CN112655211B - Image coding and decoding method and device - Google Patents
Image coding and decoding method and deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112655211B CN112655211BCN202080004809.5ACN202080004809ACN112655211BCN 112655211 BCN112655211 BCN 112655211BCN 202080004809 ACN202080004809 ACN 202080004809ACN 112655211 BCN112655211 BCN 112655211B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- pixel value
- threshold
- value
- normalized
- pixel
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/10—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding
- H04N19/134—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the element, parameter or criterion affecting or controlling the adaptive coding
- H04N19/136—Incoming video signal characteristics or properties
- H04N19/14—Coding unit complexity, e.g. amount of activity or edge presence estimation
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/10—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding
- H04N19/169—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the coding unit, i.e. the structural portion or semantic portion of the video signal being the object or the subject of the adaptive coding
- H04N19/182—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the coding unit, i.e. the structural portion or semantic portion of the video signal being the object or the subject of the adaptive coding the unit being a pixel
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/10—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding
- H04N19/169—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the coding unit, i.e. the structural portion or semantic portion of the video signal being the object or the subject of the adaptive coding
- H04N19/186—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals using adaptive coding characterised by the coding unit, i.e. the structural portion or semantic portion of the video signal being the object or the subject of the adaptive coding the unit being a colour or a chrominance component
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/42—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals characterised by implementation details or hardware specially adapted for video compression or decompression, e.g. dedicated software implementation
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N19/00—Methods or arrangements for coding, decoding, compressing or decompressing digital video signals
- H04N19/44—Decoders specially adapted therefor, e.g. video decoders which are asymmetric with respect to the encoder
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04N—PICTORIAL COMMUNICATION, e.g. TELEVISION
- H04N5/00—Details of television systems
- H04N5/14—Picture signal circuitry for video frequency region
- H04N5/20—Circuitry for controlling amplitude response
- H04N5/202—Gamma control
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Compression Or Coding Systems Of Tv Signals (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域Technical Field
本申请涉及图像处理技术领域,特别涉及一种图像编解码方法及装置。The present application relates to the field of image processing technology, and in particular to an image encoding and decoding method and device.
背景技术Background Art
摄像头具有分辨率高、非接触被动测量、使用方便、成本低廉等特点,是自动驾驶环境感知的必备传感器。随着摄像头分辨率、帧率、采样深度等的不断提高,视频图像输出对传输带宽的需求越来越大,为了缓解传输的压力,通常采用图像编码(图像压缩)的方法来降低传输带宽需求。同时,考虑到自动驾驶安全性第一的要求,图像编码应满足自动驾驶对低时延、低复杂度的需求。Cameras have the characteristics of high resolution, non-contact passive measurement, easy use, and low cost. They are essential sensors for autonomous driving environment perception. With the continuous improvement of camera resolution, frame rate, sampling depth, etc., the demand for transmission bandwidth for video image output is increasing. In order to alleviate the pressure of transmission, image coding (image compression) is usually used to reduce the demand for transmission bandwidth. At the same time, considering the safety first requirement of autonomous driving, image coding should meet the requirements of autonomous driving for low latency and low complexity.
非线性变换作为图像编码中的重要一环,通过将图像中像素点的像素值由线性域变换到非线性域,提高编码压缩性能。因此,如何降低非线性变换的复杂度,对减小图像编码的时延具有重要意义。As an important part of image coding, nonlinear transformation improves coding compression performance by transforming the pixel values of pixels in the image from the linear domain to the nonlinear domain. Therefore, how to reduce the complexity of nonlinear transformation is of great significance to reducing the delay of image coding.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本申请提供一种图像编解码方法及装置,用以降低非线性变换的复杂度,减小图像编码的时延。The present application provides an image encoding and decoding method and device to reduce the complexity of nonlinear transformation and shorten the image encoding delay.
第一方面,本申请实施例提供一种图像编码方法,该方法可由编码设备来执行,该方法包括:编码设备确定第一图像单元,所述第一图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点,其中所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值小于或等于第一阈值,所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值大于所述第一阈值;基于第一gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值进行第一变换,得到所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;基于第一线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值进行第二变换,得到所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。可选的,所述第一图像单元为Bayer raw图像单元。In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an image encoding method, which can be executed by an encoding device, and the method includes: the encoding device determines a first image unit, the first image unit includes a first pixel and a second pixel, wherein the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel is less than or equal to a first threshold, and the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel is greater than the first threshold; based on a first gamma curve, the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel is subjected to a first transformation to obtain a third normalized pixel value of the first pixel; based on a first linear curve, the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel is subjected to a second transformation to obtain a fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel. Optionally, the first image unit is a Bayer raw image unit.
在本申请实施例中,通过引入第一线性曲线对归一化像素值大于第一阈值的第二像素点进行变换,相比于仅通过gamma曲线对图像单元中的像素点的归一化像素值进行变换,可以有效降低gamma曲线的平方和/或开方带来的运算量,或降低gamma曲线带来的显示查找表存储和查找开销,从而有效降低非线性变换的复杂度,进而减小图像编码带来的时延。In an embodiment of the present application, by introducing a first linear curve to transform the second pixel point whose normalized pixel value is greater than the first threshold, compared to only transforming the normalized pixel values of the pixel points in the image unit through the gamma curve, the amount of calculation caused by the square and/or square root of the gamma curve can be effectively reduced, or the display lookup table storage and search overhead caused by the gamma curve can be reduced, thereby effectively reducing the complexity of the nonlinear transformation and further reducing the delay caused by image encoding.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一gamma曲线为其中,x表示第一像素点的第一归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;所述第一线性曲线为y=1-b+b*x,其中,x表示第二像素点的第二归一化像素值、b为斜率、y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。可选的,所述第一阈值,b,a,γ为预设的数值。In one possible design, the first gamma curve is Wherein, x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel; the first linear curve is y=1-b+b*x, where x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel. Optionally, the first threshold, b, a, and γ are preset values.
上述设计中,引入通过坐标点(1,1)的第一线性直线对第一图像单元中归一化像素值大于第一阈值的第二像素点进行变换,可以有效降低gamma曲线的平方和/或开方带来的运算量,或降低gamma曲线带来的显示查找表存储和查找开销,从而有效降低非线性变换的复杂度,进而减小图像编码带来的时延。In the above design, a first linear straight line passing through the coordinate point (1, 1) is introduced to transform the second pixel point in the first image unit whose normalized pixel value is greater than the first threshold. This can effectively reduce the amount of calculation caused by the square and/or square root of the gamma curve, or reduce the storage and search overhead of the display lookup table caused by the gamma curve, thereby effectively reducing the complexity of the nonlinear transformation and further reducing the delay caused by image encoding.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一线性曲线为还可以为y=1-b+b*x+c1,c1为预设值。In a possible design, the first linear curve may also be y=1-b+b*x+c1 , where c1 is a preset value.
上述设计中,通过引入c1可以进一步对第一线性曲线的输出范围进行调整,满足不同场景下非线性变换的需求。In the above design, by introducingc1 , the output range of the first linear curve can be further adjusted to meet the requirements of nonlinear transformation in different scenarios.
在一种可能的设计中,所述a不小于1,所述b不小于0.18、且不大于0.5。In a possible design, a is not less than 1, and b is not less than 0.18 and not greater than 0.5.
上述设计中,通过对斜率b和gamma曲线旋转系数a进行上述限定,可以将非线性变换对人眼视觉的影响控制在一定范围内,保证图像的视觉效果。In the above design, by limiting the slope b and the gamma curve rotation coefficient a, the influence of the nonlinear transformation on human vision can be controlled within a certain range, thereby ensuring the visual effect of the image.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值不小于0.4、且不大于0.6。可选的,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, the first threshold is not less than 0.4 and not greater than 0.6. Optionally, the first threshold is 0.5.
上述设计中,通过对第一阈值进行上述限定,可以确保有效降低gamma曲线的平方和/或开方带来的运算量,或降低gamma曲线带来的显示查找表存储和查找开销,同时避免对图像低亮部分的视觉效果产生影响。In the above design, by limiting the first threshold as above, it is possible to ensure that the amount of calculation caused by the square and/or square root of the gamma curve is effectively reduced, or the storage and search overhead of the display lookup table caused by the gamma curve is reduced, while avoiding affecting the visual effect of the low-brightness part of the image.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.0时,所述a为1.25、所述b为0.25,所述第一阈值为0.486;或,所述a为1.131、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.0, the a is 1.25, the b is 0.25, and the first threshold is 0.486; or, the a is 1.131, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
上述设计中,对参数的限定,可以实现在不同码率条件下对图像视觉效果有所提升。In the above design, the limitation of parameters can improve the visual effect of the image under different bit rate conditions.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.2时,所述a为1.096、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5;当所述γ为2.4时,所述a为1.068、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.2, the a is 1.096, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5; when the γ is 2.4, the a is 1.068, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
上述设计中,对参数的限定,可以实现在不同码率条件下对图像视觉效果有所提升。In the above design, the limitation of parameters can improve the visual effect of the image under different bit rate conditions.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一gamma曲线与所述第一线性曲线相交在所述第一阈值。In one possible design, the first gamma curve intersects the first linear curve at the first threshold.
上述设计中,第一gamma曲线与第一线性曲线相交在第一阈值,可以保证非线性变换的连续性。In the above design, the first gamma curve intersects the first linear curve at the first threshold, which can ensure the continuity of the nonlinear transformation.
在一种可能的设计中,所述归一化像素值根据预设最大的像素值m,预设最小的像素值n和像素点的像素值c确定,所述像素点的归一化像素值为c/(m-n)。可选的,所述预设最大的像素值m为图像传感器的饱和值,所述预设最小的像素值n为图像传感器的光学暗电平。In a possible design, the normalized pixel value is determined according to a preset maximum pixel value m, a preset minimum pixel value n and a pixel value c of a pixel point, and the normalized pixel value of the pixel point is c/(m-n). Optionally, the preset maximum pixel value m is a saturation value of an image sensor, and the preset minimum pixel value n is an optical dark level of an image sensor.
上述设计中,可以保证对像素点归一化像素值的准确确定。In the above design, accurate determination of the normalized pixel value of the pixel point can be guaranteed.
第二方面,本申请实施例提供一种图像解码方法,该方法可由解码设备来执行,该方法包括:确定第二图像单元,所述第二图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点,其中所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值小于或等于第二阈值,所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值大于所述第二阈值;基于第二gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值进行第一逆变换,得到所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值;基于第二线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值进行第二逆变换,得到所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值。In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an image decoding method, which can be executed by a decoding device, and the method includes: determining a second image unit, the second image unit includes a first pixel point and a second pixel point, wherein the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point is less than or equal to a second threshold, and the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point is greater than the second threshold; performing a first inverse transformation on the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point based on a second gamma curve to obtain the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point; performing a second inverse transformation on the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point based on a second linear curve to obtain the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二gamma曲线为x=(y/a)γ,其中,y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、x表示第一像素点第一归一化像素值;所述第二线性曲线为x=(y-1+b)/b,其中,y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值、b为斜率、x表示第二像素点第二归一化像素值。可选的,所述第二阈值,b,a,γ为预设的数值。In one possible design, the second gamma curve is x=(y/a)γ , where y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel; the second linear curve is x=(y-1+b)/b, where y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel. Optionally, the second threshold, b, a, γ are preset values.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二线性曲线为还可以为x=(y-1+b)/b+c2,c2为预设值。In a possible design, the second linear curve may also be x=(y-1+b)/b+c2 , where c2 is a preset value.
在一种可能的设计中,所述a不小于1,所述b不小于0.18、且不大于0.5。In a possible design, a is not less than 1, and b is not less than 0.18 and not greater than 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二阈值为所述th为预设的变换曲线选择参数。In one possible design, the second threshold is The th is a preset transformation curve selection parameter.
在一种可能的设计中,所述th不小于0.4、且不大于0.6。In a possible design, th is not less than 0.4 and not greater than 0.6.
在一种可能的设计中,所述th为0.5。In one possible design, th is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.0时,所述a为1.25、所述b为0.25,所述第二阈值为0.871;或,所述a为1.131、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.0, the a is 1.25, the b is 0.25, and the second threshold is 0.871; or, the a is 1.131, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.2时,所述a为1.096、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800;当所述γ为2.4时,所述a为1.068、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.2, the a is 1.096, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800; when the γ is 2.4, the a is 1.068, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二gamma曲线与所述第二线性曲线相交在所述第二阈值。In one possible design, the second gamma curve intersects the second linear curve at the second threshold.
上述第二方面的各种可能的设计的有益效果,可参考图像编码侧对应的描述,在此不再重复。The beneficial effects of various possible designs of the second aspect mentioned above can be referred to the corresponding description on the image encoding side, which will not be repeated here.
第三方面,本申请实施例提供一种图像编码装置,该装置具有实现上述第一方面或者第一方面的任一种可能的设计中方法的功能,所述功能可以通过软件实现,也可以通过硬件执行相应的软件实现。所述硬件或软件包括一个或多个与上述功能相对应的单元(模块),比如包括确定模块和变换模块。In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an image encoding device, which has the function of implementing the above-mentioned first aspect or any possible design method of the first aspect, and the function can be implemented by software, or can be implemented by hardware executing corresponding software. The hardware or software includes one or more units (modules) corresponding to the above-mentioned functions, such as a determination module and a transformation module.
在一个可能的设计中,该装置可以是芯片或者集成电路。In one possible design, the device may be a chip or an integrated circuit.
在一个可能的设计中,该装置包括处理器,所述处理器用于实现上述第一方面或者第一方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法的功能。该装置还可以包括存储器,所述存储器存储有可被处理器执行的用于实现上述第一方面或者第一方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法的程序或指令。In one possible design, the device includes a processor, the processor is used to implement the functions of the method described in the first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect. The device may also include a memory, the memory storing a program or instruction executable by the processor for implementing the method described in the first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect.
在一个可能的设计中,该装置可以为编码设备。In one possible design, the apparatus may be an encoding device.
第四方面,本申请实施例提供一种图像解码装置,该装置具有实现上述第二方面或者第二方面的任一种可能的设计中方法的功能,所述功能可以通过软件实现,也可以通过硬件执行相应的软件实现。所述硬件或软件包括一个或多个与上述功能相对应的单元(模块),比如包括确定模块和逆变换模块。In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an image decoding device, which has the function of implementing the above-mentioned second aspect or any possible design method of the second aspect, and the function can be implemented by software, or can be implemented by hardware executing corresponding software. The hardware or software includes one or more units (modules) corresponding to the above-mentioned functions, such as a determination module and an inverse transformation module.
在一个可能的设计中,该装置可以是芯片或者集成电路。In one possible design, the device may be a chip or an integrated circuit.
在一个可能的设计中,该装置包括处理器,所述处理器用于实现上述第二方面或者第二方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法的功能。该装置还可以包括存储器,所述存储器存储有可被处理器执行的用于实现上述第二方面或者第二方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法的程序或指令。In one possible design, the device includes a processor, the processor is used to implement the functions of the method described in the second aspect or any possible design of the second aspect. The device may also include a memory, the memory storing a program or instruction executable by the processor for implementing the method described in the second aspect or any possible design of the second aspect.
在一个可能的设计中,该装置可以为解码设备。In one possible design, the apparatus may be a decoding device.
第五方面,本申请实施例提供一种图像编解码系统,该图像编解码系统可以包括编码设备和解码设备,其中编码设备可以执行上述第一方面或者第一方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法,解码设备可以执行上述第二方面或者第二方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法。In a fifth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides an image coding and decoding system, which may include an encoding device and a decoding device, wherein the encoding device can execute the method described in the above-mentioned first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect, and the decoding device can execute the method described in the above-mentioned second aspect or any possible design of the second aspect.
第六方面,本申请实施例提供一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序或指令,当该计算机程序或指令被处理器执行时,使得处理器执行上述第一方面或第一方面的任一种可能的设计中的方法,或执行上述第二方面或第二方面的任一种可能的设计中的方法。In a sixth aspect, an embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium having a computer program or instructions stored thereon. When the computer program or instructions are executed by a processor, the processor executes the method of the first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect, or executes the second aspect or any possible design of the second aspect.
第七方面,本申请实施例还提供一种计算机程序产品,包括计算机程序或指令,当所述计算机程序或指令被处理器执行时,可以实现上述第一方面或者第一方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法,或实现上述第二方面或者第二方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法。In the seventh aspect, an embodiment of the present application also provides a computer program product, including a computer program or instructions. When the computer program or instructions are executed by a processor, it can implement the method described in the above-mentioned first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect, or implement the method described in the above-mentioned second aspect or any possible design of the second aspect.
第八方面,本申请还提供一种芯片,所述芯片用于实现上述第一方面或者第一方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法,或实现上述第二方面或者第二方面的任一种可能的设计中所述的方法。In an eighth aspect, the present application also provides a chip, wherein the chip is used to implement the method described in the above-mentioned first aspect or any possible design of the first aspect, or to implement the method described in the above-mentioned second aspect or any possible design of the second aspect.
上述第三方面至第八方面所能达到的技术效果请参照上述第一方面至第二方面所能达到的技术效果,这里不再重复赘述。The technical effects that can be achieved from the third to the eighth aspects mentioned above can refer to the technical effects that can be achieved from the first to the second aspects mentioned above, and will not be repeated here.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
图1为本申请实施例提供的业务场景示意图;FIG1 is a schematic diagram of a business scenario provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例提供的图像编解码流程示意图;FIG2 is a schematic diagram of an image encoding and decoding process provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图3为本申请实施例提供的图像编码过程示意图;FIG3 is a schematic diagram of an image encoding process provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请实施例提供的gamma曲线示意图;FIG4 is a schematic diagram of a gamma curve provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图5为本申请实施例提供的第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线示意图之一;FIG5 is one of the schematic diagrams of the first gamma curve and the first linear curve provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图6为本申请实施例提供的HLG曲线示意图;FIG6 is a schematic diagram of an HLG curve provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图7为本申请实施例提供的图像编解码中仿真效果示意图之一;FIG7 is a schematic diagram of a simulation effect in image encoding and decoding provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图8为本申请实施例提供的图像编解码中仿真效果示意图之二;FIG8 is a second schematic diagram of the simulation effect in image encoding and decoding provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图9为本申请实施例提供的第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线示意图之二;FIG9 is a second schematic diagram of a first gamma curve and a first linear curve provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图10为本申请实施例提供的第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线示意图之三;FIG10 is a third schematic diagram of a first gamma curve and a first linear curve provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图11为本申请实施例提供的图像编解码中仿真效果示意图之三;FIG11 is a third schematic diagram of the simulation effect in the image encoding and decoding provided in the embodiment of the present application;
图12为本申请实施例提供的图像编解码中仿真效果示意图之四;FIG12 is a fourth schematic diagram of the simulation effect in the image encoding and decoding provided in the embodiment of the present application;
图13为本申请实施例提供的图像解码过程示意图;FIG13 is a schematic diagram of an image decoding process provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图14为本申请实施例提供的图像编码装置示意图之一;FIG14 is a schematic diagram of an image encoding device according to an embodiment of the present application;
图15为本申请实施例提供的图像解码装置示意图之一;FIG15 is a schematic diagram of an image decoding device according to an embodiment of the present application;
图16为本申请实施例提供的图像编码装置示意图之二;FIG16 is a second schematic diagram of an image encoding device provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图17为本申请实施例提供的图像解码装置示意图之二。FIG17 is a second schematic diagram of the image decoding device provided in an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
本申请实施例所适用的业务场景可以如图1所示,摄像头在获取到贝叶尔原始(Bayer raw)图像后,需要将Bayer raw图像传输至图像信号处理(image signalprocessing,ISP)组件,对摄像头获取的原始图像(即Bayer raw图像)进行处理,得到RGB格式的图像或YUV格式的图像,以进行显示。然而在自动驾驶等环境下,通常要求摄像头输出高清图像,如果摄像头输出4K UHD 30fps 16bitdepth的Bayer raw图像,其带宽需求高达4Gbps(4K*2k*30*16)。为缓解网络传输的压力,一般采用图像编码(图像压缩)的方法来降低带宽需求,以便无需升级现有网络设施即可开展高清或超高清视频新业务。The business scenario applicable to the embodiment of the present application can be as shown in Figure 1. After the camera obtains the Bayer raw image, it needs to transmit the Bayer raw image to the image signal processing (ISP) component to process the original image (i.e., the Bayer raw image) obtained by the camera to obtain an image in RGB format or an image in YUV format for display. However, in environments such as autonomous driving, the camera is usually required to output high-definition images. If the camera outputs a 4K UHD 30fps 16bitdepth Bayer raw image, its bandwidth requirement is as high as 4Gbps (4K*2k*30*16). In order to alleviate the pressure of network transmission, image encoding (image compression) methods are generally used to reduce bandwidth requirements so that new high-definition or ultra-high-definition video services can be launched without upgrading existing network facilities.
应理解的是,本申请实施例描述的业务场景是为了更加清楚的说明本申请实施例的技术方案,并不构成对于本申请实施例提供的技术方案的限定,本领域普通技术人员可知,随着新业务场景的出现,本申请实施例提供的技术方案对于类似的技术问题,同样适用。It should be understood that the business scenarios described in the embodiments of the present application are intended to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application, and do not constitute a limitation on the technical solutions provided in the embodiments of the present application. Ordinary technicians in this field can know that with the emergence of new business scenarios, the technical solutions provided in the embodiments of the present application are also applicable to similar technical problems.
为了便于本领域技术人员理解,下面对本申请实施例中的部分用语进行解释说明。To facilitate understanding by those skilled in the art, some terms used in the embodiments of the present application are explained below.
1)、贝叶尔原始(Bayer raw)图像,也可以称为Bayer图像或raw图像。raw的原意就是“未经加工”,可以理解为:Bayer raw图像指的是CMOS或者CCD图像传感器将捕捉到的光源信号转化为数字信号的原始数据,也就是相机内部的原始图像。因此也可以把Bayer raw图像概念化为“原始图像编码数据”或更形象的称为“数字底片”。1) Bayer raw image, also known as Bayer image or raw image. The original meaning of raw is "unprocessed", which can be understood as: Bayer raw image refers to the raw data of the light source signal captured by CMOS or CCD image sensor converted into digital signal, that is, the original image inside the camera. Therefore, Bayer raw image can also be conceptualized as "raw image encoding data" or more vividly called "digital negative".
另外,在本申请实施例中,Bayer raw图像包括三个颜色分量,Bayer raw图像中的每个像素点只有一个颜色分量,该颜色分量的值可以等同于该像素点的像素值。在一种示例中,三个颜色分量分别为红色(red,R)分量、蓝色(blue,B)分量、绿色(green,G)分量。在另一种示例中,三个颜色分量分别为R分量、B分量、黄色(yellow,Y’)分量。Bayer raw图像包括哪些颜色分量,与摄像头中的颜色滤镜有关。In addition, in an embodiment of the present application, the Bayer raw image includes three color components, and each pixel in the Bayer raw image has only one color component, and the value of the color component can be equivalent to the pixel value of the pixel. In one example, the three color components are red (red, R) component, blue (blue, B) component, and green (green, G) component. In another example, the three color components are R component, B component, and yellow (yellow, Y') component. Which color components the Bayer raw image includes is related to the color filter in the camera.
2)、图像编码和图像解码,图像编码也可以称为图像压缩,指在满足一定质量(如信噪比的要求或主观评价得分)的条件下,以较少比特数表示图像或图像中所包含信息的技术。而图像解码是图像编码的逆过程。传统的图像编码压缩标准,如JPEG、H264或H265等,主要面向高压缩比低码率的应用场景,往往难以满足自动驾驶视觉感知和机器识别对低时延和低复杂度的需求。JPEG-XS是第一个面向Bayer raw图像的低时延图像编码压缩国际标准,应用场景包括摄像头内部的视频信号的压缩,自动驾驶Bayer raw视频压缩传输,高速视频存储接口压缩等。支持RGB格式/YUV格式图像压缩的JPEG-XS第一阶段工作已经完成,在视觉无损质量情况下达到压缩比6:1。目前正在开展第二阶段工作,如图2所示,JPEG-XS第二阶段标准中新引入的编码工具主要包括:非线性变换和颜色变换,引入的解码工具主要包括非线性逆变换和反颜色变换。其中,非线性变换也可以称为非线性校正,非线性逆变换是非线性变换的逆过程,也可以称为反非线性校正。非线性变换起着将图像中像素点的像素值由线性域变换到非线性域,方便后续编码工具处理的作用。本申请实施例旨在改进非线性变换和非线性逆变换的方法,以降低非线性变换和非线性逆变换的复杂度,提高图像编解码的性能,降低图像编解码的时延。2) Image coding and image decoding. Image coding can also be called image compression. It refers to the technology of representing an image or the information contained in an image with fewer bits under the condition of meeting certain quality requirements (such as signal-to-noise ratio requirements or subjective evaluation scores). Image decoding is the inverse process of image coding. Traditional image coding and compression standards, such as JPEG, H264 or H265, are mainly aimed at application scenarios with high compression ratio and low bit rate, and often cannot meet the requirements of low latency and low complexity for autonomous driving visual perception and machine recognition. JPEG-XS is the first international standard for low-latency image coding and compression for Bayer raw images. Application scenarios include compression of video signals inside cameras, Bayer raw video compression transmission for autonomous driving, and high-speed video storage interface compression. The first phase of JPEG-XS, which supports RGB format/YUV format image compression, has been completed, achieving a compression ratio of 6:1 with visual lossless quality. The second phase of work is currently underway. As shown in Figure 2, the newly introduced coding tools in the second phase of the JPEG-XS standard mainly include: nonlinear transformation and color transformation, and the introduced decoding tools mainly include nonlinear inverse transformation and inverse color transformation. Among them, nonlinear transformation can also be called nonlinear correction, and nonlinear inverse transformation is the inverse process of nonlinear transformation, which can also be called inverse nonlinear correction. Nonlinear transformation plays the role of transforming the pixel values of pixels in the image from the linear domain to the nonlinear domain, which is convenient for subsequent coding tool processing. The embodiments of the present application are intended to improve the methods of nonlinear transformation and nonlinear inverse transformation to reduce the complexity of nonlinear transformation and nonlinear inverse transformation, improve the performance of image encoding and decoding, and reduce the delay of image encoding and decoding.
另外,应理解,为了便于描述本申请实施例的技术方案,在本申请实施例中,“/”可以表示前后关联的对象是一种“或”的关系,例如,A/B可以表示A或B;“和/或”可以用于描述关联对象存在三种关系,例如,A和/或B,可以表示:单独存在A,同时存在A和B,单独存在B这三种情况,其中A,B可以是单数或者复数。在本申请实施例中所涉及的多个,是指两个或两个以上。在本申请实施例中,可以采用“第一”、“第二”等字样对功能相同或相似的技术特征进行区分。该“第一”、“第二”等字样并不对数量和执行次序进行限定,并且“第一”、“第二”等字样也并不限定一定不同。在本申请实施例中,“示例性的”或者“例如”等词用于表示例子、例证或说明,被描述为“示例性的”或者“例如”的实施例或设计方案不应被解释为比其它实施例或设计方案更优选或更具优势。使用“示例性的”或者“例如”等词旨在以具体方式呈现相关概念,便于理解。In addition, it should be understood that, in order to facilitate the description of the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present application, in the embodiments of the present application, "/" can indicate that the objects associated before and after are in an "or" relationship, for example, A/B can indicate A or B; "and/or" can be used to describe that there are three relationships between the associated objects, for example, A and/or B can indicate: A exists alone, A and B exist at the same time, and B exists alone, where A and B can be singular or plural. The multiple involved in the embodiments of the present application refers to two or more. In the embodiments of the present application, words such as "first" and "second" can be used to distinguish technical features with the same or similar functions. The words such as "first" and "second" do not limit the number and execution order, and the words such as "first" and "second" do not necessarily limit them to be different. In the embodiments of the present application, words such as "exemplary" or "for example" are used to indicate examples, illustrations or explanations, and embodiments or design schemes described as "exemplary" or "for example" should not be interpreted as being more preferred or more advantageous than other embodiments or design schemes. The use of words such as "exemplary" or "for example" is intended to present related concepts in a specific way for easy understanding.
下面将结合附图,对本申请实施例进行详细描述。The embodiments of the present application will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
图3为本申请实施例提供的一种图像编码过程示意图,该过程包括:FIG3 is a schematic diagram of an image encoding process provided by an embodiment of the present application, the process comprising:
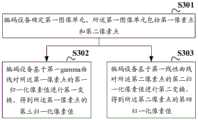
S301:编码设备确定第一图像单元,所述第一图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点。S301: The encoding device determines a first image unit, where the first image unit includes a first pixel and a second pixel.
其中,所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值小于或等于第一阈值,所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值大于所述第一阈值;或所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值小于第一阈值,所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值大于或等于所述第一阈值。Among them, the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point is less than or equal to a first threshold, and the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point is greater than the first threshold; or the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point is less than the first threshold, and the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point is greater than or equal to the first threshold.
在本申请实施例中,编码设备可以以图像单元为单位进行图像编码,在图像单元中包含一个或多个第一像素点,以及一个或多个第二像素点。具体的,图像单元可以是Bayer raw图像,也可以是Bayer raw图像中的一个图像块,本申请实施例对此不作限定。In an embodiment of the present application, the encoding device may perform image encoding in units of image units, wherein the image unit includes one or more first pixels and one or more second pixels. Specifically, the image unit may be a Bayer raw image or an image block in a Bayer raw image, which is not limited in the embodiment of the present application.
对于像素点归一化像素值的确定,在一种可能的实施中,可以根据像素点的像素值c,预设最大的像素值m以及预设的最小像素值n确定,即像素点的归一化像素值为c/(m-n)。示例的:以Bayer raw图像为RGGB格式的图像为例,Bayer raw图像中任一像素点可能是R分量对应的像素点,也可能是G分量对应的像素点,还可能是B分量对应的像素点。通常R/G/B分量对应的像素值的取值范围为0~255,也即R/G/B分量对应的预设最大像素值m通常为255,R/G/B分量对应的预设最小像素值n通常为0。假设某一像素点为R分量对应的像素点,像素点对应的像素值为102,则该像素点对应的归一化像素值为102/(255-0)=0.4。Regarding the determination of the normalized pixel value of a pixel, in a possible implementation, it can be determined according to the pixel value c of the pixel, the preset maximum pixel value m and the preset minimum pixel value n, that is, the normalized pixel value of the pixel is c/(m-n). For example: Taking the Bayer raw image in RGGB format as an example, any pixel in the Bayer raw image may be a pixel corresponding to the R component, or a pixel corresponding to the G component, or a pixel corresponding to the B component. Usually, the pixel values corresponding to the R/G/B components range from 0 to 255, that is, the preset maximum pixel value m corresponding to the R/G/B components is usually 255, and the preset minimum pixel value n corresponding to the R/G/B components is usually 0. Assuming that a certain pixel is a pixel corresponding to the R component, and the pixel value corresponding to the pixel is 102, then the normalized pixel value corresponding to the pixel is 102/(255-0)=0.4.
另外,为了对归一化像素值的准确确定,预设的最大的像素值m和预设最小的像素值n,可以根据获取图像单元的图像传感器的性能参数确定。例如:根据图像传感器的饱和值确定预设最大的像素值m;根据图像传感器的光学暗电平,确定预设最小的像素值n。示例的,对于获取RGGB格式的Bayer raw图像的图像传感器,图像传感器的饱和值为图像传感器可输出R/G/B分量的像素值的最大值,图像传感器的饱和值为图像传感器可输出R/G/B分量的像素值的最小值。In addition, in order to accurately determine the normalized pixel value, the preset maximum pixel value m and the preset minimum pixel value n can be determined according to the performance parameters of the image sensor of the image acquisition unit. For example: the preset maximum pixel value m is determined according to the saturation value of the image sensor; the preset minimum pixel value n is determined according to the optical dark level of the image sensor. For example, for an image sensor that acquires a Bayer raw image in RGGB format, the saturation value of the image sensor is the maximum value of the pixel value of the R/G/B component that the image sensor can output, and the saturation value of the image sensor is the minimum value of the pixel value of the R/G/B component that the image sensor can output.
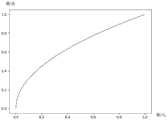
图4为现有技术中基于gamma曲线实现非线性变换的示意图,以gamma曲线γ等于2.0为例。其中横轴表示gamma曲线的输入(input),纵轴表示gamma曲线的输出(output),gamma曲线的输入和输出均为归一化的像素值。从图4中可以看出,gamma曲线在输入的信号(归一化像素值)较小时,对输入的信号放大倍数小,在输入的信号较大时,对输入的信号放大倍数小。gamma曲线实际上是对信号序列的比特(bit)重新分配,更多的bit用来表示信号的暗部,更小的bit用来表示信号的亮部。以基于gamma曲线对RGGB格式的Bayer raw图像进行变换为例,相当于对Bayer raw图像的高亮部分进行了压缩,这是利用了人眼的特性,人眼对高亮部分的变换相对并不敏感,而对低亮部分的亮度变换却相对敏感的特性。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of implementing nonlinear transformation based on a gamma curve in the prior art. Take γ equal to 2.0 as an example. The horizontal axis represents the input of the gamma curve, and the vertical axis represents the output of the gamma curve. The input and output of the gamma curve are both normalized pixel values. As can be seen from Figure 4, when the input signal (normalized pixel value) is small, the gamma curve has a small amplification factor for the input signal, and when the input signal is large, the input signal has a small amplification factor. The gamma curve is actually a reallocation of bits in the signal sequence, with more bits used to represent the dark part of the signal and smaller bits used to represent the bright part of the signal. Taking the transformation of the Bayer raw image in RGGB format based on the gamma curve as an example, it is equivalent to compressing the highlight part of the Bayer raw image. This is based on the characteristics of the human eye, which is relatively insensitive to the transformation of the highlight part, but relatively sensitive to the brightness transformation of the low-brightness part.
而基于gamma曲线实现的非线性变换,在编码侧和解码侧分别涉及平方和开方运算,尤其涉及的开方运算,会占用大量的计算资源。本申请实施例重新设计非线性变换曲线,对高亮部分进行线性化,以降低变换带来的运算量,降低对计算资源的占用量。基于此,本申请实施例中,对于第一阈值(th)的选取,可以在0.5附近选取,如在0.4至0.6之间选取,以节约一半gamma曲线带来的运算量,或节约一半gamma曲线带来的显示查找表(look-up-table,LUT)存储开销和查找开销。The nonlinear transformation based on the gamma curve involves square and square root operations on the encoding side and the decoding side, respectively, and the square root operation involved in particular will take up a lot of computing resources. The embodiment of the present application redesigns the nonlinear transformation curve and linearizes the highlighted part to reduce the amount of calculation caused by the transformation and reduce the amount of computing resources occupied. Based on this, in the embodiment of the present application, for the selection of the first threshold value (th), it can be selected near 0.5, such as between 0.4 and 0.6, to save half of the amount of calculation brought by the gamma curve, or save half of the display look-up table (look-up-table, LUT) storage overhead and search overhead brought by the gamma curve.
S302:编码设备基于第一gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值进行第一变换,得到所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值。S302: The encoding device performs a first transformation on the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point based on a first gamma curve to obtain a third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point.
S303:编码设备基于第一线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值进行第二变换,得到所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。S303: The encoding device performs a second transformation on the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point based on the first linear curve to obtain a fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point.
需要说明的是,在本申请实施例中,对S302和S303的先后顺序不作限定,可以先进行S302,也可以先进行S303,还可以同时进行S302和S303。It should be noted that in the embodiment of the present application, the order of S302 and S303 is not limited, S302 may be performed first, S303 may be performed first, or S302 and S303 may be performed simultaneously.
参照图5所示,对于第一图像单元中归一化像素值小于或等于第一阈值的第一像素点,编码设备可以基于第一gamma曲线对第一像素点的第一归一化像素值进行第一变换,得到第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;对于第一图像单元中归一化像素值大于第一阈值的第二像素点,编码设备可以基于第一线性曲线对第二像素点的第二归一化像素值进行第二变换,得到第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。As shown in Figure 5, for a first pixel point in the first image unit whose normalized pixel value is less than or equal to the first threshold, the encoding device can perform a first transformation on the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point based on the first gamma curve to obtain a third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point; for a second pixel point in the first image unit whose normalized pixel value is greater than the first threshold, the encoding device can perform a second transformation on the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point based on the first linear curve to obtain a fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point.
作为一种示例,第一gamma曲线可以为其中,x表示第一像素点的第一归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;第一线性曲线可以为y=1-b+b*x,其中,x表示第二像素点的第二归一化像素值、b为斜率、y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。As an example, the first gamma curve may be Among them, x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point; the first linear curve can be y=1-b+b*x, wherein x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point, b is the slope, and y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point.
所述第一线性曲线中还可以引入参数c1,进一步对第一线性曲线的输出范围进行调整,以满足不同场景下非线性变换的需求。即第一线性曲线为还可以为y=1-b+b*x+c1,c1为预设值。The first linear curve may also introduce a parameter c1 to further adjust the output range of the first linear curve to meet the requirements of nonlinear transformation in different scenarios. That is, the first linear curve may also be y=1-b+b*x+c1 , where c1 is a preset value.
在一种可能的实施中,为了保证非线性变换的连续性,第一gamma曲线与第一线性曲线相交在第一阈值。In a possible implementation, in order to ensure the continuity of the nonlinear transformation, the first gamma curve intersects the first linear curve at a first threshold.
对于斜率(b)的设定,可以参考gamme曲线和HLG曲线,参照图6所示,其中HLG曲线是gamma曲线和Log曲线的结合(hybrid log-gamma)。输入信号小时用gamma曲线,信号大时用对数或Log曲线。相比于标准gamma曲线,HLG曲线实现了信号的更大范围高亮部分进行了压缩,对高亮部分压缩的更厉害了。其中HLG曲线的相关参数如下:For the setting of slope (b), you can refer to the gamma curve and HLG curve, as shown in Figure 6, where the HLG curve is a combination of the gamma curve and the Log curve (hybrid log-gamma). Use the gamma curve when the input signal is small, and use the logarithmic or Log curve when the signal is large. Compared with the standard gamma curve, the HLG curve compresses a wider range of highlight parts of the signal, and compresses the highlight parts more strongly. The relevant parameters of the HLG curve are as follows:
V=a*Ln(12*LC-b)+c for 1>=LC>1÷12V=a*Ln(12*LC -b)+c for 1>=LC >1÷12
V=Sqrt(3)*LC0.5 for 1÷12>=LC>=0V=Sqrt(3)*LC0.5 for 1÷12>=LC >=0
a=0.17883277,b=0.28466892,c=0.55991073a=0.17883277, b=0.28466892, c=0.55991073
HLG曲线在输入信号为1时的斜率为0.18,此时对高亮部分的压缩,对图像性能影响较大,会较大程度的影响人眼视觉效果;gamma曲线在输入信号为1时的斜率为0.5,此时对高亮部分的压缩,对图像性能影响不大,对人眼视觉效果影响较小。因此在一种可能的实施中,直线斜率b,可以在0.18~0.5之间选取,确保对人眼视觉的影响控制在一定范围内。The slope of the HLG curve is 0.18 when the input signal is 1. At this time, the compression of the highlight part has a greater impact on the image performance and will greatly affect the visual effect of the human eye. The slope of the gamma curve is 0.5 when the input signal is 1. At this time, the compression of the highlight part has little impact on the image performance and the visual effect of the human eye. Therefore, in a possible implementation, the slope b of the straight line can be selected between 0.18 and 0.5 to ensure that the impact on the human eye's vision is controlled within a certain range.
另外,为了满足第一gamma曲线与第一线性曲线相交在0.5附近,需要对第一gamma曲线进行旋转,而gamma曲线旋转系数a大于1.0,可以使得旋转后的第一gamma曲线更加接近通常采用的γ为2.2的gamma曲线的效果(即更多的bit分配给信号的暗部)。In addition, in order to satisfy that the first gamma curve intersects the first linear curve near 0.5, the first gamma curve needs to be rotated, and the gamma curve rotation coefficient a is greater than 1.0, which can make the rotated first gamma curve closer to the effect of the commonly used gamma curve with a γ of 2.2 (that is, more bits are allocated to the dark part of the signal).
基于上述参数确定原则,对于第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线(y=1-b+b*x)中的参数γ、a、b,以及涉及的第一阈值(th)。当γ为2.0时,第一组可选的参数为:γ为2.0,a为1.25、b为0.25,th为0.486;第二组可选的参数为:γ为2.0,a为1.131、b为0.4,th为0.5。Based on the above parameter determination principle, for the first gamma curve and the parameters γ, a, b in the first linear curve (y=1-b+b*x), and the first threshold (th). When γ is 2.0, the first set of optional parameters is: γ is 2.0, a is 1.25, b is 0.25, and th is 0.486; the second set of optional parameters is: γ is 2.0, a is 1.131, b is 0.4, and th is 0.5.
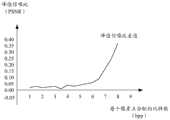
如图7所示,为采用第一组可选参数的仿真测试结果。横轴为每个像素点在编码时分配的比特数(bit per pixel,bpp),相当于码率大小;纵轴为峰值信噪比(peak signalto noise ratio,PSNR),PSNR为图像质量衡量指标,其数值越大越好。图7中曲线表示PSNR的差值,PSNR的差值为负数表示性能有损失,PSNR的差值为正数表示性能有提升。如图7所示,可见在低码率时,图像性能有一定损失,在高码率时,图像性能有提升。As shown in Figure 7, it is the simulation test result using the first set of optional parameters. The horizontal axis is the number of bits (bit per pixel, bpp) allocated to each pixel during encoding, which is equivalent to the bit rate; the vertical axis is the peak signal to noise ratio (PSNR), which is an indicator of image quality. The larger the value, the better. The curve in Figure 7 represents the difference in PSNR. A negative difference in PSNR indicates performance loss, and a positive difference in PSNR indicates performance improvement. As shown in Figure 7, it can be seen that at low bit rates, the image performance has a certain loss, and at high bit rates, the image performance is improved.
如图8所示,为采用第二组可选参数的仿真测试结果。横轴为每个像素点在编码时分配的比特数(bpp),相当于码率大小;纵轴为峰值信噪比(PSNR),PSNR为图像质量衡量指标,其数值越大越好。图8中曲线表示PSNR的差值,PSNR的差值为负数表示性能有损失,PSNR的差值为正数表示性能有提升。如图8所示,可见在整个测试码率范围内,图像性能均有提升。As shown in Figure 8, it is the simulation test result using the second set of optional parameters. The horizontal axis is the number of bits (bpp) allocated to each pixel during encoding, which is equivalent to the bit rate; the vertical axis is the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), which is an indicator of image quality. The larger the value, the better. The curve in Figure 8 represents the difference in PSNR. A negative difference in PSNR indicates a loss in performance, and a positive difference in PSNR indicates an improvement in performance. As shown in Figure 8, it can be seen that the image performance is improved in the entire test bit rate range.
另外,在非线性变换在实现时,往往采用查找显示查找表(LUT)的方法,确定每个输入值对应的输出值,而不是采用直接计算的方法。这种场景下,我们可以优化γ取值,来获得更好的性能。同时对高亮部分进行线性化,减少LUT大小,及查找LUT的开销。具体的,可以将γ的取值,设置为现实常用的取值,如2.2或2.4。可以进一步改善非线性变换的效果,提升编码压缩性能。同时设计th值在0.5附近,仍然保证LUT大小减半,降低存储开销与查找开销。基于此,当γ为2.2时,如图9所示,第三组可选的参数为:γ为2.2,a为1.096、b为0.4,th为0.5;如图10所示,当γ为2.2时,第四组可选的参数为:γ为2.4,a为1.068、b为0.4,th为0.5。In addition, when implementing nonlinear transformation, the method of looking up the display lookup table (LUT) is often used to determine the output value corresponding to each input value, rather than using a direct calculation method. In this scenario, we can optimize the γ value to obtain better performance. At the same time, the highlight part is linearized to reduce the LUT size and the overhead of looking up the LUT. Specifically, the value of γ can be set to a commonly used value in reality, such as 2.2 or 2.4. The effect of nonlinear transformation can be further improved and the encoding compression performance can be improved. At the same time, the th value is designed to be around 0.5, which still ensures that the LUT size is halved and the storage overhead and search overhead are reduced. Based on this, when γ is 2.2, as shown in Figure 9, the third group of optional parameters is: γ is 2.2, a is 1.096, b is 0.4, and th is 0.5; as shown in Figure 10, when γ is 2.2, the fourth group of optional parameters is: γ is 2.4, a is 1.068, b is 0.4, and th is 0.5.
在采用第三组参数和第四组参数的情况下,相比第一组参数和第二组参数的情况下,因为γ值变大了,在交点处的第一gamma曲线的斜率变小了,更接近第一线性直线的斜率,第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线的过度更加平缓,有助于减少非线性映射过程中的引入的突变现象。When the third and fourth groups of parameters are used, compared with the first and second groups of parameters, because the γ value becomes larger, the slope of the first gamma curve at the intersection becomes smaller and closer to the slope of the first linear line, the transition between the first gamma curve and the first linear curve is smoother, which helps to reduce the mutation phenomenon introduced in the nonlinear mapping process.
如图11所示,为采用第三组可选参数的仿真测试结果。横轴为每个像素点在编码时分配的比特数(bpp),相当于码率大小;纵轴为峰值信噪比(PSNR),PSNR为图像质量衡量指标,其数值越大越好。图11中曲线表示PSNR的差值,PSNR的差值为负数表示性能有损失,PSNR的差值为正数表示性能有提升。如图11所示,第三组参数对应的仿真效果,在低码率范围内相比于第一组参数和第二组参数,带来了图像性能提升。As shown in Figure 11, it is the simulation test result using the third set of optional parameters. The horizontal axis is the number of bits (bpp) allocated to each pixel during encoding, which is equivalent to the bit rate; the vertical axis is the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), which is an indicator of image quality. The larger the value, the better. The curve in Figure 11 represents the difference in PSNR. A negative difference in PSNR indicates a performance loss, and a positive difference in PSNR indicates an improvement in performance. As shown in Figure 11, the simulation effect corresponding to the third set of parameters has brought about an improvement in image performance compared to the first and second sets of parameters in the low bit rate range.
如图12所示,为采用第四组可选参数的仿真测试结果。横轴为每个像素点在编码时分配的比特数(bpp),相当于码率大小;纵轴为峰值信噪比(PSNR),PSNR为图像质量衡量指标,其数值越大越好。图12中曲线表示PSNR的差值1PSNR的差值为负数表示性能有损失,PSNR的差值为正数表示性能有提升。如图12所示,第四组参数对应的仿真效果,在测试码率范围内均带来了一定图像性能提升。同时相比于第三组参数,进一步在低码率范围带来了图像性能提升。As shown in Figure 12, it is the simulation test result using the fourth set of optional parameters. The horizontal axis is the number of bits (bpp) allocated to each pixel during encoding, which is equivalent to the bit rate; the vertical axis is the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR). PSNR is an indicator of image quality, and the larger the value, the better. The curve in Figure 12 represents the difference of PSNR. A negative difference of PSNR indicates performance loss, and a positive difference of PSNR indicates performance improvement. As shown in Figure 12, the simulation effect corresponding to the fourth set of parameters has brought about a certain improvement in image performance within the test bit rate range. At the same time, compared with the third set of parameters, it further brings about image performance improvement in the low bit rate range.
接下来如图13所示,为本申请实施例提供的一种解码过程示意图,该过程包括:Next, as shown in FIG. 13 , a schematic diagram of a decoding process provided in an embodiment of the present application is shown, and the process includes:
S1301:解码设备确定第二图像单元,所述第二图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点。S1301: The decoding device determines a second image unit, where the second image unit includes a first pixel and a second pixel.
其中,所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值小于或等于第二阈值,所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值大于所述第二阈值;或所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值小于第二阈值,所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值大于或等于所述第二阈值。Among them, the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point is less than or equal to the second threshold, and the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point is greater than the second threshold; or the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point is less than the second threshold, and the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point is greater than or equal to the second threshold.
在本申请实施例中,第二图像单元是指经过非线性变换后的第一图像单元,示例的,参照图3所示,第一图像单元进行如图3所示的编码过程即可获得第二图像单元。In the embodiment of the present application, the second image unit refers to the first image unit after nonlinear transformation. For example, referring to FIG. 3 , the first image unit can be encoded by the encoding process shown in FIG. 3 to obtain the second image unit.
在解码侧实现的非线性逆变换,可以理解为是编码侧实现的非线性变换的逆过程,因此,对于第二阈值的选取,可以根据编码侧第一阈值的选取进行确定。例如:可以将第一阈值代入编码侧进行非线性变换的第一gamma曲线或第一线性曲线中,根据第一阈值变换后得到的值,确定第二阈值。The nonlinear inverse transformation implemented on the decoding side can be understood as the inverse process of the nonlinear transformation implemented on the encoding side. Therefore, the selection of the second threshold can be determined according to the selection of the first threshold on the encoding side. For example, the first threshold can be substituted into the first gamma curve or the first linear curve for nonlinear transformation on the encoding side, and the second threshold is determined according to the value obtained after the first threshold transformation.
S1302:解码设备基于第二gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值进行第一逆变换,得到所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值。S1302: The decoding device performs a first inverse transformation on the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel point based on a second gamma curve to obtain a first normalized pixel value of the first pixel point.
S1303:解码设备基于第二线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值进行第二逆变换,得到所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值。S1303: The decoding device performs a second inverse transformation on the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel point based on a second linear curve to obtain a second normalized pixel value of the second pixel point.
需要说明的是,在本申请实施例中,对S1302和S1303的先后顺序不作限定,可以先进行S1302,也可以先进行S1303,还可以同时进行S1302和S1303。It should be noted that in the embodiment of the present application, the order of S1302 and S1303 is not limited, and S1302 may be performed first, or S1303 may be performed first, or S1302 and S1303 may be performed simultaneously.
作为一种示例,第二gamma曲线可以为x=(y/a)γ,其中,y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、x表示第一像素点第一归一化像素值;第二线性曲线可以为x=(y-1+b)/b,其中,y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值、b为斜率、x表示第二像素点第二归一化像素值。As an example, the second gamma curve can be x=(y/a)γ , where y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel; the second linear curve can be x=(y-1+b)/b, where y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
所述第二线性曲线中还可以引入参数c2,进一步对第二线性曲线的输出范围进行调整,以满足不同场景下非线性变换的需求。即第二线性曲线为还可以为x=(y-1+b)/b+c2,c2为预设值。The parameter c2 may be introduced into the second linear curve to further adjust the output range of the second linear curve to meet the requirements of nonlinear transformation in different scenarios. That is, the second linear curve may also be x=(y-1+b)/b+c2 , where c2 is a preset value.
在一种可能的实施中,为了保证非线性变换的连续性,第二gamma曲线与第二线性曲线相交在第二阈值。In a possible implementation, in order to ensure the continuity of the nonlinear transformation, the second gamma curve intersects the second linear curve at a second threshold.
对于斜率(b)、gamma曲线旋转系数(a)的选取原则可以参照编码侧的描述,重复之处不再进行赘述。而对于第二阈值(th’)的确定,可以根据编码侧第一阈值(th)的选取进行确定,作为一种示例,The selection principle of the slope (b) and the gamma curve rotation coefficient (a) can refer to the description of the encoding side, and the repeated parts will not be repeated. As for the determination of the second threshold (th'), it can be determined according to the selection of the first threshold (th) on the encoding side. As an example,
因此,当编码侧第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线(y=1-b+b*x)中的参数为第一组可选参数时,即γ为2.0,a为1.25、b为0.25,th为0.486时,解码侧对应的第一组可选参数为:γ为2.0,a为1.25、b为0.25、th’为0.871;当编码侧第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线(y=1-b+b*x)中的参数为第二组可选参数时,即γ为2.0,a为1.131、b为0.4,th为0.5时,解码侧对应的第二组可选参数为:γ为2.0,a为1.131、所述b为0.4、th’为0.800。Therefore, when the first gamma curve on the encoding side When the parameters in the first linear curve (y=1-b+b*x) are the first set of optional parameters, that is, γ is 2.0, a is 1.25, b is 0.25, and th is 0.486, the first set of optional parameters corresponding to the decoding side is: γ is 2.0, a is 1.25, b is 0.25, and th' is 0.871; when the first gamma curve on the encoding side When the parameters in the first linear curve (y=1-b+b*x) are the second set of optional parameters, that is, γ is 2.0, a is 1.131, b is 0.4, and th is 0.5, the second set of optional parameters corresponding to the decoding side are: γ is 2.0, a is 1.131, b is 0.4, and th' is 0.800.
同理,当编码侧第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线(y=1-b+b*x)中的参数为第三组可选参数时,即γ为2.2、a为1.096、b为0.4,th为0.5时,解码侧对应的第三组可选参数为:γ为2.2,a为1.096、b为0.4、th’为0.800;当编码侧第一gamma曲线和第一线性曲线(y=1-b+b*x)中的参数为第四组可选参数时,即γ为2.4、a为1.068、b为0.4,th为0.5时,解码侧对应的第四组可选参数为:γ为2.4,a为1.068、b为0.4、th’为0.800。Similarly, when the first gamma curve on the encoding side When the parameters in the first linear curve (y=1-b+b*x) are the third set of optional parameters, that is, γ is 2.2, a is 1.096, b is 0.4, and th is 0.5, the corresponding third set of optional parameters on the decoding side is: γ is 2.2, a is 1.096, b is 0.4, and th' is 0.800; when the first gamma curve on the encoding side When the parameters in the first linear curve (y=1-b+b*x) are the fourth group of optional parameters, that is, γ is 2.4, a is 1.068, b is 0.4, and th is 0.5, the fourth group of optional parameters corresponding to the decoding side are: γ is 2.4, a is 1.068, b is 0.4, and th' is 0.800.
每组可选参数对应的仿真效果可以参照编码侧的实施,重复之处不再进行赘述。The simulation effect corresponding to each set of optional parameters can refer to the implementation on the encoding side, and the repeated parts will not be repeated.
另外,需要理解的是,在本申请实施例中,不仅限于引入一条线性曲线(如直线),对现有仅基于gamma曲线实现的非线性变换进行改进。例如,可以引入多条线性曲线(如直线),对现有仅基于gamma曲线实现的非线性变换进行改进。In addition, it should be understood that in the embodiments of the present application, it is not limited to introducing a linear curve (such as a straight line) to improve the existing nonlinear transformation based only on the gamma curve. For example, multiple linear curves (such as straight lines) can be introduced to improve the existing nonlinear transformation based only on the gamma curve.
以引入两条线性曲线(第一线性曲线A和第一线性曲线B)对仅基于第一gamma曲线实现的非线性变换进行改进为例,对于第一图像单元中归一化像素值小于或等于第一阈值A的第一像素点,基于第一gamma曲线实现变换;对于第一图像单元中归一化像素值大于第一阈值A、且小于或等于第一阈值B的第二像素点,基于第一线性曲线A实现变换;对于第一图像单元中归一化像素值大于第一阈值B的第三像素点,基于第一线性曲线B实现变换,其中第一阈值A小于第二阈值B。Taking the introduction of two linear curves (the first linear curve A and the first linear curve B) to improve the nonlinear transformation based only on the first gamma curve as an example, for the first pixel point in the first image unit whose normalized pixel value is less than or equal to the first threshold A, the transformation is implemented based on the first gamma curve; for the second pixel point in the first image unit whose normalized pixel value is greater than the first threshold A and less than or equal to the first threshold B, the transformation is implemented based on the first linear curve A; for the third pixel point in the first image unit whose normalized pixel value is greater than the first threshold B, the transformation is implemented based on the first linear curve B, wherein the first threshold A is less than the second threshold B.
同理,对于解码侧,对应引入两条线性曲线(第二线性曲线A和第二线性曲线B)对仅基于第二gamma曲线实现的非线性逆变换进行改进,对于第二图像单元(第二图像单元由第一图像中像素点进行线性变换得到)中归一化像素值小于或等于第二阈值A的第一像素点,基于第二gamma曲线实现逆变换;对于第二图像单元中归一化像素值大于第二阈值A、且小于或等于第二阈值B的第二像素点,基于第二线性曲线A实现逆变换;对于第二图像单元中归一化像素值大于第二阈值B的第三像素点,基于第二线性曲线B实现逆变换,其中第二阈值A小于第二阈值B。Similarly, for the decoding side, two linear curves (the second linear curve A and the second linear curve B) are introduced to improve the nonlinear inverse transformation implemented only based on the second gamma curve. For the first pixel point in the second image unit (the second image unit is obtained by linearly transforming the pixels in the first image) whose normalized pixel value is less than or equal to the second threshold A, the inverse transformation is implemented based on the second gamma curve; for the second pixel point in the second image unit whose normalized pixel value is greater than the second threshold A and less than or equal to the second threshold B, the inverse transformation is implemented based on the second linear curve A; for the third pixel point in the second image unit whose normalized pixel value is greater than the second threshold B, the inverse transformation is implemented based on the second linear curve B, where the second threshold A is less than the second threshold B.
前文介绍了本申请实施例的图像编解码方法,下文中将介绍本申请实施例中的图像编解码装置。方法、装置是基于同一技术构思的,由于方法、装置解决问题的原理相似,因此装置与方法的实施可以相互参见,重复之处不再赘述。The above describes the image coding and decoding method of the embodiment of the present application, and the following describes the image coding and decoding device of the embodiment of the present application. The method and the device are based on the same technical concept. Since the principles of solving the problem by the method and the device are similar, the implementation of the device and the method can refer to each other, and the repeated parts will not be repeated.
基于与上述图像编码方法的相同的技术构思,如图14所示,提供了一种图像编码装置1400,装置1400能够执行上述图3的方法中由编码设备执行的各个步骤。装置1400可以为一个设备,或者设备中的一个芯片。装置1400可以包括:确定模块1410和变换模块1420。Based on the same technical concept as the above-mentioned image coding method, as shown in FIG14 , an image coding apparatus 1400 is provided, and the apparatus 1400 can execute each step executed by the coding device in the method of FIG3 . The apparatus 1400 can be a device, or a chip in the device. The apparatus 1400 can include: a
在一种可能的设计中,确定模块1410,用于确定第一图像单元;所述第一图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点,其中所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值小于或等于第一阈值,所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值大于所述第一阈值;变换模块1420,用于基于第一gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值进行第一变换,得到所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;所述变换模块1420,还用于基于第一线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值进行第二变换,得到所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。In one possible design, a
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一gamma曲线为其中,x表示第一像素点的第一归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;In one possible design, the first gamma curve is Wherein, x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel;
所述第一线性曲线为y=1-b+b*x,其中,x表示第二像素点的第二归一化像素值、b为斜率、y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。The first linear curve is y=1-b+b*x, wherein x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值,b,a,γ为预设的数值。In a possible design, the first thresholds, b, a, and γ are preset values.
在一种可能的设计中,所述a不小于1,所述b不小于0.18、且不大于0.5。In a possible design, a is not less than 1, and b is not less than 0.18 and not greater than 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值不小于0.4、且不大于0.6。In a possible design, the first threshold is not less than 0.4 and not greater than 0.6.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.0时,所述a为1.25、所述b为0.25,所述第一阈值为0.486;或,所述a为1.131、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.0, the a is 1.25, the b is 0.25, and the first threshold is 0.486; or, the a is 1.131, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.2时,所述a为1.096、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.2, the a is 1.096, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.4时,所述a为1.068、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.4, the a is 1.068, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一gamma曲线与所述第一线性曲线相交在所述第一阈值。In one possible design, the first gamma curve intersects the first linear curve at the first threshold.
在一种可能的设计中,所述归一化像素值根据预设最大的像素值m,预设最小的像素值n和像素点的像素值c确定。In a possible design, the normalized pixel value is determined based on a preset maximum pixel value m, a preset minimum pixel value n, and a pixel value c of the pixel point.
在一种可能的设计中,所述预设最大的像素值m为图像传感器的饱和值,所述预设最小的像素值n为图像传感器的光学暗电平。In a possible design, the preset maximum pixel value m is a saturation value of the image sensor, and the preset minimum pixel value n is an optical dark level of the image sensor.
在一种可能的设计中,所述像素点的归一化像素值为c/(m-n)。In one possible design, the normalized pixel value of the pixel point is c/(m-n).
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一图像单元为Bayer raw图像单元。In a possible design, the first image unit is a Bayer raw image unit.
基于与上述图像解码方法的同一技术构思,如图15所示,提供了一种图像解码装置1500,装置1500能够执行上述图13的方法中由解码设备执行的各个步骤。装置1500可以为一个设备,也可以为应用于一个设备中的芯片。装置1500可以包括:确定模块1510和逆变换模块1520。Based on the same technical concept as the above-mentioned image decoding method, as shown in FIG15 , an image decoding device 1500 is provided, and the device 1500 can execute each step executed by the decoding device in the method of FIG13 . The device 1500 can be a device or a chip applied to a device. The device 1500 can include: a
在一种可能的设计中,确定模块1510,用于确定第二图像单元;所述第二图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点,其中所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值小于或等于第二阈值,所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值大于所述第二阈值;逆变换模块1520,用于基于第二gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值进行第一逆变换,得到所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值;所述逆变换模块1520,还用于基于第二线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值进行第二逆变换,得到所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值。In one possible design, a
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二gamma曲线为x=(y/a)γ,其中,y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、x表示第一像素点第一归一化像素值;In a possible design, the second gamma curve is x=(y/a)γ , where y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel;
所述第二线性曲线为x=(y-1+b)/b,其中,y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值、b为斜率、x表示第二像素点第二归一化像素值。The second linear curve is x=(y-1+b)/b, wherein y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二阈值,b,a,γ为预设的数值。In a possible design, the second thresholds, b, a, and γ are preset values.
在一种可能的设计中,所述a不小于1,所述b不小于0.18、且不大于0.5。In a possible design, a is not less than 1, and b is not less than 0.18 and not greater than 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二阈值为所述th为预设的变换曲线选择参数。In one possible design, the second threshold is The th is a preset transformation curve selection parameter.
在一种可能的设计中,所述th不小于0.4、且不大于0.6。In a possible design, th is not less than 0.4 and not greater than 0.6.
在一种可能的设计中,所述th为0.5。In one possible design, th is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.0时,所述a为1.25、所述b为0.25,所述第二阈值为0.871;或,所述a为1.131、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.0, the a is 1.25, the b is 0.25, and the second threshold is 0.871; or, the a is 1.131, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.2时,所述a为1.096、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.2, the a is 1.096, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.4时,所述a为1.068、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.4, the a is 1.068, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二gamma曲线与所述第二线性曲线相交在所述第二阈值。In one possible design, the second gamma curve intersects the second linear curve at the second threshold.
图16是本申请实施例的编码装置1600的示意性框图。应理解,所述装置1600能够执行上述图3的方法中由编码设备执行的各个步骤。装置1600包括:处理器1610,可选的,还包括存储器1620。所述处理器1610和所述存储器1620之间电耦合。FIG16 is a schematic block diagram of an encoding device 1600 according to an embodiment of the present application. It should be understood that the device 1600 can perform each step performed by the encoding device in the method of FIG3 above. The device 1600 includes: a processor 1610, and optionally, a memory 1620. The processor 1610 and the memory 1620 are electrically coupled.
示例的,存储器1620,用于存储计算机程序或指令;所述处理器1610,可以用于调用所述存储器中存储的计算机程序或指令,以执行上述图像编码方法。For example, the memory 1620 is used to store computer programs or instructions; the processor 1610 can be used to call the computer program or instructions stored in the memory to execute the above-mentioned image encoding method.
在一种可能的实现中,所述处理器1610,用于确定第一图像单元,所述第一图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点,其中所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值小于或等于第一阈值,所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值大于所述第一阈值;以及基于第一gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值进行第一变换,得到所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;基于第一线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值进行第二变换,得到所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。In one possible implementation, the processor 1610 is used to determine a first image unit, where the first image unit includes a first pixel and a second pixel, wherein a first normalized pixel value of the first pixel is less than or equal to a first threshold, and a second normalized pixel value of the second pixel is greater than the first threshold; and perform a first transformation on the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel based on a first gamma curve to obtain a third normalized pixel value of the first pixel; and perform a second transformation on the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel based on a first linear curve to obtain a fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一gamma曲线为其中,x表示第一像素点的第一归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值;In one possible design, the first gamma curve is Wherein, x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel;
所述第一线性曲线为y=1-b+b*x,其中,x表示第二像素点的第二归一化像素值、b为斜率、y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值。The first linear curve is y=1-b+b*x, wherein x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值,b,a,γ为预设的数值。In a possible design, the first thresholds, b, a, and γ are preset values.
在一种可能的设计中,所述a不小于1,所述b不小于0.18、且不大于0.5。In a possible design, a is not less than 1, and b is not less than 0.18 and not greater than 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值不小于0.4、且不大于0.6。In a possible design, the first threshold is not less than 0.4 and not greater than 0.6.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.0时,所述a为1.25、所述b为0.25,所述第一阈值为0.486;或,所述a为1.131、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.0, the a is 1.25, the b is 0.25, and the first threshold is 0.486; or, the a is 1.131, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.2时,所述a为1.096、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.2, the a is 1.096, the b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.4时,所述a为1.068、所述b为0.4,所述第一阈值为0.5。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.4, a is 1.068, b is 0.4, and the first threshold is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一gamma曲线与所述第一线性曲线相交在所述第一阈值。In one possible design, the first gamma curve intersects the first linear curve at the first threshold.
在一种可能的设计中,所述归一化像素值根据预设最大的像素值m,预设最小的像素值n和像素点的像素值c确定。In a possible design, the normalized pixel value is determined based on a preset maximum pixel value m, a preset minimum pixel value n, and a pixel value c of the pixel point.
在一种可能的设计中,所述预设最大的像素值m为图像传感器的饱和值,所述预设最小的像素值n为图像传感器的光学暗电平。In a possible design, the preset maximum pixel value m is a saturation value of the image sensor, and the preset minimum pixel value n is an optical dark level of the image sensor.
在一种可能的设计中,所述像素点的归一化像素值为c/(m-n)。In one possible design, the normalized pixel value of the pixel point is c/(m-n).
在一种可能的设计中,所述第一图像单元为Bayer raw图像单元。In a possible design, the first image unit is a Bayer raw image unit.
图17是本申请实施例的解码装置1700的示意性框图。应理解,所述装置1700能够执行上述图13的方法中由解码设备执行的各个步骤。装置1700包括:处理器1710,可选的,还包括存储器1720。所述处理器1710和所述存储器1720之间电耦合。FIG17 is a schematic block diagram of a decoding device 1700 according to an embodiment of the present application. It should be understood that the device 1700 can perform each step performed by the decoding device in the method of FIG13. The device 1700 includes: a processor 1710, and optionally, a
示例的,存储器1720,用于存储计算机程序或指令;所述处理器1710,可以用于调用所述存储器中存储的计算机程序或指令,以执行上述图像解码方法。For example, the
在一种可能的实现中,所述处理器1710,用于确定第二图像单元,所述第二图像单元包括第一像素点和第二像素点,其中所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值小于或等于第二阈值,所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值大于所述第二阈值;以及基于第二gamma曲线对所述第一像素点的第三归一化像素值进行第一逆变换,得到所述第一像素点的第一归一化像素值;基于第二线性曲线对所述第二像素点的第四归一化像素值进行第二逆变换,得到所述第二像素点的第二归一化像素值。In one possible implementation, the processor 1710 is used to determine a second image unit, where the second image unit includes a first pixel and a second pixel, wherein a third normalized pixel value of the first pixel is less than or equal to a second threshold, and a fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel is greater than the second threshold; and perform a first inverse transformation on the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel based on a second gamma curve to obtain a first normalized pixel value of the first pixel; and perform a second inverse transformation on the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel based on a second linear curve to obtain a second normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二gamma曲线为x=(y/a)γ,其中,y表示第一像素点的第三归一化像素值、a表示gamma曲线旋转系数、γ表示gamma值、x表示第一像素点第一归一化像素值;In a possible design, the second gamma curve is x=(y/a)γ , where y represents the third normalized pixel value of the first pixel, a represents the gamma curve rotation coefficient, γ represents the gamma value, and x represents the first normalized pixel value of the first pixel;
所述第二线性曲线为x=(y-1+b)/b,其中,y表示第二像素点的第四归一化像素值、b为斜率、x表示第二像素点第二归一化像素值。The second linear curve is x=(y-1+b)/b, wherein y represents the fourth normalized pixel value of the second pixel, b is the slope, and x represents the second normalized pixel value of the second pixel.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二阈值,b,a,γ为预设的数值。In a possible design, the second thresholds, b, a, and γ are preset values.
在一种可能的设计中,所述a不小于1,所述b不小于0.18、且不大于0.5。In a possible design, a is not less than 1, and b is not less than 0.18 and not greater than 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二阈值为所述th为预设的变换曲线选择参数。In one possible design, the second threshold is The th is a preset transformation curve selection parameter.
在一种可能的设计中,所述th不小于0.4、且不大于0.6。In a possible design, th is not less than 0.4 and not greater than 0.6.
在一种可能的设计中,所述th为0.5。In one possible design, th is 0.5.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.0时,所述a为1.25、所述b为0.25,所述第二阈值为0.871;或,所述a为1.131、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.0, the a is 1.25, the b is 0.25, and the second threshold is 0.871; or, the a is 1.131, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.2时,所述a为1.096、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.2, the a is 1.096, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,当所述γ为2.4时,所述a为1.068、所述b为0.4,所述第二阈值为0.800。In a possible design, when the γ is 2.4, the a is 1.068, the b is 0.4, and the second threshold is 0.800.
在一种可能的设计中,所述第二gamma曲线与所述第二线性曲线相交在所述第二阈值。In one possible design, the second gamma curve intersects the second linear curve at the second threshold.
上述的处理器可以是中央处理器(central processing unit,CPU),网络处理器(network processor,NP)或者CPU和NP的组合。处理器还可以进一步包括硬件芯片或其他通用处理器。上述硬件芯片可以是专用集成电路(application-specific integratedcircuit,ASIC),可编程逻辑器件(programmable logic device,PLD)或其组合。上述PLD可以是复杂可编程逻辑器件(complex programmable logic device,CPLD),现场可编程逻辑门阵列(field-programmable gate array,FPGA),通用阵列逻辑(generic array logic,GAL)及其他可编程逻辑器件、分立门或者晶体管逻辑器件、分立硬件组件等或其任意组合。通用处理器可以是微处理器或者该处理器也可以是任何常规的处理器等。The above-mentioned processor may be a central processing unit (CPU), a network processor (NP) or a combination of a CPU and a NP. The processor may further include a hardware chip or other general-purpose processor. The above-mentioned hardware chip may be an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), a programmable logic device (PLD) or a combination thereof. The above-mentioned PLD may be a complex programmable logic device (CPLD), a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), a generic array logic (GAL) and other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, etc. or any combination thereof. The general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor or the processor may also be any conventional processor, etc.
还应理解,本申请实施例中提及的存储器可以是易失性存储器或非易失性存储器,或可包括易失性和非易失性存储器两者。其中,非易失性存储器可以是只读存储器(Read-Only Memory,ROM)、可编程只读存储器(Programmable ROM,PROM)、可擦除可编程只读存储器(Erasable PROM,EPROM)、电可擦除可编程只读存储器(Electrically EPROM,EEPROM)或闪存。易失性存储器可以是随机存取存储器(Random Access Memory,RAM),其用作外部高速缓存。通过示例性但不是限制性说明,许多形式的RAM可用,例如静态随机存取存储器(Static RAM,SRAM)、动态随机存取存储器(Dynamic RAM,DRAM)、同步动态随机存取存储器(Synchronous DRAM,SDRAM)、双倍数据速率同步动态随机存取存储器(Double DataRate SDRAM,DDR SDRAM)、增强型同步动态随机存取存储器(Enhanced SDRAM,ESDRAM)、同步连接动态随机存取存储器(Synchlink DRAM,SLDRAM)和直接内存总线随机存取存储器(Direct Rambus RAM,DR RAM)。应注意,本申请描述的存储器旨在包括但不限于这些和任意其它适合类型的存储器。It should also be understood that the memory mentioned in the embodiments of the present application may be a volatile memory or a non-volatile memory, or may include both volatile and non-volatile memories. Among them, the non-volatile memory may be a read-only memory (ROM), a programmable read-only memory (PROM), an erasable programmable read-only memory (EPROM), an electrically erasable programmable read-only memory (EEPROM), or a flash memory. The volatile memory may be a random access memory (RAM), which is used as an external cache. By way of example and not limitation, many forms of RAM are available, such as static random access memory (SRAM), dynamic random access memory (DRAM), synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM), double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory (DDR SDRAM), enhanced synchronous dynamic random access memory (ESDRAM), synchronous link dynamic random access memory (SLDRAM), and direct memory bus random access memory (DR RAM). It should be noted that the memory described in this application is intended to include, but is not limited to, these and any other suitable types of memory.
本申请实施例还提供了一种计算机存储介质,存储有计算机程序或指令,该计算机程序或指令被处理器执行时,可以使得所述处理器用于执行上述图像编码方法和/或图像解码方法。例如执行图3所示的方法。例如执行图13所示的方法。The embodiment of the present application further provides a computer storage medium storing a computer program or instruction, which, when executed by a processor, can cause the processor to execute the above-mentioned image encoding method and/or image decoding method. For example, the method shown in FIG3 is executed. For example, the method shown in FIG13 is executed.
本申请实施例还提供了一种包含指令的计算机程序产品,当其在处理器上运行时,使得处理器可以执行上述提供的图像编码方法和/或图像解码方法。例如执行图3所示的方法。例如执行图13所示的方法。The present application also provides a computer program product including instructions, which, when executed on a processor, enables the processor to execute the image encoding method and/or image decoding method provided above, such as executing the method shown in FIG3 , or executing the method shown in FIG13 .
本申请实施例还提供了一种芯片,所述芯片运行时,实现上述提供的图像编码方法和/或图像解码方法。例如实现图3所示的方法。例如实现图13所示的方法。The present application also provides a chip, which, when in operation, implements the above-mentioned image encoding method and/or image decoding method, for example, the method shown in FIG3 , or the method shown in FIG13 .
本领域内的技术人员应明白,本申请的实施例可提供为方法、系统、或计算机程序产品。因此,本申请可采用完全硬件实施例、完全软件实施例、或结合软件和硬件方面的实施例的形式。而且,本申请可采用在一个或多个其中包含有计算机可用程序代码的计算机可用存储介质(包括但不限于磁盘存储器、CD-ROM、光学存储器等)上实施的计算机程序产品的形式。Those skilled in the art will appreciate that the embodiments of the present application may be provided as methods, systems, or computer program products. Therefore, the present application may adopt the form of a complete hardware embodiment, a complete software embodiment, or an embodiment in combination with software and hardware. Moreover, the present application may adopt the form of a computer program product implemented in one or more computer-usable storage media (including but not limited to disk storage, CD-ROM, optical storage, etc.) that contain computer-usable program code.
本申请是参照根据本申请实施例的方法、设备(系统)、和计算机程序产品的流程图和/或方框图来描述的。应理解可由计算机程序指令实现流程图和/或方框图中的每一流程和/或方框、以及流程图和/或方框图中的流程和/或方框的结合。可提供这些计算机程序指令到通用计算机、专用计算机、嵌入式处理机或其他可编程数据处理设备的处理器以产生一个机器,使得通过计算机或其他可编程数据处理设备的处理器进行的指令产生用于实现在流程图一个流程或多个流程和/或方框图一个方框或多个方框中指定的功能的装置。The present application is described with reference to the flowchart and/or block diagram of the method, device (system) and computer program product according to the embodiment of the present application. It should be understood that each flow process and/or box in the flow chart and/or block diagram, and the combination of the flow process and/or box in the flow chart and/or block diagram can be realized by computer program instructions. These computer program instructions can be provided to a processor of a general-purpose computer, a special-purpose computer, an embedded processor or other programmable data processing device to produce a machine, so that the instructions performed by the processor of the computer or other programmable data processing device produce a device for realizing the function specified in one flow chart or multiple flows and/or one box or multiple boxes of the block diagram.
这些计算机程序指令也可存储在能引导计算机或其他可编程数据处理设备以特定方式工作的计算机可读存储器中,使得存储在该计算机可读存储器中的指令产生包括指令装置的制造品,该指令装置实现在流程图一个流程或多个流程和/或方框图一个方框或多个方框中指定的功能。These computer program instructions may also be stored in a computer-readable memory that can direct a computer or other programmable data processing device to work in a specific manner, so that the instructions stored in the computer-readable memory produce a manufactured product including an instruction device that implements the functions specified in one or more processes in the flowchart and/or one or more boxes in the block diagram.
这些计算机程序指令也可装载到计算机或其他可编程数据处理设备上,使得在计算机或其他可编程设备上进行一系列操作步骤以产生计算机实现的处理,从而在计算机或其他可编程设备上进行的指令提供用于实现在流程图一个流程或多个流程和/或方框图一个方框或多个方框中指定的功能的步骤。These computer program instructions may also be loaded onto a computer or other programmable data processing device so that a series of operational steps are performed on the computer or other programmable device to produce a computer-implemented process, whereby the instructions performed on the computer or other programmable device provide steps for implementing the functions specified in one or more processes in the flowchart and/or one or more boxes in the block diagram.
尽管已描述了本申请的优选实施例,但本领域内的技术人员一旦得知了基本创造性概念,则可对这些实施例作出另外的变更和修改。所以,所附权利要求意欲解释为包括优选实施例以及落入本申请范围的所有变更和修改。Although the preferred embodiments of the present application have been described, those skilled in the art may make other changes and modifications to these embodiments once they have learned the basic creative concept. Therefore, the appended claims are intended to be interpreted as including the preferred embodiments and all changes and modifications falling within the scope of the present application.
显然,本领域的技术人员可以对本申请实施例进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本申请实施例的精神和范围。这样,倘若本申请实施例的这些修改和变型属于本申请权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则本申请也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。Obviously, those skilled in the art can make various changes and modifications to the embodiments of the present application without departing from the spirit and scope of the embodiments of the present application. Thus, if these modifications and variations of the embodiments of the present application fall within the scope of the claims of the present application and their equivalents, the present application is also intended to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (40)
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2020/086516WO2021212440A1 (en) | 2020-04-23 | 2020-04-23 | Image encoding/decoding method and apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112655211A CN112655211A (en) | 2021-04-13 |
| CN112655211Btrue CN112655211B (en) | 2023-07-11 |
Family
ID=75368447
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202080004809.5AActiveCN112655211B (en) | 2020-04-23 | 2020-04-23 | Image coding and decoding method and device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112655211B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021212440A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN119946305A (en)* | 2023-10-26 | 2025-05-06 | 深圳引望智能技术有限公司 | Image processing method and system |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103281537A (en)* | 2013-05-23 | 2013-09-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Compression method and device for dynamic range of image |
| CN108200441A (en)* | 2018-01-22 | 2018-06-22 | 青岛海信电器股份有限公司 | A kind of brightness of image processing method and processing device, electronic equipment |
| CN110428379A (en)* | 2019-07-29 | 2019-11-08 | 慧视江山科技(北京)有限公司 | A kind of image grayscale Enhancement Method and system |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUPQ056099A0 (en)* | 1999-05-25 | 1999-06-17 | Silverbrook Research Pty Ltd | A method and apparatus (pprint01) |
| US9036042B2 (en)* | 2011-04-15 | 2015-05-19 | Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation | Encoding, decoding, and representing high dynamic range images |
| CN108259701A (en)* | 2018-01-17 | 2018-07-06 | 深圳市唯特视科技有限公司 | A kind of color reproduction method based on high dynamic range Color Gamut Mapping |
| CN109584182A (en)* | 2018-12-03 | 2019-04-05 | 董育理 | A kind of image processing method and system |
- 2020
- 2020-04-23CNCN202080004809.5Apatent/CN112655211B/enactiveActive
- 2020-04-23WOPCT/CN2020/086516patent/WO2021212440A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103281537A (en)* | 2013-05-23 | 2013-09-04 | 华为技术有限公司 | Compression method and device for dynamic range of image |
| CN108200441A (en)* | 2018-01-22 | 2018-06-22 | 青岛海信电器股份有限公司 | A kind of brightness of image processing method and processing device, electronic equipment |
| CN110428379A (en)* | 2019-07-29 | 2019-11-08 | 慧视江山科技(北京)有限公司 | A kind of image grayscale Enhancement Method and system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112655211A (en) | 2021-04-13 |
| WO2021212440A1 (en) | 2021-10-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US12315471B2 (en) | Gamut mapping using luminance parameters | |
| KR102531468B1 (en) | Encoding and decoding of image data | |
| CN105850129B (en) | Method and apparatus for tone mapping of high dynamic range images | |
| US20220237754A1 (en) | Image processing method and apparatus | |
| CN113099201B (en) | Video signal processing method and device and electronic equipment | |
| CN116485979B (en) | Mapping relation calculation method, color calibration method and electronic equipment | |
| CN114467298B (en) | Image signal conversion processing method and device and terminal equipment | |
| WO2023005115A1 (en) | Image processing method, image processing apparatus, electronic device, and readable storage medium | |
| WO2023010750A1 (en) | Image color mapping method and apparatus, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| CN114679626B (en) | Image processing method, storage medium and display device | |
| CN104463806B (en) | Height adaptive method for enhancing picture contrast based on data driven technique | |
| US20190147570A1 (en) | Enhancement of edges in images using depth information | |
| CN112073718B (en) | Television screen splash detection method and device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN116468636A (en) | Low illumination enhancement method, device, electronic device and readable storage medium | |
| WO2018100950A1 (en) | Image processing device, digital camera, image processing program, and recording medium | |
| CN112655211B (en) | Image coding and decoding method and device | |
| KR101634652B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for intensificating contrast in image | |
| US10846829B1 (en) | Image sharpening with edge direction based undershoot and overshoot reduction | |
| CN113891081A (en) | Video processing method, device and equipment | |
| CN103647957B (en) | Reduce the method for real-time data transmission amount of color image | |
| JP7656833B2 (en) | Information processing device, information processing method, and program | |
| CN103974052B (en) | The method of adjustment of a kind of image saturation, device and equipment | |
| US20230061368A1 (en) | Image Encoding Method and Apparatus, and Image Decoding Method and Apparatus | |
| CN114494051A (en) | Image processing method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN114240800A (en) | Coding camera image enhancement method and device for scattering scene |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | ||
| TR01 | Transfer of patent right | Effective date of registration:20241101 Address after:518129 Huawei Headquarters Office Building 101, Wankecheng Community, Bantian Street, Longgang District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Patentee after:Shenzhen Yinwang Intelligent Technology Co.,Ltd. Country or region after:China Address before:518129 Bantian HUAWEI headquarters office building, Longgang District, Guangdong, Shenzhen Patentee before:HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES Co.,Ltd. Country or region before:China |