CN111930311A - Storage method and device - Google Patents
Storage method and deviceDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111930311A CN111930311ACN202010790717.6ACN202010790717ACN111930311ACN 111930311 ACN111930311 ACN 111930311ACN 202010790717 ACN202010790717 ACN 202010790717ACN 111930311 ACN111930311 ACN 111930311A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- data
- stripe
- brushing
- dirty
- alignment
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0602—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems specifically adapted to achieve a particular effect
- G06F3/061—Improving I/O performance
- G06F3/0611—Improving I/O performance in relation to response time
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0629—Configuration or reconfiguration of storage systems
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0638—Organizing or formatting or addressing of data
- G06F3/0643—Management of files
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F3/00—Input arrangements for transferring data to be processed into a form capable of being handled by the computer; Output arrangements for transferring data from processing unit to output unit, e.g. interface arrangements
- G06F3/06—Digital input from, or digital output to, record carriers, e.g. RAID, emulated record carriers or networked record carriers
- G06F3/0601—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems
- G06F3/0628—Interfaces specially adapted for storage systems making use of a particular technique
- G06F3/0655—Vertical data movement, i.e. input-output transfer; data movement between one or more hosts and one or more storage devices
- G06F3/0656—Data buffering arrangements
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Memory System Of A Hierarchy Structure (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及数据存储领域,具体而言,涉及一种存储方法和装置。The present invention relates to the field of data storage, and in particular, to a storage method and device.
背景技术Background technique
目前存储系统为了兼顾性能和成本,一般会采用两层架构,分别是缓存层和数据持久化层。如图1所示,为了在随机IO(Input/Output,输入/输出)场景下提供高性能的读写,因此,缓存层的主要介质可以是SSD(Solid State Disk,固态硬盘),例如,可以是NVME(Non-Volatit Controller Interface,非易失性控制器接口)SSD,数据写入到缓存层就返回,由于缓存层的容量往往比后端数据持久化层的容量小,因此,数据写入到缓存层后,可以根据一定的回刷策略,将数据回刷到数据持久化层。为了考虑能够存储大容量的数据和成本,数据持久化层主要采用HDD盘(Hard Disk Drive,硬盘驱动器)或者SMR盘(ShingledMagneting Recording,叠瓦式磁记录盘)等容量大又廉价的介质。In order to take into account both performance and cost, the current storage system generally adopts a two-layer architecture, namely the cache layer and the data persistence layer. As shown in Figure 1, in order to provide high-performance read and write in the random IO (Input/Output) scenario, the main medium of the cache layer can be SSD (Solid State Disk, solid-state drive), for example, it can be It is an NVME (Non-Volait Controller Interface, non-volatile controller interface) SSD. Data is written to the cache layer and returned. Since the capacity of the cache layer is often smaller than that of the back-end data persistence layer, data writing After reaching the cache layer, the data can be flushed back to the data persistence layer according to a certain flushing strategy. In order to consider the ability to store large-capacity data and costs, the data persistence layer mainly uses HDD disks (Hard Disk Drive, hard disk drive) or SMR disk (Shingled Magneting Recording, Shingled Magnetic Recording disk) and other large-capacity and cheap media.
基于上述结构,缓存层回刷数据到持久化层,是根据写缓存的数据,根据一定的数据回刷的策略,例如LRU(Least Recently Used,最近最少使用)或者LFU(LeastFrequently Used,最不经常使用)的cache回刷处理策略去回刷对应的管理单元的数据,但上述策略没有考虑到后端扶持化的存储持久化层是否是EC pool(Erasure Coding pool,纠错码池),如果是EC pool,由于数据回刷的过程没有考虑条带对齐和条带整数倍回刷,基于检验数据的计算的需要,需要将其它列的数据读上来,再更新回刷写数据一起计算检验数据,再写回刷数据和检验数据,使得在回刷写的流程中,多了一次读的IO处理,这样导致回刷的流程IO的时延增加了一倍,导致在回刷非条带对齐和非满条带的数据的时候,回刷的效率比较低。Based on the above structure, the cache layer flushes data to the persistence layer according to the data written in the cache, according to a certain data flushing strategy, such as LRU (Least Recently Used, least recently used) or LFU (Least Frequently Used, least often Use the cache flushing processing strategy of In EC pool, since the process of data flushing does not consider strip alignment and stripe flushing in integer multiples, based on the needs of the calculation of the test data, it is necessary to read the data of other columns, and then update the data to be flushed and calculate the test data together. Then write back the flush data and check data, so that one more read IO processing is required in the flush write process, which doubles the IO delay of the flush process, resulting in non-stripe alignment and When the data of the strip is not full, the efficiency of flashback is relatively low.
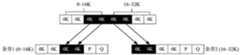
例如,如图2所示,其中,脏数据用实心方框表示,空白数据用空心方框表示。假设EC pool采用4+2的条带,条带深度是4K,也即由4个4K数据块和2个4K的检验数据组成的条带。当通过cache回刷脏数据8~24K范围的时候,回刷到后端EC pool时需要分别回刷到两个条带上,其中,检验数据P和Q是新生成的,因此需要将0~8K,24~32K的数据读出来,生成两个条带中的新的P、Q写下去,导致读放大的温度。For example, as shown in FIG. 2, the dirty data is represented by solid squares, and the blank data is represented by open squares. Assuming that the EC pool uses 4+2 stripes, the stripe depth is 4K, that is, a stripe composed of 4 4K data blocks and 2 4K test data. When the dirty data in the range of 8-24K is flushed through the cache, it needs to be flushed to two stripes respectively when flushing back to the back-end EC pool. Among them, the test data P and Q are newly generated, so it is necessary to set 0~24K. 8K, 24~32K data is read out, and new P and Q in two strips are generated and written down, resulting in the temperature of read amplification.
针对上述的问题,目前尚未提出有效的解决方案。For the above problems, no effective solution has been proposed yet.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明实施例提供了一种存储方法和装置,以至少解决现有技术中在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层的过程中,由于在回刷写的流程中,多了一次读的IO处理,导致在回刷非条带对齐和非满条带的数据的时候,回刷的效率低的技术问题。Embodiments of the present invention provide a storage method and device, so as to at least solve the problem that in the process of flushing data from the cache layer to the persistence layer in the prior art, because in the process of flushing and writing, there is one more IO processing for read. , which leads to a technical problem of low efficiency of flushing back when flushing data with non-stripe alignment and non-full stripes.
根据本发明实施例的一个方面,提供了一种存储方法,包括:在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层之前,获取后端存储的多个条带的条带大小;基于每个条带的条带大小,确定每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级;基于每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,将每个待回刷的数据按照对应的回刷优先级回刷到后端存储。According to an aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a storage method is provided, including: before the cache layer flushes data back to the persistence layer, obtaining the stripe sizes of multiple stripes stored in the backend; The size of the stripe determines the flushing priority of each data to be flushed; based on the flushing priority of each data to be flushed, each data to be flushed is flushed back to the corresponding flushing priority. backend storage.
可选地,回刷优先级依次为:条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据、条带不对齐部分数据。Optionally, the flushing priorities are sequentially as follows: strip alignment and data that is an integer multiple of the strip, and partial data that is not aligned in the strip.
可选地,该数据包括:脏数据和干净数据,其中,如果脏数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍的情况下,将缓存层中完成回刷后未淘汰的干净数据与脏数据进行合并,组成条带对齐和/或是条带整数倍的数据,并进行回刷处理。Optionally, the data includes: dirty data and clean data, wherein, if the dirty data is not aligned with the stripe and/or is not an integer multiple of the stripe, the clean data in the cache layer that is not eliminated after the flushing is completed and the dirty data The data is merged to form stripe alignment and/or data that is an integer multiple of stripes, and is flushed back.
可选地,在缓存层的脏数据空间大于预定阈值的情况下,如果未扫描到条带对齐和/或条带整数倍的脏数据,或干净数据与脏数据进行合并后组成的数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍,则对非条带对齐和/或非条带整数倍的脏数据进行回刷。Optionally, when the dirty data space of the cache layer is greater than a predetermined threshold, if the stripe alignment and/or the dirty data that is an integer multiple of the stripe is not scanned, or the data formed by merging the clean data and the dirty data is not a stripe If the stripe is aligned and/or not an integer multiple of the stripe, the dirty data that is not stripe aligned and/or not an integer multiple of the stripe is flushed back.
可选地,脏数据回刷成功后,转换为干净数据,其中,在缓存层的空白空间低于预定值的情况下,对干净数据进行淘汰操作。Optionally, after the dirty data is successfully flushed back, it is converted into clean data, wherein when the empty space of the cache layer is lower than a predetermined value, the clean data is eliminated.
根据本发明实施例的另一方面,还提供了一种存储装置,包括:获取模块,用于在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层之前,获取后端存储的多个条带的条带大小;确定模块,用于基于每个条带的条带大小,确定每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级;回刷模块,用于基于每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,将每个待回刷的数据按照对应的回刷优先级回刷到后端存储。According to another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a storage device is further provided, including: an obtaining module, configured to obtain the stripe sizes of multiple stripes stored in the backend before the cache layer flushes data back to the persistence layer ; The determination module is used to determine the flushing priority of each data to be flushed based on the stripe size of each strip; the flushing module is used to determine the flushing priority based on each data to be flushed, Each data to be refreshed is refreshed to the back-end storage according to the corresponding refresh priority.
可选地,回刷优先级依次为:条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据、条带不对齐部分数据。Optionally, the flushing priorities are sequentially as follows: strip alignment and data that is an integer multiple of the strip, and partial data that is not aligned in the strip.
可选地,该数据包括:脏数据和干净数据,其中,该装置还包括:合并模块,用于如果脏数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍的情况下,将缓存层中完成回刷后未淘汰的干净数据与脏数据进行合并,组成条带对齐和/或是条带整数倍的数据,并进行回刷处理。Optionally, the data includes: dirty data and clean data, wherein the apparatus further includes: a merging module, configured to complete the data in the cache layer if the dirty data is not strip-aligned and/or is not an integer multiple of the stripe The clean data that has not been eliminated after the flashback is merged with the dirty data to form stripe alignment and/or data that is an integer multiple of the stripe, and the flashback process is performed.
可选地,该装置还包括:第一子处理模块,用于在缓存层的脏数据空间大于预定阈值的情况下,如果未扫描到条带对齐和/或条带整数倍的脏数据,或干净数据与脏数据进行合并后组成的数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍,则对非条带对齐和/或非条带整数倍的脏数据进行回刷。Optionally, the apparatus further includes: a first sub-processing module, configured to, when the dirty data space of the cache layer is greater than a predetermined threshold, if no stripe alignment and/or dirty data of an integer multiple of the stripe is scanned, or If the data formed by merging the clean data and the dirty data is not strip-aligned and/or is not an integer multiple of the strip, then the dirty data that is not aligned and/or is not an integer multiple of the strip is flushed.
可选地,该装置还包括:第二子处理模块,用于脏数据回刷成功后,转换为干净数据,其中,在缓存层的空白空间低于预定值的情况下,对干净数据进行淘汰操作。Optionally, the apparatus further includes: a second sub-processing module for converting dirty data into clean data after successful flushing back, wherein, in the case that the empty space of the cache layer is lower than a predetermined value, the clean data is eliminated. operate.
根据本发明实施例的另一方面,还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,计算机可读存储介质包括存储的程序,其中,在程序运行时控制计算机可读存储介质所在设备执行上述的存储方法。According to another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a computer-readable storage medium is also provided, where the computer-readable storage medium includes a stored program, wherein when the program is run, the device where the computer-readable storage medium is located is controlled to execute the above-mentioned storage method .
根据本发明实施例的另一方面,还提供了一种处理器,处理器用于运行程序,其中,程序运行时执行上述的存储方法。According to another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a processor is also provided, and the processor is used for running a program, wherein the above-mentioned storage method is executed when the program is running.
在本发明实施例中,在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层之前,可以基于获取到的后端存储的每个条带的条带大小,确定每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,并基于每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,将每个待回刷的数据按照对应的回刷优先级回刷到后端存储。容易注意到的是,通过加入回刷优先级策略,按照不同的回刷优先级将不同待回刷的数据回刷到后端存储,从而达到了减少非满条带回刷带来的读放大,减少回刷的IO流程,提高回刷的效率的技术效果,进而解决了现有技术中在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层的过程中,由于在回刷写的流程中,多了一次读的IO处理,导致在回刷非条带对齐和非满条带的数据的时候,回刷的效率低的技术问题。In this embodiment of the present invention, before the cache layer flushes data to the persistence layer, the flushing priority of each data to be flushed may be determined based on the obtained stripe size of each stripe stored in the backend , and based on the refresh priority of each data to be refreshed, each data to be refreshed is refreshed to the back-end storage according to the corresponding refresh priority. It is easy to notice that by adding the flushing priority policy, different data to be flushed back to the back-end storage according to different flushing priorities, thus reducing the read amplification caused by the flushing of non-full stripes. , reducing the IO process of flushing and improving the efficiency of flushing, thus solving the problem of flushing data from the cache layer to the persistence layer in the prior art, because in the process of flushing and writing, there is one more time The IO processing of read leads to the technical problem of low flushing efficiency when flushing data that is not stripe aligned or not full.
附图说明Description of drawings
此处所说明的附图用来提供对本发明的进一步理解,构成本申请的一部分,本发明的示意性实施例及其说明用于解释本发明,并不构成对本发明的不当限定。在附图中:The accompanying drawings described herein are used to provide a further understanding of the present invention and constitute a part of the present application. The exemplary embodiments of the present invention and their descriptions are used to explain the present invention and do not constitute an improper limitation of the present invention. In the attached image:
图1是根据现有技术的一种存储系统的两层架构的示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of a two-tier architecture of a storage system according to the prior art;
图2是根据现有技术的一种数据回刷的示意图;Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of a data flashback according to the prior art;
图3是根据本发明实施例的一种存储方法的流程图;3 is a flowchart of a storage method according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4是根据本发明实施例的一种可选的数据回刷的示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of an optional data flashback according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图5是根据本发明实施例的另一种可选的数据回刷的示意图;以及FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of another optional data flashback according to an embodiment of the present invention; and
图6是根据本发明实施例的一种存储装置的示意图。FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a storage device according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本技术领域的人员更好地理解本发明方案,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例仅仅是本发明一部分的实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都应当属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make those skilled in the art better understand the solutions of the present invention, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only Embodiments are part of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts shall fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
需要说明的是,本发明的说明书和权利要求书及上述附图中的术语“第一”、“第二”等是用于区别类似的对象,而不必用于描述特定的顺序或先后次序。应该理解这样使用的数据在适当情况下可以互换,以便这里描述的本发明的实施例能够以除了在这里图示或描述的那些以外的顺序实施。此外,术语“包括”和“具有”以及他们的任何变形,意图在于覆盖不排他的包含,例如,包含了一系列步骤或单元的过程、方法、系统、产品或设备不必限于清楚地列出的那些步骤或单元,而是可包括没有清楚地列出的或对于这些过程、方法、产品或设备固有的其它步骤或单元。It should be noted that the terms "first", "second" and the like in the description and claims of the present invention and the above drawings are used to distinguish similar objects, and are not necessarily used to describe a specific sequence or sequence. It is to be understood that the data so used may be interchanged under appropriate circumstances such that the embodiments of the invention described herein can be practiced in sequences other than those illustrated or described herein. Furthermore, the terms "comprising" and "having" and any variations thereof, are intended to cover non-exclusive inclusion, for example, a process, method, system, product or device comprising a series of steps or units is not necessarily limited to those expressly listed Rather, those steps or units may include other steps or units not expressly listed or inherent to these processes, methods, products or devices.
下面对本发明实施例中出现的技术名称或技术术语进行如下解释说明:The technical names or technical terms that appear in the embodiments of the present invention are explained as follows:
EC:纠错码是一种数据保护方法,可以将数据分割成片段,把冗余数据块扩展、编码,并将其存储在不同的位置,比如磁盘、存储节点或者其它地理位置。EC: Error Correcting Code is a method of data protection that divides data into pieces, expands, encodes, and stores redundant blocks of data in different locations, such as disks, storage nodes, or other geographic locations.
脏数据:可以是写入cache没有回刷到后端存储的数据。Dirty data: It can be data that is written to the cache and not flushed back to the backend storage.
干净数据:可以是已经回刷到后端存储的数据。Clean data: It can be data that has been flushed back to the backend storage.
空白数据:没有写过数据或者原来写过数据的空间已被释放。Empty data: No data has been written or the space where the data was written has been released.
实施例1Example 1
根据本发明实施例,提供了一种存储方法,需要说明的是,在附图的流程图示出的步骤可以在诸如一组计算机可执行指令的计算机系统中执行,并且,虽然在流程图中示出了逻辑顺序,但是在某些情况下,可以以不同于此处的顺序执行所示出或描述的步骤。According to an embodiment of the present invention, a storage method is provided. It should be noted that the steps shown in the flowchart of the accompanying drawings may be executed in a computer system such as a set of computer-executable instructions. A logical order is shown, but in some cases steps shown or described may be performed in a different order than herein.
图3是根据本发明实施例的一种存储方法的流程图,如图3所示,该方法包括如下步骤:FIG. 3 is a flowchart of a storage method according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 3 , the method includes the following steps:
步骤S302,在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层之前,获取后端存储的多个条带的条带大小。Step S302, before the cache layer flushes the data back to the persistence layer, obtain the stripe sizes of multiple stripes stored in the backend.
上述步骤中的缓存层可以采用NVME SSD或者SSD,但不仅限于此。持久化层可以采用HDD盘或者SMR盘,但不仅限于此。后端存储可以是指后端数据持久化层,可以是EC pool,因此回刷数据到持久化层时需要考虑条带对齐和条带整数倍回刷。The cache layer in the above steps may use NVME SSD or SSD, but is not limited to this. The persistence layer can be an HDD disk or an SMR disk, but is not limited to this. The back-end storage can refer to the back-end data persistence layer, which can be the EC pool. Therefore, when flushing data to the persistence layer, strip alignment and stripe flushing in integer multiples must be considered.
步骤S304,基于每个条带的条带大小,确定每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级。Step S304, based on the stripe size of each stripe, determine the flushing priority of each data to be flushed back.
上述步骤中的回刷优先级可以是基于新的回刷优先级策略所确定的优先级顺序,按照从高到低的顺序,回刷优先级依次为:条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据、条带不对齐部分数据。待回刷数据可以是缓存层中存储的数据,该数据需要回刷到后端存储中。The flushing priority in the above steps may be the priority order determined based on the new flushing priority policy. In descending order, the flushing priority is: stripe alignment and data with an integer multiple of stripe , the strips are not aligned with part of the data. The data to be flushed can be data stored in the cache layer, and the data needs to be flushed back to the backend storage.
步骤S306,基于每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,将每个待回刷的数据按照对应的回刷优先级回刷到后端存储。Step S306, based on the flushing priority of each data to be flushed, flushing each data to be flushed back to the back-end storage according to the corresponding flushing priority.
在一种可选的实施例中,cache回刷前获取后端存储EC的条带大小,在常用的回刷处理策略中,在回刷一个块的数据,或者一个对象的数据的时候,加入新的回刷优先级策略。根据常用的回刷处理策略,回刷某个数据块或者对象数据时,先判断脏数据是否有满足条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据,如果有条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据,优先回刷这部分数据,不对齐部分数据暂时不回刷处理。In an optional embodiment, the stripe size of the backend storage EC is obtained before the cache is flushed. In a common flushing processing strategy, when flushing the data of a block or the data of an object, adding New flush back priority policy. According to the commonly used flushing processing strategy, when flushing a data block or object data, first determine whether the dirty data has data that satisfies the stripe alignment and an integer multiple of the stripe. This part of the data will be refreshed first, and the unaligned part of the data will not be refreshed for the time being.
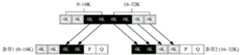
例如,如图4所示,其中,脏数据用实心方框表示,空白数据用空心方框表示。虽然连续可回刷的数据是8~32K,但是,采用回刷优先级策略,可以仅回刷16~32K的满条带数据,8~16K暂时不回刷处理。For example, as shown in FIG. 4 , dirty data is represented by solid squares, and blank data is represented by open squares. Although the data that can be continuously refreshed is 8 to 32K, using the refresh priority strategy, only 16 to 32K of full stripe data can be refreshed, and 8 to 16K will not be refreshed temporarily.
通过本发明上述实施例中,在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层之前,可以基于获取到的后端存储的每个条带的条带大小,确定每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,并基于每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,将每个待回刷的数据按照对应的回刷优先级回刷到后端存储。容易注意到的是,通过加入回刷优先级策略,按照不同的回刷优先级将不同待回刷的数据回刷到后端存储,从而达到了减少非满条带回刷带来的读放大,减少回刷的IO流程,提高回刷的效率的技术效果,进而解决了现有技术中在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层的过程中,由于在回刷写的流程中,多了一次读的IO处理,导致在回刷非条带对齐和非满条带的数据的时候,回刷的效率低的技术问题。Through the above embodiments of the present invention, before the cache layer flushes data to the persistence layer, the flushing priority of each data to be flushed can be determined based on the obtained stripe size of each stripe stored in the backend level, and based on the flushing priority of each data to be flushed, each data to be flushed is flushed back to the back-end storage according to the corresponding flushing priority. It is easy to notice that by adding the flushing priority policy, different data to be flushed back to the back-end storage according to different flushing priorities, thus reducing the read amplification caused by the flushing of non-full stripes. , reducing the IO process of flushing and improving the efficiency of flushing, thus solving the problem of flushing data from the cache layer to the persistence layer in the prior art, because in the process of flushing and writing, there is one more time The IO processing of read leads to the technical problem of low flushing efficiency when flushing data that is not stripe aligned or not full.
可选地,在本发明上述实施例中,该数据包括:脏数据和干净数据,其中,如果脏数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍的情况下,将缓存层中完成回刷后未淘汰的干净数据与脏数据进行合并,组成条带对齐和/或是条带整数倍的数据,并进行回刷处理。Optionally, in the foregoing embodiment of the present invention, the data includes: dirty data and clean data, wherein, if the dirty data is not strip-aligned and/or is not an integer multiple of the strip, the cache layer is flushed back The clean data that has not been eliminated and the dirty data are merged to form stripe-aligned and/or data that is an integer multiple of stripes, and the flushing process is performed.
在一种可选的实施例中,组成条带对其和条带整数倍写的时候,如果脏数据部分不能满足回刷优先级的要求,则可以加入干净数据部分一起凑成条带对齐或者条带整数倍的数据,从而可以对其做回刷处理。In an optional embodiment, when a stripe is formed to write to an integer multiple of the stripe, if the dirty data part cannot meet the requirement of the flushback priority, the clean data part can be added together to form stripe alignment or Strip integer multiples of data, so that it can be flushed back.
例如,如图5所示,其中,脏数据用实心方框表示,空白数据用空心方框表示,干净数据用斜线方框表示。脏数据不满足条带对齐和条带整数倍的条件,可以添加干净数据,凑成满足条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据回刷,从而后端EC pool就没有读放大的问题。For example, as shown in FIG. 5 , dirty data is represented by solid squares, blank data is represented by hollow squares, and clean data is represented by slashed squares. Dirty data does not meet the conditions of stripe alignment and stripe multiples. Clean data can be added to make data flushing that meets stripe alignment and stripe multiples, so that the back-end EC pool does not have the problem of read amplification.
可选地,在本发明上述实施例中,在缓存层的脏数据空间大于预定阈值的情况下,如果未扫描到条带对齐和/或条带整数倍的脏数据,或干净数据与脏数据进行合并后组成的数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍,则对非条带对齐和/或非条带整数倍的脏数据进行回刷。Optionally, in the foregoing embodiment of the present invention, when the dirty data space of the cache layer is greater than a predetermined threshold, if no stripe alignment and/or dirty data of an integer multiple of the stripe, or clean data and dirty data are scanned. If the data formed after merging is not strip-aligned and/or not an integer multiple of the strip, then the dirty data that is not aligned and/or not an integer multiple of the strip is flushed back.
上述步骤中的预定阈值可以是用于表征缓存层中缓存的脏数据较多,能够继续缓存脏数据的空间较小,可能会影响后续脏数据缓存在缓存层,预定阈值的具体值可以根据实际需要进行设定。The predetermined threshold in the above steps may be used to indicate that there is a lot of dirty data cached in the cache layer, and the space that can continue to cache dirty data is small, which may affect subsequent dirty data cached in the cache layer. The specific value of the predetermined threshold can be determined according to the actual situation. Setting is required.
在一种可选的实施例中,当缓存层的脏数据空间大于预定阈值,也即脏数据空间比较紧张时,如果找不到满足条带对齐和条带整数倍的脏数据,或者添加干净数据后的数据仍然不满足条带对齐和条带整数倍,则可以直接回刷非条带对齐和条带整数倍的脏数据。In an optional embodiment, when the dirty data space of the cache layer is greater than a predetermined threshold, that is, when the dirty data space is relatively tight, if the dirty data that satisfies the stripe alignment and an integer multiple of the stripe cannot be found, or add clean data If the data after the data still does not satisfy the stripe alignment and stripe integer multiples, the dirty data that is not stripe-aligned and stripe integer multiples can be directly flushed back.
可选地,在本发明上述实施例中,脏数据回刷成功后,转换为干净数据,其中,在缓存层的空白空间低于预定值的情况下,对干净数据进行淘汰操作。Optionally, in the above-mentioned embodiment of the present invention, after the dirty data is successfully flushed back, it is converted into clean data, wherein the clean data is eliminated when the empty space of the cache layer is lower than a predetermined value.
上述步骤中的预定值可以是用于表征缓存层的空白空间的剩余空间较小,可能会影响后续数据缓存在缓存层,预定值的具体值可以根据实际需要进行设定。The predetermined value in the above steps may be that the remaining space used to represent the blank space of the cache layer is small, which may affect subsequent data caching in the cache layer, and the specific value of the predetermined value may be set according to actual needs.
在一种可选的实施例中,脏数据回刷成功之后可以转换为干净数据,干净数据在空白空间紧张的时候才会被回收,也即,当空白空间较低时直接淘汰部分干净数据,从而干净数据在回收之前可以提高读的情况和方便后续非满条带的脏数据,凑满条带回刷处理。In an optional embodiment, dirty data can be converted into clean data after being flushed successfully, and clean data will be recycled only when the empty space is tight, that is, when the empty space is low, part of the clean data is directly eliminated, Therefore, before the clean data is recovered, the read condition can be improved and the subsequent dirty data of the non-full stripe can be facilitated, and the full stripe can be flushed back for processing.
通过上述方案,为了降低cache回刷数据到EC pool的时候引入的读放大问题,在回刷的策略中加入回刷优先级策略,优先回刷条带对齐和条带整数倍的数据,如果脏数据非满条带宽对齐的时候,能够根据cache回刷后未淘汰的干净数据一起凑成满条带回刷,来进一步减少非满条带回刷带来的读放大,减少回刷的IO流程,提高回刷的效率。Through the above solution, in order to reduce the read amplification problem introduced when the cache flushes data to the EC pool, the flushing priority policy is added to the flushing strategy, and the stripe alignment and the data that is an integer multiple of the stripe are preferentially flushed. When the data is not fully aligned with the bandwidth, the clean data that has not been eliminated after the cache flush can be combined into a full strip, which can further reduce the read amplification caused by the non-full strip, and reduce the IO process of the flush. , to improve the efficiency of back brushing.
实施例2Example 2
根据本发明实施例,提供了一种存储装置,该装置可以执行上述实施例中的存储方法,本实施例与上述实施例中的具体实现方案与优选应用场景相同,在此不做赘述。According to an embodiment of the present invention, a storage device is provided, and the device can execute the storage method in the above-mentioned embodiment. The specific implementation scheme and preferred application scenario of this embodiment and the above-mentioned embodiment are the same, and are not repeated here.
图6是根据本发明实施例的一种存储装置的示意图,如图6所示,该装置包括:FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a storage device according to an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 6 , the device includes:
获取模块62,用于在缓存层回刷数据到持久化层之前,获取后端存储的多个条带的条带大小;The obtaining module 62 is used to obtain the stripe size of the multiple stripes stored in the back-end before the cache layer flushes the data back to the persistence layer;
确定模块64,用于基于每个条带的条带大小,确定每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级;Determining module 64, for determining the flushing priority of each data to be flushed based on the stripe size of each strip;
回刷模块66,用于基于每个待回刷的数据的回刷优先级,将每个待回刷的数据按照对应的回刷优先级回刷到后端存储。The flushing module 66 is configured to, based on the flushing priority of each data to be flushed, flush each data to be flushed back to the back-end storage according to the corresponding flushing priority.
可选地,在本发明上述实施例中,该数据包括:脏数据和干净数据,其中,该装置还包括:合并模块,用于如果脏数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍的情况下,将缓存层中完成回刷后未淘汰的干净数据与脏数据进行合并,组成条带对齐和/或是条带整数倍的数据,并进行回刷处理。Optionally, in the above-mentioned embodiment of the present invention, the data includes: dirty data and clean data, wherein the apparatus further includes: a merging module, for if the dirty data is not strip-aligned and/or is not an integer multiple of the strip In this case, the clean data and dirty data in the cache layer that are not eliminated after the flushing is completed are combined to form stripe alignment and/or data that is an integer multiple of stripes, and the flushing process is performed.
可选地,在本发明上述实施例中,该装置还包括:第一子处理模块,用于在缓存层的脏数据空间大于预定阈值的情况下,如果未扫描到条带对齐和/或条带整数倍的脏数据,或干净数据与脏数据进行合并后组成的数据不是条带对齐和/或不是条带整数倍,则对非条带对齐和/或非条带整数倍的脏数据进行回刷。Optionally, in the above-mentioned embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus further includes: a first sub-processing module, configured to, in the case that the dirty data space of the cache layer is greater than a predetermined threshold, if no stripe alignment and/or stripe alignment is scanned Dirty data with integer multiples, or data formed by merging clean data and dirty data is not stripe-aligned and/or not an integer multiple of stripes, then the dirty data that is not aligned and/or is not an integer multiple of stripes will be processed. Brush back.
可选地,在本发明上述实施例中,该装置还包括:第二子处理模块,用于脏数据回刷成功后,转换为干净数据,其中,在缓存层的空白空间低于预定值的情况下,对干净数据进行淘汰操作。Optionally, in the above-mentioned embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus further includes: a second sub-processing module for converting dirty data into clean data after successful flushing back, wherein the empty space in the cache layer is lower than a predetermined value. In this case, the clean data is eliminated.
实施例3Example 3
根据本发明实施例,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,计算机可读存储介质包括存储的程序,其中,在程序运行时控制计算机可读存储介质所在设备执行上述实施例1中的存储方法。According to an embodiment of the present invention, a computer-readable storage medium is provided, where the computer-readable storage medium includes a stored program, wherein when the program is executed, the device where the computer-readable storage medium is located is controlled to execute the storage method in
实施例4Example 4
根据本发明实施例,提供了一种处理器,处理器用于运行程序,其中,程序运行时执行上述实施例1中的存储方法。According to an embodiment of the present invention, a processor is provided, and the processor is used for running a program, wherein the storage method in the foregoing
上述本发明实施例序号仅仅为了描述,不代表实施例的优劣。The above-mentioned serial numbers of the embodiments of the present invention are only for description, and do not represent the advantages or disadvantages of the embodiments.
在本发明的上述实施例中,对各个实施例的描述都各有侧重,某个实施例中没有详述的部分,可以参见其他实施例的相关描述。In the above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention, the description of each embodiment has its own emphasis. For parts that are not described in detail in a certain embodiment, reference may be made to related descriptions of other embodiments.
在本申请所提供的几个实施例中,应该理解到,所揭露的技术内容,可通过其它的方式实现。其中,以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,例如所述单元的划分,可以为一种逻辑功能划分,实际实现时可以有另外的划分方式,例如多个单元或组件可以结合或者可以集成到另一个系统,或一些特征可以忽略,或不执行。另一点,所显示或讨论的相互之间的耦合或直接耦合或通信连接可以是通过一些接口,单元或模块的间接耦合或通信连接,可以是电性或其它的形式。In the several embodiments provided in this application, it should be understood that the disclosed technical content can be implemented in other ways. The device embodiments described above are only illustrative, for example, the division of the units may be a logical function division, and there may be other division methods in actual implementation, for example, multiple units or components may be combined or Integration into another system, or some features can be ignored, or not implemented. On the other hand, the shown or discussed mutual coupling or direct coupling or communication connection may be through some interfaces, indirect coupling or communication connection of units or modules, and may be in electrical or other forms.
所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部单元来实现本实施例方案的目的。The units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and components shown as units may or may not be physical units, that is, may be located in one place, or may be distributed to multiple units. Some or all of the units may be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution in this embodiment.
另外,在本发明各个实施例中的各功能单元可以集成在一个处理单元中,也可以是各个单元单独物理存在,也可以两个或两个以上单元集成在一个单元中。上述集成的单元既可以采用硬件的形式实现,也可以采用软件功能单元的形式实现。In addition, each functional unit in each embodiment of the present invention may be integrated into one processing unit, or each unit may exist physically alone, or two or more units may be integrated into one unit. The above-mentioned integrated units may be implemented in the form of hardware, or may be implemented in the form of software functional units.
所述集成的单元如果以软件功能单元的形式实现并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,可以存储在一个计算机可读取存储介质中。基于这样的理解,本发明的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分或者该技术方案的全部或部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品存储在一个存储介质中,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可为个人计算机、服务器或者网络设备等)执行本发明各个实施例所述方法的全部或部分步骤。而前述的存储介质包括:U盘、只读存储器(ROM,Read-Only Memory)、随机存取存储器(RAM,Random Access Memory)、移动硬盘、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。The integrated unit, if implemented in the form of a software functional unit and sold or used as an independent product, may be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. Based on this understanding, the technical solution of the present invention is essentially or the part that contributes to the prior art, or all or part of the technical solution can be embodied in the form of a software product, and the computer software product is stored in a storage medium , including several instructions for causing a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device, etc.) to execute all or part of the steps of the methods described in the various embodiments of the present invention. The aforementioned storage medium includes: U disk, read-only memory (ROM, Read-Only Memory), random access memory (RAM, Random Access Memory), mobile hard disk, magnetic disk or optical disk and other media that can store program codes .
以上所述仅是本发明的优选实施方式,应当指出,对于本技术领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明原理的前提下,还可以做出若干改进和润饰,这些改进和润饰也应视为本发明的保护范围。The above are only the preferred embodiments of the present invention. It should be pointed out that for those skilled in the art, without departing from the principles of the present invention, several improvements and modifications can be made. It should be regarded as the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (12)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010790717.6ACN111930311A (en) | 2020-08-07 | 2020-08-07 | Storage method and device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010790717.6ACN111930311A (en) | 2020-08-07 | 2020-08-07 | Storage method and device |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111930311Atrue CN111930311A (en) | 2020-11-13 |
Family
ID=73307011
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010790717.6APendingCN111930311A (en) | 2020-08-07 | 2020-08-07 | Storage method and device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111930311A (en) |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080005465A1 (en)* | 2006-06-30 | 2008-01-03 | Matthews Jeanna N | Write ordering on disk cached platforms |
| CN106681665A (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2017-05-17 | 北京奇虎科技有限公司 | Cache data persistent storage method and device |
| CN107273048A (en)* | 2017-06-08 | 2017-10-20 | 浙江大华技术股份有限公司 | A kind of method for writing data and device |
| CN109783023A (en)* | 2019-01-04 | 2019-05-21 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | The method and relevant apparatus brushed under a kind of data |
| US20190188156A1 (en)* | 2017-12-19 | 2019-06-20 | Seagate Technology Llc | Stripe aligned cache flush |
- 2020
- 2020-08-07CNCN202010790717.6Apatent/CN111930311A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080005465A1 (en)* | 2006-06-30 | 2008-01-03 | Matthews Jeanna N | Write ordering on disk cached platforms |
| CN106681665A (en)* | 2016-12-29 | 2017-05-17 | 北京奇虎科技有限公司 | Cache data persistent storage method and device |
| CN107273048A (en)* | 2017-06-08 | 2017-10-20 | 浙江大华技术股份有限公司 | A kind of method for writing data and device |
| US20190188156A1 (en)* | 2017-12-19 | 2019-06-20 | Seagate Technology Llc | Stripe aligned cache flush |
| CN109783023A (en)* | 2019-01-04 | 2019-05-21 | 平安科技(深圳)有限公司 | The method and relevant apparatus brushed under a kind of data |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9361183B2 (en) | Aggregation of write traffic to a data store | |
| CN107784121B (en) | Lowercase optimization method of log file system based on nonvolatile memory | |
| KR101678868B1 (en) | Apparatus for flash address translation apparatus and method thereof | |
| CN108958656B (en) | Dynamic stripe system design method based on RAID5 solid state disk array | |
| CN101625897B (en) | Data writing method, storage system and controller for flash memory | |
| US11868651B2 (en) | Key-value KV storage method and apparatus, and storage device | |
| CN111443874B (en) | Content-aware-based solid-state disk memory cache management method, device, and solid-state disk | |
| CN107221351A (en) | The optimized treatment method of error correcting code and its application in a kind of solid-state disc system | |
| CN109558456A (en) | A kind of file migration method, apparatus, equipment and readable storage medium storing program for executing | |
| US11789864B2 (en) | Flush method for mapping table of SSD | |
| CN110515550B (en) | Method and device for separating cold data and hot data of SATA solid state disk | |
| CN104182176A (en) | Rapid dilatation method for RAID 5 (redundant array of independent disks) | |
| CN106406750A (en) | Data operation method and system | |
| CN109284070B (en) | Solid-state storage device power-off recovery method based on STT-MRAM | |
| CN119739340B (en) | A distributed all-flash storage data writing method, device and medium | |
| US20250165180A1 (en) | Recovery method for all-flash storage system, and related apparatus | |
| CN104794066A (en) | Storage apparatus and method for selecting storage area where data is written | |
| CN119739344A (en) | Data storage method, device and medium | |
| CN108009041B (en) | Flash memory array verification updating method based on data relevance perception | |
| US8145839B2 (en) | Raid—5 controller and accessing method with data stream distribution and aggregation operations based on the primitive data access block of storage devices | |
| CN106980471B (en) | Method and device for improving hard disk writing performance of intelligent equipment | |
| US10353642B2 (en) | Selectively improving RAID operations latency | |
| CN111930311A (en) | Storage method and device | |
| JP4040797B2 (en) | Disk control device and recording medium | |
| KR20140049327A (en) | Apparatus for logging and recovering transactions in database installed in a mobile environment and method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| CB02 | Change of applicant information | ||
| CB02 | Change of applicant information | Address after:100094 101, floors 1-5, building 7, courtyard 3, fengxiu Middle Road, Haidian District, Beijing Applicant after:Beijing Xingchen Tianhe Technology Co.,Ltd. Address before:100097 room 806-1, block B, zone 2, Jinyuan times shopping center, indigo factory, Haidian District, Beijing Applicant before:XSKY BEIJING DATA TECHNOLOGY Corp.,Ltd. | |
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20201113 |