CN111424038A - A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY40 gene and its application - Google Patents
A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY40 gene and its applicationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111424038A CN111424038ACN202010298688.1ACN202010298688ACN111424038ACN 111424038 ACN111424038 ACN 111424038ACN 202010298688 ACN202010298688 ACN 202010298688ACN 111424038 ACN111424038 ACN 111424038A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- cgwrky40
- gene
- chunlan
- centrifuge
- ser
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/415—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from plants
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/63—Introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors; Vectors; Use of hosts therefor; Regulation of expression
- C12N15/79—Vectors or expression systems specially adapted for eukaryotic hosts
- C12N15/82—Vectors or expression systems specially adapted for eukaryotic hosts for plant cells, e.g. plant artificial chromosomes (PACs)
- C12N15/8241—Phenotypically and genetically modified plants via recombinant DNA technology
- C12N15/8261—Phenotypically and genetically modified plants via recombinant DNA technology with agronomic (input) traits, e.g. crop yield
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/63—Introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors; Vectors; Use of hosts therefor; Regulation of expression
- C12N15/79—Vectors or expression systems specially adapted for eukaryotic hosts
- C12N15/82—Vectors or expression systems specially adapted for eukaryotic hosts for plant cells, e.g. plant artificial chromosomes (PACs)
- C12N15/8241—Phenotypically and genetically modified plants via recombinant DNA technology
- C12N15/8261—Phenotypically and genetically modified plants via recombinant DNA technology with agronomic (input) traits, e.g. crop yield
- C12N15/8262—Phenotypically and genetically modified plants via recombinant DNA technology with agronomic (input) traits, e.g. crop yield involving plant development
- C12N15/827—Flower development or morphology, e.g. flowering promoting factor [FPF]
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Botany (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于植物基因工程技术领域,具体涉及一种春兰CgWRKY40基因及其应用。The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, in particular to a ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene and its application.
背景技术Background technique
兰科(Orchidaceae)是开花植物中最大科之一,全世界含有25000多种,约占所有开花植物的10%。春兰(Cymbidium goeringii)属于兰科兰属中的小花型地生兰种类,其花型奇特、花色淡雅,花香清幽,叶姿优美,观赏价值和经济价值极高。春兰对生长环境要求较高,在生长过程中极易受到高温、低温、干旱等恶劣环境影响,严重时,会导致园艺观赏品质下降,甚至植株死亡。因此,研究植物应对非生物胁迫的分子机制以及鉴定具有抗逆功能的基因对春兰育种和生产具有重要意义。在植物细胞信号转导途径中,WRKY转录因子被认为是植物生长和多种胁迫响应的关键枢纽,为植物的遗传改良提供重要依据。Orchidaceae is one of the largest families of flowering plants, containing more than 25,000 species worldwide, accounting for about 10% of all flowering plants. Chunlan (Cymbidium goeringii ) belongs to the small-flowered ground orchid species in the genus Orchidaceae. Chunlan has high requirements on the growth environment, and is easily affected by harsh environments such as high temperature, low temperature, and drought during the growth process. Therefore, it is of great significance to study the molecular mechanism of plant response to abiotic stress and identify genes with stress resistance function for spring orchid breeding and production. In plant cell signal transduction pathways, WRKY transcription factors are considered to be key hubs for plant growth and responses to various stresses, providing an important basis for genetic improvement of plants.
WRKY转录因子是植物中最大的调节蛋白家族之一,参与多种生理过程,其中,最突出的是对生物和非生物胁迫的应激反应。有报道表明WRKY基因可以增强植株对逆境胁迫的耐受性。向日葵HaWRKY76转基因植株对水涝胁迫表现出更强的抗逆性,产量也明显增多。AtWRKY25的过表达增强拟南芥的耐盐性。AtWRKY57在水稻中的过表达不仅提高了水稻的抗旱性,而且增强了其对盐和PEG的耐受性。因此,利用基因工程技术,从春兰中克隆获得CgWRKY40基因,该基因在ABA胁迫下存在明显的表达差异,因此将CgWRKY40基因转入植物中,极具应用前景。WRKY transcription factors are one of the largest family of regulatory proteins in plants and are involved in a variety of physiological processes, the most prominent of which is the stress response to biotic and abiotic stresses. It has been reported that WRKY gene can enhance plant tolerance to stress. Sunflower HaWRKY76 transgenic plants showed stronger resistance to waterlogging stress and increased yield significantly. Overexpression ofAtWRKY25 enhances salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Overexpression ofAtWRKY57 in rice not only improved the drought resistance of rice, but also enhanced its tolerance to salt and PEG. Therefore, using genetic engineering technology, theCgWRKY40 gene was cloned from Chunlan. The gene has obvious expression differences under ABA stress. Therefore, it is very promising to transfer theCgWRKY40 gene into plants.
不同的植物,即使是相同的基因族,基因序列也是不同的,即使是80%以上的基因序列相同,但是因为部分基因插入的位点不同,将其转入植物中,所起到的作用也是不同的。当外源基因进入染色体上,产生了此基因编码的外源蛋白,外源蛋白或酶通过一系列的反应导致了其他酶或蛋白质活性的增强或者降低,另外当外源基因嵌入在染色体的某个区段时,必将对整个染色体产生影响,从而影响其他基因的活性或调控机制。Different plants, even the same gene family, have different gene sequences, even if more than 80% of the gene sequences are the same, but because the insertion sites of some genes are different, the effect of transferring them into plants is also different. When the exogenous gene enters the chromosome, the exogenous protein encoded by the gene is produced. The exogenous protein or enzyme leads to the enhancement or reduction of the activity of other enzymes or proteins through a series of reactions. In addition, when the foreign gene is embedded in a certain part of the chromosome When a segment is present, it will have an impact on the entire chromosome, thereby affecting the activity or regulatory mechanism of other genes.
即使插入的是同一个基因,但是由于插入位点不同或者染色体组不同,必然对所在染色体产生影响,进一步导致对所在染色体上的基因产生影响,而基因微小的改变,都有可能影响其调控机制,导致出现基因失活、活性降低、活性增强等改变,也造成基因作用的不同,而基因的作用需要通过验证才能获得,并不是通过推断就能得到。Even if the same gene is inserted, due to different insertion sites or different sets of chromosomes, it will inevitably affect the chromosome where it is located, which will further affect the genes on the chromosome where it is located. Small changes in genes may affect its regulatory mechanism. , resulting in changes such as gene inactivation, activity reduction, and activity enhancement, which also result in different gene roles, and the role of genes can only be obtained by verification, not by inference.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
发明目的:针对现有育种技术中存在的不足,本发明的目的是提供一种春兰CgWRKY40基因。本发明的另一目的是提供春兰CgWRKY40基因在兰花育种中的应用。Purpose of the invention: In view of the deficiencies in the existing breeding technology, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene. Another object of the present invention is to provide the application of ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene in orchid breeding.
技术方案:为了实现上述发明目的,本发明采用的技术方案如下:Technical scheme: in order to realize the above-mentioned purpose of the invention, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is as follows:
一种春兰CgWRKY40基因,其核苷酸序列如SEQ ID NO.1所示。A ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
所述的春兰CgWRKY40基因的表达蛋白,其氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO.2所示。The amino acid sequence of the expressed protein of the ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.
所述的春兰CgWRKY40基因在植物生产和育种中的应用。Application of the ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene in plant production and breeding.
含有所述的的春兰CgWRKY40基因的载体。The vector containing the described ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene.
含有所述的春兰CgWRKY40基因的宿主细胞。A host cell containing the ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene.
有益效果:与现有技术相比,本发明通过对春兰CgWRKY40基因的克隆与鉴定,基因的表达分析,验证其功能,发现过表达CgWRKY40基因的拟南芥植株在幼苗期,CgWRKY40转基因植株与WT相比,叶片明显较大且多,伴有明显肉眼可见的性状毛,营养生长旺盛,且开花较野生型拟南芥要迟,说明CgWRKY40促进了转基因植株的营养生长,从而延迟了开花,可见该基因在兰花和其它植物生产、育种中将有广泛的用途。Beneficial effect: Compared with the prior art, the present invention through the cloning and identification of ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene, the expression analysis of the gene, and verifying its function, it is found that the Arabidopsis plant overexpressing theCgWRKY40 gene is in the seedling stage, and theCgWRKY40 transgenic plant is similar to the WT In contrast, the leaves were significantly larger and more numerous, accompanied by obvious naked-eye hairs, vigorous vegetative growth, and flowering was later than that of wild-type Arabidopsis, indicating thatCgWRKY40 promoted the vegetative growth of transgenic plants, thereby delaying flowering. It can be seen that The gene will have a wide range of applications in the production and breeding of orchids and other plants.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1是春兰CgWRKY40基因克隆和构建的过表达载体图;Fig. 1 is a diagram of the overexpression vector cloned and constructed of ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene;
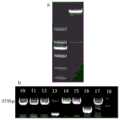
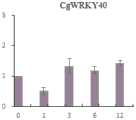
图2 中a图是CgWRKY40在春兰各组织中的表达情况,其中,R表示根,P表示假鳞茎,L表示叶,F表示花;b图是ABA胁迫下春兰CgWRKY40基因的表达情况;In Figure 2, picture a is the expression ofCgWRKY40 in various tissues of Chunlan, where R represents root, P represents pseudobulb, L represents leaf, and F represents flower; picture b is the expression ofCgWRKY40 gene in Chunlan under ABA stress;
图3中 a图是酶切结果图,其中,M:DL2000 Marker;CgWRKY40与pBI121连接后用SmaI和SnaBI双酶切;b图是阳性重组子的筛选图,其中,M:DL2000 Marker,目的条带大小为939bp;In Figure 3, picture a is the result of enzyme digestion, in which, M: DL2000 Marker;CgWRKY40 was ligated with pBI121 and then double digested with SmaI and SnaBI; picture b is the screening picture of positive recombinants, wherein, M: DL2000 Marker, the target bar The band size is 939bp;
图4是转基因拟南芥植株PCR结果图,其中,M:DL2000 Marker;1:以载体质粒DNA为阳性对照;2:野生型DNA为阴性对照;Figure 4 is a graph of the PCR results of transgenic Arabidopsis plants, wherein M: DL2000 Marker; 1: vector plasmid DNA is used as a positive control; 2: wild-type DNA is used as a negative control;
图5是转CgWRKY40基因植株与野生型拟南芥植株株型比较图,图中WT,野生型拟南芥;40-1,40-2,40-3,40-4,转CgWRKY40基因的不同株系;Figure 5 is a comparison of plant typesbetween CgWRKY40 gene transgenic plants and wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana plants. In the figure, WT, wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana; 40-1, 40-2, 40-3, 40-4, the difference of transgenicCgWRKY40 gene strain;
图6是转CgWRKY40基因植株与野生型拟南芥在ABA胁迫下的表达量;Figure 6 is the expression level ofCgWRKY40 gene transgenic plants and wild-type Arabidopsis under ABA stress;
图7是转CgWRKY40基因植株根长变化图;WT:普通野生型拟南芥;横坐标代表基因号;纵坐标代表根长(cm);ABA的浓度单位(μM)。Figure 7 is a graph showing the change of root length ofCgWRKY40 transgenic plants; WT: common wild-type Arabidopsis; the abscissa represents the gene number; the ordinate represents the root length (cm); the concentration unit of ABA (μM).
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施例对本发明做进一步的说明。The present invention will be further described below with reference to specific embodiments.
实施例1Example 1
本实施例所采用的材料是春兰‘宋梅’叶片,采后速冻于液氮中,超低温冰箱(-80℃)保存。The material used in this example is the leaves of Chunlan 'Songmei', which were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen after harvest and stored in an ultra-low temperature refrigerator (-80°C).
1)春兰叶片总RNA的提取1) Extraction of total RNA from Chunlan leaves
按照TaKaRa植物总RNA提取试剂盒的说明书进行,具体操作为:Follow the instructions of the TaKaRa Plant Total RNA Extraction Kit. The specific operations are:
将超低温冻存的春兰叶片迅速转移至用液氮预冷的研钵中,用研杵研磨组织,其间不断加入液氮,直至研磨成粉末状;将研磨成粉状的样品加入到含有450 μl Buffer PE 的1.5 mL灭菌 tube中,用移液器反复吹打直至裂解液中无明显沉淀;将裂解液12,000 rpm,4℃离心5min;将上清液小心吸取到新的1.5 mL灭菌tube 中。加入上清液 1/10体积的Buffer NB,Vortex 振荡混匀,12,000 rpm,4℃离心5 min;将上清液小心吸取到新的1.5mL灭菌 tube 中,加入450μL的 Buffer RL,使用移液枪将溶液混合均匀;加入混合液1/2体积的无水乙醇,使用移液枪将溶液混合均匀后,立即将混合液全部转入到RNA SpinColumn中; 12,000 rpm,离心1min,弃滤液,将RNA Spin Column 放回到2 ml CollectionTube 中;将500μL的 Buffer RWA 加入至RNA Spin Column 中,12,000 rpm 离心30s,弃滤液;600μL的Buffer RWB 加入至RNA Spin Column中,12,000 rpm 离心30s,弃滤液;向RNASpin Column膜中央加入50μL DNase I 反应液,室温静置15min;向RNA Spin Column膜中央加入350μL的Buffer RWB,12,000 rpm离心30s,弃滤液;将 RNA Spin Column 重新安置于2mL Collection Tube 上,12,000 rpm 离心2min;将 RNA Spin Column 安置于1.5 mL的RNase Free Collection Tube上,在RNA Spin Column 膜中央处加入50μL的 RNaseFree dH2O室温静置5min,12,000 rpm 离心2min洗脱RNA。所得RNA经浓度和纯度检测后存于-80℃冰箱保存备用。The ultra-low temperature frozen Chunlan leaves were quickly transferred to a mortar pre-cooled with liquid nitrogen, and the tissue was ground with a pestle, during which liquid nitrogen was added continuously until it was ground into powder; Buffer PE into a 1.5 mL sterilized tube, pipette repeatedly until there is no obvious precipitation in the lysate; centrifuge the lysate at 12,000 rpm and 4°C for 5 min; carefully pipette the supernatant into a new 1.5 mL sterilized tube . Add 1/10 volume of Buffer NB to the supernatant, mix with Vortex, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm and 4°C for 5 min; carefully pipette the supernatant into a new 1.5 mL sterile tube, add 450 μL of Buffer RL, and use a pipette Mix the solution evenly with a liquid gun; add 1/2 volume of anhydrous ethanol to the mixture, and use a pipette to mix the solution evenly, immediately transfer all the mixture to the RNA SpinColumn; centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, discard the filtrate, Put the RNA Spin Column back into the 2 ml CollectionTube; add 500 μL of Buffer RWA to the RNA Spin Column, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 30s, and discard the filtrate; add 600 μL of Buffer RWB to the RNA Spin Column, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 30s, and discard the filtrate ; Add 50 μL of DNase I reaction solution to the center of the RNA Spin Column membrane, and let stand for 15 min at room temperature; Add 350 μL of Buffer RWB to the center of the RNA Spin Column membrane, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 30 s, and discard the filtrate; relocate the RNA Spin Column to a 2 mL Collection Tube, Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 2 min; place the RNA Spin Column on a 1.5 mL RNase Free Collection Tube, add 50 μL of RNaseFree dH2 O to the center of the RNA Spin Column membrane, let stand for 5 min at room temperature, and centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 2 min to elute the RNA. The obtained RNA was tested for concentration and purity and stored in a -80°C refrigerator for later use.
吸取2μL RNA利用1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,结果显示28S和18S条带较为清晰,28S条带亮度约为18S的两倍,RNA质量较好。通过微量核算蛋白测定仪检测RNA纯度,OD260/OD280为2.04,OD260/OD230为2.02,完整性较好,可用于反转录。Aspirate 2 μL of RNA and detect it by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. The results show that the 28S and 18S bands are relatively clear, the 28S band is about twice as bright as the 18S, and the RNA quality is better. The RNA purity was detected by a micro-accounting protein analyzer. The OD260 /OD280 was 2.04, and the OD260 /OD230 was 2.02. The integrity was good and could be used for reverse transcription.
2)第一链cDNA的合成2) Synthesis of first-strand cDNA
以所得到的的总RNA为模板,使用TaKaRa反转录试剂盒进行反转录,使用Oligo(dT)作为锚定引物,反转录合成第一链cDNA。具体操作如下:Using the obtained total RNA as a template, reverse transcription was performed using a TaKaRa reverse transcription kit, and Oligo(dT) was used as an anchor primer to reverse transcription to synthesize the first-strand cDNA. The specific operations are as follows:
在离心管中配制按照下列模板RNA/引物的顺序配制混合物,总量为10μL:模板1μg,Oligo(dT) Primer(50μM) 1μL,dNTP Mixture(10mM each) 1μL ,剩余体积用RNase-freeddH2O补齐。65℃保温5min后,冰上迅速冷却;将该离心管离心,使离心管中的混合物均沉于管底。在新的离心管中配制反转录反应液(20μL):上述变性后反应液10μL,5×PrimeScriptBuffer 4μL,RNase Inhibitor(40U/μl) 0.5μL,PrimeScript RTase(200 U/μl) 1μL,RNase Free dH2O补齐20μL。缓慢摇匀,在PCR仪上,30℃保温10min,42℃保温30min,95℃保温5min使酶失活,冰上放置,得到cDNA溶液。Prepare the mixture in the following order of template RNA/primers in a centrifuge tube in a total amount of 10 μL:
3)目的基因引物的设计及克隆3) Design and cloning of target gene primers
根据现有的春兰转录组测序数据,利用其它物种的WRKY相关基因序列进行Blast同源比对。利用Oligo6.0,Prime5.0设计相应引物,引物序列为:Based on the existing Chunlan transcriptome sequencing data, theWRKY -related gene sequences of other species were used for Blast homology alignment. Use Oligo6.0, Prime5.0 to design the corresponding primers, the primer sequences are:
CgWRKY40-F:5'- ATGGAACCGTCCCCTC -3',CgWRKY40-F: 5'-ATGGAACCGTCCCCTC-3',
CgWRKY40-R:5'- TCAATTATGAGAAGATGGGAGTT -3'。CgWRKY40-R: 5'-TCAATTATGAGAAGATGGGAGTT-3'.
以cDNA第一链为模板,利用PrimerStar Max高保真酶进行春兰CgWRKY40基因的克隆。PCR扩增体系(50μL)为:25μlL PrimerStar Max,2μL Forward Primer,2μL ReversePrimer,2μL Template DNA,19μL ddH2O。PCR程序为:反应条件为94℃预变性3min,98℃变性10s,60℃退火5s,72℃延伸30s,32个循环,72℃总延伸5min,16℃保温。Using the first strand of cDNA as a template, the clone of ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene was carried out using PrimerStar Max high-fidelity enzyme. The PCR amplification system (50 μL) was: 25 μL PrimerStar Max, 2 μL Forward Primer, 2 μL ReversePrimer, 2 μL Template DNA, 19 μL ddH2 O. The PCR program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, denaturation at 98 °C for 10 s, annealing at 60 °C for 5 s, extension at 72 °C for 30 s, 32 cycles, total extension at 72 °C for 5 min, and incubation at 16 °C.
PCR反应完成后,取全部PCR产物通过1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测并切割目的片段,凝胶回收纯化PCR目的扩增产物。采用天根公司的DNA凝胶回收试剂盒,进行目的片段纯化回收,具体操作为:向吸附柱CA2中(吸附柱放入收集管中)加入500μL平衡液BL,12000rpm离心1min,倒掉收集管中的废液,将吸附柱重新放回收集管中;将单一目的条带从琼脂糖凝胶中切下,放入干净的离心管中,称取重量;向胶块中加入等体积溶液PN(如果凝胶为0.1g,其体积可视为100μL,则加入100μL PN溶液),50℃水浴放置,其间不断温和上下翻转离心管,直至胶块完全溶解;将上一步所得溶液加入一个吸附柱CA2中,室温放置2min,12000rpm离心1min,倒掉收集管中废液,将吸附柱CA2放入收集管中;向吸附柱CA2中加入600μL漂洗液W,12000rpm离心1min,倒掉收集管中的废液,将吸附柱放回收集管中;12000rpm离心2min,尽量除尽漂洗液,将吸附柱置于室温放置5min,彻底晾干;将吸附柱放到一个干净离心管中,向吸附膜中间位置悬空滴加30μL ddH2O,室温静置2min,12000rpm离心2min收集DNA溶液。取2μL回收纯化后的产物,使用1%琼脂糖进行凝胶电泳检测。After the PCR reaction was completed, all the PCR products were taken through 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis to detect and cut the target fragment, and the target PCR product was recovered and purified from the gel. The DNA gel recovery kit from Tiangen Company was used to purify and recover the target fragments. The specific operation is as follows: add 500 μL of equilibrium solution BL to the adsorption column CA2 (the adsorption column is placed in the collection tube), centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, and pour out the collection tube. Put the adsorption column back into the collection tube; cut the single-purpose band from the agarose gel, put it into a clean centrifuge tube, and weigh it; add an equal volume of solution PN to the gel block (If the gel is 0.1 g and its volume can be regarded as 100 μL, add 100 μL of PN solution), place it in a water bath at 50°C, and gently turn the centrifuge tube up and down until the gel block is completely dissolved; add the solution obtained in the previous step to an adsorption column In CA2, place at room temperature for 2min, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1min, pour off the waste liquid in the collection tube, put the adsorption column CA2 into the collection tube; add 600μL of rinsing solution W to the adsorption column CA2, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1min, pour out the collection tube waste liquid, put the adsorption column back into the collection tube; centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 2 min to remove the rinse solution as much as possible, place the adsorption column at room temperature for 5 min, and dry it thoroughly; put the adsorption column in a clean centrifuge tube, and place it in the middle of the adsorption membrane 30 μL of ddH2 O was added dropwise to the position, left at room temperature for 2 min, and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 2 min to collect the DNA solution. 2 μL of the purified product was recovered and detected by gel electrophoresis using 1% agarose.
4)目的片段与载体连接4) The target fragment is ligated with the vector
克隆载体为全式金公司的pEASY-Blunt载体,进行连接反应,连接体系(5μL):4μL PCR纯化产物,1μL pEASY-Blunt Vector,轻轻吸打混匀后,室温放置5min,将离心管置于冰上。The cloning vector is the pEASY-Blunt vector of Quanxingjin Company, and the ligation reaction is carried out. The ligation system (5 μL): 4 μL of PCR purified product, 1 μL of pEASY-Blunt Vector. on ice.
5)连接产物的转化5) Conversion of ligation products
从超低温冰箱中取出感受态细胞Trans5α菌株,置于冰上融化。吸取5μL的过夜连接产物加入到100μL感受态细胞中;将离心管置于冰上冰浴30 min;42℃水浴锅中水浴,热激90s,期间不要摇动;后立即置于冰上冰浴2 min;在超净台中加入800μL无抗生素的液体培养基,37℃、180 rpm摇1h复苏;4000 rpm 离心3 min,吸去800μL上清;将沉淀的菌体重悬,涂于LB平板(Amp的浓度为100 mg/L),37℃培养过夜。Remove the competent cell Trans5α strain from the ultra-low temperature freezer and thaw on ice.
6)重组质粒的筛选及验证6) Screening and verification of recombinant plasmids
挑取在含有抗生素(Amp)的LB固体培养基上过夜生长的单菌落,接种到含有同样抗生素的750μL的LB液体培养基中。200 rpm,37℃过夜培养。A single colony grown overnight on LB solid medium containing antibiotics (Amp) was picked and inoculated into 750 μL of LB liquid medium containing the same antibiotics. Incubate overnight at 37°C at 200 rpm.
PCR扩增体系为:10uL Green TaqMix,1μl M13-F/R,1μL菌液,7μL ddH2O补充到20μL。The PCR amplification system was as follows: 10uL Green TaqMix, 1 μl M13-F/R, 1 μL bacterial solution, 7 μL ddH2 O supplemented to 20 μL.
PCR程序为:94℃10min;94℃30 s,55℃30 s,72℃1 min,30 cycles;72℃5 min;16℃forever。The PCR program was: 94°C for 10 min; 94°C for 30 s, 55°C for 30 s, 72°C for 1 min, 30 cycles; 72°C for 5 min; 16°C forever.
吸取5µL的PCR产物进行琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测分析。验证后,将条带大小正确的菌液样品委托南京金斯瑞生物科技有限公司测序,测序引物为通用引物M13F/R。测序结果在NCBI上进行比对分析。
根据对测序结果的分析,最终确定克隆得到1个春兰WRKY编码基因,命名为CgWRKY40基因,其核苷酸序列如SEQ ID NO.1所示,CgWRKY40基因编码长度为939bp,含有ATG起始密码子和TGA终止密码子,其中ORF全长为939bp,编码312个氨基酸的蛋白质,该蛋白氨基酸序列如SEQ ID NO.2所示。According to the analysis of the sequencing results, it was finally determined that a ChunlanWRKY encoding gene was cloned and named asCgWRKY40 gene, its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. and TGA stop codon, wherein the ORF has a full length of 939 bp and encodes a protein of 312 amino acids, the amino acid sequence of which is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.
实施例2Example 2
研究结果表明WRKY40基因在春兰中各个组织器官中均有表达(图2a),但是该基因在春兰花中的表达量最高,说明该基因在花中功能活跃。通过对春兰ABA胁迫处理的叶片进行表达分析(图2b),证明CgWRKY40基因在春兰叶片的ABA胁迫响应中起着重要的调控作用。The results showed that theWRKY40 gene was expressed in various tissues and organs in Chunlan (Fig. 2a), but the expression of this gene was the highest in spring orchid, indicating that the gene was functionally active in flowers. The expression analysis of ABA-stressed leaves of Chunlan orchid (Fig. 2b) demonstrated thatCgWRKY40 gene plays an important regulatory role in the ABA-stress response of Chunlan leaves.
本实施例所用的植物材料为拟南芥(Arabidopsis thaliana)Col(Columbia)野生型种子。The plant material used in this example isArabidopsis thaliana Col (Columbia) wild-type seeds.
本实施例所用的大肠杆菌菌株为Trans5α;农杆菌菌株为GV3101,分别用于转化拟南芥;试验中所用植物表达载体为pBI121。所用菌株分别购自全式金生物公司和普利斯生物公司。The Escherichia coli strain used in this example was Trans5α; the Agrobacterium strain was GV3101, which were respectively used to transform Arabidopsis thaliana; the plant expression vector used in the experiment was pBI121. The strains used were purchased from Quanjin Bio and Price Bio.
1)CgWRKY40基因过表达载体的构建1) Construction ofCgWRKY40 gene overexpression vector
将实施例1获得的CgWRKY40基因ORF全长序列与植物表达载体pBI121进行连接,构建的载体如图1。The full-length sequence of theCgWRKY40 gene ORF obtained in Example 1 was connected with the plant expression vector pBI121, and the constructed vector was shown in Figure 1.
2)质粒的提取:2) Extraction of plasmids:
按照天根质粒小提中量试剂盒说明书提取质粒,具体步骤如下:Extract the plasmid according to the instructions of the Tiangen Plasmid Small Extraction Kit. The specific steps are as follows:
取过夜培养的10mL菌液,12000 rpm离心1min,去掉上清液;取500μL P1溶液(含RNaseA)加至留有菌体沉淀的离心管中,使用涡旋仪彻底悬浮菌体沉淀;取500μL P2溶液加至离心管中,温和上下翻转时菌体裂解充分,取700μL P3溶液加至离心管中,立即温和上下翻转,充分混匀,当出现白色絮状沉淀后,12000rpm离心10min;取500μL平衡液BL加至吸附柱CP4中,12000rpm离心1min,弃掉收集管中的废液,将吸附柱放回收集管,将收集的上清液分批加入过滤柱CS中,12000rpm离心2min,小心将收集管中收集的溶液分批加入吸附柱CP4中,12000rpm离心1min,弃掉收集管中的废液,将吸附柱CP4放回收集管;取500μL去蛋白液PD加至吸附柱CP4中,12000rpm离心1min,弃掉收集管中废液,将吸附柱CP4重新放回收集管;取600μl 漂洗液PW(含无水乙醇)加至吸附柱CP4中,12000rpm离心1min,弃掉收集管中的废液,将吸附柱CP4放回收集管,12000rpm离心2min,去除吸附柱中残余的漂洗液;将吸附柱CP4移至新的1.5ml离心管中,向吸附膜中间加入60μL ddH2O;室温静置2min,12000rpm离心1min,离心管中收集的溶液即为质粒。最后测定质粒浓度,为下一步实验做准备。Take 10 mL of the overnight cultured bacterial solution, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, and remove the supernatant; add 500 μL of P1 solution (containing RNaseA) to the centrifuge tube with the bacterial pellet, and use a vortexer to completely suspend the bacterial pellet; take 500 μL The P2 solution was added to the centrifuge tube, and the cells were fully lysed when gently turned up and down. Take 700 μL of the P3 solution into the centrifuge tube, and immediately turn it up and down gently and mix thoroughly. When a white flocculent precipitate appears, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes; Add the equilibrium solution BL to the adsorption column CP4, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1min, discard the waste liquid in the collection tube, put the adsorption column back into the collection tube, add the collected supernatant to the filter column CS in batches, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 2min, be careful Add the solution collected in the collection tube to the adsorption column CP4 in batches, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, discard the waste liquid in the collection tube, and put the adsorption column CP4 back into the collection tube; take 500 μL of deproteinized solution PD and add it to the adsorption column CP4, Centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, discard the waste liquid in the collection tube, and put the adsorption column CP4 back into the collection tube; take 600 μl of rinsing solution PW (containing absolute ethanol) and add it to the adsorption column CP4, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, and discard the waste in the collection tube. waste liquid, put the adsorption column CP4 back into the collection tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 2 min to remove the residual rinse solution in the adsorption column; move the adsorption column CP4 to a new 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add 60 μL ddH2 O to the middle of the adsorption membrane; room temperature Let stand for 2 min, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 1 min, and the solution collected in the centrifuge tube is the plasmid. Finally, the plasmid concentration was determined to prepare for the next experiment.
3)特异酶切位点的添加3) Addition of specific restriction sites
以cDNA为模板,通过PCR方法在目的基因的两侧添加特异性酶切位点。春兰CgWRKY40基因两侧添加SmaI和SnaBI酶切位点。PCR反应体系、程序及所使用引物如下:Using cDNA as a template, specific restriction sites are added on both sides of the target gene by PCR method. SmaI and SnaBI restriction sites were added on both sides of ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene. The PCR reaction system, procedures and primers used are as follows:
PCR扩增体系(50μL):25μL PrimerStar Max,2μL Forward Primer,2μL ReversePrimer,2μL Template DNA,19μL ddH2O。PCR程序为:反应条件为94℃预变性3min,98℃变性10s,60℃退火5s,72℃延伸30s,32个循环,72℃总延伸5min,16℃保温。PCR amplification system (50 μL): 25 μL PrimerStar Max, 2 μL Forward Primer, 2 μL ReversePrimer, 2 μL Template DNA, 19 μL ddH2 O. The PCR program was as follows: pre-denaturation at 94 °C for 3 min, denaturation at 98 °C for 10 s, annealing at 60 °C for 5 s, extension at 72 °C for 30 s, 32 cycles, total extension at 72 °C for 5 min, and incubation at 16 °C.
所使用的引物序列:Primer sequences used:
CgWRKY40-SmaI-F:5'-TCACACAAACGGTGATACGTAATTATGAGAAGATGGGAGTTCAAAGA -3',CgWRKY40-SmaI-F: 5'-TCACACAAACGGTGATACGTAATTATGAGAAGATGGGAGTTCAAAGA-3',
CgWRKY40-SnaBI-R:5'-GGACTCTAGAGGATCCCCGGGATGGAGGACGTGTTGGATGAAT-3'。CgWRKY40-SnaBI-R: 5'-GGACTCTAGAGGATCCCCGGGATGGAGGACGTGTTGGATGAAT-3'.
将得到的PCR产物用1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离,使用天根琼脂糖凝胶DNA回收试剂盒进行回收纯化,将回收后的产物与pBI121载体连接,构建表达载体。The obtained PCR product was separated by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis, recovered and purified using Tiangen agarose DNA recovery kit, and the recovered product was connected to the pBI121 vector to construct an expression vector.
4)双酶切反应4) Double enzyme digestion reaction
将提取的pBI121质粒用SmaI和SnaBI在37℃条件下酶切15min,电泳回收线性载体,-20℃保存备用。双酶切反应体系为50μL:pBI121质粒 20μL,5×buffer 5μL,SmaI 1μL,SnaBI1μL,ddH2O 23μL。酶切结果如图3a所示,其中,M:DL2000 Marker;1:CgWRKY40,与pBI121连接后用用SmaI和SnaBI双酶切。The extracted pBI121 plasmid was digested with SmaI and SnaBI at 37°C for 15 min, the linear vector was recovered by electrophoresis, and stored at -20°C for future use. The double digestion reaction system was 50 μL: pBI121 plasmid 20 μL, 5×
5)连接反应5) Ligation reaction
琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测酶切后所回收到的目的基因和载体pBI121,根据所检测出的纯度和浓度,按连接体系加入各试剂。其中,目的片段分子数:载体分子数=3:1-5:1,连接反应体系为:线性化pBI121载体7μL,插入片段3μL,5×CE II buffer 4μl,Exnase II 2μl,ddH2OUp to 20μL。在37℃下反应30min,放置于冰上降温冷却。Agarose gel electrophoresis was used to detect the target gene and the vector pBI121 recovered after enzyme digestion, and each reagent was added according to the connection system according to the detected purity and concentration. Among them, the number of target fragment molecules: the number of vector molecules = 3:1-5:1, and the ligation reaction system is: linearized
6)连接产物转入大肠杆菌6) The ligation product was transferred into E. coli
将目的片段与载体pBI121连接后的产物转入大肠杆菌Trans5α感受态细胞中,方法同实施例1。The product obtained by ligating the target fragment with the vector pBI121 was transferred into Escherichia coli Trans5α competent cells, and the method was the same as that in Example 1.
7)重组子的鉴定7) Identification of recombinants
挑取平板上的单菌落接种到含有抗生素(卡那霉素)的LB液体培养基中,37℃、200 rpm震荡培养过夜。使用目的基因全长引物进行菌液PCR,以筛选阳性克隆。筛选后的阳性克隆送南京金斯瑞公司测序。同时使用天根质粒提取试剂盒提取质粒并进行酶切验证,判断酶切后片段大小是否一致。结果如图3b所示,为目的引物PCR结果,条带大小为939bp。Pick a single colony on the plate and inoculate it into LB liquid medium containing antibiotics (kanamycin), and inoculate overnight at 37°C and 200 rpm with shaking. Bacterial PCR was performed using the full-length primers of the target gene to screen for positive clones. The screened positive clones were sent to Nanjing GenScript for sequencing. At the same time, the Tiangen plasmid extraction kit was used to extract the plasmid and carry out digestion verification to determine whether the fragment size after digestion was consistent. The result is shown in Figure 3b, which is the PCR result of the target primer, and the size of the band is 939bp.
8)农杆菌感受态细胞的制备与转化8) Preparation and transformation of Agrobacterium competent cells
本实施例利用农杆菌GV3101来制备农杆菌感受态,进行拟南芥的侵染实验;农杆菌感受态制备过程为:挑取已经活化好的农杆菌单菌落,接种于5mL液体LB培养基中,28℃、250rpm摇菌培养20-24 h;吸取2mL菌液,接种到含有50mL液体LB培养基的三角瓶中,28℃、250rpm摇菌至OD600值为0.8左右;将扩大繁殖后的菌液置于冰上冰浴30 min,4℃、5000 rpm离心5 min,弃上清;加入10mL经预冷的0.1 mo1/L CaCl2溶液,充分悬浮沉淀的菌体;4℃,5000 rpm离心5 min,弃去上清;加入1mL预冷的20 mmo1/L CaCl2溶液充分悬浮菌体,即得到所要制备的GV3101感受态细胞,用离心管将其分装成100µL/管,迅速加入20%的无菌甘油,-80℃放置保存。In this example, Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 was used to prepare Agrobacterium-competent state, and the infection experiment of Arabidopsis thaliana was carried out; the Agrobacterium-competent state preparation process was as follows: picking a single activated Agrobacterium colony and inoculating it into 5 mL of liquid LB medium , 28°C, 250rpm for 20-24 h; draw 2mL of bacterial liquid, inoculate it into a conical flask containing 50mL of liquid LB medium, shake at 28°C, 250rpm until the OD600 value is about 0.8; The bacterial solution was placed in an ice bath on ice for 30 min, centrifuged at 4°C, 5000 rpm for 5 min, and the supernatant was discarded; 10 mL of pre-cooled 0.1 mol/L CaCl2 solution was added to fully suspend the precipitated bacteria; 4°C, 5000 rpm Centrifuge for 5 min, discard the supernatant; add 1 mL of pre-cooled 20 mmol/L CaCl2 solution to fully suspend the cells to obtain the GV3101 competent cells to be prepared. 20% sterile glycerol, stored at -80°C.
重组子的农杆菌转化:冰浴,使农杆菌感受态细胞融化,将1-5 µl经回收纯化后的质粒加入到200 μl的农杆菌感受态中,轻轻混匀,冰浴30 min;使用液氮速冻l min,37℃水浴锅中热击1-5 min,迅速置于冰上1-2 min;加入800 μl不含任何抗生素的LB培养基,28℃,100 rpm复苏2-4 h; 4000 rpm离心3 min,吸掉部分培养基;使用移液枪充分混匀剩余的菌液,后涂抹于添加 50 mg/L卡那霉素和50 mg/L链霉素(EHA105)或100 mg/L的庆大霉素(GV3101)的固体 LB 培基上;28℃倒置培养30-48 h。Agrobacterium transformation of recombinants: ice bath to melt Agrobacterium competent cells, add 1-5 µl of the recovered and purified plasmid to 200 µl of Agrobacterium competent cells, mix gently, and ice bath for 30 minutes; Quick-freeze in liquid nitrogen for 1 min, heat shock in a 37°C water bath for 1-5 min, and quickly place on ice for 1-2 min; add 800 μl of LB medium without any antibiotics, recover at 28°C, 100 rpm for 2-4 h; Centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 3 min, and aspirate part of the medium; use a pipette to mix the remaining bacterial solution well, and then apply it on the addition of 50 mg/L kanamycin and 50 mg/L streptomycin (EHA105) or 100 mg/L gentamicin (GV3101) on solid LB medium; invert at 28°C for 30-48 h.
农杆菌重组子的鉴定:从平板培养基上挑取长出的单菌落,接种于含有相应抗生素的液体培养基中;28℃,220 rpm培养过夜;使用35S-F分别搭配如下引物进行菌液PCR,引物序列为:Identification of Agrobacterium recombinants: Pick out single colonies grown from the plate medium and inoculate them in liquid medium containing corresponding antibiotics; cultivate overnight at 28°C, 220 rpm; use 35S-F with the following primers to carry out bacterial culture PCR, primer sequences are:
35S-F:5'-GATAGTGGAAAAGGAAGGTG-3',35S-F: 5'-GATAGTGGAAAAGGAAGGTG-3',
35S-CgWRKY40-R:5'- GGACTCTAGAGGATCCCCGGGATGGAGGACGTGTTGGATGAAT -3'。35S-CgWRKY40-R: 5'-GGACTCTAGAGGATCCCCGGGATGGAGGACGTGTTGGATGAAT-3'.
PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,鉴定是否含有目的片段;鉴定出的阳性克隆,扩大培养后,采用碱裂解法提取质粒,进行双酶切验证;鉴定后的阳性克隆加入适量无菌甘油,于-80℃保存备用。The PCR product was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to identify whether it contained the target fragment; the identified positive clones were expanded and cultured, and the plasmid was extracted by alkaline lysis method for double-enzyme digestion verification; the identified positive clones were added to an appropriate amount of sterile Glycerol, stored at -80°C for later use.
9)农杆菌介导的拟南芥的转化9) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis
采用花序侵染法将目的基因转入拟南芥中,具体操作方法为:拟南芥(col野生型)保持健康生长状态至开花;活化携带有目的基因的农杆菌EHA105菌株。挑取单菌落,接种于5mL含有卡那霉素和链霉素的LB培养基上,28℃、250 rpm摇菌至菌液刚刚变浑浊,约8-10 h;吸取1mL菌液,接种到三角瓶中(50mL )摇菌24 h,至OD值约为0.8左右;将菌液5000 rpm在室温下离心5 min,去除上清后收集菌体,用5%蔗糖溶液悬浮;浸泡前,加入SilwetL-77,浓度为0.05%(500 μl/L),晃出泡沫;将拟南芥的地上部分在农杆菌悬浮溶液中浸泡15-30 s,期间轻轻晃动;将浸过的拟南芥平躺在托盘中,用保鲜膜覆盖,锡箔纸密封避光,4℃,放置24h;揭开锡箔纸,正长条件下培养,当种子成熟时停止浇水。The target gene was transferred into Arabidopsis thaliana by inflorescence infection method. The specific operation method was as follows: Arabidopsis thaliana (col wild type) maintained a healthy growth state until flowering; activated the Agrobacterium EHA105 strain carrying the target gene. Pick a single colony, inoculate it on 5mL of LB medium containing kanamycin and streptomycin, shake the bacteria at 28°C and 250 rpm until the bacterial solution just becomes cloudy, about 8-10 h; aspirate 1 mL of the bacterial solution and inoculate it into Shake the bacteria in a conical flask (50 mL) for 24 hours until the OD value is about 0.8; centrifuge the bacteria solution at 5000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature, remove the supernatant, collect the bacteria, and suspend with 5% sucrose solution; before soaking, add SilwetL-77, the concentration is 0.05% (500 μl/L), shake out the foam; soak the aerial part of Arabidopsis thaliana in the Agrobacterium suspension solution for 15-30 s, shaking gently during the period; immerse the immersed Arabidopsis thaliana Lie flat on the tray, cover with plastic wrap, seal with foil, and place it at 4°C for 24 hours; uncover the foil, cultivate under positive growth conditions, and stop watering when the seeds are mature.
5%蔗糖溶液重悬液各成分如下:MS培养基,添加蔗糖50g/L,MES 0.5g/L,Silwet-77 500µl/L。(注意:配制后pH调制5.8,菌液离心重悬后再加入SilwetL-77;重悬液和菌液的换算关系为:重悬液用量:菌液OD*菌液体积=0.8*重悬液)。The components of the 5% sucrose solution re-suspension are as follows: MS medium, supplemented with sucrose 50g/L, MES 0.5g/L, Silwet-77 500µl/L. (Note: After preparation, adjust the pH to 5.8, and add SilwetL-77 after centrifuging and resuspending the bacterial solution; the conversion relationship between the resuspension and the bacterial solution is: the dosage of the resuspension: the OD of the bacterial solution * the volume of the bacterial solution = 0.8 * the resuspension ).
10)转基因植株的筛选10) Screening of transgenic plants
收集的T1代转基因拟南芥的种子,用酒精和升汞进行灭菌,步骤为:取适量获得的转基因种子放置于1.5mL离心管中,用75%酒精浸泡30 s;10%次氯酸钠灭菌2 min 30 s;无菌水冲洗3-4次,第一次冲洗后更换经高压灭菌的新离心管;用0.1%琼脂糖溶液悬浮。The collected T1 generation transgenic Arabidopsis seeds were sterilized with alcohol and mercuric chloride. The steps were: take an appropriate amount of the obtained transgenic seeds and place them in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, soak them in 75% alcohol for 30 s; sterilize with 10
将灭菌后的转基因拟南芥种子播种于含有抗生素(卡那霉素50 mg/L和头孢霉素100 mg/L)的1/2MS固体培养基上。22℃,光照培养。大约一周后将培养基上可以正常生长的拟南芥移植与土中,继续生长。Sterilized transgenic Arabidopsis seeds were sown on 1/2 MS solid medium containing antibiotics (kanamycin 50 mg/L and cephalosporin 100 mg/L). 22°C, light culture. About a week later, the Arabidopsis that can grow normally on the medium were transplanted into the soil and continued to grow.
11)转基因植株的检测11) Detection of transgenic plants
取适量拟南芥和转基因植株的幼嫩叶片,采用CTAB法提取DNA,具体操作步骤为:将适量叶片置于灭菌处理后的2mL离心管中,加入700 µl的CTAB溶液,用球磨仪彻底研磨,65℃静置10 min;加入等体积的氯仿:异戊醇,数次颠倒使其混合均匀,14000 rpm离心10 min;将上清移至新的无菌离心管中,加入等体积的异丙醇,颠倒混匀数次,室温静置2 min,14000 rpm离心10 min,倒掉上清;加入70%的无水乙醇,使用移液枪吹打洗涤两次,14000rpm离心1min,弃去上清;吹干表面液体,加入20 µL ddH2O溶解。取上述提取的转基因和野生型拟南芥的DNA,用CgWRKY40基因的特异性引物进行PCR检测。Take an appropriate amount of young leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana and transgenic plants, and extract DNA by CTAB method. The specific operation steps are as follows: put an appropriate amount of leaves in a sterilized 2 mL centrifuge tube, add 700 µl of CTAB solution, and use a ball mill to thoroughly Grind, let stand at 65°C for 10 min; add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol, invert several times to mix evenly, and centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min; transfer the supernatant to a new sterile centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of Isopropanol, invert and mix several times, stand at room temperature for 2 min, centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min, and discard the supernatant; add 70% absolute ethanol, wash twice with a pipette, centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 1 min, and discard Supernatant; dry the surface liquid and add 20 µL ddH2 O to dissolve. The DNAs of transgenic and wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana extracted above were used for PCR detection with specific primers for theCgWRKY40 gene.
春兰CgWRKY40基因转化拟南芥后,共获得5个过表达CgWRKY40基因拟南芥株系。以重组质粒为阳性对照,以野生型为阴性对照,以水为空白对照,PCR结果如图4所示,阳性对照为CgWRKY40基因载体PCR结果,阴性对照以水为代替模板,WT是以野生型拟南芥DNA为模板。After the ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene was transformed into Arabidopsis thaliana, five Arabidopsis thaliana lines overexpressing theCgWRKY40 gene were obtained. Take the recombinant plasmid as the positive control, the wild type as the negative control, and the water as the blank control, the PCR results are shown in Figure 4, the positive control is the PCR result of theCgWRKY40 gene vector, the negative control uses water as the template, and the WT is the wild type Arabidopsis DNA as template.
12)表型观察12) Phenotypic observation
不同代转基因植株的获得:收获的转基因T1代种子经灭菌,筛选培养后,再移植于营养土中,22℃,16 h光照/8h黑暗培养;经检测后保留初步确认的转基因植株,待成熟后收获T1代种子,进行编号,得到T2代;同T1代一样,将T2代种子经灭菌后涂布于含抗生素的筛选培养基上,置于22℃,连续光照;10d左右,对不同编号的T2代种子进行存活率统计,选取存活比例为75%的植株移植与营养土中按照22℃,16 h光照/8h黑暗培养,并取叶片进行阳性检测;阳性T2代植株继续进行编号,收集种子,得到T3代种子;将种子灭菌后,用筛选培养基筛选,置于光下连续光照培养;10d左右,观察不同编号的T3代植株,全部存活并且没有出现分离的为T3代纯合植株。Obtainment of transgenic plants of different generations: The harvested transgenic T1 generation seeds were sterilized, screened and cultured, and then transplanted into nutrient soil at 22 °C, 16 h light/8 h dark culture; after testing, the preliminarily confirmed transgenic plants were retained for later. Harvest the seeds of the T1 generation after maturity, and number them to obtain the T2 generation; as with the T1 generation, the T2 generation seeds are sterilized and then coated on the screening medium containing antibiotics, placed at 22 ° C, and continuously illuminated; about 10 days, the The survival rate of the T2 generation seeds with different numbers was counted, and the plants with a survival rate of 75% were selected to be transplanted and cultivated in nutrient soil at 22°C, 16 h light/8 h dark, and the leaves were taken for positive detection; positive T2 generation plants continued to be numbered , collect the seeds to obtain the T3 generation seeds; after the seeds are sterilized, they are screened with a screening medium, and placed in the light for continuous light culture; about 10 days, the T3 generation plants of different numbers are observed, and all the T3 generation plants survive and do not appear to be separated. Homozygous plants.
对得到的转基因株系分批次进行观察。The obtained transgenic lines were observed in batches.
(1)选取其中表型明显的3个转基因植株进行观察,如图5,结果发现与野生型拟南芥相比,转基因拟南芥植株生长发育缓慢,CgWRKY40转基因植株在幼苗期,CgWRKY40转基因植株与WT相比,叶片明显较大且多,伴有明显肉眼可见的性状毛,营养生长旺盛,且开花较野生型拟南芥要迟,说明CgWRKY40促进了转基因植株的营养生长。(1) Three transgenic plants with obvious phenotypes were selected for observation, as shown in Figure 5. It was found that compared with wild-type Arabidopsis, the growth and development of transgenic Arabidopsis plants was slow.CgWRKY40 transgenic plants were in the seedling stage, andCgWRKY40 transgenic plants Compared with WT, the leaves were significantly larger and more numerous, accompanied by obvious visible hairs, vigorous vegetative growth, and flowering was later than that of wild-type Arabidopsis, indicating thatCgWRKY40 promoted the vegetative growth of transgenic plants.
(2)对转基因拟南芥进行ABA胁迫处理,将经过消毒处理的转基因拟南芥种子和野生型拟南芥种子播种于1/2MS培养基上生长4d左右,转移到添加100μM ABA的1/2MS培养基上,生长10d左右照相观察拟南芥根长,并记录数据,见图6,结果发现,CgWRKY40的表达模式为在1h先降低,而后上升,而在普通野生型拟南芥植株(WT)中的表达量几乎均为0,在转基因拟南芥植株中不同时刻均有不同程度的差异表达,实验结果证明CgWRKY40基因已成功转入拟南芥中;如图7,CgWRKY40过表达拟南芥在正常培养条件下根长比WT稍长,但均达到40mm以上,在不同ABA浓度下CgWRKY40转基因拟南芥根长降幅明显低于WT,说明CgWRKY40对ABA敏感,且可能减缓了ABA对根发育的抑制作用。(2) The transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana was subjected to ABA stress treatment. The sterilized transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana seeds and wild-type Arabidopsis seeds were sown on 1/2MS medium and grown for about 4 days, and then transferred to 1/2 MS medium supplemented with 100 μM ABA. On the 2MS medium, the root length of Arabidopsis thaliana was observed by photographing for about 10 d, and the data was recorded, as shown in Figure 6. It was found that the expression pattern ofCgWRKY40 first decreased at 1 h, and then increased, while in common wild-type Arabidopsis plants ( The expression level in WT) is almost 0, and there are different degrees of differential expression in transgenic Arabidopsis plants at different times. The experimental results show thatthe CgWRKY40 gene has been successfully transferred into Arabidopsis; as shown in Figure 7,CgWRKY40 overexpression Under normal culture conditions, the root length of Arabidopsis was slightly longer than that of WT, but all reached more than 40 mm. Under different ABA concentrations, the root length ofCgWRKY40 transgenic Arabidopsis decreased significantly lower than that of WT, indicating thatCgWRKY40 is sensitive to ABA and may slow down the effect of ABA on ABA. Inhibition of root development.
本实施例将过表达的春兰CgWRKY40基因的35S:CgWRKY40转入模式植物拟南芥中,进行表型观察和分析。从结果可以看出,过表达35S:CgWRKY40T2代拟南芥植株叶片明显较大且多,伴有明显肉眼可见的性状毛,营养生长旺盛,且开花较野生型拟南芥要迟;CgWRKY40超表达可能通过调控ABA信号通路相关基因的表达来减缓了ABA对根发育的抑制作用。In this example, the 35S:CgWRKY40 of the overexpressed ChunlanCgWRKY40 gene was transferred into the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana for phenotypic observation and analysis. It can be seen from the results that the T2-generation Arabidopsis plants overexpressing 35S:CgWRKY40 have significantly larger and more leaves, with obvious hairs visible to the naked eye, vigorous vegetative growth, and flowering later than wild-type Arabidopsis;CgWRKY40 overexpressed The expression may slow down the inhibitory effect of ABA on root development by regulating the expression of genes related to the ABA signaling pathway.
序列表 sequence listing
<110> 南京林业大学<110> Nanjing Forestry University
<120> 一种春兰CgWRKY40基因及其应用<120> A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY40 gene and its application
<160> 8<160> 8
<170> SIPOSequenceListing 1.0<170> SIPOSequenceListing 1.0
<210> 1<210> 1
<211> 939<211> 939
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 春兰Cymbidium goeringii<213> Cymbidium goeringii
<400> 1<400> 1
atggaaccgt cccctcggct cggctgctcc actgtaaatc tcgacctcag tgtcggtccg 60atggaaccgt cccctcggct cggctgctcc actgtaaatc tcgacctcag tgtcggtccg 60
accaacctcc tcctcgaaga tccgatcggc tcgagagctt tggcgactaa tccgatacaa 120accaacctcc tcctcgaaga tccgatcggc tcgagagctt tggcgactaa tccgatacaa 120
attctaatga atccgccaag tagagaagag actgaggata tgaagatgaa gatacaaaag 180attctaatga atccgccaag tagagaagag actgaggata tgaagatgaa gatacaaaag 180
ctaagtgaag agaattggaa gctgaatgag aagctgagtg ccatgactgt gagttacagc 240ctaagtgaag agaattggaa gctgaatgag aagctgagtg ccatgactgt gagttacagc 240
actcttcaga accagcttct tgatctcatg atctcatctc cttcggagaa gggagcggga 300actcttcaga accagcttct tgatctcatg atctcatctc cttcggagaa gggagcggga 300
tcccccacga agaaaaggaa gagcgcaagc ctcgaatctg atagccgcaa cgacgacagc 360tccccccacga agaaaaggaa gagcgcaagc ctcgaatctg atagccgcaa cgacgacagc 360
agcggctttg tcgcgcacgt ggagagcatg tctagcgacg attctcatca gaagttgagg 420agcggctttg tcgcgcacgt ggagagcatg tctagcgacg attctcatca gaagttgagg 420
gttgattcta gatcgactgt atcgaaggtt tgtgtgaagt ctgatccatc tgatcgaatg 480gttgattcta gatcgactgt atcgaaggtt tgtgtgaagt ctgatccatc tgatcgaatg 480
aacatggttg tgaaagatgg ctatcagtgg aggaaatatg ggcagaaggt tacaagagat 540aacatggttg tgaaagatgg ctatcagtgg aggaaatatg ggcagaaggt tacaagagat 540
aacccttcac cgagagctta tttcagatgc tccttcgccc cttcatgccc agttaagaag 600aacccttcac cgagagctta tttcagatgc tccttcgccc cttcatgccc agttaagaag 600
aaggtgcaga gaagtgttga tgatttgtcc atcttggttg ccacatatga aggtgagcac 660aaggtgcaga gaagtgttga tgatttgtcc atcttggttg ccacatatga aggtgagcac 660
aatcacaggc cgccattaca aggtgaagct ccgcctcgtt cgagccacgg tgtaagctcg 720aatcacaggc cgccattaca aggtgaagct ccgcctcgtt cgagccacgg tgtaagctcg 720
acgcctaatt tcaccggcca gacagtcacc gtcgatctca gggatgatcg gtggcgcgcg 780acgcctaatt tcaccggcca gacagtcacc gtcgatctca gggatgatcg gtggcgcgcg 780
gatttgaata aggttagcac agaggtagct tctctggagt ttcagaaggt catgatcgag 840gatttgaata aggttagcac agaggtagct tctctggagt ttcagaaggt catgatcgag 840
caaatggctg tggtcttgac gaaagatccc aactttagaa catcattagc gaatgcaata 900caaatggctg tggtcttgac gaaagatccc aactttagaa catcattagc gaatgcaata 900
tctgagagga tctttgaact cccatcttct cataattga 939tctgagagga tctttgaact cccatcttct cataattga 939
<210> 2<210> 2
<211> 312<211> 312
<212> PRT<212> PRT
<213> 春兰Cymbidium goeringii<213> Cymbidium goeringii
<400> 2<400> 2
Met Glu Pro Ser Pro Arg Leu Gly Cys Ser Thr Val Asn Leu Asp LeuMet Glu Pro Ser Pro Arg Leu Gly Cys Ser Thr Val Asn Leu Asp Leu
1 5 10 151 5 10 15
Ser Val Gly Pro Thr Asn Leu Leu Leu Glu Asp Pro Ile Gly Ser ArgSer Val Gly Pro Thr Asn Leu Leu Leu Leu Glu Asp Pro Ile Gly Ser Arg
20 25 30 20 25 30
Ala Leu Ala Thr Asn Pro Ile Gln Ile Leu Met Asn Pro Pro Ser ArgAla Leu Ala Thr Asn Pro Ile Gln Ile Leu Met Asn Pro Pro Ser Arg
35 40 45 35 40 45
Glu Glu Thr Glu Asp Met Lys Met Lys Ile Gln Lys Leu Ser Glu GluGlu Glu Thr Glu Asp Met Lys Met Lys Ile Gln Lys Leu Ser Glu Glu
50 55 60 50 55 60
Asn Trp Lys Leu Asn Glu Lys Leu Ser Ala Met Thr Val Ser Tyr SerAsn Trp Lys Leu Asn Glu Lys Leu Ser Ala Met Thr Val Ser Tyr Ser
65 70 75 8065 70 75 80
Thr Leu Gln Asn Gln Leu Leu Asp Leu Met Ile Ser Ser Pro Ser GluThr Leu Gln Asn Gln Leu Leu Asp Leu Met Ile Ser Ser Pro Ser Glu
85 90 95 85 90 95
Lys Gly Ala Gly Ser Pro Thr Lys Lys Arg Lys Ser Ala Ser Leu GluLys Gly Ala Gly Ser Pro Thr Lys Lys Arg Lys Ser Ala Ser Leu Glu
100 105 110 100 105 110
Ser Asp Ser Arg Asn Asp Asp Ser Ser Gly Phe Val Ala His Val GluSer Asp Ser Arg Asn Asp Asp Ser Ser Gly Phe Val Ala His Val Glu
115 120 125 115 120 125
Ser Met Ser Ser Asp Asp Ser His Gln Lys Leu Arg Val Asp Ser ArgSer Met Ser Ser Asp Asp Ser His Gln Lys Leu Arg Val Asp Ser Arg
130 135 140 130 135 140
Ser Thr Val Ser Lys Val Cys Val Lys Ser Asp Pro Ser Asp Arg MetSer Thr Val Ser Lys Val Cys Val Lys Ser Asp Pro Ser Asp Arg Met
145 150 155 160145 150 155 160
Asn Met Val Val Lys Asp Gly Tyr Gln Trp Arg Lys Tyr Gly Gln LysAsn Met Val Val Lys Asp Gly Tyr Gln Trp Arg Lys Tyr Gly Gln Lys
165 170 175 165 170 175
Val Thr Arg Asp Asn Pro Ser Pro Arg Ala Tyr Phe Arg Cys Ser PheVal Thr Arg Asp Asn Pro Ser Pro Arg Ala Tyr Phe Arg Cys Ser Phe
180 185 190 180 185 190
Ala Pro Ser Cys Pro Val Lys Lys Lys Val Gln Arg Ser Val Asp AspAla Pro Ser Cys Pro Val Lys Lys Lys Lys Val Gln Arg Ser Val Asp Asp
195 200 205 195 200 205
Leu Ser Ile Leu Val Ala Thr Tyr Glu Gly Glu His Asn His Arg ProLeu Ser Ile Leu Val Ala Thr Tyr Glu Gly Glu His Asn His Arg Pro
210 215 220 210 215 220
Pro Leu Gln Gly Glu Ala Pro Pro Arg Ser Ser His Gly Val Ser SerPro Leu Gln Gly Glu Ala Pro Pro Arg Ser Ser His Gly Val Ser Ser
225 230 235 240225 230 235 240
Thr Pro Asn Phe Thr Gly Gln Thr Val Thr Val Asp Leu Arg Asp AspThr Pro Asn Phe Thr Gly Gln Thr Val Thr Val Asp Leu Arg Asp Asp
245 250 255 245 250 255
Arg Trp Arg Ala Asp Leu Asn Lys Val Ser Thr Glu Val Ala Ser LeuArg Trp Arg Ala Asp Leu Asn Lys Val Ser Thr Glu Val Ala Ser Leu
260 265 270 260 265 270
Glu Phe Gln Lys Val Met Ile Glu Gln Met Ala Val Val Leu Thr LysGlu Phe Gln Lys Val Met Ile Glu Gln Met Ala Val Val Leu Thr Lys
275 280 285 275 280 285
Asp Pro Asn Phe Arg Thr Ser Leu Ala Asn Ala Ile Ser Glu Arg IleAsp Pro Asn Phe Arg Thr Ser Leu Ala Asn Ala Ile Ser Glu Arg Ile
290 295 300 290 295 300
Phe Glu Leu Pro Ser Ser His AsnPhe Glu Leu Pro Ser Ser His Asn
305 310305 310
<210> 3<210> 3
<211> 16<211> 16
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 人工序列(artiartificial sequence)<213> artificial sequence (artiartificial sequence)
<400> 3<400> 3
atggaaccgt cccctc 16atggaaccgt cccctc 16
<210> 4<210> 4
<211> 23<211> 23
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 人工序列(artiartificial sequence)<213> artificial sequence (artiartificial sequence)
<400> 4<400> 4
tcaattatga gaagatggga gtt 23tcaattatga gaagatggga gtt 23
<210> 5<210> 5
<211> 47<211> 47
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 人工序列(artiartificial sequence)<213> artificial sequence (artiartificial sequence)
<400> 5<400> 5
tcacacaaac ggtgatacgt aattatgaga agatgggagt tcaaaga 47tcacacaaac ggtgatacgt aattatgaga agatgggagt tcaaaga 47
<210> 6<210> 6
<211> 43<211> 43
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 人工序列(artiartificial sequence)<213> artificial sequence (artiartificial sequence)
<400> 6<400> 6
ggactctaga ggatccccgg gatggaggac gtgttggatg aat 43ggactctaga ggatccccgg gatggaggac gtgttggatg aat 43
<210> 7<210> 7
<211> 20<211> 20
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 人工序列(artiartificial sequence)<213> artificial sequence (artiartificial sequence)
<400> 7<400> 7
gatagtggaa aaggaaggtg 20gatagtggaa aaggaaggtg 20
<210> 8<210> 8
<211> 43<211> 43
<212> DNA<212> DNA
<213> 人工序列(artiartificial sequence)<213> artificial sequence (artiartificial sequence)
<400> 8<400> 8
ggactctaga ggatccccgg gatggaggac gtgttggatg aat 43ggactctaga ggatccccgg gatggaggac gtgttggatg aat 43
Claims (5)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010298688.1ACN111424038B (en) | 2020-04-16 | 2020-04-16 | Cymbidium CgWRKY40 gene and application thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010298688.1ACN111424038B (en) | 2020-04-16 | 2020-04-16 | Cymbidium CgWRKY40 gene and application thereof |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111424038Atrue CN111424038A (en) | 2020-07-17 |
| CN111424038B CN111424038B (en) | 2022-04-26 |
Family
ID=71558016
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010298688.1AExpired - Fee RelatedCN111424038B (en) | 2020-04-16 | 2020-04-16 | Cymbidium CgWRKY40 gene and application thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111424038B (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118726410A (en)* | 2024-09-03 | 2024-10-01 | 青岛农业大学 | WRKY40 transcription factor of peanut for promoting drought tolerance and early flowering in plants and its application |
| CN119592583A (en)* | 2025-02-12 | 2025-03-11 | 东北农业大学 | Application of soybean GmWRKY40 gene in soybean breeding |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040045049A1 (en)* | 1998-09-22 | 2004-03-04 | James Zhang | Polynucleotides and polypeptides in plants |
| CN107937411A (en)* | 2017-11-10 | 2018-04-20 | 中国林业科学研究院华北林业实验中心 | Chinese white poplar PtoWRKY40 genes, its expression vector and construction method and application |
| CN109628467A (en)* | 2019-01-30 | 2019-04-16 | 南京林业大学 | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY2 gene and its application |
| CN110256549A (en)* | 2019-07-29 | 2019-09-20 | 九圣禾种业股份有限公司 | Plant disease-resistant Protein G hWRKY40 and encoding gene and its application |
- 2020
- 2020-04-16CNCN202010298688.1Apatent/CN111424038B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20040045049A1 (en)* | 1998-09-22 | 2004-03-04 | James Zhang | Polynucleotides and polypeptides in plants |
| CN107937411A (en)* | 2017-11-10 | 2018-04-20 | 中国林业科学研究院华北林业实验中心 | Chinese white poplar PtoWRKY40 genes, its expression vector and construction method and application |
| CN109628467A (en)* | 2019-01-30 | 2019-04-16 | 南京林业大学 | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY2 gene and its application |
| CN110256549A (en)* | 2019-07-29 | 2019-09-20 | 九圣禾种业股份有限公司 | Plant disease-resistant Protein G hWRKY40 and encoding gene and its application |
Non-Patent Citations (8)
| Title |
|---|
| NCBI: "PREDICTED: Dendrobium catenatum probable WRKY transcription factor 40 (LOC110111426), transcript variant X2, mRNA", 《GENBANK DATABASE》* |
| NCBI: "probable WRKY transcription factor 40 isoform X2 [Dendrobium catenatum]", 《GENBANK DATABASE》* |
| RADHA YADAV等: "Transcriptome sequence analysis and mining of SSRs in Jhar Ber (Ziziphus nummularia (Burm.f.) Wight & Arn) under drought stress", 《SCIENTIFIC REPORTS》* |
| UNIPROTKB: "Putative WRKY transcription factor 40", 《EMBL》* |
| ZHANG G.Q.等: "Dendrobium catenatum putative WRKY transcription factor 40", 《EMBL》* |
| 刘戈宇等: "植物WRKY蛋白家族的结构及其功能", 《生命的化学》* |
| 刘文英: "《植物逆境与基因》", 31 May 2015, 北京理工大学出版社* |
| 张子凤等: "铁皮石斛DoWRKY6转录因子基因的克隆与分析", 《现代生物医学进展》* |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN118726410A (en)* | 2024-09-03 | 2024-10-01 | 青岛农业大学 | WRKY40 transcription factor of peanut for promoting drought tolerance and early flowering in plants and its application |
| CN119592583A (en)* | 2025-02-12 | 2025-03-11 | 东北农业大学 | Application of soybean GmWRKY40 gene in soybean breeding |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111424038B (en) | 2022-04-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN106868021B (en) | Gene OsNAC1 for controlling rice seed size and application thereof | |
| CN109628467A (en) | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY2 gene and its application | |
| CN104829700A (en) | Corn CCCH-type zinc finger protein, and encoding gene ZmC3H54 and application thereof | |
| CN111454966B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY4 gene and application thereof | |
| CN111424037B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY70 gene and application thereof | |
| CN108949786A (en) | Application of the arabidopsis E3 ubiquitinbond enzyme coding gene ATL27 in regulation plant salt resistant character | |
| CN110951771B (en) | Chinese cymbidiummiR390aApplication in controlling plant root system development | |
| CN111304198B (en) | Application of Chunlan miR390b in the control of plant vegetative organ development | |
| CN111424038B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY40 gene and application thereof | |
| CN100540665C (en) | Gene for regulating plant branching, vector containing the gene, microorganism transformed by the vector, and method for regulating plant branching using the microorganism | |
| CN111304221B (en) | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY31 gene and its application | |
| CN111304223B (en) | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY24 gene and its application | |
| CN109694874B (en) | Cloning and application of coding sequence of wheat gene TaCPSF30 | |
| CN104328127B (en) | Tumorous stem mustard stress resistance gene BjEFh1 as well as plant expression vector and application thereof | |
| CN110904106B (en) | Application of Chunlan miR159b in enhancing plant cold sensitivity | |
| CN111424041B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY49 gene and application thereof | |
| CN111304220B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY3 gene and application thereof | |
| CN111424039B (en) | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY65 gene and its application | |
| CN111304222B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY11 gene and application thereof | |
| CN109628468A (en) | A kind of Chunlan CgWRKY53 gene and its application | |
| CN111424040B (en) | Cymbidium CgWRKY21 gene and application thereof | |
| CN116254288B (en) | Application of a Chunlan MIR156b gene in regulating plant flowering time | |
| CN116179590B (en) | Application of cymbidium miR396 gene in regulation and control of thickening of plant stems | |
| CN105063062A (en) | Wheat salt-resistant drought-resistant gene TaDHN3, and expression vector and applications thereof | |
| CN104558132A (en) | DELLA gene families of peanut as well as encoding genes and applications of DELLA gene families |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20220426 |