CN111953706A - A method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information - Google Patents
A method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic informationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111953706A CN111953706ACN202010849981.2ACN202010849981ACN111953706ACN 111953706 ACN111953706 ACN 111953706ACN 202010849981 ACN202010849981 ACN 202010849981ACN 111953706 ACN111953706 ACN 111953706A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- mobile application
- https
- sni
- data packet
- data
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription32
- 238000013507mappingMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription17
- 238000012545processingMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description4
- 238000007689inspectionMethods0.000description3
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000description2
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 230000000977initiatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 238000012544monitoring processMethods0.000description1
- 238000004064recyclingMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/16—Implementing security features at a particular protocol layer
- H04L63/166—Implementing security features at a particular protocol layer at the transport layer
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/14—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for detecting or protecting against malicious traffic
- H04L63/1408—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for detecting or protecting against malicious traffic by monitoring network traffic
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/02—Protocols based on web technology, e.g. hypertext transfer protocol [HTTP]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及流量分析技术领域,尤其涉及数据抓包领域,具体是指一种基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法。The invention relates to the technical field of traffic analysis, in particular to the field of data packet capture, and in particular to a method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information.
背景技术Background technique
随着互联网技术的发展,网络数据流量越来越大,这对数据包流量分析提出了极大的挑战。而基于数据面的数据包处理框架(Data Plane Development Kit,DPDK)成为数据包分析的主流方法。使用DPDK提供的快速收发包接口在用户态进行抓包分析,同时结合数据包深度检测技术(Deep Packet Inspection,DPI),针对不同的网络协议在应用层载荷(例如HTTP、DNS等)进行深度检测,通过对报文的有效载荷检测决定其合法性。如果数据包是经过加密传输的,则采用DPI方式的流控技术则无法识别。With the development of Internet technology, the network data traffic is increasing, which poses a great challenge to the analysis of data packet traffic. The data plane-based packet processing framework (Data Plane Development Kit, DPDK) has become the mainstream method of packet analysis. Use the fast packet sending and receiving interface provided by DPDK to capture and analyze packets in the user mode, and combine the deep packet inspection technology (Deep Packet Inspection, DPI) to perform in-depth inspection of application layer loads (such as HTTP, DNS, etc.) for different network protocols , the validity of the packet is determined by checking the payload of the packet. If the data packets are encrypted and transmitted, the flow control technology using the DPI method cannot identify them.
现在很多移动应用,为了本身数据传输的安全性,会使用HTTPS协议进行数据交互。一旦移动应用使用了HTTPS进行传输,对于一些流量分析和安全监控领域,这些移动应用就是一种盲区,几乎是一无所知。HTTPS的安全基础是SSL,所以HTTPS协议中一定含有服务器域名指示(Server Name Indication,SNI)信息。SNI是一项用于改善SSL/TLS的技术,它允许客户端在发起SSL握手请求时(具体说来,是客户端发出SSL请求中的ClientHello阶段),提交请求的域名信息,从而使得服务器能够切换到正确的域并返回相应的证书。Many mobile applications now use the HTTPS protocol for data interaction for the security of their own data transmission. Once mobile applications use HTTPS for transmission, for some traffic analysis and security monitoring fields, these mobile applications are a kind of blind spot, and almost nothing is known. The security foundation of HTTPS is SSL, so the HTTPS protocol must contain Server Name Indication (SNI) information. SNI is a technology used to improve SSL/TLS. It allows the client to submit the requested domain name information when initiating an SSL handshake request (specifically, the ClientHello phase in the client's SSL request), so that the server can Switch to the correct domain and return the corresponding certificate.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的是克服了上述现有技术的缺点,提供了一种满足安全性好、操作简便、适用范围较为广泛的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the shortcomings of the above-mentioned prior art, and to provide a method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information that satisfies good security, is easy to operate, and has a wide range of applications.
为了实现上述目的,本发明的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法如下:In order to achieve the above object, the method for identifying a mobile application based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention is as follows:
该基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法,其主要特点是,所述的方法包括以下步骤:The main feature of the method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information is that the method includes the following steps:
(1)分析收集到的网络公开信息或抓取包,得到域名和移动应用的键值对样本库,创建数据库和表;(1) Analyze the collected network public information or grab packets, obtain a sample library of key-value pairs of domain names and mobile applications, and create databases and tables;
(2)完成程序运行环境配置;(2) Complete the program operating environment configuration;
(3)初始化DPDK的环境抽象层,初始化网卡和CPU核队列,连接键值对数据库,启动核上线程;(3) Initialize the environment abstraction layer of DPDK, initialize the network card and CPU core queue, connect the key-value pair database, and start the thread on the core;
(4)接收流量数据存入不同核队列,取出流量数据包,按照协议栈分析定位到应用层数据的起始位置;(4) The received traffic data is stored in different core queues, the traffic data packets are taken out, and the starting position of the application layer data is located according to the analysis of the protocol stack;
(5)对应用层数据进行分析,按照HTTPS会话中第一个数据包的结构进行解析,获取其中的SNI;(5) Analyze the application layer data, analyze the structure of the first data packet in the HTTPS session, and obtain the SNI therein;
(6)匹配识别到的SNI和样本库,查询定位移动应用。(6) Match the identified SNI and sample library, and query and locate the mobile application.
较佳地,所述的步骤(3)具体包括以下步骤:Preferably, the step (3) specifically includes the following steps:
(3.1)根据系统的运行参数,将域名规则和移动应用名的映射表读到内存中;(3.1) Read the mapping table of domain name rules and mobile application names into memory according to the operating parameters of the system;
(3.2)初始化DPDK的环境抽象层环境;(3.2) Initialize the environment abstraction layer environment of DPDK;
(3.3)初始化接收队列和发送队列,初始化内存池,初始化网卡接口;(3.3) Initialize the receive queue and send queue, initialize the memory pool, and initialize the network card interface;
(3.4)启动CPU核上线程。(3.4) Start the thread on the CPU core.
较佳地,所述的步骤(4)具体包括以下步骤:Preferably, the step (4) specifically includes the following steps:
(4.1)根据MAC地址以及源地址和目标地址的端口计算五元组的Hash值;(4.1) Calculate the hash value of the quintuple according to the MAC address and the ports of the source address and the destination address;
(4.2)通过Hash映射到对应的逻辑核的接收队列;(4.2) Map to the receive queue of the corresponding logical core through Hash;
(4.3)将数据包加入至接收队列,相同会话的数据包在逻辑核上的线程中处理;(4.3) The data packets are added to the receiving queue, and the data packets of the same session are processed in the threads on the logical core;
(4.4)处理线程从队列中取出数据包,根据网络层和传输层的五元组信息构建会话对象,加入会话对象管理器。(4.4) The processing thread takes out the data packet from the queue, constructs the session object according to the quintuple information of the network layer and the transport layer, and joins the session object manager.
较佳地,所述的步骤(5)具体包括以下步骤:Preferably, the step (5) specifically includes the following steps:
(5.1)判断应用层数据包数据一个字节是否符合握手协议,如果是,则继续步骤(5.2);否则,丢弃数据包;(5.1) Determine whether a byte of application layer data packet data conforms to the handshake protocol, and if so, proceed to step (5.2); otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.2)判断剩余数据包长度是否满足SSL头部和握手协议头部的大小,如果是,则继续步骤(5.3);否则,丢弃数据包;(5.2) Determine whether the length of the remaining data packet satisfies the size of the SSL header and the handshake protocol header, and if so, proceed to step (5.3); otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.3)解析SSL头部和握手协议头部,判断握手协议是否为ClientHello,如果是,则继续步骤(5.4);否则,丢弃数据包;(5.3) Parse the SSL header and the handshake protocol header to determine whether the handshake protocol is ClientHello, if so, continue to step (5.4); otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.4)解析握手协议ClientHello数据包,按照字节内容依次获取客户端版本号、32位随机数、会话ID、密码套件、压缩内容和扩展字段;(5.4) Parse the ClientHello data packet of the handshake protocol, and obtain the client version number, 32-bit random number, session ID, cipher suite, compressed content and extension fields in sequence according to the byte content;
(5.5)判断是否有扩展字段,如果是,则解析扩展字段;否则,丢弃数据包;(5.5) Determine whether there is an extension field, if so, parse the extension field; otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.6)判断扩展字段类型是否为0,如果是,则即为扩展信息SNI;否则,丢弃数据包。(5.6) Determine whether the extension field type is 0, if so, it is the extension information SNI; otherwise, discard the data packet.
较佳地,所述的步骤(6)具体包括以下步骤:Preferably, the step (6) specifically includes the following steps:
(6.1)匹配内存域名规则和移动应用名映射表,判断是否匹配成功,如果是,则继续步骤(6.2);否则,将SNI单独存入数据库,进行后续分析。(6.1) Match the memory domain name rules and the mobile application name mapping table to determine whether the match is successful, if so, proceed to step (6.2); otherwise, store the SNI in the database separately for subsequent analysis.
(6.2)获取对应移动应用名,通过SNI和移动应用名生成结果集,将结果集存入数据库。(6.2) Obtain the corresponding mobile application name, generate a result set through the SNI and the mobile application name, and store the result set in the database.
较佳地,所述的步骤(1)的表包括域名规则及移动应用名映射表、SNI和移动应用名结果表和未识别的SNI的采集表。Preferably, the table in the step (1) includes a domain name rule and a mobile application name mapping table, a SNI and mobile application name result table, and a collection table of unidentified SNIs.
较佳地,所述的步骤(2)的程序运行环境配置包括创建大页空间、加载驱动模块和网卡绑定驱动。Preferably, the configuration of the program running environment in the step (2) includes creating a huge page space, loading a driver module and a network card binding driver.
较佳地,所述的步骤(3)的初始化DPDK的环境抽象层包括轮询模式驱动初始化、CPU内核和DPDK线程绑定、设置HugePage大页内存。Preferably, the environment abstraction layer for initializing DPDK in step (3) includes polling mode driver initialization, CPU core and DPDK thread binding, and setting HugePage memory.
采用了本发明的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法,从HTTPS网络数据流量中解析识别出服务器名称指示SNI,把SNI和不断累积的域名和移动应用名样本库进行碰撞,最后识别出具体移动应用的方法。本发明能构建完成如下的移动应用和域名的映射关系样本库,从网络数据流量中获取HTTPS的SNI,适用范围广泛。The method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention is adopted, the server name indicating SNI is parsed and identified from the HTTPS network data traffic, the SNI is collided with the continuously accumulated domain name and mobile application name sample library, and finally the specific mobile application is identified. method of application. The present invention can construct and complete the following sample library of mapping relationship between mobile applications and domain names, obtain SNI of HTTPS from network data traffic, and has a wide range of applications.
附图说明Description of drawings
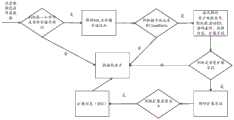
图1为本发明的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法的解析SNI的数据流程图。FIG. 1 is a data flow chart of parsing SNI in a method for identifying a mobile application based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention.
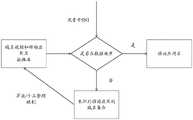
图2为本发明的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法的HTTPS获取SNI逻辑图。FIG. 2 is a logical diagram of HTTPS acquiring SNI of the method for identifying a mobile application based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention.
图3为本发明的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法的SNI定位移动应用逻辑图。FIG. 3 is a logical diagram of the SNI positioning mobile application of the method for identifying a mobile application based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了能够更清楚地描述本发明的技术内容,下面结合具体实施例来进行进一步的描述。In order to describe the technical content of the present invention more clearly, further description will be given below with reference to specific embodiments.
本发明的该基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法,其中包括以下步骤:The method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention includes the following steps:
(1)分析收集到的网络公开信息或抓取包,得到域名和移动应用的键值对样本库,创建数据库和表;(1) Analyze the collected network public information or grab packets, obtain a sample library of key-value pairs of domain names and mobile applications, and create databases and tables;
(2)完成程序运行环境配置;(2) Complete the program operating environment configuration;
(3)初始化DPDK的环境抽象层,初始化网卡和CPU核队列,连接键值对数据库,启动核上线程;(3) Initialize the environment abstraction layer of DPDK, initialize the network card and CPU core queue, connect the key-value pair database, and start the thread on the core;
(3.1)根据系统的运行参数,将域名规则和移动应用名的映射表读到内存中;(3.1) Read the mapping table of domain name rules and mobile application names into memory according to the operating parameters of the system;
(3.2)初始化DPDK的环境抽象层环境;(3.2) Initialize the environment abstraction layer environment of DPDK;
(3.3)初始化接收队列和发送队列,初始化内存池,初始化网卡接口;(3.3) Initialize the receive queue and send queue, initialize the memory pool, and initialize the network card interface;
(3.4)启动CPU核上线程;(3.4) Start the thread on the CPU core;
(4)接收流量数据存入不同核队列,取出流量数据包,按照协议栈分析定位到应用层数据的起始位置;(4) The received traffic data is stored in different core queues, the traffic data packets are taken out, and the starting position of the application layer data is located according to the analysis of the protocol stack;
(4.1)根据MAC地址以及源地址和目标地址的端口计算五元组的Hash值;(4.1) Calculate the hash value of the quintuple according to the MAC address and the ports of the source address and the destination address;
(4.2)通过Hash映射到对应的逻辑核的接收队列;(4.2) Map to the receive queue of the corresponding logical core through Hash;
(4.3)将数据包加入至接收队列,相同会话的数据包在逻辑核上的线程中处理;(4.3) The data packets are added to the receiving queue, and the data packets of the same session are processed in the threads on the logical core;
(4.4)处理线程从队列中取出数据包,根据网络层和传输层的五元组信息构建会话对象,加入会话对象管理器;(4.4) The processing thread takes out the data packet from the queue, constructs the session object according to the quintuple information of the network layer and the transport layer, and joins the session object manager;
(5)对应用层数据进行分析,按照HTTPS会话中第一个数据包的结构进行解析,获取其中的SNI;(5) Analyze the application layer data, analyze the structure of the first data packet in the HTTPS session, and obtain the SNI therein;
(5.1)判断应用层数据包数据一个字节是否符合握手协议,如果是,则继续步骤(5.2);否则,丢弃数据包;(5.1) Determine whether a byte of application layer data packet data conforms to the handshake protocol, and if so, proceed to step (5.2); otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.2)判断剩余数据包长度是否满足SSL头部和握手协议头部的大小,如果是,则继续步骤(5.3);否则,丢弃数据包;(5.2) Determine whether the length of the remaining data packet satisfies the size of the SSL header and the handshake protocol header, and if so, proceed to step (5.3); otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.3)解析SSL头部和握手协议头部,判断握手协议是否为ClientHello,如果是,则继续步骤(5.4);否则,丢弃数据包;(5.3) Parse the SSL header and the handshake protocol header to determine whether the handshake protocol is ClientHello, if so, continue to step (5.4); otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.4)解析握手协议ClientHello数据包,按照字节内容依次获取客户端版本号、32位随机数、会话ID、密码套件、压缩内容和扩展字段;(5.4) Parse the ClientHello data packet of the handshake protocol, and obtain the client version number, 32-bit random number, session ID, cipher suite, compressed content and extension fields in sequence according to the byte content;
(5.5)判断是否有扩展字段,如果是,则解析扩展字段;否则,丢弃数据包;(5.5) Determine whether there is an extension field, if so, parse the extension field; otherwise, discard the data packet;
(5.6)判断扩展字段类型是否为0,如果是,则即为扩展信息SNI;否则,丢弃数据包;(5.6) Judge whether the extension field type is 0, if so, it is the extension information SNI; otherwise, discard the data packet;
(6)匹配识别到的SNI和样本库,查询定位移动应用;(6) Match the identified SNI and sample library, and query and locate the mobile application;
(6.1)匹配内存域名规则和移动应用名映射表,判断是否匹配成功,如果是,则继续步骤(6.2);否则,将SNI单独存入数据库,进行后续分析。(6.1) Match the memory domain name rules and the mobile application name mapping table to determine whether the match is successful, if so, proceed to step (6.2); otherwise, store the SNI in the database separately for subsequent analysis.
(6.2)获取对应移动应用名,通过SNI和移动应用名生成结果集,将结果集存入数据库。(6.2) Obtain the corresponding mobile application name, generate a result set through the SNI and the mobile application name, and store the result set in the database.
作为本发明的优选实施方式,所述的步骤(1)的表包括域名规则及移动应用名映射表、SNI和移动应用名结果表和未识别的SNI的采集表。As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the table in step (1) includes a domain name rule and a mobile application name mapping table, a SNI and mobile application name result table, and a collection table of unidentified SNIs.
作为本发明的优选实施方式,所述的步骤(2)的程序运行环境配置包括创建大页空间、加载驱动模块和网卡绑定驱动。As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the program execution environment configuration of the step (2) includes creating a huge page space, loading a driver module and a network card binding driver.
作为本发明的优选实施方式,所述的步骤(3)的初始化DPDK的环境抽象层包括轮询模式驱动初始化、CPU内核和DPDK线程绑定、设置HugePage大页内存。As a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the environment abstraction layer for initializing DPDK in step (3) includes polling mode driver initialization, CPU core and DPDK thread binding, and setting HugePage memory.
本发明的具体实施方式中,公开了从HTTPS网络数据流量中识别具体移动应用的方法。其具体包括以下步骤:In a specific embodiment of the present invention, a method for identifying specific mobile applications from HTTPS network data traffic is disclosed. It specifically includes the following steps:
步骤一,通过收集网络公开信息或者在移动应用使用过程中抓取包进行分析得到域名和移动应用的键值对样本库。随着数据样本的增加,定位移动应用更加准确。In step 1, a sample library of domain names and key-value pairs of the mobile application is obtained by collecting public information on the network or by grabbing packets during the use of the mobile application for analysis. As the data sample increases, locating the mobile app becomes more accurate.
步骤二,完成程序运行环境配置:创建大页空间,加载驱动模块,网卡绑定驱动Step 2, complete the configuration of the program running environment: create a large page space, load the driver module, and bind the network card to the driver
步骤三,初始化DPDK的环境抽象层(其中包括轮询模式驱动初始化、CPU内核和DPDK线程绑定、设置HugePage大页内存等系统初始化),初始化网卡和CPU核队列,连接键值对数据库,最后启动核上线程。Step 3: Initialize the environment abstraction layer of DPDK (including polling mode driver initialization, CPU core and DPDK thread binding, setting HugePage large page memory and other system initialization), initialize the network card and CPU core queue, connect the key-value pair database, and finally Start the thread on the core.
步骤四,接收流量数据按照五元组存入不同核队列,核逻辑线程从核队列中取出流量数据包,按照协议栈分析,定位到应用层数据的起始位置。In step 4, the received traffic data is stored in different core queues according to the quintuple, and the core logic thread takes out the traffic data packets from the core queue, and locates the starting position of the application layer data according to the analysis of the protocol stack.
步骤五,接着步骤四,对应用层数据进行分析,因为SNI信息在HTTPS在第一个数据包(ClientHello)内,根据HTTPS数据包的特征值判断该数据流量是否是需要解析,然后按照HTTPS会话中第一个数据包的结构进行解析(具体解析步骤参见具体实施方式),从而获取其中的SNI。Step 5, then Step 4, analyze the application layer data, because the SNI information is in the first data packet (ClientHello) of HTTPS, according to the characteristic value of the HTTPS data packet to determine whether the data traffic needs to be parsed, and then according to the HTTPS session. parse the structure of the first data packet in (for specific parsing steps, refer to the specific implementation manner) to obtain the SNI in it.
步骤六,用识别到的SNI去样本库进行匹配查询是否可以定位移动应用,如果不能定位移动应用,可以记录该域名,后续可以通过手动定位来完善扩充样本库,从而为未知移动应用定位。Step 6: Use the identified SNI to go to the sample library for matching and query whether the mobile application can be located. If the mobile application cannot be located, the domain name can be recorded. Subsequently, the sample library can be improved and expanded by manual positioning, so as to locate the unknown mobile application.
本发明的从HTTPS网络数据流量中识别具体移动应用的方法,其中,包括以下步骤:The method for identifying a specific mobile application from HTTPS network data traffic of the present invention includes the following steps:
1、创建数据库和表:1. Create the database and tables:
创建域名规则和移动应用名的样本库,其中主要有三张表:域名规则和移动应用名映射表、SNI和移动应用名结果表以及未识别的SNI的采集表。Create a sample library of domain name rules and mobile application names, including three tables: the mapping table of domain name rules and mobile application names, the result table of SNI and mobile application names, and the collection table of unidentified SNIs.
2、配置程序运行环境:2. Configure the program operating environment:
程序主要在Linux环境下运行,在运行前需要根据NUMA设置内存大页,然后加载DPDK的生成驱动模块,最后把网卡和驱动模块绑定,这样就可以接收网卡中的流量,然后把它映射到大页中,减少内存复制,提高流量处理能力。The program mainly runs in the Linux environment. Before running, it needs to set the memory huge page according to NUMA, then load the generated driver module of DPDK, and finally bind the network card to the driver module, so that the traffic in the network card can be received, and then mapped to In large pages, memory copying is reduced and traffic processing capability is improved.
3、DPDK初始化:3. DPDK initialization:
根据系统的运行参数,将域名规则和移动应用名的映射表读到内存中,初始化DPDK的环境抽象层环境(主要是哪个网卡端口绑定哪个逻辑线程在哪个逻辑核上运行),接着初始化每个核的接收队列和发送队列,初始化内存池,初始化网卡接口,最后启动CPU核上线程。According to the operating parameters of the system, read the mapping table of domain name rules and mobile application names into the memory, initialize the environment abstraction layer environment of DPDK (mainly which network card port is bound to which logical thread runs on which logical core), and then initialize each logical core. The receive queue and send queue of each core, initialize the memory pool, initialize the network card interface, and finally start the thread on the CPU core.
4、数据包解析:4. Data packet analysis:
从网卡接收到数据包根据协议栈来解析,首先根据MAC地址以及源地址和目的地址的端口计算五元组的Hash值,通过该Hash映射到对应的逻辑核的接收队列,然后把数据包加入到该接收队列,此后,相同会话中的数据包就在该逻辑核上的线程中处理,保证了CPU核的亲和性。处理线程从队列中取出数据包,然后根据网络层和传输层的五元组信息构建会话对象,加入会话对象管理器,方便回收。The data packet received from the network card is parsed according to the protocol stack. First, the hash value of the quintuple is calculated according to the MAC address and the ports of the source and destination addresses, and the hash value is mapped to the receiving queue of the corresponding logical core, and then the data packet is added to the After reaching the receiving queue, the data packets in the same session are processed in the thread on the logical core, ensuring the affinity of the CPU core. The processing thread takes out the data packet from the queue, and then constructs the session object according to the quintuple information of the network layer and the transport layer, and joins the session object manager to facilitate recycling.
5、SNI识别:5. SNI identification:
在同一个会话中,获取应用层数据的起始地址和长度,为了说明方便从抓包如下:In the same session, the starting address and length of the application layer data are obtained. For the convenience of description, the packet capture is as follows:
选中二进值数据为应用数据。Select binary data as application data.
首先,判断应用层数据包数据一个字节是否握手协议(0x16),如果不是数据包丢弃。First, determine whether a byte of application layer data packet data is a handshake protocol (0x16), if not, the data packet is discarded.
其次,判断剩余数据包长度是否满足SSL头部和握手协议头部的大小,如果不是数据包丢弃。Second, determine whether the remaining packet length meets the size of the SSL header and the handshake protocol header, and if not, discard the packet.
接着,解析SSL头部和握手协议头部。0x16 0x03 0x01 0x02 0x00是SSL头部,0x16表示类型,0x03 0x01表示版本,0x02,0x00表示长度。0x01 0x00 0x01 0xfc是握手协议头部,0x01表示握手协议的类型0x00 0x01 0xfc表示握手协议的长度。判断0x01就是ClientHello,如果不是数据包丢弃。Next, parse the SSL header and the handshake protocol header. 0x16 0x03 0x01 0x02 0x00 is the SSL header, 0x16 is the type, 0x03 0x01 is the version, 0x02, 0x00 is the length. 0x01 0x00 0x01 0xfc is the header of the handshake protocol, 0x01 represents the type of the handshake protocol 0x00 0x01 0xfc represents the length of the handshake protocol. It is judged that 0x01 is ClientHello, if not the packet is discarded.
最后,解析握手协议ClientHello数据包,按照字节内容依次获取客户端版本号(0x030x03)、32位随机数、会话ID(2个字节长度+内容)、密码套件((2个字节长度+内容)、压缩内容((2个字节长度+内容)和扩展字段((2个字节长度+内容)等,当存在扩展字段的情况下解析扩展字段,扩展字段的结构是类型+2个字节长度+内容,当类型为0是,其内容进一步信息就是SNI。Finally, parse the ClientHello packet of the handshake protocol, and obtain the client version number (0x030x03), 32-bit random number, session ID (2 bytes length + content), cipher suite ((2 bytes length + content), compressed content ((2 byte length + content) and extension field ((2 byte length + content), etc. When there is an extension field, the extension field is parsed, and the structure of the extension field is type + 2 Byte length + content, when the type is 0, the further information of its content is SNI.
6、SNI和移动应用名对比:6. SNI and mobile application name comparison:
当获取服务器名称指示(Server Name Indication SNI)后,与内存域名规则和移动应用名映射表进行匹配,匹配方式主要是后缀匹配,如果匹配成功后,取得对应移动应用名,拿SNI和移动应用名生成结果集。把该结果集存入数据库,方便后续查看流量中识别的SNI及其对应的移动应用名。如果失败,则把SNI单独存入数据库,做后续分析。When the server name indication (Server Name Indication SNI) is obtained, it is matched with the memory domain name rules and the mobile application name mapping table. The matching method is mainly suffix matching. If the matching is successful, the corresponding mobile application name is obtained, and the SNI and mobile application name are obtained. Generate a result set. The result set is stored in the database to facilitate subsequent viewing of the SNI identified in the traffic and its corresponding mobile application name. If it fails, the SNI is stored in the database separately for subsequent analysis.
7、未识别的SNI的采集和归类总结:7. Summary of collection and classification of unidentified SNI:
对未识别的SNI进行单独存储,后续进行离线算法统计和人工标注,生成新的域名规则和移动应用名映射关系,不断扩充域名规则和移动应用名映射表。The unrecognized SNI is stored separately, followed by offline algorithm statistics and manual annotation to generate a new mapping relationship between domain name rules and mobile application names, and continuously expand the mapping table of domain name rules and mobile application names.
采用了本发明的基于HTTPS流量信息识别移动应用的方法,从HTTPS网络数据流量中解析识别出服务器名称指示SNI,把SNI和不断累积的域名和移动应用名样本库进行碰撞,最后识别出具体移动应用的方法。本发明能构建完成如下的移动应用和域名的映射关系样本库,从网络数据流量中获取HTTPS的SNI,适用范围广泛。The method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information of the present invention is adopted, the server name indicating SNI is parsed and identified from the HTTPS network data traffic, the SNI is collided with the continuously accumulated domain name and mobile application name sample library, and finally the specific mobile application is identified. method of application. The present invention can construct and complete the following sample library of mapping relationship between mobile applications and domain names, obtain SNI of HTTPS from network data traffic, and has a wide range of applications.
在此说明书中,本发明已参照其特定的实施例作了描述。但是,很显然仍可以作出各种修改和变换而不背离本发明的精神和范围。因此,说明书和附图应被认为是说明性的而非限制性的。In this specification, the invention has been described with reference to specific embodiments thereof. However, it will be evident that various modifications and changes can still be made without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. Accordingly, the specification and drawings are to be regarded in an illustrative rather than a restrictive sense.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010849981.2ACN111953706A (en) | 2020-08-21 | 2020-08-21 | A method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010849981.2ACN111953706A (en) | 2020-08-21 | 2020-08-21 | A method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111953706Atrue CN111953706A (en) | 2020-11-17 |
Family
ID=73359136
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010849981.2APendingCN111953706A (en) | 2020-08-21 | 2020-08-21 | A method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111953706A (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112615758A (en)* | 2020-12-16 | 2021-04-06 | 北京锐安科技有限公司 | Application identification method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| CN113553137A (en)* | 2021-06-17 | 2021-10-26 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | A high-speed data processing method for access capability network elements based on DPDK under NFV architecture |
| CN114125015A (en)* | 2021-11-30 | 2022-03-01 | 上海斗象信息科技有限公司 | Data acquisition method and system |
| CN114244846A (en)* | 2021-12-15 | 2022-03-25 | 山石网科通信技术股份有限公司 | Flow message forwarding method and device, intermediate device and storage medium |
| CN116112445A (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2023-05-12 | 深圳市赛柏特通信技术有限公司 | Application identification method, intelligent terminal and storage medium |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103618726A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2014-03-05 | 北京中创信测科技股份有限公司 | Method for recognizing mobile data service based on HTTPS |
| CN109413196A (en)* | 2018-11-13 | 2019-03-01 | 四川长虹电器股份有限公司 | A kind of method of intelligent Matching HTTPS access certificate |
| CN110768933A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2020-02-07 | 深信服科技股份有限公司 | Network flow application identification method, system and equipment and storage medium |
| CN110768875A (en)* | 2019-12-27 | 2020-02-07 | 北京安博通科技股份有限公司 | Application identification method and system based on DNS learning |
| CN111371779A (en)* | 2020-02-29 | 2020-07-03 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A Firewall Based on DPDK Virtualization Management System and Its Implementation Method |
- 2020
- 2020-08-21CNCN202010849981.2Apatent/CN111953706A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103618726A (en)* | 2013-12-04 | 2014-03-05 | 北京中创信测科技股份有限公司 | Method for recognizing mobile data service based on HTTPS |
| CN110768933A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2020-02-07 | 深信服科技股份有限公司 | Network flow application identification method, system and equipment and storage medium |
| CN109413196A (en)* | 2018-11-13 | 2019-03-01 | 四川长虹电器股份有限公司 | A kind of method of intelligent Matching HTTPS access certificate |
| CN110768875A (en)* | 2019-12-27 | 2020-02-07 | 北京安博通科技股份有限公司 | Application identification method and system based on DNS learning |
| CN111371779A (en)* | 2020-02-29 | 2020-07-03 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A Firewall Based on DPDK Virtualization Management System and Its Implementation Method |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112615758A (en)* | 2020-12-16 | 2021-04-06 | 北京锐安科技有限公司 | Application identification method, device, equipment and storage medium |
| WO2022127196A1 (en)* | 2020-12-16 | 2022-06-23 | 北京锐安科技有限公司 | Application identification method and apparatus, and device and storage medium |
| CN113553137A (en)* | 2021-06-17 | 2021-10-26 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | A high-speed data processing method for access capability network elements based on DPDK under NFV architecture |
| CN113553137B (en)* | 2021-06-17 | 2022-11-01 | 中国人民解放军战略支援部队信息工程大学 | A high-speed data processing method for access capability network elements based on DPDK under NFV architecture |
| CN114125015A (en)* | 2021-11-30 | 2022-03-01 | 上海斗象信息科技有限公司 | Data acquisition method and system |
| CN114244846A (en)* | 2021-12-15 | 2022-03-25 | 山石网科通信技术股份有限公司 | Flow message forwarding method and device, intermediate device and storage medium |
| CN114244846B (en)* | 2021-12-15 | 2024-02-09 | 山石网科通信技术股份有限公司 | Flow message forwarding method and device, intermediate equipment and storage medium |
| CN116112445A (en)* | 2022-12-30 | 2023-05-12 | 深圳市赛柏特通信技术有限公司 | Application identification method, intelligent terminal and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111953706A (en) | A method for identifying mobile applications based on HTTPS traffic information | |
| CN106330584B (en) | A kind of recognition methods of Business Stream and identification device | |
| KR101510432B1 (en) | Apparatus for analizing traffic | |
| US9100291B2 (en) | Systems and methods for extracting structured application data from a communications link | |
| CN103916294B (en) | The recognition methods of protocol type and device | |
| WO2021164261A1 (en) | Method for testing cloud network device, and storage medium and computer device | |
| CN102394885B (en) | Information classification protection automatic verification method based on data stream | |
| CN114157502A (en) | Terminal identification method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN105024971A (en) | A communication protocol conversion method and device | |
| CN110868409A (en) | A method and system for passive identification of operating system based on TCP/IP protocol stack fingerprint | |
| CN110213124A (en) | Passive operation system identification method and device based on the more sessions of TCP | |
| CN114124551B (en) | Malicious encryption traffic identification method based on multi-granularity feature extraction under WireGuard protocol | |
| CN110245273A (en) | A method and corresponding device for acquiring APP service feature database | |
| CN116634046A (en) | Message processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114172980A (en) | Method, system, device, equipment and medium for identifying type of operating system | |
| CN108881425A (en) | A kind of data package processing method and system | |
| CN115883381A (en) | Industrial Internet asset identification method based on network protocol fingerprints | |
| CN102893580A (en) | Anti-virus method and device and firewall equipment | |
| CN113055420B (en) | HTTPS service identification method, device and computing equipment | |
| CN111107064B (en) | Terminal equipment identification method, device, equipment and readable storage medium | |
| CN113315678A (en) | Encrypted TCP (Transmission control protocol) traffic acquisition method and device | |
| CN114666169B (en) | A scanning detection type identification method, device, equipment and medium | |
| CN114610976B (en) | Data query method, data storage method, device, computing device and medium | |
| KR101596603B1 (en) | Apparatus and method for creating signature using network packet flow sequence | |
| CN111314104B (en) | A method and device for identifying instant messaging service operation behavior |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20201117 | |
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication |