CN111047107B - Highway transit time prediction method, device, electronic device and storage medium - Google Patents
Highway transit time prediction method, device, electronic device and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN111047107B CN111047107BCN201911344130.6ACN201911344130ACN111047107BCN 111047107 BCN111047107 BCN 111047107BCN 201911344130 ACN201911344130 ACN 201911344130ACN 111047107 BCN111047107 BCN 111047107B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- road
- connection relation
- node
- data corresponding
- preset
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/04—Forecasting or optimisation specially adapted for administrative or management purposes, e.g. linear programming or "cutting stock problem"
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/40—Business processes related to the transportation industry
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及数据处理技术中的智能交通技术领域,尤其涉及一种公路通行时间预测方法、装置、电子设备和存储介质。The present application relates to the technical field of intelligent transportation in data processing technology, and in particular, to a method, device, electronic device and storage medium for predicting highway transit time.
背景技术Background technique
目前,随着全球定位系统等地理位置相关传感器的不断发展,大多数公共交通配备自动车辆定位系统,以及随着地图导航不断普及,预估到达时间是地图技术的重要组成部分。At present, with the continuous development of location-related sensors such as GPS, most public transportation is equipped with automatic vehicle positioning systems, and with the increasing popularity of map navigation, estimated time of arrival is an important part of map technology.
然而,预估到达时间是由于环境和交通存在很多的不确定性,每条公路通行时间对预估到达时间的预测起着非常重要的作用,因此,如何准确预测公路通行时间是需要解决的技术问题。However, the estimated time of arrival is due to many uncertainties in the environment and traffic. The travel time of each road plays a very important role in the prediction of the estimated time of arrival. Therefore, how to accurately predict the travel time of the road is a technology that needs to be solved. question.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本申请的第一个目的在于提出一种公路通行时间预测方法。The first purpose of the present application is to propose a road transit time prediction method.
本申请的第二个目的在于提出一种公路通行时间预测装置。The second objective of the present application is to provide a road transit time prediction device.
本申请的第三个目的在于提出一种电子设备。The third object of the present application is to propose an electronic device.
本申请的第四个目的在于提出一种存储有计算机指令的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质。A fourth object of the present application is to provide a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing computer instructions.
为达上述目的,本申请第一方面实施例提出了一种公路通行时间预测方法,包括以下步骤:In order to achieve the above purpose, a first aspect embodiment of the present application proposes a road transit time prediction method, which includes the following steps:
获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与所述目标公路节点对应的计算子图;Obtaining a target highway node, and obtaining a calculation subgraph corresponding to the target highway node according to preset map data;
通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取所述计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据;Obtain the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node in the calculation subgraph, and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node from the preset database through a preset mapping mechanism;
将所述各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和所述各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成所述目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。The highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node are input into a preset prediction model for calculation, and the predicted travel time corresponding to the target highway node is generated.
为达上述目的,本申请第二方面实施例提出了一种公路通行时间预测装置,包括:In order to achieve the above purpose, a second aspect embodiment of the present application provides a road transit time prediction device, including:
第一获取模块,用于获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与所述目标公路节点对应的计算子图;a first obtaining module, configured to obtain a target highway node, and obtain a calculation subgraph corresponding to the target highway node according to preset map data;
第二获取模块,用于通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取所述计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据;The second obtaining module is configured to obtain, from the preset database, the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node in the calculation subgraph, and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node from the preset database through a preset mapping mechanism;
计算模块,用于将所述各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和所述各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成所述目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。The calculation module is used to input the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node into a preset prediction model for calculation, and generate the predicted traffic corresponding to the target highway node time.
为达上述目的,本申请第三方面实施例提出了一种电子设备,包括:至少一个处理器;以及与所述至少一个处理器通信连接的存储器;其中,所述存储器存储有可被所述至少一个处理器执行的指令,所述指令被所述至少一个处理器执行,以使所述至少一个处理器能够执行上述实施例描述的公路通行时间预测方法。In order to achieve the above purpose, an embodiment of the third aspect of the present application provides an electronic device, comprising: at least one processor; and a memory communicatively connected to the at least one processor; Instructions executed by at least one processor, the instructions being executed by the at least one processor, so that the at least one processor can execute the highway transit time prediction method described in the above embodiments.
为达上述目的,本申请第四方面实施例提出了一种存储有计算机指令的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质,所述计算机指令用于使所述计算机执行上述实施例描述的公路通行时间预测方法。In order to achieve the above purpose, the embodiment of the fourth aspect of the present application provides a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing computer instructions, the computer instructions are used to make the computer execute the highway transit time prediction method described in the above embodiments. .
上述申请中的一个实施例具有如下优点或有益效果:An embodiment in the above application has the following advantages or beneficial effects:
获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与目标公路节点对应的计算子图;通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据;将各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。由此,通过预设映射机制来读取数据,提高了数据获取效率,以及在进行预测时考虑到各个公路之间连接关系特征数据,进一步提高公路通行时间预测的准确性,从而提高预估到达时间的准确性。Obtain the target highway node, and obtain the calculation subgraph corresponding to the target highway node according to the preset map data; obtain the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node in the calculation subgraph from the preset database through the preset mapping mechanism, and each highway node The connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship; the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to each highway node connection relationship are input into the preset prediction model for calculation, and the predicted travel time corresponding to the target highway node is generated. As a result, the data is read through the preset mapping mechanism, which improves the efficiency of data acquisition, and takes into account the characteristic data of the connection relationship between various roads when making predictions, which further improves the accuracy of road travel time prediction, thereby improving the estimated arrival time. time accuracy.
上述可选方式所具有的其他效果将在下文中结合具体实施例加以说明。Other effects of the above-mentioned optional manners will be described below with reference to specific embodiments.
附图说明Description of drawings
附图用于更好地理解本方案,不构成对本申请的限定。其中:The accompanying drawings are used for better understanding of the present solution, and do not constitute a limitation to the present application. in:
图1是根据本申请第一实施例的公路通行时间预测方法的流程图;FIG. 1 is a flowchart of a method for predicting road transit time according to a first embodiment of the present application;
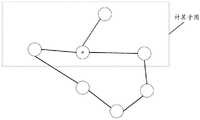
图2是根据本申请第一实施例的计算子图的示例图;FIG. 2 is an exemplary diagram of a calculation subgraph according to the first embodiment of the present application;
图3是根据本申请第二实施例的公路通行时间预测方法的流程图;3 is a flow chart of a method for predicting a highway transit time according to a second embodiment of the present application;
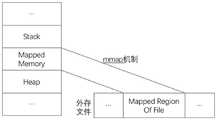
图4是根据本申请第二实施例的存储方式的示例图;FIG. 4 is an exemplary diagram of a storage mode according to the second embodiment of the present application;
图5是根据本申请第三实施例的公路通行时间预测装置的结构示意图;5 is a schematic structural diagram of a highway transit time prediction device according to a third embodiment of the present application;
图6是根据本申请第四实施例的公路通行时间预测装置的结构示意图;6 is a schematic structural diagram of a highway transit time prediction device according to a fourth embodiment of the present application;
图7是根据本申请第五实施例的公路通行时间预测装置的结构示意图;7 is a schematic structural diagram of a highway transit time prediction device according to a fifth embodiment of the present application;
图8是根据本申请第六实施例的公路通行时间预测装置的结构示意图;8 is a schematic structural diagram of a highway transit time prediction device according to a sixth embodiment of the present application;
图9是用来实现本申请实施例的公路通行时间预测方法的电子设备的框图。FIG. 9 is a block diagram of an electronic device used to implement the road transit time prediction method according to the embodiment of the present application.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
以下结合附图对本申请的示范性实施例做出说明,其中包括本申请实施例的各种细节以助于理解,应当将它们认为仅仅是示范性的。因此,本领域普通技术人员应当认识到,可以对这里描述的实施例做出各种改变和修改,而不会背离本申请的范围和精神。同样,为了清楚和简明,以下的描述中省略了对公知功能和结构的描述。Exemplary embodiments of the present application are described below with reference to the accompanying drawings, which include various details of the embodiments of the present application to facilitate understanding, and should be considered as exemplary only. Accordingly, those of ordinary skill in the art will recognize that various changes and modifications of the embodiments described herein can be made without departing from the scope and spirit of the present application. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions are omitted from the following description for clarity and conciseness.
下面参考附图描述本申请实施例的公路通行时间预测方法、装置、电子设备和存储介质。The following describes the method, apparatus, electronic device, and storage medium for predicting highway transit time according to the embodiments of the present application with reference to the accompanying drawings.
本方案通过预设映射机制来读取数据,提高了数据获取效率,以及在进行预测时同时考虑到公路特征数据和各个公路之间连接关系特征数据,进一步提高公路通行时间预测的准确性,从而提高预估到达时间的准确性。This scheme reads data through a preset mapping mechanism, improves the efficiency of data acquisition, and takes into account the characteristic data of highways and the characteristic data of the connection relationship between each highway when making predictions, further improving the accuracy of highway travel time prediction, thereby Improve the accuracy of estimated time of arrival.
具体而言,图1是根据本申请第一实施例的公路通行时间预测方法的流程图。Specifically, FIG. 1 is a flow chart of a method for predicting road transit time according to the first embodiment of the present application.
如图1所示,该方法包括:As shown in Figure 1, the method includes:
步骤101,获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与目标公路节点对应的计算子图。In
具体地,在进行公路通行时间预测时可以根据导航路线中的一条公路或者多条公路的通行时间进行同时预测,因此,将需要进行通行时间预测的公路作为目标公路节点,从而根据预设地图数据可以获取与目标公路节点对应的计算子图。Specifically, when predicting the travel time of a highway, simultaneous prediction can be made according to the travel time of one or more roads in the navigation route. Therefore, the road that needs to be predicted for the travel time is taken as the target road node, so that according to the preset map data The computation subgraph corresponding to the target highway node can be obtained.
其中,预设地图数据是预先建立的,作为一种可能实现方式,获取多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系,根据多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系构建预设地图数据,也就是说,可以将每一条公路作为节点,公路与公路之间十字路口作为边,构建预设地图数据。The preset map data is pre-established. As a possible implementation method, multiple roads and the connection relationship between the roads are obtained, and the preset map data is constructed according to the multiple roads and the connection relationship between the roads. , that is to say, each road can be used as a node, and the intersection between the road and the road can be used as an edge to construct preset map data.
因此,可以从预设地图数据中找到目标公路节点,并且将与目标公路节点相邻的全部公路节点以及连接边作为计算子图,比如图2所示,目标公路节点为A,计算子图为虚线包围各个公路节点,以及和目标公路节点A连接的连接边。Therefore, the target highway node can be found from the preset map data, and all highway nodes and connecting edges adjacent to the target highway node are used as calculation subgraphs. For example, as shown in Figure 2, the target highway node is A, and the calculation subgraph is The dotted lines enclose each road node, and the connecting edge connected to the target road node A.
步骤102,通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据。Step 102: Obtain from a preset database through a preset mapping mechanism, highway feature data corresponding to each highway node in the calculation subgraph, and connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node.
可以理解的是,预设数据库是预先设置的,作为一种可能实现方式,获取多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据,将多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据按照预设映射机制存储在预设数据库。It can be understood that the preset database is preset, and as a possible implementation method, multiple historical feature data of highways corresponding to multiple highways, and multiple historical feature data of connection relationships corresponding to the connection relationships between the highways are obtained. , and store a plurality of road historical feature data corresponding to a plurality of roads and a plurality of connection relationship historical feature data corresponding to the connection relationship between the roads in a preset database according to a preset mapping mechanism.
因此,可以通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据比如该公路节点对应的该时刻交通拥堵指数、通行时间和交通事故概率,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据,比如该十字路口红绿灯情况,交通拥堵指数等。Therefore, the highway characteristic data corresponding to each highway node in the calculation sub-graph, such as the traffic congestion index, travel time and traffic accident probability corresponding to the highway node at the moment, as well as the connection of each highway node, can be obtained from the preset database through the preset mapping mechanism. The connection relationship feature data corresponding to the relationship, such as the traffic light situation at the intersection, the traffic congestion index, etc.
其中,预设映射机制指的是存储获取和存储的一种方式,通过将文件指针存储到内存里面,使得系统通过内存操作的方式获取外存数据,提高数据读取效率。Among them, the preset mapping mechanism refers to a method of storage acquisition and storage. By storing the file pointer in the memory, the system can obtain external memory data through memory operations, thereby improving data reading efficiency.
步骤103,将各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。
具体地,预设预测模型是预先生成的,作为一种可能实现方式,确定训练公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与训练公路节点对应的训练子图,通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取训练子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据,通过预设聚合函数将各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据进行聚合处理生成训练公路特征样本数据,将多个训练公路特征样本数据输入到神经网络模型中得到多个训练结果,分别将多个训练结果与多个训练公路节点对应的多个当前通行时间进行损失函数计算和反向传播梯度处理,直到生成预测模型。Specifically, the preset prediction model is pre-generated. As a possible implementation method, the training highway nodes are determined, and the training sub-maps corresponding to the training highway nodes are obtained according to the preset map data, and the training sub-maps are obtained from the preset database through the preset mapping mechanism. Obtain the road feature sample data corresponding to each road node in the training subgraph, and the connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to the connection relationship of each road node, and connect the road feature sample data corresponding to each road node and each road node through a preset aggregation function. The connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to the relationship is aggregated to generate training highway feature sample data, and multiple training highway feature sample data is input into the neural network model to obtain multiple training results, and the multiple training results are respectively associated with multiple training highway nodes. The corresponding multiple current transit times are subjected to loss function calculation and back-propagation gradient processing until the prediction model is generated.
因此,将各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间,作为一种可能实现方式,通过预设聚合函数将各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据进行聚合处理生成目标公路特征数据,将目标公路特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。Therefore, the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node are input into the preset prediction model for calculation, and the predicted transit time corresponding to the target highway node is generated. As a possible implementation method, Through a preset aggregation function, the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node are aggregated to generate target highway feature data, and the target highway feature data is input into the preset prediction model for calculation. Generate the predicted travel time corresponding to the target highway node.
也就是说,以目标公路节点为起点,根据连接关系产生计算子图,通过mmap机制获取计算子图中各个节点对应的公路特征数据并挂载到子图中,通过聚合函数将采样子图中各个节点特征通过连接关系聚合生成目标公路特征数据,再利用目标公路特征数据进行全连接计算产出目标公路节点的预测结果即通行时间。That is to say, take the target highway node as the starting point, generate the calculation subgraph according to the connection relationship, obtain the road feature data corresponding to each node in the calculation subgraph through the mmap mechanism and mount it in the subgraph, and use the aggregation function to sample the subgraph. The characteristics of each node are aggregated through the connection relationship to generate the target highway feature data, and then the target highway feature data is used for full connection calculation to produce the predicted result of the target highway node, that is, the travel time.
举例而言,假设公路节点是B、C分布是A的邻居,预测目标公路节点A的通行时间,首先会对A的连接关系进行采样产生A、B、C构成的计算子图,通过mmap机制获取计算子图A、B、C的公路特征数据进行挂载,根据计算子图构建目标公路特征数据输入到预设预测模型中,通过全连接计算直接产生A的预测结果即通行时间。For example, assuming that the road nodes are B and C distributed as neighbors of A, to predict the transit time of the target road node A, the connection relationship of A is first sampled to generate a calculation subgraph composed of A, B, and C, and the mmap mechanism is used. Obtain the highway feature data of the calculation subgraphs A, B, and C for mounting, construct the target highway feature data according to the calculation subgraph and input it into the preset prediction model, and directly generate the prediction result of A through the full connection calculation, that is, the travel time.
综上,本申请实施例的公路通行时间预测方法,获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与目标公路节点对应的计算子图;通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据;将各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。由此,通过预设映射机制来读取数据,提高了数据获取效率,以及在进行预测时考虑到各个公路之间连接关系特征数据,进一步提高公路通行时间预测的准确性,从而提高预估到达时间的准确性。To sum up, the highway transit time prediction method of the embodiment of the present application obtains the target highway node, and obtains the calculation subgraph corresponding to the target highway node according to the preset map data; obtains the calculation subgraph from the preset database through the preset mapping mechanism The highway feature data corresponding to each highway node in , and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node; input the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node into the preset prediction model Calculated in , to generate the predicted transit time corresponding to the target highway node. As a result, the data is read through the preset mapping mechanism, which improves the efficiency of data acquisition, and takes into account the characteristic data of the connection relationship between various roads when making predictions, which further improves the accuracy of road travel time prediction, thereby improving the estimated arrival time. time accuracy.
为了实现上述实施例,为了更加清楚描述数据预处理和预设预测模型生成的具体过程,下面结合图3进行详细说明,图3是根据本申请第二实施例的公路通行时间预测方法的流程图。In order to realize the above embodiment, in order to describe the specific process of data preprocessing and preset prediction model generation more clearly, a detailed description is given below with reference to FIG. 3 , which is a flowchart of a method for predicting highway transit time according to the second embodiment of the present application. .
步骤201,获取多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系,根据多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系构建预设地图数据。Step 201: Acquire a plurality of roads and the connection relationship between the roads, and construct preset map data according to the plurality of roads and the connection relationship between the roads.
步骤202,获取多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据。Step 202: Acquire multiple historical feature data of highways corresponding to multiple highways, and multiple historical feature data of connection relationships corresponding to the connection relationships between the highways.
具体地,针将公路建模为图中的点,公路与公路之间十字路口建模为图中的边,获取多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据,可以公路历史特征数据按照和连接关系历史特征数据按照预设时间,比如5min切片粒度,并计算切片中计算均值、求和等统计值作为最终的公路历史特征数据按照和连接关系历史特征数据,其中,为了防止回归模型存在的数值爆炸的问题,可以将预测目标转换为分类问题。Specifically, the road is modeled as a point in the graph, and the intersection between the road and the road is modeled as an edge in the graph, and multiple historical feature data of roads corresponding to multiple roads are obtained, as well as the connection relationship between the roads. Corresponding multiple historical feature data of connection relationship can be based on the historical feature data of highway and the historical feature data of connection relationship according to preset time, such as 5min slice granularity, and calculate the statistical values such as the mean value and summation in the slice as the final historical highway feature The data is connected with historical feature data according to the relationship, among which, in order to prevent the problem of numerical explosion existing in the regression model, the prediction target can be converted into a classification problem.
也就是说,充分利用地图点与点之间的邻居关系,将地图中的公路建模为图的点,将地图中的十字路口建模为图的边,将公路要预测的流量分为多个等级,并利用graphsage(聚合节点邻居特征信息的一种方式)进行节点分类预测。That is to say, make full use of the neighbor relationship between map points, model the road in the map as the point of the graph, model the intersection in the map as the edge of the graph, and divide the traffic to be predicted by the road into multiple and use graphsage (a way of aggregating the feature information of node neighbors) for node classification prediction.
步骤203,将多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据按照预设映射机制存储在预设数据库。Step 203: Store a plurality of road historical feature data corresponding to the plurality of roads and a plurality of connection relationship historical feature data corresponding to the connection relationship between the roads in a preset database according to a preset mapping mechanism.
具体地,比如单纯对北京公路建模,图中公路节点的数目大概在200w左右,一个月内历史数据特征量级大概在300G左右,如果直接采用分布式图进行存储,会导致训练时候准备数据出现严重的带宽瓶颈,因此,采用预设映射机制将多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据存储在预设数据库,比如linux的mmap机制,将大规模点特征存储到外存,并通过内存映射和文件指针的形式优化数据的读取效率,mmap机制大致如下图4所示,通过将文件指针存储到内存里面,使得系统通过内存操作的方式获取外存数据。Specifically, for example, simply modeling the Beijing highway, the number of road nodes in the graph is about 200w, and the feature level of historical data within a month is about 300G. If the distributed graph is directly used for storage, it will lead to data preparation during training. A serious bandwidth bottleneck occurs. Therefore, a preset mapping mechanism is used to store multiple historical feature data of multiple highways corresponding to multiple highways and multiple historical feature data of connection relationships corresponding to each highway in a preset database, such as Linux's mmap mechanism stores large-scale point features in external memory, and optimizes data reading efficiency in the form of memory mapping and file pointers. The mmap mechanism is roughly as shown in Figure 4 below. By storing file pointers in memory, it makes The system obtains external memory data by means of memory operations.
也就是说,预处理数据冗余度低,单机即可完成,利用linux的mmap的机制,将地图中公路庞大特征存储到外存上,克服原先分布式图存储的网络带宽瓶颈。That is to say, the preprocessing data has low redundancy and can be completed by a single machine. Using the mmap mechanism of linux, the huge features of the roads in the map are stored in the external memory, which overcomes the network bandwidth bottleneck of the original distributed map storage.
步骤204,确定训练公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与训练公路节点对应的训练子图。Step 204: Determine the training highway nodes, and obtain training subgraphs corresponding to the training highway nodes according to preset map data.
步骤205,通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取训练子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据。
步骤206,通过预设聚合函数将各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据进行聚合处理生成训练公路特征样本数据。Step 206: Aggregate the highway feature sample data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to each highway node connection relationship through a preset aggregation function to generate training highway feature sample data.
步骤207,将多个训练公路特征样本数据输入到神经网络模型中得到多个训练结果,分别将多个训练结果与多个训练公路节点对应的多个当前通行时间进行损失函数计算和反向传播梯度处理,直到生成预测模型。Step 207: Inputting multiple training highway feature sample data into the neural network model to obtain multiple training results, and performing loss function calculation and back-propagation on the multiple training results and multiple current transit times corresponding to multiple training highway nodes respectively. Gradient processing until a predictive model is generated.
具体地,以其中一个公路节点作为训练公路节点进行采邻居子图即训练子图,根据该训练子图的邻接点进行随机采样,并把采样的层数以及邻居采样点数目作为模型超参数,在生成训练子图后,通过mmap的形式从外存读取训练子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据,并挂在到训练子图中。Specifically, one of the highway nodes is used as a training highway node to select a neighbor subgraph, that is, a training subgraph, random sampling is performed according to the adjacent points of the training subgraph, and the number of layers sampled and the number of neighbor sampling points are used as model hyperparameters, After the training sub-graph is generated, the road feature sample data corresponding to each road node in the training sub-graph and the connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to the connection relationship of each road node are read from the external memory in the form of mmap, and linked to the training sub-graph Figure.
对于上述随机采样训练子图,把邻居节点的表示通过聚合函数聚合为当前节点表示,然后进行梯度回传,例如,采用GATgraphsage算法时候,该聚合函数为attention函数,把各个节点的邻居表示通过attention加权到方式聚合到一起,然后再与自身表示连接起来进行全连接转换表示即通过预设聚合函数将各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据进行聚合处理生成训练公路特征样本数据。For the above random sampling training subgraph, the representation of neighbor nodes is aggregated into the representation of the current node through the aggregation function, and then the gradient is returned. The weighted to method is aggregated together, and then connected with its own representation for full connection transformation representation, that is, the highway feature sample data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node are aggregated through a preset aggregation function. The processing generates sample data for training road features.
最后,将多个训练公路特征样本数据输入到神经网络模型中得到多个训练结果,分别将多个训练结果与多个训练公路节点对应的多个当前通行时间进行损失函数计算和反向传播梯度处理,直到生成预测模型。Finally, input multiple training highway feature sample data into the neural network model to obtain multiple training results, and perform loss function calculation and backpropagation gradient respectively on multiple training results and multiple current transit times corresponding to multiple training highway nodes. Process until a predictive model is generated.
也就是说,随机选择一个起始点,获取起始点为起点游走邻居生成对应的训练子图,通过mmap机制获取训练子图中各个节点对应的公路特征数据并挂载到训练子图中,根据生成的训练子图构建训练公路特征样本数据,通过神经网络模型对练公路特征样本数据进行损失函数计算和反向传播梯度,重复此训练过程直到模型收敛,生成预测模型。实现不需要单独对地图每个十字路口节点进行单独建模,以及利用分散/聚集实现的预设预测模型,避免了对每个节点单独利用建模,每个节点都需要进行大批处理器运算的问题,利用到多机加速能够充分利用处理器进行加速训练时间,克服传统方法实现的模型重复计算问题,使得单机即可完成模型训练和预测。That is to say, randomly select a starting point, obtain the starting point as the starting point to walk neighbors to generate the corresponding training subgraph, obtain the road feature data corresponding to each node in the training subgraph through the mmap mechanism, and mount it in the training subgraph. The generated training subgraph constructs the training highway feature sample data, and uses the neural network model to perform the loss function calculation and backpropagation gradient on the training highway feature sample data. Repeat this training process until the model converges to generate a prediction model. The realization does not require separate modeling of each intersection node on the map, and uses the preset prediction model implemented by scatter/gather, which avoids the separate use of modeling for each node, and each node requires a large number of processor operations. The use of multi-machine acceleration can make full use of the processor to accelerate the training time, overcome the problem of repeated calculation of the model realized by the traditional method, so that the model training and prediction can be completed by a single machine.
举例而言,假设当前训练的节点是A,B、C和D分布是A的邻居,首先会对A的连接关系进行采样产生A、B和C构成的训练子图,通过mmap机制获取采样子图A、B和C的历史公路特征数据进行挂载,根据训练子图构建训练公路特征样本数据输入到神经网络中,与A点当前通行时间计算损失函数,进行方向梯度回传训练,直到产生预测模型。其中,还可以构建A、B和D的训练子图重复进行上述步骤进行训练。For example, assuming that the current training node is A, and the distributions of B, C, and D are neighbors of A, the connection relationship of A is first sampled to generate a training subgraph composed of A, B, and C, and the sampling subgraph is obtained through the mmap mechanism. The historical highway feature data of Figures A, B and C are mounted, and the training highway feature sample data is constructed according to the training sub-graph and input into the neural network, and the loss function is calculated with the current travel time of point A, and the directional gradient backhaul training is performed until the generation of prediction model. Among them, the training subgraphs of A, B, and D can also be constructed to repeat the above steps for training.
需要说明的是,预测过程中,由于节点的入度会非常的大,所以预测也是基于前面采样的训练子图进行计算,把邻居节点表示通过聚合函数生成当前节点表示信息。It should be noted that in the prediction process, since the in-degree of the node will be very large, the prediction is also calculated based on the previously sampled training subgraph, and the neighbor node representation is generated by the aggregation function to generate the current node representation information.
综上,本申请实施例的公路通行时间预测方法,获取多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系,根据多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系构建预设地图数据,获取多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据,将多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据按照预设映射机制存储在预设数据库,确定训练公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与训练公路节点对应的训练子图,通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取训练子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据,通过预设聚合函数将各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据进行聚合处理生成训练公路特征样本数据,将多个训练公路特征样本数据输入到神经网络模型中得到多个训练结果,分别将多个训练结果与多个训练公路节点对应的多个当前通行时间进行损失函数计算和反向传播梯度处理,直到生成预测模型。由此,通过预设映射机制来读取数据,提高了数据获取效率,以及在进行预测时考虑到各个公路之间连接关系特征数据,进一步提高公路通行时间预测的准确性,从而提高预估到达时间的准确性。To sum up, the highway transit time prediction method of the embodiment of the present application acquires multiple highways and the connection relationship between the highways, constructs preset map data according to the multiple highways and the connection relationship between the highways, and obtains multiple highways. Multiple historical feature data of highways corresponding to highways, and multiple historical feature data of connection relationships corresponding to the connection relationships between the highways The historical feature data of a plurality of connection relationships are stored in the preset database according to the preset mapping mechanism, determine the training highway nodes, and obtain the training subgraphs corresponding to the training highway nodes according to the preset map data, and use the preset mapping mechanism from the preset database. Obtain the road feature sample data corresponding to each road node in the training subgraph, and the connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to the connection relationship of each road node, and connect the road feature sample data corresponding to each road node and each road node through a preset aggregation function. The connection relationship feature sample data corresponding to the relationship is aggregated to generate training highway feature sample data, and multiple training highway feature sample data is input into the neural network model to obtain multiple training results, and the multiple training results are respectively associated with multiple training highway nodes. The corresponding multiple current transit times are subjected to loss function calculation and back-propagation gradient processing until the prediction model is generated. As a result, the data is read through the preset mapping mechanism, which improves the efficiency of data acquisition, and takes into account the characteristic data of the connection relationship between various roads when making predictions, which further improves the accuracy of road travel time prediction, thereby improving the estimated arrival time. time accuracy.
为了实现上述实施例,本申请还提出了一种公路通行时间预测装置,图5是根据本申请第四实施例的公路通行时间预测装置的结构示意图,如图5所示,该公路通行时间预测装置包括:第一获取模块501、第二获取模块502和计算模块503,其中,In order to realize the above embodiment, the present application also proposes a road travel time prediction device. FIG. 5 is a schematic structural diagram of the road travel time prediction device according to the fourth embodiment of the present application. As shown in FIG. 5 , the road travel time prediction device The apparatus includes: a
第一获取模块501,用于获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与所述目标公路节点对应的计算子图。The first obtaining
第二获取模块502,用于通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取所述计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据。The second obtaining
计算模块503,用于将所述各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和所述各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成所述目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。The
在本申请的一个实施例中,计算模块503,具体用于:In an embodiment of the present application, the
通过预设聚合函数将所述各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和所述各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据进行聚合处理生成目标公路特征数据;将所述目标公路特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成所述目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。The target highway feature data is generated by aggregating the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to each highway node connection relationship through a preset aggregation function; inputting the target highway feature data into the preset Calculation is performed in the prediction model to generate the predicted transit time corresponding to the target highway node.
在本申请的一个实施例中,如图6所示,在图5的基础上,还包括:第三获取模块504和构建模块505。In an embodiment of the present application, as shown in FIG. 6 , on the basis of FIG. 5 , it further includes: a third acquiring
第三获取模块504,用于获取多条公路,以及各公路之间的连接关系。The third obtaining
构建模块505,用于根据所述多条公路,以及所述各公路之间的连接关系构建所述预设地图数据。The
在本申请的一个实施例中,如图7所示,在图6的基础上,还包括:第四获取模块506和存储模块507。In an embodiment of the present application, as shown in FIG. 7 , on the basis of FIG. 6 , it further includes: a
第四获取模块506,用于获取所述多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及所述各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据。存储模块507,用于将所述多条公路对应的多个公路历史特征数据,以及所述各公路之间的连接关系对应的多个连接关系历史特征数据按照所述预设映射机制存储在所述预设数据库。The fourth obtaining
在本申请的一个实施例中,如图8所示,在图5的基础上,还包括:确定获取模块508、第五获取模块509、聚合模块510和生成模块511。In an embodiment of the present application, as shown in FIG. 8 , on the basis of FIG. 5 , it further includes: a determination and
其中,确定获取模块508,用于确定训练公路节点,并根据所述预设地图数据获取与所述训练公路节点对应的训练子图。The determining and obtaining
第五获取模块509,用于通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取所述训练子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据。The fifth obtaining
聚合模块510,用于通过预设聚合函数将所述各个公路节点对应的公路特征样本数据和所述各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征样本数据进行聚合处理生成训练公路特征样本数据。The
生成模块511,用于将多个所述训练公路特征样本数据输入到神经网络模型中得到多个训练结果,分别将所述多个训练结果与多个训练公路节点对应的多个当前通行时间进行损失函数计算和反向传播梯度处理,直到生成所述预测模型。The
需要说明的是,前述对公路通行时间预测方法的解释说明,也适用于本发明实施例的公路通行时间预测装置,其实现原理类似,在此不再赘述。It should be noted that the foregoing explanations of the highway transit time prediction method are also applicable to the highway transit time prediction apparatus of the embodiment of the present invention, and the implementation principle thereof is similar, which will not be repeated here.
综上,本申请实施例的公路通行时间预测装置,获取目标公路节点,并根据预设地图数据获取与目标公路节点对应的计算子图;通过预设映射机制从预设数据库中获取计算子图中各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据,以及各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据;将各个公路节点对应的公路特征数据和各个公路节点连接关系对应的连接关系特征数据输入到预设预测模型中进行计算,生成目标公路节点对应的预测通行时间。由此,通过预设映射机制来读取数据,提高了数据获取效率,以及在进行预测时考虑到各个公路之间连接关系特征数据,进一步提高公路通行时间预测的准确性,从而提高预估到达时间的准确性。To sum up, the highway transit time prediction device of the embodiment of the present application acquires the target highway node, and obtains the calculation subgraph corresponding to the target highway node according to the preset map data; obtains the calculation subgraph from the preset database through the preset mapping mechanism The highway feature data corresponding to each highway node in , and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node; input the highway feature data corresponding to each highway node and the connection relationship feature data corresponding to the connection relationship of each highway node into the preset prediction model Calculated in , to generate the predicted transit time corresponding to the target highway node. As a result, the data is read through the preset mapping mechanism, which improves the efficiency of data acquisition, and takes into account the characteristic data of the connection relationship between various roads when making predictions, which further improves the accuracy of road travel time prediction, thereby improving the estimated arrival time. time accuracy.
根据本申请的实施例,本申请还提供了一种电子设备和一种可读存储介质。According to the embodiments of the present application, the present application further provides an electronic device and a readable storage medium.
如图9所示,是根据本申请实施例的公路通行时间预测的方法的电子设备的框图。电子设备旨在表示各种形式的数字计算机,诸如,膝上型计算机、台式计算机、工作台、个人数字助理、服务器、刀片式服务器、大型计算机、和其它适合的计算机。电子设备还可以表示各种形式的移动装置,诸如,个人数字处理、蜂窝电话、智能电话、可穿戴设备和其它类似的计算装置。本文所示的部件、它们的连接和关系、以及它们的功能仅仅作为示例,并且不意在限制本文中描述的和/或者要求的本申请的实现。As shown in FIG. 9 , it is a block diagram of an electronic device of a method for predicting road transit time according to an embodiment of the present application. Electronic devices are intended to represent various forms of digital computers, such as laptops, desktops, workstations, personal digital assistants, servers, blade servers, mainframe computers, and other suitable computers. Electronic devices may also represent various forms of mobile devices, such as personal digital processors, cellular phones, smart phones, wearable devices, and other similar computing devices. The components shown herein, their connections and relationships, and their functions are by way of example only, and are not intended to limit implementations of the application described and/or claimed herein.
如图9所示,该电子设备包括:一个或多个处理器901、存储器902,以及用于连接各部件的接口,包括高速接口和低速接口。各个部件利用不同的总线互相连接,并且可以被安装在公共主板上或者根据需要以其它方式安装。处理器可以对在电子设备内执行的指令进行处理,包括存储在存储器中或者存储器上以在外部输入/输出装置(诸如,耦合至接口的显示设备)上显示GUI的图形信息的指令。在其它实施方式中,若需要,可以将多个处理器和/或多条总线与多个存储器和多个存储器一起使用。同样,可以连接多个电子设备,各个设备提供部分必要的操作(例如,作为服务器阵列、一组刀片式服务器、或者多处理器系统)。图9中以一个处理器901为例。As shown in FIG. 9, the electronic device includes: one or
存储器902即为本申请所提供的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质。其中,所述存储器存储有可由至少一个处理器执行的指令,以使所述至少一个处理器执行本申请所提供的方法。本申请的非瞬时计算机可读存储介质存储计算机指令,该计算机指令用于使计算机执行本申请所提供的公路通行时间预测方法。The
存储器902作为一种非瞬时计算机可读存储介质,可用于存储非瞬时软件程序、非瞬时计算机可执行程序以及模块,如本申请实施例中的停车位数据的有效性识别的方法对应的程序指令/模块(例如,附图5所示的第一获取模块501、第二获取模块502和计算模块503)。处理器901通过运行存储在存储器902中的非瞬时软件程序、指令以及模块,从而执行服务器的各种功能应用以及数据处理,即实现上述方法实施例中的公路通行时间预测方法。As a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium, the
存储器902可以包括存储程序区和存储数据区,其中,存储程序区可存储操作系统、至少一个功能所需要的应用程序;存储数据区可存储根据电子设备的使用所创建的数据等。此外,存储器902可以包括高速随机存取存储器,还可以包括非瞬时存储器,例如至少一个磁盘存储器件、闪存器件、或其他非瞬时固态存储器件。在一些实施例中,存储器902可选包括相对于处理器901远程设置的存储器,这些远程存储器可以通过网络连接至电子设备。上述网络的实例包括但不限于互联网、企业内部网、局域网、移动通信网及其组合。The
执行停车位数据的有效性识别的方法的电子设备还可以包括:输入装置903和输出装置904。处理器901、存储器902、输入装置903和输出装置904可以通过总线或者其他方式连接,图9中以通过总线连接为例。The electronic device for performing the method of validating the parking space data may further include: an
输入装置903可接收输入的数字或字符信息,以及产生与电子设备的用户设置以及功能控制有关的键信号输入,例如触摸屏、小键盘、鼠标、轨迹板、触摸板、指示杆、一个或者多个鼠标按钮、轨迹球、操纵杆等输入装置。输出装置904可以包括显示设备、辅助照明装置(例如,LED)和触觉反馈装置(例如,振动电机)等。该显示设备可以包括但不限于,液晶显示器(LCD)、发光二极管(LED)显示器和等离子体显示器。在一些实施方式中,显示设备可以是触摸屏。The
此处描述的系统和技术的各种实施方式可以在数字电子电路系统、集成电路系统、专用ASIC(专用集成电路)、计算机硬件、固件、软件、和/或它们的组合中实现。这些各种实施方式可以包括:实施在一个或者多个计算机程序中,该一个或者多个计算机程序可在包括至少一个可编程处理器的可编程系统上执行和/或解释,该可编程处理器可以是专用或者通用可编程处理器,可以从存储系统、至少一个输入装置、和至少一个输出装置接收数据和指令,并且将数据和指令传输至该存储系统、该至少一个输入装置、和该至少一个输出装置。Various implementations of the systems and techniques described herein can be implemented in digital electronic circuitry, integrated circuit systems, application specific ASICs (application specific integrated circuits), computer hardware, firmware, software, and/or combinations thereof. These various embodiments may include being implemented in one or more computer programs executable and/or interpretable on a programmable system including at least one programmable processor that The processor, which may be a special purpose or general-purpose programmable processor, may receive data and instructions from a storage system, at least one input device, and at least one output device, and transmit data and instructions to the storage system, the at least one input device, and the at least one output device an output device.
这些计算程序(也称作程序、软件、软件应用、或者代码)包括可编程处理器的机器指令,并且可以利用高级过程和/或面向对象的编程语言、和/或汇编/机器语言来实施这些计算程序。如本文使用的,术语“机器可读介质”和“计算机可读介质”指的是用于将机器指令和/或数据提供给可编程处理器的任何计算机程序产品、设备、和/或装置(例如,磁盘、光盘、存储器、可编程逻辑装置(PLD)),包括,接收作为机器可读信号的机器指令的机器可读介质。术语“机器可读信号”指的是用于将机器指令和/或数据提供给可编程处理器的任何信号。These computational programs (also referred to as programs, software, software applications, or codes) include machine instructions for programmable processors, and may be implemented using high-level procedural and/or object-oriented programming languages, and/or assembly/machine languages calculation program. As used herein, the terms "machine-readable medium" and "computer-readable medium" refer to any computer program product, apparatus, and/or apparatus for providing machine instructions and/or data to a programmable processor ( For example, magnetic disks, optical disks, memories, programmable logic devices (PLDs), including machine-readable media that receive machine instructions as machine-readable signals. The term "machine-readable signal" refers to any signal used to provide machine instructions and/or data to a programmable processor.
为了提供与用户的交互,可以在计算机上实施此处描述的系统和技术,该计算机具有:用于向用户显示信息的显示装置(例如,CRT(阴极射线管)或者LCD(液晶显示器)监视器);以及键盘和指向装置(例如,鼠标或者轨迹球),用户可以通过该键盘和该指向装置来将输入提供给计算机。其它种类的装置还可以用于提供与用户的交互;例如,提供给用户的反馈可以是任何形式的传感反馈(例如,视觉反馈、听觉反馈、或者触觉反馈);并且可以用任何形式(包括声输入、语音输入或者、触觉输入)来接收来自用户的输入。To provide interaction with a user, the systems and techniques described herein may be implemented on a computer having a display device (eg, a CRT (cathode ray tube) or LCD (liquid crystal display) monitor) for displaying information to the user ); and a keyboard and pointing device (eg, a mouse or trackball) through which a user can provide input to the computer. Other kinds of devices can also be used to provide interaction with the user; for example, the feedback provided to the user can be any form of sensory feedback (eg, visual feedback, auditory feedback, or tactile feedback); and can be in any form (including acoustic input, voice input, or tactile input) to receive input from the user.
可以将此处描述的系统和技术实施在包括后台部件的计算系统(例如,作为数据服务器)、或者包括中间件部件的计算系统(例如,应用服务器)、或者包括前端部件的计算系统(例如,具有图形用户界面或者网络浏览器的用户计算机,用户可以通过该图形用户界面或者该网络浏览器来与此处描述的系统和技术的实施方式交互)、或者包括这种后台部件、中间件部件、或者前端部件的任何组合的计算系统中。可以通过任何形式或者介质的数字数据通信(例如,通信网络)来将系统的部件相互连接。通信网络的示例包括:局域网(LAN)、广域网(WAN)和互联网。The systems and techniques described herein may be implemented on a computing system that includes back-end components (eg, as a data server), or a computing system that includes middleware components (eg, an application server), or a computing system that includes front-end components (eg, a user's computer having a graphical user interface or web browser through which a user may interact with implementations of the systems and techniques described herein), or including such backend components, middleware components, Or any combination of front-end components in a computing system. The components of the system may be interconnected by any form or medium of digital data communication (eg, a communication network). Examples of communication networks include: Local Area Networks (LANs), Wide Area Networks (WANs), and the Internet.
计算机系统可以包括客户端和服务器。客户端和服务器一般远离彼此并且通常通过通信网络进行交互。通过在相应的计算机上运行并且彼此具有客户端-服务器关系的计算机程序来产生客户端和服务器的关系。A computer system can include clients and servers. Clients and servers are generally remote from each other and usually interact through a communication network. The relationship of client and server arises by computer programs running on the respective computers and having a client-server relationship to each other.
应该理解,可以使用上面所示的各种形式的流程,重新排序、增加或删除步骤。例如,本发申请中记载的各步骤可以并行地执行也可以顺序地执行也可以不同的次序执行,只要能够实现本申请公开的技术方案所期望的结果,本文在此不进行限制。It should be understood that steps may be reordered, added or deleted using the various forms of flow shown above. For example, the steps described in the present application can be performed in parallel, sequentially or in different orders, and as long as the desired results of the technical solutions disclosed in the present application can be achieved, no limitation is imposed herein.
上述具体实施方式,并不构成对本申请保护范围的限制。本领域技术人员应该明白的是,根据设计要求和其他因素,可以进行各种修改、组合、子组合和替代。任何在本申请的精神和原则之内所作的修改、等同替换和改进等,均应包含在本申请保护范围之内。The above-mentioned specific embodiments do not constitute a limitation on the protection scope of the present application. It should be understood by those skilled in the art that various modifications, combinations, sub-combinations and substitutions may occur depending on design requirements and other factors. Any modifications, equivalent replacements and improvements made within the spirit and principles of this application shall be included within the protection scope of this application.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911344130.6ACN111047107B (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-23 | Highway transit time prediction method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911344130.6ACN111047107B (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-23 | Highway transit time prediction method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN111047107A CN111047107A (en) | 2020-04-21 |
| CN111047107Btrue CN111047107B (en) | 2022-05-10 |
Family
ID=70238905
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911344130.6AActiveCN111047107B (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-23 | Highway transit time prediction method, device, electronic device and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN111047107B (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111597700B (en)* | 2020-05-09 | 2023-08-15 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Signal control algorithm evaluation method, device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium |
| CN111914180B (en)* | 2020-08-19 | 2024-04-16 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | User characteristic determining method, device, equipment and medium based on graph structure |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1796058A1 (en)* | 2005-12-12 | 2007-06-13 | C.R.F. Societa Consortile per Azioni | Method and system for estimating the arrival time of a public transport means at predetermined points of its path |
| CN104269059A (en)* | 2014-10-15 | 2015-01-07 | 河海大学 | City path travel time forecasting method based on multi-source data fusion |
| CN109035761A (en)* | 2018-06-25 | 2018-12-18 | 复旦大学 | Travel time estimation method based on back-up surveillance study |
- 2019
- 2019-12-23CNCN201911344130.6Apatent/CN111047107B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP1796058A1 (en)* | 2005-12-12 | 2007-06-13 | C.R.F. Societa Consortile per Azioni | Method and system for estimating the arrival time of a public transport means at predetermined points of its path |
| CN104269059A (en)* | 2014-10-15 | 2015-01-07 | 河海大学 | City path travel time forecasting method based on multi-source data fusion |
| CN109035761A (en)* | 2018-06-25 | 2018-12-18 | 复旦大学 | Travel time estimation method based on back-up surveillance study |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 图卷积神经网络综述;徐冰冰 等;《计算机学报》;20191104;正文第5-8页* |
| 基于图卷积神经网络的旅行时间预测方法研究;虎玉鑫;《中国优秀博硕士学位论文全文数据库(硕士)信息科技辑》;20190115;正文第25-59页* |
| 虎玉鑫.基于图卷积神经网络的旅行时间预测方法研究.《中国优秀博硕士学位论文全文数据库(硕士)信息科技辑》.2019,* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN111047107A (en) | 2020-04-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7334205B2 (en) | Destination prediction method, device, electronic device, computer-readable storage medium and computer program | |
| CN111563592B (en) | Hypernetwork-based neural network model generation method and device | |
| CN112000893B (en) | Resident area prediction method, device, equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114357105B (en) | Pre-training method and model fine-tuning method of geographic pre-training model | |
| CN111968229A (en) | High-precision map making method and device | |
| EP3940556A1 (en) | Map information display method and apparatus, electronic device, and computer storage medium | |
| CN111310987B (en) | Method and device for predicting free parking space of parking lot, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111325382B (en) | Method and device for predicting free parking space of parking lot, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111859291A (en) | Traffic accident identification method, device, equipment and computer storage medium | |
| CN111353009B (en) | Route time consumption estimation model, route time consumption estimation method and corresponding device | |
| CN111612249A (en) | Method, apparatus, device and storage medium for predicting human flow | |
| CN112000763B (en) | Method, device, equipment and medium for determining competition relationship of interest points | |
| CN110705800A (en) | Mixed travel route determination method, device, device and storage medium | |
| CN112419728B (en) | Method, device, device and storage medium for determining road condition information | |
| CN113591573A (en) | Training and target detection method and device for multi-task learning deep network model | |
| CN112131335A (en) | Lane-level map data processing method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111986490A (en) | Road condition prediction method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium | |
| CN111553279A (en) | Representation learning and identification method, device, equipment and storage medium of interest point | |
| CN111982138A (en) | Predictive model acquisition and path planning method, device and storage medium | |
| CN111047107B (en) | Highway transit time prediction method, device, electronic device and storage medium | |
| CN111737636A (en) | Method, device, computer equipment and storage medium for generating path curve | |
| CN111597287A (en) | Map generation method, device and device | |
| CN110930187A (en) | Store visitor crowd mining method, device, equipment and medium | |
| KR20220122565A (en) | Multipath generation method, apparatus, device and storage medium | |
| CN111782744B (en) | A method, device, equipment and storage medium for determining traffic attributes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |