CN112507101A - Method and device for establishing pre-training language model - Google Patents
Method and device for establishing pre-training language modelDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112507101A CN112507101ACN202011504224.8ACN202011504224ACN112507101ACN 112507101 ACN112507101 ACN 112507101ACN 202011504224 ACN202011504224 ACN 202011504224ACN 112507101 ACN112507101 ACN 112507101A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- language model
- training
- character
- text
- output
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/30—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of unstructured textual data
- G06F16/33—Querying
- G06F16/332—Query formulation
- G06F16/3329—Natural language query formulation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/30—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor of unstructured textual data
- G06F16/33—Querying
- G06F16/3331—Query processing
- G06F16/334—Query execution
- G06F16/3344—Query execution using natural language analysis
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/21—Design or setup of recognition systems or techniques; Extraction of features in feature space; Blind source separation
- G06F18/214—Generating training patterns; Bootstrap methods, e.g. bagging or boosting
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
- G06N20/20—Ensemble learning
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Machine Translation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及计算机应用技术领域,特别涉及人工智能技术领域中的自然语言处理技术。The present application relates to the field of computer application technology, in particular to the natural language processing technology in the field of artificial intelligence technology.
背景技术Background technique
在NLP(Natural Language Processing,自然语言处理)领域中,预训练语言模型得到了广泛的关注和使用,同时也涌现出了很多为细分领域设计的预训练语言模型。In the field of NLP (Natural Language Processing, natural language processing), pre-trained language models have received extensive attention and use, and many pre-trained language models designed for subdivision fields have emerged.
现有的预训练语言模型大都是针对无格式的流式文本,能够对文本中各字符的一维位置信息(例如对文本中各字符的顺序)进行很好地理解并基于此建模语义信息。但对于一些具有特定格式的文本,因其体现的是文本中各字符的二维位置信息,目前却没有很好的方式来建立理解二维位置信息的预训练语言模型。Most of the existing pre-trained language models are aimed at unformatted streaming text, which can well understand the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text (such as the order of each character in the text) and model semantic information based on this. . However, for some texts with a specific format, because they reflect the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text, there is currently no good way to establish a pre-trained language model that understands the two-dimensional position information.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
有鉴于此,本申请提供了一种建立预训练语言模型的方法和装置,以使得预训练语言模型能够很好地理解文本中各字符的二维位置信息。In view of this, the present application provides a method and apparatus for establishing a pre-trained language model, so that the pre-trained language model can well understand the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text.
第一方面,本申请提供了一种建立预训练语言模型的方法,包括:In a first aspect, the present application provides a method for establishing a pre-trained language model, including:
获取训练样本,所述训练样本包括文本;obtaining training samples, the training samples including text;
将所述文本作为预先训练得到的第一预训练语言模型的输入以及第二预训练语言模型的输入,训练所述第二预训练语言模型;Using the text as the input of the first pre-training language model and the input of the second pre-training language model obtained by pre-training, and training the second pre-training language model;
其中,所述第二预训练语言模型的训练目标包括:最小化第二预训练语言模型基于所述文本中各字符的二维位置信息得到的中间层输出与第一预训练语言模型基于所述文本中各字符的一维位置信息得到的中间层输出之间的差异。Wherein, the training objective of the second pre-training language model includes: minimizing the intermediate layer output obtained by the second pre-training language model based on the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text and the first pre-training language model based on the The difference between the output of the intermediate layer obtained from the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text.
第二方面,本申请提供了一种建立预训练语言模型的装置,包括:In a second aspect, the present application provides an apparatus for establishing a pre-trained language model, including:
样本获取单元,用于获取训练样本,所述训练样本包括文本;a sample acquisition unit for acquiring training samples, the training samples including text;
模型训练单元,用于将所述文本作为预先训练得到的第一预训练语言模型的输入以及第二预训练语言模型的输入,训练所述第二预训练语言模型;a model training unit, configured to train the second pre-trained language model by using the text as the input of the first pre-trained language model and the input of the second pre-trained language model obtained by pre-training;
其中,所述第二预训练语言模型的训练目标包括:最小化第二预训练语言模型基于所述文本中各字符的二维位置信息得到的中间层输出与第一预训练语言模型基于所述文本中各字符的一维位置信息得到的中间层输出之间的差异。Wherein, the training objective of the second pre-training language model includes: minimizing the intermediate layer output obtained by the second pre-training language model based on the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text and the first pre-training language model based on the The difference between the output of the intermediate layer obtained from the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text.
第三方面,本申请提供了一种电子设备,包括:In a third aspect, the present application provides an electronic device, comprising:
至少一个处理器;以及at least one processor; and
与所述至少一个处理器通信连接的存储器;其中,a memory communicatively coupled to the at least one processor; wherein,
所述存储器存储有可被所述至少一个处理器执行的指令,所述指令被所述至少一个处理器执行,以使所述至少一个处理器能够执行上述的方法。The memory stores instructions executable by the at least one processor, the instructions being executed by the at least one processor to enable the at least one processor to perform the method described above.
第四方面,本申请提供了一种存储有计算机指令的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质,其中,所述计算机指令用于使所述计算机执行上述的方法。In a fourth aspect, the present application provides a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing computer instructions, wherein the computer instructions are used to cause the computer to execute the above method.
第五方面,本申请提供了一种计算机程序产品,包括计算机程序,所述计算机程序在被处理器执行时实现如上所述的方法。In a fifth aspect, the present application provides a computer program product, comprising a computer program that, when executed by a processor, implements the method as described above.
由以上技术方案可以看出,本申请采用已训练得到的能够很好理解一维位置信息的第一预训练语言模型来指导第二预训练语言模型对二维位置信息的理解,从而使得训练得到的第二预训练语言模型能够很好地理解文本中各字符的二维位置信息。It can be seen from the above technical solutions that the present application uses the trained first pre-training language model that can well understand the one-dimensional position information to guide the second pre-training language model to understand the two-dimensional position information, so that the training can be obtained. The second pre-trained language model of can well understand the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text.
上述可选方式所具有的其他效果将在下文中结合具体实施例加以说明。Other effects of the above-mentioned optional manners will be described below with reference to specific embodiments.
附图说明Description of drawings
附图用于更好地理解本方案,不构成对本申请的限定。其中:The accompanying drawings are used for better understanding of the present solution, and do not constitute a limitation to the present application. in:
图1为本申请实施例提供的主要方法流程图;1 is a flow chart of a main method provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例提供的模型训练架构的示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of a model training architecture provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图3a为本申请实施例提供的第一预训练语言模型的结构示意图;3a is a schematic structural diagram of a first pre-trained language model provided by an embodiment of the application;
图3b为本申请实施例提供的第二预训练语言模型的结构示意图;3b is a schematic structural diagram of a second pre-trained language model provided by an embodiment of the application;
图4为本申请实施例提供的建立预训练语言模型的装置的结构示意图;4 is a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for establishing a pre-trained language model provided by an embodiment of the present application;
图5是用来实现本申请实施例的电子设备的框图。FIG. 5 is a block diagram of an electronic device used to implement an embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下结合附图对本申请的示范性实施例做出说明,其中包括本申请实施例的各种细节以助于理解,应当将它们认为仅仅是示范性的。因此,本领域普通技术人员应当认识到,可以对这里描述的实施例做出各种改变和修改,而不会背离本申请的范围和精神。同样,为了清楚和简明,以下的描述中省略了对公知功能和结构的描述。Exemplary embodiments of the present application are described below with reference to the accompanying drawings, which include various details of the embodiments of the present application to facilitate understanding, and should be considered as exemplary only. Accordingly, those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that various changes and modifications of the embodiments described herein can be made without departing from the scope and spirit of the present application. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions are omitted from the following description for clarity and conciseness.
预训练语言模型已经广泛的应用于NLP领域,本申请所提供的方法能够在服务器端或者具有较强计算能力的计算机终端来实现,用以完成各种与NLP相关的任务。在现有技术中有一些学者提出直接利用文本中各字符的二维位置信息训练预训练语言模型,但这种方案使得预训练语言模型很难理解二维位置信息,无法很好地学习。本申请的核心思想是采用已训练得到的能够很好理解一维位置信息的第一预训练语言模型来指导第二预训练语言模型对二维位置信息的理解。下面结合实施例对本申请所提供的方法进行详细描述。Pre-trained language models have been widely used in the field of NLP, and the method provided in this application can be implemented on a server side or a computer terminal with strong computing power to complete various NLP-related tasks. In the prior art, some scholars propose to directly use the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text to train the pre-trained language model, but this solution makes it difficult for the pre-trained language model to understand the two-dimensional position information and cannot learn well. The core idea of the present application is to use the trained first pre-trained language model capable of understanding one-dimensional position information well to guide the second pre-trained language model to understand the two-dimensional position information. The method provided by the present application will be described in detail below with reference to the embodiments.
图1为本申请实施例提供的主要方法流程图,如图1中所示,该方法可以包括以下步骤:FIG. 1 is a flow chart of a main method provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 1 , the method may include the following steps:
在101中,获取训练样本,训练样本中包含文本。In 101, a training sample is obtained, and the training sample contains text.
本申请实施例中采用的训练样本可以是多种形式的文本,例如网页文本、文档扫描件、文献等等。这些文本中可以是具有一些格式或版式的文本,例如存在一些表单、表格、浮动图片、分栏等等。The training samples used in the embodiments of the present application may be texts in various forms, such as web page texts, document scans, documents, and so on. These texts may be texts with some formatting or layout, for example, there are some forms, tables, floating pictures, columns, and so on.
在102中,将训练样本中的文本作为预先训练得到的第一预训练语言模型的输入以及第二预训练语言模型的输入,训练第二预训练语言模型;训练目标包括:最小化第二预训练语言模型基于文本中各字符的二维位置信息得到的中间层输出与第一预训练语言模型基于文本中各字符的一维位置信息得到的中间层输出之间的差异。In 102, the text in the training sample is used as the input of the first pre-trained language model and the input of the second pre-trained language model obtained by pre-training, and the second pre-trained language model is trained; the training objectives include: minimizing the second pre-training language model. The difference between the intermediate layer output obtained by the training language model based on the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text and the intermediate layer output obtained by the first pre-trained language model based on the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text.
在本申请实施例中,第一预训练语言模型是预先训练好的模型,其已经能够很好的理解文本中各字符的一维位置信息。第一预训练语言模型可以采用目前通用的BERT(Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers,深度双向转换语言模型)、ERNIE(Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities,知识增强语义表示模型)等。训练任务可以使用Mask Language Model(掩码语言模型)的方式或NSP(Next Sentence Prediction,下一句子预测)的方式。其中,Mask Language Model的方式是输入文本后,基于对文本中各字符的一维位置信息(例如各字符的顺序)的理解,最小化对文本中被mask字符的预测结果与实际值之间的差异。NSP的方式是输入文本后,最小化对下一句子的预测结果与实际顺序的差异。鉴于第一预训练语言模型的训练是现有技术中较为成熟的方案,在此不做详述。In the embodiment of the present application, the first pre-trained language model is a pre-trained model, which can already well understand the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text. The first pre-trained language model may adopt the currently common BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, deep bidirectional transformation language model), ERNIE (Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities, knowledge-enhanced semantic representation model) and the like. The training task can use the Mask Language Model method or the NSP (Next Sentence Prediction, next sentence prediction) method. Among them, the method of Mask Language Model is to minimize the difference between the prediction result of the masked characters in the text and the actual value based on the understanding of the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text (such as the order of each character) after the text is input. difference. The way of NSP is to minimize the difference between the predicted result of the next sentence and the actual order after inputting the text. Since the training of the first pre-trained language model is a relatively mature solution in the prior art, it will not be described in detail here.
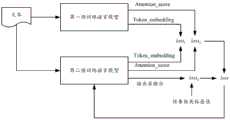
在训练第二预训练语言模型时,训练架构如图2中所示。训练样本中的文本作为第一预训练语言模型和第二预训练语言模型的输入。第一预训练语言模型基于对文本中各字符(Token)的一维位置信息的理解,经过中间层之后输出各字符的向量表示(Token_embedding)和注意力得分(Attention_score)。When training the second pre-trained language model, the training architecture is shown in Figure 2. The text in the training samples is used as input to the first pre-trained language model and the second pre-trained language model. The first pre-trained language model is based on the understanding of the one-dimensional position information of each character (Token) in the text, and outputs a vector representation (Token_embedding) and an attention score (Attention_score) of each character after passing through the middle layer.
其中,中间层包括嵌入层和隐藏层。如图3a中所示,第一预训练语言模型在输入层输入文本后,在嵌入层进行字符嵌入(Token Embeddings)、段落嵌入(SegmentEmbeddings)和位置嵌入(Position Embeddings)。在进行位置嵌入时,是对各字符的一维位置信息进行embedding,例如对各字符的顺序编号进行embedding。关于嵌入层进行上述嵌入处理的具体内容可以采用现有技术中较为成熟的方式,在此不做赘述。图3a中采用的具体嵌入值仅仅为一个示例,对本申请的保护范围不做任何限定。隐藏层可以采用多层Transformer的结构,输出各字符的向量表示(Token_embedding)和注意力得分(Attention_score)。Among them, the middle layer includes an embedded layer and a hidden layer. As shown in Figure 3a, the first pre-trained language model performs character embeddings (Token Embeddings), paragraph embeddings (Segment Embeddings) and position embeddings (Position Embeddings) in the embedding layer after inputting text in the input layer. When performing position embedding, the one-dimensional position information of each character is embedded, for example, the sequence number of each character is embedded. The specific content of the above-mentioned embedding processing performed by the embedding layer may adopt a relatively mature manner in the prior art, which will not be repeated here. The specific embedded value used in FIG. 3a is only an example, and does not limit the protection scope of the present application. The hidden layer can use a multi-layer Transformer structure to output the vector representation (Token_embedding) and attention score (Attention_score) of each character.
如图3b中所示,第二预训练语言模型在输入层输入文本后,在嵌入层同样进行字符嵌入(Token Embeddings)、段落嵌入(Segment Embeddings)和位置嵌入(PositionEmbeddings)。其中,字符嵌入和段落嵌入的方式与第一预训练语言模型相同。但在进行位置嵌入时,第二预训练语言模型采用的是各字符的二维位置信息。As shown in Figure 3b, the second pre-trained language model also performs character embedding (Token Embeddings), paragraph embedding (Segment Embeddings) and position embedding (Position Embeddings) in the embedding layer after inputting text in the input layer. Among them, the way of character embedding and paragraph embedding is the same as that of the first pre-trained language model. However, when performing position embedding, the second pre-trained language model uses the two-dimensional position information of each character.
作为一种优选的实施方式,字符的二维位置信息可以采用字符的左上角点坐标(x0,y0)和右下角点坐标(x1,y1)表示。如图3b中所示,在进行位置嵌入时,可以对上述左上角点横坐标(图中表示为2D-x0)、左上角点纵坐标(图中表示为2D-y0)、右下角点横坐标(图中表示为2D-x1)以及右下角点纵坐标(图中表示为2D-y1)分别进行嵌入处理。图3b中采用的具体嵌入值仅仅为一个示例,对本申请的保护范围不做任何限定。As a preferred embodiment, the two-dimensional position information of the character can be represented by the coordinates of the upper left corner point (x0, y0) and the lower right corner point coordinates (x1, y1) of the character. As shown in Figure 3b, when performing position embedding, the abscissa of the upper left corner (represented as 2D-x0 in the figure), the ordinate of the upper left corner (represented as 2D-y0 in the figure), the horizontal The coordinates (represented as 2D-x1 in the figure) and the ordinate of the lower right corner (represented as 2D-y1 in the figure) are respectively embedded. The specific embedded value used in FIG. 3b is only an example, and does not limit the protection scope of the present application.
除此之外,字符的二维位置信息也可以采用其他方式表示,例如采用左下角点坐标和右上角点坐标表示,或者,采用字符的中间点坐标表示,等等。In addition, the two-dimensional position information of the character can also be represented by other means, for example, by the coordinates of the lower left corner and the upper right corner, or by the coordinates of the middle point of the character, and so on.
在训练第二预训练语言模型时,实际上是将第一预训练语言模型输出的各Token_embedding和各Attention_score用于指导第二预训练语言模型的学习,目标是尽量使得两个模型输出的Token_embedding一致且Attention_score一致。以此目标可以构建两个损失函数loss1和loss2,loss1用于体现两个模型输出的各Token_embedding的差异,loss2用于体现两个模型输出的各Attention_score的差异。例如:When training the second pre-training language model, each Token_embedding and each Attention_score output by the first pre-training language model are actually used to guide the learning of the second pre-training language model. The goal is to make the Token_embedding output by the two models as consistent as possible. And the Attention_score is the same. With this goal, two loss functions loss1 and loss2 can be constructed. Loss1 is used to reflect the difference of each Token_embedding output by the two models, and loss2 is used to reflect the difference of each Attention_score output by the two models. E.g:
其中,N为文本的长度,即文本所包含字符的个数。D为每个Token_embedding的维度。eij为第一预训练语言模型的隐藏层输出的第i个字符的Token_embedding向量中的第j个向量值。e'ij为第二预训练语言模型的隐藏层输出的第i个字符的Token_embedding向量中的第j个向量值。Sijk为第一预训练语言模型的隐藏层输出的第i个字符的Attention_score向量中第j行第k列的取值,S'ijk为第二预训练语言模型的隐藏层输出的第i个字符的Attention_score向量中第j行第k列的取值。Among them, N is the length of the text, that is, the number of characters contained in the text. D is the dimension of each Token_embedding. eij is the j-th vector value in the Token_embedding vector of the i-th character output by the hidden layer of the first pre-trained language model. e'ij is the jth vector value in the Token_embedding vector of the ith character output by the hidden layer of the second pre-trained language model. Sijk is the value of the jth row and kth column of the Attention_score vector of the i-th character output by the hidden layer of the first pre-trained language model, and S'ijk is the i-th output of the hidden layer of the second pre-trained language model The value of the jth row and kth column in the Attention_score vector of the character.
作为一种实施方式,可以将上述loss1和loss2进行加和后得到一个总的损失函数,然后利用该总的损失函数进行反向传播,利用梯度下降算法调整第二预训练语言模型的模型参数。As an embodiment, the above loss1 and loss2 can be added to obtain a total loss function, and then the total loss function can be used for backpropagation, and the gradient descent algorithm is used to adjust the model of the second pre-trained language model parameter.
作为另一种优选的实施方式,在训练样本中还可以进一步包括文本中各字符对应的任务相关标签值。也就是说,对文本进行标签的标注,该标签是与第二预训练语言模型的具体下游任务相关的。在第二预训练语言模型中通过输出层进行诸如Softmax的映射,得到与任务相关的估计值。在第二预训练语言模型的训练过程中,训练目标还可以进一步包括:最小化第二预训练语言模型的输出层输出与所述各字符对应的任务相关标签值之间的差异。As another preferred embodiment, the training sample may further include task-related label values corresponding to each character in the text. That is to say, label the text, and the label is related to the specific downstream task of the second pre-trained language model. In the second pre-trained language model, a mapping such as Softmax is performed through the output layer to obtain task-related estimates. During the training process of the second pre-trained language model, the training objective may further include: minimizing the difference between the output layer output of the second pre-trained language model and the task-related label value corresponding to each character.
在此对于下游任务举两个例子,但需要说明的是,下游任务并不限于以下两个例子:Here are two examples of downstream tasks, but it should be noted that downstream tasks are not limited to the following two examples:
下游任务1:字符粒度的分类任务。Downstream Task 1: Character-grained classification task.
在文本中可能包含一些表单,每个字符可能在表单中属于一些表单区域类型。对这些表单区域类型进行划分,通过第二预训练语言模型基于字符在文本中的二维位置信息来判别该字符对应的表单区域类型。There may be some forms in the text, and each character may belong to some form area type in the form. These form area types are divided, and the form area type corresponding to the character is determined by the second pre-trained language model based on the two-dimensional position information of the character in the text.
其中,表单区域类型可以包括诸如:表单标题(title)、单元格(table cell)、属性信息(key)以及属性值(value)等等。例如,若收件人为key,具体收件人的名字,例如“张三”就是value。Wherein, the form area type may include, for example: form title (title), cell (table cell), attribute information (key), attribute value (value) and so on. For example, if the recipient is the key, the specific recipient's name, such as "Zhang San", is the value.
更具体地,可以进一步划分各种表单区域类型的开始位置、中间位置和结束位置三种类型。例如,title开始位置、title中间位置和title结束位置。通过对文本中字符的内容、段落信息、二维位置信息等进行理解,第二预训练语言模型就能够判断出一个字符是属于表单title中的开始位置、中间位置还是结束位置。More specifically, three types of start position, middle position and end position of various form area types can be further divided. For example, title start position, title middle position and title end position. By understanding the content, paragraph information, and two-dimensional position information of characters in the text, the second pre-trained language model can determine whether a character belongs to the start position, middle position, or end position of the form title.
在此任务下,第二预训练语言模型的输出层可以输出各字符属于预先划分的各种表单区域类型的概率。Under this task, the output layer of the second pre-trained language model can output the probability that each character belongs to various pre-divided form area types.
下游任务2:阅读顺序预测任务。Downstream Task 2: Reading Order Prediction Task.
在一些文本中可能包含分栏、浮动图片、表格等复杂布局,那么找到每个字符正确的阅读顺序就十分必要。只有确定正确的阅读顺序,下游解析逻辑才能够正确的理解文本正确的语义,那么第二预训练语言模型就可以基于字符在文本中的二维位置信息来预测每个字符的下一个字符是哪个字符,如果某字符的下一个字符指向它本身或者为空,则代表当前语义段结束。In some texts that may contain complex layouts such as columns, floating images, tables, etc., it is necessary to find the correct reading order for each character. Only by determining the correct reading order, the downstream parsing logic can correctly understand the correct semantics of the text, then the second pre-trained language model can predict the next character of each character based on the two-dimensional position information of the characters in the text. character, if the next character of a character points to itself or is empty, it means the end of the current semantic segment.
在此任务下,第二预训练语言模型的输出层可以输出各字符作为当前字符的下一个字符的概率。Under this task, the output layer of the second pre-trained language model can output the probability that each character is the next character of the current character.
通过任务相关标签值可以构建第三个损失函数loss3,loss3用以体现第二预训练语言模型的输出层输出与各字符对应的任务相关标签值(即训练样本中标注的值)之间的差异。例如:The third loss function loss3 can be constructed through the task-related label value, and loss3 is used to reflect the difference between the output layer output of the second pre-trained language model and the task-related label value corresponding to each character (that is, the value marked in the training sample). difference. E.g:
其中,C为相关任务标签的类别数量,即每个字符可能预测的类别数量。ti表示第i个字符对应的任务相关标签值(即训练样本中标注的值)。li表示第二预训练语言模型输出层输出的第i个字符在上述标签值对应的类别上的概率值,ln表示第二预训练语言模型输出层输出的第i个字符在第n个类别上的概率值。Among them, C is the number of categories of relevant task labels, that is, the number of categories that each character may predict. ti represents the task-related label value corresponding to the ith character (that is, the value labeled in the training sample). li represents the probability value of the i-th character output by the output layer of the second pre-training language model on the category corresponding to the above label value, and ln represents the i-th character output by the output layer of the second pre-training language model is in the n-th character The probability value on the class.
然后将上述loss1、loss2和loss3进行加和后得到一个总的损失函数loss,然后利用该总的损失函数进行反向传播,利用梯度下降算法调整第二预训练语言模型的模型参数。Then the above loss1 , loss2 and loss3 are added to obtain a total loss function loss, and then the total loss function is used for backpropagation, and the gradient descent algorithm is used to adjust the model parameters of the second pre-trained language model.
经过上述训练得到的第二预训练语言模型,可以接入下游任务对待预测文本进行任务相关的预测。例如上述的字符粒度的分类预测或阅读顺序预测,等等。The second pre-trained language model obtained through the above training can be connected to the downstream task to perform task-related prediction on the text to be predicted. For example, the above-mentioned character granularity classification prediction or reading order prediction, and so on.
以上是对本申请所提供的方法进行的详细描述,下面结合实施例对本申请所提供的装置进行详细描述。The above is a detailed description of the method provided by the present application, and the device provided by the present application is described in detail below with reference to the embodiments.
图4为本申请实施例提供的建立预训练语言模型的装置的结构示意图,如图4中所示,该装置可以包括:样本获取单元01和模型训练单元02。其中各组成单元的主要功能如下:FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for establishing a pre-trained language model provided by an embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 4 , the apparatus may include: a
样本获取单元01,用于获取训练样本,训练样本包括文本。The
模型训练单元02,用于将文本作为预先训练得到的第一预训练语言模型的输入以及第二预训练语言模型的输入,训练第二预训练语言模型;The
其中,第二预训练语言模型的训练目标包括:最小化第二预训练语言模型基于文本中各字符的二维位置信息得到的中间层输出与第一预训练语言模型基于文本中各字符的一维位置信息得到的中间层输出之间的差异。Wherein, the training objective of the second pre-trained language model includes: minimizing the output of the intermediate layer obtained by the second pre-trained language model based on the two-dimensional position information of each character in the text and the first pre-trained language model based on the output of each character in the text. The difference between the output of the intermediate layer obtained from the dimensional position information.
第一预训练语言模型是预先训练好的模型,其已经能够很好的理解文本中各字符的一维位置信息。第一预训练语言模型可以采用目前通用的BERT、ERNIE等。训练任务可以使用Mask Language Model的方式或NSP的方式。The first pre-trained language model is a pre-trained model, which can already well understand the one-dimensional position information of each character in the text. The first pre-trained language model may use currently common BERT, ERNIE, and the like. The training task can use the Mask Language Model method or the NSP method.
其中,中间层输出可以包括:各字符的向量表示和注意力得分。Among them, the output of the middle layer can include: the vector representation of each character and the attention score.
作为一种实施方式,可以利用第二预训练语言模型输出的各字符的向量表示和第一预训练语言模型输出的各字符的向量表示之间的差异构建第一损失函数,利用第二预训练语言模型输出的各字符的注意力得分和第一预训练语言模型输出的各字符的注意力得分之间的差异构建第二损失函数。将第一损失函数和第二损失函数进行加和后得到一个总的损失函数,然后利用该总的损失函数进行反向传播,利用梯度下降算法调整第二预训练语言模型的模型参数。As an implementation manner, the first loss function can be constructed by using the difference between the vector representation of each character output by the second pre-training language model and the vector representation of each character output by the first pre-training language model, and the second pre-training language model can be used to construct the first loss function. The difference between the attention score of each character output by the language model and the attention score of each character output by the first pre-trained language model constitutes a second loss function. After adding the first loss function and the second loss function, a total loss function is obtained, and then the total loss function is used for back propagation, and the gradient descent algorithm is used to adjust the model parameters of the second pre-trained language model.
作为一种优选的实施方式,上述训练样本还包括文本中各字符对应的任务相关标签值。相应地,第二预训练语言模型的训练目标进一步包括:最小化第二预训练语言模型的输出层输出与各字符对应的任务相关标签值之间的差异。As a preferred embodiment, the above-mentioned training samples also include task-related label values corresponding to each character in the text. Correspondingly, the training objective of the second pre-trained language model further includes: minimizing the difference between the output layer output of the second pre-trained language model and the task-related label value corresponding to each character.
其中,各字符对应的任务相关标签值可以包括但不限于:各字符在文本包含的表单中的类型信息;或者,各字符的正确阅读顺序信息。The task-related tag value corresponding to each character may include, but is not limited to: the type information of each character in the form included in the text; or, the correct reading sequence information of each character.
模型训练单元02在训练第二预训练语言模型过程中采用的总的损失函数由第一损失函数、第二损失函数和第三损失函数的总和得到。其中第三损失函数是利用第二预训练语言模型的输出层输出的各字符对应的任务相关估计值与各字符对应的任务相关标签值之间的差异得到的。然后利用该总的损失函数进行反向传播,利用梯度下降算法调整第二预训练语言模型的模型参数。The total loss function used by the
根据本申请的实施例,本申请还提供了一种电子设备、一种可读存储介质和一种计算机程序产品。According to the embodiments of the present application, the present application further provides an electronic device, a readable storage medium, and a computer program product.
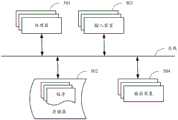
如图5所示,是根据本申请实施例的建立预训练语言模型的方法的电子设备的框图。电子设备旨在表示各种形式的数字计算机,诸如,膝上型计算机、台式计算机、工作台、个人数字助理、服务器、刀片式服务器、大型计算机、和其它适合的计算机。电子设备还可以表示各种形式的移动装置,诸如,个人数字处理、蜂窝电话、智能电话、可穿戴设备和其它类似的计算装置。本文所示的部件、它们的连接和关系、以及它们的功能仅仅作为示例,并且不意在限制本文中描述的和/或者要求的本申请的实现。As shown in FIG. 5 , it is a block diagram of an electronic device for a method for establishing a pre-trained language model according to an embodiment of the present application. Electronic devices are intended to represent various forms of digital computers, such as laptops, desktops, workstations, personal digital assistants, servers, blade servers, mainframe computers, and other suitable computers. Electronic devices may also represent various forms of mobile devices, such as personal digital processors, cellular phones, smart phones, wearable devices, and other similar computing devices. The components shown herein, their connections and relationships, and their functions are by way of example only, and are not intended to limit implementations of the application described and/or claimed herein.
如图5所示,该电子设备包括:一个或多个处理器501、存储器502,以及用于连接各部件的接口,包括高速接口和低速接口。各个部件利用不同的总线互相连接,并且可以被安装在公共主板上或者根据需要以其它方式安装。处理器可以对在电子设备内执行的指令进行处理,包括存储在存储器中或者存储器上以在外部输入/输出装置(诸如,耦合至接口的显示设备)上显示GUI的图形信息的指令。在其它实施方式中,若需要,可以将多个处理器和/或多条总线与多个存储器和多个存储器一起使用。同样,可以连接多个电子设备,各个设备提供部分必要的操作(例如,作为服务器阵列、一组刀片式服务器、或者多处理器系统)。图5中以一个处理器501为例。As shown in FIG. 5, the electronic device includes: one or
存储器502即为本申请所提供的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质。其中,所述存储器存储有可由至少一个处理器执行的指令,以使所述至少一个处理器执行本申请所提供的预训练语言模型的方法。本申请的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质存储计算机指令,该计算机指令用于使计算机执行本申请所提供的预训练语言模型的方法。The
存储器502作为一种非瞬时计算机可读存储介质,可用于存储非瞬时软件程序、非瞬时计算机可执行程序以及模块,如本申请实施例中的预训练语言模型的方法对应的程序指令/模块。处理器501通过运行存储在存储器502中的非瞬时软件程序、指令以及模块,从而执行服务器的各种功能应用以及数据处理,即实现上述方法实施例中的预训练语言模型的方法。As a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium, the
存储器502可以包括存储程序区和存储数据区,其中,存储程序区可存储操作系统、至少一个功能所需要的应用程序;存储数据区可存储根据该电子设备的使用所创建的数据等。此外,存储器502可以包括高速随机存取存储器,还可以包括非瞬时存储器,例如至少一个磁盘存储器件、闪存器件、或其他非瞬时固态存储器件。在一些实施例中,存储器502可选包括相对于处理器501远程设置的存储器,这些远程存储器可以通过网络连接至该电子设备。上述网络的实例包括但不限于互联网、企业内部网、局域网、移动通信网及其组合。The
该电子设备还可以包括:输入装置503和输出装置504。处理器501、存储器502、输入装置503和输出装置504可以通过总线或者其他方式连接,图5中以通过总线连接为例。The electronic device may further include: an
输入装置503可接收输入的数字或字符信息,以及产生与该电子设备的用户设置以及功能控制有关的键信号输入,例如触摸屏、小键盘、鼠标、轨迹板、触摸板、指示杆、一个或者多个鼠标按钮、轨迹球、操纵杆等输入装置。输出装置504可以包括显示设备、辅助照明装置(例如,LED)和触觉反馈装置(例如,振动电机)等。该显示设备可以包括但不限于,液晶显示器(LCD)、发光二极管(LED)显示器和等离子体显示器。在一些实施方式中,显示设备可以是触摸屏。The
此处描述的系统和技术的各种实施方式可以在数字电子电路系统、集成电路系统、专用ASIC(专用集成电路)、计算机硬件、固件、软件、和/或它们的组合中实现。这些各种实施方式可以包括:实施在一个或者多个计算机程序中,该一个或者多个计算机程序可在包括至少一个可编程处理器的可编程系统上执行和/或解释,该可编程处理器可以是专用或者通用可编程处理器,可以从存储系统、至少一个输入装置、和至少一个输出装置接收数据和指令,并且将数据和指令传输至该存储系统、该至少一个输入装置、和该至少一个输出装置。Various implementations of the systems and techniques described herein can be implemented in digital electronic circuitry, integrated circuit systems, application specific ASICs (application specific integrated circuits), computer hardware, firmware, software, and/or combinations thereof. These various embodiments may include being implemented in one or more computer programs executable and/or interpretable on a programmable system including at least one programmable processor that The processor, which may be a special purpose or general-purpose programmable processor, may receive data and instructions from a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device, and transmit data and instructions to the storage system, the at least one input device, and the at least one output device an output device.
这些计算程序(也称作程序、软件、软件应用、或者代码)包括可编程处理器的机器指令,并且可以利用高级过程和/或面向对象的编程语言、和/或汇编/机器语言来实施这些计算程序。如本文使用的,术语“机器可读介质”和“计算机可读介质”指的是用于将机器指令和/或数据提供给可编程处理器的任何计算机程序产品、设备、和/或装置(例如,磁盘、光盘、存储器、可编程逻辑装置(PLD)),包括,接收作为机器可读信号的机器指令的机器可读介质。术语“机器可读信号”指的是用于将机器指令和/或数据提供给可编程处理器的任何信号。These computational programs (also referred to as programs, software, software applications, or codes) include machine instructions for programmable processors, and may be implemented using high-level procedural and/or object-oriented programming languages, and/or assembly/machine languages calculation program. As used herein, the terms "machine-readable medium" and "computer-readable medium" refer to any computer program product, apparatus, and/or apparatus for providing machine instructions and/or data to a programmable processor ( For example, magnetic disks, optical disks, memories, programmable logic devices (PLDs), including machine-readable media that receive machine instructions as machine-readable signals. The term "machine-readable signal" refers to any signal used to provide machine instructions and/or data to a programmable processor.
为了提供与用户的交互,可以在计算机上实施此处描述的系统和技术,该计算机具有:用于向用户显示信息的显示装置(例如,CRT(阴极射线管)或者LCD(液晶显示器)监视器);以及键盘和指向装置(例如,鼠标或者轨迹球),用户可以通过该键盘和该指向装置来将输入提供给计算机。其它种类的装置还可以用于提供与用户的交互;例如,提供给用户的反馈可以是任何形式的传感反馈(例如,视觉反馈、听觉反馈、或者触觉反馈);并且可以用任何形式(包括声输入、语音输入或者、触觉输入)来接收来自用户的输入。To provide interaction with a user, the systems and techniques described herein may be implemented on a computer having a display device (eg, a CRT (cathode ray tube) or LCD (liquid crystal display) monitor) for displaying information to the user ); and a keyboard and pointing device (eg, a mouse or trackball) through which a user can provide input to the computer. Other kinds of devices can also be used to provide interaction with the user; for example, the feedback provided to the user can be any form of sensory feedback (eg, visual feedback, auditory feedback, or tactile feedback); and can be in any form (including acoustic input, voice input, or tactile input) to receive input from the user.
可以将此处描述的系统和技术实施在包括后台部件的计算系统(例如,作为数据服务器)、或者包括中间件部件的计算系统(例如,应用服务器)、或者包括前端部件的计算系统(例如,具有图形用户界面或者网络浏览器的用户计算机,用户可以通过该图形用户界面或者该网络浏览器来与此处描述的系统和技术的实施方式交互)、或者包括这种后台部件、中间件部件、或者前端部件的任何组合的计算系统中。可以通过任何形式或者介质的数字数据通信(例如,通信网络)来将系统的部件相互连接。通信网络的示例包括:局域网(LAN)、广域网(WAN)和互联网。The systems and techniques described herein may be implemented on a computing system that includes back-end components (eg, as a data server), or a computing system that includes middleware components (eg, an application server), or a computing system that includes front-end components (eg, a user's computer having a graphical user interface or web browser through which a user may interact with implementations of the systems and techniques described herein), or including such backend components, middleware components, Or any combination of front-end components in a computing system. The components of the system may be interconnected by any form or medium of digital data communication (eg, a communication network). Examples of communication networks include: Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), and the Internet.
计算机系统可以包括客户端和服务器。客户端和服务器一般远离彼此并且通常通过通信网络进行交互。通过在相应的计算机上运行并且彼此具有客户端-服务器关系的计算机程序来产生客户端和服务器的关系。A computer system can include clients and servers. Clients and servers are generally remote from each other and usually interact through a communication network. The relationship of client and server arises by computer programs running on the respective computers and having a client-server relationship to each other.
应该理解,可以使用上面所示的各种形式的流程,重新排序、增加或删除步骤。例如,本发申请中记载的各步骤可以并行地执行也可以顺序地执行也可以不同的次序执行,只要能够实现本申请公开的技术方案所期望的结果,本文在此不进行限制。It should be understood that steps may be reordered, added or deleted using the various forms of flow shown above. For example, the steps described in the present application can be performed in parallel, sequentially or in different orders, and as long as the desired results of the technical solutions disclosed in the present application can be achieved, no limitation is imposed herein.
上述具体实施方式,并不构成对本申请保护范围的限制。本领域技术人员应该明白的是,根据设计要求和其他因素,可以进行各种修改、组合、子组合和替代。任何在本申请的精神和原则之内所作的修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本申请保护范围之内。The above-mentioned specific embodiments do not constitute a limitation on the protection scope of the present application. It should be understood by those skilled in the art that various modifications, combinations, sub-combinations and substitutions may occur depending on design requirements and other factors. Any modifications, equivalent replacements and improvements made within the spirit and principles of this application shall be included within the protection scope of this application.
Claims (13)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011504224.8ACN112507101B (en) | 2020-12-18 | 2020-12-18 | Method and device for establishing pre-training language model |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011504224.8ACN112507101B (en) | 2020-12-18 | 2020-12-18 | Method and device for establishing pre-training language model |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112507101Atrue CN112507101A (en) | 2021-03-16 |
| CN112507101B CN112507101B (en) | 2024-04-05 |
Family
ID=74922415
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011504224.8AActiveCN112507101B (en) | 2020-12-18 | 2020-12-18 | Method and device for establishing pre-training language model |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112507101B (en) |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113094482A (en)* | 2021-03-29 | 2021-07-09 | 中国地质大学(北京) | Lightweight semantic intelligent service adaptation training evolution method and system |
| CN113255328A (en)* | 2021-06-28 | 2021-08-13 | 北京京东方技术开发有限公司 | Language model training method and application method |
| CN113807102A (en)* | 2021-08-20 | 2021-12-17 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and computer storage medium for establishing semantic representation model |
| CN113807540A (en)* | 2021-09-17 | 2021-12-17 | 北京搜狗科技发展有限公司 | A data processing method and device |
| CN114241496A (en)* | 2021-11-15 | 2022-03-25 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Pre-training model training method and device for reading task and electronic equipment thereof |
| CN114547329A (en)* | 2022-01-25 | 2022-05-27 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Method for establishing pre-training language model, semantic analysis method and device |
| CN114661904A (en)* | 2022-03-10 | 2022-06-24 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Training method, device, device, storage medium and program for document processing model |
| CN115114439A (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2022-09-27 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and device for multi-task model reasoning and multi-task information processing |
| CN116127045A (en)* | 2023-03-03 | 2023-05-16 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Generative large language model training method, model-based human-computer voice interaction method |
| CN116860999A (en)* | 2023-07-07 | 2023-10-10 | 清华大学 | Ultra-large language model distributed pre-training method, device, equipment and medium |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110309256A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2019-10-08 | 北京国双科技有限公司 | The acquisition methods and device of event data in a kind of text |
| CN111079447A (en)* | 2020-03-23 | 2020-04-28 | 深圳智能思创科技有限公司 | Chinese-oriented pre-training method and system |
| CN111159414A (en)* | 2020-04-02 | 2020-05-15 | 成都数联铭品科技有限公司 | Text classification method and system, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
| CN111709406A (en)* | 2020-08-18 | 2020-09-25 | 成都数联铭品科技有限公司 | Text line identification method and device, readable storage medium and electronic equipment |
| WO2020211275A1 (en)* | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-22 | 五邑大学 | Pre-trained model and fine-tuning technology-based medical text relationship extraction method |
| CN111859951A (en)* | 2020-06-19 | 2020-10-30 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Language model training method, device, electronic device and readable storage medium |
| WO2020220370A1 (en)* | 2019-05-01 | 2020-11-05 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Method and system of utilizing unsupervised learning to improve text to content suggestions |
- 2020
- 2020-12-18CNCN202011504224.8Apatent/CN112507101B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110309256A (en)* | 2018-03-09 | 2019-10-08 | 北京国双科技有限公司 | The acquisition methods and device of event data in a kind of text |
| WO2020211275A1 (en)* | 2019-04-18 | 2020-10-22 | 五邑大学 | Pre-trained model and fine-tuning technology-based medical text relationship extraction method |
| WO2020220370A1 (en)* | 2019-05-01 | 2020-11-05 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Method and system of utilizing unsupervised learning to improve text to content suggestions |
| CN111079447A (en)* | 2020-03-23 | 2020-04-28 | 深圳智能思创科技有限公司 | Chinese-oriented pre-training method and system |
| CN111159414A (en)* | 2020-04-02 | 2020-05-15 | 成都数联铭品科技有限公司 | Text classification method and system, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium |
| CN111859951A (en)* | 2020-06-19 | 2020-10-30 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Language model training method, device, electronic device and readable storage medium |
| CN111709406A (en)* | 2020-08-18 | 2020-09-25 | 成都数联铭品科技有限公司 | Text line identification method and device, readable storage medium and electronic equipment |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| WEI-CHENG CHANG ET AL: "PRE-TRAINING TASKS FOR EMBEDDING-BASED LARGE-SCALE RETRIEVAL", 《ARXIV》, 10 February 2020 (2020-02-10)* |
| 李舟军;范宇;吴贤杰;: "面向自然语言处理的预训练技术研究综述", 计算机科学, 31 March 2020 (2020-03-31)* |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113094482B (en)* | 2021-03-29 | 2023-10-17 | 中国地质大学(北京) | Lightweight semantic intelligent service adaptation training evolution method and system |
| CN113094482A (en)* | 2021-03-29 | 2021-07-09 | 中国地质大学(北京) | Lightweight semantic intelligent service adaptation training evolution method and system |
| CN113255328A (en)* | 2021-06-28 | 2021-08-13 | 北京京东方技术开发有限公司 | Language model training method and application method |
| CN113255328B (en)* | 2021-06-28 | 2024-02-02 | 北京京东方技术开发有限公司 | Language model training methods and application methods |
| CN113807102A (en)* | 2021-08-20 | 2021-12-17 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and computer storage medium for establishing semantic representation model |
| CN113807102B (en)* | 2021-08-20 | 2022-11-01 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method, apparatus, device and computer storage medium for establishing semantic representation model |
| CN113807540A (en)* | 2021-09-17 | 2021-12-17 | 北京搜狗科技发展有限公司 | A data processing method and device |
| CN114241496A (en)* | 2021-11-15 | 2022-03-25 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Pre-training model training method and device for reading task and electronic equipment thereof |
| CN114547329A (en)* | 2022-01-25 | 2022-05-27 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Method for establishing pre-training language model, semantic analysis method and device |
| CN114547329B (en)* | 2022-01-25 | 2025-03-25 | 阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司 | Method for establishing pre-trained language model, semantic parsing method and device |
| CN114661904A (en)* | 2022-03-10 | 2022-06-24 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Training method, device, device, storage medium and program for document processing model |
| CN115114439A (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2022-09-27 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and device for multi-task model reasoning and multi-task information processing |
| CN116127045A (en)* | 2023-03-03 | 2023-05-16 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Generative large language model training method, model-based human-computer voice interaction method |
| CN116860999A (en)* | 2023-07-07 | 2023-10-10 | 清华大学 | Ultra-large language model distributed pre-training method, device, equipment and medium |
| CN116860999B (en)* | 2023-07-07 | 2024-04-19 | 清华大学 | Distributed pre-training method, device, equipment and medium for ultra-large language model |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112507101B (en) | 2024-04-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112507101B (en) | Method and device for establishing pre-training language model | |
| KR102565673B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for generating semantic representation model,and storage medium | |
| EP3920075A1 (en) | Text recognition method and apparatus, electronic device, and storage medium | |
| KR102780053B1 (en) | Abstraction generation method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN113657100B (en) | Entity identification method, entity identification device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112100332B (en) | Word embedding representation learning method and device, text recall method and device | |
| CN111144115B (en) | Pre-training language model acquisition method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111831814B (en) | Pre-training method and device for abstract generation model, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112560479A (en) | Abstract extraction model training method, abstract extraction device and electronic equipment | |
| CN112560912A (en) | Method and device for training classification model, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111767359B (en) | Interest point classification method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111523326A (en) | Entity chain finger method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| JP2021111420A (en) | Semantics description processing method, device and device of text entity | |
| CN110619053A (en) | Training method of entity relation extraction model and method for extracting entity relation | |
| CN112507706B (en) | Training method and device for knowledge pre-training model and electronic equipment | |
| WO2021121198A1 (en) | Semantic similarity-based entity relation extraction method and apparatus, device and medium | |
| CN112395873B (en) | Method and device for generating white character labeling model and electronic equipment | |
| CN112148856B (en) | Method and device for establishing punctuation prediction model | |
| CN112000792A (en) | Extraction method, device, equipment and storage medium of natural disaster events | |
| CN112541362B (en) | Generalization processing method, device, equipment and computer storage medium | |
| CN114495130A (en) | Document reading comprehension model training method and device based on cross-modal information | |
| CN111539209B (en) | Method and apparatus for entity classification | |
| CN112541332A (en) | Form information extraction method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111858880B (en) | Methods, devices, electronic devices and readable storage media for obtaining query results | |
| CN112506949A (en) | Method and device for generating query statement of structured query language and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |