIT-BIH数据库的实验效果图,其中,(a)是原始心电采样信号,(b)是提升小波变换后得到的高频系数,(c)是提升小波变换后得到的低频系数,(d)是对低频系数做缩放处理后得到的值,(e)是对缩放后的系数进一步做平滑操作得到的值,(f)是对平滑后的系数进行双模预测,最终得到的预测误差值。Figure 2 shows the experimental results based on the MIT-BIH database, in which (a) is the original ECG sampled signal, (b) is the high-frequency coefficient obtained after boosting the wavelet transform, and (c) is the low-frequency coefficient obtained after boosting the wavelet transform coefficient, (d) is the value obtained after scaling the low-frequency coefficient, (e) is the value obtained by further smoothing the scaled coefficient, (f) is the bimodal prediction of the smoothed coefficient, and finally obtain prediction error value.
图3为数据封装形式的示意图。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of a data encapsulation form.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了本发明的技术方案更加清晰,下面结合附图和实施例对本发明进行更完整地表述。本发明的实施包括下面的实施例但不仅限于此。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the technical solutions of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be more completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. The implementation of the present invention includes the following examples but is not limited thereto. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those skilled in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
参照图1~图3,一种基于小波变换和双模预测的心电信压缩方法,具体流程如图1所示,包括以下步骤:Referring to Fig. 1 to Fig. 3 , a method for compressing ECG based on wavelet transform and bimodal prediction, the specific process is shown in Fig. 1, including the following steps:
第一步,应用5/3提升小波对心电信号采样值进行分解,具体为将心电信号采样序列X[n]分为奇偶两个序列X[2n+1]和X[2n],n为大于等于1的正整数,将这两个序列通过公式进行转换为低频系数和高频系数,转换公式表达为:The first step is to use 5/3 lifting wavelet to decompose the ECG signal sampling value, specifically, dividing the ECG signal sampling sequence X[n] into two odd and even sequences X[2n+1] and X[2n], n For a positive integer greater than or equal to 1, the two sequences are converted into low-frequency coefficients and high-frequency coefficients through the formula, and the conversion formula is expressed as:
式中X[2n+1]和X[2n]分别为输入信号X[n]分裂得到的奇偶两个序列,d[n]为提升小波变换得到的高频小波系数序列,s[n]为提升小波变换得到的低频尺度系数序列,在计算高频系数d[n]时,需要同时取得奇序列的值X[2n+1]和前后两个偶序列的值X[2n]和X[2n+2]进行计算,计算低频系数s[n]时,需要同时取得偶序列的值X[2n]和该偶序列值前后两个高频系数d[n]和d[n-1]的值。In the formula, X[2n+1] and X[2n] are the parity sequences obtained by splitting the input signal X[n], respectively, d[n] is the high-frequency wavelet coefficient sequence obtained by lifting wavelet transform, and s[n] is When calculating the high-frequency coefficient d[n] of the low-frequency scale coefficient sequence obtained by lifting the wavelet transform, it is necessary to obtain the value X[2n+1] of the odd sequence and the values X[2n] and X[2n of the two even sequences at the same time. +2] for calculation, when calculating the low-frequency coefficient s[n], it is necessary to obtain the value X[2n] of the even sequence and the values of the two high-frequency coefficients d[n] and d[n-1] before and after the even sequence value at the same time .
第二步,对分解得到的低频系数进行缩放,即对系数做除法,根据不同的应用场景选择不同的除数为2、4、8、16、32,以利于实际电路的实现,对缩放后的值做进一步的平滑操作增大最终的压缩率,对连续的三个小波系数x1、x2、x3,若满足x1=x3且|x2-x1|=1,则使x2=x1。即将中间点视为毛刺,修改该值使其与前后值相等,从而使得小波变换后的系数变化更加平滑,更有利于后续的预测。The second step is to scale the low-frequency coefficients obtained by decomposition, that is, to divide the coefficients, and select different divisors of 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32 according to different application scenarios to facilitate the realization of the actual circuit. The value is further smoothed to increase the final compression rate. For three consecutive wavelet coefficients x1 , x2 , x3 , if x1 =x3 and |x2 -x1 |=1, then x2 = x1 . That is, the middle point is regarded as a burr, and the value is modified to be equal to the value before and after, so that the coefficient change after wavelet transformation is smoother, which is more conducive to subsequent prediction.
第三步,对平滑后的小波系数进行预测,过程如下:The third step is to predict the smoothed wavelet coefficients. The process is as follows:
对非QRS区间采用0阶线性预测的方法进行预测,即对每个小波系数的值,用前一个系数预测,保留预测误差值,也就是当前的系数减去前一个系数得到的差值。The non-QRS interval is predicted by the 0-order linear prediction method, that is, the value of each wavelet coefficient is predicted by the previous coefficient, and the prediction error value is retained, that is, the difference obtained by subtracting the previous coefficient from the current coefficient.
应用R峰检测算法检测出QRS区间的位置,当心电信号采样进入QRS区域时,开始用模板预测和2阶线性预测相结合的方法对低频系数进行预测,模板数量设为Nt,对于采样频率为f的心电信号,对应的QRS区间内低频小波系数的个数为Wqrs=f/20,因此将模板长度设为Wqrs,也就是每个模板可以预测的系数个数,初始值都为0。The R peak detection algorithm is used to detect the position of the QRS interval. When the ECG signal is sampled into the QRS area, the combination of template prediction and second-order linear prediction is used to predict the low-frequency coefficients. The number of templates is set to Nt , for the sampling frequency For the ECG signal of f, the number of low-frequency wavelet coefficients in the corresponding QRS interval is Wqrs =f/20, so the template length is set to Wqrs , that is, the number of coefficients that can be predicted by each template, and the initial value is is 0.
具体的,预测首先需要在Nt个模板预测器和1个二阶线性预测器中选择一个让QRS区间所有系数预测误差绝对值的和最小的预测器,其中二阶线性预测的公式表达为:Specifically, the prediction first needs to select a predictor that minimizes the sum of the absolute values of the prediction errors of all coefficients in the QRS interval among the Nt template predictors and one second-order linear predictor, where the second-order linear prediction formula is expressed as:
其中x[n-1]、x[n-2]、x[n-3]分别是过去的三个系数值,求得QRS区间内所有Wqrs个系数的预测值,将所有预测的值和原始值做差得到Wqrs个预测误差值,将其求和得道预测误差总和。然后用所有Nt个模板预测器存储的值对当前QRS区间的值进行预测并分别求得Nt个预测误差总和,将这Nt个预测误差总和与二阶线性预测器的误差总和一共Nt+1个值相比较,选取预测误差总和最小的那个预测器,对当前QRS区间系数值进行预测。每轮QRS区间预测完成时,用当前QRS区间的所有系数值更新前面最早更新的一个模板。Where x[n-1], x[n-2], x[n-3] are the past three coefficient values, respectively, to obtain the predicted values of all Wqrs coefficients in the QRS interval, and sum all predicted values to The difference between the original values is obtained to obtain Wqrs prediction error values, which are summed to obtain the sum of the prediction errors. Then use the values stored in all Nt template predictors to predict the value of the current QRS interval and obtain the sum of Nt prediction errors respectively. The sum of these Nt prediction errors and the sum of the errors of the second-order linear predictor is a total of Nt + 1 values are compared, and the predictor with the smallest sum of prediction errors is selected to predict the coefficient value of the current QRS interval. When each round of QRS interval prediction is completed, the earliest updated template is updated with all the coefficient values of the current QRS interval.
第四步,对预测误差编码,首先先将整数预测误差映射为非负整数m,再对映射值进行二级golomb-rice编码,在进行golomb-rice编码前先对参数k的值进行预测,从而获得比较高的编码效率,预测的公式表示为和d的初始值设为64,编码方式如下:The fourth step, encoding the prediction error, firstly maps the integer prediction error to a non-negative integer m, and then performs two-level golomb-rice encoding on the mapped value, and predicts the value of the parameter k before performing the golomb-rice encoding. In order to obtain relatively high coding efficiency, the prediction formula is expressed as and The initial value of d is set to 64, and the encoding method is as follows:
对于非0值或连续为0数量小于8的数据,对每个数据我们的编码形式为常规golomb-rice编码,根据不同商值得范围在一元编码前加上相应个数的比特“1”。For data with a non-zero value or a number of consecutive zeros less than 8, our encoding form for each data is conventional golomb-rice encoding, and a corresponding number of bits "1" are added before unary encoding according to different quotient value ranges.
2.对于连续为“0”的数量大于等于8的片段,我们对该片段整体进行编码,编码形式为“1110”+该片段数据个数的golomb-rice编码值。2. For the segment with the number of consecutive "0" greater than or equal to 8, we encode the segment as a whole, and the encoding format is "1110" + the golomb-rice encoded value of the number of data in the segment.
其中golomb-rice编码值表示为{一元编码0,二元编码(m mod 2k)}。where the golomb-rice encoded value is expressed as {
第五步,对编码值进行封装,封装的数据包括所有解码需要的信息,具体形式如图3所示,其中t的值为log2(Nt+1)。首先对前三个小波系数的二进制编码进行封装,解码时可根据前三个值进行后续的预测。然后按照非QRS区间误差编码、QRS指示码、QRS模板索引、QRS区间误差编码的顺序对每个心电周期进行封装,这样可以达到实时编解码。同时在每个非QRS区间和QRS区间存在多个由前缀码“1110”指示的连续0值片段的编码。The fifth step is to encapsulate the encoded value, and the encapsulated data includes all the information required for decoding. The specific form is shown in Figure 3, where the value of t is log2 (Nt +1). Firstly, the binary codes of the first three wavelet coefficients are encapsulated, and the subsequent prediction can be performed according to the first three values during decoding. Then, encapsulate each ECG cycle in the order of non-QRS interval error coding, QRS indication code, QRS template index, and QRS interval error coding, so that real-time encoding and decoding can be achieved. At the same time, in each non-QRS interval and QRS interval, there are multiple codes of consecutive 0-valued segments indicated by the prefix code "1110".
以上所述,仅为本发明较佳的实施例,但本发明的保护范围并不仅仅局限于此,热火和采用本发明设计的原理,及在本发明基础上做出的非创造性的变化,都属于本发明专利的保护范围内。The above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to this. All belong to the protection scope of the patent of the present invention.
Claims (7)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110395294.2ACN113143284B (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2021-04-13 | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110395294.2ACN113143284B (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2021-04-13 | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113143284A CN113143284A (en) | 2021-07-23 |
| CN113143284Btrue CN113143284B (en) | 2022-10-21 |
Family
ID=76890297
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110395294.2AActiveCN113143284B (en) | 2021-04-13 | 2021-04-13 | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113143284B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2024216514A1 (en)* | 2023-04-18 | 2024-10-24 | 华为技术有限公司 | Data compression method, data decompression method, and related apparatus |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1874162A (en)* | 2005-06-01 | 2006-12-06 | 奥林巴斯映像株式会社 | Data encoding apparatus and data encoding method |
| CN101268936A (en)* | 2008-02-27 | 2008-09-24 | 天津大学 | ECG compression method and decoding method for wireless ECG monitor |
| CN101404772A (en)* | 2008-11-19 | 2009-04-08 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | VLSI image compression encoder based on wavelet transformation |
| CN101572814A (en)* | 2008-04-29 | 2009-11-04 | 合肥坤安电子科技有限公司 | Secondary run length encoding method |
| CN102368385A (en)* | 2011-09-07 | 2012-03-07 | 中科开元信息技术(北京)有限公司 | Backward block adaptive Golomb-Rice coding and decoding method and apparatus thereof |
| CN103908243A (en)* | 2014-04-01 | 2014-07-09 | 南京普澳医疗设备有限公司 | Lifting wavelet and median filter combined algorithm |
| CN104000579A (en)* | 2014-06-11 | 2014-08-27 | 复旦大学 | Multifunctional electrocardiosignal processing SoC chip for remote medical monitoring |
| US10547843B1 (en)* | 2018-07-24 | 2020-01-28 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Prefix coding method for high-throughput entropy coder in display interface compression |
| CN112134567A (en)* | 2020-08-28 | 2020-12-25 | 北京航空航天大学 | Self-adaptive real-time compression method and system for absorption spectrum data |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6735254B2 (en)* | 2001-06-29 | 2004-05-11 | Qualcomm, Inc. | DCT compression using Golomb-Rice coding |
| CN102323977B (en)* | 2011-06-29 | 2014-04-30 | 无锡市吉天通信科技有限公司 | Electrocardio data storage method based on electrocardio characteristic points |
| CN104159108B (en)* | 2014-08-11 | 2017-08-11 | 浙江大学 | Electrocardiosignal real-time lossless compression method and device based on adaptive prediction and improvement variable-length encoding |
| TWI561215B (en)* | 2014-12-16 | 2016-12-11 | Sunplus Technology Co Ltd | Method of compressing electrocardiography signal and electrocardiography signal sensing apparatus thereof |
| TWI662948B (en)* | 2018-08-10 | 2019-06-21 | 國立中央大學 | Ecg signals lossless compression system and its method |
- 2021
- 2021-04-13CNCN202110395294.2Apatent/CN113143284B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1874162A (en)* | 2005-06-01 | 2006-12-06 | 奥林巴斯映像株式会社 | Data encoding apparatus and data encoding method |
| CN101268936A (en)* | 2008-02-27 | 2008-09-24 | 天津大学 | ECG compression method and decoding method for wireless ECG monitor |
| CN101572814A (en)* | 2008-04-29 | 2009-11-04 | 合肥坤安电子科技有限公司 | Secondary run length encoding method |
| CN101404772A (en)* | 2008-11-19 | 2009-04-08 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | VLSI image compression encoder based on wavelet transformation |
| CN102368385A (en)* | 2011-09-07 | 2012-03-07 | 中科开元信息技术(北京)有限公司 | Backward block adaptive Golomb-Rice coding and decoding method and apparatus thereof |
| CN103908243A (en)* | 2014-04-01 | 2014-07-09 | 南京普澳医疗设备有限公司 | Lifting wavelet and median filter combined algorithm |
| CN104000579A (en)* | 2014-06-11 | 2014-08-27 | 复旦大学 | Multifunctional electrocardiosignal processing SoC chip for remote medical monitoring |
| US10547843B1 (en)* | 2018-07-24 | 2020-01-28 | Samsung Display Co., Ltd. | Prefix coding method for high-throughput entropy coder in display interface compression |
| CN112134567A (en)* | 2020-08-28 | 2020-12-25 | 北京航空航天大学 | Self-adaptive real-time compression method and system for absorption spectrum data |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| A Wavelet-Based EGG Compression Algorithm Using Golomb Codes;Jianhua Chen;《International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems》;20070115;全文* |
| Lossless ECG Compression with Lifting Wavelet Transform;Krzysztof Duda;《IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference》;20010523;全文* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113143284A (en) | 2021-07-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8917779B2 (en) | Electrocardiogram signal compression and de-compression system | |
| Zigel et al. | ECG signal compression using analysis by synthesis coding | |
| Vadrevu et al. | A new quality-aware quality-control data compression framework for power reduction in IoT and smartphone PPG monitoring devices | |
| Manikandan et al. | Wavelet threshold based TDL and TDR algorithms for real-time ECG signal compression | |
| CN101268936A (en) | ECG compression method and decoding method for wireless ECG monitor | |
| Tsai et al. | VLSI implementation of multi-channel ECG lossless compression system | |
| CN113143284B (en) | Electrocardiosignal compression method based on wavelet transformation and dual-mode prediction | |
| Alam et al. | Zonal complexity based measure for lossy compression of photoplethysmogram using delta encoding | |
| CN112863653B (en) | Electrocardiogram data compression method and device | |
| TWI662948B (en) | Ecg signals lossless compression system and its method | |
| CN101669819A (en) | Electrocardiogram signal lossless compression method based on PT conversion and linear prediction combination | |
| Tsai et al. | Efficient lossless compression scheme for multi-channel ECG signal | |
| WO1985005514A1 (en) | Signal processing system | |
| Kalaivani et al. | Design and implementation of hybrid compression algorithm for personal health care big data applications | |
| CN113288050B (en) | Multidimensional Enhanced Epilepsy Seizure Prediction System Based on Graph Convolutional Networks | |
| CN110381461A (en) | Electrocardio signal transmission method, device, sensor, terminal and storage medium | |
| Zigel et al. | A diagnostic meaningful distortion measure for ECG compression | |
| US9326734B1 (en) | Method of compressing electrocardiography signal and electrocardiography signal sensing apparatus thereof | |
| CN116919419A (en) | Abnormality judgment method, device and electronic equipment based on dynamic electrocardiogram | |
| Tornekar et al. | Comparative study of lossless ECG signal compression techniques for wireless networks | |
| Higgins et al. | Low power compression of EEG signals using JPEG2000 | |
| Abdali-Mohammadi | 12 lead electrocardiography signals compression by a new genetic programming based mathematical modeling algorithm | |
| Ramesh | FPGA based Implementation of a Multi-Channel ECG Lossless Compression System | |
| Manikandan et al. | Wavelet-based ECG and PCG signals compression technique for mobile telemedicine | |
| Bui et al. | Signal quality valuation with optimal power consumption and high compression ratio method for estimate heart rate applied to real-time PPG measurement |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |