CN110742708A - Fixing and sewing method for preventing rodentia animal wound skin from shrinking and application thereof - Google Patents
Fixing and sewing method for preventing rodentia animal wound skin from shrinking and application thereofDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110742708A CN110742708ACN201910839986.4ACN201910839986ACN110742708ACN 110742708 ACN110742708 ACN 110742708ACN 201910839986 ACN201910839986 ACN 201910839986ACN 110742708 ACN110742708 ACN 110742708A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- skin
- steel ring
- wound
- rat
- suture
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription76
- 241000283984RodentiaSpecies0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription35
- 238000009958sewingMethods0.000titleclaims2
- 229910000831SteelInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription116
- 239000010959steelSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription116
- 208000027418Wounds and injuryDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription85
- 239000012528membraneSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription60
- 206010033675panniculitisDiseases0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 210000004304subcutaneous tissueAnatomy0.000claimsabstractdescription15
- 241000700159RattusSpecies0.000claimsdescription84
- 230000007547defectEffects0.000claimsdescription33
- 241001465754MetazoaSpecies0.000claimsdescription13
- 235000013372meatNutrition0.000claimsdescription12
- 241000700198CaviaSpecies0.000claimsdescription6
- 241001481760Erethizon dorsatumSpecies0.000claimsdescription6
- 230000008602contractionEffects0.000claimsdescription6
- 229910001220stainless steelInorganic materials0.000claimsdescription6
- 206010072170Skin woundDiseases0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000002265preventionEffects0.000claims1
- 239000010935stainless steelSubstances0.000claims1
- 206010052428WoundDiseases0.000abstractdescription83
- 210000004379membraneAnatomy0.000abstractdescription57
- 230000029663wound healingEffects0.000abstractdescription35
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000abstractdescription18
- 230000008569processEffects0.000abstractdescription17
- 230000009193crawlingEffects0.000abstractdescription12
- 230000035876healingEffects0.000abstractdescription11
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000abstractdescription10
- 230000007246mechanismEffects0.000abstractdescription5
- 238000007634remodelingMethods0.000abstractdescription3
- 230000002500effect on skinEffects0.000abstract1
- 210000003491skinAnatomy0.000description114
- 229920001296polysiloxanePolymers0.000description27
- 238000012453sprague-dawley rat modelMethods0.000description19
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000description13
- 238000007920subcutaneous administrationMethods0.000description13
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description11
- 206010039491SarcomaDiseases0.000description9
- 238000001356surgical procedureMethods0.000description9
- 239000003550markerSubstances0.000description6
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description6
- WEXRUCMBJFQVBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-NpentobarbitalChemical compoundCCCC(C)C1(CC)C(=O)NC(=O)NC1=OWEXRUCMBJFQVBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description6
- 238000010171animal modelMethods0.000description5
- 210000004207dermisAnatomy0.000description5
- 210000000981epitheliumAnatomy0.000description5
- 238000007490hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stainingMethods0.000description5
- 208000015181infectious diseaseDiseases0.000description5
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description5
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description4
- 206010002091AnaesthesiaDiseases0.000description3
- IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-NEthylene oxideChemical compoundC1CO1IAYPIBMASNFSPL-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description3
- 229930182555PenicillinNatural products0.000description3
- JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-NPenicillin GChemical compoundN([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C(O)=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N0.000description3
- 230000037005anaesthesiaEffects0.000description3
- 210000002615epidermisAnatomy0.000description3
- 239000007927intramuscular injectionSubstances0.000description3
- 238000010255intramuscular injectionMethods0.000description3
- 239000007928intraperitoneal injectionSubstances0.000description3
- 229940049954penicillinDrugs0.000description3
- 229960001412pentobarbitalDrugs0.000description3
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description3
- 241000700157Rattus norvegicusSpecies0.000description2
- 206010048038Wound infectionDiseases0.000description2
- 238000001804debridementMethods0.000description2
- 201000010099diseaseDiseases0.000description2
- 208000037265diseases, disorders, signs and symptomsDiseases0.000description2
- 208000014674injuryDiseases0.000description2
- 230000007774longtermEffects0.000description2
- 210000003205muscleAnatomy0.000description2
- 230000008929regenerationEffects0.000description2
- 238000011069regeneration methodMethods0.000description2
- 230000003252repetitive effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000010008shearingMethods0.000description2
- 230000001954sterilising effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000004659sterilization and disinfectionMethods0.000description2
- 230000008733traumaEffects0.000description2
- 238000011282treatmentMethods0.000description2
- 230000037314wound repairEffects0.000description2
- 241000195940BryophytaSpecies0.000description1
- 102000008186CollagenHuman genes0.000description1
- 108010035532CollagenProteins0.000description1
- 208000008960Diabetic footDiseases0.000description1
- 206010056340Diabetic ulcerDiseases0.000description1
- 208000034693LacerationDiseases0.000description1
- 241000699670Mus sp.Species0.000description1
- 206010028980NeoplasmDiseases0.000description1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilicium dioxideChemical compoundO=[Si]=OVYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 208000028990Skin injuryDiseases0.000description1
- 241000282887SuidaeSpecies0.000description1
- 238000005299abrasionMethods0.000description1
- 230000002924anti-infective effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004888barrier functionEffects0.000description1
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000036760body temperatureEffects0.000description1
- 230000037396body weightEffects0.000description1
- 210000004271bone marrow stromal cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 229920001436collagenPolymers0.000description1
- 230000003111delayed effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description1
- 230000018109developmental processEffects0.000description1
- 239000003814drugSubstances0.000description1
- 229940079593drugDrugs0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 210000001339epidermal cellAnatomy0.000description1
- 229940011871estrogenDrugs0.000description1
- 239000000262estrogenSubstances0.000description1
- 238000011156evaluationMethods0.000description1
- 239000000835fiberSubstances0.000description1
- 239000003163gonadal steroid hormoneSubstances0.000description1
- 210000004209hairAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000009545invasionEffects0.000description1
- 238000011866long-term treatmentMethods0.000description1
- 230000004060metabolic processEffects0.000description1
- 230000000813microbial effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 235000011929mousseNutrition0.000description1
- 230000017074necrotic cell deathEffects0.000description1
- 230000037311normal skinEffects0.000description1
- 210000000056organAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000012188paraffin waxSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001717pathogenic effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002980postoperative effectEffects0.000description1
- 230000002035prolonged effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000002994raw materialSubstances0.000description1
- 230000001105regulatory effectEffects0.000description1
- 208000023504respiratory system diseaseDiseases0.000description1
- 238000005070samplingMethods0.000description1
- 210000000518sarcolemmaAnatomy0.000description1
- 210000001732sebaceous glandAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000035945sensitivityEffects0.000description1
- 230000001568sexual effectEffects0.000description1
- 239000000741silica gelSubstances0.000description1
- 229910002027silica gelInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000036560skin regenerationEffects0.000description1
- MHQHHBYRYFICDV-UHFFFAOYSA-Msodium;pyrimidin-3-ide-2,4,6-trioneChemical compound[Na+].O=C1CC(=O)[N-]C(=O)N1MHQHHBYRYFICDV-UHFFFAOYSA-M0.000description1
- 230000002269spontaneous effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000000106sweat glandAnatomy0.000description1
- 230000009885systemic effectEffects0.000description1
- 231100000027toxicologyToxicity0.000description1
- 238000002054transplantationMethods0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61D—VETERINARY INSTRUMENTS, IMPLEMENTS, TOOLS, OR METHODS
- A61D1/00—Surgical instruments for veterinary use
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Agricultural Chemicals And Associated Chemicals (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明具体涉及一种防止啮齿目动物创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法及其用途。The invention specifically relates to a fixation and suturing method for preventing the shrinkage of rodent wound surface skin and its application.
背景技术Background technique
皮肤是人体最大的器官,约占体重的5%~15%,总面积为1.5~2平方米。皮肤覆盖于全身表面,是人体与外界环境之间的天然屏障,一方面可以防止体内水分、电解质及其他物质的丢失,另一方面也可以保护体内各种组织和器官免受物理、化学、机械性和病原微生物性的侵袭。皮肤主要分为表皮、真皮,并借皮下组织与深部组织相连。真皮中尚有毛发、皮脂腺、汗腺等皮肤附属器,因此皮肤具有吸收、排泄、调节体温以及参与物质代谢的作用。临床上常见的皮肤损伤主要包括擦伤、撕裂伤、烧伤以及内科疾病导致的相关并发症如糖尿病溃疡等等。皮肤具有较强的自愈能力,但是严重的烧烫伤、大面积创伤和糖尿病足溃疡等往往久治不愈,长时间不愈合的创面极易发生感染,进而引起其他一系列更为严重的全身并发症。因此,难治性创面的治疗已经成为临床和科研研究的重点和热点。The skin is the largest organ of the human body, accounting for about 5% to 15% of the body weight, with a total area of 1.5 to 2 square meters. Covering the surface of the whole body, the skin is a natural barrier between the human body and the external environment. Sexual and pathogenic microbial invasion. The skin is mainly divided into epidermis and dermis, and is connected with deep tissue by subcutaneous tissue. There are still hair, sebaceous glands, sweat glands and other skin appendages in the dermis, so the skin has the functions of absorbing, excreting, regulating body temperature and participating in material metabolism. Common clinical skin injuries mainly include abrasions, lacerations, burns, and related complications caused by medical diseases such as diabetic ulcers. The skin has a strong self-healing ability, but severe burns, large-scale wounds, and diabetic foot ulcers are often unhealed for a long time. Wounds that do not heal for a long time are prone to infection, which in turn leads to a series of other more serious systemic complications. Therefore, the treatment of refractory wounds has become the focus and hotspot of clinical and scientific research.
外科治疗中,对于难治性创面多采用清创、长期换药、皮片及皮瓣移植等方法。但存在的问题是,清创后长期换药所需的治疗时间长,费用多,家庭负担大,疗效不佳,术后创面易发生感染等。皮片和皮瓣移植均存在部分或全部坏死的风险,更为严重的是皮片和皮瓣的获取会给患者带来新的创伤和风险。目前的研究中,治疗难治性创面的手段有:运用特色换药、负压吸引联合促愈合药物、组织工程全层皮肤、ADSCs或BMSCs等加速创面的愈合速度,促进创面愈合。这些研究采用的动物多为猪、SD大鼠、c57小鼠等,动物模型为全层皮肤缺损模型。其中,SD大鼠又以抗感染能力强、价格便宜、创面愈合周期短和管理方便等优势,被广泛地运用于各种创面修复的实验研究中。In surgical treatment, methods such as debridement, long-term dressing change, skin grafting and skin flap transplantation are often used for refractory wounds. However, the existing problems are that the long-term treatment time required for long-term dressing change after debridement is long, the cost is high, the family burden is large, the curative effect is not good, and the postoperative wound is prone to infection. Both skin grafts and skin flaps carry the risk of partial or total necrosis, and more seriously, the acquisition of skin grafts and skin flaps will bring new trauma and risks to the patient. In the current research, the methods of treating refractory wounds include: using special dressing changes, negative pressure suction combined with healing drugs, tissue engineering full-thickness skin, ADSCs or BMSCs, etc. to accelerate the healing speed of wounds and promote wound healing. Most of the animals used in these studies were pigs, SD rats, c57 mice, etc., and the animal models were full-thickness skin defect models. Among them, SD rats are widely used in various experimental studies of wound repair due to their strong anti-infection ability, low price, short wound healing period and convenient management.
SD(Sprague-Dawley)大鼠是大鼠的一个品系,1925年,美国Sprague Dawley农场用Wistar大鼠培育而成。其毛色白化,主要特性为:①头部狭长、尾长接近于身长,产仔多,生长发育较Wistar为快。10周龄时雄性大鼠体重可达300~400g,雌性大鼠达180~270g。②性情比Wistar大鼠稍为凶猛。③对疾病的抵抗力较强,尤其对呼吸道疾病的抵抗力很强。④自发性肿瘤的发生率较低。⑤对性激素敏感性高。因而被广泛用于药理、毒理、药效及GLP等实验。在创面修复研究方面,SD大鼠的创面愈合主要由创面周围正常皮肤的收缩和皮肤的爬行共同参与,但与其他动物不同的是,大鼠皮肤下存在一层啮齿目动物特有的类似肌肉的组织,称为肉膜,肉膜的存在使得大鼠的创面愈合过程中,收缩起到的作用比爬行更大,这也使得大鼠的创面愈合速度比其他常用实验动物更快。SD (Sprague-Dawley) rat is a strain of rat, which was bred from Wistar rat in Sprague Dawley farm in the United States in 1925. Its coat color is albino, and its main characteristics are: ① The head is long and narrow, the tail length is close to the body length, the litter is more, and the growth and development is faster than that of the Wistar. At the age of 10 weeks, the weight of male rats can reach 300-400 g, and the weight of female rats can reach 180-270 g. ②The temperament is slightly fiercer than that of Wistar rats. ③ Strong resistance to diseases, especially to respiratory diseases. ④ The incidence of spontaneous tumors is low. ⑤ high sensitivity to sex hormones. Therefore, it is widely used in experiments such as pharmacology, toxicology, efficacy and GLP. In terms of wound repair research, the wound healing of SD rats is mainly participated by the contraction of the normal skin around the wound and the crawling of the skin, but unlike other animals, there is a layer of rodent-specific muscle-like layers under the skin of rats. The presence of the tissue, called the sarcolemma, allows the rat's wound to heal more rapidly than crawling through contraction, which also makes the rat's wound heal faster than other commonly used experimental animals.
但是,人的创面愈合机制主要是以表皮细胞的爬行作用为主,因此研究者们尝试用硅胶圈固定在大鼠背部创面周围,通过防止肉膜的收缩来模拟人的创面愈合机制。如今,硅胶圈固定法已经被广泛应用于大鼠创面愈合实验研究中。但是在具体研究的实践过程中发现硅胶圈防收缩的方法存在以下不足:第一,硅胶圈的规格并没有统一的标准,而其防收缩性能会因为硅胶圈的厚薄、软硬而发生变化,可能会成为实验研究过程中影响实验本身的额外干扰因素。第二,硅胶圈需要用缝线固定在皮肤创缘周围,而在创面愈合的过程中,创缘的收缩力会变大,缝线会和硅胶圈本身形成切割作用。当硅胶圈被缝线切割之后,硅胶圈就失去了防收缩的作用。第三,硅胶圈是固定在动物皮肤表面的,缝线的大部分也是裸露在外,体型较大和身体柔软的动物能够咬到硅胶圈和缝线,使硅胶圈产生形变或者断裂,从而影响防收缩的效果。第四,硅胶圈本身属于异体材料,且其缝合后与皮肤之间的缝隙容易藏污纳垢,与创面长时间接触可能会造成创面感染,增加创面不愈的风险。因此亟需寻找一个新的更有效的方法来防止大鼠的创面收缩。However, the human wound healing mechanism is mainly based on the crawling effect of epidermal cells, so the researchers tried to use a silicone ring to fix the wound around the back of the rat to simulate the human wound healing mechanism by preventing the contraction of the flesh membrane. Nowadays, the silicone ring fixation method has been widely used in experimental research on wound healing in rats. However, in the practice process of specific research, it is found that the anti-shrinkage method of the silicone ring has the following shortcomings: First, the specifications of the silicone ring do not have a unified standard, and its anti-shrinkage performance will change due to the thickness, softness and hardness of the silicone ring. It may become an additional interference factor affecting the experiment itself during the experimental research process. Second, the silicone ring needs to be fixed around the skin wound edge with sutures. During the healing process of the wound, the contraction force of the wound edge will increase, and the suture will form a cutting effect with the silicone ring itself. When the silicone ring is cut by the suture, the silicone ring loses its anti-shrinkage effect. Third, the silicone ring is fixed on the surface of the animal's skin, and most of the sutures are also exposed. Larger and softer animals can bite the silicone ring and suture, causing the silicone ring to deform or break, thus affecting the anti-shrinkage. Effect. Fourth, the silicone ring itself is a foreign material, and the gap between it and the skin after suture is easy to hide dirt, and prolonged contact with the wound may cause wound infection and increase the risk of wound unhealing. Therefore, it is urgent to find a new and more effective method to prevent wound shrinkage in rats.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
为了解决这个问题,本发明提供了一种防止啮齿目动物创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法及其用途。In order to solve this problem, the present invention provides a fixation and suturing method for preventing rodent wound skin from shrinking and its use.
本发明提供了一种防止啮齿目动物创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法,所述的固定及缝合方法包括如下步骤:The present invention provides a fixation and suturing method for preventing rodent wound skin from shrinking, and the fixation and suturing method comprises the following steps:
沿啮齿目动物皮肤创面创缘,环形剪除肉膜,剪除的宽度为2~3mm,将钢圈外径与剪除后的肉膜边缘重合,通过连续锁边缝合法将钢圈与皮肤、肉膜及皮下组织缝合固定,即可。Along the wound edge of the rodent skin, cut off the flesh membrane in a circular shape with a width of 2 to 3 mm. The outer diameter of the steel ring is overlapped with the edge of the cut flesh membrane, and the steel ring is connected to the skin and flesh membrane by continuous seam suture. And the subcutaneous tissue is sutured and fixed.
本发明操作方法简单,本领域技术人员均可以操作。理由如下:The operation method of the present invention is simple and can be operated by those skilled in the art. The reasons are as follows:
首先,本发明的主体为啮齿目动物,本领域公知地,啮齿目动物具有皮肤以及与皮肤紧密连接的肉膜,当其皮肤出现创面后,皮肤以及肉膜结构均会清楚的地暴露出来,本领域技术人员很容易就能找到肉膜。本领域技术人员找到肉膜后,环形剪去肉膜是很容易的,剪除肉膜时,剪除的宽度为2~3mm,也是本领域技术人员可以实现的。First, the subject of the present invention is a rodent. It is well known in the art that rodents have skin and a flesh membrane closely connected to the skin. Meat membranes can be easily found by those skilled in the art. After a person skilled in the art finds the meat film, it is very easy to cut the meat film in a circular shape. When cutting the meat film, the width of the cut is 2-3 mm, which can also be realized by those skilled in the art.
其次,连续锁边缝合是一种常见的缝合方法,针从距创缘约1mm皮肤下、钢圈内缘内侧穿出皮肤,然后在皮肤外跨过皮下钢圈从钢圈外缘的皮外穿过皮肤、肉膜达皮下,再从皮下跨过钢圈穿过钢圈内缘处皮下组织,第一针缝合后打结,继而用同样的缝合方法以连续锁边缝合整圈钢圈,最后一针与第一针所留线头打结固定,即可。Secondly, continuous overlock suture is a common suture method. The needle is about 1 mm from the wound edge, under the skin, and inside the inner edge of the steel ring. The needle is passed through the skin, and then crosses the subcutaneous steel ring outside the skin from the outer edge of the steel ring. Pass through the skin and flesh membrane to the subcutaneous, and then cross the steel ring from the subcutaneous to the subcutaneous tissue at the inner edge of the steel ring. After the first stitch is sutured, tie a knot, and then use the same suture method to suture the entire ring of the steel ring with continuous overlock. The last stitch is tied with the thread left in the first stitch to fix it.
综上,连续锁边缝合是本领域的常规缝合手段,而啮齿目动物的皮肤、肉膜、皮下组织也是本领域技术人员知晓且容易找到的组织,因此利用连续锁边缝合方法将钢圈与皮肤、肉膜及皮下组织缝合是本领域技术人员很容易操作的方法。因此,本发明的固定及缝合方法是本领域技术人员容易实现,能够在产业上使用的方法,具备实用性。To sum up, continuous overlock suture is a conventional suturing method in the art, and the skin, flesh membrane, and subcutaneous tissue of rodents are also known and easily found by those skilled in the art. Suture of skin, sarcoma and subcutaneous tissue is a method that can be easily performed by those skilled in the art. Therefore, the fixing and suturing method of the present invention can be easily realized by those skilled in the art and can be used industrially, and has practicality.
进一步地,所述的啮齿目动物为大鼠、豚鼠、豪猪;优选地,所述的啮齿目动物为大鼠;更优选地,所述的大鼠为SD大鼠。Further, the rodents are rats, guinea pigs, and porcupines; preferably, the rodents are rats; more preferably, the rats are SD rats.
进一步地,所述的创面为圆形创面。Further, the wound surface is a round wound surface.
进一步地,所述的连续锁边缝合法使用的缝合线为不可吸收缝合线。Further, the suture used in the continuous overlock suture method is a non-absorbable suture.
进一步地,所述的不可吸收缝合线为3-0不可吸收缝合线。Further, the non-absorbable suture is a 3-0 non-absorbable suture.
进一步地,所述的钢圈由医用不锈钢丝制成,所述医用不锈钢丝的直径为0.8mm。Further, the steel ring is made of medical stainless steel wire, and the diameter of the medical stainless steel wire is 0.8 mm.
本发明还提供了前述的钢圈在制备啮齿目动物皮肤缺损防收缩模型中的用途。The present invention also provides the use of the aforementioned steel ring in preparing a rodent skin defect anti-shrinkage model.
进一步地,所述的啮齿目动物为大鼠、豚鼠、豪猪;优选地,所述的啮齿目动物为大鼠;更优选地,所述的大鼠为SD大鼠。Further, the rodents are rats, guinea pigs, and porcupines; preferably, the rodents are rats; more preferably, the rats are SD rats.
本发明还提供了一种啮齿目动物皮肤缺损防收缩模型,它是由前述的钢圈制备而成。The present invention also provides an anti-shrinkage model of rodent skin defect, which is prepared from the aforementioned steel ring.
进一步地,所述的啮齿目动物为大鼠、豚鼠、豪猪;优选地,所述的啮齿目动物为大鼠;更优选地,所述的大鼠为SD大鼠。Further, the rodents are rats, guinea pigs, and porcupines; preferably, the rodents are rats; more preferably, the rats are SD rats.
本发明中,3-0不可吸收缝合线是型号为3-0的强生慕丝丝线编织非吸收性缝合线。因为3-0的线粗细程度刚好合适。如果线太细,则起不到固定钢圈的作用,而且后期会因为肉膜的收缩力而断裂,起不到防收缩的效果。如果线太粗,在缝合时创伤会比较大,并且会对创面周缘的上皮产生影响,可能会影响上皮的正常爬行。In the present invention, the 3-0 non-absorbable suture is a 3-0 Johnson & Johnson mousse silk woven non-absorbable suture. Because the line thickness of 3-0 is just right. If the wire is too thin, it will not play the role of fixing the steel ring, and it will break due to the shrinkage force of the meat film in the later stage, and the effect of preventing shrinkage will not be achieved. If the thread is too thick, the trauma will be larger during suture, and it will affect the epithelium around the wound surface, which may affect the normal crawling of the epithelium.
本发明中,圈指的是任选一个顶点为起点,沿着不重复的边,经过不重复的顶点为途径,之后又回到起点的闭合途径称为圈。In the present invention, a circle refers to selecting a vertex as a starting point, along a non-repetitive edge, passing through a non-repetitive vertex as a path, and then returning to the starting point. The closed path is called a circle.
本发明中,皮下为皮下组织。In the present invention, the subcutaneous tissue is a subcutaneous tissue.
本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法防收缩效果显著,能够在不影响上皮爬行的同时,最大程度地减少大鼠创面的收缩,且不影响创面的愈合质量。利用本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法制备的大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型能够有效的模拟人的创面愈合机制,更准确评估伤口愈合过程中表皮的爬行过程,更好地观察真皮的重塑过程,能够作为研究创面愈合的优良模型,作为评估各种影响伤口愈合因素的平台。其在科学研究方面,有很强的应用价值。The fixation and suturing method for preventing rat wound skin shrinkage provided by the invention has remarkable anti-shrinkage effect, can minimize rat wound shrinkage without affecting epithelial crawling, and does not affect the wound healing quality. The rat skin defect anti-contraction model prepared by the fixation and suturing method for preventing rat wound skin shrinkage of the present invention can effectively simulate the human wound healing mechanism, more accurately evaluate the crawling process of the epidermis during the wound healing process, and better observe the dermis. The remodeling process can be used as an excellent model to study wound healing and as a platform to evaluate various factors affecting wound healing. It has strong application value in scientific research.
本发明采用统一了材质、尺寸的钢圈取代现有技术的硅胶圈,应用于啮齿目动物皮肤缺损防收缩模型的制备中,不仅统一了钢圈的使用标准,尽可能排除了额外干扰因素;而且过程中不会破坏钢圈内部结构,钢圈也不易产生形变或者断裂,能够维持良好的防收缩作用,有效的模拟人的创面愈合机制,效果非常优良。The invention adopts the steel ring with unified material and size to replace the silicone ring of the prior art, and is applied to the preparation of the rodent skin defect anti-shrinkage model, which not only unifies the use standard of the steel ring, but also eliminates additional interference factors as much as possible; In addition, the internal structure of the steel ring will not be damaged during the process, and the steel ring will not be easily deformed or broken.
显然,根据本发明的上述内容,按照本领域的普通技术知识和惯用手段,在不脱离本发明上述基本技术思想前提下,还可以做出其它多种形式的修改、替换或变更。Obviously, according to the above-mentioned content of the present invention, according to the common technical knowledge and conventional means in the field, without departing from the above-mentioned basic technical idea of the present invention, other various forms of modification, replacement or change can also be made.
以下通过实施例形式的具体实施方式,对本发明的上述内容再作进一步的详细说明。但不应将此理解为本发明上述主题的范围仅限于以下的实例。凡基于本发明上述内容所实现的技术均属于本发明的范围。The above content of the present invention will be further described in detail below through the specific implementation in the form of examples. However, this should not be construed as limiting the scope of the above-mentioned subject matter of the present invention to the following examples. All technologies implemented based on the above content of the present invention belong to the scope of the present invention.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为硅胶圈组术后即刻大体图。Figure 1 is a general view of the silicone ring group immediately after surgery.
图2为不剪肉膜单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图。Figure 2 is the general view immediately after operation of the simple intermittent suture fixed steel ring group without cutting the flesh membrane.
图3为不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图。Figure 3 is the general view immediately after operation in the simple continuous suture and fixed steel ring group without cutting the flesh membrane.
图4为剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图。Figure 4 is a general view of the group of scissors membrane combined with simple interrupted suture and fixed steel ring immediately after operation.
图5为剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图。Figure 5 is a general view of the group of scissors membrane combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring immediately after operation.
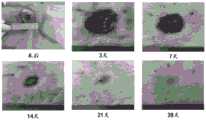
图6为空白对照组创面愈合过程。Figure 6 shows the wound healing process in the blank control group.
图7为硅胶圈组创面愈合过程。Figure 7 shows the wound healing process in the silicone ring group.
图8为不剪肉膜单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组创面愈合过程。Figure 8 shows the healing process of the wound in the simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group without cutting the flesh membrane.
图9为不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定钢圈组创面愈合过程。Figure 9 shows the wound healing process of the continuous suture and fixed steel ring group without cutting the flesh membrane.
图10为剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组创面愈合过程。Figure 10 shows the wound healing process in the group of shearing membrane combined with simple interrupted suture and fixed steel ring.
图11为剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组创面愈合过程。Figure 11 shows the healing process of the wound in the meat-cutting membrane combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group.
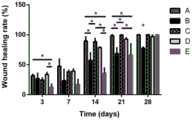
图12为动物实验一中各实验组创面愈合率;A:不剪肉膜单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组;B:不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定缝合钢圈组;C:硅胶圈组;D:剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组;E:剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组。Figure 12 shows the wound healing rate of each experimental group in
图13为3天时剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(A)、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(B)HE染色图。Figure 13 shows the HE staining images of the meat-cutting film combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (A) and the meat-cutting film combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group (B) at 3 days.
图14为7天时剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(A)、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(B)HE染色图。Figure 14 shows the HE staining images of the meat-cutting film combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (A) and the meat-cutting film combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group (B) at 7 days.
图15为14天时剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(A)、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(B)HE染色图。Figure 15 shows the HE staining images of the meat-cutting film combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (A) and the meat-cutting film combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group (B) at 14 days.
图16为21天时剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(A)、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(B)HE染色图。Figure 16 shows the HE staining images of the meat-cutting film combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (A) and the meat-cutting film combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group (B) at 21 days.
图17为28天时剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(A)、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(B)HE染色图。Figure 17 shows the HE staining images of the meat-cutting film combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (A) and the meat-cutting film combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group (B) at 28 days.
图18为21天时硅胶圈组(如图A)、剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(如图B)、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(如图C)的创面再生区域长度比较。Figure 18 shows the wounds of the silicone ring group (Figure A), the meat-cutting membrane combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (Figure B), and the meat-cutting membrane combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group (Figure C) at 21 days Comparison of regeneration area lengths.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
本发明具体实施方式中使用的原料、设备均为已知产品,通过购买市售产品获得。The raw materials and equipment used in the specific embodiments of the present invention are all known products, which are obtained by purchasing commercially available products.
实验动物:Experimental animals:
健康的12周龄的SD雄性大鼠,由北京维通利华实验动物公司和成都达硕实验动物公司提供,实验通过四川大学伦理委员会审核通过。不选择雌性大鼠是为排除创面愈合过程中雌激素的影响。Healthy 12-week-old SD male rats were provided by Beijing Weitong Lihua Laboratory Animal Company and Chengdu Dashuo Laboratory Animal Company, and the experiment was approved by the Ethics Committee of Sichuan University. Female rats were not selected to exclude the effect of estrogen during wound healing.
实验材料:Experimental Materials:
钢圈1:由直径为0.8mm的医用不锈钢丝制成,钢圈的直径(外径)为22mm,用环氧乙烷灭菌备用。Steel ring 1: It is made of medical stainless steel wire with a diameter of 0.8 mm, the diameter (outer diameter) of the steel ring is 22 mm, and is sterilized with ethylene oxide for use.
钢圈2:由直径为0.8mm的医用不锈钢丝制成,钢圈的直径(外径)为23mm,用环氧乙烷灭菌备用。Steel ring 2: It is made of medical stainless steel wire with a diameter of 0.8 mm, the diameter (outer diameter) of the steel ring is 23 mm, and is sterilized with ethylene oxide for use.
硅胶圈1:由外径30mm,内径20mm的天然硅胶柱切割而成,厚度为3mm,用环氧乙烷灭菌备用。Silicone ring 1: It is cut from a natural silica gel column with an outer diameter of 30mm and an inner diameter of 20mm, with a thickness of 3mm, and is sterilized with ethylene oxide for later use.
实施例1、利用本发明防止啮齿目动物创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法制备大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型Example 1. Preparation of rat skin defect anti-shrinkage model by using the fixation and suturing method for preventing rodent wound skin shrinkage according to the present invention
(1)大鼠皮肤缺损模型的制备(1) Preparation of rat skin defect model
选用健康的12周龄雄性SD大鼠,首先使用3%戊巴比妥30mg/kg腹腔注射麻醉。麻醉成功后,在术前给予青霉素(60w单位/天)肌肉注射,预防切口感染。接着将动物俯卧位固定于手术台,背部剃毛,于大鼠脊柱两侧背部用标记笔作对称的直径20mm的圆形,之后进行常规消毒铺巾。用高温高压灭菌过的剪刀按照标记笔作的圆形做皮肤缺损,制备直径20mm的圆形皮肤缺损模型。Healthy 12-week-old male SD rats were selected and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital at 30 mg/kg. After successful anesthesia, intramuscular injection of penicillin (60w units/day) was given before surgery to prevent incision infection. Then, fix the animal in the prone position on the operating table, shave the back, and use a marker pen to make a symmetrical circle with a diameter of 20 mm on the back of both sides of the spine of the rat, and then routinely sterilize the towel. Use high-temperature and high-pressure sterilized scissors to make a skin defect according to the circle made by a marker pen, and prepare a circular skin defect model with a diameter of 20 mm.
(2)利用本发明固定及缝合方法制备大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型(2) Using the fixation and suturing method of the present invention to prepare a rat skin defect anti-shrinkage model
皮肤缺损模型制备成功后,沿SD大鼠皮肤创面创缘,用眼科剪环形剪除肉膜,剪除的宽度为2mm,再将灭菌待用的钢圈1置于剪除肉膜处(钢圈外缘与剪除后的肉膜边缘重合),用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用连续锁边缝合法缝合钢圈、皮肤、肉膜及皮下组织,将钢圈固定,利用钢圈防止肉膜收缩。After the successful preparation of the skin defect model, along the wound edge of the SD rat skin, use ophthalmic scissors to cut off the flesh membrane in a circular shape with a width of 2 mm, and then place the sterilized
实施例2、利用本发明防止啮齿目动物创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法制备大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型Example 2. Preparation of rat skin defect anti-shrinkage model by using the fixation and suturing method for preventing rodent wound skin shrinkage according to the present invention
(1)大鼠皮肤缺损模型的制备(1) Preparation of rat skin defect model
选用健康的12周龄雄性SD大鼠,首先使用3%戊巴比妥30mg/kg腹腔注射麻醉。麻醉成功后,在术前给予青霉素(60w单位/天)肌肉注射,预防切口感染。接着将动物俯卧位固定于手术台,背部剃毛,于大鼠脊柱两侧背部用标记笔作对称的直径20mm的圆形,之后进行常规消毒铺巾。用高温高压灭菌过的剪刀按照标记笔作的圆形做皮肤缺损,制备直径20mm的圆形皮肤缺损模型。Healthy 12-week-old male SD rats were selected and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital at 30 mg/kg. After successful anesthesia, intramuscular injection of penicillin (60w units/day) was given before surgery to prevent incision infection. Then, fix the animal in the prone position on the operating table, shave the back, and use a marker pen to make a symmetrical circle with a diameter of 20 mm on the back of both sides of the spine of the rat, and then routinely sterilize the towel. Use high-temperature and high-pressure sterilized scissors to make a skin defect according to the circle made by a marker pen, and prepare a circular skin defect model with a diameter of 20 mm.
(2)利用本发明固定及缝合方法制备大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型(2) Using the fixation and suturing method of the present invention to prepare a rat skin defect anti-shrinkage model
皮肤缺损模型制备成功后,沿SD大鼠皮肤创面创缘,用眼科剪环形剪除肉膜,剪除的宽度为3mm,再将灭菌待用的钢圈2置于剪除肉膜处(钢圈外径与剪除后的肉膜边缘重合),用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用连续锁边缝合法缝合钢圈、皮肤、肉膜及皮下组织,将钢圈固定,利用钢圈防止肉膜收缩。After the successful preparation of the skin defect model, along the wound edge of the SD rat skin, use ophthalmic scissors to cut off the flesh membrane in a circular shape with a width of 3 mm, and then place the sterilized
以下通过具体的试验例证明本发明的有益效果。The beneficial effects of the present invention are demonstrated below through specific test examples.
试验例1、本发明防止啮齿目动物创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法的防收缩效果研究Test Example 1. Research on the anti-shrinkage effect of the present invention's fixation and suture method for preventing rodent wound skin from shrinking
1、大鼠皮肤缺损模型的制备1. Preparation of rat skin defect model
选用健康的12周龄雄性SD大鼠,首先使用3%戊巴比妥30mg/kg腹腔注射麻醉。麻醉成功后,在术前给予青霉素(60w单位/天)肌肉注射,预防切口感染。接着将动物俯卧位固定于手术台,背部剃毛,于大鼠脊柱两侧背部用标记笔作对称的直径20mm的圆形,之后进行常规消毒铺巾。用高温高压灭菌过的剪刀按照标记笔作的圆形做皮肤缺损,制备直径20mm的圆形皮肤缺损模型。Healthy 12-week-old male SD rats were selected and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of 3% pentobarbital at 30 mg/kg. After successful anesthesia, intramuscular injection of penicillin (60w units/day) was given before surgery to prevent incision infection. Then, fix the animal in the prone position on the operating table, shave the back, and use a marker pen to make a symmetrical circle with a diameter of 20 mm on the back of both sides of the spine of the rat, and then routinely sterilize the towel. Use high-temperature and high-pressure sterilized scissors to make a skin defect according to the circle made by a marker pen, and prepare a circular skin defect model with a diameter of 20 mm.
2、实验1:不同固定及缝合方法制备的大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型的防收缩效果2. Experiment 1: Anti-shrinkage effect of rat skin defect anti-shrinkage models prepared by different fixation and suture methods
将上述“1、大鼠皮肤缺损模型的制备”中造模成功(制备皮肤缺损模型成功)的SD大鼠随机分为5个实验组,每个实验组5只,每个实验组大鼠采用一种防止创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法处理创面,具体如下:The SD rats that were successfully established in the above "1. Preparation of rat skin defect model" (successful preparation of the skin defect model) were randomly divided into 5 experimental groups, 5 in each experimental group, and the rats in each experimental group were divided into 5 experimental groups. A fixation and suturing method for preventing wound surface skin shrinkage to treat wound surface, the details are as follows:
①硅胶圈组:将灭菌待用的硅胶圈1内缘与创面创缘重合,用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用单纯间断缝合法缝合硅胶圈与皮肤,针自硅胶圈中部向圈外缘穿入,缝挂皮肤后自圈外缘穿出,将硅胶圈固定于创缘皮肤上,均匀缝挂8针(硅胶圈组术后即刻大体图如图1所示);①Silicone ring group: The inner edge of the sterilized
②不剪肉膜单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组:将灭菌待用的钢圈1置于创缘皮肤下(钢圈1与圆形皮肤缺损为同心圆),用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用单纯间断缝合法缝合钢圈与皮肤,针从距创缘约1mm的肉膜下、钢圈内缘内侧穿出皮肤,然后在皮肤外跨过皮下钢圈从钢圈外缘的皮外穿过皮肤、肉膜达皮下;打结将钢圈固定,均匀缝挂8针(不剪肉膜单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图如图2所示);②The steel ring group was fixed by intermittent suture without cutting the flesh membrane: the sterilized
③不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定钢圈组:将灭菌待用的钢圈1置于创缘皮肤下(钢圈1与圆形皮肤缺损为同心圆),用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用单纯连续缝合法缝合钢圈与皮肤,针从距创缘约1mm肉膜下、钢圈内缘内侧穿出皮肤,然后在皮肤外跨过皮下钢圈从钢圈外缘的皮外穿过皮肤、肉膜达皮下,第一针缝合后打结,继而用同样方法连续缝合整个钢圈,最后一针与第一针所留线头打结将钢圈固定(不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图如图3所示);3. Simple continuous suture and fixed steel ring group without cutting the flesh membrane: place the
④剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组:沿SD大鼠皮肤创面创缘,用眼科剪仔细环形剪除肉膜,剪除的宽度为2mm,再将灭菌待用的钢圈1置于剪除肉膜处(钢圈外径与剪除后的肉膜边缘重合),用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用单纯间断缝合法缝合钢圈、皮肤、肉膜及皮下组织。④Scissor membrane combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group: along the wound edge of SD rat skin, carefully cut the meat membrane with ophthalmic scissors in a circular shape, and the width of the cut is 2 mm, and then place the
针从距创缘约1mm皮肤下、钢圈内缘内侧穿出皮肤,然后在皮肤外跨过皮下钢圈从钢圈外缘的皮外穿过皮肤、肉膜达皮下,再从皮下跨过钢圈穿过钢圈内缘处皮下组织,打结将钢圈固定,均匀缝挂8针(剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图如图4所示);The needle penetrates the skin under the skin about 1mm from the wound edge and inside the inner edge of the steel ring, and then crosses the subcutaneous steel ring outside the skin, passes through the skin outside the skin of the outer edge of the steel ring, reaches the subcutaneous membrane, and then crosses the subcutaneous The steel ring passes through the subcutaneous tissue at the inner edge of the steel ring, and the steel ring is fixed by knotting, and 8 stitches are evenly sutured (the general view of the group of cutting the flesh membrane combined with simple intermittent suture to fix the steel ring is shown in Figure 4);
⑤剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组:沿SD大鼠皮肤创面创缘,用眼科剪仔细环形剪除肉膜,剪除的宽度为2mm,再将灭菌待用的钢圈1置于剪除肉膜处(钢圈外径与剪除后的肉膜边缘重合),用3-0不可吸收缝合线,采用连续锁边缝合法缝合钢圈与皮肤、肉膜及皮下组织,针从距创缘约1mm皮肤下、钢圈内缘内侧穿出皮肤,然后在皮肤外跨过皮下钢圈从钢圈外缘的皮外穿过皮肤、肉膜达皮下,再从皮下跨过钢圈穿过钢圈内缘处皮下组织,第一针缝合后打结,继而用同样的缝合方法以连续锁边缝合整个钢圈,最后一针与第一针所留线头打结固定,将钢圈固定(剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组术后即刻大体图如图5所示)。⑤Scissor membrane combined with continuous overlock suture to fix the steel ring group: along the wound edge of the SD rat skin, carefully cut the meat membrane with ophthalmic scissors in a circular shape with a width of 2 mm, and then place the
缝合好后,各组都在创面上敷以油纱,再用无菌纱布覆盖,并将其四角缝合固定于皮肤。术后大鼠自由饮食和进水,单笼饲养直至实验结束。在3、7、14、21、28天时观察各组大鼠创面愈合情况,并拍照,计算各组创面愈合率。比较不同的固定及缝合方法对创面愈合率和上皮收缩的影响。创面愈合率=(1-开放性伤口的面积/原始伤口的面积)×100%。After suturing, oil gauze was applied to the wound surface in each group, then covered with sterile gauze, and the four corners of the wound were sutured and fixed to the skin. After the operation, the rats were allowed to eat and drink freely, and were kept in a single cage until the end of the experiment. At 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days, the wound healing of the rats in each group was observed, and photographs were taken to calculate the wound healing rate of each group. The effects of different fixation and suture methods on wound healing rate and epithelial shrinkage were compared. Wound healing rate=(1-area of open wound/area of original wound)×100%.
3、实验2:不同固定及缝合方法制备大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型防收缩效果3. Experiment 2: Anti-shrinkage effect of rat skin defect anti-shrink model prepared by different fixation and suture methods
将上述“1、大鼠皮肤缺损模型的制备”中造模成功(制备皮肤缺损模型成功)的SD大鼠随机分为2个实验组,每个实验组15只,各实验组采用的防止创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法具体如下:SD rats with successful modeling (successful preparation of skin defect model) in the above "1. Preparation of Rat Skin Defect Model" were randomly divided into 2 experimental groups with 15 rats in each experimental group. The skin shrinkage fixation and suture methods are as follows:
实验组Ⅰ:左侧创面为空白对照组(即不采用防止创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法处理),右侧创面为硅胶圈组(固定及缝合方法同试验例1“2”中的“①”);Experimental group I: the left wound was the blank control group (that is, the fixation and suturing methods to prevent the wound skin from shrinking were not used), and the right wound was the silicone ring group (the fixation and suturing methods were the same as those in "①" in "2" of Test Example 1). ");
实验组Ⅱ:左侧创面为剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组(固定及缝合方法同试验例1“2”中的“④”),右侧创面为剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组(固定及缝合方法同试验例1“2”中的“⑤”)。Experimental group II: The wound on the left side was cut flesh membrane combined with simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group (the fixation and suture methods were the same as "④" in "2" of Test Example 1), and the wound on the right was cut flesh membrane combined with continuous overlock suture Fixed steel ring group (fixing and suturing methods are the same as "⑤" in "2" of Test Example 1).
空白对照组,以及采用防止创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法处理后的各组,都在创面上敷以油纱,再用无菌纱布覆盖,并将其四角缝合固定于皮肤。术后大鼠自由饮食和进水,单笼饲养直至实验结束。各组分别在3、7、14、21、28天取材(取材时取大鼠皮肤,如大鼠皮肤与其下的肌层难以分离,可将肌层一起取下。每次取材时使用过量戊巴比妥钠麻醉大鼠致死),石蜡包埋后H&E染色。通过组织学评价上皮收缩情况和皮肤的再生情况。通过组织学比较并评价空白对照组、硅胶圈组、剪肉膜联合单纯间断缝合固定钢圈组、剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组的再生上皮的长度,从而评价不同防收缩方法的优缺点。The blank control group and the groups treated with the fixation and suturing methods to prevent the skin from shrinking on the wound surface were all covered with oil gauze on the wound surface, then covered with sterile gauze, and the four corners of the wound were sutured and fixed to the skin. After the operation, the rats were allowed to eat and drink freely, and were kept in a single cage until the end of the experiment. Each group was collected on 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days respectively (rat skin was taken when the material was collected. If the skin of the rat is difficult to separate from the muscle layer below, the muscle layer can be removed together. Excessive amount of pentoxide was used for each sampling. Rats were anesthetized with sodium barbiturate) and stained with H&E after paraffin embedding. Epithelial shrinkage and skin regeneration were assessed histologically. Different anti-shrinkage methods were evaluated by histological comparison and evaluation of the length of the regenerated epithelium in the blank control group, the silicone ring group, the meat-cutting membrane combined with the simple intermittent suture and fixed steel ring group, and the meat-cutting membrane combined with continuous overlock suture and fixed steel ring group. advantages and disadvantages.
4、实验结果4. Experimental results
各组防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法的防收缩效果如图6~18所示。Figures 6-18 show the anti-contraction effects of the fixation and suture methods for preventing the rat wound skin from shrinking in each group.
(1)图6为不做防止创面收缩处理(空白对照组)的创面愈合情况,图7~11为采用实验1中各组固定及缝合方法处理后创面愈合过程图,图12为实验1中各组固定及缝合方法的创面愈合率。由图6~12可知,与空白对照组相比,各组防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法都不同程度地减慢了创面的收缩。但是,与其他各组相比,本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法(剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组)防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的效果最好。从图9、图11和图12看到不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定钢圈组创面愈合也很慢,甚至在第28天其创面愈合率小于本发明剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组,这是因为不剪肉膜单纯连续缝合固定钢圈组出现了创面的感染,导致创面发生了延迟愈合,已经影响了创面的正常上皮的爬行和愈合。而本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法(剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组)能够在不影响上皮爬行的同时,最大程度地减少创面的收缩,保证创面正常愈合。(1) Figure 6 shows the wound healing without the treatment to prevent wound shrinkage (blank control group). Figures 7 to 11 show the healing process of the wounds after each group's fixation and suturing in
(2)图13~18为实验2的实验结果图,H&E切片结果显示,剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组的肉膜收缩程度最小,创面再生区域最大,而且创面的愈合质量(包括上皮完全覆盖创面的时间,真皮层的厚度,胶原纤维排列及其成熟度)与其他实验组没有明显区别。说明本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法(剪肉膜联合连续锁边缝合固定钢圈组)能够最大程度地减少创面的收缩,且不影响创面的愈合质量。(2) Figures 13-18 are the experimental results of
综上,本发明采用统一了材质、尺寸的钢圈取代现有技术的硅胶圈,应用于啮齿目动物皮肤缺损防收缩模型的制备中,不仅统一了钢圈的使用标准,尽可能排除了额外干扰因素;而且过程中不会破坏钢圈内部结构,钢圈也不易产生形变或者断裂,能够维持良好的防收缩作用,效果非常优良。同时,本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法防收缩效果显著,能够在不影响上皮爬行的同时,最大程度地减少大鼠创面的收缩,且不影响创面的愈合质量。利用本发明防止大鼠创面皮肤收缩的固定及缝合方法制备的大鼠皮肤缺损防收缩模型能够有效的模拟人的创面愈合机制,更准确评估伤口愈合过程中表皮的爬行过程,更好地观察真皮的重塑过程,能够作为研究创面愈合的优良模型,作为评估各种影响伤口愈合因素的平台。其在科学研究方面,有很强的应用价值。To sum up, the present invention uses a steel ring with unified material and size to replace the silicone ring of the prior art, and is applied to the preparation of the rodent skin defect anti-shrinkage model, which not only unifies the use standard of the steel ring, but also eliminates additional In addition, the internal structure of the steel ring will not be damaged during the process, and the steel ring will not be easily deformed or broken, and it can maintain a good anti-shrinkage effect, and the effect is very good. At the same time, the fixation and suturing method for preventing rat wound skin shrinkage of the present invention has a remarkable anti-shrinkage effect, can minimize rat wound shrinkage without affecting epithelial crawling, and does not affect the wound healing quality. The rat skin defect anti-contraction model prepared by the fixation and suturing method for preventing rat wound skin shrinkage of the present invention can effectively simulate the human wound healing mechanism, more accurately evaluate the crawling process of the epidermis during the wound healing process, and better observe the dermis. The remodeling process can be used as an excellent model to study wound healing and as a platform to evaluate various factors affecting wound healing. It has strong application value in scientific research.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910839986.4ACN110742708A (en) | 2019-09-05 | 2019-09-05 | Fixing and sewing method for preventing rodentia animal wound skin from shrinking and application thereof |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910839986.4ACN110742708A (en) | 2019-09-05 | 2019-09-05 | Fixing and sewing method for preventing rodentia animal wound skin from shrinking and application thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110742708Atrue CN110742708A (en) | 2020-02-04 |
Family
ID=69276174
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910839986.4APendingCN110742708A (en) | 2019-09-05 | 2019-09-05 | Fixing and sewing method for preventing rodentia animal wound skin from shrinking and application thereof |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110742708A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112386371A (en)* | 2020-11-24 | 2021-02-23 | 四川大学华西医院 | Valve replacement thread and use method thereof |
| CN113520657A (en)* | 2021-06-21 | 2021-10-22 | 李恭驰 | Method for establishing rat and mouse chronic wound model |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011019859A2 (en)* | 2009-08-11 | 2011-02-17 | Neodyne Biosciences, Inc. | Devices and methods for dressing applicators |
| CN202933049U (en)* | 2013-01-10 | 2013-05-15 | 申传安 | Contracture-resisting steel wire blocking ring for full-thickness skin defect wound in rodent |
| CN109330733A (en)* | 2018-11-30 | 2019-02-15 | 李永彬 | A kind of livestock wound circumference synchronization extension fixture |
| CN208582532U (en)* | 2017-07-27 | 2019-03-08 | 中国人民解放军第三军医大学第一附属医院 | Ring-shaped stent to prevent shrinkage of wound surface |
| CN110051449A (en)* | 2019-05-20 | 2019-07-26 | 贾志强 | A kind of the multi-mode apparatus for deivation and modeling method of rat hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum model |
| CN209187043U (en)* | 2018-11-30 | 2019-08-02 | 李永彬 | A kind of livestock wound circumference synchronization extension fixture |
- 2019
- 2019-09-05CNCN201910839986.4Apatent/CN110742708A/enactivePending
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011019859A2 (en)* | 2009-08-11 | 2011-02-17 | Neodyne Biosciences, Inc. | Devices and methods for dressing applicators |
| CN202933049U (en)* | 2013-01-10 | 2013-05-15 | 申传安 | Contracture-resisting steel wire blocking ring for full-thickness skin defect wound in rodent |
| CN208582532U (en)* | 2017-07-27 | 2019-03-08 | 中国人民解放军第三军医大学第一附属医院 | Ring-shaped stent to prevent shrinkage of wound surface |
| CN109330733A (en)* | 2018-11-30 | 2019-02-15 | 李永彬 | A kind of livestock wound circumference synchronization extension fixture |
| CN209187043U (en)* | 2018-11-30 | 2019-08-02 | 李永彬 | A kind of livestock wound circumference synchronization extension fixture |
| CN110051449A (en)* | 2019-05-20 | 2019-07-26 | 贾志强 | A kind of the multi-mode apparatus for deivation and modeling method of rat hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum model |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112386371A (en)* | 2020-11-24 | 2021-02-23 | 四川大学华西医院 | Valve replacement thread and use method thereof |
| CN113520657A (en)* | 2021-06-21 | 2021-10-22 | 李恭驰 | Method for establishing rat and mouse chronic wound model |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Venugopalan | Essentials of veterinary surgery | |
| Tobias | Manual of small animal soft tissue surgery | |
| Searle et al. | Equine castration: review of anatomy, approaches, techniques and complications in normal, cryptorchid and monorchid horses | |
| GHAMSARI et al. | Evaluation of low level laser therapy on primary healing of experimentally induced full thickness teat wounds in dairy cattle | |
| Yokota et al. | Partial bile duct ligation in the mouse: a controlled model of localized obstructive cholestasis | |
| CN110742708A (en) | Fixing and sewing method for preventing rodentia animal wound skin from shrinking and application thereof | |
| Miller et al. | Evaluation of sutureless scrotal castration for pediatric and juvenile dogs | |
| RU2396923C2 (en) | Method of ovariohysterectomy of cats by lateral access | |
| Greenfield et al. | Neuromuscular pedicle graft for restoration of arytenoid abductor function in dogs with experimentally induced laryngeal hemiplegia | |
| Tamura et al. | Use of the buccal fad pad for vocal cord augmentation | |
| Gouletsou et al. | Comparison of continuous intradermal with simple interrupted suture pattern: An experimental study in dogs | |
| Aston | The choice of suture material for skin closure | |
| RU2391941C2 (en) | Method of boar castration | |
| Truhlsen | The recession operation: histopathologic response, and suture reaction and absorption | |
| Prud'homme et al. | Surgical orchiectomy in fruit bats—Description of two techniques in the Ruwenzori Long-haired fruit bat (Rousettus lanosus) and the Jamaican fruit-eating bat (Artibeus jamaicensis) | |
| CN113040965A (en) | Method for postmenopausal osteoporosis model mouse | |
| Aulia et al. | Comparison of tensile strength and histopathological evaluation of wound healing process using adhesive skin tapes on laceration wounds of porcine skin | |
| Doneley | Soft tissue surgery | |
| Davies | Scalp wounds. An alternative to suture | |
| RU2130299C1 (en) | Method for performing castration of small domestic animals | |
| Azam et al. | A Clinical Report on Surgical Management of Accidentally Erosive Tongue of Cattle in Banshkhali Upazila, Chattogram | |
| RU2580660C1 (en) | Method for elimination of through defect of nose | |
| RU2672122C2 (en) | Method of modeling postoperative purulent-inflammatory complications in the experiment | |
| Malik et al. | EFFECT ON THE TESTOSTERONE ON HEPATIC REGENERATION IN RABBIT MODELS. | |
| Jing et al. | A causal analysis of intra-abdominal hemorrhage after reduced-size liver transplantation in rat |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination |