CN110084816B - Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment - Google Patents
Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipmentDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110084816B CN110084816BCN201910217342.1ACN201910217342ACN110084816BCN 110084816 BCN110084816 BCN 110084816BCN 201910217342 ACN201910217342 ACN 201910217342ACN 110084816 BCN110084816 BCN 110084816B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- feature map
- feature maps
- stage
- feature
- network
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T7/00—Image analysis
- G06T7/10—Segmentation; Edge detection
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06V—IMAGE OR VIDEO RECOGNITION OR UNDERSTANDING
- G06V10/00—Arrangements for image or video recognition or understanding
- G06V10/20—Image preprocessing
- G06V10/26—Segmentation of patterns in the image field; Cutting or merging of image elements to establish the pattern region, e.g. clustering-based techniques; Detection of occlusion
- G06V10/267—Segmentation of patterns in the image field; Cutting or merging of image elements to establish the pattern region, e.g. clustering-based techniques; Detection of occlusion by performing operations on regions, e.g. growing, shrinking or watersheds
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20081—Training; Learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06T—IMAGE DATA PROCESSING OR GENERATION, IN GENERAL
- G06T2207/00—Indexing scheme for image analysis or image enhancement
- G06T2207/20—Special algorithmic details
- G06T2207/20084—Artificial neural networks [ANN]
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Multimedia (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
- Compression Or Coding Systems Of Tv Signals (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域technical field
本申请涉及计算机技术领域,特别是涉及一种物体分割方法、装置、计算机可读存储介质和计算机设备。The present application relates to the field of computer technology, and in particular, to an object segmentation method, apparatus, computer-readable storage medium, and computer equipment.
背景技术Background technique
随着人工智能和无人驾驶技术的不断发展,也对计算机视觉提高出了更高的要求。物体分割一直是计算机视觉中长期存在的技术难题之一。物体分割包括语义分割和实例分割。其中,语义分割指的是将图中每一点像素标注为某个物体类别,同一物体的不同实例不需要单独分割出来。而实例分割是物体检测与语义分割的综合体,相对物体检测只得到物体的边界框,实例分割可精确到物体的边缘;相对语义分割,实例分割可以标注出图上同一物体的不同个体。With the continuous development of artificial intelligence and unmanned driving technology, higher requirements for computer vision have also been raised. Object segmentation has been one of the long-standing technical challenges in computer vision. Object segmentation includes semantic segmentation and instance segmentation. Among them, semantic segmentation refers to labeling each pixel in the image as a certain object category, and different instances of the same object do not need to be segmented separately. Instance segmentation is a combination of object detection and semantic segmentation. Relative object detection only obtains the bounding box of the object, and instance segmentation can be accurate to the edge of the object; relative to semantic segmentation, instance segmentation can mark different individuals of the same object on the map.
然而,目前采用传统方法对图像进行物体分割,分割结果的准确性不是太高,不能满足越来越精细化的需求。However, at present, traditional methods are used to segment objects in images, and the accuracy of segmentation results is not too high to meet the needs of more and more refinement.
发明内容SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
基于此,有必要针对传统方法对图像进行物体分割得到的分割结果的准确性不是太高的技术问题,提供一种物体分割方法、装置、计算机可读存储介质和计算机设备。Based on this, it is necessary to provide an object segmentation method, apparatus, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment for the technical problem that the accuracy of the segmentation result obtained by performing object segmentation on an image by a traditional method is not too high.
一种物体分割方法,包括:An object segmentation method, comprising:
获取待处理图像的初始特征图;Obtain the initial feature map of the image to be processed;
将所述初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,分别在所述自顶向下网络和所述自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对所述第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图;Input the initial feature map into the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network to calculate the first-stage feature map, and encode RCE according to the regional context in the top-down network and the bottom-up network respectively. updating the first-stage feature map to obtain an updated first-stage feature map;
将所述更新后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合及更新处理,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图;Using the updated first-stage feature map as an input to perform iterative fusion and update processing until a preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map;
根据所述目标特征图对所述待处理图像进行物体分割。Perform object segmentation on the to-be-processed image according to the target feature map.
在其中一个实施例中,所述连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络采用密集路径连接。In one embodiment, the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network are connected by dense paths.
在其中一个实施例中,所述将所述初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,包括:In one embodiment, the inputting the initial feature map into a continuous top-down network and a bottom-up network to obtain the first-stage feature map, including:
所述第一阶段特征图包括两组特征图;The first-stage feature map includes two sets of feature maps;
将所述初始特征图输入自顶向下网络中计算得到所述第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;Inputting the initial feature map into a top-down network to obtain the first set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map;
将所述第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图输入至自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。Inputting the first set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map into a bottom-up network to obtain a second set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map.
在其中一个实施例中,所述分别在所述自顶向下网络和所述自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对所述第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图,包括:In one embodiment, the first-stage feature map is updated in the top-down network and the bottom-up network according to regional context coding RCE, respectively, to obtain the updated first-stage features Figures, including:
在所述自顶向下网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将所述上下文特征图传播到所述自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图,对所述自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;In the top-down network, according to the region context encoding RCE, a context feature map based on sub-regions of each layer feature map is generated, and the context feature map is propagated to other layer feature maps in the top-down network. , update the feature maps of other layers in the top-down network to obtain the first group of feature maps in the updated first-stage feature map;
在所述自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将所述上下文特征图传播到所述自底向上网络中的其他层特征图对所述自底向上网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。In the bottom-up network, according to the region context encoding RCE, a context feature map based on the sub-region of each layer feature map is generated, and the context feature map is propagated to other layer feature maps in the bottom-up network. The feature maps of other layers in the bottom-up network are updated to obtain the second set of feature maps in the updated first-stage feature maps.
在其中一个实施例中,所述根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,包括:In one of the embodiments, the generating a context feature map of sub-regions based on the feature map of each layer according to the region context encoding RCE includes:
将每一层特征图划分为不同尺度的子区域;Divide the feature map of each layer into sub-regions of different scales;
将相同尺度的子区域进行加权和计算得到所述尺度的子区域的全局表示;The sub-regions of the same scale are weighted and calculated to obtain a global representation of the sub-regions of the scale;
将所述全局表示重新分配到所述尺度的子区域,将所述尺度的子区域聚合生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。The global representation is reassigned to sub-regions of the scale, and the sub-regions of the scale are aggregated to generate a contextual feature map based on the sub-regions of each layer's feature map.
在其中一个实施例中,所述区域上下文编码RCE对于每一层特征图包括多个并行分支,每个所述并行分支分别对同一尺度的子区域进行处理。In one of the embodiments, the region context encoding RCE includes a plurality of parallel branches for each layer of feature maps, and each of the parallel branches respectively processes sub-regions of the same scale.
在其中一个实施例中,所述迭代融合及更新处理的过程,包括:In one embodiment, the iterative fusion and update process includes:
将所述第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图和第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;Fusing the first set of feature maps and the second set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map to obtain the first set of feature maps in the second-stage feature map;
将所述第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图与所述第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图;fusing the first set of feature maps in the second-stage feature map with the second set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map to obtain a second set of feature maps in the second-stage feature map;
根据区域上下文编码RCE在所述自顶向下网络中对所述第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;Update the first group of feature maps in the second-stage feature map in the top-down network according to the regional context encoding RCE, to obtain the first set of feature maps in the updated second-stage feature map;
根据区域上下文编码RCE在所述自底向上网络中对所述第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图;Update the second group of feature maps in the second-stage feature map in the bottom-up network according to the regional context encoding RCE, to obtain the second set of feature maps in the updated second-stage feature map;
将所述更新后的第二阶段特征图作为下一次迭代融合及更新计算的输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图。The updated second-stage feature map is used as an input for the next iterative fusion and update calculation to perform iterative fusion and update calculation until a preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map.
在其中一个实施例中,所述获取待处理图像的初始特征图,包括:In one embodiment, the acquiring an initial feature map of the image to be processed includes:
将待处理图像输入至自底向上网络计算得到初始特征图。Input the image to be processed into the bottom-up network to calculate the initial feature map.
在其中一个实施例中,所述目标特征图为自底向上网络所得到的特征图。In one embodiment, the target feature map is a feature map obtained by a bottom-up network.
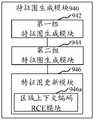
一种物体分割装置,所述装置包括:An object segmentation device, the device includes:
初始特征图获取模块,用于获取待处理图像的初始特征图;The initial feature map acquisition module is used to acquire the initial feature map of the image to be processed;
特征图生成模块,用于将所述初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,分别在所述自顶向下网络和所述自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对所述第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图;The feature map generation module is used to input the initial feature map into the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network to calculate the first-stage feature map, which are respectively used in the top-down network and the bottom-up network. In the network, the first-stage feature map is updated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the updated first-stage feature map is obtained;
迭代处理模块,用于将所述更新后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图;an iterative processing module, configured to use the updated first-stage feature map as an input to perform iterative fusion and update calculation until a preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map;
物体分割模块,用于根据所述目标特征图对所述待处理图像进行物体分割。An object segmentation module, configured to perform object segmentation on the to-be-processed image according to the target feature map.
一种计算机可读存储介质,存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被处理器执行时,使得所述处理器执行上述方法的步骤。A computer-readable storage medium stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, causes the processor to perform the steps of the above method.
一种计算机设备,包括存储器和处理器,所述存储器存储有计算机程序,所述计算机程序被所述处理器执行时,使得所述处理器执行上述方法的步骤。A computer device includes a memory and a processor, the memory stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by the processor, causes the processor to perform the steps of the above method.
上述物体分割方法、装置、计算机可读存储介质和计算机设备,获取待处理图像的初始特征图,将初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,分别在自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图。将更新后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图,根据目标特征图对待处理图像进行物体分割,目标特征图为自底向上网络所得到的特征图。区域上下文编码RCE可以利用特征图的不同子区域来计算上下文特征从而对每一阶段的特征图进行更新,能够捕获特征图中多尺度子区域的上下文信息。迭代融合能够聚合所有级别的上下文信息,避免信息的流失,进而提高物体分割的准确性。The above-mentioned object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment obtain the initial feature map of the image to be processed, and input the initial feature map into the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network to calculate the first-stage feature map , update the first-stage feature map according to the regional context encoding RCE in the top-down network and bottom-up network respectively, and obtain the updated first-stage feature map. The updated first-stage feature map is used as input to perform iterative fusion and update calculation until the preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map, and the object to be processed is segmented according to the target feature map. The target feature map is obtained by the bottom-up network. feature map. The regional context encoding RCE can use different sub-regions of the feature map to calculate the context features to update the feature map at each stage, and can capture the context information of multi-scale sub-regions in the feature map. Iterative fusion can aggregate all levels of context information, avoid information loss, and improve the accuracy of object segmentation.
附图说明Description of drawings
图1A为一个实施例中物体分割方法的分割结果图;1A is a segmentation result diagram of an object segmentation method in one embodiment;
图1B为一个实施例中物体分割方法的流程示意图;1B is a schematic flowchart of an object segmentation method in one embodiment;
图2为一个实施例中网络结构及特征图的示意图;2 is a schematic diagram of a network structure and a feature map in one embodiment;
图3为图1B中第一组特征图和第二组特征图生成方法的流程示意图;3 is a schematic flowchart of a method for generating a first group of feature maps and a second group of feature maps in FIG. 1B ;
图4为图1B中更新后的第一组特征图和第二组特征图生成方法的流程示意图;4 is a schematic flowchart of a method for generating the updated first group of feature maps and the second group of feature maps in FIG. 1B ;
图5为一个实施例中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图方法的流程示意图;5 is a schematic flowchart of a method for generating a context feature map based on a subregion of each layer feature map according to the region context encoding RCE in one embodiment;
图6为一个实施例中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图方法的示意图;6 is a schematic diagram of a method for generating a context feature map based on sub-regions of each layer feature map according to regional context coding RCE in one embodiment;
图7为图1B中迭代融合及更新处理过程的流程示意图;FIG. 7 is a schematic flowchart of the iterative fusion and update processing process in FIG. 1B ;
图8为图1B中迭代融合及更新处理过程的示意图;FIG. 8 is a schematic diagram of the iterative fusion and update processing process in FIG. 1B ;
图9为一个实施例中物体分割装置的结构框图;9 is a structural block diagram of an object segmentation apparatus in one embodiment;
图10为图9中特征图生成模块的结构框图;Fig. 10 is the structural block diagram of the feature map generation module in Fig. 9;
图11为一个实施例中计算机设备的结构框图。FIG. 11 is a structural block diagram of a computer device in one embodiment.
具体实施方式Detailed ways
为了使本申请的目的、技术方案及优点更加清楚明白,以下结合附图及实施例,对本申请进行进一步详细说明。应当理解,此处所描述的具体实施例仅仅用以解释本申请,并不用于限定本申请。In order to make the purpose, technical solutions and advantages of the present application more clearly understood, the present application will be described in further detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described herein are only used to explain the present application, but not to limit the present application.
如图1A所示,在一个实施例中,提供了一种经过物体分割方法所得到的分割结果图。在图1A中采用该物体分割方法对每张图像中不同的物体进行了分割。As shown in FIG. 1A , in one embodiment, a segmentation result graph obtained by an object segmentation method is provided. In Figure 1A, the object segmentation method is used to segment different objects in each image.
如图1B所示,在一个实施例中,提供了一种物体分割方法。参照图1B,该物体分割方法具体包括如下步骤:As shown in FIG. 1B, in one embodiment, an object segmentation method is provided. 1B, the object segmentation method specifically includes the following steps:
S102,获取待处理图像的初始特征图。S102: Acquire an initial feature map of the image to be processed.
其中,待处理图像为进行物体分割的图像。待处理图像可以是实时采集的图像,也可以是来自其他任何设备的图像。此处,待处理图像可以是视频数据,也可以是图片数据。特征图指的是对待处理图像通过卷积神经网络进行计算所得到的特征图。初始特征图具体是将待处理图像输入至主干网络进行卷积计算所得到的,在这里,主干网络可以是自底向上网络。自底向上网络是一种卷积神经网络,当然,主干网络也可以是其他类型的卷积神经网络。The image to be processed is an image for object segmentation. The images to be processed can be real-time captured images or images from any other device. Here, the image to be processed may be video data or picture data. The feature map refers to the feature map obtained by calculating the image to be processed through the convolutional neural network. Specifically, the initial feature map is obtained by inputting the image to be processed into the backbone network for convolution calculation. Here, the backbone network can be a bottom-up network. Bottom-up network is a kind of convolutional neural network, of course, the backbone network can also be other types of convolutional neural network.
S104,将初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,分别在自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图。S104, input the initial feature map into the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network to calculate the first-stage feature map, and encode RCE in the top-down network and bottom-up network respectively according to the regional context. The feature map is updated to obtain the updated first-stage feature map.
自顶向下网络和自底向上网络指的是不同类型的卷积神经网络。其中,自顶向下网络将高层大尺度语义信息向下传播到较浅的网络层,而自底向上的网络将较小尺度的可视细节编码到较深的网络层。连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络指的是在自顶向下的网络之后连接了一个自底向上的网络,从而构成了新的网络,该连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络为最顶层和最底层的特征图之间的信息传播构建了一个快捷方式。因此,连续的自顶向下和自底向上的网络被用来学习不同层次上更强大的特征图。Top-down networks and bottom-up networks refer to different types of convolutional neural networks. Among them, top-down networks propagate high-level large-scale semantic information down to shallower network layers, while bottom-up networks encode smaller-scale visual details into deeper network layers. A continuous top-down network and a bottom-up network refer to a bottom-up network connected after a top-down network to form a new network, the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network. The up network builds a shortcut for information propagation between the topmost and bottommost feature maps. Therefore, successive top-down and bottom-up networks are used to learn more powerful feature maps at different levels.
区域上下文编码(Region Context Encoding,RCE)指的是区域上下文编码(RCE)机制,该机制连接输入特征图的所有子区域,使每个子区域都能够灵活地传播其信息。区域上下文编码(RCE)机制采用多个并行分支实现,将自顶向下/自底向上网络生成的特征图输入到每个RCE分支。在每个RCE分支中,首先将特征图划分为规则的、不同尺度的子区域;然后将一层特征图中相同尺度的子区域进行加权和,从而将所有子区域聚合成一个全局表示;最后将全局表示重新分配到尺度的子区域,再将该层特征图所有分支的结果与输入特征图相加,生成该层特征图的上下文特征图。这允许每个子区域向新特征图的所有子区域传递信息。每个分支对特征图执行不同的细分,生成不同尺度的子区域。Region Context Encoding (RCE) refers to the Region Context Encoding (RCE) mechanism that connects all sub-regions of the input feature map, enabling each sub-region to flexibly propagate its information. The Region Context Encoding (RCE) mechanism is implemented with multiple parallel branches, and the feature maps generated by the top-down/bottom-up network are input to each RCE branch. In each RCE branch, the feature map is firstly divided into regular, different-scale sub-regions; then the sub-regions of the same scale in a layer of feature maps are weighted and summed to aggregate all sub-regions into a global representation; finally The global representation is reassigned to the sub-regions of the scale, and the results of all branches of the feature map of this layer are added to the input feature map to generate the contextual feature map of the feature map of this layer. This allows each subregion to pass information to all subregions of the new feature map. Each branch performs different subdivisions on the feature maps, generating sub-regions of different scales.
具体的,将初始特征图先输入自顶向下网络进行处理得到与该自顶向下网络对应的特征图,再将该处理结果输入至与自顶向下网络连接的自底向上网络进行处理,得到与该自底向上网络对应的特征图,这两个特征图构成了第一阶段特征图。然后在自顶向下网络中分别根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图通过自顶向下网络传播到自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图,从而对自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图进行更新。同理,在自底向上网络中分别根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图通过自底向上网络传播到自底向上网络中的其他层特征图,从而对自底向上网络中的其他层特征图进行更新。上述两者更新后的特征图就构成了更新后的第一阶段特征图。Specifically, the initial feature map is first input to the top-down network for processing to obtain a feature map corresponding to the top-down network, and then the processing result is input to the bottom-up network connected to the top-down network for processing. , the feature map corresponding to the bottom-up network is obtained, and these two feature maps constitute the first-stage feature map. Then, in the top-down network, the contextual feature map of the sub-region based on the feature map of each layer is generated according to the region context encoding RCE, and the context feature map is propagated to other layers in the top-down network through the top-down network. feature maps to update the feature maps of other layers in the top-down network. In the same way, in the bottom-up network, the context feature map of the sub-region based on the feature map of each layer is generated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the context feature map is propagated through the bottom-up network to other layer features in the bottom-up network. map to update the feature maps of other layers in the bottom-up network. The above two updated feature maps constitute the updated first-stage feature maps.
S106,将更新后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合及更新处理,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图。S106, performing iterative fusion and update processing with the updated first-stage feature map as an input until a preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map.
将根据区域上下文编码RCE更新之后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合处理,得到第二阶段特征图。根据区域上下文编码RCE对第二阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新之后的第二阶段特征图。再将更新之后的第二阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合处理,得到第三阶段特征图。根据区域上下文编码RCE对第三阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新之后的第四阶段特征图,如此迭代下去,直到达到预设迭代次数停止,此时,最后得到的特征图即为目标特征图。The first-stage feature map after RCE update according to the regional context encoding is used as input to perform iterative fusion processing to obtain the second-stage feature map. The second-stage feature map is updated according to the region context encoding RCE, and the updated second-stage feature map is obtained. Then, the updated second-stage feature map is used as input for iterative fusion processing, and the third-stage feature map is obtained. The third-stage feature map is updated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the fourth-stage feature map after the update is obtained, and the iteration continues until the preset number of iterations is reached. At this time, the finally obtained feature map is the target feature map.
S108,根据目标特征图对待处理图像进行物体分割,目标特征图为自底向上网络所得到的特征图。S108 , perform object segmentation on the image to be processed according to the target feature map, where the target feature map is a feature map obtained by a bottom-up network.
在得到了目标特征图之后,就可以根据目标特征图对待处理图像进行物体分割。具体的,对待处理图像进行物体分割,即可以实现将待处理图像中的不同的物体以及同一物体的不同个体进行分割开来。其中,目标特征图为自底向上网络所得到的特征图。After the target feature map is obtained, the object to be processed can be segmented according to the target feature map. Specifically, the object segmentation of the image to be processed can realize the segmentation of different objects in the image to be processed and different individuals of the same object. Among them, the target feature map is the feature map obtained by the bottom-up network.
上述物体分割方法,获取待处理图像的初始特征图,将初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,分别在自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图。将更新后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图,根据目标特征图对待处理图像进行物体分割。区域上下文编码RCE可以利用特征图的不同子区域来计算上下文特征从而对每一阶段的特征图进行更新,能够捕获特征图中多尺度子区域的上下文信息。迭代融合能够聚合所有级别的上下文信息,避免信息的流失,进而提高物体分割的准确性。For the above object segmentation method, the initial feature map of the image to be processed is obtained, and the initial feature map is input into the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network to calculate the first-stage feature map. In the upward network, the first-stage feature map is updated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the updated first-stage feature map is obtained. The updated first-stage feature map is used as input to perform iterative fusion and update calculation until the preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map, and the object to be processed is segmented according to the target feature map. The regional context encoding RCE can use different sub-regions of the feature map to calculate the context features to update the feature map at each stage, and can capture the context information of multi-scale sub-regions in the feature map. Iterative fusion can aggregate all levels of context information, avoid information loss, and improve the accuracy of object segmentation.
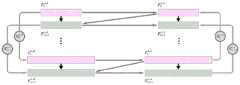
在一个实施例中,连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络采用密集路径连接。In one embodiment, the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network are connected using dense paths.
具体的,图2为一个实施例中网络结构及特征图的示意图。图2中箭头所示均为网络结构,长方形块所示均为特征图。若箭头自顶指向下,则箭头所示为自顶向下网络,若箭头自底指向上,则箭头所示为自底向上网络。Specifically, FIG. 2 is a schematic diagram of a network structure and a feature map in an embodiment. The arrows in Figure 2 are all network structures, and the rectangular blocks are all feature maps. If the arrow points from the top to the bottom, the arrow shows a top-down network, and if the arrow points from the bottom to the top, the arrow shows a bottom-up network.
在图2(a)中,左图箭头所示为主干网络,右图箭头所示为自顶向下网络。在图2(b)中,左图箭头所示为主干网络,右图箭头所示为采用密集路径连接的自顶向下网络。在图2(c)中,左图箭头所示为主干网络,将主干网络所得的特征图输入至右图箭头所示连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络。其中,在连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中,将由自顶向下网络进行卷积计算所得的特征图输入至自底向上网络中进行卷积计算得到特征图。在图2(d)中,左图箭头所示为主干网络,将主干网络所得的特征图输入至右图箭头所示连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络,该连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络均采用密集路径连接。在本申请实施例中,主干网络为自底向上网络,且在本申请实施例中,主要采用图2(d)箭头所示的网络结构实现物体分割。In Figure 2(a), the arrow on the left shows the backbone network, and the arrow on the right shows the top-down network. In Figure 2(b), the arrows on the left show the backbone network, and the arrows on the right show the top-down network connected by dense paths. In Figure 2(c), the arrow on the left shows the backbone network, and the feature map obtained by the backbone network is input to the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network shown by the arrow on the right. Among them, in the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network, the feature map obtained by the convolution calculation of the top-down network is input into the bottom-up network for convolution calculation to obtain the feature map. In Figure 2(d), the arrow on the left shows the backbone network, and the feature map obtained by the backbone network is input to the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network shown by the arrow on the right. Both the bottom network and the bottom-up network are connected by dense paths. In the embodiment of the present application, the backbone network is a bottom-up network, and in the embodiment of the present application, the network structure shown by the arrow in FIG. 2(d) is mainly used to realize object segmentation.
在图2(c)中,连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络都只能在相邻特征图之间直接传播上下文信息,而在相邻的特征图之外传播上下文信息,则需要经过多个阶段间接进行传播,间接传播必然会导致重要信息的衰减。In Figure 2(c), both the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network can only directly propagate context information between adjacent feature maps, while to propagate context information outside adjacent feature maps, it is necessary to After multiple stages of indirect propagation, indirect propagation will inevitably lead to the attenuation of important information.
本申请实施例中,连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络均采用密集路径连接,密集路径就可以在上下文信息传播的每个阶段都直接通信所有的特征图,从而能够在所有级别上直接有效地增强特征图,避免了重要信息在间接传播过程中的不断衰减,以至于降低最后物体分割结果的准确性。In the embodiment of the present application, the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network are connected by dense paths, and the dense paths can directly communicate all feature maps at each stage of context information propagation, so that all levels can be It directly and effectively enhances the feature map, avoiding the continuous attenuation of important information in the process of indirect propagation, so as to reduce the accuracy of the final object segmentation result.
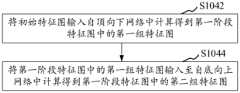
在一个实施例中,如图3所示,将初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,包括:第一阶段特征图包括两组特征图;In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 3, the initial feature map is input into the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network to obtain the first-stage feature map, including: the first-stage feature map includes two sets of feature maps ;
S1042,将初始特征图输入自顶向下网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;S1042, inputting the initial feature map into the top-down network to obtain the first group of feature maps in the first-stage feature map;
S1044,将第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图输入至自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。S1044: Input the first set of feature maps in the feature map of the first stage into a bottom-up network to calculate the second set of feature maps in the feature map of the first stage.
具体的,如图2(d)所示,由主干网络(图2(d)左图箭头所示)进行卷积计算得到初始特征图,将初始特征图输入至(图2(d)右图箭头所示)连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络,且该连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络采用密集路径连接。其中,先将初始特征图输入至密集的自顶向下网络进行卷积计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图。然后将第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图输入至密集的自底向上网络进行卷积计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。Specifically, as shown in Figure 2(d), the initial feature map is obtained by convolution calculation by the backbone network (shown by the arrow on the left of Figure 2(d)), and the initial feature map is input to (Figure 2(d) on the right). Arrows) continuous top-down network and bottom-up network, and the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network are connected by dense paths. Among them, the initial feature map is first input into a dense top-down network for convolution calculation to obtain the first set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map. Then, the first set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map is input to a dense bottom-up network for convolution calculation to obtain the second set of feature maps in the first-stage feature map.
本申请实施例中,连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络为最顶层和最底层的特征图之间的信息传播构建了一个快捷方式。因此,连续的自顶向下和自底向上的网络被用来学习不同层次上更强大的特征图。且该连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络采用密集路径连接,密集路径就可以在上下文信息传播的每个阶段都直接通信所有的特征图,从而能够在所有级别上直接有效地增强特征图,避免了重要信息在间接传播过程中的不断衰减。因此,在本申请实施例中,分别从连续和密集两个维度上提高了物体分割结果的准确性。In this embodiment of the present application, the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network construct a shortcut for information propagation between the topmost and bottommost feature maps. Therefore, successive top-down and bottom-up networks are used to learn more powerful feature maps at different levels. And the continuous top-down network and bottom-up network are connected by dense paths, and dense paths can directly communicate all feature maps at each stage of context information propagation, so that features can be directly and effectively enhanced at all levels. Graph, avoiding the continuous attenuation of important information in the process of indirect propagation. Therefore, in the embodiments of the present application, the accuracy of the object segmentation result is improved from two dimensions, continuous and dense, respectively.
在一个实施例中,如图4所示,分别在自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图,包括:In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 4 , the first-stage feature map is updated in the top-down network and the bottom-up network according to the regional context coding RCE, respectively, to obtain the updated first-stage feature map, including :
S1046,在自顶向下网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图传播到自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图,对自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图。S1046, in the top-down network, according to the regional context coding RCE, generate a context feature map based on the sub-region of each layer feature map, and propagate the context feature map to other layer feature maps in the top-down network. The feature maps of other layers in the downward network are updated to obtain the first set of feature maps in the updated first-stage feature maps.
具体的,在图2(d)中间部分箭头所示的密集连接的自顶向下网络中,根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,再通过图2(d)中间部分箭头所示的所有连接将该上下文特征图传播到自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图。从而实现对自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图。Specifically, in the densely connected top-down network shown by the arrow in the middle part of Fig. 2(d), the contextual feature map of the sub-region based on the feature map of each layer is generated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and then through Fig. 2 ( d) All connections shown by arrows in the middle part propagate this contextual feature map to other layer feature maps in the top-down network. In this way, the feature maps of other layers in the top-down network are updated, and the first group of feature maps in the updated first-stage feature maps are obtained.
S1048,在自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图传播到自底向上网络中的其他层特征图对自底向上网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。S1048, in the bottom-up network, according to the regional context encoding RCE, generate a context feature map based on the sub-region of each layer feature map, and propagate the context feature map to other layer feature maps in the bottom-up network to the bottom-up network. The feature maps of other layers are updated to obtain the second set of feature maps in the updated first-stage feature maps.
具体的,在图2(d)右侧部分箭头所示的密集连接的自底向上网络中,根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,再通过图2(d)右侧部分的所有连接将该上下文特征图传播到自底向上网络中的其他层特征图。从而实现对自底向上网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。Specifically, in the densely connected bottom-up network shown by the arrow in the right part of Figure 2(d), the contextual feature map of the sub-region based on the feature map of each layer is generated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and then through Figure 2 ( d) All connections in the right part propagate this contextual feature map to other layer feature maps in the bottom-up network. In this way, the feature maps of other layers in the bottom-up network are updated, and the second set of feature maps in the updated first-stage feature maps are obtained.
本申请实施例中,根据区域上下文编码RCE机制,并通过密集连接的路径对第一阶段特征图进行更新。该机制连接输入特征图的所有子区域,使每个子区域都能够灵活地传播其信息,从而避免每一层特征图的子区域中所包含的信息的流失。且采用密集连接的路径,将根据区域上下文编码RCE机制所得的基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,传播到同一网络中的其他层特征图。采用密集路径就可以实现上下文特征图传播时都直接通信所有的特征图,从而能够在所有级别上直接有效地增强特征图,避免了重要信息在间接传播过程中的不断衰减,以至于降低最后物体分割结果的准确性。In the embodiment of the present application, the RCE mechanism is encoded according to the regional context, and the feature map of the first stage is updated through densely connected paths. This mechanism connects all sub-regions of the input feature map, so that each sub-region can flexibly propagate its information, thereby avoiding the loss of information contained in the sub-regions of each layer of feature maps. In addition, the densely connected path is used to propagate the context feature maps of sub-regions based on the feature map of each layer obtained by the regional context encoding RCE mechanism to the feature maps of other layers in the same network. By using dense paths, all feature maps can be directly communicated when the context feature map is propagated, so that feature maps can be directly and effectively enhanced at all levels, avoiding the continuous attenuation of important information in the process of indirect propagation, so as to reduce the final object. The accuracy of segmentation results.
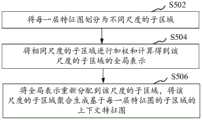
在一个实施例中,如图5所示,根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,包括:In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 5 , a context feature map of sub-regions based on each layer feature map is generated according to the region context encoding RCE, including:
S502,将每一层特征图划分为不同尺度的子区域;S502, dividing each layer of feature maps into sub-regions of different scales;
S504,将相同尺度的子区域进行加权和计算得到该尺度的子区域的全局表示;S504, weighting and calculating the sub-regions of the same scale to obtain a global representation of the sub-regions of the scale;
S506,将全局表示重新分配到该尺度的子区域,将该尺度的子区域聚合生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。S506 , reassign the global representation to the sub-regions of the scale, and aggregate the sub-regions of the scale to generate a context feature map based on the sub-regions of the feature maps of each layer.
具体的,如图6所示,区域上下文编码RCE机制对于每一层特征图的处理包括多个并行分支,在不同的分支中对输入特征图进行不同尺度的划分。例如在图6中,对输入特征图(a)采用三种不同尺度的划分,划分为3×3,5×5,7×7的子区域,每一个分支中的子区域的尺度是相同的。区域上下文编码RCE机制首先使用单独的卷积层来处理输入特征图(a),然后用处理结果来计算子区域(b)的特征,并在每个分支中将相同尺度的子区域进行加权和计算得到该尺度下子区域的全局表示。Specifically, as shown in FIG. 6 , the processing of the feature map of each layer by the region context encoding RCE mechanism includes multiple parallel branches, and the input feature map is divided into different scales in different branches. For example, in Figure 6, the input feature map (a) is divided into three different scales, divided into 3×3, 5×5, 7×7 sub-regions, and the scales of the sub-regions in each branch are the same . The region context encoding RCE mechanism first uses a separate convolutional layer to process the input feature map (a), and then uses the processing results to calculate the features of the subregions (b), and weighted sum of the subregions of the same scale in each branch A global representation of the subregion at this scale is computed.
在得到了全局表示之后,将全局表示重新分配到该尺度的子区域,将该尺度的子区域聚合生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。具体的,因为全局表示(c)分别在对应的分支中来连接所有的子区域,所以全局表示就可以向所有子区域(d)传播信息得到每个分支的处理结果。最后,再将所有分支的处理结果与输入特征图(a)相加,生成基于输入特征图(a)的上下文特征图(e),该上下文特征图(e)可以用R来表示。After the global representation is obtained, the global representation is reassigned to the sub-regions of this scale, and the sub-regions of this scale are aggregated to generate a contextual feature map based on the sub-regions of each layer of feature maps. Specifically, since the global representation (c) connects all sub-regions in corresponding branches, the global representation can propagate information to all sub-regions (d) to obtain the processing result of each branch. Finally, the processing results of all branches are added to the input feature map (a) to generate a context feature map (e) based on the input feature map (a). The context feature map (e) can be represented by R.
更具体的,给定由自顶向下/自底向上网络生成的特征图Fi∈RH×W×C,对特征图Fi∈RH×W×C进行卷积并将其划分为K×K的子区域。通过对每个子区域内的神经元进行累加,得到了一个特征图又有:More specifically, given a feature map Fi ∈ RH×W×C generated by a top-down/bottom-up network, convolve the feature map Fi ∈ RH×W×C and divide it into A subregion of K×K. By accumulating neurons in each subregion, a feature map is obtained And also:
其中(x,y)表示的位置,用S(x,y)表示中包含一组神经元的子区域,表示子区域S(x,y)的特征。通过调整所有子区域的重要性来对所有子区域的特征进行求和,从而得到连接所有子区域的全局表示。为此,可以简单地应用可学的K×K卷积与ReLU激活其中没有填充。这就产生了一个c维特征向量(如图6(c)所示)。其他的可学习的K×K卷积内核用于反卷积这个c维特征向量,其中没有填充,得到一个新的特征图然后将所有分支的特征图添加到输入特征图Fi中,生成特征图Ri∈RH×W×C:where (x, y) means The position of , represented by S(x,y) contains a subregion of a set of neurons, Represents the features of the subregion S(x,y). The features of all sub-regions are summed by adjusting the importance of all sub-regions, resulting in a global representation connecting all sub-regions. To do this, learnable K×K convolutions with ReLU activations can be simply applied There is no padding in it. This produces a c-dimensional feature vector (as shown in Fig. 6(c)). Additional learnable K×K convolution kernels are used to deconvolve this c-dimensional feature vector with no padding, resulting in a new feature map then all branches The feature map is added to the input feature map Fi to generate a feature map Ri ∈ RH×W×C :
对于公式2,使用了Fi的3个不同的细分(3×3,5×5,7×7的子区域)来计算特征图的集合通过将特征图划分成更多的子区域,可以显著地增加需要学习的参数的数量。For Equation 2, 3 differentsubdivisions of Fi (sub-regions of 3×3, 5×5, 7×7) are used to compute the set of feature maps By dividing the feature map into more sub-regions, the number of parameters that need to be learned can be significantly increased.
本申请实施例中,对于每层输入特征图,区域上下文编码RCE机制都采用多个分支,在每个分支中将特征图划分为不同尺度的子区域,再对同一尺度的子区域计算出一个全局变量。因此,每一个分支就对应一个全局变量。In the embodiment of the present application, for each layer of input feature maps, the region context encoding RCE mechanism adopts multiple branches. In each branch, the feature map is divided into sub-regions of different scales, and then a sub-region of the same scale is calculated. global variables. Therefore, each branch corresponds to a global variable.
再将某一分支的全局变量对应重新分配到该分支所对应的尺度下所划分的子区域得到每个分支的处理结果,最后将所有分支的处理结果与输入特征图相加,生成基于该输入特征图的上下文特征图。与输入特征图对应的多个全局变量就包含了输入特征图中不同尺度子区域的上下文信息,所以最终所生成的基于该输入特征图的上下文特征图所包含的信息就更加全面。Then reassign the global variables of a branch to the sub-regions divided by the scale corresponding to the branch to obtain the processing results of each branch, and finally add the processing results of all branches to the input feature map to generate Contextual feature maps for feature maps. The multiple global variables corresponding to the input feature map contain the context information of sub-regions of different scales in the input feature map, so the final generated context feature map based on the input feature map contains more comprehensive information.
通过RCE机制所得到的每层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,会通过密集连接传播到其他层特征图中。然后其他层特征图也是通过RCE机制,得到该特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。因此,由于RCE机制,每一层特征图不同尺度的子区域就可以影响其他层特征图的任何位置。相对于采用密集路径实现上下文特征图传播时都直接通信所有的特征图,从而能够在所有级别上直接有效地增强特征图,避免了重要信息在间接传播过程中的不断衰减。RCE机制进一步使得每一层特征图不同尺度的子区域就可以影响其他层特征图的任何位置。所以,进一步提高了物体分割结果的准确性。The contextual feature maps of the sub-regions of the feature maps of each layer obtained through the RCE mechanism will be propagated to the feature maps of other layers through dense connections. Then the feature maps of other layers are also obtained through the RCE mechanism to obtain the context feature maps of the sub-regions of the feature map. Therefore, due to the RCE mechanism, sub-regions of different scales in the feature maps of each layer can affect any position of the feature maps of other layers. Compared with the use of dense paths to implement context feature map propagation, all feature maps are directly communicated, so that feature maps can be directly and effectively enhanced at all levels, avoiding the continuous attenuation of important information in the process of indirect propagation. The RCE mechanism further enables sub-regions of different scales in the feature maps of each layer to affect any position of the feature maps of other layers. Therefore, the accuracy of the object segmentation result is further improved.
在一个实施例中,区域上下文编码RCE对于每一层特征图包括多个并行分支,每个并行分支分别对同一尺度的子区域进行处理。In one embodiment, the region context encoding RCE includes multiple parallel branches for each layer feature map, and each parallel branch processes sub-regions of the same scale respectively.
具体的,如图6所示,区域上下文编码RCE机制对于每一层特征图的处理包括多个并行分支(图6所示为三个分支),在不同的分支中对输入特征图进行不同尺度的划分。例如在图6中,对输入特征图(a)采用三种不同尺度的划分,划分为3×3,5×5,7×7的子区域,每一个分支中的子区域的尺度是相同的。每个并行分支分别对同一尺度的子区域进行处理。当然,上述实施例中所采用的三种不同尺度的划分只是举例,也可以采用一种、两种、四种或者更多种不同尺度的划分。还可以对输入特征图采取不规则的划分,即每个分支中的子区域的尺度是不同的,但是每个分支中的子区域的尺度具有不同的特定规律。Specifically, as shown in Figure 6, the region context encoding RCE mechanism includes multiple parallel branches (three branches shown in Figure 6) for each layer of feature maps, and different scales are performed on the input feature maps in different branches. division. For example, in Figure 6, the input feature map (a) is divided into three different scales, which are divided into 3×3, 5×5, 7×7 sub-regions, and the scales of the sub-regions in each branch are the same . Each parallel branch separately processes subregions of the same scale. Of course, the division of three different scales adopted in the above-mentioned embodiments is just an example, and one, two, four or more kinds of division of different scales may also be adopted. The input feature map can also be divided irregularly, that is, the scales of the sub-regions in each branch are different, but the scales of the sub-regions in each branch have different specific laws.
区域上下文编码RCE机制首先使用单独的卷积层来处理输入特征图(a),然后用处理结果来计算子区域(b)的特征,并在每个分支中将相同尺度的子区域进行加权和计算得到该尺度下子区域的全局表示。在得到了全局表示之后,将全局表示重新分配到该尺度的子区域,将该尺度的子区域聚合生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。The region context encoding RCE mechanism first uses a separate convolutional layer to process the input feature map (a), and then uses the processing results to calculate the features of the subregions (b), and weighted sum of the subregions of the same scale in each branch A global representation of the subregion at this scale is computed. After the global representation is obtained, the global representation is reassigned to the sub-regions of this scale, and the sub-regions of this scale are aggregated to generate a contextual feature map based on the sub-regions of each layer of feature maps.
本申请实施例中,RCE机制在不同的分支中对输入特征图进行不同尺度的划分,所以从不同分支中所计算出的全局表示是具有差异性的,这样再将全局表示重新分配到该尺度的子区域,将该尺度的子区域聚合生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。最终所生成的基于该输入特征图的上下文特征图就包括了差异性全局表示所包含的所有信息,因此最终所生成的基于该输入特征图的上下文特征图所包含的信息就更加全面,避免了单一分支所造成的信息遗失。In the embodiment of the present application, the RCE mechanism divides the input feature map at different scales in different branches, so the global representations calculated from different branches are different, so the global representation is reassigned to the scale The sub-regions of this scale are aggregated to generate a contextual feature map based on the sub-regions of each layer’s feature map. The final generated context feature map based on the input feature map includes all the information contained in the differential global representation, so the final generated context feature map based on the input feature map contains more comprehensive information, avoiding the need for Loss of information caused by a single branch.
在一个实施例中,如图7所示,迭代融合及更新处理的过程,包括:In one embodiment, as shown in Figure 7, the process of iterative fusion and update processing includes:
S702,将第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图和第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图。S702 , fuse the first set of feature maps and the second set of feature maps in the feature map of the first stage to obtain the first set of feature maps in the feature map of the second stage.
具体的,如图8所示,为迭代融合及更新处理过程的示意图,让t表示阶段(0≤t≤T)。图8中包括了两个阶段,第一阶段相关的数据用右下标为t的字母来表示,第二阶段相关的数据用右下标为t+1的字母来表示,和为自顶向下和自底向上的第t阶段第i层的特征图。假设此时t取值为1,则为自顶向下网络的第一阶段第i层的第一组特征图。为自底向上网络的第一阶段第i层的第二组特征图。Specifically, as shown in FIG. 8 , which is a schematic diagram of an iterative fusion and update process, let t represent a stage (0≤t≤T). Figure 8 includes two stages. The data related to the first stage is represented by the letter marked with t in the lower right, and the data related to the second stage is represented by the letter marked with t+1 in the lower right. and are the top-down and bottom-up feature maps of the i-th layer in the t-th stage. Assuming that t is 1 at this time, then is the first set of feature maps of the i-th layer in the first stage of the top-down network. is the second set of feature maps of the i-th layer of the first stage of the bottom-up network.
将第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图和第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图。实际为将第一阶段特征图中某层的第一组特征图和第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中该层的第一组特征图。在图8中,即为将特征图和融合为同理,对于第一阶段其他层的特征图也是将该层的第一组特征图和第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中该层的第一组特征图。The first set of feature maps and the second set of feature maps in the feature map of the first stage are fused to obtain the first set of feature maps in the feature map of the second stage. Actually, the first set of feature maps and the second set of feature maps of a certain layer in the feature map of the first stage are fused to obtain the first set of feature maps of the layer in the feature map of the second stage. In Figure 8, that is, the feature map and merged into Similarly, for the feature maps of other layers in the first stage, the first set of feature maps of the layer and the second set of feature maps are fused to obtain the first set of feature maps of the layer in the feature map of the second stage.
S704,将第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图与第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。S704, fuse the first set of feature maps in the feature map of the second stage with the second set of feature maps in the feature map of the first stage to obtain a second set of feature maps in the feature map of the second stage.
实际指的是将第二阶段特征图中某层的第一组特征图与第一阶段特征图中该层的第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中该层的第二组特征图。在图8中,即为将特征图和融合为同理,对于第二阶段其他层的第二组特征图也是按照相同的方式生成。It actually refers to the fusion of the first set of feature maps of a certain layer in the feature map of the second stage with the second set of feature maps of the layer in the feature map of the first stage to obtain the second set of feature maps of the layer in the feature map of the second stage. feature map. In Figure 8, that is, the feature map and merged into Similarly, the second set of feature maps for other layers in the second stage are also generated in the same way.
因此,上下文信息在两个网络之间以锯齿形的方式传播。所以本申请实施例中的网络也称之为锯齿形网络(ZigZagNet)。该锯齿形网络包括密集连接的、连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络,且该自顶向下网络和自底向上网络之间以锯齿形的方式迭代融合更新以传播上下文信息。Therefore, contextual information is propagated in a zigzag fashion between the two networks. Therefore, the network in the embodiment of the present application is also called a ZigZagNet (ZigZagNet). The zigzag network includes a densely connected, continuous top-down network and a bottom-up network, and the top-down network and the bottom-up network are iteratively fused and updated in a zigzag manner to propagate context information.
S706,根据区域上下文编码RCE在自顶向下网络中对第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图。S706: Update the first group of feature maps in the second-stage feature map in the top-down network according to the regional context encoding RCE, to obtain the updated first group of feature maps in the second-stage feature map.
S708,根据区域上下文编码RCE在自底向上网络中对第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。S708: Update the second set of feature maps in the second-stage feature map in the bottom-up network according to the regional context encoding RCE, to obtain the second set of feature maps in the updated second-stage feature map.
在得到了第二阶段特征图之后,根据区域上下文编码RCE在各自的网络中对第二阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图。第二阶段特征图包括第一组特征图和第二组特征图,其中第一组特征图包括多层特征图,第二组特征图包括相同数目的多层特征图。更新的过程具体为:在自顶向下网络中分别根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图通过自顶向下网络传播到自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图,从而对自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图进行更新。同理,在自底向上网络中分别根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图通过自底向上网络传播到自底向上网络中的其他层特征图,从而对自底向上网络中的其他层特征图进行更新。上述两者更新后的特征图就构成了更新后的第二阶段特征图。After the second-stage feature map is obtained, the second-stage feature map is updated in the respective networks according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the updated second-stage feature map is obtained. The second-stage feature maps include a first set of feature maps and a second set of feature maps, wherein the first set of feature maps includes multi-layer feature maps, and the second set of feature maps includes the same number of multi-layer feature maps. The update process is as follows: in the top-down network, the contextual feature map of the sub-region based on the feature map of each layer is generated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the contextual feature map is propagated to the top-down through the top-down network. The feature maps of other layers in the network are updated to update the feature maps of other layers in the top-down network. In the same way, in the bottom-up network, the context feature map of the sub-region based on the feature map of each layer is generated according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the context feature map is propagated through the bottom-up network to other layer features in the bottom-up network. map to update the feature maps of other layers in the bottom-up network. The updated feature maps of the above two constitute the updated second-stage feature maps.
S710,将更新后的第二阶段特征图作为下一次迭代融合及更新计算的输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图。S710 , using the updated second-stage feature map as an input for the next iterative fusion and update calculation, and perform iterative fusion and update calculation until a preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map.
具体的,将更新后的第二阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合,得到第三阶段特征图,再根据区域上下文编码RCE在各自的网络中对第三阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第三阶段特征图。同理进行下一次迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图。在本申请实施例中,可以取迭代次数为三次,当然在其他实施例中,迭代次数可以是其他任意数值。Specifically, iteratively fuses the updated second-stage feature maps as input to obtain the third-stage feature maps, and then updates the third-stage feature maps in their respective networks according to the regional context encoding RCE to obtain the updated first-stage feature maps. Three-stage feature map. In the same way, the next iterative fusion and update calculation is performed until the preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map. In this embodiment of the present application, the number of iterations may be three times. Of course, in other embodiments, the number of iterations may be any other value.
本申请实施例中,通过迭代融合使得特征图所包含的上下文信息在自顶向下网络和自底向上网络之间以锯齿形的方式传播。即实现了在自顶向下和自底向上的网络之间迭代地交换上下文信息,加强了两种网络直接的信息交流,避免了单一网络所造成的信息遗失,提高了物体分割的准确性。In this embodiment of the present application, the context information contained in the feature map is propagated in a zigzag manner between the top-down network and the bottom-up network through iterative fusion. That is, it realizes the iterative exchange of context information between top-down and bottom-up networks, strengthens the direct information exchange between the two networks, avoids information loss caused by a single network, and improves the accuracy of object segmentation.
在一个实施例中,对图8所示的迭代融合及更新处理的计算过程进行详细的说明。In one embodiment, the calculation process of the iterative fusion and update processing shown in FIG. 8 is described in detail.
在阶段t+1中自顶向下的网络计算特征图有The top-down network computes feature maps in stage t+1 as
其中t=0,…,T-1。在本申请实施例中T最大为3,当然也可以设定T最大取到其他数值。通过将来自更高层次的上下文特征图集与融合的特征图集的乘积相加,对特征映射进行建模,其中where t=0,...,T-1. In the embodiment of the present application, the maximum value of T is 3. Of course, the maximum value of T can also be set to other values. by bringing from higher levels The contextual feature atlas and the fused feature atlas of Add the products of , to the feature map model, where
其中是卷积内核,σ表示Relu激活函数,初始化时t=0,使用Bi表示由骨架FCN计算的特征图,用它构造在接下来的迭代中,通过卷积和激活它们的总和,将上一个迭代中自顶向下和自底向上的网络生成的和融合起来。因此,与传统的单向上下文信息传播不同,自顶向下网络接收上一个迭代的自顶向下和自底向上的上下文信息,以细化新的特征图此外,使用区域上下文编码(RCE)来生成基于的子区域的上下文特征图RCE将分区之间的关系编码到上下文特征图中。通过使用不同的子区域尺度,为提供了更丰富的上下文信息。in is the convolution kernel, σ represents the Relu activation function, t=0 during initialization, and Bi is used to represent the feature map calculated by the skeleton FCN, which is used to construct In the next iteration, the top-down and bottom-up networks generated in the previous iteration are generated by convolution and activation of their sum and fused. Therefore, unlike the traditional one-way context information propagation, the top-down network receives top-down and bottom-up context information from the previous iteration to refine new feature maps Furthermore, Region Context Encoding (RCE) is used to generate Contextual feature maps of subregions of RCE encodes the relationship between partitions into a contextual feature map. By using different subregion scales, Provides richer contextual information.
同样的,使用自底向上的网络来计算特征图有:Similarly, a bottom-up network is used to compute feature maps Have:
其中有:Including:
注意,这里不像公式4那样融合阶段t的两个特征图,而是融合图和因为在流程的这一点上已经可用,并且包含比更精确的信息。最后,利用公式(4)融合图和得到用于分割的图Note that the two feature maps of stage t are not fused here as in Equation 4, but the fusion map and because at this point in the process is already available and contains more than more precise information. Finally, use formula (4) to fuse the graph and get a graph for segmentation
在一个实施例中,获取待处理图像的初始特征图,包括:In one embodiment, acquiring the initial feature map of the image to be processed includes:
将待处理图像输入至自底向上网络计算得到初始特征图。Input the image to be processed into the bottom-up network to calculate the initial feature map.
本申请实施例中,如图2(d)左图所示为自底向上网络,将待处理图像输入至该自底向上网络进行卷积计算,就得到了初始特征图。In the embodiment of the present application, as shown in the left figure of FIG. 2(d), it is a bottom-up network, and the image to be processed is input into the bottom-up network for convolution calculation, and an initial feature map is obtained.
在一个实施例中,目标特征图为自底向上网络所得到的特征图。In one embodiment, the target feature map is a feature map obtained by a bottom-up network.
本申请实施例中,在经过多次迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数时,得到最后阶段的特征图。该最后阶段的特征图包括第一组特征图和第二组特征图。其中,第一组特征图为由自顶向下网络计算所得的特征图,第二组特征图为由自底向上网络计算所得的特征图。但是,在物体分割时是根据最后阶段的第二组特征图进行的,所以目标特征图就为最后阶段的自底向上网络所得到的特征图。最后阶段的自底向上网络所得到的特征图是最新的、且包含了最为丰富的上下文信息,所以采用最后阶段的自底向上网络所得到的特征图进行物体分割,就提高了分割结果的准确性。In the embodiment of the present application, after multiple iterations of fusion and update calculation, until the preset number of iterations is reached, the feature map of the final stage is obtained. The feature maps in this final stage include a first set of feature maps and a second set of feature maps. Among them, the first set of feature maps are the feature maps calculated by the top-down network, and the second set of feature maps are the feature maps calculated by the bottom-up network. However, the object segmentation is performed according to the second set of feature maps in the final stage, so the target feature map is the feature map obtained by the bottom-up network in the final stage. The feature map obtained by the bottom-up network in the final stage is the latest and contains the most abundant contextual information. Therefore, using the feature map obtained by the bottom-up network in the final stage for object segmentation improves the accuracy of the segmentation results. sex.
在一个实施例中,如图9所示,提供了一种物体分割装置900,装置包括:初始特征图获取模块920、特征图生成模块940、迭代处理模块960及物体分割模块980。其中,In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 9 , an object segmentation apparatus 900 is provided. The apparatus includes: an initial feature
初始特征图获取模块920,用于获取待处理图像的初始特征图;an initial feature
特征图生成模块940,用于将初始特征图输入连续的自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图,分别在自顶向下网络和自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE对第一阶段特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图;The feature
迭代处理模块960,用于将更新后的第一阶段特征图作为输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图,目标特征图为自底向上网络所得到的特征图;The iterative processing module 960 is configured to use the updated first-stage feature map as an input to perform iterative fusion and update calculation until a preset number of iterations is reached to obtain a target feature map, which is a feature map obtained by a bottom-up network;
物体分割模块980,用于根据目标特征图对待处理图像进行物体分割。The
在一个实施例中,如图10所示,特征图生成模块940包括:第一组特征图生成模块942及第二组特征图生成模块944。其中,In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 , the feature
第一组特征图生成模块942,用于将初始特征图输入自顶向下网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;The first group of feature
第二组特征图生成模块944,用于将第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图输入至自底向上网络中计算得到第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。The second set of feature
在一个实施例中,如图10所示,特征图生成模块940还包括:特征图更新模块946。其中,In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 , the feature
特征图更新模块946,用于在自顶向下网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图传播到自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图,对自顶向下网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;The feature
特征图更新模块946,还用于在自底向上网络中根据区域上下文编码RCE生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图,将上下文特征图传播到自底向上网络中的其他层特征图对自底向上网络中的其他层特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图。The feature
在一个实施例中,如图10所示,特征图更新模块946包括区域上下文编码RCE模块946a,区域上下文编码RCE模块946a用于将每一层特征图划分为不同尺度的子区域;将相同尺度的子区域进行加权和计算得到尺度的子区域的全局表示;将全局表示重新分配到尺度的子区域,将尺度的子区域聚合生成基于每一层特征图的子区域的上下文特征图。In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 , the feature
在一个实施例中,如图10所示,迭代处理模块960,还用于将第一阶段特征图中的第一组特征图和第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 , the iterative processing module 960 is further configured to fuse the first set of feature maps and the second set of feature maps in the feature map of the first stage to obtain the feature map of the second stage The first set of feature maps;
将第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图与第一阶段特征图中的第二组特征图进行融合,得到第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图;Fusion of the first set of feature maps in the second stage feature map and the second set of feature maps in the first stage feature map to obtain the second set of feature maps in the second stage feature map;
根据区域上下文编码RCE在自顶向下网络中对第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图中的第一组特征图;The first group of feature maps in the second-stage feature map is updated in the top-down network according to the regional context encoding RCE, and the first set of feature maps in the updated second-stage feature map is obtained;
根据区域上下文编码RCE在自底向上网络中对第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图进行更新,得到更新后的第二阶段特征图中的第二组特征图;The second group of feature maps in the second-stage feature map is updated in the bottom-up network according to the region context encoding RCE to obtain the second set of feature maps in the updated second-stage feature map;
将更新后的第二阶段特征图作为下一次迭代融合及更新计算的输入进行迭代融合及更新计算,直到达到预设迭代次数得到目标特征图。The updated second-stage feature map is used as the input of the next iterative fusion and update calculation to perform iterative fusion and update calculation until the preset number of iterations is reached to obtain the target feature map.
在一个实施例中,如图10所示,初始特征图获取模块920,还用于将待处理图像输入至自底向上网络计算得到初始特征图。In one embodiment, as shown in FIG. 10 , the initial feature
图11示出了一个实施例中计算机设备的内部结构图。该计算机设备具体可以是终端或服务器。如图11所示,该计算机设备包括该计算机设备包括通过系统总线连接的处理器、存储器、网络接口、输入装置、显示屏、摄像头、声音采集装置及扬声器。其中,存储器包括非易失性存储介质和内存储器。该计算机设备的非易失性存储介质存储有操作系统,还可存储有计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时,可使得处理器实现物体分割方法。该内存储器中也可储存有计算机程序,该计算机程序被处理器执行时,可使得处理器执行物体分割方法。计算机设备的显示屏可以是液晶显示屏或者电子墨水显示屏,计算机设备的输入装置可以是显示屏上覆盖的触摸层,也可以是计算机设备外壳上设置的按键、轨迹球或触控板,还可以是外接的键盘、触控板或鼠标等。Figure 11 shows an internal structure diagram of a computer device in one embodiment. The computer device may specifically be a terminal or a server. As shown in FIG. 11 , the computer equipment includes a processor, a memory, a network interface, an input device, a display screen, a camera, a sound collection device and a speaker connected through a system bus. Wherein, the memory includes a non-volatile storage medium and an internal memory. The non-volatile storage medium of the computer device stores an operating system, and also stores a computer program. When the computer program is executed by the processor, the processor can implement the object segmentation method. A computer program may also be stored in the internal memory, and when the computer program is executed by the processor, the processor may execute the object segmentation method. The display screen of the computer equipment may be a liquid crystal display screen or an electronic ink display screen, and the input device of the computer equipment may be a touch layer covered on the display screen, or a button, a trackball or a touchpad set on the shell of the computer equipment, or It can be an external keyboard, trackpad or mouse, etc.
本领域技术人员可以理解,图11中示出的结构,仅仅是与本申请方案相关的部分结构的框图,并不构成对本申请方案所应用于其上的计算机设备的限定,具体的计算机设备可以包括比图中所示更多或更少的部件,或者组合某些部件,或者具有不同的部件布置。Those skilled in the art can understand that the structure shown in FIG. 11 is only a block diagram of a partial structure related to the solution of the present application, and does not constitute a limitation on the computer equipment to which the solution of the present application is applied. Include more or fewer components than shown in the figures, or combine certain components, or have a different arrangement of components.
在一个实施例中,本申请提供的物体分割装置可以实现为一种计算机程序的形式,计算机程序可在如图11所示的计算机设备上运行。计算机设备的存储器中可存储组成该物体分割装置的各个程序模块,比如,图9所示的初始特征图获取模块920、特征图生成模块940、迭代处理模块960及物体分割模块980。各个程序模块构成的计算机程序使得处理器执行本说明书中描述的本申请各个实施例的物体分割方法中的步骤。In one embodiment, the object segmentation apparatus provided by the present application can be implemented in the form of a computer program, and the computer program can be executed on the computer device as shown in FIG. 11 . The memory of the computer device can store various program modules constituting the object segmentation device, for example, the initial feature
例如,图11所示的计算机设备可以通过如图9所示的物体分割装置中的For example, the computer equipment shown in FIG. 11 can be processed by the object segmentation device shown in FIG.
初始特征图获取模块920执行步骤S102。计算机设备可通过特征图生成模块940执行步骤S104。计算机设备可通过迭代处理模块960执行步骤S106。计算机设备可通过物体分割模块980执行步骤S108。The initial feature
在一个实施例中,提供了一种计算机设备,包括存储器和处理器,存储器存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时,使得处理器执行上述物体分割方法的步骤。此处物体分割方法的步骤可以是上述各个实施例的物体分割方法中的步骤。In one embodiment, a computer device is provided, including a memory and a processor, the memory stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by the processor, the processor causes the processor to perform the steps of the above object segmentation method. The steps of the object segmentation method here may be the steps in the object segmentation methods of the above embodiments.
在一个实施例中,提供了一种计算机可读存储介质,存储有计算机程序,计算机程序被处理器执行时,使得处理器执行上述物体分割方法的步骤。此处物体分割方法的步骤可以是上述各个实施例的物体分割方法中的步骤。In one embodiment, a computer-readable storage medium is provided, which stores a computer program, and when the computer program is executed by a processor, causes the processor to perform the steps of the above-mentioned object segmentation method. The steps of the object segmentation method here may be the steps in the object segmentation methods of the above embodiments.
本领域普通技术人员可以理解实现上述实施例方法中的全部或部分流程,是可以通过计算机程序来指令相关的硬件来完成,的程序可存储于一非易失性计算机可读取存储介质中,该程序在执行时,可包括如上述各方法的实施例的流程。其中,本申请所提供的各实施例中所使用的对存储器、存储、数据库或其它介质的任何引用,均可包括非易失性和/或易失性存储器。非易失性存储器可包括只读存储器(ROM)、可编程ROM(PROM)、电可编程ROM(EPROM)、电可擦除可编程ROM(EEPROM)或闪存。易失性存储器可包括随机存取存储器(RAM)或者外部高速缓冲存储器。作为说明而非局限,RAM以多种形式可得,诸如静态RAM(SRAM)、动态RAM(DRAM)、同步DRAM(SDRAM)、双数据率SDRAM(DDRSDRAM)、增强型SDRAM(ESDRAM)、同步链路(Synchlink)DRAM(SLDRAM)、存储器总线(Rambus)直接RAM(RDRAM)、直接存储器总线动态RAM(DRDRAM)、以及存储器总线动态RAM(RDRAM)等。Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that the realization of all or part of the processes in the methods of the above embodiments can be accomplished by instructing relevant hardware through a computer program, and the program can be stored in a non-volatile computer-readable storage medium, When the program is executed, it may include the flow of the embodiments of the above-mentioned methods. Wherein, any reference to memory, storage, database or other medium used in the various embodiments provided in this application may include non-volatile and/or volatile memory. Nonvolatile memory may include read only memory (ROM), programmable ROM (PROM), electrically programmable ROM (EPROM), electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM), or flash memory. Volatile memory may include random access memory (RAM) or external cache memory. By way of illustration and not limitation, RAM is available in various forms such as static RAM (SRAM), dynamic RAM (DRAM), synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), double data rate SDRAM (DDRSDRAM), enhanced SDRAM (ESDRAM), synchronous chain Road (Synchlink) DRAM (SLDRAM), memory bus (Rambus) direct RAM (RDRAM), direct memory bus dynamic RAM (DRDRAM), and memory bus dynamic RAM (RDRAM), etc.
以上所述实施例的各技术特征可以进行任意的组合,为使描述简洁,未对上述实施例中的各个技术特征所有可能的组合都进行描述,然而,只要这些技术特征的组合不存在矛盾,都应当认为是本说明书记载的范围。The technical features of the above-described embodiments can be combined arbitrarily. For the sake of brevity, all possible combinations of the technical features in the above-described embodiments are not described. However, as long as there is no contradiction between the combinations of these technical features, All should be regarded as the scope described in this specification.
以上所述实施例仅表达了本申请的几种实施方式,其描述较为具体和详细,但并不能因此而理解为对本申请专利范围的限制。应当指出的是,对于本领域的普通技术人员来说,在不脱离本申请构思的前提下,还可以做出若干变形和改进,这些都属于本申请的保护范围。因此,本申请专利的保护范围应以所附权利要求为准。The above-mentioned embodiments only represent several embodiments of the present application, and the descriptions thereof are relatively specific and detailed, but should not be construed as a limitation on the scope of the patent of the present application. It should be pointed out that for those skilled in the art, without departing from the concept of the present application, several modifications and improvements can be made, which all belong to the protection scope of the present application. Therefore, the scope of protection of the patent of the present application shall be subject to the appended claims.
Claims (10)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910217342.1ACN110084816B (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2019-03-21 | Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment |
| PCT/CN2019/081484WO2020186563A1 (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2019-04-04 | Object segmentation method and apparatus, computer readable storage medium, and computer device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910217342.1ACN110084816B (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2019-03-21 | Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110084816A CN110084816A (en) | 2019-08-02 |
| CN110084816Btrue CN110084816B (en) | 2021-04-06 |
Family
ID=67413426
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910217342.1AActiveCN110084816B (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2019-03-21 | Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110084816B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2020186563A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110084816B (en)* | 2019-03-21 | 2021-04-06 | 深圳大学 | Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment |
| CN113421276B (en)* | 2021-07-02 | 2023-07-21 | 深圳大学 | Image processing method, device and storage medium |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102073700A (en)* | 2010-12-30 | 2011-05-25 | 浙江大学 | Discovery method of complex network community |
| CN102074013A (en)* | 2011-01-26 | 2011-05-25 | 刘国英 | Wavelet multi-scale Markov network model-based image segmentation method |
| CN103049340A (en)* | 2012-10-26 | 2013-04-17 | 中山大学 | Image super-resolution reconstruction method of visual vocabularies and based on texture context constraint |
| US20130223740A1 (en)* | 2012-02-23 | 2013-08-29 | Microsoft Corporation | Salient Object Segmentation |
| CN104463191A (en)* | 2014-10-30 | 2015-03-25 | 华南理工大学 | Robot visual processing method based on attention mechanism |
| CN107909581A (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2018-04-13 | 杭州依图医疗技术有限公司 | Method, device, system, storage medium and equipment for lung segment segmentation of CT images |
| CN109118491A (en)* | 2018-07-30 | 2019-01-01 | 深圳先进技术研究院 | A kind of image partition method based on deep learning, system and electronic equipment |
| US10176388B1 (en)* | 2016-11-14 | 2019-01-08 | Zoox, Inc. | Spatial and temporal information for semantic segmentation |
| CN109255790A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2019-01-22 | 北京工业大学 | A kind of automatic image marking method of Weakly supervised semantic segmentation |
| CN109447990A (en)* | 2018-10-22 | 2019-03-08 | 北京旷视科技有限公司 | Image, semantic dividing method, device, electronic equipment and computer-readable medium |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101916379A (en)* | 2010-09-03 | 2010-12-15 | 华中科技大学 | An Object Search and Recognition Method Based on Object Accumulation Visual Attention Mechanism |
| US20120092357A1 (en)* | 2010-10-14 | 2012-04-19 | Microsoft Corporation | Region-Based Image Manipulation |
| CN107609460B (en)* | 2017-05-24 | 2021-02-02 | 南京邮电大学 | A Human Action Recognition Method Integrating Spatio-temporal Dual Network Flow and Attention Mechanism |
| CN107368787B (en)* | 2017-06-16 | 2020-11-10 | 长安大学 | Traffic sign identification method for deep intelligent driving application |
| CN107909082B (en)* | 2017-10-30 | 2020-07-31 | 东南大学 | Sonar image target identification method based on deep learning technology |
| CN108171711A (en)* | 2018-01-17 | 2018-06-15 | 深圳市唯特视科技有限公司 | A kind of infant's brain Magnetic Resonance Image Segmentation method based on complete convolutional network |
| CN108647695A (en)* | 2018-05-02 | 2018-10-12 | 武汉科技大学 | Soft image conspicuousness detection method based on covariance convolutional neural networks |
| CN109102513A (en)* | 2018-08-15 | 2018-12-28 | 黄淮学院 | A kind of partitioning algorithm of the medical image based on mathematical morphology |
| CN109472298B (en)* | 2018-10-19 | 2021-06-01 | 天津大学 | Deep Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Augmentation Network for Small-Scale Object Detection |
| CN110084816B (en)* | 2019-03-21 | 2021-04-06 | 深圳大学 | Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment |
- 2019
- 2019-03-21CNCN201910217342.1Apatent/CN110084816B/enactiveActive
- 2019-04-04WOPCT/CN2019/081484patent/WO2020186563A1/ennot_activeCeased
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102073700A (en)* | 2010-12-30 | 2011-05-25 | 浙江大学 | Discovery method of complex network community |
| CN102074013A (en)* | 2011-01-26 | 2011-05-25 | 刘国英 | Wavelet multi-scale Markov network model-based image segmentation method |
| US20130223740A1 (en)* | 2012-02-23 | 2013-08-29 | Microsoft Corporation | Salient Object Segmentation |
| CN103049340A (en)* | 2012-10-26 | 2013-04-17 | 中山大学 | Image super-resolution reconstruction method of visual vocabularies and based on texture context constraint |
| CN104463191A (en)* | 2014-10-30 | 2015-03-25 | 华南理工大学 | Robot visual processing method based on attention mechanism |
| US10176388B1 (en)* | 2016-11-14 | 2019-01-08 | Zoox, Inc. | Spatial and temporal information for semantic segmentation |
| CN107909581A (en)* | 2017-11-03 | 2018-04-13 | 杭州依图医疗技术有限公司 | Method, device, system, storage medium and equipment for lung segment segmentation of CT images |
| CN109255790A (en)* | 2018-07-27 | 2019-01-22 | 北京工业大学 | A kind of automatic image marking method of Weakly supervised semantic segmentation |
| CN109118491A (en)* | 2018-07-30 | 2019-01-01 | 深圳先进技术研究院 | A kind of image partition method based on deep learning, system and electronic equipment |
| CN109447990A (en)* | 2018-10-22 | 2019-03-08 | 北京旷视科技有限公司 | Image, semantic dividing method, device, electronic equipment and computer-readable medium |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| Assembly Design and Evaluation Based on Bare-Hand Interaction in an Augmented Reality Environment;Zhenbiao Wang等;《2009 International Conference on CyberWorlds》;20091006;第21-28页* |
| 一种模拟视觉机制的图像分割模型;杜馨瑜 等;《中国生物医学工程学报》;20120229;第31卷(第1期);第32-38页* |
| 探究基于视觉特性的计算机图像分割算法的应用;田源;《电脑编程技巧与维护》;20181130;第142-143,152页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110084816A (en) | 2019-08-02 |
| WO2020186563A1 (en) | 2020-09-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10796452B2 (en) | Optimizations for structure mapping and up-sampling | |
| US10586350B2 (en) | Optimizations for dynamic object instance detection, segmentation, and structure mapping | |
| CN110517278B (en) | Image segmentation and training method and device of image segmentation network and computer equipment | |
| CN111126574B (en) | Method, device and storage medium for training machine learning model based on endoscopic image | |
| CN111670457B (en) | Optimization of dynamic object instance detection, segmentation and structure mapping | |
| US11274922B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for binocular ranging | |
| CN110414344B (en) | A video-based person classification method, intelligent terminal and storage medium | |
| JP2023533907A (en) | Image processing using self-attention-based neural networks | |
| CN110929047A (en) | Knowledge Graph Reasoning Method and Apparatus Concerning Neighbor Entities | |
| WO2021151336A1 (en) | Road image target detection method based on attentional mechanism and related device | |
| CN108304761A (en) | Method for text detection, device, storage medium and computer equipment | |
| EP3493106A1 (en) | Optimizations for dynamic object instance detection, segmentation, and structure mapping | |
| CN109544559B (en) | Image semantic segmentation method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| EP3493104A1 (en) | Optimizations for dynamic object instance detection, segmentation, and structure mapping | |
| WO2024041108A1 (en) | Image correction model training method and apparatus, image correction method and apparatus, and computer device | |
| CN108898562B (en) | A deep learning-based image dehazing method for mobile devices | |
| CN115631396A (en) | A YOLOv5 target detection method based on knowledge distillation | |
| CN110363086A (en) | Image data recognition method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN114676777B (en) | Self-supervision learning fine-granularity image classification method based on twin network | |
| CN110084816B (en) | Object segmentation method, device, computer-readable storage medium and computer equipment | |
| CN111159450A (en) | Image classification method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| CN117710728A (en) | SAR image target recognition method, device, computer equipment and storage medium | |
| Martins et al. | Sparse and structured visual attention | |
| CN116091823A (en) | A single-feature anchor-free object detection method based on fast grouping residual module | |
| CN118608753B (en) | Dense pseudo tag method, device and equipment for semi-supervised rotation target detection |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |