CN112416554B - Task migration method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium - Google Patents
Task migration method and device, electronic equipment and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112416554B CN112416554BCN202011312378.7ACN202011312378ACN112416554BCN 112416554 BCN112416554 BCN 112416554BCN 202011312378 ACN202011312378 ACN 202011312378ACN 112416554 BCN112416554 BCN 112416554B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- task
- edge computing
- migrated
- user equipment
- task migration
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/48—Program initiating; Program switching, e.g. by interrupt
- G06F9/4806—Task transfer initiation or dispatching
- G06F9/4843—Task transfer initiation or dispatching by program, e.g. task dispatcher, supervisor, operating system
- G06F9/485—Task life-cycle, e.g. stopping, restarting, resuming execution
- G06F9/4856—Task life-cycle, e.g. stopping, restarting, resuming execution resumption being on a different machine, e.g. task migration, virtual machine migration
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/48—Program initiating; Program switching, e.g. by interrupt
- G06F9/4806—Task transfer initiation or dispatching
- G06F9/4843—Task transfer initiation or dispatching by program, e.g. task dispatcher, supervisor, operating system
- G06F9/4881—Scheduling strategies for dispatcher, e.g. round robin, multi-level priority queues
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及分布式计算技术领域,尤其涉及一种任务迁移方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质。The present application relates to the technical field of distributed computing, and in particular to a task migration method, device, electronic equipment and storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
目前,5G通信技术推动信息社会进入了万物互联的时代,物联网终端设备数量以及数据量呈指数级增长。为了满足数据处理需求,通常利用移动边缘计算系统对用户设备终端所产生的海量数据进行任务迁移和处理。At present, 5G communication technology has pushed the information society into the era of the Internet of Everything, and the number of IoT terminal devices and the amount of data are increasing exponentially. In order to meet the data processing requirements, the mobile edge computing system is usually used to migrate and process the massive data generated by the user equipment terminal.
在现有技术中,移动边缘计算系统通常是根据固定的任务迁移规则进行任务迁移,比如根据用户设备终端的迁移选择、发射功率、任务的大小、截止时间、用户设备终端的计算资源和边缘计算服务器的计算资源等因素,确定任务迁移策略。In the prior art, the mobile edge computing system usually performs task migration according to fixed task migration rules, such as user equipment terminal migration selection, transmit power, task size, deadline, user equipment terminal computing resources and edge computing Factors such as the computing resources of the server determine the task migration strategy.
但是,由于用户设备终端多种多样,若仅根据固定的任务迁移规则对各用户设备终端所产生的任务进行任务迁移,则存在部分低时延高可靠的任务无法及时处理,造成移动边缘计算系统的时延及能耗超标等风险。因此,急需一种可以缓解多业务并发时移动边缘计算系统的能耗压力的任务迁移方法,对提高移动边缘计算系统的任务处理效率有重要意义。However, due to the variety of user equipment terminals, if the tasks generated by each user equipment terminal are only migrated according to the fixed task migration rules, some low-latency and high-reliability tasks cannot be processed in time, causing the mobile edge computing system Risks such as time delay and excessive energy consumption. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a task migration method that can alleviate the energy consumption pressure of the mobile edge computing system when multiple services are concurrent, which is of great significance for improving the task processing efficiency of the mobile edge computing system.
发明内容Contents of the invention
本申请提供一种任务迁移方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质,以解决现有技术中的任务迁移方法所确定的任务迁移策略可能导致移动边缘计算系统的能耗超标等缺陷。The present application provides a task migration method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium to solve the defects that the task migration strategy determined by the task migration method in the prior art may lead to excessive energy consumption of the mobile edge computing system.
本申请第一个方面提供一种任务迁移方法,包括:The first aspect of this application provides a task migration method, including:
获取多个用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及所述边缘计算服务器可用资源;其中,所述待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求;Obtaining task information of tasks to be migrated generated by multiple user equipment terminals, available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and available resources of the edge computing server; wherein the task information to be migrated includes: tasks to be migrated Computing resource requirements and bandwidth requirements;
在预设的约束条件内,根据所述待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及所述边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略;Within preset constraints, generate multiple task migration strategies according to the task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server;
根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。According to the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy, the target task migration strategy is determined.
可选的,所述根据所述待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及所述边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略,包括:Optionally, generating multiple task migration strategies according to the task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server includes:
根据所述待迁移任务的带宽需求和各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽,生成所述待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策;其中,所述任务迁移决策包括各待迁移任务的执行目的地,所述执行目的地包括用户设备终端和边缘计算服务器;Generate multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated according to the bandwidth requirements of the tasks to be migrated and the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station; wherein the task migration decisions include the execution of each task to be migrated a destination, the execution destination includes a user equipment terminal and an edge computing server;
当所述待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,确定所述待迁移任务为第一任务;When the execution destination of the task to be migrated is an edge computing server, determine that the task to be migrated is the first task;
获取所述第一任务的服务质量要求,根据所述服务质量要求确定所述第一任务的优先级;根据各第一任务的优先级,确定边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配量;Acquiring the quality of service requirements of the first task, determining the priority of the first task according to the quality of service requirement; determining the allocation amount of available resources of the edge computing server according to the priority of each first task;
根据所述待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策,及边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配情况,生成多个任务迁移策略。Multiple task migration strategies are generated according to the multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated and the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server.
可选的,所述根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略,包括:Optionally, the determining the target task migration strategy according to the total system energy consumption corresponding to each task migration strategy includes:
根据各所述第一任务对应的用户设备终端的传输功率、传输时延以及预设的边缘计算服务器的属性信息,确定边缘计算服务器能耗;Determine the energy consumption of the edge computing server according to the transmission power and transmission delay of the user equipment terminal corresponding to each of the first tasks and the preset attribute information of the edge computing server;
根据第一任务以外的第二任务的计算资源需求及其对应的用户设备终端的执行周期频率,确定所述第二任务对应的各用户设备终端的本地能耗;Determine the local energy consumption of each user equipment terminal corresponding to the second task according to the computing resource requirements of the second task other than the first task and the execution cycle frequency of the corresponding user equipment terminal;
根据所述边缘计算服务器能耗和所述本地能耗,确定各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;According to the energy consumption of the edge computing server and the local energy consumption, determine the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy;
将所述系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,确定为所述目标任务迁移策略。The task migration strategy with the minimum total energy consumption of the system is determined as the target task migration strategy.
可选的,所述根据所述边缘计算服务器能耗和所述本地能耗,确定各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,包括:Optionally, the determining the total system energy consumption corresponding to each task migration strategy according to the energy consumption of the edge computing server and the local energy consumption includes:
根据如下公式确定任一任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗:Determine the total system energy consumption corresponding to any task migration strategy according to the following formula:
其中,Eall表示所述任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,T表示系统总消耗时间,θi表示第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地,其中,当所述第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,θi=1,当所述第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为对应的用户设备终端时,θi=0,表示各第一任务对应的边缘计算服务器能耗,表示各第二任务对应的本地能耗。Wherein, Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy, T represents the total consumption time of the system, and θi represents the execution destination of the i-th task to be migrated, wherein, when the i-th task to be migrated When the execution destination is an edge computing server, θi =1, when the execution destination of the ith task to be migrated is the corresponding user equipment terminal, θi =0, Indicates the energy consumption of the edge computing server corresponding to each first task, Indicates the local energy consumption corresponding to each second task.
可选的,所述根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略,包括:Optionally, the determining the target task migration strategy according to the total system energy consumption corresponding to each task migration strategy includes:
基于如下公式,根据所述系统总能耗计算所述各任务迁移策略的奖励值:Based on the following formula, the reward value of each task migration strategy is calculated according to the total energy consumption of the system:
其中,r表示所述奖励值,telocal表示各待迁移任务的执行目的地为均为对应的用户设备终端时的系统总能耗,Eall表示所述任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;Wherein, r represents the reward value, telocal represents the total energy consumption of the system when the execution destinations of the tasks to be migrated are all corresponding user equipment terminals, and Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy;
将所述奖励值最高的任务迁移策略,确定为所述目标任务迁移策略。The task migration strategy with the highest reward value is determined as the target task migration strategy.
可选的,还包括:Optionally, also include:
根据预设缓存需求,构建等待队列;Build a waiting queue according to preset cache requirements;
根据各第一任务的生成顺序,将所述各第一任务存储至所述等待队列。Store the first tasks in the waiting queue according to the generation order of the first tasks.
可选的,所述预设的约束条件,包括:Optionally, the preset constraints include:
各任务迁移策略的总传输时延小于预设的总传输时延阈值、各用户设备终端的执行周期频率小于预设的执行周期频率阈值和/或各用户设备终端的执行周期数量不大于所述边缘计算服务器的执行周期数量。The total transmission delay of each task migration strategy is less than the preset total transmission delay threshold, the execution cycle frequency of each user equipment terminal is less than the preset execution cycle frequency threshold and/or the number of execution cycles of each user equipment terminal is not greater than the specified The number of execution cycles for the edge computing server.
本申请第二个方面提供一种任务迁移装置,包括:The second aspect of the present application provides a task migration device, including:
获取模块,用于获取多个用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及所述边缘计算服务器可用资源;其中,所述待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求;An acquisition module, configured to acquire task information of tasks to be migrated generated by multiple user equipment terminals, available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and available resources of the edge computing server; wherein, the task information to be migrated Including: computing resource requirements and bandwidth requirements of the tasks to be migrated;
生成模块,用于在预设的约束条件内,根据所述待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及所述边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略;A generating module, configured to generate multiple task migration strategies according to the task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server within preset constraints;
确定模块,用于根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。The determination module is used to determine the target task migration strategy according to the total system energy consumption corresponding to each task migration strategy.
可选的,所述生成模块,具体用于:Optionally, the generating module is specifically used for:
根据所述待迁移任务的带宽需求和各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽,生成所述待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策;其中,所述任务迁移决策包括各待迁移任务的执行目的地,所述执行目的地包括用户设备终端和边缘计算服务器;Generate multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated according to the bandwidth requirements of the tasks to be migrated and the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station; wherein the task migration decisions include the execution of each task to be migrated a destination, the execution destination includes a user equipment terminal and an edge computing server;
当所述待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,确定所述待迁移任务为第一任务;When the execution destination of the task to be migrated is an edge computing server, determine that the task to be migrated is the first task;
获取所述第一任务的服务质量要求,根据所述服务质量要求确定所述第一任务的优先级;Acquire the quality of service requirement of the first task, and determine the priority of the first task according to the quality of service requirement;
根据各第一任务的优先级,确定边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配量;According to the priority of each first task, determine the allocation amount of available resources of the edge computing server;
根据所述待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策,及边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配情况,生成多个任务迁移策略。Multiple task migration strategies are generated according to the multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated and the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server.
可选的,所述确定模块,具体用于:Optionally, the determination module is specifically used for:
根据各所述第一任务对应的用户设备终端的传输功率、传输时延以及预设的边缘计算服务器的属性信息,确定边缘计算服务器能耗;Determine the energy consumption of the edge computing server according to the transmission power and transmission delay of the user equipment terminal corresponding to each of the first tasks and the preset attribute information of the edge computing server;
根据第一任务以外的第二任务的计算资源需求及其对应的用户设备终端的执行周期频率,确定所述第二任务对应的各用户设备终端的本地能耗;Determine the local energy consumption of each user equipment terminal corresponding to the second task according to the computing resource requirements of the second task other than the first task and the execution cycle frequency of the corresponding user equipment terminal;
根据所述边缘计算服务器能耗和所述本地能耗,确定各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;According to the energy consumption of the edge computing server and the local energy consumption, determine the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy;
将所述系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,确定为所述目标任务迁移策略。The task migration strategy with the minimum total energy consumption of the system is determined as the target task migration strategy.
可选的,所述确定模块具体用于:Optionally, the determination module is specifically used for:
根据如下公式确定任一任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗:Determine the total system energy consumption corresponding to any task migration strategy according to the following formula:
其中,Eall表示所述任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,T表示系统总消耗时间,θi表示第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地,其中,当所述第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,θi=1,当所述第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为对应的用户设备终端时,θi=0,表示各第一任务对应的边缘计算服务器能耗,表示各第二任务对应的本地能耗。Wherein, Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy, T represents the total consumption time of the system, and θi represents the execution destination of the i-th task to be migrated, wherein, when the i-th task to be migrated When the execution destination is an edge computing server, θi =1, when the execution destination of the ith task to be migrated is the corresponding user equipment terminal, θi =0, Indicates the energy consumption of the edge computing server corresponding to each first task, Indicates the local energy consumption corresponding to each second task.
可选的,所述确定模块具体还用于:Optionally, the determining module is specifically further configured to:
基于如下公式,根据所述系统总能耗计算所述各任务迁移策略的奖励值:Based on the following formula, the reward value of each task migration strategy is calculated according to the total energy consumption of the system:
其中,r表示所述奖励值,telocal表示各待迁移任务的执行目的地为均为对应的用户设备终端时的系统总能耗,Eall表示所述任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;Wherein, r represents the reward value, telocal represents the total energy consumption of the system when the execution destinations of the tasks to be migrated are all corresponding user equipment terminals, and Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy;
将所述奖励值最高的任务迁移策略,确定为所述目标任务迁移策略。The task migration strategy with the highest reward value is determined as the target task migration strategy.
可选的,所述生成模块,还用于:Optionally, the generating module is also used for:
根据预设缓存需求,构建等待队列;Build a waiting queue according to preset cache requirements;
根据各第一任务的生成顺序,将所述各第一任务存储至所述等待队列。Store the first tasks in the waiting queue according to the generation order of the first tasks.
可选的,所述预设的约束条件,包括:Optionally, the preset constraints include:
各任务迁移策略的总传输时延小于预设的总传输时延阈值、各用户设备终端的执行周期频率小于预设的执行周期频率阈值和/或各用户设备终端的执行周期数量不大于所述边缘计算服务器的执行周期数量。The total transmission delay of each task migration strategy is less than the preset total transmission delay threshold, the execution cycle frequency of each user equipment terminal is less than the preset execution cycle frequency threshold and/or the number of execution cycles of each user equipment terminal is not greater than the specified The number of execution cycles for the edge computing server.
本申请第三个方面提供一种电子设备,包括:至少一个处理器和存储器;A third aspect of the present application provides an electronic device, including: at least one processor and a memory;
所述存储器存储计算机执行指令;the memory stores computer-executable instructions;
所述至少一个处理器执行所述存储器存储的计算机执行指令,使得所述至少一个处理器执行如上第一个方面以及第一个方面各种可能的设计所述的方法。The at least one processor executes the computer-executed instructions stored in the memory, so that the at least one processor executes the method described in the above first aspect and various possible designs of the first aspect.
本申请第四个方面提供一种计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机可读存储介质中存储有计算机执行指令,当处理器执行所述计算机执行指令时,实现如上第一个方面以及第一个方面各种可能的设计所述的方法。The fourth aspect of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, the computer-readable storage medium stores computer-executable instructions, and when the processor executes the computer-executable instructions, the above first aspect and the first Aspects of various possible designs of the described method.
本申请技术方案,具有如下优点:The technical solution of the present application has the following advantages:
本申请提供的任务迁移方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质,通过获取多个用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源;其中,待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求;在预设的约束条件内,根据待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略;根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。上述方案提供的任务迁移方法,通过对多种可实现的任务迁移策略的系统总能耗进行预估,以筛选出系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,避免了移动边缘计算系统能耗超标的风险,提高了移动边缘计算系统的可靠性,为提高移动边缘计算系统的任务处理效率奠定了基础。The task migration method, device, electronic device, and storage medium provided by the present application obtain the task information to be migrated generated by multiple user equipment terminals, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server; wherein, The task information to be migrated includes: computing resource requirements and bandwidth requirements of the task to be migrated; within preset constraints, according to the task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server, generate Multiple task migration strategies; determine the target task migration strategy according to the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy. The task migration method provided by the above solution estimates the total system energy consumption of various achievable task migration strategies to screen out the task migration strategy with the smallest total system energy consumption, avoiding the problem of excessive energy consumption of the mobile edge computing system. Risk, improves the reliability of the mobile edge computing system, and lays the foundation for improving the task processing efficiency of the mobile edge computing system.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本申请实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作一简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图是本申请的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application or the prior art, the following will briefly introduce the drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description These are some embodiments of the present application, and those skilled in the art can also obtain other drawings according to these drawings.
图1为本申请实施例基于的移动边缘计算系统的网络结构示意图;FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a network structure of a mobile edge computing system based on an embodiment of the present application;
图2为本申请实施例提供的任务迁移方法的流程示意图;FIG. 2 is a schematic flowchart of a task migration method provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图3为本申请实施例提供的任务迁移装置的结构示意图;FIG. 3 is a schematic structural diagram of a task migration device provided in an embodiment of the present application;
图4为本申请实施例提供的电子设备的结构示意图。FIG. 4 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present application.
通过上述附图,已示出本申请明确的实施例,后文中将有更详细的描述。这些附图和文字描述并不是为了通过任何方式限制本公开构思的范围,而是通过参考特定实施例为本领域技术人员说明本申请的概念。By means of the above drawings, specific embodiments of the present application have been shown, which will be described in more detail hereinafter. These drawings and written description are not intended to limit the scope of the disclosed concept in any way, but to illustrate the concept of the application for those skilled in the art by referring to specific embodiments.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本申请实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本申请实施例中的附图,对本申请实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本申请一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本申请中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有作出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本申请保护的范围。In order to make the purposes, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present application clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the drawings in the embodiments of the present application. Obviously, the described embodiments It is a part of the embodiments of this application, not all of them. Based on the embodiments in this application, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of this application.
首先对本申请所涉及的名词进行解释:First, the nouns involved in this application are explained:
任务迁移决策:具体是指待迁移任务是迁移至边缘计算服务器来执行,还是在本地(用户设备终端)执行,即待迁移任务的执行目的地。Task migration decision: specifically refers to whether the task to be migrated is migrated to the edge computing server for execution, or executed locally (user equipment terminal), that is, the execution destination of the task to be migrated.
任务调度决策:是指针对执行目的地为边缘计算服务的第一任务,边缘计算服务器的可用资源的分配情况。Task scheduling decision: refers to the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server for the first task whose execution destination is the edge computing service.
任务迁移策略:包括任务迁移决策和任务调度决策。Task migration strategy: including task migration decision and task scheduling decision.
此外,术语“第一”、“第二”等仅用于描述目的,而不能理解为指示或暗示相对重要性或者隐含指明所指示的技术特征的数量。在以下各实施例的描述中,“多个”的含义是两个以上,除非另有明确具体的限定。In addition, the terms "first", "second", etc. are used for descriptive purposes only, and should not be understood as indicating or implying relative importance or implicitly specifying the quantity of the indicated technical features. In the descriptions of the following embodiments, "plurality" means two or more, unless otherwise specifically defined.
在现有技术中,移动边缘计算系统通常是根据固定的任务迁移规则进行任务迁移,比如根据用户设备终端的迁移选择、发射功率、任务的大小、截止时间、用户设备终端的计算资源和边缘计算服务器的计算资源等因素,确定任务迁移策略。但是,由于用户设备终端多种多样,若仅根据固定的任务迁移规则对各用户设备终端所产生的任务进行任务迁移,则存在部分低时延高可靠的任务无法及时处理,造成移动边缘计算系统的时延及能耗超标等风险。用户设备终端针对上述问题,本申请实施例提供的任务迁移方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质,通过获取多个用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源;其中,待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求;在预设的约束条件内,根据待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略;根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。上述方案提供的任务迁移方法,通过对多种可实现的任务迁移策略的系统总能耗进行预估,以筛选出系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,避免了移动边缘计算系统能耗超标的风险,提高了移动边缘计算系统的可靠性,为提高移动边缘计算系统的任务处理效率奠定了基础。In the prior art, the mobile edge computing system usually performs task migration according to fixed task migration rules, such as user equipment terminal migration selection, transmit power, task size, deadline, user equipment terminal computing resources and edge computing Factors such as the computing resources of the server determine the task migration strategy. However, due to the variety of user equipment terminals, if the tasks generated by each user equipment terminal are only migrated according to the fixed task migration rules, some low-latency and high-reliability tasks cannot be processed in time, causing the mobile edge computing system Risks such as time delay and excessive energy consumption. For the user equipment terminal to address the above problems, the task migration method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium provided in the embodiments of the present application obtain the task information to be migrated generated by multiple user equipment terminals, and the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station. and the available resources of the edge computing server; wherein, the task information to be migrated includes: computing resource requirements and bandwidth requirements of the task to be migrated; within preset constraints, according to the task information to be migrated, the available Multiple task migration strategies are generated based on the bandwidth and available resources of the edge computing server; the target task migration strategy is determined according to the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy. The task migration method provided by the above solution estimates the total system energy consumption of various achievable task migration strategies to screen out the task migration strategy with the smallest total system energy consumption, avoiding the problem of excessive energy consumption of the mobile edge computing system. Risk, improves the reliability of the mobile edge computing system, and lays the foundation for improving the task processing efficiency of the mobile edge computing system.
下面这几个具体的实施例可以相互结合,对于相同或相似的概念或过程可能在某些实施例中不再赘述。下面将结合附图,对本发明实施例进行描述。The following specific embodiments may be combined with each other, and the same or similar concepts or processes may not be repeated in some embodiments. Embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
首先,对本申请所基于的移动边缘计算系统的网络结构进行说明:First, the network structure of the mobile edge computing system on which this application is based is described:
本申请实施例提供的任务迁移方法、装置、电子设备及存储介质,适用于确定系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,以解决现有技术中的任务迁移方法所确定的任务迁移策略可能导致移动边缘计算系统的能耗超标等缺陷。如图1所示,为本申请实施例基于的移动边缘计算系统的网络结构示意图,主要包括多个用户设备终端、边缘计算服务器、基站和用于进行任务迁移的电子设备。具体地,各用户设备终端在生成待迁移任务后,在通过基站将所生成的待迁移任务发送至边缘计算服务器之前,先将这些待迁移任务对应的待迁移任务信息发送至电子设备,电子设备根据所到的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,确定目标任务迁移策略。The task migration method, device, electronic equipment, and storage medium provided in the embodiments of the present application are suitable for determining the task migration strategy with the minimum total energy consumption of the system, so as to solve the problem that the task migration strategy determined by the task migration method in the prior art may cause the The energy consumption of the edge computing system exceeds the standard and other defects. As shown in FIG. 1 , it is a schematic diagram of the network structure of the mobile edge computing system based on the embodiment of the present application, which mainly includes multiple user equipment terminals, edge computing servers, base stations, and electronic devices for task migration. Specifically, after each user equipment terminal generates tasks to be migrated, before sending the generated tasks to be migrated to the edge computing server through the base station, it first sends the task information to be migrated corresponding to these tasks to be migrated to the electronic device, and the electronic device According to the received task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server, the target task migration strategy is determined.
本申请实施例提供了一种任务迁移方法,用于确定系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略。本申请实施例的执行主体为电子设备,比如服务器、台式电脑、笔记本电脑、平板电脑及其他可用于进行任务迁移的电子设备。An embodiment of the present application provides a task migration method, which is used to determine a task migration strategy with the minimum total energy consumption of the system. The execution subject of the embodiment of the present application is an electronic device, such as a server, a desktop computer, a notebook computer, a tablet computer, and other electronic devices that can be used for task migration.
如图2所示,为本申请实施例提供的任务迁移方法的流程示意图,该方法包括:As shown in Figure 2, it is a schematic flow chart of the task migration method provided in the embodiment of the present application, the method includes:
步骤201,获取多个用户设备终端生成待迁移任务的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源。
其中,待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求。Wherein, the task information to be migrated includes: computing resource requirements and bandwidth requirements of the task to be migrated.
需要解释的是,计算资源需求是指该任务执行时需要消耗的计算资源,带宽需求是指该任务通过基站传输至边缘计算服务器时所需要的带宽。It should be explained that the computing resource requirement refers to the computing resources that need to be consumed when the task is executed, and the bandwidth requirement refers to the bandwidth required when the task is transmitted to the edge computing server through the base station.
步骤202,在预设的约束条件内,根据待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略。Step 202: Within preset constraints, multiple task migration strategies are generated according to the task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server.
其中,预设的约束条件可以是各任务迁移策略的总传输时延小于预设的总传输时延阈值、各用户设备终端的执行周期频率小于预设的执行周期频率阈值和/或各用户设备终端的执行周期数量不大于边缘计算服务器的执行周期数量。Among them, the preset constraint conditions may be that the total transmission delay of each task migration strategy is less than the preset total transmission delay threshold, the execution cycle frequency of each user equipment terminal is less than the preset execution cycle frequency threshold and/or each user equipment The number of execution cycles of the terminal is not greater than the number of execution cycles of the edge computing server.
类似的,预设的约束条件也包括基站带宽的分配比例在预设的分配比例范围内以及等待队列稳定可靠等,约束条件具体可以根据实际情况进行设定和组合,本申请实施例不做限定。Similarly, the preset constraint conditions also include that the allocation ratio of the base station bandwidth is within the preset allocation ratio range and the waiting queue is stable and reliable, etc. The specific constraints can be set and combined according to the actual situation, and are not limited in the embodiment of this application. .
具体地,任务迁移策略包括各待迁移任务的执行目的地,以及当执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配情况。Specifically, the task migration policy includes the execution destination of each task to be migrated, and when the execution destination is the edge computing server, the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server.
步骤203,根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。Step 203: Determine the target task migration strategy according to the total system energy consumption corresponding to each task migration strategy.
具体地,系统总能耗是边缘计算服务器能耗与本地能耗之和,具体是将系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略确定为目标任务迁移策略。Specifically, the total energy consumption of the system is the sum of the energy consumption of the edge computing server and the local energy consumption. Specifically, the task migration strategy with the smallest total energy consumption of the system is determined as the target task migration strategy.
在上述实施例的基础上,为了提高所生成的各任务迁移策略的可靠性,作为一种可实施的方式,在上述实施例的基础上,在一实施例中,根据待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略(步骤202),包括:On the basis of the above embodiments, in order to improve the reliability of the generated task migration strategies, as an implementable manner, on the basis of the above embodiments, in one embodiment, according to the task information to be migrated, each The available bandwidth between the user equipment terminal and the base station and the available resources of the edge computing server generate multiple task migration strategies (step 202), including:
步骤2021,根据待迁移任务的带宽需求和各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽,生成待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策;其中,任务迁移决策包括各待迁移任务的执行目的地,执行目的地包括用户设备终端和边缘计算服务器;Step 2021: Generate a plurality of task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated according to the bandwidth requirements of the tasks to be migrated and the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station; wherein, the task migration decisions include the execution destinations of the tasks to be migrated, Execution destinations include user equipment terminals and edge computing servers;
步骤2022,当待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,确定待迁移任务为第一任务;Step 2022, when the execution destination of the task to be migrated is the edge computing server, determine that the task to be migrated is the first task;
步骤2023,获取第一任务的服务质量要求,根据服务质量要求确定第一任务的优先级;Step 2023, obtaining the service quality requirement of the first task, and determining the priority of the first task according to the service quality requirement;
步骤2024,根据各第一任务的优先级,确定边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配量;Step 2024, according to the priority of each first task, determine the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server;
步骤2025,根据待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策,及边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配情况,生成多个任务迁移策略。Step 2025, generating multiple task migration strategies according to the multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated and the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server.
具体地,对于各待迁移任务的执行目的地是否可以为边缘计算服务器,重点需要考虑各用户设备终端与基站之间的带宽是否可以满足带宽需求,只有在满足带宽需求的情况下,该用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务才可以传输至边缘计算服务器,并进一步基于边缘计算服务器来执行。Specifically, for whether the execution destination of each task to be migrated can be an edge computing server, it is important to consider whether the bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station can meet the bandwidth requirement. Only when the bandwidth requirement is met, the user equipment The to-be-migrated tasks generated by the terminal can be transmitted to the edge computing server, and further executed based on the edge computing server.
需要解释的是,第一任务的服务质量要求可以包括该第一任务对应的任务处理时限和可靠性要求。It should be explained that the QoS requirement of the first task may include a task processing time limit and reliability requirement corresponding to the first task.
具体地,可以基于如下公式计算各第一任务的优先级:Specifically, the priority of each first task may be calculated based on the following formula:
Priority=α×Time+β×ReliabilityPriority=α×Time+β×Reliability
其中,Priority表示该第一任务对应的优先级;Time表示任务处理时限,也称任务处理事件的最大容忍值;Reliability表示可靠性要求,具体是指对边缘计算服务器的可靠性要求;α和β分别表示二者的系数值,其中,α+β=1,具体表示移动边缘计算系统对这两个属性考虑的侧重比例。其中,任务优先级是指该任务在移动边缘计算系统中任务的优先级值,优先级高的任务还会优先迁移并获得更多的无线资源带宽。Among them, Priority indicates the priority corresponding to the first task; Time indicates the task processing time limit, also known as the maximum tolerance value of task processing events; Reliability indicates reliability requirements, specifically referring to the reliability requirements for edge computing servers; α and β respectively represent the coefficient values of the two, where α+β=1, which specifically represents the emphasis ratio that the mobile edge computing system considers on these two attributes. Wherein, the task priority refers to the priority value of the task in the mobile edge computing system, and tasks with higher priority will be migrated first and obtain more wireless resource bandwidth.
相应的,在一实施例中,可以根据各第一任务对应的用户设备终端的传输功率、传输时延以及预设的边缘计算服务器的属性信息,确定边缘计算服务器能耗;根据第一任务以外的第二任务的计算资源需求及其对应的用户设备终端的执行周期频率,确定第二任务对应的各用户设备终端的本地能耗;根据边缘计算服务器能耗和本地能耗,确定各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;将系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,确定为目标任务迁移策略。Correspondingly, in an embodiment, the energy consumption of the edge computing server can be determined according to the transmission power and transmission delay of the user equipment terminal corresponding to each first task, and the attribute information of the preset edge computing server; According to the computing resource requirements of the second task and the execution cycle frequency of the corresponding user equipment terminal, determine the local energy consumption of each user equipment terminal corresponding to the second task; determine the migration of each task according to the energy consumption of the edge computing server and the local energy consumption The total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the strategy; the task migration strategy with the minimum total energy consumption of the system is determined as the target task migration strategy.
需要解释的是,针对上述第一任务,当第i个用户设备迁移第一任务Ai(t)到达边缘计算服务器时,整个迁移过程通常分为三个步骤。步骤1:第i个用户设备终端上传第一任务Ai(t)的输入数据,通过无线专网向基站转发数据,基站将数据转发给边缘计算服务器。步骤2:任务Ai(t)进入等待队列,等待边缘计算服务器分配计算资源来执行计算任务。步骤3:边缘计算服务器把处理后的任务返回给第i个用户设备终端。对于迁移计算的最后一步,所需的时间是处理结果的返回时延,表示为tdown。但是在现有技术中,下载数据速率一般都很高,任务处理结果的数据大小比输入数据小得多,因此在本申请实施例中可以忽略这步骤3的时延。It should be explained that, for the first task above, when the i-th user equipment migrates the first task Ai (t) to the edge computing server, the whole migration process is generally divided into three steps. Step 1: The i-th user equipment terminal uploads the input data of the first task Ai (t), forwards the data to the base station through the wireless private network, and the base station forwards the data to the edge computing server. Step 2: The task Ai (t) enters the waiting queue, waiting for the edge computing server to allocate computing resources to execute the computing task. Step 3: The edge computing server returns the processed task to the i-th user equipment terminal. For the last step of the migration calculation, the required time is the return delay of the processing result, denoted as tdown . However, in the prior art, the download data rate is generally very high, and the data size of the task processing result is much smaller than the input data, so the delay in step 3 can be ignored in the embodiment of the present application.
具体地,如果多个用户设备终端在时隙τ内选择将第一任务迁移至边缘计算服务器,则带宽将依据各第一任务的优先级排序结果按比例分配给边缘汇总段设备用于上传数据。传输速率的表达还必须加上极端延迟和传输可靠性要求。本申请实施例考虑了传输出错率的影响,不同于经典香农公式。在时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端产生的第一任务为Ai(t)迁移到边缘服务器的传输速率可表示为:Specifically, if multiple user equipment terminals choose to migrate the first task to the edge computing server within the time slot τ, the bandwidth will be proportionally allocated to the edge summary device for uploading data according to the priority ranking results of each first task . The expression of transmission rate must also add extreme delay and transmission reliability requirements. The embodiment of the present application considers the influence of the transmission error rate, which is different from the classic Shannon formula. In the time slot τ, the first task generated by the i-th user equipment terminal is Ai (t) migrating to the edge server. The transmission rate can be expressed as:
vi(t)=γi(t)·BW·(log2(1+δi(t))-ψ)vi (t) = γi (t) BW (log2 (1+δi (t))-ψ)
其中,vi(t)表示传输速率,BW表示该第一任务分配到的带宽,δi(t)表示该用户设备终端与边缘计算服务器之间的信道参数变量,γi(t)为时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端产生的任务为Ai(t)迁移到边缘计算服务器过程中所分配到的带宽比例,ψ表示信道的可靠性。Among them, vi (t) represents the transmission rate, BW represents the bandwidth allocated to the first task, δi (t) represents the channel parameter variable between the user equipment terminal and the edge computing server, γi (t) is The task generated by the i-th user equipment terminal in slot τ is the proportion of bandwidth allocated during the migration of Ai (t) to the edge computing server, and ψ represents the reliability of the channel.
需要解释的是,δi(t)具体可以表示为:What needs to be explained is that δi (t) can be specifically expressed as:
其中,ptx为时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端用于迁移第一任务Ai(t)到边缘服务器的传输功率,g0为时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端用于迁移第一任务Ai(t)到边缘服务器过程的信道增益,N0为时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端用于迁移第一任务Ai(t)到边缘计算服务器过程的加性高斯信道噪声功率。Among them, ptx is the transmission power of the i-th user equipment terminal in time slot τ for migrating the first task Ai (t) to the edge server, g0 is the i-th user equipment terminal in time slot τ for migrating the first task A i (t) to the edge server The channel gain of a task Ai (t) to the edge server process, N0 is the additive Gaussian channel noise of the i-th user equipment terminal in time slot τ for migrating the first task Ai (t) to the edge computing server process power.
需要进一步解释的是,γi(t)的值受优先级影响,可以表示为:What needs further explanation is that the value of γi (t) is affected by the priority, which can be expressed as:
其中,0≤γi(t)≤1,且∑i∈Nγi(t)=1,Pr,i(t)表示该第一任务Ai(t)对应的优先级。θi(t)=0或1,对于执行目的地为边缘计算服务器的第一任务Ai(t),θi(t)=1,反之等于0。Wherein, 0≤γi (t)≤1, and Σi∈N γi (t)=1, Pr,i (t) represents the priority corresponding to the first task Ai (t). θi (t)=0 or 1, for the first task Ai (t) whose execution destination is the edge computing server, θi (t)=1, otherwise equal to 0.
需要进一步解释的是,ψ具体可表示为:What needs further explanation is that ψ can be specifically expressed as:
其中,Vτ为信道色散,可近似为1,它表明信道相对于相同容量的确定性信道的随机变化。Q-1(·)表示高斯Q函数的逆,εi(t)表示在时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端产生的第一任务Ai(t)迁移到边缘计算服务器时的传输出错率。Among them, Vτ is the channel dispersion, which can be approximated as 1, which indicates the random variation of the channel relative to the deterministic channel of the same capacity. Q-1 ( ) represents the inverse of the Gaussian Q function, εi (t) represents the transmission error rate when the first task Ai (t) generated by the i-th user equipment terminal in the time slot τ is migrated to the edge computing server .
具体地,在步骤1中第一任务Ai(t)从边缘汇终端设备迁移到边缘计算服务器产生传输时延为tup,当边缘计算服务器执行一项任务的时候,假定占据了所有的可用资源,则表达式如下:Specifically, in step 1, the first task Ai (t) migrates from the edge sink terminal device to the edge computing server, and the transmission delay is tup . When the edge computing server executes a task, it is assumed that all available resources, the expression is as follows:
其中,bi(t)表示需要执行的第一任务Ai(t)的数据量大小,vi(t)表示第i个用户设备终端产生的第一任务为Ai(t)迁移到边缘服务器的传输速率。Among them, bi (t) represents the data size of the first task Ai (t) that needs to be executed, and vi (t) represents the first task generated by the i-th user equipment terminal is Ai (t) migrated to the edge The transfer rate of the server.
针对上述步骤2,由于边缘计算服务器可用资源受限,所有第一任务不能同时被处理,到达且未被处理的第一任务进入等待队列。假设边缘计算服务器中有所需的时间是边缘计算服务器的计算延迟texe和第一任务在等待队列中的平均等待时间边缘计算服务器的计算延迟texe可以表示为:For the above step 2, due to the limited resources available on the edge computing server, all first tasks cannot be processed at the same time, and the first tasks that arrive and have not been processed enter the waiting queue. Assuming that the edge computing server has the required time is the computing delaytexe of the edge computing server and the average waiting time of the first task in the waiting queue The calculation delaytexe of the edge computing server can be expressed as:
其中,di(t)表示待迁移任务(第一任务)在本地(对应的用户设备终端)执行时所需的计算资源,即待迁移任务的计算资源需求,fs,i(t)表示第一任务Ai(t)在边缘计算服务器中所分配到的可用资源的分配量。Among them, di (t) represents the computing resources required when the task to be migrated (the first task) is executed locally (corresponding to the user equipment terminal), that is, the computing resource requirement of the task to be migrated, fs, i (t) represents An allocation amount of available resources allocated to the first task Ai (t) in the edge computing server.
需要解释的是,根据现有技术中的Little定律,每个用户设备终端的任务Ai(t)所经历的平均等待时间与其在边缘计算服务器中任务缓存区(等待队列)的平均队列长度成正比。因此,每个用户设备终端的任务缓冲区的平均队列长度被用作执行延迟的度量之一,具体可以被表示为:What needs to be explained is that according to Little’s law in the prior art, the average waiting time experienced by each user equipment terminal task Ai (t) is proportional to the average queue length of the task buffer (waiting queue) in the edge computing server. Proportional. Therefore, the average queue length of the task buffer of each user equipment terminal is used as one of the measures of execution delay, which can be expressed as:
其中,表示第i个用户设备终端所生成的第一任务Ai(t)的平均等待时间,E[Qi(t)]表示等待队列的队列长度对应的期望值。in, represents the average waiting time of the first task Ai (t) generated by the i-th user equipment terminal, and E[Qi (t)] represents the expected value corresponding to the queue length of the waiting queue.
具体地,在本申请实施例中表示第i个用户设备终端的第一任务Ai(t)迁移到边缘计算服务器的整个过程的时延,即传输时延,具体可表示为:Specifically, in the embodiment of this application Indicates the delay of the entire process of migrating the first task Ai (t) of the i-th user equipment terminal to the edge computing server, that is, the transmission delay, which can be specifically expressed as:
具体地,在本申请实施例中用表示时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端的第一任务Ai(t)迁移到边缘计算服务器的整个计算过程中的产生的能耗,其主要发生在数据传输和任务处理过程中,表达式如下:Specifically, in the embodiment of this application, use Indicates the energy consumption during the entire calculation process of the first task Ai (t) of the i-th user equipment terminal migrating to the edge computing server in the time slot τ, which mainly occurs during data transmission and task processing, the expression as follows:
其中,κser表示边缘计算服务器中的CPU核心的有效切换电容,它与芯片体系结构有关,即κser为预设的边缘计算服务器的属性信息。Among them, κser represents the effective switching capacitance of the CPU core in the edge computing server, which is related to the chip architecture, that is, κser is the attribute information of the preset edge computing server.
进一步的,针对上述第二业务,第i个用户设备终端的CPU计算周期频率(执行周期频率)为fil,不能超过其最大值用集合表示本地CPU计算周期频率,假设边缘计算服务器的计算速度比本地CPU最大计算速度快得多,因此第二任务在本地CPU完成的时延就是任务的计算时间。在本申请实施例中用表示任务Ai(t)在本地的时延,表达式如下:Further, for the above-mentioned second service, the CPU calculation cycle frequency (execution cycle frequency) of the i-th user equipment terminal is fil and cannot exceed its maximum value use collection Indicates the calculation cycle frequency of the local CPU. It is assumed that the calculation speed of the edge computing server is much faster than the maximum calculation speed of the local CPU, so the delay for the second task to be completed by the local CPU is the calculation time of the task. In the embodiment of this application, use Indicates the local delay of task Ai (t), the expression is as follows:
其中,di(t)表示待迁移任务(第二任务)在本地执行时所需的计算资源。Wherein, di (t) represents the computing resource required when the task to be migrated (the second task) is executed locally.
进一步的,第i个用户设备终端的本地能耗可以根据如下公式进行计算:Further, the local energy consumption of the i-th user equipment terminal can be calculated according to the following formula:
其中,是指完成该第二任务的每个CPU计算周期(执行周期)的能源消耗。in, Refers to the energy consumption of each CPU calculation cycle (execution cycle) for completing the second task.
具体地,在一实施例中,可以根据如下公式确定任一任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗:Specifically, in an embodiment, the total system energy consumption corresponding to any task migration strategy can be determined according to the following formula:
其中,Eall表示任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,T表示系统总消耗时间,θi表示第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地,其中,当第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,θi=1,当第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为对应的用户设备终端时,θi=0,表示各第一任务对应的边缘计算服务器能耗,表示各第二任务对应的本地能耗。Among them, Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy, T represents the total consumption time of the system, θi represents the execution destination of the i-th task to be migrated, where, when the execution destination of the i-th task to be migrated is For the edge computing server, θi =1, when the execution destination of the ith task to be migrated is the corresponding user equipment terminal, θi =0, Indicates the energy consumption of the edge computing server corresponding to each first task, Indicates the local energy consumption corresponding to each second task.
具体地,在一实施例中,为了提高对待迁移任务的管理效率,可以根据预设缓存需求,构建等待队列;根据各第一任务的生成顺序,将各第一任务存储至等待队列。Specifically, in one embodiment, in order to improve the management efficiency of the tasks to be migrated, a waiting queue may be constructed according to preset cache requirements; and each first task may be stored in the waiting queue according to the order in which the first tasks are generated.
具体地,可以根据边缘计算服务器的预设缓存需求,构建等待队列。Specifically, a waiting queue can be constructed according to the preset cache requirements of the edge computing server.
示例性的,对于每个时隙τ内,第i个用户设备终端产生的任务,移到边缘计算服务器的任务。假设Qi(t)是时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端在边缘计算服务器中的队列长度,它被假定具有足够大的容量。Ci(t)表示边缘计算服务器在时隙τ内任务调度决策,即在时隙τ内的第i个用户设备终端在边缘计算节点中正在被处理的任务数目。通过在时隙τ内的队列长度Qi(t)、卸载到达的任务Bi(t)以及任务调度决策Ci(t),可以推导出下一个时隙τ的队列长度Qi(t+1),其表达式为:Exemplarily, for each time slot τ, the task generated by the i-th user equipment terminal is moved to the task of the edge computing server. Suppose Qi (t) is the queue length of the i-th user equipment terminal in the edge computing server within the time slot τ, which is assumed to have a large enough capacity. Ci (t) represents the task scheduling decision of the edge computing server in the time slot τ, that is, the number of tasks being processed by the i-th user equipment terminal in the time slot τ in the edge computing node. According to the queue length Qi (t) in the time slot τ, the task Bi (t) that unloads and arrives, and the task scheduling decision Ci (t), the queue length Qi (t+ 1), whose expression is:
Qi(t+1)=max{Qi(t)-Ci(t),0}+Bi(t) t∈{0,1,2,...}Qi (t+1)=max{Qi (t)-Ci (t), 0}+Bi (t) t∈{0, 1, 2,...}
其中,假设任务缓存区最初是空的,即Qi(0)=0,i∈N。边缘计算服务器的计算节点的计算资源可以分配给从不同的用户设备终端迁移过来的第一任务,因此边缘计算服务器调度决策应满足以下条件:Wherein, it is assumed that the task buffer area is initially empty, that is, Qi (0)=0, i∈N. The computing resources of the computing nodes of the edge computing server can be allocated to the first task migrated from different user equipment terminals, so the scheduling decision of the edge computing server should meet the following conditions:
∑i∈NCi(t)·bi(t)·≤Fser·τ (4)∑i∈N Ci (t) bi (t) ≤ Fser τ (4)
这意味着完成目标任务迁移策略的所需的用户设备终端的执行周期数不应大于边缘计算服务器的执行周期。This means that the execution cycles of the user equipment terminal required to complete the target task migration strategy should not be greater than the execution cycles of the edge computing server.
其中,当时隙τ内第i个用户设备在边缘服务器中正在被处理的任务集,其所分配到的边缘计算服务器可用资源同样将依据各第一任务的优先级值排序按比例分配,相同优先级的第一任务在时隙τ内第i个用户设备终端在边缘计算服务器中正在被处理的第一任务所分配到的计算资源为fs,i(t),表达式如下:Among them, when the task set of the i-th user equipment in the time slot τ is being processed in the edge server, the available resources of the edge computing server allocated to it will also be allocated in proportion according to the priority values of the first tasks, and the same priority The computing resource assigned to the first task of the i-th user equipment terminal being processed in the edge computing server in the time slot τ by the first task of the stage is fs, i (t), and the expression is as follows:
其中,Fser表示边缘计算服务器可用资源。Among them, Fser represents the available resources of the edge computing server.
具体地,在一实施例中,为了进一步提高任务迁移效率和移动边缘计算系统的任务处理效率。可以采用DQN算法、WoLF-PHC算法和A3C算法等机器学习算法实现上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法,具体本申请实施例不做限定。Specifically, in an embodiment, in order to further improve task migration efficiency and task processing efficiency of the mobile edge computing system. Machine learning algorithms such as the DQN algorithm, the WoLF-PHC algorithm, and the A3C algorithm may be used to implement the task migration method provided in the above embodiment, which is not limited in this specific embodiment of the present application.
具体地,在一实施例中,为了可以适应多种机器学习算法,并进一步提高任务迁移效率,可以基于如下公式,根据系统总能耗计算各任务迁移策略的奖励值:Specifically, in one embodiment, in order to adapt to various machine learning algorithms and further improve task migration efficiency, the reward value of each task migration strategy can be calculated according to the total energy consumption of the system based on the following formula:
其中,r表示奖励值,telocal表示各待迁移任务的执行目的地为均为对应的用户设备终端时的系统总能耗,Eall表示任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;将奖励值最高的任务迁移策略,确定为目标任务迁移策略。Among them, r represents the reward value, telocal represents the total energy consumption of the system when the execution destinations of the tasks to be migrated are all corresponding user equipment terminals, Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy; the highest reward value The task migration strategy of is determined as the target task migration strategy.
具体地,可以基于各机器学习算法构建具有深度学习能力的任务迁移模型,其中该任务迁移的模型的三要素分别为状态、动作和回报。其中,状态应包含各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源。动作具体可以包括任务迁移决策Λ(t)以及任务迁移策略C(t)对应的决策向量。例如分别有N个用户设备终端的任务迁移决策向量和任务调度决策向量因此,动作向量(任务迁移策略)可以用任务迁移决策向量和任务调度决策向量的集合[θ1,θ2…,θN,c1,c2…,cN]来表示。其中,回报是指对于每一步迭代,代理环境在执行每一个可能的动作后,都会使状态发生改变,进而得到一个奖励值。一般来说,奖励功能应该与期待功能有关。本申请实施例所提供的任务迁移方法优化问题的目标是获得最小的系统总能耗,而机器学习的目标是获得最大长远回报,因此奖励值应该与系统总能耗的大小呈负相关。Specifically, a task migration model with deep learning capabilities can be constructed based on various machine learning algorithms, where the three elements of the task migration model are state, action, and reward. Wherein, the state should include the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station and the available resources of the edge computing server. The action may specifically include a task migration decision Λ(t) and a decision vector corresponding to the task migration strategy C(t). For example, there are task migration decision vectors of N user equipment terminals respectively and task scheduling decision vector Therefore, the action vector (task migration strategy) can be expressed by the set of task migration decision vector and task scheduling decision vector [θ1 , θ2 ..., θN , c1 , c2 ..., cN ]. Among them, the reward means that for each iteration step, the agent environment will change the state after executing every possible action, and then get a reward value. In general, the reward function should be related to the expectancy function. The goal of the optimization problem of the task migration method provided by the embodiment of this application is to obtain the minimum total energy consumption of the system, while the goal of machine learning is to obtain the maximum long-term return, so the reward value should be negatively correlated with the total system energy consumption.
在实际应用中,如果有越来越多的用户设备终端设备,则动作空间将迅速增加,为了限制动作空间的大小,我们在机器学习过程之前提出了一个预处理步骤。对于用户设备终端,如果即在本地执行将不能满足延迟阈值要求,只能将这个待迁移任务上传至边缘计算服务器执行,可以直接得到这个待迁移任务对应的θi固定为1,并且分配的边缘计算资源应满足预设的约束,这样就可以减少动作的可能值,以限制强化学习代理的决策空间,从而提高任务迁移效率。In practical applications, if there are more and more user equipment terminal devices, the action space will increase rapidly, in order to limit the size of the action space, we propose a preprocessing step before the machine learning process. For user equipment terminals, if That is, local execution will not be able to meet the delay threshold requirements, and the task to be migrated can only be uploaded to the edge computing server for execution. It can be directly obtained that θi corresponding to the task to be migrated is fixed at 1, and the allocated edge computing resources should meet the preset , so that the possible values of actions can be reduced to limit the decision space of the reinforcement learning agent, thus improving the task transfer efficiency.
示例性的,当采用DQN算法实现上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法时,将所有的Q值存储在Q表中,矩阵Q(s,a)将非常大,尤其在本环境下,状态空间是三维的,用户设备终端的数目同样需要一个维度,还包括了三大类决策,Q表的维度已经到达一定的高度了。因此很难获得足够的样本来遍历每个状态,这将导致算法效率不够,也就是Q-learning的维度灾难,因此,相比Q-learning算法而言,DQN不再通过存储完整的Q表来决策,而是利用神经网络,来估计Q(s,a)。Exemplarily, when using the DQN algorithm to implement the task migration method provided by the above embodiment, all Q values are stored in the Q table, and the matrix Q(s, a) will be very large, especially in this environment, the state space is In three dimensions, the number of user equipment terminals also requires a dimension, which also includes three types of decision-making. The dimension of the Q table has reached a certain height. Therefore, it is difficult to obtain enough samples to traverse each state, which will lead to insufficient algorithm efficiency, that is, the dimension disaster of Q-learning. Therefore, compared with the Q-learning algorithm, DQN no longer stores the complete Q table. decision, but use neural networks to estimate Q(s, a).
具体的DQN算法流程如下:存储一定的(st,at,rt+1,st+1)经验池,其中,st是当前状态,at是在st状态下进行的动作,st+1是在at动作下到达的下一个状态,rt+1是st状态到st+1状态时,环境给予的奖励经验池中采样一个小批量batch,st、st+1放进网络,在a下的状态-动作值函数与st+1,st+1下的maxQ(st+1)=next_qvalue,计算期望决策的动作值函数,如下式所示:The specific DQN algorithm process is as follows: store a certain (st , at , rt+1 , st+1 ) experience pool, where st is the current state, at is the action performed in the state of st , st+1 is the next state reached under the at action, rt+1 is when the st state reaches the st+1 state, a small batch is sampled in the reward experience pool given by the environment, st , st +1 into the network, the state-action value function under a and st+1 , maxQ(stt +1)=next_qvalue under st+1 , calculate the action value function of the desired decision, as shown in the following formula:
expect_qvalue=reward+γ*next_qvalue,Loss=Lossfunction(qvalue,expected_qvalue),这里损失选择范数损失,即平方损失。本申请实施例提供的模型考虑的一个多用户,两大类的决策:任务迁移决策向量和任务调度决策向量对于每一个决策θ都有两种决策,因为θi∈{0,1}。同理,对于每一个任务调度决策,可以将它离散化,即ci∈{0,1,2,3}。于是在NN的输出层节点数应该等于节点数目*2+节点数目*4,每个节点代表某一个用户设备终端的任务迁移决策的最大长期奖励。这里可以采用全连接层构造网络,其输出地方包含了所有的决策部分,针对神经网络的设置,本申请实施例更新NN时使用小批量随机梯度(MBGD)下降方法。它是对BGD以和SGD的一个中和办法。其思想是:每次迭代使用一小批样本来对参数进行更新。假设hθ(x)是要拟合的函数,J(θ)损失函数中θ是参数,要迭代求解的值。求解θ就能得到完整的要拟合的函数。其中m是训练集的数目,j是参数的个数。expect_qvalue=reward+γ*next_qvalue, Loss=Lossfunction(qvalue, expected_qvalue), here the loss selects the norm loss, that is, the square loss. The model provided by the embodiment of this application considers a multi-user and two types of decisions: task migration decision vector and task scheduling decision vector For every decision θ there are two decisions, since θi ∈ {0, 1}. Similarly, for each task scheduling decision, it can be discretized, that is, ci ∈ {0, 1, 2, 3}. Therefore, the number of nodes in the output layer of NN should be equal to the number of nodes * 2 + the number of nodes * 4, and each node represents the maximum long-term reward for a certain user equipment terminal's task migration decision. Here, the fully connected layer can be used to construct the network, and its output contains all the decision-making parts. For the setting of the neural network, the embodiment of the present application uses the mini-batch stochastic gradient (MBGD) descent method when updating the NN. It is a neutralization method for BGD and SGD. The idea is that each iteration uses a small batch of samples to update the parameters. Assuming that hθ (x) is the function to be fitted, θ in the J(θ) loss function is a parameter, and the value to be solved iteratively. Solving for θ yields the complete function to be fitted. where m is the number of training sets and j is the number of parameters.
首先要对目标函数求偏导,然后进行参数更新,若指定每次参数更新用到的训练样本个数batch_size=s,则每次参数更新,随机选s个样本计算。这样更新方法可以减少迭代的次数和实践,具体可以基于如下公式进行计算:Firstly, the partial derivative of the objective function must be obtained, and then the parameters are updated. If the number of training samples used for each parameter update is specified as batch_size=s, then s samples are randomly selected for calculation each time the parameters are updated. In this way, the update method can reduce the number of iterations and practice, which can be calculated based on the following formula:
其中,α表示学习率,强化学习指的就是智能体与环境的不断交互最终找到解决问题的最优策略,在深度强化学习中,主要关注的就是DQN权重的学习,与深度神经网络的学习相近,都是计算一个loss,然后通过back-prop更新权重。其中,DQN算法的loss可以根据如下公式进行计算:Among them, α represents the learning rate. Reinforcement learning refers to the continuous interaction between the agent and the environment to finally find the optimal strategy to solve the problem. In deep reinforcement learning, the main concern is the learning of DQN weights, which is similar to the learning of deep neural networks. , all calculate a loss, and then update the weight through back-prop. Among them, the loss of the DQN algorithm can be calculated according to the following formula:
TDloss=Rt+γQ(st+1,at+1)-Q(st,at)TDloss=Rt +γQ(st+1 , at+1 )-Q(st , at )
其中,γ表示折扣率。Among them, γ represents the discount rate.
其中,由于深度神经网络收敛很慢,需要非常多的样本,如果只根据环境交互来训练网络,将非常的没效率。因此DQN引入了一个经验池来进行回放经验,就是把之前和环境交互的经验存下来,在训练时重复利用。ReplayBuffer主要实现两个函数:push模块将经验存入,样本将经验取出用于训练。在上述环境配置中可以将DQN算法应用于移动边缘计算系统,将任务迁移与资源分配的过程进行了重现,从环境模块中返回下一个状态及奖励。Among them, because the deep neural network converges very slowly and requires a lot of samples, it will be very inefficient to train the network only based on the interaction of the environment. Therefore, DQN introduces an experience pool for playback experience, which is to save the previous experience of interacting with the environment and reuse it during training. ReplayBuffer mainly implements two functions: the push module stores experience, and the sample takes experience out for training. In the above environment configuration, the DQN algorithm can be applied to the mobile edge computing system, and the process of task migration and resource allocation is reproduced, and the next state and reward are returned from the environment module.
示例性的,当采用WoLF-PHC算法实现上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法时,对于单个智能体,可以令所有状态-动作对的Q值为0;初始化随机策略πi及其他控制条件,令n=0。在决策时刻Tn时,根据混合策略πi选择状态si(Tn)下的动作ai(si(Tn))。执行动作ai(si(Tn)),并记录样本数据,计算累计回报计算更新更新平均策略在状态si(Tn)时的动作选择概率;更新平均策略πi在状态si(Tn)时的动作选择概率。若算法终止条件满足,学习结束;否则,n=n+1,并重新确定在决策时刻Tn时,根据混合策略πi选择状态si(Tn)下的动作ai(si(Tn)),直至满足终止条件,迭代结束。Exemplarily, when the WoLF-PHC algorithm is used to implement the task migration method provided in the above embodiment, for a single agent, the Q value of all state-action pairs can be set to 0; the random strategy πi and other control conditions are initialized, so that n=0. At the decision time Tn , the action ai (si (Tn )) in the state si (Tn ) is selected according to the mixed strategy πi . Execute the action ai (si (Tn )), record the sample data, and calculate the cumulative return calculation update update average strategy Action selection probability in state si(Tn ); update the action selection probability of the average policy πi in state si (Tn ). If the algorithm termination condition is satisfied, the learning ends; otherwise, n=n+1, and re-determine at the decision time Tn , according to the mixed strategy πi select the action ai (si (Tn ) under the state si (T n )n )), until the termination condition is met, the iteration ends.
示例性的,当采用A3C算法实现上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法时,由于A3C算法则是结合策略和价值函数的产物,A3C算法中动作策略π(s)决定了智能体的动作,这意味着,其输出并非单纯的一个动作,而是动作的概率分布,π(a|s)是选择行动a的概率,加起来为1。在这里每一次动作策略的状态回报有两种函数:Exemplarily, when the A3C algorithm is used to implement the task migration method provided by the above embodiments, since the A3C algorithm is a product of a combination of strategy and value function, the action strategy π(s) in the A3C algorithm determines the action of the agent, which means That is, its output is not simply an action, but the probability distribution of actions, π(a|s) is the probability of choosing action a, which adds up to 1. Here, the state return of each action strategy has two functions:
价值函数V(s):当前状态s所能获得的回报,是下一个s′所能获得返回和在状态转移过程中所得到奖励r的加和。Value function V(s): The return that the current state s can obtain is the sum of the return that the next s′ can obtain and the reward r obtained during the state transition process.
V(s)=Eπ(s)[r+γ·V(s′)]V(s)=Eπ(s) [r+γ·V(s')]
动作价值函数Q(s,a)状态价值回报:Action value function Q(s, a) state value return:
Q(s,a)=r+γ·V(s′)Q(s, a)=r+γ·V(s')
定义一个新的函数A(s,a),即优势函数,用此来计算每一次策略π(s)的价值,其表达了在状态s下,选择动作a有多好。如果动作a比平均值要好,那么优势函数就是处于优势的,否则,就是劣势的:Define a new function A(s, a), namely the advantage function, which is used to calculate the value of each strategy π(s), which expresses how good it is to choose action a in state s. If action a is better than the average, then the dominance function is at an advantage, otherwise, it is at a disadvantage:
A(s,a)=Q(s,a)-V(s)A(s,a)=Q(s,a)-V(s)
其中,传统的动作评价算法单步采样近似估计,在A3C算法中,采样更进一步,使用了N步采样,以加速收敛。因此:Among them, the traditional action evaluation algorithm single-step sampling approximate estimation, in the A3C algorithm, the sampling is further, using N-step sampling to speed up the convergence. therefore:
A(S,A,t)=rt+γ·rt+1+…+γn-1·rt+n-1V(S′)-V(S)A(S, A, t)=rt +γ·rt+1 +…+γn-1 ·rt+n-1 V(S′)-V(S)
从上式可以得到,只需要知道V(S)就可以计算A(s,a),而这个V(s)是容易用NN来计算的。因此可以将价值函数和动作-价值函数联合的进行预测。It can be obtained from the above formula that A(s, a) can be calculated only by knowing V(S), and this V(s) is easy to calculate with NN. Therefore, the value function and the action-value function can be jointly predicted.
为了得到更好的策略,必须进行优化更新。衡量策略的好坏则用到了一个函数J(π),表示一个策略所能得到的折扣的奖赏,从s0出发得到的所有奖励的平均,这个函数直接估计比较难,所以又引入了这个函数的梯度来进行估计。In order to get a better policy, an optimization update must be performed. To measure the quality of the strategy, a function J(π) is used, which represents the discounted reward that a strategy can get, and the average of all rewards obtained from s0. This function is difficult to estimate directly, so this function is introduced gradient to estimate.
其中,A3C算法创建了多个并行的环境,让多个代理同时在该环境上更新主结构中的参数。并行中的智能体互不干扰,而中央结构的参数更新受到不连续干扰,所以更新的相关性被降低,收敛性提高。A3C算法采用异步更新策略,该策略可以在固定的经验时间步上进行操作。它将使用这些片段计算奖励r和优势函数A(s,a)的估计值。每一个智能体都会遵循下述工作流程:获取全局网络参数;通过遵循最小化(t_max:到终极状态的步长)步长数的局部策略与环境进行交互;计算价值损失和策略损失;从损失中得到梯度;用梯度更新全局网络;重复上述工作流程。Among them, the A3C algorithm creates multiple parallel environments, allowing multiple agents to update the parameters in the main structure on the environment at the same time. The agents in parallel do not interfere with each other, while the parameter updates of the central structure are disturbed discontinuously, so the correlation of updates is reduced and the convergence is improved. The A3C algorithm adopts an asynchronous update strategy that can operate on a fixed empirical time step. It will use these pieces to compute the reward r and an estimate of the advantage function A(s, a). Each agent follows the following workflow: obtain global network parameters; interact with the environment by following a local policy that minimizes (t_max: the step size to the final state) number of steps; calculates value loss and policy loss; Get the gradient in ; update the global network with the gradient; repeat the above workflow.
本申请实施例提供的任务迁移方法,通过获取多个用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源;其中,待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求;在预设的约束条件内,根据待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略;根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。上述方案提供的任务迁移方法,通过对多种可实现的任务迁移策略的系统总能耗进行预估,以筛选出系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,避免了移动边缘计算系统能耗超标的风险,提高了移动边缘计算系统的可靠性,为提高移动边缘计算系统的任务处理效率奠定了基础。The task migration method provided in the embodiment of the present application obtains the task information to be migrated generated by multiple user equipment terminals, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server; wherein, the task information to be migrated includes: The computing resource requirements and bandwidth requirements of the tasks to be migrated; within the preset constraints, multiple task migration strategies are generated according to the task information to be migrated, the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, and the available resources of the edge computing server; According to the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy, the target task migration strategy is determined. The task migration method provided by the above solution estimates the total system energy consumption of various achievable task migration strategies to screen out the task migration strategy with the smallest total system energy consumption, avoiding the problem of excessive energy consumption of the mobile edge computing system. Risk, improves the reliability of the mobile edge computing system, and lays the foundation for improving the task processing efficiency of the mobile edge computing system.
本申请实施例提供了一种任务迁移装置,用于执行上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法。An embodiment of the present application provides a task migration device, configured to execute the task migration method provided in the foregoing embodiments.
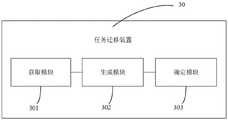
如图3所示,为本申请实施例提供的任务迁移装置的结构示意图。该任务迁移装置30包括获取模块301、生成模块302和确定模块303。As shown in FIG. 3 , it is a schematic structural diagram of a task migration device provided in the embodiment of the present application. The
其中,获取模块301,用于获取多个用户设备终端生成的待迁移任务的待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源;其中,待迁移任务信息包括:待迁移任务的计算资源需求和带宽需求;生成模块302,用于在预设的约束条件内,根据待迁移任务信息、各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽以及边缘计算服务器可用资源,生成多个任务迁移策略;确定模块303,用于根据各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,确定目标任务迁移策略。Wherein, the acquiring
具体地,在一实施例中,生成模块302,具体用于:Specifically, in an embodiment, the
根据待迁移任务的带宽需求和各用户设备终端与基站之间的可用带宽,生成待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策;其中,任务迁移决策包括各待迁移任务的执行目的地,执行目的地包括用户设备终端和边缘计算服务器;According to the bandwidth requirements of the tasks to be migrated and the available bandwidth between each user equipment terminal and the base station, multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated are generated; wherein, the task migration decisions include execution destinations of each task to be migrated, and the execution destination Including user equipment terminals and edge computing servers;
当待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,确定待迁移任务为第一任务;When the execution destination of the task to be migrated is an edge computing server, determine that the task to be migrated is the first task;
获取第一任务的服务质量要求,根据服务质量要求确定第一任务的优先级;Acquire the service quality requirements of the first task, and determine the priority of the first task according to the service quality requirements;
根据各第一任务的优先级,确定边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配量;According to the priority of each first task, determine the allocation amount of available resources of the edge computing server;
根据待迁移任务对应的多个任务迁移决策,及边缘计算服务器可用资源的分配情况,生成多个任务迁移策略。Multiple task migration strategies are generated according to the multiple task migration decisions corresponding to the tasks to be migrated and the allocation of available resources of the edge computing server.
具体地,在一实施例中,确定模块303,具体用于:Specifically, in an embodiment, the determining
根据各第一任务对应的用户设备终端的传输功率、传输时延以及预设的边缘计算服务器的属性信息,确定边缘计算服务器能耗;Determine the energy consumption of the edge computing server according to the transmission power and transmission delay of the user equipment terminal corresponding to each first task and the preset attribute information of the edge computing server;
根据第一任务以外的第二任务的计算资源需求及其对应的用户设备终端的执行周期频率,确定第二任务对应的各用户设备终端的本地能耗;Determine the local energy consumption of each user equipment terminal corresponding to the second task according to the computing resource requirements of the second task other than the first task and the execution cycle frequency of the corresponding user equipment terminal;
根据边缘计算服务器能耗和本地能耗,确定各任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;According to the energy consumption of the edge computing server and the local energy consumption, determine the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to each task migration strategy;
将系统总能耗最小的任务迁移策略,确定为目标任务迁移策略。The task migration strategy with the minimum total energy consumption of the system is determined as the target task migration strategy.
具体地,在一实施例中,确定模块303具体用于:Specifically, in an embodiment, the determining
根据如下公式确定任一任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗:Determine the total system energy consumption corresponding to any task migration strategy according to the following formula:
其中,Eall表示任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗,T表示系统总消耗时间,θi表示第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地,其中,当第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为边缘计算服务器时,θi=1,当第i个待迁移任务的执行目的地为对应的用户设备终端时,θi=0,表示各第一任务对应的边缘计算服务器能耗,表示各第二任务对应的本地能耗。Among them, Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy, T represents the total consumption time of the system, θi represents the execution destination of the i-th task to be migrated, where, when the execution destination of the i-th task to be migrated is For the edge computing server, θi =1, when the execution destination of the ith task to be migrated is the corresponding user equipment terminal, θi =0, Indicates the energy consumption of the edge computing server corresponding to each first task, Indicates the local energy consumption corresponding to each second task.
具体地,在一实施例中,确定模块303具体还用于:Specifically, in an embodiment, the determining
基于如下公式,根据系统总能耗计算各任务迁移策略的奖励值:Based on the following formula, the reward value of each task migration strategy is calculated according to the total energy consumption of the system:
其中,r表示奖励值,telocal表示各待迁移任务的执行目的地为均为对应的用户设备终端时的系统总能耗,Eall表示任务迁移策略对应的系统总能耗;Among them, r represents the reward value, telocal represents the total energy consumption of the system when the execution destinations of the tasks to be migrated are all corresponding user equipment terminals, and Eall represents the total energy consumption of the system corresponding to the task migration strategy;
将奖励值最高的任务迁移策略,确定为目标任务迁移策略。The task migration strategy with the highest reward value is determined as the target task migration strategy.
具体地,在一实施例中,生成模块302,还用于:Specifically, in an embodiment, the
根据预设缓存需求,构建等待队列;Build a waiting queue according to preset cache requirements;
根据各第一任务的生成顺序,将各第一任务存储至等待队列。According to the generation sequence of each first task, each first task is stored in a waiting queue.
具体地,在一实施例中,预设的约束条件,包括:Specifically, in one embodiment, the preset constraints include:
各任务迁移策略的总传输时延小于预设的总传输时延阈值、各用户设备终端的执行周期频率小于预设的执行周期频率阈值和/或各用户设备终端的执行周期数量不大于边缘计算服务器的执行周期数量。The total transmission delay of each task migration strategy is less than the preset total transmission delay threshold, the execution cycle frequency of each user equipment terminal is less than the preset execution cycle frequency threshold, and/or the number of execution cycles of each user equipment terminal is not greater than the edge computing The number of execution cycles for the server.
关于本实施例中的任务迁移装置,其中各个模块执行操作的具体方式已经在有关该方法的实施例中进行了详细描述,此处将不做详细阐述说明。Regarding the task migration apparatus in this embodiment, the specific manner in which each module executes operations has been described in detail in the embodiment of the method, and will not be described in detail here.
本申请实施例提供的任务迁移装置,用于执行上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法,其实现方式与原理相同,不再赘述。The task migration device provided in the embodiment of the present application is used to execute the task migration method provided in the above embodiment, and its implementation method is the same as the principle, and will not be repeated here.
本申请实施例提供了一种电子设备,用于执行上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法。An embodiment of the present application provides an electronic device configured to execute the task migration method provided in the foregoing embodiments.
如图4所示,为本申请实施例提供的电子设备的结构示意图。该电子设备40包括:至少一个处理器41和存储器42;As shown in FIG. 4 , it is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided in an embodiment of the present application. The
存储器存储计算机执行指令;至少一个处理器执行存储器存储的计算机执行指令,使得至少一个处理器执行如上实施例提供的任务迁移方法。The memory stores computer-executable instructions; at least one processor executes the computer-executable instructions stored in the memory, so that at least one processor executes the task migration method provided in the above embodiments.
本申请实施例提供的一种电子设备,用于执行上述实施例提供的任务迁移方法,其实现方式与原理相同,不再赘述。An electronic device provided in the embodiment of the present application is used to execute the task migration method provided in the above embodiment, and the implementation method is the same as the principle, and will not be repeated here.
本申请实施例提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,计算机可读存储介质中存储有计算机执行指令,当处理器执行计算机执行指令时,实现如上任一实施例提供的任务迁移方法。An embodiment of the present application provides a computer-readable storage medium, in which computer-executable instructions are stored, and when a processor executes the computer-executable instructions, the task migration method provided in any one of the above embodiments is implemented.
本申请实施例的包含计算机可执行指令的存储介质,可用于存储前述实施例中提供的任务迁移方法的计算机执行指令,其实现方式与原理相同,不再赘述。The storage medium containing the computer-executable instructions in the embodiment of the present application can be used to store the computer-executable instructions of the task migration method provided in the foregoing embodiments.
本领域技术人员可以清楚地了解到,为描述的方便和简洁,仅以上述各功能模块的划分进行举例说明,实际应用中,可以根据需要而将上述功能分配由不同的功能模块完成,即将装置的内部结构划分成不同的功能模块,以完成以上描述的全部或者部分功能。上述描述的装置的具体工作过程,可以参考前述方法实施例中的对应过程,在此不再赘述。Those skilled in the art can clearly understand that for the convenience and brevity of description, only the division of the above-mentioned functional modules is used as an example for illustration. The internal structure of the system is divided into different functional modules to complete all or part of the functions described above. For the specific working process of the device described above, reference may be made to the corresponding process in the foregoing method embodiments, and details are not repeated here.
最后应说明的是:以上各实施例仅用以说明本申请的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述各实施例对本申请进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分或者全部技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本申请各实施例技术方案的范围。Finally, it should be noted that: the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present application, and are not intended to limit it; although the application has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that: It is still possible to modify the technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments, or perform equivalent replacements for some or all of the technical features; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the technical solutions of the various embodiments of the present application. scope.
Claims (9)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011312378.7ACN112416554B (en) | 2020-11-20 | 2020-11-20 | Task migration method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011312378.7ACN112416554B (en) | 2020-11-20 | 2020-11-20 | Task migration method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112416554A CN112416554A (en) | 2021-02-26 |
| CN112416554Btrue CN112416554B (en) | 2022-12-02 |
Family
ID=74778386
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011312378.7AActiveCN112416554B (en) | 2020-11-20 | 2020-11-20 | Task migration method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112416554B (en) |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113014659B (en)* | 2021-03-11 | 2022-05-24 | 北京邮电大学 | Microservice migration method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment |
| TWI773196B (en)* | 2021-03-16 | 2022-08-01 | 和碩聯合科技股份有限公司 | Method for allocating computing resources and electronic device using the same |
| CN113141394B (en)* | 2021-03-25 | 2022-04-01 | 北京邮电大学 | A resource allocation method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
| CN112887435B (en)* | 2021-04-13 | 2022-05-20 | 中南大学 | A method to improve the cooperation rate of task offloading in edge computing |
| CN113452751B (en)* | 2021-05-20 | 2024-06-21 | 国网江苏省电力有限公司信息通信分公司 | Cloud-edge collaboration-based power Internet of things task security migration system and method |
| CN113515378A (en)* | 2021-06-28 | 2021-10-19 | 国网河北省电力有限公司雄安新区供电公司 | 5G edge computing task migration and computing resource allocation method and device |
| CN113645637B (en)* | 2021-07-12 | 2022-09-16 | 中山大学 | Method and device for unloading tasks of ultra-dense network, computer equipment and storage medium |
| CN113597013B (en)* | 2021-08-05 | 2024-03-22 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | Collaborative task scheduling method under user mobile scene in mobile edge calculation |
| CN113689001B (en)* | 2021-08-30 | 2023-12-05 | 浙江大学 | A virtual self-playing method and device based on counterfactual regret minimization |
| CN114003121B (en)* | 2021-09-30 | 2023-10-31 | 中国科学院计算技术研究所 | Data center server energy efficiency optimization method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN114281426B (en)* | 2021-12-21 | 2023-05-16 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Task unloading method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium |
| CN117440175A (en)* | 2022-07-14 | 2024-01-23 | 抖音视界有限公司 | Methods, devices, systems, equipment and media for video transmission |
| CN116112976B (en)* | 2022-12-20 | 2024-05-03 | 暨南大学 | Equipment calculation migration method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN117873689B (en)* | 2024-03-11 | 2024-05-31 | 浪潮计算机科技有限公司 | A task allocation method, device, equipment and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN119129958A (en)* | 2024-07-26 | 2024-12-13 | 中国船舶集团有限公司第七一九研究所 | Submersible energy management method and system based on demand allocation strategy |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019200716A1 (en)* | 2018-04-20 | 2019-10-24 | 上海无线通信研究中心 | Fog computing-oriented node computing task scheduling method and device thereof |
| CN111031102A (en)* | 2019-11-25 | 2020-04-17 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A cacheable task migration method in a multi-user, multi-task mobile edge computing system |
- 2020
- 2020-11-20CNCN202011312378.7Apatent/CN112416554B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2019200716A1 (en)* | 2018-04-20 | 2019-10-24 | 上海无线通信研究中心 | Fog computing-oriented node computing task scheduling method and device thereof |
| CN111031102A (en)* | 2019-11-25 | 2020-04-17 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | A cacheable task migration method in a multi-user, multi-task mobile edge computing system |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 基于边缘计算的单任务迁移策略研究;朱霞等;《金陵科技学院学报》;20200930(第03期);全文* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112416554A (en) | 2021-02-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112416554B (en) | Task migration method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111953759B (en) | Collaborative computing task unloading and transferring method and device based on reinforcement learning | |
| CN112134916B (en) | Cloud edge collaborative computing migration method based on deep reinforcement learning | |
| CN113950066A (en) | Method, system and device for offloading partial computing on a single server in a mobile edge environment | |
| CN112422644B (en) | Computing task offloading method and system, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN113950103A (en) | Multi-server complete computing unloading method and system under mobile edge environment | |
| CN113242568A (en) | Task unloading and resource allocation method in uncertain network environment | |
| CN113568727A (en) | Mobile edge calculation task allocation method based on deep reinforcement learning | |
| CN111953758A (en) | A kind of edge network computing offloading and task migration method and device | |
| CN109947545A (en) | A Decision Method for Task Offloading and Migration Based on User Mobility | |
| CN113867843B (en) | Mobile edge computing task unloading method based on deep reinforcement learning | |
| CN112291335B (en) | Optimal task scheduling method in mobile edge computing | |
| CN114340016A (en) | A method and system for offloading and distributing power grid edge computing | |
| CN116489708B (en) | Meta universe oriented cloud edge end collaborative mobile edge computing task unloading method | |
| CN116541106B (en) | Calculation task offloading method, computing device and storage medium | |
| CN112905315A (en) | Task processing method, device and equipment in Mobile Edge Computing (MEC) network | |
| KR20240072551A (en) | Method and apparatus for optimizing energy consumption and delay cost based on resource allocation in mobile edge computing in industrial Internet of Things environment | |
| CN116418808A (en) | A MEC joint computing offloading and resource allocation method and device | |
| Hu et al. | Dynamic task offloading in MEC-enabled IoT networks: A hybrid DDPG-D3QN approach | |
| CN116954866A (en) | Edge cloud task scheduling method and system based on deep reinforcement learning | |
| CN116886703A (en) | A cloud-edge collaborative computing offloading method based on priority and reinforcement learning | |
| Huang et al. | When lyapunov drift based queue scheduling meets adversarial bandit learning | |
| CN118034933A (en) | Resource scheduling decision method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN118210609A (en) | A cloud computing scheduling method and system based on DQN model | |
| CN118612855A (en) | A method for task offloading and resource optimization of heterogeneous UAVs |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |