CN111756539A - A Re-random Identification Encryption and Decryption Method - Google Patents
A Re-random Identification Encryption and Decryption MethodDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111756539A CN111756539ACN202010672997.0ACN202010672997ACN111756539ACN 111756539 ACN111756539 ACN 111756539ACN 202010672997 ACN202010672997 ACN 202010672997ACN 111756539 ACN111756539 ACN 111756539A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- ciphertext
- module
- new
- receiver
- elements
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription41
- 238000000605extractionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription13
- 239000000654additiveSubstances0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000000996additive effectEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 229910002056binary alloyInorganic materials0.000claims1
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claims1
- 238000011084recoveryMethods0.000claims1
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description3
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description3
- 238000003491arrayMethods0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description1
- 230000000977initiatory effectEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/30—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy
- H04L9/3066—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy involving algebraic varieties, e.g. elliptic or hyper-elliptic curves
- H04L9/3073—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy involving algebraic varieties, e.g. elliptic or hyper-elliptic curves involving pairings, e.g. identity based encryption [IBE], bilinear mappings or bilinear pairings, e.g. Weil or Tate pairing
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L63/00—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security
- H04L63/04—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks
- H04L63/0428—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks wherein the data content is protected, e.g. by encrypting or encapsulating the payload
- H04L63/0442—Network architectures or network communication protocols for network security for providing a confidential data exchange among entities communicating through data packet networks wherein the data content is protected, e.g. by encrypting or encapsulating the payload wherein the sending and receiving network entities apply asymmetric encryption, i.e. different keys for encryption and decryption
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/30—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy
- H04L9/3066—Public key, i.e. encryption algorithm being computationally infeasible to invert or user's encryption keys not requiring secrecy involving algebraic varieties, e.g. elliptic or hyper-elliptic curves
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L9/00—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols
- H04L9/32—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials
- H04L9/3236—Cryptographic mechanisms or cryptographic arrangements for secret or secure communications; Network security protocols including means for verifying the identity or authority of a user of the system or for message authentication, e.g. authorization, entity authentication, data integrity or data verification, non-repudiation, key authentication or verification of credentials using cryptographic hash functions
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Algebra (AREA)
- Pure & Applied Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Mathematical Analysis (AREA)
- Mathematical Optimization (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Storage Device Security (AREA)
- Computer And Data Communications (AREA)
- Data Exchanges In Wide-Area Networks (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于信息安全技术领域,涉及一种标识加解密方法,具体涉及一种具有高安全性的可重随机的标识加解密方法。The invention belongs to the technical field of information security, and relates to an identification encryption and decryption method, in particular to a re-random identification encryption and decryption method with high security.
背景技术Background technique
目前在密码领域具有代表性的可重随机的标识加解密方法有BB04方法、Waters05方法和Gentry06方法。然而,这三种方法均只能实现抗基于标识的选择明文安全(ID-CPA安全)。在实际应用中,某些具有更强能力的攻击者能够破解ID-CPA安全的加解密方法。下面将以Gentry06方法为例进行阐述。At present, the representative re-random identification encryption and decryption methods in the cryptographic field include the BB04 method, the Waters05 method and the Gentry06 method. However, all these three methods can only achieve identity-resistant chosen-plaintext security (ID-CPA security). In practical applications, some more capable attackers can crack the ID-CPA security encryption and decryption method. The following will take the Gentry06 method as an example to illustrate.
Gentry06方法:由Gentry在2006年EuroCrypt会议中提出。具体包括以下步骤:Gentry06 method: Presented by Gentry at the 2006 EuroCrypt conference. Specifically include the following steps:
第一步,密钥生成中心(指负责生成私钥的服务器)运行初始化模块生成公共参数和主密钥,并将公共参数公开。具体包括以下步骤:In the first step, the key generation center (referring to the server responsible for generating the private key) runs the initialization module to generate public parameters and the master key, and discloses the public parameters. Specifically include the following steps:
1.1初始化模块生成对称双线性群四元组其中p为素数,根据国际通用的美国国家标准与技术研究院(NIST)标准,当p的数量级约为2160时,加解密方法的安全性等级为80比特,即攻击者至少需要进行280次运算才能破解该方法,中的元素个数均为p,中的元素均为椭圆曲线上点的坐标,可表示为两个整数,中的元素为有限域中的元素,可表示为k维整数数组,为一个可有效计算的非退化的双线性映射;1.1 The initialization module generates a symmetric bilinear group quaternion Among them, p is a prime number. According to the international standard of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), when the magnitude of p is about 2160 , the security level of the encryption and decryption method is 80 bits, that is, the attacker needs to perform at least 280 It takes several operations to break the method, The number of elements in is p, The elements in are the coordinates of points on the elliptic curve, which can be expressed as two integers, The elements in are finite fields The elements in , which can be represented as a k-dimensional integer array, is an efficiently computable non-degenerate bilinear map;
1.2初始化模块生成元素个数为q的加法整数群其元素为0到p-1的整数;1.2 The initialization module generates an additive integer group with the number of elements q Its elements are integers from 0 to p-1;
1.3从中随机选取2个元素g,h;从中随机选取元素α;1.3 From Randomly select 2 elements g, h from Randomly select element α in ;
1.4计算公共参数元素g1=gα,为方便起见,椭圆曲线坐标与标量的乘法运算统一用指数运算的形式进行表示,具体的椭圆曲线坐标与标量的乘法运算步骤可以视为对椭圆曲线坐标进行多次加法运算;1.4 Calculate the common parameter element g1 =gα . For the sake of convenience, the multiplication of elliptic curve coordinates and scalars is uniformly expressed in the form of exponential operations. perform multiple addition operations;
1.5将g,g1,h组成公共参数,将α视为主私钥。1.5 Form g, g1 , h into public parameters, and regard α as the master private key.
第二步,密钥生成中心根据接收者的标识id,运行密钥提取模块为接收者生成私钥,其中接收者的标识id为中的元素。私钥生成具体包括以下步骤:In the second step, the key generation center runs the key extraction module to generate a private key for the recipient according to the recipient's ID, where the recipient's ID is elements in . Private key generation includes the following steps:
2.1检查id是否等于α。若相等,则标识非法,终止运行;2.1 Check if id is equal to α. If they are equal, the identification is illegal and the operation is terminated;
2.2从中随机选取私钥第一元素rid;2.2 From Randomly select the first element rid of the private key;
2.3计算私钥第二元素2.3 Calculate the second element of the private key
2.4将rid,hid组成接收者的私钥。2.4 Make rid and hid the recipient's private key.
第三步,发送者(即发送者所在服务器)运行加密模块生成密文,并将密文发送给公共服务器。需要加密的明文m为中的元素,具体步骤如下:In the third step, the sender (that is, the server where the sender is located) runs the encryption module to generate the ciphertext, and sends the ciphertext to the public server. The plaintext m to be encrypted is elements, the specific steps are as follows:
3.1从中随机选取元素s;3.1 From Randomly select element s in ;
3.2构建密文C,3.2 Construct ciphertext C,
第四步,公共服务器运行重随机模块,将得到的新密文发送给接收者。具体步骤如下:In the fourth step, the public server runs the re-random module and sends the obtained new ciphertext to the receiver. Specific steps are as follows:
4.1将密文C解析成三元组(u,v,w);4.1 Parse the ciphertext C into triples (u, v, w);
4.2从中随机选取元素t;4.2 From Randomly select an element t in ;
4.3构建新密文C′,4.3 Construct a new ciphertext C′,
第五步,接收者(即接收者所在服务器)运行解密模块,对收到的密文进行解密。具体步骤如下:In the fifth step, the receiver (that is, the server where the receiver is located) runs the decryption module to decrypt the received ciphertext. Specific steps are as follows:
5.1将密文C′解析成三元组(u′,v′,w′);5.1 Parse the ciphertext C' into triples (u', v', w');
5.2构建明文m,5.2 Construct the plaintext m,
考虑如下攻击场景:密钥生成中心运行初始化模块生成公共参数和主私钥,并公开公共参数。然后,密钥生成中心运行密钥提取模块为接收者生成私钥,并通过安全信道发送给接收者。攻击者选择两个明文m0和m1,并诱使发送者从m0和m1中随机挑选一个明文进行加密。攻击者可以获得发送者生成的密文。同时,攻击者还可以向密钥生成中心发起一系列解密询问。解密询问以标识和密文为输入,返回密文在该标识对应密钥下的解密结果。当解密结果等于m0或m1时,则不回答该询问。最终,攻击者的目标是猜测发送者是对m0还是m1进行了加密。Consider the following attack scenario: the key generation center runs the initialization module to generate public parameters and the master private key, and discloses the public parameters. Then, the key generation center runs the key extraction module to generate a private key for the receiver, and sends it to the receiver through a secure channel. The attacker chooses two plaintexts m0 and m1 , and induces the sender to randomly pick a plain text from m0 and m1 to encrypt. An attacker can obtain the ciphertext generated by the sender. At the same time, the attacker can also initiate a series of decryption challenges to the key generation center. The decryption query takes the identifier and the ciphertext as input, and returns the decryption result of the ciphertext under the key corresponding to the identifier. When the decryption result is equal to m0 or m1 , the query is not answered. Ultimately, the attacker's goal is to guess whether the sender encryptedm0 orm1 .
下面将解释Gentry06方法为何不能抵挡上述攻击。攻击者在获得发送者生成的密文后,可以将其解析为三元组(u,v,w)。从中随机选择元素m′,计算新密文C*=(u,v,m′·w)。假设以接收者的标识id和新密文C*发起解密询问得到的结果为m*,那么计算m*/m′即可得知发送者是对m0还是m1进行了加密。The following will explain why the Gentry06 method cannot withstand the above attacks. After obtaining the ciphertext generated by the sender, the attacker can parse it into a triple (u, v, w). from Randomly select the element m' in , and calculate the new ciphertext C* =(u, v, m'·w). Assuming that the result obtained by initiating a decryption query with the receiver's identification id and the new ciphertext C* is m* , then calculating m* /m' can know whether the sender has encrypted m0 or m1 .
目前为止,还没有公开文献涉及能够抵抗上述攻击(又称为基于标识的可重放的选择密文攻击)的可重随机的标识加解密方法。So far, there is no open document related to a re-random identifier encryption/decryption method that can resist the above attack (also known as an identifier-based replayable chosen ciphertext attack).
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明要解决的技术问题是针对现有可重随机的标识加解密方法存在的安全性缺陷,提供一种更高安全性的可重随机的标识加解密方法。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to provide a re-random re-random identification encryption and decryption method with higher security for the security defects existing in the existing re-random identification encryption and decryption methods.
本发明技术方案如下:The technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
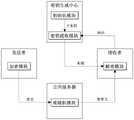
第一步:构建加解密系统。该系统中有四个角色,分别为密钥生成中心、发送者、接收者和公共服务器。加解密系统由五个模块组成,分别为初始化模块、密钥提取模块、加密模块、解密模块和重随机模块。其中初始化模块和密钥提取模块部署在密钥生成中心,加密模块部署在发送者,解密模块部署在接收者,重随机模块部署在公共服务器。Step 1: Build an encryption and decryption system. There are four roles in the system, namely, the key generation center, the sender, the receiver, and the public server. The encryption and decryption system consists of five modules, namely initialization module, key extraction module, encryption module, decryption module and re-random module. The initialization module and the key extraction module are deployed in the key generation center, the encryption module is deployed in the sender, the decryption module is deployed in the receiver, and the re-random module is deployed in the public server.
第二步:密钥生成中心运行初始化模块,生成公共参数和主私钥,并将公共参数公开。具体步骤如下:Step 2: The key generation center runs the initialization module, generates public parameters and the master private key, and exposes the public parameters. Specific steps are as follows:
2.1初始化模块生成对称双线性群四元组其中p为素数,其大小与加解密方法的安全性等级相关。p的数量级约为2160,中的元素个数均为p,中的元素为椭圆曲线上点的坐标,可表示为两个整数,中的元素为有限域中的元素,可表示为k维整数数组,e(g1,g2)为一个可有效计算的非退化的双线性映射,即g1,g2均为中的元素;2.1 The initialization module generates a symmetric bilinear group quaternion Among them, p is a prime number, and its size is related to the security level of the encryption and decryption method. The magnitude of p is about 2160 , The number of elements in is p, The elements in are the coordinates of the points on the elliptic curve, which can be expressed as two integers, The elements in are finite fields The elements in can be represented as a k-dimensional integer array, e(g1 , g2 ) is a non-degenerate bilinear map that can be efficiently calculated, namely g1 and g2 are both elements in;
2.2初始化模块生成元素个数为p的加法整数群其元素为0到p-1的整数;2.2 The initialization module generates an additive integer group with the number of elements p Its elements are integers from 0 to p-1;
2.3构造哈希函数H(m),其输入m为中的元素,输出为中的元素。H(m)采用了美国国家标准与技术研究院发布的SHA-1函数,具体为将m划分成512比特的片段,将每一段运算SHA-1函数的结果进行异或运算得到160比特长的输出,即中的元素;2.3 Construct a hash function H(m) whose input m is elements in , the output is elements in . H(m) adopts the SHA-1 function issued by the National Institute of Standards and Technology of the United States. Specifically, m is divided into 512-bit segments, and the result of each segment of the SHA-1 function is XORed to obtain a 160-bit long output, i.e. elements in;
2.4从中随机选取8个元素g,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,h7;2.4 From 8 elements g, h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6 , h7 are randomly selected from the
2.5从中随机选取3个元素α,z0,z1,其中z0≠z1;2.5 From Randomly select 3 elements α, z0 , z1 in , where z0 ≠z1 ;
2.6计算公共参数元素g1=gα。该指数运算代表椭圆曲线坐标元素g与从中随机选取的标量元素α的乘法运算,椭圆曲线坐标g与标量的乘法运算步骤可以视为对椭圆曲线坐标g进行α-1次加法运算,方法是:2.6 Calculate the common parameter element g1 =gα . The exponential operation represents the elliptic curve coordinate element g with the The multiplication operation of the randomly selected scalar element α, the multiplication operation step of the elliptic curve coordinate g and the scalar can be regarded as α-1 addition operation on the elliptic curve coordinate g, the method is:
2.6.1令椭圆曲线y2=x3+ax+b上的坐标元素g=(gx,gy),令变量i=2,令坐标元素h=(hx,hy)=g;2.6.1 Let the coordinate element g=(gx , gy ) on the elliptic curve y2 =x3 +ax+b, let the variable i=2, let the coordinate element h=(hx ,hy )=g;
2.6.2计算g和h之间的斜率λ。若g=h,则为经点g与椭圆曲线相切的切线的斜率;若g≠h,则λ=(gy-hy)/(gx-hx);2.6.2 Calculate the slope λ between g and h. If g=h, then is the slope of the tangent line tangent to the elliptic curve through point g; if g≠h, then λ=(gy -hy )/(gx -hx );
2.6.3计算g和h相加后的横坐标rx=λ2-gx-hx和g和h相加后的纵坐标ry=λ(gx-rx)-gy。r=(rx,ry)即为g与h相加的结果。2.6.3 Calculate the abscissa rx =λ2 -gx -hx after adding g and h and the ordinate ry= λ(gx -rx )-gy after adding g and h. r= (rx , ry ) is the result of adding g and h.
2.6.4若i=α,此时r即为元素g1,转2.7;否则,更新i=i+1,令h=r,转2.6.2。2.6.4 If i=α, then r is the element g1 , go to 2.7; otherwise, update i=i+1, set h=r, go to 2.6.2.
2.7将g,g1,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,h7,z0,z1,H(m)组成公共参数,α组成主私钥。h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,h7中的任意一个记为hi,i∈{1,2,3,4,5,6,7}。2.7 Form g, g1 , h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6 , h7 , z0 , z1 , H(m) as public parameters, and α as the master private key. Any one of h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6 , h7 is denoted as hi , i∈{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}.
第三步,密钥生成中心运行密钥提取模块,采用接收者的标识id为接收者生成私钥。接收者的标识id为接收者已有的身份标识在中对应的元素,私钥生成方法是:In the third step, the key generation center runs a key extraction module, and generates a private key for the recipient by using the recipient's identification id. The receiver's identification id is the receiver's existing identification. The corresponding element in , the private key generation method is:
3.1判断id是否等于α,若相等,则标识非法,转第七步;若不相等,转3.2;3.1 Judging whether the id is equal to α, if it is equal, the identification is illegal, go to the seventh step; if not, go to 3.2;
3.2令变量i=1;3.2 Let the variable i=1;
3.3从中随机选取一个元素,作为接收者的私钥中的第i个元素rid,i;3.3 From Randomly select an element in the receiver's private key as the i-th element rid,i in the receiver's private key;
3.4计算私钥元素更新i=i+1;;3.4 Calculate private key elements update i = i+1;;
3.5若i≤7,转3.3;否则,将{rid.i,hid.i|i∈{1,2,3,4,5,6,7}}组成私钥。3.5 If i≤7, go to 3.3; otherwise, combine {rid.i , hid.i |i∈{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}} to form the private key.
第四步,发送者运行加密模块,采用接收者的标识id生成密文,并将密文发送给公共服务器。需要加密的明文M为转化为十进制数后不大于p的二进制数,具体步骤如下:In the fourth step, the sender runs the encryption module, uses the receiver's identification id to generate the ciphertext, and sends the ciphertext to the public server. The plaintext M that needs to be encrypted is a binary number that is not greater than p after being converted into a decimal number. The specific steps are as follows:
4.1将明文M按照二进制转十进制的方法,转化为整数M′。令中间明文m=(0,…,0,M′),其中前k-1维元素均为0,第k维元素为M′。那么m即中的元素;k为中元素表示为整数数组时的维数;4.1 Convert the plaintext M into an integer M' according to the method of converting from binary to decimal. Let the intermediate plaintext m=(0, . . . , 0, M'), wherein the first k-1 dimension elements are all 0, and the kth dimension element is M'. Then m is elements in ; k is The number of dimensions when the elements in are represented as integer arrays;
4.2从中随机选取4个元素s,t,4.2 From Randomly select 4 elements s, t,
4.3从中随机选取元素u;4.3 From Randomly select element u in ;
4.4计算第一哈希值θ=H(m),计算第二哈希值σ=H(u);4.4 Calculate the first hash value θ=H(m), and calculate the second hash value σ=H(u);
4.5计算密文第一元素密文第二元素x2=e(gs,g),密文第三元素x3=m·e(g-s,h1),密文第四元素密文第五元素密文第六元素密文第七元素y2=e(gt,g),密文第八元素y3=e(g-t,h1),密文第九元素y4=(e(g,h2)e(gθ,h3))σt,密文第十元素y5=(e(g,h4)e(gθ,h5))σt,密文第十一元素密文第十二元素密文第十三元素密文第十四元素密文第十五元素密文第十六元素密文第十七元素密文第十八元素令元素β1,β2为从中随机选取的元素,元素γ为从中随机选取的元素,β1β2表示β1和β2进行有限域上的乘法运算,表示β1和γ进行有限域上的指数运算。例如:当β1=e(g,h2),β2=e(gθ,h3)时,表示β1和β2进行有限域上的乘法运算后的结果,再和σ(s+z0)进行有限域上的指数运算。4.5 Calculate the first element of the ciphertext The second element of the ciphertext x2 =e(gs , g), the third element of the ciphertext x3 =m·e(g-s , h1 ), the fourth element of the ciphertext The fifth element of the ciphertext The sixth element of the ciphertext The seventh element of ciphertext y2 =e(gt , g), the eighth element of ciphertext y3 =e(g-t , h1 ), the ninth element of ciphertext y4 =(e(g, h2 ) e(gθ , h3 ))σt , the tenth element of the ciphertext y5 =(e(g, h4 )e(gθ , h5 ))σt , the eleventh element of the ciphertext The twelfth element of the ciphertext Thirteenth element of ciphertext The fourteenth element of the ciphertext The fifteenth element of the ciphertext The sixteenth element of the ciphertext The seventeenth element of the ciphertext The eighteenth element of the ciphertext Let the elements β1 , β2 be from A randomly selected element in , the element γ is fromRandomlyselectedelementsin multiplication on , Represents β1 and γ for a finite field exponentiation on . For example: when β1 =e(g, h2 ), β2 =e(gθ , h3 ), Represents β1 and β2 for finite field The result of the multiplication operation on , and then perform a finite field with σ(s+z0 ) exponentiation on .
4.6将x1,x2,x3,x4,x5组成第一五元组X,将y1,y2,y3,y4,y5组成第二五元组Y,将u1,u2,u3,u4组成第一四元组U,将v1,v2,v3,v4组成第二四元组V;4.6 Form x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 into the first quintuple X, y1 , y2 , y3 , y4 , y5 form the second quintuple Y, and u1 , u2 , u3 , u4 form the first quadruple U, and v1 , v2 , v3 , and v4 form the second quadruple V;
4.7将X,Y,U,V组成密文C,将C发送给公共服务器。4.7 Form X, Y, U, V into ciphertext C, and send C to the public server.
第五步,公共服务器运行重随机模块,对从发送者接收的密文C进行重随机,将得到的新密文C′发送给接收者。具体步骤如下:In the fifth step, the public server runs the re-random module, re-randomizes the ciphertext C received from the sender, and sends the new ciphertext C' obtained to the receiver. Specific steps are as follows:
5.1重随机模块从发送者接收密文C,将密文C解析成(X,Y,U,V),其中第一五元组X=(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5),第二五元组Y=(y1,y2,y3,y4,y5),第一四元组U=(u1,u2,u3,u4)以及第二四元组V=(v1,v2,v3,v4);5.1 The re-random module receives the ciphertext C from the sender, and parses the ciphertext C into (X, Y, U, V), where the first five-tuple X=(x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 ), the second quintuple Y=(y1 , y2 , y3 , y4 , y5 ), the first quintuple U=(u1 , u2 , u3 , u4 ) and the second quaternion V=(v1 , v2 , v3 , v4 );
5.2从中随机选取4个元素s′,t′,5.2 From Randomly select 4 elements s', t',
5.3计算新密文第一元素新密文第二元素新密文第二元素新密文第四元素新密文第五元素新密文第六元素新密文第七元素新密文第八元素新密文第九元素新密文第十元素新密文第十一元素新密文第十二元素新密文第十三元素新密文第十四元素新密文第十五元素新密文第十六元素新密文第十七元素新密文第十八元素5.3 Calculate the first element of the new ciphertext The second element of the new ciphertext The second element of the new ciphertext The fourth element of the new ciphertext The fifth element of the new ciphertext The sixth element of the new ciphertext The seventh element of the new ciphertext The eighth element of the new ciphertext The ninth element of the new ciphertext The tenth element of the new ciphertext The eleventh element of the new ciphertext The twelfth element of the new ciphertext The thirteenth element of the new ciphertext The fourteenth element of the new ciphertext The fifteenth element of the new ciphertext The sixteenth element of the new ciphertext The seventeenth element of the new ciphertext The eighteenth element of the new ciphertext
5.4将x′1,x′2,x′3,x′4,x′5组成第三五元组X′,将y′1,y′2,y′3,y′4,y′5组成第四五元组Y′,将u′1,u′2,u′3,u′4组成第三四元组U′,将v′1,v′2,v′3,v′4组成第四四元组V′;5.4 Form x′1 , x′2 , x′3 , x′4 , x′5 into the third quintuple X′, and combine y′1 , y′2 , y′3 , y′4 , y′5 The fourth quintuple Y' is formed, u'1 , u'2 , u'3 , u'4 are formed into the third quaternary U', v'1 , v'2 , v'3 , v'4 Form the fourth quadruple V';
5.5将X′,Y′,U′,V′组成新密文C′,将C′发送给接收者。5.5 Combine X', Y', U', V' to form a new ciphertext C', and send C' to the receiver.
第六步,接收者运行解密模块,对从公共服务器收到的新密文C′进行解密。具体步骤如下:In the sixth step, the receiver runs the decryption module to decrypt the new ciphertext C' received from the public server. Specific steps are as follows:
6.1将密文C′解析成(X′,Y′,U′,V′),其中第三五元组X′=(x′1,x′2,x′3,x′4,x′5),第四五元组Y′=(y′1,y′2,y′3,y′4,y′5),第三四元组U′=(u′1,u′2,u′3,u′4)以及第四四元组V′=(v′1,v′2,v′3,v′4);6.1 Parse the ciphertext C' into (X', Y', U', V'), where the third quintuple X'=(x'1 , x'2 , x'3 , x'4 , x'5 ), the fourth quintuple Y′=(y′1 , y′2 , y′3 , y′4 , y′5 ), the third quintuple U′=(u′1 , u′2 , u′3 , u′4 ) and the fourth quadruple V′=(v′1 , v′2 , v′3 , v′4 );
6.2还原中间明文和元素若m不能表示为k维数组(0,…,0,M′)或者整数M′大于p,转第七步;否则,将M′按照十进制转二进制的方法,计算得到明文M。此时还不能直接输出明文M,需要进一步确定密文C′是否合法;6.2 Restoring the intermediate plaintext and elements If m cannot be represented as a k-dimensional array (0, . . . , 0, M') or the integer M' is greater than p, go to step 7; At this time, the plaintext M cannot be directly output, and it is necessary to further determine whether the ciphertext C' is legal;
6.3计算第一哈希值θ=H(m)和第二哈希值σ=H(u);6.3 Calculate the first hash value θ=H(m) and the second hash value σ=H(u);
6.4计算临时第一元素临时第二元素临时第三元素6.4 Computing the temporary first element temporary second element temporary third element
6.5判断第一三元组是否等于第二三元组(u′4,v′3,v′4),若不等于,则密文C′不合法,转第七步;若相等,转6.6;6.5 Judging the first triple Is it equal to the second triplet (u′4 , v′3 , v′4 ), if not, then the ciphertext C′ is invalid, go to step 7; if it is equal, go to 6.6;
6.6计算临时第四元素临时第五元素临时第六元素临时第七元素临时第八元素6.6 Calculating the Temporary Fourth Element temporary fifth element temporary sixth element temporary seventh element temporary eighth element
6.7判断第五五元组是否等于第六五元组(x′4,x′5,y′3,y′4,y′5),若不等于,则密文不合法,转第七步;若相等,则解密结果为M。6.7 Judging the fifth quintuple Is it equal to the sixth quintuple (x′4 , x′5 , y′3 , y′4 , y′5 ), if not equal, the ciphertext is invalid, go to the seventh step; if it is equal, the decryption result for M.
第七步,加解密系统结束运行。In the seventh step, the encryption and decryption system ends operation.
采用本发明可以得到如下效果:The following effects can be obtained by adopting the present invention:
1.本发明由于第四步的4.4,保证了抗可重放的选择密文攻击安全。具体来说,在4.4中,x4,x5,y4,y5的计算使用了第一哈希值θ,即明文m的哈希值。当攻击者尝试对通过修改本发明中的现有密文C得到具有不同底层明文的新密文C*时,攻击者需要重新计算出对应的然而严谨的数学规约可以证明攻击者无法计算正确的因此,攻击者不能通过修改密文C得到具有不同底层明文的新密文C*,本发明可以抵抗基于标识的可重放的选择密文攻击,解决了背景技术所述的攻击以及Gentry06方法存在的安全缺陷。1. Due to 4.4 of the fourth step, the present invention ensures the security against replayable selected ciphertext attacks. Specifically, in 4.4, the calculation of x4 , x5 , y4 , and y5 uses the first hash value θ, that is, the hash value of the plaintext m. When an attacker tries to obtain a new ciphertext C* with a different underlying plaintext by modifying the existing ciphertext C in the present invention, the attacker needs to recalculate the corresponding However, a rigorous mathematical specification can prove that the attacker cannot calculate the correct Therefore, an attacker cannot obtain a new ciphertext C* with a different underlying plaintext by modifying the ciphertext C. The present invention can resist the replayable selected ciphertext attack based on the identification, and solves the attack described in the background art and the existence of the Gentry06 method. security flaws.
2.相比于一般的可重随机的标识加解密方案,本发明第五步重随机模块的运行不需要接收者的标识,因此可以免去标识的分发,使得任意角色可以对密文直接进行重随机化,而不需要事先获取密文所对应的标识,这样使得公共服务器的部署和运行更加简洁和高效。2. Compared with the general re-random identification encryption and decryption scheme, the operation of the fifth step of the re-random module of the present invention does not require the identification of the receiver, so the distribution of the identification can be omitted, so that any role can directly perform the encryption on the ciphertext. Re-randomization without the need to obtain the identifier corresponding to the ciphertext in advance, which makes the deployment and operation of the public server more concise and efficient.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是本发明的加解密以及重随机逻辑结构图;Fig. 1 is the encryption and decryption of the present invention and the re-random logic structure diagram;
图2是本发明的流程图。Figure 2 is a flow chart of the present invention.
具体实施方式:Detailed ways:
以下结合说明书附图和具体实施例对本发明作进一步描述。The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
如图2所示,本发明包括以下步骤:As shown in Figure 2, the present invention comprises the following steps:
第一步:构建加解密系统。如图1所示,加解密系统中有四个角色,分别为密钥生成中心、发送者、接收者和公共服务器。加解密系统由五个模块组成,分别为初始化模块、密钥提取模块、加密模块、解密模块和重随机模块。其中初始化模块和密钥提取模块部署在密钥生成中心,加密模块部署在发送者,解密模块部署在接收者,重随机模块部署在公共服务器。Step 1: Build an encryption and decryption system. As shown in Figure 1, there are four roles in the encryption and decryption system, namely the key generation center, the sender, the receiver and the public server. The encryption and decryption system consists of five modules, namely initialization module, key extraction module, encryption module, decryption module and re-random module. The initialization module and the key extraction module are deployed in the key generation center, the encryption module is deployed in the sender, the decryption module is deployed in the receiver, and the re-random module is deployed in the public server.
第二步:密钥生成中心运行初始化模块,生成公共参数和主私钥,并将公共参数公开。具体步骤如下:Step 2: The key generation center runs the initialization module, generates public parameters and the master private key, and exposes the public parameters. Specific steps are as follows:
2.1初始化模块生成对称双线性群四元组其中p为素数,其大小与加解密方法的安全性等级相关。p的数量级约为2160,中的元素个数均为p,和的元素为椭圆曲线上点的坐标,可表示为两个整数,中的元素为有限域中的元素,可表示为k维整数数组,e(g1,g2)为一个可有效计算的非退化的双线性映射,即g1,g2均为中的元素;2.1 The initialization module generates a symmetric bilinear group quaternion Among them, p is a prime number, and its size is related to the security level of the encryption and decryption method. The magnitude of p is about 2160 , The number of elements in is p, The elements of and are the coordinates of points on the elliptic curve, which can be expressed as two integers, The elements in are finite fields The elements in can be represented as a k-dimensional integer array, e(g1 , g2 ) is a non-degenerate bilinear map that can be efficiently calculated, namely g1 and g2 are both elements in;
2.2初始化模块生成元素个数为p的加法整数群其元素为0到p-1的整数;2.2 The initialization module generates an additive integer group with the number of elements p Its elements are integers from 0 to p-1;
2.3构造哈希函数H(m),其输入m为中的元素,输出为中的元素。H(m)采用了美国国家标准与技术研究院发布的SHA-1函数,具体为将m划分成512比特的片段,将每一段运算SHA-1函数的结果进行异或运算得到160比特长的输出,即中的元素;2.3 Construct a hash function H(m) whose input m is elements in , the output is elements in . H(m) adopts the SHA-1 function issued by the National Institute of Standards and Technology of the United States. Specifically, m is divided into 512-bit segments, and the result of each segment of the SHA-1 function is XORed to obtain a 160-bit long output, i.e. elements in;
2.4从中随机选取8个元素g,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,h7;2.4 From 8 elements g, h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6 , h7 are randomly selected from the
2.5从中随机选取3个元素α,z0,z1,其中z0≠z1;2.5 From Randomly select 3 elements α, z0 , z1 in , where z0 ≠z1 ;
2.6计算公共参数元素g1=gα。该指数运算代表椭圆曲线坐标元素g与从中随机选取的标量元素α的乘法运算,椭圆曲线坐标g与标量的乘法运算步骤可以视为对椭圆曲线坐标g进行α-1次加法运算,方法是:2.6 Calculate the common parameter element g1 =gα . The exponential operation represents the elliptic curve coordinate element g with the The multiplication operation of the randomly selected scalar element α, the multiplication operation step of the elliptic curve coordinate g and the scalar can be regarded as α-1 addition operation on the elliptic curve coordinate g, the method is:
2.6.1令椭圆曲线y2=x3+ax+b上的坐标元素g=(gx,gy),令变量i=2,令坐标元素h=(hx,hy)=g;2.6.1 Let the coordinate element g=(gx , gy ) on the elliptic curve y2 =x3 +ax+b, let the variable i=2, let the coordinate element h=(hx ,hy )=g;
2.6.2计算g和h之间的斜率λ。若g=h,则为经点g与椭圆曲线相切的切线的斜率;若g≠h,则λ=(gy-hy)/(gx-hx);2.6.2 Calculate the slope λ between g and h. If g=h, then is the slope of the tangent line tangent to the elliptic curve through point g; if g≠h, then λ=(gy -hy )/(gx -hx );
2.6.3计算g和h相加后的横坐标rx=λ2-gx-hx和g和h相加后的纵坐标ry=λ(gx-rx)-gy。r=(rx,ry)即为g与h相加的结果。2.6.3 Calculate the abscissa rx =λ2 -gx -hx after adding g and h and the ordinate ry= λ(gx -rx )-gy after adding g and h. r= (rx , ry ) is the result of adding g and h.
2.6.4若i=α,此时r即为元素g1,转2.7;否则,更新i=i+1,令h=r,转2.6.2。2.6.4 If i=α, then r is the element g1 , go to 2.7; otherwise, update i=i+1, set h=r, go to 2.6.2.
2.7将g,g1,h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,h7,z0,z1,H(m)组成公共参数,α组成主私钥。h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6,h7中的任意一个记为hi,i∈{1,2,3,4,5,6,7}。2.7 Form g, g1 , h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6 , h7 , z0 , z1 , H(m) as public parameters, and α as the master private key. Any one of h1 , h2 , h3 , h4 , h5 , h6 , h7 is denoted as hi , i∈{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}.
第三步,密钥生成中心运行密钥提取模块,采用接收者的标识id为接收者生成私钥。接收者的标识id为接收者已有的身份标识在中对应的元素,私钥生成方法是:In the third step, the key generation center runs a key extraction module, and generates a private key for the recipient by using the recipient's identification id. The receiver's identification id is the receiver's existing identification. The corresponding element in , the private key generation method is:
3.1判断id是否等于α,若相等,则标识非法,转第七步;若不相等,转3.2;3.1 Judging whether the id is equal to α, if it is equal, the identification is illegal, go to the seventh step; if not, go to 3.2;
3.2令变量i=1;3.2 Let the variable i=1;
3.3从中随机选取一个元素,作为接收者的私钥中的第i个元素rid,i;3.3 From Randomly select an element in the receiver's private key as the i-th element rid,i in the receiver's private key;
3.4计算私钥元素更新i=i+1;;3.4 Calculate private key elements update i = i+1;;
3.5若i≤7,转3.3;否则,将{rid.i,hid.i|i∈{1,2,3,4,5,6,7}}组成私钥。3.5 If i≤7, go to 3.3; otherwise, combine {rid.i , hid.i |i∈{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}} to form the private key.
第四步,发送者运行加密模块,采用接收者的标识id生成密文,并将密文发送给公共服务器。需要加密的明文M为转化为十进制数后不大于p的二进制数,具体步骤如下:In the fourth step, the sender runs the encryption module, uses the receiver's identification id to generate the ciphertext, and sends the ciphertext to the public server. The plaintext M that needs to be encrypted is a binary number that is not greater than p after being converted into a decimal number. The specific steps are as follows:
4.1将明文M按照二进制转十进制的方法,转化为整数M′。令中间明文m=(0,…,0,M′),其中前k-1维元素均为0,第k维元素为M′。那么m即中的元素;k为中元素表示为整数数组时的维数;4.1 Convert the plaintext M into an integer M' according to the method of converting from binary to decimal. Let the intermediate plaintext m=(0, . . . , 0, M'), wherein the first k-1 dimension elements are all 0, and the kth dimension element is M'. Then m is elements in ; k is The number of dimensions when the elements in are represented as integer arrays;
4.2从中随机选取4个元素s,t,4.2 From Randomly select 4 elements s, t,
4.3从中随机选取元素u;4.3 From Randomly select element u in ;
4.4计算第一哈希值θ=H(m),计算第二哈希值σ=H(u);4.4 Calculate the first hash value θ=H(m), and calculate the second hash value σ=H(u);
4.5计算密文第一元素密文第二元素x2=e(gs,g),密文第三元素x3=m·e(g-s,h1),密文第四元素密文第五元素密文第六元素密文第七元素y2=e(gt,g),密文第八元素y3=e(g-t,h1),密文第九元素y4=(e(g,h2)e(gθ,h3))σt,密文第十元素y5=(e(g,h4)e(gθ,h5))σt,密文第十一元素密文第十二元素密文第十三元素密文第十四元素密文第十五元素密文第十六元素密文第十七元素密文第十八元素令元素β1,β2为从中随机选取的元素,元素y为从中随机选取的元素,β1β2表示β1和β2进行有限域上的乘法运算,表示β1和γ进行有限域上的指数运算。4.5 Calculate the first element of the ciphertext The second element of the ciphertext x2 =e(gs , g), the third element of the ciphertext x3 =m·e(g-s , h1 ), the fourth element of the ciphertext The fifth element of the ciphertext The sixth element of the ciphertext The seventh element of ciphertext y2 =e(gt , g), the eighth element of ciphertext y3 =e(g-t , h1 ), the ninth element of ciphertext y4 =(e(g, h2 ) e(gθ , h3 ))σt , the tenth element of the ciphertext y5 =(e(g, h4 )e(gθ , h5 ))σt , the eleventh element of the ciphertext The twelfth element of the ciphertext Thirteenth element of ciphertext The fourteenth element of the ciphertext The fifteenth element of the ciphertext The sixteenth element of the ciphertext The seventeenth element of the ciphertext The eighteenth element of the ciphertext Let the elements β1 , β2 be from Randomly selected elements in , element y is fromRandomlyselectedelementsin multiplication on , Represents β1 and γ for a finite field exponentiation on .
4.6将x1,x2,x3,x4,x5组成第一五元组X,将y1,y2,y3,y4,y5组成第二五元组Y,将u1,u2,u3,u4组成第一四元组U,将v1,v2,v3,v4组成第二四元组V;4.6 Form x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 into the first quintuple X, y1 , y2 , y3 , y4 , y5 form the second quintuple Y, and u1 , u2 , u3 , u4 form the first quadruple U, and v1 , v2 , v3 , and v4 form the second quadruple V;
4.7将X,Y,U,V组成密文C,将C发送给公共服务器。4.7 Form X, Y, U, V into ciphertext C, and send C to the public server.
第五步,公共服务器运行重随机模块,对从发送者接收的密文C进行重随机,将得到的新密文C′发送给接收者。具体步骤如下:In the fifth step, the public server runs the re-random module, re-randomizes the ciphertext C received from the sender, and sends the new ciphertext C' obtained to the receiver. Specific steps are as follows:
5.1重随机模块从发送者接收密文C,将密文C解析成(X,Y,U,V),其中第一五元组X=(x1,x2,x3,x4,x5),第二五元组Y=(y1,y2,y3,y4,y5),第一四元组U=(u1,u2,u3,u4)以及第二四元组V=(v1,v2,v3,v4);5.1 The re-random module receives the ciphertext C from the sender, and parses the ciphertext C into (X, Y, U, V), where the first five-tuple X=(x1 , x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 ), the second quintuple Y=(y1 , y2 , y3 , y4 , y5 ), the first quintuple U=(u1 , u2 , u3 , u4 ) and the second quaternion V=(v1 , v2 , v3 , v4 );
5.2从中随机选取4个元素s′,t′,5.2 From Randomly select 4 elements s', t',
5.3计算新密文第一元素新密文第二元素新密文第二元素新密文第四元素新密文第五元素新密文第六元素新密文第七元素新密文第八元素新密文第九元素新密文第十元素新密文第十一元素新密文第十二元素新密文第十三元素新密文第十四元素新密文第十五元素新密文第十六元素新密文第十七元素新密文第十八元素5.3 Calculate the first element of the new ciphertext The second element of the new ciphertext The second element of the new ciphertext The fourth element of the new ciphertext The fifth element of the new ciphertext The sixth element of the new ciphertext The seventh element of the new ciphertext The eighth element of the new ciphertext The ninth element of the new ciphertext The tenth element of the new ciphertext The eleventh element of the new ciphertext The twelfth element of the new ciphertext The thirteenth element of the new ciphertext The fourteenth element of the new ciphertext The fifteenth element of the new ciphertext The sixteenth element of the new ciphertext The seventeenth element of the new ciphertext The eighteenth element of the new ciphertext
5.4将x′1,x′2,x′3,x′4,x′5组成第三五元组X′,将y′1,y′2,y′3,y′4,y′5组成第四五元组Y′,将u′1,u′2,u′3,u′4组成第三四元组U′,将v′1,v′2,v′3,v′4组成第四四元组V′;5.4 Form x′1 , x′2 , x′3 , x′4 , x′5 into the third quintuple X′, and combine y′1 , y′2 , y′3 , y′4 , y′5 The fourth quintuple Y' is formed, u'1 , u'2 , u'3 , u'4 are formed into the third quaternary U', v'1 , v'2 , v'3 , v'4 Form the fourth quadruple V';
5.5将X′,Y′,U′,V′组成新密文C′,将C′发送给接收者。5.5 Combine X', Y', U', V' to form a new ciphertext C', and send C' to the receiver.
第六步,接收者运行解密模块,对从公共服务器收到的新密文C′进行解密。具体步骤如下:In the sixth step, the receiver runs the decryption module to decrypt the new ciphertext C' received from the public server. Specific steps are as follows:
6.1将密文C′解析成(X′,Y′,U′,V′),其中第三五元组X′=(x′1,x′2,x′3,x′4,x′5),第四五元组Y′=(y′1,y′2,y′3,y′4,y′5),第三四元组U′=(u′1,u′2,u′3,u′4)以及第四四元组V′=(v′1,v′2,v′3,v′4);6.1 Parse the ciphertext C' into (X', Y', U', V'), where the third quintuple X'=(x'1 , x'2 , x'3 , x'4 , x'5 ), the fourth quintuple Y′=(y′1 , y′2 , y′3 , y′4 , y′5 ), the third quintuple U′=(u′1 , u′2 , u′3 , u′4 ) and the fourth quadruple V′=(v′1 , v′2 , v′3 , v′4 );
6.2还原中间明文和元素若m不能表示为k维数组(0,…,0,M′)或者整数M′大于p,转第七步;否则,将M′按照十进制转二进制的方法,计算得到明文M。此时还不能直接输出明文M,需要进一步确定密文C′是否合法;6.2 Restoring the intermediate plaintext and elements If m cannot be represented as a k-dimensional array (0, . . . , 0, M') or the integer M' is greater than p, go to step 7; At this time, the plaintext M cannot be directly output, and it is necessary to further determine whether the ciphertext C' is legal;
6.3计算第一哈希值θ=H(m)和第二哈希值σ=H(u);6.3 Calculate the first hash value θ=H(m) and the second hash value σ=H(u);
6.4计算临时第一元素临时第二元素临时第三元素6.4 Computing the temporary first element temporary second element temporary third element
6.5判断第一三元组是否等于第二三元组(u′4,v′3,v′4),若不等于,则密文C′不合法,转第七步;若相等,转6.6;6.5 Judging the first triple Is it equal to the second triplet (u′4 , v′3 , v′4 ), if not, then the ciphertext C′ is invalid, go to step 7; if it is equal, go to 6.6;
6.6计算临时第四元素临时第五元素临时第六元素临时第七元素临时第八元素6.6 Calculating the Temporary Fourth Element temporary fifth element temporary sixth element temporary seventh element temporary eighth element
6.7判断第五五元组是否等于第六五元组(x′4,x′5,y′3,y′4,y′5),若不等于,则密文不合法,转第七步;若相等,则解密结果为M。6.7 Judging the fifth quintuple Is it equal to the sixth quintuple (x′4 , x′5 , y′3 , y′4 , y′5 ), if not equal, the ciphertext is invalid, go to the seventh step; if it is equal, the decryption result for M.
第七步,加解密系统结束运行。In the seventh step, the encryption and decryption system ends operation.
最后说明的是,以上仅是本发明的优选实施例,并非对本发明作任何形式上的限制。虽然本发明已以优选实施例揭露如上,然而并非用以限定本发明。任何熟悉本领域的技术人员,在不脱离本发明技术方案范围的情况下,都可利用上述揭示的技术内容对本发明技术方案做出许多可能的变动和修饰,或修改为等同变化的等效实施例。因此,凡是未脱离本发明技术方案的内容,依据本发明技术实质对以上实施例所做的任何简单修改、等同变化及修饰,均应落在本发明技术方案保护的范围内。Finally, it should be noted that the above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention, and do not limit the present invention in any form. Although the present invention has been disclosed above with preferred embodiments, it is not intended to limit the present invention. Any person skilled in the art, without departing from the scope of the technical solution of the present invention, can make many possible changes and modifications to the technical solution of the present invention by using the technical content disclosed above, or modify it into an equivalent implementation of equivalent changes. example. Therefore, any simple modifications, equivalent changes and modifications made to the above embodiments according to the technical essence of the present invention without departing from the content of the technical solutions of the present invention should fall within the protection scope of the technical solutions of the present invention.
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010672997.0ACN111756539B (en) | 2020-07-14 | 2020-07-14 | A Re-random Identification Encryption and Decryption Method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010672997.0ACN111756539B (en) | 2020-07-14 | 2020-07-14 | A Re-random Identification Encryption and Decryption Method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111756539Atrue CN111756539A (en) | 2020-10-09 |
| CN111756539B CN111756539B (en) | 2021-02-05 |
Family
ID=72711507
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010672997.0AActiveCN111756539B (en) | 2020-07-14 | 2020-07-14 | A Re-random Identification Encryption and Decryption Method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111756539B (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080137868A1 (en)* | 2006-12-08 | 2008-06-12 | University Technologies International, a Canadian Corporation | Distributed encryption methods and systems |
| CN107070662A (en)* | 2017-03-23 | 2017-08-18 | 西安电子科技大学 | Encryption Proxy Signature method based on obfuscation |
| CN108923921A (en)* | 2018-07-24 | 2018-11-30 | 上海声联网络科技有限公司 | A kind of cryptographic key factor generation method of root key |
| CN110601822A (en)* | 2019-08-20 | 2019-12-20 | 国家电网有限公司 | Encryption blind signature method based on quantum secret communication technology |
- 2020
- 2020-07-14CNCN202010672997.0Apatent/CN111756539B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080137868A1 (en)* | 2006-12-08 | 2008-06-12 | University Technologies International, a Canadian Corporation | Distributed encryption methods and systems |
| CN107070662A (en)* | 2017-03-23 | 2017-08-18 | 西安电子科技大学 | Encryption Proxy Signature method based on obfuscation |
| CN108923921A (en)* | 2018-07-24 | 2018-11-30 | 上海声联网络科技有限公司 | A kind of cryptographic key factor generation method of root key |
| CN110601822A (en)* | 2019-08-20 | 2019-12-20 | 国家电网有限公司 | Encryption blind signature method based on quantum secret communication technology |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| 赵青松,曾庆凯,刘西蒙,徐焕良: "基于可重随机化混淆电路的可验证计算", 《软件学报》* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111756539B (en) | 2021-02-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN108388808B (en) | Image Encryption Method Based on Hill Encryption and Dynamic DNA Coding | |
| Laiphrakpam et al. | A robust image encryption scheme based on chaotic system and elliptic curve over finite field | |
| US7657033B2 (en) | Cryptography related to keys | |
| KR102304831B1 (en) | Encryption systems and method using permutaion group based cryptographic techniques | |
| RU2691253C2 (en) | Nado cryptography with key generators | |
| US20100046755A1 (en) | Cryptography related to keys with signature | |
| CN109450640B (en) | SM 2-based two-party signature method and system | |
| Sengupta et al. | Message mapping and reverse mapping in elliptic curve cryptosystem | |
| CN112187461A (en) | Weapon equipment data hybrid encryption method based on encryption algorithm | |
| CN114362912A (en) | Identification password generation method based on distributed key center, electronic device and medium | |
| CN114793167A (en) | Network coding method, system and device based on block encryption and threshold sharing | |
| CN116094716B (en) | Text encryption and decryption method, system and device based on elliptic curve cryptography | |
| CN117114959A (en) | An image encryption method based on the key feedback mechanism of multi-parameter one-dimensional chaotic system | |
| CN1881874A (en) | Public key cipher encrypting and decrypting method based on nerval network chaotic attractor | |
| Jasra et al. | Image encryption using logistic-cosine-sine chaos map and elliptic curve cryptography | |
| CN119232351B (en) | A n-choose-k oblivious transmission method based on homomorphic encryption | |
| CN111835766B (en) | Re-random public key encryption and decryption method | |
| CN111865578B (en) | SM 2-based multi-receiver public key encryption method | |
| CN111817853B (en) | Signcryption algorithm for post-quantum security | |
| CN108124076A (en) | Image encryption method based on isomery chaos and keccak hash functions | |
| CN109495478B (en) | A distributed secure communication method and system based on blockchain | |
| CN102136911A (en) | Method for encrypting electronic document | |
| CN107359982B (en) | A Homomorphic Signature Method Against Intra-Generation/Inter-Generation Attacks | |
| CN114221753B (en) | Key data processing method and electronic equipment | |
| CN111756539B (en) | A Re-random Identification Encryption and Decryption Method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |