CN111241881A - Method, apparatus, apparatus and medium for area identification - Google Patents
Method, apparatus, apparatus and medium for area identificationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111241881A CN111241881ACN201811444648.2ACN201811444648ACN111241881ACN 111241881 ACN111241881 ACN 111241881ACN 201811444648 ACN201811444648 ACN 201811444648ACN 111241881 ACN111241881 ACN 111241881A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- area
- region
- target
- picture
- identification
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V20/00—Scenes; Scene-specific elements
- G06V20/10—Terrestrial scenes
- G06V20/13—Satellite images
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/21—Design or setup of recognition systems or techniques; Extraction of features in feature space; Blind source separation
- G06F18/214—Generating training patterns; Bootstrap methods, e.g. bagging or boosting
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/23—Clustering techniques
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F18/00—Pattern recognition
- G06F18/20—Analysing
- G06F18/24—Classification techniques
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/20—Image preprocessing
- G06V10/255—Detecting or recognising potential candidate objects based on visual cues, e.g. shapes
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/40—Extraction of image or video features
- G06V10/44—Local feature extraction by analysis of parts of the pattern, e.g. by detecting edges, contours, loops, corners, strokes or intersections; Connectivity analysis, e.g. of connected components
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Biology (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Computational Biology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Astronomy & Astrophysics (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及计算机技术领域,尤其涉及一种区域识别的方法、装置、设备和介质。The present invention relates to the field of computer technology, and in particular, to a method, apparatus, device and medium for area identification.
背景技术Background technique
网络质量评估是无线网络优化工作的重要组成部分,是运营商开展网络运行维护、优化调整以及工程建设的重要手段和依据。在对某一个区域进行网络质量评估时,首先就需要确定某一个区域的具体位置,基于确定的区域位置,才可以准确对网络质量进行评估。Network quality assessment is an important part of wireless network optimization, and it is an important means and basis for operators to carry out network operation and maintenance, optimization and adjustment, and engineering construction. When evaluating the network quality of a certain area, the specific location of the certain area needs to be determined first, and then the network quality can be accurately evaluated based on the determined area location.
目前通常是根据测量报告(Measurement Report,MR)中的数据信息对某一个区域的网络质量进行评估和优化。但是MR数据无法准确体现用户的地理位置,从而就会影响到接下来对某一个区域的网络质量进行评估的准确性。Currently, the network quality of a certain area is usually evaluated and optimized according to the data information in the measurement report (Measurement Report, MR). However, the MR data cannot accurately reflect the user's geographic location, which will affect the accuracy of the subsequent evaluation of the network quality in a certain area.
因此,存在无法准确进行区域的识别的技术问题。Therefore, there is a technical problem that the identification of the area cannot be performed accurately.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明实施例提供了一种区域识别的方法、装置、设备和介质,能够准确进行区域的识别。The embodiments of the present invention provide a method, apparatus, device and medium for area identification, which can accurately identify the area.
本发明实施例的一方面,提供一种区域识别的方法,该方法包括:An aspect of the embodiments of the present invention provides a method for area identification, the method comprising:
获取包括已知区域信息的卫星图片;Obtain satellite images including known area information;
对包括已知区域信息的卫星图片进行预处理,得到目标图片;Preprocessing satellite images including known area information to obtain target images;
以包括已知区域信息的卫星图片作为训练集,以目标图片作为目标数据,训练区域识别模型,得到训练后的区域识别模型;Taking the satellite images including known area information as the training set, and using the target image as the target data, the area identification model is trained, and the trained area identification model is obtained;
利用训练后的区域识别模型,确定需要进行区域识别的卫星图片中的目标区域。Using the trained area identification model, determine the target area in the satellite image that needs to be identified.
本发明实施例的另一方面,提供一种区域识别的装置,该装置包括:Another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention provides an apparatus for area identification, the apparatus comprising:
图片获取模块,用于获取包括已知区域信息的卫星图片;The image acquisition module is used to acquire satellite images including known area information;
图片处理模块,用于对包括已知区域信息的卫星图片进行预处理,得到目标图片;The image processing module is used to preprocess the satellite image including the known area information to obtain the target image;
模型创建模块,用于以包括已知区域信息的卫星图片作为训练集,以目标图片作为目标数据,训练区域识别模型,得到训练后的区域识别模型;The model creation module is used for training the region recognition model with the satellite images including the known region information as the training set and the target picture as the target data to obtain the trained region recognition model;
区域识别模块,用于利用训练后的区域识别模型,确定需要进行区域识别的卫星图片中的目标区域。The area identification module is used to use the trained area identification model to determine the target area in the satellite image that needs to be identified.
根据本发明实施例的另一方面,提供一种区域识别的设备,该设备包括:According to another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a device for area identification is provided, the device comprising:
处理器以及存储有计算机程序指令的存储器;a processor and a memory storing computer program instructions;
处理器执行计算机程序指令时实现如上述本发明实施例的任意一方面提供的区域识别的方法。When the processor executes the computer program instructions, the method for region identification provided by any one of the foregoing embodiments of the present invention is implemented.
根据本发明实施例的另一方面,提供一种计算机存储介质,计算机存储介质上存储有计算机程序指令,计算机程序指令被处理器执行时实现如上述本发明实施例的任意一方面提供的区域识别的方法。According to another aspect of the embodiments of the present invention, a computer storage medium is provided, and computer program instructions are stored on the computer storage medium, and when the computer program instructions are executed by a processor, the area identification provided in any aspect of the foregoing embodiments of the present invention is implemented Methods.
本发明实施例提供的区域识别的方法、装置、设备和介质。基于已知区域信息的卫星图片以及经过预处理后得到的目标图片,训练区域识别模型,通过调整超参数可以使得区域识别模型越加精准,从而使得通过该区域识别模型得到的区域识别结果也更加精准。同时利用训练后的区域识别模型来对需要进行区域识别的卫星图片进行区域识别,提高了区域识别的效率以及准确性。The method, apparatus, device, and medium for area identification provided by the embodiments of the present invention. Based on the satellite images of known area information and the preprocessed target images, the area recognition model is trained. By adjusting the hyperparameters, the area recognition model can be made more accurate, so that the area recognition results obtained by the area recognition model are also more accurate. Precise. At the same time, the trained region identification model is used to perform region identification on satellite images that need region identification, which improves the efficiency and accuracy of region identification.
附图说明Description of drawings
为了更清楚地说明本发明实施例的技术方案,下面将对本发明实施例中所需要使用的附图作简单地介绍,对于本领域普通技术人员来讲,在不付出创造性劳动的前提下,还可以根据这些附图获得其他的附图。In order to illustrate the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention more clearly, the accompanying drawings required in the embodiments of the present invention will be briefly introduced below. For those of ordinary skill in the art, without creative work, the Additional drawings can be obtained from these drawings.
图1示出本发明一实施例的区域识别的方法的示意图;FIG. 1 shows a schematic diagram of a method for area identification according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图2示出本发明一实施例的卫星图片示意图;FIG. 2 shows a schematic diagram of a satellite image according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图3示出本发明一实施例的卷积神经网络的原理示意图;FIG. 3 shows a schematic diagram of the principle of a convolutional neural network according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图4示出本发明另一实施例的区域识别的方法的流程图;FIG. 4 shows a flowchart of a method for area identification according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图5示出本发明一实施例的村庄区域示意图;FIG. 5 shows a schematic diagram of a village area according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图6a示出本发明一实施例的曼哈顿距离示意图;FIG. 6a shows a schematic diagram of Manhattan distance according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图6b示出本发明一实施例的像素点之间的曼哈顿距离;FIG. 6b shows the Manhattan distance between pixels according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图7示出本发明一实施例的聚类处理的方法的流程图;7 shows a flowchart of a method for clustering processing according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图8示出本发明一实施例的聚类结果示意图;FIG. 8 shows a schematic diagram of a clustering result according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图9示出本发明一实施例的8连通检测轮廓跟踪算法的定义示意图;9 shows a schematic diagram of the definition of an 8-connection detection contour tracking algorithm according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图10示出本发明一实施例的连通邻居像素点的示意图;10 shows a schematic diagram of connected neighbor pixels according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图11示出本发明又一实施例的区域识别的方法的流程图;11 shows a flowchart of a method for area identification according to another embodiment of the present invention;
图12示出本发明一实施例的区域识别的装置的结构示意图;FIG. 12 shows a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for area identification according to an embodiment of the present invention;
图13示出了能够实现根据本发明实施例的区域识别的方法和装置的计算设备的示例性硬件架构的结构图。FIG. 13 shows a structural diagram of an exemplary hardware architecture of a computing device capable of implementing the method and apparatus for area identification according to an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面将详细描述本发明的各个方面的特征和示例性实施例,为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细描述。应理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅被配置为解释本发明,并不被配置为限定本发明。对于本领域技术人员来说,本发明可以在不需要这些具体细节中的一些细节的情况下实施。下面对实施例的描述仅仅是为了通过示出本发明的示例来提供对本发明更好的理解。The features and exemplary embodiments of various aspects of the present invention will be described in detail below. In order to make the objects, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention more clear, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only configured to explain the present invention, and are not configured to limit the present invention. It will be apparent to those skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without some of these specific details. The following description of the embodiments is only intended to provide a better understanding of the present invention by illustrating examples of the invention.
需要说明的是,在本文中,诸如第一和第二等之类的关系术语仅仅用来将一个实体或者操作与另一个实体或操作区分开来,而不一定要求或者暗示这些实体或操作之间存在任何这种实际的关系或者顺序。而且,术语“包括”、“包含”或者其任何其他变体意在涵盖非排他性的包含,从而使得包括一系列要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备不仅包括那些要素,而且还包括没有明确列出的其他要素,或者是还包括为这种过程、方法、物品或者设备所固有的要素。在没有更多限制的情况下,由语句“包括……”限定的要素,并不排除在包括所述要素的过程、方法、物品或者设备中还存在另外的相同要素。It should be noted that, in this document, relational terms such as first and second are only used to distinguish one entity or operation from another entity or operation, and do not necessarily require or imply any relationship between these entities or operations. any such actual relationship or sequence exists. Moreover, the terms "comprising", "comprising" or any other variation thereof are intended to encompass a non-exclusive inclusion such that a process, method, article or device that includes a list of elements includes not only those elements, but also includes not explicitly listed or other elements inherent to such a process, method, article or apparatus. Without further limitation, an element defined by the phrase "comprises" does not preclude the presence of additional identical elements in a process, method, article, or device that includes the element.
下面结合附图,详细描述根据本发明实施例的区域识别的方法、装置、设备和介质。应注意,这些实施例并不是用来限制本发明公开的范围。The method, apparatus, device, and medium for area identification according to embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings. It should be noted that these examples are not intended to limit the scope of the present disclosure.
下面通过图1至图11详细介绍根据本发明实施例的区域识别的方法。The method for region identification according to an embodiment of the present invention is described in detail below with reference to FIG. 1 to FIG. 11 .
在本发明的一个实施例中,如图1所示,图1是示出本发明一实施例的区域识别的方法的示意图。下面以农村区域作为需要识别的区域即目标区域为例,详细介绍本发明实施例中的区域识别方法。In an embodiment of the present invention, as shown in FIG. 1 , FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram illustrating a method for region identification according to an embodiment of the present invention. The following takes a rural area as an area to be identified, that is, a target area, as an example, to describe the area identification method in the embodiment of the present invention in detail.
如图1所示,本发明实施例中的区域识别的方法100包括以下步骤:As shown in FIG. 1 , the
S110,获取包括已知区域信息的卫星图片。S110, acquiring satellite pictures including known area information.
具体的,如图2所示,图2是示出本发明实施例中卫星图片示意图。首先获取预设数量的包括农村区域的卫星图片。Specifically, as shown in FIG. 2 , FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram showing a satellite picture in an embodiment of the present invention. First acquire a preset number of satellite images including rural areas.
S120,对包括已知区域信息的卫星图片进行预处理,得到目标图片。S120: Preprocess the satellite image including the known area information to obtain a target image.
在本发明的一个实施例中,继续参见图2。将获取的卫星图片中的农村区域标注出来。例如,可以将获取的卫星图片中的农村区域的像素值设置为0,即将卫星图片中的农村区域设置为黑色,得到目标图片。其中,目标图片中包括黑色区域的农村区域以及非农村区域。In one embodiment of the present invention, continued reference is made to FIG. 2 . The rural areas in the acquired satellite images are marked. For example, the pixel value of the rural area in the acquired satellite image can be set to 0, that is, the rural area in the satellite image can be set to be black to obtain the target image. Among them, the target image includes rural areas in black areas and non-rural areas.
S130,以包括已知区域信息的卫星图片作为训练集,以目标图片作为目标数据,训练区域识别模型,得到训练后的区域识别模型。S130 , using the satellite images including the known area information as the training set and the target image as the target data, train the area identification model to obtain the trained area identification model.
在本发明的一个实施例中,将上述获取到的卫星图片作为区域识别模型的训练集。其中,训练集用于估计模型。将目标图片作为区域识别模型的目标数据,即将目标图片作为区域识别模型的标签。In an embodiment of the present invention, the obtained satellite image is used as a training set of the region identification model. Among them, the training set is used to estimate the model. The target image is used as the target data of the region recognition model, that is, the target image is used as the label of the region recognition model.
首先,将训练集中包括已知区域信息的卫星图片按照预设规格进行划分。例如,可以将训练集中包括已知区域信息的卫星图片以及目标数据中的目标图片按照8×8预设规格进行划分,得到模型栅格图片。应当注意的是,区域识别模型的训练集以及区域识别模型的目标数据共同组成区域识别模型的数据集。First, the satellite images including known area information in the training set are divided according to preset specifications. For example, the satellite pictures including known area information and the target pictures in the target data in the training set can be divided according to 8×8 preset specifications to obtain model grid pictures. It should be noted that the training set of the region identification model and the target data of the region identification model together constitute the data set of the region identification model.
其次,将目标数据即区域识别模型的标签转换为离散标签,例如,标签[0,1]代表非农村区域,标签[1,0]代表农村区域。Second, the target data, that is, the labels of the region recognition model, are converted into discrete labels, for example, labels [0, 1] represent non-rural areas, and labels [1, 0] represent rural areas.
最后,将模型栅格图片以及离散标签通过多层卷积神经网络模型进行模型训练,通过对超参数进行调整使得经过迭代后的模型收敛,进而得到训练后的区域识别模型。应当理解的是,超参数是指在开始模型训练前,为训练模型设置的参数,在模型训练的过程中,通过对超参数不断地调整,使得模型的训练结果越加接近目标数据,从而提高训练模型的性能。Finally, the model grid image and discrete labels are trained through the multi-layer convolutional neural network model, and the iterative model is converged by adjusting the hyperparameters, and then the trained region recognition model is obtained. It should be understood that hyperparameters refer to the parameters set for the training model before starting the model training. During the model training process, by continuously adjusting the hyperparameters, the training results of the model are made closer to the target data, thereby improving the performance of the model. The performance of the trained model.
如图3所示,图3是示出本发明实施例中卷积神经网络的原理示意图。As shown in FIG. 3 , FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing the principle of a convolutional neural network in an embodiment of the present invention.
卷积神经网络主要是模拟人类对物体识别和认知。从图3中可以看出,对于不同的物体,在最底层的特征基本上是类似的。越往上,越能提取出此类物体的一些特征,例如:轮子、眼睛和躯干等。到最上层,不同的高级特征最终组合成相应的图像,从而能够让人类准确的区分不同的物体。Convolutional neural networks mainly simulate human recognition and cognition of objects. As can be seen from Figure 3, for different objects, the features at the bottom layer are basically similar. The higher you go, the more you can extract some features of such objects, such as wheels, eyes, and torso. To the top layer, different high-level features are finally combined into corresponding images, allowing humans to accurately distinguish different objects.
卷积神经网络就是首先通过较底层的网络识别初级的图像特征。其次,由若干底层特征组成更上一层特征。通过多个层级的组合,最终在顶层做出分类。卷积网络通过一系列方法,成功将数据量庞大的图像识别问题不断降维,最终使其能够被训练。The convolutional neural network is to first identify the primary image features through the lower-level network. Second, a higher-level feature is composed of several underlying features. Through the combination of multiple levels, classification is finally made at the top level. Through a series of methods, the convolutional network successfully reduces the dimensionality of the image recognition problem with a large amount of data, and finally enables it to be trained.
在本发明实施例中,基于卷积神经网络进行模型训练,得到训练后的区域识别模型,可以将区域识别技术问题转换为基于卷积神经网络的二分类问题。即将区域识别的结果分为目标区域和非目标区域。可以对卫星图片中的区域进行更加精准的识别。In the embodiment of the present invention, model training is performed based on a convolutional neural network to obtain a trained region identification model, which can convert the technical problem of region identification into a two-classification problem based on a convolutional neural network. The result of region recognition is divided into target region and non-target region. More accurate identification of areas in satellite images is possible.
S140,利用训练后的区域识别模型,确定需要进行区域识别的卫星图片中的目标区域。S140, using the trained area identification model to determine the target area in the satellite image that needs to be identified.
在本发明的一个实施例中,首先,将需要进行区域识别的卫星图片按照训练后的区域识别模型中的预设规格划分,例如,将需要进行区域识别的卫星图片按照8×8预设规格进行划分,得到待识别栅格图片。In an embodiment of the present invention, firstly, the satellite pictures that need to be identified are divided according to the preset specifications in the trained region identification model, for example, the satellite pictures that need to be identified are divided according to the preset specifications of 8×8 Divide to obtain the raster image to be recognized.
其次,待识别栅格图片经过训练后的区域识别模型的训练,得到训练结果。其中,基于训练后的区域识别模型的目标数据经过转换得到的离散标签,得到待识别栅格图片的训练结果为[0,1]或[1,0]。Secondly, the raster image to be recognized is trained by the trained region recognition model, and the training result is obtained. Wherein, based on the discrete labels obtained by transforming the target data of the trained region recognition model, the training result of the raster image to be recognized is obtained as [0,1] or [1,0].
当待识别栅格图片的训练结果为[1,0]时,将该待识别栅格图片标注为第一标识。例如,可以将该待识别栅格图片设置为黑色。当待识别栅格图片的训练结果为[0,1]时,将该待识别栅格图片标注为第二标识。例如,可以将该待识别栅格图片设置为白色。When the training result of the grid image to be recognized is [1,0], the grid image to be recognized is marked as the first identifier. For example, the to-be-recognized raster image can be set to black. When the training result of the grid image to be recognized is [0, 1], the grid image to be recognized is marked as the second identifier. For example, the to-be-recognized raster picture can be set as white.
最后,具有第一标识的待识别栅格图片以及具有第二标识的待识别栅格图片拼接在一起,作为结果图片。应当注意的是,为了防止噪声,还可以将得到的训练结果进行多次区域识别模型的训练。Finally, the to-be-recognized grid picture with the first identification and the to-be-identified grid picture with the second identification are spliced together as a result picture. It should be noted that, in order to prevent noise, the obtained training results can also be trained for multiple region recognition models.
接下来,可以将结果图片等比扩大为和原始卫星图片的大小一致。通过开源计算机视觉库(Open Source Computer Vision Library,OpenCV)获取扩大处理后的结果图片中具有第一标识的待识别栅格图片的轮廓,从而确定需要进行区域识别的卫星图片中的目标区域。其中,通过OpenCV可以实现图像处理。Next, the resulting image can be scaled up to match the size of the original satellite image. The outline of the raster image to be identified with the first identifier in the enlarged result image is obtained through an open source computer vision library (Open Source Computer Vision Library, OpenCV), thereby determining the target area in the satellite image that needs to be identified. Among them, image processing can be realized through OpenCV.
通过上述实施例所述的区域识别方法,利用卷积神经网络训练区域识别模型,可以将区域识别技术问题转换为基于卷积神经网络的二分类问题。即将区域识别的结果分为目标区域和非目标区域。将需要进行区域识别的卫星图片经过训练后的区域识别模型的训练以及OpenCV的图像处理,可以对卫星图片中的需要进行识别的区域进行更加精准的识别。Through the region identification method described in the above embodiment, the region identification model is trained by using the convolutional neural network, and the region identification technology problem can be converted into a two-classification problem based on the convolutional neural network. The result of region recognition is divided into target region and non-target region. The satellite images that need to be identified can be more accurately identified by the training of the regional identification model and the image processing of OpenCV.
为了便于理解,图4示出了本发明另一实施例的区域识别的方法的流程图。图4与图1相同的步骤使用相同的编号。For ease of understanding, FIG. 4 shows a flowchart of a method for region identification according to another embodiment of the present invention. Steps in Figure 4 that are identical to Figure 1 use the same numbers.
如图4所示,区域识别的方法400和图1所示的区域识别的方法100相同的步骤,在此不再赘述。本发明实施例中的区域识别的方法400还包括以下步骤:As shown in FIG. 4 , the
S410,根据区域兴趣点(Point of Interest,POI)点对目标区域进行聚类处理,确定与区域POI点对应的目标区域。S410: Perform clustering processing on the target area according to the area Point of Interest (POI) points, and determine the target area corresponding to the area POI points.
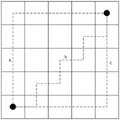
具体的,基于在卫星图片上识别出的农村区域,还可以具体识别出特定村庄的区域。应当理解的是,在地理信息系统中,一个区域POI点可以是一栋房子、一个商铺、一个邮筒或一个公交站等。Specifically, based on the rural area identified on the satellite image, the area of a specific village can also be specifically identified. It should be understood that, in a geographic information system, an area POI point can be a house, a shop, a post box, a bus stop, and so on.
在本发明的一个实施例中,以POI点作为村庄的中心点。如图5所示,图5是示出本发明实施例中的村庄区域示意图。将POI点标注为黑色,将在卫星图片中识别出的农村区域标注为灰色,将卫星图片中的非农村区域标注为白色。当需要具体识别出特定村庄所在的区域时,即需要标注出哪些灰色区域是属于当前POI点。In an embodiment of the present invention, the POI point is used as the center point of the village. As shown in FIG. 5 , FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram showing a village area in an embodiment of the present invention. Mark the POI points in black, the rural areas identified in the satellite image as gray, and the non-rural areas in the satellite image as white. When it is necessary to specifically identify the area where a specific village is located, it is necessary to mark which gray areas belong to the current POI point.
如图6a所示,图6a是示出本发明一实施例中曼哈顿距离示意图。图6a中的三条路线a、b和c,皆表示曼哈顿路径,其长度就是曼哈顿距离值。在平面上,例如坐标(xi,yi)与坐标(xj,yj)的曼哈顿距离可根据表达式(1)计算得到。As shown in FIG. 6a, FIG. 6a is a schematic diagram illustrating the Manhattan distance in an embodiment of the present invention. The three routes a, b and c in Fig. 6a all represent Manhattan paths, and their lengths are the Manhattan distance values. On a plane, for example, the Manhattan distance between the coordinates (xi , yi ) and the coordinates (xj , yj ) can be calculated according to the expression (1).
D(i,j)=|xi-xj|+|yi-yj| (1)D(i,j)=|xi -xj |+|yi -yj | (1)
其中,D(i,j)表示坐标(xi,yi)与坐标(xj,yj)的曼哈顿距离。Among them, D(i,j) represents the Manhattan distance between the coordinates (xi , yi ) and the coordinates (xj , yj ).
如图6b所示,图6b是示出本发明一实施例的像素点之间的曼哈顿距离。例如,距离A点曼哈顿距离为1的点为B,距离A点曼哈顿距离为2的点为C。As shown in FIG. 6b, FIG. 6b shows the Manhattan distance between pixel points according to an embodiment of the present invention. For example, a point with a Manhattan distance of 1 from point A is B, and a point with a Manhattan distance of 2 from point A is C.
作为一个具体的示例,如图7所示,图7是示出本发明实施例中聚类处理流程示意图。当根据POI点对目标区域即农村区域进行聚类处理时,可以首先设置曼哈顿距离的最大距离值Dmax、设置曼哈顿距离Dist的初始值为1,设置所有POI点Pi对应的轮廓边界为Edgei={(xi,yi)},设置所有POI点Pi(xi,yi),i=1,2,…,Np对应的区域集合为Areai={(xi,yi)},其中,i为正整数。As a specific example, as shown in FIG. 7 , FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram illustrating a clustering processing flow in an embodiment of the present invention. When the target area, that is, the rural area, is clustered according to POI points, you can first set the maximum distance value Dmax of the Manhattan distance, set the initial value of the Manhattan distance Dist to 1, and set the contour boundaries corresponding to all POI points Pi as Edgei = {(xi , yi )}, set all POI points Pi (xi , yi ), i=1, 2, ..., the area set corresponding to Np is Areai={(xi , yi ) }, where i is a positive integer.
其次,初始化边界改变数量NUM为0,i的初始值为1。确认当前Pi对应的轮廓边界Edgei={(xi,yi)}的集合中与当前Pi的曼哈顿距离为Dist的像素点。当得到的像素点(xn,yn)的像素值为0.5即像素点为灰色点,就将(xn,yn)加入Edgei和Areai中,并将(xn,yn)的灰度值设置为0,即将像素点(xn,yn)设置为黑色点。应当理解的是,n为正整数。Second, initialize the boundary change number NUM to 0, and the initial value of i to 1. Confirm the pixel points whose Manhattan distance from the current Pi in the set of the contour boundary Edgei={(xi,yi)} corresponding to the current Pi is Dist. When the pixel value of the obtained pixel point (xn , yn ) is 0.5, that is, the pixel point is a gray point, then (xn , yn ) is added to Edgei and Areai , and (xn , yn ) The gray value of is set to 0, that is, the pixel point (xn , yn ) is set as a black point. It should be understood that n is a positive integer.
当Edgei发生改变时,设置NUM=NUM+1,并对Edgei集合中的像素点进行筛选,如果一个像素点的四周已经被黑色点包围,则从轮廓边界Edgei中剔除。When Edgei changes, set NUM=NUM+1, and filter the pixels in the Edgei set. If a pixel is surrounded by black points, it will be removed from the contour boundary Edgei .
按照上述方法,依次遍历Edgei集合中的每一个像素点,直到满足Dist=Dmax。According to the above method, each pixel point in the Edgei set is traversed in turn until Dist=Dmax is satisfied.
如图8所示,图8是示出本发明一实施例中的聚类结果示意图。由图中可以看到,从POI点出发,以曼哈顿距离为1不断往外延伸,直到连通域,即没有被白色区域阻断的区域,全被分配完毕如图8d所示。然后增加曼哈顿距离,直到如图8e所示,跨过白色区域到达另一边的未分配区域,接着再重复曼哈顿距离为1并往外延伸,最终当曼哈顿距离达到预先设定的最大阈值Dmax时,也没有找到新的未分配区域,那么完成整个聚类过程,得到的整个黑色区域即为与POI点对应的目标区域。As shown in FIG. 8 , FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram showing a clustering result in an embodiment of the present invention. It can be seen from the figure that starting from the POI point, the Manhattan distance is 1 and continues to extend outwards until the connected domain, that is, the area that is not blocked by the white area, is all allocated as shown in Figure 8d. Then increase the Manhattan distance until, as shown in Figure 8e, across the white area to the unallocated area on the other side, then repeat the Manhattan distance to 1 and extend outwards, and finally when the Manhattan distance reaches the preset maximum thresholdDmax , If no new unallocated area is found, then the entire clustering process is completed, and the entire black area obtained is the target area corresponding to the POI point.
在本发明实施例中,对于不同的像素点之间的距离,采用曼哈顿距离则只需要计算加减法,大大提升了运行效率并且保证不会出现误差。通过聚类处理可以准确识别出属于特定村庄的区域。使得区域的识别更加精准。In the embodiment of the present invention, for the distance between different pixel points, the Manhattan distance only needs to be calculated by addition and subtraction, which greatly improves the operation efficiency and ensures that no error occurs. Areas belonging to specific villages can be accurately identified through clustering. This makes the region identification more accurate.
S420,通过轮廓跟踪算法,获得与POI点对应的目标区域的区域轮廓。S420 , obtain an area outline of the target area corresponding to the POI point through an outline tracking algorithm.
具体的,轮廓跟踪算法可以采用8连通检测轮廓跟踪算法。在本发明实施例中,输入一个二值图像,即像素值或者灰度值只有0和1。其中,0表示黑色和1表示白色。Specifically, the contour tracking algorithm may adopt an 8-connection detection contour tracking algorithm. In the embodiment of the present invention, a binary image is input, that is, the pixel values or grayscale values are only 0 and 1. where 0 means black and 1 means white.
如图9所示,图9是示出本发明的一个实施例中8连通检测轮廓跟踪算法的定义示意图。As shown in FIG. 9 , FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram showing the definition of an 8-connection detection contour tracking algorithm in an embodiment of the present invention.
框架是指图片最外围的一层像素点,即图片的最上和最下的俩行、最左和最右的两列围成的矩形框。The frame refers to the outermost layer of pixels in the picture, that is, the rectangular frame enclosed by the uppermost and lowermost rows and the leftmost and rightmost columns of the picture.
背景S1是与框架在同一层级且像素值为0的像素点。The background S1 is a pixel that is at the same level as the frame and has a pixel value of 0.
连通块S2和S5是一块由连通的白点像素构成的区域。Connected blocks S2 and S5 are an area composed of connected white dot pixels.
洞S3是除背景之外其余由连通的黑点构成的区域。The hole S3 is an area consisting of connected black dots except for the background.
外轮廓B1、B3和B4,是指包裹一个连通块的最外围白点。The outer contours B1, B3 and B4 refer to the outermost white dots surrounding a connected block.
内轮廓B2,是包裹一个洞的最外围白点或一个连通块最内围的白点。The inner contour B2 is the outermost white point surrounding a hole or the innermost white point of a connected block.
如图10所示,图10是示出本发明一实施例中连通邻居像素点示意图。对目标像素点A而言,4连通的情况下是指只有上下左右四个方向直接相连的B点才算邻居像素点。而8连通加入了左上、左下、右上和右下四个角落的B和C点才算邻居像素点。As shown in FIG. 10 , FIG. 10 is a schematic diagram showing connected neighboring pixels in an embodiment of the present invention. For the target pixel A, in the case of 4-connection, it means that only the B points that are directly connected in four directions, up, down, left, and right, are considered neighbor pixels. And 8 connected points B and C in the four corners of the upper left, lower left, upper right and lower right are counted as neighbor pixels.
在本发明的一个实施例中,记输入的图像为F={f(i,j)},用NBD表示当前边界的序号,将NBD初始化为1,表示F的框架,其余的边界从2开始标注。按照从上到下(i增加)、从左到右(j增加)的顺序遍历图片中的每一个像素点,且每次扫描一个新行的时候,将变量LNBD重置为1,当f(i,j)≠0的时候执行以下步骤:In an embodiment of the present invention, the input image is denoted as F={f(i,j)}, the sequence number of the current boundary is represented by NBD, and the NBD is initialized to 1 to represent the frame of F, and the rest of the boundaries start from 2 callout. Traverse each pixel in the picture in the order from top to bottom (i increases) and from left to right (j increases), and each time a new line is scanned, the variable LNBD is reset to 1, when f( When i,j)≠0, perform the following steps:
Step1,如果f(i,j)=1且f(i,j-1)=0,此时认为像素(i,j)是外轮廓的一个起点,令NBD=NBD+1以及(i2,j2)=(i,j-1)。若f(i,j)≥1且f(i,j+1)=0,此时认为像素(i,j)是内轮廓的一个起点,令NBD=NBD+1以及(i2,j2)=(i,j+1),若f(i,j)>1再令LNBD=f(i,j)。否则,跳转至Step4。Step1, if f(i,j)=1 and f(i,j-1)=0, consider the pixel (i,j) as a starting point of the outer contour, let NBD=NBD+1 and (i2 , j2 )=(i, j-1). If f(i,j)≥1 and f(i,j+1)=0, then the pixel (i,j) is considered to be a starting point of the inner contour, let NBD=NBD+1 and (i2 , j2 )=(i,j+1), if f(i,j)>1, then let LNBD=f(i,j). Otherwise, skip to Step4.
Step2,根据新发现的轮廓的类型和顺序序号为LNBD的轮廓,即在当前行中上一个相遇的轮廓,然后确定当前轮廓的父节点。其中,新发现的轮廓B的父轮廓的决策规则如表1所示。Step 2: According to the type of the newly discovered contour and the contour whose sequence serial number is LNBD, that is, the last encountered contour in the current line, then determine the parent node of the current contour. Among them, the decision rules of the parent contour of the newly discovered contour B are shown in Table 1.
表1Table 1
Step3,从起始点(i,j)开始跟踪检测到的边界。Step 3, track the detected boundary from the starting point (i, j).
在本发明的一个实施例中,Step3具体还包括以下四个步骤:In an embodiment of the present invention, Step3 specifically further includes the following four steps:
第一步骤,从(i2,j2)开始,以顺时针方向检查(i,j)的邻居像素点,并找到一个非0的像素点,记第一个非0像素点为(i1,j1)。如果没有找到,将-NBD分配给f(i,j),跳转至Step4。The first step, starting from (i2 , j2 ), checks the neighbor pixels of (i, j) in a clockwise direction, and finds a non-0 pixel, and denote the first non-0 pixel as (i1 ,j1 ). If not found, assign -NBD to f(i,j) and go to Step4.
第二步骤,令(i2,j2)=(i1,j1),(i3,j3)=(i,j)。In the second step, let (i2 , j2 )=(i1 , j1 ), (i3 , j3 )=(i, j).
第三步骤,从(i2,j2)按逆时针方向的下一个像素点开始,以逆时针方向检测当前像素点(i3,j3)的邻居像素点,找到第一个非0像素记为(i4,j4)。The third step, starting from the next pixel point in the counterclockwise direction of (i2 , j2 ), detects the neighbor pixels of the current pixel point (i3 , j3 ) in the counter-clockwise direction, and finds the first non-zero pixel Denoted as (i4 ,j4 ).
第四步骤,若(i3,j3+1)是一个0像素点,那么令f(i3,j3)=-NBD。若f(i3,j3)=1且(i3,j3+1)是一个非0像素点,那么令f(i3,j3)=NBD。否则,f(i3,j3)不发生改变。In the fourth step, if (i3 , j3 +1) is a 0 pixel, then let f(i3 , j3 )=-NBD. If f(i3 , j3 )=1 and (i3 , j3 +1) is a non-zero pixel, then let f(i3 , j3 )=NBD. Otherwise, f(i3 , j3 ) does not change.
第五步骤,如果(i4,j4)=(i,j)且(i3,j3)=(i1,j1),即回到了起始点,则跳转至Step4。否则,令(i2,j2)=(i3,j3),(i3,j3)=(i4,j4),返回至第三步骤。In the fifth step, if (i4 , j4 )=(i, j) and (i3 , j3 )=(i1 , j1 ), that is, returning to the starting point, then jump to Step 4. Otherwise, let (i2 , j2 )=(i3 , j3 ), (i3 , j3 )=(i4 , j4 ), and return to the third step.
Step4,如果f(i,j)≠1,则令LNBD=|f(i,j)|。并从像素点(i,j+1)继续恢复遍历,当遍历到图像的右下角时,8连通检测轮廓跟踪算法终止。Step4, if f(i,j)≠1, then let LNBD=|f(i,j)|. And continue to resume the traversal from the pixel point (i, j+1), when the traversal reaches the lower right corner of the image, the 8-connection detection contour tracking algorithm terminates.
在本发明实施例中,通过8连通检测轮廓跟踪算法,按照设定顺序找出边缘点来跟踪边界,可以准确识别出区域的边界点,进而得到区域的轮廓。In the embodiment of the present invention, through the 8-connection detection contour tracking algorithm, the edge points are found according to the set order to track the boundary, the boundary points of the area can be accurately identified, and then the outline of the area can be obtained.
在本发明的另一个实施例中,当需要具体识别出目标村庄的区域轮廓时,由于一幅卫星图片可能无法覆盖一个村庄区域,所以需要对具有目标区域的图片进行拼接和筛选。In another embodiment of the present invention, when the area outline of the target village needs to be specifically identified, since a satellite image may not cover a village area, it is necessary to splicing and filtering the images with the target area.
首先,找出目标村庄点所在的轮廓图片,以该轮廓图片为中心,找出周围的8幅图片进行拼接,得到拼接图片。First, find the contour picture where the target village point is located, take the contour picture as the center, find the surrounding 8 pictures and stitch them together to get the stitched picture.
其次,由于该拼接图片可能会存在多个轮廓,所以首先找出离目标村庄最近的轮廓,若该轮廓区域内只有一个村庄点,则该轮廓即为目标村庄的区域轮廓。若该轮廓区域内有多个村庄点,即可能有连接的村庄,则对轮廓进行距离判断。与轮廓区域距离最近的村庄点,即为该轮廓区域所属村庄区域。Secondly, since there may be multiple contours in the stitched image, first find the contour closest to the target village. If there is only one village point in the contour area, the contour is the regional contour of the target village. If there are multiple village points in the contour area, that is, there may be connected villages, the distance judgment is performed on the contour. The village point closest to the contour area is the village area to which the contour area belongs.
S430,在与区域POI点对应的目标区域的区域轮廓内,进行与区域POI点对应的目标区域的网络质量评估。S430 , within the area outline of the target area corresponding to the area POI point, perform network quality evaluation of the target area corresponding to the area POI point.
在本发明的一个实施例中,利用全球移动通信系统(Global System forMobileCommunication,GSM)网络的测量报告(Measurement Report,MR)数据中在所述区域轮廓内的OTT采样点,进行网络质量评估。其中,长期演进技术(Long Term Evolution,LTE)网络的MR测量周期是演进型Node B(Evolved Node B,eNodeB)或用户设备(User Equipment,UE)按照要求实现,其测量周期可以是120毫秒(ms)、240ms、640ms、1024ms、2048ms、5120ms或10240ms,测量得到的数据可用于网络评估和优化。In an embodiment of the present invention, the network quality assessment is performed by using the OTT sampling points in the area outline in the measurement report (Measurement Report, MR) data of the Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) network. The MR measurement period of the Long Term Evolution (Long Term Evolution, LTE) network is implemented by an evolved Node B (Evolved Node B, eNodeB) or user equipment (User Equipment, UE) as required, and the measurement period may be 120 milliseconds ( ms), 240ms, 640ms, 1024ms, 2048ms, 5120ms or 10240ms, the measured data can be used for network evaluation and optimization.
在本发明的一个实施例中,可以对网络覆盖进行评估。具体的,可以按照各轮廓区域的平均场强或者按照弱覆盖采样点比例统计弱覆盖区域,进而对网络覆盖进行评估。其中,可以将各轮廓区域的平均场强门限值设定为-105分贝(dB),弱覆盖采样点比例可以设定为大于10%,可以将小于平均场强门限值的区域称为弱覆盖区域。In one embodiment of the invention, network coverage can be assessed. Specifically, the weak coverage area can be counted according to the average field strength of each contour area or according to the ratio of weak coverage sampling points, and then the network coverage can be evaluated. Among them, the average field strength threshold value of each contour area can be set to -105 decibels (dB), the proportion of weak coverage sampling points can be set to be greater than 10%, and the area less than the average field strength threshold value can be called as Weak coverage area.
在本发明的一个实施例中,可以通过各轮廓区域的平均上行信噪比(Signal toInterference plus Noise Ratio UL,SinrUL)和参考信号接收质量(Reference SignalReceiving Quality,RSRQ),评估各区域的通信质量情况。在本发明的另一个实施例中,也可以按轮廓区域的平均SinrUL和平均RSRQ来统计质差区域或者按照弱质量采样点比例来统计质差区域。In an embodiment of the present invention, the communication quality of each area can be evaluated by the average uplink signal-to-noise ratio (Signal to Interference plus Noise Ratio UL, SinrUL) and reference signal receiving quality (Reference Signal Receiving Quality, RSRQ) of each contour area . In another embodiment of the present invention, the poor quality area may also be counted according to the average SinrUL and the average RSRQ of the contour area, or the poor quality area may be counted according to the ratio of weak quality sampling points.
在本发明的一个实施例中,还可以通过统计Uu接口和X2接口的XDR格式文件的切换数据,统计各区域的切换成功率。其中,切换成功率(%)=(换成功次数×100)/切换请求次数。统计切换失败率超过指定门限的区域,发现切换失败的问题轮廓区域。In an embodiment of the present invention, the handover success rate of each area can also be counted by counting the handover data of the XDR format files of the Uu interface and the X2 interface. Wherein, the handover success rate (%)=(the number of successful exchanges×100)/the number of handover requests. Count the areas where the handover failure rate exceeds the specified threshold, and find the problem contour area of the handover failure.
在本发明的一个实施例中,掉线事件是指Uu接口发生无线资源控制(RadioResource Control,RRC)连接释放异常。In an embodiment of the present invention, the disconnection event refers to that a radio resource control (RadioResource Control, RRC) connection release exception occurs on the Uu interface.
通过统计掉线率超过指定门限的轮廓区域,发现掉线问题区域。Find out the problem area of disconnection by counting the contour areas where the disconnection rate exceeds the specified threshold.
在本发明的一个实施例中,采样点重叠覆盖度是指与主小区场强差绝对值在6dB以内的小区(含主小区)个数。统计范围包括异频邻区和不包含异频邻区。In an embodiment of the present invention, the overlapping coverage of sampling points refers to the number of cells (including the main cell) whose absolute value of field strength difference with the main cell is within 6dB. The statistical scope includes inter-frequency adjacent cells and does not include inter-frequency adjacent cells.
区域平均重叠覆盖度是指将区域内采样点的重叠覆盖度计算均值,代表此区域的平均重叠覆盖度。The average overlap coverage of an area refers to the calculation of the average of the overlap coverage of sampling points in the area, which represents the average overlap coverage of this area.
通过平均重叠覆盖度和高重叠覆盖比例评估一个区域的重叠覆盖情况,通过统计高重叠覆盖度比例超过指定门限,发现重叠覆盖问题区域。The overlapping coverage of an area is evaluated by the average overlapping coverage and the high overlapping coverage ratio, and the overlapping coverage problem area is found by counting the high overlapping coverage ratio exceeding the specified threshold.
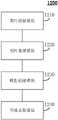
如图11所示,图11是示出本发明又一个实施例的区域识别的方法的流程图。区域识别的方法1100包括:As shown in FIG. 11 , FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating a method for region identification according to still another embodiment of the present invention. The
S1110,农村居民区卫星图片样本数据处理。S1110, processing the sample data of satellite images of rural residential areas.
S1120,农村居民区模型建模。S1120, Modeling of Rural Residential Areas.
S1130,总体农村居民区标注。S1130, overall rural residential area labeling.
S1140,农村POI信息点对应的居民区聚类。S1140, clustering the residential areas corresponding to the rural POI information points.
S1150,农村POI信息点对应的居民区轮廓获取。S1150, obtaining the outline of the residential area corresponding to the rural POI information point.
S1160,农村居民区无线网络质量评估。S1160, wireless network quality assessment in rural residential areas.
下面通过图12详细介绍根据本发明实施例的区域识别的装置,区域识别的装置与区域识别的方法相对应。The apparatus for area identification according to the embodiment of the present invention is described in detail below with reference to FIG. 12 , and the apparatus for area identification corresponds to the method for area identification.
图12示出了本发明一实施例的区域识别的装置的结构示意图。FIG. 12 shows a schematic structural diagram of an apparatus for region identification according to an embodiment of the present invention.
如图12所示,区域识别的装置1200包括:As shown in Figure 12, the
图片获取模块1210,用于获取包括已知区域信息的卫星图片。The
图片处理模块1220,用于对包括已知区域信息的卫星图片进行预处理,得到目标图片。The
模型创建模块1230,用于以包括已知区域信息的卫星图片作为训练集,以目标图片作为目标数据,训练区域识别模型。The
区域识别模块1240,用于利用训练后的区域识别模型,确定需要进行区域识别的卫星图片中的目标区域。The
通过本发明实施例中的区域识别装置,基于图片获取模块1210、图片处理模块1220以及模型创建模块1230,训练区域识别模型,可以基于已知区域信息的卫星图片以及经过预处理后得到的目标图片,训练区域识别模型,通过调整超参数可以使得区域识别模型越加精准,从而使得通过该区域识别模型得到的区域识别结果也更加精准。通过区域识别模块1240,利用训练后的区域识别模型来对需要进行区域识别的卫星图片进行区域识别,提高了区域识别的效率以及准确性。With the region identification device in the embodiment of the present invention, based on the
在本发明的一个实施例中,图片处理模块1220具体用于对包括已知区域信息的卫星图片中目标区域进行标注,将包括标注后的目标区域的卫星图片作为目标图片。In an embodiment of the present invention, the
在本发明的一个实施例中,模型创建模块1230具体用于基于预设规格划分训练集中包括已知区域信息的卫星图片以及目标数据中的目标图片,得到模型栅格图片,以及利用卷积神经网络和模型栅格图片,训练区域识别模型。In one embodiment of the present invention, the
在本发明的一个实施例中,区域识别模块1240具体用于将需要进行区域识别的卫星图片按照预设规格进行划分,得到待识别栅格图片。In an embodiment of the present invention, the
基于训练后的区域识别模型对待识别栅格图片进行模型训练,得到训练结果。Model training is performed on the raster image to be recognized based on the trained region recognition model, and the training result is obtained.
将训练结果为目标区域的待识别栅格图片标注为第一标识,将训练结果为非目标区域的待识别栅格图片标注为第二标识。The to-be-recognized raster picture whose training result is the target area is marked as the first identifier, and the to-be-recognized raster image whose training result is the non-target area is marked as the second identifier.
将具有第一标识的待识别栅格图片以及具有第二标识的待识别栅格图片拼接,得到结果图片,并获取扩大处理后的结果图片中具有第一标识的待识别栅格图片的轮廓,确定需要进行区域识别的卫星图片中的目标区域。splicing the to-be-identified grid picture with the first identification and the to-be-identified grid picture with the second identification to obtain a result picture, and obtaining the outline of the to-be-identified grid picture with the first identification in the enlarged result picture, Identify target areas in satellite images that require area identification.
在本发明的另一个实施例中,区域识别的装置1200还包括:In another embodiment of the present invention, the
聚类处理模块1250,用于根据区域兴趣点POI点对目标区域进行聚类处理,确定与区域POI点对应的目标区域。The clustering processing module 1250 is configured to perform clustering processing on the target area according to the regional POI points, and determine the target area corresponding to the regional POI points.
轮廓跟踪模块1260,用于利用轮廓跟踪算法,获得与区域POI点对应的目标区域的区域轮廓。The contour tracking module 1260 is configured to obtain the regional contour of the target area corresponding to the regional POI points by using the contour tracking algorithm.
质量评估模块1270,用于在与区域POI点对应的目标区域的区域轮廓内,进行与区域POI点对应的目标区域的网络质量评估。The quality assessment module 1270 is configured to perform network quality assessment of the target area corresponding to the area POI points within the area outline of the target area corresponding to the area POI points.
在本发明的一个实施例中,聚类处理模块1250具体用于设置曼哈顿距离的初始值以及设置曼哈顿距离的最大值。In an embodiment of the present invention, the clustering processing module 1250 is specifically configured to set the initial value of the Manhattan distance and the maximum value of the Manhattan distance.
依据预设增量增加曼哈顿距离的初始值,得到当前曼哈顿距离值。Increase the initial value of Manhattan distance according to the preset increment to get the current Manhattan distance value.
以区域POI点为起点,确定目标区域内与区域POI点的距离为当前曼哈顿距离值的区域边界点。Taking the area POI point as the starting point, determine the area boundary point whose distance from the area POI point in the target area is the current Manhattan distance value.
当当前曼哈顿距离值为曼哈顿距离的最大值时,将得到的区域边界点所构成的区域作为与区域POI点对应的目标区域。When the current Manhattan distance value is the maximum value of the Manhattan distance, the area formed by the obtained area boundary points is used as the target area corresponding to the area POI points.
在本发明的一个实施例中,轮廓跟踪模块1260具体用于采用8连通检测轮廓跟踪算法进行轮廓跟踪。In an embodiment of the present invention, the contour tracking module 1260 is specifically configured to perform contour tracking using an 8-connectivity detection contour tracking algorithm.
在本发明的一个实施例中,质量评估模块1270具体用于利用测量报告MR数据中在区域轮廓内的OTT采样点,进行质量评估,质量评估至少包括以下一种:网络覆盖评估、网络质量评估、切换评估、掉线评估和重复覆盖评估。In an embodiment of the present invention, the quality assessment module 1270 is specifically configured to use the OTT sampling points in the MR data of the measurement report within the region outline to perform quality assessment, and the quality assessment includes at least one of the following: network coverage assessment, network quality assessment , Toggle Evaluation, Dropped Call Evaluation, and Duplicate Coverage Evaluation.
图13示出了能够实现根据本发明实施例的区域识别的方法和装置的计算设备的示例性硬件架构的结构图。FIG. 13 shows a structural diagram of an exemplary hardware architecture of a computing device capable of implementing the method and apparatus for area identification according to an embodiment of the present invention.
如图13所示,计算设备1300包括输入设备1301、输入接口1302、中央处理器1303、存储器1304、输出接口1305、以及输出设备1306。其中,输入接口1302、中央处理器1303、存储器1304、以及输出接口1305通过总线1310相互连接,输入设备1301和输出设备1306分别通过输入接口1302和输出接口1305与总线1310连接,进而与计算设备1300的其他组件连接。As shown in FIG. 13 , the computing device 1300 includes an input device 1301 , an input interface 1302 , a central processing unit 1303 , a memory 1304 , an output interface 1305 , and an output device 1306 . The input interface 1302, the central processing unit 1303, the memory 1304, and the output interface 1305 are connected to each other through the bus 1310, and the input device 1301 and the output device 1306 are respectively connected to the bus 1310 through the input interface 1302 and the output interface 1305, and then to the computing device 1300. connections to other components.
具体地,输入设备1301接收来自外部的输入信息,并通过输入接口1302将输入信息传送到中央处理器1303;中央处理器1303基于存储器1304中存储的计算机可执行指令对输入信息进行处理以生成输出信息,将输出信息临时或者永久地存储在存储器1304中,然后通过输出接口1305将输出信息传送到输出设备1306;输出设备1306将输出信息输出到计算设备1300的外部供用户使用。Specifically, the input device 1301 receives input information from the outside, and transmits the input information to the central processing unit 1303 through the input interface 1302; the central processing unit 1303 processes the input information based on the computer-executable instructions stored in the memory 1304 to generate output information, temporarily or permanently store the output information in the memory 1304, and then transmit the output information to the output device 1306 through the output interface 1305; the output device 1306 outputs the output information to the outside of the computing device 1300 for the user to use.
也就是说,图13所示的计算设备也可以被实现区域识别的设备,该区域识别的设备可以包括:存储有计算机可执行指令的存储器;以及处理器,该处理器在执行计算机可执行指令时可以实现结合图1至图12描述的区域识别的方法和装置。That is, the computing device shown in FIG. 13 can also be implemented as a region-identified device, and the region-identified device can include: a memory storing computer-executable instructions; and a processor that executes the computer-executable instructions. The method and apparatus for region identification described in conjunction with FIG. 1 to FIG. 12 can be implemented.
本发明实施例还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质上存储有计算机程序指令;该计算机程序指令被处理器执行时实现本发明实施例提供的区域识别。Embodiments of the present invention further provide a computer-readable storage medium, where computer program instructions are stored thereon; when the computer program instructions are executed by a processor, the region identification provided by the embodiments of the present invention is implemented.
需要明确的是,本发明并不局限于上文所描述并在图中示出的特定配置和处理。为了简明起见,这里省略了对已知方法的详细描述。在上述实施例中,描述和示出了若干具体的步骤作为示例。但是,本发明的方法过程并不限于所描述和示出的具体步骤,本领域的技术人员可以在领会本发明的精神后,作出各种改变、修改和添加,或者改变步骤之间的顺序。以上所述的结构框图中所示的功能块可以实现为硬件、软件、固件或者它们的组合。当以硬件方式实现时,其可以例如是电子电路、专用集成电路(ASIC)、适当的固件、插件、功能卡等等。当以软件方式实现时,本发明的元素是被用于执行所需任务的程序或者代码段。程序或者代码段可以存储在机器可读介质中,或者通过载波中携带的数据信号在传输介质或者通信链路上传送。“机器可读介质”可以包括能够存储或传输信息的任何介质。机器可读介质的例子包括电子电路、半导体存储器设备、ROM、闪存、可擦除ROM(EROM)、软盘、CD-ROM、光盘、硬盘、光纤介质、射频(RF)链路,等等。代码段可以经由诸如因特网、内联网等的计算机网络被下载。It is to be understood that the present invention is not limited to the specific arrangements and processes described above and shown in the figures. For the sake of brevity, detailed descriptions of known methods are omitted here. In the above-described embodiments, several specific steps are described and shown as examples. However, the method process of the present invention is not limited to the specific steps described and shown, and those skilled in the art can make various changes, modifications and additions, or change the sequence of steps after comprehending the spirit of the present invention. The functional blocks shown in the above-described structural block diagrams may be implemented as hardware, software, firmware, or a combination thereof. When implemented in hardware, it may be, for example, an electronic circuit, an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC), suitable firmware, a plug-in, a function card, or the like. When implemented in software, elements of the invention are programs or code segments used to perform the required tasks. The program or code segments may be stored in a machine-readable medium or transmitted over a transmission medium or communication link by a data signal carried in a carrier wave. A "machine-readable medium" may include any medium that can store or transmit information. Examples of machine-readable media include electronic circuits, semiconductor memory devices, ROM, flash memory, erasable ROM (EROM), floppy disks, CD-ROMs, optical disks, hard disks, fiber optic media, radio frequency (RF) links, and the like. The code segments may be downloaded via a computer network such as the Internet, an intranet, or the like.
本发明可以以其他的具体形式实现,而不脱离其精神和本质特征。例如,特定实施例中所描述的算法可以被修改,而设备体系结构并不脱离本发明的基本精神。因此,当前的实施例在所有方面都被看作是示例性的而非限定性的,本发明的范围由所附权利要求而非上述描述定义,并且,落入权利要求的含义和等同物的范围内的全部改变从而都被包括在本发明的范围之中。The present invention may be embodied in other specific forms without departing from its spirit or essential characteristics. For example, the algorithms described in specific embodiments may be modified without departing from the basic spirit of the invention. Accordingly, the present embodiments are to be considered in all respects as illustrative and not restrictive, and the scope of the present invention is defined by the appended claims rather than the foregoing description, and falls within the meaning and equivalents of the claims. All changes within the scope are thus included in the scope of the invention.
Claims (11)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811444648.2ACN111241881B (en) | 2018-11-29 | 2018-11-29 | Method, apparatus, device and medium for region identification |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811444648.2ACN111241881B (en) | 2018-11-29 | 2018-11-29 | Method, apparatus, device and medium for region identification |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111241881Atrue CN111241881A (en) | 2020-06-05 |
| CN111241881B CN111241881B (en) | 2022-12-27 |
Family
ID=70865512
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201811444648.2AActiveCN111241881B (en) | 2018-11-29 | 2018-11-29 | Method, apparatus, device and medium for region identification |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111241881B (en) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111818557A (en)* | 2020-08-04 | 2020-10-23 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Network coverage problem identification method, device and system |
| CN112200012A (en)* | 2020-09-15 | 2021-01-08 | 汉海信息技术(上海)有限公司 | Map data processing method, device and electronic device |
| CN113192229A (en)* | 2021-05-12 | 2021-07-30 | 西安图迹信息科技有限公司 | Power plant inspection method based on wireless Bluetooth equipment |
| CN113723405A (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2021-11-30 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and device for determining area outline and electronic equipment |
| CN114639023A (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2022-06-17 | 国网浙江省电力有限公司经济技术研究院 | A Machine Learning-Based Approach for Rooftop Photovoltaic Potential Assessment |
| CN114842416A (en)* | 2022-04-27 | 2022-08-02 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | Method for counting number of targets in region, and method and device for training region recognition model |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6850497B1 (en)* | 1995-09-19 | 2005-02-01 | Mobile Satellite Ventures, Lp | Satellite trunked radio service system |
| CN104378635A (en)* | 2014-10-28 | 2015-02-25 | 西交利物浦大学 | Video region-of-interest (ROI) encoding method based on microphone array assistance |
| CN105095838A (en)* | 2014-05-20 | 2015-11-25 | 中国移动通信集团广东有限公司 | Target detection method and device |
| CN107067003A (en)* | 2017-03-09 | 2017-08-18 | 百度在线网络技术(北京)有限公司 | Extracting method, device, equipment and the computer-readable storage medium of region of interest border |
| CN107527109A (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2017-12-29 | 中国辐射防护研究院 | Dose of radiation caused by gaseous state radionuclide and the evaluation method of safeguard procedures suggestion |
| CN107646118A (en)* | 2015-03-24 | 2018-01-30 | 开利公司 | System and method for determining the RF sensor performance related to floor plan |
| CN108052876A (en)* | 2017-11-28 | 2018-05-18 | 广东数相智能科技有限公司 | Regional development appraisal procedure and device based on image identification |
| CN108124279A (en)* | 2017-12-12 | 2018-06-05 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | The appraisal procedure and device of network coverage quality |
| CN108399454A (en)* | 2018-03-05 | 2018-08-14 | 山东领能电子科技有限公司 | A kind of completely new sectional convolution neural network target recognition |
| WO2018209057A1 (en)* | 2017-05-11 | 2018-11-15 | The Research Foundation For The State University Of New York | System and method associated with predicting segmentation quality of objects in analysis of copious image data |
- 2018
- 2018-11-29CNCN201811444648.2Apatent/CN111241881B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6850497B1 (en)* | 1995-09-19 | 2005-02-01 | Mobile Satellite Ventures, Lp | Satellite trunked radio service system |
| CN105095838A (en)* | 2014-05-20 | 2015-11-25 | 中国移动通信集团广东有限公司 | Target detection method and device |
| CN104378635A (en)* | 2014-10-28 | 2015-02-25 | 西交利物浦大学 | Video region-of-interest (ROI) encoding method based on microphone array assistance |
| CN107646118A (en)* | 2015-03-24 | 2018-01-30 | 开利公司 | System and method for determining the RF sensor performance related to floor plan |
| CN107527109A (en)* | 2016-06-21 | 2017-12-29 | 中国辐射防护研究院 | Dose of radiation caused by gaseous state radionuclide and the evaluation method of safeguard procedures suggestion |
| CN107067003A (en)* | 2017-03-09 | 2017-08-18 | 百度在线网络技术(北京)有限公司 | Extracting method, device, equipment and the computer-readable storage medium of region of interest border |
| WO2018209057A1 (en)* | 2017-05-11 | 2018-11-15 | The Research Foundation For The State University Of New York | System and method associated with predicting segmentation quality of objects in analysis of copious image data |
| CN108052876A (en)* | 2017-11-28 | 2018-05-18 | 广东数相智能科技有限公司 | Regional development appraisal procedure and device based on image identification |
| CN108124279A (en)* | 2017-12-12 | 2018-06-05 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | The appraisal procedure and device of network coverage quality |
| CN108399454A (en)* | 2018-03-05 | 2018-08-14 | 山东领能电子科技有限公司 | A kind of completely new sectional convolution neural network target recognition |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| J.B.MENA .ETC: "An automatic method for road extraction in rural and semi-urban areas starting from high resolution satellite imagery", 《PATTERN RECOGNITION LETTERS》* |
| 黄莎: "基于多数据源关联的市网分析产品终端战略地图", 《电信工程技术与标准化》* |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111818557A (en)* | 2020-08-04 | 2020-10-23 | 中国联合网络通信集团有限公司 | Network coverage problem identification method, device and system |
| CN112200012A (en)* | 2020-09-15 | 2021-01-08 | 汉海信息技术(上海)有限公司 | Map data processing method, device and electronic device |
| CN113192229A (en)* | 2021-05-12 | 2021-07-30 | 西安图迹信息科技有限公司 | Power plant inspection method based on wireless Bluetooth equipment |
| CN113723405A (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2021-11-30 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and device for determining area outline and electronic equipment |
| CN113723405B (en)* | 2021-08-31 | 2024-09-13 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Method and device for determining regional outline and electronic equipment |
| CN114639023A (en)* | 2021-11-16 | 2022-06-17 | 国网浙江省电力有限公司经济技术研究院 | A Machine Learning-Based Approach for Rooftop Photovoltaic Potential Assessment |
| CN114842416A (en)* | 2022-04-27 | 2022-08-02 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | Method for counting number of targets in region, and method and device for training region recognition model |
| CN114842416B (en)* | 2022-04-27 | 2025-07-04 | 杭州海康威视数字技术股份有限公司 | Method for counting target quantity in region, method and device for training region recognition model |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111241881B (en) | 2022-12-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN111241881B (en) | Method, apparatus, device and medium for region identification | |
| CN104700099B (en) | The method and apparatus for recognizing traffic sign | |
| CN104021394B (en) | Insulator image-recognizing method based on AdaBoost algorithms | |
| WO2020248957A1 (en) | Method, system and apparatus for detecting occluded target object, and storage medium | |
| CN113591967A (en) | Image processing method, device and equipment and computer storage medium | |
| CN112543411B (en) | Interference positioning method, device and system of wireless communication system | |
| US20220398400A1 (en) | Methods and apparatuses for determining object classification | |
| CN110390261A (en) | Object detection method, device, computer readable storage medium and electronic equipment | |
| CN112613348B (en) | Character recognition method and electronic equipment | |
| CN108764235B (en) | Object detection method, equipment and medium | |
| CN103902981A (en) | Method and system for identifying license plate characters based on character fusion features | |
| CN108271176A (en) | Determine base station cell matter difference root because method and system | |
| CN117115415B (en) | Image marking processing method and system based on big data analysis | |
| CN105335952A (en) | Matching cost calculation method and apparatus, and parallax value calculation method and equipment | |
| CN113610770A (en) | License plate recognition method, device and equipment | |
| JP6347155B2 (en) | Image processing apparatus, image determination method, and program | |
| CN115830302B (en) | Multi-scale feature extraction fusion power distribution network equipment positioning identification method | |
| CN114219073A (en) | Method, device, storage medium and electronic device for determining attribute information | |
| CN108401222A (en) | Localization method and device | |
| CN111666953B (en) | A method and device for tidal zone mapping based on semantic segmentation | |
| CN119501364A (en) | A new energy welding quality detection method and system based on image processing | |
| CN103065315B (en) | A kind of multichannel chromatogram fusion method, system and Medical Devices | |
| WO2022263908A1 (en) | Methods and apparatuses for determining object classification | |
| CN113642553A (en) | An accurate positioning method of unconstrained license plate combining whole and component target detection | |
| CN115830342A (en) | Method, device, storage medium and electronic device for determining detection frame |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |