CN110712491A - A layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling - Google Patents
A layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decouplingDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110712491A CN110712491ACN201910983324.4ACN201910983324ACN110712491ACN 110712491 ACN110712491 ACN 110712491ACN 201910983324 ACN201910983324 ACN 201910983324ACN 110712491 ACN110712491 ACN 110712491A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- modal
- vehicle
- control
- decoupling
- matrix
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription41
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription87
- 239000000725suspensionSubstances0.000claimsabstractdescription51
- 230000009466transformationEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription10
- 238000013016dampingMethods0.000claimsdescription20
- 238000006073displacement reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription9
- 230000005284excitationEffects0.000claimsdescription7
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000004590computer programMethods0.000claimsdescription6
- 238000010276constructionMethods0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000000694effectsEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000004364calculation methodMethods0.000claims1
- 230000008878couplingEffects0.000abstractdescription11
- 238000010168coupling processMethods0.000abstractdescription11
- 238000005859coupling reactionMethods0.000abstractdescription11
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000abstractdescription4
- 239000013598vectorSubstances0.000description25
- 230000007704transitionEffects0.000description6
- -1verticalSubstances0.000description3
- 230000006872improvementEffects0.000description2
- 230000008859changeEffects0.000description1
- 244000145845chatteringSpecies0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description1
- 238000012986modificationMethods0.000description1
- 230000004048modificationEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60G—VEHICLE SUSPENSION ARRANGEMENTS
- B60G17/00—Resilient suspensions having means for adjusting the spring or vibration-damper characteristics, for regulating the distance between a supporting surface and a sprung part of vehicle or for locking suspension during use to meet varying vehicular or surface conditions, e.g. due to speed or load
- B60G17/015—Resilient suspensions having means for adjusting the spring or vibration-damper characteristics, for regulating the distance between a supporting surface and a sprung part of vehicle or for locking suspension during use to meet varying vehicular or surface conditions, e.g. due to speed or load the regulating means comprising electric or electronic elements
- B60G17/018—Resilient suspensions having means for adjusting the spring or vibration-damper characteristics, for regulating the distance between a supporting surface and a sprung part of vehicle or for locking suspension during use to meet varying vehicular or surface conditions, e.g. due to speed or load the regulating means comprising electric or electronic elements characterised by the use of a specific signal treatment or control method
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60G—VEHICLE SUSPENSION ARRANGEMENTS
- B60G2600/00—Indexing codes relating to particular elements, systems or processes used on suspension systems or suspension control systems
- B60G2600/18—Automatic control means
- B60G2600/187—Digital Controller Details and Signal Treatment
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Vehicle Body Suspensions (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明涉及车辆控制技术,具体涉及一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法、系统及介质,用于实现车辆模态解耦的分层控制。The invention relates to vehicle control technology, in particular to a layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling, which are used to realize the layered control of vehicle modal decoupling.
背景技术Background technique
车辆在行驶过程中有7种耦合运动模式,即车身主导的垂向、俯仰和侧倾模式,以及车轮组主导的垂向、俯仰、侧倾和扭曲模式,车辆行驶时,各振动模态之间相互耦合,即汽车悬挂质量和非悬挂质量产生的耦合振动,这不仅降低了车辆行驶平顺性,还降低了驾乘者的舒适度。悬架系统连接了车轮与车身,对悬架的控制能够直接改变车辆的运动模态,但是传统的对悬架的控制方式往往针对某一种模态进行控制,由于模态之间存在耦合,因此在对某一种模态进行控制的同时也会影响其它模态运动的性能,导致该模态运动性能提高了,但是降低了其他模态运动的性能。The vehicle has 7 coupled motion modes during driving, namely the vertical, pitch and roll modes dominated by the body, and the vertical, pitch, roll and twist modes dominated by the wheel group. The mutual coupling, that is, the coupled vibration generated by the suspension mass and the non-suspension mass of the vehicle, not only reduces the ride comfort of the vehicle, but also reduces the comfort of the driver and occupant. The suspension system connects the wheel and the body, and the control of the suspension can directly change the motion mode of the vehicle, but the traditional control method of the suspension is often controlled for a certain mode, due to the coupling between the modes, Therefore, while controlling a certain mode, it will also affect the performance of other modes of motion, resulting in the improvement of the motion performance of this mode, but the decrease of the performance of other modes of motion.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明要解决的技术问题:针对现有技术的上述问题,提供一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法、系统及介质,本发明能够使车辆的几种模态之间相互解耦,从而实现单独控制某一种模态而不影响其他运动模态,本发明分层控制利用模块化设计的优点,能够有效地提高整体控制质量,在设计控制器时采用分层控制方法可以避免控制模式的切换,有利于降低控制系统的复杂性。本发明解决了传统控制方法在针对某一种模态进行控制的同时不能保证其它模态的性能问题,车辆模态解耦分层控制方法的应用,对研究车辆运动、分析复杂的车辆模型、解决车辆运动时的多干扰、非线性、滞后、不确定性以及强耦合等问题具有深远的意义。The technical problem to be solved by the present invention: in view of the above-mentioned problems of the prior art, a layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling are provided. The present invention can decouple several modes of the vehicle from each other. In order to achieve independent control of a certain mode without affecting other motion modes, the layered control of the present invention utilizes the advantages of modular design, which can effectively improve the overall control quality. When designing the controller, the layered control method can be used. Avoiding the switching of control modes is beneficial to reduce the complexity of the control system. The invention solves the problem that the traditional control method cannot guarantee the performance of other modes while controlling a certain mode. The application of the vehicle mode decoupling layered control method is useful for studying vehicle motion, analyzing complex vehicle models, It has far-reaching significance to solve the problems of multiple disturbances, nonlinearity, hysteresis, uncertainty and strong coupling during vehicle motion.
为了解决上述技术问题,本发明采用的技术方案为:In order to solve the above-mentioned technical problems, the technical scheme adopted in the present invention is:
一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法,实施步骤包括:A layered control method for vehicle modal decoupling, the implementation steps include:
1)获取车辆的构造数据和行车数据;1) Obtain the structural data and driving data of the vehicle;
2)根据构造数据和行车数据建立车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型;2) Establish a vehicle seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model of the vehicle according to the structural data and driving data;
3)将车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型用模态转换矩阵TF转换,得到一个用于将车辆模型表示为解耦模态坐标方程的新七自由度模态解耦方程;3) Transform the vehicle's seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model with a modal transformation matrix TF to obtain a new seven-degree-of-freedom modal decoupling equation for representing the vehicle model as a decoupled modal coordinate equation;
4)基于新七自由度模态解耦方程通过上层控制器根据控制目标求出期望模态控制力;4) Based on the new 7-DOF modal decoupling equation, the desired modal control force is obtained through the upper controller according to the control objective;
5)通过下层控制器结合具体的悬架作动器系统模型跟踪获取的期望模态控制力。5) Track the desired modal control force obtained by the lower controller combined with the specific suspension actuator system model.
优选地,步骤2)的详细步骤包括:Preferably, the detailed steps of step 2) include:
2.1)根据构造数据和行车数据建立车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型,且所述整车七自由度振动参考模型的函数表达式如式(1)所示;2.1) According to the construction data and the driving data, a vehicle seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model of the vehicle is established, and the function expression of the vehicle seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model is shown in formula (1);
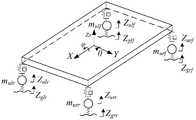
式(1)中,Zs表示车身的垂直位移,Zgij表示每个轮胎的路面轮廓激励,Zuij表示非簧载质量四角处的垂直位移,Fsij表示每个角落的悬架力,Faij表示每个角落的控制力,Mr是侧向激励产生的侧倾力矩,muij表示四个非簧载质量,ms表示簧载质量,Iy表示俯仰转动惯量,Ix表示侧倾转动惯量,θ为俯仰角,为侧倾角,a为车辆质心到前轴的距离,b为车辆质心到后轴的距离,tr为二分之一车辆后轮轮距,tf为二分之一车辆前轮轮距,Ktij表示垂向刚度,其中i=f,r,j=l,r;In formula (1), Zs represents the vertical displacement of the vehicle body, Zgij represents the road profile excitation of each tire, Zuij represents the vertical displacement at the four corners of the unsprung mass, Fsij represents the suspension force at each corner, Faij is the control force at each corner, Mr is the roll moment generated by the lateral excitation, muij is the four unsprung masses, ms is the sprung mass, Iy is the pitch moment of inertia, and Ix is the side Tilt inertia, θ is the pitch angle, is the roll angle, a is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the front axle, b is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the rear axle, tr is one-half of the rear wheel track of the vehicle, tf is one-half of the front wheel track of the vehicle, Ktij represents the vertical stiffness, where i=f,r,j=l,r;
2.2)将所述整车七自由度振动参考模型改写成如式(2)所示矩阵形式;2.2) Rewrite the vehicle seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model into a matrix form as shown in formula (2);
式(2)中,M表示质量系数矩阵,C表示阻尼系数矩阵,K表示刚度系数矩阵,F表示力矩阵,Z表示状态量,表示Z的一阶微分,表示Z的二阶微分。In formula (2), M is the quality coefficient matrix, C is the damping coefficient matrix, K is the stiffness coefficient matrix, F is the force matrix, Z is the state quantity, represents the first derivative of Z, represents the second derivative of Z.
优选地,步骤3)中使用的模态转换矩阵TF的函数表达式如式(3)所示;Preferably, the functional expression of the modal transition matrix TF used in step 3) is as shown in formula (3);
式(3)中,a为车辆质心到前轴的距离,b为车辆质心到后轴的距离,c=2(a+b),q1=4tf,q2=4tr,tr为二分之一车辆后轮轮距,tf为二分之一车辆前轮轮距。In formula (3), a is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the front axle, b is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the rear axle, c=2(a+b), q1 =4tf , q2 =4tr , andtr is One-half the rear wheel track of the vehicle, and tf is one-half the wheel track of the front wheel of the vehicle.
优选地,步骤3)中得到的新七自由度模态解耦方程的函数表达式如式(4)所示;Preferably, the functional expression of the new seven-degree-of-freedom modal decoupling equation obtained in step 3) is shown in formula (4);
式(4)中,Mm表示模态质量系数矩阵,Cm表示模态阻尼系数矩阵,Km表示模态刚度系数矩阵,Lr表示路面模态输入系数矩阵,qr表示路面模态输入,Du表示模态控制量系数矩阵,u模态控制量,Zm表示模态状态量,表示Zm的一阶微分,表示Zm的二阶微分。In formula (4), Mm represents the modal quality coefficient matrix, Cm represents the modal damping coefficient matrix, Km represents the modal stiffness coefficient matrix, Lr represents the pavement modal input coefficient matrix, and qr represents the pavement modal input , Du represents the modal control quantity coefficient matrix, u modal control quantity, Zm represents the modal state quantity, represents the first derivative of Zm , represents the second derivative of Zm .
优选地,步骤4)中的上层控制器为H∞控制器、H2控制器、滑膜控制器、线性二次调节器、线性二次高斯控制器、模糊控制器中的一种。Preferably, the upper controller in step 4) is one of H∞ controller, H2 controller, synovial controller, linear quadratic regulator, linear quadratic Gaussian controller, and fuzzy controller.
优选地,步骤4)中的上层控制器根据控制目标求出期望模态控制力时,控制目标的函数表达式如式(5)所示,且求出期望模态控制力为u=[Fb Fp Fr Fw]T,其中Fb、Fp、Fr、Fw分别是垂向、俯仰、侧倾、扭曲四个模态的悬架力;Preferably, when the upper controller in step 4) obtains the desired modal control force according to the control target, the functional expression of the control target is as shown in formula (5), and the desired modal control force is obtained as u=[Fb Fp Fr Fw ]T , where Fb , Fp , Fr , and Fw are the suspension forces of the four modes of vertical, pitch, roll, and twist, respectively;
式(5)中,J是目标函数,x是状态量,u是控制量,Q、R分别是状态量和控制量的权重矩阵。In formula (5), J is the objective function, x is the state quantity, u is the control quantity, Q and R are the weight matrices of the state quantity and the control quantity, respectively.
优选地,步骤5)通过下层控制器结合具体的悬架作动器系统模型跟踪获取的期望模态控制力的详细步骤包括:Preferably, step 5) the detailed steps of tracking the desired modal control force obtained by the lower controller in combination with the specific suspension actuator system model include:
5.1)通过模态转换矩阵TF将求出的期望模态控制力转换成自然坐标下的期望控制力,该期望控制力为四个角点处悬架提供的主动垂向力;5.1) Convert the obtained desired modal control force into the desired control force in natural coordinates through the modal conversion matrix TF, and the desired control force is the active vertical force provided by the suspension at the four corner points;
5.2)设计控制器跟期望模态控制力,求出最优控制量作为系统的控制输入最终达到期望的控制效果。5.2) Design the controller and the expected modal control force, and obtain the optimal control amount as the control input of the system to finally achieve the desired control effect.
本发明还提供一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制系统,包括计算机设备,该计算机设备被编程以执行本发明前述用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的步骤。The present invention also provides a hierarchical control system for vehicle modal decoupling, comprising a computer device programmed to perform the steps of the aforementioned hierarchical control method for vehicle modal decoupling of the present invention.
本发明还提供一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制系统,包括计算机设备,该计算机设备的存储介质上存储有被编程以执行本发明前述用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的计算机程序。The present invention also provides a layered control system for vehicle modal decoupling, comprising a computer device, the computer device having stored on a storage medium programmed to execute the aforementioned layered control for vehicle modal decoupling of the present invention A computer program of the method.
本发明还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质上存储有被编程以执行本发明前述用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的计算机程序。The present invention also provides a computer-readable storage medium on which a computer program programmed to execute the aforementioned hierarchical control method for vehicle modal decoupling is stored.
和现有技术相比,本发明具有下述优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
1、本发明通过转换矩阵将车辆模型表示为解耦模态坐标方程,从而定量描述七种模态之间的耦合关系,能够使车辆的几种模态之间相互解耦,从而实现单独控制某一种模态而不影响其他运动模态,解决了传统控制方法在针对某一种模态进行控制的同时不能保证其它模态的性能问题,车辆模态解耦分层控制方法的应用,对研究车辆运动、分析复杂的车辆模型、解决车辆运动时的多干扰、非线性、滞后、不确定性以及强耦合等问题具有深远的意义。1. The present invention expresses the vehicle model as a decoupling modal coordinate equation through a transformation matrix, thereby quantitatively describing the coupling relationship between the seven modes, enabling the decoupling of several modes of the vehicle, thereby realizing independent control A certain mode does not affect other motion modes, which solves the problem that the traditional control method cannot guarantee the performance of other modes while controlling a certain mode. The application of the vehicle mode decoupling layered control method, It has far-reaching significance for studying vehicle motion, analyzing complex vehicle models, and solving problems such as multiple disturbances, nonlinearity, lag, uncertainty and strong coupling during vehicle motion.
2、本发明采用分层控制方法,使上层控制器求出期望的控制量,下层控制器跟踪期望的控制量,可广泛用于研究主动悬架各模态的独立控制。分层控制利用模块化设计的优点,能够有效地提高整体控制质量,在设计控制器时采用分层控制方法可以避免控制模式的切换,有利于降低控制系统的复杂性。2. The present invention adopts a layered control method, so that the upper controller obtains the desired control quantity, and the lower controller tracks the desired control quantity, which can be widely used to study the independent control of each mode of the active suspension. Hierarchical control utilizes the advantages of modular design, which can effectively improve the overall control quality. When designing the controller, the hierarchical control method can avoid the switching of control modes, which is beneficial to reduce the complexity of the control system.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1为本发明方法的基本流程示意图。FIG. 1 is a schematic flow chart of the basic flow of the method of the present invention.
图2为本发明方法的七自由度参考模型示意图。FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a seven-degree-of-freedom reference model of the method of the present invention.
图3为本发明方法的分层控制设计流程图。FIG. 3 is a flow chart of the hierarchical control design of the method of the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
下面结合附图,对本发明中的技术方案进行清晰完整地阐述说明。The technical solutions in the present invention will be clearly and completely described below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
车辆在行驶过程中有7种耦合运动模式,即车身主导的垂向、俯仰和侧倾模式,以及车轮组主导的垂向、俯仰、侧倾和扭曲模式,本发明所设计的模态解耦分层控制方法能使车辆的这几种模态之间相互解耦,现以车辆的侧倾模态控制为例对此方法进行说明,基于车辆的侧倾和扭曲模态坐标方程和模态状态变量,实现侧倾模态的控制,由于垂向和俯仰运动模态在模态坐标下已经和侧倾/扭曲运动模态相互解耦了,因此只需要设计侧倾和扭曲运动模态解耦的控制器即可。The vehicle has 7 coupled motion modes during driving, namely the vertical, pitch and roll modes dominated by the body, and the vertical, pitch, roll and twist modes dominated by the wheel group. The modal decoupling designed by the present invention The layered control method can decouple these modes of the vehicle from each other. Now, the roll mode control of the vehicle is taken as an example to illustrate this method. Based on the roll and twist modal coordinate equations and modes of the vehicle State variables to realize the control of the roll mode. Since the vertical and pitch motion modes have been decoupled from the roll/twist motion modes in the modal coordinates, only the roll and twist motion modes need to be designed. A coupled controller is sufficient.
如图1所示,本实施例用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的实施步骤包括:As shown in FIG. 1 , the implementation steps of the layered control method for vehicle modal decoupling in this embodiment include:
1)获取车辆的构造数据和行车数据;1) Obtain the structural data and driving data of the vehicle;
2)根据构造数据和行车数据建立车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型;2) Establish a vehicle seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model of the vehicle according to the structural data and driving data;
3)将车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型用模态转换矩阵TF转换,得到一个用于将车辆模型表示为解耦模态坐标方程的新七自由度模态解耦方程;3) Transform the vehicle's seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model with a modal transformation matrix TF to obtain a new seven-degree-of-freedom modal decoupling equation for representing the vehicle model as a decoupled modal coordinate equation;
4)基于新七自由度模态解耦方程通过上层控制器根据控制目标求出期望模态控制力;4) Based on the new 7-DOF modal decoupling equation, the desired modal control force is obtained through the upper controller according to the control objective;
5)通过下层控制器结合具体的悬架作动器系统模型跟踪获取的期望模态控制力。5) Track the desired modal control force obtained by the lower controller combined with the specific suspension actuator system model.
本实施例1)中获取车辆的构造数据和行车数据时,构造数据包括车辆的簧载质量ms、非簧载质量muij、侧倾转动惯量Ix、俯仰转动惯量Iy、车辆质心到前轴的距离a、车辆质心到后轴的距离b、车辆前轮轮距tf、车辆后轮轮距2tr;行车数据包括侧倾角俯仰角θ。When acquiring the structural data and driving data of the vehicle in this embodiment 1), the structural data includes the sprung mass ms of the vehicle, the unsprung mass muij , the roll moment of inertia Ix , the pitch moment of inertia Iy , the center of mass of the vehicle to Distance a from front axle, distance b from vehicle center of mass to rear axle, vehicle front wheel track tf , vehicle rear wheel track 2tr ; driving data including roll angle Pitch angle θ.
本实施例中,步骤2)的详细步骤包括:In this embodiment, the detailed steps of step 2) include:
2.1)根据构造数据和行车数据建立车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型,如图2所示,且整车七自由度振动参考模型的函数表达式如式(1)所示;2.1) According to the construction data and driving data, establish the vehicle's seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model, as shown in Figure 2, and the function expression of the vehicle's seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model is shown in formula (1);
式(1)中,Zs表示车身的垂直位移,Zgij表示每个轮胎的路面轮廓激励,Zuij表示非簧载质量四角处的垂直位移,Fsij表示每个角落的悬架力,Faij表示每个角落的控制力,Mr是侧向激励产生的侧倾力矩,muij表示四个非簧载质量,ms表示簧载质量,Iy表示俯仰转动惯量,Ix表示侧倾转动惯量,θ为俯仰角,为侧倾角,a为车辆质心到前轴的距离,b为车辆质心到后轴的距离,tr为二分之一车辆后轮轮距,tf为二分之一车辆前轮轮距,Ktij表示垂向刚度,其中i=f,r,j=l,r;In formula (1), Zs represents the vertical displacement of the vehicle body, Zgij represents the road profile excitation of each tire, Zuij represents the vertical displacement at the four corners of the unsprung mass, Fsij represents the suspension force at each corner, Faij is the control force at each corner, Mr is the roll moment generated by the lateral excitation, muij is the four unsprung masses, ms is the sprung mass, Iy is the pitch moment of inertia, and Ix is the side Tilt inertia, θ is the pitch angle, is the roll angle, a is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the front axle, b is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the rear axle, tr is one-half of the rear wheel track of the vehicle, tf is one-half of the front wheel track of the vehicle, Ktij represents the vertical stiffness, where i=f,r,j=l,r;
2.2)将整车七自由度振动参考模型改写成如式(2)所示矩阵形式;2.2) Rewrite the seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model of the vehicle into a matrix form as shown in formula (2);
式(2)中,M表示质量系数矩阵,C表示阻尼系数矩阵,K表示刚度系数矩阵,F表示力矩阵,Z表示状态量,表示Z的一阶微分,表示Z的二阶微分。In formula (2), M is the quality coefficient matrix, C is the damping coefficient matrix, K is the stiffness coefficient matrix, F is the force matrix, Z is the state quantity, represents the first derivative of Z, represents the second derivative of Z.
式(2-1)中,ms表示簧载质量,Iy表示俯仰转动惯量,Ix表示侧倾转动惯量,mu1~mu4分别表示四个非簧载质量。In formula (2-1), ms represents the sprung mass, Iy represents the pitch moment of inertia, Ix represents the roll moment of inertia, and mu1 to mu4 represent the four unsprung masses, respectively.
式(2-2)中,ksf表示前轮悬架弹簧刚度,ksr表示后轮悬架弹簧刚度,ktf表示前轮轮胎刚度,ktr表示后轮轮胎刚度,a为车辆质心到前轴的距离,b为车辆质心到后轴的距离,tr为二分之一车辆后轮轮距,tf为二分之一车辆前轮轮距。In formula (2-2), ksf is the spring stiffness of the front wheel suspension, ksr is the spring stiffness of the rear wheel suspension, ktf is the stiffness of the front wheel tire, ktr is the stiffness of the rear wheel tire, and a is the center of mass of the vehicle to the front The distance between the axles, b is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the rear axle, tr is one-half the track of the rear wheel of the vehicle, and tf is one-half the track of the front wheel of the vehicle.
式(2-3)中,csf表示前轮悬架阻尼,csr表示后轮悬架阻尼,a为车辆质心到前轴的距离,b为车辆质心到后轴的距离,tr为二分之一车辆后轮轮距,tf为二分之一车辆前轮轮距。In formula (2-3), csf is the front wheel suspension damping, csr is the rear wheel suspension damping, a is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the front axle, b is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the rear axle, andtr is two One-half the track of the rear wheel of the vehicle, and tf is one-half the track of the front wheel of the vehicle.
式(2-4)中,ktf表示前轮轮胎刚度,ktr表示后轮轮胎刚度,Zg1~Zg4分别表示四个轮胎路面输入。In formula (2-4), ktf represents the front tire stiffness, ktr represents the rear tire stiffness, and Zg1 to Zg4 represent the four tire road surface inputs respectively.
本实施例中,步骤3)中使用的模态转换矩阵TF的函数表达式如式(3)所示;In the present embodiment, the functional expression of the modal transition matrix TF used in step 3) is shown in formula (3);
式(3)中,a为车辆质心到前轴的距离,b为车辆质心到后轴的距离,c=2(a+b),q1=4tf,q2=4tr,tr为二分之一车辆后轮轮距,tf为二分之一车辆前轮轮距。In formula (3), a is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the front axle, b is the distance from the center of mass of the vehicle to the rear axle, c=2(a+b), q1 =4tf , q2 =4tr , andtr is One-half the rear wheel track of the vehicle, and tf is one-half the wheel track of the front wheel of the vehicle.
本实施例中,3)将车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型用模态转换矩阵TF转换,得到一个用于将车辆模型表示为解耦模态坐标方程的新七自由度模态解耦方程。将车辆的整车七自由度振动参考模型表示为如式(3-1)所示解耦模态坐标方程;In this embodiment, 3) transform the vehicle's seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model with a modal transformation matrix TF to obtain a new seven-degree-of-freedom modal decoupling for expressing the vehicle model as a decoupled modal coordinate equation equation. The seven-degree-of-freedom vibration reference model of the vehicle is expressed as the decoupled modal coordinate equation as shown in equation (3-1);
式(3-1)中,Fmodal和Zmodal分别表示模态力和模态位移,TF表示模态转换矩阵,Fcorner和Zcorner分别表示垂直方向上的力和位移;模态转换矩阵TF的函数表达式如式(3)所示;In formula (3-1), Fmodal and Zmodal represent the modal force and modal displacement, respectively, TF represents the modal transformation matrix, Fcorner and Zcorner represent the force and displacement in the vertical direction, respectively; the modal transformation matrix TF The function expression of is shown in formula (3);
将悬架力转换成模态坐标表示如式(3-2)所示的形式;Convert the suspension force into the form of modal coordinate representation as shown in equation (3-2);
式(3-2)中,FS表示模态悬架力,CS表示四个悬架的阻尼构成的对角矩阵,表示QS的一阶微分,是新的悬架变形模态向量(包括垂向、俯仰、侧倾和扭曲模态向量),KS表示四个悬架的刚度构成的对角矩阵,TF表示模态转换矩阵。In formula (3-2), FS represents the modal suspension force, CS represents the diagonal matrix formed by the damping of the four suspensions, represents the first-order differential of QS , is the new suspension deformation modal vector (including vertical, pitch, roll and twist modal vectors), KS represents the diagonal matrix formed by the stiffness of the four suspensions, and TF represents the modal transition matrix.
将簧载质量看作刚体,因此在簧载质量方程中加入虚构的扭曲运动,如式(3-3)所示;The sprung mass is regarded as a rigid body, so an imaginary twisting motion is added to the sprung mass equation, as shown in equation (3-3);
式(3-3)中,diag(ms,Iy,Ix,Iw)表示簧载质量和三个转动惯量构成的对角矩阵,表示Q的二阶微分,是新的簧载质量模态向量(由垂向、俯仰、侧倾和虚构的扭曲模态向量组成),TF表示模态转换矩阵,FS表示模态悬架力,FA表示模态控制力,MR表示侧向激励产生的模态侧倾力矩。ms表示簧载质量,Iy表示俯仰转动惯量,Ix表示侧倾转动惯量,Iw表示扭曲转动惯量,因为簧载质量是刚性的,因此扭曲转动惯量Iw无穷大、扭曲转动惯量Iw的倒数等于零。In formula (3-3), diag(ms , Iy , Ix , Iw ) represents the diagonal matrix composed of sprung mass and three moments of inertia, represents the second-order differential of Q, is the new sprung mass modal vector (consisting of vertical, pitch, roll, and imaginary twist modal vectors), TF is the modal transition matrix, FS is the modal suspension force, and FA is the modal control force, MR represents the modal roll moment produced by the lateral excitation. ms represents the sprung mass, Iy represents the pitch moment of inertia, Ix represents the roll moment of inertia, and Iw represents the twist moment of inertia, because the sprung mass is rigid, so the twist moment of inertia Iw is infinite, and the twist moment of inertia Iw The reciprocal of is equal to zero.
将(3-2)中的悬架力代入(3-3),改写为式(3-4);Substitute the suspension force in (3-2) into (3-3), and rewrite it as formula (3-4);
式(3-4)中,表示Q的二阶微分,diag(ms,Iy,Ix,Iw)表示簧载质量和三个转动惯量构成的对角矩阵,TF表示模态转换矩阵,CS表示四个悬架的刚度构成的对角矩阵,表示QS的一阶微分,是新的悬架变形模态向量(包括垂向、俯仰、侧倾和扭曲模态向量),KS表示四个悬架的阻尼构成的对角矩阵,FA表示模态控制力,MR表示侧向激励产生的模态侧倾力矩。ms表示簧载质量,Iy表示俯仰转动惯量,Ix表示侧倾转动惯量,Iw表示扭曲转动惯量。hu表示悬架垂向模态向量,θu表示悬架俯仰模态向量,表示悬架侧倾模态向量,ωu表示悬架扭曲模态向量。In formula (3-4), Represents the second-order differential of Q, diag(ms , Iy , Ix , Iw ) represents the diagonal matrix formed by the sprung mass and the three moments of inertia, TF represents the mode transition matrix, and CS represents the four suspensions The diagonal matrix formed by the stiffness of , represents the first-order differential of QS , is the new suspension deformation modal vector (including vertical, pitch, roll and twist modal vectors), KS represents the diagonal matrix formed by the damping of the four suspensions, FA represents the modal control force, and MR represents the Modal roll moment due to lateral excitation. ms is the sprung mass, Iy is the pitch moment of inertia, Ix is the roll moment of inertia, and Iw is the twist moment of inertia. hu is the suspension vertical modal vector, θu is the suspension pitch modal vector, is the suspension roll mode vector, and ωu is the suspension twist mode vector.
将簧下质量运动方程转化为模态形式;Convert the equation of motion of the unsprung mass into a modal form;
在力和位移转换后,簧下质量运动方程可以写为式(3-5);After the force and displacement conversion, the motion equation of the unsprung mass can be written as equation (3-5);
式(3-5)中,TF表示模态转换矩阵,表示QS的二阶微分,表示QS的一阶微分,是新的悬架变形模态向量(包括垂向、俯仰、侧倾和扭曲模态向量),表示Q的二阶微分,是新的簧载质量模态向量(由垂向、俯仰、侧倾和虚构的扭曲模态向量组成),Mu表示簧下质量矩阵,KT表示轮胎模态刚度矩阵,QG表示轮胎模态路面输入,CS表示四个悬架的模态阻尼构成的对角矩阵,KS表示四个悬架的模态刚度构成的对角矩阵,FA表示模态控制力。In formula (3-5), TF represents the mode transition matrix, represents the second-order differential of QS , represents the first-order differential of QS , are the new suspension deformation modal vectors (including vertical, pitch, roll, and twist modal vectors), represents the second-order differential of Q, is the new sprung mass modal vector (consisting of vertical, pitch, roll and imaginary twisting modal vectors), Mu is the unsprung mass matrix, KT is the tire modal stiffness matrix, QG is the tire modulus CS represents the diagonal matrix formed by the modal damping of the four suspensions, KS represents the diagonal matrix formed by the modal stiffness of the four suspensions, and FA represents the modal control force.
将(3-4)代入(3-5),可得簧下质量模态方程。Substituting (3-4) into (3-5), the unsprung mass modal equation can be obtained.
最终,将式(3-4)的前三行与簧下质量模态运动方程相结合,推导出一种新七自由度模态解耦方程,用模态状态变量表示,写成矩阵形式如式(4)所示。本实施例中,步骤3)中得到的新七自由度模态解耦方程的函数表达式如式(4)所示。Finally, combining the first three lines of Equation (3-4) with the modal motion equation of the unsprung mass, a new modal decoupling equation with seven degrees of freedom is derived, which is represented by modal state variables and written in the form of a matrix such as Eq. (4). In this embodiment, the functional expression of the new seven-degree-of-freedom modal decoupling equation obtained in step 3) is shown in formula (4).
式(4)中,Mm表示模态质量系数矩阵,其函数表达式如式(4-1)所示。表示Zm的二阶微分,表示Zm的一阶微分;Zm表示模态状态量,其函数表达式如式(4-2)所示。Km表示模态刚度矩阵,其函数表达式如式(4-3)所示。Cm表示模态阻尼矩阵,其函数表达式如式(4-4)所示。Lr表示路面模态输入系数矩阵,其函数表达式如式(4-4)所示。Du表示模态控制量系数矩阵,其函数表达式如式(4-5)所示。qr表示四轮路面的模态输入,u表示模态控制力输入。In formula (4), Mm represents the modal quality coefficient matrix, and its function expression is shown in formula (4-1). represents the second derivative of Zm , Represents the first-order differential of Zm ; Zm represents the modal state quantity, and its function expression is shown in formula (4-2). Km represents the modal stiffness matrix, and its function expression is shown in formula (4-3). Cm represents the modal damping matrix, and its function expression is shown in formula (4-4). Lr represents the pavement modal input coefficient matrix, and its function expression is shown in formula (4-4). Du represents the modal control quantity coefficient matrix, and its function expression is shown in formula (4-5). qr represents the modal input of the four-wheel road surface, and u represents the modal control force input.
式(4-1)中,ms表示簧载质量,Iy表示俯仰转动惯量,Ix表示侧倾转动惯量。模态质量系数矩阵Mm中,簧下质量的四项可以是1,也可以从模态阻尼矩阵Cm、模态刚度矩阵Km和路面模态输入系数矩阵Lr的对应行中提出公因式。In formula (4-1), ms represents the sprung mass, Iy represents the pitch moment of inertia, and Ix represents the roll moment of inertia. In the modal mass coefficient matrix Mm , the four terms of the unsprung mass can be 1, or a common formula can be proposed from the corresponding rows of the modal damping matrix Cm , the modal stiffness matrix Km and the road modal input coefficient matrix Lr . factor.
式(4-2)中,Zs表示车身垂向模态向量,θ表示车身俯仰模态向量,表示车身侧倾模态向量,hu表示悬架垂向模态向量,θu表示悬架俯仰模态向量,表示悬架侧倾模态向量,ωu表示悬架扭曲模态向量。前三个变量表示车身的三个模态坐标,后四个表示悬架变形的四个模态坐标。In formula (4-2), Zs represents the vertical modal vector of the vehicle body, θ represents the vehicle body pitch modal vector, is the body roll mode vector, hu is the suspension vertical mode vector, θu is the suspension pitch mode vector, is the suspension roll mode vector, and ωu is the suspension twist mode vector. The first three variables represent the three modal coordinates of the body, and the last four represent the four modal coordinates of the suspension deformation.
式(4-3)中,kij表示第i行第j列的模态刚度,i和j的取值范围均小于等7。In formula (4-3), kij represents the modal stiffness of the i-th row and the j-th column, and the value ranges of i and j are both less than equal to 7.
式(4-4)中,cij表示第i行第j列的模态阻尼,i和j的取值范围均小于等7。In formula (4-4), cij represents the modal damping of the i-th row and the j-th column, and the value ranges of i and j are both less than equal to 7.
式(4-5)中,kij表示第i行第j列的模态刚度,i的取值范围小于等7,j的取值范围小于等4。In formula (4-5), kij represents the modal stiffness of the i-th row and the j-th column, the value range of i is less than or equal to 7, and the value range of j is less than or equal to 4.
式(4-6)中,dij表示第i行第j列的模态控制量系数,i的取值范围小于等7,j的取值范围小于等4。In formula (4-6), dij represents the modal control quantity coefficient of the i-th row and the j-th column, the value range of i is less than or equal to 7, and the value range of j is less than or equal to 4.
由于车辆侧向是不对称的,所以在模态刚度矩阵Km和模态阻尼矩阵Cm中,垂向模态和俯仰模态耦合刚度(k15、k24、k45和k54)和阻尼(c15、c24、c45和c54)是非零的。但由于车辆的纵向对称,固有的侧倾/扭曲模态耦合刚度(k37、k67、k76)和阻尼(c37、c67、c76)均为零。因此为了设计出侧倾/扭曲模态解耦控制器,模态控制量系数矩阵Du中的非对角元素(d64和d73)必须为零。Since the vehicle is laterally asymmetric, in the modal stiffness matrix Km and the modal damping matrix Cm , the vertical and pitching modal coupling stiffnesses (k15 , k24 , k45 and k54 ) and Damping (c15 , c24 , c45 and c54 ) are non-zero. However, due to the longitudinal symmetry of the vehicle, the inherent roll/twist modal coupling stiffness (k37 , k67 , k76 ) and damping (c37 , c67 , c76 ) are all zero. Therefore in order to design a roll/twist modal decoupled controller, the off- diagonal elements (d64 and d73 ) in the modal control quantity coefficient matrix Du must be zero.
模态刚度矩阵Km、模态阻尼矩阵Cm中各项通过(3-4)、(3-5)计算得到。这些矩阵表明,垂向、俯仰模态相互耦合,并与侧倾、扭曲模态解耦,而侧倾、扭曲模态相互耦合,分块矩阵Km1和Cm1(Km3和Cm2)的对角线元素分别表示簧载质量(悬架变形)的垂向、俯仰、侧倾和扭曲模态刚度和阻尼,非对角线元素表示振型耦合刚度和阻尼。由以上矩阵可知,车辆的垂向和俯仰运动模态是相互耦合的,而与侧倾和扭曲运动模态是相互解耦、互不影响的,同样地,侧倾和扭曲运动模态之间也是相互耦合的。利用模态方程的物理意义,通过模态力的控制,我们可以直接为单个运动模态设计控制器,而不影响其他运动模态。为了实现解耦控制,控制输入必须使车身和悬架变形的模态耦合刚度/阻尼为零。The items in the modal stiffness matrix Km and the modal damping matrix Cm are calculated by (3-4) and (3-5). These matrices show that the vertical and pitch modes are coupled with each other and decoupled from the roll and twist modes, while the roll and twist modes are coupled with each other, and the block matrix Km1 and Cm1 (Km3 and Cm2 ) have The diagonal elements represent the vertical, pitch, roll and torsional modal stiffness and damping of the sprung mass (suspension deformation), respectively, and the off-diagonal elements represent the modal coupling stiffness and damping. It can be seen from the above matrix that the vertical and pitch motion modes of the vehicle are coupled with each other, while the roll and torsion motion modes are decoupled from each other and do not affect each other. Similarly, the roll and torsion motion modes are are also coupled to each other. Using the physical meaning of modal equations, through the control of modal forces, we can directly design controllers for a single motion mode without affecting other motion modes. In order to achieve decoupled control, the control input must be such that the modal coupling stiffness/damping of the body and suspension deformations is zero.
为实现单个运动模态的控制而不影响其他运动模态,设计分层控制器,有很多控制方法可以实现分层控制,例如H∞和H2控制、滑膜控制、线性二次调节器/线性二次高斯控制和模糊控制等,根据具体情况选取控制方法。因此,步骤4)中的上层控制器可以根据需要选择为H∞控制器、H2控制器、滑膜控制器、线性二次调节器、线性二次高斯控制器、模糊控制器中的一种。In order to realize the control of a single motion mode without affecting other motion modes, a hierarchical controller is designed. There are many control methods to achieve hierarchical control, such as H∞ and H2 control, synovial control, linear quadratic regulator/linear Quadratic Gaussian control and fuzzy control, etc., the control method is selected according to the specific situation. Therefore, the upper-layer controller in step 4) can be selected as one of H∞ controller, H2 controller, synovial controller, linear quadratic regulator, linear quadratic Gaussian controller, and fuzzy controller as required.
本实施例中,步骤4)中的上层控制器根据控制目标求出期望模态控制力时,控制目标的函数表达式如式(5)所示,且求出期望模态控制力为u=[Fb Fp Fr Fw]T,其中Fb,Fp,Fr,Fw分别是垂向、俯仰、侧倾、扭曲四个模态的控制力;In this embodiment, when the upper controller in step 4) obtains the desired modal control force according to the control target, the functional expression of the control target is as shown in formula (5), and the desired modal control force is obtained as u= [Fb Fp Fr Fw ]T , where Fb , Fp , Fr , and Fw are the control forces of the vertical, pitch, roll, and twist modes, respectively;
式(5)中,J是目标函数,x是状态量,u是控制量,Q、R分别是状态量和控制量的权重矩阵。In formula (5), J is the objective function, x is the state quantity, u is the control quantity, Q and R are the weight matrices of the state quantity and the control quantity, respectively.
如式(4)所示新七自由度模态解耦方程改写成如式(6)所示As shown in Equation (4), the new 7-DOF modal decoupling equation is rewritten as shown in Equation (6)
式(6)中,表示Xm的一阶微分,Am表示模态状态量系数矩阵,Bm表示路面模态输入系数矩阵,Mym表示主动模态控制力矩输入,Dm表示模态控制量系数矩阵,qr表示四轮路面的模态输入,u表示控制力输入。Xm表示模态状态量,如式(7)所示In formula (6), represents the first-order differential of Xm , Am represents the modal state quantity coefficient matrix, Bm represents the road modal input coefficient matrix, Mym represents the active modal control torque input, Dm represents the modal control quantity coefficient matrix, qr represents the modal input of the four-wheel road surface, and u represents the control force input. Xm represents the modal state quantity, as shown in equation (7)
表示Zm的一阶微分;Zm表示模态状态量,如式(4-2)所示。 Represents the first-order differential of Zm ; Zm represents the modal state quantity, as shown in formula (4-2).
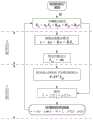
本实施例中设计一种上层控制器求得期望的模态控制力,实现单个运动模态的控制而不影响其他运动模态,图3为本实施例中的分层控制器的设计流程图,下面以LQR(线性二次调节器)控制为例。In this embodiment, an upper-layer controller is designed to obtain the desired modal control force and realize the control of a single motion mode without affecting other motion modes. FIG. 3 is a design flow chart of the layered controller in this embodiment. , the following takes LQR (Linear Quadratic Regulator) control as an example.
如图3所示,系统输入为经过模态转换的模态状态量,为了实现控制单一运动模态,需要通过控制器求出期望的模态控制力。状态向量为:As shown in Figure 3, the system input is the modal state quantity that has undergone modal conversion. In order to control a single motion mode, it is necessary to obtain the desired modal control force through the controller. The state vector is:
式(7-1)中,是簧载质量侧倾模态向量,是悬架侧倾模态向量,ωu是悬架扭曲模态向量,是的一阶微分,是的一阶微分,是ωu的一阶微分。In formula (7-1), is the sprung mass roll mode vector, is the suspension roll mode vector, ωu is the suspension twist mode vector, Yes the first-order differential of , Yes the first-order differential of , is the first derivative of ωu .
状态方程如下:The equation of state is as follows:
式(7-2)中,表示x的一阶微分,x表示模态状态量,A1表示状态量系数矩阵,w表示外部输入,B1表示外部输入系数矩阵,Fm表示模态控制力,B2表示模态控制力系数矩阵。In formula (7-2), Represents the first derivative of x, x represents the modal state quantity, A1 represents the state quantity coefficient matrix, w represents the external input, B1 represents the external input coefficient matrix, Fm represents the modal control force, and B2 represents the modal control force coefficient matrix.
状态反馈控制律定义为:The state feedback control law is defined as:
Fmd=-Kx (7-3)Fmd = -Kx (7-3)
式(7-3)中,Fmd表示模态控制量,K表示增益矩阵,x表示模态状态量。In formula (7-3), Fmd represents the modal control quantity, K represents the gain matrix, and x represents the modal state quantity.
根据式(5)所示控制目标,则有式(7-4)所示目标函数;According to the control objective shown in formula (5), there is the objective function shown in formula (7-4);
式(7-4)中,J表示目标函数,x表示状态量,Fmd表示控制量,Q和R表示权重矩阵。控制器求出权重矩阵Q和R后,增益矩阵K的计算如下:In formula (7-4), J represents the objective function, x represents the state quantity, Fmd represents the control quantity, and Q and R represent the weight matrix. After the controller obtains the weight matrices Q and R, the gain matrix K is calculated as follows:
K=R-1B2TP (7-5)K=R-1 B2T P (7-5)
式(7-5)中,R表示权重矩阵,B2表示模态控制力系数矩阵,P表示代数Riccati方程的解,代数Riccati方程参见式(7-6)。In equation (7-5), R represents the weight matrix, B2 represents the modal control force coefficient matrix, and P represents the solution of the algebraic Riccati equation. See equation (7-6) for the algebraic Riccati equation.
A1P+A1TP-PB2R-1B2TP+Q=0 (7-6)A1 P+A1T P-PB2 R-1 B2T P+Q=0 (7-6)
式(7-6)中,A1表示状态量系数矩阵,B2表示模态控制力系数矩阵,P表示代数Riccati方程的解,Q和R表示权重矩阵。In formula (7-6), A1 represents the state quantity coefficient matrix, B2 represents the modal control force coefficient matrix, P represents the solution of the algebraic Riccati equation, and Q and R represent the weight matrix.
将求出的增益矩阵K代入式(7-3)中便可得到期望的模态控制力,其中包括垂向、俯仰、侧倾、扭曲模态控制力,由于本例中控制器的状态量只有侧倾和扭曲模态,因此垂向和俯仰的模态控制力均为零。Substitute the obtained gain matrix K into Equation (7-3) to obtain the desired modal control force, including vertical, pitch, roll, and twist modal control forces. There are only roll and twist modes, so the modal control forces for both vertical and pitch are zero.
本实施例中,步骤5)通过下层控制器结合具体的悬架作动器系统模型跟踪获取的期望模态控制力的详细步骤包括:In this embodiment, the detailed steps of step 5) tracking the desired modal control force obtained by the lower controller in combination with the specific suspension actuator system model include:
5.1)通过模态转换矩阵TF将求出的期望模态控制力转换成自然坐标下的期望控制力,该期望控制力为四个角点处悬架提供的主动垂向力,如式(8)所示;5.1) Convert the obtained expected modal control force into the expected control force in natural coordinates through the modal transformation matrix TF, which is the active vertical force provided by the suspension at the four corner points, as shown in Eq. (8 ) shown;
F=TFTFm (8)F=TFT Fm (8)
式(8)中,F表示自然坐标下的期望控制力,Fm表示求出的期望模态控制力,TF表示模态转换矩阵。In formula (8), F represents the expected control force in natural coordinates, Fm represents the obtained expected modal control force, and TF represents the modal transformation matrix.
5.2)设计控制器跟期望模态控制力,求出最优控制量作为系统的控制输入最终达到期望的控制效果。5.2) Design the controller and the expected modal control force, and obtain the optimal control amount as the control input of the system to finally achieve the desired control effect.
如图3所示,本实施例中下层控制器的系统输入为上层控制器求出的期望模态控制力,然后经过模态转换,转换成自然坐标下的控制力,再用下层控制器跟踪此控制力而求出所需要的控制量,最后将控制量作用于系统。作动器模型可写为如式(8-1)所示;设计滑膜函数如式(8-2)所示;趋近率如式(8-3)所示;联立上式可求得控制量如式(8-4)所示;As shown in Figure 3, the system input of the lower-level controller in this embodiment is the desired modal control force obtained by the upper-level controller, which is then converted into the control force in natural coordinates through modal conversion, and then tracked by the lower-level controller. The required control amount is obtained from this control force, and finally the control amount is applied to the system. The actuator model can be written as shown in Equation (8-1); the designed synovial function is shown in Equation (8-2); the approach rate is shown in Equation (8-3); The control amount is shown in formula (8-4);
式(8-1)中,表示作动器输出的一阶微分,f(ξ)表示作动器输出的函数,g(ξ)表示动器输出的函数,u表示控制量。In formula (8-1), Represents the first-order differential of the actuator output, f(ξ) represents the function of the actuator output, g(ξ) represents the function of the actuator output, and u represents the control amount.
s=ξ-ξd (8-2)s=ξ-ξd (8-2)
式(8-2)中,s表示输出误差,ξ表示实际输出,ξd表示期望输出。In formula (8-2), s represents the output error, ξ represents the actual output, and ξd represents the expected output.
式(8-3)中,表示输出误差的一阶微分,表示实际输出的一阶微分,表示期望输出的一阶微分,η1表示相关系数,η2表示相关系数,s表示作动器输出误差,sign为符号函数。In formula (8-3), represents the first derivative of the output error, represents the first derivative of the actual output, Represents the first-order differential of the desired output, η1 represents the correlation coefficient, η2 represents the correlation coefficient, s represents the actuator output error, and sign is a sign function.
式(8-4)中,u表示控制量,η1表示相关系数,η2表示相关系数,s表示输出误差,sat(s/d)表示饱和函数,表示期望输出的一阶微分,f(ξ)表示作动器输出的函数,g(ξ)表示作动器输出的函数。sat(s/d)用来代替趋近特征函数sign(s),从而消除抖振。然后将控制量u作为控制输入,最终达到期望的控制效果。In formula (8-4), u represents the control variable, η1 represents the correlation coefficient, η2 represents the correlation coefficient, s represents the output error, and sat(s/d) represents the saturation function, is the first derivative of the desired output, f(ξ) is a function of the actuator output, and g(ξ) is a function of the actuator output. sat(s/d) is used to replace the approach characteristic function sign(s), thereby eliminating chattering. Then the control quantity u is used as the control input, and finally the desired control effect is achieved.
本实施例所设计的模态解耦分层控制方法能使车辆的几种模态之间相互解耦,将车辆模型表示为解耦模态坐标方程,定量描述七种模态之间的耦合关系,从而实现单独控制某一种模态而不影响其他运动模态。采用分层控制方法可以避免控制模式的切换,有利于降低控制系统的复杂性,同时分层控制利用模块化设计的优点,有效地提高整体控制质量。The modal decoupling layered control method designed in this embodiment can decouple several modes of the vehicle from each other, express the vehicle model as a decoupled modal coordinate equation, and quantitatively describe the coupling between the seven modes relationship, so as to achieve independent control of a certain mode without affecting other motion modes. Using the hierarchical control method can avoid the switching of control modes, which is beneficial to reduce the complexity of the control system. At the same time, the hierarchical control uses the advantages of modular design to effectively improve the overall control quality.
此外,本实施例还提供一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制系统,包括计算机设备,该计算机设备被编程以执行本实施例前述用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的步骤。In addition, this embodiment also provides a layered control system for vehicle modal decoupling, including a computer device programmed to execute the aforementioned layered control method for vehicle modal decoupling in this embodiment. step.
此外,本实施例还提供一种用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制系统,包括计算机设备,该计算机设备的存储介质上存储有被编程以执行本实施例前述用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的计算机程序。In addition, this embodiment also provides a layered control system for vehicle modal decoupling, including a computer device, and the computer device has a storage medium stored on a storage medium that is programmed to execute the aforementioned vehicle modal decoupling in this embodiment. A computer program for a hierarchical control method.
此外,本实施例还提供一种计算机可读存储介质,该计算机可读存储介质上存储有被编程以执行本实施例前述用于车辆模态解耦的分层控制方法的计算机程序。In addition, this embodiment also provides a computer-readable storage medium, where a computer program programmed to execute the aforementioned hierarchical control method for vehicle modal decoupling is stored on the computer-readable storage medium.
以上所述仅是本发明的优选实施方式,本发明的保护范围并不仅局限于上述实施例,凡属于本发明思路下的技术方案均属于本发明的保护范围。应当指出,对于本技术领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本发明原理前提下的若干改进和润饰,这些改进和润饰也应视为本发明的保护范围。The above are only the preferred embodiments of the present invention, and the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the above-mentioned embodiments, and all technical solutions under the idea of the present invention belong to the protection scope of the present invention. It should be pointed out that for those skilled in the art, some improvements and modifications without departing from the principle of the present invention should also be regarded as the protection scope of the present invention.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910983324.4ACN110712491B (en) | 2019-10-16 | 2019-10-16 | Layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910983324.4ACN110712491B (en) | 2019-10-16 | 2019-10-16 | Layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110712491Atrue CN110712491A (en) | 2020-01-21 |
| CN110712491B CN110712491B (en) | 2022-01-21 |
Family
ID=69211751
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910983324.4AActiveCN110712491B (en) | 2019-10-16 | 2019-10-16 | Layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110712491B (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112124028A (en)* | 2020-09-21 | 2020-12-25 | 华南理工大学 | An electronically controlled air suspension system and its control method and system, and electronic control unit |
| CN113239471A (en)* | 2021-06-25 | 2021-08-10 | 湖南大学 | Motion modal displacement and force calculation method for three-axis vehicle suspension system |
| CN113378408A (en)* | 2021-07-01 | 2021-09-10 | 合肥工业大学 | Optimal control method for whole vehicle coupling of electric control suspension |
| CN113820085A (en)* | 2021-08-12 | 2021-12-21 | 广州大学 | An acceleration layered control method for seismic simulation shaking table |
| CN114516251A (en)* | 2022-02-17 | 2022-05-20 | 上海新纪元机器人有限公司 | Vehicle dynamic parameter identification method and system, vehicle and storage medium |
Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2567650A1 (en)* | 1984-07-13 | 1986-01-17 | Thomson Csf | OPTOELECTRIC SYSTEM FOR DETECTION AND ANGULAR LOCATION OF LIGHT SOURCES WITH HIGH IMMUNITY AGAINST COUNTERMEASURES |
| US5473767A (en)* | 1992-11-03 | 1995-12-05 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for asynchronously stopping the clock in a processor |
| GB2402108A (en)* | 2003-05-24 | 2004-12-01 | Gibbs Tech Ltd | Amphibious vehicle retractable suspension |
| US20050038584A1 (en)* | 2003-08-13 | 2005-02-17 | Kim Jeong Hoon | Suspension of a vehicle and method for controlling the same |
| US20050240326A1 (en)* | 2004-04-27 | 2005-10-27 | Tenneco Automotive Operating Company, Inc. | Model free semi-active vehicle suspension system |
| CN1807135A (en)* | 2006-01-28 | 2006-07-26 | 重庆大学 | Apery intelligent control method for harmonizing auto magnetorheological half-initiative suspension according to posture |
| CN1950222A (en)* | 2004-04-27 | 2007-04-18 | 田纳科自动化操作有限公司 | Model-free semi-active vehicle suspension system |
| CN101916113A (en)* | 2010-07-23 | 2010-12-15 | 江苏大学 | A body attitude decoupling control method based on active suspension evaluation index |
| CN102609551A (en)* | 2011-01-21 | 2012-07-25 | 北京汽车研究总院有限公司 | Design optimization method and optimization device of power assembly mounting system |
| CN103419588A (en)* | 2013-07-30 | 2013-12-04 | 江苏大学 | Active energy-feedback suspension layered controller with adjustable three-level damping and construction method thereof |
| CN104385873A (en)* | 2014-09-24 | 2015-03-04 | 湖南大学 | Multi-objective optimization method of car suspension system |
| CN105539052A (en)* | 2016-02-16 | 2016-05-04 | 南京师范大学 | Controllable suspension sliding mode tracking controller taking vehicle steady state as reference |
| CN107009866A (en)* | 2017-04-06 | 2017-08-04 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of oscillation damping method towards vehicle motor vertical vibration |
| CN107160990A (en)* | 2017-04-06 | 2017-09-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of oscillation damping method of the longitudinally twisted vibration of vehicle motor |
| CN107554229A (en)* | 2017-09-04 | 2018-01-09 | 吉林大学 | A kind of frequency division control method of vehicle suspension |
| CN107791773A (en)* | 2017-09-04 | 2018-03-13 | 昆明理工大学 | A kind of vehicle active suspension system vibration control method based on regulation performance function |
| CN108891221A (en)* | 2018-07-24 | 2018-11-27 | 山东大学 | A kind of active suspension system and its working method based on mode energy distribution method |
| CN109606133A (en)* | 2019-01-16 | 2019-04-12 | 浙江科技学院 | Torque vector control method for distributed drive electric vehicle based on double-layer control |
- 2019
- 2019-10-16CNCN201910983324.4Apatent/CN110712491B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR2567650A1 (en)* | 1984-07-13 | 1986-01-17 | Thomson Csf | OPTOELECTRIC SYSTEM FOR DETECTION AND ANGULAR LOCATION OF LIGHT SOURCES WITH HIGH IMMUNITY AGAINST COUNTERMEASURES |
| US5473767A (en)* | 1992-11-03 | 1995-12-05 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for asynchronously stopping the clock in a processor |
| GB2402108A (en)* | 2003-05-24 | 2004-12-01 | Gibbs Tech Ltd | Amphibious vehicle retractable suspension |
| US20050038584A1 (en)* | 2003-08-13 | 2005-02-17 | Kim Jeong Hoon | Suspension of a vehicle and method for controlling the same |
| US20050240326A1 (en)* | 2004-04-27 | 2005-10-27 | Tenneco Automotive Operating Company, Inc. | Model free semi-active vehicle suspension system |
| CN1950222A (en)* | 2004-04-27 | 2007-04-18 | 田纳科自动化操作有限公司 | Model-free semi-active vehicle suspension system |
| CN1807135A (en)* | 2006-01-28 | 2006-07-26 | 重庆大学 | Apery intelligent control method for harmonizing auto magnetorheological half-initiative suspension according to posture |
| CN101916113A (en)* | 2010-07-23 | 2010-12-15 | 江苏大学 | A body attitude decoupling control method based on active suspension evaluation index |
| CN102609551A (en)* | 2011-01-21 | 2012-07-25 | 北京汽车研究总院有限公司 | Design optimization method and optimization device of power assembly mounting system |
| CN103419588A (en)* | 2013-07-30 | 2013-12-04 | 江苏大学 | Active energy-feedback suspension layered controller with adjustable three-level damping and construction method thereof |
| CN104385873A (en)* | 2014-09-24 | 2015-03-04 | 湖南大学 | Multi-objective optimization method of car suspension system |
| CN105539052A (en)* | 2016-02-16 | 2016-05-04 | 南京师范大学 | Controllable suspension sliding mode tracking controller taking vehicle steady state as reference |
| CN107009866A (en)* | 2017-04-06 | 2017-08-04 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of oscillation damping method towards vehicle motor vertical vibration |
| CN107160990A (en)* | 2017-04-06 | 2017-09-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | A kind of oscillation damping method of the longitudinally twisted vibration of vehicle motor |
| CN107554229A (en)* | 2017-09-04 | 2018-01-09 | 吉林大学 | A kind of frequency division control method of vehicle suspension |
| CN107791773A (en)* | 2017-09-04 | 2018-03-13 | 昆明理工大学 | A kind of vehicle active suspension system vibration control method based on regulation performance function |
| CN108891221A (en)* | 2018-07-24 | 2018-11-27 | 山东大学 | A kind of active suspension system and its working method based on mode energy distribution method |
| CN109606133A (en)* | 2019-01-16 | 2019-04-12 | 浙江科技学院 | Torque vector control method for distributed drive electric vehicle based on double-layer control |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| 刘旭晖等: "车身动态稳定系统抗侧倾性能的研究", 《汽车工程》* |
| 王芃: "整车主动悬架系统天棚阻尼控制策略", 《科学技术与工程》* |
| 董小闵等: "汽车磁流变半主动悬架整车分姿态协调控制研究", 《功能材料》* |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN112124028A (en)* | 2020-09-21 | 2020-12-25 | 华南理工大学 | An electronically controlled air suspension system and its control method and system, and electronic control unit |
| CN112124028B (en)* | 2020-09-21 | 2022-07-12 | 华南理工大学 | An electronically controlled air suspension system and its control method and system, and electronic control unit |
| CN113239471A (en)* | 2021-06-25 | 2021-08-10 | 湖南大学 | Motion modal displacement and force calculation method for three-axis vehicle suspension system |
| CN113239471B (en)* | 2021-06-25 | 2022-04-15 | 湖南大学 | Calculation method of motion modal displacement and force of three-axle vehicle suspension system |
| CN113378408A (en)* | 2021-07-01 | 2021-09-10 | 合肥工业大学 | Optimal control method for whole vehicle coupling of electric control suspension |
| CN113378408B (en)* | 2021-07-01 | 2022-09-13 | 合肥工业大学 | Optimal control method for whole vehicle coupling of electric control suspension |
| CN113820085A (en)* | 2021-08-12 | 2021-12-21 | 广州大学 | An acceleration layered control method for seismic simulation shaking table |
| CN114516251A (en)* | 2022-02-17 | 2022-05-20 | 上海新纪元机器人有限公司 | Vehicle dynamic parameter identification method and system, vehicle and storage medium |
| CN114516251B (en)* | 2022-02-17 | 2024-08-30 | 上海新纪元机器人有限公司 | Vehicle dynamics parameter identification method, system, vehicle and storage medium |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110712491B (en) | 2022-01-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110712491A (en) | A layered control method, system and medium for vehicle modal decoupling | |
| CN107791773B (en) | Whole vehicle active suspension system vibration control method based on specified performance function | |
| Thoresson et al. | Efficient optimisation of a vehicle suspension system, using a gradient-based approximation method, Part 1: Mathematical modelling | |
| CN113239450B (en) | Interconnected air suspension multi-objective optimization method based on interval analysis | |
| CN110096750B (en) | Adaptive Dynamic Surface Control Method Considering Nonlinear Active Suspension Actuators | |
| Wang et al. | Optimization and static output-feedback control for half-car active suspensions with constrained information | |
| CN110435377B (en) | Fault-tolerant tracking control method for nonlinear active suspension based on proportional integral observer | |
| CN110673480B (en) | Robust control method of time-varying displacement constrained active suspension system | |
| CN113467233B (en) | Time-lag finite frequency domain output feedback control method based on fuzzy model | |
| CN111791660B (en) | Active suspension fault-tolerant control method based on sliding-mode observer | |
| CN111439087B (en) | Vehicle ISD suspension active control method based on model reference adaptive control | |
| CN101464696B (en) | Vibration Control Method for Automobile Layered Modeling | |
| CN116278570B (en) | An adaptive collaborative control system and method for commercial vehicle semi-automatic suspension based on data-driven model | |
| CN111679575A (en) | A Robust Model Predictive Control-Based Intelligent Vehicle Trajectory Tracking Controller and Its Construction Method | |
| Yang et al. | Active suspension robust preview control by considering actuator delay | |
| Hu et al. | Robust adaptive backstepping sliding mode control for motion mode decoupling of two‐axle vehicles with active kinetic dynamic suspension systems | |
| CN117111475A (en) | A multi-agent based active suspension output consistency control method | |
| CN110901326A (en) | A control method of active suspension system with state constraints and dead zone input | |
| CN108681257A (en) | A kind of design method of the controller of active heeling-proof inclining system | |
| CN102975587A (en) | Vehicle semiactive suspension based on double controllable dampers and control method thereof | |
| CN115099035B (en) | Suspension vibration reduction design method with negative stiffness and inertial cooperation under random displacement excitation | |
| Ahmed et al. | Improving the performance of the electric vehicle suspension system using sliding mode controller and PID controller | |
| CN118358310A (en) | Heavy-duty vehicle composite attitude control method with electrohydraulic actuator active suspension | |
| CN104972860A (en) | Holographic optimal sliding mode controller used for vehicle active suspension | |
| CN107168279A (en) | Based on H∞Control method of active suspension system of vehicle with preview control |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |