CN112016680B - Reconfigurable autonomous learning impulse neural network processor - Google Patents
Reconfigurable autonomous learning impulse neural network processorDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN112016680B CN112016680BCN202011135965.3ACN202011135965ACN112016680BCN 112016680 BCN112016680 BCN 112016680BCN 202011135965 ACN202011135965 ACN 202011135965ACN 112016680 BCN112016680 BCN 112016680B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- updated
- synapse
- target neuron
- module
- calculation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/04—Architecture, e.g. interconnection topology
- G06N3/049—Temporal neural networks, e.g. delay elements, oscillating neurons or pulsed inputs
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/02—Neural networks
- G06N3/06—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons
- G06N3/063—Physical realisation, i.e. hardware implementation of neural networks, neurons or parts of neurons using electronic means
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Feedback Control In General (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及脉冲神经网络技术领域,尤其涉及一种可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器。The invention relates to the technical field of spiking neural networks, in particular to a reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor.
背景技术Background technique
神经网络是根据生物脑部神经系统特点抽象出来的数学模型,可用来解决物体识别等实际问题,其发展过程可分为三代:感知机(Perceptron)、人工神经网络(ArtificialNeural Network,ANN)、脉冲神经网络(Spiking Neural Network,SNN)。早期的感知机仅能够解决线性问题,对非线性问题(如异或问题)则无能为力;ANN在感知机的基础上增加了非线性的激活函数,使其能够解决非线性的问题。近年来,随着计算机计算能力的提升,ANN在一些复杂问题的解决上有较好的表现,但随着问题复杂度的提高,需要更深的网络才能解决问题,这导致完成任务的功耗和硬件开销大大增大,且ANN学习算法的计算量大,导致其难以实现在线学习。为降低网络运行的功耗和硬件资源使用,科研人员提出了SNN的概念。一方面,SNN从人脑神经元更底层的生理特征进行建模,仅在有输入时才更新网络部分神经元,相比于ANN每个时刻更新网络全部神经元,功耗显著降低;另一方面SNN主要采用无监督学习的算法,算法复杂度低,更适合于实现在线学习。Neural network is an abstract mathematical model based on the characteristics of biological brain nervous system, which can be used to solve practical problems such as object recognition. Its development process can be divided into three generations: Perceptron, Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Pulse Neural Network (Spiking Neural Network, SNN). Early perceptrons were only able to solve linear problems, but were powerless to nonlinear problems (such as XOR problems); ANN added a nonlinear activation function to the perceptron, enabling it to solve nonlinear problems. In recent years, with the improvement of computer computing power, ANN has a better performance in solving some complex problems, but with the increase of the complexity of the problem, a deeper network is required to solve the problem, which leads to the power consumption and The hardware overhead is greatly increased, and the computational load of the ANN learning algorithm is large, which makes it difficult to realize online learning. In order to reduce the power consumption and hardware resource usage of network operation, researchers put forward the concept of SNN. On the one hand, SNN models the lower-level physiological characteristics of human brain neurons, and only updates some neurons in the network when there is input. Compared with ANN, which updates all neurons in the network at every moment, the power consumption is significantly reduced; In terms of SNN, it mainly adopts unsupervised learning algorithm, which has low algorithm complexity and is more suitable for online learning.
目前,对于SNN的算法已经有了很多研究,在一些任务上取得了很好的效果,但在硬件上的研究仍然不够充分,还存在一些问题,主要是以下几个方面:At present, there have been a lot of researches on the SNN algorithm, and good results have been achieved in some tasks, but the research on hardware is still insufficient, and there are still some problems, mainly in the following aspects:
1.由于SNN每次输入仅更新部分神经元,因此,硬件需要实现大量稀疏的并行计算,最好的实现方式是使用阵列式架构。阵列由若干处理单元组成,每个处理单元独立完成网络某一部分的计算。由于各处理单元是相互独立的,会存在一些处理单元没有被充分利用,另一些处理单元忙碌的情形,这就不能充分利用硬件资源。1. Since SNN only updates some neurons for each input, the hardware needs to implement a large number of sparse parallel calculations, and the best way to implement it is to use an array architecture. The array consists of several processing units, each processing unit independently completes the calculation of a certain part of the network. Since each processing unit is independent of each other, some processing units are not fully utilized, and other processing units are busy, so that hardware resources cannot be fully utilized.
2.SNN内部传递的信息主要是脉冲,通过脉冲信息路由的方式实现。现有的设计是,当源神经元发射脉冲时,根据目的神经元的ID,由源神经元所在处理单元发射与目的神经元个数相同的脉冲包,这些脉冲包由脉冲产生时间和目的神经元ID构成。由于网络结构比较大,这种设计对系统的传输带宽要求高,导致系统性能降低。2. The information transmitted inside the SNN is mainly pulse, which is realized by the way of pulse information routing. The existing design is that when the source neuron emits a pulse, according to the ID of the target neuron, the processing unit where the source neuron is located emits the same number of pulse packets as the target neuron. Meta ID composition. Due to the relatively large network structure, this design has high requirements on the transmission bandwidth of the system, resulting in a decrease in system performance.
3. 要想支持SNN的在线学习,现有的设计需要额外设计学习电路,大大增加硬件资源的开销。3. In order to support the online learning of SNN, the existing design needs to design additional learning circuits, which greatly increases the cost of hardware resources.
4. 实现SNN的更新主要有两种机制,一种是时间驱动(clock-driven)的方式,另一种是事件驱动(event-driven)的方式。前者每个时刻都要更新网络全部的神经元,虽然不能体现SNN每次输入仅更新部分神经元的特性,但更新网络的运算复杂度低;后者仅根据输入,每次更新与输入相关的部分神经元,能够体现SNN每次输入仅更新部分神经元的特性,但更新网络的运算复杂度高。以全连接网络为例,网络的每个神经元都与下层所有神经元相连接,这就意味着,当输入脉冲的频率高时,event-driven的方式需要短时间进行大量复杂度高的运算,反而会增大系统的功耗;输入脉冲的频率低时,event-driven的方式会使系统功耗降低。因此,对于不同的脉冲输入情形,应当加以区分地使用不同的更新方式,以使系统的功耗尽可能地低,但目前的设计均未有此考虑。4. There are two main mechanisms for implementing SNN updates, one is a clock-driven approach, and the other is an event-driven approach. The former needs to update all the neurons of the network at every moment. Although it cannot reflect the characteristic that SNN only updates part of the neurons for each input, the computational complexity of updating the network is low; Some neurons can reflect the characteristic that SNN only updates some neurons for each input, but the computational complexity of updating the network is high. Taking the fully connected network as an example, each neuron of the network is connected to all the neurons in the lower layer, which means that when the frequency of input pulses is high, the event-driven method requires a large number of complex operations in a short time. , but will increase the power consumption of the system; when the frequency of the input pulse is low, the event-driven method will reduce the power consumption of the system. Therefore, for different pulse input situations, different update methods should be used to make the power consumption of the system as low as possible, but the current design has not considered this.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对上述问题,本发明提供了一种可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器。In view of the above problems, the present invention provides a reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor.
为实现上述发明目的,本发明采用的技术方案如下:For realizing the above-mentioned purpose of the invention, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is as follows:
一种可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器,其特征在于,包括由多个处理单元组成的处理单元阵列,同步模块,以及分布在处理单元阵列周围的东向通道、南向通道、西向通道、北向通道;所述处理单元包括数据端口、控制端口、外部路由模块、排序模块、脉冲队列模块、控制器模块、搜索模块、存储器模块、客户端模块、服务器模块、内部路由模块和多个计算资源;所述多个计算资源中一部分为独占计算资源,其余为可借用计算资源,所述独占计算资源为仅处理单元自己所用的计算资源,所述可借用计算资源为处理单元中可借用给其他处理单元的计算资源;所述存储器模块存有以源神经元ID为地址的目的神经元ID表、以源神经元ID为地址的突触ID表、以目的神经元ID为地址的目的神经元状态信息、以突触ID为地址的突触状态信息;其中,突触ID表包括突触ID和突触更新计数值,所述突触更新计数值用于控制计算资源执行学习模式第一阶段或学习模式第二阶段的更新计算;A reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor is characterized by comprising a processing unit array composed of a plurality of processing units, a synchronization module, and an eastward channel, a southward channel, and a westward channel distributed around the processing unit array. channel, northbound channel; the processing unit includes a data port, a control port, an external routing module, a sequencing module, a pulse queue module, a controller module, a search module, a memory module, a client module, a server module, an internal routing module and a plurality of Computing resources; a part of the multiple computing resources are exclusive computing resources, and the rest are borrowable computing resources, the exclusive computing resources are computing resources only used by the processing unit itself, and the borrowable computing resources are the processing units that can be borrowed Computing resources for other processing units; the memory module stores a destination neuron ID table with the source neuron ID as an address, a synapse ID table with the source neuron ID as an address, and a destination neuron ID as an address. Neuron state information, synapse state information with the synapse ID as the address; wherein, the synapse ID table includes the synapse ID and the synapse update count value, and the synapse update count value is used to control the computing resource to execute the learning mode first. Update calculation of the first stage or the second stage of the learning mode;
处理单元的外部路由模块通过数据端口与指定的处理单元的外部路由模块连接,指定的处理单元发送脉冲包至处理单元的外部路由模块,所述脉冲包由脉冲产生时间和源神经元ID组成,所述源神经元ID由发送脉冲包的指定的处理单元ID 和产生脉冲的源神经元在处理单元中的相对ID组成;外部路由模块根据预先配置的路由表查询脉冲包是否需要进行本地处理或通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元,所述路由表包括全局的源神经元ID,及源神经元对应的脉冲包传送至本地、东、南、西、北五个方向处理单元的方向信息,需要传送脉冲包的方向的方向信息为1,否则为0;The external routing module of the processing unit is connected with the external routing module of the designated processing unit through the data port, and the designated processing unit sends a pulse packet to the external routing module of the processing unit, and the pulse packet is composed of the pulse generation time and the source neuron ID, The source neuron ID is composed of the designated processing unit ID that sends the pulse packet and the relative ID of the source neuron that generates the pulse in the processing unit; the external routing module queries whether the pulse packet needs to be processed locally or not according to the preconfigured routing table. The routing table includes the global source neuron ID, and the pulse packets corresponding to the source neuron are sent to the local, east, south, west, and north through the data port. The direction information of the five direction processing units, the direction information of the direction in which the pulse packet needs to be transmitted is 1, otherwise it is 0;
若处理单元需要对接收的脉冲包进行本地处理,外部路由模块将脉冲包传输至排序模块进行时间戳排序,得到排序后脉冲包,排序后脉冲包传输至脉冲队列模块等待,待排序模块将接收的脉冲包全部排序完成,脉冲队列模块将代表排序完成的排序信号传输至控制器模块,控制器模块通过控制端口传输至同步模块,待所有处理单元均向同步模块传输排序信号后,同步模块回传处理信号至控制器模块;之后控制器模块触发搜索模块将脉冲队列模块中的排序后脉冲包依次取出,搜索模块根据排序后脉冲包的源神经元ID在存储器查找对应目的神经元ID、突触ID和突触更新计数值信息,并将脉冲产生时间与目的神经元ID、突触ID、突触更新计数值组成目的神经元-突触ID信息;搜索模块将查到的目的神经元-突触ID信息传输至客户端模块,客户端模块再根据目的神经元-突触ID信息,在存储器中查找对应目的神经元状态信息和突触状态信息,并将脉冲产生时间与目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息组成待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息,其中,所述目的神经元状态信息包括待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元上次更新时间和目的神经元阈值,所述突触状态信息包括待更新突触权值相关变量、上次更新后突触权值和突触上次更新时间;客户端模块将待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息传输至服务器模块,服务器模块按照分配规则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至处理单元的独占计算资源,处理单元的可借用计算资源,和/或东、南、西、北四个方向处理单元的可借用计算资源执行计算,执行计算的计算资源在从自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器外部传输的推理/学习标志位的控制下执行推理模式或学习模式;计算完成后,执行计算的计算资源将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息经服务器模块回传至客户端模块,客户端模块将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息写回存储器,更新目的神经元状态信息和/或突触状态信息;If the processing unit needs to perform local processing on the received pulse packets, the external routing module transmits the pulse packets to the sorting module for timestamp sorting, and obtains the sorted pulse packets. After sorting, the pulse packets are transmitted to the pulse queue module for waiting. After all the pulse packets are sorted, the pulse queue module transmits the sorting signal representing the completion of the sorting to the controller module, and the controller module transmits it to the synchronization module through the control port. After all processing units transmit the sorting signal to the synchronization module, the synchronization module returns The processing signal is transmitted to the controller module; then the controller module triggers the search module to take out the sorted pulse packets in the pulse queue module in turn, and the search module searches the memory for the corresponding destination neuron ID, burst according to the source neuron ID of the sorted pulse packet. Contact ID and synapse update count value information, and combine the pulse generation time with the target neuron ID, synapse ID, synapse update count value to form the target neuron-synapse ID information; the search module will find the target neuron- The synapse ID information is transmitted to the client module, and the client module searches for the corresponding target neuron state information and synapse state information in the memory according to the target neuron-synapse ID information, and compares the pulse generation time with the target neuron ID. , target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and synapse state information to form the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated, wherein the target neuron state information includes the target neuron membrane potential to be updated , the last update time of the target neuron and the threshold value of the target neuron, the synaptic state information includes the relevant variables of the synaptic weight to be updated, the synaptic weight after the last update and the last update time of the synapse; the client module will The target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated is transmitted to the server module, and the server module allocates the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated to the exclusive computing resources of the processing unit according to the allocation rules, the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit, and/or The computing resources of the processing units in the four directions of east, south, west, and north can be borrowed to perform the computation, and the computing resources that perform the computation perform the inference mode or learning under the control of the inference/learning flag bit transmitted from the outside of the self-learning spiking neural network processor mode; after the calculation is completed, the computing resources that perform the calculation will return the updated target neuron-synaptic state information to the client module through the server module, and the client module will write the updated target neuron-synaptic state information back to the memory, Update the target neuron state information and/or synapse state information;
计算资源执行计算的模式分为推理模式和学习模式,所述推理模式需要更新目的神经元膜电位,所述学习模式需要更新目的神经元膜电位、突触权值相关变量和突触权值,采用的计算用以下通式表示:The modes in which the computing resources perform computation are divided into an inference mode and a learning mode. The inference mode needs to update the target neuron membrane potential, and the learning mode needs to update the target neuron membrane potential, synaptic weight-related variables, and synaptic weights. The calculations employed are represented by the following general formula:
其中,为泄露后目的神经元膜电位或更新后突触权值相关变量;为待更新目的神经元膜电位或待更新突触权值相关变量;为脉冲产生时间与目的神经元上次更新时间的更新时间间隔,或脉冲产生时间与突触上次更新时间的更新时间间隔;为目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的静息值;为目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的时间常数;为上次更新后突触权值;为更新后目的神经元膜电位;为目的神经元复位值;为更新后突触权值;为目的神经元阈值;代表为神经元状态更新。in, It is the relevant variable of the target neuron membrane potential after leakage or the updated synaptic weight; For the target neuron membrane potential to be updated or the variable related to the synaptic weight to be updated; is the update time interval between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, or the update time interval between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse; The resting value of the variable related to the target neuron membrane potential or synaptic weight; The time constant of the variable related to the target neuron membrane potential or synaptic weight; is the synaptic weight after the last update; is the membrane potential of the target neuron after updating; reset value for the target neuron; is the updated synaptic weight; for the target neuron threshold; Represents the neuron state update.
进一步地,在推理模式,先对待更新目的神经元膜电位使用公式(1)执行一次更新计算,再执行公式(2),将公式(1)所得泄露后目的神经元膜电位与上次更新后突触权值之和作为更新后目的神经元膜电位;Further, in the inference mode, use formula (1) to perform an update calculation first, and then execute formula (2), and compare the leaked target neuron membrane potential obtained by formula (1) with that after the last update. The sum of synaptic weights is used as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
若更新后目的神经元膜电位高于目的神经元阈值,则执行公式(3),将更新后目的神经元膜电位重置为目的神经元复位值,同时产生新脉冲;否则不产生新脉冲;If the updated target neuron membrane potential is higher than the target neuron threshold, execute formula (3) to reset the updated target neuron membrane potential to the target neuron reset value , and a new pulse is generated at the same time; otherwise, no new pulse is generated;
在学习模式,分为两个阶段:In learning mode, there are two stages:
第一阶段,先对待更新目的神经元膜电位使用公式(1)执行一次更新计算,再执行公式(2),将公式(1)所得泄露后目的神经元膜电位与上次更新后突触权值之和作为更新后目的神经元膜电位;In the first stage, use formula (1) to perform an update calculation on the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, and then execute formula (2). The sum of the values is used as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
若更新后目的神经元膜电位高于目的神经元阈值,则执行公式(3),将更新后目的神经元膜电位重置为目的神经元复位值,同时产生新脉冲;否则不产生新脉冲;If the updated target neuron membrane potential is higher than the target neuron threshold, execute formula (3) to reset the updated target neuron membrane potential to the target neuron reset value , and a new pulse is generated at the same time; otherwise, no new pulse is generated;
然后对待更新突触权值相关变量使用公式(1)执行一次更新计算,得到更新后突触权值相关变量;Then, use formula (1) to perform an update calculation on the variables related to the updated synaptic weights to obtain the updated synaptic weight-related variables;
再对上次更新后突触权值使用公式(4)执行一次更新计算,得到更新后突触权值;若第一阶段未产生新脉冲,则不执行第二阶段,否则执行第二阶段;Then use formula (4) to perform an update calculation on the synaptic weights after the last update to obtain the updated synaptic weights; if no new pulses are generated in the first stage, the second stage is not executed, otherwise the second stage is executed;
第二阶段,对待更新突触权值相关变量使用公式(1)执行二次更新计算,此时公式(1)中待更新突触权值相关变量为第一阶段所得更新后突触权值相关变量,得到更新后突触权值相关变量;In the second stage, the relevant variables of the synaptic weights to be updated are calculated using the formula (1) to perform the second update calculation. At this time, the relevant variables of the synaptic weights to be updated in the formula (1) are the relevant variables of the updated synaptic weights obtained in the first stage. variable, obtain the relevant variables of the updated synaptic weights;
对上次更新后突触权值使用公式(4)执行二次更新计算,此时公式(4)中上次更新后突触权值为第一阶段所得更新后突触权值,得到更新后突触权值;Use formula (4) to perform a second update calculation on the synaptic weight after the last update. At this time, the synaptic weight after the last update in formula (4) is the updated synapse weight obtained in the first stage, and the updated synaptic weight is obtained. synaptic weight;
进一步地,所述分配规则具体为:服务器模块依次查询处理单元的独占计算资源和可借用计算资源中是否存在空闲的计算资源,若存在空闲的独占计算资源,则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至空闲的处理单元的独占计算资源执行计算;若处理单元的独占计算资源均忙碌,而处理单元的可借用计算资源存在空闲,则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至处理单元的可借用计算资源执行计算;若处理单元的独占计算资源和可借用计算资源均处于忙碌状态,则服务器模块查询东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元中是否存在空闲的可借用计算资源,若存在空闲的可借用计算资源,则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至空闲的可借用计算资源执行计算,若东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元的可借用计算资源均处于忙碌状态,则服务器模块依次重复查询处理单元的独占计算资源,处理单元的可借用计算资源,东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元的可借用计算资源中是否存在空闲的计算资源,直至存在空闲的计算资源再分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息;Further, the allocation rule is specifically as follows: the server module sequentially queries the exclusive computing resources and the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit whether there are idle computing resources; The state information is sent to the exclusive computing resources of the idle processing units to perform the calculation; if the exclusive computing resources of the processing units are busy, and the borrowable computing resources of the processing units are idle, the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated is allocated to the processing unit. The borrowable computing resources of the unit perform the calculation; if the exclusive computing resources and the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit are both in a busy state, the server module queries whether there is any idle available for borrowing in the processing units in the four directions of east, south, west, and north. Computing resources, if there are idle borrowable computing resources, allocate the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated to the idle borrowable computing resources to perform calculations, if the processing units in the east, south, west, and north directions are available If the borrowed computing resources are in a busy state, the server module repeatedly inquires about the exclusive computing resources of the processing unit, the available computing resources of the processing unit, and the available computing resources of the processing units in the four directions of east, south, west, and north. Idle computing resources, until there are idle computing resources, redistribute the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated;
进一步地,所述计算资源包括数据包打包/拆分模块、可重构控制器模块、自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块和计算单元;Further, the computing resources include a data packet packing/splitting module, a reconfigurable controller module, an adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module and a computing unit;
所述数据包打包/拆分模块用于将待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息拆分成脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值和突触状态信息,并缓存,所述数据包打包/拆分模块还将更新后目的神经元状态信息、更新后突触状态信息、脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、突触ID、突触更新计数值打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息,并缓存;The data packet packing/splitting module is used to split the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated into pulse generation time, target neuron ID, target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value and Synapse state information, and cache, the data packet packing/splitting module will also update the target neuron state information, the updated synapse state information, the pulse generation time, the destination neuron ID, the synapse ID, and the synapse update. The count value is packaged into the updated target neuron-synaptic state information and cached;
所述可重构控制器模块根据突触更新计数值、从自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器外部传输的推理/学习标志位的状态,输出神经元/突触标志位,以控制计算单元,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取不同的数据完成计算,从而实现推理与学习的可重构;The reconfigurable controller module outputs neuron/synaptic flags according to the synaptic update count value and the state of the inference/learning flags transmitted from the outside of the autonomous learning spiking neural network processor to control the computing unit, adaptive The clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules pull different data from the data packet packing/splitting module to complete the calculation, thereby realizing the reconfiguration of reasoning and learning;
所述自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块根据脉冲产生时间与目的神经元上次更新时间,或脉冲产生时间与突触上次更新时间的差值,自适应地改变计算单元执行更新计算的计算方式;当小于预设定的最小时间阈值时,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块控制计算单元执行clock-driven机制的计算,采用公式(5)取代公式(1)计算;The adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module is based on the difference between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, or the difference between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse , adaptively change the calculation method of the calculation unit to perform the update calculation; when less than a preset minimum time threshold When , the self-adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module controls the computing unit to perform the calculation of the clock-driven mechanism, and adopts the formula (5) to replace the formula (1) for calculation;
其中,为推理泄露值或学习泄露值;in, For inference leaked values or learning leaked values;
当大于最小时间阈值而小于预设定的最大时间阈值时,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块控制计算单元执行event-driven机制的计算,采用公式(1)计算;当大于最大时间阈值时,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块控制计算单元用目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的静息值分别覆盖待更新目的神经元膜电位或待更新突触权值相关变量,得到泄露后目的神经元膜电位或更新后突触权值相关变量,取代公式(1)计算;when greater than the minimum time threshold while less than the preset maximum time threshold , the self-adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module controls the computing unit to perform the calculation of the event-driven mechanism, using formula (1) to calculate; when greater than the maximum time threshold At the same time, the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules control the computing unit to cover the target neuron membrane potential or the to-be-updated synaptic weight with the target neuron membrane potential or the resting value of the synaptic weight-related variable, respectively. Value-related variables, obtain the target neuron membrane potential after leakage or the updated synaptic weight-related variables, replace formula (1) for calculation;
所述计算单元根据推理/学习标志位、神经元/突触标志位、自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号,采用可重构的电路更新目的神经元膜电位、突触权值相关变量或突触权值;The computing unit adopts a reconfigurable circuit to update the target neuron membrane potential, synapse according to the inference/learning flag, neuron/synaptic flag, and the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules. Weight-related variables or synaptic weights;
其中,最小时间阈值为所述自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器映射网络采用clock-driven计算机制仿真时,根据网络仿真的单步步长决定的最小间隔,最大时间阈值为目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的时间常数的3~5倍。Among them, the minimum time threshold When using clock-driven computer simulation for the self-learning impulse neural network processor mapping network, the minimum interval determined according to the single step size of the network simulation, the maximum time threshold Time constants of variables related to the membrane potential of the target neuron or
进一步地,所述可重构控制器模块包括第一有限状态机;所述自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块包括第一数据选择器、第二数据选择器、第三数据选择器、第一减法器、第一比较器和第二比较器;所述计算单元包括控制通路和计算通路,所述控制通路包括第二有限状态机,所述计算通路包括第四数据选择器、第五数据选择器、第六数据选择器、第七数据选择器、第八数据选择器、第九数据选择器、除法器、指数计算模块、第二减法器、乘法器、第一加法器、第二加法器、第三加法器、第三比较器和数据分配器;Further, the reconfigurable controller module includes a first finite state machine; the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module includes a first data selector, a second data selector, and a third data selector a first subtractor, a first comparator and a second comparator; the calculation unit includes a control path and a calculation path, the control path includes a second finite state machine, the calculation path includes a fourth data selector, Fifth data selector, sixth data selector, seventh data selector, eighth data selector, ninth data selector, divider, exponent calculation module, second subtractor, multiplier, first adder, a second adder, a third adder, a third comparator, and a data distributor;
计算资源的数据包打包/拆分模块将处理单元中服务器模块或东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元中服务器模块传递的待更新的目的神经元-突触状态信息拆分成脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值和突触状态信息,并缓存,进一步将目的神经元状态信息拆分成待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元上次更新时间和目的神经元阈值,并缓存,将突触状态信息拆分成待更新突触权值相关变量、上次更新后突触权值和突触上次更新时间,并缓存;将突触更新计数值、从自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器外部传输的推理/学习标志位传输至可重构控制器模块,可重构控制器模块内部的第一有限状态机根据突触更新计数值和推理/学习标志位的状态输出神经元/突触标志位,以控制计算单元,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取不同的数据完成计算,从而实现推理与学习的可重构,具体为:The data packet packing/splitting module of the computing resource splits the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated transmitted by the server module in the processing unit or the server module in the processing unit in the four directions of east, south, west and north into pulses Generate time, target neuron ID, target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value and synapse state information, and cache them, and further split the target neuron state information into the target neuron membrane potential to be updated, The last update time of the target neuron and the threshold value of the target neuron are cached, and the synapse state information is divided into variables related to the synapse weight to be updated, the synapse weight after the last update, and the last update time of the synapse, and Cache; transfer the synaptic update count value and the inference/learning flag bit transmitted from the outside of the autonomous learning spiking neural network processor to the reconfigurable controller module, and the first finite state machine inside the reconfigurable controller module according to the synaptic Update count value and state of inference/learning flags Output neuron/synaptic flags to control computing units, adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules pull different from packet packing/splitting modules The data completes the calculation, so as to realize the reconfiguration of reasoning and learning, specifically:
当推理/学习标志位为0、突触更新计数值为0时,计算资源处于推理模式,执行目的神经元膜电位的更新计算,此时神经元/突触标志位为0,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间和目的神经元上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元阈值和上次更新后突触权值;When the inference/learning flag is 0 and the synapse update count is 0, the computing resource is in inference mode, and the update calculation of the target neuron membrane potential is performed. At this time, the neuron/synapse flag is 0, and the adaptive The clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules pull the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, and control the computing unit to pull the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, the target neuron threshold and the synaptic weight after the last update. ;
当推理/学习标志位为1、突触更新计数值为0时,计算资源处于学习模式的第一阶段,将执行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算、待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算;此时神经元/突触标志位先为0,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间和目的神经元上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元阈值和上次更新后突触权值,以进行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算;计算完后,神经元/突触标志位为1,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间和突触上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新突触权值相关变量和上次更新后突触权值,进行待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算;When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the synaptic update count is 0, the computing resource is in the first stage of the learning mode, and an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated will be performed, and the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated will be executed. An update calculation of the last update and an update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update; at this time, the neuron/synaptic flag bit is first 0, which controls the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules to pull the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, control the computing unit to pull the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, the threshold of the target neuron and the synaptic weight after the last update, so as to perform an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated; After the calculation, the neuron/synapse flag is set to 1, which controls the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules to pull the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse, and controls the calculation unit to pull the synapse to be updated. Weight-related variables and synaptic weights after the last update, perform one update calculation of the synaptic weight related variables to be updated and one update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update;
当推理/学习标志位为1、突触更新计数值为1时,计算资源处于学习模式的第二阶段,将执行待更新突触权值相关变量的二次更新计算、上次更新后突触权值的二次更新计算,此时神经元/突触标志位为1,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间和突触上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新突触权值相关变量和上次更新后突触权值,进行待更新突触权值相关变量的二次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的二次更新计算;When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the synaptic update count is 1, the computing resource is in the second stage of the learning mode, and will perform the second update calculation of the variables related to the synapse weights to be updated, and the synapse after the last update. The second update calculation of the weight, at this time the neuron/synaptic flag is 1, which controls the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module to pull the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse, and controls the computing unit Pull the relevant variables of the synaptic weights to be updated and the synaptic weights after the last update, and perform the secondary update calculation of the variables related to the synaptic weights to be updated and the secondary update calculation of the synaptic weights after the last update;
所述自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块中第一数据选择器连接数据包打包/拆分模块,为0的神经元/突触标志位控制第一数据选择器从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取脉冲产生时间和目的神经元上次更新时间,为1的神经元/突触标志位控制第一数据选择器从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取脉冲产生时间和突触上次更新时间,再传输至第一减法器计算更新时间间隔;与最小时间阈值一起作为第一比较器的输入信号,若,则输出1,反之输出0,再与最大时间阈值一起作为第二比较器的输入信号,若,则输出1,反之输出0,将第二比较器的输出作为第三数据选择器的控制信号;第一比较器的输出信号作为第二数据选择器的控制信号,clock-driven标志与event-driven标志作为第二数据选择器的输入信号,若第二数据选择器控制信号为1,则输出clock-driven标志,反之输出event-driven标志;第二数据选择器的输出信号与跳过计算标志共同作为第三数据选择器的输入信号,若第三数据选择器控制信号为1,则输出跳过计算标志,反之输出第二数据选择器的输出信号,第三数据选择器的输出信号用于控制计算单元的计算,此时自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为clock-driven标志、event-driven标志或跳过计算标志,分别用00、01、11表示;The first data selector in the self-adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module is connected to the data packet packing/splitting module, and the neuron/synaptic flag bit of 0 controls the first data selector to pack from the data packet / The split module pulls the pulse generation time and the last update time of the destination neuron, and the neuron/synaptic flag bit is 1 to control the first data selector from the packet packing / The split module pulls the pulse generation time and synapse The last update time, and then transmitted to the first subtractor to calculate the update time interval ; with minimum time threshold together as the input signal of the first comparator, if , then
推理/学习标志位,神经元/突触标志位,和自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号共同决定控制通路中第二有限状态机的工作状态,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号再控制计算通路更新目的神经元膜电位、突触权值相关变量或突触权值,第二有限状态机不同工作状态下的计算通路执行计算的情况如下:The reasoning/learning flag, the neuron/synaptic flag, and the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanisms jointly determine the working state of the second finite state machine in the control pathway, the second finite state machine The output control signal then controls the computing pathway to update the membrane potential of the target neuron, the variable related to the synaptic weight or the synaptic weight. The computations performed by the computing pathway under different working states of the second finite state machine are as follows:
当推理/学习标志位为0,神经元/突触标志位为0时,计算资源处于推理模式,执行目的神经元膜电位的更新计算,具体为:When the inference/learning flag is 0 and the neuron/synapse flag is 0, the computing resource is in inference mode, and the update calculation of the target neuron membrane potential is performed, specifically:
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为01时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号,分别控制第四数据选择器输出预设定的推理时间常数负值,第五数据选择器输出从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的待更新目的神经元膜电位,第六数据选择器输出预设定的目的神经元膜电位静息值;第一减法器输出的与第四数据选择器输出的推理时间常数负值共同作为除法器的输入,所得商再输入至指数计算模块,得到以自然常数e为底、商为指数的指数函数;自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号01控制第八数据选择器输出第六数据选择器输出的目的神经元膜电位静息值;第五数据选择器和第八数据选择器的输出共同作为第二减法器的输入,所得差再与指数计算模块输出的指数函数共同输入至乘法器相乘,所得积与第八数据选择器的输出共同输入至第一加法器,所得和为泄露后目的神经元膜电位;将所得泄露后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第二加法器,所得和为更新后目的神经元膜电位;所得更新后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的目的神经元阈值共同输入至第三比较器作比较,若更新后目的神经元膜电位大于目的神经元阈值,则第三比较器输出新脉冲信号至数据包打包/拆分模块,同时控制第九数据选择器输出目的神经元复位值,否则第三比较器控制第九数据选择器输出第二加法器所得更新后目的神经元膜电位;控制信号控制数据分配器输出第九数据选择器的输出,作为更新后目的神经元膜电位传输至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 01, the control signal output by the second finite state machine respectively controls the fourth data selector to output a preset negative value of the inference time constant. The fifth data selector outputs the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated pulled from the data packet packing/splitting module, the sixth data selector outputs the preset resting value of the target neuron membrane potential; the first subtractor outputs the The negative value of the inference time constant output by the fourth data selector is used as the input of the divider, and the obtained quotient is then input to the exponential calculation module to obtain an exponential function with the natural constant e as the base and the quotient as the exponent; self-adaptive clock-driven The output signal 01 of the event-driven computer mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the target neuron membrane potential resting value output by the sixth data selector; the outputs of the fifth data selector and the eighth data selector are jointly used as the first The input of the second subtractor, the difference obtained and the exponential function output by the exponential calculation module are jointly input to the multiplier for multiplication, and the obtained product and the output of the eighth data selector are jointly input to the first adder. Membrane potential; input the obtained membrane potential of the target neuron after the leak together with the synaptic weight after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module to the second adder, and the resulting sum is the membrane of the target neuron after the update potential; the obtained updated target neuron membrane potential and the target neuron threshold pulled from the data packet packaging/splitting module are input to the third comparator for comparison. If the updated target neuron membrane potential is greater than the target neuron threshold, Then the third comparator outputs a new pulse signal to the data packet packing/splitting module, and at the same time controls the ninth data selector to output the reset value of the destination neuron, otherwise the third comparator controls the ninth data selector to output the update obtained by the second adder After the target neuron membrane potential; the control signal controls the data distributor to output the output of the ninth data selector, which is transmitted to the data packet packaging/splitting module as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为00时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第七数据选择器输出预设定的推理泄露值,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号00控制第八数据选择器输出第七数据选择器输出的推理泄露值,再与第五数据选择器输出的待更新目的神经元膜电位共同输入至第二减法器,所得差在控制信号下输入至第二加法器,与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值求和,所得和为更新后目的神经元膜电位;所得更新后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的目的神经元阈值共同输入至第三比较器作比较,若更新后目的神经元膜电位大于目的神经元阈值,则第三比较器输出新脉冲信号至数据包打包/拆分模块,同时控制第九数据选择器输出目的神经元复位值,否则第三比较器控制第九数据选择器输出第二加法器所得更新后目的神经元膜电位;控制信号控制数据分配器输出第九数据选择器的输出,作为更新后目的神经元膜电位传输至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 00, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the seventh data selector to output a preset inference leakage value, and the adaptive clock- The output signal 00 of the driven and event-driven computing mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the inference leakage value output by the seventh data selector, and then together with the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated outputted by the fifth data selector is input to the first Two subtractors, the difference is input to the second adder under the control signal, and the synaptic weights after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module are summed, and the obtained sum is the target neuron membrane potential after the update ; The obtained updated target neuron membrane potential and the target neuron threshold pulled from the data packet packaging/splitting module are input to the third comparator for comparison. If the updated target neuron membrane potential is greater than the target neuron threshold, then The third comparator outputs a new pulse signal to the data packet packing/splitting module, and controls the ninth data selector to output the reset value of the target neuron, otherwise the third comparator controls the ninth data selector to output the updated value obtained by the second adder The target neuron membrane potential; the control signal controls the data distributor to output the output of the ninth data selector, which is transmitted to the data packet packaging/splitting module as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为11时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第六选择器将输出的目的神经元膜电位静息值输入至第二加法器,与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值求和,所得和为更新后目的神经元膜电位;所得更新后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的目的神经元阈值共同输入至第三比较器作比较,若更新后目的神经元膜电位大于目的神经元阈值,则第三比较器输出新脉冲信号至数据包打包/拆分模块,同时控制第九数据选择器输出目的神经元复位值,否则第三比较器控制第九数据选择器输出第二加法器所得更新后目的神经元膜电位;控制信号控制数据分配器输出第九数据选择器的输出,作为更新后目的神经元膜电位传输至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signal of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module is 11, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the sixth selector to input the output resting value of the target neuron membrane potential to the second The adder sums the synaptic weights after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module, and the resulting sum is the updated target neuron membrane potential; / The threshold value of the target neuron pulled by the splitting module is jointly input to the third comparator for comparison. If the membrane potential of the target neuron after the update is greater than the target neuron threshold, the third comparator outputs a new pulse signal to the packet packaging/demolition It is divided into modules and controls the ninth data selector to output the reset value of the target neuron at the same time, otherwise the third comparator controls the ninth data selector to output the updated target neuron membrane potential obtained by the second adder; the control signal controls the data distributor to output the first The output of the nine data selectors is transmitted to the data packet packing/splitting module as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
当推理/学习标志位为1、更新计数器为0时,计算资源处于学习模式的第一阶段,将执行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算、待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算;此时神经元/突触更新标志位先为0,执行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算,更新计算方法与计算资源处于推理模式时执行目的神经元膜电位的更新计算的方法一致;数据包打包/拆分模块接收到更新后目的神经元膜电位后,输入计算单元计算完成信号至可重构控制器模块中的第一有限状态机,控制第一有限状态机输出的神经元/突触更新标志位为1,执行待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算,具体为:When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the update counter is 0, the computing resource is in the first stage of the learning mode, and an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated and an update of the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated will be performed. Calculation and an update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update; at this time, the neuron/synapse update flag is first 0, and an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated is performed. The update calculation method and computing resources are in the process of inference. The method of performing the update calculation of the target neuron membrane potential in the mode is the same; after the data packet packing/splitting module receives the updated target neuron membrane potential, it inputs the calculation unit to calculate the completion signal to the first in the reconfigurable controller module. The finite state machine controls the neuron/synaptic update flag bit output by the first finite state machine to be 1, and performs an update calculation of the relevant variables of the synaptic weight to be updated and an update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update, Specifically:
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为01时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号,分别控制第四数据选择器输出预设定的学习时间常数负值,第五数据选择器输出从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的待更新突触权值相关变量,第六数据选择器输出预设定的突触权值相关变量静息值;第一减法器输出的与第四数据选择器输出的学习时间常数负值共同作为除法器的输入,所得商再输入至指数计算模块,得到以自然常数e为底、商为指数的指数函数;自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号01控制第八数据选择器输出第六数据选择器输出的突触权值相关变量静息值;第五数据选择器和第八数据选择器的输出共同作为第二减法器的输入,所得差再与指数计算模块输出的指数函数共同输入至乘法器相乘,所得积与第八数据选择器的输出共同输入至第一加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值相关变量,更新后突触权值相关变量输入至数据分配器后,在控制信号下输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;然后将数据分配器输出的更新后突触权值相关变量与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第三加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值,输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 01, the control signal output by the second finite state machine respectively controls the fourth data selector to output the preset negative value of the learning time constant. The fifth data selector outputs the synaptic weight-related variable to be updated pulled from the data packet packing/splitting module, the sixth data selector outputs the preset resting value of the synaptic weight-related variable; the first subtractor outputs of The negative value of the learning time constant output by the fourth data selector is used as the input of the divider, and the obtained quotient is then input to the exponential calculation module to obtain an exponential function with the natural constant e as the base and the quotient as the exponent; self-adaptive clock-driven The output signal 01 of the event-driven computer mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the synaptic weight-related variable rest value output by the sixth data selector; the outputs of the fifth data selector and the eighth data selector are used together as The input of the second subtractor, the obtained difference and the exponential function output by the exponential calculation module are jointly input to the multiplier for multiplication, and the obtained product and the output of the eighth data selector are jointly input to the first adder, and the obtained sum is the sum after the update. After the synaptic weight-related variables are updated, the updated synaptic weight-related variables are input to the data distributor, and then output to the data packet packing/splitting module under the control signal; then the updated synaptic weight-related variables output by the data distributor are It is input to the third adder together with the synaptic weight after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module, and the obtained sum is the updated synaptic weight, which is output to the packet packing/splitting module;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为00时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第七数据选择器输出预设定的学习泄露值,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号00控制第八数据选择器输出第七数据选择器输出的学习泄露值,再与第五数据选择器输出的待更新突触权值相关变量共同输入至第二减法器,所得差为更新后突触权值相关变量,更新后突触权值相关变量输入至数据分配器后,在控制信号下输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;然后将数据分配器输出的更新后突触权值相关变量与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第三加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值,输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 00, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the seventh data selector to output a preset learning leakage value, and the adaptive clock- The output signal 00 of the driven and event-driven computer mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the learning leakage value output by the seventh data selector, and is then jointly input with the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated output by the fifth data selector to The second subtractor, the difference obtained is the updated synaptic weight related variable, after the updated synaptic weight related variable is input to the data distributor, it is output to the data packet packing/splitting module under the control signal; then the data is distributed The relevant variables of the updated synaptic weight output by the adder and the last updated synaptic weight pulled from the packet packing/splitting module are jointly input to the third adder, and the resulting sum is the updated synaptic weight, and the output to the packet packing/splitting module;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为11时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第六选择器将输出的突触权值相关变量静息值输入至数据分配器,作为更新后突触权值相关变量,在控制信号下输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;然后将数据分配器输出的更新后突触权值相关变量与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第三加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值,输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signal of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module is 11, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the sixth selector to input the output synaptic weight related variable rest value into the data The distributor, as the relevant variable of the updated synaptic weight, is output to the data packet packing/splitting module under the control signal; The synaptic weights after the last update pulled by the module are jointly input to the third adder, and the resulting sum is the updated synaptic weights, which are output to the packet packing/splitting module;
当推理/学习标志位为1、更新计数器为1时,计算资源处于学习模式的第二阶段,此时神经元/突触更新标志位为1,将执行待更新突触权值相关变量的二次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的二次更新计算, 更新计算方法与计算资源处于学习模式第一阶段时执行待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算的更新计算的方法一致;When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the update counter is 1, the computing resource is in the second stage of the learning mode. At this time, the neuron/synaptic update flag is 1, and the second step of the variable related to the synaptic weight to be updated will be executed. The second update calculation and the second update calculation of the synaptic weights after the last update, the update calculation method and the computing resources are in the first stage of the learning mode to perform one update calculation of the variables related to the synaptic weights to be updated and synaptic weights after the last update. The method of update calculation of one update calculation of touch value is the same;
此时,第二有限状态机任意工作状态下的计算通路执行计算完毕;At this time, the calculation path of the second finite state machine in any working state has completed the calculation;
当计算资源处于推理模式时,数据包打包/拆分模块将接收的更新后目的神经元膜电位,与从待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息中拆分出的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元上次更新时间、目的神经元阈值、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息;当计算资源处于学习模式第一阶段时,数据包打包/拆分模块将接收的更新后目的神经元膜电位、更新后突触权值相关变量、更新后突触权值,与从待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息中拆分出的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元上次更新时间、目的神经元阈值、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触上次更新时间打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息;当计算资源处于学习模式第二阶段时,数据包打包/拆分模块将接收的更新后突触权值相关变量、更新后突触权值,与从待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息中拆分出的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触上次更新时间打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息;When the computing resource is in the inference mode, the packet packing/splitting module compares the received updated target neuron membrane potential with the pulse generation time and target neuron split from the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated. ID, target neuron last update time, target neuron threshold, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and synapse state information are packaged into updated target neuron-synapse state information; when the computing resource is in the learning mode, the first During the phase, the packet packing/splitting module will receive the updated target neuron membrane potential, the updated synaptic weight related variables, and the updated synaptic weight, and compare the received neuron-synaptic state information from the updated target neuron-synaptic state information. The split pulse generation time, destination neuron ID, destination neuron last update time, destination neuron threshold, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and synapse last update time are packaged into the updated destination neuron- Synapse state information; when the computing resource is in the second stage of the learning mode, the data packet packing/splitting module will receive the updated synaptic weight related variables, the updated synaptic weight, and the target neuron- The pulse generation time, destination neuron ID, destination neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and last update time of the synapse split from the synapse state information are packaged into the updated destination neuron-synapse status information;
所得更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息与推理/学习标志位共同经服务器模块传输至客户端模块,客户端模块将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息写回存储器,更新目的神经元和/或突触的状态信息,其中,采用脉冲产生时间更新目的神经元上次更新时间和/或突触上次更新时间;若数据包打包/拆分模块有接收到新脉冲信号,数据包打包/拆分模块还将新脉冲信号经服务器模块传输至客户端模块;客户端模块接收到新脉冲信号后,将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息中的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID与进行本地处理的处理单元的ID共同组成一个新脉冲包,并由进行本地处理的处理单元的ID和目的神经元ID组成新脉冲包的源神经元ID;客户端模块将新脉冲包和推理/学习标志位传递给内部路由模块,若推理/学习标志位为0,内部路由模块将新脉冲包传输至外部路由模块,外部路由模块再根据预先配置的路由表查询新脉冲包是否需要通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元;若推理/学习标志位为1,内部路由模块将新脉冲包传输至外部路由模块,外部路由模块再根据预先配置的路由表查询新脉冲包是否需要通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元,内部路由模块还将新脉冲包传输至脉冲队列模块,根据新脉冲包的源神经元ID,通过控制器模块、搜索模块、存储器、客户端模块查找对应脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息,组成待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息,经服务器模块输入至执行计算的计算资源,进行学习模式第二阶段;The obtained updated target neuron-synaptic state information and the inference/learning flag are jointly transmitted to the client module through the server module, and the client module writes the updated target neuron-synaptic state information back to the memory, and updates the target neuron and / or the status information of the synapse, wherein the pulse generation time is used to update the last update time of the target neuron and/or the last update time of the synapse; if the packet packing/splitting module receives a new pulse signal, the packet packing / The splitting module also transmits the new pulse signal to the client module through the server module; after the client module receives the new pulse signal, it will update the target neuron-synaptic state information in the pulse generation time, target neuron ID and The IDs of the processing units that perform local processing together form a new pulse packet, and the ID of the processing unit that performs local processing and the destination neuron ID form the source neuron ID of the new pulse packet; the client module combines the new pulse packet with the inference/ The learning flag is passed to the internal routing module. If the inference/learning flag is 0, the internal routing module transmits the new pulse packet to the external routing module. The external routing module then queries whether the new pulse packet needs to pass through the data port according to the pre-configured routing table. Routing to processing units in four directions: east, south, west, and north; if the inference/learning flag is 1, the internal routing module transmits the new pulse packet to the external routing module, and the external routing module queries the new pulse packet according to the pre-configured routing table. Whether the pulse packet needs to be routed to the processing units in the four directions of east, south, west and north through the data port, the internal routing module also transmits the new pulse packet to the pulse queue module, according to the source neuron ID of the new pulse packet, through the controller Module, search module, memory, client module look up the corresponding pulse generation time, target neuron ID, target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, synapse state information, and form the target neuron to be updated - synapse The touch state information is input to the computing resources that perform the calculation through the server module, and the second stage of the learning mode is carried out;
进一步地,外界的脉冲包先经东向通道、南向通道、西向通道或北向通道输入至预设定处理单元的外部路由模块,外部路由模块根据预先配置的路由表查询脉冲包是否需要进行本地处理或通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元。Further, the external pulse packet is first input to the external routing module of the preset processing unit through the east channel, south channel, west channel or north channel, and the external routing module queries whether the pulse packet needs to be localized according to the preconfigured routing table. Processing or routing through data ports to processing units in the east, south, west, and north directions.
本发明的有益效果为:The beneficial effects of the present invention are:
1、本发明通过设计多个独占计算资源和可借用计算资源,实现计算资源共享技术,可充分利用脉冲神经网络处理器的硬件资源,提高处理器的运行速度和能效;1. The present invention realizes the computing resource sharing technology by designing a plurality of exclusive computing resources and borrowable computing resources, which can make full use of the hardware resources of the pulse neural network processor and improve the running speed and energy efficiency of the processor;
2、本发明采用由脉冲产生时间和源神经元ID组成的脉冲包进行信息传送,相比于现有由脉冲产生时间和目的神经元ID构成的脉冲包,本发明无需在处理单元间传送与待更新目的神经元个数相同的脉冲包,而是采用中继的方式,以每个处理单元的外部路由模块为中继,仅向需要传送脉冲包的方向传送脉冲包,大大降低传送的脉冲包数量,进而降低对处理器的传输带宽要求;2. The present invention uses pulse packets composed of pulse generation time and source neuron ID for information transmission. Compared with the existing pulse packets composed of pulse generation time and destination neuron ID, the present invention does not need to transmit and communicate between processing units. The pulse packets with the same number of target neurons to be updated are relayed, and the external routing module of each processing unit is used as a relay to transmit the pulse packets only to the direction that needs to transmit the pulse packets, which greatly reduces the transmitted pulse packets. The number of packets, thereby reducing the transmission bandwidth requirements of the processor;
3、本发明提出的一种可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器,无需采用额外的学习电路,通过复用推理过程采用的电路,即可支持脉冲神经网络的在线学习,有效降低使用的硬件资源;3. The reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor proposed by the present invention does not need to use additional learning circuits, and can support the online learning of spiking neural networks by reusing the circuits used in the reasoning process, effectively reducing the use of hardware resources;
4、本发明优选地在计算资源中设计一个自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块,根据不同的更新时间间隔,采用clock-driven或event-driven计算机制更新目的神经元或/和突触的状态信息,进而降低脉冲神经网络处理器的功耗。4. The present invention preferably designs an adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module in the computing resource, and according to different update time intervals, adopts the clock-driven or event-driven computing mechanism to update the target neuron or/and Synaptic state information, thereby reducing the power consumption of spiking neural network processors.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明实施例1提供的可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器的结构图;1 is a structural diagram of a reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor provided in
图2是本发明实施例1提供的可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器中处理单元的结构图;2 is a structural diagram of a processing unit in the reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor provided in
图3是本发明实施例1提供的可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器中外部路由模块预先配置的路由表的组成图;3 is a composition diagram of a routing table preconfigured by an external routing module in the reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor provided in
图4是本发明实施例1提供的可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器中计算资源的结构图;4 is a structural diagram of computing resources in the reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor provided in
图5是本发明实施例1提供的可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器中计算资源的分配规则图。FIG. 5 is a diagram of the allocation rule of computing resources in the reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor provided in
附图包括以下附图标记:The drawings include the following reference numbers:
1:推理/学习标志位;1: Reasoning/learning flag bit;
2:更新后的目的神经元-突触状态信息;2: The updated target neuron-synaptic state information;
3:新脉冲信号;3: new pulse signal;
4:计算单元计算完成信号;4: The calculation unit calculates the completion signal;
5:待更新的目的神经元-突触状态信息;5: target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated;
6:突触更新计数器;6: Synaptic update counter;
7:目的神经元上次更新时间;7: The last update time of the target neuron;
8:突触上次更新时间;8: The last update time of the synapse;
9:脉冲产生时间;9: pulse generation time;
10:待更新目的神经元膜电位;10: The membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated;
11:待更新突触权值相关变量;11: variables related to synaptic weights to be updated;
12:跳过计算标志;12: Skip calculation flag;
13:更新后目的神经元膜电位;13: Membrane potential of the target neuron after updating;
14:更新后突触权值相关变量;14: Related variables of synaptic weights after updating;
15:上次更新后突触权值;15: The synaptic weight after the last update;
16:更新后突触权值;16: The updated synaptic weight;
17:更新时间间隔;17: Update interval ;
18:最小时间阈值;18: Minimum time threshold ;
19:最大时间阈值;19: Maximum time threshold ;
20:Clock-Driven机制标志;20: Clock-Driven mechanism flag;
21:Event-Driven机制标志;21: Event-Driven mechanism flag;
22:神经元/突触标志位;22: neuron/synaptic flag bit;
23:自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号;23: The output signal of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module;
24:控制信号;24: control signal;
25:目的神经元阈值;25: target neuron threshold;
26:推理时间常数负值;26: Negative value of inference time constant;
27:学习时间常数负值;27: negative value of learning time constant;
28:目的神经元膜电位静息值;28: resting value of target neuron membrane potential;
29:突触权值相关变量静息值;29: The resting value of the variable related to the synaptic weight;
30:推理泄露值;30: Inference leakage value;
31:学习泄露值;31: learn leakage value;
32:目的神经元复位值。32: The reset value of the target neuron.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清晰,结合以下具体实施例,并参照附图,对本发明做进一步的说明。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in conjunction with the following specific embodiments and with reference to the accompanying drawings.
实施例1Example 1
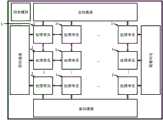
本实施例提出了一种可重构的自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器,如图1所示,包括由M×N个处理单元组成的处理单元阵列,同步模块,以及分布在处理单元阵列周围的东向通道、南向通道、西向通道、北向通道;This embodiment proposes a reconfigurable self-learning spiking neural network processor, as shown in FIG. 1 , which includes a processing unit array composed of M×N processing units, a synchronization module, and a processing unit array distributed around the processing unit array. East channel, south channel, west channel, north channel;
所述处理单元如图2所示,包括数据端口、控制端口、外部路由模块、排序模块、脉冲队列模块、控制器模块、搜索模块、存储器模块、客户端模块、服务器模块、内部路由模块、K+P个计算资源;所述K+P个计算资源由K个独占计算资源和P个可借用计算资源组成,所述独占计算资源为仅处理单元自己所用的计算资源,所述可借用计算资源为处理单元中可借用给其他处理单元的计算资源;所述存储器模块存有以源神经元ID为地址的目的神经元ID表、以源神经元ID为地址的突触ID表、以目的神经元ID为地址的目的神经元状态信息、以突触ID为地址的突触状态信息;其中,突触ID表包括突触ID和突触更新计数值;The processing unit, as shown in Figure 2, includes a data port, a control port, an external routing module, a sorting module, a pulse queue module, a controller module, a search module, a memory module, a client module, a server module, an internal routing module, a K +P computing resources; the K+P computing resources are composed of K exclusive computing resources and P borrowable computing resources, the exclusive computing resources are computing resources only used by the processing unit itself, and the borrowable computing resources It is a computing resource that can be borrowed to other processing units in the processing unit; the memory module stores the destination neuron ID table with the source neuron ID as the address, the synapse ID table with the source neuron ID as the address, and the destination neuron ID table. The element ID is the destination neuron state information of the address, and the synapse state information with the synapse ID as the address; wherein, the synapse ID table includes the synapse ID and the synapse update count value;
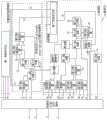
所述计算资源支持可重构的推理模式和学习模式,如图4所示,计算资源包括数据包打包/拆分模块、可重构控制器模块、自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块和计算单元;其中,所述可重构控制器模块包括第一有限状态机;所述自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块包括第一数据选择器、第二数据选择器、第三数据选择器、第一减法器、第一比较器、第二比较器;所述计算单元包括控制通路和计算通路,所述控制通路包括第二有限状态机,所述计算通路包括第四数据选择器、第五数据选择器、第六数据选择器、第七数据选择器、第八数据选择器、第九数据选择器、除法器、指数计算模块、第二减法器、乘法器、第一加法器、第二加法器、第三加法器、第三比较器和数据分配器;The computing resources support reconfigurable reasoning mode and learning mode. As shown in Figure 4, the computing resources include data packet packing/splitting modules, reconfigurable controller modules, adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computers A control module and a computing unit; wherein, the reconfigurable controller module includes a first finite state machine; the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules include a first data selector, a second data selector , a third data selector, a first subtractor, a first comparator, and a second comparator; the calculation unit includes a control path and a calculation path, the control path includes a second finite state machine, and the calculation path includes a first Four data selectors, fifth data selectors, sixth data selectors, seventh data selectors, eighth data selectors, ninth data selectors, divider, exponent calculation module, second subtractor, multiplier, a first adder, a second adder, a third adder, a third comparator and a data distributor;
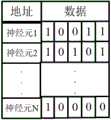
源处理单元发送的脉冲包先依次通过数据端口输入至处理单元的外部路由模块,所述脉冲包为30比特,由16比特的脉冲产生时间和14比特的源神经元ID组成,所述源神经元ID由4比特的源处理单元ID 和10比特的产生脉冲的源神经元在处理单元中的相对ID组成;外部路由模块根据预先配置的路由表查询脉冲包是否需要进行本地处理或通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元,所述路由表的组成图如图3所示,由地址和数据组成,地址为全局的源神经元ID,包括神经元1,神经元2,…,神经元N,数据中从左到右依次为源神经元对应的脉冲包传送至本地、北、南、西、东五个方向处理单元的方向信息,需要传送脉冲包的方向的方向信息为1,否则为0;The pulse packet sent by the source processing unit is firstly input to the external routing module of the processing unit through the data port. The pulse packet is 30 bits and consists of 16 bits of pulse generation time and 14 bits of source neuron ID. The element ID is composed of the 4-bit source processing unit ID and the 10-bit relative ID of the source neuron that generates the pulse in the processing unit; the external routing module queries whether the pulse packet needs to be processed locally or through the data port according to the pre-configured routing table. Routing to processing units in four directions: east, south, west, and north. The composition diagram of the routing table is shown in Figure 3, which is composed of addresses and data. The address is the global source neuron ID, including
若处理单元需要对接收的脉冲包进行本地处理,外部路由模块将脉冲包传输至排序模块进行时间戳排序,得到排序后脉冲包,排序后脉冲包传输至脉冲队列模块等待,待排序模块将接收的脉冲包全部排序完成,脉冲队列模块将代表排序完成的排序信号传输至控制器模块,控制器模块通过控制端口传输至同步模块,待所有处理单元均向同步模块传输排序信号后,同步模块回传处理信号至控制器模块;之后控制器模块触发搜索模块将脉冲队列模块中的排序后脉冲包依次取出,搜索模块根据排序后脉冲包的源神经元ID在存储器查找对应目的神经元ID、突触ID、突触更新计数值信息,并将脉冲产生时间与目的神经元ID、突触ID、突触更新计数值组成目的神经元-突触ID信息;搜索模块将查到的目的神经元-突触ID信息传输至客户端模块,客户端模块再根据目的神经元-突触ID信息,在存储器中查找对应目的神经元状态信息、突触状态信息,并将脉冲产生时间与目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息组成待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息,其中,所述目的神经元状态信息包括待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元上次更新时间、目的神经元阈值,所述突触状态信息包括待更新突触权值相关变量、上次更新后突触权值、突触上次更新时间,所述突触更新计数值用于控制计算资源执行学习模式第一阶段或学习模式第二阶段的更新计算,0为学习模式第一阶段,1为学习模式第二阶段;客户端模块将待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息传输至服务器模块,服务器模块按照分配规则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至处理单元的独占计算资源,处理单元的可借用计算资源,和/或北、南、西、东四个方向处理单元的可借用计算资源执行计算,并采用从自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器外部传输的推理/学习标志位控制执行计算的计算资源执行推理模式或学习模式,0为推理模式,1为学习模式;计算完成后,执行计算的计算资源将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息经服务器模块回传至客户端模块,客户端模块将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息写回存储器,更新目的神经元状态信息和突触状态信息;If the processing unit needs to perform local processing on the received pulse packets, the external routing module transmits the pulse packets to the sorting module for timestamp sorting, and obtains the sorted pulse packets. After sorting, the pulse packets are transmitted to the pulse queue module for waiting. After all the pulse packets are sorted, the pulse queue module transmits the sorting signal representing the completion of sorting to the controller module, and the controller module transmits it to the synchronization module through the control port. After all processing units transmit the sorting signal to the synchronization module, the synchronization module returns to the synchronization module. The processing signal is transmitted to the controller module; then the controller module triggers the search module to take out the sorted pulse packets in the pulse queue module in turn, and the search module searches the memory for the corresponding destination neuron ID, burst according to the source neuron ID of the sorted pulse packet. Contact ID, synapse update count value information, and combine the pulse generation time with the target neuron ID, synapse ID, synapse update count value to form the target neuron-synapse ID information; the search module will find the target neuron- The synapse ID information is transmitted to the client module, and the client module searches for the corresponding target neuron state information and synapse state information in the memory according to the target neuron-synapse ID information, and compares the pulse generation time with the target neuron ID. , target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and synapse state information to form the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated, wherein the target neuron state information includes the target neuron membrane potential to be updated , the last update time of the target neuron, the threshold value of the target neuron, the synapse state information includes the relevant variables of the synapse weight to be updated, the synapse weight after the last update, the last update time of the synapse, the synapse The update count value is used to control the computing resources to perform the update calculation of the first stage of the learning mode or the second stage of the learning mode, 0 is the first stage of the learning mode, 1 is the second stage of the learning mode; the client module will update the target neuron- The synaptic state information is transmitted to the server module, and the server module allocates the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated according to the allocation rules to the exclusive computing resources of the processing unit, the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit, and/or north, south, west, The computing resources of the processing units in the four east directions can be borrowed to perform calculations, and the inference/learning flag bits transmitted from the outside of the self-learning spiking neural network processor are used to control the computing resources that perform the calculations to execute the inference mode or the learning mode, 0 is the inference mode, 1 is the learning mode; after the calculation is completed, the computing resources that perform the calculation will return the updated target neuron-synaptic state information to the client module through the server module, and the client module will write the updated target neuron-synaptic state information Back to the memory, update the target neuron state information and synapse state information;
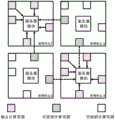
所述分配规则如图5所示,具体为:服务器模块依次查询处理单元的独占计算资源和可借用计算资源中是否存在空闲的计算资源,若存在空闲的独占计算资源,则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至空闲的处理单元的独占计算资源执行计算;若处理单元的独占计算资源均忙碌,而处理单元的可借用计算资源存在空闲,则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至处理单元的可借用计算资源执行计算;若处理单元的独占计算资源和可借用计算资源均处于忙碌状态,则服务器模块查询北、南、西、东四个方向的处理单元中是否存在空闲的可借用计算资源,若存在空闲的可借用计算资源,则分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息至空闲的可借用计算资源执行计算,若北、南、西、东四个方向的处理单元的可借用计算资源均处于忙碌状态,则服务器模块依次重复查询处理单元的独占计算资源,处理单元的可借用计算资源,北、南、西、东四个方向的处理单元的可借用计算资源中是否存在空闲的计算资源,直至存在空闲的计算资源再分配待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息;The allocation rules are shown in Figure 5, and are specifically as follows: the server module sequentially queries the exclusive computing resources and the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit whether there are idle computing resources, and if there are idle exclusive computing resources, then allocate the target neural network to be updated. Meta-synaptic state information is sent to the exclusive computing resources of the idle processing units to perform calculations; if the exclusive computing resources of the processing units are busy, and the borrowable computing resources of the processing units are idle, the target neuron-synaptic state to be updated is allocated. The information is sent to the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit to perform the calculation; if the exclusive computing resources and the borrowable computing resources of the processing unit are both in a busy state, the server module queries whether there are idle processing units in the four directions of north, south, west, and east. If there are idle borrowable computing resources, the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated will be allocated to the idle borrowable computing resources to perform calculations. If processing in the four directions of north, south, west, and east If the available computing resources of the unit are in a busy state, the server module repeatedly queries the exclusive computing resources of the processing unit, the available computing resources of the processing unit, and the available computing resources of the processing units in the north, south, west, and east directions. Whether there are idle computing resources in the system, until there are idle computing resources, the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated is redistributed;
计算资源执行计算的模式分为推理模式和学习模式,区别在于,对于神经元与突触状态的更新,推理模式仅更新目的神经元膜电位,学习模式既需要更新目的神经元膜电位,还需要更新突触权值相关变量和突触权值,这些更新计算可以用一组通式表示:Computational resource execution modes are divided into inference mode and learning mode. The difference is that, for the update of neuron and synapse states, inference mode only updates the membrane potential of the target neuron, while the learning mode needs to update the membrane potential of the target neuron and also Update the variables related to synaptic weights and synaptic weights. These update calculations can be expressed by a set of general formulas:
其中,为泄露后目的神经元膜电位或更新后突触权值相关变量;为待更新目的神经元膜电位或待更新突触权值相关变量;为脉冲产生时间与目的神经元上次更新时间的更新时间间隔,或脉冲产生时间与突触上次更新时间的更新时间间隔;为目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的静息值;为目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的时间常数;为上次更新后突触权值;为更新后目的神经元膜电位;为目的神经元复位值;为更新后突触权值;为目的神经元阈值;代表为神经元状态更新;in, It is the relevant variable of the target neuron membrane potential after leakage or the updated synaptic weight; For the target neuron membrane potential to be updated or the variable related to the synaptic weight to be updated; is the update time interval between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, or the update time interval between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse; The resting value of the variable related to the target neuron membrane potential or synaptic weight; The time constant of the variable related to the target neuron membrane potential or synaptic weight; is the synaptic weight after the last update; is the membrane potential of the target neuron after updating; reset value for the target neuron; is the updated synaptic weight; for the target neuron threshold; Represents the neuron state update;
公式(1)在更新目的神经元膜电位与突触权值相关变量中都要执行;公式(2)、(3)在更新目的神经元膜电位时执行,将泄露后目的神经元膜电位与上次更新后突触权值之和作为更新后目的神经元膜电位,若更新后目的神经元膜电位超过目的神经元阈值,则将更新后目的神经元膜电位重置为目的神经元复位值,同时还会产生新脉冲,否则不产生新脉冲;公式(4)仅在更新突触权值时执行,将突触权值更新为待更新突触权值与更新后突触权值相关变量之和。Formula (1) is executed in updating the relevant variables of the target neuron membrane potential and synaptic weight; formulas (2) and (3) are executed when updating the target neuron membrane potential. Synaptic weights since last update The sum is used as the updated target neuron membrane potential. If the updated target neuron membrane potential exceeds the target neuron threshold , then reset the updated target neuron membrane potential to the target neuron reset value , and a new pulse will be generated at the same time, otherwise no new pulse will be generated; formula (4) is only executed when the synaptic weight is updated, and the synaptic weight is Update the synaptic weights to be updated Sum of variables associated with updated synaptic weights.
从第一个等式可以看到,待更新目的神经元膜电位与待更新突触权值相关变量采用相似的微分方程进行描述,且公式(2)与公式(4)的计算方式也是近似的,因此可以用同样的硬件电路实现目的神经元膜电位与突触权值的更新,这就实现了推理与学习的可重构;It can be seen from the first equation that the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated and the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated are described by similar differential equations, and the calculation methods of formula (2) and formula (4) are also similar , so the same hardware circuit can be used to update the target neuron membrane potential and synaptic weight, which realizes the reconfiguration of reasoning and learning;
在推理模式,先对待更新目的神经元膜电位使用公式(1)执行一次更新计算,再执行公式(2),将公式(1)所得泄露后目的神经元膜电位与上次更新后突触权值之和作为更新后目的神经元膜电位,若更新后目的神经元膜电位高于目的神经元阈值,则执行公式(3),将更新后目的神经元膜电位重置为目的神经元复位值,同时产生新脉冲,否则不产生新脉冲;推理模式后得到更新后目的神经元膜电位;In the inference mode, use formula (1) to perform an update calculation on the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, and then execute formula (2), and compare the leaked target neuron membrane potential obtained by formula (1) with the synaptic weight after the last update. The sum of the values is used as the updated target neuron membrane potential. If the updated target neuron membrane potential is higher than the target neuron threshold, formula (3) is executed to reset the updated target neuron membrane potential to the target neuron reset value. , and generate new pulses at the same time, otherwise no new pulses are generated; after inference mode, the updated target neuron membrane potential is obtained;
在学习模式,分为两个阶段:In learning mode, there are two stages:
第一阶段,先对待更新目的神经元膜电位使用公式(1)执行一次更新计算,再执行公式(2),将公式(1)所得泄露后目的神经元膜电位与上次更新后突触权值之和作为更新后目的神经元膜电位,若更新后目的神经元膜电位高于目的神经元阈值,则执行公式(3),将更新后目的神经元膜电位重置为目的神经元复位值,同时产生新脉冲,否则不产生新脉冲;然后对待更新突触权值相关变量使用公式(1)执行一次更新计算,对上次更新后突触权值使用公式(4)执行一次更新计算;第一阶段得到更新后目的神经元膜电位、更新后突触权值相关变量、更新后突触权值,若第一阶段未产生新脉冲,则不执行第二阶段,否则执行第二阶段;In the first stage, use formula (1) to perform an update calculation on the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, and then execute formula (2). The sum of the values is used as the updated target neuron membrane potential. If the updated target neuron membrane potential is higher than the target neuron threshold, formula (3) is executed to reset the updated target neuron membrane potential to the target neuron reset value , and generate a new pulse at the same time, otherwise no new pulse will be generated; then use formula (1) to perform an update calculation for the relevant variables of the synaptic weight to be updated, and use formula (4) to perform an update calculation for the synaptic weight after the last update; The first stage obtains the updated target neuron membrane potential, the updated synaptic weight related variables, and the updated synaptic weight. If no new pulses are generated in the first stage, the second stage is not executed, otherwise the second stage is executed;
第二阶段,对待更新突触权值相关变量使用公式(1)执行二次更新计算,此时公式(1)中待更新突触权值相关变量为第一阶段所得更新后突触权值相关变量;对上次更新后突触权值使用公式(4)执行二次更新计算,此时公式(4)中上次更新后突触权值为第一阶段所得更新后突触权值;第二阶段得到更新后突触权值相关变量、更新后突触权值;In the second stage, the relevant variables of the synaptic weights to be updated are calculated using the formula (1) to perform the second update calculation. At this time, the relevant variables of the synaptic weights to be updated in the formula (1) are the relevant variables of the updated synaptic weights obtained in the first stage. variable; use the formula (4) to perform the second update calculation for the synaptic weight after the last update, at this time, the synapse weight after the last update in the formula (4) is the updated synapse weight obtained in the first stage; In the second stage, the relevant variables of the updated synaptic weight and the updated synaptic weight are obtained;
计算资源执行更新计算的具体过程如下:The specific process for the computing resource to perform the update calculation is as follows:
计算资源的数据包打包/拆分模块将处理单元中服务器模块或东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元中服务器模块传递的待更新的目的神经元-突触状态信息拆分成脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息,并缓存,进一步将目的神经元状态信息拆分成待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元上次更新时间、目的神经元阈值,并缓存,将突触状态信息拆分成待更新突触权值相关变量、上次更新后突触权值、突触上次更新时间,并缓存;将突触更新计数值、从自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器外部传输的推理/学习标志位传输至可重构控制器模块,可重构控制器模块内部的第一有限状态机根据突触更新计数值和推理/学习标志位的状态输出神经元/突触标志位,以控制计算单元,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取不同的数据完成计算,从而实现推理与学习的可重构,具体为:The data packet packing/splitting module of the computing resource splits the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated transmitted by the server module in the processing unit or the server module in the processing unit in the four directions of east, south, west and north into pulses Generate time, target neuron ID, target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, synapse state information, and cache them, and further split the target neuron state information into the target neuron membrane potential to be updated, The last update time of the target neuron and the threshold value of the target neuron are cached, and the synapse state information is divided into variables related to the synapse weight to be updated, the synapse weight after the last update, the last update time of the synapse, and the Cache; transfer the synaptic update count value and the inference/learning flag bit transmitted from the outside of the autonomous learning spiking neural network processor to the reconfigurable controller module, and the first finite state machine inside the reconfigurable controller module according to the synaptic Update count value and state of inference/learning flags Output neuron/synaptic flags to control computing units, adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules pull different from packet packing/splitting modules The data completes the calculation, so as to realize the reconfiguration of reasoning and learning, specifically:
当推理/学习标志位为0、突触更新计数值为0时,计算资源处于推理模式,执行目的神经元膜电位的更新计算,此时神经元/突触标志位为0,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间、目的神经元上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元阈值、上次更新后突触权值;When the inference/learning flag is 0 and the synapse update count is 0, the computing resource is in inference mode, and the update calculation of the target neuron membrane potential is performed. At this time, the neuron/synapse flag is 0, and the adaptive The clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules pull the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, and control the computing unit to pull the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, the target neuron threshold, and the synaptic weight after the last update. ;
当推理/学习标志位为1、突触更新计数值为0时,计算资源处于学习模式的第一阶段,将执行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算、待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算、上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算;此时神经元/突触标志位先为0,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间、目的神经元上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新目的神经元膜电位、目的神经元阈值、上次更新后突触权值,以进行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算;计算完后,神经元/突触标志位为1,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间、突触上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新突触权值相关变量、上次更新后突触权值,进行待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算;When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the synaptic update count is 0, the computing resource is in the first stage of the learning mode, and an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated will be performed, and the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated will be executed. An update calculation of the last update and an update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update; at this time, the neuron/synaptic flag bit is first 0, and the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are controlled to pull the pulse generation time , the last update time of the target neuron, and control the computing unit to pull the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated, the threshold of the target neuron, and the synaptic weight after the last update, so as to perform an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated; After the calculation, the neuron/synapse flag is set to 1, which controls the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules to pull the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse, and controls the calculation unit to pull the synapse to be updated. Weight-related variables and synaptic weights after the last update, perform one update calculation of the synaptic weight related variables to be updated and one update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update;
当推理/学习标志位为1、突触更新计数值为1时,计算资源处于学习模式的第二阶段,将执行待更新突触权值相关变量的二次更新计算、上次更新后突触权值的二次更新计算,此时神经元/突触更新标志位为1,控制自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块拉取脉冲产生时间、突触上次更新时间,控制计算单元拉取待更新突触权值相关变量、上次更新后突触权值,进行待更新突触权值相关变量的二次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的二次更新计算;When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the synaptic update count is 1, the computing resource is in the second stage of the learning mode, and will perform the second update calculation of the variables related to the synapse weights to be updated, and the synapse after the last update. The secondary update calculation of weights, at this time, the neuron/synaptic update flag is 1, which controls the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules to pull the pulse generation time, the last update time of the synapse, and control the calculation. The unit pulls the variables related to the synaptic weights to be updated and the synaptic weights after the last update, and performs the secondary update calculation of the variables related to the synaptic weights to be updated and the secondary update calculation of the synaptic weights after the last update;
所述自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块功能是根据脉冲包输入至处理单元的频率,自适应地改变计算单元执行更新计算的计算方式;当脉冲包输入至处理单元的频率高时,不同的脉冲包可能对应同一目的神经元,需要在短时间内对同一个目的神经元或者同一条突触执行多次公式(1)的计算,复杂度大,大大增加系统功耗,但这是毫无必要的,因为在短时间间隔,采用clock-driven机制的差分计算替代微分计算,亦能实现公式(1)的功能,而差分计算仅需要减法器或者乘法器就能实现,复杂度低,计算时功耗小;当脉冲包输入至处理单元的频率低时,一个神经元可能需要经历很久才能被更新,由于我们不知道其每次更新经过了多久,此时再使用差分替代微分进行公式(1)的计算就极其不准确,而且由于采用clock-driven机制,无论有没有输入脉冲到处理单元,每个短时间间隔都要计算,此时总的功耗采用clock-driven机制要比采用event-driven机制高,故使用能够实现公式(1)的电路进行计算;总的功耗还有一种情况,当脉冲包输入至处理单元的频率极低时,一个目的神经元的膜电位或突触权值相关变量可能衰减至静息值还不会更新,这时为了降低功耗,在更新时让其直接置为相应静息值,再进行公式(2)、(3)、(4)的计算;The self-adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module function is to adaptively change the calculation method of the calculation unit to perform the update calculation according to the frequency of the pulse packet input to the processing unit; when the frequency of the pulse packet input to the processing unit is high When , different pulse packets may correspond to the same target neuron, and it is necessary to perform multiple calculations of formula (1) on the same target neuron or the same synapse in a short time, which is complicated and greatly increases the system power consumption, but This is unnecessary, because in a short time interval, the differential calculation using the clock-driven mechanism can replace the differential calculation, and the function of formula (1) can also be realized, and the differential calculation only needs a subtractor or a multiplier. Low power consumption and low power consumption during calculation; when the frequency of pulse packets input to the processing unit is low, a neuron may take a long time to be updated. Since we do not know how long it takes for each update, we use differential replacement at this time. The calculation of formula (1) by differentiation is extremely inaccurate, and because of the clock-driven mechanism, regardless of whether there is an input pulse to the processing unit, each short time interval must be calculated. At this time, the total power consumption adopts the clock-driven mechanism. It is higher than the event-driven mechanism, so use a circuit that can realize formula (1) for calculation; there is also a case of total power consumption, when the frequency of pulse packets input to the processing unit is extremely low, the membrane of a target neuron The potential or synaptic weight-related variables may decay to the resting value and will not be updated. In this case, in order to reduce power consumption, let it be directly set to the corresponding resting value when updating, and then perform formulas (2), (3), (4) calculation;
当脉冲产生时间与目的神经元上次更新时间,或脉冲产生时间与突触上次更新时间的差值小于预设定的最小时间阈值时,控制计算单元执行clock-driven机制的计算,使用下述公式(5)取代公式(1)计算;When the pulse generation time and the last update time of the target neuron, or the difference between the pulse generation time and the last update time of the synapse less than a preset minimum time threshold When , the control computing unit performs the calculation of the clock-driven mechanism, and uses the following formula (5) to replace the formula (1) for calculation;
其中,为推理泄露值或学习泄露值;in, For inference leaked values or learning leaked values;
当大于最小时间阈值而小于预设定的最大时间阈值时,控制计算单元执行event-driven机制的计算,采用公式(1)计算;当大于最大时间阈值时,控制计算单元用目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的静息值分别覆盖待更新目的神经元膜电位或待更新突触权值相关变量,得到泄露后目的神经元膜电位或更新后突触权值相关变量,取代公式(1)计算;when greater than the minimum time threshold while less than the preset maximum time threshold , the control computing unit performs the calculation of the event-driven mechanism, using formula (1) to calculate; when greater than the maximum time threshold When , the control computing unit covers the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated or the variable related to the synaptic weight with the resting value of the target neuron membrane potential or the synaptic weight-related variable, respectively, and obtains the target neuron membrane potential after leakage or After the update, the relevant variables of synaptic weights are replaced by formula (1);
所述自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块中第一数据选择器连接数据包打包/拆分模块,为0的神经元/突触标志位控制第一数据选择器从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取脉冲产生时间和目的神经元上次更新时间,为1的神经元/突触标志位控制第一数据选择器从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取脉冲产生时间和突触上次更新时间,再传输至第一减法器计算更新时间间隔;与最小时间阈值一起作为第一比较器的输入信号,若,则输出1,反之输出0,再与最大时间阈值一起作为第二比较器的输入信号,若,则输出1,反之输出0,将第二比较器的输出作为第三数据选择器的控制信号;第一比较器的输出信号作为第二数据选择器的控制信号,clock-driven标志与event-driven标志作为第二数据选择器的输入信号,若第二数据选择器控制信号为1,则输出clock-driven标志,反之输出event-driven标志;第二数据选择器的输出信号与跳过计算标志共同作为第三数据选择器的输入信号,若第三数据选择器控制信号为1,则输出跳过计算标志,反之输出第二数据选择器的输出信号,第三数据选择器的输出信号用于控制计算单元的计算,此时自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为clock-driven标志、event-driven标志或跳过计算标志,分别用00、01、11表示;其中最小时间阈值为所述自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器映射网络采用clock-driven计算机制仿真时,根据网络仿真的单步步长决定的最小间隔,最大时间阈值为目的神经元膜电位或突触权值相关变量的时间常数的3~5倍;The first data selector in the self-adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module is connected to the data packet packing/splitting module, and the neuron/synaptic flag bit of 0 controls the first data selector to pack from the data packet / The split module pulls the pulse generation time and the last update time of the destination neuron, and the neuron/synaptic flag bit is 1 to control the first data selector from the packet packing / The split module pulls the pulse generation time and synapse The last update time, and then transmitted to the first subtractor to calculate the update time interval ; with minimum time threshold together as the input signal of the first comparator, if , then
从自主学习脉冲神经网络处理器外部传输的推理/学习标志位,可重构控制器模块输出的神经元/突触推理标志位,和自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号共同决定控制通路中第二有限状态机的工作状态,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号再控制计算通路更新目的神经元膜电位、突触权值相关变量或突触权值,第二有限状态机不同工作状态下的计算通路执行计算的情况如下:Inference/learning flags transmitted from outside the self-learning spiking neural network processor, neuron/synaptic inference flags output from the reconfigurable controller module, and outputs from the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism modules The signals jointly determine the working state of the second finite state machine in the control pathway, and the control signal output by the second finite state machine then controls the calculation pathway to update the target neuron membrane potential, synaptic weight-related variables or synaptic weights. The computations performed by the computation paths in different working states of the state machine are as follows:
当推理/学习标志位为0,神经元/突触标志位为0,计算资源处于推理模式,执行目的神经元膜电位的更新计算,具体为:When the inference/learning flag is 0, the neuron/synapse flag is 0, the computing resource is in the inference mode, and the update calculation of the target neuron membrane potential is performed, specifically:
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为01时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号,分别控制第四数据选择器输出预设定的推理时间常数负值,第五数据选择器输出从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的待更新目的神经元膜电位,第六数据选择器输出预设定的目的神经元膜电位静息值;第一减法器输出的与第四数据选择器输出的推理时间常数负值共同作为除法器的输入,所得商再输入至指数计算模块,得到以自然常数e为底、商为指数的指数函数;自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号01控制第八数据选择器输出第六数据选择器输出的目的神经元膜电位静息值;第五数据选择器和第八数据选择器的输出共同作为第二减法器的输入,所得差再与指数计算模块输出的指数函数共同输入至乘法器相乘,所得积与第八数据选择器的输出共同输入至第一加法器,所得和为泄露后目的神经元膜电位;将所得泄露后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第二加法器,所得和为更新后目的神经元膜电位;所得更新后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的目的神经元阈值共同输入至第三比较器作比较,若更新后目的神经元膜电位大于目的神经元阈值,则第三比较器输出新脉冲信号至数据包打包/拆分模块,同时控制第九数据选择器输出目的神经元复位值,否则第三比较器控制第九数据选择器输出第二加法器所得更新后目的神经元膜电位;控制信号控制数据分配器输出第九数据选择器的输出,作为更新后目的神经元膜电位传输至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 01, the control signal output by the second finite state machine respectively controls the fourth data selector to output a preset negative value of the inference time constant. The fifth data selector outputs the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated pulled from the data packet packing/splitting module, the sixth data selector outputs the preset resting value of the target neuron membrane potential; the first subtractor outputs the The negative value of the inference time constant output by the fourth data selector is used as the input of the divider, and the obtained quotient is then input to the exponential calculation module to obtain an exponential function with the natural constant e as the base and the quotient as the exponent; self-adaptive clock-driven The output signal 01 of the event-driven computer mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the target neuron membrane potential resting value output by the sixth data selector; the outputs of the fifth data selector and the eighth data selector are jointly used as the first The input of the second subtractor, the difference obtained and the exponential function output by the exponential calculation module are jointly input to the multiplier for multiplication, and the obtained product and the output of the eighth data selector are jointly input to the first adder. Membrane potential; input the obtained membrane potential of the target neuron after the leak together with the synaptic weight after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module to the second adder, and the resulting sum is the membrane of the target neuron after the update potential; the obtained updated target neuron membrane potential and the target neuron threshold pulled from the data packet packaging/splitting module are input to the third comparator for comparison. If the updated target neuron membrane potential is greater than the target neuron threshold, Then the third comparator outputs a new pulse signal to the data packet packing/splitting module, and at the same time controls the ninth data selector to output the reset value of the destination neuron, otherwise the third comparator controls the ninth data selector to output the update obtained by the second adder After the target neuron membrane potential; the control signal controls the data distributor to output the output of the ninth data selector, which is transmitted to the data packet packaging/splitting module as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为00时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第七数据选择器输出预设定的推理泄露值,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号00控制第八数据选择器输出第七数据选择器输出的推理泄露值,再与第五数据选择器输出的待更新目的神经元膜电位共同输入至第二减法器,所得差在控制信号下输入至第二加法器,与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值求和,所得和为更新后目的神经元膜电位;所得更新后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的目的神经元阈值共同输入至第三比较器作比较,若更新后目的神经元膜电位大于目的神经元阈值,则第三比较器输出新脉冲信号至数据包打包/拆分模块,同时控制第九数据选择器输出目的神经元复位值,否则第三比较器控制第九数据选择器输出第二加法器所得更新后目的神经元膜电位;控制信号控制数据分配器输出第九数据选择器的输出,作为更新后目的神经元膜电位传输至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 00, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the seventh data selector to output a preset inference leakage value, and the adaptive clock- The output signal 00 of the driven and event-driven computing mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the inference leakage value output by the seventh data selector, and then together with the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated outputted by the fifth data selector is input to the first Two subtractors, the difference is input to the second adder under the control signal, and the synaptic weights after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module are summed, and the obtained sum is the target neuron membrane potential after the update ; The obtained updated target neuron membrane potential and the target neuron threshold pulled from the data packet packaging/splitting module are input to the third comparator for comparison. If the updated target neuron membrane potential is greater than the target neuron threshold, then The third comparator outputs a new pulse signal to the data packet packing/splitting module, and controls the ninth data selector to output the reset value of the target neuron, otherwise the third comparator controls the ninth data selector to output the updated value obtained by the second adder The target neuron membrane potential; the control signal controls the data distributor to output the output of the ninth data selector, which is transmitted to the data packet packaging/splitting module as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为11时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第六选择器将输出的目的神经元膜电位静息值输入至第二加法器,与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值求和,所得和为更新后目的神经元膜电位;所得更新后目的神经元膜电位与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的目的神经元阈值共同输入至第三比较器作比较,若更新后目的神经元膜电位大于目的神经元阈值,则第三比较器输出新脉冲信号至数据包打包/拆分模块,同时控制第九数据选择器输出目的神经元复位值,否则第三比较器控制第九数据选择器输出第二加法器所得更新后目的神经元膜电位;控制信号控制数据分配器输出第九数据选择器的输出,作为更新后目的神经元膜电位传输至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signal of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism module is 11, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the sixth selector to input the output resting value of the target neuron membrane potential to the second The adder sums the synaptic weights after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module, and the resulting sum is the updated target neuron membrane potential; / The threshold value of the target neuron pulled by the splitting module is jointly input to the third comparator for comparison. If the membrane potential of the target neuron after the update is greater than the target neuron threshold, the third comparator outputs a new pulse signal to the packet packaging/demolition It is divided into modules and controls the ninth data selector to output the reset value of the target neuron at the same time, otherwise the third comparator controls the ninth data selector to output the updated target neuron membrane potential obtained by the second adder; the control signal controls the data distributor to output the first The output of the nine data selectors is transmitted to the data packet packing/splitting module as the updated target neuron membrane potential;
当推理/学习标志位为1、更新计数器为0时,计算资源处于学习模式的第一阶段,将执行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算、待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算、上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算;此时神经元/突触更新标志位先为0,执行待更新目的神经元膜电位的一次更新计算,更新计算方法与计算资源处于推理模式时执行的目的神经元膜电位的更新计算方法一致;数据包打包/拆分模块接收到更新后目的神经元膜电位后,输入计算单元计算完成信号至可重构控制器模块中的第一有限状态机,用于控制第一有限状态机输出的神经元/突触更新标志位为1,执行待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算和上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算,具体为:When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the update counter is 0, the computing resource is in the first stage of the learning mode, and an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated and an update of the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated will be performed. Calculation, an update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update; at this time, the neuron/synapse update flag is first 0, and an update calculation of the membrane potential of the target neuron to be updated is performed. The update calculation method and computing resources are in the process of inference. The update calculation method of the target neuron membrane potential executed in the mode is the same; after the data packet packing/splitting module receives the updated target neuron membrane potential, it inputs the calculation unit to calculate the completion signal to the first in the reconfigurable controller module. The finite state machine is used to control the neuron/synaptic update flag bit output by the first finite state machine to be 1, and perform an update calculation of the variables related to the synaptic weights to be updated and an update of the synaptic weights after the last update. Calculate, specifically:
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为01时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号,分别控制第四数据选择器输出预设定的学习时间常数负值,第五数据选择器输出从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的待更新突触权值相关变量,第六数据选择器输出预设定的突触权值相关变量静息值;第一减法器输出的与第四数据选择器输出的学习时间常数负值共同作为除法器的输入,所得商再输入至指数计算模块,得到以自然常数e为底、商为指数的指数函数;自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号01控制第八数据选择器输出第六数据选择器输出的突触权值相关变量静息值;第五数据选择器和第八数据选择器的输出共同作为第二减法器的输入,所得差再与指数计算模块输出的指数函数共同输入至乘法器相乘,所得积与第八数据选择器的输出共同输入至第一加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值相关变量,更新后突触权值相关变量输入至数据分配器后,在控制信号下输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;然后将数据分配器输出的更新后突触权值相关变量与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第三加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值,输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 01, the control signal output by the second finite state machine respectively controls the fourth data selector to output the preset negative value of the learning time constant. The fifth data selector outputs the synaptic weight-related variable to be updated pulled from the data packet packing/splitting module, the sixth data selector outputs the preset resting value of the synaptic weight-related variable; the first subtractor outputs of The negative value of the learning time constant output by the fourth data selector is used as the input of the divider, and the obtained quotient is then input to the exponential calculation module to obtain an exponential function with the natural constant e as the base and the quotient as the exponent; self-adaptive clock-driven The output signal 01 of the event-driven computer mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the synaptic weight-related variable rest value output by the sixth data selector; the outputs of the fifth data selector and the eighth data selector are used together as The input of the second subtractor, the obtained difference and the exponential function output by the exponential calculation module are jointly input to the multiplier for multiplication, and the obtained product and the output of the eighth data selector are jointly input to the first adder, and the obtained sum is the sum after the update. After the synaptic weight-related variables are updated, the updated synaptic weight-related variables are input to the data distributor, and then output to the data packet packing/splitting module under the control signal; then the updated synaptic weight-related variables output by the data distributor are It is input to the third adder together with the synaptic weight after the last update pulled from the packet packing/splitting module, and the obtained sum is the updated synaptic weight, which is output to the packet packing/splitting module;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为00时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第七数据选择器输出预设定的学习泄露值,自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号00控制第八数据选择器输出第七数据选择器输出的学习泄露值,再与第五数据选择器输出的待更新突触权值相关变量共同输入至第二减法器,所得差为更新后突触权值相关变量,更新后突触权值相关变量输入至数据分配器后,在控制信号下输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;然后将数据分配器输出的更新后突触权值相关变量与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第三加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值,输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signals of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computer mechanism modules are 00, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the seventh data selector to output a preset learning leakage value, and the adaptive clock- The output signal 00 of the driven and event-driven computer mechanism module controls the eighth data selector to output the learning leakage value output by the seventh data selector, and is then jointly input with the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated output by the fifth data selector to The second subtractor, the difference obtained is the updated synaptic weight related variable, after the updated synaptic weight related variable is input to the data distributor, it is output to the data packet packing/splitting module under the control signal; then the data is distributed The relevant variables of the updated synaptic weight output by the adder and the last updated synaptic weight pulled from the packet packing/splitting module are jointly input to the third adder, and the resulting sum is the updated synaptic weight, and the output to the packet packing/splitting module;
当自适应的clock-driven与event-driven计算机制模块的输出信号为11时,第二有限状态机输出的控制信号控制第六选择器将输出的突触权值相关变量静息值输入至数据分配器,作为更新后突触权值相关变量,在控制信号下输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;然后将数据分配器输出的更新后突触权值相关变量与从数据包打包/拆分模块拉取的上次更新后突触权值共同输入至第三加法器,所得和为更新后突触权值,输出至数据包打包/拆分模块;When the output signal of the adaptive clock-driven and event-driven computing mechanism module is 11, the control signal output by the second finite state machine controls the sixth selector to input the output synaptic weight related variable rest value into the data The distributor, as the relevant variable of the updated synaptic weight, is output to the data packet packing/splitting module under the control signal; The synaptic weights after the last update pulled by the module are jointly input to the third adder, and the resulting sum is the updated synaptic weights, which are output to the packet packing/splitting module;
当推理/学习标志位为1、更新计数器为1时,计算资源处于学习模式的第二阶段,此时神经元/突触更新标志位为1,将执行待更新突触权值相关变量的二次更新计算、上次更新后突触权值的二次更新计算, 更新计算方法与计算资源处于学习模式第一阶段时执行待更新突触权值相关变量的一次更新计算、上次更新后突触权值的一次更新计算的更新计算的方法一致;When the inference/learning flag is 1 and the update counter is 1, the computing resource is in the second stage of the learning mode. At this time, the neuron/synaptic update flag is 1, and the second step of the variable related to the synaptic weight to be updated will be executed. The second update calculation, the second update calculation of the synaptic weight after the last update, the update calculation method and the computing resource are in the first stage of the learning mode to perform one update calculation of the variables related to the synaptic weight to be updated, and the synapse after the last update. The method of update calculation of one update calculation of touch value is the same;
此时,第二有限状态机任意工作状态下的计算通路执行计算完毕;At this time, the calculation path of the second finite state machine in any working state has completed the calculation;
当计算资源处于推理模式时,数据包打包/拆分模块将接收的更新后目的神经元膜电位,与从待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息中拆分出的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元上次更新时间、目的神经元阈值、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息;当计算资源处于学习模式第一阶段时,数据包打包/拆分模块将接收的更新后目的神经元膜电位、更新后突触权值相关变量、更新后突触权值,与从待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息中拆分出的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元上次更新时间、目的神经元阈值、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触上次更新时间打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息;当计算资源处于学习模式第二阶段时,数据包打包/拆分模块将接收的更新后突触权值相关变量、更新后突触权值,与从待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息中拆分出的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触上次更新时间打包成更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息;When the computing resource is in the inference mode, the packet packing/splitting module compares the received updated target neuron membrane potential with the pulse generation time and target neuron split from the target neuron-synaptic state information to be updated. ID, target neuron last update time, target neuron threshold, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and synapse state information are packaged into updated target neuron-synapse state information; when the computing resource is in the learning mode, the first During the phase, the packet packing/splitting module will receive the updated target neuron membrane potential, the updated synaptic weight related variables, and the updated synaptic weight, and compare the received neuron-synaptic state information from the updated target neuron-synaptic state information. The split pulse generation time, destination neuron ID, destination neuron last update time, destination neuron threshold, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and synapse last update time are packaged into the updated destination neuron- Synapse state information; when the computing resource is in the second stage of the learning mode, the data packet packing/splitting module will receive the updated synaptic weight related variables, the updated synaptic weight, and the target neuron- The pulse generation time, destination neuron ID, destination neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, and last update time of the synapse split from the synapse state information are packaged into the updated destination neuron-synapse status information;
所得更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息与推理/学习标志位共同经服务器模块传输至客户端模块,客户端模块将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息写回存储器,更新目的神经元或/和突触的状态信息,其中,采用脉冲产生时间更新目的神经元上次更新时间或/和突触上次更新时间;若数据包打包/拆分模块有接收到新脉冲信号,数据包打包/拆分模块还将新脉冲信号经服务器模块传输至客户端模块;客户端模块接收到新脉冲信号后,得知此次更新计算产生了一个新脉冲,将更新后目的神经元-突触状态信息中的脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID与进行本地处理的处理单元的ID共同组成一个新脉冲包,并由4比特的进行本地处理的处理单元的ID和10比特的目的神经元ID组成新脉冲包的源神经元ID;将新脉冲包和推理/学习标志位传递给内部路由模块,若推理/学习标志位为0,表示为推理模式,此时没有学习模式的第二阶段,内部路由模块将新脉冲包传输至外部路由模块,外部路由模块再根据预先配置的路由表查询新脉冲包是否需要通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元或者输出回电脑;若推理/学习标志位为1,此时为学习模式第一阶段,内部路由模块将新脉冲包传输至外部路由模块,外部路由模块再根据预先配置的路由表查询新脉冲包是否需要通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元或者输出回电脑;内部路由模块还将新脉冲包传输至脉冲队列模块,根据新脉冲包的源神经元ID,通过控制器模块、搜索模块、存储器、客户端模块查找对应脉冲产生时间、目的神经元ID、目的神经元状态信息、突触ID、突触更新计数值、突触状态信息,组成待更新目的神经元-突触状态信息,经服务器模块输入至执行计算的计算资源,进行学习模式第二阶段;The obtained updated target neuron-synaptic state information and the inference/learning flag are jointly transmitted to the client module through the server module, and the client module writes the updated target neuron-synaptic state information back to the memory, and updates the target neuron or / and the status information of the synapse, in which the pulse generation time is used to update the last update time of the target neuron or/and the last update time of the synapse; if the packet packing/splitting module receives a new pulse signal, the packet packing / The splitting module also transmits the new pulse signal to the client module through the server module; after the client module receives the new pulse signal, it knows that a new pulse has been generated by the update calculation, and the updated target neuron-synaptic state The pulse generation time, destination neuron ID and the ID of the processing unit performing local processing in the information together form a new pulse packet, which is composed of the 4-bit ID of the processing unit performing local processing and the 10-bit destination neuron ID. The source neuron ID of the impulse packet; pass the new impulse packet and the inference/learning flag to the internal routing module. If the inference/learning flag is 0, it indicates the inference mode. At this time, there is no second stage of the learning mode, and the internal routing The module transmits the new pulse packet to the external routing module, and the external routing module inquires whether the new pulse packet needs to be routed to the processing units in the four directions of east, south, west and north through the data port according to the pre-configured routing table or output back to the computer; If the inference/learning flag is 1, this is the first stage of the learning mode, the internal routing module transmits the new pulse packet to the external routing module, and the external routing module then queries whether the new pulse packet needs to pass through the data port according to the pre-configured routing table. Routing to the processing units in the four directions of east, south, west and north or output back to the computer; the internal routing module also transmits the new pulse packet to the pulse queue module, according to the source neuron ID of the new pulse packet, through the controller module, search The module, memory, and client module look up the corresponding pulse generation time, target neuron ID, target neuron state information, synapse ID, synapse update count value, synapse state information, and form the target neuron to be updated - synapse state information , the second stage of the learning mode is carried out through the server module input to the computing resources that perform the calculation;
外界的脉冲包先经东向通道、南向通道、西向通道或北向通道输入至预设定处理单元的外部路由模块,外部路由模块根据预先配置的路由表查询脉冲包是否需要进行本地处理或通过数据端口路由至东、南、西、北四个方向的处理单元。The external pulse packet is first input to the external routing module of the preset processing unit through the east channel, south channel, west channel or north channel. The external routing module queries whether the pulse packet needs to be processed locally or through Data ports are routed to processing units in four directions: east, south, west, and north.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011135965.3ACN112016680B (en) | 2020-10-22 | 2020-10-22 | Reconfigurable autonomous learning impulse neural network processor |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011135965.3ACN112016680B (en) | 2020-10-22 | 2020-10-22 | Reconfigurable autonomous learning impulse neural network processor |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN112016680A CN112016680A (en) | 2020-12-01 |
| CN112016680Btrue CN112016680B (en) | 2021-02-05 |
Family
ID=73527806
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202011135965.3AActiveCN112016680B (en) | 2020-10-22 | 2020-10-22 | Reconfigurable autonomous learning impulse neural network processor |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN112016680B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114186665B (en)* | 2021-11-01 | 2024-12-20 | 南京航空航天大学 | A GPU-based spiking neural network simulation method |
| CN114091652A (en)* | 2021-11-05 | 2022-02-25 | 上海新氦类脑智能科技有限公司 | Pulse neural network model training method, processing chip and electronic device |
| CN114638360A (en)* | 2022-05-19 | 2022-06-17 | 之江实验室 | A computing platform and method for spiking neural network learning and simulation |
| CN114781633B (en)* | 2022-06-17 | 2022-10-14 | 电子科技大学 | A processor integrating artificial neural network and spiking neural network |
| CN115906952B (en)* | 2022-08-17 | 2025-07-22 | 北京俱生智能科技有限公司 | Low-complexity brain simulation method, device, equipment and medium |
| CN115470449B (en)* | 2022-08-30 | 2025-09-05 | 无锡江南计算技术研究所 | A matrix multiplication operation systolic array device and interval configuration accumulation method |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110188874A (en)* | 2019-07-08 | 2019-08-30 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Recursive network topology digital-analog hybrid neural network circuit |
| CN210627259U (en)* | 2019-07-08 | 2020-05-26 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Pulse neural network digital-analog hybrid circuit system for realizing liquid state machine |
- 2020
- 2020-10-22CNCN202011135965.3Apatent/CN112016680B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110188874A (en)* | 2019-07-08 | 2019-08-30 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Recursive network topology digital-analog hybrid neural network circuit |
| CN210627259U (en)* | 2019-07-08 | 2020-05-26 | 中国人民解放军陆军工程大学 | Pulse neural network digital-analog hybrid circuit system for realizing liquid state machine |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN112016680A (en) | 2020-12-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112016680B (en) | Reconfigurable autonomous learning impulse neural network processor | |
| JP7366274B2 (en) | Adaptive search method and device for neural networks | |
| CN110728364B (en) | Arithmetic device and arithmetic method | |
| Geng et al. | A framework for acceleration of CNN training on deeply-pipelined FPGA clusters with work and weight load balancing | |
| Chen et al. | Rubik: A hierarchical architecture for efficient graph neural network training | |
| CN109104876A (en) | Computing device and related products | |
| CN110197270A (en) | Integrated circuit chip device and Related product | |
| CN111105023B (en) | Data stream reconstruction method and reconfigurable data stream processor | |
| JP2024506073A (en) | Internet of Things device-based task assignment method, network training method, and device thereof | |
| WO2008067676A1 (en) | Architecture, system and method for artificial neural network implementation | |
| CN106528357A (en) | FPGA system and implementation method based on on-line training neural network of quasi-newton method | |
| Zhang et al. | Enabling highly efficient capsule networks processing through a PIM-based architecture design | |
| CN115470889A (en) | Network-on-chip autonomous optimal mapping exploration system and method based on reinforcement learning | |
| CN111275173A (en) | Neural network training method, device and equipment | |
| CN118133908A (en) | A Transformer-based acceleration system and method | |
| Zhang et al. | Low-latency mini-batch gnn inference on cpu-fpga heterogeneous platform | |
| Chen et al. | Exploiting on-chip heterogeneity of versal architecture for gnn inference acceleration | |
| Lin et al. | Latency-driven model placement for efficient edge intelligence service | |
| Maliţa et al. | Heterogeneous computing system for deep learning | |
| Zou et al. | Learn-to-scale: Parallelizing deep learning inference on chip multiprocessor architecture | |
| TW201931216A (en) | Integrated circuit chip device and related products comprise a compression mapping circuit for executing the compressing processing of each of the data; the main processing circuit for executing each successive operation in the neural network operation, etc. | |
| KR20220114228A (en) | Processor, method for operating the same, and electronic device including the same | |
| Zhu et al. | Core placement optimization of many-core brain-inspired near-storage systems for spiking neural network training | |
| WO2024221872A1 (en) | Quantum error correction hardware decoder and chip | |
| Su et al. | Processing element architecture design for deep reinforcement learning with flexible block floating point exploiting signal statistics |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |