CN112420997B - A method for constructing a metal oxide coating with a controllable thickness in a solution phase - Google Patents
A method for constructing a metal oxide coating with a controllable thickness in a solution phaseDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112420997B CN112420997BCN201910770861.0ACN201910770861ACN112420997BCN 112420997 BCN112420997 BCN 112420997BCN 201910770861 ACN201910770861 ACN 201910770861ACN 112420997 BCN112420997 BCN 112420997B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- lithium
- coated
- oxide
- metal
- core
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription39
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription38
- 229910044991metal oxideInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription37
- 150000004706metal oxidesChemical class0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription37
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription32
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription53
- 239000011258core-shell materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription36
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription28
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription28
- 239000011247coating layerSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 150000003839saltsChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription18
- HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-NLithium ionChemical compound[Li+]HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 229910001416lithium ionInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription16
- 239000003125aqueous solventSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 239000011259mixed solutionSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 230000001376precipitating effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 239000003795chemical substances by applicationSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 239000002244precipitateSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription4
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000claimsdescription88
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilicium dioxideChemical compoundO=[Si]=OVYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription49
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron oxideInorganic materials[Fe]=OUQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription44
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-NLithiumChemical compound[Li]WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription29
- 229910052744lithiumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription29
- BDKWOJYFHXPPPT-UHFFFAOYSA-Nlithium dioxido(dioxo)manganese nickel(2+)Chemical compound[Mn](=O)(=O)([O-])[O-].[Ni+2].[Li+]BDKWOJYFHXPPPT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription29
- XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntin dioxideChemical compoundO=[Sn]=OXOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription28
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-NZrO2Inorganic materialsO=[Zr]=OMCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription25
- WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-MLithium hydroxideChemical compound[Li+].[OH-]WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription24
- VKYKSIONXSXAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-NhexamethylenetetramineChemical compoundC1N(C2)CN3CN1CN2C3VKYKSIONXSXAKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription20
- RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-Noxygen(2-);zirconium(4+)Chemical compound[O-2].[O-2].[Zr+4]RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription17
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitaniumChemical compound[Ti]RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription15
- 239000007774positive electrode materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthanolChemical groupCCOLFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription14
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 239000000377silicon dioxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- PFYQFCKUASLJLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Co].[Ni].[Li]Chemical compound[Co].[Ni].[Li]PFYQFCKUASLJLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription11
- 239000012298atmosphereSubstances0.000claimsdescription11
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription11
- 238000001354calcinationMethods0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000004312hexamethylene tetramineSubstances0.000claimsdescription10
- 235000010299hexamethylene tetramineNutrition0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000010410layerSubstances0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000003570airSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-NArgonChemical compound[Ar]XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-Natomic oxygenChemical compound[O]QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 229910003002lithium saltInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription8
- 159000000002lithium saltsChemical class0.000claimsdescription8
- -1oxidesChemical class0.000claimsdescription8
- 229910052760oxygenInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription8
- 239000001301oxygenSubstances0.000claimsdescription8
- KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-MPotassium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[K+]KWYUFKZDYYNOTN-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription6
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-MSodium hydroxideChemical compound[OH-].[Na+]HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000claimsdescription6
- 235000012239silicon dioxideNutrition0.000claimsdescription6
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NAtomic nitrogenChemical compoundN#NIJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910019142PO4Inorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-NPalladiumChemical compound[Pd]KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-NTinChemical compound[Sn]ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitan oxideChemical compoundO=[Ti]=OGWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-NZinc monoxideChemical compound[Zn]=OXLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052786argonInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910017052cobaltInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000010941cobaltSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncobalt atomChemical compound[Co]GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- GNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndivanadium pentaoxideChemical compoundO=[V](=O)O[V](=O)=OGNTDGMZSJNCJKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910021389grapheneInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- AMWRITDGCCNYAT-UHFFFAOYSA-Lhydroxy(oxo)manganese;manganeseChemical compound[Mn].O[Mn]=O.O[Mn]=OAMWRITDGCCNYAT-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription4
- VCJMYUPGQJHHFU-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron(3+);trinitrateChemical group[Fe+3].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OVCJMYUPGQJHHFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 150000002739metalsChemical class0.000claimsdescription4
- 150000004767nitridesChemical class0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052755nonmetalInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000011146organic particleSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052698phosphorusInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000011574phosphorusSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-NplatinumChemical compound[Pt]BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910052718tinInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription4
- OERNJTNJEZOPIA-UHFFFAOYSA-Nzirconium nitrateChemical compound[Zr+4].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OOERNJTNJEZOPIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription4
- UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-NSulphideChemical compound[S-2]UCKMPCXJQFINFW-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- ZYXUQEDFWHDILZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Ni].[Mn].[Li]Chemical compound[Ni].[Mn].[Li]ZYXUQEDFWHDILZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- QHGJSLXSVXVKHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndilithium;dioxido(dioxo)manganeseChemical compound[Li+].[Li+].[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=OQHGJSLXSVXVKHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000003960organic solventSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000010452phosphateSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-KphosphateChemical compound[O-]P([O-])([O-])=ONBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription3
- INZDTEICWPZYJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N1-(chloromethyl)-4-[4-(chloromethyl)phenyl]benzeneChemical compoundC1=CC(CCl)=CC=C1C1=CC=C(CCl)C=C1INZDTEICWPZYJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- KXGFMDJXCMQABM-UHFFFAOYSA-N2-methoxy-6-methylphenolChemical compound[CH]OC1=CC=CC([CH])=C1OKXGFMDJXCMQABM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052580B4CInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052582BNInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-NBoronChemical compound[B]ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- PZNSFCLAULLKQX-UHFFFAOYSA-NBoron nitrideChemical compoundN#BPZNSFCLAULLKQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- XMWRBQBLMFGWIX-UHFFFAOYSA-NC60 fullereneChemical classC12=C3C(C4=C56)=C7C8=C5C5=C9C%10=C6C6=C4C1=C1C4=C6C6=C%10C%10=C9C9=C%11C5=C8C5=C8C7=C3C3=C7C2=C1C1=C2C4=C6C4=C%10C6=C9C9=C%11C5=C5C8=C3C3=C7C1=C1C2=C4C6=C2C9=C5C3=C12XMWRBQBLMFGWIX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000005997Calcium carbideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920001661ChitosanPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 229930091371FructoseNatural products0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000005715FructoseSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- RFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-NFructoseChemical compoundOC[C@H]1O[C@](O)(CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1ORFSUNEUAIZKAJO-ARQDHWQXSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910002601GaNInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-NGallium nitrideChemical compound[Ga]#NJMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-NGlucoseNatural productsOC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1OWQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-NHydrogenChemical compound[H][H]UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000877Melamine resinPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004640Melamine resinSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- MKGYHFFYERNDHK-UHFFFAOYSA-KP(=O)([O-])([O-])[O-].[Ti+4].[Li+]Chemical compoundP(=O)([O-])([O-])[O-].[Ti+4].[Li+]MKGYHFFYERNDHK-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphorusChemical compound[P]OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004793PolystyreneSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-NRutheniumChemical compound[Ru]KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- BUGBHKTXTAQXES-UHFFFAOYSA-NSeleniumChemical compound[Se]BUGBHKTXTAQXES-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052581Si3N4Inorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NSiliconChemical compound[Si]XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilverChemical compound[Ag]BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-NSulfurChemical compound[S]NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-NTitanium nitrideChemical compound[Ti]#NNRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920001807Urea-formaldehydePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000005083Zinc sulfideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- NRJJZXGPUXHHTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Li+].[O--].[O--].[O--].[O--].[Zr+4].[La+3]Chemical compound[Li+].[O--].[O--].[O--].[O--].[Zr+4].[La+3]NRJJZXGPUXHHTC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- YWJVFBOUPMWANA-UHFFFAOYSA-H[Li+].[V+5].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OChemical compound[Li+].[V+5].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OYWJVFBOUPMWANA-UHFFFAOYSA-H0.000claimsdescription2
- FBDMTTNVIIVBKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N[O-2].[Mn+2].[Co+2].[Ni+2].[Li+]Chemical compound[O-2].[Mn+2].[Co+2].[Ni+2].[Li+]FBDMTTNVIIVBKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-SLPGGIOYSA-Naldehydo-D-glucoseChemical compoundOC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=OGZCGUPFRVQAUEE-SLPGGIOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- CVJYOKLQNGVTIS-UHFFFAOYSA-Kaluminum;lithium;titanium(4+);phosphateChemical compound[Li+].[Al+3].[Ti+4].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OCVJYOKLQNGVTIS-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052787antimonyInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-Nantimony atomChemical compound[Sb]WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- CFJRGWXELQQLSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NazanylidyneniobiumChemical compound[Nb]#NCFJRGWXELQQLSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- SKKMWRVAJNPLFY-UHFFFAOYSA-NazanylidynevanadiumChemical compound[V]#NSKKMWRVAJNPLFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052796boronInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- INAHAJYZKVIDIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-Nboron carbideChemical compoundB12B3B4C32B41INAHAJYZKVIDIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- BRPQOXSCLDDYGP-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncalcium oxideChemical compound[O-2].[Ca+2]BRPQOXSCLDDYGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000000292calcium oxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- ODINCKMPIJJUCX-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncalcium oxideInorganic materials[Ca]=OODINCKMPIJJUCX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- NNLOHLDVJGPUFR-UHFFFAOYSA-Lcalcium;3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxy-2-oxohexanoateChemical compound[Ca+2].OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(=O)C([O-])=O.OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(=O)C([O-])=ONNLOHLDVJGPUFR-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052799carbonInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910021393carbon nanotubeInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000002041carbon nanotubeSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- CETPSERCERDGAM-UHFFFAOYSA-Nceric oxideChemical compoundO=[Ce]=OCETPSERCERDGAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910000422cerium(IV) oxideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- GVEHJMMRQRRJPM-UHFFFAOYSA-Nchromium(2+);methanidylidynechromiumChemical compound[Cr+2].[Cr]#[C-].[Cr]#[C-]GVEHJMMRQRRJPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- INPLXZPZQSLHBR-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncobalt(2+);sulfideChemical compound[S-2].[Co+2]INPLXZPZQSLHBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- AJNVQOSZGJRYEI-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndigallium;oxygen(2-)Chemical compound[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Ga+3].[Ga+3]AJNVQOSZGJRYEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910003472fullereneInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910001195gallium oxideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000007789gasSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052732germaniumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-Ngermanium atomChemical compound[Ge]GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000008103glucoseSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-NgoldChemical compound[Au]PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052737goldInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000010931goldSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052739hydrogenInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000001257hydrogenSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910003437indium oxideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- PJXISJQVUVHSOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-Nindium(iii) oxideChemical compound[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[In+3].[In+3]PJXISJQVUVHSOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910000398iron phosphateInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- VAKIVKMUBMZANL-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron phosphideChemical compoundP.[Fe].[Fe].[Fe]VAKIVKMUBMZANL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- WBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-Kiron(3+) phosphateChemical group[Fe+3].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OWBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910000664lithium aluminum titanium phosphates (LATP)Inorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- GELKBWJHTRAYNV-UHFFFAOYSA-Klithium iron phosphateChemical compound[Li+].[Fe+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OGELKBWJHTRAYNV-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- FUJCRWPEOMXPAD-UHFFFAOYSA-Nlithium oxideChemical compound[Li+].[Li+].[O-2]FUJCRWPEOMXPAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910001947lithium oxideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- SBWRUMICILYTAT-UHFFFAOYSA-Klithium;cobalt(2+);phosphateChemical compound[Li+].[Co+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OSBWRUMICILYTAT-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- DVATZODUVBMYHN-UHFFFAOYSA-Klithium;iron(2+);manganese(2+);phosphateChemical compound[Li+].[Mn+2].[Fe+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=ODVATZODUVBMYHN-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- ILXAVRFGLBYNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-Klithium;manganese(2+);phosphateChemical compound[Li+].[Mn+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OILXAVRFGLBYNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000claimsdescription2
- NFFIWVVINABMKP-UHFFFAOYSA-NmethylidynetantalumChemical compound[Ta]#CNFFIWVVINABMKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- CWQXQMHSOZUFJS-UHFFFAOYSA-Nmolybdenum disulfideChemical compoundS=[Mo]=SCWQXQMHSOZUFJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910000476molybdenum oxideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- FBMUYWXYWIZLNE-UHFFFAOYSA-Nnickel phosphideChemical compound[Ni]=P#[Ni]FBMUYWXYWIZLNE-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052757nitrogenInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-Noxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumaneChemical compoundO=[Al]O[Al]=OTWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- PQQKPALAQIIWST-UHFFFAOYSA-NoxomolybdenumChemical compound[Mo]=OPQQKPALAQIIWST-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052763palladiumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000005011phenolic resinSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920001568phenolic resinPolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- AMWVZPDSWLOFKA-UHFFFAOYSA-NphosphanylidynemolybdenumChemical compound[Mo]#PAMWVZPDSWLOFKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052697platinumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920001690polydopaminePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920002223polystyrenePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000001267polyvinylpyrrolidoneSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229920000036polyvinylpyrrolidonePolymers0.000claimsdescription2
- 235000013855polyvinylpyrrolidoneNutrition0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052703rhodiumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000010948rhodiumSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-Nrhodium atomChemical compound[Rh]MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052707rutheniumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052711seleniumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011669seleniumSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052710siliconInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000010703siliconSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910010271silicon carbideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsilicon carbideChemical compound[Si+]#[C-]HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-Nsilicon nitrideChemical compoundN12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052709silverInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004332silverSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- YPMOSINXXHVZIL-UHFFFAOYSA-NsulfanylideneantimonyChemical compound[Sb]=SYPMOSINXXHVZIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- WWNBZGLDODTKEM-UHFFFAOYSA-NsulfanylidenenickelChemical compound[Ni]=SWWNBZGLDODTKEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052717sulfurInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011593sulfurSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910003468tantalcarbideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052714telluriumInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- PORWMNRCUJJQNO-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntellurium atomChemical compound[Te]PORWMNRCUJJQNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- CLZWAWBPWVRRGI-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntert-butyl 2-[2-[2-[2-[bis[2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-5-bromophenoxy]ethoxy]-4-methyl-n-[2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-2-oxoethyl]anilino]acetateChemical compoundCC1=CC=C(N(CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)C(OCCOC=2C(=CC=C(Br)C=2)N(CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)CC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)=C1CLZWAWBPWVRRGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- AFNRRBXCCXDRPS-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntin(ii) sulfideChemical compound[Sn]=SAFNRRBXCCXDRPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000004408titanium dioxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- CFJRPNFOLVDFMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntitanium disulfideChemical compoundS=[Ti]=SCFJRPNFOLVDFMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- JUWGUJSXVOBPHP-UHFFFAOYSA-Btitanium(4+);tetraphosphateChemical compound[Ti+4].[Ti+4].[Ti+4].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OJUWGUJSXVOBPHP-UHFFFAOYSA-B0.000claimsdescription2
- ADDWXBZCQABCGO-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntitanium(iii) phosphideChemical compound[Ti]#PADDWXBZCQABCGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910003470tongbaiteInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- BHZCMUVGYXEBMY-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntrilithium;azanideChemical compound[Li+].[Li+].[Li+].[NH2-]BHZCMUVGYXEBMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- MTPVUVINMAGMJL-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntrimethyl(1,1,2,2,2-pentafluoroethyl)silaneChemical compoundC[Si](C)(C)C(F)(F)C(F)(F)FMTPVUVINMAGMJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052721tungstenInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000010937tungstenSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- UONOETXJSWQNOL-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntungsten carbideChemical compound[W+]#[C-]UONOETXJSWQNOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- ITRNXVSDJBHYNJ-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntungsten disulfideChemical compoundS=[W]=SITRNXVSDJBHYNJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000011787zinc oxideSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 229910052984zinc sulfideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription2
- DRDVZXDWVBGGMH-UHFFFAOYSA-Nzinc;sulfideChemical compound[S-2].[Zn+2]DRDVZXDWVBGGMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription2
- NDLPOXTZKUMGOV-UHFFFAOYSA-Noxo(oxoferriooxy)iron hydrateChemical compoundO.O=[Fe]O[Fe]=ONDLPOXTZKUMGOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims7
- 235000021317phosphateNutrition0.000claims2
- ZMVMBTZRIMAUPN-UHFFFAOYSA-H[Na+].[V+5].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OChemical compound[Na+].[V+5].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OZMVMBTZRIMAUPN-UHFFFAOYSA-H0.000claims1
- 239000005456alcohol based solventSubstances0.000claims1
- 239000005453ketone based solventSubstances0.000claims1
- RSNHXDVSISOZOB-UHFFFAOYSA-Nlithium nickelChemical compound[Li].[Ni]RSNHXDVSISOZOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 239000000395magnesium oxideSubstances0.000claims1
- CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-Nmagnesium oxideInorganic materials[Mg]=OCPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-Nmagnesium;oxygen(2-)Chemical compound[O-2].[Mg+2]AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims1
- 150000001247metal acetylidesChemical class0.000claims1
- 150000002843nonmetalsChemical class0.000claims1
- 150000003013phosphoric acid derivativesChemical class0.000claims1
- 150000004763sulfidesChemical class0.000claims1
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000abstractdescription13
- 239000012467final productSubstances0.000abstract1
- 239000012716precipitatorSubstances0.000abstract1
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-Nferric oxideChemical compoundO=[Fe]O[Fe]=OJEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description45
- 239000002904solventSubstances0.000description18
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-NIronChemical compound[Fe]XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description12
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description12
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000description11
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description10
- 238000001556precipitationMethods0.000description10
- 238000010992refluxMethods0.000description9
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000description8
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000description8
- 239000010406cathode materialSubstances0.000description7
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000description7
- SZQUEWJRBJDHSM-UHFFFAOYSA-Niron(3+);trinitrate;nonahydrateChemical compoundO.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.O.[Fe+3].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OSZQUEWJRBJDHSM-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description7
- 238000005245sinteringMethods0.000description7
- HFCVPDYCRZVZDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Li+].[Co+2].[Ni+2].[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=OChemical compound[Li+].[Co+2].[Ni+2].[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=OHFCVPDYCRZVZDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 230000001066destructive effectEffects0.000description6
- 229910052742ironInorganic materials0.000description6
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description5
- LRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-NN-ButanolChemical compoundCCCCOLRHPLDYGYMQRHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- QXZUUHYBWMWJHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Co].[Ni]Chemical compound[Co].[Ni]QXZUUHYBWMWJHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 239000007864aqueous solutionSubstances0.000description4
- 238000005119centrifugationMethods0.000description4
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description4
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000description4
- 230000007062hydrolysisEffects0.000description4
- 238000006460hydrolysis reactionMethods0.000description4
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description4
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000description4
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene glycolChemical compoundOCCOLYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-NMethanolChemical compoundOCOKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-NPropylene glycolChemical compoundCC(O)CODNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-NZirconiumChemical compound[Zr]QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000description3
- 239000007791liquid phaseSubstances0.000description3
- 229910021645metal ionInorganic materials0.000description3
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-Npropan-1-olChemical compoundCCCOBDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 239000000376reactantSubstances0.000description3
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description3
- 229910052726zirconiumInorganic materials0.000description3
- WXKDNDQLOWPOBY-UHFFFAOYSA-Nzirconium(4+);tetranitrate;pentahydrateChemical compoundO.O.O.O.O.[Zr+4].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OWXKDNDQLOWPOBY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- DLFVBJFMPXGRIB-UHFFFAOYSA-NAcetamideChemical compoundCC(N)=ODLFVBJFMPXGRIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-NAcetoneChemical compoundCC(C)=OCSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- ATRRKUHOCOJYRX-UHFFFAOYSA-NAmmonium bicarbonateChemical compound[NH4+].OC([O-])=OATRRKUHOCOJYRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- ZHNUHDYFZUAESO-UHFFFAOYSA-NFormamideChemical compoundNC=OZHNUHDYFZUAESO-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-NIsopropanolChemical compoundCC(C)OKFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphoric acidChemical compoundOP(O)(O)=ONBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- PPPKZBCCLMQHSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Co++].[Ni++].[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=O.[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=OChemical compound[Co++].[Ni++].[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=O.[O-][Mn]([O-])(=O)=OPPPKZBCCLMQHSN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 230000002378acidificating effectEffects0.000description2
- 239000001099ammonium carbonateSubstances0.000description2
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description2
- 239000007853buffer solutionSubstances0.000description2
- 238000005253claddingMethods0.000description2
- 238000000151depositionMethods0.000description2
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description2
- MNNHAPBLZZVQHP-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndiammonium hydrogen phosphateChemical compound[NH4+].[NH4+].OP([O-])([O-])=OMNNHAPBLZZVQHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 239000007772electrode materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000006138lithiation reactionMethods0.000description2
- XGZVUEUWXADBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-Llithium carbonateChemical compound[Li+].[Li+].[O-]C([O-])=OXGZVUEUWXADBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description2
- 229910052808lithium carbonateInorganic materials0.000description2
- FRMOHNDAXZZWQI-UHFFFAOYSA-Nlithium manganese(2+) nickel(2+) oxygen(2-)Chemical compound[O-2].[Mn+2].[Ni+2].[Li+]FRMOHNDAXZZWQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 239000011824nuclear materialSubstances0.000description2
- 239000000047productSubstances0.000description2
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description2
- 238000007086side reactionMethods0.000description2
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description2
- USFZMSVCRYTOJT-UHFFFAOYSA-NAmmonium acetateChemical compoundN.CC(O)=OUSFZMSVCRYTOJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000005695Ammonium acetateSubstances0.000description1
- 229910000013Ammonium bicarbonateInorganic materials0.000description1
- VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-NAmmonium hydroxideChemical compound[NH4+].[OH-]VHUUQVKOLVNVRT-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000004254Ammonium phosphateSubstances0.000description1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-LCarbonateChemical compound[O-]C([O-])=OBVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- 229910002993LiMnO2Inorganic materials0.000description1
- 229910013870LiPF 6Inorganic materials0.000description1
- 229910000572Lithium Nickel Cobalt Manganese Oxide (NCM)Inorganic materials0.000description1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-NMagnesiumChemical compound[Mg]FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910002651NO3Inorganic materials0.000description1
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-NNitrateChemical compound[O-][N+]([O-])=ONHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000002033PVDF binderSubstances0.000description1
- GSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-NTriethanolamineChemical compoundOCCN(CCO)CCOGSEJCLTVZPLZKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- QTHKJEYUQSLYTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Co]=O.[Ni].[Li]Chemical compound[Co]=O.[Ni].[Li]QTHKJEYUQSLYTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- CFVBFMMHFBHNPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Na].[V]Chemical compound[Na].[V]CFVBFMMHFBHNPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 150000001242acetic acid derivativesChemical class0.000description1
- 125000005595acetylacetonate groupChemical group0.000description1
- 239000011149active materialSubstances0.000description1
- 150000004703alkoxidesChemical class0.000description1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-Naluminium oxideInorganic materials[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3]PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910000147aluminium phosphateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 235000019257ammonium acetateNutrition0.000description1
- 229940043376ammonium acetateDrugs0.000description1
- 235000012538ammonium bicarbonateNutrition0.000description1
- 235000012501ammonium carbonateNutrition0.000description1
- LFVGISIMTYGQHF-UHFFFAOYSA-Nammonium dihydrogen phosphateChemical compound[NH4+].OP(O)([O-])=OLFVGISIMTYGQHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910000387ammonium dihydrogen phosphateInorganic materials0.000description1
- VZTDIZULWFCMLS-UHFFFAOYSA-Nammonium formateChemical compound[NH4+].[O-]C=OVZTDIZULWFCMLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 235000011114ammonium hydroxideNutrition0.000description1
- 229910000148ammonium phosphateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 235000019289ammonium phosphatesNutrition0.000description1
- 238000000231atomic layer depositionMethods0.000description1
- XJMWHXZUIGHOBA-UHFFFAOYSA-Nazane;propanoic acidChemical compoundN.CCC(O)=OXJMWHXZUIGHOBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000011230binding agentSubstances0.000description1
- 230000033228biological regulationEffects0.000description1
- 239000004202carbamideSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description1
- 150000003841chloride saltsChemical class0.000description1
- 239000002482conductive additiveSubstances0.000description1
- 230000007797corrosionEffects0.000description1
- 238000005260corrosionMethods0.000description1
- 229910052593corundumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 229910000388diammonium phosphateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 235000019838diammonium phosphateNutrition0.000description1
- 238000005538encapsulationMethods0.000description1
- 238000004146energy storageMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000011065in-situ storageMethods0.000description1
- 150000002576ketonesChemical class0.000description1
- 150000003893lactate saltsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000011031large-scale manufacturing processMethods0.000description1
- VGYDTVNNDKLMHX-UHFFFAOYSA-Nlithium;manganese;nickel;oxocobaltChemical compound[Li].[Mn].[Ni].[Co]=OVGYDTVNNDKLMHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000011777magnesiumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052749magnesiumInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000014759maintenance of locationEffects0.000description1
- 230000003446memory effectEffects0.000description1
- 229910001960metal nitrateInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000002923metal particleSubstances0.000description1
- 235000019837monoammonium phosphateNutrition0.000description1
- 239000007773negative electrode materialSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052759nickelInorganic materials0.000description1
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-NnickelSubstances[Ni]PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 150000002823nitratesChemical class0.000description1
- 230000001590oxidative effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000012071phaseSubstances0.000description1
- 229920002981polyvinylidene fluoridePolymers0.000description1
- QLNJFJADRCOGBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NpropionamideChemical compoundCCC(N)=OQLNJFJADRCOGBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229940080818propionamideDrugs0.000description1
- 230000035484reaction timeEffects0.000description1
- 229910052814silicon oxideInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000007858starting materialSubstances0.000description1
- 150000003467sulfuric acid derivativesChemical class0.000description1
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-Nurea groupChemical groupNC(=O)NXSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910001845yogo sapphireInorganic materials0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/362—Composites
- H01M4/366—Composites as layered products
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/052—Li-accumulators
- H01M10/0525—Rocking-chair batteries, i.e. batteries with lithium insertion or intercalation in both electrodes; Lithium-ion batteries
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/48—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides
- H01M4/483—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides for non-aqueous cells
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/48—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides
- H01M4/485—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides of mixed oxides or hydroxides for inserting or intercalating light metals, e.g. LiTi2O4 or LiTi2OxFy
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/48—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides
- H01M4/50—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides of manganese
- H01M4/505—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides of manganese of mixed oxides or hydroxides containing manganese for inserting or intercalating light metals, e.g. LiMn2O4 or LiMn2OxFy
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/48—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides
- H01M4/52—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides of nickel, cobalt or iron
- H01M4/525—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic oxides or hydroxides of nickel, cobalt or iron of mixed oxides or hydroxides containing iron, cobalt or nickel for inserting or intercalating light metals, e.g. LiNiO2, LiCoO2 or LiCoOxFy
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M2004/026—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material characterised by the polarity
- H01M2004/028—Positive electrodes
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Inorganic Compounds Of Heavy Metals (AREA)
- Battery Electrode And Active Subsutance (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于材料领域,具体涉及一种溶液相中构筑厚度可控的金属氧化物包覆层的方法。The invention belongs to the field of materials, and in particular relates to a method for constructing a metal oxide coating layer with a controllable thickness in a solution phase.
背景技术Background technique
锂离子电池相比于传统电池体系,具有能量密度高、工作电压高、无记忆效应、环境友好等优势,在电子产品、电动汽车等领域中得到了广泛应用。为了满足市场日益增长的需求,应开发出具有更高能量密度、功率密度及可靠的安全性能的锂离子电池。正极材料作为锂离子电池的关键组成部分,是决定电池性能好坏的重要因素。因此,发展更高能量密度的锂离子电池,势必对正极材料提出更高的要求。但是,由于正极材料所处的电势较高,且脱锂态正极材料具有较强的氧化性,易与电解液发生副反应,导致材料结构劣化,造成电化学性能恶化。对正极材料表面进行包覆改性是改善正极材料电化学性能的重要手段之一。Compared with traditional battery systems, lithium-ion batteries have the advantages of high energy density, high operating voltage, no memory effect, and environmental friendliness, and have been widely used in electronic products, electric vehicles and other fields. In order to meet the growing demands of the market, lithium-ion batteries with higher energy density, power density and reliable safety performance should be developed. As a key component of lithium-ion batteries, the cathode material is an important factor determining the performance of the battery. Therefore, the development of lithium-ion batteries with higher energy density is bound to put forward higher requirements for cathode materials. However, due to the high potential of the positive electrode material and the strong oxidizing property of the delithiated positive electrode material, it is prone to side reactions with the electrolyte, resulting in the deterioration of the material structure and the deterioration of the electrochemical performance. Coating and modifying the surface of the cathode material is one of the important means to improve the electrochemical performance of the cathode material.
金属氧化物由于具有稳定的化学性质,常被用作正极材料表面包覆改性的物质。大量研究工作表明,在正极材料表面引入金属氧化物包覆层,可以避免正极材料与电解液直接接触,降低副反应发生的几率,有效提升材料结构稳定性,从而使材料电化学性能得到显著提升。构筑金属氧化物包覆层最常用的方法为液相沉积法,通过在水溶液中利用碱性沉淀剂沉淀金属盐,使产物沉积在材料表面从而获得包覆物质。但是此方法存在很多问题,例如由于金属盐在水溶液中易快速水解,沉淀过程难以控制,因而得到的包覆层效果差,均匀性、连续性及厚度均无法得到有效调节,不能最大限度地优化电极材料性能。原子层沉积法是获得良好包覆效果的主要手段,但是此法所涉及的设备价格昂贵、成本高、对样品处理能力有限,不适用于大规模生产应用。因此,基于实际应用对合成方案提出的要求,结合液相过程适用范围广、工艺简单、成本低的特点,开发可行的液相体系以实现包覆层的精准构筑具有重要的研究意义。发明专利CN201310545860.9报道了一种可控构筑均匀三氧化二铝包覆层的方法。通过在水溶液中添加酸性缓冲溶液调节反应体系的pH值,能够对金属离子沉淀过程进行动力学控制,从而实现金属氧化物包覆层的精准构筑,包覆层均匀连续,且厚度精确可调。但是,此法所涉及的水溶液反应体系会不适用于吸湿性强的电极材料特别是目前备受关注的高镍三元正极材料,由于对水分尤其敏感,不能在水溶液中进行处理。此外,此法需要使用酸性缓冲溶液来抑制金属离子的快速沉淀,会对材料结构造成腐蚀。因此,开发基于非水反应体系的构筑方案,以实现材料表面的无损处理具有重要的研究价值。此外,还需要在非水体系中获得包覆层的精准构筑,以最大限度优化材料的性能。因此,如何通过合理设计合成方案,在确保核材料无损处理的前提下,实现物质沉淀过程的有效控制,从而获得包覆层的精准构筑,是目前面临的一大挑战。Due to their stable chemical properties, metal oxides are often used as surface coating modification substances for cathode materials. A large number of research works have shown that the introduction of a metal oxide coating layer on the surface of the positive electrode material can avoid the direct contact between the positive electrode material and the electrolyte, reduce the probability of side reactions, and effectively improve the structural stability of the material, thereby significantly improving the electrochemical performance of the material. . The most common method for constructing the metal oxide coating layer is the liquid phase deposition method. The coating substance is obtained by precipitating the metal salt with an alkaline precipitant in an aqueous solution, and depositing the product on the surface of the material. However, there are many problems in this method. For example, due to the rapid hydrolysis of metal salts in the aqueous solution, the precipitation process is difficult to control, so the obtained coating layer has poor effect, and the uniformity, continuity and thickness cannot be effectively adjusted, and cannot be optimized to the maximum extent. Electrode material properties. Atomic layer deposition is the main method to obtain good coating effect, but the equipment involved in this method is expensive, high in cost, and limited in sample handling capacity, so it is not suitable for large-scale production applications. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop a feasible liquid-phase system to realize the precise construction of the coating layer based on the requirements of the practical application for the synthesis scheme, combined with the characteristics of the liquid-phase process with wide application range, simple process and low cost. Invention patent CN201310545860.9 reports a method for controllably constructing a uniform Al2O3 coating layer. By adding an acidic buffer solution to the aqueous solution to adjust the pH value of the reaction system, the kinetic control of the metal ion precipitation process can be performed, thereby realizing the precise construction of the metal oxide coating layer, the coating layer is uniform and continuous, and the thickness is precisely adjustable. However, the aqueous reaction system involved in this method is not suitable for electrode materials with strong hygroscopicity, especially the high-nickel ternary cathode materials that have attracted much attention at present. Since they are particularly sensitive to moisture, they cannot be processed in aqueous solutions. In addition, this method requires the use of an acidic buffer solution to inhibit the rapid precipitation of metal ions, which can cause corrosion to the material structure. Therefore, it is of great research value to develop a construction scheme based on non-aqueous reaction systems to achieve non-destructive treatment of material surfaces. In addition, precise construction of the cladding layer in non-aqueous systems is required to maximize the performance of the material. Therefore, how to effectively control the material precipitation process and obtain the precise construction of the cladding layer on the premise of ensuring the non-destructive treatment of nuclear materials by rationally designing the synthesis scheme is a major challenge currently facing.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的第一个目的是提供一种基于非水溶剂中在材料表面实现精准、无损构筑金属氧化物包覆层的方法。The first object of the present invention is to provide a method for realizing precise and non-destructive construction of a metal oxide coating layer on the surface of a material based on a non-aqueous solvent.
本发明提供一种金属氧化物的包覆方法,该方法包括如下步骤:在非水溶剂中加入包覆底物材料、金属盐和沉淀剂,得到混合液;所述沉淀剂与金属盐反应生成的沉淀均匀沉积在所述包覆底物材料的表面,形成金属氧化物包覆层。The present invention provides a method for coating metal oxides. The method comprises the following steps: adding a coating substrate material, a metal salt and a precipitating agent to a non-aqueous solvent to obtain a mixed solution; the precipitating agent reacts with the metal salt to generate The precipitates are uniformly deposited on the surface of the coating substrate material to form a metal oxide coating layer.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述非水溶剂选自无水有机溶剂,例如选自无水醇溶剂和/或无水酮溶剂;优选地,所述非水溶剂选自无水的甲醇、乙醇、丙醇、丁醇、乙二醇、丙二醇、正丙醇、异丙醇、正丁醇和丙酮中的至少一种;更优选为无水乙醇。进一步地,所述非水溶剂的纯度为色谱纯级别,其含水量≤0.1wt%。According to the technical solution of the present invention, the non-aqueous solvent is selected from anhydrous organic solvents, for example, selected from anhydrous alcohol solvent and/or anhydrous ketone solvent; preferably, the non-aqueous solvent is selected from anhydrous methanol, ethanol , at least one of propanol, butanol, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, n-propanol, isopropanol, n-butanol and acetone; more preferably absolute ethanol. Further, the purity of the non-aqueous solvent is chromatographic grade, and its water content is less than or equal to 0.1 wt%.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述包覆底物材料选自金属、氧化物、碳化物、硫化物、磷化物、氮化物、锂盐、磷酸盐、非金属和有机物颗粒中的至少一种;According to the technical solution of the present invention, the coating substrate material is selected from at least one of metal, oxide, carbide, sulfide, phosphide, nitride, lithium salt, phosphate, non-metal and organic particles;
其中,所述金属选自以下金属及其形成的合金中的至少一种:金、银、钯、铂、钌、铑、锡、锗和锑;Wherein, the metal is selected from at least one of the following metals and alloys thereof: gold, silver, palladium, platinum, ruthenium, rhodium, tin, germanium and antimony;
其中,所述氧化物选自二氧化硅、二氧化锡、三氧化二铝、氧化钼、五氧化二钒、二氧化钛、四氧化三锰、四氧化三钴、二氧化锆、氧化锌、二氧化铈、氧化镁、氧化钙、氧化铟、氧化镓、氧化锂、四氧化三铁和锂镧锆氧中的至少一种;优选为二氧化硅和/或二氧化锡;Wherein, the oxide is selected from silicon dioxide, tin dioxide, aluminum oxide, molybdenum oxide, vanadium pentoxide, titanium dioxide, manganese tetroxide, cobalt tetroxide, zirconium dioxide, zinc oxide, ceria, oxide At least one of magnesium, calcium oxide, indium oxide, gallium oxide, lithium oxide, triiron tetroxide and lithium lanthanum zirconium oxide; preferably silicon dioxide and/or tin dioxide;
其中,所述碳化物选自碳化钙、碳化钛、碳化铬、碳化钒、碳化钨、碳化硅、碳化硼和碳化钽中的至少一种;Wherein, the carbide is selected from at least one of calcium carbide, titanium carbide, chromium carbide, vanadium carbide, tungsten carbide, silicon carbide, boron carbide and tantalum carbide;
其中,所述硫化物选自硫化钼、硫化锌、硫化镍、硫化钴、硫化铋、硫化锡、硫化钨、硫化锑和二硫化钛中的至少一种;Wherein, the sulfide is selected from at least one of molybdenum sulfide, zinc sulfide, nickel sulfide, cobalt sulfide, bismuth sulfide, tin sulfide, tungsten sulfide, antimony sulfide and titanium disulfide;
其中,所述磷化物选自磷化钴、磷化钼、磷化钛、磷化镍、磷化铁和磷化锡中的至少一种;Wherein, the phosphide is selected from at least one of cobalt phosphide, molybdenum phosphide, titanium phosphide, nickel phosphide, iron phosphide and tin phosphide;
其中,所述氮化物选自氮化镓、氮化硼、氮化硅、氮化磷、氮化钨、氮化钒、氮化钛、氮化铌和氮化锂中的至少一种;Wherein, the nitride is selected from at least one of gallium nitride, boron nitride, silicon nitride, phosphorus nitride, tungsten nitride, vanadium nitride, titanium nitride, niobium nitride and lithium nitride;
其中,所述锂盐选自锰酸锂、钴酸锂、镍酸锂、镍锰酸锂、镍锰钴酸锂、镍钴铝酸锂、镍钴酸锂、富锂镍钴锰酸锂和钛酸锂中的至少一种;优选为镍锰酸锂、镍锰钴酸锂、镍钴铝酸锂和钛酸锂中的至少一种;Wherein, the lithium salt is selected from lithium manganate, lithium cobaltate, lithium nickelate, lithium nickel manganate, lithium nickel manganese cobaltate, lithium nickel cobalt aluminate, lithium nickel cobalt oxide, lithium rich nickel cobalt manganate and At least one of lithium titanate; preferably at least one of lithium nickel manganese oxide, lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide, lithium nickel cobalt aluminate and lithium titanate;
其中,所述磷酸盐选自磷酸铁、磷酸钛、磷酸钛锂、磷酸钛铝锂、磷酸铁锂、磷酸钴锂、磷酸锰锂、磷酸锰钴锂、磷酸铁锰锂、磷酸钒锂和磷酸钒钠中的至少一种;Wherein, the phosphate is selected from iron phosphate, titanium phosphate, lithium titanium phosphate, lithium aluminum titanium phosphate, lithium iron phosphate, lithium cobalt phosphate, lithium manganese phosphate, lithium manganese cobalt phosphate, lithium iron manganese phosphate, lithium vanadium phosphate and phosphoric acid At least one of sodium vanadium;
其中,所述非金属选自碳、碳纳米管、石墨烯、氧化石墨烯、富勒烯、硅、磷、硫、硒、碲和硼中的至少一种;Wherein, the non-metal is selected from at least one of carbon, carbon nanotubes, graphene, graphene oxide, fullerenes, silicon, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, tellurium and boron;
其中,所述有机物颗粒选自酚醛树脂、脲醛树脂、三聚氰胺树脂、聚苯乙烯、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮、聚多巴胺、葡萄糖、壳聚糖和果糖中的至少一种。Wherein, the organic particles are selected from at least one of phenolic resin, urea-formaldehyde resin, melamine resin, polystyrene, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polydopamine, glucose, chitosan and fructose.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述金属盐选自所述金属对应的氯化盐、硫酸盐、硝酸盐、醋酸盐、乙酰丙酮盐、乳酸盐和醇盐中的至少一种;例如选自硝酸盐;示例性地,选自硝酸铁或其水合物,硝酸锆或其水合物。According to the technical solution of the present invention, the metal salt is selected from at least one of chloride salts, sulfates, nitrates, acetates, acetylacetonates, lactates and alkoxides corresponding to the metals; From nitrate; exemplarily, selected from ferric nitrate or its hydrate, zirconium nitrate or its hydrate.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述沉淀剂选自尿素、甲酰胺、乙酰胺、丙酰胺、三乙醇胺、六次甲基四胺、氨水、甲酸铵、乙酸铵、丙酸铵、碳酸氢铵、碳酸铵、磷酸铵、磷酸氢二铵、磷酸二氢铵、氢氧化锂、氢氧化钠和氢氧化钾中的至少一种;例如选自六次甲基四胺或氢氧化锂。According to the technical scheme of the present invention, the precipitating agent is selected from urea, formamide, acetamide, propionamide, triethanolamine, hexamethylenetetramine, ammonia water, ammonium formate, ammonium acetate, ammonium propionate, ammonium bicarbonate, At least one of ammonium carbonate, ammonium phosphate, diammonium hydrogen phosphate, ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, lithium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide; for example, selected from hexamethylenetetramine or lithium hydroxide.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述混合液中,包覆底物材料的浓度为0.01~100g/L;例如浓度为0.5~50g/L、1~10g/L;示例性地,浓度为1.67g/L、3.33g/L、6.67g/L。According to the technical solution of the present invention, in the mixed solution, the concentration of the coating substrate material is 0.01-100 g/L; for example, the concentration is 0.5-50 g/L, 1-10 g/L; exemplarily, the concentration is 1.67 g /L, 3.33g/L, 6.67g/L.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述包覆底物材料的平均粒径为10nm~20μm;例如20nm~10μm、50nm~5μm、100nm~1μm;示例性地,平均粒径为200nm或600nm。According to the technical solution of the present invention, the average particle size of the coating substrate material is 10 nm-20 μm; for example, 20 nm-10 μm, 50 nm-5 μm, 100 nm-1 μm; exemplarily, the average particle size is 200 nm or 600 nm.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述混合液中,金属盐的浓度为1×10-4~0.1mol/L;例如浓度为1×10-3~0.05mol/L、5×10-3~0.01mol/L;示例性地,浓度为8.2×10-3mol/L、2×10-4mol/L。According to the technical solution of the present invention, in the mixed solution, the concentration of the metal salt is 1×10-4 to 0.1mol/L; for example, the concentration is 1×10-3 to 0.05mol/L, 5×10-3 to 0.01 mol/L; exemplarily, the concentrations are 8.2×10−3 mol/L, 2×10−4 mol/L.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述混合液中,沉淀剂的浓度为1×10-3~1mol/L;例如,浓度为5×10-3~0.5mol/L、1×10-2~0.1mol/L;示例性地,浓度为0.024mol/L、0.004mol/L。According to the technical solution of the present invention, in the mixed solution, the concentration of the precipitant is 1×10-3 to 1mol/L; for example, the concentration is 5×10-3 to 0.5mol/L, 1×10-2 to 0.1 mol/L; exemplarily, the concentrations are 0.024 mol/L, 0.004 mol/L.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述反应的温度为10~100℃,例如为50-90℃,示例性地,温度为80℃。According to the technical solution of the present invention, the temperature of the reaction is 10-100°C, for example, 50-90°C, and exemplarily, the temperature is 80°C.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述反应的时间为0.5h~10h,例如为2-8h,示例性地,时间为4h。According to the technical solution of the present invention, the reaction time is 0.5h-10h, for example, 2-8h, and exemplarily, the time is 4h.
根据本发明的技术方案,所述方法还包括对含有金属包覆层的金属氧化物进行煅烧处理,得到以金属氧化物为壳层的核-壳结构包覆型颗粒。According to the technical solution of the present invention, the method further includes calcining the metal oxide containing the metal coating layer to obtain core-shell structure coated particles with the metal oxide as the shell layer.
其中,所述煅烧的气氛为空气、氧气、氮气、氩气、氢气/氩气混合气中的至少一种;优选为空气或氧气。Wherein, the calcining atmosphere is at least one of air, oxygen, nitrogen, argon, and hydrogen/argon gas mixture; preferably air or oxygen.
其中,所述煅烧的温度为400~1000℃,例如温度为500~800℃,示例性地,温度为500℃、700℃。Wherein, the temperature of the calcination is 400-1000°C, for example, the temperature is 500-800°C, exemplarily, the temperature is 500°C and 700°C.
其中,所述煅烧的时间为0.5~10h,例如时间为1-5h,示例性地,时间为2h、4h。Wherein, the calcination time is 0.5-10 h, for example, the time is 1-5 h, exemplarily, the time is 2 h, 4 h.
根据本发明的实施方案,所述方法包括如下步骤:According to an embodiment of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of:
(1)在非水溶剂中加入包覆底物材料、金属硝酸盐和沉淀剂,得到混合液;所述沉淀剂与金属盐反应生成的沉淀均匀沉积在所述包覆底物材料的表面,形成包覆层;(1) adding a coating substrate material, a metal nitrate and a precipitant in a non-aqueous solvent to obtain a mixed solution; the precipitation generated by the reaction of the precipitating agent and the metal salt is uniformly deposited on the surface of the coating substrate material, forming a coating;
所述包覆底物材料选自氧化物或锂盐;The coating substrate material is selected from oxides or lithium salts;
(2)对步骤(1)得到的含有金属包覆层的金属氧化物进行煅烧,得到以金属氧化物为壳层的核-壳结构包覆型颗粒。(2) calcining the metal oxide containing the metal coating layer obtained in step (1) to obtain core-shell structure coated particles with the metal oxide as the shell layer.
进一步地,本发明第二个目的提供由上述方法制备得到的以金属氧化物为壳层的核-壳结构包覆型颗粒。其中,所述壳层均匀、连续、完整地包覆在所述包覆底物材料上,且包覆底物材料表面无损。优选地,所述金属氧化物可以为三氧化二铁、二氧化锆。进一步地,所述壳层的厚度为1-200nm,例如3-100nm、5-50nm,示例性地,厚度为3nm、5nm、9nm、10nm、25nm、28nm、32nm、45nm。其中,所述核为所述包覆底物材料。Further, the second object of the present invention is to provide core-shell structure coated particles with metal oxides as shell layers prepared by the above method. Wherein, the shell layer is uniformly, continuously and completely coated on the coated substrate material, and the surface of the coated substrate material is not damaged. Preferably, the metal oxide can be ferric oxide and zirconium dioxide. Further, the thickness of the shell layer is 1-200 nm, such as 3-100 nm, 5-50 nm, exemplarily, the thickness is 3 nm, 5 nm, 9 nm, 10 nm, 25 nm, 28 nm, 32 nm, 45 nm. Wherein, the core is the coating substrate material.
根据本发明的实施方案,所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒可以为三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化硅、三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化锡、三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴锰酸锂、三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴铝酸锂、三氧化二铁包覆的钛酸锂、三氧化二铁包覆的镍锰酸锂、二氧化锆包覆的二氧化硅、二氧化锆包覆的镍锰酸锂。According to an embodiment of the present invention, the core-shell structure-coated particles may be ferric oxide-coated silica, ferric oxide-coated tin dioxide, and ferric oxide-coated nickel-cobalt particles Lithium manganate, ferric oxide-coated nickel-cobalt aluminate, ferric oxide-coated lithium titanate, ferric oxide-coated lithium nickel manganate, zirconium dioxide-coated silica, Zirconium dioxide coated lithium nickel manganate.
本发明方法中,在所利用的非水溶剂中,反应物离子活度减弱,金属盐水解得到有效抑制,沉淀剂能够缓慢与金属盐发生反应,逐渐生成沉淀,并均匀、连续地沉积在包覆底物材料的表面,从而获得完整、厚度可控的包覆层。经过煅烧处理,得到以金属氧化物为壳的核-壳结构包覆型颗粒。In the method of the present invention, in the used non-aqueous solvent, the ionic activity of the reactant is weakened, the hydrolysis of the metal salt is effectively suppressed, and the precipitant can slowly react with the metal salt to gradually form a precipitate, which is uniformly and continuously deposited on the package. The surface of the substrate material is coated to obtain a complete coating with controllable thickness. After calcination treatment, core-shell structure coated particles with metal oxides as shells are obtained.
进一步地,本发明第三个目的提供所述方法得到的具有核-壳结构的包覆型颗粒在锂电池中的应用,优选作为锂电池的正极材料。Further, the third object of the present invention is to provide the application of the coated particles with a core-shell structure obtained by the method in a lithium battery, preferably as a positive electrode material for a lithium battery.
进一步地,本发明还提供一种含有所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒的锂离子正极材料。Further, the present invention also provides a lithium ion positive electrode material containing the core-shell structure coated particles.
根据本发明的实施方案,当所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒的核选自所述锂盐时,所述锂离子正极材料即为所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒。According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the core of the core-shell structure coated particle is selected from the lithium salt, the lithium ion positive electrode material is the core-shell structure coated particle.
根据本发明的实施方案,当所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒的核选自非所述锂盐时,所述锂离子正极材料可由所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒锂化处理得到。进一步地,所述的锂化包括如下步骤:所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒与氢氧化锂或碳酸锂混合烧结。其中,所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒与氢氧化锂或碳酸锂的摩尔比为1:(1-1.1),例如1:(1-1.08)、1:(1.02-1.06)。所述烧结在含氧气氛下进行,例如空气或氧气气氛下。所述烧结的温度为400-1000℃,例如500-900℃、600-800℃。所述烧结的时间为1-10h,例如2-8h、4-6h。所述烧结可以为一步烧结,或两次以上的多步烧结,每步烧结温度和时间可以相同或不同。According to an embodiment of the present invention, when the core of the core-shell structure-coated particle is selected from a non-lithium salt, the lithium ion positive electrode material can be obtained by lithiation of the core-shell structure-coated particle . Further, the lithiation includes the following steps: the core-shell structure coated particles are mixed and sintered with lithium hydroxide or lithium carbonate. Wherein, the molar ratio of the core-shell structure-coated particles to lithium hydroxide or lithium carbonate is 1:(1-1.1), for example, 1:(1-1.08), 1:(1.02-1.06). The sintering is carried out in an oxygen-containing atmosphere, such as air or oxygen. The sintering temperature is 400-1000°C, such as 500-900°C, 600-800°C. The sintering time is 1-10h, such as 2-8h, 4-6h. The sintering can be one-step sintering, or two or more multi-step sintering, and the sintering temperature and time of each step can be the same or different.
进一步地,本发明还提供一种含有所述核-壳结构包覆型颗粒或含有所述锂离子正极材料的锂离子电池。Further, the present invention also provides a lithium ion battery containing the core-shell structure coated particles or containing the lithium ion positive electrode material.
由本发明的具有核-壳结构的金属氧化物包覆型颗粒对锂离子电池或锂电池的正极材料进行原位厚度可控的包覆后得到的金属氧化物包覆型正极材料,能够作为高能量型储能器件的锂离子电池或锂电池的正极材料。The metal oxide-coated positive electrode material obtained by the in-situ thickness-controllable coating of the positive electrode material of a lithium ion battery or a lithium battery by the metal oxide-coated particles having a core-shell structure of the present invention can be used as a high Lithium-ion battery or positive electrode material of lithium battery for energy storage device.
本发明的有益效果:Beneficial effects of the present invention:
本发明提供了一种能够在非水环境中实现金属氧化物包覆层精准构筑的方法,工艺简单、反应条件温和,对核材料表面能够实现无损处理,适用范围广。该方法基于非水溶剂提供的反应环境,能够减弱反应物的离子活度,抑制金属离子的水解,有效控制金属盐的沉淀过程,实现沉淀物析出方式的调节,从而获得材料表面均匀连续的包覆层,且厚度可在纳米精度范围内调控。通过进一步的煅烧处理即可得到所述的金属氧化物包覆的核-壳结构颗粒。以此方法得到的金属氧化物包覆锂离子电池正极材料的核-壳结构颗粒,能够表现出优异的电化学性能。The invention provides a method for realizing precise construction of a metal oxide coating layer in a non-aqueous environment, with simple process, mild reaction conditions, non-destructive treatment of the surface of the nuclear material, and wide application range. The method is based on the reaction environment provided by the non-aqueous solvent, which can weaken the ionic activity of the reactants, inhibit the hydrolysis of metal ions, effectively control the precipitation process of metal salts, and realize the adjustment of the precipitation method, so as to obtain uniform and continuous encapsulation on the surface of the material. coating, and the thickness can be adjusted in the nanometer precision range. The metal oxide-coated core-shell structure particles can be obtained by further calcination treatment. The core-shell structure particles of the metal oxide-coated cathode material of lithium ion batteries obtained in this way can exhibit excellent electrochemical performance.
本发明提供的金属氧化物包覆型颗粒,可以在不同包覆底物的表面上得到均匀、连续、完整且厚度可控的金属氧化物包覆层,且确保材料表面获得无损处理。本发明利用非水溶剂提供的反应环境,减弱反应物的离子活度,抑制金属盐的水解,使金属盐的沉淀过程变得可控,从而获得对沉淀析出方式的调控,成功实现均匀、连续、完整、厚度可控包覆层的制备。本发明提供的包覆方法工艺简单、普适性强、能够实现材料表面无损处理,获得的包覆层均匀、连续、完整、厚度可实现纳米精度内精确调节,在高能量型储能器件即锂离子电池或锂电池领域有着很高的实用性和应用前景。The metal oxide-coated particles provided by the present invention can obtain a uniform, continuous, complete and controllable thickness of the metal oxide coating layer on the surfaces of different coating substrates, and ensure that the surface of the material can be non-destructively treated. The invention utilizes the reaction environment provided by the non-aqueous solvent, weakens the ionic activity of the reactants, inhibits the hydrolysis of the metal salt, and makes the precipitation process of the metal salt controllable, so as to obtain the regulation of the precipitation and precipitation mode, and successfully realize uniform and continuous , Preparation of complete, thickness-controllable coating. The coating method provided by the invention has simple process, strong universality, and can realize non-destructive treatment of material surface. The obtained coating layer is uniform, continuous and complete, and the thickness can be precisely adjusted within nanometer precision. The field of lithium ion batteries or lithium batteries has high practicability and application prospects.
附图说明Description of drawings
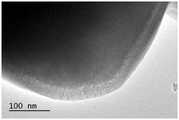
图1为实施例1的三氧化二铁包覆二氧化硅颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 1 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the ferric oxide-coated silica particles of Example 1. FIG.
图2为实施例2的三氧化二铁包覆二氧化锡颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 2 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the ferric oxide-coated tin dioxide particles of Example 2. FIG.
图3为实施例3的三氧化二铁包覆镍钴锰酸锂颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。3 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the ferric oxide-coated nickel cobalt lithium manganate particles of Example 3. FIG.
图4为实施例4的三氧化二铁包覆镍钴铝酸锂颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 4 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the ferric oxide-coated nickel-cobalt aluminate particles of Example 4. FIG.
图5为实施例5的三氧化二铁包覆钛酸锂颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 5 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the Fe2O3-coated lithium titanate particles of Example 5. FIG.
图6为实施例6的二氧化锆包覆二氧化硅颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。6 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the zirconia-coated silica particles of Example 6. FIG.
图7为实施例7的二氧化锆包覆镍锰酸锂颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 7 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the zirconium dioxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles of Example 7. FIG.
图8为实施例8的三氧化二铁包覆镍锰酸锂颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 8 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of the Fe2O3-coated lithium nickel manganate particles of Example 8. FIG.
图9为实施例8的三氧化二铁包覆镍锰酸锂颗粒在0.1C下的循环性能。FIG. 9 shows the cycle performance of the Fe2O3-coated lithium nickel manganate particles of Example 8 at 0.1C.
图10为对比例1的以去离子水为溶剂下三氧化二铁包覆二氧化硅颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。FIG. 10 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of Fe2O3-coated silica particles using deionized water as a solvent of Comparative Example 1. FIG.
图11为对比例2的以去离子水为溶剂下二氧化锆包覆二氧化硅颗粒的透射电子显微镜照片。11 is a transmission electron microscope photograph of zirconium dioxide-coated silica particles of Comparative Example 2 using deionized water as a solvent.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下文将结合具体实施例对本发明的技术方案做更进一步的详细说明。应当理解,下列实施例仅为示例性地说明和解释本发明,而不应被解释为对本发明保护范围的限制。凡基于本发明上述内容所实现的技术均涵盖在本发明旨在保护的范围内。The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to specific embodiments. It should be understood that the following examples are only for illustrating and explaining the present invention, and should not be construed as limiting the protection scope of the present invention. All technologies implemented based on the above content of the present invention are covered within the intended protection scope of the present invention.
除非另有说明,以下实施例中使用的原料和试剂均为市售商品,或者可以通过已知方法制备。Unless otherwise stated, the starting materials and reagents used in the following examples are commercially available or can be prepared by known methods.
以下实施例中所用到的无水乙醇为色谱纯级别,其含水量≤0.1wt%。The absolute ethanol used in the following examples is of chromatographically pure grade, and its water content is less than or equal to 0.1 wt%.
实施例1Example 1
制备三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化硅颗粒Preparation of Fe2O3-Coated Silica Particles
(1)将二氧化硅颗粒0.05g(平均粒径为600nm)、九水硝酸铁0.1g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含铁包覆型的二氧化硅颗粒,再在500℃空气气氛下煅烧2h,得到三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化硅颗粒。(1) Mix 0.05 g of silica particles (average particle size of 600 nm), 0.1 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent absolute ethanol, and reflux at 80°C with stirring The reaction was carried out for 4 hours, centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain iron-coated silica particles, and then calcined in an air atmosphere at 500° C. for 2 hours to obtain ferric oxide-coated silica particles.
(2)该三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化硅颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图1所示。构成核的材料为粒径为600nm的二氧化硅,构成壳的材料为三氧化二铁,厚度为32nm;且三氧化二铁连续、均匀、完整地包覆在二氧化硅的表面,且二氧化硅表面为无损包覆。(2) The ferric oxide-coated silica particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 1 . The material constituting the core is silica with a particle size of 600 nm, and the material constituting the shell is ferric oxide with a thickness of 32 nm; and the ferric oxide is continuously, uniformly and completely coated on the surface of the silica, and the two The silicon oxide surface is a non-destructive coating.
实施例2Example 2
制备三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化锡颗粒Preparation of ferric oxide-coated tin dioxide particles
(1)将二氧化锡颗粒0.05g(粒径为20~100nm)、九水硝酸铁0.1g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含铁包覆型的二氧化锡颗粒,再在500℃空气气氛下煅烧2h,得到三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化锡颗粒。(1) Mix 0.05 g of tin dioxide particles (with a particle size of 20 to 100 nm), 0.1 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent anhydrous ethanol, and stir at 80° C. The reaction was carried out under reflux for 4 hours, centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain iron-coated tin dioxide particles, and then calcined in an air atmosphere at 500° C. for 2 hours to obtain ferric oxide-coated tin dioxide particles.
(2)该三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化锡颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图2所示。构成核的材料为粒径为20~100nm的二氧化锡,构成壳的材料为三氧化二铁,厚度为10nm;且三氧化二铁均匀包覆在二氧化锡的表面。(2) The tin dioxide particles coated with ferric oxide have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 2 . The material constituting the core is tin dioxide with a particle size of 20-100 nm, and the material constituting the shell is ferric oxide with a thickness of 10 nm; and the ferric oxide is uniformly coated on the surface of the tin dioxide.
实施例3Example 3
制备三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴锰酸锂颗粒Preparation of Fe2O3-Coated Nickel Cobalt Lithium Manganate Particles
(1)将镍钴锰酸锂颗粒0.2g(粒径为1~10μm)、九水硝酸铁0.1g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含铁包覆型的镍钴锰酸锂颗粒,再在700℃氧气气氛下煅烧2h,得到三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴锰酸锂颗粒。(1) Mix 0.2 g of nickel cobalt lithium manganate particles (particle size is 1 to 10 μm), 0.1 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent anhydrous ethanol, under stirring The reaction was carried out under reflux at 80°C for 4 hours, and then centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain iron-coated nickel-cobalt manganate particles, and then calcined at 700°C in an oxygen atmosphere for 2 hours to obtain iron trioxide-coated lithium nickel-cobalt manganate particles. particles.
(2)该三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴锰酸锂颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图3所示。构成核的材料为粒径为1~10μm的镍钴锰酸锂,构成壳的材料为三氧化二铁,厚度为5nm;且三氧化二铁均匀包覆在镍钴锰酸锂的表面。(2) The ferric oxide-coated nickel-cobalt lithium manganate particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 3 . The material constituting the core is lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide with a particle size of 1-10 μm, and the material constituting the shell is ferric oxide with a thickness of 5 nm; and the ferric oxide is uniformly coated on the surface of the lithium nickel cobalt manganate.
实施例4Example 4
制备三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴铝酸锂颗粒Preparation of Fe2O3-Coated Nickel-Cobalt-Lithium Aluminate Particles
(1)将镍钴铝酸锂颗粒0.1g(粒径为1~10μm)、九水硝酸铁0.3g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.3g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含铁包覆型的镍钴铝酸锂颗粒,再在700℃氧气气氛下煅烧2h,得到三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴铝酸锂颗粒。(1) Mix 0.1 g of nickel cobalt lithium aluminate particles (particle size is 1 to 10 μm), 0.3 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.3 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent absolute ethanol, and stir under stirring. The reaction was carried out under reflux at 80 °C for 4 hours, and then centrifuged, washed and dried to obtain iron-coated nickel-cobalt aluminate lithium particles, and then calcined at 700 °C in an oxygen atmosphere for 2 hours to obtain ferric oxide-coated lithium nickel-cobalt aluminate. particles.
(2)该三氧化二铁包覆的镍钴铝酸锂颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图4所示。构成核的材料为粒径为1~10μm的镍钴铝酸锂,构成壳的材料为三氧化二铁,厚度为25nm;且三氧化二铁均匀包覆在镍钴铝酸锂的表面。(2) The ferric oxide-coated nickel-cobalt lithium aluminate particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 4 . The material constituting the core is lithium nickel cobalt aluminate with a particle size of 1-10 μm, and the material constituting the shell is ferric oxide with a thickness of 25 nm; and ferric oxide is uniformly coated on the surface of the lithium nickel cobalt aluminate.
实施例5Example 5
制备三氧化二铁包覆的钛酸锂颗粒Preparation of Fe2O3-Coated Lithium Titanate Particles
(1)将钛酸锂颗粒0.2g(粒径为50~200nm)、九水硝酸铁0.1g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含铁包覆型的钛酸锂颗粒,再在700℃空气气氛下煅烧2h,得到三氧化二铁包覆的钛酸锂颗粒。(1) Mix 0.2 g of lithium titanate particles (with a particle size of 50 to 200 nm), 0.1 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent anhydrous ethanol, and stir at 80° C. The reaction was carried out under reflux for 4 hours, centrifuged, washed, and dried to obtain iron-coated lithium titanate particles, and then calcined at 700° C. in an air atmosphere for 2 hours to obtain iron trioxide-coated lithium titanate particles.
(2)该三氧化二铁包覆的钛酸锂颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图5所示。构成核的材料为粒径为50~200nm的钛酸锂,构成壳的材料为三氧化二铁,厚度为9nm;且三氧化二铁均匀包覆在钛酸锂的表面。(2) The ferric oxide-coated lithium titanate particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 5 . The material constituting the core is lithium titanate with a particle size of 50-200 nm, the material constituting the shell is ferric oxide with a thickness of 9 nm; and the surface of the lithium titanate is uniformly coated with ferric oxide.
实施例6Example 6
制备二氧化锆包覆的二氧化硅颗粒Preparation of zirconia-coated silica particles
(1)将二氧化硅颗粒0.05g(平均粒径为600nm)、五水硝酸锆0.1g、沉淀剂氢氧化锂0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在室温下搅拌回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含锆包覆型的二氧化硅颗粒,再在500℃空气气氛下煅烧2h,得到二氧化锆包覆的二氧化硅颗粒。(1) Mix 0.05 g of silica particles (average particle size of 600 nm), 0.1 g of zirconium nitrate pentahydrate, and 0.1 g of lithium hydroxide as a precipitant in 30 mL of solvent absolute ethanol, and stir and reflux at room temperature to react for 4 h, After centrifugation, washing and drying, zirconium-coated silica particles were obtained, and then calcined in an air atmosphere at 500° C. for 2 h to obtain zirconia-coated silica particles.
(2)该二氧化锆包覆的二氧化硅颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图6所示。构成核的材料为粒径为600nm的二氧化硅,构成壳的材料为二氧化锆,厚度为28nm;且二氧化锆均匀包覆在二氧化硅的表面。(2) The zirconium dioxide-coated silica particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 6 . The material constituting the core is silicon dioxide with a particle size of 600 nm, and the material constituting the shell is zirconium dioxide with a thickness of 28 nm; and the surface of the silicon dioxide is uniformly coated by the zirconium dioxide.
实施例7Example 7
制备二氧化锆包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒Preparation of zirconia-coated lithium nickel manganate particles
(1)将镍锰酸锂颗粒0.2g(粒径为1~10μm)、五水硝酸锆0.1g、沉淀剂氢氧化锂0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在室温下搅拌进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含锆包覆型的镍锰酸锂颗粒,再在700℃空气气氛下煅烧2h,得到二氧化锆包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒。(1) Mix 0.2 g of lithium nickel manganate particles (with a particle size of 1 to 10 μm), 0.1 g of zirconium nitrate pentahydrate, and 0.1 g of lithium hydroxide as a precipitant in 30 mL of solvent absolute ethanol, and stir at room temperature for 4 h. , after centrifugation, washing, and drying to obtain zirconium-coated lithium nickel manganate particles, and then calcined at 700 °C for 2 hours in an air atmosphere to obtain zirconium dioxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles.
(2)该二氧化锆包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图7所示。构成核的材料为粒径为1~10μm的镍锰酸锂,构成壳的材料为二氧化锆,厚度约为45nm;且二氧化锆均匀包覆在镍锰酸锂的表面。(2) The zirconium dioxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 7 . The material constituting the core is lithium nickel manganate with a particle size of 1-10 μm, and the material constituting the shell is zirconium dioxide with a thickness of about 45 nm; and the surface of the lithium nickel manganate is uniformly coated by the zirconium dioxide.
实施例8Example 8
一、制备三氧化二铁包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒1. Preparation of ferric oxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles
(1)将镍锰酸锂颗粒0.2g(粒径为1~5μm)、九水硝酸铁0.1g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.1g在30mL溶剂无水乙醇中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到含铁包覆型的镍锰酸锂颗粒,再在700℃氧气气氛下煅烧2h,得到三氧化二铁包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒。(1) Mix 0.2 g of lithium nickel manganate particles (with a particle size of 1 to 5 μm), 0.1 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent absolute ethanol, and stir for 80 The reaction was carried out under reflux for 4 hours, centrifuged, washed, and dried to obtain iron-coated lithium nickel manganate particles, and then calcined at 700 °C in an oxygen atmosphere for 2 hours to obtain iron trioxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles.
(2)该三氧化二铁包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒为核-壳结构,其电镜照片如图8所示。构成核的材料为粒径为1~5μm的镍锰酸锂,构成壳的材料为三氧化二铁,厚度为3nm;且三氧化二铁均匀包覆在镍锰酸锂的表面。(2) The ferric oxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles have a core-shell structure, and the electron microscope photograph thereof is shown in FIG. 8 . The material constituting the core is lithium nickel manganate with a particle size of 1-5 μm, and the material constituting the shell is ferric oxide with a thickness of 3 nm; and the surface of the lithium nickel manganate is uniformly coated with ferric oxide.
二、制备三氧化二铁包覆型的镍锰酸锂电极2. Preparation of Fe2O3-coated LiMnO2 electrode
将步骤一中制备的三氧化二铁包覆的镍锰酸锂颗粒0.2136g、导电添加剂Super P0.0267g、粘结剂PVDF 0.534g与少许溶剂NMP混合均匀,经制浆、涂片(铝片作为集流体)、干燥,得到三氧化二铁包覆型的镍锰酸锂电极。The ferric oxide-coated lithium nickel manganate particles 0.2136g prepared in
三、组装电池3. Assemble the battery
以上述制备的三氧化二铁包覆型的镍锰酸锂电极作为正极材料,以金属锂作为负极材料组装成电池。电解液选择浓度为1M的碳酸酯电解液,溶剂为DMC:DEC:EC=1:1:1(w/w/w),溶质为LiPF6。A battery is assembled by using the ferric oxide-coated lithium nickel manganate electrode prepared above as a positive electrode material, and using metallic lithium as a negative electrode material. The electrolyte is selected as carbonate electrolyte with a concentration of 1M, the solvent is DMC:DEC:EC=1:1:1 (w/w/w), and the solute is LiPF6 .
四、电池测试Fourth, battery test
(1)使用充放电仪对上述电池进行恒流充放电测试,测试电压区间为3~5V,测试温度为25℃。电池容量和充放电电流均以镍锰酸锂的质量计算。(1) Use a charge-discharge instrument to carry out a constant-current charge-discharge test on the above-mentioned battery. The test voltage range is 3-5V, and the test temperature is 25°C. The battery capacity and charge-discharge current are calculated by the mass of lithium nickel manganate.
(2)图9为此材料在0.1C下(0.1C是按理论容量的0.1倍的安培电流进行充放电,对于镍锰酸锂0.1C=0.1×146.7mAh/g×活性物质的质量)的循环性能。电池在经过100圈循环后,容量为125.5mAh/g(未包覆的镍锰酸锂100圈循环后容量为105mAh/g),库伦效率在98%以上,具有良好的容量保持率和寿命。(2) Figure 9 shows the material at 0.1C (0.1C is charged and discharged at an ampere current of 0.1 times the theoretical capacity, for lithium nickel manganate 0.1C=0.1×146.7mAh/g×mass of active material) cycle performance. After 100 cycles, the battery has a capacity of 125.5mAh/g (uncoated lithium nickel manganese oxide has a capacity of 105mAh/g after 100 cycles), and the Coulomb efficiency is over 98%, with good capacity retention and life.
对比例1Comparative Example 1
以去离子水为溶剂,制备三氧化二铁包覆的二氧化硅颗粒Preparation of Fe2O3-Coated Silica Particles Using Deionized Water as Solvent
将二氧化硅颗粒0.05g(平均粒径为600nm)、九水硝酸铁0.1g、沉淀剂六次甲基四胺0.1g在30mL溶剂去离子水中混合,在搅拌下80℃回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到处理后的二氧化硅颗粒,其电镜照片如图10所示,二氧化硅颗粒表面没有形成包覆层,说明在去离子水中包覆无法成功进行。Mix 0.05 g of silica particles (average particle size is 600 nm), 0.1 g of ferric nitrate nonahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant hexamethylenetetramine in 30 mL of solvent deionized water, and reflux at 80 °C for 4 h under stirring. After centrifugation, washing, and drying, the treated silica particles were obtained. The electron microscope photo of the silica particles was shown in Figure 10. No coating layer was formed on the surface of the silica particles, indicating that the coating in deionized water could not be successfully carried out.
对比例2Comparative Example 2
以去离子水为溶剂,制备二氧化锆包覆的二氧化硅颗粒Preparation of Zirconium Dioxide-Coated Silica Particles Using Deionized Water as Solvent
将二氧化硅颗粒0.05g(平均粒径为600nm)、五水硝酸锆0.1g、沉淀剂氢氧化锂0.1g在30mL溶剂去离子水中混合,在室温下搅拌回流进行反应4h,经离心、洗涤、干燥得到处理后的二氧化硅颗粒,其电镜照片如图11所示,二氧化硅颗粒表面没有形成包覆层,说明在去离子水中包覆无法成功进行。Mix 0.05 g of silica particles (average particle size of 600 nm), 0.1 g of zirconium nitrate pentahydrate, and 0.1 g of precipitant lithium hydroxide in 30 mL of deionized water as a solvent, and stir and reflux at room temperature for 4 hours. After centrifugation, washing , and dried to obtain the treated silica particles. The electron microscope photo of the silica particles is shown in Figure 11. No coating layer is formed on the surface of the silica particles, indicating that the coating cannot be successfully carried out in deionized water.
以上,对本发明的实施方式进行了说明。但是,本发明不限定于上述实施方式。凡在本发明的精神和原则之内,所做的任何修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明的保护范围之内。The embodiments of the present invention have been described above. However, the present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments. Any modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made within the spirit and principle of the present invention shall be included within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (14)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910770861.0ACN112420997B (en) | 2019-08-20 | 2019-08-20 | A method for constructing a metal oxide coating with a controllable thickness in a solution phase |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910770861.0ACN112420997B (en) | 2019-08-20 | 2019-08-20 | A method for constructing a metal oxide coating with a controllable thickness in a solution phase |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112420997A CN112420997A (en) | 2021-02-26 |
| CN112420997Btrue CN112420997B (en) | 2022-07-01 |
Family
ID=74779705
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910770861.0AActiveCN112420997B (en) | 2019-08-20 | 2019-08-20 | A method for constructing a metal oxide coating with a controllable thickness in a solution phase |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112420997B (en) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI743017B (en) | 2021-05-10 | 2021-10-11 | 台灣中油股份有限公司 | Lithium titanate/titanium niobate core-shell composite material and preparation method thereof |
| CN115566260B (en)* | 2021-07-01 | 2024-03-19 | 北京理工大学 | Polymer gel electrolyte and preparation method thereof |
| CN113652081B (en)* | 2021-08-23 | 2023-03-28 | 湖北世丰新材料有限公司 | Antibacterial flame-retardant foamed plastic |
| CN115710493A (en)* | 2021-08-23 | 2023-02-24 | 中国石油天然气集团有限公司 | Ultralow-density high-strength ceramsite proppant and preparation method thereof |
| CN115732647A (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2023-03-03 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Low-alkalinity high-lattice-stability coated modified cathode material and preparation method and application thereof |
| CN114373892B (en)* | 2021-12-22 | 2023-12-26 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Method for controllably constructing phosphate coating and application thereof |
| CN116344806A (en)* | 2021-12-22 | 2023-06-27 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | A method and application of a controllable construction of a carbon composite coating layer containing phosphate by polymerization |
| CN114784368B (en)* | 2022-03-14 | 2025-09-23 | 深圳市杰创新能源有限责任公司 | A method for removing and coating the passivation layer on the surface of an LLZO-type solid electrolyte and its application |
| CN114976007B (en)* | 2022-06-08 | 2024-02-20 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Method for controllably constructing sulfide coating layer |
| CN115432751A (en)* | 2022-10-25 | 2022-12-06 | 格林美股份有限公司 | A kind of modified cathode material and its preparation method and application |
| CN116230413B (en)* | 2022-12-23 | 2025-09-12 | 山东大学 | A gallium nitride/metal oxide composite electrode material and its preparation method and application |
| CN117913344B (en)* | 2024-03-19 | 2024-06-25 | 苏州大学 | A method for controllably constructing a fast ion conductor coating layer and its application |
| CN119637941A (en)* | 2025-01-17 | 2025-03-18 | 湘潭电化科技股份有限公司 | Preparation method and application of modified sea urchin type manganous oxide |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100691908B1 (en)* | 2005-09-08 | 2007-03-09 | 한화석유화학 주식회사 | Method for coating metal oxide ultrafine particles on the surface of metal oxide and a coating prepared therefrom |
| CN103606660A (en)* | 2013-11-06 | 2014-02-26 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Alumina-coated granules, as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN103618064A (en)* | 2013-11-08 | 2014-03-05 | 宁夏共享集团有限责任公司 | Preparation method of alumina composite nickel-cobalt lithium manganate ternary material |
| CN104134795A (en)* | 2014-07-25 | 2014-11-05 | 江南大学 | Preparation method of spherical layer-structured anode material externally coated with nanocrystalline metal oxide for lithium ion battery |
| WO2017101233A1 (en)* | 2015-12-15 | 2017-06-22 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Anode material, preparation method therefor and use thereof |
- 2019
- 2019-08-20CNCN201910770861.0Apatent/CN112420997B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100691908B1 (en)* | 2005-09-08 | 2007-03-09 | 한화석유화학 주식회사 | Method for coating metal oxide ultrafine particles on the surface of metal oxide and a coating prepared therefrom |
| CN103606660A (en)* | 2013-11-06 | 2014-02-26 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Alumina-coated granules, as well as preparation method and application thereof |
| CN103618064A (en)* | 2013-11-08 | 2014-03-05 | 宁夏共享集团有限责任公司 | Preparation method of alumina composite nickel-cobalt lithium manganate ternary material |
| CN104134795A (en)* | 2014-07-25 | 2014-11-05 | 江南大学 | Preparation method of spherical layer-structured anode material externally coated with nanocrystalline metal oxide for lithium ion battery |
| WO2017101233A1 (en)* | 2015-12-15 | 2017-06-22 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | Anode material, preparation method therefor and use thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112420997A (en) | 2021-02-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112420997B (en) | A method for constructing a metal oxide coating with a controllable thickness in a solution phase | |
| CN104966823B (en) | Material surface has nickel cobalt lithium aluminate cathode material of component concentration gradient and preparation method thereof | |
| CN107069023B (en) | A kind of preparation method of hollow structure lithium ion battery electrode material | |
| CN106410157B (en) | High-magnification long-life cathode material and preparation method thereof | |
| WO2008068905A1 (en) | Li-Ni COMPOSITE OXIDE PARTICLE POWDER FOR RECHARGEABLE BATTERY WITH NONAQUEOUS ELECTROLYTE, PROCESS FOR PRODUCING THE Li-Ni COMPOSITE OXIDE PARTICLE POWDER, AND RECHARGEABLE BATTERY WITH NONAQUEOUS ELECTROLYTE | |
| CN110061228A (en) | Anode material of lithium-ion battery and synthetic method based on MXene Yu fake capacitance type transition metal oxide nano composite construction | |
| EP4407748A1 (en) | Method for synthesizing high-safety positive electrode material by recycling positive electrode leftover materials, and application | |
| CN105473507A (en) | Alkali metal titanium oxide having anisotropic structure, titanium oxide, electrode active material containing said oxides, and electricity storage device | |
| CN114976007B (en) | Method for controllably constructing sulfide coating layer | |
| CN106711419A (en) | Core-shell NiO/C porous composite lithium ion battery negative electrode material | |
| CN105161686A (en) | Double-coated manganese-base layered lithium-rich material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN117913344B (en) | A method for controllably constructing a fast ion conductor coating layer and its application | |
| CN112151781A (en) | Rapid composite coating modification method for lithium battery positive electrode material | |
| CN107799747A (en) | A preparation method of ion-doped lithium-rich manganese-based solid solution/carbon conductive network composite positive electrode material | |
| CN111816866B (en) | Method for preparing lithium-rich manganese-based positive electrode material by co-precipitation-hydrothermal combination | |
| CN113764633A (en) | Surface modified lithium ion battery positive electrode material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114373892B (en) | Method for controllably constructing phosphate coating and application thereof | |
| CN110482604B (en) | Cu2V2O7Nanorod potassium ion battery positive electrode material, potassium ion battery and preparation method thereof | |
| CN113753963B (en) | A kind of tin cobalt disulfide nanoparticle and its preparation method and application | |
| CN105375004B (en) | Long-life high-energy lithium secondary battery positive electrode material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116344806A (en) | A method and application of a controllable construction of a carbon composite coating layer containing phosphate by polymerization | |
| CN108565416B (en) | A kind of surface phase change modified lithium ion battery electrode material and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN101928044B (en) | A preparation method of nanometer cobalt tetroxide that can be used as negative electrode material of lithium ion battery | |
| CN115732647A (en) | Low-alkalinity high-lattice-stability coated modified cathode material and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN108023079B (en) | Mixed transition metal borate anode material and preparation method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |