CN111338802B - Method, system, equipment and medium for optimizing performance of big data cluster - Google Patents
Method, system, equipment and medium for optimizing performance of big data clusterDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111338802B CN111338802BCN202010132949.2ACN202010132949ACN111338802BCN 111338802 BCN111338802 BCN 111338802BCN 202010132949 ACN202010132949 ACN 202010132949ACN 111338802 BCN111338802 BCN 111338802B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- cpu
- reserved
- intensive
- cores
- resource
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/50—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU]
- G06F9/5005—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request
- G06F9/5027—Allocation of resources, e.g. of the central processing unit [CPU] to service a request the resource being a machine, e.g. CPUs, Servers, Terminals
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F9/00—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units
- G06F9/06—Arrangements for program control, e.g. control units using stored programs, i.e. using an internal store of processing equipment to receive or retain programs
- G06F9/46—Multiprogramming arrangements
- G06F9/52—Program synchronisation; Mutual exclusion, e.g. by means of semaphores
- G06F9/526—Mutual exclusion algorithms
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Debugging And Monitoring (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及大数据集群领域,更具体地,特别是指一种优化大数据集群性能的方法、系统、计算机设备及可读介质。The present invention relates to the field of big data clusters, and more particularly, to a method, system, computer equipment and readable medium for optimizing the performance of big data clusters.
背景技术Background technique
伴随着服务器的快速发展,很多国产CPU及相似产品也广泛被人们接受使用,在目前,国产CPU的发展方向是放弃超线程技术而使用多物理核聚合到一颗CPU中来提高CPU整体性能。因为国产CPU与目前主流CPU的结构差异较大,所以虽然国产CPU的综合硬件性能与一些主流CPU的性能相当,但是在搭配了国产CPU的服务器运行大数据方面任务时,却达不到期望的性能值。With the rapid development of servers, many domestic CPUs and similar products are widely accepted and used. At present, the development direction of domestic CPUs is to abandon hyper-threading technology and use multiple physical cores to aggregate into one CPU to improve the overall performance of the CPU. Because the structure of domestic CPUs is quite different from that of current mainstream CPUs, although the comprehensive hardware performance of domestic CPUs is comparable to that of some mainstream CPUs, when servers equipped with domestic CPUs run big data tasks, they cannot meet expectations. performance value.
目前使用多物理核服务器集群搭建的大数据平台上,其资源调度器yar n会继续将物理核使用虚拟核技术,因为国产CPU其使用的物理核数很多,且单核能力逊色于主流的英特尔gold系列等CPU,经常出现多个调用CPU较少的进程使一个CPU密集调度的进程无法得到执行,因为显示核数较多,多个调用CPU较少进程并不是通过队列的形式排队快速执行,而是并发执行,CPU密集调度进程在与其共同并发时,其调用CPU核数单核能力不足且因为与其他进程共同并发而得到核数不多,会引起该任务GC(Allocation Failure,分配失败)时间过长,执行效率过慢且长时间不能释放该进程占用资源加剧性能问题,从而大大影响集群性能。On the big data platform currently built with multi-physical core server clusters, the resource scheduler yarn will continue to use virtual core technology for physical cores, because domestic CPUs use a lot of physical cores, and the single-core capability is inferior to mainstream Intel. For CPUs such as the gold series, there are often multiple processes that call less CPU, so that a process that is intensively scheduled cannot be executed, because the number of displayed cores is large, and multiple processes that call less CPU are not queued for fast execution in the form of a queue. Instead, it is executed concurrently. When a CPU-intensive scheduling process is concurrently concurrent with it, its ability to call a single core of CPU cores is insufficient, and the number of cores obtained because it is concurrently concurrent with other processes is small, which will cause the task GC (Allocation Failure, allocation failure) If the time is too long, the execution efficiency is too slow, and the resources occupied by the process cannot be released for a long time, aggravating performance problems and greatly affecting the cluster performance.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
有鉴于此,本发明实施例的目的在于提出一种优化大数据集群性能的方法、系统、计算机设备及计算机可读存储介质,通过设置虚拟核作为预留CPU来执行CPU密集调度的进程,有效防止了在大数据集群中CPU密集调度的进程因CPU核数不够而无法执行的问题,大幅提高了大数据集群的性能。In view of this, the purpose of the embodiments of the present invention is to provide a method, system, computer equipment and computer-readable storage medium for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster. By setting a virtual core as a reserved CPU to perform a CPU-intensive scheduling process, effectively It prevents the CPU-intensive scheduling process in the big data cluster from being executed due to insufficient CPU cores, and greatly improves the performance of the big data cluster.
基于上述目的,本发明实施例的一方面提供了一种优化大数据集群性能的方法,包括如下步骤:基于CPU物理核的数量创建多个CPU虚拟核,并将其中预定数量的所述CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定;判断当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源是否超过阈值;响应于当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源超过阈值,判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程;以及响应于存在CPU密集调度的进程,对所述预留CPU解锁并使用所述预留CPU执行所述CPU密集调度的进程。Based on the above object, one aspect of the embodiments of the present invention provides a method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster, including the following steps: creating multiple CPU virtual cores based on the number of physical CPU cores, and virtualizing a predetermined number of the CPU virtual cores. The cores are locked as reserved CPUs; determine whether the number of CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeds the threshold; in response to the number of CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeding the threshold, determine whether there are CPU-intensive scheduling processes; For a process of intensive scheduling, unlock the reserved CPU and use the reserved CPU to execute the process of the CPU intensive scheduling.
在一些实施方式中,所述判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程包括:依次判断每个进程是否存在密集响应标识。In some embodiments, the judging whether there is a process of CPU intensive scheduling includes: sequentially judging whether each process has an intensive response identifier.
在一些实施方式中,所述判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程包括:监控进程对应的资源容器,判断所述资源容器中内存释放时间大于预定时间的任务数是否超过第二阈值。In some embodiments, the judging whether there is a process of CPU-intensive scheduling includes: monitoring a resource container corresponding to the process, and judging whether the number of tasks in the resource container whose memory release time is greater than a predetermined time exceeds a second threshold.
在一些实施方式中,所述将其中预定数量的所述CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定包括:向资源管理器发出所述预留CPU资源被占用的信号。In some implementation manners, locking a predetermined number of the CPU virtual cores as reserved CPUs includes: sending a signal to a resource manager that the reserved CPU resources are occupied.
本发明实施例的另一方面,还提供了一种优化大数据集群性能的系统,包括:预留模块,配置用于基于CPU物理核的数量创建多个CPU虚拟核,并将其中预定数量的所述CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定;第一判断模块,配置用于判断当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源是否超过阈值;第二判断模块,配置用于响应于当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源超过阈值,判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程;以及执行模块,配置用于响应于存在CPU密集调度的进程,对所述预留CPU解锁并使用所述预留CPU执行所述CPU密集调度的进程。Another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention further provides a system for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster, including: a reservation module configured to create a plurality of CPU virtual cores based on the number of physical CPU cores, and allocate a predetermined number of CPU virtual cores among them. The CPU virtual core is locked as a reserved CPU; the first judgment module is configured to judge whether the number of CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeds a threshold; the second judgment module is configured to respond to the CPU occupied by the current number of processes The number of core resources exceeds a threshold, and it is judged whether there is a process of CPU-intensive scheduling; and an execution module is configured to, in response to the existence of a process of CPU-intensive scheduling, unlock the reserved CPU and use the reserved CPU to execute the CPU-intensive process Scheduled process.
在一些实施方式中,所述第二判断模块还配置用于:依次判断每个进程是否存在密集响应标识。In some embodiments, the second judging module is further configured to: judge in turn whether each process has a dense response identifier.
在一些实施方式中,所述第二判断模块还配置用于:监控进程对应的资源容器,判断所述资源容器中内存释放时间大于预定时间的任务数是否超过第二阈值。In some embodiments, the second judgment module is further configured to: monitor the resource container corresponding to the process, and judge whether the number of tasks in the resource container whose memory release time is greater than a predetermined time exceeds a second threshold.
在一些实施方式中,所述预留模块还配置用于:向资源管理器发出所述预留CPU资源被占用的信号。In some embodiments, the reservation module is further configured to: send a signal to the resource manager that the reserved CPU resource is occupied.
本发明实施例的又一方面,还提供了一种计算机设备,包括:至少一个处理器;以及存储器,所述存储器存储有可在所述处理器上运行的计算机指令,所述指令由所述处理器执行时实现如上方法的步骤。In yet another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, there is also provided a computer device, comprising: at least one processor; and a memory, where the memory stores computer instructions that can be executed on the processor, and the instructions are executed by the processor. The processor implements the steps of the above method when executed.
本发明实施例的再一方面,还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,计算机可读存储介质存储有被处理器执行时实现如上方法步骤的计算机程序。In yet another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a computer-readable storage medium is also provided, where the computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program that implements the above method steps when executed by a processor.
本发明具有以下有益技术效果:通过设置虚拟核作为预留CPU来执行CPU密集调度的进程,有效防止了在大数据集群中CPU密集调度的进程因CPU核数不够而无法执行的问题,大幅提高了大数据集群的性能。The present invention has the following beneficial technical effects: by setting virtual cores as reserved CPUs to perform CPU-intensive scheduling processes, the problem that the CPU-intensive scheduling processes in big data clusters cannot be executed due to insufficient CPU cores is effectively prevented, thereby greatly improving performance of big data clusters.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例或现有技术中的技术方案,下面将对实施例或现有技术描述中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,显而易见地,下面描述中的附图仅仅是本发明的一些实施例,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的实施例。In order to explain the embodiments of the present invention or the technical solutions in the prior art more clearly, the following briefly introduces the accompanying drawings that need to be used in the description of the embodiments or the prior art. Obviously, the accompanying drawings in the following description are only These are some embodiments of the present invention. For those of ordinary skill in the art, other embodiments can also be obtained according to these drawings without creative efforts.
图1为本发明提供的优化大数据集群性能的方法的实施例的示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster provided by the present invention;
图2为本发明提供的优化大数据集群性能的方法的实施例的计算机设备结构示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic structural diagram of a computer device according to an embodiment of the method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster provided by the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为使本发明的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚明白,以下结合具体实施例,并参照附图,对本发明实施例进一步详细说明。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more clearly understood, the embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the specific embodiments and the accompanying drawings.
需要说明的是,本发明实施例中所有使用“第一”和“第二”的表述均是为了区分两个相同名称非相同的实体或者非相同的参量,可见“第一”“第二”仅为了表述的方便,不应理解为对本发明实施例的限定,后续实施例对此不再一一说明。It should be noted that all expressions using "first" and "second" in the embodiments of the present invention are for the purpose of distinguishing two entities with the same name but not the same or non-identical parameters. It can be seen that "first" and "second" It is only for the convenience of expression and should not be construed as a limitation to the embodiments of the present invention, and subsequent embodiments will not describe them one by one.
基于上述目的,本发明实施例的第一个方面,提出了一种优化大数据集群性能的方法的实施例。图1示出的是本发明提供的优化大数据集群性能的方法的实施例的示意图。如图1所示,本发明实施例包括如下步骤:Based on the above objective, in the first aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, an embodiment of a method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster is proposed. FIG. 1 shows a schematic diagram of an embodiment of a method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster provided by the present invention. As shown in Figure 1, the embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
S1、基于CPU物理核的数量创建多个CPU虚拟核,并将其中预定数量的CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定;S1. Create multiple CPU virtual cores based on the number of CPU physical cores, and lock a predetermined number of CPU virtual cores as reserved CPUs;
S2、判断当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源是否超过阈值;S2. Determine whether the number of CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeds the threshold;
S3、响应于当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源超过阈值,判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程;以及S3. In response to the CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeding the threshold, determine whether there is a process of CPU intensive scheduling; and
S4、响应于存在CPU密集调度的进程,对预留CPU解锁并使用预留CPU执行CPU密集调度的进程。S4. In response to the existence of a process with CPU-intensive scheduling, unlock the reserved CPU and use the reserved CPU to perform the process of CPU-intensive scheduling.
基于CPU物理核的数量创建多个CPU虚拟核,并将预定数量的CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定。在大数据集群设置CPU虚拟核,例如可以将CPU虚拟核的数量设置为CPU物理核数的2倍,可以通过管理CPU虚拟核来对CPU物理核进行管理与调度。可以将预定数量的CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定,预定数量可以根据具体的情况进行设定,例如,可以设置12%的虚拟核为reserved cpu(预留CPU)。Create multiple CPU virtual cores based on the number of CPU physical cores, and lock a predetermined number of CPU virtual cores as reserved CPUs. Set CPU virtual cores in a big data cluster. For example, you can set the number of CPU virtual cores to twice the number of physical CPU cores. You can manage and schedule CPU physical cores by managing CPU virtual cores. A predetermined number of CPU virtual cores may be locked as reserved CPUs, and the predetermined number may be set according to specific conditions. For example, 12% of the virtual cores may be set as reserved CPUs (reserved CPUs).
在一些实施方式中,所述将预定数量的所述CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定包括:向资源管理器发出所述预留CPU资源被占用的信号。例如,被选入reserved cpu的虚拟核通过各个节点的nodemanager(节点管理器)向ResourceManager(资源管理器)发送资源被占用的信号,这样,这些预留CPU就会显示占用状态。In some embodiments, locking the predetermined number of the CPU virtual cores as reserved CPUs includes: sending a signal to the resource manager that the reserved CPU resources are occupied. For example, the virtual core selected into the reserved CPU sends a signal that the resource is occupied to the ResourceManager (resource manager) through the nodemanager (node manager) of each node, so that these reserved CPUs will display the occupied state.
判断当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源是否超过阈值。响应于当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源超过阈值,判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程。可以在大数据平台的资源管理器设置监控,监控从集群各个节点管理器向AppliacationMaster(应用管理器)发起的进程及相应container(资源容器)请求。可以通过ResourceManager获取可用资源报告,当进程数占用资源容器中的CPU资源大于全部可用CPU核数资源的70%时,则判定集群处于多进程并发及CPU使用频繁状态。此时检测是否存在CPU密集调度的进程。Determines whether the number of CPU cores occupied by the current number of processes exceeds the threshold. In response to the CPU core resource occupied by the current number of processes exceeding the threshold, it is determined whether there is a process that is CPU intensively scheduled. You can set up monitoring in the resource manager of the big data platform to monitor the processes and corresponding container (resource container) requests initiated from each node manager of the cluster to the ApplicationMaster (application manager). You can obtain the available resource report through the ResourceManager. When the number of processes occupying the CPU resources in the resource container is greater than 70% of all available CPU core resources, it is determined that the cluster is in a state of multi-process concurrency and frequent CPU usage. At this point, it is detected whether there is a CPU-intensive scheduling process.
在一些实施方式中,所述判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程包括:依次判断每个进程是否存在密集响应标识。在向Applicationmaster发送资源请求时,可以对该进程设置标识,也即是将其标识为CPU密集调度的进程,在ResourceManager与Applicationmaster调度资源时,在资源调度器分配的CPU核数的基础上将reserved cpu释放打包成container以支撑其算力。In some embodiments, the judging whether there is a process of CPU intensive scheduling includes: sequentially judging whether each process has an intensive response identifier. When sending a resource request to Applicationmaster, you can set an identifier for the process, that is, identify it as a CPU-intensive scheduling process. When ResourceManager and Applicationmaster schedule resources, they will be reserved on the basis of the number of CPU cores allocated by the resource scheduler. The cpu is released and packaged into a container to support its computing power.
在一些实施方式中,所述判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程包括:监控进程对应的资源容器,判断所述资源容器中内存释放时间大于预定时间的任务数是否超过第二阈值。监控并发进程任务下的container,设定container下内存正常释放时间为m。如果container下内存释放时间超过m的任务数大于30%,则可以确定该进程为CPU密集调度的进程。In some embodiments, the judging whether there is a process of CPU-intensive scheduling includes: monitoring a resource container corresponding to the process, and judging whether the number of tasks in the resource container whose memory release time is greater than a predetermined time exceeds a second threshold. Monitor the container under the concurrent process task, and set the normal memory release time under the container to m. If the number of tasks in the container whose memory release time exceeds m is greater than 30%, it can be determined that the process is a CPU-intensive scheduling process.
响应于存在CPU密集调度的进程,对预留CPU解锁并使用预留CPU执行CPU密集调度的进程。可以将reserved cpu释放打包为container加入此进程。In response to the existence of a CPU-intensive scheduled process, the reserved CPU is unlocked and the CPU-intensive scheduled process is performed using the reserved CPU. The reserved cpu release can be packaged as a container to join this process.
需要特别指出的是,上述优化大数据集群性能的方法的各个实施例中的各个步骤均可以相互交叉、替换、增加、删减,因此,这些合理的排列组合变换之于优化大数据集群性能的方法也应当属于本发明的保护范围,并且不应将本发明的保护范围局限在实施例之上。It should be particularly pointed out that the steps in each embodiment of the above-mentioned method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster can be intersected, replaced, added, and deleted. The method should also belong to the protection scope of the present invention, and the protection scope of the present invention should not be limited to the embodiments.
基于上述目的,本发明实施例的第二个方面,提出了一种优化大数据集群性能的系统,包括:预留模块,配置用于基于CPU物理核的数量创建多个CPU虚拟核,并将其中预定数量的所述CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定;第一判断模块,配置用于判断当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源是否超过阈值;第二判断模块,配置用于响应于当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源超过阈值,判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程;以及执行模块,配置用于响应于存在CPU密集调度的进程,对所述预留CPU解锁并使用所述预留CPU执行所述CPU密集调度的进程。Based on the above purpose, in a second aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a system for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster is proposed, including: a reservation module configured to create multiple CPU virtual cores based on the number of physical CPU cores, and A predetermined number of the CPU virtual cores are locked as reserved CPUs; the first judgment module is configured to judge whether the number of CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeds a threshold; the second judgment module is configured to respond to the current process The number of CPU core resources occupied by the number of CPU cores exceeds a threshold, and it is judged whether there is a process of CPU-intensive scheduling; and an execution module, configured to respond to a process with CPU-intensive scheduling, unlock the reserved CPU and use the reserved CPU to execute The CPU-intensive scheduled process.
在一些实施方式中,所述第二判断模块还配置用于:依次判断每个进程是否存在密集响应标识。In some embodiments, the second judging module is further configured to: judge in turn whether each process has a dense response identifier.
在一些实施方式中,所述第二判断模块还配置用于:监控进程对应的资源容器,判断所述资源容器中内存释放时间大于预定时间的任务数是否超过第二阈值。In some embodiments, the second judgment module is further configured to: monitor the resource container corresponding to the process, and judge whether the number of tasks in the resource container whose memory release time is greater than a predetermined time exceeds a second threshold.
在一些实施方式中,所述预留模块还配置用于:向资源管理器发出所述预留CPU资源被占用的信号。In some embodiments, the reservation module is further configured to: send a signal to the resource manager that the reserved CPU resource is occupied.
基于上述目的,本发明实施例的第三个方面,提出了一种计算机设备,包括:至少一个处理器;以及存储器,存储器存储有可在处理器上运行的计算机指令,指令由处理器执行以实现如下步骤:S1、基于CPU物理核的数量创建多个CPU虚拟核,并将其中预定数量的CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定;S2、判断当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源是否超过阈值;S3、响应于当前进程数占用的CPU核数资源超过阈值,判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程;以及S4、响应于存在CPU密集调度的进程,对预留CPU解锁并使用预留CPU执行CPU密集调度的进程。Based on the above objective, in a third aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a computer device is provided, including: at least one processor; and a memory, where the memory stores computer instructions that can be executed on the processor, and the instructions are executed by the processor to The following steps are implemented: S1. Create multiple CPU virtual cores based on the number of physical CPU cores, and lock a predetermined number of CPU virtual cores as reserved CPUs; S2. Determine whether the CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceed a threshold. ; S3, in response to the number of CPU core resources occupied by the current number of processes exceeding the threshold, determine whether there is a process of CPU-intensive scheduling; and S4, in response to a process with CPU-intensive scheduling, unlock the reserved CPU and use the reserved CPU to execute the CPU Intensively scheduled processes.
在一些实施方式中,所述判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程包括:依次判断每个进程是否存在密集响应标识。In some embodiments, the judging whether there is a process of CPU intensive scheduling includes: sequentially judging whether each process has an intensive response identifier.
在一些实施方式中,所述判断是否存在CPU密集调度的进程包括:监控进程对应的资源容器,判断所述资源容器中内存释放时间大于预定时间的任务数是否超过第二阈值。In some embodiments, the judging whether there is a process of CPU-intensive scheduling includes: monitoring a resource container corresponding to the process, and judging whether the number of tasks in the resource container whose memory release time is greater than a predetermined time exceeds a second threshold.
在一些实施方式中,所述将其中预定数量的所述CPU虚拟核作为预留CPU进行锁定包括:向资源管理器发出所述预留CPU资源被占用的信号。In some implementation manners, locking a predetermined number of the CPU virtual cores as reserved CPUs includes: sending a signal to a resource manager that the reserved CPU resources are occupied.
如图2所示,为本发明提供的上述优化大数据集群性能的方法的一个实施例的计算机设备结构示意图。As shown in FIG. 2 , it is a schematic structural diagram of a computer device according to an embodiment of the above-mentioned method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster provided by the present invention.
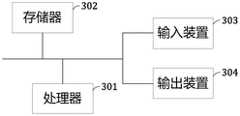
以如图2所示的装置为例,在该装置中包括一个处理器301以及一个存储器302,并还可以包括:输入装置303和输出装置304。Taking the device shown in FIG. 2 as an example, the device includes a
处理器301、存储器302、输入装置303和输出装置304可以通过总线或者其他方式连接,图2中以通过总线连接为例。The
存储器302作为一种非易失性计算机可读存储介质,可用于存储非易失性软件程序、非易失性计算机可执行程序以及模块,如本申请实施例中的优化大数据集群性能的方法对应的程序指令/模块。处理器301通过运行存储在存储器302中的非易失性软件程序、指令以及模块,从而执行服务器的各种功能应用以及数据处理,即实现上述方法实施例的优化大数据集群性能的方法。As a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium, the
存储器302可以包括存储程序区和存储数据区,其中,存储程序区可存储操作系统、至少一个功能所需要的应用程序;存储数据区可存储根据优化大数据集群性能的方法的使用所创建的数据等。此外,存储器302可以包括高速随机存取存储器,还可以包括非易失性存储器,例如至少一个磁盘存储器件、闪存器件、或其他非易失性固态存储器件。在一些实施例中,存储器302可选包括相对于处理器301远程设置的存储器,这些远程存储器可以通过网络连接至本地模块。上述网络的实例包括但不限于互联网、企业内部网、局域网、移动通信网及其组合。The
输入装置303可接收输入的用户名和密码等信息。输出装置304可包括显示屏等显示设备。The
一个或者多个优化大数据集群性能的方法对应的程序指令/模块存储在存储器302中,当被处理器301执行时,执行上述任意方法实施例中的优化大数据集群性能的方法。The program instructions/modules corresponding to one or more methods for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster are stored in the
执行上述优化大数据集群性能的方法的计算机设备的任何一个实施例,可以达到与之对应的前述任意方法实施例相同或者相类似的效果。Any embodiment of the computer device that executes the above method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster can achieve the same or similar effects as any of the foregoing method embodiments corresponding to it.
本发明还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,计算机可读存储介质存储有被处理器执行时执行如上方法的计算机程序。The present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium, where the computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program that executes the above method when executed by a processor.
最后需要说明的是,本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例方法中的全部或部分流程,可以通过计算机程序来指令相关硬件来完成,优化大数据集群性能的方法的程序可存储于一计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,可包括如上述各方法的实施例的流程。其中,程序的存储介质可为磁碟、光盘、只读存储记忆体(ROM)或随机存储记忆体(RAM)等。上述计算机程序的实施例,可以达到与之对应的前述任意方法实施例相同或者相类似的效果。Finally, it should be noted that those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the processes in the methods of the above embodiments can be implemented by instructing relevant hardware through a computer program. The program of the method for optimizing the performance of a big data cluster can be stored in a computer In the readable storage medium, when the program is executed, it may include the processes of the foregoing method embodiments. Wherein, the storage medium of the program may be a magnetic disk, an optical disk, a read only memory (ROM) or a random access memory (RAM) or the like. The above computer program embodiments can achieve the same or similar effects as any of the foregoing method embodiments corresponding thereto.
此外,根据本发明实施例公开的方法还可以被实现为由处理器执行的计算机程序,该计算机程序可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中。在该计算机程序被处理器执行时,执行本发明实施例公开的方法中限定的上述功能。In addition, the methods disclosed according to the embodiments of the present invention may also be implemented as a computer program executed by a processor, and the computer program may be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. When the computer program is executed by the processor, the above-mentioned functions defined in the methods disclosed in the embodiments of the present invention are executed.
此外,上述方法步骤以及系统单元也可以利用控制器以及用于存储使得控制器实现上述步骤或单元功能的计算机程序的计算机可读存储介质实现。In addition, the above-mentioned method steps and system units can also be implemented by using a controller and a computer-readable storage medium for storing a computer program that enables the controller to implement the functions of the above-mentioned steps or units.
此外,应该明白的是,本文的计算机可读存储介质(例如,存储器)可以是易失性存储器或非易失性存储器,或者可以包括易失性存储器和非易失性存储器两者。作为例子而非限制性的,非易失性存储器可以包括只读存储器(ROM)、可编程ROM(PROM)、电可编程ROM(EPROM)、电可擦写可编程ROM(EEPROM)或快闪存储器。易失性存储器可以包括随机存取存储器(RAM),该RAM可以充当外部高速缓存存储器。作为例子而非限制性的,RAM可以以多种形式获得,比如同步RAM(DRAM)、动态RAM(DRAM)、同步DRAM(SDRAM)、双数据速率SDRAM(DDRSDRAM)、增强SDRAM(ESDRAM)、同步链路DRAM(SLDRAM)、以及直接Rambus RAM(DRRAM)。所公开的方面的存储设备意在包括但不限于这些和其它合适类型的存储器。In addition, it should be understood that computer-readable storage media (eg, memory) herein can be volatile memory or non-volatile memory, or can include both volatile and non-volatile memory. By way of example and not limitation, nonvolatile memory may include read only memory (ROM), programmable ROM (PROM), electrically programmable ROM (EPROM), electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM), or flash memory memory. Volatile memory may include random access memory (RAM), which may act as external cache memory. By way of example and not limitation, RAM is available in various forms such as synchronous RAM (DRAM), dynamic RAM (DRAM), synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), double data rate SDRAM (DDRSDRAM), enhanced SDRAM (ESDRAM), synchronous Link DRAM (SLDRAM), and Direct Rambus RAM (DRRAM). The storage devices of the disclosed aspects are intended to include, but not be limited to, these and other suitable types of memory.
本领域技术人员还将明白的是,结合这里的公开所描述的各种示例性逻辑块、模块、电路和算法步骤可以被实现为电子硬件、计算机软件或两者的组合。为了清楚地说明硬件和软件的这种可互换性,已经就各种示意性组件、方块、模块、电路和步骤的功能对其进行了一般性的描述。这种功能是被实现为软件还是被实现为硬件取决于具体应用以及施加给整个系统的设计约束。本领域技术人员可以针对每种具体应用以各种方式来实现的功能,但是这种实现决定不应被解释为导致脱离本发明实施例公开的范围。Those skilled in the art will also appreciate that the various exemplary logical blocks, modules, circuits, and algorithm steps described in connection with the disclosure herein may be implemented as electronic hardware, computer software, or combinations of both. To clearly illustrate this interchangeability of hardware and software, various illustrative components, blocks, modules, circuits, and steps have been described generally in terms of their functionality. Whether such functionality is implemented as software or hardware depends on the specific application and design constraints imposed on the overall system. Those skilled in the art may implement the functions in various ways for each specific application, but such implementation decisions should not be interpreted as causing a departure from the scope of the disclosed embodiments of the present invention.
结合这里的公开所描述的各种示例性逻辑块、模块和电路可以利用被设计成用于执行这里功能的下列部件来实现或执行:通用处理器、数字信号处理器(DSP)、专用集成电路(ASIC)、现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)或其它可编程逻辑器件、分立门或晶体管逻辑、分立的硬件组件或者这些部件的任何组合。通用处理器可以是微处理器,但是可替换地,处理器可以是任何传统处理器、控制器、微控制器或状态机。处理器也可以被实现为计算设备的组合,例如,DSP和微处理器的组合、多个微处理器、一个或多个微处理器结合DSP和/或任何其它这种配置。The various exemplary logical blocks, modules, and circuits described in connection with the disclosure herein can be implemented or executed using the following components designed to perform the functions herein: general purpose processors, digital signal processors (DSPs), application specific integrated circuits (ASIC), Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) or other programmable logic device, discrete gate or transistor logic, discrete hardware components, or any combination of these components. A general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor, but in the alternative, the processor may be any conventional processor, controller, microcontroller, or state machine. A processor may also be implemented as a combination of computing devices, eg, a combination of a DSP and a microprocessor, multiple microprocessors, one or more microprocessors in combination with a DSP, and/or any other such configuration.
结合这里的公开所描述的方法或算法的步骤可以直接包含在硬件中、由处理器执行的软件模块中或这两者的组合中。软件模块可以驻留在RAM存储器、快闪存储器、ROM存储器、EPROM存储器、EEPROM存储器、寄存器、硬盘、可移动盘、CD-ROM、或本领域已知的任何其它形式的存储介质中。示例性的存储介质被耦合到处理器,使得处理器能够从该存储介质中读取信息或向该存储介质写入信息。在一个替换方案中,存储介质可以与处理器集成在一起。处理器和存储介质可以驻留在ASIC中。ASIC可以驻留在用户终端中。在一个替换方案中,处理器和存储介质可以作为分立组件驻留在用户终端中。The steps of a method or algorithm described in connection with the disclosures herein may be embodied directly in hardware, in a software module executed by a processor, or in a combination of the two. A software module may reside in RAM memory, flash memory, ROM memory, EPROM memory, EEPROM memory, registers, hard disk, removable disk, CD-ROM, or any other form of storage medium known in the art. An exemplary storage medium is coupled to the processor, such that the processor can read information from, and write information to, the storage medium. In an alternative, the storage medium may be integrated with the processor. The processor and storage medium may reside in an ASIC. The ASIC may reside in the user terminal. In an alternative, the processor and storage medium may reside in the user terminal as discrete components.
在一个或多个示例性设计中,功能可以在硬件、软件、固件或其任意组合中实现。如果在软件中实现,则可以将功能作为一个或多个指令或代码存储在计算机可读介质上或通过计算机可读介质来传送。计算机可读介质包括计算机存储介质和通信介质,该通信介质包括有助于将计算机程序从一个位置传送到另一个位置的任何介质。存储介质可以是能够被通用或专用计算机访问的任何可用介质。作为例子而非限制性的,该计算机可读介质可以包括RAM、ROM、EEPROM、CD-ROM或其它光盘存储设备、磁盘存储设备或其它磁性存储设备,或者是可以用于携带或存储形式为指令或数据结构的所需程序代码并且能够被通用或专用计算机或者通用或专用处理器访问的任何其它介质。此外,任何连接都可以适当地称为计算机可读介质。例如,如果使用同轴线缆、光纤线缆、双绞线、数字用户线路(DSL)或诸如红外线、无线电和微波的无线技术来从网站、服务器或其它远程源发送软件,则上述同轴线缆、光纤线缆、双绞线、DSL或诸如红外线、无线电和微波的无线技术均包括在介质的定义。如这里所使用的,磁盘和光盘包括压缩盘(CD)、激光盘、光盘、数字多功能盘(DVD)、软盘、蓝光盘,其中磁盘通常磁性地再现数据,而光盘利用激光光学地再现数据。上述内容的组合也应当包括在计算机可读介质的范围内。In one or more exemplary designs, functions may be implemented in hardware, software, firmware, or any combination thereof. If implemented in software, the functions may be stored on or transmitted over as one or more instructions or code on a computer-readable medium. Computer-readable media includes both computer storage media and communication media including any medium that facilitates transfer of a computer program from one place to another. A storage medium can be any available medium that can be accessed by a general purpose or special purpose computer. By way of example and not limitation, the computer-readable medium may include RAM, ROM, EEPROM, CD-ROM or other optical disk storage devices, magnetic disk storage devices or other magnetic storage devices, or may be used to carry or store instructions in the form of or data structures and any other medium that can be accessed by a general purpose or special purpose computer or a general purpose or special purpose processor. Also, any connection is properly termed a computer-readable medium. For example, if coaxial cable, fiber optic cable, twisted pair, digital subscriber line (DSL), or wireless technologies such as infrared, radio, and microwave are used to send software from a website, server, or other remote source, the above coaxial cable Cable, fiber optic cable, twisted pair, DSL or wireless technologies such as infrared, radio and microwave are all included in the definition of medium. As used herein, magnetic disks and optical disks include compact disks (CDs), laser disks, optical disks, digital versatile disks (DVDs), floppy disks, blu-ray disks, where disks usually reproduce data magnetically, while optical disks reproduce data optically with lasers . Combinations of the above should also be included within the scope of computer-readable media.
以上是本发明公开的示例性实施例,但是应当注意,在不背离权利要求限定的本发明实施例公开的范围的前提下,可以进行多种改变和修改。根据这里描述的公开实施例的方法权利要求的功能、步骤和/或动作不需以任何特定顺序执行。此外,尽管本发明实施例公开的元素可以以个体形式描述或要求,但除非明确限制为单数,也可以理解为多个。The above are exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure, but it should be noted that various changes and modifications may be made without departing from the scope of the disclosure of the embodiments of the present invention as defined in the claims. The functions, steps and/or actions of the method claims in accordance with the disclosed embodiments described herein need not be performed in any particular order. Furthermore, although elements disclosed in the embodiments of the present invention may be described or claimed in the singular, unless explicitly limited to the singular, the plural may also be construed.
应当理解的是,在本文中使用的,除非上下文清楚地支持例外情况,单数形式“一个”旨在也包括复数形式。还应当理解的是,在本文中使用的“和/或”是指包括一个或者一个以上相关联地列出的项目的任意和所有可能组合。It should be understood that, as used herein, the singular form "a" is intended to include the plural form as well, unless the context clearly supports an exception. It will also be understood that "and/or" as used herein is meant to include any and all possible combinations of one or more of the associated listed items.
上述本发明实施例公开实施例序号仅仅为了描述,不代表实施例的优劣。The above-mentioned embodiments of the present invention disclose the serial numbers of the embodiments only for description, and do not represent the advantages and disadvantages of the embodiments.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例的全部或部分步骤可以通过硬件来完成,也可以通过程序来指令相关的硬件完成,程序可以存储于一种计算机可读存储介质中,上述提到的存储介质可以是只读存储器,磁盘或光盘等。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that all or part of the steps of implementing the above embodiments can be completed by hardware, or can be completed by instructing relevant hardware through a program, and the program can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium. The storage medium can be a read-only memory, a magnetic disk or an optical disk, and the like.
所属领域的普通技术人员应当理解:以上任何实施例的讨论仅为示例性的,并非旨在暗示本发明实施例公开的范围(包括权利要求)被限于这些例子;在本发明实施例的思路下,以上实施例或者不同实施例中的技术特征之间也可以进行组合,并存在如上的本发明实施例的不同方面的许多其它变化,为了简明它们没有在细节中提供。因此,凡在本发明实施例的精神和原则之内,所做的任何省略、修改、等同替换、改进等,均应包含在本发明实施例的保护范围之内。Those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that the discussion of any of the above embodiments is only exemplary, and is not intended to imply that the scope (including the claims) disclosed by the embodiments of the present invention is limited to these examples; under the idea of the embodiments of the present invention , the technical features in the above embodiments or different embodiments can also be combined, and there are many other changes in different aspects of the above embodiments of the present invention, which are not provided in detail for the sake of brevity. Therefore, any omission, modification, equivalent replacement, improvement, etc. made within the spirit and principle of the embodiments of the present invention should be included within the protection scope of the embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010132949.2ACN111338802B (en) | 2020-02-29 | 2020-02-29 | Method, system, equipment and medium for optimizing performance of big data cluster |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010132949.2ACN111338802B (en) | 2020-02-29 | 2020-02-29 | Method, system, equipment and medium for optimizing performance of big data cluster |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111338802A CN111338802A (en) | 2020-06-26 |
| CN111338802Btrue CN111338802B (en) | 2022-08-09 |
Family
ID=71185887
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202010132949.2AActiveCN111338802B (en) | 2020-02-29 | 2020-02-29 | Method, system, equipment and medium for optimizing performance of big data cluster |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111338802B (en) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112134752B (en) | 2020-09-10 | 2022-05-13 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A method, system, device and medium for monitoring switches based on BMC |
| CN112231066B (en)* | 2020-10-29 | 2024-02-13 | 北京思特奇信息技术股份有限公司 | Optimization processing method and system based on JVM memory use |
| CN113448749B (en)* | 2021-06-04 | 2023-03-24 | 山东英信计算机技术有限公司 | Method, system, device and medium for optimizing execution of expected timing task |
| CN113608834A (en)* | 2021-07-29 | 2021-11-05 | 济南浪潮数据技术有限公司 | Resource scheduling method, device and equipment based on super-fusion and readable medium |
| CN114840340A (en)* | 2022-05-07 | 2022-08-02 | 中国银行股份有限公司 | Method and device for automatically adjusting system performance |
| CN115941679A (en)* | 2022-10-14 | 2023-04-07 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | Method, device, equipment and medium for improving cluster link service carrying capacity |
| CN116149846B (en)* | 2022-12-05 | 2025-10-03 | 中国科学院深圳先进技术研究院 | Application performance optimization method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105550040A (en)* | 2015-12-29 | 2016-05-04 | 四川中电启明星信息技术有限公司 | KVM platform based virtual machine CPU resource reservation algorithm |
| US20160179560A1 (en)* | 2014-12-22 | 2016-06-23 | Mrittika Ganguli | CPU Overprovisioning and Cloud Compute Workload Scheduling Mechanism |
| CN110442423A (en)* | 2019-07-09 | 2019-11-12 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A kind of method and apparatus for realizing that virtual machine reserves CPU using control group |
- 2020
- 2020-02-29CNCN202010132949.2Apatent/CN111338802B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20160179560A1 (en)* | 2014-12-22 | 2016-06-23 | Mrittika Ganguli | CPU Overprovisioning and Cloud Compute Workload Scheduling Mechanism |
| CN105550040A (en)* | 2015-12-29 | 2016-05-04 | 四川中电启明星信息技术有限公司 | KVM platform based virtual machine CPU resource reservation algorithm |
| CN110442423A (en)* | 2019-07-09 | 2019-11-12 | 苏州浪潮智能科技有限公司 | A kind of method and apparatus for realizing that virtual machine reserves CPU using control group |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111338802A (en) | 2020-06-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111338802B (en) | Method, system, equipment and medium for optimizing performance of big data cluster | |
| CN111756811B (en) | Method, system, device and medium for actively pushing distributed system | |
| CN111367659B (en) | Resource management method, equipment and medium for nodes in Kubernetes | |
| CN109992366B (en) | Task scheduling method and task scheduling device | |
| CN108429631A (en) | Method and device for instantiating network services | |
| CN111367693B (en) | Method, system, device and medium for scheduling plug-in tasks based on message queue | |
| CN110677305A (en) | Automatic scaling method and system in cloud computing environment | |
| CN113031870A (en) | Dynamic management method, device, storage medium and equipment for cluster system | |
| WO2021018011A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for accessing critical resource, computer device, and readable storage medium | |
| JP2016530625A (en) | Method, system, and program for efficient task scheduling using a locking mechanism | |
| CN113157411B (en) | Celery-based reliable configurable task system and device | |
| CN114461668A (en) | MYSQL database query method and device based on thread pool | |
| CN113867954A (en) | A thread processing method, system and medium based on thread pool and object pool | |
| CN103778002A (en) | Method and device for recycling critical resources in multi-core system | |
| WO2019109948A1 (en) | Paas management method and device, and storage medium | |
| CN116468124B (en) | Quantum task scheduling method and related device | |
| CN118484262A (en) | Resource scheduling method and server | |
| CN112153114A (en) | A method, system, device and medium for time-sharing access to a shared device | |
| CN114816678B (en) | Virtual machine scheduling method, system, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN112130900A (en) | User information management method, system, equipment and medium for BMC | |
| CN115033501A (en) | System, method, equipment and medium for invalidation cache data | |
| CN111338792B (en) | A cluster resource release method, device and medium | |
| WO2023103434A1 (en) | Lock management method, apparatus and system | |
| TWI381315B (en) | Synchronization elements for multi-core embedded systems | |
| CN115714771A (en) | Double-current mutual backup high-availability method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CP03 | Change of name, title or address | Address after:Building 9, No.1, guanpu Road, Guoxiang street, Wuzhong Economic Development Zone, Wuzhong District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province Patentee after:Suzhou Yuannao Intelligent Technology Co.,Ltd. Country or region after:China Address before:Building 9, No.1, guanpu Road, Guoxiang street, Wuzhong Economic Development Zone, Wuzhong District, Suzhou City, Jiangsu Province Patentee before:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGY Co.,Ltd. Country or region before:China |