CN111435489A - Agriculture dealing system - Google Patents
Agriculture dealing systemDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111435489A CN111435489ACN202010040611.4ACN202010040611ACN111435489ACN 111435489 ACN111435489 ACN 111435489ACN 202010040611 ACN202010040611 ACN 202010040611ACN 111435489 ACN111435489 ACN 111435489A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- work
- farmland
- farm
- plan
- file
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0631—Resource planning, allocation, distributing or scheduling for enterprises or organisations
- G06Q10/06313—Resource planning in a project environment
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/02—Agriculture; Fishing; Forestry; Mining
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01B—SOIL WORKING IN AGRICULTURE OR FORESTRY; PARTS, DETAILS, OR ACCESSORIES OF AGRICULTURAL MACHINES OR IMPLEMENTS, IN GENERAL
- A01B76/00—Parts, details or accessories of agricultural machines or implements, not provided for in groups A01B51/00 - A01B75/00
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01B—SOIL WORKING IN AGRICULTURE OR FORESTRY; PARTS, DETAILS, OR ACCESSORIES OF AGRICULTURAL MACHINES OR IMPLEMENTS, IN GENERAL
- A01B79/00—Methods for working soil
- A01B79/005—Precision agriculture
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A01—AGRICULTURE; FORESTRY; ANIMAL HUSBANDRY; HUNTING; TRAPPING; FISHING
- A01C—PLANTING; SOWING; FERTILISING
- A01C11/00—Transplanting machines
- A01C11/02—Transplanting machines for seedlings
- A01C11/025—Transplanting machines using seedling trays; Devices for removing the seedlings from the trays
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0631—Resource planning, allocation, distributing or scheduling for enterprises or organisations
- G06Q10/06315—Needs-based resource requirements planning or analysis
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Soil Sciences (AREA)
- Environmental Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Mining & Mineral Resources (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Marine Sciences & Fisheries (AREA)
- Animal Husbandry (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Agronomy & Crop Science (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Biodiversity & Conservation Biology (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及务农系统。The present invention relates to farming systems.
背景技术Background technique
以往,存在管理由农田作业机进行的农田作业的务农系统、以及利用农田作业机管理被区分成多个区间的农田的务农系统。Conventionally, there are farming systems that manage farm work performed by farm work machines, and farming systems that manage farm fields divided into a plurality of sections by the farm work machines.
专利文献1的务农系统具有:农业区间管理部,管理农业区间;农作业管理部,按照每个农业区间管理经时实施的施肥、收割等农作业活动;数据记录部,将实施的农作业活动的内容(施肥量、收割量等)以及成本作为农作业实绩进行记录;实绩输出数据生成部,生成用于将农作业活动的履历作为农作业实绩表输出的实绩输出数据;以及计划输出数据生成部,用于根据通过农作业实绩计算的农作业活动的标准输出农作业计划书的计划输出数据。农作业者一边观察输出的农作业计划书,一边实施农作业。The farming system of Patent Document 1 includes an agricultural section management unit that manages agricultural sections; an agricultural operation management section that manages agricultural operations such as fertilization and harvesting performed over time for each agricultural section; and a data recording section that manages agricultural operations to be implemented The content (fertilization amount, harvesting amount, etc.) and cost are recorded as agricultural work performance; the actual performance output data generation unit generates actual performance output data for outputting the history of agricultural work activities as an agricultural work performance table; and plan output data generation The part is used to output the planned output data of the agricultural work plan according to the standard of the agricultural work activity calculated by the agricultural work performance. The farmer carries out the farm work while observing the output farm work plan.
专利文献2的务农系统具有:地图数据记录部,记录农田地图数据;农田作业数据记录部,记录以每个通过各种农作业机对农田进行的作业为单位生成的农田作业数据;数据管理部,以共通的坐标位置对农田地图数据和农田作业数据进行数据管理;以及评价部,根据农田作业数据进行农田的务农评价。农田作业数据包含每个微小区间的收量、味道和施肥量。根据基于农田的每个微小区间的收量输出的农田的微小区间收量分布,判断比平均好的优良区间和比平均差的不良区间。根据该判断结果,设立包含对优良区间的肥料投入的减少、以及对不良区间的肥料投入的增加等的农作业计划。The farming system of Patent Document 2 includes: a map data recording unit that records farmland map data; a farmland operation data recording unit that records farmland operation data generated for each operation performed on the farmland by various agricultural work machines; and a data management unit , which manages the farmland map data and farmland operation data with a common coordinate position; and the evaluation department, which conducts farming evaluation of the farmland based on the farmland operation data. Fieldwork data includes yield, taste, and fertilization for each microinterval. Based on the yield distribution of the micro-section of the farmland output based on the yield of each micro-section of the farmland, an excellent section that is better than the average and a poor section that is worse than the average are determined. Based on the result of this determination, an agricultural work plan including a reduction in fertilizer input in an excellent section, an increase in fertilizer input in a poor section, and the like is established.
(1)在上述现有的务农系统中,以农田为单位记录有涉及过去实施的施肥作业等农田作业的作业数据、以及作为该农田作业的成果的收割量等实绩数据。当设立新的农田作业计划时,参照记录的作业数据和实绩数据,制作能够期待效率较高的收割的农田作业计划。然而,在上述务农系统中,当涉及将要制作的农田作业计划的作业数据和实绩数据并未记录时,由于没有需要参照的数据,因此导致无法制作农田作业计划的麻烦。(1) In the above-described conventional farming system, work data related to farm work such as fertilization work performed in the past, and performance data such as harvesting amount as a result of the farm work are recorded in units of farm fields. When creating a new farm work plan, the recorded work data and actual performance data are referred to, and a farm work plan that can expect efficient harvesting is created. However, in the above-mentioned farming system, when the work data and actual performance data related to the farm work plan to be prepared are not recorded, there is no data to be referenced, and thus it is troublesome that the farm work plan cannot be prepared.
(2)并且,在上述现有的务农系统中,以农田为单位记录有过去实施的施肥作业等涉及农田作业的作业数据、以及作为该农田作业的成果的收割量等实绩数据。当设立新的农田作业计划时,重要的是,参照记录的作业数据和实绩数据,以能够期待效率较高的收割的方式进行计划。务农者通过显示器或印刷物掌握作为作业对象的农田的形状,根据该形状构思作业内容,进行农田作业计划。因此,务农者以规定农田形状的畦或农道作为境界线对农田进行分割,并为分割的农田区域(区间)分配最合适的作业内容。当制作上述农田作业计划时,以能够实现该农田作业计划的方式,使农田作业机在农田进行作业行驶。此时,由于农田作业机设定了作业宽度,因此,必须以具有该作业宽度(包含重叠部)的行驶轨迹涵盖农田的方式行驶。在作业计划时,对于农田作业机的作业宽度并未严格考虑。并且,在农田可能存在无法预料的行驶障碍物等,因此,农田作业车的行驶路径在作业计划时和实际作业行驶时不一定一致。结果是,实际作业进行的实际作业实绩与作业计划预想的预想作业实绩不同。然而,在当前的务农系统中,很难简单地评价上述预想作业实绩与实际作业实绩之间的差异。(2) Furthermore, in the above-mentioned conventional farming system, work data related to farm work such as fertilization work performed in the past, and actual performance data such as harvesting amount as a result of the farm work are recorded in units of farm fields. When setting up a new farm work plan, it is important to make a plan so that efficient harvesting can be expected with reference to the recorded work data and actual performance data. The farmer grasps the shape of the farmland to be worked on on the display or printed matter, conceives the contents of the work based on the shape, and makes a farmwork plan. Therefore, the farmer divides the farmland with a border or a farm road that defines the shape of the farmland as a boundary line, and assigns the most suitable work content to the divided farmland area (section). When the above-mentioned farm work plan is prepared, the farm work machine is caused to work and travel on the farm so that the farm work plan can be realized. At this time, since the working width of the farm working machine is set, it is necessary to travel so that the running locus having the working width (including the overlapping portion) covers the farmland. In the operation planning, the working width of the farm work machine is not strictly considered. In addition, there may be unexpected driving obstacles or the like in the farmland, and therefore, the travel path of the farm work vehicle does not necessarily match when the work is planned and when the work is actually traveled. As a result, the actual work performance performed by the actual work is different from the expected work performance expected in the work plan. However, in the current farming system, it is difficult to simply evaluate the above-mentioned difference between the expected work performance and the actual work performance.
(现有技术文献)(Prior Art Literature)
(专利文献)(patent literature)
专利文献1:日本发明专利申请公布“特开2014-194653号”公报Patent Document 1: Japanese Patent Application Publication "Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2014-194653"
专利文献2:日本发明专利申请公布“特开2017-068533号”公报Patent Document 2: Japanese Patent Application Publication "Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 2017-068533"
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
(本发明要解决的问题)(Problems to be Solved by the Invention)
(1)与背景技术(1)相对应的问题如下。(1) The problems corresponding to the background art (1) are as follows.
鉴于上述情况,本发明的目的在于,提供一种务农系统,即使没有涉及过去进行的农作业的数据,也能够尽可能制作效果较好的农田作业计划。In view of the above-mentioned circumstances, an object of the present invention is to provide a farming system capable of creating an effective farm work plan as much as possible even if there is no data related to the farming work performed in the past.
(2)与背景技术(2)相对应的问题如下。(2) The problems corresponding to the background art (2) are as follows.
本发明的目的在于,提供一种务农系统,能够简单地评价预想作业实绩和实际作业实绩之间的差异。An object of the present invention is to provide a farming system that can easily evaluate the difference between the expected work performance and the actual work performance.
(解决问题的方案)(solution to the problem)
(1)与问题(1)相对应的解决方案如下。(1) The solution corresponding to the problem (1) is as follows.
管理农田作业机进行的农田作业的本发明的务农系统具有:农田文件存储部,存储包含各农田的农田特征文件、农田作业履历文件以及农田收割文件的农田文件;作业计划制作部,利用所述农田文件制作指定农田的农田作业计划;以及模拟文件制作部,当用于所述指定农田的所述农田文件未存储在所述农田文件存储部时,制作用于所述指定农田的模拟农田文件,并赋予所述作业计划制作部。The farming system of the present invention that manages farm work performed by a farm work machine includes a farm file storage unit that stores a farm field file including a farm field characteristic file, a farm work history file, and a farm field harvest file for each farm field, and an operation plan creation unit that uses the a farmland file creating a farmland operation plan for a designated farmland; and a simulation file making unit that, when the farmland file for the designated farmland is not stored in the farmland file storage unit, creates a simulated farmland file for the designated farmland , and assigned to the operation plan making department.
在该结构中,在将要制作的农田作业计划中,当不存在要参照的农田文件,例如农田特征文件、农田作业履历文件以及农田收割文件中的至少1个时,模拟制作该缺失的文件。当将模拟制作的文件(模拟文件)赋予作业计划制作部时,作业计划制作部参照该模拟文件制作农田作业计划。模拟文件是根据存储在农田文件存储部的文件中的与相似农田或相似农田作业相对应的文件数据制作的。需要包含在未存储于农田文件存储部的文件中的数据的类似数据还能够通过访问上位云系统的数据库、公用农业数据库或商用农业数据库的方式获取。能够利用如上所述地获得的类似数据制作模拟农田文件。或者,通过将数据未知(或空白)的农田文件作为模拟农田文件赋予作业计划制作部,作业计划制作部至少能够制作未知(空白)的农田作业计划。此时,通过用人为输入的输入数据置换未知(空白),从而完成正式的农田作业计划。In this configuration, when there is no farmland file to be referenced in the farmland operation plan to be prepared, such as at least one of the farmland characteristic file, the farmland operation history file, and the farmland harvesting file, the missing file is simulated and created. When a simulated file (simulation file) is given to the work plan preparation unit, the work plan preparation unit generates a farm work plan with reference to the simulation file. The simulation file is created based on the file data corresponding to similar farmland or similar farmland operations in the file stored in the farmland file storage unit. Similar data requiring data contained in files not stored in the field file storage unit can also be obtained by accessing a database of an upper cloud system, a public agricultural database, or a commercial agricultural database. Simulated farmland files can be made using similar data obtained as described above. Alternatively, by assigning a farmland file with unknown (or blank) data to the operation plan creation unit as a simulated farmland file, the operation plan creation unit can create at least an unknown (blank) farmland operation plan. At this time, by replacing the unknown (blank) with the input data inputted manually, a formal farm work plan is completed.
农作物的生产每年或每半年周期性(季节性)重复,因此,当设立农田作业计划时,优选参照过去多次的农田作业数据。The production of crops is periodically (seasonally) repeated every year or every six months, and therefore, when setting up a farm work plan, it is preferable to refer to the farm work data of the past many times.
由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述农田文件为由以年度为单位获取的数据构成的经时构造文件,所述作业计划制作部根据多个年度的所述农田文件输出所述农田作业计划。多个年度的农田文件的对应数据群通过统计计算等执行预处理,通过该预处理计算的数据被作为用于制作农田作业计划的输入数据加以利用。或者,作业计划制作部也可以以能够直接输入多个年度的农田文件本身的方式构成。Therefore, in one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention, the farmland file is a time-lapse structure file composed of data acquired on a yearly basis, and the work plan preparation unit outputs the data based on the farmland file for a plurality of years. Describe the farm work plan. Preprocessing is performed on the corresponding data groups of the farmland files for a plurality of years by statistical calculation or the like, and the data calculated by the preprocessing is used as input data for making a farmland work plan. Alternatively, the work plan preparation unit may be configured so that the farmland documents themselves for a plurality of years can be directly input.
农田特征文件包含杂草状态、土质、表土深、气候风土、日照等数据,农田作业履历文件包含肥料散布量、药剂散布量、秧苗量等数据,农田收割文件包含味道、收量、生长状况等数据。并且,农田作业机为了按照制作的农田作业计划进行农田作业,需要以装备的行驶设备和作业设备适合该农田作业的方式调整各作业参数。为了使农田作业机执行通过参照包含在各农田文件中的多个数据而制作的农田作业计划,需要正确的作业参数。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述作业计划制作部由计算单元构成,所述计算单元以所述农田特征文件、所述农田作业履历文件以及所述农田收割文件的数据作为输入参数,输出设定在进行所述农田作业的所述农田作业机的作业参数。农田作业机被设计成能够以在各种农田执行各种农田作业的方式自由调整,为了实施合适的农田作业,需要适当进行该调整。在该结构中,采用了计算单元,所述计算单元将从涉及指定的农田和农田作业的各文件中读取的数据作为输入参数,输出当在该农田进行农田作业时需要的作业参数。上述计算单元的优选例子为学习型计算单元。通过利用预先采用多个样本进行学习的学习型计算单元,能够输出当在具有特定的农田特征的农田进行特定的农田作业时需要的作业参数。根据输出的作业参数,以适合特定农田作业机进行的特定农田作业的方式调整行驶设备和作业设备。The farmland characteristic file includes data such as weed status, soil quality, topsoil depth, climate and terroir, and sunshine. The farmland operation history file includes data such as fertilizer distribution, chemical distribution, and seedling amount. The farmland harvest file includes taste, yield, growth status, etc. data. In addition, in order to perform the farm work according to the prepared farm work plan, the farm work machine needs to adjust each work parameter so that the equipped traveling equipment and work equipment are suitable for the farm work. In order for the farm working machine to execute the farm work plan prepared by referring to a plurality of data included in each farm file, accurate work parameters are required. Therefore, in one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention, the operation plan preparation unit is constituted by a calculation unit, and the calculation unit uses data of the farmland characteristic file, the farmland operation history file, and the farmland harvesting file as data A parameter is input, and an operation parameter set to the farm working machine that performs the farm operation is output. The farm work machine is designed to be freely adjustable so as to perform various farm work on various farm fields, and the adjustment needs to be appropriately performed in order to perform suitable farm work. In this configuration, a calculation unit is employed that outputs, as input parameters, data read from each file related to a designated farmland and farmland work, and outputs work parameters required when performing farmland work on the farmland. A preferred example of the above computing unit is a learning computing unit. By using a learning-type computing unit that performs learning by using a plurality of samples in advance, it is possible to output work parameters required when specific farmland work is performed on a farmland having specific farmland characteristics. Based on the output work parameters, the traveling equipment and work equipment are adjusted in a manner suitable for the specific field work performed by the specific field work machine.
农田作业中的最重要项目随着各务农者的想法不同而不同。例如,存在最重视收量的务农者、最重视品质的务农者以及最重视轻劳动的务农者。并且,即使是同一务农者,随着农作物的不同,有时最重视的项目也有所不同。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,在所述计算单元中准备有多个计算模式,所述计算模式符合从多个务农目标项目中选择的需要重视的所述务农目标项目,各个所述计算模式下的计算中的所述数据的权重系数不同。并且,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述务农目标项目为收量、味道、减少农药、轻劳动、低成本以及高效益中的任一个。在该结构中,能够制作符合务农者各自重视的项目的农田作业计划。而且,通过根据将要进行的农田作业变更重视的项目,即变更权重系数,从而能够制作符合该项目的农田作业计划。The most important items in farm work vary with each farmer's thinking. For example, there are farmers who value yield the most, those who value quality the most, and those who value light labor the most. Also, even for the same farmer, depending on the crops, sometimes the most important items are different. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention is that a plurality of calculation modes are prepared in the calculation unit, and the calculation modes conform to the agricultural target item that needs attention selected from a plurality of agricultural target items, and each The weight coefficients of the data in the calculation in the calculation mode are different. Furthermore, in one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention, the farming target item is any one of yield, taste, reduction of pesticides, light labor, low cost, and high efficiency. With this configuration, it is possible to create a farm work plan in accordance with the item that each farmer attaches importance to. Then, by changing the item of importance, that is, the weight coefficient, according to the farm work to be performed, a farm work plan corresponding to the item can be created.
在农田作业中的重视项目的选择和其重要程度基于务农者的想法,可能随着农作物的种类或年度不同而不同。因此,即使参照过去的数据自动进行,也未必能够获得满意的结果。因此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述权重系数能够人为调整。The selection and importance of items of importance in field operations are based on the ideas of the farmers and may vary by crop type or year. Therefore, even if it is done automatically with reference to past data, it is not always possible to obtain satisfactory results. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention is that the weight coefficient can be adjusted manually.
即使从作业计划制作部输出了作为农田作业计划的合适的作业参数,该作业参数有时并不与设定在使用的农田作业机的作业参数相匹配。例如,当由作业参数规定的施肥量与施肥作业机能够按等级设定的施肥量不一致时,设定成能够设定的施肥量中的与由作业参数规定的施肥量最接近的施肥量。并且,当由作业参数规定的最小施肥量比施肥作业机的最小施肥量小时,可以采用施肥作业机的最小施肥量,或者,也可以将施肥作业机的车速提高至超过标准车速,从而减少实质上每单位面积的施肥量。因此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,具有规格调整部,所述规格调整部使从所述作业计划制作部输出的所述作业参数适用于所述农田作业机的规格。Even if suitable work parameters as the farm work plan are output from the work plan creation unit, the work parameters may not match the work parameters set for the farm work machine being used. For example, when the fertilization rate specified by the work parameters does not match the fertilization rate that can be set by the fertilization work machine, the fertilization rate that is closest to the fertilization rate specified by the work parameter is set among the settable fertilization rates. In addition, when the minimum fertilization rate specified by the operation parameters is smaller than the minimum fertilization rate of the fertilization work machine, the minimum fertilization rate of the fertilization work machine may be used, or the vehicle speed of the fertilization work machine may be increased to exceed the standard speed, thereby reducing the actual amount of fertilization. The amount of fertilizer applied per unit area. Therefore, one of preferred embodiments of the present invention includes a specification adjustment unit that applies the operation parameters output from the operation plan creation unit to the specifications of the farm working machine.
即使在同一农田,农田的肥沃状态、农作物的生长状态、农作物的日照等也会随着农田的场所不同而不同。因此,包含在农田特征文件、农田作业履历文件、农田收割文件中的数据优选以场所为单位进行管理。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述农田文件由分配在每个通过将所述农田分割成多个从而获得的区间的以区间为单位的数据构成,所述作业计划制作部为每个所述区间制作所述农田作业计划。Even in the same farmland, the fertile state of the farmland, the growth state of the crops, the sunshine of the crops, etc. will vary depending on the location of the farmland. Therefore, it is preferable to manage the data contained in the farmland characteristic file, the farmland work history file, and the farmland harvesting file on a site-by-site basis. Therefore, in one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention, the farmland file is composed of section-by-section data allocated to each section obtained by dividing the farmland into a plurality of pieces, and the work plan creation unit The farm work plan is made for each of the sections.
在农田作业中,务农者的多年经验至关重要。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,具有修正部,所述修正部通过人为操作修正由所述作业计划制作部制作的所述农田作业计划。由此,务农者至少对于认为依赖经验更为合适的农田作业计划项目,能够发挥自己的经验。In field operations, the farmer's years of experience are crucial. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention includes a correction unit that corrects the farm work plan created by the work plan creation unit by manual operation. As a result, farmers can at least make use of their own experience with respect to the farmland operation planning items that rely on experience as more appropriate.
(2)与问题(2)相对应的解决方案如下。(2) The solution corresponding to the problem (2) is as follows.
本发明的务农系统利用农田作业机管理被区分成多个区间的农田,所述务农系统具有:作业计划图制作部,制作表示每个所述区间的农田作业的计划的作业计划图;作业预测图制作部,根据所述作业计划图模拟所述农田作业,从而制作作为该模拟结果的作业预测图;作业实绩图制作部,根据由实施了所述农田作业的农田作业机生成的作业数据制作作业实绩图;以及显示控制部,将所述作业计划图、所述作业预测图以及所述作业实绩图中的任一个显示在显示器上,或将其中至少2个以能够相互比较的方式显示在显示器上。The farming system of the present invention manages farmland divided into a plurality of sections by using a farm working machine, and the farming system includes: an operation plan drawing unit that creates an operation plan diagram showing a plan of farmland operation for each of the sections; and an operation forecast A map creation unit simulates the farm work based on the work plan, and creates a work forecast map as a result of the simulation, and a work performance map creation unit creates a work performance map based on work data generated by a farm work machine that has performed the farm work. a work record; and a display control unit that displays any one of the work plan, the work forecast, and the work record on a display, or displays at least two of them in a mutually comparable manner on the display.
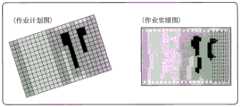
在该结构中,当制作农田作业的作业计划图时,根据该作业计划图模拟该农田作业。将该模拟结果作为作业预测图进行制作。由此,务农者能够一边观察显示在显示器上的作业计划图和作业预测图,一边评价作业计划,在有必要时,能够修正作业计划,改善作业计划图。并且,当根据作业计划图通过农田作业机实施农田作业时,根据通过该农田作业获得的作业数据制作作业实绩图。如上所述制作的一系列作业计划图、作业预测图以及作业实绩图中的任一个显示在显示器上,或者其中至少2个以能够相互比较的方式显示在显示器上,因此,务农者能够通过该显示器的显示界面,获得用于下一次农田作业计划的有益指导。In this configuration, when creating a work plan for farm work, the farm work is simulated based on the work plan. This simulation result is produced as a work forecast map. Thereby, the farmer can evaluate the work plan while viewing the work plan and the work forecast displayed on the display, and when necessary, can correct the work plan and improve the work plan. Then, when the farm work is performed by the farm work machine based on the work plan, a work performance map is created based on the work data obtained by the farm work. Any one of a series of work plan charts, work forecast charts, and work performance charts prepared as described above is displayed on the display, or at least two of them are displayed on the display so that they can be compared with each other. Therefore, farmers can use this The display interface of the monitor to get helpful guidance for planning your next field operation.
当计划施肥作业和药剂投放作业等农田作业时,务农者将农田大致区分成多个区域,考虑每个该区域的过去的农田作业结果和现在的农田状态,为每个该区域决定农田作业内容。此时,务农者以规定农田形状的畦或农道为境界线分割农田,为分割的农田区域(区间)分配最合适的作业内容,设立作业计划。对此,在模拟的农田作业和实际的农田作业中,以通过农田作业机的行驶轨迹和其作业宽度所划分的农田区域(区间)为单位,计算该作业结果。由此,作为优选,在制作各个图时,作业计划图以与作业预测图和作业实绩图不同的坐标系表示。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述作业计划图以第一坐标系表示,所述作业预测图和所述作业实绩图以不同于所述第一坐标系的第二坐标系表示。When planning farmland operations such as fertilization and chemical administration, the farmer roughly divides the farmland into a plurality of areas, and determines the contents of farmland work for each area in consideration of the past farmland operation results and current farmland conditions for each area. . At this time, the farmer divides the farmland with a border or a farm road that defines the shape of the farmland as a boundary line, assigns the most suitable work content to the divided farmland area (section), and establishes a work plan. On the other hand, in the simulated farm work and the actual farm work, the work result is calculated in units of the farm field area (section) divided by the travel path of the farm work machine and the work width. Therefore, it is preferable that the work plan map is represented by a coordinate system different from the work forecast map and the work performance map when each map is created. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention is that the work plan map is represented by a first coordinate system, and the work forecast map and the work performance map are represented by a second coordinate system different from the first coordinate system. express.
一边进行自动行驶一边进行农田作业的农田作业机始终通过卫星测位计算本车的坐标位置。因此,作为优选,将通过卫星测位获得的坐标值与农田作业的内容组合,从而制作作业预测图和作业实绩图。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述第一坐标系为将给所述农田划界的2个境界线作为纵轴和横轴的农田坐标系,所述第二坐标系为将通过卫星测位数据获取的纬度和经度作为纵轴和横轴的卫星测位坐标系。A farm work machine that performs farm work while running autonomously always calculates the coordinate position of the vehicle through satellite positioning. Therefore, preferably, the coordinate values obtained by satellite positioning are combined with the content of the farm work to create a work forecast map and an actual work performance map. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention is that the first coordinate system is a farmland coordinate system with two boundary lines delimiting the farmland as the vertical axis and the horizontal axis, and the second coordinate system is A satellite positioning coordinate system with the latitude and longitude obtained from the satellite positioning data as the vertical axis and the horizontal axis.
当作业计划图以第一坐标系表示,作业预测图和作业实绩图以第二坐标系表示时,为了将作业计划图中的每个区间的农田计划内容正确地传递至作业预测图生成部或农田作业机,需要从第一坐标系向第二坐标系进行坐标转换。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,具有坐标转换部,所述坐标转换部进行从所述第一坐标系向所述第二坐标系的坐标转换。When the work plan is represented by the first coordinate system, and the work forecast map and the work performance map are represented by the second coordinate system, in order to correctly transmit the farmland plan content of each section in the work plan to the work forecast map generation unit or The farm work machine needs to perform coordinate transformation from the first coordinate system to the second coordinate system. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention includes a coordinate conversion unit that performs coordinate conversion from the first coordinate system to the second coordinate system.
务农者一边根据农田形状在大局上掌握农田状态,一边设立农田作业计划。与此相对,该农田作业计划的模拟结果和实绩通过农田作业机的作业行驶获得。由此,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,所述坐标计划图所使用的所述区间的形状与所述作业预测图所使用的所述区间的形状不同,所述作业预测图和所述作业实绩图所使用的所述区间的形状相同。此时,考虑到基于农田作业计划图的模拟结果和实绩通过农田作业机的作业行驶获得,作为优选,所述作业预测图和所述作业实绩图所使用的所述区间的形状由实施所述农田作业的农田作业机的作业宽度来规定。The farmer establishes a farm operation plan while grasping the overall situation of the farm according to the shape of the farm. On the other hand, the simulation result and actual performance of the farm work plan are obtained by the work travel of the farm work machine. Therefore, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention is that the shape of the section used in the coordinate planning map is different from the shape of the section used in the work forecast map, and the work forecast map and the work forecast map have different shapes. The shape of the section used in the work performance graph is the same. In this case, considering that the simulation results and actual results based on the farm work plan are obtained through the work travel of the farm work machine, preferably, the shapes of the sections used in the work forecast map and the work performance map are determined by implementing the The working width of the farm work machine for farm work is specified.
在农田作业中,当租用农田作业车等时,有时会在农田作业之前变更作业宽度等作业车规格。并且,根据农田的状态,有时会在作业过程中变更作业宽度。农田作业车的作业宽度的变更导致已作业区间的形状变更。为了解决该问题,本发明的优选实施方式之一为,具有区间数据转换部,所述区间数据转换部将分配在所述作业计划图的所述区间的作业计划数据分配在所述作业预测图的所述区间。In farm work, when a farm work vehicle or the like is rented, the specifications of the work vehicle such as the work width may be changed before the farm work. Furthermore, depending on the state of the farmland, the work width may be changed during the work. Changes in the working width of the farm work vehicle lead to a change in the shape of the worked section. In order to solve this problem, one of the preferred embodiments of the present invention includes a section data conversion unit that allocates work plan data allocated to the section of the work plan map to the work forecast map of said interval.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是表示第一实施方式的图(以下至图6均相同),是表示务农系统的概略结构的说明图。FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the first embodiment (the same applies to FIG. 6 hereinafter), and is an explanatory diagram showing a schematic configuration of a farming system.
图2是利用务农系统进行农田作业管理的一个例子的图解说明图。FIG. 2 is a diagrammatic explanatory diagram of an example of farm work management using the farming system.
图3是作为农田作业机的一个例子的带施肥功能的插秧机的侧视图。Fig. 3 is a side view of a rice transplanter with a fertilization function as an example of a farm working machine.
图4是表示取苗量调节机构和送出量调节机构的概略构造的说明图。Fig. 4 is an explanatory diagram showing a schematic structure of a seedling-taking amount adjusting mechanism and a feeding amount adjusting mechanism.
图5是嵌入务农系统的插秧机的控制系统的功能框图。Fig. 5 is a functional block diagram of a control system of a rice transplanter embedded in a farming system.
图6是农田作业计划的制作流程的图解说明图。FIG. 6 is a diagrammatic explanatory diagram of a production flow of a farm work plan.
图7是表示第二实施方式的图(以下至图14均相同),是表示务农系统的概略结构的说明图。FIG. 7 is a diagram showing a second embodiment (the same applies to FIG. 14 hereinafter), and is an explanatory diagram showing a schematic configuration of a farming system.
图8是表示参加务农系统的插秧机的控制系统的功能框图。It is a functional block diagram which shows the control system of the rice transplanter which participated in a farming system.
图9是表示作业计划图的一个例子的界面图。FIG. 9 is an interface diagram showing an example of a work schedule diagram.
图10是表示作业预测图的一个例子的界面图。FIG. 10 is an interface diagram showing an example of a job prediction map.
图11是用于比较作业计划图和作业预测图的界面图。FIG. 11 is an interface diagram for comparing the work plan map and the work forecast map.
图12是表示作业实绩图的一个例子的界面图。FIG. 12 is an interface diagram showing an example of a work record diagram.
图13是用于比较作业计划图和作业实绩图的界面图。FIG. 13 is an interface diagram for comparing the work plan chart and the work record chart.
图14是用于比较作业预测图和作业实绩图的界面图。FIG. 14 is an interface diagram for comparing the work forecast map and the work record map.
附图标记说明Description of reference numerals
1:机体1: Body
1A:行驶设备群1A: Driving equipment group
1B:作业设备群1B: Working equipment group
4:施肥装置4: Fertilizer device
40:送出量调节机构40: Delivery volume adjustment mechanism
402:调节体402: Regulator
403:螺丝轴403: Screw shaft
404:肥料调节马达404: Fertilizer regulating motor
405:位置检测传感器405: Position detection sensor
41:料斗41: Hopper
42:送出机构42: Sending Agency
43:鼓风机43: Blower
44:施肥管44: Fertilizer Tube
45:开沟器45: Opener
51:农田文件存储部51: Farmland File Storage Department
52:作业计划制作部52: Work plan production department
52a:作业计划计算单元(计算单元)52b:作业参数表52a: work plan calculation unit (calculation unit) 52b: work parameter table
53:模拟文件制作部53: Simulation file production department
54:修正部54: Correction Department
55:数据处理部55: Data Processing Department
6:控制单元6: Control unit
61:行驶控制部61: Driving Control Department
62:作业控制部62: Operation Control Department
63:本车位置计算部63: Own Vehicle Position Calculation Department
64:规格调整部64: Specification Adjustment Department
65:作业结果文件制作部65: Work Result Document Creation Department
8:测位单元8: Positioning unit
9:通用终端9: Universal Terminal
91:行驶路径生成部91: Driving Route Generation Section
105:外部计算机系统105: External Computer Systems
151:数据存储部151: Data Storage Department
152:作业计划图制作部152: Work Plan Drawing Department
153:作业预测图制作部153: Job Forecast Chart Production Department
154:作业实绩图制作部154: Work Performance Chart Production Department
155:显示控制部155: Display Control Section
156:坐标转换部156: Coordinate conversion section
157:区间数据转换部157: Interval data conversion section
158:显示器158: Display
164:作业参数设定部164: Operation parameter setting section
165:作业数据制作部165: Job Data Creation Department
CS:务农云服务CS: Farming Cloud Services
具体实施方式Detailed ways
(第一实施方式)(first embodiment)
首先,参照图1至图6,对第一实施方式进行说明。First, the first embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 6 .
用图1说明本发明的务农系统的概略。在此说明的务农系统主要用于种植麦子和稻子,但也可以用于小麦、玉米、胡萝卜、圆葱等各种农作物。该务农系统用于管理农田作业机进行的农田作业,优选作为云服务而构成,被登录的各地的务农者所利用。当然,该务农系统也可以由务农者个人所有,作为封闭的系统加以利用。The outline of the farming system of this invention is demonstrated using FIG. 1. FIG. The farming system described here is mainly used for growing wheat and rice, but can also be used for various crops such as wheat, corn, carrots, and onions. This farming system is used to manage the farm work performed by the farm work machine, and is preferably configured as a cloud service, and is used by farmers in registered localities. Of course, the farming system can also be used as a closed system by the individual farmer.
该务农系统由具有农田文件存储部51、作业计划制作部52、模拟文件制作部53、修正部54以及数据处理部55的云计算机系统构成,与进行农田作业的农田作业机之间交换涉及农田作业的信息。This farming system is composed of a cloud computer system including a farmland
农田文件存储部51存储有包含农田特征文件、农田作业履历文件以及农田收割文件的农田文件。农田特征文件包含各农田的地图数据、环境数据以及土壤数据。地图数据包含农田名、农田的地图位置、形状以及面积等。环境数据包含日照时间、雨量、通风以及农田地温等。土壤数据包含土质、表土深以及肥沃度等。这些数据以将农田以格子状分割成多个所获得的区间为单位进行记录。也就是说,数据分配在每个区间。一个区间的宽度优选为投入的农田作业机的作业宽度的倍数。当投入了作业宽度不同的多个农田作业机时,优选为这些作业宽度的最大公约数的倍数。区间长度优选为从1m至数m。并且,在农田文件中记录有每年度或每季度的作物种类的信息(稻、麦、玉米等)和品种信息(XX光米、OO小町米等)。The farmland
农田作业履历文件为经时构造文件,通过农田作业机实施的农田作业作为年度文件或季度文件被层级化。在农田作业履历文件中,以区间为单位记录有农田的农田作业的详细数据。记录在农田作业履历文件中的农田作业的种类为插秧作业、施肥作业(包含追肥作业)、施药作业、水管理作业、生长状况监视作业以及收割作业等。根据农田作业的种类选择投入的农田作业机。选择的农田作业机所实施的农田作业的详细数据从农田作业机或驾驶农田作业机的驾驶员的电子设备发送。例如,在施肥作业和施药作业中,从施肥作业机发送农田的每个区间的施肥量和施药量,并记录在农田作业履历文件中。The farm work history file is a file structured over time, and the farm work performed by the farm work machine is hierarchized as an annual file or a quarterly file. In the farm work history file, detailed data of farm work on farm fields are recorded in units of sections. The types of farm work recorded in the farm work history file are rice transplanting work, fertilization work (including top dressing work), pesticide application work, water management work, growth condition monitoring work, harvesting work, and the like. Select the input farm work machine according to the type of farm work. Detailed data of the farm work performed by the selected farm work machine is transmitted from the farm work machine or the electronic device of the driver who drives the farm work machine. For example, in the fertilization work and the chemical application work, the fertilizer application amount and the chemical application amount for each section of the farmland are transmitted from the fertilizer application machine, and recorded in the farmland operation history file.
农田收割文件也是经时构造文件,农田作业机所实施的农田作业作为年度文件或季度文件被层级化。记录在农田收割文件的数据为农田的每个区间的收量(收割量),当为稻子时,通过在收割时进行的味道测量获得的味道(水分和蛋白质成分)也记录在农田收割文件中。The farmland harvesting document is also a document that is structured over time, and the farmland work performed by the farmer is hierarchized as an annual document or a quarterly document. The data recorded in the field harvest file is the harvest amount (harvested amount) for each section of the field, and in the case of rice, the taste (moisture and protein content) obtained by the taste measurement performed at the time of harvest is also recorded in the field harvest file .
作业计划制作部52从农田文件存储部51中读取涉及指定了的指定农田的农田文件,并根据记录在该农田文件中的数据,制作对该指定农田需要进行的农田作业的农田作业计划。在农田作业计划中,还附带有选择的农田作业机进行符合该农田作业计划的农田作业所必须的作业参数(表示对行驶设备群1A和作业设备群1B的调整内容)。The operation
当涉及指定的农田的农田文件未存储在农田文件存储部51时,模拟文件制作部53制作用于该农田的模拟农田文件,并赋予作业计划制作部52。例如,当找到类似农田的涉及相同农田作业的农田作业履历文件时,能够援用该文件作为模拟农田文件。当未找到能够援用的农田作业履历文件时,模拟文件制作部53将数据未知(或空白)的农田文件作为模拟农田文件赋予作业计划制作部52。此时,作业计划制作部52制作由未知(空白)构成的农田作业计划。制作的农田作业计划中的未知(空白)被通过人为操作向修正部54发送指令从而输入的规定数据替换。When the farmland file related to the designated farmland is not stored in the farmland
对于数据全部记入的农田作业计划而言,也能够通过人为操作向修正部54发送指令,从而进行特定数据的重写。Even in a farm work plan in which all data is entered, it is possible to rewrite specific data by sending a command to the
农田作业机具有将在实施的农田作业中制作的农田作业数据通过数据通信网络NET发送给务农系统的功能。数据处理部55处理从农田作业机发送的农田作业数据,并记录在农田特征文件、农田作业履历文件以及农田收割文件中的任一个中。例如,若农田作业机为施肥作业机,则将肥料种类和施肥量作为农田作业数据进行发送,若农田作业机为插秧机,则将插植量、插植间隔等作为农田作业数据进行发送。并且,若农田作业机为联合收割机等收割作业机,则将收量、味道作为农田作业数据进行发送。大多数农田作业机具有通过GNSS(GPS等全球测位卫星系统)进行的本车位置计算功能,因此,各种农田作业数据以区间为单位生成。The farm work machine has a function of transmitting the farm work data created in the implemented farm work to the farming system through the data communication network NET. The
图2表示利用该务农系统进行农田作业管理的示意图。在该示意图中,作为农田特征文件,利用了以区间为单位的表示表土深的表土深图。并且,作为农田作业履历文件利用了由无人机获取的稻子的生长图,作为农田收割文件利用了收量图,二者均以区间为单位进行数据化。将表土深图、生长图以及收量图各自的以区间为单位的数据作为输入参数,输出表示以区间为单位的施肥量和车速的农田作业计划(施肥计划)。该农田作业计划附带有表示为了实现以区间为单位的施肥量的肥料送出量设定值和车速设定值的作业参数。因此,接收该农田作业计划的农田作业机(插秧机)利用该作业参数调整行驶设备群1A和作业设备群1B。当农田作业机的规格不能按作业参数进行调整时,尽量以得到相近的作业结果的方式修正作业参数,调整行驶设备群1A和作业设备群1B。在图1中,对上述作业参数配合农田作业机的规格进行调整的规格调整部64设置在农田作业机侧。代替该结构,规格调整部64也可以设置在云计算机系统侧。此时,当鉴于实际实施农田作业的农田作业机的规格,不能按照农田作业计划所包含的作业参数进行设定时,规格调整部64尽可能以与该作业参数接近的方式制作修正作业参数,并发送给农田作业机。FIG. 2 shows a schematic diagram of farm work management using the farming system. In this schematic diagram, a topsoil depth map representing the topsoil depth in units of intervals is used as the farmland characteristic file. In addition, the growth chart of the rice acquired by the drone was used as the farm work history file, and the yield chart was used as the farm field harvesting file, and both of them were digitized in units of sections. Using the data of each of the topsoil depth map, the growth map, and the yield map in units of sections as input parameters, a farm work plan (fertilization plan) representing the fertilization amount and vehicle speed in the units of sections is output. The farm work plan is accompanied by work parameters indicating a set value of a fertilizer delivery amount and a set value of a vehicle speed for realizing the fertilization amount in units of sections. Therefore, the farm work machine (rice transplanter) that received the farm work plan adjusts the traveling
下面,作为本发明的务农系统管理的农田作业的一个例子,对种植稻子的施肥作业进行说明。该施肥作业利用了作为农田作业机的图3所示的乘坐型插秧机。Next, as an example of the farm work managed by the farming system of the present invention, the fertilization work for planting rice will be described. This fertilization work utilized the riding type rice transplanter shown in FIG. 3 as a farm work machine.
如图3所示,插秧机具有乘坐型四轮驱动式行驶机体(以下称为机体1)。机体1具有:平行四连杆式的连杆机构11,以能够升降摆动的方式连结在机体1的后部;液压式升降缸11a,摆动驱动连杆机构11;秧苗插植装置3(作业设备群的一个例子),以能够横摆的方式连结在连杆机构11的后端部;以及施肥装置4(作业设备群的一个例子),从机体1的后端部架设至秧苗插植装置3;等。As shown in FIG. 3, a rice transplanter has a riding type four-wheel-drive type traveling body (henceforth a body 1). The body 1 has: a parallel four-link
机体1具有作为用于行驶的设备的车轮12、发动机13以及液压式无级变速装置14。车轮12具有能够转向操作的左右前轮12A和不能转向操作的左右后轮12B。发动机13和无级变速装置14装载在机体1的前部。来自发动机13的动力经由无级变速装置14等提供给前轮12A和后轮12B等。The body 1 has
秧苗插植装置3作为一个例子构成为8行插植型。秧苗插植装置3具有载秧台31、8行插植机构32等。该秧苗插植装置3通过未图示的各行离合器的控制,能够变更成2行插植、4行插植、6行插植等形式。The
载秧台31为载置8行毯状秧苗的基座。载秧台31以与毯状秧苗的左右宽度相对应的一定行程在左右方向上往返移动,每当载秧台31到达左右行程端部时,纵向移送机构33将载秧台31上的各毯状秧苗向载秧台31的下端以规定的间隔纵向移送。8个插植机构32为旋转式,以与插植行距相对应的一定间隔配置在左右方向上。并且,各插植机构32通过来自机体1的动力,从载置在载秧台31的各毯状秧苗的下端切取一株秧苗,并插植在整地后的泥土部。由此,在秧苗插植装置3的动作状态下,能够从载置在载秧台31的毯状秧苗取出秧苗并插植在水田的泥土部。The
如图4所示,秧苗插植装置3具有通过插植机构32调节取苗量的取苗量调节机构30。插植机构32经过形成于滑动引导载秧台31的下端的导轨31a的取苗口取出一株秧苗并进行插植。通过在上下方向对载秧台31和滑动引导载秧台31的下端的导轨31a进行位置变更,从而调节取苗量。As shown in FIG. 4 , the
取苗量调节机构30具有:带减速机构的取苗量调节马达36,为用于在上下方向上对载秧台31和导轨31a进行位置变更的执行器;以及扇形齿轮35,与设置在该取苗量调节马达36的输出轴的小齿轮啮合。并且,取苗量调节机构30具有:支承臂301,插入导轨31a的前部;以及支承轴302,以能够摆动的方式支承在该支承臂301。支承臂301和扇形齿轮35通过连结臂303连杆结合。The seedling
在扇形齿轮35的转动轴304设有检测扇形齿轮35的转动角度(取苗量)的取苗量传感器305。通过对取苗量调节马达36向一个方向驱动,从而使载秧台31和导轨31a向上升侧移动,通过对取苗量调节马达36向另一方向驱动,从而使载秧台31和导轨31a向下降侧移动。通过载秧台31和导轨31a的上下移动,能够改变取苗量。The
如图3所示,施肥装置4具有横长的料斗41、送出机构42、电动式鼓风机43、多个施肥管44以及设置于各行的开沟器45。料斗41存储颗粒状或粉末状的肥料。送出机构42以从发动机13传递的动力进行动作,从料斗41将2行肥料按规定量不断送出。As shown in FIG. 3, the
鼓风机43通过来自装载在机体1的电池(未图示)的电力进行动作,产生通过各送出机构42将送出的肥料向农田的泥面搬运的搬运风。施肥装置4通过鼓风机43等的连通切断操作,能够在将存储在料斗41中的肥料按规定量提供给农田的动作状态和停止提供的非动作状态之间切换。The
各施肥管44将由搬运风搬运的肥料引导至各开沟器45。各开沟器45配备在各整地浮板15。并且,各开沟器45与各整地浮板15共同升降,当进行各整地浮板15接地的作业行驶时,在水田的泥土部形成施肥槽,将肥料引导至施肥槽内。Each fertilization pipe 44 guides the fertilizer conveyed by the conveyance wind to each
如图4所示,施肥装置4具有能够变更调整送出机构42的肥料送出量的送出量调节机构40。送出量调节机构40具有:螺丝轴403,能够改变用于调节送出机构42的送出量的调节体402的位置;肥料调节马达404,经由齿轮使螺丝轴403向正向和逆向旋转;以及位置检测传感器405,检测调节体402基于螺丝轴403的旋转的变位位置;等。As shown in FIG. 4, the
如图3所示,机体1在其后部侧具有驾驶部20。驾驶部20具有前轮转向用方向盘21、通过进行无级变速装置14的变速操作调整车速的主变速杆22;能够进行副变速装置的变速操作的副变速杆23、能够进行秧苗插植装置3的升降操作和动作状态的切换等的作业操作杆25、具有显示(通知)各种信息并通知(输出)给操作员且接收各种信息的输入的触屏的通用终端9、以及操作者用驾驶座椅16等。并且,在驾驶部20的前方设置有收纳预备秧苗的预备秧苗框架17。As shown in FIG. 3 , the body 1 has a driving
方向盘21经由未图示的转向机构与前轮12A连结,通过方向盘21的旋转操作,能够调整前轮12A的转向角。并且,如图4所示,转向机构还连结有转向马达M1,在自动行驶时,根据来自控制单元6的指令使转向马达M1动作,由此调整前轮12A的转向角。并且,还具有用于自动操作主变速杆22的变速操作用马达M2,在自动行驶时,根据来自控制单元6的指令使变速操作用马达M2动作,由此调整无级变速装置14的变速位置。The
图5示出了表示能够与具有上述云计算机系统的务农云服务CS进行数据交换的插秧机的控制系统的控制框图。作为插秧机的控制系统的中枢的控制单元6与通信部81和通用终端9连接,通信部81与包含务农云服务CS的外部计算机之间进行数据交换。控制单元6被输入有来自测位单元8、自动切换开关27、行驶传感器群28以及作业传感器群29的信号。来自控制单元6的控制信号输出至行驶设备群1A和作业设备群1B。Fig. 5 is a control block diagram showing a control system of a rice transplanter capable of exchanging data with the farming cloud service CS having the above-mentioned cloud computer system. The
测位单元8输出用于计算机体1的位置和方位的测位数据。测位单元8包含接收来自全地球导航卫星系统(GNSS)的卫星的电波的卫星测位模块8A和检测机体1的三轴的倾斜和加速度的惯性测量模块8B。自动切换开关27为选择使机体1自动行驶的自动行驶模式和使机体1手动行驶的手动行驶模式的开关。行驶传感器群28包含检测转向角、车速、发动机转数等状态以及这些状态的设定值的各种传感器。作业传感器群29包含检测连杆机构11、秧苗插植装置3、施肥装置4的状态以及这些状态的设定值的各种传感器。The
行驶设备群1A例如包含转向马达M1和变速操作用马达M2,根据来自控制单元6的控制信号,通过控制转向马达M1调节转向角,通过控制变速操作用马达M2调节车速。The traveling
作业设备群1B例如包含升降缸11a、取苗量调节机构30以及送出量调节机构40。根据来自控制单元6的控制信号,通过控制取苗量调节马达36调节取苗量,通过控制肥料调节马达404调节施肥量。The
控制单元6具有行驶控制部61、作业控制部62、本车位置计算部63、规格调整部64以及作业结果文件制作部65。The
本车位置计算部63根据从测位单元8逐次发送的卫星测位数据,计算机体1的地图坐标(本车位置)。该插秧机能够自动行驶和手动行驶。在行驶控制部61,根据自动切换开关27的指令,设定有进行自动行驶的自动行驶模式或进行手动行驶的手动行驶模式中的任一个。在自动行驶模式下,自动行驶控制部611根据通过比较本车位置和目标行驶路径计算的横偏差和方位偏差,以使横偏差和方位偏差缩小的方式计算转向控制量。根据转向控制量控制转向马达M1,从而调整前轮12A的转向角。在手动行驶模式下,手动行驶控制部612根据方向盘21的操作量控制转向马达M1,从而调整前轮12A的转向角。The own vehicle
在自动行驶模式下,作业控制部62根据预先赋予的程序自动控制作业设备群1B,在手动行驶模式下,作业控制部62根据驾驶员的操作控制作业设备群1B。In the automatic travel mode, the
用图1说明如下,规格调整部64将由务农云服务CS发送的农田作业计划所包含的作业参数以符合该插秧机的规格的方式进行修正,制作修正作业参数,并赋予作业控制部62。1 , the
作业结果文件制作部65将插秧机基于农田作业计划实施的农田作业的作业结果进行数据化,从而制作作业结果文件。在该例子中,插秧机实施作为农田作业的施肥作业。因此,该作业结果文件包含作业日期时间、识别农田的数据、机体1的行驶轨迹、肥料种类以及以区间为单位的施肥量等。在行驶轨迹的数据化中,以能够识别非作业行驶的行驶轨迹和作业行驶的行驶轨迹的方式进行数据化。制作的作业结果文件通过通信部81上传至务农云服务CS。The work result
当农田作业为插秧作业时,在从插秧机上传至务农云服务CS的作业结果文件中,代替以区间为单位的施肥量,包含以区间为单位的秧苗插植量。并且,当农田作业为收割作业时,利用作为农田作业机的联合收割机,在作业结果文件中包含每个区间的收量和味道。当农田作业为表土作业时,作业结果文件中包含每个区间的表土深。并且,当农田作业为通过无人机等监视生长状态时,作业结果文件中包含以区间为单位的生长分布。如上所述,在以季度为单位(时序)实施的农田作业中制作的作业结果文件在数据处理部55以能够计算的方式数据化,并作为农田文件存储在农田文件存储部51。When the field operation is rice transplanting, in the operation result file uploaded from the rice transplanter to the farming cloud service CS, instead of the fertilization amount in the unit of interval, the amount of seedling planting in the unit of interval is included. Furthermore, when the farm work is harvesting work, using a combine which is a farm work machine, the work result file includes the yield and taste for each section. When the farmland operation is topsoil operation, the topsoil depth of each interval is included in the operation result file. In addition, when the farm work is to monitor the growth state by drones or the like, the work result file includes the growth distribution in units of sections. As described above, the work result files created in the field work performed on a quarterly basis (sequence) are converted into computable data in the
在作业计划制作部52,将从存储在农田文件存储部51的农田文件中读取的数据作为输入参数,制作包含作业参数的农田作业计划。作业计划制作部52的农田作业计划的制作如图6所示。在图6所示的例子中,利用2016年度和2017年度的种植稻子的表土深文件、施肥量文件和收量文件、以及2018年度的表土深文件,制作2018年度的施肥计划。作为优选,这些农田文件为用于将要进行作业计划而指定的指定农田的农田文件,当上述农田文件缺失时,如图1所示,能够用模拟文件替代。模拟文件中的数据援用了类似农田的农田文件的数据。当上述农田文件不存在时,采用具有默认数据的默认农田文件。In the work
将从表土深文件中读取的以区间为单位的表土深数据、从施肥量文件中读取的以区间为单位的施肥量数据、以及从收量文件中读取的以区间为单位的收量数据作为输入参数输入至作业计划制作部52。在该例子中,表示每个区间的施肥量的施肥计划作为作业计划输出,因此,输入至设置在作业计划制作部52的计算单元群中的一个用于决定施肥量的作业计划计算单元52a。该作业计划计算单元52a将包含在过去的农田文件中的以区间为单位的数据作为输入参数,从而输出以区间为单位的施肥量。在该例子中的作业计划计算单元52a中,求出2016年度和2017年度的每个区间的表土深、施肥量和收量之间的相关关系,通过将2018年度的每个区间的表土深分配在该每个区间的相关关系中,从而计算2018年度的每个区间的施肥量。在该实施方式中,作业计划计算单元52a以采用多个样本预先进行学习的学习型计算单元的方式构建。上述作业计划计算单元52a将由过去年度的以区间为单位的表土深、以区间为单位的施肥量以及以区间为单位的收量的组合构成的多个数据作为学习数据,根据这些数据的相关关系,输出以区间为单位的表土深、以区间为单位的施肥量以及以区间为单位的收量中的任一个数据的最优解。The topsoil depth data in intervals read from the topsoil depth file, the fertilization amount data in intervals read from the fertilization rate file, and the income in intervals read from the yield file. The quantity data is input to the work
在作业计划计算单元52a中,在施肥量的计算中,能够选择要优先的务农目标项目。例如,作为务农目标项目,有收量、味道、减少农药、轻劳动、低成本、高效益等。在此,作为需要优先的务农目标项目,能够从收量、成本、味道中选择1个。在收量优先时,输出表示利用能够获得高收量的相关关系计算的施肥量的施肥计划。在成本优先时,输出表示利用在能够维持平均收量和味道的范围内的最小施肥量的相关关系计算的施肥量的施肥计划。在味道优选时,输出表示利用能够获得好味道的相关关系计算的施肥量的施肥计划。需要优先的务农目标项目随着各务农者的不同而不同,因此,在进行计算前,以在符合需要重视的务农目标项目的计算模式下动作的方式调整作业计划计算单元52a。在该调整中,通过变更作业计划计算单元52a的计算式的权重系数,作业计划计算单元52a成为符合需要优先的务农目标项目的计算单元。In the operation plan calculation means 52a, it is possible to select a farming target item to be prioritized in the calculation of the fertilization amount. For example, as agricultural target items, there are yield, taste, reduction of pesticides, light labor, low cost, and high efficiency. Here, as a farming target item that needs priority, one can be selected from yield, cost, and taste. When the yield is given priority, a fertilization plan representing the fertilization amount calculated using the correlation that high yield can be obtained is output. When priority is given to cost, a fertilization plan showing the fertilization amount calculated using the correlation of the minimum fertilization amount within the range in which the average yield and the taste can be maintained is output. When the taste is preferred, a fertilization plan showing the fertilization amount calculated using the correlation for obtaining a good taste is output. Since the farming target item that needs to be prioritized varies with each farmer, the work plan calculation unit 52a is adjusted so as to operate in the calculation mode corresponding to the farming target item that needs attention before the calculation is performed. In this adjustment, by changing the weighting coefficient of the calculation formula of the work plan calculation means 52a, the work plan calculation means 52a becomes a calculation means for the farming target item that needs priority.
嵌入作业计划制作部52的施肥量/作业参数表52b将表示以区间为单位的施肥量的施肥计划作为输入,输出做出该施肥量所需的插秧机的作业参数。由于该作业参数也以每个区间为单位决定,因此,以区间为单位调节作业参数,由此,插秧机能够以区间为单位,按照施肥计划的施肥量向农田投放肥料。The fertilization amount/operation parameter table 52b embedded in the operation
(第一实施方式的其他实施方式)(Other embodiments of the first embodiment)
(1)在图5所示的实施方式中,修正部54设置在务农云服务CS,但也可以设置在农田作业机的控制单元6或通用终端9,还可以设置在务农云服务CS和农田作业机双方。(1) In the embodiment shown in FIG. 5 , the
(2)在图5所示的实施方式中,农田作业机为能够自动行驶的车辆,也可以为不能够自动行驶的车辆。此时,根据来自测位单元8的测位数据计算本车位置(作业位置),通过组合该本车位置和作业结果,从而制作作业结果文件。(2) In the embodiment shown in FIG. 5 , the farm working machine is a vehicle capable of autonomous travel, but may be a vehicle not capable of autonomous travel. At this time, the host vehicle position (work position) is calculated from the positioning data from the
(3)在图6所示的例子中,作业计划计算单元52a以学习型计算单元构成,但也可以代替该结构,根据1个以上农田文件(例如,生长分布文件、表土深分布文件、收量分布文件等)的以区间为单位的数据,以导出特定的作业计划(例如,施肥计划)的以区间为单位的作业量的一元或多元表构成。(3) In the example shown in FIG. 6, the operation plan calculation unit 52a is constituted by a learning-type calculation unit, but instead of this configuration, it may be based on one or more farmland files (for example, a growth distribution file, a topsoil depth distribution file, a The interval-unit data of the amount distribution file, etc.) is composed of a univariate or multivariate table that derives the interval-unit operation amount of a specific work plan (for example, a fertilization plan).
(4)当为作业宽度可变的农田作业机时,也可以采用制作与作业宽度的变更连动的具有区间宽度的作业计划的结构。并且,也可以采用制作与农田作业机进行的农田作业中的最小应答时机相配合的具有行驶方向上的区间长度的作业计划。(4) In the case of a farm working machine with a variable working width, it is also possible to adopt a configuration in which a working plan having a section width is created in conjunction with the change of the working width. In addition, it is also possible to prepare a work plan having a section length in the traveling direction in accordance with the minimum response timing in the field work performed by the field work machine.
(5)本发明能够适用于管理农田作业机进行的农田作业的务农系统。(5) The present invention can be applied to a farming system for managing farm work performed by a farm working machine.
(第二实施方式)(Second Embodiment)
下面,参照图7至图14对第二实施方式进行说明。对于与第一实施方式相同的结构,省略其说明。Next, the second embodiment will be described with reference to FIGS. 7 to 14 . The description of the same structure as that of the first embodiment is omitted.
用图7说明本发明的务农系统的概略。务农系统主要用于种植麦子和稻子,也可以用于小麦、玉米、胡萝卜、圆葱等各种农作物。该务农系统适合管理农田作业机进行的农田作业,特别是施肥作业和药剂散布作业,由计算机系统构成。该务农系统既可以构建成务农者个人(独立地)利用的计算机系统,又可以构建成多个务农者共同利用的云计算机系统。务农者利用该务农系统计划被区分成多个区间的农田的农田作业,并根据该计划使农田作业机进行作业行驶。The outline of the farming system of this invention is demonstrated using FIG. 7. FIG. The farming system is mainly used to grow wheat and rice, but can also be used for various crops such as wheat, corn, carrots, and onions. The farming system is suitable for managing farm operations performed by farm work machines, especially fertilization operations and chemical distribution operations, and is composed of a computer system. The farming system can be constructed as a computer system used by farmers individually (independently), or as a cloud computer system commonly used by a plurality of farmers. Using this farming system, a farmer plans farmland work on the farmland divided into a plurality of sections, and drives the farmland working machine to work on the basis of the plan.
务农系统具有作为基本构成要件的数据存储部151、作业计划图制作部152、作业预测图制作部153、作业实绩图制作部154以及显示控制部155。该实施方式的务农系统还具有坐标转换部156和区间数据转换部157。并且,务农系统与为了进行农田作业而投入的农田作业机之间能够直接(利用数据通信网)或间接(利用可搬运型存储器)进行数据交换。The farming system includes a
数据存储部151将由该务农系统生成的全部数据、以及从农田作业机发送的数据以每个农田为单位进行存储。数据以每个农田为单位存储,该数据的种类为农田的特征数据、农田作业计划数据以及农田实绩数据等。The
作业计划图制作部152将务农者设立的农田作业计划进行数据化,制作表示每个区间的农田作业的计划的作业计划图。在该作业计划图中,附带有包含表示基于该作业计划图进行的农田作业的内容的作业内容数据、以及表示进行农田作业的农田作业车的作业规格(作业宽度、每单位距离的作业量、车速等)的规格数据的农田作业机数据。作业预测图制作部153根据由作业计划图制作部152制作的作业计划图,模拟农田作业,从而制作作为该模拟结果的作业预测图。在该模拟之前,选择投入该农田作业的农田作业机,将选择的农田作业机的作业宽度和作业性能等规格作为模拟输入参数赋予作业预测图制作部153。作业实绩图制作部154根据实施农田作业的农田作业机生成的作业数据制作作业实绩图。例如,当农田作业机为施肥作业机时,作业实绩图中包含每个区间的施肥量。The work plan
农田作业机的相对于行驶方向的横断方向的区间长度优选为,与根据农田作业机的规格决定的作业宽度一致,或者为该作业宽度的倍数。农田作业机的行驶方向上的合适的最小区间长度依赖于作业控制速度。也就是说,行驶方向上的区间长度依赖于装备在农田作业机的作业设备的控制应答性。即使缩小行驶方向上的区间长度,当对该连续区间没有分配有意义的作业结果值时,该较短区间也成为浪费。因此,行驶方向上的区间长度在最大的控制应答性上为分配了有意义的作业结果值的区间长度以上。作业计划图和作业预测图作为农田作业计划数据,作业实绩图作为农田实绩数据,存储在数据存储部151。The section length of the farm working machine in the transverse direction with respect to the traveling direction is preferably the same as the working width determined according to the specifications of the farm working machine, or a multiple of the working width. A suitable minimum section length in the direction of travel of the farm working machine depends on the work control speed. That is, the section length in the traveling direction depends on the control responsiveness of the work equipment equipped in the farm working machine. Even if the length of the section in the traveling direction is reduced, if no meaningful work result value is assigned to the continuous section, the short section is wasted. Therefore, the section length in the traveling direction is equal to or larger than the section length to which a meaningful work result value is assigned in terms of maximum control responsiveness. The work plan map and the work forecast map are stored in the
显示控制部155提取存储在数据存储部151的数据,并显示在显示器158上。例如,能够将作业计划图、作业预测图以及作业实绩体中的任一个、或者其中至少2个以能够相互比较的方式显示在显示器158上。因此,务农者在进行本年度的施肥计划时,能够查看显示在显示器158上的过去的农田作业的状况。The
务农者在头脑中描绘农田的样子,一边参照上年度的施肥作业和收割作业的结果,一边设立农田作业计划。因此,作为作业计划图制作部152制作的作业计划图所使用的坐标系(第一坐标系),在此,采用了将给农田划界的2个境界线作为纵轴(在图7中用Y表示)和横轴(在图7中用X表示)的农田坐标系。与此相对,作业预测图和作业实绩图是根据由卫星测位系统计算本车位置的农田作业车的作业轨迹制作的,因此,作为用于这些图的坐标系(第二坐标系),在此,采用了将从卫星测位数据获取的纬度和经度作为纵轴(在图7中用M表示)和横轴(在图7中用L表示)的卫星测位坐标系。因此,在将作业计划图赋予作业预测图制作部153和作业实绩图制作部154之前,坐标转换部156将作业计划图的数据从第一坐标系向所述第二坐标系进行坐标转换。Farmers draw a picture of the farmland in their minds, and set up a farmland operation plan while referring to the results of the previous year's fertilization and harvesting operations. Therefore, as the coordinate system (first coordinate system) used for the work plan chart created by the work plan
在作业计划图中,采用容易设立作业计划的区间形状,相对地,作业预测图和作业实绩图所使用的区间形状由农田作业机的作业宽度来规定。因此,在此,作业计划图采用3m×3m的正方形区间(计划区间),在作业预测图中,农田作业车的作业宽度为2m,因此,采用2m×2m的正方形区间(预测区间)。也就是说,区间的形状在作业计划图和作业预测图中不同。因此,在将作业计划图赋予作业预测图制作部153和作业实绩图制作部154之前,通过坐标转换部156进行坐标转换,并且,区间数据转换部157进行将分配在作业区间的作业计划数据的值(区间数据值)分配在作业预测图的区间的区间数据转换。此时,通过将与作为目标的预测区间相对应的位置的计划区间和位于该计划区间的周边的计划区间的区间数据值的平均值(算数平均值或加权平均值)除以计划区间的面积获得的数据密度乘以预测区间的面积,从而计算作为目标的预测区间的区间数据值。通过将该计算处理对于全部预测区间进行,从而能够完成从作业计划图到作业预测图的区间数据的转换。In the work plan map, a section shape that makes it easy to set up a work plan is adopted, while the section shape used in the work forecast map and the work performance map is defined by the work width of the farm work machine. Therefore, here, a 3m×3m square section (planned section) is used in the work plan map, and a 2m×2m square section (prediction section) is used because the working width of the farm work vehicle is 2m in the work forecast map. That is, the shape of the interval is different between the job plan graph and the job forecast graph. Therefore, the coordinate
图8示出了该插秧机的控制系统和构建上述务农系统的外部计算机系统105的控制框图。构成插秧机的控制系统的中枢的控制单元6连接在与外部计算机系统105之间进行数据交换时使用的通信部81和设置在插秧机的通用终端9。在通用终端9构建了生成作为自动行驶时的目标的行驶路径的行驶路径生成部91。控制单元6输入有来自测位单元8、自动切换开关27、行驶传感器群28以及作业传感器群29的信号。来自控制单元6的控制信号输出至行驶设备群1A和作业设备群1B。FIG. 8 shows the control block diagram of the control system of this rice transplanter and the
测位单元8输出用于计算机体1的位置和方位的测位数据。测位单元8包含有接收来自全地球导航卫星系统(GNSS)的卫星的电波的卫星测位模块8A、和检测机体1的三轴的倾斜和加速度的惯性测量模块8B。自动切换开关27为选择沿着由行驶路径生成部91生成的行驶路径使机体1自动行驶的自动行驶模式或使机体1手动行驶的手动行驶模式的开关。行驶传感器群28包含检测转向角、车速、发动机转数等状态以及这些状态的设定值的各种传感器。作业传感器群29包含检测连杆机构11、秧苗插植装置3以及施肥装置4的状态以及这些状态的设定值的各种传感器。The
行驶设备群1A例如包含转向马达M1和变速操作用马达M2,根据来自控制单元6的控制信号,通过控制转向马达M1调节转向角,通过控制变速操作用马达M2调节车速。The traveling
作业设备群1B包含例如升降缸11a、取苗量调节机构30以及送出量调节机构40。根据来自控制单元6的控制信号,通过控制取苗量调节马达36(参照图4)调节取苗量,通过控制肥料调节马达404(参照图4)调节施肥量。The
控制单元6具有行驶控制部61、作业控制部62、本车位置计算部63、作业参数设定部164以及作业数据制作部165。The
本车位置计算部63根据从测位单元8逐次发送的卫星测位数据,计算机体1的地图坐标(本车位置)。该插秧机能够进行自动行驶和手动行驶,行驶控制部61根据自动切换开关27的指令,设定进行自动行驶的自动行驶模式、或进行手动行驶的手动行驶模式中的任一模式。在自动行驶模式下,自动行驶控制部611根据通过比较本车位置和目标行驶路径计算的横偏差和方位偏差,以缩小横偏差和方位偏差的方式计算转向控制量。根据转向控制量控制转向马达M1,从而调整前轮12A的转向角。在手动行驶模式下,手动行驶控制部612根据方向盘21的操作量,通过控制转向马达M1,从而调整前轮12A的转向角。The own vehicle
在自动行驶模式下,作业控制部62根据预先获得的程序自动控制作业设备群1B,在手动行驶模式下,作业控制部62根据驾驶员的操作控制作业设备群1B。In the automatic travel mode, the
作业参数设定部164根据从外部计算机系统105下载的作业计划图所包含的作业内容,为作业设备群1B设定作业参数。该作业内容以农田的每个区间为单位进行设定。在农田作业为施肥作业时,作业参数设定部164根据由本车位置计算部63计算的本车位置,识别开沟器45所处的区间,计算作为与分配在该识别的区间的肥料投入量相对应的作业参数的调整量。以实现计算的调整量的方式控制送出量调节机构40。The work
作业数据制作部165将插秧机基于农田作业计划实施的农田作业的作业结果进行数据化生成作业数据,从而制作包含该作业数据的作业结果文件。当插秧机实施作为农田作业的施肥作业时,该作业结果文件中包含作业日期时间、识别农田的数据、机体1的行驶轨迹、肥料种类以及每个区间的施肥量等。制作的作业结果文件通过通信部81上传至外部计算机系统105。The work
当农田作业为插秧作业时,在从插秧机向外部计算机系统105上传的作业结果文件的作业数据中,代替每个区间的施肥量,包含每个区间的秧苗插植量。当农田作业为收割作业时,采用作为农田作业机的联合收割机,作业结果文件的作业数据包含每个区间的收量和味道。当农田作业为表土作业时,作业结果文件的作业数据包含每个区间的表土深。When the field work is rice transplanting work, the work data of the work result file uploaded from the rice transplanter to the
外部计算机系统105具有与用图7说明的务农系统相同的功能,因而省略其说明。在此,对在务农者利用该务农系统设立作业计划,经过模拟,制作向插秧机发送的最终作业计划图的过程中,显示在显示器158的内容的一部分进行说明。Since the
图9示出了通过作业计划图制作部152制作的显示在显示器158的作业计划图(在此为施肥计划图)。本年度的施肥计划图是务农者参照同一农田的上一年度的收量实绩图(作业实绩图的一个例子)输入每个区间的施肥量而制作的。只要设定了收量和施肥量之间的一定的关系,该作业计划图制作部152就能够自动根据收量实绩图制作施肥计划图。自动制作的施肥计划图显示在显示器界面上,并且,务农者能够通过指定任意的区间修改其施肥量。FIG. 9 shows a work plan (here, a fertilization plan) created by the work
图10示出了通过作业预测图制作部153制作,并显示在显示器158的作业预测图(在此为施肥预测图)。作业预测图制作部153具有模拟计算功能,以在将输入的施肥计划图所包含的每个区间的施肥量的肥料通过指定的施肥作业机投放时的肥料分布,作为施肥预测图进行计算。在该模拟过程中,指定的施肥作业机的作业宽度为区间一边的长度。插秧机和施肥作业机通过各行离合器等的控制能够变更作业宽度,因此,也可以采用随着变更了的作业宽度而变更区间宽度的可变区间宽度。区间的另一边的长度即施肥作业机的行驶方向上的区间长度根据肥料投放间隔的不同能够采用不同的值。然而,小于投放间隔的区间长度会产生浪费区间,因此不采用。如图11所示,制作的施肥预测图与施肥计划图并排显示。上述显示器界面用于施肥计划的好坏判断。在图11中,为了便于比较,施肥计划图与施肥预测图并排显示,也可以代替该结构,使施肥计划图和施肥预测图以能够选择的方式重叠显示。FIG. 10 shows an operation prediction map (here, a fertilization prediction map) created by the operation prediction
图12示出了通过作业实绩图制作部154制作的显示在显示器158的作业实绩图(在此为施肥实绩图)。作业实绩图制作部154由插秧机的作业数据制作部165制作,根据上传至外部计算机系统105的作业结果文件的作业数据所包含的每个区间的施肥量,制作施肥实绩图。当模拟与实绩的作业的作业宽度不同时,作业预测图与作业实绩图也可以采用不同尺寸的区间。作业结果文件包含插秧机的行驶轨迹,因此,也能够在施肥实绩图上使进行施肥作业的插秧机的行驶轨迹重叠显示。在图12中,以虚线表示行驶轨迹的一部分。在图13的显示器界面图中,施肥计划图与施肥实绩图并排显示,在图14的显示器界面图中,施肥预测图和施肥实绩图并排显示。务农者评价图13的显示器界面,从而能够探讨施肥计划与实际的施肥实绩的不同之处、以及产生较大差别的地点。并且,通过图14的显示器界面观察比较模拟结果和实绩,从而能够发现模拟的改进点。FIG. 12 shows a work record graph (here, a fertilization record graph) created by the work record
(第二实施方式的其他实施方式)(Other embodiments of the second embodiment)
(1)在图8所示的实施方式中,务农系统由外部计算机系统105构建,也可以在通用终端9等农田作业机侧构建。或者,也可以分配在外部计算机系统105和通用终端9来构建。(1) In the embodiment shown in FIG. 8 , the farming system is constructed by the
(2)在上述实施方式中,农田作业机为能够自动行驶的车辆,也可以为不能够自动行驶的车辆。此时,根据来自测位单元8的测位数据计算本车位置(作业位置),组合该本车位置和作业结果,从而制作作业实绩图。在手动行驶时,由行驶路径生成部91生成的行驶路径用作行驶辅助图。(2) In the above-described embodiments, the farm working machine is a vehicle capable of autonomous driving, but may be a vehicle that is not capable of autonomous driving. At this time, the own vehicle position (work position) is calculated based on the positioning data from the
(3)当为作业宽度可变的农田作业机时,也可以采用制作具有与作业宽度的变更连动的区间宽度的作业预测图和作业实绩图。并且,也可以采用制作配合农田作业机进行的农田作业的最小应答时机的具有行驶方向上的区间长度的作业预测图和作业实绩图的结构。(3) In the case of a farm working machine with a variable working width, it is also possible to create a work forecast map and an actual work performance map having a section width linked to the change of the work width. In addition, it is also possible to adopt a configuration in which a work forecast map and a work performance map with section lengths in the traveling direction are created in accordance with the minimum response timing of the farm work performed by the farm work machine.
(4)本发明在上述实施方式中作为农田作业机采用了带施肥装置的插秧机,此外,施肥专用机等也能够组装进本发明的务农系统。(4) In the present invention, a rice transplanter with a fertilization device is employed as the farm working machine in the above-described embodiments, but a dedicated machine for fertilization and the like can also be incorporated into the farming system of the present invention.
Claims (16)
Translated fromChineseApplications Claiming Priority (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019004537AJP7158291B2 (en) | 2019-01-15 | 2019-01-15 | farming system |
| JP2019004538AJP7158292B2 (en) | 2019-01-15 | 2019-01-15 | farming system |
| JP2019-004538 | 2019-01-15 | ||
| JP2019-004537 | 2019-01-15 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111435489Atrue CN111435489A (en) | 2020-07-21 |
Family
ID=71580421
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010040611.4APendingCN111435489A (en) | 2019-01-15 | 2020-01-15 | Agriculture dealing system |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR20200088768A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN111435489A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114303614A (en)* | 2020-10-09 | 2022-04-12 | 迪尔公司 | Graph generation and control system |
| CN119698999A (en)* | 2023-09-26 | 2025-03-28 | 广州极飞科技股份有限公司 | UAV seedling throwing control method and device, seedling throwing system and readable storage medium |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1713198A (en)* | 2004-06-22 | 2005-12-28 | 东芝解决方案株式会社 | Culturing plan management server, method and program |
| CN103562949A (en)* | 2012-05-09 | 2014-02-05 | 株式会社久保田 | Farm operation support system |
| CN104077646A (en)* | 2013-03-28 | 2014-10-01 | 株式会社久保田 | Agricultural management system and agricultural machine |
| JP2015049864A (en)* | 2013-09-04 | 2015-03-16 | 株式会社クボタ | Agricultural support system |
| CN106461807A (en)* | 2014-04-21 | 2017-02-22 | 克莱米特公司 | Generating an agriculture prescription |
| CN108510107A (en)* | 2018-03-07 | 2018-09-07 | 深圳远佳智慧科技有限公司 | A kind of agricultural planting guidance method, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6363579B2 (en) | 2015-09-30 | 2018-07-25 | 株式会社クボタ | Field management system |
- 2020
- 2020-01-06KRKR1020200001233Apatent/KR20200088768A/ennot_activeCeased
- 2020-01-15CNCN202010040611.4Apatent/CN111435489A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1713198A (en)* | 2004-06-22 | 2005-12-28 | 东芝解决方案株式会社 | Culturing plan management server, method and program |
| CN103562949A (en)* | 2012-05-09 | 2014-02-05 | 株式会社久保田 | Farm operation support system |
| CN104077646A (en)* | 2013-03-28 | 2014-10-01 | 株式会社久保田 | Agricultural management system and agricultural machine |
| JP2015049864A (en)* | 2013-09-04 | 2015-03-16 | 株式会社クボタ | Agricultural support system |
| CN106461807A (en)* | 2014-04-21 | 2017-02-22 | 克莱米特公司 | Generating an agriculture prescription |
| CN108510107A (en)* | 2018-03-07 | 2018-09-07 | 深圳远佳智慧科技有限公司 | A kind of agricultural planting guidance method, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114303614A (en)* | 2020-10-09 | 2022-04-12 | 迪尔公司 | Graph generation and control system |
| CN119698999A (en)* | 2023-09-26 | 2025-03-28 | 广州极飞科技股份有限公司 | UAV seedling throwing control method and device, seedling throwing system and readable storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20200088768A (en) | 2020-07-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102639478B1 (en) | Farming system | |
| CN111093355B (en) | Agricultural support device and agricultural support system | |
| JP7158291B2 (en) | farming system | |
| US10362733B2 (en) | Agricultural harvester configured to control a biomass harvesting rate based upon soil effects | |
| US8738244B2 (en) | Agricultural machine having a system for automatic setting of a working parameter, and associated method | |
| CN112889007B (en) | Use of spatially distributed values specific to an agronomic field to improve a digital nutrient model | |
| CN113163710B (en) | System and method for identifying and utilizing test sites in an agricultural field | |
| US6070673A (en) | Location based tractor control | |
| US20180035622A1 (en) | Method for optimizing an operating parameter of a machine for application of agricultural material to a field and a corresponding machine | |
| JP7158292B2 (en) | farming system | |
| JP2023509344A (en) | Responsive farming systems that are exceptionally optimized during the season | |
| UA126111C2 (en) | SYSTEMS AND METHODS FOR IMAGE CAPTURE AND ANALYSIS OF AGRICULTURAL FIELDS | |
| CN112889063A (en) | Automatic yield prediction and seed rate recommendation based on weather data | |
| JP7206118B2 (en) | farming system | |
| CN114846431A (en) | Method for generating field regions for agricultural data analysis based on conditional data file generation | |
| EP4445711A1 (en) | A method and system for estimating performance for position-specific control of an agricultural machine | |
| WO2023106158A1 (en) | Route planning system for automatically operated farm machine | |
| JP2020004438A (en) | Farm field management system | |
| CN111435489A (en) | Agriculture dealing system | |
| JP7080627B2 (en) | Agricultural support system and agricultural support equipment | |
| JP2022036524A (en) | Work management system, work management method, and work management program | |
| JP6938356B2 (en) | Agricultural support system and agricultural support equipment | |
| Fulton et al. | GPS, GIS, Guidance, and Variable‐rate Technologies for Conservation Management | |
| JP2022040342A (en) | Farming system | |
| Ayanniran et al. | Design and Implementation of Robotic Maize Seed Planter |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |