CN110856227B - Data unloading method based on greedy algorithm and reverse auction - Google Patents
Data unloading method based on greedy algorithm and reverse auctionDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110856227B CN110856227BCN201911132825.8ACN201911132825ACN110856227BCN 110856227 BCN110856227 BCN 110856227BCN 201911132825 ACN201911132825 ACN 201911132825ACN 110856227 BCN110856227 BCN 110856227B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- wifi access
- reverse auction
- access point
- mno
- greedy
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0055—Transmission or use of information for re-establishing the radio link
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
- G06Q30/0207—Discounts or incentives, e.g. coupons or rebates
- G06Q30/0222—During e-commerce, i.e. online transactions
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/06—Buying, selling or leasing transactions
- G06Q30/0645—Rental transactions; Leasing transactions
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/06—Buying, selling or leasing transactions
- G06Q30/08—Auctions
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q50/00—Information and communication technology [ICT] specially adapted for implementation of business processes of specific business sectors, e.g. utilities or tourism
- G06Q50/40—Business processes related to the transportation industry
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/0005—Control or signalling for completing the hand-off
- H04W36/0055—Transmission or use of information for re-establishing the radio link
- H04W36/0072—Transmission or use of information for re-establishing the radio link of resource information of target access point
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/14—Reselecting a network or an air interface
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W36/00—Hand-off or reselection arrangements
- H04W36/16—Performing reselection for specific purposes
- H04W36/22—Performing reselection for specific purposes for handling the traffic
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W48/00—Access restriction; Network selection; Access point selection
- H04W48/20—Selecting an access point
Landscapes
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Computer Security & Cryptography (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及通信技术领域,尤其涉及一种基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法。The present invention relates to the field of communication technologies, in particular to a data unloading method based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction.
背景技术Background technique
近年来,随着移动设备(例如,Ipad,笔记本电脑,智能手机)的迅速普及,移动互联网服务正在经历爆炸式增长,并提供各种应用,包括视频、音频和图像等。蜂窝网络是当今提供移动互联网服务的最流行的方式,特别是随着5G网络的出现。然而,移动服务和用户需求的爆炸性增长很可能在不久的将来使蜂窝网络过载和拥塞。特别是在高峰时段或城市地区,移动用户可能在低网络带宽,错失语音呼叫,较差的信号覆盖等方面面临极端情况。因此,移动网络运营商(MNO)迫切需要提供有效且有前景的解决方案来减轻蜂窝网络的负担。In recent years, with the rapid popularity of mobile devices (eg, Ipads, laptops, smartphones), mobile Internet services are experiencing explosive growth and provide various applications including video, audio, and images, among others. Cellular networks are the most popular way to provide mobile internet services today, especially with the advent of 5G networks. However, the explosive growth in mobile services and user demand is likely to overload and congest cellular networks in the near future. Especially during peak hours or urban areas, mobile users can face extremes in terms of low network bandwidth, missed voice calls, poor signal coverage, and more. Therefore, there is an urgent need for mobile network operators (MNOs) to provide effective and promising solutions to relieve the burden on cellular networks.
移动数据卸载是使用互补网络通信技术来传输那些最初计划通过蜂窝网络传输的移动流量。随着移动网络流量持续快速增长,它已成为关键的工业细分领域。蜂窝流量可以通过其他互补网络卸载,例如小型基站(Small Base Station,SBS),机会移动网络,Wi-Fi接入点(Access Point,AP)或异构网络。通过SBS卸载的数据(SBS卸载)使用诸如微小区,微微小区和毫微微小区的低功率小型基站(SBS)来卸载异构网络中的蜂窝流量。通过机会移动网络卸载数据(机会卸载),利用机会移动网络从蜂窝网络卸载移动流量。通过Wi-Fi网络卸载数据(Wi-Fi卸载),当移动设备进入Wi-Fi覆盖区域时将流量从蜂窝网络切换到Wi-Fi AP,以此降低蜂窝网络的成本和流量负载。综上所述,通过异构网络卸载数据是上述三种数据卸载方法的结合。Mobile data offloading is the use of complementary network communication technologies to transport mobile traffic that was originally intended to be transmitted over a cellular network. As mobile network traffic continues to grow rapidly, it has become a key industrial segment. Cellular traffic can be offloaded through other complementary networks, such as Small Base Stations (SBS), Opportunistic Mobile Networks, Wi-Fi Access Points (APs), or heterogeneous networks. Data offloaded by SBS (SBS offload) uses low-power small base stations (SBS) such as micro cells, pico cells and femto cells to offload cellular traffic in heterogeneous networks. Offloading data over opportunistic mobile networks (opportunistic offloading) utilizes opportunistic mobile networks to offload mobile traffic from cellular networks. Data offload via Wi-Fi network (Wi-Fi offload), which reduces the cost and traffic load of the cellular network by switching traffic from the cellular network to the Wi-Fi AP when the mobile device enters the Wi-Fi coverage area. To sum up, offloading data through a heterogeneous network is a combination of the above three data offloading methods.
据报道,2017年移动设备和仅限Wi-Fi设备的Wi-Fi流量将占移动数据流量的60%以上。由于Wi-Fi AP的广泛部署,将过载的蜂窝流量卸载到Wi-Fi AP已经成为一种有效且有前景的方法。最近的研究已经证明了Wi-Fi卸载在缓解蜂窝网络数据流量负担方面的可行性和有效性。然而,Wi-Fi AP在没有接收适当的经济激励(例如,支付或奖励)时可能不愿意参与数据卸载过程。这是因为为MNO提供数据卸载服务将不可避免地产生额外的资源消耗,例如能量消耗,带宽消耗等。此外,在为移动用户提供数据卸载服务时,Wi-Fi AP可能不得不牺牲自己的用户利益,如带宽,传输速率,服务质量等。因此,迫切需要设计有效的激励机制来刺激Wi-Fi AP参与数据卸载过程。According to reports, Wi-Fi traffic from mobile devices and Wi-Fi-only devices will account for more than 60% of mobile data traffic in 2017. Due to the widespread deployment of Wi-Fi APs, offloading overloaded cellular traffic to Wi-Fi APs has become an effective and promising approach. Recent studies have demonstrated the feasibility and effectiveness of Wi-Fi offloading in alleviating the data traffic burden on cellular networks. However, Wi-Fi APs may be reluctant to participate in the data offloading process without receiving appropriate financial incentives (eg, payments or rewards). This is because providing data offloading services for MNOs will inevitably generate additional resource consumption, such as energy consumption, bandwidth consumption, etc. In addition, Wi-Fi APs may have to sacrifice their own user interests, such as bandwidth, transmission rate, quality of service, etc., when providing data offloading services for mobile users. Therefore, it is urgent to design an effective incentive mechanism to stimulate Wi-Fi APs to participate in the data offloading process.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明实施例提供一种基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法,用于解决现有技术中的上述技术问题。The embodiment of the present invention provides a data unloading method based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction, which is used to solve the above-mentioned technical problems in the prior art.
为了解决上述技术问题,一方面,本发明实施例提供一种基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法,包括:In order to solve the above technical problems, on the one hand, an embodiment of the present invention provides a data unloading method based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction, including:
获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;Obtain the maximum delay that can be tolerated by the application in each mobile user MU;
基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;A reverse auction optimization algorithm model is constructed based on the maximum delay. The goal of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model is to maximize the revenue of the operator MNO. The constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model include ensuring that each MU has a The transmission delay does not exceed the corresponding maximum delay threshold;
利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。A greedy winner selection algorithm is used to select the winning WiFi access point to assign to the MU.
进一步地,所述基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型之前,还包括:Further, before constructing the reverse auction optimization algorithm model based on the maximum delay, the method further includes:
获取每一WiFi接入点上报的资源和出价。Get the resources and bids reported by each WiFi access point.
进一步地,所述基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型之前,还包括:Further, before constructing the reverse auction optimization algorithm model based on the maximum delay, the method further includes:
获取每一MU上报的可用WiFi接入点。Obtain the available WiFi access points reported by each MU.
进一步地,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件还包括确保AP向MU租用的频谱带宽与最大可用频谱资源块匹配。Further, the constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model further include ensuring that the spectrum bandwidth leased by the AP from the MU matches the maximum available spectrum resource block.
进一步地,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件还包括只能分配获胜者来协助MU数据卸载。Further, the constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model further include that only winners can be allocated to assist in MU data unloading.
进一步地,所述利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU,具体包括:Further, using the greedy winner selection algorithm to select the winning WiFi access point and assign it to the MU specifically includes:
计算所有WiFi接入点的边际贡献值减去其总出价的差值,确定差值最大的WiFi接入点来得到WiFi接入点的索引;Calculate the difference between the marginal contribution values of all WiFi access points minus their total bids, and determine the WiFi access point with the largest difference to obtain the index of the WiFi access point;
基于差值排序来选择获胜的WiFi接入点,直到所选WiFi接入点的总出价大于或等于其边际贡献。The winning WiFi access point is selected based on the difference ranking until the total bid of the selected WiFi access point is greater than or equal to its contribution margin.
进一步地,在选择获胜的WiFi接入点之后,MNO采用标准VCG机制确定为每一WiFi接入点支付的报酬。Further, after selecting the winning WiFi access point, the MNO uses the standard VCG mechanism to determine the compensation to be paid for each WiFi access point.
另一方面,本发明实施例提供一种基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载装置,包括:On the other hand, an embodiment of the present invention provides a data unloading apparatus based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction, including:
获取模块,用于获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;an acquisition module, used to acquire the maximum delay that can be tolerated by the application in each mobile user MU;
模型构建模块,用于基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;A model building module for constructing a reverse auction optimization algorithm model based on the maximum delay, the goal of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model is to maximize the revenue of the operator MNO, and the constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model Including ensuring that the transmission delay of each MU does not exceed the corresponding maximum delay threshold;
分配模块,用于利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。The allocation module is used to select the winning WiFi access point to be allocated to the MU using the greedy winner selection algorithm.
再一方面,本发明实施例提供一种电子设备,包括:存储器、处理器,以及存储在所述存储器上并可在所述处理器上运行的计算机程序,所述处理器执行所述计算机程序时,实现上述方法的步骤。In another aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides an electronic device, including: a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored on the memory and executable on the processor, where the processor executes the computer program , implement the steps of the above method.
又一方面,本发明实施例提供一种非暂态计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,当所述计算机程序被处理器执行时,实现上述方法的步骤。In yet another aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps of the above method are implemented.
本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法,从商业角度将Wi-Fi卸载问题转化为基于反向拍卖的激励问题,旨在最大化MNO的收益,并且提出一种新的基于延迟约束和反向竞价的激励机制来刺激Wi-Fi接入点参与数据卸载过程。The data offloading method based on the greedy algorithm and the reverse auction provided by the embodiment of the present invention transforms the Wi-Fi offloading problem into the incentive problem based on the reverse auction from a commercial point of view, aiming at maximizing the income of the MNO, and proposes a new The incentive mechanism based on delay constraints and reverse bidding to stimulate Wi-Fi access points to participate in the data offloading process.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法示意图;1 is a schematic diagram of a data unloading method based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图2为本发明实施例提供的Wi-Fi卸载的网络场景示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of a network scenario of Wi-Fi offloading provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
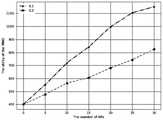
图3为本发明实施例提供的在不同AP的数量下MNO的收益示意图;3 is a schematic diagram of the revenue of MNOs under different numbers of APs provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图4为本发明实施例提供的在不同AP的数量下MNO的流量负载示意图;4 is a schematic diagram of the traffic load of an MNO under different numbers of APs provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图5为本发明实施例提供的在不同MU的数量下MNO的收益示意图;FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of the benefits of MNOs under different numbers of MUs provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明实施例提供的在不同MU的数量下MNO的流量负载示意图;FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of the traffic load of the MNO under different numbers of MUs provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图7为本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载装置示意图;7 is a schematic diagram of a data unloading device based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction provided by an embodiment of the present invention;
图8为本发明实施例提供的电子设备的结构示意图。FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明实施例的目的、技术方案和优点更加清楚,下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部的实施例。基于本发明的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都属于本发明保护的范围。In order to make the purposes, technical solutions and advantages of the embodiments of the present invention clearer, the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention will be described clearly and completely below with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments These are some embodiments of the present invention, but not all embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by those of ordinary skill in the art without creative work fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
图1为本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法示意图,如图1所示,本发明实施例提供一种基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法。该方法包括:FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of a data unloading method based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1 , an embodiment of the present invention provides a data unloading method based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction. The method includes:
步骤S101、获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;Step S101, obtaining the maximum delay that the application program in each mobile user MU can tolerate;
步骤S102、基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;Step S102, constructing a reverse auction optimization algorithm model based on the maximum delay, the goal of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model is to maximize the revenue of the operator MNO, and the constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model include ensuring that every The transmission delay of a MU does not exceed the corresponding maximum delay threshold;
步骤S103、利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。Step S103, using the greedy winner selection algorithm to select the winning WiFi access point and assign it to the MU.
具体来说,图2为本发明实施例提供的Wi-Fi卸载的网络场景示意图,如图2所示,本发明实施例考虑单个蜂窝网络中移动数据卸载的场景,网络由移动网络运营商(MobileNetwork Operator,MNO)的基站(Base Station,BS),若干Wi-Fi接入点(Access Point,AP)和一组移动用户(Mobile User,MU)构成。这里,BS由MNO部署,并且AP由不同的第三方公司部署。此外假设所有MU都在BS的服务覆盖范围内,而每个AP由于其较小的传输功率而仅覆盖部分MU,并且MU均匀分布在覆盖区域中。每个MU可以从BS下载其喜爱的内容。由于BS具有有限的回程和无线电接入容量,因此MNO可以选择由AP服务的一些MU以最大化网络吞吐量并改善整体网络性能,尤其是在发生网络拥塞时。Specifically, FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a network scenario of Wi-Fi offloading provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 2 , an embodiment of the present invention considers a scenario of mobile data offloading in a single cellular network. Operator, MNO) base station (Base Station, BS), several Wi-Fi access points (Access Point, AP) and a group of mobile users (Mobile User, MU). Here, the BS is deployed by the MNO, and the AP is deployed by different third-party companies. Furthermore, it is assumed that all MUs are within the service coverage of the BS, while each AP only covers part of the MUs due to its small transmission power, and the MUs are uniformly distributed in the coverage area. Each MU can download its favorite content from the BS. Since the BS has limited backhaul and radio access capacity, the MNO can select some MUs served by the AP to maximize network throughput and improve overall network performance, especially when network congestion occurs.
然而AP属于不同的第三方公司,由于它们是自私且理性的,因此通过AP卸载的数据通常不是免费的。为了刺激这些自私且理性的AP参与数据卸载过程,MNO需要向AP提供一些支付以补偿其资源消耗。此外,MU可以运行不同的应用程序,因此当MNO做出卸载决定时应考虑不同应用程序可容忍的最大时延。AP将其可用的频谱资源块租赁给MNO以换取报酬。通过租用的频谱资源块,MU可以在不同的频谱带宽中进行数据传输。具体来说,每个AP周期性地报告其可用频谱资源块并向MNO提供报价,而MNO基于所收集的信息选择一些AP参与数据卸载过程并向其支付相应的报酬。However APs belong to different third-party companies, and since they are selfish and rational, data offloaded through APs is usually not free. To stimulate these selfish and rational APs to participate in the data offloading process, the MNO needs to provide some payments to the APs to compensate for their resource consumption. Furthermore, MUs can run different applications, so the maximum latency that different applications can tolerate should be considered when the MNO makes an offload decision. The AP leases its available blocks of spectrum resources to the MNO in exchange for payment. Through the leased spectrum resource blocks, the MU can perform data transmission in different spectrum bandwidths. Specifically, each AP periodically reports its available spectrum resource blocks and provides offers to the MNO, and the MNO selects some APs to participate in the data offloading process based on the collected information and pays them accordingly.
相关模型如下:The relevant models are as follows:
1)移动运营商收入模型:在上述网络中,MNO通过向MU提供内容服务来获得收入。本发明实施例假设系统中MU请求总的移动数据流量是q,其中AP可以协助卸载的流量是f。因此,由BS传输的总流量为(q-f)。由于MNO在早期阶段建设和维护BS所投入的成本是固定的,因此可以将单位移动数据的成本设置为e,将价格设置为d。然后可以得到MNO从单位流量中获取的收入为(d-e)。1) Mobile operator revenue model: In the above network, MNOs earn revenue by providing content services to MUs. The embodiment of the present invention assumes that the total mobile data traffic requested by the MU in the system is q, and the traffic that the AP can assist in offloading is f. Therefore, the total traffic transmitted by the BS is (q-f). Since the cost of building and maintaining the BS in the early stage of the MNO is fixed, the cost per unit of mobile data can be set as e and the price as d. Then it can be obtained that the MNO's income from unit traffic is (d-e).
如果不考虑支付给参与数据卸载过程的AP的报酬,则MNO的收入函数表示如下:If the remuneration paid to APs participating in the data offloading process is not considered, the revenue function of the MNO is expressed as follows:
U(q,f)=(d-e)(q-f)+df (1)U(q, f)=(d-e)(q-f)+df (1)
其中,U(q,f)为MNO的收入,(d-e)(q-f)是由BS传输的流量产生的收入,df是由AP卸载的流量产生的收入,d为MNO单位移动数据的价格,e为MNO单位移动数据的成本,q为MU请求总的移动数据流量,f为AP可以协助卸载的流量。Among them, U(q, f) is the revenue of the MNO, (d-e)(q-f) is the revenue generated by the traffic transmitted by the BS, df is the revenue generated by the traffic offloaded by the AP, d is the price of the MNO unit mobile data, e is the unit mobile data cost of the MNO, q is the total mobile data traffic requested by the MU, and f is the traffic that the AP can assist in offloading.
本发明实施例将数据卸载过程划分为多个时隙,其中每个时隙至少大于MU的最大容忍延迟。MNO在每个时段发起拍卖并收集AP的出价。根据周围MU的请求信息,MNO可以根据其可用的频谱资源块来评估每个AP的卸载潜力。然后,MNO选择最有价值的AP参与数据卸载。当MU请求内容服务时,MNO首先检查它们是否可以由附近可用的AP服务。如果没有可用的AP,则MU仍然能够直接访问蜂窝网络下载内容。In the embodiment of the present invention, the data offloading process is divided into multiple time slots, wherein each time slot is at least greater than the maximum tolerated delay of the MU. The MNO initiates an auction and collects bids from APs at each time slot. According to the request information of the surrounding MUs, the MNO can evaluate the offloading potential of each AP according to its available spectrum resource blocks. Then, the MNO selects the most valuable APs to participate in data offloading. When MUs request content services, MNOs first check if they can be served by nearby available APs. If no AP is available, the MU can still directly access the cellular network to download content.
2)传输模型:假设表示MU的集合,并且每个MU有以下属性:2) Transmission Model: Assumptions represents the set of MUs, and each MU Has the following properties:
流量需求sj:系统中的每个MU都有自己的流量需求,这是需要基于不同类型的应用程序并有指定的传输延迟限制。Traffic requirements sj : Each MU in the system has its own traffic requirements, which are required based on different types of applications and have specified transmission delay limits.
最大延迟阈值δj:这取决于每个MU的服务类型,不同类型应用程序的MU容忍不同的最大延迟。例如,文件传输程序(例如网盘)比视频应用程序(例如网络直播)有更高的容忍延迟。Maximum delay thresholdδj : This depends on the service type of each MU, MUs for different types of applications tolerate different maximum delays. For example, file transfer programs (such as web drives) have a higher latency tolerance than video applications (such as webcasting).
信道传输速率Rij:对于每个AP和MU之间的信道模型,本发明实施例考虑路径损耗和小规模衰落。AP i∈K和MU j∈N之间的信道传输速率可表示如下:Channel transmission rate Rij : For the channel model between each AP and MU, the embodiment of the present invention considers path loss and small-scale fading. The channel transmission rate between AP i∈K and MU j∈N can be expressed as follows:
其中,Bij是AP i和MU j之间租用传输信道的带宽,N0是信道噪声功率,dij是AP i和MU j之间的距离,α是路径损失指数,hj表示瑞利分布的小规模信道衰落。为了便于分析,本发明实施例假设所有AP都采用固定功率传输,并且令Pi=Pt,where Bij is the bandwidth of the leased transmission channel between AP i and MU j, N0 is the channel noise power, dij is the distance between AP i and MU j, α is the path loss index, and hj is the Rayleigh distribution small-scale channel fading. For the convenience of analysis, the embodiment of the present invention assumes that all APs use fixed power transmission, and let Pi =Pt ,
3)AP的竞标模型:假设表示AP的集合,并且每个有以下属性:3) AP's bidding model: Assumptions represents the set of APs, and each Has the following properties:
可用的频谱资源块由于第三方公司拥有的每个AP都有自己的任务,因此AP可能有不同的备用频谱资源块可用于执行数据卸载。Available spectrum resource blocks Since each AP owned by a third-party company has its own task, the APs may have different spare spectrum resource blocks available to perform data offloading.
单位租用频谱资源块的真实值vi:它表示通过帮助MNO服务数据卸载过程而导致的消耗的真实值。并且vi是AP i的私人信息,任何其他AP或MNO都无法知道。Real value vi per unitleased spectrum resource block: It represents the real value of consumption caused by helping the MNO service data offloading process. And vi is AP i's private information, which cannot be known by any other AP or MNO.
单位租用频谱资源块的出价φi:这是AP i想要从MNO收到的奖励或支付,以补偿因进行数据卸载而导致的资源消耗。但是,如果AP i可以通过要求其他价格获得更高的报酬,则出价φi可能不等于消费vi的真实值。MU j的通信成本与租用频谱的带宽Bij以及占用的持续时间tij=sj/Rij相关联,表示为εij,计算如下:Bid φi per unit leased spectrum resource block: This is the reward or payment that AP i wants to receive from the MNO to compensate for resource consumption due to data offloading. However, if APi can get a higher reward by asking other prices, the bid φi may not be equal to the true value of consumption vi. The communication cost of MU j is associated with the bandwidth Bij of the leased spectrum and the occupied duration tij =sj /Rij , expressed as εij , calculated as follows:
εij=φiBijtij (3)εij = φi Bij tij (3)
其中,εij为MU j的通信成本,φi为单位租用频谱资源块的出价,Bij为租用频谱的带宽,tij为占用时间。Among them, εij is the communication cost of MU j, φi is the bid price of the leased spectrum resource block, Bij is the bandwidth of the leased spectrum, and tij is the occupied time.
在拍卖过程中,每个AP i将其出价向量提交给MNO,其中φi代表其出价,以及可用频谱资源块为了使拍卖过程公平,AP之间的交易互惠互利,应设计适当的激励机制,鼓励AP的参与。During the auction, each AP i puts its bid vector Submitted to the MNO, whereφi represents its bid, and the available spectrum resource block In order to make the auction process fair and the transactions between APs mutually beneficial, an appropriate incentive mechanism should be designed to encourage the participation of APs.
4)反向拍卖模型:本发明使用反向拍卖来激励AP参与数据卸载过程,其中MNO充当购买AP容量的拍卖者,而AP充当提供其可用频谱资源以服务于卸载流量的卖方。具体而言,每个AP报告其可用容量并向MNO出价,而MNO根据收集的信息(即所有AP的可用资源和出价)选择一些AP参与数据卸载过程并支付它们相应的报酬。整个拍卖程序包括三个步骤:4) Reverse auction model: The present invention uses reverse auctions to incentivize APs to participate in the data offloading process, where the MNO acts as an auctioneer buying AP capacity and the AP acts as a seller providing its available spectrum resources to serve offload traffic. Specifically, each AP reports its available capacity and makes a bid to the MNO, and the MNO selects some APs to participate in the data offloading process according to the collected information (ie, the available resources and bids of all APs) and pays their corresponding remuneration. The entire auction process consists of three steps:
1、每个AP将其出价向量提交给MNO。1. Each AP puts its bid vector Submit to MNO.
2、每个MU向MNO报告其附近可用的Wi-Fi连接,以及所请求数据可容忍的最大延迟和数据大小(即sj和δj,)。根据报告的信息,MNO可以生成AP-MU关联集这反映了每个AP覆盖范围内的MU集合,其中Fi表示AP i覆盖的MU集合。例如,如图2所示,MU 6,MU 8和MU 10由AP 3覆盖。也就是说,AP 3覆盖范围内MU的集合是同样,AP 4覆盖范围内MU的集合是2. Each MU reports to the MNO the available Wi-Fi connections in its vicinity, as well as the maximum delay and data size that the requested data can tolerate (i.e. sj and δj , ). Based on the reported information, the MNO can generate an AP-MU association set This reflects the set of MUs covered by each AP, where Fi represents the set of MUs covered by APi . For example, as shown in Figure 2, MU 6, MU 8 and
3、MNO确定将参与数据卸载过程的AP的子集,并计算给与每个AP的报酬。3. The MNO determines the subset of APs that will participate in the data offloading process, and calculates a reward for each AP.
本发明实施例假设所有信道状态信息和MU的传输功率在MNO处是已知的。现在,本发明实施例将xi∈{0,1}和aij∈{0,1}定义为两个指示变量,以指示AP i最终是否被选中协助卸载数据流量,以及是否选择AP i来分别协助MU j进行数据流量卸载。如果选择AP i来执行卸载任务,xi=1;否则,xi=0。同样,如果MU j连接到AP i,aij=1;否则,aij=0。Embodiments of the present invention assume that all channel state information and the transmit power of the MU are known at the MNO. Now, the embodiment of the present invention defines xi ∈ {0, 1} and aij ∈ {0, 1} as two indicator variables to indicate whether AP i is finally selected to assist in offloading data traffic, and whether AP i is selected to Assist MU j in data traffic offloading respectively. If AP i is selected to perform the offload task, xi =1; otherwise, xi =0. Likewise, if MU j is connected to AP i, aij =1; otherwise, aij =0.
然后,可以得到MNO的收益函数如下:Then, the profit function of MNO can be obtained as follows:
其中,是数据卸载的总收入与获胜者的总支付之间的差异,U(·)是MNO的收入函数,如公式(1)所示,xi为指示变量,xi∈{0,1},aij为指示变量,aij∈{0,1},sj为MU j的流量需求,εij为MU j的通信成本。in, is the difference between the total revenue of data unloading and the total payout of the winner, U( ) is the revenue function of the MNO, as shown in formula (1), xi is the indicator variable, xi ∈ {0, 1}, aij is an indicator variable, aij ∈ {0, 1}, sj is the traffic demand of MU j, and εij is the communication cost of MU j.
从MNO的角度来看,它的目标是通过减少支付来获得尽可能多的收入。最大化MNO收益的总体问题如下:From an MNO's perspective, its goal is to generate as much revenue as possible by paying less. The overall problem of maximizing MNO returns is as follows:
上述公式中约束条件的含义如下:The meaning of the constraints in the above formula is as follows:
约束(6)确保AP向MU租用的频谱带宽与最大可用频谱资源块匹配。Constraint (6) ensures that the spectrum bandwidth leased by the AP to the MU matches the maximum available spectrum resource block.
约束(7)确保MU传输延迟不超过其最大延迟阈值。Constraint (7) ensures that the MU propagation delay does not exceed its maximum delay threshold.
约束(8)表示只能分配获胜者来协助MU数据卸载。Constraint (8) states that only winners can be assigned to assist in MU data offloading.
约束(9)保证二进制变量的整数性质。Constraint (9) guarantees the integer nature of binary variables.
解决具有整数约束和变量分数运算的问题是难以处理的。目标函数(5)是混合整数非线性规划问题(MINLP),它通常是NP-hard问题。为了使问题易于处理,本发明实施例首先分析目标函数。为了获得上述公式中的AP选择问题的最优解,广泛使用现有的分支定界(BNB)方法。然而,当存在大量AP时,BNB方法的时间复杂度总是呈指数增长。因此,本发明实施例提出如下解决该问题的方法:Solving problems with integer constraints and variable fraction operations is intractable. The objective function (5) is a mixed integer nonlinear programming problem (MINLP), which is usually NP-hard. In order to make the problem easy to deal with, the embodiment of the present invention first analyzes the objective function. To obtain the optimal solution to the AP selection problem in the above formulation, existing branch and bound (BNB) methods are widely used. However, the time complexity of the BNB method always grows exponentially when there are a large number of APs. Therefore, the embodiment of the present invention proposes the following method for solving this problem:
本发明实施例将使用启发式算法来解决上述优化问题,并降低计算复杂度。解决上述优化问题的一种简单方法是选择能给MNO增加收益最大的AP。因此,本发明实施例首先介绍一种贪婪获胜者选择算法(Greedy Winner Selection Method,GWSM)。The embodiment of the present invention will use a heuristic algorithm to solve the above-mentioned optimization problem and reduce the computational complexity. A simple way to solve the above optimization problem is to choose the AP that can add the most benefit to the MNO. Therefore, the embodiments of the present invention first introduce a greedy winner selection method (Greedy Winner Selection Method, GWSM).
首先,本发明介绍一些定义。然后,详细说明在GWSM中提出的AP选择规则。First, the present invention introduces some definitions. Then, the AP selection rules proposed in GWSM are explained in detail.
定义1(AP的贡献值):的贡献值被定义为选择AP i协助数据卸载后MNO的收入增量,其计算公式如下:Definition 1 (contribution value of AP): The contribution value of is defined as the income increment of MNO after selecting AP i to assist data unloading, and its calculation formula is as follows:
其中,ui为AP i的贡献值,Ti表示由AP i服务的MU的最优集合,它可以最大化每个时隙中AP i卸载的数据量。sj为MU j的流量需求,d为MNO单位移动数据的价格。Among them,ui is the contribution value of AP i, and Ti represents the optimal set of MUs served by AP i, which can maximize the amount of data unloaded by AP i in each time slot. sj is the traffic demand of MU j, and d is the price of MNO unit mobile data.
定义2(AP的总出价):的总出价定义为AP i所服务的MU在其单位租用频谱资源块的出价下的通信成本之和,其计算公式如下:Definition 2 (total bid for AP): The total bid is defined as the sum of the communication costs of the MUs served by AP i under the bids of its unit leased spectrum resource blocks, and its calculation formula is as follows:
其中,bi为AP i的总出价,Ti表示由AP i服务的MU的最优集合,εij表示MU j与AP i的通信费用。Among them, bi is the total bid of AP i, Ti represents the optimal set of MUs served by AP i, and εij represents the communication cost between MU j and AP i.
定义3(获胜者集合贡献值):用来表示一组获胜的AP,获胜者集合的贡献值被定义为中所有AP的贡献之和,其计算公式如下:Definition 3 (winner set contribution value): use to represent a set of winning APs, the set of winners The contribution value of is defined as The sum of the contributions of all APs in the calculation formula is as follows:
定义4(AP的边际贡献值):用来表示一组获胜的AP,的边际贡献值被定义为当其被选择为获胜AP后获胜者集合贡献值的增量,其计算公式如下:Definition 4 (the marginal contribution value of AP): use to represent a set of winning APs, The marginal contribution value of is defined as the increment of the winner set contribution value when it is selected as the winning AP, and its calculation formula is as follows:
根据上述定义,当MN0选择一组AP参与数据卸载过程,并且目标为最大化MNO的效益,可以表述为:According to the above definition, when the MN0 selects a group of APs to participate in the data offloading process, and the goal is to maximize the benefits of the MNO, it can be expressed as:
其中表示获胜AP服务的MU集合。in Represents the set of MUs served by the winning AP.
为了有效地解决优化问题,本发明实施例设计了一种贪婪算法来选择最有价值的AP。AP根据其边际贡献值减去总出价进行排序。获胜的AP可以排序为:In order to effectively solve the optimization problem, the embodiment of the present invention designs a greedy algorithm to select the most valuable AP. APs are sorted by their contribution margin minus total bids. Winning APs can be sorted as:
其中,θ(n)表示排序中第n个AP索引。因为在每个while循环中的获胜者集合都会被更新,因此在式(17)中本发明使用来简化表示本发明通过计算所有AP的边际贡献值减去其总出价的差值中最大的AP来得到AP的索引。然后,基于其边际贡献值减去总出价的差值排序来选择获胜AP,直到所选AP的总出价大于或等于其边际贡献。Among them, θ(n) represents the nth AP index in the sorting. because in each while loop the set of winners will be updated, so in formula (17) the present invention uses to simplify the representation The present invention obtains the index of the AP by calculating the marginal contribution value of all APs minus the largest AP in the difference between their total bids. The winning APs are then selected based on their contribution margin minus the total bid, until the selected AP's total bid is greater than or equal to its contribution margin.
在选择获胜的AP之后,MN0应该确定对他们的付款。由于自私性和合理性的性质,每个AP可能会通过宣布不真实的出价来欺骗更高的报酬。因此,本发明提出了一种新颖的基于标准Vickrey-Clarke-Groves(VCG)机制的支付方案。支付方案可以激励自私和理性的AP参与数据卸载过程,并保证个体的合理性和真实性。After selecting the winning AP, the MN0 should determine the payment to them. Due to the nature of selfishness and rationality, each AP may deceive higher payouts by announcing untrue bids. Therefore, the present invention proposes a novel payment scheme based on the standard Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) mechanism. The payment scheme can motivate selfish and rational APs to participate in the data offloading process and guarantee the rationality and authenticity of individuals.
在标准的VCG方案中,每个获胜者将支付给其他参与者的“机会成本”。竞标人i的“机会成本”定义为:在没有竞标人i参与的情况下,将所有竞标获胜者的出价总和减去所有其他实际竞标人的出价总和。根据定义1与定义2可知ui表示选择AP i后MNO收入的增量,bi表示AP i协助数据卸载所产生的通信成本总和。In a standard VCG scheme, each winner will pay an "opportunity cost" to the other participants. Bidder i's "opportunity cost" is defined as the sum of all bid winners' bids minus the sum of all other actual bidders' bids in the absence of bidder i's participation. According to Definition 1 and Definition 2,ui represents the increment of MNO revenue after selecting APi , and bi represents the sum of communication costs generated by AP i assisting data offloading.
为了用数学的形式表达,将定义为不考虑AP i的贡献值情况下的最优解,可以公式表述为:In order to express it in mathematical form, the Defined as the optimal solution without considering the contribution value of AP i, it can be expressed as:
并且用表示不考虑AP i参与数据卸载过程的最优解决方案。然后,支付给AP i的报酬可以表示如下:and use Represents the optimal solution that does not consider the participation of AP i in the data offloading process. Then, the remuneration paid to AP i can be expressed as follows:
令表示AP i在参与数据卸载的过程中所消耗的真实价值。因此,每个的收益可以表示为:make It represents the real value consumed by AP i in the process of participating in data offloading. Therefore, each The income can be expressed as:
μi=pi-γi (20)μi =pi -γ i( 20)
另外,将支付给的报酬定义为0。In addition, will be paid to The reward is defined as 0.
下面结合具体的实验数据对上述实施例中的方法进行说明:Below in conjunction with concrete experimental data, the method in the above-mentioned embodiment is described:
在实验中,本发明实施例考虑在BS的覆盖范围内随机布置若干个传输距离为[50,100]m的AP。单位频谱资源块的出价均匀分布于[0.2,0.5]货币单位(例如,美元或人民币)/(MHzsec)。每个MU的最大延迟均匀分布在[0.1,1]sec内。MU数量的取值范围为[0,100],AP数量的取值范围为[0,30],并且AP的最大可用频谱资源块Bmax的取值范围为[0,80]。路径损耗指数是α=2.5。本发明实施例将提出的GWSM(S.1)的性能与随机获胜者选择方法(S.2)进行比较,该方法选择一组AP随机参与数据卸载过程。为了公平起见,随机获胜者选择方法中所选AP的总数与本发明提出的方法相同,本发明使用MNO的收益(或效益)和MNO的流量负载作为评估指标。这里,MNO的收益定义为公式(4),MNO的流量负载表示BS发送的总数据量。In the experiment, the embodiment of the present invention considers randomly arranging several APs with a transmission distance of [50, 100] m within the coverage area of the BS. Bids per unit spectrum resource block are evenly distributed in [0.2, 0.5] currency units (eg, US dollars or RMB)/(MHzsec). The maximum delay of each MU is uniformly distributed within [0.1, 1] sec. The value range of the number of MUs is [0, 100], the value range of the number of APs is [0, 30], and the value range of the maximum available spectrum resource block Bmax of the AP is [0, 80]. The path loss exponent is α=2.5. The embodiments of the present invention compare the performance of the proposed GWSM (S.1) with the random winner selection method (S.2), which selects a group of APs to randomly participate in the data offloading process. For the sake of fairness, the total number of APs selected in the random winner selection method is the same as the method proposed by the present invention, which uses the MNO's revenue (or benefit) and the MNO's traffic load as evaluation indicators. Here, the revenue of the MNO is defined as formula (4), and the traffic load of the MNO represents the total amount of data sent by the BS.
图3为本发明实施例提供的在不同AP的数量下MNO的收益示意图,图3显示了当MU的数量设置为|N|=100,AP的可用频谱资源块为20MHz时,在GWSM(S.1)和随机优胜者选择方法(S.2)中MNO的收益随着AP数量增加的变化情况。随着AP数量的增加,更多的AP可以帮助MNO卸载流量,因此MNO的效益将不断增加。可以发现,当AP的数量增加时,GWSM比随机优胜者选择方法表现得更好,特别是当AP的数量较大时。FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of the benefits of MNOs under different numbers of APs according to an embodiment of the present invention. .1) and the random winner selection method (S.2), the change of the MNO's return with the increase of the number of APs. As the number of APs increases, more APs can help MNOs offload traffic, so the benefits of MNOs will continue to increase. It can be found that when the number of APs increases, GWSM performs better than the random winner selection method, especially when the number of APs is large.
图4为本发明实施例提供的在不同AP的数量下MNO的流量负载示意图,图4显示了当MU的数量设置为|N|=100,AP的可用频谱资源块为20MHz时,GWSM(S.1)和随机优胜者选择方法(S.2)中MNO的流量负载随着AP数量增加的变化情况。随着AP数量的增加,更多的AP可以帮助MNO卸载流量,因此MNO的流量负载不断减少。可以发现,与随机获胜者选择方法相比,随着AP数量的增加,GWSM中MNO的流量负载显著减少,这表明GWSM表现最佳。FIG. 4 is a schematic diagram of the traffic load of the MNO under different numbers of APs according to an embodiment of the present invention. .1) and the random winner selection method (S.2), the traffic load of the MNO as the number of APs increases. As the number of APs increases, more APs can help the MNO to offload traffic, so the traffic load of the MNO keeps decreasing. It can be found that the traffic load of MNOs in GWSM decreases significantly as the number of APs increases compared to the random winner selection method, which indicates that GWSM performs the best.
图5为本发明实施例提供的在不同MU的数量下MNO的收益示意图,图5显示了当AP的数量设置为|K|=30,AP的可用频谱资源块为20MHz时,GWSM(S.1)和随机优胜者选择方法(S.2)中MNO的收益随着MU数量增加的变化情况。随着MU数量的增加,MU将请求的总流量会不断增加,这意味着AP可以卸载的流量也在增加。因此,MNO的效益将不断增加。类似地,可以发现,随着MU数量的增加,GWSM仍然比随机获胜者选择方法执行得更好,特别是当AP的数量较大时。FIG. 5 is a schematic diagram of the benefits of the MNO under different numbers of MUs according to an embodiment of the present invention. 1) and the random winner selection method (S.2), the change of the return of MNO with the increase of the number of MU. As the number of MUs increases, the total traffic that the MUs will request will continue to increase, which means that the traffic that the AP can offload also increases. Therefore, the benefits of MNOs will continue to increase. Similarly, it can be found that as the number of MUs increases, GWSM still performs better than the random winner selection method, especially when the number of APs is large.
图6为本发明实施例提供的在不同MU的数量下MNO的流量负载示意图,图6显示了当AP的数量设置为|K|=30,AP的可用频谱资源块为20MHz时,GWSM(S.1)和随机优胜者选择方法(S.2)中MNO流量负载随着MU个数增加的变化情况。随着MU数量的增加,MU要求更多的流量需求,因此MNO的流量负载将不断增加。可以发现,GWSM与随机优胜者选择方法相比,随着MU的数量增加,GWSM中的MNO的业务负载增加最慢,这表明GWSM表现最佳。FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of the traffic load of the MNO under different numbers of MUs according to an embodiment of the present invention. .1) and the random winner selection method (S.2), the change of MNO traffic load with the increase of the number of MUs. As the number of MUs increases, the MUs demand more traffic, so the traffic load of the MNO will continue to increase. It can be found that compared with the random winner selection method, as the number of MUs increases, the traffic load of MNOs in GWSM increases the slowest, which indicates that GWSM performs the best.
本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载方法,从商业角度将Wi-Fi卸载问题转化为基于反向拍卖的激励问题,旨在最大化MNO的收益,并且提出一种新的基于延迟约束和反向竞价的激励机制来刺激Wi-Fi接入点参与数据卸载过程。The data offloading method based on the greedy algorithm and the reverse auction provided by the embodiment of the present invention transforms the Wi-Fi offloading problem into the incentive problem based on the reverse auction from a commercial point of view, aiming at maximizing the income of the MNO, and proposes a new The incentive mechanism based on delay constraints and reverse bidding to stimulate Wi-Fi access points to participate in the data offloading process.
本发明实施例通过考虑不同应用的延迟约束将优化问题建模为非线性整数规划问题,并引入一种低复杂度算法:贪婪获胜者选择算法(Greedy Winner SelectionMethod,GWSM)来解决优化问题。The embodiments of the present invention model the optimization problem as a nonlinear integer programming problem by considering delay constraints of different applications, and introduce a low-complexity algorithm: Greedy Winner Selection Method (GWSM) to solve the optimization problem.
本发明实施例提出了一种新颖的基于标准Vickrey-Clarke-Groves(VCG)机制的支付规则,该规则可以保证GWSM的个体合理性和真实性。The embodiment of the present invention proposes a novel payment rule based on the standard Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) mechanism, which can ensure the individual rationality and authenticity of the GWSM.
通过仿真实验表明,在不同场景下本发明提出的GWSM在MNO的效益和流量负载方面比随机获胜者选择算法表现更好。Simulation experiments show that the GWSM proposed by the present invention performs better than the random winner selection algorithm in terms of MNO benefit and traffic load in different scenarios.
基于上述任一实施例,图7为本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载装置示意图,如图7所示,本发明实施例提供一种基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载装置,包括获取模块701、模型构建模块702和分配模块703,其中:Based on any of the foregoing embodiments, FIG. 7 is a schematic diagram of a data unloading apparatus based on a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 7 , an embodiment of the present invention provides a greedy algorithm and a reverse auction-based data unloading device The data unloading apparatus includes an
获取模块701用于获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;模型构建模块702用于基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;分配模块703用于利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。The obtaining
本发明实施例提供的基于贪婪算法和反向拍卖的数据卸载装置,从商业角度将Wi-Fi卸载问题转化为基于反向拍卖的激励问题,旨在最大化MNO的收益,并且提出一种新的基于延迟约束和反向竞价的激励机制来刺激Wi-Fi接入点参与数据卸载过程。The data offloading device based on the greedy algorithm and the reverse auction provided by the embodiment of the present invention transforms the Wi-Fi offloading problem into the incentive problem based on the reverse auction from a commercial point of view, aiming at maximizing the income of the MNO, and proposes a new The incentive mechanism based on delay constraints and reverse bidding to stimulate Wi-Fi access points to participate in the data offloading process.
图8为本发明实施例提供的电子设备的结构示意图,如图8所示,该电子设备包括:处理器(processor)801、通信接口(Communications Interface)802、存储器(memory)803和通信总线804,其中,处理器801,通信接口802,存储器803通过通信总线804完成相互间的通信。处理器801和存储器802通过总线803完成相互间的通信。处理器801可以调用存储器803中的逻辑指令,以执行如下方法:FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of an electronic device provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 8 , the electronic device includes: a processor (processor) 801, a communications interface (Communications Interface) 802, a memory (memory) 803, and a
获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;Obtain the maximum delay that can be tolerated by the application in each mobile user MU;
基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;A reverse auction optimization algorithm model is constructed based on the maximum delay. The goal of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model is to maximize the revenue of the operator MNO. The constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model include ensuring that each MU has a The transmission delay does not exceed the corresponding maximum delay threshold;
利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。A greedy winner selection algorithm is used to select the winning WiFi access point to assign to the MU.
此外,上述的存储器中的逻辑指令可以通过软件功能单元的形式实现并作为独立的产品销售或使用时,可以存储在一个计算机可读取存储介质中。基于这样的理解,本发明的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分或者该技术方案的部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品存储在一个存储介质中,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以是个人计算机,服务器,或者网络设备等)执行本发明各个实施例所述方法的全部或部分步骤。而前述的存储介质包括:U盘、移动硬盘、只读存储器(ROM,Read-Only Memory)、随机存取存储器(RAM,Random Access Memory)、磁碟或者光盘等各种可以存储程序代码的介质。In addition, the above-mentioned logic instructions in the memory can be implemented in the form of software functional units and can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium when sold or used as an independent product. Based on this understanding, the technical solution of the present invention can be embodied in the form of a software product in essence, or the part that contributes to the prior art or the part of the technical solution. The computer software product is stored in a storage medium, including Several instructions are used to cause a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device, etc.) to execute all or part of the steps of the methods described in the various embodiments of the present invention. The aforementioned storage medium includes: U disk, mobile hard disk, Read-Only Memory (ROM, Read-Only Memory), Random Access Memory (RAM, Random Access Memory), magnetic disk or optical disk and other media that can store program codes .
进一步地,本发明实施例提供一种计算机程序产品,所述计算机程序产品包括存储在非暂态计算机可读存储介质上的计算机程序,所述计算机程序包括程序指令,当所述程序指令被计算机执行时,计算机能够执行上述各方法实施例中的步骤,例如包括:Further, an embodiment of the present invention provides a computer program product, the computer program product includes a computer program stored on a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium, the computer program includes program instructions, and when the program instructions are executed by a computer When executed, the computer can execute the steps in the above method embodiments, for example, including:
获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;Obtain the maximum delay that can be tolerated by the application in each mobile user MU;
基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;A reverse auction optimization algorithm model is constructed based on the maximum delay. The goal of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model is to maximize the revenue of the operator MNO. The constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model include ensuring that each MU has a The transmission delay does not exceed the corresponding maximum delay threshold;
利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。A greedy winner selection algorithm is used to select the winning WiFi access point to assign to the MU.
进一步地,本发明实施例提供一种非暂态计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,当所述计算机程序被处理器执行时,实现上述各方法实施例中的步骤,例如包括:Further, an embodiment of the present invention provides a non-transitory computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored. When the computer program is executed by a processor, the steps in the above method embodiments are implemented, for example, including:
获取每一移动用户MU中的应用程序可容忍的最大时延;Obtain the maximum delay that can be tolerated by the application in each mobile user MU;
基于所述最大时延构建反向拍卖优化算法模型,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的目标是最大化运营商MNO的收益,所述反向拍卖优化算法模型的约束条件包括确保每一MU的传输延迟不超过对应的最大延迟阈值;A reverse auction optimization algorithm model is constructed based on the maximum delay. The goal of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model is to maximize the revenue of the operator MNO. The constraints of the reverse auction optimization algorithm model include ensuring that each MU has a The transmission delay does not exceed the corresponding maximum delay threshold;
利用贪婪获胜者选择算法选择获胜WiFi接入点分配给MU。A greedy winner selection algorithm is used to select the winning WiFi access point to assign to the MU.
以上所描述的装置实施例仅仅是示意性的,其中所述作为分离部件说明的单元可以是或者也可以不是物理上分开的,作为单元显示的部件可以是或者也可以不是物理单元,即可以位于一个地方,或者也可以分布到多个网络单元上。可以根据实际的需要选择其中的部分或者全部模块来实现本实施例方案的目的。本领域普通技术人员在不付出创造性的劳动的情况下,即可以理解并实施。The device embodiments described above are only illustrative, wherein the units described as separate components may or may not be physically separated, and the components shown as units may or may not be physical units, that is, they may be located in One place, or it can be distributed over multiple network elements. Some or all of the modules may be selected according to actual needs to achieve the purpose of the solution in this embodiment. Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand and implement it without creative effort.
通过以上的实施方式的描述,本领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到各实施方式可借助软件加必需的通用硬件平台的方式来实现,当然也可以通过硬件。基于这样的理解,上述技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中,如ROM/RAM、磁碟、光盘等,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以是个人计算机,服务器,或者网络设备等)执行各个实施例或者实施例的某些部分所述的方法。From the description of the above embodiments, those skilled in the art can clearly understand that each embodiment can be implemented by means of software plus a necessary general hardware platform, and certainly can also be implemented by hardware. Based on this understanding, the above-mentioned technical solutions can be embodied in the form of software products in essence or the parts that make contributions to the prior art, and the computer software products can be stored in computer-readable storage media, such as ROM/RAM, magnetic A disc, an optical disc, etc., includes several instructions for causing a computer device (which may be a personal computer, a server, or a network device, etc.) to perform the methods described in various embodiments or some parts of the embodiments.
最后应说明的是:以上实施例仅用以说明本发明的技术方案,而非对其限制;尽管参照前述实施例对本发明进行了详细的说明,本领域的普通技术人员应当理解:其依然可以对前述各实施例所记载的技术方案进行修改,或者对其中部分技术特征进行等同替换;而这些修改或者替换,并不使相应技术方案的本质脱离本发明各实施例技术方案的精神和范围。Finally, it should be noted that the above embodiments are only used to illustrate the technical solutions of the present invention, but not to limit them; although the present invention has been described in detail with reference to the foregoing embodiments, those of ordinary skill in the art should understand that it can still be The technical solutions described in the foregoing embodiments are modified, or some technical features thereof are equivalently replaced; and these modifications or replacements do not make the essence of the corresponding technical solutions deviate from the spirit and scope of the technical solutions of the embodiments of the present invention.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911132825.8ACN110856227B (en) | 2019-11-19 | 2019-11-19 | Data unloading method based on greedy algorithm and reverse auction |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911132825.8ACN110856227B (en) | 2019-11-19 | 2019-11-19 | Data unloading method based on greedy algorithm and reverse auction |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110856227A CN110856227A (en) | 2020-02-28 |
| CN110856227Btrue CN110856227B (en) | 2021-08-10 |
Family
ID=69602311
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911132825.8AActiveCN110856227B (en) | 2019-11-19 | 2019-11-19 | Data unloading method based on greedy algorithm and reverse auction |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110856227B (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111639993B (en)* | 2020-05-29 | 2023-06-09 | 郑州轻工业大学 | A Mobile Data Offloading and Pricing Method Based on Multi-item Auction Mechanism |
| CN112492656B (en)* | 2020-11-25 | 2022-08-05 | 重庆邮电大学 | Wireless network access point switching method based on reinforcement learning |
| CN113115367B (en)* | 2021-03-23 | 2022-09-02 | 三峡大学 | Data unloading excitation method and device based on greedy assistant selection algorithm |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106376058A (en)* | 2015-07-24 | 2017-02-01 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | A Distributed Method for Dynamic Access Point Selection in Wireless Networks |
| CN107426804A (en)* | 2017-06-06 | 2017-12-01 | 重庆邮电大学 | A kind of wlan system WAP energy-saving control method based on auction mechanism |
| CN109302709A (en)* | 2018-09-14 | 2019-02-01 | 重庆邮电大学 | Task offloading and resource allocation strategy of Internet of Vehicles for mobile edge computing |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9723532B2 (en)* | 2013-12-09 | 2017-08-01 | Nec Corporation | Intelligent WiFi-offloading for next-generation mobile networks |
| US20170230871A1 (en)* | 2016-02-04 | 2017-08-10 | Sooktha Consulting Private Limited | Cellular Wireless Access Data Offload System |
| US20180077587A1 (en)* | 2016-09-12 | 2018-03-15 | Telefonaktiebolaget Lm Ericsson (Publ) | Apparatus and method for assigning cells to coordination sets for optimizing coordination performance |
- 2019
- 2019-11-19CNCN201911132825.8Apatent/CN110856227B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN106376058A (en)* | 2015-07-24 | 2017-02-01 | 上海贝尔股份有限公司 | A Distributed Method for Dynamic Access Point Selection in Wireless Networks |
| CN107426804A (en)* | 2017-06-06 | 2017-12-01 | 重庆邮电大学 | A kind of wlan system WAP energy-saving control method based on auction mechanism |
| CN109302709A (en)* | 2018-09-14 | 2019-02-01 | 重庆邮电大学 | Task offloading and resource allocation strategy of Internet of Vehicles for mobile edge computing |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110856227A (en) | 2020-02-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Zhou et al. | DRAIM: A novel delay-constraint and reverse auction-based incentive mechanism for WiFi offloading | |
| CN110856228B (en) | Data unloading method based on dynamic programming algorithm and reverse auction | |
| CN113228600B (en) | Method and apparatus for stimulating participation in a mist network | |
| Wang et al. | TODA: Truthful online double auction for spectrum allocation in wireless networks | |
| CN110856227B (en) | Data unloading method based on greedy algorithm and reverse auction | |
| Bourdena et al. | Efficient radio resource management algorithms in opportunistic cognitive radio networks | |
| Zhang et al. | A double auction mechanism for virtual resource allocation in SDN-based cellular network | |
| CN106604282B (en) | Small cell micro base station spectrum auction method with power distribution and beam forming | |
| Wu et al. | Collusion-resistant multi-winner spectrum auction for cognitive radio networks | |
| Liu et al. | Multi-item auction based mechanism for mobile data offloading: A robust optimization approach | |
| CN113703970A (en) | Auction mechanism-based server resource allocation method, device, equipment and medium | |
| WO2019213950A1 (en) | A sequential auction game for qos-aware user association in heterogeneous cellular networks | |
| Noreen et al. | A review on game-theoretic incentive mechanisms for mobile data offloading in heterogeneous networks | |
| Song et al. | Incentive framework for mobile data offloading market under QoE‐aware users | |
| Ndikumana et al. | Pricing mechanism for virtualized heterogeneous resources in wireless network virtualization | |
| Zhang et al. | Competitive auctions for cost-aware cellular traffic offloading with optimized capacity gain | |
| Shajaiah et al. | An auction-based resource leasing mechanism for under-utilized spectrum | |
| Gupta et al. | Efficient spectrum sharing in 5G and beyond network: a survey | |
| CN118071377A (en) | A UAV on-demand spectrum trading system and method based on double-layer Stackelberg game | |
| CN106658518A (en) | Variable step stepping-type frequency spectrum auction method for femtocell base stations in two-layer heterogeneous network | |
| Tong et al. | Deep reinforcement learning based multi-attribute auction model for resource allocation in vehicular AIGC services | |
| JP7335592B2 (en) | Program and Server | |
| Du et al. | Second-price auction based cognitive traffic offloading in heterogeneous networks | |
| Shafiq et al. | Adaptive auction framework for spectrum market in cognitive radio networks | |
| Parzy et al. | On-line spectrum auctions in TV white spaces for supporting mobile services—A practical manual |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| OL01 | Intention to license declared | ||
| OL01 | Intention to license declared |