CN110046713B - Robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application - Google Patents
Robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its applicationDownload PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN110046713B CN110046713BCN201910318891.8ACN201910318891ACN110046713BCN 110046713 BCN110046713 BCN 110046713BCN 201910318891 ACN201910318891 ACN 201910318891ACN 110046713 BCN110046713 BCN 110046713B
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- model
- ranking
- sorting
- function
- archive
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06F—ELECTRIC DIGITAL DATA PROCESSING
- G06F16/00—Information retrieval; Database structures therefor; File system structures therefor
- G06F16/90—Details of database functions independent of the retrieved data types
- G06F16/95—Retrieval from the web
- G06F16/953—Querying, e.g. by the use of web search engines
- G06F16/9535—Search customisation based on user profiles and personalisation
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N20/00—Machine learning
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING OR CALCULATING; COUNTING
- G06N—COMPUTING ARRANGEMENTS BASED ON SPECIFIC COMPUTATIONAL MODELS
- G06N3/00—Computing arrangements based on biological models
- G06N3/004—Artificial life, i.e. computing arrangements simulating life
- G06N3/006—Artificial life, i.e. computing arrangements simulating life based on simulated virtual individual or collective life forms, e.g. social simulations or particle swarm optimisation [PSO]
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02D—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES [ICT], I.E. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES AIMING AT THE REDUCTION OF THEIR OWN ENERGY USE
- Y02D10/00—Energy efficient computing, e.g. low power processors, power management or thermal management
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Databases & Information Systems (AREA)
- Software Systems (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computing Systems (AREA)
- Artificial Intelligence (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Computational Linguistics (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Information Retrieval, Db Structures And Fs Structures Therefor (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Translated fromChinese技术领域Technical Field
本发明涉及信息检索与机器学习领域,尤其是涉及一种基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法及其应用。The present invention relates to the fields of information retrieval and machine learning, and in particular to a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application.
背景技术Background Art
排序学习是利用机器学习技术去自动训练出排序模型以解决排序问题。它是信息检索与机器学习领域中研究的热点问题,在信息检索、搜索引擎、推荐系统和问答系统等方面有着广泛的应用前景。Ranking learning is the use of machine learning technology to automatically train a ranking model to solve the ranking problem. It is a hot topic in the field of information retrieval and machine learning, and has broad application prospects in information retrieval, search engines, recommendation systems, and question-answering systems.
由于Web的动态性和用户信息需求的多样性,在不同的排序模型下,一些Web搜索的查询的性能也许会发生较大的变化,并且可能遭受显著性损失,从而降低用户的体验。一个鲁棒的检索系统应确保用户体验不因性能表现差的查询出现而受到损害。因此,为了尽可能地提高整体用户的体验,除了传统的相关性和重要性准则外,如何保证排序模型的鲁棒性,即相对于简单基准,尽管整体上获得了一个平均增益,但新的排序模型通常会在许多查询的性能上受到损失,是近年来排序学习研究面临的一个重要问题。因此,开发鲁棒性排序学习方法以训练鲁棒性感知的排序模型从而尽可能地改进所有用户的整体满意度是非常有必要。Due to the dynamic nature of the Web and the diversity of user information needs, the performance of some Web search queries may vary significantly under different ranking models, and may suffer significant losses, thereby reducing the user experience. A robust retrieval system should ensure that the user experience is not impaired by the appearance of poorly performing queries. Therefore, in order to improve the overall user experience as much as possible, in addition to the traditional relevance and importance criteria, how to ensure the robustness of the ranking model, that is, relative to the simple benchmark, although an average gain is obtained overall, the new ranking model usually suffers a performance loss on many queries, is an important issue facing ranking learning research in recent years. Therefore, it is very necessary to develop robust ranking learning methods to train robustness-aware ranking models to improve the overall satisfaction of all users as much as possible.
当前,排序学习研究者们主要是通过设计高级的排序特征和/或通过开发先进的排序学习方法,比较和评估多个排序模型,基于一些有效性度量标准,例如归一化折扣累积增益(Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain,NDCG)和期望倒数排序(Expectedreciprocal rank,ERR)等,选择一个最佳有效性的排序模型,其目标是聚焦于改进排序模型的平均有效性,这些方法往往忽视了排序模型的鲁棒性。鲁棒性差的排序模型会导致排序系统的不稳定,即一些查询的性能表现很好,而另一些查询的性能表现却很差,导致所呈现给用户的排序结果不稳定,难以尽可能地满足不同用户的信息需求,从而难以给用户带来满意的体验。为此,在排序模型的训练过程中,有必要建立符合实际需求的优化目标,考虑同时优化排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性。Currently, researchers in ranking learning mainly design advanced ranking features and/or develop advanced ranking learning methods, compare and evaluate multiple ranking models, and select a ranking model with the best effectiveness based on some effectiveness metrics, such as Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG) and Expected Reciprocal Rank (ERR). The goal is to focus on improving the average effectiveness of the ranking model. These methods often ignore the robustness of the ranking model. Ranking models with poor robustness will lead to instability in the ranking system, that is, the performance of some queries is very good, while the performance of other queries is very poor, resulting in unstable ranking results presented to users, making it difficult to meet the information needs of different users as much as possible, and thus difficult to provide users with a satisfactory experience. To this end, in the training process of the ranking model, it is necessary to establish an optimization goal that meets actual needs and consider optimizing the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model at the same time.
发明内容Summary of the invention
本发明的目的就是为了克服上述现有技术存在的缺陷而提供一种基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法及其应用。The purpose of the present invention is to overcome the defects of the above-mentioned prior art and to provide a robust sorting learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application.
本发明的目的可以通过以下技术方案来实现:The purpose of the present invention can be achieved by the following technical solutions:
一种基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法,包括以下步骤:A robust sorting learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization includes the following steps:
步骤一,基于偏差-方差均衡理论,设计排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数,构建排序学习的两个优化性能指标;Step 1: Based on the bias-variance equilibrium theory, the effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function of the sorting model are designed to construct two optimization performance indicators for sorting learning.
步骤二,在排序学习数据集上,基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架,迭代优化排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数这两个目标以训练排序模型,从而产生排序模型归档解集;Step 2: Based on the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm framework, the effectiveness deviation function and robustness variance function of the sorting model are iteratively optimized to train the sorting model on the sorting learning dataset, thereby generating a sorting model archive solution set;
步骤三,基于多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想,从上一步骤所产生的排序模型归档解集中选择一个具有最大“净流”排序值的Pareto最优的排序模型以此作为训练出的最终排序模型。Step three, based on the idea of PROMETHEE II, a preference order structure evaluation method in multi-attribute decision-making theory, a Pareto optimal sorting model with the largest "net flow" sorting value is selected from the sorting model archive solution set generated in the previous step as the final sorting model trained.
优选地,所述的设计排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数,构建排序学习的两个优化性能指标具体为:Preferably, the validity deviation function and robustness variance function of the design ranking model are designed to construct two optimization performance indicators of ranking learning:
查询和查询集在排序模型下的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数分别定义如下:The validity deviation function and robustness variance function of the query and query set under the ranking model are defined as follows:
定义1.查询qi的有效性偏差函数BiasR(qi)定义为:
其中,表示查询qi下的所有文档Di在理想排序模型I,即所有文档全部正确排序下所获得的最佳有效性,表示查询qi下的所有文档Di在排序模型R下所获得的实际有效性,BiasR(qi)表示查询qi在排序模型R下的实际有效性相对于理想排序模型I的最佳有效性的偏差;in, represents the best effectiveness of all documentsDi under queryqi under the ideal ranking model I, that is, all documents are correctly ranked. represents the actual effectiveness of all documents Di under query qi under ranking model R, and BiasR (qi ) represents the deviation of the actual effectiveness of query qi under ranking model R relative to the optimal effectiveness of ideal ranking model I;
定义2.查询集Q的有效性偏差函数BiasR(Q)定义为:
其中,BiasR(Q)表示在排序模型R下查询集Q中所有查询qi的有效性偏差的平均值,|Q|表示查询集Q中查询qi的总个数;Where BiasR (Q) represents the average validity bias of all queries qi in the query set Q under the ranking model R, and |Q| represents the total number of queries qi in the query set Q;
定义3.查询qi的鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(qi)定义为:Definition 3. The robustness variance function VarianceR (qi ) of query qi is defined as:
VarianceR(qi)=[BiasR(qi)-BiasR(Q)]2…(3)VarianceR (qi )=[BiasR (qi )-BiasR (Q)]2 ...(3)
其中,VarianceR(qi)表示在排序模型R下查询qi的有效性偏差BiasR(qi)离查询集Q的有效性偏差BiasR(Q)的离散程度;Wherein, VarianceR (qi ) represents the degree of dispersion of the validity deviation BiasR (qi ) of query qi from the validity deviation BiasR (Q) of query set Q under ranking model R;
定义4.查询集Q的鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(Q)定义为:Definition 4. The robustness variance function VarianceR (Q) of the query set Q is defined as:
其中,VarianceR(Q)表示在排序模型R下查询集Q中所有查询qi的鲁棒性方差的平均值;Where VarianceR (Q) represents the average robustness variance of all queries qi in the query set Q under the ranking model R;
将鲁棒性排序学习问题转化为一个同时考虑有效性和鲁棒性的多目标优化问题,依据上述有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数的定义,则鲁棒性排序学习问题可形式化描述为:The robust ranking learning problem is transformed into a multi-objective optimization problem that considers both effectiveness and robustness. According to the definitions of the effectiveness deviation function and the robustness variance function, the robust ranking learning problem can be formally described as:
Utility(Q)={min BiasR(Q),min VarianceR(Q)}…(5)Utility(Q)={min BiasR (Q),min VarianceR (Q)}…(5)
即在排序学习的过程中,同时最小化有效性偏差函数BiasR(Q)和鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(Q)以训练排序模型,为此,基于上述所构建的排序模型的优化性能指标BiasR(Q)和VarianceR(Q),可采用多目标智能优化算法,如多目标粒子群优化算法,同时最小化BiasR(Q)和VarianceR(Q)的值以达到均衡优化排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性的目的。That is, in the process of sorting learning, the effectiveness deviation function BiasR (Q) and the robustness variance function VarianceR (Q) are minimized at the same time to train the sorting model. To this end, based on the optimization performance indicators BiasR (Q) and VarianceR (Q) of the sorting model constructed above, a multi-objective intelligent optimization algorithm, such as a multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm, can be adopted to simultaneously minimize the values of BiasR (Q) and VarianceR (Q) to achieve the purpose of balancing the effectiveness and robustness of the optimized sorting model.
优选地,所述的基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架,迭代优化排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数这两个目标以训练排序模型,从而产生排序模型归档解集具体为:Preferably, the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm framework is based on which the two objectives of the validity deviation function and the robustness variance function of the sorting model are iteratively optimized to train the sorting model, thereby generating a sorting model archive solution set specifically as follows:
步骤1.初始化粒子群的相关参数;
步骤2.基于所给定的排序学习数据集,在理想排序模型I下,计算每个查询qi的最佳有效性
步骤3.对每个粒子的相关信息进行初始化以产生初始排序模型集合P;Step 3. Initialize the relevant information of each particle to generate an initial sorting model set P;
步骤4.初始化迭代计数器t=0;Step 4. Initialize iteration counter t=0;
步骤5.创建初始排序模型归档解集Archive,在初始排序模型P中,选择非支配排序模型,存储于排序模型归档解集Archive中;Step 5. Create an initial sorting model archive solution set Archive, select a non-dominated sorting model in the initial sorting model P, and store it in the sorting model archive solution set Archive;
步骤6.计算排序模型归档解集Archive中每个非支配解的拥挤距离;Step 6. Calculate the crowding distance of each non-dominated solution in the sorting model archive solution set Archive;
步骤7.按拥挤距离大小将Archive中的非支配解降序排列;Step 7. Arrange the non-dominated solutions in Archive in descending order according to the crowding distance;
步骤8.对每个粒子执行操作以更新粒子的位置和速度信息;Step 8. Perform operations on each particle to update the position and velocity information of the particle;
步骤9.更新排序模型归档解集Archive;Step 9. Update the sorting model archive solution set Archive;
步骤10.更新粒子群P中每个粒子的个体极值Pbest[i];Step 10. Update the individual extreme value Pbest[i] of each particle in the particle swarm P;
步骤11.t=t+1,若t<MAXT,则转步骤6,否则,输出排序模型归档解集Archive中的各排序模型,即产生最终排序模型集合。Step 11. t=t+1, if t<MAXT, go to step 6, otherwise, output each sorting model in the sorting model archive solution set Archive, that is, generate the final sorting model set.
优选地,所述的步骤1的相关参数包括种群规模Pop、加速因子c1和c2、初始惯性权重ω0、最终惯性权重ω1、最大迭代次数MAXT、目标函数个数N和变异概率Mu。Preferably, the relevant parameters of
优选地,所述的步骤3的对每个粒子的相关信息进行初始化以产生初始排序模型集合P具体为:Preferably, the step 3 of initializing the relevant information of each particle to generate an initial sorting model set P is specifically:
31)随机初始化各粒子的位置P[i];31) Randomly initialize the position P[i] of each particle;
采用实数编码,在排序学习问题的可行排序模型域内,随机产生每个粒子的初始位置P[i],即各排序特征所对应的权值,其中1≤i≤Pop;Using real number coding, in the feasible sorting model domain of the sorting learning problem, the initial position P[i] of each particle is randomly generated, that is, the weight corresponding to each sorting feature, where 1≤i≤Pop;
32)初始化各粒子的速度V[i]=0;32) Initialize the velocity of each particle V[i]=0;
33)计算排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数值;33) Calculate the validity deviation function and robustness variance function values of the sorting model;
按照各粒子的位置P[i]和线性排序评分函数计算各查询qi下的每个文档dij的评分,其中fijm(qi,dij)表示查询—文档对(qi,dij)的第M维排序特征,依据不同的Score(qi,dij)值从大到小对各查询qi下各文档dij进行top-n快速排序,再依据文档的排序位置及其相关性标注Yi,联合理想排序模型I,按照公式(1)至公式(4)分别计算查询qi和查询集Q的有效性偏差函数BiasR(qi)和BiasR(Q)以及鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(qi)和VarianceR(Q)的各个值,以获得排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数的目标值;According to the position P[i] of each particle and the linear sorting scoring function Calculate the score of each documentdij under each queryqi , wherefijm (qi ,dij ) represents the Mth dimension ranking feature of the query-document pair (qi ,dij ). Perform top-n quick sorting on each documentdij under each queryqi from large to small according to different Score(qi ,dij ) values. Then, labelYi according to the ranking position and relevance of the document. Combined with the ideal ranking model I, calculate the validity bias function BiasR (qi ) and BiasR (Q) of the queryqi and the query set Q and the robustness variance function VarianceR (qi ) and VarianceR (Q) according to formulas (1) to (4) respectively, so as to obtain the target values of the validity bias function and robustness variance function of the ranking model.
34)初始化粒子的个体极值Pbest[i]=P[i];34) Initialize the individual extreme value of the particle Pbest[i]=P[i];
35)根据各个粒子的Pbest[i]确定初始种群的全局极值Gbest。35) Determine the global extreme value Gbest of the initial population based on Pbest[i] of each particle.
优选地,所述的步骤8对每个粒子执行操作以更新粒子的位置和速度信息具体为:Preferably, the step 8 performs an operation on each particle to update the position and velocity information of the particle as follows:
81)从已排序的排序模型归档解集Archive中的拥挤距离较大的前端的非劣解集中随机选择某一个粒子i,将其位置设置为全局极值Gbest;81) Randomly select a particle i from the non-inferior solution set of the front end with a larger crowding distance in the sorted sorting model archive solution set Archive, and set its position to the global extreme value Gbest;
82)依公式(6)更新粒子i的速度V[i]:82) Update the velocity V[i] of particle i according to formula (6):
Vim(t+1)=ωt*Vim(t)+c1*rand()*[Xim(t)-Pim(t)]+c2*rand()*[XGm(t)-Pim(t)]…(6)Vim (t+1)=ωt *Vim (t)+c1*rand()*[Xim (t)-Pim (t)]+c2*rand()*[XGm (t)- Pim (t)]…(6)
其中,第t次迭代时的惯性权重c1和c2为加速常数因子,rand()是[0,1]间的随机数,Xim(t)和XGm(t)分别表示第t次迭代时粒子i的个体极值Pbest[i]的第m维分量和全局极值Gbest的第m维分量,整数i为粒子编号,取值为1,2,……,Pop;Among them, the inertia weight at the tth iteration c1 and c2 are acceleration constant factors, rand() is a random number between [0, 1],Xim (t) andXGm (t) represent the m-th dimensional component of the individual extreme value Pbest[i] and the m-th dimensional component of the global extreme value Gbest of particle i at the t-th iteration, respectively, and the integer i is the particle number, which takes values of 1, 2, ..., Pop;
83)依公式(7)更新粒子i的位置P[i]:83) Update the position P[i] of particle i according to formula (7):
Pim(t+1)=Pim(t)+Vim(t+1)…(7)Pim (t+1)=Pim (t)+Vim (t+1)…(7)
84)检查P[i]是否在变量给定的界限内,如果超出了其位置范围,则将P[i]中相应的维变量设置为对应的边界值,同时速度设置为逆向,即-V[i];84) Check whether P[i] is within the given limit of the variable. If it exceeds its position range, set the corresponding dimension variable in P[i] to the corresponding boundary value, and set the speed to the reverse direction, that is, -V[i];
85)若t<MAXT*Mu,则以Mu为变异率对粒子的位置P[i]执行变异操作;85) If t<MAXT*Mu, then perform mutation operation on the particle position P[i] with Mu as the mutation rate;
86)计算粒子的目标函数值;86) Calculate the objective function value of the particle;
按照粒子的位置P[i]和线性排序评分函数计算各查询qi下的每个文档dij的评分,其中fijm(qi,dij)表示查询—文档对(qi,dij)的第M维排序特征,依据不同的Score(qi,dij)值从大到小对各查询qi下各文档dij进行top-n快速排序,再依据文档的排序位置及其相关性标注Yi,联合理想排序模型I,按照公式(1)至公式(4)分别计算查询qi和查询集Q的有效性偏差函数BiasR(qi)和BiasR(Q)以及鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(qi)和VarianceR(Q)的各个值,以获得排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数的目标值。According to the particle position P[i] and the linear sorting scoring function Calculate the score of each document dij under each query qi , wherefijm (qi ,dij ) represents the Mth dimension ranking feature of the query-document pair (qi ,dij ). Perform top-n quick sorting on each document dij under each query qi from large to small according to different Score(qi ,dij ) values, and then labelYi according to the ranking position and relevance of the document. Combined with the ideal ranking model I, calculate the validity bias function BiasR (qi ) and BiasR (Q) and the robust variance function VarianceR (qi ) and VarianceR (Q) of query qi and query set Q respectively according to formulas (1) to (4), so as to obtain the target values of the validity bias function and robust variance function of the ranking model.
优选地,所述的步骤9更新排序模型归档解集Archive具体为:Preferably, the step 9 of updating the sorting model archive solution set Archive is specifically as follows:
如果种群P中的粒子不受排序模型归档解集Archive中的任何粒子支配,则插入所有新的非支配粒子于排序模型归档解集Archive中,并删除排序模型归档解集Archive中的所有被新粒子支配的粒子,如果排序模型归档解集Archive满,则按以下步骤替换粒子:If the particles in the population P are not dominated by any particles in the sorting model archive solution set Archive, then insert all new non-dominated particles into the sorting model archive solution set Archive, and delete all particles dominated by new particles in the sorting model archive solution set Archive. If the sorting model archive solution set Archive is full, replace the particles according to the following steps:
步骤1.计算排序模型归档解集Archive中每个非支配解的拥挤距离,并按拥挤距离大小降序排列;
步骤2.从排序模型归档解集Archive的底端中随机选择拥挤距离较小的前端的非支配解中的一个粒子,用新粒子替换它。
优选地,所述的步骤10更新粒子群P中每个粒子的个体极值Pbest[i]具体为:Preferably, the step 10 of updating the individual extreme value Pbest[i] of each particle in the particle group P is specifically as follows:
依据支配关系,比较粒子P[i]的新位置和Pbest[i]的优劣,当P[i]占优时,更新个体最优,即Pbest[i]=P[i]。According to the dominance relationship, compare the new position of particle P[i] and Pbest[i]. When P[i] is dominant, update the individual optimal value, that is, Pbest[i] = P[i].
优选地,所述的步骤三,基于多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEEII的思想,从上一步骤所产生的排序模型归档解集中选择一个具有最大“净流”排序值的Pareto最优的排序模型以此作为训练出的最终排序模型具体为:Preferably, in step three, based on the idea of the preference order structure evaluation method PROMETHEEII in the multi-attribute decision-making theory, a Pareto optimal sorting model with the maximum "net flow" sorting value is selected from the sorting model archive solution set generated in the previous step as the final sorting model trained, specifically:
步骤1.计算每个排序模型的“出流”函数;
对步骤二中最终产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,分别计算每个排序模型的“出流”函数Out(Ri)值,将Out(Ri)定义为:For the final sorting model archive solution set Archive generated in
其中,|A|表示排序模型归档解集Archive中Pareto优化解的总数量;Where |A| represents the total number of Pareto optimization solutions in the sorting model archive solution set Archive;
步骤2.计算每个排序模型的“入流”函数;
对步骤二中最终产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,分别计算每个排序模型的“入流”函数In(Ri)值,将In(Ri)定义为:For the final sorting model archive solution set Archive generated in
步骤3.计算每个排序模型的“净流”函数;Step 3. Calculate the “net flow” function of each sorting model;
对步骤二中最终产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,分别计算每个排序模型的“净流”函数Net(Ri)值,将Net(Ri)定义为:For the final sorting model archive solution set Archive generated in
Net(Ri)=Out(Ri)-In(Ri)Net(Ri )=Out(Ri )-In(Ri )
步骤4.依据“净流”函数Net(Ri)获得排序模型归档解集Archive中每个排序模型Ri的“净流”排序值,选择一个具有最大“净流”排序值的Pareto优化解作为最终的排序模型R。Step 4. Obtain the "net flow" ranking value of each sorting model Ri in the sorting model archive solution set Archive according to the "net flow" function Net(Ri ), and select a Pareto optimization solution with the maximum "net flow" ranking value as the final sorting model R.
一种所述的基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法的应用,将基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法应用于搜索引擎中,其中的搜索引擎包括百度Baidu、谷歌Google、必应Bing、搜狗Sogou和雅虎Yahoo,将该方法所训练出的排序模型嵌入搜索引擎的排序系统中,以此排序模型去预测用户需要搜索的查询词的网页排序结果,从而可提高整体用户的满意度,增强用户的体验感,具体应用过程如下:An application of the robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization is to apply the robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization to search engines, wherein the search engines include Baidu, Google, Bing, Sogou and Yahoo, and embed the ranking model trained by the method into the ranking system of the search engine, and use this ranking model to predict the ranking results of web pages of the query words that users need to search, thereby improving the overall user satisfaction and enhancing the user experience. The specific application process is as follows:
步骤1.将基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法融入搜索引擎中;
首先,对搜索引擎网页索引数据库中的部分网页进行数据预处理,对网页进行排序特征的提取和标注以构建搜索引擎排序学习数据集;Firstly, data preprocessing is performed on some web pages in the search engine web page index database, and ranking features of web pages are extracted and annotated to construct a search engine ranking learning dataset;
其次,在所构建的排序学习数据集上,运用基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法去迭代训练排序模型以产生鲁棒性感知的排序模型;Secondly, on the constructed ranking learning dataset, a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization is used to iteratively train the ranking model to generate a robustness-aware ranking model;
最后,将所产生的鲁棒性感知的排序模型嵌入搜索引擎的排序系统中;Finally, the generated robustness-aware ranking model is embedded into the search engine’s ranking system;
步骤2.执行网页搜索,呈现排序结果;
在融入了基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法的搜索引擎中,用户可循环多次执行网页搜索;In the search engine that incorporates the robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization, users can perform web page searches multiple times in a loop;
首先,用户在搜索引擎的搜索框中,输入想要搜索的查询词,并点击搜索;First, the user enters the query word they want to search in the search box of the search engine and clicks search;
其次,搜索引擎的排序系统调用搜索引擎网页索引数据库,从中找出所有包含了该查询词的网页,并计算出哪些网页应该排在前面,哪些网页应该排在后面以预测出网页搜索的排序结果;Secondly, the search engine's ranking system calls the search engine's web page index database to find all the web pages that contain the query word, and calculates which web pages should be ranked first and which should be ranked last to predict the ranking results of the web page search;
最后,将网页搜索排序结果按照设定的方式返回到“搜索”页面以呈现给搜索用户。Finally, the web page search ranking results are returned to the "Search" page in a set manner to be presented to the search user.
与现有技术相比,本发明具有以下优点:Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the following advantages:
1)排序学习的多目标优化模型新。1) A new multi-objective optimization model for ranking learning.
构建了同时考虑有效性和鲁棒性的多目标排序学习模型,将偏差-方差均衡理论引入到排序学习任务中,给出了相应的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数以分别度量排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性,它们各自独立设计目标函数,不用考虑多个目标的权重指派。A multi-objective ranking learning model that considers both effectiveness and robustness is constructed, the bias-variance equilibrium theory is introduced into the ranking learning task, and the corresponding effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function are given to measure the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model respectively. They design their objective functions independently without considering the weight assignment of multiple objectives.
2)排序学习的方法新。2) The method of ranking learning is new.
基于多目标粒子群优化框架和多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想,设计了一种基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法以同时优化排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性,使得所训练出的排序模型具有较好的有效性和鲁棒性间的均衡,从而提高整体用户体验。Based on the multi-objective particle swarm optimization framework and the idea of PROMETHEE II, a preference order structure evaluation method in multi-attribute decision-making theory, a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization is designed to simultaneously optimize the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model, so that the trained ranking model has a good balance between effectiveness and robustness, thereby improving the overall user experience.
附图说明BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
图1为本发明基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法流程框架图;FIG1 is a flowchart of a robust sorting learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization according to the present invention;
图2为本发明排序模型优化性能指标的构建流程图;FIG2 is a flow chart of constructing a ranking model optimization performance index according to the present invention;
图3为本发明排序模型的训练的具体实施流程图;FIG3 is a flowchart of a specific implementation of the training of the sorting model of the present invention;
图4为本发明排序模型的优选的具体实施流程图;FIG4 is a flowchart of a preferred specific implementation of the sorting model of the present invention;
图5为本发明具体实施例一的示意图;FIG5 is a schematic diagram of a first specific embodiment of the present invention;
图6为本发明具体实施例二的示意图。FIG. 6 is a schematic diagram of a second specific embodiment of the present invention.
具体实施方式DETAILED DESCRIPTION
下面将结合本发明实施例中的附图,对本发明实施例中的技术方案进行清楚、完整地描述,显然,所描述的实施例是本发明的一部分实施例,而不是全部实施例。基于本发明中的实施例,本领域普通技术人员在没有做出创造性劳动的前提下所获得的所有其他实施例,都应属于本发明保护的范围。The following will be combined with the drawings in the embodiments of the present invention to clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are part of the embodiments of the present invention, not all of the embodiments. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by ordinary technicians in this field without creative work should fall within the scope of protection of the present invention.
本专利针对鲁棒性排序学习问题,同时考虑排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性并分别优化,将鲁棒性排序学习问题建模为多目标优化问题,基于偏差-方差均衡理论,给出了相应的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数以分别度量排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性,并基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架和多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想,设计了一种基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法,该方法是一种鲁棒性感知的多目标排序学习方法。This patent aims at the problem of robust ranking learning, considers the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model at the same time and optimizes them separately, models the robust ranking learning problem as a multi-objective optimization problem, and based on the bias-variance equilibrium theory, gives the corresponding effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function to measure the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model respectively. Based on the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm framework and the idea of the preference order structure evaluation method PROMETHEE II in multi-attribute decision-making theory, a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization is designed. This method is a robustness-aware multi-objective ranking learning method.
现有排序学习方法主要是将排序学习问题建模为分类、回归、序数回归和凸优化等问题,所采用的技术主要有支持向量机、神经网络、多重加法回归树、极限学习机、Boosting和遗传编程等,这些技术难以同时优化多个性能指标。与现有排序学习方法相比,本发明是针对鲁棒性排序学习而进行设计的一种基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法。该排序学习方法将排序学习问题建模为多目标优化问题,所采用的技术是多目标粒子群优化技术。该方法独立设计多个目标函数,不用指派多个目标的权值,并可在排序模型的训练过程中同时优化排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性,使得所训练出的排序模型具有较好的有效性和鲁棒性间的均衡,从而提高整体用户的满意度体验。The existing ranking learning methods mainly model the ranking learning problem as classification, regression, ordinal regression and convex optimization problems. The technologies used mainly include support vector machines, neural networks, multiple additive regression trees, extreme learning machines, Boosting and genetic programming, etc. These technologies are difficult to optimize multiple performance indicators at the same time. Compared with the existing ranking learning methods, the present invention is a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization designed for robust ranking learning. The ranking learning method models the ranking learning problem as a multi-objective optimization problem, and the technology used is multi-objective particle swarm optimization technology. The method independently designs multiple objective functions without assigning weights to multiple objectives, and can simultaneously optimize the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model during the training process of the ranking model, so that the trained ranking model has a good balance between effectiveness and robustness, thereby improving the overall user satisfaction experience.
本发明基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法是同时考虑排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性,将排序学习任务构建为一个多目标优化问题;基于偏差-方差均衡理论,设计了相应的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数以分别度量排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性,其中有效性偏差函数用来度量排序模型的有效性,鲁棒性方差函数用来度量排序模型的鲁棒性;基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架和多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想所设计的。The robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization of the present invention considers the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model at the same time, and constructs the ranking learning task as a multi-objective optimization problem; based on the bias-variance equilibrium theory, the corresponding effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function are designed to measure the effectiveness and robustness of the ranking model respectively, wherein the effectiveness bias function is used to measure the effectiveness of the ranking model, and the robustness variance function is used to measure the robustness of the ranking model; it is designed based on the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm framework and the idea of the preference order structure evaluation method PROMETHEE II in the multi-attribute decision-making theory.
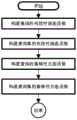
本发明基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法的流程框架如图1所示,主要包含排序模型优化性能指标的构建、排序模型的训练和排序模型的优选三大阶段。首先,基于偏差-方差均衡理论,设计排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数,构建排序学习的两个优化性能指标;其次,在排序学习数据集上,基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架,迭代优化排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数这两个目标以训练排序模型,从而产生排序模型归档解集;最后,基于多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想,从上一阶段所产生的排序模型归档解集中选择一个具有最大“净流”排序值的Pareto最优的排序模型以此作为训练出的最终排序模型。The process framework of the robust sorting learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization of the present invention is shown in Figure 1, which mainly includes three stages: construction of sorting model optimization performance indicators, training of sorting models and optimization of sorting models. First, based on the bias-variance equilibrium theory, the effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function of the sorting model are designed to construct two optimization performance indicators for sorting learning; secondly, on the sorting learning data set, based on the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm framework, the effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function of the sorting model are iteratively optimized to train the sorting model, thereby generating a sorting model archive solution set; finally, based on the idea of the preference order structure evaluation method PROMETHEE II in the multi-attribute decision theory, a Pareto optimal sorting model with the largest "net flow" sorting value is selected from the sorting model archive solution set generated in the previous stage as the final sorting model trained.
本发明基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法主要包含排序模型优化性能指标的构建、排序模型的训练和排序模型的优选三大阶段,各阶段的具体步骤如下:The robust sorting learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization of the present invention mainly includes three stages: construction of sorting model optimization performance index, training of sorting model and optimization of sorting model. The specific steps of each stage are as follows:
阶段一:排序模型优化性能指标的构建。Phase 1: Construction of ranking model optimization performance indicators.
基于偏差-方差均衡理论,设计排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数以构建排序学习的两个优化性能指标:有效性和鲁棒性,从而表征排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性指标。Based on the bias-variance equilibrium theory, the effectiveness bias function and robustness variance function of the ranking model are designed to construct two optimization performance indicators of ranking learning: effectiveness and robustness, thereby characterizing the effectiveness and robustness indicators of the ranking model.
构建排序模型的优化性能指标的步骤如图2所示,查询和查询集在排序模型下的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数分别定义在各步骤中,阐述如下:The steps of constructing the optimization performance index of the ranking model are shown in Figure 2. The validity deviation function and robustness variance function of the query and query set under the ranking model are defined in each step, as follows:
步骤1.构建查询的有效性偏差函数。
定义1.查询qi的有效性偏差函数BiasR(qi)定义为:
其中,表示查询qi下的所有文档Di在理想排序模型I,即所有文档全部正确排序下所获得的最佳有效性,表示查询qi下的所有文档Di在排序模型R下所获得的实际有效性,BiasR(qi)表示查询qi在排序模型R下的实际有效性相对于理想排序模型I的最佳有效性的偏差。此处,有效性可指信息检索领域中一些常用的性能指标,如归一化折扣累积增益(Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain,NDCG)和期望倒数排序(Expectedreciprocal rank,ERR)等,各有效性指标的计算公式在此忽略。in, represents the best effectiveness of all documentsDi under queryqi under the ideal ranking model I, that is, all documents are correctly ranked. represents the actual effectiveness of all documents Di under query qi under ranking model R, and BiasR (qi ) represents the deviation of the actual effectiveness of query qi under ranking model R relative to the optimal effectiveness of ideal ranking model I. Here, effectiveness can refer to some commonly used performance indicators in the field of information retrieval, such as Normalized Discounted Cumulative Gain (NDCG) and Expected Reciprocal Rank (ERR), etc. The calculation formulas of various effectiveness indicators are ignored here.
步骤2.构建查询集的有效性偏差函数。
定义2.查询集Q的有效性偏差函数BiasR(Q)定义为:
其中,BiasR(Q)表示在排序模型R下查询集Q中所有查询qi的有效性偏差的平均值,|Q|表示查询集Q中查询qi的总个数。Among them, BiasR (Q) represents the average validity deviation of all queries qi in the query set Q under the ranking model R, and |Q| represents the total number of queries qi in the query set Q.
步骤3.构建查询的鲁棒性方差函数。Step 3. Construct a robust variance function for the query.
定义3.查询qi的鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(qi)定义为:Definition 3. The robustness variance function VarianceR (qi ) of query qi is defined as:
VarianceR(qi)=[BiasR(qi)-BiasR(Q)]2…(3)VarianceR (qi )=[BiasR (qi )-BiasR (Q)]2 ...(3)
其中,VarianceR(qi)表示在排序模型R下查询qi的有效性偏差BiasR(qi)离查询集Q的有效性偏差BiasR(Q)的离散程度。Wherein, VarianceR (qi ) represents the degree of dispersion of the validity deviation BiasR (qi ) of query qi from the validity deviation BiasR (Q) of query set Q under ranking model R.
步骤4.构建查询集的鲁棒性方差函数。Step 4. Construct a robust variance function for the query set.
定义4.查询集Q的鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(Q)定义为:Definition 4. The robustness variance function VarianceR (Q) of the query set Q is defined as:
其中,VarianceR(Q)表示在排序模型R下查询集Q中所有查询qi的鲁棒性方差的平均值。Where VarianceR (Q) represents the average robustness variance of all queries qi in the query set Q under the ranking model R.
将鲁棒性排序学习问题转化为一个同时考虑有效性和鲁棒性的多目标优化问题,依据上述有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数的定义,则鲁棒性排序学习问题可形式化描述为:The robust ranking learning problem is transformed into a multi-objective optimization problem that considers both effectiveness and robustness. According to the definitions of the effectiveness deviation function and the robustness variance function, the robust ranking learning problem can be formally described as:
Utility(Q)={min BiasR(Q),min VarianceR(Q)}…(5)Utility(Q)={min BiasR (Q),min VarianceR (Q)}…(5)
即在排序学习的过程中,同时最小化有效性偏差函数BiasR(Q)和鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(Q)以训练排序模型。为此,基于上述所构建的排序模型的优化性能指标BiasR(Q)和VarianceR(Q),可采用多目标智能优化算法,如多目标粒子群优化算法同时最小化BiasR(Q)和VarianceR(Q)的值以达到均衡优化排序模型的有效性和鲁棒性的目的。That is, in the process of sorting learning, the effectiveness deviation function BiasR (Q) and the robustness variance function VarianceR (Q) are minimized at the same time to train the sorting model. To this end, based on the optimization performance indicators BiasR (Q) and VarianceR (Q) of the sorting model constructed above, a multi-objective intelligent optimization algorithm can be used, such as a multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm, to simultaneously minimize the values of BiasR (Q) and VarianceR (Q) to achieve the purpose of balancing the effectiveness and robustness of the optimization sorting model.
阶段二:排序模型的训练。Phase 2: Training of the sorting model.
基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架,在排序学习数据集上优化上一阶段所设计的排序模型的有效性偏差和鲁棒性方差这两个目标函数以迭代训练排序模型,从而产生排序模型归档解集。Based on the framework of multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm, the two objective functions of validity deviation and robustness variance of the sorting model designed in the previous stage are optimized on the sorting learning dataset to iteratively train the sorting model, thereby generating a sorting model archive solution set.
在具体实施中,针对排序学习问题,采用实数编码方式表示粒子,一个粒子代表一种排序模型,粒子的搜索空间为M维(即每个粒子由M维组成,M表示排序模型中所需要考虑的排序特征的总维数)。粒子的位置P和速度V可用M维向量表示,粒子的位置P代表了排序模型中各个排序特征所对应的权值,粒子i的位置P[i]是由第i个排序模型中M维排序特征各自所对应的权值组成,即用向量P[i]=(Pi1,Pi2,Pi3,…,Pim,…,PiM)T来表示,其中Pim表示第i个排序模型中第m维排序特征所对应的权值,而整数i=1,2,…,Pop,整数m=1,2,…,M,整数Pop表示粒子群体总规模,整数M表示排序模型中排序特征的总维数;粒子的速度V是用来改变粒子的位置P,即用来调整排序模型中各排序特征的权值,与粒子位置的定义类似,粒子i的速度V[i]用向量V[i]=(vi1,vi2,vi3,…,vim,…,viM)T来表示。In the specific implementation, for the sorting learning problem, real number coding is used to represent particles. One particle represents a sorting model, and the search space of the particle is M-dimensional (that is, each particle consists of M dimensions, and M represents the total dimension of the sorting features that need to be considered in the sorting model). The position P and velocity V of a particle can be represented by an M-dimensional vector. The position P of a particle represents the weight corresponding to each sorting feature in the sorting model. The position P[i] of particle i is composed of the weights corresponding to the M-dimensional sorting features in the ith sorting model, that is, it is represented by the vector P[i]=(Pi1 ,Pi2 ,Pi3 ,…,Pim ,…,PiM )T , where Pim represents the weight corresponding to the m-dimensional sorting feature in the ith sorting model, and the integer i=1,2,…,Pop, the integer m=1,2,…,M, the integer Pop represents the total size of the particle population, and the integer M represents the total dimension of the sorting features in the sorting model; the velocity V of the particle is used to change the position P of the particle, that is, to adjust the weights of each sorting feature in the sorting model. Similar to the definition of the particle position, the velocity V[i] of particle i is represented by the vector V[i]=(vi1 ,vi2 ,vi3 ,…,vim ,…,viM )T .
在基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法中,其排序模型的训练的具体实施流程如图3所示,其详细步骤如下:In the robust sorting learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization, the specific implementation process of the sorting model training is shown in Figure 3, and the detailed steps are as follows:
步骤1.初始化粒子群的相关参数。
相关参数包括种群规模Pop、加速因子c1和c2、初始惯性权重ω0、最终惯性权重ω1、最大迭代次数MAXT、目标函数个数N和变异概率Mu等参数。The relevant parameters include population size Pop, acceleration factors c1 and c2, initial inertia weight ω0 , final inertia weight ω1 , maximum number of iterations MAXT, number of objective functions N and mutation probability Mu.
步骤2.基于所给定的排序学习数据集,在理想排序模型I下,计算每个查询qi的最佳有效性
步骤3.对每个粒子的相关信息进行初始化以产生初始排序模型集合P。Step 3. Initialize the relevant information of each particle to generate an initial sorting model set P.
①随机初始化各粒子的位置P[i]。① Randomly initialize the position P[i] of each particle.
采用实数编码,在排序学习问题的可行排序模型域内,随机产生每个粒子的初始位置P[i],即各排序特征所对应的权值,其中1≤i≤Pop。Using real number coding, the initial position P[i] of each particle is randomly generated in the feasible sorting model domain of the sorting learning problem, that is, the weight corresponding to each sorting feature, where 1≤i≤Pop.
②初始化各粒子的速度V[i]=0。② Initialize the velocity of each particle V[i]=0.
③计算排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数值。③ Calculate the validity deviation function and robustness variance function values of the sorting model.
按照各粒子的位置P[i]和线性排序评分函数计算各查询qi下的每个文档dij的评分,其中fijm(qi,dij)表示查询-文档对(qi,dij)的第M维排序特征。依据不同的Score(qi,dij)值从大到小对各查询qi下各文档dij进行top-n快速排序,再依据文档的排序位置及其相关性标注Yi,联合理想排序模型I,按照公式(1)至公式(4)分别计算查询qi和查询集Q的有效性偏差函数BiasR(qi)和BiasR(Q)以及鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(qi)和VarianceR(Q)的各个值,以获得排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数的目标值。According to the position P[i] of each particle and the linear sorting scoring function Calculate the score of each documentdij under each queryqi , wherefijm (qi ,dij ) represents the Mth dimension ranking feature of the query-document pair (qi ,dij ). Perform top-n quick sorting on each documentdij under each queryqi from large to small according to different Score(qi ,dij ) values, and then annotateYi according to the ranking position and relevance of the document, and combine with the ideal ranking model I to calculate the validity bias function BiasR (qi ) and BiasR (Q) of queryqi and query set Q and the robustness variance function VarianceR (qi) and VarianceR (Q) according to formulas (1 ) to (4) respectively, so as to obtain the target values of the validity bias function and robustness variance function of the ranking model.
④初始化粒子的个体极值Pbest[i]=P[i]。④ Initialize the individual extreme value of the particle Pbest[i] = P[i].
⑤根据各个粒子的Pbest[i]确定初始种群的全局极值Gbest。⑤Determine the global extreme value Gbest of the initial population based on Pbest[i] of each particle.
步骤4.初始化迭代计数器t=0。Step 4. Initialize iteration counter t=0.
步骤5.创建初始排序模型归档解集Archive。Step 5. Create an initial sorting model archive solution set Archive.
在初始排序模型P中,选择非支配排序模型,存储于排序模型归档解集Archive中。In the initial sorting model P, a non-dominated sorting model is selected and stored in the sorting model archive solution set Archive.
步骤6.计算排序模型归档解集Archive中每个非支配解的拥挤距离。Step 6. Calculate the crowding distance of each non-dominated solution in the sorting model archive solution set Archive.
步骤7.按拥挤距离大小将Archive中的非支配解降序排列。Step 7. Arrange the non-dominated solutions in Archive in descending order according to the crowding distance.
步骤8.对每个粒子执行以下操作以更新粒子的位置和速度等信息。Step 8. Perform the following operations on each particle to update the particle's position, velocity and other information.
①从已排序的排序模型归档解集Archive中的拥挤距离较大的前端的非劣解集中随机选择某一个粒子i,将其位置设置为全局极值Gbest。① Randomly select a particle i from the non-inferior solution set with a larger crowding distance in the sorted sorting model archive solution set Archive, and set its position to the global extreme value Gbest.
②依公式(6)更新粒子i的速度V[i]:② Update the velocity V[i] of particle i according to formula (6):
Vim(t+1)=ωt*Vim(t)+c1*rand()*[Xim(t)-Pim(t)]+c2*rand()*[XGm(t)-Pim(t)]…(6)其中,第t次迭代时的惯性权重c1和c2为加速常数因子,rand()是[0,1]间的随机数,Xim(t)和XGm(t)分别表示第t次迭代时粒子i的个体极值Pbest[i]的第m维分量和全局极值Gbest的第m维分量,整数i为粒子编号,取值为1,2,……,Pop。Vim (t+1) =ωt *Vim (t) + c1 * rand() * [Xim (t) -Pim (t)] + c2 * rand() * [XGm (t) -Pim (t)] (6) where the inertia weight at the tth iteration is c1 and c2 are acceleration constant factors, rand() is a random number between [0, 1],Xim (t) andXGm (t) represent the m-th dimensional component of the individual extremum Pbest[i] and the m-th dimensional component of the global extremum Gbest of particle i at the t-th iteration, respectively. The integer i is the particle number, which takes values of 1, 2, …, Pop.
③依公式(7)更新粒子i的位置P[i]:③ Update the position P[i] of particle i according to formula (7):
Pim(t+1)=Pim(t)+Vim(t+1)…(7)Pim (t+1)=Pim (t)+Vim (t+1)…(7)
④检查P[i]是否在变量给定的界限内,如果超出了其位置范围,则将P[i]中相应的维变量设置为对应的边界值,同时速度设置为逆向,即-V[i]。④ Check whether P[i] is within the limits given by the variable. If it exceeds its position range, set the corresponding dimension variable in P[i] to the corresponding boundary value, and set the speed to the reverse, that is, -V[i].
⑤若t<MAXT*Mu,则以Mu为变异率对粒子的位置P[i]执行变异操作。⑤If t<MAXT*Mu, then perform mutation operation on the particle position P[i] with Mu as the mutation rate.
⑥计算粒子的目标函数值。⑥Calculate the objective function value of the particle.
按照粒子的位置P[i]和线性排序评分函数计算各查询qi下的每个文档dij的评分,其中fijm(qi,dij)表示查询—文档对(qi,dij)的第M维排序特征。依据不同的Score(qi,dij)值从大到小对各查询qi下各文档dij进行top-n快速排序,再依据文档的排序位置及其相关性标注Yi,联合理想排序模型I,按照公式(1)至公式(4)分别计算查询qi和查询集Q的有效性偏差函数BiasR(qi)和BiasR(Q)以及鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(qi)和VarianceR(Q)的各个值,以获得排序模型的有效性偏差函数和鲁棒性方差函数的目标值。According to the particle position P[i] and the linear sorting scoring function Calculate the score of each documentdij under each queryqi , wherefijm (qi ,dij ) represents the Mth dimension ranking feature of the query-document pair (qi ,dij ). Perform top-n quick sorting on each documentdij under each queryqi from large to small according to different Score(qi ,dij ) values, and then labelYi according to the ranking position and relevance of the document. Combined with the ideal ranking model I, calculate the validity bias function BiasR (qi ) and BiasR (Q) of queryqi and query set Q and the robustness variance function VarianceR (qi) and VarianceR (Q) according to formulas (1 ) to (4) respectively, so as to obtain the target values of the validity bias function and robustness variance function of the ranking model.
步骤9.更新排序模型归档解集Archive。Step 9. Update the sorting model archive solution set Archive.
如果种群P中的粒子不受排序模型归档解集Archive中的任何粒子支配,则插入所有新的非支配粒子于排序模型归档解集Archive中,并删除排序模型归档解集Archive中的所有被新粒子支配的粒子。如果排序模型归档解集Archive满,则按以下步骤替换粒子:If the particles in the population P are not dominated by any particles in the sorted model archive solution set Archive, insert all new non-dominated particles into the sorted model archive solution set Archive, and delete all particles in the sorted model archive solution set Archive that are dominated by new particles. If the sorted model archive solution set Archive is full, replace the particles according to the following steps:
①计算排序模型归档解集Archive中每个非支配解的拥挤距离,并按拥挤距离大小降序排列。① Calculate the crowding distance of each non-dominated solution in the sorting model archive solution set Archive, and arrange them in descending order according to the crowding distance.
②从排序模型归档解集Archive的底端中随机选择拥挤距离较小的前端的非支配解中的一个粒子,用新粒子替换它。② Randomly select a particle from the non-dominated solution at the front end with a smaller crowding distance from the bottom of the sorting model archive solution set Archive and replace it with a new particle.
步骤10.更新粒子群P中每个粒子的个体极值Pbest[i]。Step 10. Update the individual extreme value Pbest[i] of each particle in the particle swarm P.
依据支配关系,比较粒子P[i]的新位置和Pbest[i]的优劣,当P[i]占优时,更新个体最优,即Pbest[i]=P[i]。According to the dominance relationship, compare the new position of particle P[i] and Pbest[i]. When P[i] is dominant, update the individual optimal value, that is, Pbest[i] = P[i].
步骤11.t=t+1,若t<MAXT,则转步骤6,否则,输出排序模型归档解集Archive中的各排序模型,即产生最终排序模型集合。Step 11. t=t+1, if t<MAXT, go to step 6, otherwise, output each sorting model in the sorting model archive solution set Archive, that is, generate the final sorting model set.
阶段三:排序模型的优选。Stage 3: Optimization of sorting model.
通过基于多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想,结合各排序模型的有效性偏差函数BiasR(Q)和鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(Q),从上一阶段所产生的排序模型归档解集中选择一个具有最大净流排序值的Pareto优化解,即最优排序模型,以此作为训练出的最终排序模型。排序模型的优选具体实施流程如图4所示,其具体实施步骤如下:Based on the idea of PROMETHEE II, a preference order structure evaluation method in multi-attribute decision-making theory, and combined with the effectiveness bias function BiasR (Q) and robustness variance function VarianceR (Q) of each sorting model, a Pareto optimization solution with the maximum net flow sorting value is selected from the sorting model archive solution set generated in the previous stage, that is, the optimal sorting model, which is used as the final sorting model trained. The specific implementation process of the optimization of the sorting model is shown in Figure 4, and its specific implementation steps are as follows:
步骤1.计算每个排序模型的“出流”函数。
对阶段二中最终产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,分别计算每个排序模型的“出流”函数Out(Ri)值,将Out(Ri)定义为:For the final sorting model archive solution set Archive generated in
其中,|A|表示排序模型归档解集Archive中Pareto优化解的总数量。Where |A| represents the total number of Pareto optimization solutions in the sorting model archive solution set Archive.
步骤2.计算每个排序模型的“入流”函数。
对阶段二中最终产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,分别计算每个排序模型的“入流”函数In(Ri)值,将In(Ri)定义为:For the final sorting model archive solution set Archive generated in
步骤3.计算每个排序模型的“净流”函数。Step 3. Calculate the “net flow” function for each sorting model.
对阶段二中最终产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,分别计算每个排序模型的“净流”函数Net(Ri)值,将Net(Ri)定义为:For the final sorting model archive solution set Archive generated in
Net(Ri)=Out(Ri)-In(Ri)Net(Ri )=Out(Ri )-In(Ri )
步骤4.依据“净流”函数Net(Ri)获得排序模型归档解集Archive中每个排序模型Ri的“净流”排序值,选择一个具有最大“净流”排序值的Pareto优化解作为最终的排序模型R。Step 4. Obtain the "net flow" ranking value of each sorting model Ri in the sorting model archive solution set Archive according to the "net flow" function Net(Ri ), and select a Pareto optimization solution with the maximum "net flow" ranking value as the final sorting model R.
具体实施例一如下:
如图5所示,假定现有一个标准排序学习数据集L2Rdataset,用集合的方式表示为:L2Rdataset={(<qi,dij>,yij)|qi∈Q,dij∈Di,yij∈Yi,1≤i≤|Q|,1≤j≤|Di|},其中qi表示第i个查询,Q表示排序学习数据集中的有限查询集,|Q|表示查询集中查询的总个数,dij表示文档集合Di中的第j个文档,Di表示关联于查询qi的文档集合,|Di|表示文档集合Di中文档的总个数,yij表示相关性标注,反映了查询qi和文档dij之间的相关性程度,取值可为一些等级值,如{1,2,3,4,5},Yi={yi1,yi2,…,yi|Di|}表示关联于查询的标签集。查询-文档对<qi,dij>通过M维排序特征f来描述,可表示为<qi,dij>={qi,fij1,fij1,…,fijm,…,fijM}。通过第一阶段的“排序模型优化性能指标的构建”,产生了四个性能指标:BiasR(qi)、BiasR(Q)、VarianceR(qi)和VarianceR(Q),其中BiasR(Q)和VarianceR(Q)是要在第二阶段通过多目标粒子群优化算法优化的目标函数。在第二阶段“排序模型的训练”中,针对所给定的排序学习数据集L2Rdataset,读取L2Rdataset中的查询-文档对<qi,dij>的特征值{qi,fij1,fij1,…,fijm,…,fijM}以及相关性标注yij等数据,在初始排序模型R下,计算BiasR(qi)、BiasR(Q)、VarianceR(qi)和VarianceR(Q)的值,基于多目标粒子群优化算法框架,迭代优化排序模型的有效性偏差函数BiasR(Q)和鲁棒性方差函数VarianceR(Q)以不断更新排序模型,最终产生排序模型的归档解集Archive。在第三阶段“排序模型的优选”中,针对上一阶段所产生的排序模型归档解集Archive,通过基于多属性决策理论中的偏好顺序结构评估法PROMETHEE II的思想,分别按照对应方法计算每个排序模型的“出流”函数值、“入流”函数值和“净流”函数值,再从Archive解集中选择一个具有最大净流排序值的Pareto优化解,即最优排序模型,以此作为训练出的最终排序模型R,该排序模型是一个鲁棒性感知的排序模型,可以运用该排序模型去预测新的查询的文档排序。当有新的查询q需要检索文档时,通过排序系统在文档数据库D中筛选出对应的文档集,基于所产生的排序模型R,对所反馈的文档集进行评分,再按照评分大小对文档集进行降序排列,生成新查询q的预测文档的排序结果并输出显示。As shown in Figure 5, assume that there is a standard ranking learning dataset L2Rdataset, which is expressed in a set way: L2Rdataset = {(<qi ,dij >,yij )|qi ∈Q,dij ∈Di ,yij ∈Yi ,1≤i≤|Q|,1≤j≤|Di |}, whereqi represents the i-th query, Q represents the finite query set in the ranking learning dataset, |Q| represents the total number of queries in the query set,dij represents the j-th document in the document setDi ,Di represents the document set associated with the queryqi , |Di | represents the total number of documents in the document setDi ,yij represents the relevance annotation, which reflects the degree of relevance between the queryqi and the documentdij , and the value can be some level values, such as {1, 2, 3, 4, 5},Yi = {yi1 ,yi2 ,…,yi|Di| } represents the label set associated with the query. The query-document pair <qi ,dij > is described by the M-dimensional sorting feature f, which can be expressed as <qi ,dij >={qi ,fij1 ,fij1 ,…,fijm ,…,fijM }. Through the first stage of "construction of sorting model optimization performance indicators", four performance indicators are generated: BiasR (qi ), BiasR (Q), VarianceR (qi ) and VarianceR (Q), among which BiasR (Q) and VarianceR (Q) are the objective functions to be optimized by the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm in the second stage. In the second stage “training of the ranking model”, for the given ranking learning dataset L2Rdataset, the feature values {qi ,fij1 ,fij1 ,…,fijm ,…,fijM } of the query-document pair <qi ,dij > and the relevance annotation yij and other data in the L2Rdataset are read. Under the initial ranking model R, the values of BiasR (qi ), BiasR (Q), VarianceR (qi ) and VarianceR (Q) are calculated. Based on the multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm framework, the effectiveness bias function BiasR (Q) and the robustness variance function VarianceR (Q) of the ranking model are iteratively optimized to continuously update the ranking model, and finally the archive solution set Archive of the ranking model is generated. In the third stage, "optimization of ranking model", for the archive solution set Archive of the ranking model generated in the previous stage, the "outflow" function value, "inflow" function value and "net flow" function value of each ranking model are calculated according to the corresponding method based on the idea of PROMETHEE II, a preference order structure evaluation method in multi-attribute decision theory, and then a Pareto optimization solution with the maximum net flow ranking value is selected from the Archive solution set, that is, the optimal ranking model, which is used as the final ranking model R trained. This ranking model is a robustness-aware ranking model, which can be used to predict the document ranking of new queries. When there is a new query q that needs to retrieve documents, the ranking system selects the corresponding document set in the document database D, and the feedback document set is scored based on the generated ranking model R, and then the document set is sorted in descending order according to the score size, and the ranking result of the predicted document of the new query q is generated and output for display.
具体实施例二如下:
如图6所示,一种采用所述的基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法可以应用于信息检索、搜索引擎、推荐系统和问答系统等实际需求排序的应用场景中。此处,将基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法应用于如百度(Baidu)、谷歌(Google)、必应(Bing)、搜狗(Sogou)和雅虎(Yahoo)等搜索引擎中,以作应用示例。将该方法所训练出的排序模型嵌入搜索引擎的排序系统中,以此排序模型去预测用户需要搜索的查询词的网页排序结果,从而可提高整体用户的满意度,增强用户的体验感。As shown in FIG6 , a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization can be applied to application scenarios of actual demand ranking such as information retrieval, search engines, recommendation systems, and question-answering systems. Here, the robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization is applied to search engines such as Baidu, Google, Bing, Sogou, and Yahoo as an application example. The ranking model trained by this method is embedded in the ranking system of the search engine, and this ranking model is used to predict the web page ranking results of the query words that the user needs to search, thereby improving the overall user satisfaction and enhancing the user experience.
基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法应用于搜索引擎中的操作实施流程如图6所示,其实施步骤如下所述:The operational implementation process of the robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization applied to the search engine is shown in Figure 6, and its implementation steps are as follows:
步骤1.将基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法融入搜索引擎中。
首先,对搜索引擎网页索引数据库中的部分网页进行数据预处理,对网页进行排序特征的提取和标注以构建搜索引擎排序学习数据集。Firstly, data preprocessing is performed on some web pages in the search engine web page index database, and the ranking features of the web pages are extracted and annotated to construct a search engine ranking learning dataset.
其次,在所构建的排序学习数据集上,运用基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法去迭代训练排序模型以产生鲁棒性感知的排序模型。Secondly, on the constructed ranking learning dataset, a robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization is used to iteratively train the ranking model to generate a robustness-aware ranking model.
最后,将所产生的鲁棒性感知的排序模型嵌入搜索引擎的排序系统中。Finally, the generated robustness-aware ranking model is embedded into the search engine's ranking system.
步骤2.执行网页搜索,呈现排序结果。
在融入了基于多目标粒子群优化的鲁棒性排序学习方法的搜索引擎中,用户可循环多次执行网页搜索。In the search engine that incorporates the robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization, users can perform web page searches multiple times in a loop.
首先,用户在搜索引擎的搜索框中,输入想要搜索的查询词,并点击搜索。First, the user enters the query word he wants to search in the search box of the search engine and clicks search.
其次,搜索引擎的排序系统调用搜索引擎网页索引数据库,从中找出所有包含了该查询词的网页,并计算出哪些网页应该排在前面,哪些网页应该排在后面以预测出网页搜索的排序结果。Secondly, the search engine's ranking system calls the search engine's web page index database to find all web pages that contain the query term, and calculates which web pages should be ranked first and which should be ranked last to predict the ranking results of the web page search.
最后,将网页搜索排序结果按照一定的方式返回到“搜索”页面以呈现给搜索用户。Finally, the web page search ranking results are returned to the "Search" page in a certain manner to be presented to the search user.
以上所述,仅为本发明的具体实施方式,但本发明的保护范围并不局限于此,任何熟悉本技术领域的技术人员在本发明揭露的技术范围内,可轻易想到各种等效的修改或替换,这些修改或替换都应涵盖在本发明的保护范围之内。因此,本发明的保护范围应以权利要求的保护范围为准。The above is only a specific embodiment of the present invention, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited thereto. Any person skilled in the art can easily think of various equivalent modifications or substitutions within the technical scope disclosed by the present invention, and these modifications or substitutions should be included in the protection scope of the present invention. Therefore, the protection scope of the present invention shall be based on the protection scope of the claims.
Claims (8)
Translated fromChinesePriority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910318891.8ACN110046713B (en) | 2019-04-19 | 2019-04-19 | Robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910318891.8ACN110046713B (en) | 2019-04-19 | 2019-04-19 | Robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN110046713A CN110046713A (en) | 2019-07-23 |
| CN110046713Btrue CN110046713B (en) | 2023-05-12 |
Family
ID=67278070
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201910318891.8AActiveCN110046713B (en) | 2019-04-19 | 2019-04-19 | Robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN110046713B (en) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN111581546B (en)* | 2020-05-13 | 2023-10-03 | 北京达佳互联信息技术有限公司 | Method, device, server and medium for determining multimedia resource ordering model |
| CN111783209B (en)* | 2020-07-03 | 2022-09-27 | 吉林大学 | Self-adaptive structure reliability analysis method combining learning function and kriging model |
| CN111881359B (en)* | 2020-08-04 | 2023-11-17 | 携程计算机技术(上海)有限公司 | Ordering method, ordering system, ordering equipment and ordering storage medium in internet information retrieval |
| CN112100529B (en)* | 2020-11-17 | 2021-03-19 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | Search content ordering method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment |
| CN112508202B (en)* | 2021-02-07 | 2021-07-30 | 北京淇瑀信息科技有限公司 | Method and device for adjusting model stability and electronic equipment |
| CN113642632B (en)* | 2021-08-11 | 2023-10-27 | 国网冀北电力有限公司计量中心 | Power system customer classification method and device based on adaptive competition and equilibrium optimization |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108229657A (en)* | 2017-12-25 | 2018-06-29 | 杭州健培科技有限公司 | A kind of deep neural network training and optimization algorithm based on evolution algorithmic |
| CN108469983A (en)* | 2018-04-02 | 2018-08-31 | 西南交通大学 | A kind of virtual machine deployment method based on particle cluster algorithm under cloud environment |
| CN109063242A (en)* | 2018-06-20 | 2018-12-21 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Guidance tool error identification method based on particle swarm optimization |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2011055145A1 (en)* | 2009-11-05 | 2011-05-12 | Bae Systems Plc | Generating a set of solutions to a multi-objective problem |
- 2019
- 2019-04-19CNCN201910318891.8Apatent/CN110046713B/enactiveActive
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108229657A (en)* | 2017-12-25 | 2018-06-29 | 杭州健培科技有限公司 | A kind of deep neural network training and optimization algorithm based on evolution algorithmic |
| CN108469983A (en)* | 2018-04-02 | 2018-08-31 | 西南交通大学 | A kind of virtual machine deployment method based on particle cluster algorithm under cloud environment |
| CN109063242A (en)* | 2018-06-20 | 2018-12-21 | 中国人民解放军国防科技大学 | Guidance tool error identification method based on particle swarm optimization |
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| "Dynamic Multiple Swarms in Multiobjective Particle Swarm Optimization";Gary G. Yen 等;《IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part A: Systems and Humans》;第39卷(第4期);第890-911页* |
| "利用粒子群算法计算AHP判断矩阵排序权重";张建华 等;《太原科技大学学报》;第33卷(第02期);第149-154页* |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN110046713A (en) | 2019-07-23 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN110046713B (en) | Robust ranking learning method based on multi-objective particle swarm optimization and its application | |
| CN102495860B (en) | Expert recommendation method based on language model | |
| CN105893641B (en) | A job recommendation method | |
| CN108846050B (en) | Intelligent core process knowledge pushing method and system based on multi-model fusion | |
| CN109408600B (en) | Book recommendation method based on data mining | |
| CN118839021A (en) | Intelligent knowledge graph driven dynamic correlation enhancement retrieval generation system and method | |
| CN112182221B (en) | A Knowledge Retrieval Optimization Method Based on Improved Random Forest | |
| CN107145519B (en) | Image retrieval and annotation method based on hypergraph | |
| CN108021658A (en) | A kind of big data intelligent search method and system based on whale optimization algorithm | |
| CN102081668A (en) | Information retrieval optimizing method based on domain ontology | |
| CN108399213B (en) | User-oriented personal file clustering method and system | |
| CN102968419A (en) | Disambiguation method for interactive Internet entity name | |
| Wang et al. | Effective similarity search on heterogeneous networks: A meta-path free approach | |
| CN109933720A (en) | A Dynamic Recommendation Method Based on Adaptive Evolution of User Interests | |
| CN102768679A (en) | A search method and search system | |
| CN110609950B (en) | Public opinion system search word recommendation method and system | |
| CN108733745A (en) | A kind of enquiry expanding method based on medical knowledge | |
| CN112667876B (en) | Opinion leader group identification method based on PSOTVCF-Kmeans algorithm | |
| Kumar | Efficient k-mean clustering algorithm for large datasets using data mining standard score normalization | |
| Zamani et al. | Stochastic retrieval-conditioned reranking | |
| CN109783709B (en) | Sorting method based on Markov decision process and k-nearest neighbor reinforcement learning | |
| CN119377281A (en) | A data intelligent retrieval optimization method based on large models and deep learning | |
| CN111444414A (en) | An Information Retrieval Model for Modeling Diverse Relevant Features in Ad-hoc Retrieval Tasks | |
| Subbaiah | Extracting knowledge using probabilistic classifier for text mining | |
| CN114549868A (en) | Method for improving image correlation based on discrete quantum walking image reordering algorithm |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant |