CN112632997A - Chinese entity identification method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion - Google Patents
Chinese entity identification method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112632997A CN112632997ACN202011462808.3ACN202011462808ACN112632997ACN 112632997 ACN112632997 ACN 112632997ACN 202011462808 ACN202011462808 ACN 202011462808ACN 112632997 ACN112632997 ACN 112632997A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- word
- bert
- word vector
- sentence
- vector
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/20—Natural language analysis
- G06F40/279—Recognition of textual entities
- G06F40/289—Phrasal analysis, e.g. finite state techniques or chunking
- G06F40/295—Named entity recognition
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F40/00—Handling natural language data
- G06F40/30—Semantic analysis
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Audiology, Speech & Language Pathology (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Machine Translation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于命名实体识别领域,具体涉及一种基于BERT和Word2Vec 向量融合的中文实体识别方法。The invention belongs to the field of named entity recognition, in particular to a Chinese entity recognition method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion.
背景技术Background technique
命名实体识别是一项识别文本中指定类型的实体成分并对其进行分类的 任务,常见的实体类型包括:人名、地名、机构名等。在网络数据日益剧增 的今天,命名实体识别为数据挖掘提供了强有力的支持,同时它也是信息检 索、问答系统、知识图谱等任务的重要组成部分。常用的命名实体识别方法 主要分为以下三类:基于规则和词典的方法、基于统计机器学习的方法和基 于深度学习的方法。Named entity recognition is a task of identifying and classifying entity components of a specified type in text. Common entity types include: person name, place name, institution name, etc. Today, with the increasing number of network data, named entity recognition provides strong support for data mining, and it is also an important part of tasks such as information retrieval, question answering systems, and knowledge graphs. Commonly used named entity recognition methods are mainly divided into the following three categories: methods based on rules and dictionary, methods based on statistical machine learning and methods based on deep learning.
基于规则和词典的方法,需要依靠语言学专家手工设计规则模板,选取 能够描述预定义类型的实体特征,包括:统计信息、关键字、指示词、位置 词以及标点符号等,结合领域内的词典,通过规则模板与字符串匹配的方式 进行实体识别。The rule-based and dictionary-based methods need to rely on linguistic experts to manually design rule templates, select entity features that can describe predefined types, including statistical information, keywords, demonstrative words, positional words, and punctuation marks, etc., combined with the dictionary in the field , and perform entity recognition by matching the rule template with the string.
基于统计机器学习的方法,把命名实体识别当作序列标注任务处理,该 类方法不需要拥有深厚语言学知识的专家来挑选和设计特征,普通研究人员 就可以挑选出能有效反映该类实体特性的特征集合,包括:单词特征、上下 文特征、词性特征以及语义特征等。通常采用人工标注的语料训练模型,常 用的机器学习模型包括:隐马尔可夫模型、最大熵模型、支持向量机、条件 随机场等。The method based on statistical machine learning treats named entity recognition as a sequence labeling task. This type of method does not require experts with deep linguistic knowledge to select and design features. Ordinary researchers can select features that can effectively reflect the characteristics of such entities. The feature set includes: word features, context features, part-of-speech features, and semantic features. Manually labeled corpus is usually used to train the model, and the commonly used machine learning models include: Hidden Markov Model, Maximum Entropy Model, Support Vector Machine, Conditional Random Field, etc.
基于深度学习的方法,能够进行端到端的模型训练,避免了人工挑选和 设计特征的问题。随着人工神经网络在词嵌入技术中的应用,使用大量未标 注语料进行无监督预训练,可以获得更贴近词语表达含义的低维稠密的原生 词向量,常用的词向量训练模型包括:Word2Vec、Glove等。在特征提取上 常用的深度学习模型有卷积神经网络、循环神经网络等,其中双向长短时记 忆(Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory,Bi-LSTM)网络是最经典,也是效 果较好的一个模型,而标签解码一般采用条件随机场(ConditionalRandom Fields,CRF)模型。The method based on deep learning can perform end-to-end model training, avoiding the problem of manual selection and design of features. With the application of artificial neural network in word embedding technology, a large amount of unlabeled corpus is used for unsupervised pre-training, and low-dimensional and dense native word vectors that are closer to the meaning of words can be obtained. Commonly used word vector training models include: Word2Vec, Glove et al. Deep learning models commonly used in feature extraction include convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks, etc. Among them, the Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (Bi-LSTM) network is the most classic and a model with better effects. Label decoding generally adopts a Conditional Random Fields (CRF) model.
基于预训练语言模型的方法,使用海量文本对语言模型进行无监督预训 练,常用的预训练语言模型是BERT(Bidirectional Encoder Representations fromTransformers),利用获得的预训练模型在实体识别数据集上通过微调参 数的方式进行实体识别。Based on the method of pre-training language model, unsupervised pre-training of language model is carried out using massive text. The commonly used pre-training language model is BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), and the obtained pre-training model is used to fine-tune the parameters on the entity recognition data set. way of entity recognition.
但上述技术在下列缺陷:But the above technology has the following drawbacks:
基于规则和词典的方法具有较强的领域性,且有限的规则无法覆盖所有 的语言现象,缺乏鲁棒性和可移植性;The methods based on rules and dictionaries have strong domain, and limited rules cannot cover all language phenomena, lacking robustness and portability;
基于统计机器学习的方法,需要人工进行特征的挑选和组合,且人类语 言的使用通常具有很大的随意性,仅仅使用基于统计的方法会使状态搜索空 间非常庞大,导致实体识别效果不好;The method based on statistical machine learning requires manual selection and combination of features, and the use of human language is usually very arbitrary. Only using the method based on statistics will make the state search space very large, resulting in poor entity recognition effect;
基于深度学习的方法,采用Word2Vec等模型训练获得固定的静态词向 量来表示词语的语义含义,无法解决一词多义的问题,且分词错误会导致误 差传播,影响实体识别效果;Based on the method of deep learning, using Word2Vec and other models to train to obtain a fixed static word vector to represent the semantic meaning of words, which cannot solve the problem of polysemy, and word segmentation errors will lead to error propagation and affect the effect of entity recognition;
基于BERT预训练语言模型微调的方法,通常模型参数量巨大,训练和 预测都要花费很长的时间,且在训练和部署方面对硬件设施的要求较高。The method of fine-tuning the language model based on BERT pre-training usually has a huge amount of model parameters, and it takes a long time for training and prediction, and requires high hardware facilities in terms of training and deployment.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的是为了解决现有技术存在的上述所列问题,提供了一种基 于BERT和Word2Vec向量融合的中文实体识别方案,在保证实体识别效果 的前提下提高模型训练和预测的效率。The purpose of the present invention is to solve the above-mentioned problems existing in the prior art, provide a Chinese entity recognition scheme based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion, and improve the efficiency of model training and prediction under the premise of ensuring the effect of entity recognition.
为实现上述目的,本发明采用的技术方案为:使用BERT模型获取包含 上下文信息的动态字向量,使用Word2Vec模型获取静态词向量,之后通过 两种词向量融合策略对候选词向量进行融合,最后将字向量和融合后的词向 量拼接作为后续模型的输入向量,且使用了经典的Bi-LSTM-CRF模型进行 特征编码和标签的解码。In order to achieve the above object, the technical solution adopted in the present invention is: use the BERT model to obtain dynamic word vectors containing context information, use the Word2Vec model to obtain static word vectors, then use two word vector fusion strategies to fuse the candidate word vectors, and finally fuse the word vectors. The word vector and the fused word vector are concatenated as the input vector of the subsequent model, and the classic Bi-LSTM-CRF model is used for feature encoding and label decoding.
基于BERT和Word2Vec进行向量融合的中文实体识别方法,具体包括 以下步骤:A Chinese entity recognition method based on BERT and Word2Vec for vector fusion, which includes the following steps:
步骤1,获取海量中文文本语料,利用Python中的jieba模块对文本进 行分词,训练Word2Vec模型,获取静态词向量表;
步骤2,对BERT模型进行预训练,把中文文本构造成BERT模型需要 的输入格式,具体分为以下几步:
2.1对于原始语料,通过换行来分割句子,通过空行来分割上下文;2.1 For the original corpus, the sentences are separated by line breaks, and the context is separated by blank lines;
2.2构建BERT下一句预测预训练任务需要的样本,其中正样本表示的是 输入的两个句子是存在上下文关系的连续的两个句子;负样本表示的是不存 在语义关系的随机选择的两个句子;2.2 Construct the samples required for the BERT next sentence prediction pre-training task, where the positive samples indicate that the two input sentences are two consecutive sentences with a contextual relationship; the negative samples indicate that there is no semantic relationship. Two randomly selected two sentences sentence;
2.3对于超过设定的最大长度的句子,随机选择从句首或句尾进行截断;2.3 For sentences exceeding the set maximum length, randomly select the beginning or end of the clause for truncation;
2.4将待输入的两个句子用[SEP]标签连接,并且在整个句首添加[CLS] 标签,整个句尾添加[SEP]标签,若句子长度不够,用[PAD]标签进行填充;2.4 Connect the two sentences to be input with the [SEP] tag, and add the [CLS] tag at the beginning of the entire sentence, and the [SEP] tag at the end of the entire sentence. If the sentence length is not enough, fill it with the [PAD] tag;
2.5构建BERT遮蔽语言模型预训练任务需要的样本,随机选择句子中 15%的字符进行遮蔽,对于选中的字符80%的时间用[MASK]代替,10%的时 间用随机选择的一个字符代替,10%的时间保持原字符不变;2.5 Build the samples required for the BERT masking language model pre-training task, randomly select 15% of the characters in the sentence for masking, replace the selected characters with [MASK] 80% of the time, and replace them with a randomly selected character for 10% of the time, 10% of the time keep the original characters unchanged;
步骤3,根据上述两个预训练任务训练BERT模型,训练目标分别是预 测当前输入的句子对是否是存在上下文关系的句子和预测被遮蔽掉字符的原 始内容,最终获得预训练好的BERT模型;Step 3: Train the BERT model according to the above two pre-training tasks. The training objectives are to predict whether the currently input sentence pair is a sentence with a contextual relationship and predict the original content of the masked characters, and finally obtain a pre-trained BERT model;
步骤4,中文命名实体识别数据集的获取、预处理以及标注,具体标注 方式一般采用BIO标注法,其中B表示实体开始字符,I表示实体中间和结 尾字符,O表示非实体字符;Step 4, the acquisition, preprocessing and labeling of Chinese named entity recognition data set, and the specific labeling method generally adopts the BIO labeling method, wherein B represents the start character of the entity, I represents the middle and end characters of the entity, and O represents the non-entity character;
步骤5,对步骤4得到的数据集进行预处理,给每一个句子的句首添加 [CLS]标签,句尾添加[SEP]标签,将处理好的句子输入步骤3获得的预训练 BERT模型,最终获得BERT模型输出句子中每一个字符的字向量;Step 5: Preprocess the data set obtained in step 4, add a [CLS] tag to the beginning of each sentence, add a [SEP] tag to the end of the sentence, and input the processed sentence into the pre-trained BERT model obtained in step 3. Finally, the word vector of each character in the output sentence of the BERT model is obtained;
步骤6,对步骤4得到的数据集中的每一个句子,通过与词汇表进行匹 配获取该句子包含的所有候选词语,查询步骤1获得的静态词向量表,获得 每一个候选词语的词向量,将句子中每个字对应的候选词语的词向量通过两 种向量融合策略进行融合,来表示每个字在词汇层面的语义含义,具体包含 以下两种词向量融合策略:Step 6: For each sentence in the data set obtained in step 4, obtain all the candidate words contained in the sentence by matching with the vocabulary, query the static word vector table obtained in
6.1词向量融合策略一:对句子中每个字的候选词向量进行求和取均值, 以“广州市长隆公园”句子为例,“广”字包含“广州”和“广州市”两个 候选词语,首先查询词向量表获得两个词语的词向量,然后对两个词向量求 和取均值作为“广”字的词向量表示部分。6.1 Word vector fusion strategy 1: Sum the candidate word vectors of each word in the sentence and take the mean value. Taking the sentence "Guangzhou Changlong Park" as an example, the word "Guang" contains two words "Guangzhou" and "Guangzhou City" For candidate words, first query the word vector table to obtain the word vectors of the two words, and then sum the two word vectors and take the average as the word vector representation part of the word "Guang".
6.2词向量融合策略二:对句子中每个字的候选词向量以词频作为权重进 行加权求和,同样以上述例子为例,首先统计“广州”和“广州市”在数据 集中出现的总次数,然后将两个词出现的次数分别除以两个词的总次数作为 两个词向量的权重,最后将权重和词向量相乘并求和作为“广”字的词向量 表示部分,其余字符同理,当某个字不存在匹配词语时,用[None]的词向量 表示该字的词向量部分,维度同其他词向量维度一样。6.2 Word vector fusion strategy 2: The candidate word vector of each word in the sentence is weighted and summed with the word frequency as the weight. Also taking the above example as an example, first count the total number of occurrences of "Guangzhou" and "Guangzhou City" in the data set , and then divide the number of occurrences of the two words by the total number of the two words as the weight of the two word vectors, and finally multiply the weight and the word vector and sum it up as the word vector representation part of the word "Guang", and the rest of the characters Similarly, when a word does not have a matching word, the word vector of [None] is used to represent the word vector part of the word, and the dimension is the same as that of other word vectors.
步骤7,将步骤6得到的每个字的词向量与步骤5得到的每个字的字向 量进行拼接,获得每个字符的最终字向量;Step 7, the word vector of each word obtained in step 6 is spliced with the word vector of each word obtained in step 5, and the final word vector of each character is obtained;
步骤8,将步骤7得到的字向量输入Bi-LSTM-CRF模型进行训练预测, 得到实体识别结果。In step 8, the word vector obtained in step 7 is input into the Bi-LSTM-CRF model for training prediction, and an entity recognition result is obtained.
本发明的有益效果是:The beneficial effects of the present invention are:
1.本发明针对传统词向量特征表达能力不强,提出使用预训练BERT模 型获取包含上下文信息的动态字向量,增强字的语义含义,解决一词多义的 问题;1. the present invention is not strong for traditional word vector feature expression ability, proposes to use pre-training BERT model to obtain the dynamic word vector that contains context information, enhances the semantic meaning of word, and solves the problem of polysemy;
2.为了解决在传统词向量使用过程中存在的分词错误问题,更好的引入 词语以及实体边界信息,提出了词向量融合的策略,且引入了词频信息来给 可能性更大的词向量赋予更高的权重,减少错误分词带来的影响。2. In order to solve the problem of word segmentation errors in the use of traditional word vectors, and better introduce word and entity boundary information, a word vector fusion strategy is proposed, and word frequency information is introduced to give more likely word vectors. Higher weights reduce the impact of wrong word segmentation.
3.通过词向量与字向量拼接的方式,实现字与词的融合,丰富了初始向 量的特征表示,提高了实体识别的精度和召回率;3. By splicing word vectors and word vectors, the fusion of words and words is realized, which enriches the feature representation of the initial vector and improves the precision and recall rate of entity recognition;
4.本发明在输入向量的表示上进行改进,而没有涉及到特征编码模型结 构的改进,因此也可以适用于其他特征编码模型,而不仅仅局限于Bi-LSTM 模型,具有很强的灵活性;4. The present invention improves the representation of the input vector without involving the improvement of the structure of the feature encoding model, so it can also be applied to other feature encoding models, not only limited to the Bi-LSTM model, and has strong flexibility ;
5.为了减少模型训练时间,没有对预训练模型微调,而是采用特征抽取 的方式获取字向量,大大减少了模型训练的参数,提高了模型训练效率。5. In order to reduce the model training time, the pre-training model is not fine-tuned, but the word vector is obtained by means of feature extraction, which greatly reduces the parameters of model training and improves the efficiency of model training.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明的基于BERT和Word2vec向量融合的中文实体识别流程示意 图;Fig. 1 is the schematic flow chart of Chinese entity recognition based on BERT and Word2vec vector fusion of the present invention;
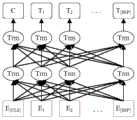
图2为本发明实施例的基于BERT和Word2Vec向量融合的中文实体识别模 型整体结构示意图;Fig. 2 is the overall structure schematic diagram of the Chinese entity recognition model based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion of the embodiment of the present invention;
图3为本发明实施例的BERT预训练语言模型结构示意图;3 is a schematic structural diagram of a BERT pre-training language model according to an embodiment of the present invention;
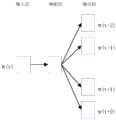
图4为本发明实施例的Word2vec中的Skip-gram模型结构示意图。FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of a Skip-gram model in Word2vec according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明所要解决的技术问题、技术方案及有益效果更加清楚、明 白,以下结合附图和实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此 处所描述的具体实施例仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and beneficial effects to be solved by the present invention more clear and comprehensible, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention.
如图1所示,本发明基于BERT和Word2vec向量融合的中文实体识别 方法,具体包括以下步骤:As shown in Figure 1, the present invention is based on the Chinese entity recognition method of BERT and Word2vec vector fusion, specifically comprises the following steps:
步骤1,获取Word2vec模型的训练语料并进行预处理;
步骤2,根据步骤1预处理后的训练语料训练Word2vec中的Skip-gram 模型,如图4所示,通过输入中心词来预测指定大小窗口内的上下文的词, 训练完成获得的映射层的权重矩阵就是词向量表:W∈R|V|*d,其中|V|是词 汇表长度,d是词向量维度。Step 2: Train the Skip-gram model in Word2vec according to the training corpus preprocessed in
步骤3,通过查询步骤2训练获得的静态词向量表来获取每个词对应的 词向量:其中vi是长度为|V|的one-hot向量,对应 维度的值为1,其余维度为0。Step 3, obtain the word vector corresponding to each word by querying the static word vector table obtained by the training in Step 2: where vi is a one-hot vector of length |V |, the value of the corresponding dimension is 1, and the other dimensions are 0.
步骤4,根据步骤1预处理后的训练语料自己预训练BERT语言模型, 也可直接下载其它已经预训练好的中文BERT模型。Step 4: Pre-train the BERT language model by yourself according to the training corpus preprocessed in
步骤5,将实体识别数据集输入到BERT模型获取包含具体语境的字向 量,ci表示句子中的每一个字符,l表示字向量的维度。Step 5, input the entity recognition data set into the BERT model to obtain the word vector containing the specific context, ci represents each character in the sentence, and l represents the dimension of the word vector.
步骤6,输入句子与预先训练好的词汇表进行匹配,获取每个字符的候 选词向量ew,如图2所示,之后通过词向量融合策略对候选词向量进行融合, 策略一为求和取均值,其计算如下:Step 6, the input sentence is matched with the pre-trained vocabulary, and the candidate word vectorew of each character is obtained, as shown in Figure 2, and then the candidate word vector is fused through the word vector fusion strategy, and the strategy one is summation Take the mean, which is calculated as follows:
其中,ew(w)表示该词语的词向量,S表示字符所对应的候选词语集合, N表示集合中词语的个数,ew(None)表示[None]标签的词向量,表示该集合 为空集,即该字符不包含任何匹配词语。Among them, ew (w) represents the word vector of the word, S represents the candidate word set corresponding to the character, N represents the number of words in the set, ew (None) represents the word vector of the [None] label, Indicates that the set is empty, that is, the character does not contain any matching words.
策略二为词频加权求和,其计算如下:The second strategy is the weighted summation of word frequency, which is calculated as follows:
其中,z(w)表示每个词语的词频,词频通过统计每个词在训练集和测试 集上出现的频率获得,其他参数同上。Among them, z(w) represents the word frequency of each word, and the word frequency is obtained by counting the frequency of each word in the training set and test set, and other parameters are the same as above.
将融合的词向量与BERT输出的字向量进行拼接,获得每个字符的最终 向量表示,表示向量拼接。Splicing the fused word vector with the word vector output by BERT to obtain the final vector representation of each character, Represents vector concatenation.
步骤7,将句子中每一个字的字向量输入到LSTM模型中,学习句子中 较长距离的前后依赖关系,LSTM通过输入门、遗忘门、输出门控制和保持 信息的传递,其参数化表示如下所示:Step 7: Input the word vector of each word in the sentence into the LSTM model to learn the long-distance front and back dependencies in the sentence. LSTM controls and maintains the transmission of information through the input gate, forget gate, and output gate, and its parameterized representation As follows:
it=σ(Wixt+Uiht-1+bi)it =σ(Wi xt +Ui ht-1 +bi )
ft=σ(Wfxt+Ufht-1+bf)ft =σ(Wf xt +Uf ht-1 +bf )
ot=σ(Woxt+Uoht-1+bo)ot =σ(Wo xt +Uo ht-1 +bo )
ht=ot e tanh(ct)ht =ot e tanh(ct )
其中,σ是Sigmoid激活函数,tanh表示tanh激活函数,表示点乘运 算,W、U分别表示对应每个门的权重矩阵,b表示偏置,xt表示步骤6获得 的当前时刻的输入向量,ht-1和ct-1分别表示上一时刻的输出和上一时刻的细 胞状态。where σ is the sigmoid activation function, tanh is the tanh activation function, Represents the point multiplication operation, W and U represent the weight matrix corresponding to each gate respectively, b represents the bias, xt represents the input vector of the current moment obtained in step 6, ht-1 and ct-1 represent the previous moment respectively output and the cell state at the previous moment.
步骤8,如图2所示,Bi-LSTM包含前向传递和反向传递两个过程,能 够编码双向语言信息,对于输入的句子向量序列S={e1,e2,L,en},ei∈R1×(d+l), 其中1≤i≤n,d,l分别表示词向量和字向量的维度。前向传递过程为:Step 8, as shown in Figure 2, Bi-LSTM includes two processes of forward pass and reverse pass, which can encode bidirectional language information. For the input sentence vector sequence S={e1 ,e2 ,L,en } , ei ∈R1×(d+l) , where 1≤i≤n, d, l represent the dimension of word vector and word vector, respectively. The forward pass process is:
反向传递过程为:The reverse transfer process is:
其中,是前向t-1时刻的隐藏状态,是反向t+1时刻的隐藏状态, et是t时刻的输入向量。in, is the hidden state at time t-1 forward, is the hidden state at time t+1 in reverse, and et is the input vector at time t.
步骤9,最后对前向和反向LSTM的输出进行拼接获得t时刻的隐藏状 态ht:Step 9, finally splicing the output of the forward and reverse LSTM to obtain the hidden state h t at timet :
步骤10,CRF层在Bi-LSTM输出的基础上考虑了标签之间的转移信息, 能够获得全局最优标签序列,计算过程如下:In step 10, the CRF layer considers the transfer information between labels on the basis of the Bi-LSTM output, and can obtain the global optimal label sequence. The calculation process is as follows:
其中,s表示评估得分,W是标签间的转移矩阵,P表示对应标签的得 分。根据评估得分计算序列x到标签y的概率为:Among them, s is the evaluation score, W is the transition matrix between labels, and P is the score of the corresponding label. Calculate the probability of sequence x to label y based on the evaluation score as:
步骤11,训练损失函数为:Step 11, the training loss function is:
至此,具体实施例流程结束。So far, the process of the specific embodiment ends.
步骤12,本发明训练基于BERT和Word2Vec向量融合的Bi-LSTM-CRF 模型参数时,将已标注好的文本和标签作为输入,然后采用梯度下降法或其 他优化方法训练该模型,训练中只更新Bi-LSTM层和CRF层的参数,BERT 模型参数保持不变,当模型产生的损失值满足设定要求或达到最大迭代次数 时,则终止该模型的训练。
上述说明示出并描述了本发明的优选实施例,如前所述,应当理解本发 明并非局限于本文所披露的形式,不应看作是对其他实施例的排除,而可用 于各种其他组合、修改和环境,并能够在本文所述发明构想范围内,通过上 述教导或相关领域的技术或知识进行改动。而本领域人员所进行的改动和变 化不脱离本发明的精神和范围,则都应在本发明所附权利要求的保护范围内。The foregoing specification illustrates and describes preferred embodiments of the present invention, and as previously stated, it should be understood that the present invention is not limited to the form disclosed herein, and should not be construed as an exclusion of other embodiments, but may be used in a variety of other Combinations, modifications and environments are possible within the scope of the inventive concepts described herein, from the above teachings or from skill or knowledge in the relevant fields. And the modification and change that those skilled in the art carry out do not depart from the spirit and scope of the present invention, then all should be within the protection scope of the appended claims of the present invention.
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011462808.3ACN112632997A (en) | 2020-12-14 | 2020-12-14 | Chinese entity identification method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011462808.3ACN112632997A (en) | 2020-12-14 | 2020-12-14 | Chinese entity identification method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112632997Atrue CN112632997A (en) | 2021-04-09 |
Family
ID=75312414
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011462808.3APendingCN112632997A (en) | 2020-12-14 | 2020-12-14 | Chinese entity identification method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112632997A (en) |
Cited By (43)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113128199A (en)* | 2021-05-11 | 2021-07-16 | 济南大学 | Word vector generation method based on pre-training language model and multiple word information embedding |
| CN113221735A (en)* | 2021-05-11 | 2021-08-06 | 润联软件系统(深圳)有限公司 | Multimodal-based scanned part paragraph structure restoration method and device and related equipment |
| CN113239689A (en)* | 2021-07-07 | 2021-08-10 | 北京语言大学 | Selection question interference item automatic generation method and device for confusing word investigation |
| CN113254628A (en)* | 2021-05-18 | 2021-08-13 | 北京中科智加科技有限公司 | Event relation determining method and device |
| CN113342930A (en)* | 2021-05-24 | 2021-09-03 | 北京明略软件系统有限公司 | String vector-based text representation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN113392629A (en)* | 2021-06-29 | 2021-09-14 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for eliminating pronouns of personal expressions based on pre-training model |
| CN113450760A (en)* | 2021-06-07 | 2021-09-28 | 北京一起教育科技有限责任公司 | Method and device for converting text into voice and electronic equipment |
| CN113505200A (en)* | 2021-07-15 | 2021-10-15 | 河海大学 | Sentence-level Chinese event detection method combining document key information |
| CN113505587A (en)* | 2021-06-23 | 2021-10-15 | 科大讯飞华南人工智能研究院(广州)有限公司 | Entity extraction method, related device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN113554168A (en)* | 2021-06-29 | 2021-10-26 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | Model training, vector generation method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
| CN113657105A (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2021-11-16 | 平安医疗健康管理股份有限公司 | Medical entity extraction method, device, equipment and medium based on vocabulary enhancement |
| CN113672727A (en)* | 2021-07-28 | 2021-11-19 | 重庆大学 | Financial text entity relation extraction method and system |
| CN113673248A (en)* | 2021-08-23 | 2021-11-19 | 中国人民解放军32801部队 | Named entity identification method for testing and identifying small sample text |
| CN113849597A (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2021-12-28 | 艾迪恩(山东)科技有限公司 | Illegal advertising word detection method based on named entity recognition |
| CN113889259A (en)* | 2021-09-06 | 2022-01-04 | 浙江工业大学 | Automatic diagnosis dialogue system under assistance of knowledge graph |
| CN113901843A (en)* | 2021-09-07 | 2022-01-07 | 昆明理工大学 | BERT and word embedding dual-representation fused Hanyue neural machine translation method |
| CN113935327A (en)* | 2021-10-09 | 2022-01-14 | 新华智云科技有限公司 | Method and device for identifying domain entity |
| CN113988073A (en)* | 2021-10-26 | 2022-01-28 | 迪普佰奥生物科技(上海)股份有限公司 | Text recognition method and system suitable for life science |
| CN114281934A (en)* | 2021-09-16 | 2022-04-05 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Text recognition method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN114298048A (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2022-04-08 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Named Entity Recognition Method and Device |
| CN114356116A (en)* | 2021-12-31 | 2022-04-15 | 科大讯飞股份有限公司 | Text input methods and related devices |
| CN114416991A (en)* | 2022-01-18 | 2022-04-29 | 中山大学 | A Prompt-based Text Sentiment Analysis Method and System |
| CN114528840A (en)* | 2022-01-21 | 2022-05-24 | 深圳大学 | Chinese entity identification method, terminal and storage medium fusing context information |
| CN114757184A (en)* | 2022-04-11 | 2022-07-15 | 中国航空综合技术研究所 | Method and system for realizing knowledge question answering in aviation field |
| CN114781380A (en)* | 2022-03-21 | 2022-07-22 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Chinese named entity recognition method, equipment and medium fusing multi-granularity information |
| CN115017901A (en)* | 2022-06-08 | 2022-09-06 | 上海金仕达软件科技有限公司 | Information prediction method, system, device and storage medium of bulletin corpus |
| CN115129892A (en)* | 2022-06-24 | 2022-09-30 | 武汉大学 | Method and device for constructing knowledge graph of fault handling in distribution network |
| CN115146642A (en)* | 2022-07-21 | 2022-10-04 | 北京市科学技术研究院 | Automatic training set labeling method and system for named entity recognition |
| CN115238691A (en)* | 2022-06-02 | 2022-10-25 | 哈尔滨理工大学 | Knowledge fusion based embedded multi-intention recognition and slot filling model |
| CN115270803A (en)* | 2022-09-30 | 2022-11-01 | 北京道达天际科技股份有限公司 | Entity extraction method based on BERT and fused with N-gram characteristics |
| CN115329766A (en)* | 2022-08-23 | 2022-11-11 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | A Named Entity Recognition Method Based on Dynamic Word Information Fusion |
| CN115422362A (en)* | 2022-10-09 | 2022-12-02 | 重庆邮电大学 | A Text Matching Method Based on Artificial Intelligence |
| CN115687577A (en)* | 2023-01-04 | 2023-02-03 | 交通运输部公路科学研究所 | A method and system for discovering road transport normalization problem appeals |
| CN115859977A (en)* | 2022-10-31 | 2023-03-28 | 浙江工业大学 | Named entity identification method based on fusion sequence characteristics |
| CN116011456A (en)* | 2023-03-17 | 2023-04-25 | 北京建筑大学 | Chinese building specification text entity identification method and system based on prompt learning |
| CN116029354A (en)* | 2022-08-09 | 2023-04-28 | 中国搜索信息科技股份有限公司 | Text pair-oriented Chinese language model pre-training method |
| CN116415007A (en)* | 2023-01-10 | 2023-07-11 | 西北工业大学 | Text retrieval method based on self-adaptive triplet updating |
| CN116720520A (en)* | 2023-08-07 | 2023-09-08 | 烟台云朵软件有限公司 | Text data-oriented alias entity rapid identification method and system |
| CN117094322A (en)* | 2023-08-21 | 2023-11-21 | 天翼物联科技有限公司 | Named entity identification method, device, equipment and medium based on knowledge graph |
| CN117195877A (en)* | 2023-11-06 | 2023-12-08 | 中南大学 | Word vector generation method, system and equipment for electronic medical record and storage medium |
| CN117350283A (en)* | 2023-10-11 | 2024-01-05 | 西安栗子互娱网络科技有限公司 | Text defect detection method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| WO2024045318A1 (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2024-03-07 | 北京龙智数科科技服务有限公司 | Method and apparatus for training natural language pre-training model, device, and storage medium |
| CN118690722A (en)* | 2024-07-30 | 2024-09-24 | 山东政通科技发展有限公司 | A method and system for automatically formatting official documents |
- 2020
- 2020-12-14CNCN202011462808.3Apatent/CN112632997A/enactivePending
Cited By (66)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113128199A (en)* | 2021-05-11 | 2021-07-16 | 济南大学 | Word vector generation method based on pre-training language model and multiple word information embedding |
| CN113221735A (en)* | 2021-05-11 | 2021-08-06 | 润联软件系统(深圳)有限公司 | Multimodal-based scanned part paragraph structure restoration method and device and related equipment |
| CN113221735B (en)* | 2021-05-11 | 2025-04-25 | 华润数字科技有限公司 | Method, device and related equipment for restoring paragraph structure of scanned documents based on multimodality |
| CN113128199B (en)* | 2021-05-11 | 2022-06-21 | 济南大学 | Word vector generation method based on pre-training language model and multiple word information embedding |
| CN113254628A (en)* | 2021-05-18 | 2021-08-13 | 北京中科智加科技有限公司 | Event relation determining method and device |
| CN113342930A (en)* | 2021-05-24 | 2021-09-03 | 北京明略软件系统有限公司 | String vector-based text representation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN113342930B (en)* | 2021-05-24 | 2024-03-08 | 北京明略软件系统有限公司 | Text representing method and device based on string vector, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN113450760A (en)* | 2021-06-07 | 2021-09-28 | 北京一起教育科技有限责任公司 | Method and device for converting text into voice and electronic equipment |
| CN113505587A (en)* | 2021-06-23 | 2021-10-15 | 科大讯飞华南人工智能研究院(广州)有限公司 | Entity extraction method, related device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN113505587B (en)* | 2021-06-23 | 2024-04-09 | 科大讯飞华南人工智能研究院(广州)有限公司 | Entity extraction method, related device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN113554168A (en)* | 2021-06-29 | 2021-10-26 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | Model training, vector generation method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
| CN113392629A (en)* | 2021-06-29 | 2021-09-14 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Method for eliminating pronouns of personal expressions based on pre-training model |
| CN113392629B (en)* | 2021-06-29 | 2022-10-28 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Human-term pronoun resolution method based on pre-training model |
| CN113239689B (en)* | 2021-07-07 | 2021-10-08 | 北京语言大学 | Selection question interference item automatic generation method and device for confusing word investigation |
| CN113239689A (en)* | 2021-07-07 | 2021-08-10 | 北京语言大学 | Selection question interference item automatic generation method and device for confusing word investigation |
| CN113505200A (en)* | 2021-07-15 | 2021-10-15 | 河海大学 | Sentence-level Chinese event detection method combining document key information |
| CN113505200B (en)* | 2021-07-15 | 2023-11-24 | 河海大学 | A method for sentence-level Chinese event detection combining key information of documents |
| CN113672727A (en)* | 2021-07-28 | 2021-11-19 | 重庆大学 | Financial text entity relation extraction method and system |
| CN113672727B (en)* | 2021-07-28 | 2024-04-05 | 重庆大学 | Financial text entity relation extraction method and system |
| CN113673248B (en)* | 2021-08-23 | 2022-02-01 | 中国人民解放军32801部队 | Named entity identification method for testing and identifying small sample text |
| CN113673248A (en)* | 2021-08-23 | 2021-11-19 | 中国人民解放军32801部队 | Named entity identification method for testing and identifying small sample text |
| CN113849597B (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2024-04-30 | 艾迪恩(山东)科技有限公司 | Illegal advertisement word detection method based on named entity recognition |
| CN113849597A (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2021-12-28 | 艾迪恩(山东)科技有限公司 | Illegal advertising word detection method based on named entity recognition |
| CN113657105A (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2021-11-16 | 平安医疗健康管理股份有限公司 | Medical entity extraction method, device, equipment and medium based on vocabulary enhancement |
| CN113889259A (en)* | 2021-09-06 | 2022-01-04 | 浙江工业大学 | Automatic diagnosis dialogue system under assistance of knowledge graph |
| CN113901843B (en)* | 2021-09-07 | 2025-05-30 | 昆明理工大学 | Chinese-Vietnamese neural machine translation method integrating BERT and word embedding dual representation |
| CN113901843A (en)* | 2021-09-07 | 2022-01-07 | 昆明理工大学 | BERT and word embedding dual-representation fused Hanyue neural machine translation method |
| CN114281934A (en)* | 2021-09-16 | 2022-04-05 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Text recognition method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN113935327A (en)* | 2021-10-09 | 2022-01-14 | 新华智云科技有限公司 | Method and device for identifying domain entity |
| CN113988073A (en)* | 2021-10-26 | 2022-01-28 | 迪普佰奥生物科技(上海)股份有限公司 | Text recognition method and system suitable for life science |
| CN114298048B (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2025-02-11 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Named entity recognition method and device |
| CN114298048A (en)* | 2021-12-29 | 2022-04-08 | 中国电信股份有限公司 | Named Entity Recognition Method and Device |
| CN114356116B (en)* | 2021-12-31 | 2024-11-01 | 科大讯飞股份有限公司 | Text input method and related device |
| CN114356116A (en)* | 2021-12-31 | 2022-04-15 | 科大讯飞股份有限公司 | Text input methods and related devices |
| CN114416991A (en)* | 2022-01-18 | 2022-04-29 | 中山大学 | A Prompt-based Text Sentiment Analysis Method and System |
| CN114416991B (en)* | 2022-01-18 | 2025-08-05 | 中山大学 | A prompt-based text sentiment analysis method and system |
| CN114528840A (en)* | 2022-01-21 | 2022-05-24 | 深圳大学 | Chinese entity identification method, terminal and storage medium fusing context information |
| CN114781380B (en)* | 2022-03-21 | 2025-06-24 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | A Chinese named entity recognition method, device and medium integrating multi-granularity information |
| CN114781380A (en)* | 2022-03-21 | 2022-07-22 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Chinese named entity recognition method, equipment and medium fusing multi-granularity information |
| CN114757184A (en)* | 2022-04-11 | 2022-07-15 | 中国航空综合技术研究所 | Method and system for realizing knowledge question answering in aviation field |
| CN114757184B (en)* | 2022-04-11 | 2023-11-10 | 中国航空综合技术研究所 | Method and system for realizing knowledge question and answer in aviation field |
| CN115238691A (en)* | 2022-06-02 | 2022-10-25 | 哈尔滨理工大学 | Knowledge fusion based embedded multi-intention recognition and slot filling model |
| CN115017901A (en)* | 2022-06-08 | 2022-09-06 | 上海金仕达软件科技有限公司 | Information prediction method, system, device and storage medium of bulletin corpus |
| CN115129892A (en)* | 2022-06-24 | 2022-09-30 | 武汉大学 | Method and device for constructing knowledge graph of fault handling in distribution network |
| CN115146642B (en)* | 2022-07-21 | 2023-08-29 | 北京市科学技术研究院 | Named entity recognition-oriented training set automatic labeling method and system |
| CN115146642A (en)* | 2022-07-21 | 2022-10-04 | 北京市科学技术研究院 | Automatic training set labeling method and system for named entity recognition |
| CN116029354A (en)* | 2022-08-09 | 2023-04-28 | 中国搜索信息科技股份有限公司 | Text pair-oriented Chinese language model pre-training method |
| CN115329766A (en)* | 2022-08-23 | 2022-11-11 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | A Named Entity Recognition Method Based on Dynamic Word Information Fusion |
| WO2024045318A1 (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2024-03-07 | 北京龙智数科科技服务有限公司 | Method and apparatus for training natural language pre-training model, device, and storage medium |
| CN115270803A (en)* | 2022-09-30 | 2022-11-01 | 北京道达天际科技股份有限公司 | Entity extraction method based on BERT and fused with N-gram characteristics |
| CN115422362B (en)* | 2022-10-09 | 2023-10-31 | 郑州数智技术研究院有限公司 | Text matching method based on artificial intelligence |
| CN115422362A (en)* | 2022-10-09 | 2022-12-02 | 重庆邮电大学 | A Text Matching Method Based on Artificial Intelligence |
| CN115859977A (en)* | 2022-10-31 | 2023-03-28 | 浙江工业大学 | Named entity identification method based on fusion sequence characteristics |
| CN115687577A (en)* | 2023-01-04 | 2023-02-03 | 交通运输部公路科学研究所 | A method and system for discovering road transport normalization problem appeals |
| CN116415007A (en)* | 2023-01-10 | 2023-07-11 | 西北工业大学 | Text retrieval method based on self-adaptive triplet updating |
| CN116415007B (en)* | 2023-01-10 | 2025-08-01 | 西北工业大学 | Text retrieval method based on self-adaptive triplet updating |
| CN116011456A (en)* | 2023-03-17 | 2023-04-25 | 北京建筑大学 | Chinese building specification text entity identification method and system based on prompt learning |
| CN116720520A (en)* | 2023-08-07 | 2023-09-08 | 烟台云朵软件有限公司 | Text data-oriented alias entity rapid identification method and system |
| CN116720520B (en)* | 2023-08-07 | 2023-11-03 | 烟台云朵软件有限公司 | Text data-oriented alias entity rapid identification method and system |
| CN117094322A (en)* | 2023-08-21 | 2023-11-21 | 天翼物联科技有限公司 | Named entity identification method, device, equipment and medium based on knowledge graph |
| CN117350283B (en)* | 2023-10-11 | 2024-10-01 | 西安栗子互娱网络科技有限公司 | Text defect detection method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN117350283A (en)* | 2023-10-11 | 2024-01-05 | 西安栗子互娱网络科技有限公司 | Text defect detection method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN117195877A (en)* | 2023-11-06 | 2023-12-08 | 中南大学 | Word vector generation method, system and equipment for electronic medical record and storage medium |
| CN117195877B (en)* | 2023-11-06 | 2024-01-30 | 中南大学 | A word vector generation method, system, equipment and storage medium for electronic medical records |
| CN118690722B (en)* | 2024-07-30 | 2025-02-14 | 山东政通科技发展有限公司 | A method and system for automatically formatting official documents |
| CN118690722A (en)* | 2024-07-30 | 2024-09-24 | 山东政通科技发展有限公司 | A method and system for automatically formatting official documents |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112632997A (en) | Chinese entity identification method based on BERT and Word2Vec vector fusion | |
| CN109657239B (en) | Chinese Named Entity Recognition Method Based on Attention Mechanism and Language Model Learning | |
| CN113609859B (en) | A Chinese named entity recognition method for special equipment based on pre-training model | |
| CN109992782B (en) | Legal document named entity identification method and device and computer equipment | |
| CN110083831B (en) | Chinese named entity identification method based on BERT-BiGRU-CRF | |
| CN111626056B (en) | Chinese named entity identification method and device based on RoBERTA-BiGRU-LAN model | |
| CN111966812B (en) | An automatic question answering method and storage medium based on dynamic word vector | |
| CN108460013A (en) | A kind of sequence labelling model based on fine granularity vocabulary representation model | |
| CN113312453B (en) | A model pre-training system for cross-language dialogue understanding | |
| CN115392259B (en) | Microblog text sentiment analysis method and system based on confrontation training fusion BERT | |
| CN108388560A (en) | GRU-CRF meeting title recognition methods based on language model | |
| CN107729309A (en) | A kind of method and device of the Chinese semantic analysis based on deep learning | |
| CN110008469A (en) | A Multi-level Named Entity Recognition Method | |
| CN113190656A (en) | Chinese named entity extraction method based on multi-label framework and fusion features | |
| CN110263325A (en) | Chinese automatic word-cut | |
| CN110781290A (en) | Extraction method of structured text abstract of long chapter | |
| CN111931496B (en) | A text style conversion system and method based on a recurrent neural network model | |
| CN114153973A (en) | Mongolian multimodal sentiment analysis method based on T-M BERT pre-training model | |
| CN114818717A (en) | Chinese named entity recognition method and system fusing vocabulary and syntax information | |
| CN114528368A (en) | Spatial relationship extraction method based on pre-training language model and text feature fusion | |
| CN112818698A (en) | Fine-grained user comment sentiment analysis method based on dual-channel model | |
| CN113076718B (en) | Commodity attribute extraction method and system | |
| CN115510230A (en) | Mongolian emotion analysis method based on multi-dimensional feature fusion and comparative reinforcement learning mechanism | |
| CN117725964A (en) | Multi-congratulation text generation method based on BART model | |
| CN114021549A (en) | Chinese Named Entity Recognition Method and Device Based on Vocabulary Enhancement and Multi-feature |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20210409 |