CN110340894B - Teleoperation system self-adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logic - Google Patents
Teleoperation system self-adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logicDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110340894B CN110340894BCN201910648989.XACN201910648989ACN110340894BCN 110340894 BCN110340894 BCN 110340894BCN 201910648989 ACN201910648989 ACN 201910648989ACN 110340894 BCN110340894 BCN 110340894B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- robot
- fuzzy logic
- slave
- function
- master
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034methodMethods0.000titleclaimsabstractdescription12
- 230000003044adaptive effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription23
- 238000004891communicationMethods0.000claimsabstractdescription19
- 230000007613environmental effectEffects0.000claimsabstractdescription9
- 238000013461designMethods0.000claimsdescription18
- 239000011159matrix materialSubstances0.000claimsdescription12
- 238000005312nonlinear dynamicMethods0.000claimsdescription12
- 230000005540biological transmissionEffects0.000claimsdescription5
- 230000001133accelerationEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 230000006978adaptationEffects0.000claimsdescription4
- 238000005457optimizationMethods0.000claimsdescription3
- 238000013528artificial neural networkMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000006243chemical reactionMethods0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000003111delayed effectEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 230000005484gravityEffects0.000claimsdescription2
- 238000011161developmentMethods0.000description2
- 238000005516engineering processMethods0.000description2
- 230000009286beneficial effectEffects0.000description1
- 238000010586diagramMethods0.000description1
- 230000003993interactionEffects0.000description1
- 238000011160researchMethods0.000description1
- 230000008054signal transmissionEffects0.000description1
Images
Classifications
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B25—HAND TOOLS; PORTABLE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS; MANIPULATORS
- B25J—MANIPULATORS; CHAMBERS PROVIDED WITH MANIPULATION DEVICES
- B25J9/00—Programme-controlled manipulators
- B25J9/16—Programme controls
- B25J9/1602—Programme controls characterised by the control system, structure, architecture
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B25—HAND TOOLS; PORTABLE POWER-DRIVEN TOOLS; MANIPULATORS
- B25J—MANIPULATORS; CHAMBERS PROVIDED WITH MANIPULATION DEVICES
- B25J9/00—Programme-controlled manipulators
- B25J9/16—Programme controls
- B25J9/1615—Programme controls characterised by special kind of manipulator, e.g. planar, scara, gantry, cantilever, space, closed chain, passive/active joints and tendon driven manipulators
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Robotics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Automation & Control Theory (AREA)
- Feedback Control In General (AREA)
- Manipulator (AREA)
Abstract
Translated fromChineseDescription
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本发明属于遥操作控制领域,具体来说是一种基于模糊逻辑的遥操作系统自适应多边控制方法,同时保证非线性多边遥操作系统的稳定性、透明性和多从机器人的协同作业性能。The invention belongs to the field of teleoperation control, in particular to a fuzzy logic-based teleoperating system adaptive multilateral control method, which simultaneously ensures the stability and transparency of the nonlinear multilateral teleoperation system and the cooperative operation performance of multi-slave robots.
背景技术Background technique
随着机电技术的不断发展,机器人系统的研究越来越成为现阶段的热门课题,其中依靠人机交互的遥操作机器人技术已经取得了阶段性的进展,并在军事、工业和医疗领域有着广泛的应用。With the continuous development of electromechanical technology, the research on robotic systems has become a hot topic at this stage. Among them, the tele-operation robot technology relying on human-computer interaction has achieved staged progress, and has a wide range of applications in military, industrial and medical fields. Applications.
然而,随着作业任务往复杂、精细的方向发展,需要作业环境中存在多个具有多自由度的机器人进行协同作业,这类机器人往往存在非线性和各种不确定性;此外,随着协同作业机器人数量的增多,多机器人间的信号通信会使存在时延的通信通道中的信号传输变得更加复杂,甚至恶化遥操作系统的稳定性和透明性。However, with the development of complex and delicate tasks, multiple robots with multiple degrees of freedom are required to work collaboratively in the work environment. Such robots often have nonlinearities and various uncertainties; in addition, with the cooperation of With the increase of the number of working robots, the signal communication between multiple robots will make the signal transmission in the communication channel with delay more complicated, and even deteriorate the stability and transparency of the teleoperating system.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
本发明的目的在于提出一种基于模糊逻辑的遥操作系统自适应多边控制方法,以解决传统多边遥操作系统中的稳定性与透明性权衡,主从机器人的非线性和各种不确定性,以及多机器人的协同作业等技术问题。The purpose of the present invention is to propose an adaptive multilateral control method of teleoperating system based on fuzzy logic, so as to solve the trade-off between stability and transparency in traditional multilateral teleoperating system, nonlinearity and various uncertainties of master-slave robot, And technical problems such as multi-robot collaborative operation.
为实现上述目的,本发明的技术方案具体内容如下:To achieve the above object, the specific content of the technical scheme of the present invention is as follows:
一种基于模糊逻辑的遥操作系统自适应多边控制方法,包括以下步骤:An adaptive multilateral control method for teleoperating systems based on fuzzy logic, comprising the following steps:
(一)建立多边遥操作系统的非线性动力学模型。(1) Establish the nonlinear dynamic model of the multilateral teleoperating system.
(二)基于模糊逻辑系统的作业环境估计与主端环境重构。(2) Operating environment estimation and master-side environment reconstruction based on fuzzy logic system.
(三)基于模糊逻辑系统设计主机器人的自适应多边控制器。(3) Design the adaptive multilateral controller of the main robot based on the fuzzy logic system.
(四)基于模糊逻辑系统设计从机器人的自适应多边控制器。(4) The adaptive multilateral controller of slave robot is designed based on fuzzy logic system.
与现有技术相比,本发明具有如下有益效果:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following beneficial effects:
1、基于模糊逻辑系统,估计了非线性环境动力学的非功率参数,并通过存在时延的通信通道传输回主端,进行主端环境力的重构,从而避免了因功率信号在通信通道中的传输造成的遥操作系统的失稳问题,并为操作者提供准确的力反馈信息。1. Based on the fuzzy logic system, the non-power parameters of nonlinear environmental dynamics are estimated, and transmitted back to the main end through the communication channel with delay to reconstruct the environmental force of the main end, thereby avoiding the power signal in the communication channel. The instability problem of the teleoperating system caused by the transmission in the middle, and provide accurate force feedback information for the operator.
2、基于模糊逻辑系统,通过设计自适应率在线更新包含未知系统模型信息的非线性函数的参数,从而解决了主从机器人存在的各种不确定性问题。2. Based on the fuzzy logic system, the parameters of the nonlinear function containing the unknown system model information are updated online by designing the adaptive rate, thus solving the various uncertainties of the master-slave robot.
3、通过基于模糊逻辑系统的非线性自适应多边控制方法,当系统存在通信时延时,使从机器人准确地跟踪主机器人的轨迹信号,从而提升系统的位置追踪性能。3. Through the nonlinear adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logic system, when there is a delay in communication in the system, the slave robot can accurately track the trajectory signal of the master robot, thereby improving the position tracking performance of the system.
4、通过设计多机器人的协同控制算法,实现了多个从机器人的作业力分配,从而提升了多个从机器人对作业任务的协同作业性能。4. By designing a multi-robot collaborative control algorithm, the work force distribution of multiple slave robots is realized, thereby improving the collaborative operation performance of multiple slave robots for work tasks.
5、通过设计李雅普诺夫函数,保证了非线性多边遥操作系统中所有信号的有界性,从而保住了系统的全局渐进稳定性;5. By designing the Lyapunov function, the boundedness of all signals in the nonlinear multilateral teleoperating system is guaranteed, thereby maintaining the global asymptotic stability of the system;
附图说明Description of drawings
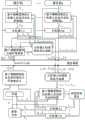
图1是本发明提出的基于模糊逻辑系统的非线性遥操作系统的自适应多边控制框图。FIG. 1 is a block diagram of the adaptive multilateral control of the nonlinear teleoperating system based on the fuzzy logic system proposed by the present invention.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本发明的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本发明进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅用以解释本发明,并不用于限定本发明。此外,下面所描述的本发明各个实施方式中所涉及到的技术特征只要彼此之间未构成冲突就可以相互组合。In order to make the objectives, technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present invention, but not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as they do not conflict with each other.
现结合实施例、附图1对本发明作进一步描述:Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying
本发明的实施技术方案为:The technical implementation scheme of the present invention is:
1)建立多边遥操作系统的非线性动力学模型,具体为:1) Establish a nonlinear dynamic model of the multilateral teleoperating system, specifically:
1-1)建立主机器人、从机器人与作业环境的非线性动力学模型1-1) Establish the nonlinear dynamic model of the master robot, slave robot and working environment
其中,qm,i,和qs,i,表示第i个主从机器人位置、速度和加速度信号,xm,i,表示第i个主机器人的末端位置,xs,o,表示作业任务中抓取目标的质心位置,Mm,i和Ms表示质量惯性矩阵,Cm,i和Cs表示科氏力/向心力矩阵,Gm,i和Gs表示重力矩阵,Dm,i和Ds表示外干扰和建模误差,um,i和us表示控制输入,Fh,i表示第i个操作者的操作力,Fe表示从机器人与作业任务中的环境力,i=1,2,....,n。Among them, qm,i , and qs,i , Indicates the position, velocity and acceleration signals of the i-th master-slave robot, xm,i , represents the end position of the i-th master robot, xs,o , Indicates the position of the center of mass of the grasping target in the task, Mm, i and Ms represent the mass inertia matrix, Cm, i and Cs represent the Coriolis force/centripetal force matrix, Gm, i and Gs represent the gravity matrix, Dm, i and Ds represent external disturbance and modeling error,um, i and us represent the control input, Fh, irepresent the operating force of the ith operator, and Fe represent the environment from the robot and the task Force, i=1,2,....,n.
上述系统具有如下特性:The above system has the following characteristics:
①0<Mm,i≤δm0,iI,0<Ms≤δs0I,其中,δm0,i,δs0>0表示单位矩阵I的缩放系数;①0<Mm,i ≤δm0,i I, 0<Ms ≤δs0 I, where δm0,i ,δs0 >0 represents the scaling factor of the identity matrix I;
②和为斜对称矩阵;② and is an obliquely symmetric matrix;
③公式(1)和(2)中的部分动力学方程可以写成如下线性方程的形式:③Part of the kinetic equations in equations (1) and (2) can be written in the form of the following linear equations:
其中,θm,i和θs表示主从机器人的模型未知参数,ζ表示模糊逻辑矩阵。Among them, θm,i and θs represent the unknown parameters of the master-slave robot model, and ζ represents the fuzzy logic matrix.
1-2)建立作业环境的非线性动力学模型1-2) Establish a nonlinear dynamic model of the working environment
其中,θe表示未知的非功率环境参数。where θe represents an unknown non-power environmental parameter.
2)基于模糊逻辑系统的作业环境估计与主端环境重构,具体为:2) Based on fuzzy logic system operating environment estimation and master-end environment reconstruction, specifically:
2-1)将从端作业环境的动力学模型(3)写成径向基神经网络函数的形式,则:2-1) Write the dynamic model (3) of the slave operating environment in the form of a radial basis neural network function, then:
Fe=ζT(xew)θe (4)Fe =ζT (xew )θe (4)
其中,xew表示模糊逻辑函数的输入量,且与xs,o,相关。Among them, xew represents the input of the fuzzy logic function, and is the same as xs,o , related.
2-2)定义为环境的最优估计参数,Ωe和Ωe0分别表示xew和We的有界集,通过MATLAB的模糊逻辑工具箱能够实现从端作业环境的在线估计。2-2) Definition For the optimal estimation parameters of the environment, Ωe and Ωe0 represent the bounded sets of xew and We respectively, and the online estimation of the slave operating environment can be realized by the fuzzy logic toolbox of MATLAB.
2-3)由于通信时延T(t)的存在,为避免功率信号在通信通道间的传递影响多边遥操作系统的稳定性,将非功率环境参数估计值传递到主端,从而得到主端的重构环境力为:2-3) Due to the existence of the communication delay T(t), in order to avoid the transmission of power signals between communication channels from affecting the stability of the multilateral teleoperating system, the estimated value of the non-power environment parameters is Pass it to the master, so as to obtain the reconstructed environment force of the master as:
其中,xemw表示模糊逻辑函数的输入量,且与xmd,i,相关。Among them, xemw represents the input of the fuzzy logic function, and is the same as xmd,i , related.
3)基于模糊逻辑系统设计主机器人的自适应多边控制器,具体为:3) Design the adaptive multilateral controller of the main robot based on the fuzzy logic system, specifically:
3-1)设计主机器人的理想轨迹生成器如下:3-1) The ideal trajectory generator for designing the master robot is as follows:
其中,i=1,2,...,n,Md,Cd,Gd表示轨迹生成器的优化参数。通过选取适当的优化系数,(6)-(7)能够生成无源的主机器人理想轨迹信号xmd,i。Among them, i=1,2,...,n, Md , Cd , Gd represent the optimization parameters of the trajectory generator. By choosing appropriate optimization coefficients, (6)-(7) can generate the passive ideal trajectory signal xmd,i of the master robot.
3-2)定义xm1,i=xm,i,则第i个主机器人的非线性动力学模型(1)可改写为:3-2) Define xm1,i =xm,i , Then the nonlinear dynamic model (1) of the i-th master robot can be rewritten as:
3-3)定义第i个主机器人的跟踪误差为:3-3) Define the tracking error of the i-th master robot as:
其中,αm1,i表示主机器人的虚拟跟踪量。Among them, αm1,i represents the virtual tracking amount of the main robot.
3-4)定义(8)中的第一个子系统的李雅普诺夫函数Vm1,i如下:3-4) Define the Lyapunov function Vm1,i of the first subsystem in (8) as follows:
通过选取虚拟跟踪量αm1,i为则By selecting the virtual tracking amount αm1, i is but
3-5)定义(8)中的第二个子系统的李雅普诺夫函数Vm2,i如下:3-5) Define the Lyapunov function Vm2,i of the second subsystem in (8) as follows:
3-6)基于(8)和(9),可得zm2,i的导数为3-6) Based on (8) and (9), the derivative of zm2,i can be obtained as
于是,可得Vm2,i的导数为Therefore, the derivative of Vm2,i can be obtained as
其中,表示未知主机器人系统动力学函数。in, represents the unknown master robot system dynamics function.
3-7)根据(14)设计主控制器,保证主端子系统的稳定性,设计的控制器um,i为:3-7) Design the main controller according to (14) to ensure the stability of the main terminal system. The designed controllerum,i is:
um,i=-μm2,izm2,i-zm1,i-Φm,i-Fh,i (15)um,i =-μm2,i zm2,i -zm1,i -Φm,i -Fh,i (15)
其中,μm2,i>0表示主控制器性能调整参数。Among them, μm2,i >0 represents the main controller performance adjustment parameter.
在从控制器(15)中,Φm,i表示一种用于估计ηm,i的模糊逻辑函数,可定义为:In the slave controller (15), Φm,i represents a fuzzy logic function for estimating ηm,i , which can be defined as:
其中,θm,i表示未知的主机器人系统动力学参数,表示模糊逻辑函数的输入量,表示第j个局部模糊逻辑函数。where θm,i represents the unknown dynamic parameters of the main robot system, represents the input quantity of the fuzzy logic function, represents the jth local fuzzy logic function.
3-8)设计主端系统的李雅普诺夫函数Vm,i为:3-8) Design the Lyapunov function Vm,i of the master-end system as:
其中,γm,i>0表示李雅普诺夫函数Vm,i的系数,表示模糊逻辑函数的估计误差,表示最优估计参数。。where γm,i >0 represents the coefficient of the Lyapunov function Vm,i , represents the estimation error of the fuzzy logic function, represents the optimal estimated parameter. .
基于李雅普诺夫函数Vm,i设计θm,i的自适应率为:Based on the Lyapunov function Vm,i, the design adaptive rate of θm,i is:
其中,km,i>0和Γm,i>0表示自适应率的性能调节参数。where km,i >0 and Γm,i >0 represent the performance tuning parameters of the adaptation rate.
4)基于模糊逻辑系统设计从机器人的自适应多边控制器,具体为:4) Design the adaptive multilateral controller of the slave robot based on the fuzzy logic system, specifically:
4-1)由于信号在通信通道的传输会不可避免地产生通信时延,主机器人的位置信号xm,i(t)通过通信通道传输到从端得到时延的位置信号xm,i(t-T(t)),设计从机器人的理想轨迹生成器为Hf(s)=1/(ofs+1)2,其中,of表示时间常数,通过输入时延的平均位置信号能够输出理想的从机器人跟踪轨迹xsd,o(t),其中,lo,i表示抓取目标与机器人末端位置间的关系转换,T(t)为系统的通信时延。4-1) Since the transmission of the signal in the communication channel will inevitably generate a communication delay, the position signal xm,i (t) of the master robot is transmitted to the slave through the communication channel to obtain the delayed position signal xm,i ( tT(t )), the ideal trajectory generator of the design slave robot is Hf (s)=1/(of s+ 1)2 , where of represents the time constant, the average position signal through the input time delay Able to output ideal slave robot tracking trajectory xsd,o (t), Among them, lo,i represents the relationship conversion between the grasping target and the end position of the robot, and T(t) is the communication delay of the system.
4-2)定义xs1=xs,o,则非线性动力学模型(2)可改写为:4-2) Define xs1 =xs,o , Then the nonlinear dynamic model (2) can be rewritten as:
4-3)定义从机器人与抓取目标的跟踪误差为:4-3) Define the tracking error between the slave robot and the grab target as:
其中,αs1表示从机器人的虚拟跟踪量。Among them, αs1 represents the virtual tracking amount of the slave robot.
4-4)定义(19)中的第一个子系统的李雅普诺夫函数Vs1如下:4-4) Define the Lyapunov function Vs1 of the first subsystem in (19) as follows:
通过选取虚拟跟踪量αs1为则By selecting the virtual tracking amount αs1 as but
4-5)定义(19)中的第二个子系统的李雅普诺夫Vs2如下:4-5) The Lyapunov Vs2 of the second subsystem in (19) is defined as follows:
4-6)基于(19)和(20),可得zs2的导数为4-6) Based on (19) and (20), the derivative of zs2 can be obtained as
于是,可得Vs2的导数为Therefore, the derivative of Vs2 can be obtained as
其中,表示未知从机器人系统动力学函数。in, represents the unknown slave robot system dynamics function.
4-7)根据(25)设计从控制器,保证从端子系统的稳定性,设计的控制器us为:4-7) Design the slave controller according to (25) to ensure the stability of the slave terminal system. The designed controller us is:
us=-μs2zs2-zs1-Φs+Fe (26)us = -μs2 zs2 -zs1 -Φs +Fe (26)
其中,μs2>0表示从控制器性能调整参数。Among them, μs2 > 0 means to adjust the parameters from the controller performance.
在从控制器(26)中,Φs表示一种用于估计ηs的模糊逻辑函数,可定义为:In the slave controller (26), Φs represents a fuzzy logic function for estimating ηs , which can be defined as:
其中,θs表示未知的从机器人系统动力学参数,表示模糊逻辑函数的输入量,表示第j个局部模糊逻辑函数。where θs represents the unknown dynamic parameters of the slave robot system, represents the input quantity of the fuzzy logic function, represents the jth local fuzzy logic function.
4-8)设计从端系统的李雅普诺夫函数Vs为:4-8) Design the Lyapunov function Vs of the slave system as:
其中,γs>0表示李雅普诺夫函数Vs的系数,表示模糊逻辑函数的估计误差,表示最优估计参数。where γs >0 represents the coefficient of the Lyapunov function Vs , represents the estimation error of the fuzzy logic function, represents the optimal estimated parameter.
基于李雅普诺夫函数Vs设计θs的自适应率为:The adaptive rate of designing θs based on the Lyapunov function Vs is:
其中,ks>0和Γs>0表示自适应率的性能调节参数。where ks >0 and Γs >0 represent the performance tuning parameters of the adaptation rate.
4-9)根据从控制器(26),为得到每个从机器人的控制输入us,i,设计多机器人的协同控制算法如下:4-9) According to the slave controller (26), in order to obtain the control input us,i of each slave robot, the cooperative control algorithm of multiple robots is designed as follows:
其中,表示分配系数,且W表示不同作业需求的权重系数,表示各个从机器人与抓取目标的内部力,且in, represents the distribution coefficient, and W represents the weight coefficient of different job requirements, represents the internal force of each slave robot and grasping target, and
Claims (4)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910648989.XACN110340894B (en) | 2019-07-18 | 2019-07-18 | Teleoperation system self-adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logic |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910648989.XACN110340894B (en) | 2019-07-18 | 2019-07-18 | Teleoperation system self-adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logic |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110340894A CN110340894A (en) | 2019-10-18 |
| CN110340894Btrue CN110340894B (en) | 2020-10-16 |
Family
ID=68178689
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910648989.XAActiveCN110340894B (en) | 2019-07-18 | 2019-07-18 | Teleoperation system self-adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logic |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110340894B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111136633B (en)* | 2020-01-13 | 2021-04-09 | 燕山大学 | Full-state control method for flexible master-slave robot system with time-varying delay |
| CN111198502B (en)* | 2020-02-28 | 2021-04-09 | 浙江大学 | Track tracking control method of unmanned aerial vehicle based on disturbance observer and fuzzy system |
| CN111427264B (en)* | 2020-03-15 | 2021-12-14 | 中国地质大学(武汉) | A Neural Adaptive Fixed Time Control Method for Complex Telemanipulation Technology |
| CN112859596B (en)* | 2021-01-07 | 2022-01-04 | 浙江大学 | A Nonlinear Teleoperation Multilateral Control Method Considering Formation Obstacle Avoidance |
| CN114474051B (en)* | 2021-12-30 | 2023-05-23 | 西北工业大学 | A Personalized Gain Teleoperation Control Method Based on Operator Physiological Signals |
| CN114527664B (en)* | 2022-02-28 | 2025-07-15 | 北京航空航天大学 | An adaptive tracking control method for dynamic uncertain systems with asymmetric time delay |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103324196A (en)* | 2013-06-17 | 2013-09-25 | 南京邮电大学 | Multi-robot path planning and coordination collision prevention method based on fuzzy logic |
| JP6201126B2 (en)* | 2013-11-07 | 2017-09-27 | 株式会社人機一体 | Master-slave system |
| CN103831831B (en)* | 2014-03-18 | 2016-07-06 | 西华大学 | There is non-linear remote control system position and the force tracing control system of time-vary delay system |
| WO2016025941A1 (en)* | 2014-08-15 | 2016-02-18 | University Of Central Florida Research Foundation, Inc. | Control interface for robotic humanoid avatar system and related methods |
| WO2017033365A1 (en)* | 2015-08-25 | 2017-03-02 | 川崎重工業株式会社 | Remote control robot system |
| CN106938462B (en)* | 2016-12-07 | 2019-05-31 | 北京邮电大学 | A kind of remote operating bilateral control method based on adaptive PD and fuzzy logic |
| CN107932506B (en)* | 2017-11-15 | 2020-10-16 | 电子科技大学 | Force feedback bilateral teleoperation stability control method |
| CN108227497B (en)* | 2018-01-11 | 2021-01-08 | 燕山大学 | Control method of networked teleoperation system under condition of considering system performance limitation |
| CN108469733B (en)* | 2018-03-22 | 2020-01-14 | 浙江大学 | Four-channel teleoperation multilateral control method for improving wave variable |
| CN108500983B (en)* | 2018-06-26 | 2023-06-16 | 西华大学 | Nonlinear teleoperation bilateral control system |
| CN108803344B (en)* | 2018-07-25 | 2019-11-22 | 西北工业大学 | A Symmetric Predictive Control Method for Bilateral Teleoperation of Robots Based on Mode Switching |
| CN109085749B (en)* | 2018-08-07 | 2020-02-28 | 浙江大学 | A Nonlinear Teleoperation Bilateral Control Method Based on Adaptive Fuzzy Inversion |
| CN109240086B (en)* | 2018-10-16 | 2020-02-28 | 浙江大学 | An Adaptive Robust Control Method for a Nonlinear Bilateral Teleoperating System |
| CN109358506B (en)* | 2018-10-26 | 2021-07-23 | 南京理工大学 | An Adaptive Fuzzy Teleoperation Control Method Based on Disturbance Observer |
- 2019
- 2019-07-18CNCN201910648989.XApatent/CN110340894B/enactiveActive
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110340894A (en) | 2019-10-18 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110340894B (en) | Teleoperation system self-adaptive multilateral control method based on fuzzy logic | |
| CN110262256B (en) | Multilateral self-adaptive sliding mode control method of nonlinear teleoperation system | |
| CN109240086B (en) | An Adaptive Robust Control Method for a Nonlinear Bilateral Teleoperating System | |
| Wang et al. | Adaptive event-triggered control for nonlinear systems with asymmetric state constraints: A prescribed-time approach | |
| CN109085749B (en) | A Nonlinear Teleoperation Bilateral Control Method Based on Adaptive Fuzzy Inversion | |
| CN104865829B (en) | Multi-robot system distributed self-adaption neutral net continuous tracking control method of electro | |
| CN109807902B (en) | A dual manipulator force/position fuzzy hybrid control method based on backstepping method | |
| CN105068427B (en) | A kind of multi-robot system finite time robust cooperates with tracking and controlling method | |
| CN103439975B (en) | Become Sliding Mode Attitude during a kind of distributed index and work in coordination with tracking and controlling method | |
| CN110434858B (en) | Force/position hybrid control method of multi-mechanical-arm system based on command filtering | |
| Wang et al. | Adaptive asymptotic tracking control for flexible-joint robots with prescribed performance: Design and experiments | |
| CN108227497B (en) | Control method of networked teleoperation system under condition of considering system performance limitation | |
| CN111459016B (en) | Cutting machine track contour tracking control method | |
| CN110116409B (en) | Four-channel teleoperation bilateral control method based on disturbance observer | |
| Zhao et al. | Low-pass-filter-based position synchronization sliding mode control for multiple robotic manipulator systems | |
| CN103728988B (en) | SCARA robot trajectory tracking control method based on internal model | |
| CN117506896A (en) | Control method for single-connecting-rod mechanical arm embedded with direct-current motor | |
| CN111427264B (en) | A Neural Adaptive Fixed Time Control Method for Complex Telemanipulation Technology | |
| CN118357919A (en) | Preset time event triggering control method for flexible joint manipulator under error constraints | |
| Wei et al. | Asymmetric time‐varying BLF‐based model‐free hybrid force/position control for SEA‐based 2‐DOF manipulator | |
| Zhang et al. | Predictive tracking control of network-based agents with communication delays | |
| CN119858164A (en) | Control method and system of flexible joint robot under input delay | |
| CN110095989B (en) | Distributed multi-Lagrange system tracking control strategy based on back stepping method | |
| CN107263455A (en) | The Position Tracking Control method of two degrees of freedom SCARA robots | |
| CN109176529B (en) | Self-adaptive fuzzy control method for coordinated movement of space robot |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |