CN110734556B - A kind of preparation method of metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel - Google Patents
A kind of preparation method of metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogelDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110734556B CN110734556BCN201911111130.1ACN201911111130ACN110734556BCN 110734556 BCN110734556 BCN 110734556BCN 201911111130 ACN201911111130 ACN 201911111130ACN 110734556 BCN110734556 BCN 110734556B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- hydrogel
- polyglutamic acid
- gamma
- metal ion
- solution
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000000017hydrogelSubstances0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription91
- 229920002643polyglutamic acidPolymers0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription65
- 229910021645metal ionInorganic materials0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription26
- 238000002360preparation methodMethods0.000titleclaimsdescription7
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription24
- 230000009920chelationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription12
- -1cerium ionChemical class0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- CZMAIROVPAYCMU-UHFFFAOYSA-Nlanthanum(3+)Chemical compound[La+3]CZMAIROVPAYCMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsabstractdescription8
- 229910052684CeriumInorganic materials0.000claimsabstractdescription7
- 229910052751metalInorganic materials0.000claimsabstract3
- 239000002184metalSubstances0.000claimsabstract3
- 239000000243solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription31
- 238000003756stirringMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-NwaterSubstancesOXLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claimsdescription8
- 239000007864aqueous solutionSubstances0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000001035dryingMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 239000012295chemical reaction liquidSubstances0.000claims3
- BPSIOYPQMFLKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntrimethoxy-[3-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)propyl]silaneChemical compoundCO[Si](OC)(OC)CCCOCC1CO1BPSIOYPQMFLKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000claims2
- HQYALQRYBUJWDH-UHFFFAOYSA-Ntrimethoxy(propyl)silaneChemical compoundCCC[Si](OC)(OC)OCHQYALQRYBUJWDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000abstractdescription8
- 239000003431cross linking reagentSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 239000000178monomerSubstances0.000abstractdescription3
- 210000000845cartilageAnatomy0.000abstractdescription2
- 239000013522chelantSubstances0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000008569processEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 230000017423tissue regenerationEffects0.000abstractdescription2
- 238000005728strengtheningMethods0.000abstract1
- 229920003169water-soluble polymerPolymers0.000abstract1
- 108700022290poly(gamma-glutamic acid)Proteins0.000description16
- 150000002500ionsChemical class0.000description6
- 238000010587phase diagramMethods0.000description4
- 108010020346Polyglutamic AcidProteins0.000description3
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description3
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description3
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description2
- 229920001222biopolymerPolymers0.000description2
- 230000007423decreaseEffects0.000description2
- 230000003247decreasing effectEffects0.000description2
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description2
- 238000002474experimental methodMethods0.000description2
- 239000000499gelSubstances0.000description2
- 229910052746lanthanumInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000000463materialSubstances0.000description2
- 231100000252nontoxicToxicity0.000description2
- 230000003000nontoxic effectEffects0.000description2
- 229920000642polymerPolymers0.000description2
- 238000002791soakingMethods0.000description2
- 230000008961swellingEffects0.000description2
- 229910021642ultra pure waterInorganic materials0.000description2
- 239000012498ultrapure waterSubstances0.000description2
- 235000014469Bacillus subtilisNutrition0.000description1
- 244000063299Bacillus subtilisSpecies0.000description1
- BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-NSilaneChemical compound[SiH4]BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 229910002808Si–O–SiInorganic materials0.000description1
- 150000001875compoundsChemical class0.000description1
- 238000004132cross linkingMethods0.000description1
- 125000004122cyclic groupChemical group0.000description1
- 239000008367deionised waterSubstances0.000description1
- 229910021641deionized waterInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000003937drug carrierSubstances0.000description1
- 230000009977dual effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000000855fermentationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004151fermentationEffects0.000description1
- 239000003292glueSubstances0.000description1
- 230000012010growthEffects0.000description1
- DKAGJZJALZXOOV-UHFFFAOYSA-Nhydrate;hydrochlorideChemical compoundO.ClDKAGJZJALZXOOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N0.000description1
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description1
- 239000007788liquidSubstances0.000description1
- 238000003760magnetic stirringMethods0.000description1
- 229910001510metal chlorideInorganic materials0.000description1
- 230000000813microbial effectEffects0.000description1
- 210000000963osteoblastAnatomy0.000description1
- 239000011148porous materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000843powderSubstances0.000description1
- 125000001436propyl groupChemical group[H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H]0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 230000004044responseEffects0.000description1
- 229910000077silaneInorganic materials0.000description1
- 239000007779soft materialSubstances0.000description1
- 239000000126substanceSubstances0.000description1
- 238000006467substitution reactionMethods0.000description1
- 238000009864tensile testMethods0.000description1
- 238000012360testing methodMethods0.000description1
- 210000001519tissueAnatomy0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J3/00—Processes of treating or compounding macromolecular substances
- C08J3/02—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques
- C08J3/03—Making solutions, dispersions, lattices or gels by other methods than by solution, emulsion or suspension polymerisation techniques in aqueous media
- C08J3/075—Macromolecular gels
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08J—WORKING-UP; GENERAL PROCESSES OF COMPOUNDING; AFTER-TREATMENT NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASSES C08B, C08C, C08F, C08G or C08H
- C08J2377/00—Characterised by the use of polyamides obtained by reactions forming a carboxylic amide link in the main chain; Derivatives of such polymers
- C08J2377/04—Polyamides derived from alpha-amino carboxylic acids
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/16—Halogen-containing compounds
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/54—Silicon-containing compounds
- C08K5/541—Silicon-containing compounds containing oxygen
- C08K5/5435—Silicon-containing compounds containing oxygen containing oxygen in a ring
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Dispersion Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers With Sulfur, Phosphorus Or Metals In The Main Chain (AREA)
- Materials For Medical Uses (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于水凝胶的制备方法,特别涉及一种强化水凝胶的制备方法。The invention belongs to a preparation method of a hydrogel, in particular to a preparation method of a strengthened hydrogel.
背景技术Background technique
水凝胶是一类由三维聚合物网络组成的材料,它能吸收大量的水。可生物降解水凝胶是一种典型的软性材料,已被应用于多种生物医学领域,如组织工程支架和药物载体等。聚谷氨酸(γ-PGA),又称纳豆菌胶、多聚谷氨酸,它是一种水溶性,生物降解,不含毒性,使用微生物发酵法制得的生物高分子。Hydrogels are a class of materials composed of three-dimensional polymer networks that can absorb large amounts of water. Biodegradable hydrogels are typical soft materials that have been applied in various biomedical fields, such as tissue engineering scaffolds and drug carriers. Polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA), also known as natto bacteria gum, polyglutamic acid, is a water-soluble, biodegradable, non-toxic, biopolymer obtained by microbial fermentation.
γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性,pH响应等特性,γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶因其自身具备的优越特性, 近年来一直是研究的热点, 是一类非常有应用潜力的生物高分子材料。但其也存在一些不足,比如在较高含水量时机械强度有所下降,导致其在应用方面有很大的限制,因此提高γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶的强度是其应用的关键。γ-Polyglutamic acid hydrogel has good biocompatibility, pH response and other characteristics. Because of its own superior characteristics, γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel has been a research hotspot in recent years. A very promising biopolymer material. However, it also has some shortcomings, such as the decrease of mechanical strength at higher water content, which leads to great limitations in its application. Therefore, improving the strength of γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel is the key to its application.
检索国内外相关专利,并没有有关金属离子强化γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶的相关报道。Searching related domestic and foreign patents, there is no relevant report on metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于提供一种金属离子强化γ 聚谷氨酸水凝胶的制备方法,解决目前γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶在较高含水量时机械强度下降的技术问题,所述制备的γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶具有较强拉伸强度,同时,其溶胀系数变小。The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing a metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel, which solves the technical problem that the mechanical strength of the current γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel decreases when the water content is relatively high. The γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel has strong tensile strength, and at the same time, its swelling coefficient becomes smaller.
为此,本发明提供的一种金属离子强化γ 聚谷氨酸水凝胶的制备方法,包括以下步骤:For this reason, the preparation method of a metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
(1)将γ-聚谷氨酸(γ-PGA)溶于水中并搅拌均匀,直至γ-聚谷氨酸完全溶解,得到γ-聚谷氨酸水溶液,作为第一反应液;(1) Dissolve γ-polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA) in water and stir evenly until the γ-polyglutamic acid is completely dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of γ-polyglutamic acid as the first reaction solution;
(2)将γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧基)丙基三甲氧基硅烷(GPTMS)边搅拌边缓慢的加入到第一反应液中,搅拌均匀;(2) Slowly add γ-(2,3-glycidoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane (GPTMS) into the first reaction solution while stirring, and stir evenly;
(3)将搅拌均匀后的溶液取出,放入烘箱中在35-38℃下静置6-12h,得到γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶;(3) Take out the well-stirred solution, put it in an oven and let it stand at 35-38°C for 6-12 hours to obtain γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel;
(4)将制得的水凝胶浸入三价金属离子溶液中,进行螯合反应,即得到金属离子强化的γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶,所述三价金属离子为铈离子或镧离子。(4) Immerse the prepared hydrogel in a trivalent metal ion solution and carry out a chelation reaction to obtain a metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel, wherein the trivalent metal ion is cerium ion or lanthanum ion.
进一步地,所选γ-聚谷氨酸的分子量为20万~200万单位。分子量为20万~200万单位的γ-聚谷氨酸具有良好的亲水性与保水能力,易于在水中溶解。Further, the molecular weight of the selected γ-polyglutamic acid is 200,000 to 2,000,000 units. Gamma-polyglutamic acid with a molecular weight of 200,000 to 2 million units has good hydrophilicity and water retention capacity, and is easy to dissolve in water.
进一步地,所述γ-聚谷氨酸质量浓度为5-20wt%。该浓度范围内的γ-聚谷氨酸更加容易形成凝胶。Further, the mass concentration of the γ-polyglutamic acid is 5-20wt%. The γ-polyglutamic acid in this concentration range is more likely to form a gel.
优选地,加入γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧基)丙基三甲氧基硅烷与第一反应液的质量比为1:(9-11)。γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧基)丙基三甲氧基硅烷作为交联剂与γ-聚谷氨酸交联反应,在溶液环境中静置后形成水凝胶。Preferably, the mass ratio of γ-(2,3-glycidoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane to the first reaction solution is 1:(9-11). γ-(2,3-glycidoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane was used as a cross-linking agent to cross-link with γ-polyglutamic acid to form a hydrogel after standing in a solution environment.
作为本发明的优选方案,三价金属离子溶液中的铈离子或镧离子的浓度为0.02-0.2M。As a preferred solution of the present invention, the concentration of cerium ions or lanthanum ions in the trivalent metal ion solution is 0.02-0.2M.
作为本发明的优先方案,所述水凝胶浸入三价金属离子溶液的时间为14-18h;烘干时间为30-45min。As a preferred solution of the present invention, the time for the hydrogel to be immersed in the trivalent metal ion solution is 14-18h; the drying time is 30-45min.
与现有技术相比,本发明的有益效果在于:Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects of the present invention are:
(1)以对人体无毒的γ-聚谷氨酸为反应单体,以对成骨细胞生长有利的无机硅烷体γ-(2.3环氧丙氧)丙基三甲氧基硅烷(GPTMS)为反应的交联剂制取γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶以廉价的三价金属氯化水合物为水凝胶螯合金属离子的来源采用金属离子的螯合反应,反应温度低,工艺简单,实施成本低廉。(1) The non-toxic γ-polyglutamic acid is used as the reaction monomer, and the inorganic silane γ-(2.3 glycidoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane (GPTMS), which is beneficial to the growth of osteoblasts, is used as the reaction monomer. Preparation of γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel by reacting cross-linking agent, using cheap trivalent metal chloride hydrate as the source of chelating metal ions for hydrogel, adopting the chelating reaction of metal ions, the reaction temperature is low, and the process is simple , the implementation cost is low.
(2)本发明方法制备的强化水凝胶韧性较好,且能在较快时间完成螯合反应,形成强度均一的螯合物,同时,其溶胀系数变小,适合后期应用。(2) The reinforced hydrogel prepared by the method of the present invention has good toughness, and can complete the chelation reaction in a relatively fast time to form a chelate compound with uniform strength. At the same time, its swelling coefficient becomes smaller, which is suitable for later application.
(3)本发明方法制备的强化水凝胶在进行拉伸实验时具有较高的拉伸强度,与未进行螯合的γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶相比,与铈离子螯合的水凝胶相比,0.02M/L的铈离子溶液浓度所制备的水凝胶强度最好,杨氏模量提升了661倍,拉伸强度提高了53倍,镧离子螯合的水凝胶在不同的浓度下,0.15M/L的镧离子溶液所制备的水凝胶强度最好,杨氏模量提升了960倍,拉伸强度提高了118倍,水凝胶的力学强度得到了极大的提高。(3) The reinforced hydrogel prepared by the method of the present invention has higher tensile strength in the tensile test, and compared with the γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel without chelation, the Compared with the hydrogel, the hydrogel prepared with the concentration of 0.02M/L cerium ion solution has the best strength, the Young's modulus is increased by 661 times, the tensile strength is increased by 53 times, and the lanthanum ion chelated hydrogel Under different concentrations, the hydrogel prepared by 0.15M/L lanthanum ion solution has the best strength, the Young's modulus is increased by 960 times, the tensile strength is increased by 118 times, and the mechanical strength of the hydrogel is extremely high. big improvement.
(4)本发明方法制备的强化水凝胶可用于软骨组织修复,软体机器人,生物传感器等方面。(4) The reinforced hydrogel prepared by the method of the present invention can be used for cartilage tissue repair, soft robots, biosensors and the like.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为Ce3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶的拉伸强度相图。Figure 1 is a phase diagram of the tensile strength of chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of Ce3+ .
图2为Ce3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶的断裂伸长率相图。Figure 2 is a phase diagram of elongation at break of chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of Ce3+ .
图3为Ce3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶杨氏模量。Figure 3 shows the Young's modulus of chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of Ce3+ .
图4为Ce3+螯合水凝胶的原理示意图。Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the principle of Ce3+ chelating hydrogel.
图5为La3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶的拉伸强度相图。Figure 5 is a phase diagram of the tensile strength of the chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of La3+ .
图6为La3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶的断裂伸长率相图。Figure 6 is a phase diagram of elongation at break of chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of La3+ .
图7为La3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶杨氏模量。Figure 7 shows the Young's modulus of chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of La3+ .
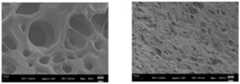
图8为实施例1水凝胶与La3+离子强化后水凝胶扫描电子显微镜图片。FIG. 8 is a scanning electron microscope picture of the hydrogel of Example 1 after being reinforced with La3+ ions.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合具体实施例和附图对本发明作进一步详述。The present invention will be described in further detail below with reference to specific embodiments and accompanying drawings.
实施例1Example 1
称取分子量为20万~200万单位的γ-PGA粉末1g,溶解于10ml去离子水中,利用磁力搅拌2-3h使其完全溶解,再加入1mlGPTMS,做为交联剂,利用磁力搅拌4-5h,使γ-PGA与GPTMS发生交联反应,再将液态高分子溶液倒入模具中,放入37℃烘箱中静置8-12h待其成胶取出,获得γ-PGA水凝胶,将水凝胶切成长度、宽度基本相同的条状样品。Weigh 1g of γ-PGA powder with a molecular weight of 200,000 to 2 million units, dissolve it in 10ml of deionized water, and use magnetic stirring for 2-3h to completely dissolve it. 5h, make the γ-PGA and GPTMS cross-linking reaction, then pour the liquid polymer solution into the mold, put it in a 37 ℃ oven for 8-12h until it gels and take it out to obtain γ-PGA hydrogel. The hydrogel was cut into strip samples with substantially the same length and width.
实施例2Example 2
进一步地,分别称取0.373g,1.118g,1.863g,2.795g,3.726g CeCl3·7H2O溶解于50ml超纯水中,配制成0.02M(mol/L),0.06M,0.1M,0.15M,0.2M的Ce3+浓度的水溶液,将实施例1中制好的水凝胶样条分别浸入不同Ce3+浓度的溶液中16h,取出烘干30-45min,获得金属离子强化γ-PGA水凝胶。Further, 0.373g, 1.118g, 1.863g, 2.795g, 3.726g CeCl3 ·7H2 O were weighed and dissolved in 50ml ultrapure water, respectively, and prepared into 0.02M (mol/L), 0.06M, 0.1M, 0.15M, 0.2M Ce3+ concentration aqueous solutions, the hydrogel splines prepared in Example 1 were immersed in solutions of different Ce3+ concentrations for 16h, taken out and dried for 30-45min to obtain metal ion-enhanced γ -PGA hydrogel.
通过拉伸实验测得与Ce3+发生螯合反应的γ-PGA水凝胶的拉伸强度,图1、2为Ce3+离子不同浓度下螯合水凝胶拉伸强度及断裂伸长率的对比图,分别对应的是未浸泡Ce3+离子的γ-PGA水凝胶样品及0.02M(mol/L),0.06M,0.1M,0.15M,0.2M的Ce3+浓度的水溶液浸泡后的样品,试验结果表明:与γ-PGA水凝胶的拉伸强度相比经过Ce3+离子螯合反应后的水凝胶拉伸强度最高提升了53倍,断裂伸长率略有下降,但拉伸强度有明显提高。图3为Ce3+离子不同浓度下螯合水凝胶杨氏模量,与γ-PGA水凝胶的拉伸强度相比经过Ce3+螯合反应后的水凝胶杨氏模量最高提升了661倍。水凝胶的力学强度有了明显的提升。图4为γ-PGA水凝胶与三价金属离子发生螯合反应的原理示意图,首先γ-聚谷氨酸与γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧基)丙基三甲氧基硅烷(GPTMS)发生反应,生成环状的Si-O-Si结构的γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶,将生成的γ-聚谷氨酸水凝胶浸入CeCl3溶液中,水凝胶与Ce3+离子发生螯合反应,生成物理和化学网络双网络交联的水凝胶。The tensile strength of γ-PGA hydrogels chelated with Ce3+ was measured by tensile experiments. Figures 1 and 2 show the tensile strength and elongation at break of chelated hydrogels under different concentrations of Ce3+ ions. The comparison chart of the ratio of γ-PGA hydrogel samples and 0.02M (mol/L), 0.06M, 0.1M, 0.15M, 0.2M Ce3+ concentration aqueous solution respectively without soaking Ce3+ ions After soaking the samples, the test results show that compared with the tensile strength of γ-PGA hydrogels, the tensile strength of hydrogels after Ce3+ ion chelation reaction is up to 53 times higher, and the elongation at break is slightly higher than that of γ-PGA hydrogels. decreased, but the tensile strength increased significantly. Figure 3 shows the Young's modulus of chelated hydrogels at different concentrations of Ce3+ ions. Compared with the tensile strength of γ-PGA hydrogels, the Young's modulus of hydrogels after Ce3+ chelation reaction is the highest An increase of 661 times. The mechanical strength of the hydrogel has been significantly improved. Figure 4 is a schematic diagram of the chelation reaction between γ-PGA hydrogel and trivalent metal ions. First, γ-polyglutamic acid and γ-(2,3-glycidoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane ( GPTMS) reacted to generate a cyclic Si-O-Si structure γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel, the generated γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel was immersed in CeCl3 solution, and the hydrogel was mixed with Ce3 + ions undergo a chelation reaction, resulting in a hydrogel cross-linked with a dual network of physical and chemical networks.
实施例3Example 3
分别称取0.258g,0.775g,1.293g,1.938g,2.584gCeCl3·7H2O溶解于50ml超纯水中,配制成0.02M(mol/L),0.06M,0.1M,0.15M,0.2M的La3+浓度的水溶液,将实施例1中制好的水凝胶样条分别浸入不同La3+浓度的溶液中16h,取出烘干30-45min,获得金属离子强化γ-PGA水凝胶。Weigh 0.258g, 0.775g, 1.293g, 1.938g, 2.584g of CeCl3 ·7H2 O and dissolve them in 50ml of ultrapure water to prepare 0.02M (mol/L), 0.06M, 0.1M, 0.15M, 0.2 La3+ concentration aqueous solution of M, the hydrogel splines prepared in Example 1 were immersed in solutions of different La3+ concentrations for 16 h, taken out and dried for 30-45 min to obtain metal ion-enhanced γ-PGA hydrogelation glue.
通过拉伸实验测得与La3+发生螯合反应的γ-PGA水凝胶的拉伸强度,图5、6为La3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶的拉伸强度与断裂伸长率对比相图,与γ-PGA水凝胶的拉伸强度相比经过La3+螯合反应后的水凝胶拉伸强度最高提升了118倍,断裂伸长率略有下降,但拉伸强度有明显提高,图7为La3+不同浓度下螯合水凝胶杨氏模量,与γ-PGA水凝胶的拉伸强度相比经过La3+螯合反应后的水凝胶杨氏模量最高提升了960倍。水凝胶的力学强度有了明显的提升。The tensile strength of γ-PGA hydrogels chelated with La3+ was measured by tensile experiments. Figures 5 and 6 show the tensile strength and elongation at break of chelated hydrogels with different concentrations of La3+ Compared with the tensile strength of γ-PGA hydrogel, the tensile strength of the hydrogel after La3+ chelation reaction increased by a maximum of 118 times, and the elongation at break decreased slightly, but the tensile strength The strength is significantly improved. Figure 7 shows the Young's modulus of the chelated hydrogel at different concentrations of La3+ . Compared with the tensile strength of the γ-PGA hydrogel, the Young's modulus of the hydrogel after La3+ chelation reaction The modulus is up to 960 times higher. The mechanical strength of the hydrogel has been significantly improved.
实施例4Example 4
一种金属离子强化γ 聚谷氨酸水凝胶的制备方法,包括以下步骤:A preparation method of metal ion-enhanced gamma polyglutamic acid hydrogel, comprising the following steps:
(1)将分子量为20万~200万单位的γ-聚谷氨酸溶于水中并搅拌均匀,直至γ-聚谷氨酸完全溶解,得到γ-聚谷氨酸水溶液,作为第一反应液,第一反应液中,γ-聚谷氨酸质量浓度为5-20wt%;(1) Dissolve γ-polyglutamic acid with a molecular weight of 200,000 to 2 million units in water and stir evenly until the γ-polyglutamic acid is completely dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of γ-polyglutamic acid as the first reaction solution , in the first reaction solution, the mass concentration of γ-polyglutamic acid is 5-20wt%;
(2)将γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧基)丙基三甲氧基硅烷边搅拌边缓慢的加入到第一反应液中,搅拌均匀;γ-(2,3-环氧丙氧基)丙基三甲氧基硅烷与第一反应液的质量比为1:(9-11);(2) Slowly add γ-(2,3-glycidoxy)propyltrimethoxysilane to the first reaction solution while stirring, and stir evenly; γ-(2,3-glycidoxy) The mass ratio of propyl)propyltrimethoxysilane and the first reaction solution is 1:(9-11);
(3)将搅拌均匀后的溶液取出,放入烘箱中在35-38℃下静置6-12h,得到γ 聚谷氨酸水凝胶;(3) Take out the well-stirred solution, put it in an oven and let it stand at 35-38°C for 6-12 hours to obtain γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel;
(4)将制得的浸入三价镧离子溶液中14-18h,进行螯合反应,取出水凝胶烘干30-45mi即得到强化的水凝胶即得到金属离子强化的γ 聚谷氨酸水凝胶,镧离子的浓度为0.02-0.2M。(4) Immerse the prepared lanthanum ion solution for 14-18 hours, carry out chelation reaction, take out the hydrogel and dry it for 30-45 minutes to obtain a strengthened hydrogel, namely, a metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid The hydrogel, the concentration of lanthanum ions is 0.02-0.2M.
所获得的金属离子强化γ 聚谷氨酸水凝胶具有拉伸强度高,水凝胶的力学强度有了明显的提升。The obtained metal ion reinforced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel has high tensile strength, and the mechanical strength of the hydrogel has been significantly improved.
实施例1中的获得的γ-PGA水凝胶与本实施例La3+螯合后的水凝胶进行冷冻干燥进行SEM拍摄得到图8,图片中可以明显看出水凝胶的孔径明显减小而且更为致密。The obtained γ-PGA hydrogel in Example 1 and the La3+ chelated hydrogel in this example were freeze-dried and photographed by SEM to obtain Figure 8. It can be clearly seen from the picture that the pore size of the hydrogel is significantly reduced And more dense.
上述三价镧离子溶液可为三价铈离子溶液所取代,也能取得提高水凝胶强度的目的。The trivalent lanthanum ion solution can be replaced by the trivalent cerium ion solution, and the purpose of improving the strength of the hydrogel can also be achieved.
本发明并不局限于上述实施例,在本发明公开的技术方案的基础上,本领域的技术人员根据所公开的技术内容,不需要创造性的劳动就可以对其中的一些技术特征作出一些替换和变形,这些替换和变形均在本发明的保护范围内。The present invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments. On the basis of the technical solutions disclosed in the present invention, those skilled in the art can make some substitutions and modifications to some of the technical features according to the disclosed technical contents without creative work. Modifications, replacements and modifications are all within the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (4)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911111130.1ACN110734556B (en) | 2019-11-14 | 2019-11-14 | A kind of preparation method of metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911111130.1ACN110734556B (en) | 2019-11-14 | 2019-11-14 | A kind of preparation method of metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110734556A CN110734556A (en) | 2020-01-31 |
| CN110734556Btrue CN110734556B (en) | 2022-07-22 |
Family
ID=69272867
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201911111130.1AActiveCN110734556B (en) | 2019-11-14 | 2019-11-14 | A kind of preparation method of metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110734556B (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112708147B (en)* | 2020-12-01 | 2022-03-15 | 扬州大学 | Preparation method of Mg/Sr-NBG enhanced gamma-PGA hydrogel |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101848737A (en)* | 2007-09-07 | 2010-09-29 | 皇家创新公司 | Bioactive nanocomposite material |
| CN106589409A (en)* | 2016-11-28 | 2017-04-26 | 上海大学 | Polyglutamic acid/sodium alginate adhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
| CN110092922A (en)* | 2019-05-31 | 2019-08-06 | 成都金开生物工程有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of gamma-polyglutamic acid plural gel |
- 2019
- 2019-11-14CNCN201911111130.1Apatent/CN110734556B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101848737A (en)* | 2007-09-07 | 2010-09-29 | 皇家创新公司 | Bioactive nanocomposite material |
| CN106589409A (en)* | 2016-11-28 | 2017-04-26 | 上海大学 | Polyglutamic acid/sodium alginate adhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof |
| CN110092922A (en)* | 2019-05-31 | 2019-08-06 | 成都金开生物工程有限公司 | A kind of preparation method of gamma-polyglutamic acid plural gel |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| Fabrication, characterization and in vitro drug release behavior of electrospun PLGA/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold;Meng Z. X.,et al;《MATERIALS CHEMISTRY AND PHYSICS》;20110215;第125卷(第3期);第606-611页* |
| Modification of polyglutamic acid with silanol groups and calcium salts to induce calcification in a simulated body fluid;Koh Mi-Young,et al;《JOURNAL OF BIOMATERIALS APPLICATIONS》;20100305;第25卷(第6期);第581-594页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110734556A (en) | 2020-01-31 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| Gan et al. | Plant-inspired adhesive and tough hydrogel based on Ag-Lignin nanoparticles-triggered dynamic redox catechol chemistry | |
| Seidi et al. | Self‐healing polyol/borax hydrogels: fabrications, properties and applications | |
| CN102206342B (en) | Conductive polymer and its synthesis method, electroactive electrode whose surface is covered with said conductive polymer | |
| CN112266486A (en) | A kind of tannic acid-coated nanocellulose/polyacrylic acid adhesive hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| US9275771B2 (en) | Conductive polymer, synthesis method thereof, and electroactive electrode covered with said conductive polymer | |
| CN106750478B (en) | Preparation method of high-strength dual-network antibacterial biological hydrogel | |
| CN104194023A (en) | Dopamine-based method for improving surface hydrophilicity and biocompatibility of medical polyurethane material | |
| WO2022041429A1 (en) | Anti-fouling gel particles containing rare earth/anti-fouling agent and preparation method therefor | |
| CN109880127B (en) | Preparation method of high-strength triple-network polypyrrole-based conductive composite hydrogel material | |
| CN109897316B (en) | Preparation method of polyaniline/polyvinyl alcohol composite conductive gel | |
| CN109912816B (en) | A kind of preparation method of polypyrrole/polyurethane composite conductive hydrogel | |
| CN109734842A (en) | A kind of transparent conductive flexible bacterial cellulose composite material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110790885A (en) | Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan quaternary ammonium salt antibacterial self-healing hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN104130540A (en) | Cellulose based conductive hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof | |
| CN104262648A (en) | Collagen-based biomedical material by taking dialdehyde polyethylene glycol as cross-linking agent and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106832135A (en) | A kind of modified poly ethylene alcohol copolymer and its preparation and gel polymer electrolyte | |
| CN110734556B (en) | A kind of preparation method of metal ion-enhanced γ-polyglutamic acid hydrogel | |
| CN107987285A (en) | A kind of conduction injection aquagel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN110407982A (en) | A kind of antibacterial hydrogel material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116589735A (en) | A kind of preparation method and application of agarose-bacterial cellulose composite gel | |
| Zhang et al. | Preparation and properties of a chitosan–hyaluronic acid-polypyrrole conductive hydrogel catalyzed by Laccase | |
| CN108314868A (en) | A kind of lignin composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof | |
| CN115895281A (en) | A kind of tannic acid modified protein-based hydrogel and its preparation method and application | |
| CN112480435B (en) | Injectable antibacterial hydrogel material and preparation method thereof | |
| CN106750349A (en) | Peptide modified polyamide-amine type branch-shape polymer and preparation method and application |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |