CN111414274A - Remote exclusion method for abnormal state of cabinets in data centers - Google Patents
Remote exclusion method for abnormal state of cabinets in data centersDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111414274A CN111414274ACN201910014424.6ACN201910014424ACN111414274ACN 111414274 ACN111414274 ACN 111414274ACN 201910014424 ACN201910014424 ACN 201910014424ACN 111414274 ACN111414274 ACN 111414274A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- bmc
- rmc
- management system
- cabinet
- bmc22
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F11/00—Error detection; Error correction; Monitoring
- G06F11/07—Responding to the occurrence of a fault, e.g. fault tolerance
- G06F11/14—Error detection or correction of the data by redundancy in operation
- G06F11/1402—Saving, restoring, recovering or retrying
- G06F11/1415—Saving, restoring, recovering or retrying at system level
- G06F11/1441—Resetting or repowering
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L43/00—Arrangements for monitoring or testing data switching networks
- H04L43/08—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters
- H04L43/0805—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters by checking availability
- H04L43/0817—Monitoring or testing based on specific metrics, e.g. QoS, energy consumption or environmental parameters by checking availability by checking functioning
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/01—Protocols
- H04L67/02—Protocols based on web technology, e.g. hypertext transfer protocol [HTTP]
- H04L67/025—Protocols based on web technology, e.g. hypertext transfer protocol [HTTP] for remote control or remote monitoring of applications
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Environmental & Geological Engineering (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Debugging And Monitoring (AREA)
- Computer And Data Communications (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及数据中心,尤其涉及对数据中心中的机柜的异常状态的分析与排除的方法。The invention relates to a data center, in particular to a method for analyzing and eliminating abnormal states of cabinets in the data center.
背景技术Background technique
一般来说,一个数据中心通常会通过智能型平台管理界面(IntelligentPlatform Management Interface,IPMI)对数据中心内的机柜、端点服务器等设备的机柜管理控制器(Rack Management Controller,RMC)及基板管理控制器(BaseboardManagement Controller,BMC)进行远端管理。Generally speaking, a data center usually uses the Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) to monitor the rack management controller (RMC) and baseboard management controller of the cabinets, endpoint servers and other equipment in the data center. (Baseboard Management Controller, BMC) for remote management.
不论使用何种方式进行远端管理,只要任一机柜或端点服务器的RMC或BMC出现异常,管理者就会收到许多警告信件。然而,管理者一般难以通过这些警告信件在第一时间直接得知状态的真正问题点,往往需要随着时间不断推进,直到收到数百封警告信件并且与设备失去连线后,才能确定所述RMC、BMC发生了异常。No matter what method is used for remote management, as long as the RMC or BMC of any cabinet or endpoint server is abnormal, the administrator will receive many warning letters. However, it is generally difficult for managers to directly know the real problem point of the state through these warning letters at the first time. It often needs to continue to advance over time until hundreds of warning letters are received and the connection with the equipment is lost. The above mentioned RMC and BMC are abnormal.
更甚者,即使部分的管理平台从不同的监控管道收集到错误信息,并且进行汇整后提交故障评估报告给管理者,但这样的监控方式仍然需要由管理者进行最后的判断,并且决定处理方式。然而,只要有人为因素的介入,就无法全然避免误判的可能。What's more, even if some management platforms collect error information from different monitoring channels, and submit a fault assessment report to the manager after aggregation, such monitoring method still requires the manager to make the final judgment and decide to deal with it. Way. However, as long as there are human factors involved, the possibility of misjudgment cannot be completely avoided.
有鉴于此,本领域确实需要发展一套新颖的系统与方法,可针对处于异常状态的RMC及BMC自动实施远端修复机制,藉此强化数据中心的监控能力,使得机柜管理能够高度自动化,同时减少人为判定所间接流失的时间,并且避免人为误判。In view of this, it is indeed necessary to develop a novel system and method in the field, which can automatically implement a remote repair mechanism for the RMC and BMC in an abnormal state, thereby strengthening the monitoring capability of the data center, making the cabinet management highly automated, and at the same time. Reduce the time lost indirectly by human judgment, and avoid human misjudgment.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的主要目的,在于提供一种运用于数据中心的机柜异常状态的远端排除方法,可以在判断机柜管理控制器或基板管理控制器连线正常但判断可能即将出现异常状态时,直接于远端避免机柜管理控制器或基板管理控制器进入所述异常状态。The main purpose of the present invention is to provide a remote elimination method applied to the abnormal state of the cabinet in the data center. When it is judged that the connection of the cabinet management controller or the baseboard management controller is normal, but it is judged that the abnormal state may be about to occur, it can be directly The remote end prevents the cabinet management controller or the baseboard management controller from entering the abnormal state.
为了达成上述的目的,本发明的远端排除方法是运用于具有一机柜及由远端与该机柜连接的一机柜服务器管理系统的一数据中心,其中该机柜具有一机柜管理控制器(Rack Management Controller,RMC)及多个端点服务器,各该端点服务器分别具有一基板管理控制器(Baseboard Management Controller,BMC),该远端排除方法包括:In order to achieve the above object, the remote exclusion method of the present invention is applied to a data center having a rack and a rack server management system connected to the rack remotely, wherein the rack has a rack management controller (Rack Management Controller). Controller, RMC) and a plurality of endpoint servers, each of the endpoint servers has a baseboard management controller (Baseboard Management Controller, BMC) respectively, and the remote exclusion method includes:
a)该机柜服务器管理系统定时存取一数据库以取得该RMC及各该BMC的状态数据,并判断该RMC及各该BMC的状态变化;a) The rack server management system regularly accesses a database to obtain the status data of the RMC and each of the BMCs, and judges the status changes of the RMC and each of the BMCs;
b)依据该状态数据及该状态变化判断该RMC及各该BMC的其中之一是否处于预设的多种关注状态的其中之一;及b) judging whether one of the RMC and each of the BMCs is in one of a plurality of preset attention states according to the state data and the state change; and
c)于判断任一RMC或BMC处于该多种关注状态中的一第二类关注状态时,该机柜服务器管理系统自动对处于该第二类关注状态的该RMC或该BMC实施一远端服务重启机制,以避免该RMC或该BMC进入一异常状态,其中该第二类关注状态指该RMC或该BMC与该机柜服务器管理系统的连线正常,但判断可能即将出现该异常状态。c) When judging that any RMC or BMC is in a second type of concern state among the multiple concern states, the rack server management system automatically implements a remote service for the RMC or the BMC in the second type of concern state A restart mechanism is used to prevent the RMC or the BMC from entering an abnormal state, wherein the second type of concern state means that the connection between the RMC or the BMC and the rack server management system is normal, but it is determined that the abnormal state may occur soon.
如上所述,其中更包括下列步骤:As mentioned above, it further includes the following steps:
a01)该机柜服务器管理系统启动;a01) The cabinet server management system is started;
a02)该步骤a01)后,该机柜服务器管理系统定时主动远程访问该机柜内的该RMC及各该BMC;a02) After the step a01), the rack server management system regularly and actively remotely accesses the RMC and each of the BMCs in the rack;
a03)取得该RMC及各该BMC的该状态数据;a03) Obtain the status data of the RMC and each of the BMCs;
a04)将该状态数据储存至该数据库;及a04) store the status data in the database; and
a05)于该机柜服务器管理系统关闭前持续执行该步骤a02)至该步骤a04)。a05) Continue to execute the steps a02) to a04) before the rack server management system is shut down.
如上所述,其中更包括下列步骤:As mentioned above, it further includes the following steps:
a11)该机柜服务器管理系统启动;a11) The cabinet server management system is started;
a12)该步骤a11)后,该机柜服务器管理系统提供一操作界面;a12) After this step a11), the rack server management system provides an operation interface;
a13)于通过该操作界面接受一管理者的一操作行为时,依据该操作行为的内容对该RMC及各该BMC实施一远端管理程序;a13) When accepting an operation behavior of a manager through the operation interface, implement a remote management program to the RMC and each of the BMCs according to the content of the operation behavior;
a14)取得该远端管理程序对应的反馈信息;a14) Obtain the feedback information corresponding to the remote management program;
a15)将该操作行为及该反馈信息储存至该数据库;及a15) Store the operation behavior and the feedback information in the database; and
a16)于该机柜服务器管理系统关闭前持续执行该步骤a12)至该步骤a15)。a16) Continue to perform the steps a12) to a15) before the rack server management system is shut down.
如上所述,其中该步骤a)是取得该RMC及各该BMC目前的一智能平台管理界面(Intelligent Platform Management Interface,IPMI)的会话期间(session)总数,该步骤b)是于任一RMC或BMC的该IPMI session总数高于一第一门槛值时,判断该RMC或该BMC处于该第二类关注状态。As mentioned above, wherein the step a) is to obtain the total number of sessions (sessions) of an intelligent platform management interface (Intelligent Platform Management Interface, IPMI) of the RMC and each of the BMCs, and the step b) is performed in any RMC or When the total number of IPMI sessions of the BMC is higher than a first threshold, it is determined that the RMC or the BMC is in the second type of concern state.
如上所述,其中该步骤a)还取得该RMC及各该BMC的一系统资源使用率,该步骤b)是于任一RMC或BMC的该IPMI session总数高于该第一门槛值,并且该系统资源使用率高于一第二门槛值时,判断该RMC或该BMC处于该第二类关注状态。As described above, wherein the step a) also obtains a system resource utilization rate of the RMC and each of the BMCs, the step b) is that the total number of the IPMI sessions in any RMC or BMC is higher than the first threshold value, and the When the system resource usage rate is higher than a second threshold value, it is determined that the RMC or the BMC is in the second type of concern state.
如上所述,其中该系统资源使用率为该RMC或该BMC的中央处理单元或记忆体的使用率。As mentioned above, wherein the system resource usage rate is the usage rate of the central processing unit or the memory of the RMC or the BMC.
如上所述,其中该系统资源使用率为该RMC或该BMC主要用以提供HTTP服务或IPMI服务的系统资源的使用率。As described above, the system resource usage rate is the usage rate of system resources that the RMC or the BMC mainly uses to provide the HTTP service or the IPMI service.
如上所述,其中该步骤c)是由该机柜服务器管理系统发出一控制指令至处于该第二类关注状态的该RMC或该BMC,以令该RMC或该BMC重启IPMI服务。As described above, in the step c), the rack server management system sends a control command to the RMC or the BMC in the second type of concern state, so that the RMC or the BMC restarts the IPMI service.
如上所述,其中该步骤c)是由该机柜服务器管理系统发出一重置指令至处于该第二类关注状态的该RMC或该BMC,以强制该RMC或该BMC进行重置作业以重启IPMI服务。As described above, wherein in step c), the rack server management system sends a reset command to the RMC or the BMC in the second type of concern state, so as to force the RMC or the BMC to perform a reset operation to restart the IPMI Serve.
相对于相关技术,本发明的方法由与机柜连线的机柜服务器管理系统来进行分析并自动实施远端服务重启机制,无需等待管理者对于异常状态的人为判定,可大幅降低管理成本,亦使得机柜的监控无需人为干涉,也不受距离与时间的影响。Compared with the related art, the method of the present invention is analyzed by the cabinet server management system connected to the cabinet and automatically implements the remote service restart mechanism, without waiting for the administrator to manually determine the abnormal state, which can greatly reduce the management cost, and also make The monitoring of the cabinet does not require human intervention, nor is it affected by distance and time.
以下结合附图和具体实施例对本发明进行详细描述,但不作为对本发明的限定。The present invention is described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments, but is not intended to limit the present invention.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明的数据中心的示意图;Fig. 1 is the schematic diagram of the data center of the present invention;
图2为本发明的机柜的方框图的第一具体实施例;Fig. 2 is the first specific embodiment of the block diagram of the cabinet of the present invention;
图3A为本发明的数据搜集流程图的第一具体实施例;3A is a first specific embodiment of a data collection flowchart of the present invention;
图3B为本发明的数据搜集流程图的第二具体实施例;3B is a second specific embodiment of the data collection flow chart of the present invention;
图4为本发明的分析与排除流程图的第一具体实施例;Fig. 4 is the first specific embodiment of the analysis and elimination flow chart of the present invention;
图5为本发明的第一类关注状态排除流程图的第一具体实施例;FIG. 5 is a first specific embodiment of the first type of attention state exclusion flow chart of the present invention;
图6为本发明的第一类关注状态排除流程图的第二具体实施例;FIG. 6 is a second specific embodiment of the first type of attention state exclusion flow chart of the present invention;
图7为本发明的第二类关注状态排除流程图的第一具体实施例;Fig. 7 is the first specific embodiment of the second type of attention state exclusion flow chart of the present invention;
图8为本发明的第三类关注状态排除流程图的第一具体实施例。FIG. 8 is a first specific embodiment of the third type of attention state exclusion flowchart of the present invention.
其中,附图标记:Among them, reference numerals:
1…数据中心;1...data center;
2…机柜;2...cabinet;
21…机柜管理控制器;21 ... cabinet management controller;
211、221…网络接口控制器;211, 221... network interface controller;
22…基板管理控制器;22... baseboard management controller;
23…内部网络交换机;23...internal network switch;
24…内部硬件线路;24...internal hardware circuit;
3…机柜服务器管理系统;3... Cabinet server management system;
31…数据库;31...database;
4…公共网络交换机;4...Public network switches;
S11~S15、S21~S28…搜集步骤;S11~S15, S21~S28... collection steps;
S31~S39…分析与排除步骤;S31~S39...Analysis and elimination steps;
S41~S47、S51~S58、S61~S66、S71~S80…排除步骤。S41~S47, S51~S58, S61~S66, S71~S80...Exclusion steps.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
兹就本发明之一较佳实施例,配合附图,详细说明如后。Hereinafter, a preferred embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with the accompanying drawings.
本发明揭露了一种机柜异常状态的远端排除方法(下面将于说明书中简称为排除方法),所述排除方法主要运用于数据中心内,以协助管理者自动监控、分析并且排除数据中心内的异常状态。The present invention discloses a remote elimination method (hereinafter referred to as the elimination method in the specification) for the abnormal state of the cabinet. The elimination method is mainly used in the data center to assist the administrator to automatically monitor, analyze and eliminate the data in the data center. abnormal state.
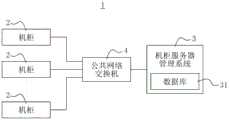
参阅图1,为本发明的数据中心的示意图。如图1所示,本发明所述的数据中心1主要具有多个机柜2,以及由远端与多个机柜2连线的机柜服务器管理系统3(下面简称为管理系统3)。所述管理系统3可设置于数据中心1的内部或外部,并且经由网络连接公共网络交换机4,再经由公共网络交换机4连接数据中心1内的多个机柜2。Referring to FIG. 1 , it is a schematic diagram of the data center of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1 , the
本发明的管理系统3可实时监控数据中心1内的多个机柜2、获取多个机柜2的各项信息、并且对这些信息进行分析。当发现任一机柜2发生异常状态或即将发生异常状态时,本发明的管理系统3可自动实施对应的处理机制以进行状况排除。藉此,本发明可以在完全不需要人为介入、大幅降低人为误判并且提升处理速度的前提下,对机柜2已发生的异常状态进行排除,或对可能即将发生的异常状态进行预防。The management system 3 of the present invention can monitor
于一实施例中,所述管理系统3可为个人电脑或云端服务器,内部具有一或多个中央处理单元(图未标示)。管理系统3被启动后,可通过公共网络交机4连接至数据中心1内的多个机柜2,并可藉由一或多个中央处理单元执行特定的应用程序与演算法,以实现对这些机柜2的监控、数据分析及异常状态排除。In one embodiment, the management system 3 can be a personal computer or a cloud server, and has one or more central processing units (not shown) inside. After the management system 3 is activated, it can be connected to a plurality of
所述管理系统3还具有数据库31,用以暂存或永久保存从数据中心1内的多个机柜2所获得的各项信息。于图1的实施例中,所述数据库31是内建于管理系统3。于其他实施例中,管理系统3亦可从外部连接一或多个数据库31,不加以限定。The management system 3 also has a
参阅图2,为本发明的机柜的方框图的第一具体实施例。图2的实施例中以数据中心1内的单一台机柜2连接至所述管理系统3为例,进行说明,然而数据中心1可依实际所需设置多台的机柜2,而不以图2所示者为限。Referring to FIG. 2 , it is a first specific embodiment of a block diagram of a cabinet of the present invention. In the embodiment of FIG. 2 , a
如图2所示,本发明的机柜2内主要包括至少一个机柜管理控制器(RackManagement Controller,RMC)21,以及与RMC21连接的多台端点服务器220,其中各个端点服务器220分别具备至少一个基板管理控制器(Baseboard Management Controller,BMC)22。As shown in FIG. 2, the
所述RMC21为一种嵌入式系统,设置于机柜2内,通过各式硬件线路协助处理机柜2的内部硬件设备(降温风扇,各式感测器或电源供应器等等设备)的所有对外通讯,并与机柜2内的所有端点服务器220的BMC22进行沟通。所述BMC22也为嵌入式系统,设置于端点服务器220中并协助处理端点服务器220的内部硬件设备(各式感测器等等设备)的所有对外通讯。The RMC21 is an embedded system, which is installed in the
本实施例中,RMC21通过内部硬件线路24连接机柜2内的所有端点服务器220的BMC22,藉由与各个BMC22沟通来控制各个端点服务器220并且获取所需信息。本实施例中,所述端点服务器可例如为直立式服务器(Tower Model Server)或刀锋服务器(BladeServer)等,但不加以限定。In this embodiment, the
如图2所示,设置在机柜2内的每一个端点服务器220分别具有一个固定的位置号码(如图2中的#1、#2、#n等),当端点服务器220或是BMC22对外的网络功能失效时,RMC21可通过内部硬件线路24连接至机柜2内的指定位置(如上述的#1、#2、#n),进而与该指定位置上的端点服务器220及BMC22沟通。如此一来,即使端点服务器220或是BMC22失去网络连线,机柜2仍可藉由RMC21来进行监控、管理各个BMC22并且排除各个BMC22的异常状况。As shown in FIG. 2, each
另,本发明的RMC21内设置有网络接口控制器(Network Interface Controller,NIC)211,各个BMC22内亦分别设置有网络接口控制器221。RMC21通过NIC211连接机柜2内部的内部网络交换机23,各个BMC22分别通过各自的NIC221连接所述内部网络交换机23。机柜2通过内部网络交换机23连接公共网络交换机4,并且藉由公共网络交换机4与所述管理系统3建立网络连线。如此一来,管理系统3可经由网络远程访问数据中心1内的机柜2,藉此查询并获取机柜2内的所有RMC21及BMC22的各项信息,并且储存于数据库31内。In addition, the
本发明的主要技术特征在于,管理系统3可经由网络定时访问机柜2,并获取机柜2内所有RMC21及BMC22的各项信息(例如状态数据、事件日志(event log)、系统资源使用率、端点服务器220内部感测器的感测数值等等),藉由这些信息来主动分析RMC21及BMC22是否发生异常状态,或即将发生异常状态。当管理系统3经分析后认为有必要时,即可主动于远端实施对应的机制,以于远端直接排除RMC21及/或BMC22的异常状态,或是预先避免RMC21及/或BMC22进入所述异常状态。The main technical feature of the present invention is that the management system 3 can regularly access the
本发明的技术方案可以在完全不需人为介入的情况下进行异常状态的处理,大幅降低了人为误判的可能,并且可令机柜2的监控达到高度自动化。The technical solution of the present invention can handle the abnormal state without human intervention, greatly reduces the possibility of human misjudgment, and can make the monitoring of the
续请参阅图3A,为本发明的数据搜集流程图的第一具体实施例。Please refer to FIG. 3A , which is a first specific embodiment of the data collection flowchart of the present invention.
如图3A所示,若管理者欲对数据中心1内的机柜2进行监控,则管理者可直接启动远端的管理系统3(步骤S11)。当管理系统3被启动后,即会主动远程访问数据中心1中的机柜2(以图2中的单一个机柜2为例)内的RMC21及所有BMC22(步骤S12)。并且,管理系统3藉由远程访问来取得机柜2中的RMC21及所有BMC22的各项信息(步骤S13),再将所取得的信息储存于本地端的数据中31中(步骤S14)。As shown in FIG. 3A , if the administrator wants to monitor the
具体地,本实施例中,管理系统3是在启动后定时主动访问机柜2,也就是将步骤S12、S13、S14的访问动作、信息取得动作及储存动作视为启动后的例行程序(routine)。于执行上述routine时,持续判断管理系统3是否关闭(步骤S15),并且于管理系统3关闭前持续执行上述步骤S12至步骤S14,以持续对机柜2内的RMC21与BMC22进行监控。Specifically, in this embodiment, the management system 3 actively accesses the
参阅图3B,为本发明的数据搜集流程图的第二具体实施例。Referring to FIG. 3B , it is a second specific embodiment of the data collection flowchart of the present invention.
本实施例中,当管理者启动了所述管理系统3后(步骤S21),管理系统3可以提供一个操作界面(步骤S22)。通过这个操作界面,管理者可以登入管理系统3,并且藉由管理系统3来于远端对数据中心1中的各个机柜2进行信息监控以及控制。本实施例中,所述操作界面可为一个实体界面或网页(Web)界面,不加以限定。In this embodiment, after the administrator starts the management system 3 (step S21 ), the management system 3 may provide an operation interface (step S22 ). Through this operation interface, the administrator can log in to the management system 3 and use the management system 3 to remotely monitor and control the information of each
在提供了所述操作界面后,管理系统3持续判断是否通过操作界面接受了由管理者所进行的操作(步骤S23)。若确实接受到管理者的操作,则管理系统3依据管理者的操作行为,从远端对机柜2以及机柜2内的RMC21及BMC22实施对应的远端管理(步骤S24)。接着,管理系统3可记录管理者的上述操作行为(步骤S25),并且,还可取得并记录管理系统3、机柜2、各端点服务器220以及RMC21、BMC22因为所述远端管理而产生的反馈、系统参数及执行数据等反馈信息(步骤S26)。最后,管理系统3同样将所述操作行为及反馈信息储存于数据库31中(步骤S27),以利于后续对于异常状态的分析动作。After the operation interface is provided, the management system 3 continuously judges whether the operation performed by the administrator is accepted through the operation interface (step S23). If the operation of the administrator is indeed received, the management system 3 performs corresponding remote management on the
相同地,本实施例的管理系统3会将步骤S22至步骤S27的动作视为启动后的routine。于执行上述routine时,持续判断管理系统3是否关闭(步骤S28),并且于管理系统3关闭前持续执行上述步骤S22至步骤S27,以持续监控并分析管理者所实施的操作行为对机柜2内的RMC21与BMC22所造成的影响。Similarly, the management system 3 of this embodiment regards the actions from step S22 to step S27 as a routine after starting. During the execution of the above routine, it is continuously determined whether the management system 3 is closed (step S28 ), and the above steps S22 to S27 are continuously executed before the management system 3 is closed, so as to continuously monitor and analyze the operation behaviors implemented by the administrator on the
续请参阅图4,为本发明的分析与排除流程图的第一具体实施例。Please refer to FIG. 4 , which is a first specific embodiment of the analysis and elimination flow chart of the present invention.
如图4所示,本实施例中管理系统3会定时存取数据库31(步骤S31),并且从数据库31中取得机柜2中的RMC21及BMC22各项信息、管理者的操作行为、以及各项反馈信息(步骤S32),并且加以进行分析。藉由上述数据,管理系统3可以分析出机柜2内的RMC21及各个BMC22是否处于预设的多种关注状态的其中之一(步骤S33)。As shown in FIG. 4 , in this embodiment, the management system 3 regularly accesses the database 31 (step S31 ), and obtains various information of the RMC21 and BMC22 in the
于一实施例中,所述管理系统3可以实时地取得机柜2中的RMC21与BMC22的各项信息、实时地从操作界面取得管理者的操作行为,并且据以进行分析。于另一实施例中,管理系统3可藉由图3A的步骤S14及图3B的步骤S27定时将上述数据储存至数据库31中,并且定时从数据库31中读取上述数据以进行分析,不加以限定。In one embodiment, the management system 3 can obtain various information of the
于一实施例中,上述RMC21及BMC22的各项信息,可例如为状态数据(如目前处于工作模式或更新模式、IP地址、MAC地址、子网络遮罩、闸道器IP地址、IPMI session数量等)、事件日志(event log)等,而上述操作行为可例如为管理者针对特定机柜2、端点服务器220或RMC21、BMC22所实行的数据查询作业、更新作业、重置作业等,但不加以限定。通过上述数据,管理系统3可以藉由执行对应演算法而分析出机柜2中目前是否具有需要即时救援的RMC21或BMC22。In one embodiment, the various information of the above-mentioned RMC21 and BMC22 can be, for example, status data (such as currently in working mode or update mode, IP address, MAC address, subnet mask, gateway IP address, number of IPMI sessions) etc.), event log (event log), etc., and the above-mentioned operation behaviors can be, for example, data query operations, update operations, reset operations, etc. performed by the administrator for a
于图4的实施例中,管理系统3主要可预设至少三个种类的关注状态,包括第一类关注状态、第二类关注状态及第三类关注状态,其中这三类的关注状态分别对应至RMC21/BMC22不同的异常状况,并且分别需要由管理系统3于远端直接实施不同的机制来加以排除或加以预防。In the embodiment of FIG. 4 , the management system 3 can mainly preset at least three types of attention states, including a first type of attention state, a second type of attention state, and a third type of attention state, wherein the three types of attention states are respectively Corresponding to different abnormal conditions of RMC21/BMC22, the management system 3 needs to directly implement different mechanisms at the remote end to eliminate or prevent them.
如图4所示,若管理系统3依据上述数据(主要依据状态数据、事件日志及管理者的操作行为)进行分析后发现有任一RMC21或BMC22已处于异常状态,但尚未与管理系统3失去连线,则会认定这个RMC21或BMC22是处于所述第一类关注状态(步骤S34)。当发现任一RMC21、BMC22处于第一类关注状态时,管理系统3可自动对处于第一类关注状态的RMC21、BMC22实施远端恢复机制,以远程解除RMC21或BMC22的异常状态(步骤S37)。As shown in FIG. 4 , if the management system 3 analyzes the above data (mainly based on the status data, event logs and the operation behavior of the administrator) and finds that any RMC21 or BMC22 is in an abnormal state, but has not yet lost contact with the management system 3 If the connection is made, the RMC21 or the BMC22 will be determined to be in the first type of attention state (step S34). When any RMC21 and BMC22 are found to be in the first type of concern state, the management system 3 can automatically implement a remote recovery mechanism for the RMC21 and BMC22 in the first type of concern state, so as to remotely release the abnormal state of the RMC21 or BMC22 (step S37 ) .
若管理系统3依据上述数据(主要依据RMC21与BMC22状态数据)进行分析后发现有任一RMC21或BMC22与管理系统3的连线正常,但判断可能即将出现异常状态,则会认定这个RMC21或BMC22是处于所述第二类关注状态(步骤S35)。当发现任一RMC21、BMC22处于第二类关注状态时,管理系统3可自动对处于第二类关注状态的RMC21、BMC22实施远端服务重启机制,以远程避免RMC21或BMC22进入可能的异常状态(步骤S38)。If the management system 3 analyzes the above data (mainly based on the status data of RMC21 and BMC22) and finds that the connection between any RMC21 or BMC22 and the management system 3 is normal, but it is judged that an abnormal state may occur, the RMC21 or BMC22 will be identified. is in the second type of attention state (step S35). When any RMC21 and BMC22 are found to be in the second type of concern state, the management system 3 can automatically implement a remote service restart mechanism for the RMC21 and BMC22 in the second type of concern state, so as to remotely prevent the RMC21 or BMC22 from entering a possible abnormal state ( step S38).
若管理系统3依据上述数据(主要依据状态数据、管理者的操作行为以及各项反馈信息)进行分析后发现有任一BMC22已失去了网络连线(即,管理系统3无法远程直接访问这个BMC22),则会认定这个BMC22是处于所述第三类关注状态(步骤S36)。当发现任一BMC22处于第三类关注状态时,管理系统3可自动对处于第三类关注状态的BMC22实施远端救援机制,以远程排除BMC22失去连线的状态,并且使BMC22的网络连线恢复正常(步骤S39)。If the management system 3 analyzes the above data (mainly based on the status data, the operation behavior of the administrator and various feedback information) and finds that any BMC22 has lost the network connection (that is, the management system 3 cannot directly access this BMC22 remotely). ), it will be determined that the
下面段落讨论所述第一类关注状态。The following paragraphs discuss the first type of attention states.
由于部分的RMC21/BMC22不具备基本输入输出系统(Basic Input/OutputSystem,BIOS),因此需要通过外部服务器所提供的网络时间协定(Network TimeProtocol,NTP)服务,或是硬件时钟芯片提供的实时时钟(Real-time Clock,RTC)服务来设定时间,以与其他设备达到时间同步。Since some RMC21/BMC22 do not have a Basic Input/Output System (BIOS), they need to use the Network Time Protocol (NTP) service provided by an external server, or the real-time clock ( Real-time Clock, RTC) service to set the time to achieve time synchronization with other devices.
如上所述,若在RMC21或BMC22的时间同步程序尚未完成前发生了系统事件,则虽然该系统事件仍然会被记录在RMC21、BMC22的事件日志中,但该系统事件的时间栏位将无法记录正确的事件发生时间,而只会记录例如“Pre-init”的字样。若没有正确的事件发生时间,则管理者无法将事件日志做为所述系统事件的参考指标,这样将会导致判断错误。除此之外,若所述RMC21、BMC22需要进行重置(Reset)作业,也可能会造成上述系统事件的事件发生时间记录错误或异常的情况。As mentioned above, if a system event occurs before the time synchronization procedure of RMC21 or BMC22 is completed, although the system event will still be recorded in the event log of RMC21 and BMC22, the time field of the system event will not be recorded. The correct event time, but only words such as "Pre-init" are logged. If there is no correct event occurrence time, the administrator cannot use the event log as a reference index of the system event, which will lead to a judgment error. In addition, if the
参阅图5,为本发明的第一类关注状态排除流程图的第一具体实施例。本实施例中,所述管理系统3会定时存取数据库31(步骤S41),以由数据库31中取得机柜2内的RMC21及BMC22的状态数据及事件日志,并且判断RMC21及BMC22的状态变化(步骤S42)。Referring to FIG. 5 , it is a first specific embodiment of the first type of attention state exclusion flow chart of the present invention. In this embodiment, the management system 3 periodically accesses the database 31 (step S41 ), so as to obtain the status data and event logs of the
本实施例中,管理系统3主要是判断所获得的事件日志中,是否有任一系统事件的事件发生时间不明或错误(步骤S43)。若所述事件日志中的所有系统事件皆记录了正确的事件发生时间,则管理系统3不主动实施任何动作。In this embodiment, the management system 3 mainly judges whether there is any system event in the obtained event log with an unknown event occurrence time or an error (step S43 ). If all the system events in the event log record the correct event occurrence time, the management system 3 does not take any action actively.
若经分析后,管理系统3发现任一RMC21或BMC22具有时间不明或错误的系统事件,则管理系统3会将该RMC21或BMC22视为处于所述第一类关注状态(步骤S44),即,认定这个RMC21或BMC22处于异常状态,但尚未失去网络连线。If, after analysis, the management system 3 finds that any RMC21 or BMC22 has an unknown or wrong system event, the management system 3 will regard the RMC21 or BMC22 as being in the first type of concern state (step S44), that is, It is determined that this RMC21 or BMC22 is in an abnormal state, but the network connection has not been lost.
于一实施例中,管理系统3主要可于所述事件日志中的任一系统事件的事件发生时间被记录为“Pre-init”或类似字样时(即,无法正确说明系统事件的发生时间),判断所述系统事件的事件发生时间不明或错误。于另一实施例中,管理系统3主要可以在从事件日志中发现任一RMC21或BMC22具有事件发生时间不明的系统事件,并且从状态数据中发现这个RMC21或BMC22尚未完成时间同步程序或是需要进行重置作业时,判断所述系统事件的事件发生时间不明或错误。In one embodiment, the management system 3 can mainly record the occurrence time of any system event in the event log as "Pre-init" or similar words (ie, the occurrence time of the system event cannot be correctly specified) , judging that the event occurrence time of the system event is unknown or wrong. In another embodiment, the management system 3 can mainly find from the event log that any RMC21 or BMC22 has a system event with an unknown event occurrence time, and find from the status data that the RMC21 or BMC22 has not completed the time synchronization procedure or needs to be When the reset operation is performed, it is determined that the event occurrence time of the system event is unknown or wrong.
当管理系统3于步骤S44中认定一个RMC21或BMC22处于第一类关注状态后,管理系统3首先取得本次存取事件日志的时间戳记(步骤S45),将这个时间戳记做为所述系统事件的备位时间识别信息,并储存于数据库31中(步骤S46)。于一实施例中,管理系统3是将本次存取数据库31以读取所述事件日志的时间做为上述时间戳记。于另一实施例中,管理系统3是将本次远程访问机柜2并从RMC21、BMC22取得所述事件日志的时间做为上述时间戳记,但不加以限定。When the management system 3 determines in step S44 that an
举例来说,所述事件日志的原始内容可例如下表所示:For example, the original content of the event log can be as shown in the following table:
若管理系统3在2018年12月22日的下午11时32分23秒时存取了所述事件日志,并发现事件二的事件发生时间有误,则管理系统3可以主动为事件二产生所述备位时间识别信息,并且修改事件日志的内容或是产生新的事件日志。新的事件日志可例如下表所示:If the management system 3 accesses the event log at 11:32:23 pm on December 22, 2018, and finds that the event occurrence time of the second event is wrong, the management system 3 can take the initiative to generate the second event. Describe the identification information of the backup time, and modify the content of the event log or generate a new event log. The new event log can look like the following table:
当管理者通过所述操作界面登入管理系统3,并且于管理系统3中查询所述事件日志时,管理系统3即可如上表所示,显示所述备位时间识别信息以做为事件二的事件发生时间。如此一来,即使RMC21或BMC22在时间同步未完成前发生一个系统事件,管理系统3仍可为该系统事件设定一个可供识别的备位时间,以利管理系统3以及管理者于对该系统事件的解读,并藉此强化远端恢复的效果。When the administrator logs into the management system 3 through the operation interface and queries the event log in the management system 3, the management system 3 can display the identification information of the standby time as the second event log as shown in the above table. The time the event occurred. In this way, even if a system event occurs in RMC21 or BMC22 before time synchronization is completed, the management system 3 can still set an identifiable backup time for the system event, so that the management system 3 and the administrator can Interpretation of system events, and thereby enhance the effect of remote recovery.
步骤S46后,管理系统3可进一步通过网络发出控制指令(例如第一控制指令)至处于第一类关注状态的RMC21或BMC22,以对具有时间错误的异常状态的RMC21或BMC22执行时间校正程序(步骤S47)。于一实施例中,所述时间校正程序是控制RMC21或BMC22藉由NTP服务进行时间校正。于另一实施例中,所述时间校正程序是强制RMC21或BMC22进行重置作业,但不加以限定。After step S46, the management system 3 can further issue a control command (such as a first control command) to the RMC21 or BMC22 in the first type of concern state through the network, so as to execute the time correction procedure ( step S47). In one embodiment, the time correction procedure controls the RMC21 or the BMC22 to perform time correction through the NTP service. In another embodiment, the time calibration procedure is to force the
下面段落继续说明其他可能发生的第一类关注状态。The following paragraphs go on to describe other possible first-class states of concern.
由于数据中心1内部的机柜2数量众多,当管理者有更新的需求时,实难以通过人工方式逐台进行更新。因此,当管理者要对机柜2内的RMC21、BMC22实施更新作业时(例如固件更新),可对管理系统3进行操作,以通过管理系统3的相关程序码来发送更新指令以及最新版本的固件,藉此于远端同时更新数据中心1内的多个机柜2的RMC21及BMC22。Due to the large number of
若于更新过程中遇到网络拥塞或网络信号不稳定造成网络连线中断等问题,使得部分RMC21、BMC22无法依循正常的更新流程完成更新作业,就有可能造成更新作业失败。然而,部分RMC21、BMC22在更新作业失败后仅会造成系统无法正常运作,但并未失去网络连线(例如进入更新模式后无法恢复为工作模式),此时就需要由管理系统3于远端介入以进行异常状况排除。If the network connection is interrupted due to network congestion or unstable network signal during the update process, some RMC21 and BMC22 cannot follow the normal update process to complete the update operation, which may cause the update operation to fail. However, some RMC21 and BMC22 will only cause the system to fail to operate normally after the update operation fails, but the network connection will not be lost (for example, it cannot be restored to the working mode after entering the update mode). Intervention for abnormal condition exclusion.
参阅图6,为本发明的第一类关注状态排除流程图的第二具体实施例。本实施例中,管理系统3同样定时存取数据库31(步骤S51),以由数据库31中取得机柜2内的RMC21及BMC22的状态数据及事件日志,同时取得管理者通过操作界面所实施的操作行为,并且判断RMC21及BMC22的状态变化(步骤S52)。Referring to FIG. 6, it is a second specific embodiment of the first type of attention state exclusion flow chart of the present invention. In this embodiment, the management system 3 also regularly accesses the database 31 (step S51 ), so as to obtain the status data and event logs of the
本实施例中,管理系统3首先可对RMC21及BMC22的状态数据以及事件日志进行分析,以判断是否有任一RMC21、BMC22的更新作业已逾时(步骤S54)或发生错误,并且判断所述更新作业逾时或发生错误的RMC21或BMC22的网络连线是否正常(步骤S55)。若管理系统3在分析后发现有任一RMC21或BMC22的更新作业逾时或发生错误但网络连线仍然正常,则可将这个RMC21或BMC22视为处于所述第一类关注状态(步骤S56),即,处于异常状态,但尚未失去连线。In this embodiment, the management system 3 can first analyze the status data and event logs of the RMC21 and the BMC22 to determine whether any update operation of the RMC21 and the BMC22 has timed out (step S54 ) or an error occurs, and determine whether the Check whether the network connection of the
更具体地,于上述步骤S52后,管理系统3可先依据所述操作行为来判断管理者是否曾对机柜2中的RMC21及/或BMC22实施了更新作业(步骤S53)。并且,于确定了管理者曾经实施了更新作业后,管理系统3再接续执行步骤S54以及步骤S55,以判断这些RMC21、BMC22的更新作业是否逾时或发生错误,以及网络连线是否正常。More specifically, after the above step S52, the management system 3 may first determine whether the administrator has performed an update operation on the
所述RMC21、BMC22在接受了管理者实施的更新作业后,将会自动进入更新模式。此时,RMC21、BMC22会在状态数据中设定已进入更新模式的标记(flag)。当周边设备与RMC21、BMC22沟通并且读到更新模式的标记时,就会自动停止与这个RMC21、BMC22的互动。因此,只要RMC21、BMC22更新作业失败而无法离开更新模式,这个RMC21、BMC22就无法正常运作。当管理系统3发现任一RMC21、BMC22接受了更新作业、更新作业已逾时或发生错误、但是尚未失去网络连线时,就可认定这个RMC21、BMC22处于所述第一关注状态。The RMC21 and the BMC22 will automatically enter the update mode after accepting the update operation performed by the administrator. At this time, the RMC21 and the BMC22 will set a flag (flag) that has entered the update mode in the status data. When the peripheral device communicates with RMC21 and BMC22 and reads the update mode mark, it will automatically stop interacting with this RMC21 and BMC22. Therefore, as long as the RMC21, BMC22 update job fails and cannot leave the update mode, the RMC21, BMC22 cannot function normally. When the management system 3 finds that any RMC21 and BMC22 have accepted the update operation, the update operation has timed out or an error has occurred, but the network connection has not been lost, it can be determined that this RMC21 and BMC22 is in the first attention state.
步骤S56后,管理系统3可进一步通过网络发出控制指令(例如第二控制指令)至处于第一类关注状态的RMC21或BMC22,以强制更新作业失败的RMC21或BMC22离开所述更新模式(步骤S57)。After step S56, the management system 3 may further issue a control command (eg, a second control command) to the
如上所述,在本实施例所指的更新作业失败情况下(即,无法离开更新模式),所述RMC21、BMC22仍可接收并处理相关的指令,只是周边设备在读到更新模式的标记(flag)时就会自动停止与RMC21、BMC22的互动。本实施例中,管理系统3已判断所述RMC21、BMC22发生异常状态,因此会无视于上述标记,而藉由控制指令的发出来强制RMC21、BMC22离开更新模式。As described above, in the case of failure of the update operation referred to in this embodiment (that is, unable to leave the update mode), the RMC21 and the BMC22 can still receive and process the relevant instructions, but the peripheral devices are reading the update mode flag (flag ) will automatically stop the interaction with RMC21 and BMC22. In this embodiment, the management system 3 has determined that the
步骤S57后,管理系统3还可进一步通过网络发出另一控制指令(例如第三控制指令)至已离开更新模式的RMC21或BMC22,以强制RMC21或BMC22进行重置作业,或是再次实施所述更新作业(步骤S58)。藉此,管理系统3可以确保RMC21、BMC22已恢复正常运作,并且固件或软件处于更新完成的最新版本。After step S57, the management system 3 may further send another control command (eg, a third control command) to the RMC21 or BMC22 that has left the update mode through the network, so as to force the RMC21 or the BMC22 to perform the reset operation, or implement the above-mentioned operation again. The job is updated (step S58). In this way, the management system 3 can ensure that the
下面段落接着讨论所述第二类关注状态。The following paragraphs then discuss the second type of attention states.
本发明中的RMC21、BMC22为一种嵌入式系统(Embbeded System),因此即使机柜2内的端点服务器220未开机,管理系统3仍可藉由与RMC21、BMC22的沟通来实现远程开机、远程关机、查看设备状态等远程管理功能。The RMC21 and BMC22 in the present invention are an embedded system, so even if the
一般来说,管理者在实施远程管理程序时,可在管理系统3上使用智能平台管理界面(Intelligent Platform Management Interface,IPMI)工具程序来通过网络发送IPMI指令,藉此与机柜2内的RMC21、BMC22沟通。于使用IPMI工具程序的情况下,每一道指令的发送都需与目的地的RMC21、BMC22建立一个IPMI会话期间(session),藉此才能与目的地的RMC21、BMC22进行沟通。具体地,在IPMI session建立完成后,管理系统3才能通过网络与RMC21、BMC22以及机柜2、端点服务器220的底层硬件设备沟通,进而取得所述指令的执行结果(例如取得固件版本、端点服务器220内的所有感测器的感测数值等)。Generally speaking, when implementing the remote management program, the administrator can use the intelligent platform management interface (Intelligent Platform Management Interface, IPMI) tool program on the management system 3 to send the IPMI command through the network, thereby communicating with the RMC21, BMC22 communication. In the case of using the IPMI tool program, the sending of each command needs to establish an IPMI session with the destination RMC21 and BMC22, so as to communicate with the destination RMC21 and BMC22. Specifically, after the establishment of the IPMI session is completed, the management system 3 can communicate with the RMC21, BMC22 and the underlying hardware devices of the
惟,嵌入式系统本身的运算资源是相当有限的,除了运作所需的基本资源消耗外,与RMC21的沟通、与BMC22的沟通以及回复数据中心1内的各式监控系统等动作皆会进一步消耗嵌入式系统的运算资源。However, the computing resources of the embedded system itself are quite limited. In addition to the basic resource consumption required for operation, the communication with the RMC21, the communication with the BMC22, and the response to various monitoring systems in the
再者,当管理者通过管理系统3对各个RMC21、BMC22实施远端管理程序时,也需消耗RMC21、BMC22的运算资源,最明显的就是令RMC21、BMC22的IPMI session数量大幅增加,使得RMC21、BMC22出现回应不及或是请求超时(timeout)的现象。此时,虽然所述RMC21、BMC22尚未发生异常状态,但可能需要由管理系统3于远端介入以避免RMC21、BMC22将来发生异常状态而影响机柜2的运作。Furthermore, when the administrator implements the remote management program for each RMC21 and BMC22 through the management system 3, the computing resources of the RMC21 and BMC22 are also consumed. The BMC22 fails to respond in time or the request times out. At this time, although the
参阅图7,为本发明的第二类关注状态排除流程图的第一具体实施例。本实施例中,所述管理系统3同样会定时存取数据库31(步骤S61),以由数据库31中取得机柜2内的RMC21及BMC22的状态数据,并且判断RMC21及BMC22的状态变化(步骤S62)。于一实施例中,管理系统3在步骤S62中主要是取得RMC21及各个BMC22目前的IPMI session总数。于另一实施例中,管理系统3在步骤S62中同时取得RMC21及各个BMC22目前的系统资源使用率。Referring to FIG. 7 , it is a first specific embodiment of the second type of attention state exclusion flowchart of the present invention. In this embodiment, the management system 3 also regularly accesses the database 31 (step S61 ), so as to obtain the status data of the
步骤S63后,管理系统3判断是否有任一RMC21、BMC22的IPMI session总数高于第一门槛值(步骤S63),并且于任一RMC21、BMC22的IPMI session总数高于第一门槛值时,认定这个RMC21、BMC22处于所述第二关注状态(步骤S65),即,RMC21或BMC22的连线正常,但判断可能即将出现异常状态。After step S63, the management system 3 determines whether the total number of IPMI sessions of any one of RMC21 and BMC22 is higher than the first threshold value (step S63), and when the total number of IPMI sessions of any one of RMC21 and BMC22 is higher than the first threshold value, it is determined that The RMC21 and the BMC22 are in the second attention state (step S65 ), that is, the connection of the RMC21 or the BMC22 is normal, but it is judged that an abnormal state may occur soon.
值得一提的是,若管理系统3于步骤S62中同时取得了RMC21及各个BMC22的系统资源使用率,则管理系统3可同时判断是否有任一RMC21、BMC22的系统资源使用率高于第二门槛值(步骤S64)。于此情境下,管理系统3会认定目前的IPMI session总数高于第一门槛值,并且系统资源使用率高于第二门槛值的RMC21或BMC22处于所述第二关注状态。It is worth mentioning that, if the management system 3 obtains the system resource usage rates of the RMC21 and each BMC22 at the same time in step S62, the management system 3 can simultaneously determine whether the system resource usage rates of any one of the RMC21 and BMC22 are higher than the second one. threshold value (step S64). In this situation, the management system 3 will determine that the current total number of IPMI sessions is higher than the first threshold value, and the
于一实施例中,所述系统资源使用率为RMC21、BMC22的中央处理单元或记忆体的使用率。于另一实施例中,所述系统资源使用率为RMC21、BMC22内部主要用来提供各项服务(如超文本传输协议(HyperText Transfer Protocol,HTTP)服务或IPMI服务等)所使用的系统资源的使用率,但不加以限定。In one embodiment, the system resource usage rate is the usage rate of the central processing unit or the memory of the RMC21 and the BMC22. In another embodiment, the system resource usage rate is the percentage of system resources used by RMC21 and BMC22 mainly for providing various services (such as HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) services or IPMI services, etc.). usage, but not limited.
当管理系统3认定一个RMC21或BMC22处于第二类关注状态后,管理系统3可进一步通过网络发出控制指令(例如第四控制指令)至处于第二类关注状态的RMC21或BMC22,以令所述RMC21或BMC22重启IPMI服务(步骤S66)。藉此,RMC21、BMC22可将目前累积的IPMIsession清空,以避免异常状态的发生。After the management system 3 determines that an
于一实施例中,所述第四控制指令为重置指令,管理系统3是通过网络发出重置指令至处于第二类关注状态的RMC21或BMC22,以强制RMC21或BMC22进行重置作业。如此一来,重置后的RMC21、BMC22即可直接重启IPMI服务。惟,上述仅为本发明的其中一个具体实施例,但不以上述为限。In one embodiment, the fourth control command is a reset command, and the management system 3 sends a reset command to the
通过上述技术方案,管理系统3可以经由分析提早发现RMC21或BMC22可能即将发生异常状态,因此可主动于远端实施服务重启机制,以避免RMC21或BMC22真的发生异常状态而影响机柜2的运作。Through the above technical solution, the management system 3 can find out that the RMC21 or the BMC22 may be in an abnormal state in advance through analysis, so it can actively implement the service restart mechanism at the remote end, so as to avoid the abnormal state of the RMC21 or the BMC22 from affecting the operation of the
下面段落接着讨论所述第三类关注状态。The following paragraphs then discuss the third type of attention state.
如前文中所述,本发明的管理系统3主要是通过网络与数据中心1内的机柜2中的RMC21、BMC22进行沟通,并且管理者也是通过网络对这些RMC21、BMC22实施远程管理程序。因此,当机柜2中的BMC22失去网络连线时,管理系统3将无法与BMC22进行沟通,管理者也无法对BMC22进行管理。于本实施例中,BMC22失去网络连线的异常状况,可能是因为IP地址设定错误所引起的。As mentioned above, the management system 3 of the present invention mainly communicates with the RMC21 and BMC22 in the
一般来说,机柜2内的BMC22可能被设定成使用动态IP地址(即,BMC22的网络模式被设定为动态IP模式)或静态IP地址(即,BMC22的网络模式被设定为静态IP模式)。若BMC22的网络模式为动态IP模式,则可由数据中心1内的动态主机设定协定(Dynamic HostConfiguration Protocol,DHCP)服务器(图未标示)来主动配发一组动态IP地址给BMC22使用。若BMC22的网络模式为静态IP模式,则管理者可通过管理系统3的操作界面来自行为BMC22设定一组静态IP地址。Generally speaking, the BMC22 in
要对BMC22实施网络设定作业以设定一组可用的静态IP地址,管理者需经由管理系统3下达至少四道指令给BMC22(即,需建立四个IPMI session),包括:(1)设定BMC22的网络模式为静态IP模式;(2)设定静态IP地址;(3)设定子网络遮罩(netmask);(4)设定闸道器(Gateway)IP地址。To implement the network setting operation for the BMC22 to set a set of available static IP addresses, the administrator needs to issue at least four instructions to the BMC22 via the management system 3 (that is, four IPMI sessions need to be established), including: (1) Setting Set the network mode of BMC22 as static IP mode; (2) set static IP address; (3) set subnet mask (netmask); (4) set gateway IP address.
如上所述,若管理者设定的静态IP地址错误(例如与DHCP服务器所配发的多组动态IP地址的其中之一重复),或是闸道器IP地址设定错误,则在多个子网域共存的环境,或是需要通过闸道器才能沟通的环境下,所述BMC22将无法与管理系统3连线。对于管理系统3来说,虽然这个BMC22所属的端点服务器220仍然存在,但因为管理系统3失去了与这个BMC22间的连线,因此将无法对这个BMC22(及其所属的端点服务器220)进行管理。此时,管理系统3可能需要于远端介入以令BMC22恢复网络连线。As mentioned above, if the static IP address set by the administrator is incorrect (for example, it is duplicated with one of the multiple sets of dynamic IP addresses distributed by the DHCP server), or the IP address of the gateway is incorrectly set, the In an environment where network domains coexist, or in an environment where communication requires a gateway, the
参阅图8,为本发明的第三类关注状态排除流程图的第一具体实施例。本实施例中,所述管理系统3会定时存取数据库31(步骤S71),以由数据库31中取得机柜2内的各个BMC22的状态数据、管理者通过管理系统3实施的操作行为、以及管理系统3基于所述操作行为所获得的各项反馈信息,并且判断BMC22的状态变化(步骤S72)。Referring to FIG. 8 , it is a first specific embodiment of the third type of attention state exclusion flowchart of the present invention. In this embodiment, the management system 3 periodically accesses the database 31 (step S71 ) to obtain from the
于一实施例中,管理系统3在步骤S72中取得的状态数据至少包括各个BMC22的网络模式(静态IP模式或动态IP模式)、目前使用的静态IP地址、子网络遮罩及闸道器IP地址等,不加以限定。并且,管理系统3在步骤S72中取得的反馈信息主要包括所述操作行为实施时,管理系统3、机柜2及各个端点服务器220(以及各个BMC22)基于这个操作行为所产生的反馈、系统参数及执行数据等数据,但不加以限定。In one embodiment, the status data obtained by the management system 3 in step S72 includes at least the network mode (static IP mode or dynamic IP mode), currently used static IP address, subnet mask and gateway IP of each
步骤S72后,管理系统3首先依据所述状态数据以及反馈信息判断机柜2中是否有任一BMC22失去了与管理系统3间的连线(步骤S73),并且,依据所述操作行为判断管理者是否刚刚为机柜2中的任一BMC22实施了网络设定作业(步骤S74)。若经分析后发现管理者刚刚对某一BMC22实施了网络设定作业,并且这个BMC22在网络设定作业后即失去连线,则管理系统3即可将这个BMC22视为处于所述第三类关注状态(步骤S75),即,BMC22已失去连线。After step S72, the management system 3 first judges whether any
值得一提的是,于前述步骤S73中,管理系统3主要可于任一BMC22的网络模式被设定为静态IP模式,并且这个BMC22的静态IP地址与DHCP服务器所配发的多组动态IP地址的其中之一重复时,判断这个BMC22失去网络连线(已经失去连线,或可能失去连线)。It is worth mentioning that, in the aforementioned step S73, the management system 3 can be set to the static IP mode mainly in the network mode of any BMC22, and the static IP address of the BMC22 and the multiple groups of dynamic IPs distributed by the DHCP server. When one of the addresses is repeated, it is judged that the BMC22 has lost the network connection (has lost the connection, or may lose the connection).
另,于前述步骤S73中,管理系统3还可于任一BMC22的网络模式被设定为静态IP模式,并且这个BMC22的闸道器IP地址设定错误时,判断这个BMC22失去网络连线(已经失去连线,或可能失去连线)。惟,上述仅为本发明的部分具体实施范例,但不应以上述为限。In addition, in the aforementioned step S73, the management system 3 can also determine that the BMC22 loses the network connection when the network mode of any BMC22 is set to the static IP mode, and the gateway IP address of the BMC22 is incorrectly set ( has lost connection, or may lose connection). However, the above are only some specific implementation examples of the present invention, but should not be limited to the above.
于步骤S75后,管理系统3已可认定某一BMC22处于所述第三类关注状态,接着,管理系统3判断在数据中心1中主要负责这个BMC22的RMC21为何(步骤S76),并且控制这个RMC21通过机柜2的内部硬件线路24检查所述BMC22所属的端点服务器220(步骤S77),以确认这个端点服务器220是否存在(步骤S78)。After step S75, the management system 3 can already determine that a
如图2所示,一个机柜2内的RMC21主要可通过内部硬件线路24实体连接机柜2中的所有端点服务器220中的BMC22,因此,即使BMC22失去网络连线,同一个机柜2内的RMC21仍可通过内部硬件线路24来与BMC22进行沟通。As shown in FIG. 2 , the RMC21 in one
若于上述步骤S78中判断所述端点服务器220不存在(例如已被抽离机柜2,或已经损坏),则管理系统3对应发出警示信号(步骤S79)。于一实施例中,管理系统3可通过操作界面发出警示信号(例如文字、灯光或声响),以对管理者进行警示。于另一实施例中,管理系统3可通过网络发送警示信号(例如简讯、电子邮件或通讯软件)给管理者,以达到警示作用。If it is determined in the above step S78 that the
若于上述步骤S78中判断所述端点服务器220仍然存在,则管理系统3控制所述RMC21通过内部硬件线路24发送一组IPMI指令至所述BMC22,以令BMC22恢复网络连线(步骤S80)。于一实施例中,管理系统3可通过RMC21将IPMI指令发送至所述BMC22,以重新设定所述BMC22的静态IP地址,或是重新设定所述BMC22的闸道器IP地址,藉此令BMC22恢复与管理系统3间的连线。If it is determined in the above step S78 that the
通过上述技术方案,管理系统3可以在BMC22失去连线后主动于远端对BMC22实施救援机制,以令BMC22恢复网络连线。Through the above technical solution, the management system 3 can actively implement a rescue mechanism to the
本发明的方法可由管理系统3自动搜集所需信息并对所有RMC21及BMC22的状态进行分析,同时于任一RMC21、BMC22处于多种关注状态之一时自动实施对应机制以排除异常状态。如此一来,本发明的技术方案可大幅降低管理成本,亦使得数据中心1的监控无需人为干涉,也不受距离与时间的影响。In the method of the present invention, the management system 3 can automatically collect the required information and analyze the states of all the RMCs 21 and
当然,本发明还可有其它多种实施例,在不背离本发明精神及其实质的情况下,熟悉本领域的技术人员当可根据本发明作出各种相应的改变和变形,但这些相应的改变和变形都应属于本发明所附的权利要求的保护范围。Of course, the present invention can also have other various embodiments, without departing from the spirit and essence of the present invention, those skilled in the art can make various corresponding changes and modifications according to the present invention, but these corresponding Changes and deformations should belong to the protection scope of the appended claims of the present invention.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910014424.6ACN111414274A (en) | 2019-01-04 | 2019-01-04 | Remote exclusion method for abnormal state of cabinets in data centers |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910014424.6ACN111414274A (en) | 2019-01-04 | 2019-01-04 | Remote exclusion method for abnormal state of cabinets in data centers |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111414274Atrue CN111414274A (en) | 2020-07-14 |
Family
ID=71490707
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910014424.6APendingCN111414274A (en) | 2019-01-04 | 2019-01-04 | Remote exclusion method for abnormal state of cabinets in data centers |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111414274A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI771759B (en)* | 2020-09-16 | 2022-07-21 | 新加坡商鴻運科股份有限公司 | Power failure monitoring method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001098857A2 (en)* | 2000-06-20 | 2001-12-27 | Bae Young Ju | Remote server management method on the network |
| CN102495785A (en)* | 2011-12-23 | 2012-06-13 | 创新科存储技术(深圳)有限公司 | Centralized management method and device for servers of whole equipment cabinet |
| CN104378218A (en)* | 2013-08-12 | 2015-02-25 | 鸿富锦精密工业(深圳)有限公司 | System and method for managing servers in cabinet |
| CN104598329A (en)* | 2015-02-12 | 2015-05-06 | 浪潮电子信息产业股份有限公司 | Automatic BMC (baseboard management controller) fault solution method based on RMC (rack server management center) management |
| WO2016165242A1 (en)* | 2015-04-14 | 2016-10-20 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method of adjusting number of nodes in system and device utilizing same |
| CN106547660A (en)* | 2015-09-23 | 2017-03-29 | 鸿富锦精密工业(深圳)有限公司 | Baseboard management controller state detecting system and method |
| TW201714432A (en)* | 2015-10-14 | 2017-04-16 | 廣達電腦股份有限公司 | Management methods, service controller devices and non-stransitory, computer-readable media |
| CN107346163A (en)* | 2016-05-06 | 2017-11-14 | 广达电脑股份有限公司 | Server rack power management |
| CN108616428A (en)* | 2018-05-14 | 2018-10-02 | 郑州云海信息技术有限公司 | A kind of mobile APP implementations of remote management RACK computer rooms |
- 2019
- 2019-01-04CNCN201910014424.6Apatent/CN111414274A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2001098857A2 (en)* | 2000-06-20 | 2001-12-27 | Bae Young Ju | Remote server management method on the network |
| CN102495785A (en)* | 2011-12-23 | 2012-06-13 | 创新科存储技术(深圳)有限公司 | Centralized management method and device for servers of whole equipment cabinet |
| CN104378218A (en)* | 2013-08-12 | 2015-02-25 | 鸿富锦精密工业(深圳)有限公司 | System and method for managing servers in cabinet |
| CN104598329A (en)* | 2015-02-12 | 2015-05-06 | 浪潮电子信息产业股份有限公司 | Automatic BMC (baseboard management controller) fault solution method based on RMC (rack server management center) management |
| WO2016165242A1 (en)* | 2015-04-14 | 2016-10-20 | 中兴通讯股份有限公司 | Method of adjusting number of nodes in system and device utilizing same |
| CN106547660A (en)* | 2015-09-23 | 2017-03-29 | 鸿富锦精密工业(深圳)有限公司 | Baseboard management controller state detecting system and method |
| TW201714432A (en)* | 2015-10-14 | 2017-04-16 | 廣達電腦股份有限公司 | Management methods, service controller devices and non-stransitory, computer-readable media |
| CN107346163A (en)* | 2016-05-06 | 2017-11-14 | 广达电脑股份有限公司 | Server rack power management |
| CN108616428A (en)* | 2018-05-14 | 2018-10-02 | 郑州云海信息技术有限公司 | A kind of mobile APP implementations of remote management RACK computer rooms |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI771759B (en)* | 2020-09-16 | 2022-07-21 | 新加坡商鴻運科股份有限公司 | Power failure monitoring method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107612787B (en) | Cloud host fault detection method based on Openstack open source cloud platform | |
| US7213179B2 (en) | Automated and embedded software reliability measurement and classification in network elements | |
| CN107147540A (en) | Fault Handling Method and Fault Handling Cluster in High Availability System | |
| US9021317B2 (en) | Reporting and processing computer operation failure alerts | |
| CN106844162A (en) | Storage server cabinet management system and method based on BMC | |
| US7788520B2 (en) | Administering a system dump on a redundant node controller in a computer system | |
| CN103607297A (en) | Fault processing method of computer cluster system | |
| CN114090184B (en) | Method and equipment for realizing high availability of virtualization cluster | |
| CN116483613B (en) | Processing method and device of fault memory bank, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| US10754722B1 (en) | Method for remotely clearing abnormal status of racks applied in data center | |
| CN108199901B (en) | Hardware repair report method, system, device, hardware management server and storage medium | |
| TWI698741B (en) | Method for remotely clearing abnormal status of racks applied in data center | |
| WO2024230401A1 (en) | Baseboard management controller system operation method and apparatus, device, and non-volatile readable storage medium | |
| CN108616428A (en) | A kind of mobile APP implementations of remote management RACK computer rooms | |
| US20200305300A1 (en) | Method for remotely clearing abnormal status of racks applied in data center | |
| CN107562601A (en) | A kind of alarm method and device | |
| CN110611603A (en) | A cluster network card monitoring method and device | |
| RU2710288C1 (en) | Method of remote abnormal state reset of racks used in data center | |
| US10842041B2 (en) | Method for remotely clearing abnormal status of racks applied in data center | |
| US11237892B1 (en) | Obtaining data for fault identification | |
| CN111416721A (en) | Far-end eliminating method for abnormal state of cabinet applied to data center | |
| CN111342986B (en) | Distributed node management method and device, distributed system and storage medium | |
| CN115499294A (en) | A distributed storage environment network sub-health detection and fault automatic processing method | |
| CN119383170A (en) | ADDRESS CONFIGURATION METHOD, DEVICE, STORAGE MEDIUM AND PROGRAM PRODUCT | |
| US8677323B2 (en) | Recording medium storing monitoring program, monitoring method, and monitoring system |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication | Application publication date:20200714 |