CN111428938A - Power transmission network scheme optimization method based on function difference and full life cycle - Google Patents
Power transmission network scheme optimization method based on function difference and full life cycleDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111428938A CN111428938ACN202010289415.0ACN202010289415ACN111428938ACN 111428938 ACN111428938 ACN 111428938ACN 202010289415 ACN202010289415 ACN 202010289415ACN 111428938 ACN111428938 ACN 111428938A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- scheme
- evaluation
- index
- indicators
- transmission network
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/04—Forecasting or optimisation specially adapted for administrative or management purposes, e.g. linear programming or "cutting stock problem"
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/06—Resources, workflows, human or project management; Enterprise or organisation planning; Enterprise or organisation modelling
- G06Q10/063—Operations research, analysis or management
- G06Q10/0639—Performance analysis of employees; Performance analysis of enterprise or organisation operations
- G06Q10/06393—Score-carding, benchmarking or key performance indicator [KPI] analysis
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/06—Energy or water supply
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Educational Administration (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Water Supply & Treatment (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Supply And Distribution Of Alternating Current (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及输电网方案投资效益评估领域,具体地,涉及一种基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选方法。The invention relates to the field of investment benefit evaluation of transmission network schemes, in particular to a method for optimizing transmission network schemes based on functional differences and full life cycle.
背景技术Background technique
输电网规划在电网规划中处于举足轻重的地位,其主要规划根据电力系统中负荷的增长及大电源的发展,对输电网进行科学的新建或改造。伴随着不断深化的电力改革与大规模新能源接入带来的挑战,直接由优化模型得出满足可靠性、经济型、安全性、灵活性、适应性等各维度的理想方案十分困难,并会导致约束条件与决策变量的成指数增长,使得规划模型的难以求解。虽然启发式智能算法得到了大规模的应用,但其容易陷入局部最优解的缺点在面对如此复杂模型依然难以保证准确性。因此,目前输电网规划往往通过简化约束条件,产生多个有竞争力的可行性方案,通过建立综合评估体系,综合评估各技术路线的收益,在多个难以取舍的方案中选出一个最优方案,以期在满足约束条件下,实现投资效益的最大化。因此从输电网规划特点出发,开展全面、目的性明确的综合评价具有重要的理论与应用意义。Transmission network planning plays an important role in power grid planning. Its main planning is to scientifically build or transform the transmission network according to the growth of the load in the power system and the development of large power sources. With the challenges brought about by the deepening power reform and large-scale new energy access, it is very difficult to directly obtain an ideal solution that satisfies reliability, economy, safety, flexibility, adaptability and other dimensions from the optimization model. It will lead to the exponential growth of constraints and decision variables, making the planning model difficult to solve. Although the heuristic intelligent algorithm has been applied on a large scale, it is easy to fall into the local optimal solution, and it is still difficult to guarantee the accuracy in the face of such a complex model. Therefore, the current transmission network planning often generates multiple competitive and feasible schemes by simplifying the constraints. By establishing a comprehensive evaluation system to comprehensively evaluate the benefits of each technical route, an optimal one is selected from among multiple difficult-to-choose schemes. In order to meet the constraints, to maximize the return on investment. Therefore, starting from the characteristics of transmission network planning, it is of great theoretical and practical significance to carry out comprehensive and purposeful comprehensive evaluation.
现阶段输电网方案的综合评价决策主要从指标体系和评价决策方法开展了大量的研究。在指标体系方面:文献“曹芳.基于两级模糊综合评判的输变电工程方案决策研究[J].水电能源科学,2010,28(09):145-147.”从工程管理与监理方面考虑,缺乏对电网方案在运行安全与效益方面的评估。文献“王滔.输电网规划方案投资价值评估和优先级排序研究[D].华南理工大学,2016.”从提升输电网可靠性贡献角度出发,构建了基于可靠性贡献值的投资价值综合指标。文献“顾洁,秦玥,包海龙,等.基于熵权与系统动力学的配电网规划动态综合评价[J].电力系统保护与控制,2013,41(01):76-83.”从系统动力学的角度分析了配电网规划方案的技术经济评价的关键影响因素,文献“电力市场下基于实物期权理论的电网投资经济评价[J].电网技术,2007,(S1):78-80.”提出了经济学中包含投资汇率、投资回收周期和内部收益率等指标用以分析方案的经济效益。文献“胡殿刚,张雪佼,陈乃仕,等.新能源发电方案多维度后评价方法体系研究[J].电力系统保护与控制,2015,43(04):10-17.”开展了技术性能、经济效益、社会多个维度构建评估指标体系,更加能体现电力企业作为公共事业单位承担的社会责任。评估方法的角度上:文献“聂宏展,聂耸,乔怡,等.基于主成分分析法的输电网规划方案综合决策[J].电网技术,2010,34(06):134-138.”采用主成分分析法避免依赖专家决策中指标权重具有主观随意的特定。文献“高庆敏,张乾业.基于SE-DEA的交叉效率模型的城市电网规划综合评判决策[J].电力系统保护与控制,2011,39(08):60-64.”针对综合评判性因素的复杂性问题及超效率数据包络分相似(SE-DEA)模型,提出了基于SE-DEA的交叉效率评判模型。文献“王瑞莲,赵万里.基于模糊决策的城市高压输电网规划方案评价方法[J].电网技术,2013,37(02):488-492.”与“曹芳.基于两级模糊综合评判的输变电工程方案决策研究[J].水电能源科学,2010,28(09):145-147.”等方案采用了模糊数学与层次分析法的结合,定量指标与定性指标的组合选择。近年来,文献“欧阳森,陈丹伶,刘丽媛.考虑用户需求的配电网规划对象选优分析方法[J].电测与仪表,2018,55(23):15-21.”与“李龙.基于LCC理论的输电网规划方案评价研究[D].浙江大学,2012.”组合赋权法综合了决策者的决策偏好与数据的隐藏数据特征,逐渐开始了在投资决策中的应用。综上,目前研究中评价指标体系固定且单一,不具备自适应能力,鲜有从投资目的或类型角度出发,制定不同类型方案评估偏向性不同的评估决策指标体系。针对投资方案经济性方面,多采用经济学指标,忽略了电力系统自身的特点,且面临着忽视中长期成本,注重短期投资的不足。At present, a large number of researches have been carried out on the comprehensive evaluation and decision-making of transmission network schemes mainly from the index system and evaluation and decision-making methods. In the aspect of the index system: the literature "Cao Fang. Research on the decision-making of power transmission and transformation projects based on two-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation [J]. Hydropower and Energy Science, 2010, 28(09): 145-147." Considering from the aspects of project management and supervision , there is a lack of evaluation of the power grid scheme in terms of operational safety and efficiency. Literature "Wang Tao. Research on investment value evaluation and prioritization of transmission network planning scheme [D]. South China University of Technology, 2016." From the perspective of improving the reliability of transmission network, a comprehensive index of investment value based on reliability contribution value is constructed. . Literature "Gu Jie, Qin Yue, Bao Hailong, et al. Dynamic Comprehensive Evaluation of Distribution Network Planning Based on Entropy Weight and System Dynamics [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41(01): 76-83." From the perspective of system dynamics, the key influencing factors of the technical and economic evaluation of the distribution network planning scheme are analyzed. The document "Economic Evaluation of Power Grid Investment Based on Real Option Theory in the Electricity Market [J]. Power Grid Technology, 2007, (S1): 78 -80." put forward indicators in economics including investment exchange rate, investment payback period and internal rate of return to analyze the economic benefits of the program. The document "Hu Diangang, Zhang Xuejiao, Chen Naishi, et al. Research on multi-dimensional post-evaluation method system of new energy power generation scheme [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(04): 10-17." carried out technical performance, economic benefits , The construction of an evaluation index system from multiple dimensions of society can better reflect the social responsibility of power companies as public institutions. From the perspective of evaluation methods: Literature "Nie Hongzhan, Nie Song, Qiao Yi, et al. Comprehensive Decision-Making of Transmission Network Planning Scheme Based on Principal Component Analysis [J]. Power Grid Technology, 2010, 34(06): 134-138. "The principal component analysis method is used to avoid relying on the subjective and arbitrary specificity of indicator weights in expert decision-making. Literature "Gao Qingmin, Zhang Qianye. Comprehensive evaluation and decision-making of urban power grid planning based on SE-DEA cross-efficiency model [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2011, 39(08): 60-64." A cross-efficiency evaluation model based on SE-DEA is proposed. Literature "Wang Ruilian, Zhao Wanli. Evaluation method of urban high-voltage transmission network planning scheme based on fuzzy decision [J]. Power grid technology, 2013, 37(02): 488-492." and "Cao Fang. Transmission based on two-level fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Substation Engineering Scheme Decision-making Research [J]. Hydropower and Energy Science, 2010, 28(09): 145-147.” and other schemes adopt the combination of fuzzy mathematics and analytic hierarchy process, and the combination of quantitative indicators and qualitative indicators. In recent years, the literature "Ouyang Sen, Chen Danling, Liu Liyuan. Analysis method of distribution network planning object selection considering user needs [J]. Electrical Measurement and Instrumentation, 2018, 55(23): 15-21." and "Li Long . Research on evaluation of transmission network planning scheme based on LCC theory [D]. Zhejiang University, 2012. "Combination weighting method integrates decision-makers' decision-making preferences and data's hidden data characteristics, and gradually began to be applied in investment decision-making. To sum up, the evaluation index system in the current research is fixed and single, without self-adaptive ability. From the perspective of investment purpose or type, there are few evaluation decision-making index systems with different evaluation biases for different types of schemes. For the economic aspects of investment programs, economic indicators are mostly used, ignoring the characteristics of the power system itself, and facing the problem of ignoring medium and long-term costs and focusing on short-term investment.
上述研究存在着没有考虑全寿命周期成本的方案投资成本,对计及全寿命周期的增量效益考虑较少,方案建设时期与运行时期的颗粒度计算不够等缺点。实践中常常由于因为只考虑了成本,没有考虑全寿命周期的收益,忽略了投入产出比较高的方案。此外,现阶段输电网方案的投资常常是具有特定目的,目前投资绩效评估体系常常将所有不同类型的方案置于同一个评估指标体系下进行评估,缺乏对不同类型方案的差异化投资导向的思考。因此,结合模糊决策方法,建立一个以投资方案类型为导向的功能差异化评估指标体系,细化投资效益与增量效益计算颗粒度。最后运用模糊层次分析法与相对优属度矩阵计算等方法,建立了输电网方案优选模型对各方案进行全方位效益评估,抉择出优秀方案。The above studies have some shortcomings, such as the investment cost of the scheme without considering the cost of the whole life cycle, less consideration of the incremental benefits taking into account the whole life cycle, and insufficient granularity calculation during the construction period and operation period of the scheme. In practice, because only the cost is considered, the benefits of the whole life cycle are not considered, and the scheme with relatively high input and output is ignored. In addition, the investment in the current transmission grid scheme is often for a specific purpose. The current investment performance evaluation system often places all different types of schemes under the same evaluation index system for evaluation, and lacks thinking about the differentiated investment orientation of different types of schemes. . Therefore, combined with the fuzzy decision-making method, a functional differentiation evaluation index system oriented by the type of investment scheme is established, and the granularity of investment benefit and incremental benefit calculation is refined. Finally, using fuzzy analytic hierarchy process and relative superiority matrix calculation method, a transmission network scheme optimization model is established to evaluate the benefits of each scheme in an all-round way, and an excellent scheme is selected.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
针对上述问题,提供一种基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选方法,从现阶段输电网方案规划与投资领域方案决策与评估的特点出发,建立针对满足新增负荷、主网架加强、安全供电和电源送出四类方案的评估指标体系,包含技术层面、经济层面、社会层面,其中有线路平均负载率改善、全寿命周期成本、单位资产增供负荷等指标。Aiming at the above problems, this paper provides a transmission network scheme optimization method based on functional differences and the whole life cycle. Starting from the characteristics of the current transmission network scheme planning and investment field scheme decision-making and evaluation, it establishes a method to meet the new load and strengthen the main network frame. The evaluation index system of four types of schemes including safe power supply and power delivery, including technical level, economic level, and social level, including the improvement of the average load rate of the line, the cost of the whole life cycle, and the increased supply load per unit asset.
本发明通过下述技术方案实现:The present invention is achieved through the following technical solutions:
一种基于功能差异化的全寿命周期输电网方案优选方法,包括以下步骤:A method for optimizing a full life cycle transmission network scheme based on functional differentiation, comprising the following steps:
S1:构建基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选实施流程,定义关键阶段,包含了两个阶段,分别为评价指标设置阶段、规划评价阶段;评价指标设置阶段:分析方案特点和负荷特性、根据方案类型选取评价指标、选取指标评估的判据与指标评分标准、设置指标权重;规划评价阶段:规划数据的导入、数据预处理与边界条件的确定、综合评估技术效益、经济效益以及社会环保效益并投资决策;S1: Construct the optimal implementation process of the transmission network scheme based on functional differences and the whole life cycle, and define the key stages, including two stages, namely the evaluation index setting stage and the planning evaluation stage; the evaluation index setting stage: analyzing the characteristics of the scheme and the load characteristics , Select evaluation indicators according to the type of scheme, select the criteria for evaluation of indicators and indicator scoring standards, and set indicator weights; planning evaluation stage: import of planning data, data preprocessing and determination of boundary conditions, comprehensive evaluation of technical benefits, economic benefits and social benefits Environmental benefits and investment decisions;
S2:总结归纳在工程应用中输电网不同类型方案的特点,包含其作用对象,作用范围,方案收益要素;筛选出共性强的方案属性,提炼其特点与重要指标,将输变电方案按功能区别为四大类:满足新增负荷、主网架加强、安全供电和电源送出四类方案;S2: Summarize the characteristics of different types of transmission network schemes in engineering applications, including their role objects, scope of action, and scheme benefit elements; screen out the scheme attributes with strong commonality, refine their characteristics and important indicators, and classify power transmission and transformation schemes according to their functions. The difference is four categories: four types of schemes to meet the new load, strengthen the main grid, safe power supply and power delivery;
S3:构建不同类型方案的功能差异化评价指标体系,包含不同方案选取其区分度好,特征性强的指标,亦包含传统意义上经济性、技术性、社会性指标;S3: Build a functional differentiation evaluation index system for different types of schemes, including the selection of indicators with good discrimination and strong characteristics for different schemes, as well as economic, technical and social indicators in the traditional sense;
S4:根据地区输电网运行参数和设备参数,构建地区输电网稳态仿真模型;S4: According to the operating parameters and equipment parameters of the regional power transmission network, construct a steady state simulation model of the regional power transmission network;
S5:根据地区输电网稳态仿真模型计算定量指标、全寿命成本与投资收益指标,定性指标初根据始投资数据、电网运行数据、社会经济发展状况、拟达到的目的,做出模糊判断评价;S5: Calculate quantitative indicators, life-cycle cost and investment income indicators according to the steady-state simulation model of the regional transmission network, and initially make fuzzy judgments and evaluations for qualitative indicators based on initial investment data, power grid operation data, social and economic development status, and the intended purpose;
S6:根据模糊判断评价,构建指标模糊判断一致矩阵,进而确定各项指标权重,引入三角模糊数形成模糊判断矩阵,利用模糊判断矩阵确定各指标的重要性排序与其权重值;S6: According to the fuzzy judgment evaluation, construct the index fuzzy judgment consistency matrix, and then determine the weight of each index, introduce the triangular fuzzy number to form the fuzzy judgment matrix, and use the fuzzy judgment matrix to determine the importance order of each index and its weight value;
S7:将指标归一化,计算得到方案、指标相互比较优属度,结合权重矩阵计算各方案综合评分;S7: Normalize the indicators, calculate the mutual superiority of the scheme and the indicators, and calculate the comprehensive score of each scheme in combination with the weight matrix;
S8:计算各方案综合评分,分析比较其各方面优劣,优选出最优方案并实施。S8: Calculate the comprehensive score of each scheme, analyze and compare the advantages and disadvantages of each aspect, and select the optimal scheme and implement it.
进一步的,一种基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选方法,所述步骤S1包括:方案效益评价应从评价对象出发,考虑其投资建设的目的,涉及到的对象特点、作用范畴、负荷特性要点,以此为依据建立全面的评价指标,形成科学合理的评价指标体系;根据电网投资方案特点,选择代表性定性指标或定量指标,根据前期指标数据的收集与积累(包括可靠性、经济性、安全性、社会性)选择综合评价模型,是否考虑投资者的风险偏好因素,对数据进行预处理,测算出各指标的权重,最后计算出评价对象的最终评价结果,并对评价结果进行分析,对上述的评价结果进行横向或纵向对比,以衡量规划方案之间的实施结果的优劣。Further, a method for optimizing a transmission network scheme based on functional differences and a full life cycle, the step S1 includes: the scheme benefit evaluation should start from the evaluation object, consider the purpose of its investment and construction, the characteristics of the objects involved, the scope of action, the load According to the characteristics of the power grid investment plan, select representative qualitative or quantitative indicators, according to the collection and accumulation of early indicator data (including reliability, economic security, safety, and sociality) select a comprehensive evaluation model, consider whether investors’ risk preference factors are considered, preprocess the data, calculate the weight of each index, and finally calculate the final evaluation result of the evaluation object, and carry out the evaluation results. Analyze and compare the above evaluation results horizontally or vertically to measure the pros and cons of the implementation results between the planning schemes.
进一步的,所述步骤S2包括:Further, described step S2 comprises:
1.满足新增负荷方案:此类方案投资多为新建变电站与输电线路,其应着重考虑方案投产后提升的变电容量与输送电量方面的效益;1. Meet the new load scheme: Most of the investment in this type of scheme is to build new substations and transmission lines, and it should focus on the benefits of the increased substation capacity and transmission power after the scheme is put into operation;
2.主网架加强方案:此类方案主要是为了增强网架结构可靠性,多为新建输电线路,应着重考虑改善线路或改善主变负载情况方面的效益;2. Main network frame strengthening scheme: This type of scheme is mainly to enhance the reliability of the network frame structure, mostly for new transmission lines, and should focus on the benefits of improving the line or improving the load situation of the main transformer;
3.安全供电方案:此类方案考虑的是为了预防大规模范围停电的重大事故安全隐患,着重考虑于“N-1通过率”、“N-2通过率”、“联络率指标”,包括方案建设周期的不同或建设效率的不同给系统带来的系统性停电风险;3. Safe power supply scheme: This type of scheme considers the potential safety hazards of major accidents in order to prevent large-scale power outages, and focuses on "N-1 pass rate", "N-2 pass rate", "contact rate index", including The risk of systemic power outages brought to the system by different construction periods or different construction efficiencies;
4.电源送出方案:此类方案应依据电源类型,受电侧的特点,包含了输电线路的建设,着重考虑与发电侧电源的协调性,用户满意程度;4. Power delivery scheme: This type of scheme should be based on the type of power source and the characteristics of the power receiving side, including the construction of transmission lines, focusing on the coordination with the power source on the power generation side and the degree of user satisfaction;
进一步的,所述步骤S3包括:具体为:Further, described step S3 comprises: be specially:
1.满足新增负荷方案:技术层面:线路平均负载率改善、主变平均负载率改善、解决高压重载线路、解决高压重载主变、新增变电容量;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益、单位资产增供负荷;社会层面:用户满意度,节能减排,满足新能源接入;1. Meet the new load plan: technical level: improve the average load rate of the line, improve the average load rate of the main transformer, solve the high-voltage heavy-duty line, solve the high-voltage heavy-load main transformer, and increase the substation capacity; economic level: the whole life cycle cost , incremental benefits, increased supply and load per unit asset; social level: user satisfaction, energy conservation and emission reduction, and new energy access;
2.主网架加强方案:技术层面:线路平均负载率改善、主变平均负载率改善、解决高压重载线路、解决高压重载主变、新增输电能力、系统协调性改善程度;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益、单位资产增加线路长度;社会层面:用户满意度,满足新能源接入;2. Main network frame strengthening plan: technical level: improvement of the average load rate of the line, improvement of the average load rate of the main transformer, solving the high-voltage heavy-duty line, solving the high-voltage heavy-load main transformer, adding power transmission capacity, and improving the degree of system coordination; economic level; : whole life cycle cost, incremental benefit, increased line length per unit asset; social level: user satisfaction, meeting new energy access;
3.安全供电方案:线路平均负载率改善、主变平均负载率改善、减少系统平均停电时间、电压质量改善、大规模停电风险、线路联络率;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益;社会层面:用户满意度,满足新能源接入;3. Safe power supply scheme: improvement of the average load rate of the line, improvement of the average load rate of the main transformer, reduction of the average power outage time of the system, improvement of voltage quality, large-scale power outage risk, line connection rate; economic level: life cycle cost, incremental benefit; Social level: user satisfaction, meet new energy access;
4.电源送出方案:接入装机容量、主变平均负载率改善、单位投资增供线路长度、导线截面积、新增变电容量;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益;社会层面:用户满意度、节能减排、满足新能源接入;4. Power delivery scheme: access to installed capacity, improvement of the average load rate of main transformers, increased supply line length per unit investment, cross-sectional area of conductors, new substation capacity; economic level: full life cycle cost, incremental benefit; social level: User satisfaction, energy conservation and emission reduction, and new energy access;
其计算方式分别如下:The calculation methods are as follows:
线路平均负载率改善=建设前线路平均负载率—建设后线路平均负载率Improvement of line average load rate = average line load rate before construction - line average load rate after construction
主变平均负载率改善=建设前主变平均负载率—建设后主变平均负载率The improvement of the average load rate of the main transformer = the average load rate of the main transformer before construction - the average load rate of the main transformer after the construction
解决高压重载线路=建设前重载线路数量—建设后重载线路的数量Solving high-voltage and heavy-duty lines = the number of heavy-duty lines before construction - the number of heavy-duty lines after construction
解决高压重载主变=建设前重载主变数量—建设后重载主变数量Solve the problem of high-voltage and heavy-duty main transformers = the number of overloaded main transformers before construction - the number of overloaded main transformers after construction
新增变电容量=新增变压器容量之和Newly added transformer capacity = the sum of newly added transformer capacity
单位资产增供负荷=预期增供负荷/项目总投资Additional supply load per unit asset = expected additional supply load / total project investment
新增输电能力=新增线路容量之和New transmission capacity = sum of new line capacity
系统协调性改善程度=建设前系统协调性-建设后系统协调性System coordination improvement degree = system coordination before construction - system coordination after construction
系统协调性=负荷增长/电源容量增长System coordination = load growth / power supply capacity growth
减少系统平均停电时间=建设前输电网用户平均停电时间—建设后输电网用户平均停电时间Reduce the average power outage time of the system = the average power outage time of the transmission network users before the construction - the average power outage time of the transmission network users after the construction
电压质量的改善=建设前输电网用户综合电压合格率—建设后输电网用户综合电压合格率Improvement of voltage quality = comprehensive voltage qualification rate of transmission network users before construction - comprehensive voltage qualification rate of transmission network users after construction
大规模停电风险="N-2"通过率Mass blackout risk = "N-2" pass rate
单位投资增供线路长度=线路增加长度×增加输送容量/投资总额Length of additional supply line per unit investment = additional line length × increased transmission capacity/total investment
用户满意度=满意用户总数量/调查用户总数量User satisfaction = total number of satisfied users / total number of surveyed users
新能源接入=增加可接入新能源容量New energy access = increase the new energy capacity that can be connected
节能减排=减少排放二氧化碳Energy saving and emission reduction = reducing carbon dioxide emissions
进一步的,所述步骤S4包括:针对输电网方案收集其初始投资数据,其所处电网运行数据,其所处社会经济发展状况、其投资后拟达到的目的,具体为:Further, the step S4 includes: collecting its initial investment data for the transmission network scheme, the power grid operation data where it is located, the social and economic development status where it is located, and the purpose to be achieved after its investment, specifically:
初始投资数据:折现率、输变电工程寿命、变电容量单位成本、线路单位成本、变电站年运维费用、线路年运维费用、损耗利用小时数、购电价、产电比、损失费与产值比例、电力设备残值率;Initial investment data: discount rate, service life of power transmission and transformation projects, unit cost of substation capacity, unit cost of line, annual operation and maintenance cost of substation, annual operation and maintenance cost of line, hours of loss utilization, electricity purchase price, production-to-power ratio, and loss fee Proportion to output value, residual value ratio of power equipment;
所处电网运行数据包含电网运行参数与设备参数,构建基于pandapower的地区电网稳态仿真模型(PSSM),具体为:基于PandaPower的地区电网稳态仿真模型(PSSM)构建包括三个步骤:The operating data of the power grid where it is located includes power grid operating parameters and equipment parameters, and the construction of the regional power grid steady state simulation model (PSSM) based on pandapower is as follows: The construction of the regional power grid steady state simulation model (PSSM) based on PandaPower includes three steps:
(1)根据PandaPower软件所需数据格式,从实际电网遥测遥信数据库中提取对应数据,提取格式为QS文件;(1) According to the data format required by the PandaPower software, extract the corresponding data from the actual power grid telemetry and remote signaling database, and the extraction format is a QS file;
(2)使用Python对QS文件进行解析,解析成与PandaPower对应的数据格式;(2) Use Python to parse the QS file and parse it into a data format corresponding to PandaPower;
PandaPower最优潮流计算所需数据格式为:The data format required for PandaPower optimal power flow calculation is:
节点(Bus):名称(Name)、类型(Type)、电压上限(max_vm_pu)、电压下限(min_vm_pu),区域(zone)、电压基准(vn_kv);Node (Bus): Name (Name), Type (Type), Voltage Upper Limit (max_vm_pu), Voltage Lower Limit (min_vm_pu), Zone (zone), Voltage Reference (vn_kv);
线路(Line):名称(Name)、每公里线电阻(r_ohm_per_km)、每公里线电抗(x_ohm_per_km)、每公里线电容(c_nf_per_km)、首节点(from_bus)、末节点(to_bus)、连接状态(in_service);Line: name (Name), line resistance per kilometer (r_ohm_per_km), line reactance per kilometer (x_ohm_per_km), line capacitance per kilometer (c_nf_per_km), first node (from_bus), last node (to_bus), connection status (in_service) );
发电机(Gen):名称(Name)、节点(Bus)、有功出力(p_mw)、电压(vm_pu)、有功出力上限(max_p_mw)、有功出力下限(min_p_mw)、无功出力上限(max_q_mw)、无功出力下限(min_q_mw)、连接状态(in_service);Generator (Gen): Name (Name), Node (Bus), Active Output (p_mw), Voltage (vm_pu), Active Output Upper Limit (max_p_mw), Active Output Lower Limit (min_p_mw), Reactive Output Upper Limit (max_q_mw), None Work output lower limit (min_q_mw), connection status (in_service);
负荷(Load):名称(Name)、节点(Bus)、有功负荷(p_mw)、无功负荷(q_mw);Load (Load): name (Name), node (Bus), active load (p_mw), reactive load (q_mw);
所处电网运行数据:GDP增长速度、负荷增长数据、负荷组成结构;Power grid operation data: GDP growth rate, load growth data, load composition structure;
拟达到目的:解决负荷增长、满足安全供电,其并不局限于一个目的,可能包含两个及以上目的。The purpose to be achieved: to solve the load growth and meet the safe power supply, it is not limited to one purpose, and may include two or more purposes.
进一步的,一种基于功能差异的全寿命周期输电网方案优选的方法,所述步骤S5包括定性指标由专家给出模糊比较判断,定量成本与收益指标,根据步骤S4建立的仿真模型着重计算其全寿命成本与收益指标,具体为:Further, a method for optimizing a life cycle power transmission network scheme based on functional differences, the step S5 includes that qualitative indicators are given by experts to give fuzzy comparison and judgment, quantitative cost and benefit indicators, and the simulation model established in step S4 focuses on calculating its value. Life-cycle cost and benefit indicators, specifically:
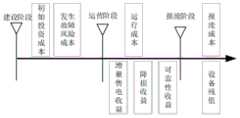
全寿命周期成本以时间划分为初始投资、运行成本、故障成本和报废成本四大类;The whole life cycle cost is divided into four categories: initial investment, operating cost, failure cost and scrapping cost according to time;
LCC=CI+CO+CF+CDLCC=CI+CO+CF+CD
式中CI指初始投资;CO指运行成本;CF指故障成本(惩罚性成本);CD指设备退役处置成本;In the formula, CI refers to the initial investment; CO refers to the operating cost; CF refers to the failure cost (punitive cost); CD refers to the decommissioning and disposal cost of the equipment;
初始投资成本包含规划设计成本与采购建设期成本,通常折算成按每年新增变电容量的投资成本和每年新增线路输电线路的投资成本:The initial investment cost includes the cost of planning and design and the cost of the procurement and construction period, which is usually converted into the investment cost of new substation capacity and the investment cost of new transmission lines each year:
式中n是建设年限,第i年新增变电容量为nsi,第i年新增的投运输电线路长度为nli,CIstation为新增单位变电容量的投资成本;CIline表示新增单位长度输电线路的投资成本;经修正后初始投资成本应为:where n is the construction period, the newly added substation capacity in the i-th year is nsi , the length of the newly added transmission line in the i-th year is nlii , and CIstation is the investment cost of the new unit substation capacity; CIline represents The investment cost of newly added transmission line per unit length; the initial investment cost after correction shall be:
运行成本主要包含运行维护成本(检修运维成本、工资及相关附加费用)与损耗成本;Operation cost mainly includes operation and maintenance costs (overhaul operation and maintenance costs, wages and related additional expenses) and wear and tear costs;
CO=COope+COlossCO=COope +COloss
式中,运行维护成本(COope)常常采取根据经验取CIEAC的一定比例:In the formula, the operation and maintenance cost (COope ) often takes a certain proportion of CIEAC based on experience:
COope=λope·CIEACCOope =λope ·CIEAC
其中λope为运维成本的比例系数,损耗成本涵概输变电设备的损耗累计值及线路的损耗作用,工程上可根据《电力系统设计手册》的方法来估算逐年的电能损耗即:Among them, λope is the proportional coefficient of the operation and maintenance cost, and the loss cost includes the accumulated loss value of the power transmission and transformation equipment and the loss effect of the line. In the project, the annual power loss can be estimated according to the method of the "Power System Design Manual", namely:
式中n为运行的年份,τi,max为第i年的损耗小时数;ΔPi,max为第i年最大负荷的功率损耗;Pprice是电网企业平均购电价格;where n is the year of operation, τi,max is the number of hours of loss in the ith year; ΔPi,max is the power loss of the maximum load in the ith year; Pprice is the average power purchase price of power grid enterprises;
在方案建成后,由于不同方案之间由于电网拓扑结构的不同,存在可靠性差别,因此由于系统元件存在故障率,或因其结构缺陷导致缺失负荷,计算故障还需计算在故障时的缺供电量:After the scheme is completed, due to the difference in reliability between different schemes due to the difference in the topology of the power grid, due to the failure rate of system components or the lack of load due to structural defects, the calculation of the fault also needs to calculate the lack of power supply at the time of the fault. quantity:
式中,t(x)表示从故障状态下切负荷恢复供电所需时间;Lc(x)表示在系统故障状态x下,恢复到静态稳定运行状态下所需的最小切负荷量;If(x)表示以系统状态x为自变量的函数:In the formula, t(x) represents the time required to restore power supply from load shedding under the fault state; Lc (x) represents the minimum load shedding amount required to restore the static and stable operation state under the system fault statex ; If ( x) represents a function that takes the system state x as an independent variable:
其故障成本表示如下:Its failure cost is expressed as follows:
式中i表示建设期中第i年;Pprice表示为电价;KGDP表示为每千瓦时产值与电价的比例;KVOLL表示停电损失费与每千瓦时产值的比值;In the formula, i represents the ith year in the construction period; Pprice represents the electricity price; KGDP represents the ratio of output value per kWh to electricity price; KVOLL represents the ratio of power outage cost to output value per kWh;
报废成本是指方案在技术改造、设备采购、方案建设的情况下形成得固定资产在方案报废时期进行拆除、处置引起的各项费用;Scrap cost refers to various expenses incurred by the dismantling and disposal of fixed assets formed under the circumstances of technical transformation, equipment procurement, and scheme construction during the scheme scrapping period;
CD=CDdis+CDvalCD=CDdis +CDval
式中CDdis为报废处置管理费用,CDval为报废设备残值回收收入;在实际应用中,常将报废处置成本这算成现值,再折算成具有实际意义的等年值,处理的方式如下:In the formula, CDdis is the management cost of scrapped disposal, and CDval is the income from the recovery of the residual value of scrapped equipment; in practical applications, the scrapped disposal cost is often calculated as the present value, and then converted into an equivalent annual value with practical significance. as follows:
CD=(λdis-λval)·CI/(1+γ)TCD=(λdis -λval )·CI/(1+γ)T
式中λdis和λval为报废处置管理费用和报废资产残值回收处理相对初始投资成本所占比例。In the formula,λdis andλval are the proportion of the management cost of scrap disposal and the recovery and treatment of the residual value of scrapped assets relative to the initial investment cost.
效益主要包括增量售电收入(EP)、电网可靠性提升收益(ER)、降损收益(EL)、资产利用率提升收益(EO)四类指标:The benefits mainly include four types of indicators: Incremental Electricity Sales Revenue (EP ), Grid Reliability Improvement Revenue (ER ), Loss Reduction (EL ), and Asset Utilization Improvement (EO ):
增量售电收入指方案建成,由于电网的供电能力提高,供电量增加带来新的售电收入。其模型如下:Incremental electricity sales revenue refers to new electricity sales revenue due to the increase in the power supply capacity of the grid due to the completion of the plan. Its model is as follows:
式中,Epi为第i年的增售电量的收益;Pi为第i年的负荷;PA为方案投运后第i年的供电能力;PB为原电网的供电能力;Tmax为最大负荷利用小时数;ΔP为购售电价差。In the formula, Epi is the income from the increase in electricity sales in the ith year; Pi is the load in theith year; PA is the power supply capacity in the ith year after the scheme is put into operation; PB is the power supply capacity of the original power grid; Tmax is the maximum load utilization hours; ΔP is the price difference between purchasing and selling electricity.
方案建设实施后,优化了原有网架结构与潮流分布,减少了重载线路等。与LCC成本分析中的损耗成本不同,此类降损效益体现于对相邻电网设备的降损效益,而LCC中损耗成本只针对新建设备在全寿命周期内的损耗。计算方式如下:After the implementation of the scheme construction, the original grid structure and power flow distribution were optimized, and the heavy-duty lines were reduced. Different from the loss cost in the LCC cost analysis, this kind of loss reduction benefit is reflected in the loss reduction benefit of the adjacent grid equipment, while the loss cost in the LCC is only for the loss of the new equipment in the whole life cycle. It is calculated as follows:
式中Eli为全寿命周期内第i年电网的降损效益;ΔPAi,j是建成后第i年第j个相关设备或线路网损;ΔPBi,j是原电网结构第i年第j个设备的网损;τmax损失小时数;Pprice为购买电价。In the formula, Eli is the loss reduction benefit of the power grid in the ith year in the whole life cycle; ΔPAi,j is the network loss of the jth related equipment or line in the ith year after completion; ΔPBi,j is the ith year of the original power grid structure. The network loss of j devices; τmax is the number of hours lost; Pprice is the purchase price.
输电网方案实施后,由于电网的可靠性提高,电网拓扑结构的互联率提升,因此期望负荷削量LEENS指标也随之变化,为量化其可靠性的提升,通过建设前后LEENS的变化量化其转换关系,公式如下:After the implementation of the transmission network scheme, due to the improvement of the reliability of the power grid and the improvement of the interconnection rate of the power grid topology, the expected load reductionLEENS index also changesaccordingly . Its conversion relationship, the formula is as follows:
式中LB是方案建设前LEENS值,LA是方案建设后LEENS值,通过此式可以计算出每年因为可靠性提升得到的对电网的收益。In the formula, LB is the LEENS value before the scheme construction, and LA is the LEENS value after the scheme construction. Through this formula, the annual benefit to the power grid due to reliability improvement can be calculated.
在建设方案实施后,在建成初期会缓解相邻重载设备的运行工况,但从长远来看容易存在两种情况:过度超前投资造成设备的闲置与浪费;对负荷增长情况预估不足,初始投资容量较小,不能跟上负荷的发展,限制了负荷的正常需求。上诉两种情况都需要避免,因此提出了资产利用收益指标来衡量,如下所示:After the implementation of the construction plan, the operating conditions of adjacent heavy-duty equipment will be alleviated in the early stage of construction, but in the long run, two situations are likely to exist: excessive and advanced investment causes idleness and waste of equipment; insufficient estimation of load growth, The initial investment capacity is small and cannot keep up with the development of the load, which limits the normal demand of the load. Appeals Both situations need to be avoided, so an asset utilization metric is proposed to measure, as follows:
式中Eoi为第i年的资产利用效率,α为电网设备剩余容量的影响因素,β为电网容量不足的影响系数,η为资产合理利用系数,L为整个电网系统平均负荷。In the formula, Eoi is the asset utilization efficiency in the ith year, α is the influence factor of the remaining capacity of the grid equipment, β is the influence coefficient of insufficient grid capacity, η is the rational utilization coefficient of assets, and L is the average load of the entire grid system.
进一步的,一种基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选方法,所述步骤S6构建指标模糊判断一致矩阵,进而确定各项指标权重。具体为:Further, in a method for optimizing a transmission network scheme based on functional differences and a full life cycle, the step S6 constructs an index fuzzy judgment consistency matrix, and then determines the weights of each index. Specifically:
为了度量专家在两两比较指标之间重要性时产生的不确定性问题,引入三角模糊数形成模糊判断矩阵,利用模糊判断矩阵确定各指标的重要性排序与其权重值。在实际应用中,通常采用1~9标度优先关系比较度量,其含义如下表所示:In order to measure the uncertainty caused by experts when comparing the importance of indicators, triangular fuzzy numbers are introduced to form a fuzzy judgment matrix, and the fuzzy judgment matrix is used to determine the importance order and weight value of each indicator. In practical applications, the 1-9 scale priority relationship comparison measure is usually used, and its meaning is shown in the following table:
每个子准则层下底层指标有m个,指标集为X={x1,x2,……,xm}。专家对指标i相对于指标j的重要程度的模糊判断为[lij,eij,pij],其中pij>lij,其中左右拓展lij、pij表示为判断的模糊程度,pij-pij越大表示决策者的模糊程度越高,准确性越低。最后得出模糊比较判断矩阵B:There are m bottom indicators under each sub-criteria layer, and the indicator set is X={x1 ,x2 ,...,xm }. The fuzzy judgment of experts on the importance of index i relative to index j is [liij , eij , pij ], where pij >lij , where left and right extensions lij and pij represent the fuzzy degree of judgment, pij The larger the -pij , the higher the ambiguity of the decision maker and the lower the accuracy. Finally, the fuzzy comparison judgment matrix B is obtained:
同理可得子准则之间的模糊比较判断矩阵。在模糊比较判断矩阵中,需要将模糊判断矩阵转化为重要程度表示,指标i相对于本层其他指标的模糊权重相对向量为:In the same way, the fuzzy comparison judgment matrix between sub-criteria can be obtained. In the fuzzy comparison judgment matrix, the fuzzy judgment matrix needs to be transformed into the importance degree representation. The fuzzy weight relative vector of the index i relative to other indexes in this layer is:
将模糊相对权重向量中每个三角模糊数明晰化。Qi(lj,ei,pi)对应的主观权重为:Clarifies each triangular fuzzy number in the fuzzy relative weight vector. The subjective weight corresponding to Qi (lj , ei , pi ) is:
由此算出各指标的主观权重赋权,由于输电网规划方案数量较少,如若采用客观赋权法如变异系数法、熵权法等会因为样本数量少造成评价决策不合理。因此方案只采用了主观赋权法:由此可得每个指标归一化后权重ai为:From this, the subjective weighting of each index is calculated. Due to the small number of transmission network planning schemes, if an objective weighting method such as the coefficient of variation method and the entropy weighting method is used, the evaluation decision will be unreasonable due to the small number of samples. Therefore, the scheme only adopts the subjective weighting method: from this, the normalized weight ai of each index can be obtained as:
式中ai为指标i在此层级的权重。where ai is the weight of indicator i at this level.
进一步的,一种基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选方法,所述步骤S7:计算得到各方案各指标相互间比较优属度,结合权重矩阵计算各方案的隶属度,具体为:Further, a method for optimizing a transmission network scheme based on functional differences and a full life cycle, the step S7: calculating and obtaining the mutual superiority of each index of each scheme, and calculating the membership degree of each scheme in combination with the weight matrix, specifically:
定量指标采用借鉴模糊数学中隶属度的评价模型,因不同指标具有不同的量纲,取值范围也大有不同,为了准确评价各方案在不同指标下的隶属度,因此需要将其归一化处理。根据输电网效益评估体系的特点,其指标体系可以分为成本型、效益型、区间型三种目标类型:The quantitative index adopts the evaluation model of membership degree borrowed from fuzzy mathematics. Because different indicators have different dimensions, the value range is also very different. In order to accurately evaluate the membership degree of each scheme under different indicators, it needs to be normalized. deal with. According to the characteristics of the transmission network benefit evaluation system, its index system can be divided into three target types: cost type, benefit type and interval type:
成本型指标:Cost indicators:
式中xik为第i个评价方案对于第k个指标值;共有m个方案;min(xk)为m个方案中第k个指标值最小值where xik is the ith evaluation scheme for the k th index value; there are m schemes in total; min(xk ) is the minimum value of the k th index value among the m schemes
效益型指标:Benefit indicators:
式中fLk和fHk是第k个区间指标的最佳下界与上界;ηk为xik的偏移区间最大值:where fLk and fHk are the optimal lower and upper bounds of the k-th interval index; ηk is the maximum value of the offset interval of xik :
ηk=max{fLk-xik,xik-fHk}ηk =max{fLk-xik ,xik -fHk }
将各定量指标归一化后,修构造各指标层下,两两比较的模糊优先关系矩阵:After normalizing each quantitative index, construct a fuzzy priority relationship matrix for pairwise comparison under each index layer:
式中:rik和rjk为第i,j个评价方案对第k个评价指标之间的隶属度值;bijk体现第i个与第j个方案的优劣程度。In the formula: rik and rjk are the membership values between the i and j th evaluation schemes to the k th evaluation index; bijk reflects the pros and cons of the i th and j th schemes.
定性指标的模糊优先关系矩阵对于定性指标,采用多个专家打分的方法,采用0.1~0.9的标度法,由于与表1类似,从而得到其模糊优先关系矩阵B=(bijk)m×n模糊一致矩阵;The fuzzy priority relationship matrix of qualitative indicators For qualitative indicators, the method of scoring by multiple experts is adopted, and the scale method of 0.1 to 0.9 is adopted. Because it is similar to Table 1, the fuzzy priority relationship matrix B=(bijk )m× n fuzzy consistent matrix;
由定性指标与定量指标得到的模糊优先关系矩阵B改造成为模糊一致矩阵A。The fuzzy priority relationship matrix B obtained by qualitative and quantitative indicators is transformed into a fuzzy consensus matrix A.
如下所示:As follows:
式中:ri为矩阵B各行之和;m为方案个数,其中:In the formula:ri is the sum of the rows of matrix B; m is the number of solutions, where:
进一步的,一种基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选方法,所述步骤S8:根据各方案隶属度,分析比较其优劣,得出最优方案并实施。具体为:单目标优属度的计算Further, a method for optimizing a transmission network scheme based on functional differences and full life cycle, the step S8: according to the membership degree of each scheme, analyze and compare the advantages and disadvantages, and obtain the optimal scheme and implement it. Specifically: Calculation of single-objective superiority degree
单目标优属度计算有最小二乘法、方根法等,方案采用方根法计算方案i在单目标优属度值Sik:The single-objective preference calculation includes the least squares method, the square root method, etc. The scheme adopts the square root method to calculate the single-objective preference value Sik of scheme i:
其中in
总目标排序Overall goal ranking
在单目标排序的基础上,利用下式计算各方案的全局优属度值,即最后得分:On the basis of single-objective ranking, the following formula is used to calculate the global superiority value of each scheme, that is, the final score:
式中ai为计算所得各指标权重;Ti为第i个方案的总得分。In the formula, ai is the calculated weight of each indicator; Ti is the total score of the i-th scheme.
本发明与现有技术相比,具有如下的优点和有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages and beneficial effects:
1、本发明由实际电网运行与投资的特点出发,根据现有阶段已有的不同投资方案类型其侧重点不同的投资效益评估体系,针对其投资目的的不同建立了不同评估指标体系的方法。传统的输变电方案的投资效益评估都是将不同类型的方案纳入同一个评价指标体系下进行评估的方法,无法满足电力体制改革的新形势下开展精细化评估和投资分配的需求。1. The present invention starts from the characteristics of actual power grid operation and investment, and establishes a method for different evaluation index systems according to the different investment plan types in the existing stage with different emphasis on investment benefit evaluation systems. The traditional investment benefit evaluation of power transmission and transformation schemes is a method of incorporating different types of schemes into the same evaluation index system for evaluation, which cannot meet the needs of refined evaluation and investment allocation under the new situation of power system reform.
2、针对许多对全寿命周期下对成本与效益的计算颗粒度较低的缺点,本文提出的全寿命周期计算的方法,包含建设前、建设中、建设后等多维度的计算比较,并针对了在建设中的存在的运行风险,能给与决策者的更多信息。2. Aiming at the shortcomings of low granularity in the calculation of costs and benefits under the whole life cycle, the calculation method of the whole life cycle proposed in this paper includes multi-dimensional calculation and comparison before, during and after construction. It can give more information to decision makers by understanding the operational risks that exist in the construction.
3、各个指标的权重系数为综合评价模型的核心,相较于以往的主观赋权法,采用三角模糊层次分析法,可减少因主观认知对评定标准造成的偏移,保证了评定结果的科学性和合理性。3. The weight coefficient of each index is the core of the comprehensive evaluation model. Compared with the previous subjective weighting method, the triangular fuzzy AHP method can reduce the deviation of the evaluation standard caused by subjective cognition and ensure the accuracy of the evaluation results. scientific and rational.
4、本发明通过构建输电网投资方案评价流程与指标体系,结合高度细化的全寿命周期成本(LCC)与效益的计算方式对整体输电网方案各指标进行了初步的计算,运用模糊层次分析法求出各指标的主观权重,运用各权重与相对优属度的排序最终得到最后的优胜方案,达到投资决策的目的。4. The present invention preliminarily calculates each index of the overall transmission network scheme by constructing the evaluation process and index system of the transmission network investment scheme, combined with the highly refined calculation method of the whole life cycle cost (LCC) and benefit, and uses the fuzzy analysis hierarchy process. The subjective weight of each index is obtained by the method, and the ranking of each weight and relative superiority is used to finally obtain the final winning plan to achieve the purpose of investment decision-making.
附图说明Description of drawings
此处所说明的附图用来提供对本发明实施例的进一步理解,构成本申请的一部分,并不构成对本发明实施例的限定;The accompanying drawings described herein are used to provide further understanding of the embodiments of the present invention, and constitute a part of the present application, and do not constitute limitations to the embodiments of the present invention;
图1为输电网规划评价实施流程图。Figure 1 is a flow chart of the implementation of transmission network planning and evaluation.
图2为输电网方案综合评价指标体系流程图。Figure 2 is the flow chart of the comprehensive evaluation index system of the transmission network scheme.
图3为输电网方案成本收益一览图。Figure 3 is a list of costs and benefits of transmission grid solutions.
图4为输电网方案评估策略图。Figure 4 is a diagram of the evaluation strategy of the transmission grid scheme.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了能够更清楚地理解本发明的上述目的、特征和优点,下面结合附图和具体实施方式对本发明进行进一步的详细描述。需要说明的是,在相互不冲突的情况下,本申请的实施例及实施例中的特征可以相互组合。In order to understand the above objects, features and advantages of the present invention more clearly, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. It should be noted that the embodiments of the present application and the features in the embodiments may be combined with each other under the condition that they do not conflict with each other.
实施例1:Example 1:
步骤S1包括:从评价对象出发,考虑其投资建设的目的,涉及到的对象特点、作用范畴、负荷特性要点,建立全面的评价指标,构建基于功能差异与全寿命周期的输电网方案优选实施流程。根据电网投资方案特点,选择代表性定性指标或定量指标,根据前期指标数据的收集与积累(包括可靠性、经济性、安全性、社会性)选择综合评价模型,是否考虑投资者的风险偏好等因素,对数据进行预处理,测算出各指标的权重,最后计算出评价对象的最终评价结果,并对评价结果进行分析,对上述的评价结果进行横向或纵向对比,以衡量规划方案之间的实施结果的优劣,如图1所示。其具体流程为:Step S1 includes: starting from the evaluation object, considering the purpose of its investment and construction, the characteristics of the objects involved, the scope of action, and the main points of the load characteristics, establishing a comprehensive evaluation index, and constructing the optimal implementation process of the transmission network scheme based on functional differences and full life cycle. . According to the characteristics of the power grid investment plan, select representative qualitative indicators or quantitative indicators, select a comprehensive evaluation model according to the collection and accumulation of previous indicator data (including reliability, economy, safety, and sociality), whether to consider investors' risk preferences, etc. Factors, preprocess the data, calculate the weight of each index, and finally calculate the final evaluation result of the evaluation object, analyze the evaluation results, and compare the above evaluation results horizontally or vertically to measure the difference between the planning schemes. The pros and cons of the implementation results are shown in Figure 1. The specific process is:
评价指标设置阶段:分析方案特点和负荷特性、根据方案类型选取评价指标、选取指标评估的判据与指标评分标准、设置指标权重。Evaluation index setting stage: analyze scheme characteristics and load characteristics, select evaluation indexes according to scheme types, select index evaluation criteria and index scoring standards, and set index weights.
规划评价阶段:规划数据的导入、数据预处理与边界条件的确定、综合评估(技术效益、经济效益、社会环保效益)并投资决策。Planning evaluation stage: import of planning data, data preprocessing and determination of boundary conditions, comprehensive evaluation (technical benefits, economic benefits, social and environmental benefits) and investment decisions.
步骤S2包括:结合方案特点、作用对象、作用范围、方案收益四大要素,定义输电网方案类别,对不同输电网方案按功能类别进行分类,并给出各类方案的重点与特点,将输变电方案按功能区别为四大类:满足新增负荷、主网架加强、安全供电和电源送出四类方案:Step S2 includes: combining the four major elements of the scheme features, the role object, the scope of action, and the scheme benefit, define the transmission network scheme category, classify different transmission network schemes according to functional categories, and give the key points and characteristics of various schemes, and the transmission network scheme. The substation schemes are divided into four categories according to their functions: meeting the new load, strengthening the main grid, safe power supply and power delivery:
1.满足新增负荷方案:此类方案投资多为新建变电站与输电线路,其应着重考虑方案投产后提升的变电容量与输送电量等方面的效益;1. Meet the new load scheme: Most of the investment in this type of scheme is to build new substations and transmission lines, and it should focus on the benefits of the increased substation capacity and transmission power after the scheme is put into operation;
2.主网架加强方案:此类方案主要是为了增强网架结构可靠性,多为新建输电线路,应着重考虑改善线路或改善主变负载情况方面的效益;2. Main network frame strengthening scheme: This type of scheme is mainly to enhance the reliability of the network frame structure, mostly for new transmission lines, and should focus on the benefits of improving the line or improving the load situation of the main transformer;
3.安全供电方案:此类方案考虑的是为了预防大规模范围停电的重大事故安全隐患,着重考虑于“N-1通过率”、“N-2通过率”、“联络率等指标”,包括方案建设周期的不同或建设效率的不同给系统带来的系统性停电风险;3. Safe power supply scheme: This type of scheme considers the safety hazards of major accidents in order to prevent large-scale power outages, and focuses on "N-1 pass rate", "N-2 pass rate", "contact rate and other indicators", Including the risk of systemic power outages brought to the system by different construction periods or different construction efficiencies;
4.电源送出方案:此类方案应依据电源类型,受电侧的特点,包含了输电线路的建设,着重考虑与发电侧电源的协调性,用户满意程度等4. Power delivery scheme: This type of scheme should be based on the type of power source and the characteristics of the power receiving side, including the construction of transmission lines, focusing on the coordination with the power source on the power generation side, and the degree of user satisfaction, etc.
步骤S3包括:构建基于功能差异的输电网投资效益评估体系,包含技术层面、经济层面、社会层面三方面,不同功能差异的指标与其他方案的功能差异亦有所不同,包含此类特定的指标,如图2所示。具体为:Step S3 includes: constructing a transmission network investment benefit evaluation system based on functional differences, including three aspects: technical level, economic level, and social level. The indicators of different functional differences are also different from those of other schemes, including such specific indicators. ,as shown in picture 2. Specifically:
1.满足新增负荷方案:技术层面:线路平均负载率改善、主变平均负载率改善、解决高压重载线路、解决高压重载主变、新增变电容量;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益、单位资产增供负荷;社会层面:用户满意度,节能减排,满足新能源接入。1. Meet the new load plan: technical level: improve the average load rate of the line, improve the average load rate of the main transformer, solve the high-voltage heavy-duty line, solve the high-voltage heavy-load main transformer, and increase the substation capacity; economic level: the whole life cycle cost , incremental benefits, increased supply and load per unit asset; social level: user satisfaction, energy conservation and emission reduction, and new energy access.
2.主网架加强方案:技术层面:线路平均负载率改善、主变平均负载率改善、解决高压重载线路、解决高压重载主变、新增输电能力、系统协调性改善程度;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益、单位资产增加线路长度;社会层面:用户满意度,满足新能源接入。2. Main network frame strengthening plan: technical level: improvement of the average load rate of the line, improvement of the average load rate of the main transformer, solving the high-voltage heavy-duty line, solving the high-voltage heavy-load main transformer, adding power transmission capacity, and improving the degree of system coordination; economic level; : whole life cycle cost, incremental benefit, increase line length per unit asset; social level: user satisfaction, meet new energy access.
3.安全供电方案:线路平均负载率改善、主变平均负载率改善、减少系统平均停电时间、电压质量改善、大规模停电风险、线路联络率;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益;社会层面:用户满意度,满足新能源接入。3. Safe power supply scheme: improvement of the average load rate of the line, improvement of the average load rate of the main transformer, reduction of the average power outage time of the system, improvement of voltage quality, large-scale power outage risk, line connection rate; economic level: life cycle cost, incremental benefit; Social level: user satisfaction, meet new energy access.
4.电源送出方案:接入装机容量、主变平均负载率改善、单位投资增供线路长度、导线截面积、新增变电容量;经济层面:全寿命周期成本、增量效益;社会层面:用户满意度、节能减排、满足新能源接入。4. Power delivery scheme: access to installed capacity, improvement of the average load rate of main transformers, increased supply line length per unit investment, cross-sectional area of conductors, new substation capacity; economic level: full life cycle cost, incremental benefit; social level: User satisfaction, energy conservation and emission reduction, and new energy access.
步骤S4包括:根据地区输电网运行参数与设备参数,构建地区输电网稳态仿真模型,收集初始投资数据等。Step S4 includes: constructing a steady state simulation model of the regional power transmission network according to the operating parameters and equipment parameters of the regional power transmission network, collecting initial investment data, and the like.
初始投资数据:折现率、输变电工程寿命、变电容量单位成本、线路单位成本、变电站年运维费用、线路年运维费用、损耗利用小时数、购电价、产电比、损失费与产值比例、电力设备残值率。所处电网运行数据包含电网运行参数与设备参数,含GDP增长速度、负荷增长数据、负荷组成结构。构建基于pandapower的地区电网稳态仿真模型。Initial investment data: discount rate, service life of power transmission and transformation projects, unit cost of substation capacity, unit cost of line, annual operation and maintenance cost of substation, annual operation and maintenance cost of line, hours of loss utilization, electricity purchase price, production-to-power ratio, and loss fee Proportion to output value, residual value rate of power equipment. The power grid operation data includes power grid operation parameters and equipment parameters, including GDP growth rate, load growth data, and load composition structure. Build a regional power grid steady state simulation model based on pandapower.
拟达到目的:解决负荷增长、满足安全供电等,其并不局限于一个目的,可能包含两个及以上目的The purpose to be achieved: solve the load growth, meet the safe power supply, etc., which is not limited to one purpose, may include two or more purposes
所述步骤S5包括定性指标由专家给出模糊比较判断,定量指标如成本与收益指标,根据步骤S4建立的仿真模型着重计算其全寿命成本与收益指标,如图3所示。The step S5 includes that the qualitative index is given by an expert to give a fuzzy comparison judgment, and the quantitative index is such as the cost and benefit index.
全寿命周期成本以时间划分为初始投资、运行成本、故障成本和报废成本等四大类:The whole life cycle cost is divided into four categories by time: initial investment, operating cost, failure cost and scrapping cost:
LCC=CI+CO+CF+CDLCC=CI+CO+CF+CD
式中CI指初始投资;CO指运行成本;CF指故障成本(惩罚性成本);CD指设备退役处置成本。In the formula, CI refers to the initial investment; CO refers to the operation cost; CF refers to the failure cost (punitive cost); CD refers to the decommissioning and disposal cost of the equipment.
效益主要包括增量售电收入(EP)、电网可靠性提升收益(ER)、降损收益(EL)、资产利用率提升收益(EO)四类指标:The benefits mainly include four types of indicators: Incremental Electricity Sales Revenue (EP ), Grid Reliability Improvement Revenue (ER ), Loss Reduction (EL ), and Asset Utilization Improvement (EO ):
所述步骤S6根据各专家的经验与主观意向,构建指标模糊判断一致矩阵,进而确定各项指标权重,如图4所示。每个子准则层下底层指标有m个,指标集为X={x1,x2,……,xm}。专家对指标i相对于指标j的重要程度的模糊判断为[lij,eij,pij],其中pij>lij,其中左右拓展lij、pij表示为判断的模糊程度,pij-pij越大表示决策者的模糊程度越高,准确性越低。最后得出模糊比较判断矩阵B:In the step S6, according to the experience and subjective intention of each expert, a consensus matrix of index fuzzy judgment is constructed, and then the weight of each index is determined, as shown in FIG. 4 . There are m bottom indicators under each sub-criteria layer, and the indicator set is X={x1 ,x2 ,...,xm }. The fuzzy judgment of experts on the importance of index i relative to index j is [liij , eij , pij ], where pij >lij , where left and right extensions lij and pij represent the fuzzy degree of judgment, pij The larger the -pij , the higher the ambiguity of the decision maker and the lower the accuracy. Finally, the fuzzy comparison judgment matrix B is obtained:
同理可得子准则之间的模糊比较判断矩阵。在模糊比较判断矩阵中,需要将模糊判断矩阵转化为重要程度表示,指标i相对于本层其他指标的模糊权重相对向量为:In the same way, the fuzzy comparison judgment matrix between sub-criteria can be obtained. In the fuzzy comparison judgment matrix, the fuzzy judgment matrix needs to be transformed into the importance degree representation. The fuzzy weight relative vector of the index i relative to other indexes in this layer is:
将模糊相对权重向量中每个三角模糊数明晰化。Qi(lj,ei,pi)对应的主观权重为:Clarifies each triangular fuzzy number in the fuzzy relative weight vector. The subjective weight corresponding to Qi (lj , ei , pi ) is:
步骤S7:计算得到各方案各指标相互间比较优属度,结合权重矩阵计算各方案的隶属度,将各定量指标归一化后,修构造各指标层下,两两比较的模糊优先关系矩阵:Step S7: Calculate the relative superiority of each indicator of each scheme, calculate the membership degree of each scheme in combination with the weight matrix, normalize each quantitative indicator, and construct a fuzzy priority relationship matrix for pairwise comparison under each indicator layer. :
式中:rik和rjk为第i,j个评价方案对第k个评价指标之间的隶属度值;bijk体现第i个与第j个方案的优劣程度。In the formula: rik and rjk are the membership values between the i and j th evaluation schemes to the k th evaluation index; bijk reflects the pros and cons of the i th and j th schemes.
定性指标的模糊优先关系矩阵对于定性指标,采用多个专家打分的方法,采用0.1~0.9的标度法,从而得到其模糊优先关系矩阵B=(bijk)m×n模糊一致矩阵由定性指标与定量指标得到的模糊优先关系矩阵B改造成为模糊一致矩阵A。The fuzzy priority relationship matrix of qualitative indicators For qualitative indicators, the method of scoring by multiple experts and the scaling method of 0.1 to 0.9 are used to obtain the fuzzy priority relationship matrix B=(bijk )m×n fuzzy consistent matrix is determined by qualitative The fuzzy priority relationship matrix B obtained from the indicators and quantitative indicators is transformed into a fuzzy consensus matrix A.
如下所示:As follows:
式中:ri为矩阵B各行之和;m为方案个数,其中:In the formula:ri is the sum of the rows of matrix B; m is the number of solutions, where:
步骤S8:根据方案的综合评分,分析比较其各方面优劣,得出最优方案并实施。Step S8: According to the comprehensive score of the scheme, analyze and compare the advantages and disadvantages of various aspects, and obtain the optimal scheme and implement it.
具体为:Specifically:
单目标优属度的计算Calculation of single-objective preference
单目标优属度值Sik:Single-objective preference value Sik :
其中in
总目标排序Overall goal ranking
在单目标排序的基础上,利用下式计算各方案的全局优属度值,即最后得分:On the basis of single-objective ranking, the following formula is used to calculate the global superiority value of each scheme, that is, the final score:
式中ai为计算所得权重;Ti为第i个方案的总得分。where ai is the calculated weight; Ti is the total score of the i-th scheme.
尽管已描述了本发明的优选实施例,但本领域内的技术人员一旦得知了基本创造性概念,则可对这些实施例作出另外的变更和修改。所以,所附权利要求意欲解释为包括优选实施例以及落入本发明范围的所有变更和修改。Although preferred embodiments of the present invention have been described, additional changes and modifications to these embodiments may occur to those skilled in the art once the basic inventive concepts are known. Therefore, the appended claims are intended to be construed to include the preferred embodiment and all changes and modifications that fall within the scope of the present invention.
显然,本领域的技术人员可以对本发明进行各种改动和变型而不脱离本发明的精神和范围。这样,倘若本发明的这些修改和变型属于本发明权利要求及其等同技术的范围之内,则本发明也意图包含这些改动和变型在内。It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that various modifications and variations can be made in the present invention without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. Thus, provided that these modifications and variations of the present invention fall within the scope of the claims of the present invention and their equivalents, the present invention is also intended to include these modifications and variations.
Claims (9)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010289415.0ACN111428938A (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2020-04-14 | Power transmission network scheme optimization method based on function difference and full life cycle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010289415.0ACN111428938A (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2020-04-14 | Power transmission network scheme optimization method based on function difference and full life cycle |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111428938Atrue CN111428938A (en) | 2020-07-17 |
Family
ID=71556276
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010289415.0APendingCN111428938A (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2020-04-14 | Power transmission network scheme optimization method based on function difference and full life cycle |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111428938A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113642886A (en)* | 2021-08-12 | 2021-11-12 | 国网经济技术研究院有限公司 | Method, system, medium and computing device for analyzing utilization rate of planned power grid line |
| CN114462692A (en)* | 2022-01-26 | 2022-05-10 | 国网湖北省电力有限公司经济技术研究院 | Power grid old and old equipment technical improvement strategy optimization and adjustment method |
| CN114493208A (en)* | 2022-01-14 | 2022-05-13 | 国核电力规划设计研究院有限公司 | Method and device for evaluating engineering project full life cycle, electronic equipment and medium |
| CN118674484A (en)* | 2024-07-24 | 2024-09-20 | 国网陕西招标有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and medium for evaluating total life cycle cost of transformer equipment |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104680254A (en)* | 2015-02-14 | 2015-06-03 | 浙江大学 | Method for optimizing power grid planning scheme based on comprehensive cost model |
| CN105427051A (en)* | 2015-12-02 | 2016-03-23 | 中国南方电网有限责任公司 | Comprehensive evaluation method of power grid based on asset life cycle |
| CN109003010A (en)* | 2018-10-17 | 2018-12-14 | 国网湖南省电力有限公司 | Evaluation method for investment benefit of power grid project |
| CN109102116A (en)* | 2018-08-03 | 2018-12-28 | 国网山东省电力公司经济技术研究院 | A kind of power network development multi-stage optimization appraisal procedure |
| US20190392360A1 (en)* | 2017-04-04 | 2019-12-26 | Korea Electric Power Corporation | Power transformer asset management device and method therefor |
- 2020
- 2020-04-14CNCN202010289415.0Apatent/CN111428938A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN104680254A (en)* | 2015-02-14 | 2015-06-03 | 浙江大学 | Method for optimizing power grid planning scheme based on comprehensive cost model |
| CN105427051A (en)* | 2015-12-02 | 2016-03-23 | 中国南方电网有限责任公司 | Comprehensive evaluation method of power grid based on asset life cycle |
| US20190392360A1 (en)* | 2017-04-04 | 2019-12-26 | Korea Electric Power Corporation | Power transformer asset management device and method therefor |
| CN109102116A (en)* | 2018-08-03 | 2018-12-28 | 国网山东省电力公司经济技术研究院 | A kind of power network development multi-stage optimization appraisal procedure |
| CN109003010A (en)* | 2018-10-17 | 2018-12-14 | 国网湖南省电力有限公司 | Evaluation method for investment benefit of power grid project |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| 郑旭 等: "基于全寿命周期SEC指标的输电网规划模糊决策评价", 《武汉大学学报(工学版)》* |
| 陈大宇: "层次分析法在城市电网规划中的应用", 《中国优秀博硕士学位论文全文数据库(硕士)工程科技Ⅱ辑》* |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113642886A (en)* | 2021-08-12 | 2021-11-12 | 国网经济技术研究院有限公司 | Method, system, medium and computing device for analyzing utilization rate of planned power grid line |
| CN113642886B (en)* | 2021-08-12 | 2024-05-28 | 国网经济技术研究院有限公司 | Method, system, medium and computing equipment for analyzing utilization rate of planned power grid line |
| CN114493208A (en)* | 2022-01-14 | 2022-05-13 | 国核电力规划设计研究院有限公司 | Method and device for evaluating engineering project full life cycle, electronic equipment and medium |
| CN114462692A (en)* | 2022-01-26 | 2022-05-10 | 国网湖北省电力有限公司经济技术研究院 | Power grid old and old equipment technical improvement strategy optimization and adjustment method |
| CN118674484A (en)* | 2024-07-24 | 2024-09-20 | 国网陕西招标有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and medium for evaluating total life cycle cost of transformer equipment |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN112907129B (en) | Energy storage comprehensive benefit evaluation index system | |
| CN111428938A (en) | Power transmission network scheme optimization method based on function difference and full life cycle | |
| CN111967776A (en) | Assessment method for operation value chain of park comprehensive energy system | |
| Yang et al. | Bi-level planning model of distributed PV-energy storage system connected to distribution network under the coordinated operation of electricity-carbon market | |
| CN106056290A (en) | Power transmission network operating efficiency and benefit detection method considering new energy access | |
| CN116823008A (en) | Park energy utilization efficiency evaluation method, system, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112001598A (en) | Energy storage configuration evaluation and operation optimization method for different users based on energy storage selection | |
| Zhang et al. | Evaluation of the multi-dimensional growth potential of China's public charging facilities for electric vehicles through 2030 | |
| CN108364238A (en) | A kind of diversified powering mode selection method based on power supply area grade classification | |
| Yang et al. | Optimal investment decision of distribution network with investment ability and project correlation constraints | |
| CN113255957A (en) | Quantitative optimization analysis method and system for uncertain factors of comprehensive service station | |
| CN111008769B (en) | Energy transformation optimization method and system considering power blockage | |
| Tang et al. | New Electric Power System Stability Evaluation Based on Game Theory Combination Weighting and Improved Cloud Model. | |
| Liu et al. | Optimal selection of energy storage nodes based on improved cumulative prospect theory in China | |
| CN119228398A (en) | Park energy carbon supervision method and system | |
| Ma et al. | Evaluation model for economic operation of active distribution network orienting to energy internet | |
| Zhao et al. | Study on Comprehensive Efficiency Evaluation of Rural Power Grid under Rural Revitalization Strategy Considering Regional Differences. | |
| CN117314239A (en) | Optimization method, device, equipment and medium for weak links in power grid development | |
| CN115481861A (en) | Power distribution network comprehensive benefit evaluation method and system | |
| CN115983664A (en) | A comprehensive evaluation method for the effect of energy storage participating in power market transactions based on fuzzy analysis | |
| CN115619252A (en) | Evaluation method, device, storage medium and equipment for AC/DC hybrid distribution network | |
| Zhong et al. | [Retracted] Analysis and Design of the Project Risk Management System Based on the Fuzzy Clustering Algorithm | |
| Liu et al. | Research on Investment Classification and Comprehensive Benefit Evaluation Method for Power Grid under New Power System. | |
| CN107294091A (en) | A kind of power network drop based on cost damages Scheme Optimum Seeking Methods | |
| Gu et al. | Provincial technical loss reduction platform with interactive management and control considering reactive power compensation potential of power supply and consumption sides |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | ||
| RJ01 | Rejection of invention patent application after publication | Application publication date:20200717 |