CN111449757A - Telemedicine robot, control method and charging method thereof - Google Patents
Telemedicine robot, control method and charging method thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111449757A CN111449757ACN202010279038.2ACN202010279038ACN111449757ACN 111449757 ACN111449757 ACN 111449757ACN 202010279038 ACN202010279038 ACN 202010279038ACN 111449757 ACN111449757 ACN 111449757A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- charging
- telemedicine
- manipulator
- moving
- robot
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B34/00—Computer-aided surgery; Manipulators or robots specially adapted for use in surgery
- A61B34/30—Surgical robots
- A61B34/35—Surgical robots for telesurgery
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Manipulator (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本说明书一个或多个实施例涉及医疗技术领域,尤其涉及一种远程医疗机器人、控制方法及其充电方法。One or more embodiments of this specification relate to the field of medical technology, and in particular, to a telemedicine robot, a control method, and a charging method thereof.
背景技术Background technique
当前各地医疗水平存在差异,发达地区高水平医生集中,偏远地区高水平医生缺乏。对于农村或偏远地区的患者来说,求医治病并不是一件容易的事情。通常患者需要长途跋涉才能到达医院,而医生问诊时间可能只有十几分钟。患者和医生的空间距离不仅增加了患者的身体负担,同时也增加了患者的经济负担。At present, there are differences in the level of medical care in various regions. There are many high-level doctors in developed areas, and there is a lack of high-level doctors in remote areas. For patients in rural or remote areas, seeking medical treatment is not an easy task. Usually patients need to travel long distances to reach the hospital, and the doctor's consultation time may only be ten minutes. The spatial distance between patients and doctors not only increases the physical burden of patients, but also increases the economic burden of patients.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
有鉴于此,本说明书一个或多个实施例的目的在于提出一种远程医疗机器人、控制方法及其充电方法,以解决农村或偏远地区的患者求医治病难的问题。In view of this, the purpose of one or more embodiments of this specification is to provide a telemedicine robot, a control method and a charging method thereof, so as to solve the problem of difficulty in seeking medical treatment for patients in rural or remote areas.
基于上述目的,本说明书实施例的第一方面,提供了一种远程医疗机器人,包括:Based on the above purpose, a first aspect of the embodiments of this specification provides a telemedicine robot, including:
具有多个自由度的调整平台;Adjustment platform with multiple degrees of freedom;
机械手,设置于所述调整平台的端部,被配置为操作检测设备对患者进行医学检测;a manipulator, disposed at the end of the adjustment platform, configured to operate the detection device to perform medical detection on the patient;
交互模块,设置于所述调整平台,被配置为实现与远端控制设备间的多媒体信息交互;以及An interaction module, arranged on the adjustment platform, is configured to realize the interaction of multimedia information with the remote control device; and
控制模块,被配置为:获取远端控制设备发送的控制指令,并根据所述控制指令,控制所述调整平台、所述机械手和所述交互模块的工作状态。The control module is configured to: acquire the control instruction sent by the remote control device, and control the working state of the adjustment platform, the manipulator and the interaction module according to the control instruction.
进一步的,所述调整平台,包括:Further, the adjustment platform includes:
旋转组件,连接所述机械手,被配置为带动所述机械手旋转以调节所述机械手的姿态;a rotating component, connected to the manipulator, and configured to drive the manipulator to rotate to adjust the posture of the manipulator;
直线移动组件,连接所述旋转组件,被配置为带动所述旋转组件和所述机械手直线移动以调节所述机械手的位置;以及a linear moving component, connected to the rotating component, configured to drive the rotating component and the manipulator to move linearly to adjust the position of the manipulator; and
移动底盘,被配置为承载所述直线移动组件,并带动所述直线移动组件、所述旋转组件和所述机械手移动。The moving chassis is configured to carry the linear moving component and drive the linear moving component, the rotating component and the manipulator to move.
进一步的,所述移动底盘,具体包括:Further, the mobile chassis specifically includes:
盘体,包括:相对设置的第一表面和第二表面,以及连接所述第一表面和第二表面的外周面;所述第一表面用于设置所述直线移动组件;a disk body, comprising: a first surface and a second surface arranged oppositely, and an outer peripheral surface connecting the first surface and the second surface; the first surface is used for setting the linear movement component;
避障传感器,均匀设置于所述外周面;以及obstacle avoidance sensors, uniformly arranged on the outer peripheral surface; and
移动轮,设置于所述第二表面。A moving wheel is arranged on the second surface.
进一步的,所述旋转组件,具体包括:Further, the rotating assembly specifically includes:
第一旋转单元,连接所述机械手,被配置为调节所述机械手在第一平面的角度;a first rotation unit, connected to the manipulator, configured to adjust the angle of the manipulator on the first plane;
第二旋转单元,连接所述第一旋转单元,被配置为调节所述第一旋转单元在第二平面的角度;其中,所述第二平面垂直所述第一平面;以及A second rotation unit, connected to the first rotation unit, configured to adjust the angle of the first rotation unit on a second plane; wherein the second plane is perpendicular to the first plane; and
第三旋转单元,连接所述第二旋转单元,被配置为调节所述第二旋转单元在第三平面的角度;其中,所述第三平面垂直所述第一平面以及所述第二平面。A third rotating unit, connected to the second rotating unit, is configured to adjust the angle of the second rotating unit on a third plane; wherein the third plane is perpendicular to the first plane and the second plane.
进一步的,所述直线移动组件,具体包括:Further, the linear moving component specifically includes:
第一移动单元,连接所述旋转组件,被配置为调节所述旋转组件在第一方向的位置;a first moving unit, connected to the rotating assembly, configured to adjust the position of the rotating assembly in a first direction;
第二移动单元,连接所述第一移动单元,被配置为调节所述第一移动单元在第二方向的位置;其中,所述第二方向垂直所述第一方向;以及A second moving unit, connected to the first moving unit, configured to adjust the position of the first moving unit in a second direction; wherein the second direction is perpendicular to the first direction; and
第三移动单元,设置于所述移动底盘上且连接所述第二移动单元,被配置为调节所述第二移动单元在第三方向的位置;其中,所述第三方向垂直所述第二方向以及所述第一方向。A third moving unit, disposed on the moving chassis and connected to the second moving unit, is configured to adjust the position of the second moving unit in a third direction; wherein the third direction is perpendicular to the second moving unit direction and the first direction.
进一步的,所述控制指令包括移动指令,所述控制模块,还被配置为:Further, the control instruction includes a movement instruction, and the control module is further configured to:
根据所述移动指令,控制所述调整平台进行相应的移动,以调整与患者的相对位置。According to the movement instruction, the adjustment platform is controlled to move accordingly, so as to adjust the relative position with the patient.
进一步的,所述检测设备包括压力传感器;所述控制模块,还被配置为:Further, the detection device includes a pressure sensor; the control module is further configured to:
获取压力传感器提供的压力信息和对应时段内所述交互模块提供的多媒体信息;Obtain the pressure information provided by the pressure sensor and the multimedia information provided by the interaction module in the corresponding time period;
将所述压力信息和远端控制设备的登录账号对应的压力等级库进行比较,确定所述压力信息对应的压力等级;comparing the pressure information with the pressure level library corresponding to the login account of the remote control device, and determining the pressure level corresponding to the pressure information;
将所述压力等级和所述多媒体信息传给所述远端控制设备;transmitting the pressure level and the multimedia information to the remote control device;
获取所述远端控制设备的反馈指令,根据所述反馈指令控制所述机械手对所述压力传感器进行调整。The feedback instruction of the remote control device is acquired, and the manipulator is controlled to adjust the pressure sensor according to the feedback instruction.
进一步的,所述检测设备包括肤色板;Further, the detection device includes a skin color plate;
利用所述交互模块实现与远端控制设备间的多媒体信息交互之前,所述控制单元,还被配置为:Before using the interaction module to realize the multimedia information interaction with the remote control device, the control unit is further configured as:
获取包括患者脸部和所述肤色板的第一图像;acquiring a first image including the patient's face and the skin tone panel;
提取所述第一图像中的所述肤色板对应的像素信息;extracting pixel information corresponding to the skin color plate in the first image;
根据所述像素信息,确定所述第一图像对应的色温;determining the color temperature corresponding to the first image according to the pixel information;
基于所述色温,调节所述多媒体信息交互中的图像的白平衡。Based on the color temperature, the white balance of the image in the multimedia information interaction is adjusted.
在本说明书实施例的第二方面,还提供了前述任一所述的远程医疗机器人的充电方法,所述远程医疗机器人还包括电源模块,所述充电方法包括:In a second aspect of the embodiments of this specification, there is also provided a charging method for any of the foregoing telemedicine robots, the telemedicine robot further includes a power supply module, and the charging method includes:
获取电池的剩余电量;Get the remaining power of the battery;
将所述剩余电量和预设安全电量进行比较;comparing the remaining power with a preset safe power;
若所述剩余电量小于所述预设安全电量,则获取充电路径;If the remaining power is less than the preset safe power, acquiring a charging path;
基于所述充电路径,向目标充电座移动;based on the charging path, moving to the target charging base;
利用感应信号,确定所述目标充电座并定位充电;其中,所述感应信号由所述目标充电座发出。Using the induction signal, the target charging base is determined and positioned for charging; wherein, the induction signal is sent by the target charging base.
进一步的,所述获取充电路径的步骤,具体包括:Further, the step of acquiring the charging path specifically includes:
获取当前位置,基于所述当前位置,按预设的规则,查找目标充电座;Obtain the current position, and based on the current position, according to preset rules, find the target charging base;
根据所述当前位置和所述目标充电座的位置,确定所述充电路径。The charging path is determined according to the current position and the position of the target charging base.
进一步的,所述利用感应信号,确定所述目标充电座并定位充电的步骤,具体包括:Further, the step of determining the target charging base and positioning and charging by using the induction signal specifically includes:
搜索感应信号,基于所述感应信号确定所述目标充电座;searching for an induction signal, and determining the target charging base based on the induction signal;
调整所述远程医疗机器人和所述目标充电座的相对位置,直至获取预设角度的所述感应信号即可。The relative positions of the telemedicine robot and the target charging base are adjusted until the sensing signal at a preset angle is obtained.
进一步的,还包括:Further, it also includes:
保存剩余电量小于所述预设安全电量时对应的充电前状态;Save the pre-charging state corresponding to when the remaining power is less than the preset safe power;
监测充电过程中的所述电池的电量;monitoring the power of the battery during charging;
若所述电池的电量达到所述预设安全电量的最大值,则停止充电;If the power of the battery reaches the maximum value of the preset safe power, stop charging;
根据保存的充电前状态,恢复所述远程医疗机器人的状态。According to the saved state before charging, the state of the telemedicine robot is restored.
在本说明书实施例的第三方面,还提供了前述任一所述的远程医疗机器人的控制方法,所述调整平台包括激光导航雷达;所述交互模块包括摄像头;所述远程医疗诊断机器人还包括光电编码器;In a third aspect of the embodiments of this specification, there is also provided a control method of any one of the aforementioned telemedicine robots, wherein the adjustment platform includes a laser navigation radar; the interaction module includes a camera; the telemedicine diagnosis robot further includes Photoelectric encoder;
所述控制方法,具体包括:The control method specifically includes:
利用所述激光导航雷达和所述摄像头的至少一者,获取环境信息;利用所述光电编码器,获取运动里程信息;At least one of the laser navigation radar and the camera is used to obtain environmental information; the photoelectric encoder is used to obtain motion mileage information;
根据所述环境信息和所述运动里程信息,基于同步定位与建图方法,得到本地地图;According to the environmental information and the motion mileage information, based on the synchronous positioning and mapping method, a local map is obtained;
获取远端控制器发送的控制指令,所述控制指令包括目标位置信息;Obtaining the control instruction sent by the remote controller, the control instruction includes target location information;
基于所述目标位置信息、所述本地地图以及远程医疗机器人定位信息,确定所述远程医疗机器人至所述目标位置的移动路径;其中,所述远程医疗机器人定位信息基于所述本地地图和当前的环境信息确定;Based on the target location information, the local map and the remote medical robot positioning information, determine the movement path of the remote medical robot to the target position; wherein the remote medical robot positioning information is based on the local map and the current determination of environmental information;
根据所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人移动至所述目标位置。According to the movement path, the telemedicine robot is controlled to move to the target position.
进一步的,根据所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人移动至所述目标位置,包括:Further, according to the movement path, controlling the telemedicine robot to move to the target position includes:
根据预设时段起止时刻对应的定位信息,确定所述远程医疗机器人的移动距离;Determine the moving distance of the telemedicine robot according to the positioning information corresponding to the start and end times of the preset time period;
若所述移动距离小于预设距离,则重新确定移动路径。If the moving distance is less than the preset distance, the moving path is re-determined.
进一步的,所述根据所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人移动至所述目标位置的步骤,包括:Further, the step of controlling the telemedicine robot to move to the target position according to the moving path includes:
利用避障传感器,获取路障数据;Use obstacle avoidance sensors to obtain roadblock data;
根据所述路障数据和所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人进行避障。According to the roadblock data and the moving path, the telemedicine robot is controlled to avoid obstacles.
从上面所述可以看出,本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的远程医疗机器人,包括具有多个自由度的调整平台、机械手、交互模块和控制模块。通过多自由度的调整平台调整所述机械手的位置和姿态,机械手操作检测设备对患者进行医学检测。同时,通过交互模块实现与远端控制设备间的多媒体信息交互。医生通过远端控制设备将控制指令发送给控制模块,所述控制模块能够根据所述控制指令,控制所述调整平台、所述机械手和所述交互模块的工作状态,进而实现患者和医生间的远程检查、诊断。As can be seen from the above, the telemedicine robot provided by one or more embodiments of this specification includes an adjustment platform with multiple degrees of freedom, a manipulator, an interaction module, and a control module. The position and posture of the manipulator are adjusted through a multi-degree-of-freedom adjustment platform, and the manipulator operates the detection device to perform medical detection on the patient. At the same time, the multimedia information interaction with the remote control device is realized through the interaction module. The doctor sends the control instruction to the control module through the remote control device, and the control module can control the working state of the adjustment platform, the manipulator and the interaction module according to the control instruction, thereby realizing the communication between the patient and the doctor. Remote inspection and diagnosis.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本说明书一个或多个实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本说明书一个或多个实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to more clearly illustrate one or more embodiments of the present specification or the technical solutions in the prior art, the following briefly introduces the accompanying drawings used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, in the following description The accompanying drawings are only one or more embodiments of the present specification, and for those of ordinary skill in the art, other drawings can also be obtained from these drawings without any creative effort.
图1为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的远程医疗机器人的结构示意图;1 is a schematic structural diagram of a telemedicine robot provided by one or more embodiments of this specification;
图2为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的移动底盘的结构示意图;2 is a schematic structural diagram of a mobile chassis provided by one or more embodiments of the present specification;
图3为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的调整平台的部分结构结构示意图;FIG. 3 is a partial structural schematic diagram of an adjustment platform provided by one or more embodiments of the present specification;
图4为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的充电方法的流程示意图;FIG. 4 is a schematic flowchart of a charging method according to one or more embodiments of the present specification;
图5为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的获取充电路径的流程示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic flowchart of obtaining a charging path according to one or more embodiments of the present specification;
图6为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的控制方法的流程示意图;6 is a schematic flowchart of a control method provided by one or more embodiments of the present specification;
图7为本说明书一个或多个实施例提供的SLAM模块的结构示意图。FIG. 7 is a schematic structural diagram of a SLAM module provided by one or more embodiments of the present specification.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本公开的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚明白,以下结合具体实施例,并参照附图,对本公开进一步详细说明。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present disclosure clearer, the present disclosure will be further described in detail below with reference to the specific embodiments and the accompanying drawings.
需要说明的是,除非另外定义,本说明书一个或多个实施例使用的技术术语或者科学术语应当为本公开所属领域内具有一般技能的人士所理解的通常意义。本说明书一个或多个实施例中使用的“第一”、“第二”以及类似的词语并不表示任何顺序、数量或者重要性,而只是用来区分不同的组成部分。“包括”或者“包含”等类似的词语意指出现该词前面的元件或者物件涵盖出现在该词后面列举的元件或者物件及其等同,而不排除其他元件或者物件。“连接”或者“相连”等类似的词语并非限定于物理的或者机械的连接,而是可以包括电性的连接,不管是直接的还是间接的。“上”、“下”、“左”、“右”等仅用于表示相对位置关系,当被描述对象的绝对位置改变后,则该相对位置关系也可能相应地改变。It should be noted that, unless otherwise defined, the technical or scientific terms used in one or more embodiments of the present specification shall have the usual meanings understood by those with ordinary skill in the art to which this disclosure belongs. The terms "first," "second," and similar terms used in one or more embodiments of this specification do not denote any order, quantity, or importance, but are merely used to distinguish the various components. "Comprises" or "comprising" and similar words mean that the elements or things appearing before the word encompass the elements or things recited after the word and their equivalents, but do not exclude other elements or things. Words like "connected" or "connected" are not limited to physical or mechanical connections, but may include electrical connections, whether direct or indirect. "Up", "Down", "Left", "Right", etc. are only used to represent the relative positional relationship, and when the absolute position of the described object changes, the relative positional relationship may also change accordingly.
目前,远程医疗设备大多是静态的,比如远程音视频设备,医生与患者缺仅限于视频通话交流,医生无法控制本地的检测设备,也无法多角度灵活观测病人情况,更无法获取患者相关体征等检测记录。此外,对于一些检测设备,患者通常不懂操作,特别是对于老人、儿童、或行动不便人士,即便医生通过视频进行指导,也难以正确使用相关检测设备。At present, most of the telemedicine equipment is static, such as remote audio and video equipment. The lack of doctors and patients is limited to video calls. The doctor cannot control the local testing equipment, and cannot flexibly observe the patient's condition from multiple angles, and it is impossible to obtain the relevant signs of the patient, etc. Inspection record. In addition, for some testing equipment, patients usually do not understand the operation, especially for the elderly, children, or people with limited mobility, even if the doctor guides through video, it is difficult to use the relevant testing equipment correctly.
随着5G技术的应用,信息传递的速度大幅度提高,为远程医疗提供了可靠的数据传递基础,使得医生远程控制医疗终端成为可能。With the application of 5G technology, the speed of information transmission has been greatly improved, providing a reliable data transmission basis for telemedicine, making it possible for doctors to remotely control medical terminals.
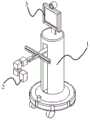
由此,为从根本上解决患者求医治病难的问题,在本说明书的第一方面,提供一种远程医疗机器人。如图1所示,所述远程医疗机器人,包括:Therefore, in order to fundamentally solve the problem of difficulty in seeking medical treatment for patients, a first aspect of the present specification provides a telemedicine robot. As shown in Figure 1, the telemedicine robot includes:
具有多个自由度的调整平台1。
这里,所述调整平台1能够提供所述远程医疗机器人各自由度的调整,包括但不限于与患者的相对位置、与检测设备的相对位置。Here, the
机械手2,设置于所述调整平台1的端部,被配置为操作检测设备对患者进行医学检测。The
需要说明的是,利用所述调整平台1,能够实现对所述机械手2的位置和姿态的调节,以保证所述检测设备位于适宜的位置,方便完成对患者的医生检测。It should be noted that, using the
交互模块3,设置于所述调整平台1,被配置为实现与远端控制设备间的多媒体信息交互;以及An
控制模块(图中未示出),被配置为:获取远端控制设备发送的控制指令,并根据所述控制指令,控制所述调整平台、所述机械手和所述交互模块的工作状态。A control module (not shown in the figure) is configured to: acquire a control instruction sent by a remote control device, and control the working state of the adjustment platform, the manipulator and the interaction module according to the control instruction.
从上述的实施例可知,通过多自由度的调整平台1调整所述机械手2的位置和姿态,机械手2操作检测设备对患者进行医学检测。同时,通过交互模块3实现与远端控制设备间的多媒体信息交互。医生通过远端控制设备将控制指令发送给控制模块,所述控制模块能够根据所述控制指令,控制所述调整平台、所述机械手和所述交互模块的工作状态,进而实现患者和医生间的远程检查、诊断。It can be known from the above-mentioned embodiments that the position and posture of the
进一步的,所述交互模块3包括摄像头、扬声器、麦克风和显示屏。其中,所述摄像头用于采集所述患者、检测设备、环境等图像信息。麦克风用于采集患者、检测设备、环境等具有的声音信息。将摄像头和麦克风采集的患者、检测设备以及环境的多媒体信息,通过控制模块发送给远端控制设备,这样,使用所述远端控制设备的医生即可获取患者相关的多媒体信息。同时,所述控制模块还能够获取远端控制设备采集的医生的多媒体信息,利用扬声器和显示屏进行展示,这样,患者即可获取医生相关的多媒体信息。Further, the
应当理解的,所述远端控制设备可以包括手机、平板电脑、PDA(Personal DigitalAssistant,个人数字助理)、POS(Point of Sales,销售终端)、车载电脑、PC(PersonalComputer)等任意终端设备。It should be understood that the remote control device may include any terminal device such as a mobile phone, a tablet computer, a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant), a POS (Point of Sales, a sales terminal), a vehicle computer, and a PC (Personal Computer).
可选的,所述检测设备可以包括听诊器、压舌板、血氧仪、血压仪、压力传感器、体温计、肤色板、电筒、心电图监测仪等任何检测设备。Optionally, the detection device may include any detection device such as a stethoscope, a tongue depressor, an oximeter, a blood pressure meter, a pressure sensor, a thermometer, a skin color board, a torch, an electrocardiogram monitor, and the like.
作为一个可选的实施例,通过交互模块3采集的图像信息,医生确定需要的检测设备的位置,由此控制所述远程医疗机器人利用机械手获取对应的检测设备。应当理解的,这里的检测设备为医院通常的检测设备,无需额外采购,有利于降低医疗成本。应当理解的,若患者或周围其他人员,例如护士等,能够帮助提供检测设备时,则无需医生根据图像信息确定检测设备的位置,患者或者护士可以将As an optional embodiment, through the image information collected by the
当然,作为一个可替换的实施例,所述检测设备也可以集成在所述机械手上,例如压力传感器、肤色板等。这样的方式,机械手的功能更佳全面,能够节约额外获取检测设备的时间,有利于提高医生和患者的检测诊疗效率。Of course, as an alternative embodiment, the detection device may also be integrated on the manipulator, for example, a pressure sensor, a skin color plate, and the like. In this way, the functions of the manipulator are better and more comprehensive, which can save time for additional acquisition of testing equipment, and is conducive to improving the efficiency of testing and diagnosis and treatment for doctors and patients.
需要说明的是,这里对所述检测设备的类别和设置形式不做具体限定。根据远程医疗机器人的使用环境、检测设备的特性可以灵活设置。It should be noted that the type and setting form of the detection device are not specifically limited here. It can be flexibly set according to the use environment of the telemedicine robot and the characteristics of the detection equipment.
参考图3,在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,所述调整平台1,包括:Referring to FIG. 3, in one or more embodiments of this specification, the
旋转组件11,连接所述机械手2,被配置为带动所述机械手2旋转以调节所述机械手2的姿态;A rotating
直线移动组件12,连接所述旋转组件11,被配置为带动所述旋转组件11和所述机械手2直线移动以调节所述机械手2的位置;以及A linear moving
移动底盘13,被配置为承载所述直线移动组件12,并带动所述直线移动组件12、所述旋转组件11和所述机械手2移动。The moving
通过移动底盘13,实现所述远程医疗机器人的整体移动,极大的提高所述远程医疗机器人的灵活性,使得远程医疗机器人不仅能够靠近患者,而且能够位于患者的不同方向,有利于医生对患者进行全面的观察。进一步的,利用直线移动组件12和旋转组件11,实现对机械手2的位置和姿态的调节,使得机械手2上的检测设备能够以适宜位置、角度方便的对患者进行检测。借助远程医疗机械人,医生能够实现对患者的远程检测,且无需患者操作,患者体验好,具有广泛的适用性。By moving the
如图2所示,在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,所述移动底盘13,具体包括:As shown in FIG. 2, in one or more embodiments of this specification, the
盘体131,包括:相对设置的第一表面和第二表面,以及连接所述第一表面和第二表面的外周面;所述第一表面用于设置所述直线移动组件12;The
避障传感器132,均匀设置于所述外周面;以及The
移动轮133,设置于所述第二表面。The moving
这里,所述避障传感器132可以包括超声波传感器、红外传感器、激光传感器等。应当理解的,避障传感器132可以采用一种传感器,也可以采用多种传感器,这里不做限定。通过避障传感器探测障碍物,所述控制模块利用所述障碍物信息,能够控制所述移动底盘13自动避开障碍物,无需人工控制,高效智能。Here, the
可选的,所述移动轮可以是电机驱动轮。所述控制模块可以通过控制电机驱动轮的工作状态,即可实现对移动底盘的移动控制。结合前述所述移动底盘承载所述直线移动组件,进而实现整个远程医疗机器人的位置移动。应当理解的,这里的位置移动不仅包括前后左右,同时还包括原地转动。Optionally, the moving wheel may be a motor-driven wheel. The control module can control the movement of the mobile chassis by controlling the working state of the motor drive wheel. In combination with the aforementioned moving chassis, the linear moving assembly is carried, thereby realizing the position movement of the entire telemedicine robot. It should be understood that the position movement here not only includes front, back, left and right, but also includes in-situ rotation.
这样的结构设置,能够保障所述远程医疗机器人在所述控制模块的控制下,自动移动,使得所述远程医疗机器人具有高度的灵活性。Such a structural arrangement can ensure that the telemedicine robot moves automatically under the control of the control module, so that the telemedicine robot has a high degree of flexibility.
参考图3,在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,所述旋转组件11,具体包括:Referring to FIG. 3, in one or more embodiments of the present specification, the rotating
第一旋转单元111,连接所述机械手2,被配置为调节所述机械手2在第一平面的角度;a
第二旋转单元112,连接所述第一旋转单元111,被配置为调节所述第一旋转单元111在第二平面的角度;其中,所述第二平面垂直所述第一平面;以及The
第三旋转单元113,连接所述第二旋转单元112,被配置为调节所述第二旋转单元112在第三平面的角度;其中,所述第三平面垂直所述第一平面以及所述第二平面。The third
通过这样的技术方案,所述旋转组件11能够实现所述机械手2三个相互垂直平面内的角度调节,使得所述机械手2的姿态满足操作检测设备的需要。Through such a technical solution, the rotating
进一步的,所述第一旋转单元111、第二旋转单元112和第三旋转单元113可以具有相同的结构,例如电动转台。具体地,电动转台包括电机和涡轮蜗杆减速机;其中,所述电机带动涡轮蜗杆减速机实现旋转运动,利用涡轮蜗杆减速机将电机的回转数减速到所要的回转数,进而实现角度的调节。Further, the first
如图3所示,在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,所述直线移动组件12,具体包括:As shown in FIG. 3 , in one or more embodiments of this specification, the
第一移动单元121,连接所述旋转组件11,被配置为调节所述旋转组件在第一方向的位置;具体地,所述第一移动单元121连接所述第三旋转单元113。The first moving
第二移动单元122,连接所述第一移动单元121,被配置为调节所述第一移动单元121在第二方向的位置;其中,所述第二方向垂直所述第一方向;以及The second moving
第三移动单元123,设置于所述移动底盘13上且连接所述第二移动单元122,被配置为调节所述第二移动单元122在第三方向的位置;其中,所述第三方向垂直所述第二方向以及所述第一方向。The third moving
作为一个更具体的实施例,所述第三方向为竖直方向,所述第二方向和所述第一方向为水平面内的两个相互垂直的方向。As a more specific embodiment, the third direction is a vertical direction, and the second direction and the first direction are two mutually perpendicular directions in a horizontal plane.
由此可见,结合前述的移动底盘13,所述直线移动组件能够灵活调整所述旋转组件11的空间位置,以使机械手2能够对准患者的不同部位,便于利用检测设备对患者进行检测。这里,所述不同部位,可以是头部、腹部、腿部等。It can be seen that, combined with the aforementioned moving
进一步的,所述第一移动单元121、第二移动单元122和第三移动单元123可以是电动滑台调整。具体地,所述电动滑台包括电机、滚珠丝杠和导轨。这里,利用滚珠丝杠将电机的轴向转动转化为直线运动,进而实现直线位置的调节。应当理解的,导轨的设置方向分别和第一方向、第二方向和第三方向相对应,这里不再详述。Further, the first moving
可选的,所述电动滑台还可以包括皮带,所述皮带连接所述电机和滚珠丝杠。通过设置皮带,能够灵活的设置所述电机的位置,使得整个直线移动组件12的结构更加均衡、稳固。Optionally, the electric sliding table may further include a belt connecting the motor and the ball screw. By setting the belt, the position of the motor can be flexibly set, so that the structure of the entire linear moving
通过交互模块3,操作远端控制设备的医生能够获得所述远程医疗机器人所处环境的多媒体信息,所述多媒体信息包括但不限于远程医疗机器人相对于患者的位置。基于此,在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,所述控制指令包括移动指令,所述控制模块,还被配置为:Through the
根据所述移动指令,控制所述调整平台进行相应的移动,以调整与患者的相对位置。According to the movement instruction, the adjustment platform is controlled to move accordingly, so as to adjust the relative position with the patient.
这里,所述移动指令包括但不限于前进、后退、左移、右移、转动等。Here, the movement instruction includes, but is not limited to, forward, backward, left, right, rotation, and the like.
通过这样的技术方案,医生能够直接控制所述远程医疗机器人的移动,使其靠近、远离或者以特点角度对准患者,实现医生对患者的多角度、灵活的观察。Through such a technical solution, the doctor can directly control the movement of the telemedicine robot to make it approach, move away from, or aim at the patient at a characteristic angle, so as to realize the doctor's multi-angle and flexible observation of the patient.
医生对患者进行检查时,除利用检测仪器外,还可以通过手部接触患者身体,观察患者在按、压等动作下相应身体部位是否有疼痛等生理反应。When the doctor examines the patient, in addition to using the detection instrument, he can also touch the patient's body with his hand to observe whether the patient has a physiological response such as pain in the corresponding body part under the action of pressing and pressing.
在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,可以利用机械手操作压力传感器来对患者进行检测。如前所述,所述检测设备包括压力传感器。具体地,机械手将所述压力传感器压向患者身体,患者身体对压力传感器产生反作用力,所述反作用力能够被所述压力传感器获取。由于每个医生的经验和手部力量的差异,导致医生对于患者身体对手部的反作用力的感受不同。In one or more embodiments of the present specification, a manipulator may be used to operate a pressure sensor to detect a patient. As previously mentioned, the detection device includes a pressure sensor. Specifically, the manipulator presses the pressure sensor toward the patient's body, and the patient's body generates a reaction force on the pressure sensor, and the reaction force can be acquired by the pressure sensor. Due to the difference of each doctor's experience and hand strength, the doctor's perception of the reaction force of the patient's body to the hand is different.
为使医生能够准确确定患者身体的情况,所述控制模块,还被配置为:In order to enable the doctor to accurately determine the condition of the patient's body, the control module is further configured to:
获取压力传感器提供的压力信息和对应时段内所述交互模块提供的多媒体信息;这里,所述压力信息为患者身体对压力传感器产生的反作用力。Obtain the pressure information provided by the pressure sensor and the multimedia information provided by the interaction module in the corresponding time period; here, the pressure information is the reaction force generated by the patient's body on the pressure sensor.
将所述压力信息和远端控制设备的登录账号对应的压力等级库进行比较,确定所述压力信息对应的压力等级。The pressure information is compared with the pressure level library corresponding to the login account of the remote control device, and the pressure level corresponding to the pressure information is determined.
需要说明的是,医生通过个人账号登录远端控制设备,由此根据远端控制设备的登录账号能够确定使用所述远端控制设备的医生。这里,所述压力等级库包括压力信息和医生感受的压力(患者身体的反作用力)等级的对应关系。It should be noted that the doctor logs in to the remote control device through a personal account, so that the doctor who uses the remote control device can be determined according to the login account of the remote control device. Here, the pressure level library includes the correspondence between pressure information and the level of pressure (reaction force of the patient's body) felt by the doctor.
应当理解的,所述压力等级库可以在医生个人账号建立之时,通过多次试验建立,明确医生感受的压力等级与压力信息的对应关系。可选的,根据试验,确定医生通常感受的压力范围并划分子范围,每一个子范围对应一个压力等级。通过所述压力信息处于的子范围,即可确定压力等级。显然,对于相同的压力信息,医生感受的压力等级可能完全不同。It should be understood that the pressure level library can be established through multiple tests when the doctor's personal account is established, so as to clarify the correspondence between the pressure level felt by the doctor and the pressure information. Optionally, according to the test, determine the pressure range that the doctor usually feels and divide it into sub-ranges, and each sub-range corresponds to a pressure level. The pressure level can be determined by the sub-range in which the pressure information is located. Obviously, for the same pressure information, the pressure level felt by the doctor may be completely different.
由此,将压力信息转化为与医生经验相对应的、便于判断的压力等级,有助于医生根据经验,准确判断患者的身体状况。Thus, the pressure information is converted into a pressure level corresponding to the doctor's experience and easy to judge, which helps the doctor to accurately judge the physical condition of the patient according to the experience.
将所述压力等级和所述多媒体信息传给所述远端控制设备。The pressure level and the multimedia information are communicated to the remote control device.
这里,使用所述远端控制设备的医生,不仅能够获取压力等级信息,还能够获取患者在该压力等级下的多媒体信息,包括但不限于表情、声音等,使得医生能够根据患者的反应,确定下一步的操作,例如机械手继续将压力传感器压向患者。Here, the doctor using the remote control device can not only obtain the pressure level information, but also obtain the multimedia information of the patient under the pressure level, including but not limited to facial expressions, voices, etc., so that the doctor can determine according to the patient's response. Next steps, such as the manipulator, continue to press the pressure sensor towards the patient.
获取所述远端控制设备的反馈指令,根据所述反馈指令控制所述机械手对所述压力传感器进行调整。The feedback instruction of the remote control device is acquired, and the manipulator is controlled to adjust the pressure sensor according to the feedback instruction.
从此可见,通过这样的技术方案,利用压力传感器,医生能够对患者进行触诊检测,更全面的了解患者的身体状况。From this, it can be seen that through such a technical solution, using the pressure sensor, the doctor can palpate and detect the patient, so as to have a more comprehensive understanding of the patient's physical condition.
除了触诊检测之外,医生也常通过观察患者的脸色、精神状态等,判断患者的身体状况。远程医疗的过程中,受环境光线的影响,交互模块提供的图像信息,存在失真的可能,不能真实反映患者的脸色。In addition to palpation testing, doctors often judge the patient's physical condition by observing the patient's face, mental state, etc. In the process of telemedicine, due to the influence of ambient light, the image information provided by the interactive module may be distorted and cannot truly reflect the patient's face.
为解决该技术问题,在本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,所述检测设备包括肤色板。利用所述肤色板,实现对图像信息的调节,以保证医生准确获取患者的脸色信息,避免因图像失真导致误判。To solve this technical problem, in one or more embodiments of the present specification, the detection device includes a skin color plate. Using the skin color plate, the image information can be adjusted, so as to ensure that the doctor can accurately obtain the patient's complexion information and avoid misjudgment caused by image distortion.
具体地,利用所述交互模块实现与远端控制设备间的多媒体信息交互之前,所述控制单元,还被配置为:Specifically, before using the interaction module to realize the multimedia information interaction with the remote control device, the control unit is further configured to:
获取包括患者脸部和所述肤色板的第一图像。A first image is acquired that includes the patient's face and the skin tone panel.
这里,肤色板包括多个肤色的像素点。Here, the skin color plate includes a plurality of skin color pixels.
可选的,所述肤色板可以由机械手置于患者脸部的附件。Optionally, the skin tone plate can be placed on the attachment of the patient's face by a manipulator.
此外,作为一种可替代的方式,所述肤色板设置于所述机械手上。当使用肤色板时,只需将机械手放置于患者脸部附件即可。In addition, as an alternative, the skin color plate is provided on the manipulator. When using the skin tone plate, simply place the manipulator on the attachment to the patient's face.
提取所述第一图像中的所述肤色板对应的像素信息。Extract pixel information corresponding to the skin color panel in the first image.
根据所述像素信息,确定所述第一图像对应的色温。According to the pixel information, the color temperature corresponding to the first image is determined.
应当理解的,在不同的色温下,肤色的像素信息位于不同的区域,根据所述像素信息处于的区域,就能够判断出周围环境的色温。对于根据所述像素信息,确定色温的方式有多种,不在一一例举。It should be understood that under different color temperatures, the pixel information of the skin color is located in different regions, and the color temperature of the surrounding environment can be determined according to the region where the pixel information is located. There are many ways to determine the color temperature according to the pixel information, which will not be listed one by one.
基于所述色温,调节所述多媒体信息交互中的图像的白平衡。Based on the color temperature, the white balance of the image in the multimedia information interaction is adjusted.
这里,调节后的图像能够反应患者的真实脸色,有助于医生判断患者的身体状况。Here, the adjusted image can reflect the real face of the patient, which is helpful for the doctor to judge the physical condition of the patient.
为了便于远程医疗机器人的自由活动,不受电力供应的限制,本说明书的一个或多个实施例中的所述远程医疗机器人还包括电源模块。所述电源模块被配置为给控制模块、机械手2、调整平台1和交互模块3供电。In order to facilitate the free movement of the telemedicine robot without being limited by the power supply, the telemedicine robot in one or more embodiments of this specification further includes a power supply module. The power supply module is configured to supply power to the control module, the
可选的,所述电源模块包括至少一个充电座、电池和电源管理单元。其中,所述电源管理单元包括充电管理子单元、电量检测子单元、电源转换子单元及分配子单元。Optionally, the power module includes at least one charging base, a battery and a power management unit. Wherein, the power management unit includes a charge management subunit, a power detection subunit, a power conversion subunit and a distribution subunit.
进一步的,在本说明书的第二方面,还提供一种充电方法。如图4所示,所述充电方法,具体包括:Further, in the second aspect of the present specification, a charging method is also provided. As shown in Figure 4, the charging method specifically includes:
步骤101:获取电池的剩余电量。Step 101: Obtain the remaining power of the battery.
这里,利用电量检测子单元,能够获取电池的剩余电量。Here, the remaining power of the battery can be obtained by using the power detection sub-unit.
步骤102:将所述剩余电量和预设安全电量进行比较。Step 102: Compare the remaining power with a preset safe power.
需要说明的是,预设安全电量可以根据远程医疗机器人的使用环境进行设置。例如,远程医疗机器人的活动范围小,则预设安全电量可以设置的较低,例如10%;远程医疗机器人的活动范围大,则预设安全电量可以设置的较高,例如20%,以保障远程医疗机器人保留足够的电量移动至充电座的位置。It should be noted that the preset safe power can be set according to the usage environment of the telemedicine robot. For example, if the scope of activity of the telemedicine robot is small, the preset safe power can be set to a lower value, such as 10%; if the scope of activity of the telemedicine robot is large, the preset safe power can be set to a higher value, such as 20%, to ensure The telemedicine robot retains enough power to move to the position of the charging base.
步骤103:若所述剩余电量小于所述预设安全电量,则获取充电路径。Step 103: Obtain a charging path if the remaining power is less than the preset safe power.
应当理解的,若所述剩余电量大于等于所述预设安全电量,则无需获取充电路径。It should be understood that, if the remaining power is greater than or equal to the preset safe power, there is no need to acquire a charging path.
对于充电路径,可以由远端控制设备确定。For the charging path, it can be determined by the remote control device.
例如,若所述剩余电量小于所述预设安全电量,则所述控制模块向远端控制设备发送充电请求。远端控制设备,利用本地地图(远程医疗机器人所在地)查找目标充电座,并制定充电路径。For example, if the remaining power is less than the preset safe power, the control module sends a charging request to the remote control device. Remotely control the device, use the local map (where the telemedicine robot is located) to find the target charging base, and formulate a charging path.
步骤104:基于所述充电路径,向目标充电座移动。Step 104: Based on the charging path, move to the target charging base.
步骤105:利用感应信号,确定所述目标充电座并定位充电;其中,所述感应信号由所述目标充电座发出。Step 105: Determine the target charging base and locate and charge by using an induction signal; wherein, the induction signal is sent by the target charging base.
在本步骤中,在靠近所述目标充电座的过程中,利用感应信号,所述远程医疗机器人能够方便的确定所述目标充电座、定位充电。这里,所述感应信号可以是红外信号。In this step, in the process of approaching the target charging base, the telemedicine robot can conveniently determine the target charging base and locate and charge by using the induction signal. Here, the induction signal may be an infrared signal.
本说明书一个或多个实施例还提供另一种获取充电路径的方法,参考图5,所述获取充电路径的步骤,具体包括:One or more embodiments of this specification also provide another method for acquiring a charging path. Referring to FIG. 5 , the steps of acquiring a charging path specifically include:
步骤201:获取当前位置,基于所述当前位置,按预设的规则,查找目标充电座。Step 201: Obtain the current position, and based on the current position, search for a target charging stand according to a preset rule.
需要特别说明的是,由于充电座的数量可以是多个,因此需要查找目标充电座。这里,预设的规则可以是距离最近,也可以是时间最短,也可以是其他规则,例如障碍物最少,这里不作限定。It should be noted that, since the number of charging bases can be multiple, it is necessary to search for the target charging base. Here, the preset rule may be the shortest distance, the shortest time, or other rules, such as the least obstacles, which is not limited here.
步骤202:根据所述当前位置和所述目标充电座的位置,确定所述充电路径。Step 202: Determine the charging path according to the current location and the location of the target charging base.
这样的技术方案,无需远端控制设备的参与,远程医疗机器人能够独立完成充电,更加智能、高效。Such a technical solution does not require the participation of remote control equipment, and the telemedicine robot can complete the charging independently, which is more intelligent and efficient.
应当理解的,采用这样获取充电路径的方法,可以向所述远端控制设备发送充电通知。这样,使用所述远端控制设备的医生能够及时了解远程医疗机器人的状态。It should be understood that by adopting the method for acquiring the charging path in this way, a charging notification can be sent to the remote control device. In this way, the doctor using the remote control device can know the status of the telemedicine robot in time.
进一步的,所述利用感应信号,确定所述目标充电座并定位充电的步骤,具体包括:Further, the step of determining the target charging base and positioning and charging by using the induction signal specifically includes:
搜索感应信号,基于所述感应信号确定所述目标充电座。Search for inductive signals, and determine the target charging base based on the inductive signals.
这里,在靠近所述目标充电座的过程中,所述远程医疗机器人虽然知道目标充电座的大体位置,但是其周围可能存在其他物品,因此需要利用感应信号,确定所述目标充电座。Here, in the process of approaching the target charging base, although the telemedicine robot knows the general position of the target charging base, there may be other objects around it, so it is necessary to use the induction signal to determine the target charging base.
调整所述远程医疗机器人和所述目标充电座的相对位置,直至获取预设角度的所述感应信号即可。The relative positions of the telemedicine robot and the target charging base are adjusted until the sensing signal at a preset angle is obtained.
应当理解的,目标充电座和所述远程医疗机器人对准,才能进行充电。这里,对准可以是充电接触点对准,也可以是所述远程医疗机器人处于能够实现充电的范围(适用于无接触式充电)。当所述感应信号以预设角度被检测,则表明所述远程医疗机器人已经对准所述目标充电座,因此完成定位能够进行充电。It should be understood that charging can be performed only when the target charging base and the telemedicine robot are aligned. Here, the alignment may be charging contact point alignment, or the telemedicine robot may be in a range capable of charging (suitable for contactless charging). When the sensing signal is detected at a preset angle, it indicates that the telemedicine robot has been aimed at the target charging base, so that the positioning can be completed and charging can be performed.
在本发明的一个或多个实施例中,所述充电方法,还包括:In one or more embodiments of the present invention, the charging method further includes:
保存剩余电量小于所述预设安全电量时对应的充电前状态;Save the pre-charging state corresponding to when the remaining power is less than the preset safe power;
监测充电过程中的所述电池的电量;monitoring the power of the battery during charging;
若所述电池的电量达到所述预设安全电量的最大值,则停止充电;If the power of the battery reaches the maximum value of the preset safe power, stop charging;
根据保存的充电前状态,恢复所述远程医疗机器人的状态。According to the saved state before charging, the state of the telemedicine robot is restored.
通过这样的技术方案,能够无需医生干预,所述远程医疗机器人自动完成状态的恢复,继续充电前的动作。Through such a technical solution, the telemedicine robot can automatically complete the state recovery without the intervention of a doctor, and continue the actions before charging.
在本说明书的第三个方面,还提供前述任一所述的远程医疗机器人的控制方法。所述调整平台包括激光导航雷达134(参考图2),所述激光导航雷达134可以设置于移动底盘13上;所述交互模块包括摄像头;所述远程医疗诊断机器人还包括光电编码器。进一步的,如图6所示,所述控制方法,具体包括:In a third aspect of the present specification, there is also provided a control method of any one of the aforementioned telemedicine robots. The adjustment platform includes a laser navigation radar 134 (refer to FIG. 2 ), and the
步骤301:利用所述激光导航雷达和所述摄像头的至少一者,获取环境信息;利用所述光电编码器,获取运动里程信息。Step 301: Use at least one of the laser navigation radar and the camera to obtain environmental information; use the photoelectric encoder to obtain motion mileage information.
步骤302:根据所述环境信息和所述运动里程信息,基于同步定位与建图方法,得到本地地图。Step 302: Obtain a local map based on the synchronous positioning and mapping method according to the environmental information and the motion mileage information.
需要说明的是,同步定位与建图(simultaneous localization and mapping,缩写SLAM),也称即时定位与地图构建(Concurrent Mapping and Localization,缩写CML)。It should be noted that simultaneous localization and mapping (simultaneous localization and mapping, abbreviated SLAM) is also called simultaneous localization and map building (Concurrent Mapping and Localization, abbreviated CML).
具体地,通过SLAM模块执行同步定位与建图方法。如图7所示,SLAM模块包括位姿更新模块、地图构建模块、特征提取模块、位姿估计模块、地图匹配模块、实时数据融合模块。以下对同步定位与建图方法,进行简单说明。Specifically, the synchronous positioning and mapping method is performed by the SLAM module. As shown in Figure 7, the SLAM module includes a pose update module, a map construction module, a feature extraction module, a pose estimation module, a map matching module, and a real-time data fusion module. The following is a brief description of the synchronous positioning and mapping method.
通过特征提取模块,对所述环境信息进行特征提取。根据所述运动里程信息,所述位姿估计模块确定所述远程医疗机器人的位姿。根据提取的特征和位姿,与现有地图进行匹配(地图匹配模块),根据匹配的结果对现有地图进行更新及构建新地图(地图构建及更新模块)。当然,提取的特征也可以先输入实时数据融合模块,将其与原有的特征数据进行融合之后,再与现有地图进行匹配。所述位姿更新模块可以根据所述地图匹配模块中的现有地图、地图构建及更新模块中的新地图对远程医疗机器人的位姿进行更新,由此所述位姿更新模块确定所述远程医疗机器人的定位信息。Through the feature extraction module, feature extraction is performed on the environmental information. According to the motion mileage information, the pose estimation module determines the pose of the telemedicine robot. According to the extracted features and poses, it is matched with the existing map (map matching module), and the existing map is updated and a new map is constructed according to the matching result (map construction and update module). Of course, the extracted features can also be input into the real-time data fusion module first, and then fused with the original feature data, and then matched with the existing map. The pose update module can update the pose of the telemedicine robot according to the existing map in the map matching module, the map construction and the new map in the update module, so that the pose update module determines the remote Positioning information of medical robots.
应当理解的,以上仅是对同步定位与建图方法的示例性说明。任何能够实现同步定位与建图的方法均适用于本说明书的本地地图构建,不再详述。It should be understood that the above is only an exemplary description of the simultaneous positioning and mapping method. Any method that can achieve synchronous positioning and mapping is applicable to the local map construction in this specification, and will not be described in detail.
步骤303:获取远端控制器发送的控制指令,所述控制指令包括目标位置信息;Step 303: Obtain a control instruction sent by the remote controller, where the control instruction includes target location information;
在本步骤中,目标可以是患者、目标充电座、检测设备等。这里,医生通常知晓患者的位置,例如病房号和床位。医生可以基于本地地图,确定目标充电座。利用多媒体信息,可以确定检测设备的位置。In this step, the target may be a patient, a target charging stand, a detection device, and the like. Here, the doctor usually knows the location of the patient, such as the ward number and the bed. The doctor can determine the target charging base based on the local map. Using the multimedia information, the location of the detection device can be determined.
步骤304:基于所述目标位置信息、所述本地地图以及远程医疗机器人定位信息,确定所述远程医疗机器人至所述目标位置的移动路径;其中,所述远程医疗机器人定位信息基于所述本地地图和当前的环境信息确定;Step 304: Based on the target location information, the local map and the telemedicine robot positioning information, determine the movement path of the telemedicine robot to the target position; wherein, the telemedicine robot positioning information is based on the local map and current environmental information to determine;
可以理解的,当所述目标是充电座时,所述移动路径即为充电路径。It can be understood that when the target is a charging stand, the moving path is a charging path.
步骤305:根据所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人移动至所述目标位置。Step 305: Control the telemedicine robot to move to the target position according to the moving path.
由此可见,通过本实施例的控制方法,所述远程医疗机器人在任何环境中,利用所述激光导航雷达、所述摄像头和所述光电编码器提供的信息,均能够实现本地地图的构建,这一过程无需医生操作。进一步的,只需远程控制设备提供目标的位置信息,所述远程医疗机器人即可实现自动移动,具有高度的灵活性,满足远程医疗的各种需求。It can be seen that, through the control method of this embodiment, the telemedicine robot can construct a local map in any environment by using the information provided by the laser navigation radar, the camera and the photoelectric encoder. This procedure does not require a doctor. Further, as long as the remote control device provides the position information of the target, the telemedicine robot can realize automatic movement, has a high degree of flexibility, and meets various needs of telemedicine.
在本发明的一个或多个实施例中,根据所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人移动至所述目标位置,包括:In one or more embodiments of the present invention, controlling the telemedicine robot to move to the target position according to the movement path includes:
根据预设时段起止时刻对应的定位信息,确定所述远程医疗机器人的移动距离。The moving distance of the telemedicine robot is determined according to the positioning information corresponding to the start and end times of the preset time period.
对于预设时段,可以对所述远程医疗机器人完成移动路径所需的总时长进行划分得到,例如划分为3份、4份。这里的总时长,根据所述远程医疗机器人的平均移动速度确定。当所述远程医疗机器人开始移动时开始计时,当达到预设时段时,例如2min,则根据开始移动时的位置(时段起始的时刻)和2min后的位置(时段终止的时刻)计算移动距离;依次类推,每隔2min确定移动距离。For the preset time period, the total time required for the telemedicine robot to complete the moving path can be divided, for example, divided into 3 parts and 4 parts. The total duration here is determined according to the average moving speed of the telemedicine robot. When the telemedicine robot starts to move, the timing starts, and when a preset time period is reached, such as 2 minutes, the moving distance is calculated according to the position at the start of the movement (the time when the time period starts) and the position after 2 minutes (the time when the time period ends). ; And so on, determine the moving distance every 2min.
若所述移动距离小于预设距离,则重新确定移动路径。If the moving distance is less than the preset distance, the moving path is re-determined.
应当理解的,所述预设距离为依据所述远程医疗机器人的平均移动速度和预设时段计算得到。It should be understood that the preset distance is calculated according to the average moving speed and preset time period of the telemedicine robot.
通过这样的方式,利用预设时段和预设距离,有效判断所述远程医疗机器人的状态,当所述远程医疗机器人遇到无法跨越的障碍,可以重新确定移动路径,避免所述远程医疗机器人因障碍无法到达目标位置的问题。这里,所述障碍可以是临时工具占据通道、通道门锁定等。In this way, the state of the telemedicine robot can be effectively judged by using the preset time period and the preset distance. When the telemedicine robot encounters an obstacle that cannot be crossed, the moving path can be re-determined to avoid the telemedicine robot due to The problem of obstacles not reaching the target location. Here, the obstacle may be a temporary tool occupying a passage, passage door locking, or the like.
进一步的,本说明书的一个或多个实施例中,还包括处理可跨越路障的方法。具体地,所述根据所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人移动至所述目标位置的步骤,包括:Further, in one or more embodiments of the present specification, a method for handling a surmountable roadblock is also included. Specifically, the step of controlling the telemedicine robot to move to the target position according to the moving path includes:
利用避障传感器,获取路障数据;Use obstacle avoidance sensors to obtain roadblock data;
根据所述路障数据和所述移动路径,控制所述远程医疗机器人进行避障。According to the roadblock data and the moving path, the telemedicine robot is controlled to avoid obstacles.
需要说明的是,控制所述远程医疗机器人进行避障的方法,可以是Bug避障算法。例如,避障传感器发现障碍后,控制所述远程医疗机器人围着检测到的障碍物轮廓行走,从而绕开它。It should be noted that the method for controlling the telemedicine robot to avoid obstacles may be a bug obstacle avoidance algorithm. For example, after an obstacle avoidance sensor detects an obstacle, the telemedicine robot is controlled to walk around the detected obstacle contour, thereby avoiding it.
除此之外,控制所述远程医疗机器人进行避障的方法,还可以是势场法、神经网络、模糊逻辑等,这里不再详述。Besides, the method for controlling the telemedicine robot to avoid obstacles may also be a potential field method, a neural network, fuzzy logic, etc., which will not be described in detail here.
需要说明的是,本说明书一个或多个实施例的方法可以由单个设备执行,例如一台计算机或服务器等。本实施例的方法也可以应用于分布式场景下,由多台设备相互配合来完成。在这种分布式场景的情况下,这多台设备中的一台设备可以只执行本说明书一个或多个实施例的方法中的某一个或多个步骤,这多台设备相互之间会进行交互以完成所述的方法。It should be noted that the methods of one or more embodiments of this specification may be executed by a single device, such as a computer or a server. The method in this embodiment can also be applied in a distributed scenario, and is completed by the cooperation of multiple devices. In the case of such a distributed scenario, one device among the multiple devices may only execute one or more steps in the method of one or more embodiments of the present specification, and the multiple devices may perform operations on each other. interact to complete the described method.
上述对本说明书特定实施例进行了描述。其它实施例在所附权利要求书的范围内。在一些情况下,在权利要求书中记载的动作或步骤可以按照不同于实施例中的顺序来执行并且仍然可以实现期望的结果。另外,在附图中描绘的过程不一定要求示出的特定顺序或者连续顺序才能实现期望的结果。在某些实施方式中,多任务处理和并行处理也是可以的或者可能是有利的。The foregoing describes specific embodiments of the present specification. Other embodiments are within the scope of the appended claims. In some cases, the actions or steps recited in the claims can be performed in an order different from that in the embodiments and still achieve desirable results. Additionally, the processes depicted in the figures do not necessarily require the particular order shown, or sequential order, to achieve desirable results. In some embodiments, multitasking and parallel processing are also possible or may be advantageous.
所属领域的普通技术人员应当理解:以上任何实施例的讨论仅为示例性的,并非旨在暗示本公开的范围(包括权利要求)被限于这些例子;在本公开的思路下,以上实施例或者不同实施例中的技术特征之间也可以进行组合,步骤可以以任意顺序实现,并存在如上所述的本说明书一个或多个实施例的不同方面的许多其它变化,为了简明它们没有在细节中提供。It should be understood by those of ordinary skill in the art that the discussion of any of the above embodiments is only exemplary, and is not intended to imply that the scope of the present disclosure (including the claims) is limited to these examples; under the spirit of the present disclosure, the above embodiments or Technical features in different embodiments may also be combined, steps may be carried out in any order, and there are many other variations of the different aspects of one or more embodiments of this specification as described above, which are not in detail for the sake of brevity supply.
另外,为简化说明和讨论,并且为了不会使本说明书一个或多个实施例难以理解,在所提供的附图中可以示出或可以不示出与集成电路(IC)芯片和其它部件的公知的电源/接地连接。此外,可以以框图的形式示出装置,以便避免使本说明书一个或多个实施例难以理解,并且这也考虑了以下事实,即关于这些框图装置的实施方式的细节是高度取决于将要实施本说明书一个或多个实施例的平台的(即,这些细节应当完全处于本领域技术人员的理解范围内)。在阐述了具体细节(例如,电路)以描述本公开的示例性实施例的情况下,对本领域技术人员来说显而易见的是,可以在没有这些具体细节的情况下或者这些具体细节有变化的情况下实施本说明书一个或多个实施例。因此,这些描述应被认为是说明性的而不是限制性的。Additionally, in order to simplify illustration and discussion, and in order not to obscure one or more embodiments of this specification, the figures provided may or may not be shown in connection with integrated circuit (IC) chips and other components. Well known power/ground connections. Furthermore, devices may be shown in block diagram form in order to avoid obscuring one or more embodiments of this description, and this also takes into account the fact that details regarding the implementation of such block diagram devices are highly dependent on the implementation of the invention (ie, these details should be well within the understanding of those skilled in the art) of the platform describing one or more embodiments. Where specific details (eg, circuits) are set forth to describe exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, it will be apparent to those skilled in the art that these specific details may be used without or with variations One or more embodiments of this specification are implemented below. Accordingly, these descriptions are to be considered illustrative rather than restrictive.
尽管已经结合了本公开的具体实施例对本公开进行了描述,但是根据前面的描述,这些实施例的很多替换、修改和变型对本领域普通技术人员来说将是显而易见的。例如,其它存储器架构(例如,动态RAM(DRAM))可以使用所讨论的实施例。Although the present disclosure has been described in conjunction with specific embodiments thereof, many alternatives, modifications, and variations to these embodiments will be apparent to those of ordinary skill in the art from the foregoing description. For example, other memory architectures (eg, dynamic RAM (DRAM)) may use the discussed embodiments.
本说明书一个或多个实施例旨在涵盖落入所附权利要求的宽泛范围之内的所有这样的替换、修改和变型。因此,凡在本说明书一个或多个实施例的精神和原则之内,所做的任何省略、修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本公开的保护范围之内。The embodiment or embodiments of this specification are intended to cover all such alternatives, modifications and variations that fall within the broad scope of the appended claims. Therefore, any omission, modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made within the spirit and principle of one or more embodiments of the present specification should be included within the protection scope of the present disclosure.
Claims (15)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010279038.2ACN111449757B (en) | 2020-04-10 | 2020-04-10 | Telemedicine robot, control method and charging method thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010279038.2ACN111449757B (en) | 2020-04-10 | 2020-04-10 | Telemedicine robot, control method and charging method thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111449757Atrue CN111449757A (en) | 2020-07-28 |
| CN111449757B CN111449757B (en) | 2022-01-11 |
Family
ID=71671660
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010279038.2AActiveCN111449757B (en) | 2020-04-10 | 2020-04-10 | Telemedicine robot, control method and charging method thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111449757B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112809696A (en)* | 2020-12-31 | 2021-05-18 | 山东大学 | Omnibearing intelligent nursing system and method for high-infectivity isolated disease area |
| CN114642408A (en)* | 2022-03-17 | 2022-06-21 | 南京华脉科技股份有限公司 | Intelligent medical diagnosis device and system based on big data |
Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040015079A1 (en)* | 1999-06-22 | 2004-01-22 | Teratech Corporation | Ultrasound probe with integrated electronics |
| CN203693567U (en)* | 2014-01-20 | 2014-07-09 | 王爽 | Dual examination comprehensive diagnosis instrument utilizing infrared thermal image guide pressure-sensitive palpation |
| CN104742139A (en)* | 2015-03-23 | 2015-07-01 | 长源动力(北京)科技有限公司 | Tele medicine auxiliary robot |
| CN104856650A (en)* | 2015-05-09 | 2015-08-26 | 深圳市前海安测信息技术有限公司 | Patient-end remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment equipment and remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment method |
| CN104881572A (en)* | 2015-05-09 | 2015-09-02 | 深圳市前海安测信息技术有限公司 | Remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment system based on network hospital and remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment method |
| CN106843198A (en)* | 2015-12-07 | 2017-06-13 | 北京奇虎科技有限公司 | Sweeping robot auto-returned charging method, sweeping robot and cradle |
| CN108375373A (en)* | 2018-01-30 | 2018-08-07 | 深圳市同川科技有限公司 | Robot and its air navigation aid, navigation device |
| CN108712639A (en)* | 2018-05-29 | 2018-10-26 | 凌云光技术集团有限责任公司 | Image color correction method, apparatus and system |
| CN208096761U (en)* | 2018-01-18 | 2018-11-16 | 中实医疗科技江苏有限公司 | It is long-range to check control device |
| CN109561291A (en)* | 2018-10-23 | 2019-04-02 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Color temperature compensation method and device, storage medium and mobile terminal |
| CN110379272A (en)* | 2019-06-12 | 2019-10-25 | 南京梦宇三维技术有限公司 | Chinese medicine diagnosis training method and system based on digital patient |
| CN110709024A (en)* | 2017-11-21 | 2020-01-17 | 直观外科手术操作公司 | System and method for master/tool registration and control of intuitive motion |
| CN209966410U (en)* | 2018-12-29 | 2020-01-21 | 上海宜硕网络科技有限公司 | Telemedicine service robot |
| CN110882061A (en)* | 2019-11-18 | 2020-03-17 | 北京唯迈医疗设备有限公司 | Four-point type tactile force feedback device of interventional operation robot |
- 2020
- 2020-04-10CNCN202010279038.2Apatent/CN111449757B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040015079A1 (en)* | 1999-06-22 | 2004-01-22 | Teratech Corporation | Ultrasound probe with integrated electronics |
| CN203693567U (en)* | 2014-01-20 | 2014-07-09 | 王爽 | Dual examination comprehensive diagnosis instrument utilizing infrared thermal image guide pressure-sensitive palpation |
| CN104742139A (en)* | 2015-03-23 | 2015-07-01 | 长源动力(北京)科技有限公司 | Tele medicine auxiliary robot |
| CN104856650A (en)* | 2015-05-09 | 2015-08-26 | 深圳市前海安测信息技术有限公司 | Patient-end remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment equipment and remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment method |
| CN104881572A (en)* | 2015-05-09 | 2015-09-02 | 深圳市前海安测信息技术有限公司 | Remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment system based on network hospital and remote auxiliary diagnosis and treatment method |
| CN106843198A (en)* | 2015-12-07 | 2017-06-13 | 北京奇虎科技有限公司 | Sweeping robot auto-returned charging method, sweeping robot and cradle |
| CN110709024A (en)* | 2017-11-21 | 2020-01-17 | 直观外科手术操作公司 | System and method for master/tool registration and control of intuitive motion |
| CN208096761U (en)* | 2018-01-18 | 2018-11-16 | 中实医疗科技江苏有限公司 | It is long-range to check control device |
| CN108375373A (en)* | 2018-01-30 | 2018-08-07 | 深圳市同川科技有限公司 | Robot and its air navigation aid, navigation device |
| CN108712639A (en)* | 2018-05-29 | 2018-10-26 | 凌云光技术集团有限责任公司 | Image color correction method, apparatus and system |
| CN109561291A (en)* | 2018-10-23 | 2019-04-02 | Oppo广东移动通信有限公司 | Color temperature compensation method and device, storage medium and mobile terminal |
| CN209966410U (en)* | 2018-12-29 | 2020-01-21 | 上海宜硕网络科技有限公司 | Telemedicine service robot |
| CN110379272A (en)* | 2019-06-12 | 2019-10-25 | 南京梦宇三维技术有限公司 | Chinese medicine diagnosis training method and system based on digital patient |
| CN110882061A (en)* | 2019-11-18 | 2020-03-17 | 北京唯迈医疗设备有限公司 | Four-point type tactile force feedback device of interventional operation robot |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112809696A (en)* | 2020-12-31 | 2021-05-18 | 山东大学 | Omnibearing intelligent nursing system and method for high-infectivity isolated disease area |
| CN114642408A (en)* | 2022-03-17 | 2022-06-21 | 南京华脉科技股份有限公司 | Intelligent medical diagnosis device and system based on big data |
| CN114642408B (en)* | 2022-03-17 | 2023-10-31 | 湖南提奥医疗科技有限公司 | Intelligent medical diagnosis device and diagnosis system based on big data |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111449757B (en) | 2022-01-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US9610685B2 (en) | Graphical interface for a remote presence system | |
| CN205750782U (en) | Telemedicine System based on intelligent glasses | |
| US20060052676A1 (en) | Tele-presence system that allows for remote monitoring/observation and review of a patient and their medical records | |
| CN111758137A (en) | Method and apparatus for telemedicine | |
| US20150320343A1 (en) | Motion information processing apparatus and method | |
| KR20180068336A (en) | Surgical system with training or auxiliary functions | |
| CN108113705A (en) | It is long-range to check control device | |
| Lin et al. | Toward unobtrusive patient handling activity recognition for injury reduction among at-risk caregivers | |
| CN206597027U (en) | A kind of ultrasonic scanner accessory system | |
| CN107115106A (en) | A kind of tele-medicine auxiliary robot | |
| CN112826458B (en) | Pulse diagnosis system and pulse diagnosis method | |
| CN111449757A (en) | Telemedicine robot, control method and charging method thereof | |
| CN204537060U (en) | A kind of human-computer interaction device based on myoelectricity stream and multi-sensor cooperation effect | |
| WO2021153863A1 (en) | Method for determining objective target location of body | |
| CN108498102A (en) | Rehabilitation training method and device, storage medium, electronic equipment | |
| JP2002085353A (en) | Remote diagnostic system | |
| CN116453715A (en) | A remote palpation method and system | |
| CN106419957B (en) | Auxiliary system of ultrasonic scanning device | |
| CN119299850A (en) | Remote image acquisition method and related products | |
| Shin | A study on the tele-medicine robot system with face to face interaction | |
| CN111356407A (en) | Ultrasonic detection device, ultrasonic control device, ultrasonic system and ultrasonic imaging method | |
| CN112802594B (en) | Remote diagnosis and treatment system | |
| Lin et al. | A vision-based compensation detection approach during robotic stroke rehabilitation therapy | |
| CN208598426U (en) | Supersonic detection device, trolley and ultrasonic system | |
| JP2008167866A (en) | Diagnostic robot, and control method and control program of diagnostic robot |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| OL01 | Intention to license declared | ||
| OL01 | Intention to license declared |