CN110794392A - Vehicle positioning method and device, vehicle and storage medium - Google Patents
Vehicle positioning method and device, vehicle and storage mediumDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110794392A CN110794392ACN201910978766.XACN201910978766ACN110794392ACN 110794392 ACN110794392 ACN 110794392ACN 201910978766 ACN201910978766 ACN 201910978766ACN 110794392 ACN110794392 ACN 110794392A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- precision map
- point cloud
- cloud data
- target object
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/02—Systems using reflection of radio waves, e.g. primary radar systems; Analogous systems
- G01S13/06—Systems determining position data of a target
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01S—RADIO DIRECTION-FINDING; RADIO NAVIGATION; DETERMINING DISTANCE OR VELOCITY BY USE OF RADIO WAVES; LOCATING OR PRESENCE-DETECTING BY USE OF THE REFLECTION OR RERADIATION OF RADIO WAVES; ANALOGOUS ARRANGEMENTS USING OTHER WAVES
- G01S13/00—Systems using the reflection or reradiation of radio waves, e.g. radar systems; Analogous systems using reflection or reradiation of waves whose nature or wavelength is irrelevant or unspecified
- G01S13/88—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications
- G01S13/93—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes
- G01S13/931—Radar or analogous systems specially adapted for specific applications for anti-collision purposes of land vehicles
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Radar, Positioning & Navigation (AREA)
- Remote Sensing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明实施例涉及智能驾驶领域,尤其涉及一种车辆定位方法、装置、车辆及存储介质。Embodiments of the present invention relate to the field of intelligent driving, and in particular, to a vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle, and storage medium.
背景技术Background technique
智能驾驶定位技术可以帮助汽车实现准确定位,进而通过精确的路径规划实现无人驾驶。同时,智能驾驶定位技术也是人工智能技术的一个部分,是实现智能驾驶最重要的一环。Intelligent driving positioning technology can help cars achieve accurate positioning, and then realize unmanned driving through precise path planning. At the same time, intelligent driving positioning technology is also a part of artificial intelligence technology, which is the most important part of realizing intelligent driving.
目前,可以通过基于摄像头的同时定位与地图构建(Simultaneous Localizationand Mapping,SLAM)技术对车辆进行定位,主要原理是通过摄像头在没有环境先验信息的情况下,于运动过程中建立环境的模型,同时估计车辆的运动。At present, the vehicle can be positioned through the camera-based Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) technology. Estimate the motion of the vehicle.
但是,上述方式过于依赖摄像头,当天气条件较为恶劣时,无法实现定位,可靠性较低,同时,上述方式的定位精度也较低。However, the above method relies too much on the camera. When the weather conditions are relatively bad, the positioning cannot be achieved, and the reliability is low. At the same time, the positioning accuracy of the above method is also low.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明提供一种车辆定位方法、装置、车辆及存储介质,以解决目前车辆定位方式可靠性低以及定位精度低的技术问题。The present invention provides a vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle and storage medium to solve the technical problems of low reliability and low positioning accuracy of the current vehicle positioning method.
第一方面,本发明实施例提供一种车辆定位方法,包括:In a first aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a vehicle positioning method, including:
获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于所述车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据;acquiring the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar disposed on the vehicle during the driving of the vehicle;
根据所述目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定所述目标点云数据对应的目标物体在所述高精度地图中的位置;其中,所述高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子;According to the target point cloud data and the pre-established high-precision map, determine the position of the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in the high-precision map; The feature descriptor determined by the point cloud data;
根据所述目标物体在所述高精度地图中的位置以及所述目标点云数据,确定所述车辆在所述高精度地图中的位置。According to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data, the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map is determined.
第二方面,本发明实施例提供一种车辆定位装置,包括:In a second aspect, an embodiment of the present invention provides a vehicle positioning device, including:
获取模块,用于获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于所述车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据;an acquisition module, configured to acquire the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar disposed on the vehicle during the driving of the vehicle;
第一确定模块,用于根据所述目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定所述目标点云数据对应的目标物体在所述高精度地图中的位置;其中,所述高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子;a first determination module, configured to determine the position of the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in the high-precision map according to the target point cloud data and the pre-established high-precision map; wherein, the high-precision map Including feature descriptors determined according to point cloud data collected by millimeter-wave radar;
第二确定模块,用于根据所述目标物体在所述高精度地图中的位置以及所述目标点云数据,确定所述车辆在所述高精度地图中的位置。The second determining module is configured to determine the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map according to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data.
第三方面,本发明实施例还提供了一种车辆,所述车辆包括:In a third aspect, an embodiment of the present invention further provides a vehicle, the vehicle comprising:
一个或多个处理器;one or more processors;
存储器,用于存储一个或多个程序;memory for storing one or more programs;
一个或多个毫米波雷达;one or more millimeter wave radars;
当所述一个或多个程序被所述一个或多个处理器执行,使得所述一个或多个处理器实现如第一方面提供的车辆定位方法。When the one or more programs are executed by the one or more processors, the one or more processors implement the vehicle positioning method provided by the first aspect.
第四方面,本发明实施例还提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,其上存储有计算机程序,该程序被处理器执行时实现如第一方面提供的车辆定位方法。In a fourth aspect, an embodiment of the present invention further provides a computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program is stored, and when the program is executed by a processor, implements the vehicle positioning method provided in the first aspect.
本实施例提供一种车辆定位方法、装置、车辆及存储介质,该方法包括:获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据,根据目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置,其中,高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子,根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标点云数据,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。实现了根据毫米波雷达采集的目标点云数据确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置,相较于现有技术,成本较低、定位精度较高以及定位的可靠性较高。This embodiment provides a vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle, and storage medium. The method includes: acquiring target point cloud data collected by a millimeter-wave radar installed on the vehicle during the driving process of the vehicle; The established high-precision map determines the position of the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in the high-precision map. The high-precision map includes the feature descriptors determined according to the point cloud data collected by the millimeter wave radar. The position in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data determine the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map. The position of the vehicle in the high-precision map is determined according to the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar. Compared with the prior art, the cost is lower, the positioning accuracy is higher, and the positioning reliability is higher.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1A为本发明提供的车辆定位方法实施例应用场景的示意图;1A is a schematic diagram of an application scenario of an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method provided by the present invention;
图1B为本发明提供的车辆的示意图;1B is a schematic diagram of a vehicle provided by the present invention;
图2为本发明提供的车辆定位方法实施例的流程示意图;2 is a schematic flowchart of an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method provided by the present invention;
图3为车辆定位方法实施例中构建的未闭合的高精度地图的示意图;3 is a schematic diagram of an unclosed high-precision map constructed in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图4A为车辆定位方法实施例中进行表面法线估计前的点云数据示意图;4A is a schematic diagram of point cloud data before surface normal estimation is performed in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图4B为车辆定位方法实施例中进行表面法线估计后的结果示意图;4B is a schematic diagram of a result of performing surface normal estimation in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图5A为车辆定位方法实施例中确定点特征直方图描述子时影响区域的示意图;5A is a schematic diagram of an influence area when determining a point feature histogram descriptor in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图5B为车辆定位方法实施例确定点特征直方图描述子时坐标系的示意图;5B is a schematic diagram of determining a point feature histogram descriptor time coordinate system according to an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图6为车辆定位方法实施例中确定快速点特征直方图描述子时影响区域的示意图;6 is a schematic diagram of an influence area when determining a fast point feature histogram descriptor in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图7A为车辆定位方法实施例中确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置的一种实现方式的示意图;7A is a schematic diagram of an implementation manner of determining the position of a vehicle in a high-precision map in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图7B为车辆定位方法实施例中确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置的另一种实现方式的示意图;7B is a schematic diagram of another implementation manner of determining the position of a vehicle in a high-precision map in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method;
图8为本发明提供的车辆定位装置实施例的结构示意图;8 is a schematic structural diagram of an embodiment of a vehicle positioning device provided by the present invention;
图9为本发明提供的车辆的结构示意图。FIG. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of a vehicle provided by the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图和实施例对本发明作进一步的详细说明。可以理解的是,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用于解释本发明,而非对本发明的限定。另外还需要说明的是,为了便于描述,附图中仅示出了与本发明相关的部分而非全部结构。The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. In addition, it should be noted that, for the convenience of description, the drawings only show some but not all structures related to the present invention.
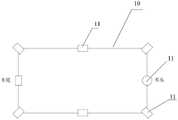
图1A为本发明提供的车辆定位方法实施例应用场景的示意图。图1B为本发明提供的车辆的示意图。如图1B所示,本发明提供的车辆10上安装有毫米波雷达11。其中,一个毫米波雷达11可以安装在车头处,具体可以安装在车头在左右方向的中点处。可选地,两个毫米波雷达11分别安装在车头左右方向的两端,两个毫米波雷达11分别安装在车辆两侧前后方向的中点处,两个毫米波雷达11分别安装在车尾左右方向的两端,一个毫米波雷达11安装在车尾左右方向的中点处。如图1A所示,车辆在行驶过程中,可以通过其上安装的毫米波雷达采集路况信息。本实施例中,毫米波雷达可以采集目标点13对应的目标点云数据。在智能驾驶领域,车辆可以根据毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据确定车辆在高精度地图中位置,实现对车辆的定位。FIG. 1A is a schematic diagram of an application scenario of an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method provided by the present invention. FIG. 1B is a schematic diagram of a vehicle provided by the present invention. As shown in FIG. 1B , the
图2为本发明提供的车辆定位方法实施例的流程示意图。本实施例适用于智能驾驶领域中,对车辆进行定位的场景。本实施例可以由车辆定位装置来执行,该车辆定位装置可以由软件和/或硬件的方式实现,该车辆定位装置可以集成于车辆中。如图2所示,本实施例提供的车辆定位方法包括如下步骤:FIG. 2 is a schematic flowchart of an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method provided by the present invention. This embodiment is applicable to a scenario of positioning a vehicle in the field of intelligent driving. This embodiment may be implemented by a vehicle positioning device, which may be implemented in software and/or hardware, and the vehicle positioning device may be integrated into a vehicle. As shown in FIG. 2 , the vehicle positioning method provided by this embodiment includes the following steps:
步骤201:获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据。Step 201: Acquire target point cloud data collected by a millimeter-wave radar installed on the vehicle during the driving of the vehicle.
具体地,毫米波是一种电磁波,由交变电场和磁场构成,可以在真空、空气和自由空间中传播。其频段比较特殊,频率高于无线电,低于可见光和红外线,频率大致范围是10GHz~200GHz。在这个频段,毫米波相关的特性使其非常适合应用于车载领域。车载领域的毫米波雷达频段主要有三段:24GHz频段、 77GHz频段以及79GHz频段。其中,24GHz频段主要用于汽车的盲点监测、变道辅助。24GHz频段的毫米波雷达可以安装在车辆的后保险杠内,用于监测车辆后方两侧的车道是否有车、可否进行变道。77GHz频段的毫米波雷达主要用来装配在车辆的前保险杠上,探测与前车的距离以及前车的速度,实现紧急制动、自动跟车等主动安全领域的功能。79GHz频段的毫米波雷达具备非常高的分辨率,可以达到5cm。这个分辨率在智能驾驶领域非常有价值,因为智能驾驶汽车要区分行人等诸多精细物体。示例性地,目前一种毫米波雷达的性能参数可以如下所示:频率为76~77GHz,探测距离为0.5~250米,视角为±15°,分辨率为0.5米,相对速度为-75~+60米每秒,速度分辨率为0.6米每秒。本实施例所涉及的毫米波雷达可以是上述任一种频段的毫米波雷达,本实施例对此不做限制。Specifically, millimeter waves are electromagnetic waves composed of alternating electric and magnetic fields that can propagate in vacuum, air, and free space. Its frequency band is relatively special, the frequency is higher than radio, lower than visible light and infrared, and the frequency range is roughly 10GHz ~ 200GHz. In this frequency band, mmWave-related characteristics make it ideal for automotive applications. There are mainly three frequency bands for millimeter-wave radar in the automotive field: the 24GHz frequency band, the 77GHz frequency band, and the 79GHz frequency band. Among them, the 24GHz frequency band is mainly used for blind spot monitoring and lane change assistance of automobiles. The millimeter-wave radar in the 24GHz frequency band can be installed in the rear bumper of the vehicle to monitor whether there are cars in the lanes on both sides of the rear of the vehicle and whether lane changes can be made. The millimeter-wave radar in the 77GHz frequency band is mainly used to be assembled on the front bumper of the vehicle to detect the distance to the vehicle in front and the speed of the vehicle in front, and realize functions in the field of active safety such as emergency braking and automatic following. The millimeter-wave radar in the 79GHz band has a very high resolution and can reach 5cm. This resolution is very valuable in the field of intelligent driving, because intelligent driving cars have to distinguish many fine objects such as pedestrians. Exemplarily, the performance parameters of a current millimeter-wave radar may be as follows: the frequency is 76-77 GHz, the detection distance is 0.5-250 meters, the viewing angle is ±15°, the resolution is 0.5 meters, and the relative velocity is -75-75 +60 meters per second with a velocity resolution of 0.6 meters per second. The millimeter-wave radar involved in this embodiment may be a millimeter-wave radar in any of the foregoing frequency bands, which is not limited in this embodiment.
毫米波雷达通过发射天线发出相应波段的有指向性的毫米波,当毫米波遇到目标点后反射回来,通过接收天线接收反射回来的毫米波。根据毫米波收发之间的时间差测得目标点的位置,延时时间td=2R/C,其中,R为目标点与车辆之间的距离,C为光速。对于目标点的方向角,毫米波雷达的探测原理是:通过毫米波雷达的发射天线发射出毫米波后,遇到目标点反射回来,毫米波雷达并列的接收天线接收反射回来的毫米波。通过收到同一目标点反射回来的毫米波的相位差,就可以计算出目标点相对于车辆的方位角。The millimeter-wave radar emits directional millimeter-waves in the corresponding band through the transmitting antenna. When the millimeter-wave encounters the target point, it is reflected back, and the reflected millimeter-wave is received through the receiving antenna. The position of the target point is measured according to the time difference between millimeter wave transmission and reception, and the delay time td=2R/C, where R is the distance between the target point and the vehicle, and C is the speed of light. For the direction angle of the target point, the detection principle of the millimeter wave radar is: after the millimeter wave is transmitted through the transmitting antenna of the millimeter wave radar, it is reflected back when it encounters the target point, and the receiving antenna of the millimeter wave radar is parallel to receive the reflected millimeter wave. By receiving the phase difference of the millimeter waves reflected from the same target point, the azimuth angle of the target point relative to the vehicle can be calculated.
本实施例中,车辆定位装置具体可以集成于车辆的整车控制器中。在车辆行驶过程中,设置于车辆上的毫米波雷达实时采集目标点云数据。一种实现方式中,车辆定位装置可以主动获取毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据。另一种实现方式中,毫米波雷达将采集到的目标点云数据主动发送给车辆定位装置。In this embodiment, the vehicle positioning device may be specifically integrated into the vehicle controller of the vehicle. During the driving process of the vehicle, the millimeter-wave radar installed on the vehicle collects the target point cloud data in real time. In an implementation manner, the vehicle positioning device can actively acquire the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar. In another implementation manner, the millimeter-wave radar actively sends the collected target point cloud data to the vehicle positioning device.
可选地,本实施例中的目标点云数据可以包括采集到的目标点在车辆坐标系中的坐标值。本实施例中的车辆坐标系是以车辆上的一点为原点建立的坐标系。本实施例中的车辆坐标系可以是三维坐标系,也可以是极坐标系。更具体地,车辆坐标系的原点为车辆的后轴中心点,车辆坐标系的X轴正方向为车辆面向前方时,车辆的左侧方向,Y轴正方向为车辆前进方向,Z轴正方向为车辆的上方方向。Optionally, the target point cloud data in this embodiment may include the collected coordinate values of the target point in the vehicle coordinate system. The vehicle coordinate system in this embodiment is a coordinate system established with a point on the vehicle as the origin. The vehicle coordinate system in this embodiment may be a three-dimensional coordinate system or a polar coordinate system. More specifically, the origin of the vehicle coordinate system is the center point of the rear axle of the vehicle, the positive direction of the X axis of the vehicle coordinate system is the left direction of the vehicle when the vehicle faces forward, the positive direction of the Y axis is the forward direction of the vehicle, and the positive direction of the Z axis the upward direction of the vehicle.
需要说明的是,目标点云数据中可以包括采集到的多个目标点在车辆坐标系中的坐标值。It should be noted that the target point cloud data may include the collected coordinate values of multiple target points in the vehicle coordinate system.
本实施例中毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据对应的目标点为散点,而非确定好的某一物体上的点。这种实现方式,一方面不需要毫米波雷达确定目标点是否为某一物体上的点,降低了成本,另一方面,兼容性较好。In this embodiment, the target points corresponding to the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar are scattered points, rather than points on a determined object. This implementation method, on the one hand, does not require millimeter-wave radar to determine whether the target point is a point on an object, which reduces the cost, and on the other hand, has better compatibility.
步骤202:根据目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置。Step 202: Determine the position of the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in the high-precision map according to the target point cloud data and the pre-established high-precision map.
其中,高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子。Among them, the high-precision map includes feature descriptors determined according to the point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar.
具体地,本实施例中预先建立了高精度地图,具体可以通过设置于采集车上的毫米波雷达采集点云数据。在采集到点云数据后,对这些点云数据进行拼接,形成高精度地图。具体过程为:(1)对点云数据进行聚类,形成多个点云数据集合;(2)从两个点云数据集合中按照同样的关键点选取标准,提取关键点;(3)对选择的所有关键点分别计算其特征描述子;(4)结合特征描述子在两个点云数据集和中的坐标位置,以二者之间的特征和位置的相似度为基础,来估算它们的对应关系,初步估计对应点对;(5)假定数据是有噪声的,除去对拼接有影响的错误的对应点对;(6)利用剩余的正确的对应关系来估算刚体变换,完成点云数据集合的拼接。Specifically, in this embodiment, a high-precision map is pre-established, and the point cloud data can be collected by a millimeter-wave radar installed on the collecting vehicle. After the point cloud data is collected, these point cloud data are spliced to form a high-precision map. The specific process is: (1) clustering point cloud data to form multiple point cloud data sets; (2) extracting key points from the two point cloud data sets according to the same key point selection criteria; (3) pairing All the selected key points calculate their feature descriptors respectively; (4) Combine the coordinate positions of the feature descriptors in the two point cloud datasets and, based on the similarity of the features and positions between the two, to estimate them (5) Assuming that the data is noisy, remove the wrong corresponding point pairs that affect the stitching; (6) Use the remaining correct correspondence to estimate the rigid body transformation and complete the point cloud Concatenation of datasets.
在构建基于毫米波雷达的高精度地图时,要借助全球定位系统(GlobalPositioning System,GPS)对采集车的行驶轨迹进行记录。点云数据经过拼接后形成初始的高精度地图,高精度地图的闭合需要对比车辆的行驶轨迹。因为在拼接过程中点云数据会有角度误差,随着高精度地图的构建误差累积会逐渐增大,因此需要借助GPS记录的行车轨迹对初始的高精度地图进行修正,完成高精度地图的闭合。图3为车辆定位方法实施例中构建的未闭合的高精度地图的示意图。如图3所示,深色线条为GPS记录的车辆轨迹,浅色线条为通过点云数据构建的未闭合的初始高精度地图。When constructing a high-precision map based on millimeter-wave radar, the driving trajectory of the collecting vehicle should be recorded with the help of a global positioning system (Global Positioning System, GPS). After the point cloud data is spliced, an initial high-precision map is formed, and the closing of the high-precision map needs to compare the driving trajectory of the vehicle. Because the point cloud data will have angular errors during the splicing process, and the accumulation of errors in the construction of the high-precision map will gradually increase. Therefore, it is necessary to use the driving track recorded by GPS to correct the initial high-precision map to complete the closure of the high-precision map. . FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram of an unclosed high-precision map constructed in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method. As shown in Figure 3, the dark line is the vehicle trajectory recorded by GPS, and the light line is the unclosed initial high-precision map constructed from point cloud data.
进一步地,为了提高后续车辆定位的效率,高精度地图中还包括点云数据的特征描述子。高精度地图中还可以包括物体的尺寸信息。Further, in order to improve the efficiency of subsequent vehicle positioning, the high-precision map also includes feature descriptors of point cloud data. The size information of objects can also be included in the high-resolution map.
可选地,步骤202的具体实现过程可以是:从目标点云数据中,确定关键点云数据;根据点云数据特征描述子提取算法,确定关键点云数据的特征描述子;根据关键点云数据的特征描述子,以及,高精度地图中的特征描述子,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置。Optionally, the specific implementation process of step 202 may be: from the target point cloud data, determine the key point cloud data; according to the point cloud data feature descriptor extraction algorithm, determine the feature descriptor of the key point cloud data; according to the key point cloud data The feature descriptor of the data, and the feature descriptor in the high-precision map, determine the position of the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in the high-precision map.
可以根据关键点提取标准从目标点云数据中确定关键点云数据。本实施例中的点云数据特征描述子提取算法包括如下四种算法:估计点云的表面法线、点特征直方图(Point Feature Histograms,PFH)描述子、快速点特征直方图(Fast Point FeatureHistograms,FPFH)以及视点特征直方图(Viewpoint Feature Histogram,VFH)描述子。以下对这四种算法进行详细描述。The key point cloud data can be determined from the target point cloud data according to the key point extraction criteria. The feature descriptor extraction algorithm for point cloud data in this embodiment includes the following four algorithms: estimating the surface normal of the point cloud, Point Feature Histograms (PFH) descriptors, Fast Point Feature Histograms (Fast Point Feature Histograms) , FPFH) and the Viewpoint Feature Histogram (VFH) descriptor. These four algorithms are described in detail below.
(1)估计点云的表面法线:(1) Estimate the surface normal of the point cloud:
表面法线是几何体表面的重要属性,对于一个已知的几何体表面,根据垂直于点表面的矢量,可以推断表面某一点的法线方向。点云数据集在真实物体的表面表现为一组定点样本,本实施例中可以直接从关键点云数据中近似推断表面法线。The surface normal is an important property of the geometric surface. For a known geometric surface, the normal direction of a point on the surface can be inferred based on the vector perpendicular to the surface of the point. The point cloud data set is represented as a set of fixed-point samples on the surface of the real object. In this embodiment, the surface normal can be approximately inferred directly from the key point cloud data.
确定表面一点法线的问题近似于估计表面的一个相切面法线的问题,因此转换过来以后就变成一个最小二乘法平面拟合估计问题。因此估计表面法线的解决方案就变成了分析一个协方差矩阵的特征矢量和特征值,这个协方差矩阵从查询点的近邻元素中创建。这里的查询点指的是关键点云数据。更具体地说,对于每一个点Pi,对应的协方差矩阵C,公式如下所示:The problem of determining a point normal to a surface is similar to the problem of estimating a tangent normal to a surface, so after conversion it becomes a least squares plane fitting estimation problem. So the solution for estimating surface normals becomes to analyze the eigenvectors and eigenvalues of a covariance matrix created from the nearest neighbors of the query point. The query point here refers to the key point cloud data. More specifically, for each point Pi, the corresponding covariance matrix C, the formula is as follows:
其中,k是点Pi邻近点的数目,表示最近邻元素的三维质心,λj是协方差矩阵的第j个特征值,是第j个特征向量。where k is the number of neighboring points of point Pi, represents the three-dimensional centroid of the nearest neighbor element, λj is thejth eigenvalue of the covariance matrix, is the jth eigenvector.
图4A为车辆定位方法实施例中进行表面法线估计前的点云数据示意图。4A is a schematic diagram of point cloud data before surface normal estimation is performed in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method.
图4B为车辆定位方法实施例中进行表面法线估计后的结果示意图。FIG. 4B is a schematic diagram of a result of performing surface normal estimation in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method.
(2)PFH描述子:(2) PFH descriptor:
PFH与坐标轴的三维数据和表面法线有关,因此可以更好的用来描述点云数据集合的三维特征。PFH计算方式通过参数化查询点与邻域点之间的空间差异,并形成一个多维直方图对查询点的k邻域几何属性进行描述。直方图所在的高维超空间为特征表示提供了一个可度量的信息空间,对点云对应曲面的6 维姿态来说它具有不变性,并且在不同的采样密度或邻域的噪音等级下具有鲁棒性。PFH表示法是基于查询点与其k邻域之间的关系以及它们的估计法线,简言之,它考虑估计法线方向之间所有的相互作用,试图捕获最好的样本表面变化情况,以描述样本的几何特征。因此,特征超空间的合成取决于每个点的表面法线估计的质量。图5A为车辆定位方法实施例中确定点特征直方图描述子时影响区域的示意图。如图5A所示,表示的是一个查询点(Pq)的PFH计算的影响区域,Pq位于在圆球的中间位置,半径为r,Pq的所有k邻元素(即与点 Pq的距离小于半径r的所有点)全部互相连接在一个网络中。最终的PFH描述子通过计算邻域内所有两点之间关系而得到的直方图。PFH is related to the three-dimensional data of the coordinate axis and the surface normal, so it can be better used to describe the three-dimensional characteristics of the point cloud data set. The PFH calculation method describes the geometric properties of the k-neighborhood of the query point by parameterizing the spatial difference between the query point and the neighborhood point, and forming a multi-dimensional histogram. The high-dimensional hyperspace in which the histogram resides provides a measurable information space for feature representation, which is invariant to the 6-dimensional pose of the surface corresponding to the point cloud and robust to different sampling densities or noise levels in the neighborhood sex. The PFH notation is based on the relationship between query points and their k-neighbors and their estimated normals. In short, it considers all interactions between the estimated normal directions, trying to capture the best case of sample surface variation to Describe the geometrical features of the sample. Therefore, the synthesis of the feature hyperspace depends on the quality of the surface normal estimates for each point. FIG. 5A is a schematic diagram of an influence area when determining a point feature histogram descriptor in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method. As shown in Figure 5A, it represents the influence area of the PFH calculation of a query point (Pq ), Pq is located in the middle of the sphere, the radius is r, and all k-neighbors of Pq (that is, with the point Pq ) All points whose distance is less than radius r) are all connected to each other in a network. The final PFH descriptor is a histogram obtained by computing the relationship between all two points in the neighborhood.
图5B为车辆定位方法实施例确定点特征直方图描述子时坐标系的示意图。如图5B所示,为了计算两点Pi和Pj及与它们对应的法线ni和nj之间的相对偏差,在其中的一个点上定义一个固定的局部坐标系。FIG. 5B is a schematic diagram of determining a point feature histogram describing a sub-time coordinate system according to an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method. As shown in Fig. 5B, in order to calculate the relative deviation between two points Pi and Pj and their corresponding normalsni and nj , a fixed local coordinate system is defined on one of the points.
u=nsu=ns
u=nsu=ns
w=u×vw=u×v
使用图5B中u-v-w坐标系,法线ns和nt之间的偏差可以用一组角度来表示,如下所示:Using the uvw coordinate system in Figure 5B, the deviation between the normalsns andnt can be represented by a set of angles as follows:
α=v·ntα=v·nt
θ=arctan(w·nt,u·nt)θ=arctan(w·nt , u·nt )
其中,d是两点Ps和Pt之间的欧氏距离,d=||Pt–Ps||2。计算k邻域内的每一对点的四组值。Among them, d is the Euclidean distance between two points Ps and Pt, d=||Pt –Ps ||2 . Compute four sets of values for each pair of points within the k neighborhood.
为查询点创建最终的PFH描述子,所有的四元组将会以某种统计的方式放进直方图中,这个过程首先把每个特征值范围划分为b个子区间,并统计落在每个子区间的点数目,因为四分之三的特征在上述中为法线之间的角度计量,在三角化圆上可以将它们的参数值非常容易地归一到相同的区间内。一个统计的例子是:把每个特征区间划分成等分的相同数目,为此在一个完全关联的空间内创建有b4个区间的直方图。在这个空间中,一个直方图中某一区间统计个数的增一对应一个点的4个特征值。To create the final PFH descriptor for the query point, all quadruplets will be put into the histogram in some statistical way. This process first divides each eigenvalue range into b sub-intervals, and counts the fall in each sub-interval The number of points in the interval, since three-quarters of the features are measured in the angle between the normals in the above, their parameter values can be very easily normalized to the same interval on the triangulation circle. A statistical example is: dividing each feature interval into equal numbers of equal parts, creating a histogram with b4 intervals in a fully associative space for this. In this space, an increase in the number of statistics in a certain interval in a histogram corresponds to the 4 eigenvalues of a point.
综上所述,计算PFH描述子的过程中,对点云数据P中的每个点p实际计算过程为:得到p点的最近邻元素;对于邻域内的每对点,计算其三个角度特征参数值;将所有结果统计到一个输出直方图中。To sum up, in the process of calculating the PFH descriptor, the actual calculation process for each point p in the point cloud data P is: to obtain the nearest neighbor element of point p; for each pair of points in the neighborhood, calculate its three angles Feature parameter values; count all results into an output histogram.
(3)FPFH描述子:(3) FPFH descriptor:
已知点云数据P中有n个点,在它的PFH的理论计算中k是点云P中每个点p计算特征向量时考虑的邻域数量。实际应用中,密集点云的PFH的计算需要大量计算资源。因此将PFH计算方式进行简化后,可以得到FPFH来描述点云的特征。It is known that there are n points in the point cloud data P, and in the theoretical calculation of its PFH, k is the number of neighborhoods considered when calculating the feature vector of each point p in the point cloud P. In practical applications, the calculation of PFH of dense point clouds requires a lot of computing resources. Therefore, after the PFH calculation method is simplified, the FPFH can be obtained to describe the characteristics of the point cloud.
为了简化直方图的特征计算,我们执行以下过程:To simplify feature computation for histograms, we perform the following process:
第一步:对于每一个查询点,计算这个点和它的邻域点之间的一个元组,称之为简化的点特征直方图(Simple Point Feature Histograms,SPFH);Step 1: For each query point, calculate a tuple between this point and its neighbor points, called Simple Point Feature Histograms (SPFH);
第二步,重新确定每个点的k邻域,使用邻近的SPFH值来计算的最终直方图(称为FPFH),公式如下:The second step is to re-determine the k-neighborhood of each point, and use the adjacent SPFH values to calculate the final histogram (called FPFH), the formula is as follows:
上式中,权重wk在一些给定的度量空间中,表示查询点Pq和其邻近点Pk之间的距离,因此可用来评定一对点(Pq,Pk)。图6为车辆定位方法实施例中确定快速点特征直方图描述子时影响区域的示意图。In the above formula, the weight wk represents the distance between the query point Pq and its neighboring point Pk in some given metric space, so it can be used to evaluate a pair of points (Pq , Pk ). FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of an influence area when determining a fast point feature histogram descriptor in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method.
因此,对于一个已知查询点,这个算法首先只利用Pq和它邻域点之间对应对(图6以线段31来说明),来估计它的SPFH值,很明显这样比PFH的标准计算少了邻域点之间的互联。点云数据集中的所有点都要执行这一计算获取 SPFH,接下来使用它的邻近点Pk的SPFH值和Pq点的SPFH值重新权重计算,从而得到Pq点的最终FPFH值。Therefore, for a known query point, the algorithm first only uses the correspondence between Pq and its neighbor points (illustrated by
(4)VFH描述子:(4) VFH descriptor:
VFH描述子主要应用在点云聚类识别和六自由度位姿估计问题上。VFH描述子源于FPFH描述子。通过以下两种计算来构造特征,以应用于目标识别问题和位姿估计:(1)扩展FPFH,使其利用整个点云对象来进行计算估计,在计算FPFH时以物体中心点与物体表面其他所有点之间的点对作为计算单元; (2)添加视点方向与每个点估计法线之间额外的统计信息,在FPFH计算中将视点方向变量直接融入到相对法线角计算当中。The VFH descriptor is mainly used in point cloud clustering recognition and 6DOF pose estimation. The VFH descriptor is derived from the FPFH descriptor. Features are constructed by the following two calculations to apply to target recognition problems and pose estimation: (1) Extend FPFH so that it uses the entire point cloud object for computational estimation, and when calculating FPFH, the center point of the object and the surface of the object are used for other calculations. The point pairs between all points are used as calculation units; (2) Additional statistical information between the viewpoint direction and the estimated normal of each point is added, and the viewpoint direction variable is directly integrated into the relative normal angle calculation in the FPFH calculation.
通过统计视点方向与每个法线之间角度的直方图来计算视点相关的特征分量。并不是每条法线的视角,因为法线的视角在尺度变换下具有可变性,此处指的是平移视点到查询点后的视点方向和每条法线间的角度。第二组特征分量就是PFH中讲述的三个角度,现在测量的是在中心点的视点方向和每条表面法线之间的角度。VFH的独特性主要体现以下两方面:一个视点方向相关的分量以及一个包含扩展FPFH的描述表面形状的分量。The viewpoint-dependent feature components are calculated by counting the histogram of the angle between the viewpoint direction and each normal. It is not the viewpoint of each normal, because the viewpoint of the normal is variable under scale transformation, which refers to the viewpoint direction after translating the viewpoint to the query point and the angle between each normal. The second set of characteristic components are the three angles described in PFH, which now measure the angle between the viewpoint direction at the center point and each surface normal. The uniqueness of the VFH is mainly reflected in the following two aspects: a component related to the viewpoint direction and a component that describes the surface shape including the extended FPFH.
通过上述四种方式中的任一种方式计算出关键点云数据的特征描述子之后,根据该关键点云数据的特征描述子,以及,高精度地图中的特征描述子,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置。通过应用一个估计得到的表示平移和旋转的4*4刚体变换矩阵来使一个点云数据集精确的与另一个点云数据集进行配准。具体过程可以是:结合特征描述子在两个数据集中的坐标位置,以二者之间特征和位置的相似度为基础,来估算它们的对应关系,初步估计对应点对;假定数据是有噪声的,除去对配准有影响的错误的对应点对;利用剩余的正确对应关系来估算刚体变换,完成配准。整个配准的过程最重要的是关键点的提取以及关键点的特征描述。以确保对应估计的准确性和效率,这样才能保证后续流程中刚体变换矩阵估计的无误性。After the feature descriptor of the key point cloud data is calculated by any of the above four methods, the target point cloud data is determined according to the feature descriptor of the key point cloud data and the feature descriptor in the high-precision map The position of the corresponding target object in the high-precision map. A point cloud dataset is precisely registered with another point cloud dataset by applying an estimated 4*4 rigid body transformation matrix representing translation and rotation. The specific process can be: combining the coordinate positions of the feature descriptors in the two data sets, based on the similarity of the features and positions between the two, to estimate their correspondence, and preliminarily estimate the corresponding point pairs; assuming that the data is noisy , remove the wrong corresponding point pairs that have an impact on the registration; use the remaining correct correspondence to estimate the rigid body transformation to complete the registration. The most important thing in the whole registration process is the extraction of key points and the feature description of key points. In order to ensure the accuracy and efficiency of the corresponding estimation, so as to ensure the correctness of the rigid body transformation matrix estimation in the subsequent process.
需要说明的是,本实施例中的目标点云数据对应的目标物体可以是点云数据所包含的目标点中的某个或者某几个目标点对应的目标物体。示例性地,目标物体可以是道路边沿或者路边的栏杆等。It should be noted that the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in this embodiment may be a target object corresponding to one or several target points in the target points included in the point cloud data. Exemplarily, the target object may be a road edge or a roadside railing or the like.
可选地,可以以高精度地图上的某一点为原点建立坐标系,目标物体在高精度地图中的位置可以以坐标的形式示出。Optionally, a coordinate system can be established with a certain point on the high-precision map as the origin, and the position of the target object in the high-precision map can be shown in the form of coordinates.
步骤203:根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标点云数据,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。Step 203: Determine the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map according to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data.
具体地,在确定出目标物体在高精度地图中的位置后,可以根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标点云数据,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置,实现对车辆的定位。Specifically, after the position of the target object in the high-precision map is determined, the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map can be determined according to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data, so as to realize the positioning of the vehicle.
一种实现方式中,可以根据目标点云数据,确定目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值;根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。在该实现方式中,车辆坐标系的原点为车辆的后轴中心点,车辆坐标系的X轴正方向为车辆面向前方时,车辆的左侧方向,Y轴正方向为车辆前进方向,Z轴正方向为车辆的上方方向。In an implementation manner, the coordinate value of the target object in the vehicle coordinate system can be determined according to the target point cloud data; The location in the high-resolution map. In this implementation, the origin of the vehicle coordinate system is the center point of the rear axle of the vehicle, the positive direction of the X-axis of the vehicle coordinate system is the left direction of the vehicle when the vehicle faces forward, the positive direction of the Y-axis is the forward direction of the vehicle, and the Z-axis is the forward direction of the vehicle. The positive direction is the upward direction of the vehicle.
如步骤202中所描述的,目标点云数据对应的目标物体可以是点云数据所包含的目标点中的某个或者某几个目标点对应的目标物体,也即,目标点云数据所包含的有些目标点并不属于目标物体对应的点。本实施例中,在根据目标点云数据,确定目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值时,可以是将属于目标物体的目标点对应的目标点云数据的平均值或者中心点的值作为目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值。之后,根据目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定目标物体与车辆之间的距离以及目标物体与车辆前进方向的夹角;根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置、目标物体与车辆之间的距离以及目标物体与车辆前进方向的夹角,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。As described in step 202, the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data may be the target object corresponding to one or several target points in the target points included in the point cloud data, that is, the target point cloud data contains Some of the target points do not belong to the corresponding points of the target object. In this embodiment, when determining the coordinate value of the target object in the vehicle coordinate system according to the target point cloud data, the average value of the target point cloud data corresponding to the target point belonging to the target object or the value of the center point may be used as the target The coordinate value of the object in the vehicle coordinate system. After that, according to the coordinate value of the target object in the vehicle coordinate system, the distance between the target object and the vehicle and the angle between the target object and the vehicle's forward direction are determined; according to the position of the target object in the high-precision map, the relationship between the target object and the vehicle The distance between them and the angle between the target object and the vehicle's forward direction determine the vehicle's position in the high-precision map.
图7A为车辆定位方法实施例中确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置的一种实现方式的示意图。如图7A所示,根据目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,可以确定出目标物体与车辆之间的距离,以及,目标物体与车辆前进方向,即Y 轴的夹角。本实施例中,可以以车辆坐标系的原点表示车辆。已知目标物体在高精度地图中的位置、目标物体与车辆之间的距离以及目标物体与车辆前进方向的夹角,根据三角几何原理可以计算出车辆在高精度地图中的位置。FIG. 7A is a schematic diagram of an implementation manner of determining the position of a vehicle in a high-precision map in an embodiment of a vehicle positioning method. As shown in FIG. 7A , according to the coordinate value of the target object in the vehicle coordinate system, the distance between the target object and the vehicle, and the angle between the target object and the vehicle's forward direction, that is, the Y axis can be determined. In this embodiment, the vehicle may be represented by the origin of the vehicle coordinate system. Knowing the position of the target object in the high-precision map, the distance between the target object and the vehicle, and the angle between the target object and the vehicle's forward direction, the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map can be calculated according to the principle of triangular geometry.
一种实现方式中,当目标点云数据对应的目标物体为多个时,上述实现方式中,根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置的具体过程可以是:根据每个目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及对应的目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定车辆在高精度地图中的多个初始位置;确定每个初始位置与其他初始位置之间的距离和;将最小的距离和对应的初始位置确定为车辆在高精度地图中的位置。In one implementation, when there are multiple target objects corresponding to the target point cloud data, in the above implementation, according to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the coordinate value of the target object in the vehicle coordinate system, it is determined that the vehicle is in the vehicle coordinate system. The specific process of the position in the high-precision map may be: according to the position of each target object in the high-precision map and the coordinate value of the corresponding target object in the vehicle coordinate system, determine multiple initial positions of the vehicle in the high-precision map ; Determine the distance sum between each initial position and other initial positions; determine the minimum distance and the corresponding initial position as the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map.
图7B为车辆定位方法实施例中确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置的另一种实现方式的示意图。如图7B所示,基于目标物体1、目标物体2、目标物体 3、……、目标物体n可以对应计算出车辆的初始位置集合(P1,P2,P3….Pn)。之后,确定每个初始位置与其他初始位置之间的距离和,将最小的距离和对应的初始位置确定为车辆在高精度地图中的位置。这种方式可以提高车辆定位的精度。FIG. 7B is a schematic diagram of another implementation manner of determining the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map in the embodiment of the vehicle positioning method. As shown in FIG. 7B , based on target object 1, target object 2, target object 3, . After that, the distance sum between each initial position and other initial positions is determined, and the minimum distance and the corresponding initial position are determined as the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map. In this way, the accuracy of vehicle positioning can be improved.
更进一步地,为了提高车辆定位的效率,可以根据多个初始位置确定车辆在高精度地图中的平均位置;确定每个与平均位置的距离小于预设阈值的初始位置与其他初始位置之间的距离和;将最小的距离和对应的初始位置确定为车辆在高精度地图中的位置。这种实现方式中,在确定距离和时,只是确定与平均位置的距离小于预设阈值的初始位置与其他初始位置之间的距离和,相较于以枚举方式计算距离和,减少了计算量,提高了算法的效率。Further, in order to improve the efficiency of vehicle positioning, the average position of the vehicle in the high-precision map can be determined according to multiple initial positions; the distance between each initial position whose distance from the average position is less than a preset threshold and other initial positions is determined. Distance and; determine the minimum distance and the corresponding initial position as the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map. In this implementation, when determining the distance sum, only the distance sum between the initial position whose distance from the average position is less than the preset threshold and other initial positions is determined. Compared with calculating the distance sum by enumeration, the calculation is reduced. , which improves the efficiency of the algorithm.
本实施例提供的车辆定位方法,利用毫米波雷达采集目标点云数据进行车辆定位,相较于激光雷达、基站定位、SLAM等方式具有成本低、定位精度高的优点,并且,对黑色物体也可以进行识别,在云雾等恶劣天气下也可以使用,定位的可靠性更高。The vehicle positioning method provided in this embodiment uses millimeter-wave radar to collect target point cloud data for vehicle positioning. Compared with lidar, base station positioning, SLAM and other methods, it has the advantages of low cost and high positioning accuracy, and also has the advantages of low cost and high positioning accuracy for black objects. It can be identified and used in bad weather such as clouds and fog, and the positioning reliability is higher.
本实施例提供的车辆定位方法,包括:获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据,根据目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置,其中,高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子,根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标点云数据,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。实现了根据毫米波雷达采集的目标点云数据确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置,相较于现有技术,成本较低、定位精度较高以及定位的可靠性较高。The vehicle positioning method provided in this embodiment includes: acquiring target point cloud data collected by a millimeter-wave radar installed on the vehicle during the driving process of the vehicle, and determining the target point cloud according to the target point cloud data and a pre-established high-precision map The position of the target object corresponding to the data in the high-precision map, wherein the high-precision map includes the feature descriptor determined according to the point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar, according to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data. , to determine the position of the vehicle on the high-resolution map. The position of the vehicle in the high-precision map is determined according to the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar. Compared with the prior art, the cost is lower, the positioning accuracy is higher, and the positioning reliability is higher.
图8为本发明提供的车辆定位装置实施例的结构示意图。如图8所示,本实施例提供的车辆定位装置包括:获取模块81、第一确定模块82以及第二确定模块83。FIG. 8 is a schematic structural diagram of an embodiment of a vehicle positioning device provided by the present invention. As shown in FIG. 8 , the vehicle positioning apparatus provided in this embodiment includes: an
获取模块81,用于获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据。The
第一确定模块82,用于根据目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置。The first determining
其中,高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子。Among them, the high-precision map includes feature descriptors determined according to the point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar.
可选地,第一确定模块82具体用于:从目标点云数据中,确定关键点云数据;根据点云数据特征描述子提取算法,确定关键点云数据的特征描述子;根据关键点云数据的特征描述子,以及,高精度地图中的特征描述子,确定目标点云数据对应的目标物体在高精度地图中的位置。Optionally, the
第二确定模块83,用于根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标点云数据,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。The second determining
可选地,第二确定模块83具体包括:第一确定子模块以及第二确定子模块。第一确定子模块,用于根据目标点云数据,确定目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值。其中,车辆坐标系为以车辆上的一点为原点建立的坐标系。第二确定子模块,用于根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。Optionally, the
一种实现方式中,车辆坐标系的原点为车辆的后轴中心点,车辆坐标系的 X轴正方向为车辆面向前方时,车辆的左侧方向,Y轴正方向为车辆前进方向, Z轴正方向为车辆的上方方向。第二确定子模块具体用于:根据目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定目标物体与车辆之间的距离以及目标物体与车辆前进方向的夹角;根据目标物体在高精度地图中的位置、目标物体与车辆之间的距离以及目标物体与车辆前进方向的夹角,确定车辆在高精度地图中的位置。In one implementation, the origin of the vehicle coordinate system is the center point of the rear axle of the vehicle, the positive direction of the X-axis of the vehicle coordinate system is the left direction of the vehicle when the vehicle faces forward, the positive direction of the Y-axis is the forward direction of the vehicle, and the Z-axis is the forward direction of the vehicle. The positive direction is the upward direction of the vehicle. The second determination sub-module is specifically used to: determine the distance between the target object and the vehicle and the angle between the target object and the vehicle's forward direction according to the coordinate value of the target object in the vehicle coordinate system; The position, the distance between the target object and the vehicle, and the angle between the target object and the vehicle's forward direction determine the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map.
可选地,当目标点云数据对应的目标物体为多个时,第二确定子模块具体包括:第一确定单元、第二确定单元以及第三确定单元。第一确定单元,用于根据每个目标物体在高精度地图中的位置以及对应的目标物体在车辆坐标系中的坐标值,确定车辆在高精度地图中的多个初始位置。第二确定单元,用于确定每个初始位置与其他初始位置之间的距离和。第三确定单元,用于将最小的距离和对应的初始位置确定为车辆在高精度地图中的位置。更进一步地,基于该实现方式,车辆定位装置还可以包括:第四确定单元,用于根据多个初始位置确定车辆在高精度地图中的平均位置。相应地,第二确定单元具体用于:确定每个与平均位置的距离小于预设阈值的初始位置与其他初始位置之间的距离和。Optionally, when there are multiple target objects corresponding to the target point cloud data, the second determination sub-module specifically includes: a first determination unit, a second determination unit, and a third determination unit. The first determining unit is configured to determine a plurality of initial positions of the vehicle in the high-precision map according to the position of each target object in the high-precision map and the coordinate value of the corresponding target object in the vehicle coordinate system. The second determining unit is configured to determine the sum of distances between each initial position and other initial positions. The third determining unit is configured to determine the minimum distance and the corresponding initial position as the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map. Further, based on this implementation, the vehicle positioning apparatus may further include: a fourth determining unit, configured to determine the average position of the vehicle in the high-precision map according to multiple initial positions. Correspondingly, the second determining unit is specifically configured to: determine the sum of the distances between each initial position whose distance from the average position is smaller than the preset threshold and other initial positions.
本发明实施例所提供的车辆定位装置可执行本发明任意实施例所提供的车辆定位方法,具备执行方法相应的功能模块和有益效果。The vehicle positioning device provided by the embodiment of the present invention can execute the vehicle positioning method provided by any embodiment of the present invention, and has functional modules and beneficial effects corresponding to the execution method.
图9为本发明提供的车辆的结构示意图。如图9所示,该车辆包括处理器 70、存储器71以及毫米波雷达72。该车辆中处理器70的数量可以是一个或多个,毫米波雷达72的数量可以是一个或多个,图9中以一个处理器70以及一个毫米波雷达72为例;该车辆的处理器70和存储器71可以通过总线或其他方式连接,图9中以通过总线连接为例。FIG. 9 is a schematic structural diagram of a vehicle provided by the present invention. As shown in FIG. 9 , the vehicle includes a
存储器71作为一种计算机可读存储介质,可用于存储软件程序、计算机可执行程序以及模块,如本发明实施例中的车辆定位方法对应的程序指令以及模块(例如,车辆定位装置中的获取模块81、第一确定模块82以及第二确定模块83)。处理器70通过运行存储在存储器71中的软件程序、指令以及模块,从而执行车辆的各种功能应用以及数据处理,即实现上述的车辆定位方法。As a computer-readable storage medium, the
存储器71可主要包括存储程序区和存储数据区,其中,存储程序区可存储操作系统、至少一个功能所需的应用程序;存储数据区可存储根据车辆的使用所创建的数据等。此外,存储器71可以包括高速随机存取存储器,还可以包括非易失性存储器,例如至少一个磁盘存储器件、闪存器件、或其他非易失性固态存储器件。在一些实施例中,存储器71可进一步包括相对于处理器70远程设置的存储器,这些远程存储器可以通过网络连接至车辆。上述网络的实施例包括但不限于互联网、企业内部网、局域网、移动通信网及其组合。The
本发明还提供一种包含计算机可执行指令的存储介质,所述计算机可执行指令在由计算机处理器执行时用于执行一种车辆定位方法,该方法包括:The present invention also provides a storage medium containing computer-executable instructions, when executed by a computer processor, the computer-executable instructions are used to execute a vehicle positioning method, the method comprising:
获取车辆行驶过程中通过设置于所述车辆上的毫米波雷达采集到的目标点云数据;acquiring the target point cloud data collected by the millimeter-wave radar disposed on the vehicle during the driving of the vehicle;
根据所述目标点云数据以及预先建立的高精度地图,确定所述目标点云数据对应的目标物体在所述高精度地图中的位置;其中,所述高精度地图包括根据毫米波雷达采集到的点云数据确定的特征描述子;According to the target point cloud data and the pre-established high-precision map, determine the position of the target object corresponding to the target point cloud data in the high-precision map; The feature descriptor determined by the point cloud data;
根据所述目标物体在所述高精度地图中的位置以及所述目标点云数据,确定所述车辆在所述高精度地图中的位置。According to the position of the target object in the high-precision map and the target point cloud data, the position of the vehicle in the high-precision map is determined.
当然,本发明实施例所提供的一种包含计算机可执行指令的存储介质,其计算机可执行指令不限于如上所述的方法操作,还可以执行本发明任意实施例所提供的车辆定位方法中的相关操作。Of course, a storage medium containing computer-executable instructions provided by an embodiment of the present invention, the computer-executable instructions of which are not limited to the above-mentioned method operations, and can also execute any of the vehicle positioning methods provided in any embodiment of the present invention. related operations.
通过以上关于实施方式的描述,所属领域的技术人员可以清楚地了解到,本发明可借助软件及必需的通用硬件来实现,当然也可以通过硬件实现,但很多情况下前者是更佳的实施方式。基于这样的理解,本发明的技术方案本质上或者说对现有技术做出贡献的部分可以以软件产品的形式体现出来,该计算机软件产品可以存储在计算机可读存储介质中,如计算机的软盘、只读存储器 (Read-Only Memory,ROM)、随机存取存储器(RandomAccess Memory,RAM)、闪存(FLASH)、硬盘或光盘等,包括若干指令用以使得一台计算机设备(可以是个人计算机,车辆,或者网络设备等)执行本发明各个实施例所述的方法。From the above description of the embodiments, those skilled in the art can clearly understand that the present invention can be realized by software and necessary general-purpose hardware, and of course can also be realized by hardware, but in many cases the former is a better embodiment . Based on such understanding, the technical solutions of the present invention can be embodied in the form of software products in essence or the parts that make contributions to the prior art, and the computer software products can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium, such as a floppy disk of a computer , read-only memory (Read-Only Memory, ROM), random access memory (Random Access Memory, RAM), flash memory (FLASH), hard disk or CD, etc., including several instructions to make a computer device (which can be a personal computer, vehicle, or network device, etc.) to execute the methods described in the various embodiments of the present invention.
值得注意的是,上述车辆定位装置的实施例中,所包括的各个单元和模块只是按照功能逻辑进行划分的,但并不局限于上述的划分,只要能够实现相应的功能即可;另外,各功能单元的具体名称也只是为了便于相互区分,并不用于限制本发明的保护范围。It is worth noting that in the above embodiments of the vehicle positioning device, the units and modules included are only divided according to functional logic, but are not limited to the above division, as long as the corresponding functions can be realized; The specific names of the functional units are only for the convenience of distinguishing from each other, and are not used to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
注意,上述仅为本发明的较佳实施例及所运用技术原理。本领域技术人员会理解,本发明不限于这里所述的特定实施例,对本领域技术人员来说能够进行各种明显的变化、重新调整和替代而不会脱离本发明的保护范围。因此,虽然通过以上实施例对本发明进行了较为详细的说明,但是本发明不仅仅限于以上实施例,在不脱离本发明构思的情况下,还可以包括更多其他等效实施例,而本发明的范围由所附的权利要求范围决定。Note that the above are only preferred embodiments of the present invention and applied technical principles. Those skilled in the art will understand that the present invention is not limited to the specific embodiments described herein, and various obvious changes, readjustments and substitutions can be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the protection scope of the present invention. Therefore, although the present invention has been described in detail through the above embodiments, the present invention is not limited to the above embodiments, and can also include more other equivalent embodiments without departing from the concept of the present invention. The scope is determined by the scope of the appended claims.
Claims (10)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910978766.XACN110794392B (en) | 2019-10-15 | 2019-10-15 | Vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle and storage medium |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910978766.XACN110794392B (en) | 2019-10-15 | 2019-10-15 | Vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle and storage medium |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110794392Atrue CN110794392A (en) | 2020-02-14 |
| CN110794392B CN110794392B (en) | 2024-03-19 |
Family
ID=69439175
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910978766.XAExpired - Fee RelatedCN110794392B (en) | 2019-10-15 | 2019-10-15 | Vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle and storage medium |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110794392B (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111505662A (en)* | 2020-04-29 | 2020-08-07 | 北京理工大学 | Unmanned vehicle positioning method and system |
| CN111638528A (en)* | 2020-05-26 | 2020-09-08 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Positioning method, positioning device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN111812658A (en)* | 2020-07-09 | 2020-10-23 | 北京京东乾石科技有限公司 | Location determination method, apparatus, system, and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN112287557A (en)* | 2020-11-09 | 2021-01-29 | 东风汽车集团有限公司 | Radar point cloud data loop playback method and system for assisting driving simulation test |
| CN113419235A (en)* | 2021-05-28 | 2021-09-21 | 同济大学 | Unmanned aerial vehicle positioning method based on millimeter wave radar |
| CN114252883A (en)* | 2020-09-24 | 2022-03-29 | 北京万集科技股份有限公司 | Target detection method, apparatus, computer device and medium |
| TWI833122B (en)* | 2021-10-22 | 2024-02-21 | 中光電智能機器人股份有限公司 | Method and system for building a spatial static map |
| US12112645B2 (en) | 2021-05-28 | 2024-10-08 | Tongji University | Unmanned aerial vehicle positioning method based on millimeter-wave radar |
Citations (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102928816A (en)* | 2012-11-07 | 2013-02-13 | 东南大学 | High-reliably integrated positioning method for vehicles in tunnel environment |
| US9140792B2 (en)* | 2011-06-01 | 2015-09-22 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | System and method for sensor based environmental model construction |
| WO2017150059A1 (en)* | 2016-03-02 | 2017-09-08 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Autonomous travel assistance device, roadside device, and autonomous travel assistance system |
| US20170314926A1 (en)* | 2016-04-28 | 2017-11-02 | Rogerson Aircraft Corporation | System and method for effectuating presentation of a terrain around a vehicle on a display in the vehicle |
| US20180306922A1 (en)* | 2017-04-20 | 2018-10-25 | Baidu Online Network Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd | Method and apparatus for positioning vehicle |
| CN108983248A (en)* | 2018-06-26 | 2018-12-11 | 长安大学 | It is a kind of that vehicle localization method is joined based on the net of 3D laser radar and V2X |
| CN109031269A (en)* | 2018-06-08 | 2018-12-18 | 上海西井信息科技有限公司 | Localization method, system, equipment and storage medium based on millimetre-wave radar |
| CN109425365A (en)* | 2017-08-23 | 2019-03-05 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method, apparatus, equipment and the storage medium of Laser Scanning Equipment calibration |
| CN109459750A (en)* | 2018-10-19 | 2019-03-12 | 吉林大学 | A kind of more wireless vehicle trackings in front that millimetre-wave radar is merged with deep learning vision |
| WO2019099802A1 (en)* | 2017-11-17 | 2019-05-23 | DeepMap Inc. | Iterative closest point process based on lidar with integrated motion estimation for high definitions maps |
| US20190171212A1 (en)* | 2017-11-24 | 2019-06-06 | Baidu Online Network Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd | Method and apparatus for outputting information of autonomous vehicle |
| CN109870689A (en)* | 2019-01-08 | 2019-06-11 | 武汉中海庭数据技术有限公司 | Millimetre-wave radar and the matched lane grade localization method of high-precision map vector and system |
| US20190195998A1 (en)* | 2017-12-22 | 2019-06-27 | Waymo Llc | Radar Based Three Dimensional Point Cloud for Autonomous Vehicles |
| CN110044371A (en)* | 2018-01-16 | 2019-07-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | A kind of method and vehicle locating device of vehicle location |
| CN110084272A (en)* | 2019-03-26 | 2019-08-02 | 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳) | A kind of cluster map creating method and based on cluster map and the matched method for relocating of location expression |
| CN110148144A (en)* | 2018-08-27 | 2019-08-20 | 腾讯大地通途(北京)科技有限公司 | Dividing method and device, storage medium, the electronic device of point cloud data |
| CN110208739A (en)* | 2019-05-29 | 2019-09-06 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Assist method, apparatus, equipment and the computer readable storage medium of vehicle location |
- 2019
- 2019-10-15CNCN201910978766.XApatent/CN110794392B/ennot_activeExpired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9140792B2 (en)* | 2011-06-01 | 2015-09-22 | GM Global Technology Operations LLC | System and method for sensor based environmental model construction |
| CN102928816A (en)* | 2012-11-07 | 2013-02-13 | 东南大学 | High-reliably integrated positioning method for vehicles in tunnel environment |
| WO2017150059A1 (en)* | 2016-03-02 | 2017-09-08 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Autonomous travel assistance device, roadside device, and autonomous travel assistance system |
| US20170314926A1 (en)* | 2016-04-28 | 2017-11-02 | Rogerson Aircraft Corporation | System and method for effectuating presentation of a terrain around a vehicle on a display in the vehicle |
| US20180306922A1 (en)* | 2017-04-20 | 2018-10-25 | Baidu Online Network Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd | Method and apparatus for positioning vehicle |
| CN108732582A (en)* | 2017-04-20 | 2018-11-02 | 百度在线网络技术(北京)有限公司 | Vehicle positioning method and device |
| CN109425365A (en)* | 2017-08-23 | 2019-03-05 | 腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司 | Method, apparatus, equipment and the storage medium of Laser Scanning Equipment calibration |
| WO2019099802A1 (en)* | 2017-11-17 | 2019-05-23 | DeepMap Inc. | Iterative closest point process based on lidar with integrated motion estimation for high definitions maps |
| US20190171212A1 (en)* | 2017-11-24 | 2019-06-06 | Baidu Online Network Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd | Method and apparatus for outputting information of autonomous vehicle |
| US20190195998A1 (en)* | 2017-12-22 | 2019-06-27 | Waymo Llc | Radar Based Three Dimensional Point Cloud for Autonomous Vehicles |
| CN110044371A (en)* | 2018-01-16 | 2019-07-23 | 华为技术有限公司 | A kind of method and vehicle locating device of vehicle location |
| CN109031269A (en)* | 2018-06-08 | 2018-12-18 | 上海西井信息科技有限公司 | Localization method, system, equipment and storage medium based on millimetre-wave radar |
| CN108983248A (en)* | 2018-06-26 | 2018-12-11 | 长安大学 | It is a kind of that vehicle localization method is joined based on the net of 3D laser radar and V2X |
| CN110148144A (en)* | 2018-08-27 | 2019-08-20 | 腾讯大地通途(北京)科技有限公司 | Dividing method and device, storage medium, the electronic device of point cloud data |
| CN109459750A (en)* | 2018-10-19 | 2019-03-12 | 吉林大学 | A kind of more wireless vehicle trackings in front that millimetre-wave radar is merged with deep learning vision |
| CN109870689A (en)* | 2019-01-08 | 2019-06-11 | 武汉中海庭数据技术有限公司 | Millimetre-wave radar and the matched lane grade localization method of high-precision map vector and system |
| CN110084272A (en)* | 2019-03-26 | 2019-08-02 | 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳) | A kind of cluster map creating method and based on cluster map and the matched method for relocating of location expression |
| CN110208739A (en)* | 2019-05-29 | 2019-09-06 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Assist method, apparatus, equipment and the computer readable storage medium of vehicle location |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 张会平 著: "《基于可视化技术的知识转化研究》", 电子科技大学出版社, pages: 107 - 108* |
| 王仁礼, 陈天泽, 王冬红: "智能型地图匹配综合算法的研究", 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, no. 11* |
| 王庆闪等: "基于NDT与ICP结合的点云配准算法", 计算机工程与应用, pages 107 - 108* |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111505662A (en)* | 2020-04-29 | 2020-08-07 | 北京理工大学 | Unmanned vehicle positioning method and system |
| CN111505662B (en)* | 2020-04-29 | 2021-03-23 | 北京理工大学 | Unmanned vehicle positioning method and system |
| CN111638528A (en)* | 2020-05-26 | 2020-09-08 | 北京百度网讯科技有限公司 | Positioning method, positioning device, electronic equipment and storage medium |
| CN111812658A (en)* | 2020-07-09 | 2020-10-23 | 北京京东乾石科技有限公司 | Location determination method, apparatus, system, and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN111812658B (en)* | 2020-07-09 | 2021-11-02 | 北京京东乾石科技有限公司 | Location determination method, apparatus, system, and computer-readable storage medium |
| CN114252883A (en)* | 2020-09-24 | 2022-03-29 | 北京万集科技股份有限公司 | Target detection method, apparatus, computer device and medium |
| CN114252883B (en)* | 2020-09-24 | 2022-08-23 | 北京万集科技股份有限公司 | Target detection method, apparatus, computer device and medium |
| CN112287557A (en)* | 2020-11-09 | 2021-01-29 | 东风汽车集团有限公司 | Radar point cloud data loop playback method and system for assisting driving simulation test |
| CN112287557B (en)* | 2020-11-09 | 2023-04-07 | 东风汽车集团有限公司 | Radar point cloud data loop playback method and system for assisting driving simulation test |
| CN113419235A (en)* | 2021-05-28 | 2021-09-21 | 同济大学 | Unmanned aerial vehicle positioning method based on millimeter wave radar |
| US12112645B2 (en) | 2021-05-28 | 2024-10-08 | Tongji University | Unmanned aerial vehicle positioning method based on millimeter-wave radar |
| TWI833122B (en)* | 2021-10-22 | 2024-02-21 | 中光電智能機器人股份有限公司 | Method and system for building a spatial static map |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110794392B (en) | 2024-03-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110794392B (en) | Vehicle positioning method, device, vehicle and storage medium | |
| US11885872B2 (en) | System and method for camera radar fusion | |
| US10677907B2 (en) | Method to determine the orientation of a target vehicle | |
| WO2021104497A1 (en) | Positioning method and system based on laser radar, and storage medium and processor | |
| US9563808B2 (en) | Target grouping techniques for object fusion | |
| Knill et al. | A direct scattering model for tracking vehicles with high-resolution radars | |
| WO2021012254A1 (en) | Target detection method, system, and mobile platform | |
| Kellner et al. | Instantaneous lateral velocity estimation of a vehicle using Doppler radar | |
| CN108845574A (en) | Target identification and method for tracing, device, equipment and medium | |
| TWI470257B (en) | Method and electronic device for angle estimation verification | |
| EP3882664B1 (en) | Histogram based l-shape detection of target objects | |
| CN114972532A (en) | Method, device and equipment for calibrating external parameters between laser radars and storage medium | |
| Dai et al. | Multiple vehicle tracking based on labeled multiple Bernoulli filter using pre-clustered laser range finder data | |
| Ram | Fusion of inverse synthetic aperture radar and camera images for automotive target tracking | |
| Zhu et al. | DeepEgo: Deep instantaneous ego-motion estimation using automotive radar | |
| CN113627569A (en) | Data fusion method for radar video all-in-one machine used for traffic large scene | |
| WO2021189206A1 (en) | Radar signal processing method and radar signal processing apparatus | |
| Chen et al. | A robust robot perception framework for complex environments using multiple mmwave radars | |
| Polychronopoulos et al. | Integrated object and road border tracking using 77 GHz automotive radars | |
| CN114839615A (en) | Target course angle fitting method for 4D millimeter wave radar and storage medium | |
| CN113888637A (en) | A vehicle positioning method, system and computer-readable storage medium | |
| Berthold et al. | Deriving spatial occupancy evidence from radar detection data | |
| Guo et al. | Doppler velocity-based algorithm for clustering and velocity estimation of moving objects | |
| EP4369028A1 (en) | Interface for detection representation of hidden activations in neural networks for automotive radar | |
| CN115171378B (en) | A long-distance multi-vehicle high-precision detection and tracking method based on roadside radar |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee | Granted publication date:20240319 |