CN112680382B - Bacillus belgii and application thereof - Google Patents
Bacillus belgii and application thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112680382B CN112680382BCN202110093588.XACN202110093588ACN112680382BCN 112680382 BCN112680382 BCN 112680382BCN 202110093588 ACN202110093588 ACN 202110093588ACN 112680382 BCN112680382 BCN 112680382B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- bacillus
- strain
- velesi
- plant
- application
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于农业生物防治技术领域,具体涉及一株贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillusvelezensis)及其应用。The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural biological control, in particular to a strain of Bacillus velezensis and its application.
背景技术Background technique
植物病害对世界粮食生产及安全造成了严重的威胁。长期以来,化学农药和肥料的使用,使得环境污染、菌株抗药性以及土壤微生态失衡等问题日益加重。亟待挖掘可替代化学农药和肥料的微生物产品。尽管已有大量微生物产品的存在,但由于其在田间定殖力低、持效期短等现象,使得从根际、根内生等植物相关微生物群落中挖掘广谱、高效的微生物成为国内外学者的研究热点。Plant diseases pose a serious threat to world food production and security. For a long time, the use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers has made problems such as environmental pollution, bacterial resistance and soil microecological imbalances increasingly aggravated. There is an urgent need to discover microbial products that can replace chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Despite the existence of a large number of microbial products, due to their low colonization in the field and short duration of validity, mining broad-spectrum and high-efficiency microorganisms from plant-related microbial communities such as rhizosphere and root endophyte has become a domestic and foreign topic. scholars' research hotspots.
芽孢杆菌是一类产芽孢的革兰氏阳性细菌,大部分芽孢杆菌具有抗菌谱广、生长迅速、易分离培养、抗逆性强和生物安全性高等优点,从而作为益生菌在农业、食品、工业、医学、冶金、林业、环保以及军事等方面被广泛研究。贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillusvelezensis)作为芽孢杆菌中新发现的一个种,在自然界中广泛分布,可从海洋和河流沉积物、土壤、植株根际、植物组织中分离得到,其对人畜无害,对环境无污染,并且能产生对多种病原微生物有拮抗作用的次生代谢物。近年来,关于贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的研究主要集中在饲料、医药、纺织、水产、污水处理、植物保护等领域。作为一种新型生防微生物因子,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌在植物病害防控、促进植物生长等方面备受关注。Bacillus is a class of spore-producing Gram-positive bacteria, most of which have the advantages of broad antibacterial spectrum, rapid growth, easy isolation and culture, strong stress resistance and high biosafety, so they are used as probiotics in agriculture, food, Industry, medicine, metallurgy, forestry, environmental protection and military are widely studied. Bacillus velezensis, a newly discovered species of Bacillus, is widely distributed in nature and can be isolated from marine and river sediments, soil, plant rhizosphere, and plant tissues. It is harmless to humans and animals. It is non-polluting to the environment and can produce secondary metabolites that have antagonistic effects on a variety of pathogenic microorganisms. In recent years, the research on Bacillus velesi has mainly focused on the fields of feed, medicine, textile, aquatic products, sewage treatment, plant protection and so on. As a new biocontrol microbial factor, Bacillus velesi has attracted much attention in the aspects of plant disease prevention and control and plant growth promotion.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的是提供一株贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9及其应用。本发明提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9,已于2020年12月07日保藏于中国微生物菌种保藏委员会普通微生物中心(简称CGMCC,地址为:北京市朝阳区北辰西路1号院3号),CGMCC No.21318The purpose of the present invention is to provide a strain of Bacillus velezensis TYGF10-2F9 and its application. The Bacillus velezensis TYGF10-2F9 provided by the present invention has been deposited in the General Microbiology Center of the China Microorganism Culture Collection Committee (CGMCC for short) on December 07, 2020, and the address is: Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing No. 1 Courtyard No. 3), CGMCC No.21318
一株贝莱斯芽孢杆菌,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)的保藏编号为CGMCC No.21318。One strain of Bacillus velezensis, Bacillus velezensis, has the deposit number of CGMCC No. 21318.
本发明所述的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌用于制备植物抑菌剂的应用,或用于制备防治植物病原菌引起的植物病害药物的应用。The application of the Bacillus velesi described in the present invention for preparing a plant bacteriostatic agent, or an application for preparing a medicine for preventing and treating plant diseases caused by plant pathogenic bacteria.
可选的,所述的植物病原菌选自油菜菌核(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)病菌、水稻纹枯(Rhizoctonia solani)病菌、小麦赤霉(Fusarium graminearum)病菌、苹果轮纹(Botryospuaeria berengeriana)病菌、烟草赤星(Alteraria alternata)病菌、辣椒疫霉(Phytophthora capsici)病菌、西瓜枯萎(Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum)病菌、黄瓜枯萎(Fusarium oxysporum.sp.cucumebrium Owen)病菌、草莓枯萎(Fusarium oxysporumf.sp.fragariae)病菌、番茄灰霉(Botrytis cinerea)病菌、苹果腐烂(Valsa mali MiyabeetYamada)病菌和小麦全蚀(Gaeu-mannomyces graminsis(sacc.)Arx&Olivier Vartritici J.walker)病菌。Optionally, the phytopathogenic bacteria are selected from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) pathogen, Rhizoctonia solani (Rhizoctonia solani) pathogen, Fusarium graminearum (Fusarium graminearum) pathogen, Botryospuaeria berengeriana pathogen, Tobacco red star ( Alteraria alternata, Phytophthora capsici, Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum, Fusarium oxysporum.sp.cucumebrium Owen, Fusarium oxysporumf.sp.fragariae Pathogens, Botrytis cinerea, apple rot (Valsa mali Miyabeet Yamada) and wheat total eclipse (Gaeu-mannomyces graminsis (sacc.) Arx & Olivier Vartritici J. walker).
本发明所述的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌用于制备植物定殖剂、植物生防剂、生物有机肥或植物促生剂的应用。The Bacillus velesi described in the present invention is used for the preparation of plant colonizers, plant biocontrol agents, biological organic fertilizers or plant growth promoters.
一种制剂,其特征在于,所述的制剂为发明所述的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的菌悬液、发酵液、发酵产物或次生代谢产物。A preparation is characterized in that the preparation is the bacterial suspension, fermentation liquid, fermentation product or secondary metabolite of Bacillus velesi described in the invention.
本发明所述的制剂用于制备植物抑菌剂的应用,或用于制备防治植物病原菌引起的植物病害药物的应用。The preparation of the present invention is used for the preparation of plant bacteriostatic agents, or the preparation of medicines for preventing and treating plant diseases caused by plant pathogens.
可选的,所述的植物病原菌选自油菜菌核(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)病菌、水稻纹枯(Rhizoctonia solani)病菌、小麦赤霉(Fusarium graminearum)病菌、苹果轮纹(Botryospuaeria berengeriana)病菌、烟草赤星(Alteraria alternata)病菌、辣椒疫霉(Phytophthora capsici)病菌、西瓜枯萎(Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum)病菌、黄瓜枯萎(Fusarium oxysporum.sp.cucumebrium Owen)病菌、草莓枯萎(Fusarium oxysporumf.sp.fragariae)病菌、番茄灰霉(Botrytis cinerea)病菌、苹果腐烂(Valsa mali MiyabeetYamada)病菌和小麦全蚀(Gaeu-mannomyces graminsis(sacc.)Arx&Olivier Vartritici J.walker)病菌。Optionally, the phytopathogenic bacteria are selected from Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum) pathogen, Rhizoctonia solani (Rhizoctonia solani) pathogen, Fusarium graminearum (Fusarium graminearum) pathogen, Botryospuaeria berengeriana pathogen, Tobacco red star ( Alteraria alternata, Phytophthora capsici, Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum, Fusarium oxysporum.sp.cucumebrium Owen, Fusarium oxysporumf.sp.fragariae Pathogens, Botrytis cinerea, apple rot (Valsa mali Miyabeet Yamada) and wheat total eclipse (Gaeu-mannomyces graminsis (sacc.) Arx & Olivier Vartritici J. walker).
一种IAA的制备方法,采用本发明所述的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌制备IAA。A preparation method of IAA, using the Bacillus velesi described in the present invention to prepare IAA.
一种铁载体的制备方法,采用本发明所述的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌制备铁载体。A preparation method of a siderophore, using the Bacillus velesi described in the present invention to prepare a siderophore.
本发明的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌应用于农业生物防治领域,可形成生物膜在植物根际稳定定殖,可对12种植物病原真菌和卵菌产生较强且广谱的抑制作用,可产生IAA、铁载体等物质来促进植物生长。该贝莱斯芽孢杆菌发酵液对油菜菌核病盆栽防效高达80.99%;该贝莱斯芽孢杆菌菌悬液和发酵液对黄瓜枯萎盆栽防效均高达66.67%,且对黄瓜具有一定的促生作用,是一株性能优良的生防菌株,具有良好的开发应用前景。The Bacillus velesi of the present invention is applied to the field of agricultural biological control, can form a biofilm and stably colonize the plant rhizosphere, can have a strong and broad-spectrum inhibitory effect on 12 kinds of plant pathogenic fungi and oomycetes, and can produce IAA , siderophores and other substances to promote plant growth. The fermented liquid of Bacillus velesi has a control effect of up to 80.99% on rape sclerotinia; both the Bacillus velesi bacterial suspension and the fermentation liquid have a control effect of 66.67% on potted cucumber wither, and has a certain promotion effect on cucumber. It is a biocontrol strain with excellent performance and has good development and application prospects.
附图说明Description of drawings
附图是用来提供对本公开的进一步理解,并且构成说明书的一部分,与下面的具体实施方式一起用于解释本公开,但并不构成对本公开的限制。在附图中:The accompanying drawings are used to provide a further understanding of the present disclosure, and constitute a part of the specification, and together with the following detailed description, are used to explain the present disclosure, but not to limit the present disclosure. In the attached image:
图1是本发明实施例1提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9发育树;Fig. 1 is the Bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) TYGF10-2F9 developmental tree provided in Example 1 of the present invention;
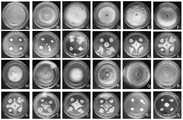
图2是本发明实施例2提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9对12株病原真菌的抑菌活性;A,G表示水稻纹枯;B,H表示小麦赤霉;C,I表示油菜菌核;D,J表示苹果轮纹;E,K表示烟草赤星;F,L表示辣椒疫霉;M,S表示西瓜枯萎;N,T表示黄瓜枯萎;O,U表示草莓枯萎;P,V表示番茄灰霉;O,W表示苹果腐烂;R,X表示小麦全蚀;Fig. 2 is the bacteriostatic activity of Bacillus velezensis TYGF10-2F9 provided in Example 2 of the present invention to 12 strains of pathogenic fungi; A, G represent rice sheath blight; B, H represent Gibberella thorn; C, I means rape sclerotium; D, J means apple ring pattern; E, K means tobacco red star; F, L means Phytophthora capsicum; M, S means watermelon wilt; N, T means cucumber wilt; O, U means strawberry wilt; P, V means tomato gray mold; O, W means apple rot; R, X means wheat total erosion;
图3是本发明实施例3提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9产IAA的标准曲线;Fig. 3 is the standard curve of IAA produced by Bacillus velezensis TYGF10-2F9 provided in Example 3 of the present invention;
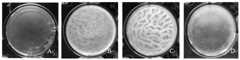
图4是本发明实施例4提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9在不同培养基中生物膜的形成;A,B,C,D分别表示菌株TYGF10-2F9在培养基LBG、LBM、LBGM和LB中的生物膜;Fig. 4 is the formation of biofilm of Bacillus velezensis TYGF10-2F9 provided in Example 4 of the present invention in different culture medium; A, B, C, D respectively represent strain TYGF10-2F9 in culture medium LBG, Biofilms in LBM, LBGM and LB;
图5是本发明实施例5提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9对油菜菌核病的盆栽防效;Fig. 5 is the potted control effect of Bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) TYGF10-2F9 provided in Example 5 of the present invention to rape sclerotinia;
图6是本发明实施例5提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9对油菜菌核的防效;Fig. 6 is the control effect of Bacillus velezensis (Bacillus velezensis) TYGF10-2F9 on rape sclerotia provided in Example 5 of the present invention;
图7是本发明实施例6提供的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)TYGF10-2F9对黄瓜枯萎病的盆栽防效。Fig. 7 shows the pot control effect of Bacillus velezensis TYGF10-2F9 on cucumber fusarium wilt provided in Example 6 of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下述实施例中所使用的实验方法如无特殊说明,均为常规方法。The experimental methods used in the following examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified.
下述实施例中所用的材料、试剂等,如无特殊说明,均可从商业途径中得到。The materials, reagents, etc. used in the following examples can be obtained from commercial sources unless otherwise specified.
本发明中提到的植物定殖剂、植物生防剂、生物有机肥、植物促生剂等均为农业中常用的肥料或营养液等常用剂型。本发明的贝莱斯芽孢杆菌应用于农业生物防治领域,可形成生物膜在植物根际稳定定殖,可对12种植物病原真菌和卵菌产生较强且广谱的抑制作用,可产生IAA、铁载体等物质来促进植物生长。该贝莱斯芽孢杆菌发酵液对油菜菌核病盆栽防效高达80.99%;该贝莱斯芽孢杆菌菌悬液和发酵液对黄瓜枯萎盆栽防效均高达66.67%,且对黄瓜具有一定的促生作用,是一株性能优良的生防菌株,具有良好的开发应用前景。The plant colonizers, plant biocontrol agents, bio-organic fertilizers, plant growth promoters and the like mentioned in the present invention are commonly used formulations such as fertilizers or nutrient solutions in agriculture. The Bacillus velesi of the present invention is applied to the field of agricultural biological control, can form a biofilm and stably colonize the plant rhizosphere, can have a strong and broad-spectrum inhibitory effect on 12 kinds of plant pathogenic fungi and oomycetes, and can produce IAA , siderophores and other substances to promote plant growth. The fermented liquid of Bacillus velesi has a control effect of up to 80.99% on rape sclerotinia; both the Bacillus velesi bacterial suspension and the fermentation liquid have a control effect of 66.67% on potted cucumber wither, and has a certain promotion effect on cucumber. It is a biocontrol strain with excellent performance and has good development and application prospects.
实施例1菌株TYGF10-2F9分离纯化及分子生物学鉴定Example 1 Isolation, purification and molecular biology identification of strain TYGF10-2F9
称取10g小麦根际土壤加入200mL 0.01M无菌PBS缓冲液,在室温、180r/min条件下震荡30min得到根际土悬浮液,用无菌水梯度稀释为10-1、10-2和10-3,用涂布棒均匀涂布在TYG培养基(Tryptone Yeast extract Glucose Medium,TYG)上,其组成为:胰蛋白胨1g、酵母提取物1g、葡萄糖0.5g、KCl 6.34g、NaCl 1.2g、MgSO4·7H2O 0.25g、K2HPO4 0.13g、CaCl2·2H2O 0.22g、K2SO4 0.17g、Na2SO4 2.4g、NaHCO3 0.5g、Na2CO3 0.09g、FeEDTA 0.07g、琼脂15g、蒸馏水1000mL、PH=7.2-7.4;于28℃下恒温培养2d后挑取单菌落进行纯化培养。Weigh 10g of wheat rhizosphere soil, add 200mL of 0.01M sterile PBS buffer, shake at room temperature for 30min under the conditions of 180r/min to obtain a rhizosphere soil suspension, and dilute with sterile water gradient to10-1 ,10-2 and 10-3 , spread evenly on TYG medium (Tryptone Yeast extract Glucose Medium, TYG) with a coating rod, which consists of: 1 g of tryptone, 1 g of yeast extract, 0.5 g of glucose, 6.34 g of KCl, 1.2 g of NaCl, MgSO4 ·7H2 O 0.25g, K2 HPO4 0.13g, CaCl2 ·2H2 O 0.22g, K2 SO4 0.17g, Na2 SO4 2.4g, NaHCO3 0.5g, Na2 CO3 0.09g , FeEDTA 0.07g, agar 15g, distilled water 1000mL, PH=7.2-7.4; after culturing at a constant temperature of 28°C for 2d, a single colony was picked for purification and culture.
DNA提取按照上海生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司的柱式细菌DNA提取试剂盒的程序操作。选用细菌通用引物对:F27 5'-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AGG-3',P1541 5'-AAG GAG GTG GTG ATC CAG CCG CA-3'。反应条件为:94℃变性45s,50℃退火45s,72℃延伸75s,50μL反应体系30个循环。PCR产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,经克隆测序得到序列结果。所得到的16S rDNA全序列与从Genbank等数据库中获得的16S rDNA序列进行比对,通过Mega 6.0软件包进行系统发育树的构建。DNA extraction was performed according to the procedure of the column-type bacterial DNA extraction kit of Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. Use bacterial universal primer pairs: F27 5'-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AGG-3', P1541 5'-AAG GAG GTG GTG ATC CAG CCG CA-3'. The reaction conditions were: denaturation at 94 °C for 45 s, annealing at 50 °C for 45 s, extension at 72 °C for 75 s, and a 50 μL reaction system for 30 cycles. PCR products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis, and sequence results were obtained by cloning and sequencing. The obtained complete 16S rDNA sequence was compared with the 16S rDNA sequence obtained from databases such as Genbank, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed by the Mega 6.0 software package.
采用分子生物学方法对菌株TYGF10-2F9进行鉴定。菌株TYGF10-2F9的16S rDNA碱基序列测定结果如序列表所示,共测定菌株TYGF10-2F9的16S rDNA有1444个碱基。The strain TYGF10-2F9 was identified by molecular biology method. The determination results of the 16S rDNA base sequence of the strain TYGF10-2F9 are shown in the sequence table, and the 16S rDNA of the strain TYGF10-2F9 has 1444 bases in total.
自菌株的基因组DNA中扩增获得片段大小为所得到的16S rDNA全序列与从Genbank数据库中获得的16S rDNA序列进行比对后获取登录号为:TYGF10-2F9(MW314755)。系统发育树的构建:选取10株模式菌株,采用MEGA 6软件中的Neighbor-Joining方法进行系统发育分析,构建的系统发育树见图1所示。The fragment size obtained by amplification from the genomic DNA of the strain is 16S rDNA obtained from the complete sequence and the 16S rDNA sequence obtained from the Genbank database. The accession number is: TYGF10-2F9 (MW314755). Construction of phylogenetic tree: 10 model strains were selected, and the Neighbor-Joining method in MEGA 6 software was used for phylogenetic analysis. The constructed phylogenetic tree is shown in Figure 1.
实施例2菌株TYGF10-2F9抑菌作用测定Example 2 Determination of antibacterial effect of strain TYGF10-2F9
采用平板对峙法,对油菜菌核(Sclerotinia sclerotiorum)、水稻纹枯(Rhizoctonia solani)、小麦赤霉(Fusarium graminearum)、苹果轮纹(Botryospuaeriaberengeriana)、烟草赤星(Alteraria alternata)、辣椒疫霉(Phytophthora capsici)、西瓜枯萎(Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum)、黄瓜枯萎(Fusariumoxysporum.sp.cucumebrium Owen)、草莓枯萎(Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.fragariae)、番茄灰霉(Botrytis cinerea)、苹果腐烂(Valsa mali Miyabe et Yamada)和小麦全蚀(Gaeu-mannomyces graminsis(sacc.)Arx&Olivier Var tritici J.walker)共12株植物病原真菌的抑制作用进行测定。首先,以培养皿中心为中心点,在培养皿底部十字交叉划线,距离中心点2.5cm处接种已经在LB培养基上活化的菌株;然后,用5mm打孔器将已活化的植物病原真菌打孔后接种于PDA培养基平板中央,对培养皿进行封口、于28℃条件下培养至病原菌对照长到培养皿三分之二的时候进行病原菌半径及所形成透明圈宽度的统计。Using the plate confrontation method, the Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium graminearum, Botryospuaeria berengriana, Alteraria alternata, Phytophthora capsici ), watermelon wilt (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.niveum), cucumber wilt (Fusarium oxysporum.sp.cucumebrium Owen), strawberry wilt (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp.fragariae), tomato gray mold (Botrytis cinerea), apple rot (Valsa mali) Miyabe et Yamada) and wheat total eclipse (Gaeu-mannomyces graminsis (sacc.) Arx & Olivier Var tritici J. walker) a total of 12 phytopathogenic fungi were tested. First, take the center of the petri dish as the center point, cross the bottom of the petri dish, and inoculate the strains that have been activated on the LB medium at a distance of 2.5cm from the center point; After punching, it was inoculated in the center of the PDA medium plate, and the petri dish was sealed and cultivated at 28°C until the pathogen control grew to two-thirds of the petri dish, and the radius of the pathogen and the width of the transparent circle formed were counted.
采用“平板对峙”法,以12种病原真菌为靶标,对菌株TYGF10-2F9抑菌谱进行评价。结果表明,菌株TYGF10-2F9对12种病原真菌具有广谱的抑制活性(图2)。其中,菌株TYGF10-2F9对苹果腐烂病病原菌的抑制活性最高,抑制率为94.06%;对油菜菌核病病原菌、番茄灰霉和小麦全蚀病原菌的抑制活性较为明显,抑制率分别为88.18%、85.24%和82.03%;水稻纹枯、苹果轮纹、烟草赤星、辣椒疫霉、西瓜枯萎、黄瓜枯萎和草莓枯萎病原菌的抑制率介于60.00%-70.00%之间;对小麦赤霉病原菌的抑制活性最小,抑制率为58.31%(表1及图2)。The "plate confrontation" method was used to evaluate the antibacterial spectrum of strain TYGF10-2F9 with 12 pathogenic fungi as targets. The results showed that strain TYGF10-2F9 had broad-spectrum inhibitory activity against 12 pathogenic fungi (Fig. 2). Among them, the strain TYGF10-2F9 had the highest inhibitory activity against the pathogenic bacteria of apple rot, with an inhibition rate of 94.06%; the inhibitory activity against the pathogenic bacteria of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, tomato gray mold and wheat total rot pathogen was more obvious, with the inhibition rates of 88.18% and 88.18%, respectively. 85.24% and 82.03%; the inhibition rate of rice sheath blight, apple ring striae, tobacco red star, pepper phytophthora, watermelon wilt, cucumber wilt and strawberry wilt pathogens were between 60.00% and 70.00%; inhibition of wheat scab pathogens The activity was the smallest, and the inhibition rate was 58.31% (Table 1 and Figure 2).
表1菌株TYGF10-2F9对12株病原真菌的抑制作用Table 1 Inhibitory effect of strain TYGF10-2F9 on 12 strains of pathogenic fungi
实施例3菌株TYGF10-2F9促生指标测定Example 3 Determination of growth-promoting indexes of strain TYGF10-2F9
首先将-80℃保存的菌株于LB培养基上进行划线,于28℃恒温箱中培养24h活化。然后将活化后的菌株接种一菌针于盛装有100mL LB液体培养基的250mL的锥形瓶中,同时在锥形瓶中添加1mL L-色氨酸,使其终浓度为100μg/mL,于28℃、180r/min条件下培养5d,每株菌进行2次生物学重复。取8mL菌株发酵液,于8000r/min、4℃条件下进行离心,吸取上清进行菌株IAA含量的定量测定。对于IAA含量的定量测定而言,吸取60μL上清于2mL离心管中,然后加入120μL Salkowski试剂于黑暗条件下进行显色,用紫外分光光度计测定530nm条件下各个处理的吸光度。同时,用梯度稀释的IAA溶液(50、10、5、2.5、1.25、0.625和0μg/mL)制作IAA含量与吸光度值的标准曲线,根据标准曲线对菌株产IAA能力进行评价。First, the strains stored at -80°C were streaked on LB medium, and then cultured in a 28°C incubator for 24 hours for activation. Then the activated strain was inoculated into a 250 mL conical flask containing 100 mL of LB liquid medium, and 1 mL of L-tryptophan was added to the conical flask to make the
采用点接种法,将活化后的菌株于无机磷培养基((NH4)2SO4 0.5g,NaCl 0.3g,KCl0.3g,MgSO4·7H2O 0.3g,Ca3(PO4)2 25g,FeSO4·7H2O 0.03g,MnSO4·H2O 0.03g,葡萄糖10g,PH 7.4-7.6)上,于28℃条件下恒温培养5d,根据菌株周围是否有透明圈产生及透明圈的大小来对菌株解无机磷能力进行评价。Using the spot inoculation method, the activated strains were placed in inorganic phosphorus medium ((NH4 )2 SO4 0.5g, NaCl 0.3g, KCl 0.3g, MgSO4 ·7H2 O 0.3g, Ca3 (PO4 )2 25g, FeSO4 ·7H2 O 0.03g, MnSO4 ·H2 O 0.03g, glucose 10g, PH 7.4-7.6), incubated at 28°C for 5d at a constant temperature, according to whether there is a transparent circle around the strain and a transparent circle The size of the strain was used to evaluate the ability of the strain to dissolve inorganic phosphorus.
采用点接种法,将活化后的菌株接种到以3mM ACC为唯一氮源的DF培养基(葡萄糖2.0g,葡萄糖酸2.0g,柠檬酸2.0g,微量元素溶液(CaCl2 200mg、FeSO4·7H2O 200mg、H3BO315mg、ZnSO4·7H2O 20mg、Na2MoO4 10mg、KI 10mg、NaBr 10mg、MnCl2 10mg、COCl2 5mg、CuCl25mg、AlCl3 2mg、NiSO4 2mg、去离子水1,000mL)10mL、去离子水990mL)上,以0.2%(w/v)(NH4)2SO4为唯一氮源的DF培养为阳性对照,以DF培养基为阴性对照。将接种后的平板于28℃条件下恒温培养5d,根据三种培养基上菌株的生长状况对菌株产ACC能力进行综合评价。Using the spot inoculation method, the activated strains were inoculated into DF medium with 3 mM ACC as the sole nitrogen source (glucose 2.0 g, gluconic acid 2.0 g, citric acid 2.0 g, trace element solution (CaCl2 200 mg, FeSO4 ·7H)2 O 200mg, H3 BO3 15mg, ZnSO4 7H2 O 20mg, Na2 MoO4 10mg, KI 10mg, NaBr 10mg, MnCl2 10mg, COCl2 5mg, CuCl2 5mg, AlCl3 2mg, NiSO4 2mg, Deionized water 1,000 mL) 10 mL, deionized water 990 mL), DF cultured with 0.2% (w/v) (NH4 )2 SO4 as the sole nitrogen source was used as a positive control, and DF medium was used as a negative control. The inoculated plates were incubated at a constant temperature of 28°C for 5 days, and the ACC-producing ability of the strains was comprehensively evaluated according to the growth conditions of the strains on the three media.
采用点接种法,将活化菌株接种于铬天青培养基(CAS)上,接种后的平板置于28℃条件下培养7d后,根据菌落周围黄色晕圈的出现与否以及大小来对菌株产铁载体的能力进行评价。Using the spot inoculation method, the activated strains were inoculated on chrome azurite medium (CAS). Siderophore capacity was evaluated.
对分离得到的菌株TYGF10-2F9产IAA能力、解磷能力、产ACC能力和产铁载体能力等促生指标的测定。通过构建IAA标准曲线(图3),测定菌株TYGF10-2F9在100μg/mL条件下可产生5.97μg/mL的IAA;具有产铁载体的能力(表2),但不具有解磷、解钾、固氮和产ACC的能力(表2)。Determination of the growth-promoting indicators of the isolated strain TYGF10-2F9, such as IAA-producing ability, phosphate-solubilizing ability, ACC-producing ability and siderophore-producing ability. By constructing the IAA standard curve (Fig. 3), it was determined that the strain TYGF10-2F9 could produce 5.97 μg/mL IAA under the condition of 100 μg/mL; it had the ability to produce siderophore (Table 2), but did not have the ability to dissolve phosphorus, potassium, Nitrogen fixation and ACC production capacity (Table 2).
表2菌株TYGF10-2F9促生特性评价Table 2 Evaluation of growth-promoting properties of strain TYGF10-2F9
实施例4菌株TYGF10-2F9生物膜形成测定Example 4 Biofilm formation assay of strain TYGF10-2F9
挑取单菌落接种于盛装有100mL LB液体培养基的250mL锥形瓶中,于160rpm/min、30℃条件下过夜培养。在16孔板中分别加入200μL LB、LBG(含有1%甘油(v/v))、LBM(含有0.1mM MnSO4)和LBGM(含有1%甘油(v/v)和0.1mM MnSO4)培养基,取2μL过夜培养的菌液轻轻滴加于不同培养基的液面上,16孔板于30℃条件下静置培养3d,观察生物膜形成情况,并记录。A single colony was picked and inoculated into a 250 mL conical flask containing 100 mL of LB liquid medium, and cultured overnight at 160 rpm/min and 30°C. 200 μL of LB, LBG (containing 1% glycerol (v/v)), LBM (containing 0.1 mM MnSO4 ) and LBGM (containing 1% glycerol (v/v) and 0.1 mM MnSO4 ) were added to the 16-well plate, respectively. Take 2 μL of the overnight cultured bacterial solution and gently drop it on the liquid surface of different media, and incubate the 16-well plate at 30 °C for 3 d to observe the biofilm formation and record.
菌株TYGF10-2F9的生物膜测定结果表明:该菌株在LBGM培养基中可形成明显的生物膜,培养基LBG次之,LBG和LB培养基中无明显生物膜的形成(图4)。The biofilm assay results of strain TYGF10-2F9 showed that the strain could form obvious biofilm in LBGM medium, followed by LBG medium, and no obvious biofilm formation in LBG and LB medium (Fig. 4).
实施例5菌株TYGF10-2F9对油菜菌核病的盆栽防效测定Example 5 Determination of pot-plant control effect of strain TYGF10-2F9 against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum
首先将-80℃保存的菌株于LB固体培养基(胰蛋白胨10g、酵母浸粉5g、NaCl 10g、琼脂20g、蒸馏水1000mL、PH=7.2-7.4)上进行划线,于28℃恒温箱中培养24h活化。然后将活化后的菌株接种一菌针于盛装有100mL LB液体培养基(胰蛋白胨10g、酵母浸粉5g、NaCl10g、蒸馏水1000mL、PH=7.2-7.4))的250mL的锥形瓶中。于160rpm/min、28℃条件下振荡培养48h,将发酵液在10000g条件下离心5min,上清液即为去菌体发酵液,菌体用等量无菌水重悬得到菌悬液。菌悬液和发酵液保存于4℃冰箱备用。First streak the strains stored at -80°C on LB solid medium (10g tryptone, 5g yeast extract, 10g NaCl, 20g agar, 1000mL distilled water, PH=7.2-7.4), and cultivate in a 28°C incubator 24h activation. Then the activated strain was inoculated into a 250 mL conical flask containing 100 mL of LB liquid medium (10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of NaCl, 1000 mL of distilled water, PH=7.2-7.4)). Shake culture at 160rpm/min and 28°C for 48h, centrifuge the fermentation broth at 10000g for 5min, the supernatant is the cell-free fermentation broth, and the cells are resuspended with an equal amount of sterile water to obtain a bacterial suspension. The bacterial suspension and fermentation broth were stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use.
分别用小喷壶将菌株发酵液和菌悬液(108CFU/mL)均匀喷洒在油菜幼苗叶片表面,稍干后接种直径为3mm的油菜菌核病菌的菌丝块,以喷洒500μg/mL多菌灵的处理为药剂对照。每处理重复2盆,每盆1株幼苗,每株幼苗选择大小相近的2个叶片,每个叶片中央用灭菌后的注射器针头刺伤后再进行接种。接种后,20℃保湿培养3d后测定病斑直径,计算抑制率。The bacterial strain fermentation broth and bacterial suspension (108 CFU/mL) were evenly sprayed on the surface of the leaves of rape seedlings with a small watering can respectively, and after a little drying, inoculated with the mycelial block of rape sclerotiorum with a diameter of 3 mm, and sprayed more than 500 μg/mL. The treatment of bacteriostat was the drug control. Each treatment was repeated in 2 pots, with 1 seedling in each pot, and 2 leaves of similar size were selected for each seedling, and the center of each leaf was stabbed with a sterilized syringe needle before inoculation. After inoculation, the lesion diameter was measured after 3 days of moisturizing at 20°C, and the inhibition rate was calculated.
抑制率=(对照病斑直径-处理病斑直径)/对照病斑直径×100%Inhibition rate=(control lesion diameter-treated lesion diameter)/control lesion diameter×100%
对具有广谱活性的菌株TYGF10-2F9进行油菜菌核病的盆栽防效评价。结果表明,菌株TYGF10-2F9菌体对油菜菌核无显著活性(IR=2.69%),发酵液对油菜菌核防效(IR=80.99%)显著高于药剂对照多菌灵的防效(IR=64.91%)(图5和图6)。The pot-plant control effect of rape sclerotinia was evaluated on the strain TYGF10-2F9 with broad-spectrum activity. The results showed that the strain TYGF10-2F9 had no significant activity (IR=2.69%) on the sclerotium of rapeseed, and the control effect (IR=80.99%) of the fermentation broth on the sclerotium of rapeseed was significantly higher than that of the control carbendazim (IR=80.99%). = 64.91%) (Fig. 5 and Fig. 6).
实施例6菌株TYGF10-2F9对黄瓜枯萎病的盆栽防效测定Example 6 Determination of potted control effect of strain TYGF10-2F9 on cucumber fusarium wilt
首先将-80℃保存的菌株于LB固体培养基(胰蛋白胨10g、酵母浸粉5g、NaCl 10g、琼脂20g、蒸馏水1000mL、PH=7.2-7.4)上进行划线,于28℃恒温箱中培养24h活化。然后将活化后的菌株接种一菌针于盛装有100mL LB液体培养基(胰蛋白胨10g、酵母浸粉5g、NaCl10g、蒸馏水1000mL、PH=7.2-7.4))的250mL的锥形瓶中。于160rpm/min、28℃条件下振荡培养48h,将发酵液在10000g条件下离心5min,上清液即为去菌体发酵液,菌体用等量无菌水重悬得到菌悬液。菌悬液和发酵液保存于4℃冰箱备用。First streak the strains stored at -80°C on LB solid medium (10g tryptone, 5g yeast extract, 10g NaCl, 20g agar, 1000mL distilled water, PH=7.2-7.4), and cultivate in a 28°C incubator 24h activation. Then the activated strain was inoculated into a 250 mL conical flask containing 100 mL of LB liquid medium (10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of NaCl, 1000 mL of distilled water, PH=7.2-7.4)). Shake culture at 160rpm/min and 28°C for 48h, centrifuge the fermentation broth at 10,000g for 5min, the supernatant is the cell-free fermentation broth, and the cells are resuspended with an equal amount of sterile water to obtain a bacterial suspension. The bacterial suspension and fermentation broth were stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use.
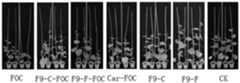
将黄瓜种子播种在育苗盘中进行育苗,育苗一周后,移栽到苗盆中,每盆一株幼苗。移栽后,待黄瓜生长至2叶一心期,采用灌根法进行防效测定试验。试验处理包括:1)只接种25mL黄瓜枯萎和等量无菌水(FOC);2)同时接种25mL黄瓜枯萎和等量的菌悬液(108CFU/mL)(F9-C-FOC);3)同时接种25mL黄瓜枯萎和等量的无菌体发酵液(F9-F-FOC);4)只接种菌悬液(108CFU/mL)(F9-C);5)只接种无菌体发酵液(F9-F);6)同时接种25mL黄瓜枯萎和等量的多菌灵药剂(500μg/mL)(Car.)和7)接种25mL无菌水(CK)。每个处理重复4次。接种一个月后进行病情指数、株高、鲜重的统计,并根据病情指数计算防效。The cucumber seeds were sown in seedling trays for seedling raising, and after one week of seedling raising, they were transplanted into seedling pots, one seedling per pot. After transplanting, when the cucumber grew to the 2-leaf and one-heart stage, the control effect was measured by the root irrigation method. The experimental treatments included: 1) only inoculate 25 mL of withered cucumber and an equal volume of sterile water (FOC); 2) simultaneously inoculate 25 mL of withered cucumber and an equal amount of bacterial suspension (108 CFU/mL) (F9-C-FOC); 3) Simultaneously inoculate 25 mL of cucumber withered and the same amount of sterile body fermentation broth (F9-F-FOC); 4) Only inoculate the bacterial suspension (108 CFU/mL) (F9-C); 5) Only inoculate sterile Body fermentation broth (F9-F); 6) Simultaneously inoculate 25 mL of cucumber wilt and an equal amount of carbendazim (500 μg/mL) (Car.) and 7) inoculate 25 mL of sterile water (CK). Each treatment was repeated 4 times. One month after inoculation, the disease index, plant height and fresh weight were counted, and the control effect was calculated according to the disease index.
黄瓜枯萎病情指数:Cucumber wilting disease index:
0级:无病症;Level 0: no symptoms;
1级:植株1/4以下的叶面表现出萎焉症状,茎基部无症状,植株正常生长;Grade 1: The leaves below 1/4 of the plant show wilting symptoms, the base of the stem is asymptomatic, and the plant grows normally;
2级:植株1/4-1/2叶面表现出萎焉症状,茎基部1/2以下出现褐变,植株矮化;Grade 2: 1/4-1/2 of the plant shows wilting symptoms on the leaves, browning below 1/2 of the stem base, and dwarfing of the plant;
3级:植株1/2以上叶面表现出萎焉症状,茎基部1/2以上出现褐变,植株明显矮化;Grade 3: more than half of the plant shows wilting symptoms on the leaves, more than 1/2 of the stem base shows browning, and the plant is obviously dwarfed;
4级:全株萎焉死亡。Level 4: The whole plant wilts and dies.
表3菌株TYGF10-2F9对黄瓜枯萎病的防病促生效果Table 3 The disease prevention and growth promotion effect of strain TYGF10-2F9 on cucumber fusarium wilt
菌株TYGF10-2F9菌体和发酵液对黄瓜枯萎病具有显著的防效,防效分别为66.67%和66.67%,均高于药剂对照多菌灵的防效(50.00%)(表3,图7)。此外,与空白对照相比,菌株TYGF10-2F9发酵液处理叶绿素含量(28.68),显著高于对照叶绿素含量(26.60),而菌体处理较对照低;菌株TYGF10-2F9发酵液处理黄瓜植株株高(67.25cm)显著高于对照株高(64.45cm),而菌体处理与对照无显著差异(64.13cm);菌株TYGF10-2F9菌体和发酵液处理黄瓜植株茎粗均高于空白对照黄瓜植株茎粗(4.35cm),分别为4.94cm和4.63cm;菌株TYGF10-2F9菌体和发酵液处理黄瓜植株鲜重显著高于空白对照黄瓜植株鲜重(17.62g),分别为21.67g和21.27g;菌株TYGF10-2F9菌体和发酵液处理黄瓜植株干重均高于空白对照黄瓜植株的干重(2.12g),分别为2.49g和2.37g。可见菌株TYGF10-2F9菌体和发酵液对黄瓜植株具有一定的促生作用(表3)。Strain TYGF10-2F9 cells and fermentation broth have significant control effects on cucumber Fusarium wilt, with control effects of 66.67% and 66.67%, respectively, which are higher than the control effect of drug control carbendazim (50.00%) (Table 3, Figure 7 ). In addition, compared with the blank control, the chlorophyll content of strain TYGF10-2F9 fermentation broth treatment (28.68) was significantly higher than the control chlorophyll content (26.60), while the bacterial cell treatment was lower than the control; strain TYGF10-2F9 fermentation broth treated cucumber plant height (67.25cm) was significantly higher than the control plant height (64.45cm), while there was no significant difference between the cell treatment and the control (64.13cm); the stem diameter of cucumber plants treated with strain TYGF10-2F9 cells and fermentation broth were higher than those in the blank control cucumber plants Stem diameters (4.35cm) were 4.94cm and 4.63cm, respectively; the fresh weight of cucumber plants treated with strain TYGF10-2F9 cells and fermentation broth was significantly higher than that of blank control cucumber plants (17.62g), 21.67g and 21.27g, respectively The dry weight of cucumber plants treated with strain TYGF10-2F9 and fermentation broth was higher than that of blank control cucumber plants (2.12g), which were 2.49g and 2.37g, respectively. It can be seen that the bacterial cells and fermentation broth of strain TYGF10-2F9 have a certain growth-promoting effect on cucumber plants (Table 3).
以上结合附图详细描述了本公开的优选实施方式,但是,本公开并不限于上述实施方式中的具体细节,在本公开的技术构思范围内,可以对本公开的技术方案进行多种简单变型,这些简单变型均属于本公开的保护范围。The preferred embodiments of the present disclosure have been described above in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. However, the present disclosure is not limited to the specific details of the above-mentioned embodiments. Various simple modifications can be made to the technical solutions of the present disclosure within the scope of the technical concept of the present disclosure. These simple modifications all fall within the protection scope of the present disclosure.
另外需要说明的是,在上述具体实施方式中所描述的各个具体技术特征,在不矛盾的情况下,可以通过任何合适的方式进行组合,为了避免不必要的重复,本公开对各种可能的组合方式不再另行说明。In addition, it should be noted that the various specific technical features described in the above-mentioned specific embodiments can be combined in any suitable manner unless they are inconsistent. In order to avoid unnecessary repetition, the present disclosure provides The combination method will not be specified otherwise.
此外,本公开的各种不同的实施方式之间也可以进行任意组合,只要其不违背本公开的思想,其同样应当视为本公开所公开的内容。In addition, the various embodiments of the present disclosure can also be arbitrarily combined, as long as they do not violate the spirit of the present disclosure, they should also be regarded as the contents disclosed in the present disclosure.
Claims (7)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110093588.XACN112680382B (en) | 2021-01-22 | 2021-01-22 | Bacillus belgii and application thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110093588.XACN112680382B (en) | 2021-01-22 | 2021-01-22 | Bacillus belgii and application thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112680382A CN112680382A (en) | 2021-04-20 |
| CN112680382Btrue CN112680382B (en) | 2022-06-28 |
Family
ID=75459041
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110093588.XAActiveCN112680382B (en) | 2021-01-22 | 2021-01-22 | Bacillus belgii and application thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112680382B (en) |
Families Citing this family (27)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111394281B (en)* | 2020-04-16 | 2022-08-23 | 山东省科学院生态研究所 | Bacillus belgii BV03 microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN113416104A (en)* | 2021-06-10 | 2021-09-21 | 中国农业科学院油料作物研究所 | Spraying type preparation for biologically preventing sclerotinia and promoting high yield of rape and preparation method thereof |
| CN113403211B (en)* | 2021-06-16 | 2022-02-01 | 青岛农业大学 | Hansenula polymorpha MP1861 with bacteriostatic effect on grape juice and application thereof |
| CN113717901B (en)* | 2021-09-30 | 2023-06-30 | 中国农业科学院蔬菜花卉研究所 | Bacillus bailii and application thereof in preventing and controlling various vegetable diseases |
| CN114395504A (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2022-04-26 | 内蒙古农业大学 | Biocontrol strain for antagonizing phytopathogens and application thereof |
| CN113969254B (en)* | 2021-12-07 | 2023-05-26 | 山东农业大学 | Sesbania endophytic bacillus ZH60, composite microbial inoculant and corn seed culture method |
| CN114317371B (en)* | 2022-01-12 | 2024-05-07 | 中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所 | Rice blast biocontrol growth promoting bacteria and application thereof |
| CN114437972A (en)* | 2022-01-26 | 2022-05-06 | 云南农业大学 | Application of Bacillus beleisi YC89 or metabolite thereof in promoting plant growth |
| CN114854618B (en)* | 2022-03-02 | 2024-06-18 | 上海交通大学 | A strain of Bacillus Velezii SF327 and its application |
| CN114806925B (en)* | 2022-03-15 | 2023-09-22 | 中国农业大学 | A strain of Bacillus belleis and its application |
| CN114891674B (en)* | 2022-05-07 | 2023-09-19 | 浙江大学 | Bacillus belicus for preventing and treating vegetable sclerotinia and application thereof |
| CN115820461B (en)* | 2022-08-11 | 2024-02-02 | 上海市农业科学院 | High-yield indoleacetic acid strain JB0319 and application thereof |
| CN115819150A (en)* | 2022-09-05 | 2023-03-21 | 元泰丰(包头)生物科技有限公司 | A special fertilizer for improving apple fruit and yield |
| CN115786172B (en)* | 2022-09-19 | 2023-12-19 | 许耀鹏 | A strain of Bacillus veleis and its composition and application |
| CN115975864B (en)* | 2022-11-04 | 2024-10-25 | 黄山学院 | Endogenous Bacillus Velezii from Atractylodes macrocephala, screening method and application thereof |
| CN115572702B (en)* | 2022-11-24 | 2023-03-21 | 云南省农业科学院农业环境资源研究所 | Bacillus belgii, microbial inoculum and biological agent and application thereof |
| CN115786212B (en)* | 2022-12-21 | 2024-05-28 | 中国科学院东北地理与农业生态研究所 | A biocontrol and growth-promoting bacterium for root rot of Atractylodes lancea and its application |
| CN115786218B (en)* | 2023-01-05 | 2024-06-25 | 东北林业大学 | Bacillus bailii and application thereof |
| CN116333927A (en)* | 2023-02-24 | 2023-06-27 | 中国农业科学院植物保护研究所 | Bacillus bailii and application thereof in control of melon bacterial fruit blotch |
| CN116731932B (en)* | 2023-07-20 | 2024-01-23 | 中国农业科学院郑州果树研究所 | A strain of Bacillus veleis NBT78-2 and its application |
| CN117551572B (en)* | 2023-11-13 | 2024-10-22 | 内蒙古农业大学 | Bacillus bailii CMC-3, application thereof and biocontrol microbial agent |
| CN117535196A (en)* | 2023-12-01 | 2024-02-09 | 淮北师范大学 | Bacillus bailii and application thereof |
| CN118126903B (en)* | 2024-04-19 | 2024-10-18 | 青岛农业大学 | A multifunctional acid-resistant and alkali-producing Bacillus velez, its microbial agent and its application |
| CN118546816B (en)* | 2024-04-19 | 2025-04-11 | 贵州大学 | Bacillus Velez and its application |
| CN118345014B (en)* | 2024-06-12 | 2024-08-30 | 潍坊学院 | Bacillus belicus and application thereof |
| CN118716143A (en)* | 2024-07-19 | 2024-10-01 | 浙江大学 | A method for improving the vitality of crop seeds and its application |
| CN119506128A (en)* | 2024-10-31 | 2025-02-25 | 四川省农业科学院植物保护研究所 | Bacillus Velez and its application |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20120051284A (en)* | 2010-11-12 | 2012-05-22 | 한국화학연구원 | Promotion of nitrogen mineralization of organic fertilizers and control of plant diseases using bacillus velezensis krict934 |
| CN111394281A (en)* | 2020-04-16 | 2020-07-10 | 山东省科学院生态研究所 | Bacillus belgii BV03 microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN111690572A (en)* | 2020-07-15 | 2020-09-22 | 西北农林科技大学 | Bacillus belgii and application and preparation thereof |
- 2021
- 2021-01-22CNCN202110093588.XApatent/CN112680382B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR20120051284A (en)* | 2010-11-12 | 2012-05-22 | 한국화학연구원 | Promotion of nitrogen mineralization of organic fertilizers and control of plant diseases using bacillus velezensis krict934 |
| CN111394281A (en)* | 2020-04-16 | 2020-07-10 | 山东省科学院生态研究所 | Bacillus belgii BV03 microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN111690572A (en)* | 2020-07-15 | 2020-09-22 | 西北农林科技大学 | Bacillus belgii and application and preparation thereof |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Genomic Insights Into the Antifungal Activity and Plant Growth-Promoting Ability in Bacillus velezensis CMRP 4490;Gustavo Manoel Teixeira et al.;《Frontiers in Microbiology》;20210115;第11卷;第1-14页* |
| 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌3A3-15生防和促生机制;刘雪娇等;《河北大学学报(自然科学版)》;20191231;第39卷(第3期);第302-310页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112680382A (en) | 2021-04-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112680382B (en) | Bacillus belgii and application thereof | |
| CN112680381B (en) | A strain of Paenibacillus polymyxa and its application | |
| CN112646755B (en) | Bacillus tequilensis and application thereof | |
| CN111088191B (en) | A kind of Bacillus and Trichoderma co-cultivation method and application | |
| CN102485880B (en) | A strain of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and its application | |
| CN108102991B (en) | One plant of Bei Laisi bacillus and its application in prevention and treatment watermelon blight | |
| CN102851243A (en) | Paenibacillus polymyxa and applications thereof | |
| CN112899205B (en) | A strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa MN225969 and its application | |
| CN116286500B (en) | Salt-tolerant bacillus bailii grown in halophytes and application thereof | |
| CN105886428A (en) | Streptomyces albidoflavus and applications thereof in microbial fertilizers | |
| CN104762223A (en) | Bacillus amyloliquefaciense BA-KA3 and application thereof | |
| CN105734000A (en) | Paenibacillus polymyxa NSY50 with capabilities of promoting growth and preventing diseases | |
| CN105018366A (en) | Bacillus methylotrophicus and application thereof | |
| CN104651260A (en) | Brevibacillus brevis BBC-3 and application thereof as well as preparation method of microbial inoculum of brevibacillus brevis | |
| CN107099474A (en) | A kind of Pseudomonas chlororaphis and its application with broad spectrum antibiotic activity | |
| CN113699065A (en) | Bacillus vallismortis and application thereof | |
| CN116515691A (en) | A kind of Bacillus Velez LG001 and its application | |
| KR20080045346A (en) | Novel Bacillus subtilis M27 strain and method for controlling plant fungal disease comprising the active ingredient | |
| CN105123763A (en) | Applications of bacillus subtilis fermentation broth, microbial fungicide containing bacillus subtilis, and preparation method of microbial fungicide | |
| CN116445354A (en) | Pseudomonas friedrisburgh and application thereof in disease prevention | |
| CN114836345B (en) | Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HZ11-4 and application thereof | |
| CN119372083A (en) | A strain of Bacillus pumilus WYH-1275 and its application in plant disease prevention and growth promotion | |
| CN108441453B (en) | Saraca pseudomonas with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and application thereof | |
| CN119410517A (en) | Bacillus, biocontrol agent made from the bacillus and application thereof | |
| CN107058180B (en) | Bacillus subtilis strain, microbial inoculum and preparation method and application of endophytic bacteria in alpine grassland |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |