CN111370678A - Preparation method of modified lithium iron phosphate material for coated lithium battery - Google Patents
Preparation method of modified lithium iron phosphate material for coated lithium batteryDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111370678A CN111370678ACN202010461312.8ACN202010461312ACN111370678ACN 111370678 ACN111370678 ACN 111370678ACN 202010461312 ACN202010461312 ACN 202010461312ACN 111370678 ACN111370678 ACN 111370678A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- iron phosphate
- lithium iron
- polymer fiber
- preparation
- solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- GELKBWJHTRAYNV-UHFFFAOYSA-Klithium iron phosphateChemical class[Li+].[Fe+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OGELKBWJHTRAYNV-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription57
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription44
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription16
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-NLithiumChemical compound[Li]WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription8
- 229910052744lithiumInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription8
- 229920005594polymer fiberPolymers0.000claimsabstractdescription24
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription22
- 238000002074melt spinningMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription6
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsdescription23
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription22
- 239000006087Silane Coupling AgentSubstances0.000claimsdescription15
- 239000006185dispersionSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription10
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 239000004094surface-active agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription9
- 229910002651NO3Inorganic materials0.000claimsdescription8
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-NNitrateChemical compound[O-][N+]([O-])=ONHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 239000011888foilSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910044991metal oxideInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription6
- 150000004706metal oxidesChemical class0.000claimsdescription6
- 239000011259mixed solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription5
- 238000001816coolingMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000004544sputter depositionMethods0.000claimsdescription4
- 239000012298atmosphereSubstances0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000000151depositionMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000002156mixingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000001681protective effectEffects0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000005245sinteringMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 230000008021depositionEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 239000003085diluting agentSubstances0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000005406washingMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000claims1
- 238000009210therapy by ultrasoundMethods0.000claims1
- 238000000576coating methodMethods0.000abstractdescription17
- 239000000835fiberSubstances0.000abstractdescription17
- 239000011248coating agentSubstances0.000abstractdescription14
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-NCarbonChemical compound[C]OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription7
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000abstractdescription6
- 239000003792electrolyteSubstances0.000abstractdescription5
- 229910052799carbonInorganic materials0.000abstractdescription4
- 239000004974Thermotropic liquid crystalSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 238000005056compactionMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 230000000704physical effectEffects0.000abstractdescription3
- 229920000106Liquid crystal polymerPolymers0.000abstractdescription2
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000010406cathode materialSubstances0.000description10
- 239000007774positive electrode materialSubstances0.000description9
- 229910010707LiFePO 4Inorganic materials0.000description8
- 230000000052comparative effectEffects0.000description7
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000description6
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000description6
- 1250000052744-hydroxybenzoic acid groupChemical group0.000description5
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-NCopperChemical compound[Cu]RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description5
- 238000000231atomic layer depositionMethods0.000description5
- -1hydrothermal methodChemical compound0.000description5
- 239000000203mixtureSubstances0.000description5
- 239000002861polymer materialSubstances0.000description5
- 239000000758substrateSubstances0.000description5
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-NArgonChemical compound[Ar]XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-NLithium ionChemical compound[Li+]HBBGRARXTFLTSG-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-NPhosphoric acidChemical compoundOP(O)(O)=ONBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 239000002202Polyethylene glycolSubstances0.000description4
- ZCCIPPOKBCJFDN-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncalcium nitrateChemical compound[Ca+2].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OZCCIPPOKBCJFDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- HSJPMRKMPBAUAU-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncerium(3+);trinitrateChemical compound[Ce+3].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=OHSJPMRKMPBAUAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 239000011889copper foilSubstances0.000description4
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-NetherSubstancesCCOCCRTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 239000010408filmSubstances0.000description4
- 229910001416lithium ionInorganic materials0.000description4
- 239000002070nanowireSubstances0.000description4
- 229920001223polyethylene glycolPolymers0.000description4
- FGIUAXJPYTZDNR-UHFFFAOYSA-Npotassium nitrateChemical compound[K+].[O-][N+]([O-])=OFGIUAXJPYTZDNR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description4
- 239000000843powderSubstances0.000description4
- 229910052782aluminiumInorganic materials0.000description3
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-NaluminiumChemical compound[Al]XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-Ncitric acidChemical compoundOC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=OKRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 238000000975co-precipitationMethods0.000description3
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000description3
- 238000001027hydrothermal synthesisMethods0.000description3
- 239000011261inert gasSubstances0.000description3
- 230000014759maintenance of locationEffects0.000description3
- 230000008569processEffects0.000description3
- 238000003980solgel methodMethods0.000description3
- ZSYNKHJUSDFTCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Li].[Fe].P(O)(O)(O)=OChemical compound[Li].[Fe].P(O)(O)(O)=OZSYNKHJUSDFTCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description2
- 238000005299abrasionMethods0.000description2
- 229910000147aluminium phosphateInorganic materials0.000description2
- 229910052786argonInorganic materials0.000description2
- 238000007796conventional methodMethods0.000description2
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000011049fillingMethods0.000description2
- 229910000398iron phosphateInorganic materials0.000description2
- WBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-Kiron(3+) phosphateChemical compound[Fe+3].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=OWBJZTOZJJYAKHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-K0.000description2
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description2
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description2
- 239000012299nitrogen atmosphereSubstances0.000description2
- 239000002736nonionic surfactantSubstances0.000description2
- 238000011056performance testMethods0.000description2
- 229920000728polyesterPolymers0.000description2
- 235000010333potassium nitrateNutrition0.000description2
- 239000004323potassium nitrateSubstances0.000description2
- 239000002243precursorSubstances0.000description2
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000description2
- 238000001878scanning electron micrographMethods0.000description2
- 239000010409thin filmSubstances0.000description2
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-NAtomic nitrogenChemical compoundN#NIJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- QSNQXZYQEIKDPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N[Li].[Fe]Chemical compound[Li].[Fe]QSNQXZYQEIKDPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 239000011149active materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000013543active substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000654additiveSubstances0.000description1
- 238000005054agglomerationMethods0.000description1
- 230000002776aggregationEffects0.000description1
- 239000000956alloySubstances0.000description1
- 229910045601alloyInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000007864aqueous solutionSubstances0.000description1
- 239000012300argon atmosphereSubstances0.000description1
- 125000003118aryl groupChemical group0.000description1
- 230000015572biosynthetic processEffects0.000description1
- 238000012512characterization methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000003153chemical reaction reagentSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011247coating layerSubstances0.000description1
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000description1
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 229910052802copperInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000010949copperSubstances0.000description1
- 239000011258core-shell materialSubstances0.000description1
- 238000002425crystallisationMethods0.000description1
- 230000008025crystallizationEffects0.000description1
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000006866deteriorationEffects0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 229910001873dinitrogenInorganic materials0.000description1
- 238000007599dischargingMethods0.000description1
- GVGUFUZHNYFZLC-UHFFFAOYSA-Ndodecyl benzenesulfonate;sodiumChemical compound[Na].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1GVGUFUZHNYFZLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000005518electrochemistryEffects0.000description1
- 229960002089ferrous chlorideDrugs0.000description1
- 239000002657fibrous materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002803fossil fuelSubstances0.000description1
- 229910021389grapheneInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000005431greenhouse gasSubstances0.000description1
- 239000001307heliumSubstances0.000description1
- 229910052734heliumInorganic materials0.000description1
- SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-Nhelium atomChemical compound[He]SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- NMCUIPGRVMDVDB-UHFFFAOYSA-Liron dichlorideChemical compoundCl[Fe]ClNMCUIPGRVMDVDB-UHFFFAOYSA-L0.000description1
- XIXADJRWDQXREU-UHFFFAOYSA-Mlithium acetateChemical compound[Li+].CC([O-])=OXIXADJRWDQXREU-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- 238000001755magnetron sputter depositionMethods0.000description1
- 238000002715modification methodMethods0.000description1
- 239000002114nanocompositeSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002105nanoparticleSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002073nanorodSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002135nanosheetSubstances0.000description1
- 239000007773negative electrode materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000002245particleSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009467reductionEffects0.000description1
- 238000012827research and developmentMethods0.000description1
- 229940080264sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonateDrugs0.000description1
- 230000000087stabilizing effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003786synthesis reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000010998test methodMethods0.000description1
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000description1
- 238000000844transformationMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/362—Composites
- H01M4/366—Composites as layered products
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B25/00—Phosphorus; Compounds thereof
- C01B25/16—Oxyacids of phosphorus; Salts thereof
- C01B25/26—Phosphates
- C01B25/45—Phosphates containing plural metal, or metal and ammonium
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M10/00—Secondary cells; Manufacture thereof
- H01M10/05—Accumulators with non-aqueous electrolyte
- H01M10/052—Li-accumulators
- H01M10/0525—Rocking-chair batteries, i.e. batteries with lithium insertion or intercalation in both electrodes; Lithium-ion batteries
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M4/36—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids
- H01M4/58—Selection of substances as active materials, active masses, active liquids of inorganic compounds other than oxides or hydroxides, e.g. sulfides, selenides, tellurides, halogenides or LiCoFy; of polyanionic structures, e.g. phosphates, silicates or borates
- H01M4/5825—Oxygenated metallic salts or polyanionic structures, e.g. borates, phosphates, silicates, olivines
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01P—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO STRUCTURAL AND PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF SOLID INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
- C01P2004/00—Particle morphology
- C01P2004/01—Particle morphology depicted by an image
- C01P2004/03—Particle morphology depicted by an image obtained by SEM
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01M—PROCESSES OR MEANS, e.g. BATTERIES, FOR THE DIRECT CONVERSION OF CHEMICAL ENERGY INTO ELECTRICAL ENERGY
- H01M4/00—Electrodes
- H01M4/02—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material
- H01M2004/026—Electrodes composed of, or comprising, active material characterised by the polarity
- H01M2004/028—Positive electrodes
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E60/00—Enabling technologies; Technologies with a potential or indirect contribution to GHG emissions mitigation
- Y02E60/10—Energy storage using batteries
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Electrochemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Composite Materials (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Battery Electrode And Active Subsutance (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及锂电技术领域,具体涉及一种改性包覆锂电池用磷酸铁锂材料的制备方法。The invention relates to the technical field of lithium batteries, in particular to a preparation method of a lithium iron phosphate material for modified coating lithium batteries.
背景技术Background technique
随着化石燃料资源供应的减少及温室气体过度排放导致环境恶化问题的加剧,新型可再生绿色清洁能源的研究和发展越来越重要。锂离子电池由于具有放电平台高、比能量密度高、材质较轻、适用温度区间较宽等优点,使其成为一种具有广阔的应用前景的二次电池。自1997年Padhi等提出锂离子电池正极材料LiFePO4以来,LiFePO4因其安全性高、稳定性好、成本低廉和环境友好等优点,已经成为锂离子二次电池最有潜力的正极材料之一。然而磷酸铁锂自身的离子导电性和电子导电性较弱,因此,通常需要对其进行改性。With the reduction in the supply of fossil fuel resources and the aggravation of environmental deterioration caused by excessive greenhouse gas emissions, the research and development of new renewable green and clean energy is becoming more and more important. Due to the advantages of high discharge platform, high specific energy density, light material, and wide applicable temperature range, lithium-ion batteries have become a kind of secondary batteries with broad application prospects. Since Padhi et al. proposed LiFePO4 as a cathode material for lithium ion batteries in 1997, LiFePO 4has become one of the most potential cathode materials for lithium ion secondary batteries due to its high safety, good stability, low cost and environmental friendliness. . However, the ionic and electronic conductivity of lithium iron phosphate itself is weak, so it usually needs to be modified.
表面包覆是一种常用的改性方法,现有技术中通常采用的是在磷酸铁锂合成过程(如水热法、溶胶凝胶法、共沉淀法等)中加入一些碳源实现碳包覆改性。张卫新等用水热法合成了形貌可控的LiFePO4/C正极材料,加入不同的十二烷基苯磺酸钠的量形成可控形貌的LiFePO4/C,如磷酸铁锂纳米粒子、纳米棒和纳米片,三种样品0.1C倍率下的首次放电比容量分别为145.3 mAh/g、149.0 mAh/g和162.9 mAh/g;5C倍率下的放电比容量分别为79.3、100.6和129.5 mAh/g(《Hydrothermal synthesis of morphology-controlledLiFePO4 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries》. Journal of PowerSources, 2012, 220: 317-323.)。Liu等以乙酸锂、氯化亚铁和磷酸为原料,采用溶胶-凝胶法制备磷酸铁锂纳米复合材料,在2.5-4.2V充放电,0.1C首次放电比容量达到166 mAh/g,50次循环以后比容量为165 mAh/g,保持率为99.4%(《A core-shell LiFePO4/Cnanocomposite prepared via a sol-gel method assisted by citric acid》. Journalof Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 574: 155-160.)。 Ding等采用共沉淀法制备出LiFePO4/石墨烯复合材料,石墨烯薄片作为添加剂可以大大的改善正极材料的导电性。0.2C倍率放电容量达到 160 mAh/g,5C、10C倍率放电比容量分别为120 mAh/g和109 mAh/g,且80次循环以后容量保持率在97%,显示出良好的电化学性能(《Preparation of nano-structured LiFePO4/graphene composites by co-precipitation method》.Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12 (1): 10-13.)。Surface coating is a commonly used modification method. In the prior art, some carbon sources are usually added to the synthesis process of lithium iron phosphate (such as hydrothermal method, sol-gel method, co-precipitation method, etc.) to realize carbon coating. modified. Zhang Weixin et al. synthesized LiFePO4 /C cathode materials with controllable morphology by hydrothermal method, adding different amounts of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate to form LiFePO4 /C with controllable morphology, such as lithium iron phosphate nanoparticles, Nanorods and nanosheets, the first discharge specific capacities of the three samples at 0.1C rate are 145.3 mAh/g, 149.0 mAh/g and 162.9 mAh/g, respectively; the discharge specific capacities at 5C rate are 79.3, 100.6 and 129.5 mAh, respectively /g ("Hydrothermal synthesis of morphology-controlled LiFePO4 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries". Journal of PowerSources, 2012, 220: 317-323.). Liu et al. used lithium acetate, ferrous chloride and phosphoric acid as raw materials to prepare lithium iron phosphate nanocomposites by sol-gel method. The charge and discharge at 2.5-4.2V, the first discharge specific capacity at 0.1C reached 166 mAh/g, 50 After the first cycle, the specific capacity is 165 mAh/g, and the retention rate is 99.4% ("A core-shell LiFePO4 /Cnanocomposite prepared via a sol-gel method assisted by citric acid". Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 574: 155- 160.). Ding et al. prepared LiFePO4 /graphene composites by co-precipitation method, and graphene flakes as additives can greatly improve the conductivity of cathode materials. The 0.2C rate discharge capacity reaches 160 mAh/g, the 5C and 10C rate discharge specific capacities are 120 mAh/g and 109 mAh/g, respectively, and the capacity retention rate after 80 cycles is 97%, showing good electrochemical performance ( "Preparation of nano-structured LiFePO4 /graphene composites by co-precipitation method". Electrochemistry Communications, 2010, 12 (1): 10-13.).
尽管上述方法的包覆均可使得其具有较好的充放电性能,然而其易在材料表面形成过厚的致密包覆层,影响材料压实,降低材料的体积能量密度。包覆不均匀会降低后端极片制程的机械加工性能,而且低温条件下,活性材料体积收缩,传统的碳包覆材料容易陷于由活性材料形成的空隙中,无法形成连续的导电通道,因此,在低温环境下循环和倍率性能下降幅度较大。Although the above-mentioned coating methods can make it have better charge-discharge performance, it is easy to form an excessively thick dense coating layer on the surface of the material, which affects the compaction of the material and reduces the volume energy density of the material. The uneven coating will reduce the machinability of the back-end pole piece process, and under low temperature conditions, the volume of the active material shrinks. , the cycle and rate performance decreased greatly in low temperature environment.
因此,如何在提高磷酸铁锂正极材料电子导电性的基础上,保证材料的压实,并且提高其低温性能是磷酸铁锂材料需要不断改进的方向。Therefore, how to ensure the compaction of the material and improve its low temperature performance on the basis of improving the electronic conductivity of the lithium iron phosphate cathode material is the direction that the lithium iron phosphate material needs to be continuously improved.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明旨在至少解决现有技术中存在的技术问题之一。为此,本发明提出一种改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料,该材料导电性好及低温性能。The present invention aims to solve at least one of the technical problems existing in the prior art. To this end, the present invention proposes a modified coated lithium iron phosphate material, which has good electrical conductivity and low temperature performance.
本发明的目的还在于提供一种改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料的制备方法,该方法制得的磷酸铁锂材料的导电性好且低温性能佳。The present invention also aims to provide a method for preparing a modified coated lithium iron phosphate material, and the lithium iron phosphate material prepared by the method has good electrical conductivity and good low temperature performance.
本发明的目的还在于提供一种上述磷酸铁锂材料的应用。The present invention also aims to provide an application of the above-mentioned lithium iron phosphate material.
根据本发明的第一方面实施方式的改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料,所述磷酸铁锂表面包覆有高分子纤维骨架,所述高分子纤维骨架中填充有纳米金属线;其中,所述高分子纤维骨架通过熔融纺丝法制备而得。According to the modified coated lithium iron phosphate material according to the first aspect of the present invention, the surface of the lithium iron phosphate is coated with a polymer fiber skeleton, and the polymer fiber skeleton is filled with nano metal wires; wherein, the The polymer fiber skeleton is prepared by melt spinning.
根据本发明实施方式的磷酸铁锂材料,至少具有如下有益效果:本发明方案在纤维骨架内填充纳米金属线,从而有效提高正极材料的电子导电性;纳米金属线颗粒结晶度较高,热致结晶得到的高分子材料纤维骨架机械强度高和化学稳定性好,其表面部分不易被氧化,即使与电解液接触也不易溶解;常规纳米金属线在充放电过程中易因体积变化造成的应力破坏也会在高分子纤维骨架结构包覆下得到相对缓解,因此,本发明方案采用的高分子纤维骨架包覆方法相较于传统的致密碳包覆,多孔改性高分子导电薄膜,电解液能充分填充到孔洞中,有利于增大电极与电解液间的接触面积,使磷酸铁锂的导电性能更加优异,同时,本发明方案的磷酸铁锂材料具有较高的压实密度(可达2.6g/cc);同时,包覆的热致液晶高分子纤维,具有良好的非吸湿性、极低气温下的高机械物理性、耐湿耐磨耗性及较强的低温特性,有利于提升磷酸铁锂材材料的低温性能。The lithium iron phosphate material according to the embodiment of the present invention has at least the following beneficial effects: the solution of the present invention fills nano metal wires in the fiber skeleton, thereby effectively improving the electronic conductivity of the positive electrode material; The polymer material fiber skeleton obtained by crystallization has high mechanical strength and good chemical stability, and its surface part is not easy to be oxidized, and it is not easy to dissolve even if it is in contact with the electrolyte; conventional nano metal wires are prone to stress damage caused by volume changes during the charging and discharging process. It will also be relatively relieved under the coating of the polymer fiber skeleton structure. Therefore, compared with the traditional dense carbon coating, the porous modified polymer conductive film, the polymer fiber skeleton coating method adopted by the solution of the present invention, the electrolyte can Fully filling the holes is beneficial to increase the contact area between the electrode and the electrolyte, so that the electrical conductivity of the lithium iron phosphate is more excellent. g/cc); at the same time, the coated thermotropic liquid crystal polymer fiber has good non-hygroscopicity, high mechanical and physical properties at extremely low temperature, moisture resistance and abrasion resistance and strong low temperature characteristics, which is conducive to improving phosphoric acid Low temperature properties of iron-lithium materials.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述高分子纤维骨架由聚(4-羟基苯甲酸-co-6-羟基-2-萘酸)通过熔融纺丝法制备而得。通过热致液晶制得的高分子纤维材料作为包覆支架,结合以芳族聚酯纤维为原料,使得制得的高分子纤维骨架具有更好的低蠕变性、良好的非吸湿性、极低气温下的高机械物理性及耐湿耐磨耗性,强度约为普通聚酯纤维的6倍,与金属纤维强度相当,因此,以该高分子纤维骨架包覆在正极材料表面时,结构稳定性好且低温特性强,即使在超低温下也不会结冰,有利于在低温情况下稳定正极材料结构,进而保证材料容量的发挥,本发明方案的磷酸铁锂材料具有更优异的低温性能。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the polymer fiber skeleton is prepared from poly(4-hydroxybenzoic acid-co-6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid) by a melt spinning method. The polymer fiber material prepared by thermotropic liquid crystal is used as a covering stent, combined with aromatic polyester fiber as raw material, so that the obtained polymer fiber skeleton has better low creep, good non-hygroscopic, extremely High mechanical and physical properties and moisture and abrasion resistance at low temperature, the strength is about 6 times that of ordinary polyester fibers, which is equivalent to the strength of metal fibers. Therefore, when the polymer fiber skeleton is wrapped on the surface of the positive electrode material, the structure is stable It has good performance and strong low-temperature characteristics, and will not freeze even at ultra-low temperature, which is conducive to stabilizing the structure of the positive electrode material at low temperature, thereby ensuring the performance of the material capacity. The lithium iron phosphate material of the solution of the present invention has more excellent low-temperature performance.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述高分子纤维骨架中纤维的细度为500~800旦。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the fineness of the fibers in the polymer fiber skeleton is 500-800 deniers.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述纳米金属线选自纳米铝线或纳米铜线。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the nano metal wires are selected from nano aluminum wires or nano copper wires.
根据本发明的第二方面实施方式的制备方法,包括以下步骤:The preparation method according to the embodiment of the second aspect of the present invention comprises the following steps:
S1、制备纳米金属线及高分子纤维骨架,并将所述纳米金属线与高分子纤维骨架混合分散得到分散液,其中,所述高分子纤维骨架通过熔融纺丝法制备而得;S1, prepare nano metal wire and polymer fiber skeleton, and mix and disperse the nano metal wire and polymer fiber skeleton to obtain a dispersion, wherein, the polymer fiber skeleton is prepared by melt spinning method;
S2、向所述分散液中加入磷酸铁锂、硅烷偶联剂进行分散连接,得到混合液;S2, adding lithium iron phosphate and silane coupling agent to the dispersion liquid for dispersion connection to obtain a mixed solution;
S3、将步骤S2得到的混合液在保护气氛下高温烧结后,得所述改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料。S3. After the mixed solution obtained in step S2 is sintered at a high temperature in a protective atmosphere, the modified coated lithium iron phosphate material is obtained.
根据本发明实施方式的制备方法,至少具有如下有益效果:通过高分子材料作为骨架,填充纳米线后通过硅烷偶联剂分散连接在磷酸铁锂正极材料表面进行改性包覆,将其应用于磷酸铁锂正极材料的制备中,可以有效提升磷酸铁锂的低温循环性能。The preparation method according to the embodiment of the present invention has at least the following beneficial effects: using a polymer material as a skeleton, filling nanowires with a silane coupling agent, dispersing and connecting on the surface of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material for modification and coating, and applying it to In the preparation of lithium iron phosphate cathode material, the low temperature cycle performance of lithium iron phosphate can be effectively improved.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述高分子纤维骨架由聚(4-羟基苯甲酸-co-6-羟基-2-萘酸)通过熔融纺丝法制备而得。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the polymer fiber skeleton is prepared from poly(4-hydroxybenzoic acid-co-6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid) by a melt spinning method.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述纳米金属线的制备方法如下:在金属箔上进行溅射沉积得到带有该金属的氧化物薄膜基材,将所述基材放置于含有硝酸盐及表面活性剂的溶液中,在70~80℃下反应6~8h后,将金属箔移出溶液,水洗后,将洗出物冷却干燥得纳米金属线。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the preparation method of the nano metal wire is as follows: perform sputtering deposition on a metal foil to obtain an oxide film substrate with the metal, and place the substrate on a surface containing nitrate and In the solution of the active agent, after reacting at 70-80° C. for 6-8 hours, the metal foil is removed from the solution, and after washing with water, the eluate is cooled and dried to obtain nano-metal wires.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述溅射沉积采用的方法选自原子沉积法(atomiclayer deposition,ALD)、射频溅射法或磁控溅射法中的至少一种。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the sputtering deposition method is selected from at least one of atomic layer deposition (ALD), radio frequency sputtering or magnetron sputtering.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述金属氧化物薄膜的厚度为30~60nm。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the thickness of the metal oxide thin film is 30-60 nm.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述含有硝酸盐及表面活性剂的溶液的制备方法如下:取0.1~0.3份体积量的硝酸盐溶液与2~4份体积量的表面活性剂混合后,加入到50~100份体积量的水中,在35~45℃下超声搅拌后得到;优选地,超声时间为3min以上;更优选地,超声时间为3~5min。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the preparation method of the solution containing nitrate and surfactant is as follows: after mixing 0.1-0.3 parts by volume of nitrate solution and 2-4 parts by volume of surfactant, adding into 50-100 parts by volume of water, and obtain after ultrasonic stirring at 35-45°C; preferably, the ultrasonic time is more than 3 min; more preferably, the ultrasonic time is 3-5 min.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述表面活性剂为非离子表面活性剂;优选地,所述非离子表面活性剂选自聚乙二醇三甲基壬基醚。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the surfactant is a nonionic surfactant; preferably, the nonionic surfactant is selected from polyethylene glycol trimethyl nonyl ether.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述硝酸盐选自硝酸钾、硝酸钙或硝酸铈中的至少一种。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the nitrate is selected from at least one of potassium nitrate, calcium nitrate or cerium nitrate.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述硝酸盐的质量百分浓度为30~40%;优选为32~38%;更优选为35%。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the mass percentage concentration of the nitrate is 30-40%; preferably 32-38%; more preferably 35%.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述步骤S2中硅烷偶联剂以含有质量浓度为30~40%的硅烷偶联剂的水溶液(也可称稀释液)的形式添加;优选地,质量浓度为32~38%;更优选为35%。According to some embodiments of the present invention, in the step S2, the silane coupling agent is added in the form of an aqueous solution (also called a diluent) containing a silane coupling agent with a mass concentration of 30-40%; preferably, the mass concentration is 32 to 38%; more preferably 35%.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述步骤S3中的高温为700~900℃,烧结时间为1~2h。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the high temperature in the step S3 is 700-900° C., and the sintering time is 1-2 h.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述保护气氛选自氮气或惰性气体中的至少一种。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the protective atmosphere is selected from at least one of nitrogen gas or inert gas.
根据本发明的一些实施方式,所述惰性气体选自氦气或氩气中的至少一种;更优选地,所述惰性气体选自氩气。According to some embodiments of the present invention, the inert gas is selected from at least one of helium or argon; more preferably, the inert gas is selected from argon.
根据本发明的第三方面实施方式的应用,一种锂电池,所述锂电池包括正极材料和负极材料,所述正极材料为上述磷酸铁锂材料。According to the application of the embodiment of the third aspect of the present invention, a lithium battery includes a positive electrode material and a negative electrode material, and the positive electrode material is the above-mentioned lithium iron phosphate material.
根据本发明实施方式的锂电池,至少具有如下有益效果:本发明方案的锂电池具有良好的低温性能,同时,还具有良好的充放电性能。The lithium battery according to the embodiment of the present invention has at least the following beneficial effects: the lithium battery of the solution of the present invention has good low temperature performance, and at the same time, also has good charge and discharge performance.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明实施例1制得的磷酸铁锂的SEM图;Fig. 1 is the SEM image of the lithium iron phosphate prepared in Example 1 of the present invention;
图2为本发明对比例1中的磷酸铁锂的SEM图;Fig. 2 is the SEM image of the lithium iron phosphate in Comparative Example 1 of the present invention;
图3为本发明实施例1~3及对比例1中的磷酸铁锂的低温循环性能测试结果图。Fig. 3 is the low-temperature cycle performance test result diagram of the lithium iron phosphate in Examples 1-3 of the present invention and Comparative Example 1.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为详细说明本发明的技术内容、所实现目的及效果,以下结合实施方式并配合附图予以说明。实施例中所使用的试验方法如无特殊说明,均为常规方法;所使用的材料、试剂等,如无特殊说明,均可从商业途径得到的试剂和材料。In order to describe the technical content, achieved objects and effects of the present invention in detail, the following descriptions are given with reference to the embodiments and the accompanying drawings. The test methods used in the examples are conventional methods unless otherwise specified; the materials, reagents, etc. used, unless otherwise specified, can be obtained from commercial sources.
本发明的实施例一为:一种磷酸铁锂正极材料改性包覆的制备方法,具体如下:Embodiment 1 of the present invention is: a preparation method of modified coating of lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material, the details are as follows:
(1) 将0.2mL 35%的硝酸钾溶液和3mL表面活性剂Tergitol® TMN 10(聚乙二醇三甲基壬基醚(C12H26O.(C2H4O)n,n大于0),加入到80ml去离子水中,在40℃的环境下超声搅拌4分钟。(1) Mix 0.2 mL of 35% potassium nitrate solution and 3 mL of surfactant Tergitol® TMN 10 (polyethylene glycol trimethyl nonyl ether (C12 H26 O.(C2 H4 O)n , where n is greater than 0), added to 80 ml of deionized water, and ultrasonically stirred for 4 minutes at 40 °C.
(2) 将在铜箔上进行原子层沉积厚度为45nm的金属氧化物薄膜基材,放置入步骤(1)得到的溶液内,在75℃的温度下加热7小时。然后将铜箔移出溶液,并通过去离子水进行清洗,自然冷却干燥。(2) Atomic layer deposition of a metal oxide film substrate with a thickness of 45 nm on the copper foil was performed, placed in the solution obtained in step (1), and heated at a temperature of 75° C. for 7 hours. The copper foil was then removed from the solution, washed with deionized water, and naturally cooled to dry.
(3) 通过熔融纺丝法(150℃下)将高分子材料聚(4-羟基苯甲酸-co-6-羟基-2-萘酸) (天津希恩思生化科技有限公司,cas no.:70679-92-4)制备为纤维骨架,纤维细度约为700旦。(3) The polymer material poly(4-hydroxybenzoic acid-co-6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid) (Tianjin Xiensi Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., cas no.: 70679-92-4) is prepared as a fiber skeleton with a fiber fineness of about 700 denier.
(4) 将步骤(2)中生长制备的纳米金属线,与步骤(3)中得到的纤维骨架按质量比1:1进行混合分散得分散液(物料浓度为75g/ml),加入220g磷酸铁锂材料粉末,再添加浓度为35%的C11H24O6Si(硅烷偶联剂)(分散液、磷酸铁锂、硅烷偶联剂的质量比为1.5:7.5:1)进行分散连接后,将处到的溶液于氮气气氛中800℃烧结1.5h,自然冷却后得到有纳米线填充的高分子纤维骨架包覆的磷酸铁锂正极材料。(4) Mix and disperse the nano metal wire grown in step (2) with the fiber skeleton obtained in step (3) at a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain a dispersion (material concentration is 75g/ml), add 220g phosphoric acid Lithium iron material powder, and then add C11 H24 O6 Si (silane coupling agent) with a concentration of 35% (the mass ratio of dispersion liquid, lithium iron phosphate and silane coupling agent is 1.5:7.5:1) for dispersion connection Then, the obtained solution was sintered at 800° C. for 1.5 h in a nitrogen atmosphere, and after natural cooling, a lithium iron phosphate cathode material coated with a polymer fiber skeleton filled with nanowires was obtained.
本发明实施例二为:一种磷酸铁锂正极材料改性包覆的制备方法,具体如下:The second embodiment of the present invention is: a preparation method for modification and coating of a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material, the details are as follows:
(1) 将0.1mL 35%的硝酸钙溶液和2mL表面活性剂Tergitol® TMN 10(聚乙二醇三甲基壬基醚(C12H26O.(C2H4O)n,n大于0),加入到50ml去离子水中,在35℃的环境下超声搅拌3分钟。(1) 0.1mL of 35% calcium nitrate solution and 2mL of surfactant Tergitol® TMN 10 (polyethylene glycol trimethyl nonyl ether (C12 H26 O.(C2 H4 O)n , n greater than 0), added to 50 ml of deionized water, and ultrasonically stirred for 3 minutes at 35 °C.
(2) 将在铜箔上进行原子层沉积厚度为30nm的金属氧化物薄膜基材,放置入步骤(1)得到的溶液内,在70℃的温度下加热6小时。然后将铜箔移出溶液,并通过去离子水进行清洗,自然冷却干燥。(2) A metal oxide thin film substrate with a thickness of 30 nm by atomic layer deposition on copper foil is placed into the solution obtained in step (1), and heated at a temperature of 70° C. for 6 hours. The copper foil was then removed from the solution, washed with deionized water, and naturally cooled to dry.
(3) 通过熔融纺丝法(150℃下)将高分子材料聚(4-羟基苯甲酸-co-6-羟基-2-萘酸) (天津希恩思生化科技有限公司,cas no.:70679-92-4)制备为纤维骨架,纤维细度约为500旦。(3) The polymer material poly(4-hydroxybenzoic acid-co-6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid) (Tianjin Xiensi Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., cas no.: 70679-92-4) is prepared as a fiber skeleton with a fiber fineness of about 500 denier.
(4) 将步骤(2)中生长制备的纳米金属线,与步骤(3)中得到的纤维骨架按质量比为1:1进行混合分散得分散液(物料浓度为75g/ml),加入200g磷酸铁锂材料粉末,再添加浓度为35%的C11H24O6Si硅烷偶联剂(分散液、磷酸铁锂、硅烷偶联剂的质量比为1.5:7.5:1)进行分散链接。将混合液于氩气气氛中700℃烧结1h,自然冷却后得到有纳米线填充的高分子纤维骨架包覆的磷酸铁锂正极材料。(4) Mix and disperse the nano metal wire grown in step (2) with the fiber skeleton obtained in step (3) in a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain a dispersion liquid (material concentration is 75g/ml), add 200g Lithium iron phosphate material powder, and then add C11 H24 O6 Si silane coupling agent with a concentration of 35% (the mass ratio of dispersion liquid, lithium iron phosphate and silane coupling agent is 1.5:7.5:1) to disperse and link. The mixed solution was sintered at 700°C for 1 h in an argon atmosphere, and after natural cooling, a lithium iron phosphate cathode material covered with a polymer fiber skeleton filled with nanowires was obtained.
本发明实施例三为:一种磷酸铁前驱体及磷酸铁锂正极材料的制备方法,磷酸铁前驱体的制备方法具体如下:The third embodiment of the present invention is: a preparation method of an iron phosphate precursor and a lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material, and the preparation method of the iron phosphate precursor is as follows:
(1) 将0.3mL 35%的硝酸铈溶液和4mL表面活性剂Tergitol® TMN 10(聚乙二醇三甲基壬基醚(C12H26O.(C2H4O)n,n大于0),加入到100ml去离子水中,在35-45℃的环境下超声搅拌5分钟。(1) 0.3mL of 35% cerium nitrate solution and 4mL of surfactant Tergitol® TMN 10 (polyethylene glycol trimethyl nonyl ether (C12 H26 O.(C2 H4 O)n , n greater than 0), added to 100 ml of deionized water, and ultrasonically stirred at 35-45 °C for 5 minutes.
(2) 将在铝箔上进行原子层沉积厚度为60nm的金属氧化物薄膜基材,放置入步骤(1)内的溶液,在80℃的温度下加热8小时。然后将铝箔移出溶液,并通过去离子水进行清洗,自然冷却干燥。(2) Atomic layer deposition of a metal oxide film substrate with a thickness of 60 nm is performed on the aluminum foil, placed in the solution in step (1), and heated at a temperature of 80° C. for 8 hours. The aluminum foil was then removed from the solution, washed with deionized water, and allowed to cool to dry.
(3)通过熔融纺丝法(150℃下)将高分子材料聚(4-羟基苯甲酸-co-6-羟基-2-萘酸) (天津希恩思生化科技有限公司,cas no.:70679-92-4)制备为纤维骨架,纤维细度约为800旦。(3) The polymer material poly(4-hydroxybenzoic acid-co-6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid) (Tianjin Xiensi Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., cas no.: 70679-92-4) is prepared as a fiber skeleton with a fiber fineness of about 800 denier.
(4) 将步骤(2)中生长制备的纳米金属线,与步骤(3)中得到的纤维骨架按质量比1:1进行混合分散得分散液(物料浓度为75g/ml),加入250g磷酸铁锂材料粉末,再添加浓度为35%的C11H24O6Si硅烷偶联剂(分散液、磷酸铁锂、硅烷偶联剂的质量比为1.5:7.5:1)进行分散链接。将混合液于氮气气氛中900℃烧结2h,自然冷却后得到有纳米线填充的高分子纤维骨架包覆的磷酸铁锂正极材料。(4) Mix and disperse the nano metal wire grown in step (2) with the fiber skeleton obtained in step (3) at a mass ratio of 1:1 to obtain a dispersion liquid (material concentration is 75g/ml), add 250g phosphoric acid Lithium iron material powder, and then add C11 H24 O6 Si silane coupling agent with a concentration of 35% (the mass ratio of dispersion liquid, lithium iron phosphate and silane coupling agent is 1.5:7.5:1) to disperse and link. The mixed solution was sintered at 900° C. for 2 h in a nitrogen atmosphere, and after natural cooling, a lithium iron phosphate cathode material coated with a polymer fiber skeleton filled with nanowires was obtained.
本发明对比例一为:一种磷酸铁锂材料,其为与实施例1中相同来源且未经改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料粉末。Comparative Example 1 of the present invention is: a lithium iron phosphate material, which is from the same source as in Example 1 and unmodified and coated with lithium iron phosphate material powder.
取实施例1制得的改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料和对照例1中的磷酸铁锂材料进行扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)表征,结果如图1和2所示。从图1中可以看出,本发明实施例方案制得的磷酸铁锂材料表面光滑,包覆效果较好。从图2中可以看出,未经改性的磷酸铁锂材料表面粗糙,颗粒间团聚明显。经实施例1包覆改性后的磷酸铁锂样品表面光滑,包覆效果良好。The modified coated lithium iron phosphate material prepared in Example 1 and the lithium iron phosphate material in Comparative Example 1 were used for scanning electron microscope (SEM) characterization, and the results are shown in FIGS. 1 and 2 . It can be seen from FIG. 1 that the lithium iron phosphate material prepared in the embodiment of the present invention has a smooth surface and a good coating effect. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the surface of the unmodified lithium iron phosphate material is rough and the agglomeration between particles is obvious. The surface of the lithium iron phosphate sample modified by coating in Example 1 is smooth and the coating effect is good.
其他实施例制得的磷酸铁锂材料进行形貌及性能表征,结果与实施例1类似,在此不赘述。The morphology and performance of the lithium iron phosphate materials prepared in other examples were characterized, and the results were similar to those in Example 1, which will not be repeated here.
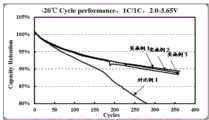
取实施例1~3制得的改性包覆磷酸铁锂材料及对比例1中的磷酸铁锂样品在同等条件下按照常规方法制备成32135圆柱电池,并对制得的圆柱电池在-20℃下进行电化学循环性能测试,结果如图3所示。从图3中结果可以看出,利用本发明实施例1~3制备的磷酸铁锂材料,具有显著优异于对比例1中未经包覆的磷酸铁锂的低温性能,本实施例1~3制得的磷酸铁锂材料在350个循环后仍具有约90%的容量保持率,而对比例1产品在约280个循环时,循环性能已降低至80%以下,由此表明本发明实施例方案制得的磷酸铁锂材料具有良好的低温性能。Take the modified coated lithium iron phosphate materials prepared in Examples 1 to 3 and the lithium iron phosphate samples in Comparative Example 1 to prepare a 32135 cylindrical battery according to a conventional method under the same conditions, and the obtained cylindrical battery was tested at -20. The electrochemical cycle performance test was carried out at ℃, and the results are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen from the results in FIG. 3 that the lithium iron phosphate materials prepared by using Examples 1 to 3 of the present invention have significantly better low-temperature properties than the uncoated lithium iron phosphate in Comparative Example 1. Examples 1 to 3 The obtained lithium iron phosphate material still has a capacity retention rate of about 90% after 350 cycles, while the cycle performance of the product of Comparative Example 1 has been reduced to below 80% at about 280 cycles, thus indicating the embodiment of the present invention. The lithium iron phosphate material prepared by the scheme has good low temperature performance.
以上所述仅为本发明的实施例,并非因此限制本发明的专利范围,凡是利用本发明说明书及附图内容所作的等同变换,或直接或间接运用在相关的技术领域,均同理包括在本发明的专利保护范围内。The above descriptions are only examples of the present invention, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention. Any equivalent transformations made by using the contents of the description and drawings of the present invention, or directly or indirectly applied in related technical fields, are similarly included in the within the scope of patent protection of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010461312.8ACN111370678B (en) | 2020-05-27 | 2020-05-27 | A kind of preparation method of modified-coated lithium iron phosphate material for lithium battery |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010461312.8ACN111370678B (en) | 2020-05-27 | 2020-05-27 | A kind of preparation method of modified-coated lithium iron phosphate material for lithium battery |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111370678Atrue CN111370678A (en) | 2020-07-03 |
| CN111370678B CN111370678B (en) | 2020-10-27 |
Family
ID=71212302
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010461312.8AActiveCN111370678B (en) | 2020-05-27 | 2020-05-27 | A kind of preparation method of modified-coated lithium iron phosphate material for lithium battery |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111370678B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115050955A (en)* | 2022-03-15 | 2022-09-13 | 中南大学 | Preparation and modification method of high-nickel single crystal ternary cathode material |
Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100176337A1 (en)* | 2009-01-13 | 2010-07-15 | Aruna Zhamu | Process for producing nano graphene reinforced composite particles for lithium battery electrodes |
| US20130171502A1 (en)* | 2011-12-29 | 2013-07-04 | Guorong Chen | Hybrid electrode and surface-mediated cell-based super-hybrid energy storage device containing same |
| CN103531814A (en)* | 2013-10-28 | 2014-01-22 | 深圳格林德能源有限公司 | Composite conductive agent, dispersion method thereof, positive plate and lithium ion battery |
| CN103545525A (en)* | 2012-07-17 | 2014-01-29 | 南京宏德纳米材料有限公司 | Lithium ion battery nano composite positive-negative electrode material containing three-dimensional conductive network as well as preparation method thereof |
| KR20140040388A (en)* | 2012-09-26 | 2014-04-03 | 주식회사 포스코이에스엠 | Method for the preparation of a lithium iron phosphate of olivine crystal structure and carbon-coated lithium iron phosphate of olivine crystal structure prepared thereby, including carbon inside |
| CN103975468A (en)* | 2011-11-15 | 2014-08-06 | 电气化学工业株式会社 | Composite particle, method for producing same, electrode material for secondary battery, and secondary battery |
| CN106340395A (en)* | 2016-10-21 | 2017-01-18 | 苏州捷迪纳米科技有限公司 | Fibrous composite electrode material and preparation method thereof |
| US20170125802A1 (en)* | 2015-10-28 | 2017-05-04 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods for making conformational conductive coated materials |
| KR20170056310A (en)* | 2015-11-13 | 2017-05-23 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Cable-type secondary battery |
| KR101815212B1 (en)* | 2017-03-22 | 2018-01-05 | 한국과학기술원 | Fiber Woven Fabric Based Structural Battery Composites |
| CN108140786A (en)* | 2015-10-02 | 2018-06-08 | 纳米技术仪器公司 | For producing the method for the lithium battery with ultra high energy density |
| CN108292744A (en)* | 2015-10-07 | 2018-07-17 | 瓦尔达微电池有限责任公司 | Composite material, electrode, the method for producing the material and the electrode and the electrochemistry list pond comprising the electrode |
| CN108735997A (en)* | 2018-05-28 | 2018-11-02 | 深圳市贝特瑞纳米科技有限公司 | A kind of LiFePO4 based composites, preparation method and the usage more than LiFePO4 theoretical capacity |
| CN109524658A (en)* | 2018-12-06 | 2019-03-26 | 深圳市德方纳米科技股份有限公司 | Anode material for lithium-ion batteries and preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery |
| US20190173079A1 (en)* | 2017-12-05 | 2019-06-06 | Nanotek Instruments, Inc. | Method of Producing Participate Electrode Materials for Alkali Metal Batteries |
| CN109860603A (en)* | 2019-01-21 | 2019-06-07 | 珠海光宇电池有限公司 | Lithium battery pole slice and preparation method thereof and lithium battery |
| CN110582872A (en)* | 2017-02-27 | 2019-12-17 | 纳米技术仪器公司 | Lithium battery cathode and method of manufacture |
| CN110720153A (en)* | 2017-04-10 | 2020-01-21 | 纳米技术仪器公司 | Encapsulated cathode active material particles, lithium secondary battery comprising the same, and method of manufacturing the same |
- 2020
- 2020-05-27CNCN202010461312.8Apatent/CN111370678B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20100176337A1 (en)* | 2009-01-13 | 2010-07-15 | Aruna Zhamu | Process for producing nano graphene reinforced composite particles for lithium battery electrodes |
| CN103975468A (en)* | 2011-11-15 | 2014-08-06 | 电气化学工业株式会社 | Composite particle, method for producing same, electrode material for secondary battery, and secondary battery |
| US20130171502A1 (en)* | 2011-12-29 | 2013-07-04 | Guorong Chen | Hybrid electrode and surface-mediated cell-based super-hybrid energy storage device containing same |
| CN103545525A (en)* | 2012-07-17 | 2014-01-29 | 南京宏德纳米材料有限公司 | Lithium ion battery nano composite positive-negative electrode material containing three-dimensional conductive network as well as preparation method thereof |
| KR20140040388A (en)* | 2012-09-26 | 2014-04-03 | 주식회사 포스코이에스엠 | Method for the preparation of a lithium iron phosphate of olivine crystal structure and carbon-coated lithium iron phosphate of olivine crystal structure prepared thereby, including carbon inside |
| CN103531814A (en)* | 2013-10-28 | 2014-01-22 | 深圳格林德能源有限公司 | Composite conductive agent, dispersion method thereof, positive plate and lithium ion battery |
| CN108140786A (en)* | 2015-10-02 | 2018-06-08 | 纳米技术仪器公司 | For producing the method for the lithium battery with ultra high energy density |
| CN108292744A (en)* | 2015-10-07 | 2018-07-17 | 瓦尔达微电池有限责任公司 | Composite material, electrode, the method for producing the material and the electrode and the electrochemistry list pond comprising the electrode |
| US20170125802A1 (en)* | 2015-10-28 | 2017-05-04 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods for making conformational conductive coated materials |
| KR20170056310A (en)* | 2015-11-13 | 2017-05-23 | 주식회사 엘지화학 | Cable-type secondary battery |
| CN106340395A (en)* | 2016-10-21 | 2017-01-18 | 苏州捷迪纳米科技有限公司 | Fibrous composite electrode material and preparation method thereof |
| CN110582872A (en)* | 2017-02-27 | 2019-12-17 | 纳米技术仪器公司 | Lithium battery cathode and method of manufacture |
| KR101815212B1 (en)* | 2017-03-22 | 2018-01-05 | 한국과학기술원 | Fiber Woven Fabric Based Structural Battery Composites |
| CN110720153A (en)* | 2017-04-10 | 2020-01-21 | 纳米技术仪器公司 | Encapsulated cathode active material particles, lithium secondary battery comprising the same, and method of manufacturing the same |
| US20190173079A1 (en)* | 2017-12-05 | 2019-06-06 | Nanotek Instruments, Inc. | Method of Producing Participate Electrode Materials for Alkali Metal Batteries |
| CN108735997A (en)* | 2018-05-28 | 2018-11-02 | 深圳市贝特瑞纳米科技有限公司 | A kind of LiFePO4 based composites, preparation method and the usage more than LiFePO4 theoretical capacity |
| CN109524658A (en)* | 2018-12-06 | 2019-03-26 | 深圳市德方纳米科技股份有限公司 | Anode material for lithium-ion batteries and preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery |
| CN109860603A (en)* | 2019-01-21 | 2019-06-07 | 珠海光宇电池有限公司 | Lithium battery pole slice and preparation method thereof and lithium battery |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115050955A (en)* | 2022-03-15 | 2022-09-13 | 中南大学 | Preparation and modification method of high-nickel single crystal ternary cathode material |
| CN115050955B (en)* | 2022-03-15 | 2024-03-22 | 中南大学 | Preparation and modification method of a high-nickel single crystal ternary cathode material |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111370678B (en) | 2020-10-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Zheng et al. | Fabrication and understanding of Cu 3 Si-Si@ carbon@ graphene nanocomposites as high-performance anodes for lithium-ion batteries | |
| Zhang et al. | One-pot sol-gel synthesis of Si/C yolk-shell anodes for high performance lithium-ion batteries | |
| CN109713286B (en) | Silicon-based composite material for lithium ion secondary battery and preparation method thereof | |
| Xu et al. | Improved cycling performance of SiOx/MgO/Mg2SiO4/C composite anode materials for lithium-ion battery | |
| Lv et al. | B2O3/LiBO2 dual-modification layer stabilized Ni-rich cathode for lithium-ion battery | |
| CN105206839B (en) | A modified carbon nanotube and preparation method thereof, positive electrode of lithium ion battery and preparation method thereof, and lithium ion battery | |
| CN115207304B (en) | A graphite negative electrode composite material and preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery | |
| CN102324497A (en) | A kind of preparation method of lithium battery negative electrode material of graphene supported carbon coating tin antimony | |
| Tan et al. | High performance sodium ion anodes based on Sn4P3 encapsulated within amphiphilic graphene tubes | |
| CN110085811A (en) | SiOx/carbon composite material, preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery | |
| Cao et al. | High-temperature solid-phase synthesis of lithium iron phosphate using polyethylene glycol grafted carbon nanotubes as the carbon source for rate-type lithium-ion batteries | |
| CN110808364A (en) | Graphene silicon-based negative electrode slurry, lithium ion battery negative electrode and preparation method thereof, and lithium ion battery | |
| CN114583137B (en) | Method for modifying carbon surface by sulfur doped phosphorus and application thereof | |
| CN110571416A (en) | A kind of transition metal selenium sulfur complex and preparation method thereof | |
| Yu et al. | High performance of porous silicon/carbon/RGO network derived from rice husks as anodes for lithium-ion batteries | |
| CN112794310B (en) | Potassium ion battery anode material and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN115513453A (en) | A silver-doped hard carbon composite material, its preparation method and application | |
| CN115954443B (en) | Preparation method of carbon-coated silicon-copper alloy negative electrode material of lithium ion battery | |
| CN109950503B (en) | Preparation method of CoMoOx/carbon/sulfur composite nanomaterial, negative electrode of lithium ion battery and lithium ion half battery | |
| Chen et al. | Achieving long-term cycling stability in Na3V2 (PO4) 3 cathode material through polymorphic carbon network coating | |
| Zhu et al. | Polypyrrole-modified prussian blue for enhanced conductivity and cycling stability in sodium-ion batteries | |
| CN113896177B (en) | Battery anode material, preparation method thereof, anode and lithium ion battery | |
| Ai et al. | A new lithium-ion batteries derivated from waste bagasse: Preparation, characterization and application | |
| CN114975964A (en) | A kind of polypyrrole-coated tin dioxide/nano carbon ball negative electrode material and its preparation method and sodium ion battery | |
| CN111370678B (en) | A kind of preparation method of modified-coated lithium iron phosphate material for lithium battery |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| PE01 | Entry into force of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | Denomination of invention:A preparation method of lithium iron phosphate material for modified coated lithium battery Effective date of registration:20210831 Granted publication date:20201027 Pledgee:Gaoxin sub branch of Bank of Changsha Co.,Ltd. Pledgor:HUNAN YACHENG NEW MATERIAL Co.,Ltd. Registration number:Y2021430000040 | |
| PE01 | Entry into force of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | ||
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder | ||
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder | Address after:410600 Xinkang Road, Ningxiang Economic and Technological Development Zone, Changsha City, Hunan Province Patentee after:Hunan Yacheng New Energy Co.,Ltd. Address before:410600 Xinkang Road, Ningxiang Economic and Technological Development Zone, Changsha City, Hunan Province Patentee before:HUNAN YACHENG NEW MATERIAL CO.,LTD. | |
| PM01 | Change of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | ||
| PM01 | Change of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | Change date:20221024 Registration number:Y2021430000040 Pledgor after:Hunan Yacheng New Energy Co.,Ltd. Pledgor before:HUNAN YACHENG NEW MATERIAL CO.,LTD. | |
| PM01 | Change of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | ||
| PM01 | Change of the registration of the contract for pledge of patent right | Change date:20250113 Registration number:Y2021430000040 Pledgee after:Bank of Changsha Co.,Ltd. Kaifu sub branch Pledgee before:Gaoxin sub branch of Bank of Changsha Co.,Ltd. |