CN113064930B - Cold and hot data identification method and device of data warehouse and electronic equipment - Google Patents
Cold and hot data identification method and device of data warehouse and electronic equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN113064930B CN113064930BCN202011603968.5ACN202011603968ACN113064930BCN 113064930 BCN113064930 BCN 113064930BCN 202011603968 ACN202011603968 ACN 202011603968ACN 113064930 BCN113064930 BCN 113064930B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- period
- data table
- access frequency
- hot
- cold
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/24—Querying
- G06F16/245—Query processing
- G06F16/2458—Special types of queries, e.g. statistical queries, fuzzy queries or distributed queries
- G06F16/2462—Approximate or statistical queries
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/20—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of structured data, e.g. relational data
- G06F16/28—Databases characterised by their database models, e.g. relational or object models
- G06F16/283—Multi-dimensional databases or data warehouses, e.g. MOLAP or ROLAP
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Probability & Statistics with Applications (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Fuzzy Systems (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Complex Calculations (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域Technical Field
本申请涉及计算机技术领域,尤其涉及一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法、装置及电子设备。The present application relates to the field of computer technology, and in particular to a method, device and electronic equipment for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse.
背景技术Background Art
数据仓库(Data Warehouse,DW)出于企业的分析性报告和决策支持多点目的而创建的一个数据存储集合,其用于对多样的业务数据进行筛选与整合。数据仓库具有业务数据量大、种类多样等特征。如何有效识别数据仓库中业务数据的冷热属性,以便对不同属性的业务数据进行分离存储、备份或者销毁等处理,对于数据仓库的管理尤为重要。A data warehouse (DW) is a data storage collection created for the purpose of analytical reporting and decision support for an enterprise. It is used to filter and integrate various business data. Data warehouses have the characteristics of large amounts of business data and diverse types. How to effectively identify the hot and cold attributes of business data in a data warehouse so as to separate, store, back up or destroy business data with different attributes is particularly important for data warehouse management.
目前,对数据仓库中业务数据的冷热属性的识别,主要通过人工逐个统计各个业务数据的访问情况,根据统计结果来区分业务数据的冷热属性,比如,如果某个业务数据频繁被访问,则可将该业务数据作为热数据,反之,则可将该业务数据作为冷数据。可见,现有技术中的冷热数据识别方法主要依赖于业务人员的经验,因而识别结果的准确率无法得到保证。并且,随着数据仓库对接的业务规模的数量级不断增大,数据仓库中的业务数据的数据量也会急剧增长,若通过人工逐个统计业务数据的访问情况,将会影响识别效率。At present, the identification of hot and cold attributes of business data in data warehouses is mainly done by manually counting the access of each business data one by one, and distinguishing the hot and cold attributes of business data based on the statistical results. For example, if a certain business data is frequently accessed, the business data can be regarded as hot data, and vice versa. It can be seen that the hot and cold data identification method in the prior art mainly relies on the experience of business personnel, so the accuracy of the identification result cannot be guaranteed. In addition, as the order of magnitude of the business scale connected to the data warehouse continues to increase, the amount of business data in the data warehouse will also increase sharply. If the access of business data is manually counted one by one, the identification efficiency will be affected.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本申请实施例提供一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法、装置及电子设备,以至少解决现有技术中的冷热数据识别方法存在的识别效率和准确率低的问题。The embodiments of the present application provide a method, device and electronic device for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse, so as to at least solve the problems of low recognition efficiency and accuracy of the hot and cold data recognition methods in the prior art.
为了解决上述技术问题,本申请实施例采用下述技术方案:In order to solve the above technical problems, the embodiments of the present application adopt the following technical solutions:
第一方面,本申请实施例提供一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法,包括:In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a method for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse, comprising:
获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录;Obtain the historical access records of the business data tables in the data warehouse within the specified statistical period;
基于所述指定统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期及在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息;Based on the historical access records within the specified statistical period, determining the processing period of the business data table and the access frequency information within the specified statistical period;
基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述指定统计周期,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点;Based on the pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period and the specified statistical period, determine the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period;
基于所述冷热数据分界时间点,识别所述业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据。Based on the hot and cold data demarcation time point, cold data and hot data in the business data table are identified.
可选地,所述访问频率信息包括总访问频率和在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率;Optionally, the access frequency information includes a total access frequency and an access frequency in each sub-period of the specified statistical period;
基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述指定统计周期,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,包括:Based on the pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period, and the specified statistical period, determining the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period includes:
将所述业务数据表的处理周期、所述指定统计周期及在所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率输入到所述冷热数据识别模型,以得到所述业务数据表的冷热数据比例,其中,所述冷热数据识别模型是以样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的总访问频率及统计周期作为训练样本,以所述样本数据表的冷热数据比例作为标签,基于预设的第一分类算法进行训练得到;The processing period of the business data table, the designated statistical period, and the total access frequency within the designated statistical period are input into the hot and cold data identification model to obtain the hot and cold data ratio of the business data table, wherein the hot and cold data identification model is obtained by training based on a preset first classification algorithm using the processing period of the sample data table, the total access frequency within the statistical period, and the statistical period as training samples and the hot and cold data ratio of the sample data table as labels;
基于所述冷热数据比例和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,确定与所述业务数据表相匹配的访问频率阈值;Determine an access frequency threshold matching the business data table based on the cold and hot data ratio and the total access frequency of the business data table in the specified statistical period;
基于所述访问频率阈值和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period of the specified statistical period, a cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period is determined.
可选地,基于所述访问频率阈值和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,包括:Optionally, based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period of the specified statistical period, determining the cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period includes:
基于所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,所述子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从所述指定统计周期的起始时间点起至所述子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;Based on the total access frequency in the specified statistical period, respectively determine the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period;
从所述指定统计周期的各个子周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到所述访问频率阈值的子周期;From each sub-period of the specified statistical period, select a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold;
将选取出的子周期确定为所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。The selected sub-period is determined as the boundary time point of the cold and hot data of the business data table within the specified statistical period.
可选地,基于所述访问频率阈值和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,包括:Optionally, based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period of the specified statistical period, determining the cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period includes:
基于所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,所述子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从所述指定统计周期的起始时间点起至所述子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;Based on the total access frequency in the specified statistical period, respectively determine the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period;
从所述指定统计周期的各个子周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到所述访问频率阈值的子周期,作为候选子周期;From each sub-period of the specified statistical period, select a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold as a candidate sub-period;
确定与所述候选子周期相邻的各个子周期对应的累计访问频率与所述候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值以及与所述访问频率阈值之间的差值;Determine a difference between a cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period and the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the candidate sub-period, and a difference between the cumulative access frequency and the access frequency threshold;
从与所述候选子周期相邻的各个子周期中,选取与所述候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值最小、且与所述访问频率阈值之间的差值位于设定范围内的子周期;From each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period, select a sub-period whose difference between the accumulated access frequencies corresponding to the candidate sub-period is the smallest and whose difference with the access frequency threshold is within a set range;
基于选取出的子周期确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Based on the selected sub-period, a time point for dividing the cold and hot data in the business data table within the specified statistical period is determined.
可选地,所述历史访问记录包括所述指定统计周期内对所述业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点;Optionally, the historical access record includes a time point of a write operation performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period;
基于所述指定统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期,包括:Determining a processing period of the business data table based on historical access records within the specified statistical period includes:
基于所述指定统计周期内对所述业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点,分别确定对所述业务数据表执行的最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期;Based on the time points of the write operations performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period, respectively determine the average write cycles between the last write operation performed on the business data table and the other write operations;
基于所述最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期,确定所述业务数据表的平均写入周期;Determine the average write cycle of the business data table based on the average write cycles between the last write operation and other write operations;
基于数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的预设对应关系以及所述业务数据表的平均写入周期,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期。Based on a preset correspondence between an average writing cycle and a processing cycle of a data table and an average writing cycle of the business data table, a processing cycle of the business data table is determined.
可选地,在确定所述业务数据表的处理周期之前,所述方法还包括:Optionally, before determining the processing cycle of the business data table, the method further includes:
获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及处理周期;Obtain historical access records and processing cycles of the sample data table within the statistical period;
基于所述统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表的平均写入周期;Determine an average write cycle of the sample data table based on the historical access records within the statistical period;
以所述样本数据表的平均写入周期作为训练样本、以所述样本数据表的处理周期作为所述训练样本的标签,基于预设的第二分类算法进行训练,以得到所述预设对应关系。The average writing cycle of the sample data table is used as a training sample, and the processing cycle of the sample data table is used as a label of the training sample. Training is performed based on a preset second classification algorithm to obtain the preset corresponding relationship.
可选地,在基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、所述指定统计周期及在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点之前,所述方法还包括:Optionally, before determining the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period based on a pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing period of the business data table, the specified statistical period, and the access frequency information in the specified statistical period, the method further includes:
获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及冷热数据比例;Obtain the historical access records and hot and cold data ratios of the sample data table within the statistical period;
基于所述历史访问记录,确定所述样本数据表的处理周期及在所述统计周期内的累计访问频率;Based on the historical access records, determining the processing period of the sample data table and the cumulative access frequency within the statistical period;
以所述样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的累计访问频率及所述统计周期作为训练样本,以所述样本数据表在所述统计周期内的冷热数据比例作为所述训练样本的标签,基于所述第一分类算法进行训练,以得到所述冷热数据识别模型。The processing period of the sample data table, the cumulative access frequency within the statistical period and the statistical period are used as training samples, and the ratio of hot and cold data in the sample data table within the statistical period is used as the label of the training sample. Training is performed based on the first classification algorithm to obtain the hot and cold data recognition model.
第二方面,本申请实施例提供一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别装置,包括:In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a device for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse, including:
第一获取模块,用于获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录;The first acquisition module is used to acquire the historical access records of the business data table in the data warehouse within a specified statistical period;
第一确定模块,用于基于所述历史访问记录,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期及在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息;A first determination module, configured to determine the processing period of the business data table and the access frequency information within the specified statistical period based on the historical access records;
第二确定模块,用于基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述指定统计周期,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,其中,所述冷热数据识别模型为基于第一分类算法对样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述统计周期进行训练得到;The second determination module is used to determine the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period based on a pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing period of the business data table, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period, and the specified statistical period, wherein the hot and cold data identification model is obtained by training the processing period of the sample data table, the access frequency information within the statistical period, and the statistical period based on the first classification algorithm;
识别模块,用于基于所述冷热数据分界时间点,识别所述业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据。The identification module is used to identify the cold data and the hot data in the business data table based on the cold and hot data demarcation time point.
可选地,所述访问频率信息包括总访问频率和在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率;Optionally, the access frequency information includes a total access frequency and an access frequency in each sub-period of the specified statistical period;
所述第二确定模块具体用于:The second determining module is specifically used for:
将所述业务数据表的处理周期、所述指定统计周期及在所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率输入到所述冷热数据识别模型,以得到所述业务数据表的冷热数据比例,其中,所述冷热数据识别模型是以样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的总访问频率及统计周期作为训练样本,以所述样本数据表的冷热数据比例作为标签,基于预设的第一分类算法进行训练得到;The processing period of the business data table, the designated statistical period, and the total access frequency within the designated statistical period are input into the hot and cold data identification model to obtain the hot and cold data ratio of the business data table, wherein the hot and cold data identification model is obtained by training based on a preset first classification algorithm using the processing period of the sample data table, the total access frequency within the statistical period, and the statistical period as training samples and the hot and cold data ratio of the sample data table as labels;
基于所述冷热数据比例和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,确定与所述业务数据表相匹配的访问频率阈值;Determine an access frequency threshold matching the business data table based on the cold and hot data ratio and the total access frequency of the business data table in the specified statistical period;
基于所述访问频率阈值和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period of the specified statistical period, a cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period is determined.
可选地,所述第二确定模块具体用于:Optionally, the second determining module is specifically configured to:
基于所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,所述子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从所述指定统计周期的起始时间点起至所述子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;Based on the total access frequency in the specified statistical period, respectively determine the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period;
从所述指定统计周期的各个子周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到所述访问频率阈值的子周期;From each sub-period of the specified statistical period, select a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold;
将选取出的子周期确定为所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。The selected sub-period is determined as the boundary time point of the cold and hot data of the business data table within the specified statistical period.
可选地,所述第二确定模块具体用于:Optionally, the second determining module is specifically configured to:
基于所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,所述子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从所述指定统计周期的起始时间点起至所述子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;Based on the total access frequency in the specified statistical period, respectively determine the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period;
从所述指定统计周期的各个子周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到所述访问频率阈值的子周期,作为候选子周期;From each sub-period of the specified statistical period, select a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold as a candidate sub-period;
确定与所述候选子周期相邻的各个子周期对应的累计访问频率与所述候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值以及与所述访问频率阈值之间的差值;Determine a difference between the accumulated access frequencies corresponding to each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period and the accumulated access frequency corresponding to the candidate sub-period, and a difference between the accumulated access frequencies and the access frequency threshold;
从与所述候选子周期相邻的各个子周期中,选取与所述候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值最小、且与所述访问频率阈值之间的差值位于设定范围内的子周期;From each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period, select a sub-period whose difference between the accumulated access frequencies corresponding to the candidate sub-period is the smallest and whose difference with the access frequency threshold is within a set range;
基于选取出的子周期确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Based on the selected sub-period, a time point for dividing the cold and hot data in the business data table within the specified statistical period is determined.
可选地,所述历史访问记录包括所述指定统计周期内对所述业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点;Optionally, the historical access record includes a time point of a write operation performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period;
所述第一确定模块具体用于:The first determining module is specifically used for:
基于所述指定统计周期内对所述业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点,分别确定对所述业务数据表执行的最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期;Based on the time points of the write operations performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period, respectively determine the average write cycles between the last write operation performed on the business data table and the other write operations;
基于所述最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期,确定所述业务数据表的平均写入周期;Determine the average write cycle of the business data table based on the average write cycles between the last write operation and other write operations;
基于数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的预设对应关系以及所述业务数据表的平均写入周期,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期。Based on a preset correspondence between an average writing cycle and a processing cycle of a data table and an average writing cycle of the business data table, a processing cycle of the business data table is determined.
可选地,所述装置还包括:Optionally, the device further comprises:
第二获取模块,用于获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及处理周期;The second acquisition module is used to obtain the historical access records and processing cycles of the sample data table within the statistical period;
第三确定模块,用于基于所述统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表的平均写入周期;A third determination module, configured to determine an average write cycle of the sample data table based on historical access records within the statistical period;
第一训练模块,用于以所述样本数据表的平均写入周期作为训练样本、以所述样本数据表的处理周期作为所述训练样本的标签,基于预设的第二分类算法进行训练,以得到所述预设对应关系。The first training module is used to use the average writing cycle of the sample data table as a training sample and the processing cycle of the sample data table as a label of the training sample, and to perform training based on a preset second classification algorithm to obtain the preset corresponding relationship.
可选地,所述装置还包括:Optionally, the device further comprises:
第三获取模块,用于获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及冷热数据比例;The third acquisition module is used to obtain the historical access records and the ratio of hot and cold data of the sample data table within the statistical period;
第四确定模块,用于基于所述历史访问记录,确定所述样本数据表的处理周期及在所述统计周期内的累计访问频率;A fourth determination module, configured to determine the processing period of the sample data table and the cumulative access frequency within the statistical period based on the historical access records;
第二训练模块,用于以所述样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的累计访问频率及所述统计周期作为训练样本,以所述样本数据表在所述统计周期内的冷热数据比例作为所述训练样本的标签,基于所述第一分类算法进行训练,以得到所述冷热数据识别模型。The second training module is used to use the processing period of the sample data table, the cumulative access frequency within the statistical period and the statistical period as training samples, and the ratio of cold and hot data in the sample data table within the statistical period as labels of the training samples, and to perform training based on the first classification algorithm to obtain the cold and hot data recognition model.
第三方面,本申请实施例提供一种电子设备,包括:In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an electronic device, including:
处理器;processor;
用于存储所述处理器可执行指令的存储器;a memory for storing instructions executable by the processor;
其中,所述处理器被配置为执行所述指令,以实现第一方面所述的方法。The processor is configured to execute the instructions to implement the method described in the first aspect.
第四方面,本申请实施例提供一种计算机可读存储介质,当所述存储介质中的指令由电子设备的处理器执行时,使得电子设备能够执行第一方面所述的方法。In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium. When instructions in the storage medium are executed by a processor of an electronic device, the electronic device can execute the method described in the first aspect.
本申请实施例采用的上述至少一个技术方案能够达到以下有益效果:At least one of the above technical solutions adopted in the embodiments of the present application can achieve the following beneficial effects:
通过对数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录进行分析,确定业务数据表的处理周期及在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息,进一步基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和确定出的处理周期、在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及指定统计周期,确定业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,最后基于冷热数据分界时间点识别业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据,整个过程无需人工参与,实现了冷热数据的自动化识别,相较于现有技术中通过人工统计和识别冷热数据的方式,准确率和效率更高;并且,对冷热数据的识别是以业务数据表为单位进行,基于业务数据表的冷热数据分界时间点来识别冷热数据,相较于对数据仓库中的业务数据逐个进行统计和识别的方式,效率更高。By analyzing the historical access records of the business data table in the data warehouse within the specified statistical period, the processing period of the business data table and the access frequency information within the specified statistical period are determined, and further based on the pre-established cold and hot data identification model and the determined processing period, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period and the specified statistical period, the cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period is determined. Finally, the cold data and hot data in the business data table are identified based on the cold and hot data demarcation time point. The whole process does not require human participation, and the automatic identification of cold and hot data is realized. Compared with the method of manually counting and identifying cold and hot data in the prior art, the accuracy and efficiency are higher; and the identification of cold and hot data is carried out in units of business data tables, and cold and hot data are identified based on the cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table. Compared with the method of counting and identifying business data in the data warehouse one by one, the efficiency is higher.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
此处所说明的附图用来提供对本申请的进一步理解,构成本申请的一部分,本申请的示意性实施例及其说明用于解释本申请,并不构成对本申请的不当限定。在附图中:The drawings described herein are used to provide a further understanding of the present application and constitute a part of the present application. The illustrative embodiments of the present application and their descriptions are used to explain the present application and do not constitute an improper limitation on the present application. In the drawings:
图1为本申请实施例提供的一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法的流程图;FIG1 is a flow chart of a method for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例提供的另一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法的流程图;FIG2 is a flow chart of another method for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图3为本申请实施例提供的一种数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的访问频率分布示意图;3 is a schematic diagram of access frequency distribution of a business data table in a data warehouse within a specified statistical period provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请实施例提供的一种冷热数据识别模型的训练方法的流程图;FIG4 is a flow chart of a method for training a cold and hot data recognition model provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图5为本申请实施例提供的一种电子设备的结构示意图;FIG5 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an electronic device provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图6为本申请实施例提供的一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别装置的结构示意图。FIG6 is a schematic diagram of the structure of a cold and hot data identification device for a data warehouse provided in an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
为使本申请的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本申请具体实施例及相应的附图对本申请技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述。显然,所描述的实施例仅是本申请一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本申请中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本申请保护的范围。In order to make the purpose, technical solution and advantages of the present application clearer, the technical solution of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in combination with the specific embodiments of the present application and the corresponding drawings. Obviously, the described embodiments are only part of the embodiments of the present application, not all of the embodiments. Based on the embodiments in the present application, all other embodiments obtained by ordinary technicians in this field without making creative work are within the scope of protection of this application.
以下结合附图,详细说明本申请各实施例提供的技术方案。The technical solutions provided by various embodiments of the present application are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
实施例1Example 1
请参考图1,本申请实施例提供一种数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法,该方法可由电子设备执行,例如,电子设备可以为服务器。如图1所示,该方法包括以下步骤:Referring to FIG1 , an embodiment of the present application provides a method for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse, which can be executed by an electronic device, for example, the electronic device can be a server. As shown in FIG1 , the method includes the following steps:
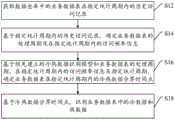
S12,获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录。S12, obtaining historical access records of the business data table in the data warehouse within a specified statistical period.
数据仓库中的业务数据按照所属的业务的业务信息分散存储于不同的业务数据表中。The business data in the data warehouse is stored in different business data tables according to the business information of the business to which it belongs.
指定统计周期可以是当前时刻之前的任意历史时间段。实际应用中,指定统计周期可以是当前时刻之前的某一天,如10月1日、上周一等;或者,指定统计周期也可以是当前时刻之前的某一时间段,如昨天上午等;或者,指定统计周期也可以是当前时刻之前的某一个月,如1月、2月等;或者,指定统计周期还可以是当前时刻之前的某几年,如2017年至2019年等。The specified statistical period can be any historical time period before the current time. In actual applications, the specified statistical period can be a day before the current time, such as October 1, last Monday, etc.; or, the specified statistical period can also be a time period before the current time, such as yesterday morning, etc.; or, the specified statistical period can also be a month before the current time, such as January, February, etc.; or, the specified statistical period can also be a few years before the current time, such as 2017 to 2019, etc.
需要说明的是,指定统计周期的粒度可以根据实际业务需要自定义设置,本申请实施例对此不作具体限定。例如,对于时效性要求较高的业务对应的业务数据表,其指定统计周期可以为一个月;对于时效性要求不高的业务对应的业务数据表,其指定统计周期可以为一年,等等。It should be noted that the granularity of the specified statistical period can be customized according to actual business needs, and the embodiments of the present application do not specifically limit this. For example, for a business data table corresponding to a business with high timeliness requirements, the specified statistical period can be one month; for a business data table corresponding to a business with low timeliness requirements, the specified statistical period can be one year, and so on.
在对数据仓库进行访问的过程中通常会产生访问日志,通过对访问日志进行分类整合,可以获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录。其中,对数据仓库的访问操作可以例如包括但不限于:写入数据、删除数据、修改数据等类型的操作。历史访问记录可以包括但不限于:对业务数据表执行的每次访问操作的类型、时间点等。Access logs are usually generated during the access to the data warehouse. By classifying and integrating the access logs, historical access records of the business data tables in the data warehouse within a specified statistical period can be obtained. Among them, the access operations to the data warehouse may include, but are not limited to, operations such as writing data, deleting data, and modifying data. Historical access records may include, but are not limited to, the type and time point of each access operation performed on the business data table.
S14,基于指定统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定业务数据表的处理周期及在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息。S14, based on the historical access records in the specified statistical period, determine the processing period of the business data table and the access frequency information in the specified statistical period.
通过对业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录进行统计和分析,可以确定业务数据的处理周期及在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息。By collecting statistics and analyzing the historical access records of the business data table within a specified statistical period, the processing period of the business data and the access frequency information within the specified statistical period can be determined.
本申请实施例中,业务数据表的指定周期用于表征对业务数据表中的业务数据进行处理的时间规律。考虑到对业务数据表中的业务数据进行处理的时间规律通常与对业务数据表的数据写入操作是一致的,例如,若对业务数据表通常是按照日为单位进行数据写入的,那么,业务数据表的处理周期也通常是以日为单位;若对业务数据表通常是按照月为单位进行数据写入的,那么,业务数据表的处理周期也通常是以月为单位,等等。基于此,可通过在指定统计周期内对业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点来确定业务数据表的处理周期。In the embodiment of the present application, the specified period of the business data table is used to characterize the time regularity of processing the business data in the business data table. Considering that the time regularity of processing the business data in the business data table is usually consistent with the data writing operation to the business data table, for example, if the business data table is usually written with data in units of days, then the processing period of the business data table is also usually in units of days; if the business data table is usually written with data in units of months, then the processing period of the business data table is also usually in units of months, and so on. Based on this, the processing period of the business data table can be determined by the time point of the write operation performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period.
在可选的方案中,具体来说,确定业务数据表的处理周期可以包括以下步骤:In an optional solution, specifically, determining the processing cycle of the business data table may include the following steps:
首先,可基于指定统计周期内对业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点,分别确定对业务数据表执行的最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期。First, based on the time points of the write operations performed on the business data table within a specified statistical period, the average write cycles between the last write operation performed on the business data table and the other write operations can be determined respectively.
更为具体地,上述最后一次写入操作与其他写入操作之间的平均写入周期可通过以下公式(1)确定。More specifically, the average write cycle between the last write operation and other write operations can be determined by the following formula (1).
其中,Ti表示上述最后一次写入操作与第i次写入操作之间的平均写入周期;An表示上述最后一次写入操作的时间点;Ai表示上述第i次写入操作的时间点;n表示在上述指定统计周期内对业务数据表执行的写入操作的次数。Among them,Ti represents the average write cycle between the last write operation and the i-th write operation;An represents the time point of the last write operation;Ai represents the time point of the i-th write operation; n represents the number of write operations performed on the business data table within the above specified statistical period.
接着,基于最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期,确定业务数据表的平均写入周期。Next, based on the average write cycles between the last write operation and the other write operations, the average write cycle of the service data table is determined.
更为具体地,业务数据表的平均写入周期可通过以下公式(2)确定。More specifically, the average write cycle of the service data table can be determined by the following formula (2).
其中,TableCycle表示上述业务数据表的平均写入周期。Among them, TableCycle represents the average write cycle of the above business data table.
最后,基于数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的预设对应关系以及业务数据表的平均写入周期,确定业务数据表的处理周期。Finally, based on the preset corresponding relationship between the average writing cycle and the processing cycle of the data table and the average writing cycle of the business data table, the processing cycle of the business data table is determined.
例如,表1示出了数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的一种预设对应关系示例。For example, Table 1 shows an example of a preset corresponding relationship between an average writing cycle and a processing cycle of a data table.
表1Table 1
需要说明的是,由于不同业务的业务属性不同,对应的业务数据表的平均写入周期也不同,因而数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的预设对应关系可以是根据实际业务需要自定义设置的。例如,对于电信行业的数据仓库中的业务数据表的处理,对业务数据的时效性要求不高,因而可将写入周期小于12小时的业务数据表的处理周期确定为小时,将写入周期在12-24小时的业务数据表的处理周期确定为天,等等。又如,对于金融行业、证券行业等,由于业务数据的时效性要求较高,因而可将写入周期在1-2小时的业务数据表的处理周期确定为小时,将写入周期大于2小时的业务数据表的处理周期确定为天,等等。It should be noted that, due to the different business attributes of different businesses, the average write cycle of the corresponding business data table is also different, so the preset correspondence between the average write cycle of the data table and the processing cycle can be customized according to actual business needs. For example, for the processing of business data tables in the data warehouse of the telecommunications industry, the timeliness requirements for business data are not high, so the processing cycle of business data tables with a write cycle of less than 12 hours can be determined as hours, and the processing cycle of business data tables with a write cycle of 12-24 hours can be determined as days, etc. For another example, for the financial industry, securities industry, etc., due to the high timeliness requirements for business data, the processing cycle of business data tables with a write cycle of 1-2 hours can be determined as hours, and the processing cycle of business data tables with a write cycle of more than 2 hours can be determined as days, etc.
为了使得到的业务数据表的处理周期更准确,以进一步提高后续对业务数据表中冷热数据的识别结果的准确性,本申请实施例中,还可以通过对大量样本数据表的平均写入周期及处理周期进行学习和训练,来得到上述数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的对应关系。具体来说,在通过上述步骤S14确定业务数据表的处理周期之前,本申请实施例提供的数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法还可以包括:首先,获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及处理周期;接着,基于统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表的平均写入周期;最后,以样本数据表的平均写入周期作为训练样本、以样本数据表的处理周期作为训练样本的标签,基于预设的第二分类算法进行训练,以得到上述数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的对应关系。In order to make the processing cycle of the obtained business data table more accurate, so as to further improve the accuracy of the subsequent identification results of hot and cold data in the business data table, in the embodiment of the present application, the average write cycle and processing cycle of a large number of sample data tables can also be studied and trained to obtain the correspondence between the average write cycle and the processing cycle of the above data table. Specifically, before determining the processing cycle of the business data table through the above step S14, the hot and cold data identification method of the data warehouse provided by the embodiment of the present application can also include: first, obtaining the historical access records and processing cycles of the sample data table within the statistical period; then, based on the historical access records within the statistical period, determining the average write cycle of the sample data table; finally, using the average write cycle of the sample data table as a training sample and the processing cycle of the sample data table as a label of the training sample, training is performed based on the preset second classification algorithm to obtain the correspondence between the average write cycle and the processing cycle of the above data table.
其中,样本数据表可以是数据仓库中已知处理周期的业务数据表。预设的第二分类算法可以例如包括以下一种或多种算法的组合:决策树算法、贝叶斯算法、人工神经网络算法、k-近邻算法(k-NearestNeighbor,KNN)等。The sample data table may be a business data table with a known processing cycle in a data warehouse. The preset second classification algorithm may include, for example, a combination of one or more of the following algorithms: decision tree algorithm, Bayesian algorithm, artificial neural network algorithm, k-nearest neighbor algorithm (kNN), etc.
需要说明的是,基于样本数据表的历史访问记录确定样本数据表的平均写入周期的具体实施方式,与上述步骤S14中确定业务数据表的平均写入周期的具体实施方式大致相同,具体请参见上述步骤S14中确定业务数据表的平均写入周期的实现过程,在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the specific implementation method of determining the average write period of the sample data table based on the historical access records of the sample data table is roughly the same as the specific implementation method of determining the average write period of the business data table in the above step S14. For details, please refer to the implementation process of determining the average write period of the business data table in the above step S14, which will not be repeated here.
业务数据表在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息用于表征在指定周期内对业务数据表的访问频率。业务数据表在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息具体可以包括但不限业务数据表在指定统计周期内的总访问频率以及在指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率。其中,子周期的粒度可根据指定统计周期的粒度及实际业务需求自定义设置,本申请实施例对此不作具体限定。例如,若指定统计周期为一年,则子周期可以为一个月;若指定统计周期为一个月,则子周期可以为一天,等等。The access frequency information of the business data table within the specified statistical period is used to characterize the access frequency to the business data table within the specified period. The access frequency information of the business data table within the specified statistical period may specifically include but is not limited to the total access frequency of the business data table within the specified statistical period and the access frequency within each sub-period of the specified statistical period. Among them, the granularity of the sub-period can be customized according to the granularity of the specified statistical period and actual business needs, and the embodiments of the present application do not specifically limit this. For example, if the specified statistical period is one year, the sub-period can be one month; if the specified statistical period is one month, the sub-period can be one day, and so on.
具体而言,业务数据表在指定统计周期内的总访问频率可基于在指定统计周期内对业务数据表的访问次数及指定统计周期的时长确定;业务数据表在子周期内的访问频率则可基于在子周期内对业务数据表的访问次数及该子周期的时长确定。Specifically, the total access frequency of the business data table within a specified statistical period can be determined based on the number of visits to the business data table within the specified statistical period and the duration of the specified statistical period; the access frequency of the business data table within a sub-period can be determined based on the number of visits to the business data table within the sub-period and the duration of the sub-period.
S16,基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和业务数据表的处理周期、在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及指定统计周期,确定业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。S16, based on the pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period and the specified statistical period, determine the hot and cold data boundary time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period.
本申请实施例中,冷热数据识别模型是预先建立的用于识别冷热数据的模型。可选地,冷热数据识别模型可以是基于样本数据表的存储周期、在统计周期内的访问频率以及统计周期作为训练样本,以样本数据表的冷热数据比例作为标签,基于预设第一分类算法进行训练得到。其中,第一分类算法可以例如包括但不限于以下一种或多种算法的组合:决策树算法、贝叶斯算法、人工神经网络算法、k-近邻算法(k-NearestNeighbor,KNN)等。In the embodiment of the present application, the hot and cold data identification model is a pre-established model for identifying hot and cold data. Optionally, the hot and cold data identification model can be based on the storage period of the sample data table, the access frequency within the statistical period, and the statistical period as training samples, with the hot and cold data ratio of the sample data table as labels, and trained based on a preset first classification algorithm. Among them, the first classification algorithm can, for example, include but is not limited to a combination of one or more of the following algorithms: decision tree algorithm, Bayesian algorithm, artificial neural network algorithm, k-nearest neighbor algorithm (k-NearestNeighbor, KNN), etc.
相应地,可将确定出的业务数据表的处理周期、在指定统计周期内的访问频率及指定统计周期输入到上述冷热数据识别模型中,以得到该业务数据表的冷热数据比例,进一步可基于冷热数据比例确定该业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热分界时间点。其中,冷热数据分界时间点是指用于划分冷数据和热数据的时间点。Accordingly, the determined processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency in the specified statistical period, and the specified statistical period can be input into the above-mentioned hot and cold data identification model to obtain the hot and cold data ratio of the business data table, and further based on the hot and cold data ratio, the hot and cold demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period can be determined. The hot and cold data demarcation time point refers to the time point used to divide cold data and hot data.
需要说明的是,训练得到的上述冷热数据识别模型的过程将在下文图4所示的实施例中进行详细说明,此处不再展开。It should be noted that the process of training the above-mentioned cold and hot data recognition model will be described in detail in the embodiment shown in FIG4 below, which will not be expanded here.
S18,基于冷热数据分界时间点,识别业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据。S18, identifying the cold data and hot data in the business data table based on the cold and hot data demarcation time point.
在确定出业务数据表的冷热数据分界时间点后,可根据冷热数据分界时间点对业务数据表中的业务数据进行划分,得到冷数据和热数据。例如,指定统计周期为2017年1月至2019年12月,基于上述步骤确定出的冷热数据分界时间点为2017年10月,由此,可将业务数据表中产生时间位于2017年1月至2017年10月的业务数据确定为冷数据,而将产生时间位于2017年11月至2019年12月的业务数据确定为热数据。After determining the time point of the cold and hot data demarcation of the business data table, the business data in the business data table can be divided according to the time point of the cold and hot data demarcation to obtain cold data and hot data. For example, if the statistical period is specified to be from January 2017 to December 2019, and the time point of the cold and hot data demarcation determined based on the above steps is October 2017, the business data in the business data table generated between January 2017 and October 2017 can be determined as cold data, and the business data generated between November 2017 and December 2019 can be determined as hot data.
本申请实施例提供的数据仓库的冷热数据识别方法,通过对数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录进行分析,确定业务数据表的处理周期及在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息,进一步基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和确定出的处理周期、在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及指定统计周期,确定业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,最后基于冷热数据分界时间点识别业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据,整个过程无需人工参与,实现了冷热数据的自动化识别,相较于现有技术中通过人工统计和识别冷热数据的方式,准确率和效率更高;并且,对冷热数据的识别是以业务数据表为单位进行,基于业务数据表的冷热数据分界时间点来识别冷热数据,相较于对数据仓库中的业务数据逐个进行统计和识别的方式,效率更高。The method for identifying hot and cold data in a data warehouse provided in an embodiment of the present application analyzes historical access records of a business data table in a data warehouse within a specified statistical period to determine a processing period of the business data table and access frequency information within the specified statistical period, further determines a cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period based on a pre-established cold and hot data identification model and the determined processing period, access frequency information within the specified statistical period, and the specified statistical period, and finally identifies cold data and hot data in the business data table based on the cold and hot data demarcation time point. The entire process does not require human intervention, thereby realizing automatic identification of cold and hot data. Compared with the method of manually counting and identifying cold and hot data in the prior art, the method has higher accuracy and efficiency. Moreover, the identification of cold and hot data is performed in units of business data tables, and cold and hot data are identified based on the cold and hot data demarcation time points of the business data tables. Compared with the method of counting and identifying business data in the data warehouse one by one, the method has higher efficiency.
为了使本领域技术人员更加理解本申请实施例提供的技术方案,下面对本申请实施例提供的技术方案进行详细说明。In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present application, the technical solutions provided by the embodiments of the present application are described in detail below.
对于上述步骤S16,在一种可选的方案中,如图2所示,上述步骤S16可以包括:For the above step S16, in an optional solution, as shown in FIG2 , the above step S16 may include:
S161,将业务数据表的处理周期、在指定统计周期内的访问频率及指定统计周期输入到预先建立的冷热数据识别模型,以得到业务数据表的冷热数据比例。S161, inputting the processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency within the specified statistical period, and the specified statistical period into a pre-established cold and hot data identification model to obtain the cold and hot data ratio of the business data table.
S162,基于业务数据表的冷热数据比例及在指定统计周期内的总访问频率,确定与业务数据表相匹配的访问频率阈值。S162: Determine an access frequency threshold that matches the business data table based on the ratio of hot and cold data in the business data table and the total access frequency in a specified statistical period.
由于不同业务数据表存储的业务数据不同,因而对不同业务数据表中的业务数据的访问频率存在差异,基于此,可针对不同的业务数据表确定不同的访问频率阈值。在可选的方案中,可将业务数据表的冷热数据比例与其在指定统计周期内的总访问频率的乘积,作为与业务数据表相匹配得到访问频率阈值。Since different business data tables store different business data, the access frequencies to the business data in different business data tables are different. Based on this, different access frequency thresholds can be determined for different business data tables. In an optional solution, the product of the ratio of hot and cold data in a business data table and its total access frequency in a specified statistical period can be used as the access frequency threshold to match the business data table.
例如,若某业务数据表的冷热数据比例为20%(即冷数据占20%),且该业务数据表在指定统计周期内的总访问频率为1380次,则可确定该业务数据表的访问频率阈值为1380×20%=276次。For example, if the ratio of hot and cold data in a business data table is 20% (i.e., cold data accounts for 20%), and the total access frequency of the business data table in a specified statistical period is 1380 times, then the access frequency threshold of the business data table can be determined to be 1380×20%=276 times.
S163,基于访问频率阈值和业务数据表在指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率,确定业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。S163, determining a cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period of the specified statistical period.
通常情况下,数据仓库中的热数据通常被频繁访问,而冷数据则较少被访问,因此,在可选的方案中,可以基于业务数据表在指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从指定统计周期的起始时间点起至该子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;接着,可以从指定统计周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到该访问频率阈值的子周期,并将该子周期确定为业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Typically, hot data in a data warehouse is frequently accessed, while cold data is less frequently accessed. Therefore, in an optional solution, the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period can be determined based on the total access frequency of the business data table within a specified statistical period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to a sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period; then, a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold can be selected from the specified statistical period, and the sub-period can be determined as the boundary time point for hot and cold data in the business data table within the specified statistical period.
例如,以图3所示的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的访问频率信息、且相匹配的访问频率阈值为276次为例,通过上述步骤S163可以确定该业务数据表中对应的累计访问频率达到该访问频率阈值的子周期为17年10月,因此,可将该子周期作为业务数据表在指定统计周期(即17年1月至19年12月)的冷热数据分界时间点。进一步地,可确定该业务数据表中写入时间点位于17年1月至17年10之间的业务数据为冷数据,而写入时间点位于17年11月至19年12月之间的业务数据为热数据。For example, taking the access frequency information of the business data table shown in FIG. 3 in the specified statistical period, and the matching access frequency threshold of 276 times as an example, through the above step S163, it can be determined that the sub-period in which the corresponding cumulative access frequency in the business data table reaches the access frequency threshold is October 2017. Therefore, the sub-period can be used as the cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period (i.e., January 2017 to December 2019). Further, it can be determined that the business data in the business data table with a writing time point between January 2017 and October 2017 is cold data, and the business data with a writing time point between November 2017 and December 2019 is hot data.
可以理解,通过上述方案,基于热数据通常被频繁访问而冷数据则较少被访问这一规律,基于业务数据表的冷热数据比例及在指定统计周期中的总访问频率确定与该业务数据表匹配的访问频率阈值,进而基于该访问频率阈值及该业务数据表在各个子周期内的访问频率来确定该业务数据表的冷热数据分界时间点,实现简单、且效率高。It can be understood that through the above scheme, based on the rule that hot data is usually frequently accessed while cold data is less frequently accessed, the access frequency threshold matching the business data table is determined based on the ratio of hot and cold data in the business data table and the total access frequency in a specified statistical period, and then the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table is determined based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period, which is simple to implement and efficient.
考虑到在实际识别过程中基于冷热数据识别模型得到的冷热数据比例与实际冷热数据比例之间可能存在一定误差,为了更为精准的确定冷热数据分界时间点,在另一种可选的方案中,可以考虑冷热数据比例的上下浮动。具体来说,在从指定统计周期中选取出对应的累计访问频率达到该访问频率阈值的子周期后,可将选取出的子周期作为候选子周期。接着,确定与候选子周期相邻的各个子周期对应的累计访问频率与该候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值以及与访问频率阈值之间的差值。进一步地,从与候选子周期相邻的各个子周期中,选取与候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值最小、且与访问频率阈值之间的差值位于预设范围内的子周期。最后,基于选取出的子周期确定业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Considering that there may be a certain error between the ratio of hot and cold data obtained based on the hot and cold data recognition model and the actual ratio of hot and cold data in the actual identification process, in order to more accurately determine the time point of the cold and hot data demarcation, in another optional scheme, the up and down fluctuation of the ratio of hot and cold data can be considered. Specifically, after selecting the sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold from the specified statistical period, the selected sub-period can be used as a candidate sub-period. Next, determine the difference between the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period and the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the candidate sub-period and the difference with the access frequency threshold. Further, from each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period, select the sub-period whose cumulative access frequency corresponding to the candidate sub-period is the smallest and whose difference with the access frequency threshold is within a preset range. Finally, determine the time point of the hot and cold data demarcation of the business data table within the specified statistical period based on the selected sub-period.
更为具体地,可基于业务数据表在各个子周期内的访问频率及各个子周期的时间先后顺序,生成各个子周期对应的数组,即a[0]至a[n],子周期对应的数组用于存储业务数据表在该子周期内的访问频率。接着,计算该候选子周期对应的累计访问频率si在指定统计周期内的总访问频率S中的比例p,即p=s/S,其中,si=a[0]+a[1]+a[2]+……+a[i],S=a[0]+a[1]+a[2]+……+a[n],i<n。进一步地,假设冷热数据比例的误差为c%,若p>(50%-c%),则可确定下标i-1为右界限,即i=r;若p>(50%+c%),则可确定下标i-1为左界限,即i=l。对数组中r至l个元素中相邻元素取查找,确定最大差值的元素对应的下标(记为k)。最后,通过以下公式(3)进行计算,将下标k+1对应的子周期作为业务数据表在指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。More specifically, based on the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period and the time sequence of each sub-period, an array corresponding to each sub-period, i.e., a[0] to a[n], can be generated. The array corresponding to the sub-period is used to store the access frequency of the business data table in the sub-period. Next, the proportion p of the cumulative access frequencysi corresponding to the candidate sub-period in the total access frequency S in the specified statistical period is calculated, i.e., p=s/S, wheresi =a[0]+a[1]+a[2]+…+a[i], S=a[0]+a[1]+a[2]+…+a[n], i<n. Further, assuming that the error of the ratio of cold and hot data is c%, if p>(50%-c%), then the subscript i-1 can be determined as the right limit, i.e., i=r; if p>(50%+c%), then the subscript i-1 can be determined as the left limit, i.e., i=l. Search for adjacent elements from r to l in the array and determine the subscript corresponding to the element with the largest difference (denoted as k). Finally, calculate using the following formula (3) and use the subperiod corresponding to subscript k+1 as the boundary time point between hot and cold data in the business data table within the specified statistical period.
a[k]-a[k+1]=Max((a[r]-a[r+1]),((a[r+1]-a[r+2]),...,(a[l-1]-a[l]))(3)a[k]-a[k+1]=Max((a[r]-a[r+1]),((a[r+1]-a[r+2]),...,( a[l-1]-a[l]))(3)
可以理解,通过上述方案,在确定冷热数据分界时间点时,考虑了基于冷热数据识别模型得到的业务数据表的冷热数据比例与实际比例之间的误差,进而得到的冷热数据分界时间点更准确,由此,基于该冷热数据分界时间点得到的冷热数据识别结果也更准确、可靠。It can be understood that through the above scheme, when determining the cold and hot data demarcation time point, the error between the cold and hot data ratio of the business data table obtained based on the cold and hot data identification model and the actual ratio is taken into account, so that the obtained cold and hot data demarcation time point is more accurate. Therefore, the cold and hot data identification result obtained based on the cold and hot data demarcation time point is also more accurate and reliable.
对于上述步骤S161中的冷热数据识别模型,本申请实施例还包括对冷热数据识别模型的训练方法。Regarding the hot and cold data recognition model in the above step S161, the embodiment of the present application also includes a training method for the hot and cold data recognition model.
值得说明的是,对上述冷热数据识别模型的训练是基于从数据仓库获取的大量样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的访问频率信息以及统计周期预先进行的,后续在对数据仓库中的业务数据表进行冷热数据识别的过程中,无需每次对上述冷热数据识别模型进行训练,或者,可以周期性地从数据仓库新采集的大量样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的访问频率信息以及统计周期对上述冷热数据识别模型进行更新,以提升上述冷热数据识别模型的准确率和可信度。其中,上述大量样本数据表可以是已知数据冷热属性的业务数据表。It is worth noting that the training of the above-mentioned hot and cold data identification model is based on the processing cycle of a large number of sample data tables obtained from the data warehouse, the access frequency information within the statistical cycle, and the statistical cycle in advance. In the subsequent process of cold and hot data identification of business data tables in the data warehouse, it is not necessary to train the above-mentioned hot and cold data identification model every time, or the above-mentioned hot and cold data identification model can be periodically updated from the processing cycle of a large number of sample data tables newly collected from the data warehouse, the access frequency information within the statistical cycle, and the statistical cycle to improve the accuracy and credibility of the above-mentioned hot and cold data identification model. Among them, the above-mentioned large number of sample data tables can be business data tables with known data hot and cold attributes.
具体来说,如图4所示,对上述冷热数据识别模型的训练方法可以包括以下步骤:Specifically, as shown in FIG4 , the training method for the above-mentioned hot and cold data recognition model may include the following steps:
S42,获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及冷热数据比例。S42, obtaining the historical access records and the ratio of hot and cold data of the sample data table within the statistical period.
S44,基于获取的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表的处理周期及在统计周期内的总访问频率。S44, based on the acquired historical access records, determine the processing period of the sample data table and the total access frequency within the statistical period.
需要说明的是,基于样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表的处理周期与上述步骤S14中确定业务数据表的处理周期的具体实施方式类似,具体可参见对上述步骤S14的描述,在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the specific implementation method of determining the processing cycle of the sample data table based on the historical access records of the sample data table within the statistical period is similar to the specific implementation method of determining the processing cycle of the business data table in the above step S14. For details, please refer to the description of the above step S14, which will not be repeated here.
同样地,基于样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表在统计周期内的总访问频率的具体实施方式,与上述步骤S14中确定业务数据表在指定统计周期内的总访问频率的具体实施方式类似,具体可参见对上述步骤S14的描述,在此不再赘述。Similarly, based on the historical access records of the sample data table during the statistical period, the specific implementation method of determining the total access frequency of the sample data table during the statistical period is similar to the specific implementation method of determining the total access frequency of the business data table during the specified statistical period in the above step S14. For details, please refer to the description of the above step S14, which will not be repeated here.
另外,不同的样本数据表可具有不同的统计周期,具体可根据样本数据表对应的业务自定义设置。为了进一步提升训练得到的冷热数据识别模型的准确率和可靠性,样本数据表可以采用与业务数据表对应相同业务的数据表。In addition, different sample data tables can have different statistical periods, which can be customized according to the business corresponding to the sample data table. In order to further improve the accuracy and reliability of the trained cold and hot data recognition model, the sample data table can use a data table corresponding to the same business as the business data table.
还需要说明的是,在实际应用中,在基于训练样本对冷热数据识别模型进行训练时,可以将样本数据以表结构形式表示,其中,表结构形式包括字段属性名称及字段描述。进一步地,为了对不同的样本数据进行区分,还可以在表结构中增加用于描述样本数据表的名称的字段。例如,表2示出了一种训练样本的表结构。It should also be noted that, in practical applications, when training the hot and cold data recognition model based on training samples, the sample data can be represented in a table structure, wherein the table structure includes field attribute names and field descriptions. Furthermore, in order to distinguish different sample data, a field for describing the name of the sample data table can be added to the table structure. For example, Table 2 shows a table structure of a training sample.
表2Table 2
S46,以样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的总访问频率及统计周期作为训练样本,以样本数据表在统计周期内的冷热数据比例作为训练样本的标签,基于预设的第一分类算法进行训练,以得到冷热数据识别模型。S46, using the processing period of the sample data table, the total access frequency within the statistical period and the statistical period as training samples, using the ratio of hot and cold data in the sample data table within the statistical period as labels of the training samples, and training based on the preset first classification algorithm to obtain a hot and cold data recognition model.
本申请实施例中的第一分类算法可以例如包括以下一种或多种算法的组合:决策树算法、贝叶斯算法、人工神经网络算法、k-近邻算法(k-NearestNeighbor,KNN)等,本申请实施例对第一分类算法不做具体限定。The first classification algorithm in the embodiment of the present application may, for example, include a combination of one or more of the following algorithms: decision tree algorithm, Bayesian algorithm, artificial neural network algorithm, k-nearest neighbor algorithm (k-NearestNeighbor, KNN), etc. The embodiment of the present application does not specifically limit the first classification algorithm.
可以理解,由于数据表的处理周期、访问频率、统计周期以及冷热数据比例之间存在一定的关联关系,通过以大量样本数据表的处理周期、访问频率及统计周期作为训练样本,以样本数据表的冷热数据比例作为标签,通过相应的分类算法进行训练以得到冷热数据识别模型,使得得到的冷热数据识别模型能够准确地识别不同业务数据表的处理周期、访问频率及统计周期与冷热数据比例之间的关系,进而基于该冷热数据识别模型可以有效、准确地获取业务数据表的冷热数据比例,进而能够有效、准确地提取冷热数据分界时间点,以得到对业务数据表中冷热数据的准确识别结果。It can be understood that since there is a certain correlation between the processing cycle, access frequency, statistical cycle and hot and cold data ratio of a data table, by taking the processing cycle, access frequency and statistical cycle of a large number of sample data tables as training samples and the hot and cold data ratio of the sample data tables as labels, training is performed through the corresponding classification algorithm to obtain a hot and cold data recognition model, so that the obtained hot and cold data recognition model can accurately identify the relationship between the processing cycle, access frequency and statistical cycle of different business data tables and the hot and cold data ratio, and then based on the hot and cold data recognition model, the hot and cold data ratio of the business data table can be effectively and accurately obtained, and then the hot and cold data boundary time point can be effectively and accurately extracted to obtain accurate recognition results of cold and hot data in the business data table.
上述对本说明书特定实施例进行了描述。其它实施例在所附权利要求书的范围内。在一些情况下,在权利要求书中记载的动作或步骤可以按照不同于实施例中的顺序来执行并且仍然可以实现期望的结果。另外,在附图中描绘的过程不一定要求示出的特定顺序或者连续顺序才能实现期望的结果。在某些实施方式中,多任务处理和并行处理也是可以的或者可能是有利的。The above is a description of a specific embodiment of the specification. Other embodiments are within the scope of the appended claims. In some cases, the actions or steps recorded in the claims can be performed in an order different from that in the embodiments and still achieve the desired results. In addition, the processes depicted in the drawings do not necessarily require the specific order or continuous order shown to achieve the desired results. In some embodiments, multitasking and parallel processing are also possible or may be advantageous.
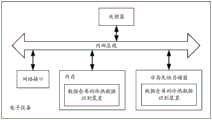
图5是本申请的一个实施例电子设备的结构示意图。请参考图5,在硬件层面,该电子设备包括处理器,可选地还包括内部总线、网络接口、存储器。其中,存储器可能包含内存,例如高速随机存取存储器(Random-Access Memory,RAM),也可能还包括非易失性存储器(non-volatile memory),例如至少1个磁盘存储器等。当然,该电子设备还可能包括其他业务所需要的硬件。FIG5 is a schematic diagram of the structure of an electronic device of an embodiment of the present application. Please refer to FIG5. At the hardware level, the electronic device includes a processor, and optionally also includes an internal bus, a network interface, and a memory. Among them, the memory may include a memory, such as a high-speed random access memory (Random-Access Memory, RAM), and may also include a non-volatile memory (non-volatile memory), such as at least one disk storage, etc. Of course, the electronic device may also include hardware required for other services.
处理器、网络接口和存储器可以通过内部总线相互连接,该内部总线可以是ISA(Industry Standard Architecture,工业标准体系结构)总线、PCI(PeripheralComponent Interconnect,外设部件互连标准)总线或EISA(Extended Industry StandardArchitecture,扩展工业标准结构)总线等。所述总线可以分为地址总线、数据总线、控制总线等。为便于表示,图5中仅用一个双向箭头表示,但并不表示仅有一根总线或一种类型的总线。The processor, the network interface and the memory may be interconnected via an internal bus, which may be an ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) bus, a PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) bus or an EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) bus, etc. The bus may be divided into an address bus, a data bus, a control bus, etc. For ease of representation, FIG5 only uses one bidirectional arrow, but does not mean that there is only one bus or one type of bus.
存储器,用于存放程序。具体地,程序可以包括程序代码,所述程序代码包括计算机操作指令。存储器可以包括内存和非易失性存储器,并向处理器提供指令和数据。The memory is used to store the program. Specifically, the program may include a program code, and the program code includes a computer operation instruction. The memory may include a memory and a non-volatile memory, and provides instructions and data to the processor.
处理器从非易失性存储器中读取对应的计算机程序到内存中然后运行,在逻辑层面上形成数据仓库的冷热数据识别装置。处理器,执行存储器所存放的程序,并具体用于执行以下操作:The processor reads the corresponding computer program from the non-volatile memory into the memory and then runs it, forming a cold and hot data identification device of the data warehouse at the logical level. The processor executes the program stored in the memory and is specifically used to perform the following operations:
获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录;Obtain the historical access records of the business data tables in the data warehouse within the specified statistical period;
基于所述指定统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期及在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息;Based on the historical access records within the specified statistical period, determining the processing period of the business data table and the access frequency information within the specified statistical period;
基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述指定统计周期,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点;Based on the pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period and the specified statistical period, determine the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period;
基于所述冷热数据分界时间点,识别所述业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据。Based on the hot and cold data demarcation time point, cold data and hot data in the business data table are identified.
上述如本申请图1所示实施例揭示的数据仓库的冷热数据识别装置执行的方法可以应用于处理器中,或者由处理器实现。处理器可能是一种集成电路芯片,具有信号的处理能力。在实现过程中,上述方法的各步骤可以通过处理器中的硬件的集成逻辑电路或者软件形式的指令完成。上述的处理器可以是通用处理器,包括中央处理器(CentralProcessing Unit,CPU)、网络处理器(Network Processor,NP)等;还可以是数字信号处理器(Digital Signal Processor,DSP)、专用集成电路(Application Specific IntegratedCircuit,ASIC)、现场可编程门阵列(Field-Programmable Gate Array,FPGA)或者其他可编程逻辑器件、分立门或者晶体管逻辑器件、分立硬件组件。可以实现或者执行本申请实施例中的公开的各方法、步骤及逻辑框图。通用处理器可以是微处理器或者该处理器也可以是任何常规的处理器等。结合本申请实施例所公开的方法的步骤可以直接体现为硬件译码处理器执行完成,或者用译码处理器中的硬件及软件模块组合执行完成。软件模块可以位于随机存储器,闪存、只读存储器,可编程只读存储器或者电可擦写可编程存储器、寄存器等本领域成熟的存储介质中。该存储介质位于存储器,处理器读取存储器中的信息,结合其硬件完成上述方法的步骤。The method performed by the cold and hot data identification device of the data warehouse disclosed in the embodiment shown in FIG. 1 of the present application can be applied to a processor or implemented by a processor. The processor may be an integrated circuit chip with signal processing capabilities. In the implementation process, each step of the above method can be completed by an integrated logic circuit of hardware in the processor or an instruction in the form of software. The above processor can be a general-purpose processor, including a central processing unit (CPU), a network processor (NP), etc.; it can also be a digital signal processor (DSP), an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gates or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components. The methods, steps and logic block diagrams disclosed in the embodiments of the present application can be implemented or executed. The general-purpose processor can be a microprocessor or the processor can also be any conventional processor, etc. The steps of the method disclosed in the embodiments of the present application can be directly embodied as a hardware decoding processor for execution, or a combination of hardware and software modules in the decoding processor for execution. The software module can be located in a mature storage medium in the field such as random access memory, flash memory, read-only memory, programmable read-only memory or electrically erasable programmable memory, register, etc. The storage medium is located in the memory, and the processor reads the information in the memory and completes the steps of the above method in combination with its hardware.
该电子设备还可执行图1的方法,并实现数据仓库的冷热数据识别装置在图1至图4所示实施例的功能,本申请实施例在此不再赘述。The electronic device can also execute the method of Figure 1 and realize the functions of the cold and hot data identification device of the data warehouse in the embodiments shown in Figures 1 to 4, and the embodiments of the present application will not be repeated here.
当然,除了软件实现方式之外,本申请的电子设备并不排除其他实现方式,比如逻辑器件抑或软硬件结合的方式等等,也就是说以下处理流程的执行主体并不限定于各个逻辑单元,也可以是硬件或逻辑器件。Of course, in addition to software implementation methods, the electronic device of the present application does not exclude other implementation methods, such as logic devices or a combination of software and hardware, etc., that is to say, the execution subject of the following processing flow is not limited to each logic unit, but can also be hardware or logic devices.
本申请实施例还提出了一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质存储一个或多个程序,该一个或多个程序包括指令,该指令当被包括多个应用程序的便携式电子设备执行时,能够使该便携式电子设备执行图1所示实施例的方法,并具体用于执行以下操作:The embodiment of the present application further proposes a computer-readable storage medium, which stores one or more programs, and the one or more programs include instructions. When the instructions are executed by a portable electronic device including multiple application programs, the portable electronic device can execute the method of the embodiment shown in FIG. 1, and is specifically used to perform the following operations:
获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录;Obtain the historical access records of the business data tables in the data warehouse within the specified statistical period;
基于所述指定统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期及在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息;Based on the historical access records within the specified statistical period, determining the processing period of the business data table and the access frequency information within the specified statistical period;
基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述指定统计周期,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点;Based on the pre-established hot and cold data identification model and the processing cycle of the business data table, the access frequency information within the specified statistical period and the specified statistical period, determine the hot and cold data demarcation time point of the business data table within the specified statistical period;
基于所述冷热数据分界时间点,识别所述业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据。Based on the hot and cold data demarcation time point, cold data and hot data in the business data table are identified.
图6是本申请的一个实施例数据仓库的冷热数据识别装置的结构示意图。请参考图6,在一种软件实施方式中,数据仓库的冷热数据装置600可包括:FIG6 is a schematic diagram of the structure of a cold and hot data identification device of a data warehouse according to an embodiment of the present application. Referring to FIG6 , in a software implementation, a cold and hot
第一获取模块610,用于获取数据仓库中的业务数据表在指定统计周期内的历史访问记录;The
第一确定模块620,用于基于所述历史访问记录,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期及在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息;A
第二确定模块630,用于基于预先建立的冷热数据识别模型和所述业务数据表的处理周期、在所述指定统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述指定统计周期,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点,其中,所述冷热数据识别模型为基于第一分类算法对样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的访问频率信息及所述统计周期进行训练得到;The
识别模块640,用于基于所述冷热数据分界时间点,识别所述业务数据表中的冷数据和热数据。The
可选地,所述访问频率信息包括总访问频率和在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率;Optionally, the access frequency information includes a total access frequency and an access frequency in each sub-period of the specified statistical period;
所述第二确定模块630具体用于:The second determining
将所述业务数据表的处理周期、所述指定统计周期及在所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率输入到所述冷热数据识别模型,以得到所述业务数据表的冷热数据比例,其中,所述冷热数据识别模型是以样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的总访问频率及统计周期作为训练样本,以所述样本数据表的冷热数据比例作为标签,基于预设的第一分类算法进行训练得到;The processing period of the business data table, the designated statistical period, and the total access frequency within the designated statistical period are input into the hot and cold data identification model to obtain the hot and cold data ratio of the business data table, wherein the hot and cold data identification model is obtained by training based on a preset first classification algorithm using the processing period of the sample data table, the total access frequency within the statistical period, and the statistical period as training samples and the hot and cold data ratio of the sample data table as labels;
基于所述冷热数据比例和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,确定与所述业务数据表相匹配的访问频率阈值;Determine an access frequency threshold matching the business data table based on the cold and hot data ratio and the total access frequency of the business data table in the specified statistical period;
基于所述访问频率阈值和所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期的各个子周期内的访问频率,确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Based on the access frequency threshold and the access frequency of the business data table in each sub-period of the specified statistical period, a cold and hot data demarcation time point of the business data table in the specified statistical period is determined.
可选地,所述第二确定模块630具体用于:Optionally, the second determining
基于所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,所述子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从所述指定统计周期的起始时间点起至所述子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;Based on the total access frequency in the specified statistical period, respectively determine the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period;
从所述指定统计周期的各个子周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到所述访问频率阈值的子周期;From each sub-period of the specified statistical period, select a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold;
将选取出的子周期确定为所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。The selected sub-period is determined as the boundary time point of the cold and hot data of the business data table within the specified statistical period.
可选地,所述第二确定模块630具体用于:Optionally, the second determining
基于所述指定统计周期内的总访问频率,分别确定各个子周期对应的累计访问频率,其中,所述子周期对应的累计访问频率是指从所述指定统计周期的起始时间点起至所述子周期的结束时间点之间的累计访问频率;Based on the total access frequency in the specified statistical period, respectively determine the cumulative access frequency corresponding to each sub-period, wherein the cumulative access frequency corresponding to the sub-period refers to the cumulative access frequency from the start time point of the specified statistical period to the end time point of the sub-period;
从所述指定统计周期的各个子周期中,选取对应的累计访问频率达到所述访问频率阈值的子周期,作为候选子周期;From each sub-period of the specified statistical period, select a sub-period whose corresponding cumulative access frequency reaches the access frequency threshold as a candidate sub-period;
确定与所述候选子周期相邻的各个子周期对应的累计访问频率与所述候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值以及与所述访问频率阈值之间的差值;Determine a difference between the accumulated access frequencies corresponding to each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period and the accumulated access frequency corresponding to the candidate sub-period, and a difference between the accumulated access frequencies and the access frequency threshold;
从与所述候选子周期相邻的各个子周期中,选取与所述候选子周期对应的累计访问频率之间的差值最小、且与所述访问频率阈值之间的差值位于设定范围内的子周期;From each sub-period adjacent to the candidate sub-period, select a sub-period whose difference between the accumulated access frequencies corresponding to the candidate sub-period is the smallest and whose difference with the access frequency threshold is within a set range;
基于选取出的子周期确定所述业务数据表在所述指定统计周期内的冷热数据分界时间点。Based on the selected sub-period, a time point for dividing the cold and hot data in the business data table within the specified statistical period is determined.
可选地,所述历史访问记录包括所述指定统计周期内对所述业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点;Optionally, the historical access record includes a time point of a write operation performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period;
所述第一确定模块620具体用于:The first determining
基于所述指定统计周期内对所述业务数据表执行的写入操作的时间点,分别确定对所述业务数据表执行的最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期;Based on the time points of the write operations performed on the business data table within the specified statistical period, respectively determine the average write cycles between the last write operation performed on the business data table and the other write operations;
基于所述最后一次写入操作分别与其他各次写入操作之间的平均写入周期,确定所述业务数据表的平均写入周期;Determine the average write cycle of the business data table based on the average write cycles between the last write operation and other write operations;
基于数据表的平均写入周期与处理周期之间的预设对应关系以及所述业务数据表的平均写入周期,确定所述业务数据表的处理周期。Based on a preset correspondence between an average writing cycle and a processing cycle of a data table and an average writing cycle of the business data table, a processing cycle of the business data table is determined.
可选地,所述装置还包括:Optionally, the device further comprises:
第二获取模块,用于获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及处理周期;The second acquisition module is used to obtain the historical access records and processing cycles of the sample data table within the statistical period;
第三确定模块,用于基于所述统计周期内的历史访问记录,确定样本数据表的平均写入周期;A third determination module, configured to determine an average write cycle of the sample data table based on historical access records within the statistical period;
第一训练模块,用于以所述样本数据表的平均写入周期作为训练样本、以所述样本数据表的处理周期作为所述训练样本的标签,基于预设的第二分类算法进行训练,以得到所述预设对应关系。The first training module is used to use the average writing cycle of the sample data table as a training sample and the processing cycle of the sample data table as a label of the training sample, and to perform training based on a preset second classification algorithm to obtain the preset corresponding relationship.
可选地,所述装置还包括:Optionally, the device further comprises:
第三获取模块,用于获取样本数据表在统计周期内的历史访问记录及冷热数据比例;The third acquisition module is used to obtain the historical access records and the ratio of hot and cold data of the sample data table within the statistical period;
第四确定模块,用于基于所述历史访问记录,确定所述样本数据表的处理周期及在所述统计周期内的累计访问频率;A fourth determination module, configured to determine the processing period of the sample data table and the cumulative access frequency within the statistical period based on the historical access records;
第二训练模块,用于以所述样本数据表的处理周期、在统计周期内的累计访问频率及所述统计周期作为训练样本,以所述样本数据表在所述统计周期内的冷热数据比例作为所述训练样本的标签,基于所述第一分类算法进行训练,以得到所述冷热数据识别模型。The second training module is used to use the processing period of the sample data table, the cumulative access frequency within the statistical period and the statistical period as training samples, and the ratio of cold and hot data in the sample data table within the statistical period as labels of the training samples, and to perform training based on the first classification algorithm to obtain the cold and hot data recognition model.
总之,以上所述仅为本申请的较佳实施例而已,并非用于限定本申请的保护范围。凡在本申请的精神和原则之内,所作的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本申请的保护范围之内。In short, the above is only a preferred embodiment of the present application and is not intended to limit the protection scope of the present application. Any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made within the spirit and principle of the present application shall be included in the protection scope of the present application.
上述实施例阐明的系统、装置、模块或单元,具体可以由计算机芯片或实体实现,或者由具有某种功能的产品来实现。一种典型的实现设备为计算机。具体的,计算机例如可以为个人计算机、膝上型计算机、蜂窝电话、相机电话、智能电话、个人数字助理、媒体播放器、导航设备、电子邮件设备、游戏控制台、平板计算机、可穿戴设备或者这些设备中的任何设备的组合。The systems, devices, modules or units described in the above embodiments may be implemented by computer chips or entities, or by products with certain functions. A typical implementation device is a computer. Specifically, the computer may be, for example, a personal computer, a laptop computer, a cellular phone, a camera phone, a smart phone, a personal digital assistant, a media player, a navigation device, an email device, a game console, a tablet computer, a wearable device, or a combination of any of these devices.
计算机可读介质包括永久性和非永久性、可移动和非可移动媒体可以由任何方法或技术来实现信息存储。信息可以是计算机可读指令、数据结构、程序的模块或其他数据。计算机的存储介质的例子包括,但不限于相变内存(PRAM)、静态随机存取存储器(SRAM)、动态随机存取存储器(DRAM)、其他类型的随机存取存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、电可擦除可编程只读存储器(EEPROM)、快闪记忆体或其他内存技术、只读光盘只读存储器(CD-ROM)、数字多功能光盘(DVD)或其他光学存储、磁盒式磁带,磁带磁磁盘存储或其他磁性存储设备或任何其他非传输介质,可用于存储可以被计算设备访问的信息。按照本文中的界定,计算机可读介质不包括暂存电脑可读媒体(transitory media),如调制的数据信号和载波。Computer readable media include permanent and non-permanent, removable and non-removable media that can be implemented by any method or technology to store information. Information can be computer readable instructions, data structures, program modules or other data. Examples of computer storage media include, but are not limited to, phase change memory (PRAM), static random access memory (SRAM), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), other types of random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM), flash memory or other memory technology, compact disk read-only memory (CD-ROM), digital versatile disk (DVD) or other optical storage, magnetic cassettes, magnetic tape magnetic disk storage or other magnetic storage devices or any other non-transmission media that can be used to store information that can be accessed by a computing device. As defined herein, computer readable media does not include temporary computer readable media (transitory media), such as modulated data signals and carrier waves.
还需要说明的是,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其任何其他变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、商品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、商品或者设备所固有的要素。在没有更多限制的情况下,由语句“包括一个……”限定的要素,并不排除在包括所述要素的过程、方法、商品或者设备中还存在另外的相同要素。It should also be noted that the terms "include", "comprises" or any other variations thereof are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion, so that a process, method, commodity or device including a series of elements includes not only those elements, but also other elements not explicitly listed, or also includes elements inherent to such process, method, commodity or device. In the absence of more restrictions, the elements defined by the sentence "comprises a ..." do not exclude the existence of other identical elements in the process, method, commodity or device including the elements.
本说明书中的各个实施例均采用递进的方式描述,各个实施例之间相同相似的部分互相参见即可,每个实施例重点说明的都是与其他实施例的不同之处。尤其,对于系统实施例而言,由于其基本相似于方法实施例,所以描述的比较简单,相关之处参见方法实施例的部分说明即可。Each embodiment in this specification is described in a progressive manner, and the same or similar parts between the embodiments can be referred to each other, and each embodiment focuses on the differences from other embodiments. In particular, for the system embodiment, since it is basically similar to the method embodiment, the description is relatively simple, and the relevant parts can be referred to the partial description of the method embodiment.
Claims (9)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011603968.5ACN113064930B (en) | 2020-12-29 | 2020-12-29 | Cold and hot data identification method and device of data warehouse and electronic equipment |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011603968.5ACN113064930B (en) | 2020-12-29 | 2020-12-29 | Cold and hot data identification method and device of data warehouse and electronic equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN113064930A CN113064930A (en) | 2021-07-02 |
| CN113064930Btrue CN113064930B (en) | 2023-04-28 |
Family
ID=76558709
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011603968.5AActiveCN113064930B (en) | 2020-12-29 | 2020-12-29 | Cold and hot data identification method and device of data warehouse and electronic equipment |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN113064930B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113886382B (en) | 2021-08-23 | 2024-12-27 | 阿里云计算有限公司 | Database task processing method, device and storage medium |
| CN115994168A (en)* | 2021-10-18 | 2023-04-21 | 中国移动通信集团贵州有限公司 | Data volatility inspection method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN114169401A (en)* | 2021-11-15 | 2022-03-11 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Data processing, predictive model training methods and equipment |
| CN113835986B (en)* | 2021-11-25 | 2022-04-08 | 中航金网(北京)电子商务有限公司 | Dynamic switching method and device for system cold and hot logs and computer equipment |
| CN114138944A (en)* | 2021-12-10 | 2022-03-04 | 云知声(上海)智能科技有限公司 | Hot-warm-cold field data grading speech recognition model modeling system and modeling method thereof |
| CN117149049A (en)* | 2022-05-24 | 2023-12-01 | 华为技术有限公司 | Memory access heat statistics method, related devices and equipment |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102388374A (en)* | 2011-09-28 | 2012-03-21 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for storing data |
| CN109739646A (en)* | 2018-12-28 | 2019-05-10 | 北京神州绿盟信息安全科技股份有限公司 | A kind of data processing method and device |
| CN110321348A (en)* | 2019-06-04 | 2019-10-11 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | A kind of data processing method, device and computer equipment |
| CN110502452A (en)* | 2019-07-12 | 2019-11-26 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for accessing hybrid cache in electronic equipment |
| US10699002B1 (en)* | 2019-11-22 | 2020-06-30 | Capital One Services, Llc | Identification of database intrusion by changes in data tables |
| CN111459900A (en)* | 2020-04-22 | 2020-07-28 | 广州虎牙科技有限公司 | Big data life cycle setting method and device, storage medium and server |
Family Cites Families (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11443166B2 (en)* | 2018-10-29 | 2022-09-13 | Oracle International Corporation | Datacenter level utilization prediction without operating system involvement |
| US11544596B2 (en)* | 2019-04-08 | 2023-01-03 | Google Llc | Creating a machine learning model with k-means clustering |
- 2020
- 2020-12-29CNCN202011603968.5Apatent/CN113064930B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102388374A (en)* | 2011-09-28 | 2012-03-21 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for storing data |
| CN109739646A (en)* | 2018-12-28 | 2019-05-10 | 北京神州绿盟信息安全科技股份有限公司 | A kind of data processing method and device |
| CN110321348A (en)* | 2019-06-04 | 2019-10-11 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | A kind of data processing method, device and computer equipment |
| CN110502452A (en)* | 2019-07-12 | 2019-11-26 | 华为技术有限公司 | Method and device for accessing hybrid cache in electronic equipment |
| US10699002B1 (en)* | 2019-11-22 | 2020-06-30 | Capital One Services, Llc | Identification of database intrusion by changes in data tables |
| CN111459900A (en)* | 2020-04-22 | 2020-07-28 | 广州虎牙科技有限公司 | Big data life cycle setting method and device, storage medium and server |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Online fuzzy logic control with decision tree for improving hybrid cache performance & symposia;Junpeng Niu;《2016 12th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation (ICCA)》;20160717;511-516* |
| 基于数据温度的冷热数据识别机制研究;解玉琳;《中国优秀硕士学位论文全文数据库 信息科技辑》;20190815;I138-461* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113064930A (en) | 2021-07-02 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN113064930B (en) | Cold and hot data identification method and device of data warehouse and electronic equipment | |
| CN109544166B (en) | Risk identification method and risk identification device | |
| CN108615119B (en) | Abnormal user identification method and equipment | |
| US10504120B2 (en) | Determining a temporary transaction limit | |
| WO2019128526A1 (en) | Method, apparatus, and device for training risk control model and risk control | |
| US9996594B2 (en) | Method, article and system for time dependent search | |
| CN111539811B (en) | Risk account identification method and device | |
| CN108549569B (en) | A method and device for searching information in an application program | |
| WO2020147488A1 (en) | Method and device for identifying irregular group | |
| CN113535817B (en) | Feature broad table generation and service processing model training method and device | |
| CN105589917B (en) | Method and device for analyzing log information of browser | |
| CN110751515A (en) | Decision-making method and device based on user consumption behaviors, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN110008986B (en) | Batch risk case identification method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN111209929A (en) | Access data processing method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| WO2019184582A1 (en) | Electronic book consumption demand determining method, electronic device, and computer storage medium | |
| CN116362823A (en) | Recommendation model training method, recommendation method and recommendation device for behavior sparse scene | |
| WO2020253369A1 (en) | Method and device for generating interest tag, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| US11308130B1 (en) | Constructing ground truth when classifying data | |
| CN114611850A (en) | Service analysis method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN110661913B (en) | User sorting method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN111191046A (en) | Method, device, computer storage medium and terminal for realizing information search | |
| CN109410052A (en) | A kind of data predication method and device | |
| CN113076451B (en) | Abnormal behavior identification and risk model library establishment method, device and electronic equipment | |
| CN110708414B (en) | Telephone number sorting method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN110163470B (en) | Event evaluation method and device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |